

Essay Writing: A complete guide for students and teachers
P LANNING, PARAGRAPHING AND POLISHING: FINE-TUNING THE PERFECT ESSAY
Essay writing is an essential skill for every student. Whether writing a particular academic essay (such as persuasive, narrative, descriptive, or expository) or a timed exam essay, the key to getting good at writing is to write. Creating opportunities for our students to engage in extended writing activities will go a long way to helping them improve their skills as scribes.
But, putting the hours in alone will not be enough to attain the highest levels in essay writing. Practice must be meaningful. Once students have a broad overview of how to structure the various types of essays, they are ready to narrow in on the minor details that will enable them to fine-tune their work as a lean vehicle of their thoughts and ideas.

In this article, we will drill down to some aspects that will assist students in taking their essay writing skills up a notch. Many ideas and activities can be integrated into broader lesson plans based on essay writing. Often, though, they will work effectively in isolation – just as athletes isolate physical movements to drill that are relevant to their sport. When these movements become second nature, they can be repeated naturally in the context of the game or in our case, the writing of the essay.
THE ULTIMATE NONFICTION WRITING TEACHING RESOURCE

- 270 pages of the most effective teaching strategies
- 50+ digital tools ready right out of the box
- 75 editable resources for student differentiation
- Loads of tricks and tips to add to your teaching tool bag
- All explanations are reinforced with concrete examples.
- Links to high-quality video tutorials
- Clear objectives easy to match to the demands of your curriculum
Planning an essay

The Boys Scouts’ motto is famously ‘Be Prepared’. It’s a solid motto that can be applied to most aspects of life; essay writing is no different. Given the purpose of an essay is generally to present a logical and reasoned argument, investing time in organising arguments, ideas, and structure would seem to be time well spent.
Given that essays can take a wide range of forms and that we all have our own individual approaches to writing, it stands to reason that there will be no single best approach to the planning stage of essay writing. That said, there are several helpful hints and techniques we can share with our students to help them wrestle their ideas into a writable form. Let’s take a look at a few of the best of these:
BREAK THE QUESTION DOWN: UNDERSTAND YOUR ESSAY TOPIC.
Whether students are tackling an assignment that you have set for them in class or responding to an essay prompt in an exam situation, they should get into the habit of analyzing the nature of the task. To do this, they should unravel the question’s meaning or prompt. Students can practice this in class by responding to various essay titles, questions, and prompts, thereby gaining valuable experience breaking these down.
Have students work in groups to underline and dissect the keywords and phrases and discuss what exactly is being asked of them in the task. Are they being asked to discuss, describe, persuade, or explain? Understanding the exact nature of the task is crucial before going any further in the planning process, never mind the writing process .
BRAINSTORM AND MIND MAP WHAT YOU KNOW:
Once students have understood what the essay task asks them, they should consider what they know about the topic and, often, how they feel about it. When teaching essay writing, we so often emphasize that it is about expressing our opinions on things, but for our younger students what they think about something isn’t always obvious, even to themselves.
Brainstorming and mind-mapping what they know about a topic offers them an opportunity to uncover not just what they already know about a topic, but also gives them a chance to reveal to themselves what they think about the topic. This will help guide them in structuring their research and, later, the essay they will write . When writing an essay in an exam context, this may be the only ‘research’ the student can undertake before the writing, so practicing this will be even more important.
RESEARCH YOUR ESSAY
The previous step above should reveal to students the general direction their research will take. With the ubiquitousness of the internet, gone are the days of students relying on a single well-thumbed encyclopaedia from the school library as their sole authoritative source in their essay. If anything, the real problem for our students today is narrowing down their sources to a manageable number. Students should use the information from the previous step to help here. At this stage, it is important that they:
● Ensure the research material is directly relevant to the essay task
● Record in detail the sources of the information that they will use in their essay
● Engage with the material personally by asking questions and challenging their own biases
● Identify the key points that will be made in their essay
● Group ideas, counterarguments, and opinions together
● Identify the overarching argument they will make in their own essay.
Once these stages have been completed the student is ready to organise their points into a logical order.
WRITING YOUR ESSAY
There are a number of ways for students to organize their points in preparation for writing. They can use graphic organizers , post-it notes, or any number of available writing apps. The important thing for them to consider here is that their points should follow a logical progression. This progression of their argument will be expressed in the form of body paragraphs that will inform the structure of their finished essay.
The number of paragraphs contained in an essay will depend on a number of factors such as word limits, time limits, the complexity of the question etc. Regardless of the essay’s length, students should ensure their essay follows the Rule of Three in that every essay they write contains an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Generally speaking, essay paragraphs will focus on one main idea that is usually expressed in a topic sentence that is followed by a series of supporting sentences that bolster that main idea. The first and final sentences are of the most significance here with the first sentence of a paragraph making the point to the reader and the final sentence of the paragraph making the overall relevance to the essay’s argument crystal clear.
Though students will most likely be familiar with the broad generic structure of essays, it is worth investing time to ensure they have a clear conception of how each part of the essay works, that is, of the exact nature of the task it performs. Let’s review:
Common Essay Structure
Introduction: Provides the reader with context for the essay. It states the broad argument that the essay will make and informs the reader of the writer’s general perspective and approach to the question.
Body Paragraphs: These are the ‘meat’ of the essay and lay out the argument stated in the introduction point by point with supporting evidence.
Conclusion: Usually, the conclusion will restate the central argument while summarising the essay’s main supporting reasons before linking everything back to the original question.
ESSAY WRITING PARAGRAPH WRITING TIPS

● Each paragraph should focus on a single main idea
● Paragraphs should follow a logical sequence; students should group similar ideas together to avoid incoherence
● Paragraphs should be denoted consistently; students should choose either to indent or skip a line
● Transition words and phrases such as alternatively , consequently , in contrast should be used to give flow and provide a bridge between paragraphs.
HOW TO EDIT AN ESSAY

Students shouldn’t expect their essays to emerge from the writing process perfectly formed. Except in exam situations and the like, thorough editing is an essential aspect in the writing process.
Often, students struggle with this aspect of the process the most. After spending hours of effort on planning, research, and writing the first draft, students can be reluctant to go back over the same terrain they have so recently travelled. It is important at this point to give them some helpful guidelines to help them to know what to look out for. The following tips will provide just such help:
One Piece at a Time: There is a lot to look out for in the editing process and often students overlook aspects as they try to juggle too many balls during the process. One effective strategy to combat this is for students to perform a number of rounds of editing with each focusing on a different aspect. For example, the first round could focus on content, the second round on looking out for word repetition (use a thesaurus to help here), with the third attending to spelling and grammar.
Sum It Up: When reviewing the paragraphs they have written, a good starting point is for students to read each paragraph and attempt to sum up its main point in a single line. If this is not possible, their readers will most likely have difficulty following their train of thought too and the paragraph needs to be overhauled.
Let It Breathe: When possible, encourage students to allow some time for their essay to ‘breathe’ before returning to it for editing purposes. This may require some skilful time management on the part of the student, for example, a student rush-writing the night before the deadline does not lend itself to effective editing. Fresh eyes are one of the sharpest tools in the writer’s toolbox.
Read It Aloud: This time-tested editing method is a great way for students to identify mistakes and typos in their work. We tend to read things more slowly when reading aloud giving us the time to spot errors. Also, when we read silently our minds can often fill in the gaps or gloss over the mistakes that will become apparent when we read out loud.
Phone a Friend: Peer editing is another great way to identify errors that our brains may miss when reading our own work. Encourage students to partner up for a little ‘you scratch my back, I scratch yours’.
Use Tech Tools: We need to ensure our students have the mental tools to edit their own work and for this they will need a good grasp of English grammar and punctuation. However, there are also a wealth of tech tools such as spellcheck and grammar checks that can offer a great once-over option to catch anything students may have missed in earlier editing rounds.

Putting the Jewels on Display: While some struggle to edit, others struggle to let go. There comes a point when it is time for students to release their work to the reader. They must learn to relinquish control after the creation is complete. This will be much easier to achieve if the student feels that they have done everything in their control to ensure their essay is representative of the best of their abilities and if they have followed the advice here, they should be confident they have done so.
WRITING CHECKLISTS FOR ALL TEXT TYPES

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
ESSAY WRITING video tutorials

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Teach Essay Writing
Last Updated: June 26, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 89,400 times.
Teaching students how to write an essay is a big undertaking, but this is a crucial process for any high school or college student to learn. Start by assigning essays to read and then encourage students to choose an essay topic of their own. Spend class time helping students understand what makes a good essay. Then, use your assignments to guide students through writing their essays.
Choosing Genres and Topics

- Narrative, which is a non-fiction account of a personal experience. This is a good option if you want your students to share a story about something they did, such as a challenge they overcame or a favorite vacation they took. [2] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Expository , which is when you investigate an idea, discuss it at length, and make an argument about it. This might be a good option if you want students to explore a specific concept or a controversial subject. [3] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Descriptive , which is when you describe a person, place, object, emotion, experience, or situation. This can be a good way to allow your students to express themselves creatively through writing. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Argumentative or persuasive essays require students to take a stance on a topic and make an argument to support that stance. This is different from an expository essay in that students won't be discussing a concept at length and then taking a position. The goal of an argumentative essay is to take a position right away and defend it with evidence. [5] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- Make sure to select essays that are well-structured and interesting so that your students can model their own essays after these examples. Include essays written by former students, if you can, as well as professionally written essays.
Tip : Readers come in many forms. You can find readers that focus on a specific topic, such as food or pop culture. You can also find reader/handbook combos that will provide general information on writing along with the model essays.

- For example, for each of the essays you assign your students, you could ask them to identify the author's main point or focus, the structure of the essay, the author's use of sources, and the effect of the introduction and conclusion.
- Ask the students to create a reverse outline of the essay to help them understand how to construct a well-written essay. They'll identify the thesis, the main points of the body paragraphs, the supporting evidence, and the concluding statement. Then, they'll present this information in an outline. [8] X Research source

- For example, if you have assigned your students a narrative essay, then encourage them to choose a story that they love to tell or a story they have always wanted to tell but never have.
- If your students are writing argumentative essays, encourage them to select a topic that they feel strongly about or that they'd like to learn more about so that they can voice their opinion.
Explaining the Parts of an Essay

- For example, if you read an essay that begins with an interesting anecdote, highlight that in your class discussion of the essay. Ask students how they could integrate something like that into their own essays and have them write an anecdotal intro in class.
- Or, if you read an essay that starts with a shocking fact or statistic that grabs readers' attention, point this out to your students. Ask them to identify the most shocking fact or statistic related to their essay topic.

- For example, you could provide a few model thesis statements that students can use as templates and then ask them to write a thesis for their topic as an in-class activity or have them post it on an online discussion board.
Tip : Even though the thesis statement is only 1 sentence, this can be the most challenging part of writing an essay for some students. Plan to spend a full class session on writing thesis statements and review the information multiple times as well.

- For example, you could spend a class session going over topic sentences, and then look at how the authors of model essays have used topic sentences to introduce their claims. Then, identify where the author provides support for a claim and how they expand on the source.

- For example, you might direct students to a conclusion in a narrative essay that reflects on the significance of an author's experience. Ask students to write a paragraph where they reflect on the experience they are writing about and turn it in as homework or share it on class discussion board.
- For an expository or argumentative essay, you might show students conclusions that restate the most important aspect of a topic or that offer solutions for the future. Have students write their own conclusions that restate the most important parts of their subject or that outline some possible solutions to the problem.
Guiding Students Through the Writing Process

- Try giving students a sample timeline for how to work on their essays. For example, they might start brainstorming a topic, gathering sources (if required), and taking notes 4 weeks before the paper is due.
- Then, students might begin drafting 2 weeks before the paper is due with a goal of having a full draft 1 week before the essay's due date.
- Students could then plan to start revising their drafts 5 days before the essay is due. This will provide students with ample time to read through their papers a few times and make changes as needed.

- Freewriting, which is when you write freely about anything that comes to mind for a set amount of time, such as 10, 15, or 20 minutes.
- Clustering, which is when you write your topic or topic idea on a piece of paper and then use lines to connect that idea to others.
- Listing, which is when you make a list of any and all ideas related to a topic and ten read through it to find helpful information for your paper.
- Questioning, such as by answering the who, what, when, where, why, and how of their topic.
- Defining terms, such as identifying all of the key terms related to their topic and writing out definitions for each one.

- For example, if your students are writing narrative essays, then it might make the most sense for them to describe the events of a story chronologically.
- If students are writing expository or argumentative essays, then they might need to start by answering the most important questions about their topic and providing background information.
- For a descriptive essay, students might use spatial reasoning to describe something from top to bottom, or organize the descriptive paragraphs into categories for each of the 5 senses, such as sight, sound, smell, taste, and feel.

- For example, if you have just gone over different types of brainstorming strategies, you might ask students to choose 1 that they like and spend 10 minutes developing ideas for their essay.

- Try having students post a weekly response to a writing prompt or question that you assign.
- You may also want to create a separate discussion board where students can post ideas about their essay and get feedback from you and their classmates.

- You could also assign specific parts of the writing process as homework, such as requiring students to hand in a first draft as a homework assignment.

- For example, you might suggest reading the paper backward 1 sentence at a time or reading the paper out loud as a way to identify issues with organization and to weed out minor errors. [21] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
- Try peer-review workshops that ask students to review each others' work. Students can work in pairs or groups during the workshop. Provide them with a worksheet, graphic organizer, or copy of the assignment rubric to guide their peer-review.
Tip : Emphasize the importance of giving yourself at least a few hours away from the essay before you revise it. If possible, it is even better to wait a few days. After this time passes, it is often easier to spot errors and work out better ways of describing things.
Community Q&A
- Students often need to write essays as part of college applications, for assignments in other courses, and when applying for scholarships. Remind your students of all the ways that improving their essay writing skills can benefit them. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/index.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/narrative_essays.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/expository_essays.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/descriptive_essays.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/argumentative_essays.html
- ↑ https://wac.colostate.edu/jbw/v1n2/petrie.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uww.edu/learn/restiptool/improve-student-writing
- ↑ https://twp.duke.edu/sites/twp.duke.edu/files/file-attachments/reverse-outline.original.pdf
- ↑ https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide/brainstorming.shtml
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/faculty-resources/tips-on-teaching-writing/situating-student-writers/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/faculty-resources/tips-on-teaching-writing/in-class-writing-exercises/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Oct 13, 2017
Did this article help you?

Jul 11, 2017
Jan 26, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- Utility Menu
- Writing Center
- Writing Program
- Guides to Teaching Writing
The Harvard Writing Project publishes resource guides for faculty and teaching fellows that help them integrate writing into their courses more effectively — for example, by providing ideas about effective assignment design and strategies for responding to student writing.
A list of current HWP publications for faculty and teaching fellows is provided below. Most of the publications are available for download as PDF files. If you would like to be added to the Bulletin mailing list or to receive printed copies of any of the guides listed below, email James Herron at [email protected].
HARVARD WRITING PROJECT BRIEF GUIDES TO TEACHING WRITING
OTHER HARVARD WRITING PROJECT TEACHING GUIDES
- Pedagogy Workshops
- Advice for Teaching Fellows
- HarvardWrites Instructor Toolkit
- Additional Resources for Teaching Fellows
Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
Four Strategies for Effective Writing Instruction

- Share article
(This is the first post in a two-part series.)
The new question-of-the-week is:
What is the single most effective instructional strategy you have used to teach writing?
Teaching and learning good writing can be a challenge to educators and students alike.
The topic is no stranger to this column—you can see many previous related posts at Writing Instruction .
But I don’t think any of us can get too much good instructional advice in this area.
Today, Jenny Vo, Michele Morgan, and Joy Hamm share wisdom gained from their teaching experience.
Before I turn over the column to them, though, I’d like to share my favorite tool(s).
Graphic organizers, including writing frames (which are basically more expansive sentence starters) and writing structures (which function more as guides and less as “fill-in-the-blanks”) are critical elements of my writing instruction.
You can see an example of how I incorporate them in my seven-week story-writing unit and in the adaptations I made in it for concurrent teaching.
You might also be interested in The Best Scaffolded Writing Frames For Students .
Now, to today’s guests:
‘Shared Writing’
Jenny Vo earned her B.A. in English from Rice University and her M.Ed. in educational leadership from Lamar University. She has worked with English-learners during all of her 24 years in education and is currently an ESL ISST in Katy ISD in Katy, Texas. Jenny is the president-elect of TexTESOL IV and works to advocate for all ELs:
The single most effective instructional strategy that I have used to teach writing is shared writing. Shared writing is when the teacher and students write collaboratively. In shared writing, the teacher is the primary holder of the pen, even though the process is a collaborative one. The teacher serves as the scribe, while also questioning and prompting the students.
The students engage in discussions with the teacher and their peers on what should be included in the text. Shared writing can be done with the whole class or as a small-group activity.
There are two reasons why I love using shared writing. One, it is a great opportunity for the teacher to model the structures and functions of different types of writing while also weaving in lessons on spelling, punctuation, and grammar.
It is a perfect activity to do at the beginning of the unit for a new genre. Use shared writing to introduce the students to the purpose of the genre. Model the writing process from beginning to end, taking the students from idea generation to planning to drafting to revising to publishing. As you are writing, make sure you refrain from making errors, as you want your finished product to serve as a high-quality model for the students to refer back to as they write independently.
Another reason why I love using shared writing is that it connects the writing process with oral language. As the students co-construct the writing piece with the teacher, they are orally expressing their ideas and listening to the ideas of their classmates. It gives them the opportunity to practice rehearsing what they are going to say before it is written down on paper. Shared writing gives the teacher many opportunities to encourage their quieter or more reluctant students to engage in the discussion with the types of questions the teacher asks.
Writing well is a skill that is developed over time with much practice. Shared writing allows students to engage in the writing process while observing the construction of a high-quality sample. It is a very effective instructional strategy used to teach writing.

‘Four Square’
Michele Morgan has been writing IEPs and behavior plans to help students be more successful for 17 years. She is a national-board-certified teacher, Utah Teacher Fellow with Hope Street Group, and a special education elementary new-teacher specialist with the Granite school district. Follow her @MicheleTMorgan1:
For many students, writing is the most dreaded part of the school day. Writing involves many complex processes that students have to engage in before they produce a product—they must determine what they will write about, they must organize their thoughts into a logical sequence, and they must do the actual writing, whether on a computer or by hand. Still they are not done—they must edit their writing and revise mistakes. With all of that, it’s no wonder that students struggle with writing assignments.
In my years working with elementary special education students, I have found that writing is the most difficult subject to teach. Not only do my students struggle with the writing process, but they often have the added difficulties of not knowing how to spell words and not understanding how to use punctuation correctly. That is why the single most effective strategy I use when teaching writing is the Four Square graphic organizer.
The Four Square instructional strategy was developed in 1999 by Judith S. Gould and Evan Jay Gould. When I first started teaching, a colleague allowed me to borrow the Goulds’ book about using the Four Square method, and I have used it ever since. The Four Square is a graphic organizer that students can make themselves when given a blank sheet of paper. They fold it into four squares and draw a box in the middle of the page. The genius of this instructional strategy is that it can be used by any student, in any grade level, for any writing assignment. These are some of the ways I have used this strategy successfully with my students:
* Writing sentences: Students can write the topic for the sentence in the middle box, and in each square, they can draw pictures of details they want to add to their writing.
* Writing paragraphs: Students write the topic sentence in the middle box. They write a sentence containing a supporting detail in three of the squares and they write a concluding sentence in the last square.
* Writing short essays: Students write what information goes in the topic paragraph in the middle box, then list details to include in supporting paragraphs in the squares.
When I gave students writing assignments, the first thing I had them do was create a Four Square. We did this so often that it became automatic. After filling in the Four Square, they wrote rough drafts by copying their work off of the graphic organizer and into the correct format, either on lined paper or in a Word document. This worked for all of my special education students!
I was able to modify tasks using the Four Square so that all of my students could participate, regardless of their disabilities. Even if they did not know what to write about, they knew how to start the assignment (which is often the hardest part of getting it done!) and they grew to be more confident in their writing abilities.
In addition, when it was time to take the high-stakes state writing tests at the end of the year, this was a strategy my students could use to help them do well on the tests. I was able to give them a sheet of blank paper, and they knew what to do with it. I have used many different curriculum materials and programs to teach writing in the last 16 years, but the Four Square is the one strategy that I have used with every writing assignment, no matter the grade level, because it is so effective.

‘Swift Structures’
Joy Hamm has taught 11 years in a variety of English-language settings, ranging from kindergarten to adult learners. The last few years working with middle and high school Newcomers and completing her M.Ed in TESOL have fostered stronger advocacy in her district and beyond:
A majority of secondary content assessments include open-ended essay questions. Many students falter (not just ELs) because they are unaware of how to quickly organize their thoughts into a cohesive argument. In fact, the WIDA CAN DO Descriptors list level 5 writing proficiency as “organizing details logically and cohesively.” Thus, the most effective cross-curricular secondary writing strategy I use with my intermediate LTELs (long-term English-learners) is what I call “Swift Structures.” This term simply means reading a prompt across any content area and quickly jotting down an outline to organize a strong response.
To implement Swift Structures, begin by displaying a prompt and modeling how to swiftly create a bubble map or outline beginning with a thesis/opinion, then connecting the three main topics, which are each supported by at least three details. Emphasize this is NOT the time for complete sentences, just bulleted words or phrases.
Once the outline is completed, show your ELs how easy it is to plug in transitions, expand the bullets into detailed sentences, and add a brief introduction and conclusion. After modeling and guided practice, set a 5-10 minute timer and have students practice independently. Swift Structures is one of my weekly bell ringers, so students build confidence and skill over time. It is best to start with easy prompts where students have preformed opinions and knowledge in order to focus their attention on the thesis-topics-supporting-details outline, not struggling with the rigor of a content prompt.
Here is one easy prompt example: “Should students be allowed to use their cellphones in class?”
Swift Structure outline:
Thesis - Students should be allowed to use cellphones because (1) higher engagement (2) learning tools/apps (3) gain 21st-century skills
Topic 1. Cellphones create higher engagement in students...
Details A. interactive (Flipgrid, Kahoot)
B. less tempted by distractions
C. teaches responsibility
Topic 2. Furthermore,...access to learning tools...
A. Google Translate description
B. language practice (Duolingo)
C. content tutorials (Kahn Academy)
Topic 3. In addition,...practice 21st-century skills…
Details A. prep for workforce
B. access to information
C. time-management support
This bare-bones outline is like the frame of a house. Get the structure right, and it’s easier to fill in the interior decorating (style, grammar), roof (introduction) and driveway (conclusion). Without the frame, the roof and walls will fall apart, and the reader is left confused by circuitous rubble.
Once LTELs have mastered creating simple Swift Structures in less than 10 minutes, it is time to introduce complex questions similar to prompts found on content assessments or essays. Students need to gain assurance that they can quickly and logically explain and justify their opinions on multiple content essays without freezing under pressure.

Thanks to Jenny, Michele, and Joy for their contributions!
Please feel free to leave a comment with your reactions to the topic or directly to anything that has been said in this post.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email (The RSS feed for this blog, and for all Ed Week articles, has been changed by the new redesign—new ones are not yet available). And if you missed any of the highlights from the first nine years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below.
- This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
- Race & Racism in Schools
- School Closures & the Coronavirus Crisis
- Classroom-Management Advice
- Best Ways to Begin the School Year
- Best Ways to End the School Year
- Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
- Implementing the Common Core
- Facing Gender Challenges in Education
- Teaching Social Studies
- Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
- Using Tech in the Classroom
- Student Voices
- Parent Engagement in Schools
- Teaching English-Language Learners
- Reading Instruction
- Writing Instruction
- Education Policy Issues
- Differentiating Instruction
- Math Instruction
- Science Instruction
- Advice for New Teachers
- Author Interviews
- Entering the Teaching Profession
- The Inclusive Classroom
- Learning & the Brain
- Administrator Leadership
- Teacher Leadership
- Relationships in Schools
- Professional Development
- Instructional Strategies
- Best of Classroom Q&A
- Professional Collaboration
- Classroom Organization
- Mistakes in Education
- Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In


- All topics A-Z
- Grammar
- Vocabulary
- Speaking
- Reading
- Listening
- Writing
- Pronunciation
- Virtual Classroom
- Worksheets by season
- 600 Creative Writing Prompts
- Warmers, fillers & ice-breakers
- Coloring pages to print
- Flashcards
- Classroom management worksheets
- Emergency worksheets
- Revision worksheets
- Resources we recommend
- Copyright 2007-2021 пїЅ
- Submit a worksheet
- Mobile version
How To Teach Argumentative Essay Writing

Teaching argumentative essay writing can be a real challenge. In addition to teaching writing, you’re also teaching skills like research and refutation. Luckily, this post includes the tips you need for effectively teaching argumentative essay writing.
I have great news for any of you gearing up to teach argumentative essay writing. Those students of yours love to argue. (Don’t believe me? Just ask their parents!) Students love to stand up for their opinion, proving their view is correct. The challenge, then, is getting them to look at the whole picture, find supporting evidence and understand the opposing viewpoints. Only then can they craft an argument that is both factually strong and persuasive. Overall, it’s about moving them beyond the blinders of their opinions and taking a more sound evidence-based approach.
Teaching argumentative essay writing doesn’t have to be such a painful experience for both you and your students. Follow the steps and strategies below to learn how to approach the dreaded argumentative essay more easily.
The Challenge with Teaching Argumentative Essay Writing
Why is teaching argumentative essay writing so difficult, you ask? I’ve been there. The truth is, when teaching argumentative essay writing, you’re teaching more than writing . You’re also teaching research skills and encouraging critical thought and analysis. You also need to explain how to evaluate sources and evidence and the difference between fact and opinion. In many ways, you’re teaching tolerance and perspective. (The list goes on.)
Long story short, it makes sense that it’s a challenge. The key is to not rush into it. Take it step-by-step, building upon what students already know.
Moving Beyond Persuasion
The good news? Many of your students have a foundational knowledge of persuasive writing that you can use as a springboard for teaching argumentative essay writing. However, it’s important to note that, while many use the terms interchangeably, they’re not quite the same. The main difference? Factual evidence. Your students might be used to persuasive writing, meaning writing to convince the reader of a claim rooted in their personal opinion . While it’s likely that students will argue something they are in favor of, argumentative essay writing involves using claims supported by factual evidence. Additionally, a hallmark of the argumentative essay is addressing the opposing viewpoint, a step that many students are unfamiliar with– and find rather challenging.
Consider the following steps as you move from persuasion to argumentative essay writing:
Step 1: Start with Casual Augmentation
Engage your students in a low-stakes debate before formally teaching argumentative essay writing. This approach will help get students in the right mindset as you begin to lay the foundation for effective argumentation. Don’t even mention the word essay at this point. Keep it fun and casual to break the ice.
There are many ways to approach casual argumentation in class. You can begin with an anticipation guide of controversial yet appropriate statements. After students fill it out, foster a group discussion in which students share their thoughts regarding each statement. Encourage them to move beyond simple opinions by asking why to get them to dig deeper as they support their stance.
To get your students up and moving, consider playing a game like Four Corners to get them to take a stance on a topic. Regardless of which activity you choose, spend time discussing the students’ stances. Small debates are likely to unfold right then and there.
Step 2: Add In Evidence, But Still Keep It Casual
You’ve causally engaged students in basic argumentation. However, before moving into a full-blown argumentative essay, dip students’ toes into the world of supporting evidence. Use the same activity above or write a simple yet controversial topic on the board for them to take a stance on. This time, give students a chance to gather supporting evidence. It might be worth quickly reviewing what makes a sound piece of evidence (research, studies, statistics, expert quotes, etc.). Then, once they pick their stance, allow five to ten minutes to gather the best piece of supportive evidence they can find. After, give them another five to ten minutes to work with the others in their corner/on their side to determine the strongest two or three pieces of evidence to share with the class. Once each team does this, have them take turns sharing their stance and supporting evidence. I like to leave room at the end for “final words” where they can respond to a point made by the other side.
During this simple activity, begin to unpack the importance of solid and relevant supporting evidence.
Step 3: Bring in the Opposing Viewpoints
Don’t stop there. One of the most challenging aspects of argumentative writing for students to grasp is acknowledging and responding to the opposition. They are often blinded by their experiences, perspectives, and opinions that they neglect the opposing side altogether.
Here’s what you can do: Repeat either activity above with a slight twist. Once students pick their side, switch it up. Instead of supporting the side they chose, ask them to research the other side and find the best supporting evidence to bring back to the class. Therefore, students will engage in a casual debate, supporting an opposing viewpoint. (For a simpler, more independent version of this, write a controversial statement on the board, have students take a stance, and then find evidence for the opposing side, putting it all into a written response.) While many students might complain at first, you’d be surprised how quickly they get into the task. Activities like these lay the groundwork for making evidence-based claims. Additionally, students will begin to recognize the role of perspective in argumentation.
Step 4: Introduce the Argumentative Essay
Now it’s time to introduce the argumentative essay. Many students will be tempted to jump right into writing. Therefore, make it clear that argumentative essay writing involves deeply investigating a topic before writing.
Next, explain how argumentative writing aims to take a stance on a topic and back it up with substantial supporting evidence. Additionally, include how argumentative essay writing requires acknowledging the opposing viewpoint. As for persuasion, explain that it must work in coordination with collected evidence rather than being rooted solely in one’s opinion.
When introducing the argumentative essay, it helps to outline the essay structure, showing students where it is both similar and different from the essays they are used to:
- Begin with an introductory paragraph. This is where the students will hook their readers and provide a summary of the issue, any relative background information, and a well-defined claim. (This is a great place to explain that claim is another word for a thesis statement used in argumentative writing.)
- Then comes the logically organized body paragraphs, each unpacking evidential support of the claim. While students are used to using body paragraphs to support their claim, remind them one body paragraph must reference and refute the opposing side.
- Finally comes the conclusion. Students are no strangers to writing conclusions. However, they should be moving beyond simply restating the thesis at the secondary level. Guide them through readdressing it in a way that acknowledges the presented evidence and leaves the author with something to think about.
Students will likely recognize the similarity between this and the traditional five-paragraph essay. Therefore, focus your teaching on the newer elements thrown into the mix that truly make it an argumentative essay.
Teacher Tip.
Incorporate various mentor texts to help students grasp the elements of argumentative essay writing. There are tons you can pull offline written by students and experts alike. ( The New York Times Learning Network has some great mentor text resources!) The more interesting your students find the subject matter, the better. Controversial topics always stir up an engaging conversation as well.
Teaching the Argumentative Essay Writing Process
Remember, students can quickly fall into old habits, neglecting some of the most imperative aspects of argumentative writing. Take it slow, walking students through the following steps – trust me, you’ll be thankful you did when it comes time to read a pile of these essays:
- Choose a topic. I recommend providing a list of argumentative essay writing topics for students to choose from. This prevents students’ classic “I can’t think of anything” roadblock. However, encourage students to choose a topic they are interested in or feel passionate about. With that said, I always give the option of letting students convince me (ha!) to let them use a topic they came up with if not on the list.
- Start the research. This is where students begin gathering evidence and is an opportunity to review what constitutes strong evidence in the first place.
- Understand the opposing side: Students are always confused about why I have them start here. One reason? It’s more challenging for students to see the other side, so this gets it out of the way first. Another? Some students never took the time to understand the other side, and in some cases, they switch their stance before writing their argument. It’s better to do so now than after you’ve done all your research and drafting. Lastly, I explain how understanding the opposing side can help guide your research for your side.
- Make a claim. While students may have an idea of their claim, the strongest claims are driven by evidence . Therefore, remind students that a claim is a statement that can be supported with evidence and reasoning and debated. Playing a quick game of two truths and an opinion (a spin on two truths and a lie) can reinforce the notion of facts vs. opinions.
- Write the body paragraphs. Each body paragraph should focus on supporting the claim with specific evidence. However, don’t forget to rebut the opposition! While they find it challenging, students learn to love this part. (After all, they love being right.) However, their instinct tends to be just to prove the other side wrong without using evidence as to why.
- Round out the intro and the conclusion, put it all together, and voila! An argumentative essay is born.
More Tips for Teaching Argumentative Essay Writing
- Begin with what they know: Build on the well-known five-paragraph essay model. Start with something students know. Many are already familiar with the classic five-paragraph essay, right? Use that as a reference point, noting out where they will add new elements, such as opposing viewpoints and rebuttal.
- Use mentor texts: Mentor texts help give students a frame of reference when learning a new genre of writing. However, don’t stop at reading the texts. Instead, have students analyze them, looking for elements such as the authors’ claims, types of evidence, and mentions of the opposing side. Additionally, encourage students to discuss where the author made the most substantial arguments and why.
- In [ARTICLE NAME/STUDY], the author states…
- According to…,
- This shows/illustrates/explains…
- This means/confirms/suggests…
- Opponents of this idea claim/maintain that… however…
- Those who disagree/are against these ideas may say/ assert that… yet…
- On the other hand…
- This is not to say that…
- Provide clear guidelines: I love using rubrics, graphic organizers, and checklists to help students stay on track throughout the argumentative essay writing process. Use these structured resources to help them stay on track every step of the way– and makes grading much easier for you .
The bottom line? Teaching argumentative essay writing is a skill that transcends the walls of our classrooms. The art of making and supporting a sound, evidence-based argument is a real-life skill. If our goal as teachers is to prepare students to be skilled, active, and engaged citizens of the 21st century, effectively teaching argumentative essay writing is a must. So, what are you waiting for? Teach those kids how to argue the write way.
1 thought on “How To Teach Argumentative Essay Writing”
This is very helpful. I am preparing to teach my student how to write an argumentative essay. This help me know that I am on the right path and to change how I organize some things in a different way. I really like how you recommended they pick out the elements of the writing. This will help them focus on the parts they dislike doing the most. Thanks for the writing.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Search form
- About Faculty Development and Support
- Programs and Funding Opportunities
Consultations, Observations, and Services
- Strategic Resources & Digital Publications
- Canvas @ Yale Support
- Learning Environments @ Yale
- Teaching Workshops
- Teaching Consultations and Classroom Observations
- Teaching Programs
- Spring Teaching Forum
- Written and Oral Communication Workshops and Panels
- Writing Resources & Tutorials
- About the Graduate Writing Laboratory
- Writing and Public Speaking Consultations
- Writing Workshops and Panels
- Writing Peer-Review Groups
- Writing Retreats and All Writes
- Online Writing Resources for Graduate Students
- About Teaching Development for Graduate and Professional School Students
- Teaching Programs and Grants
- Teaching Forums
- Resources for Graduate Student Teachers
- About Undergraduate Writing and Tutoring
- Academic Strategies Program
- The Writing Center
- STEM Tutoring & Programs
- Humanities & Social Sciences
- Center for Language Study
- Online Course Catalog
- Antiracist Pedagogy
- NECQL 2019: NorthEast Consortium for Quantitative Literacy XXII Meeting
- STEMinar Series
- Teaching in Context: Troubling Times
- Helmsley Postdoctoral Teaching Scholars
- Pedagogical Partners
- Instructional Materials
- Evaluation & Research
- STEM Education Job Opportunities
- Yale Connect
- Online Education Legal Statements
You are here
Teaching students to write good papers.
This module is designed to help you teach students to write good papers. You will find useful examples of activities that guide students through the writing process. This resource will be helpful for anyone working with students on research papers, book reviews, and other analytical essays. The Center for Teaching and Learning also has comprehensive writing resources featuring general writing tips, citation guidelines, model papers, and ways to get more help at Yale.
There are several steps TFs and faculty can take to prepare students to write good papers. If you are responsible for making writing assignments, remember that most students need to practice the basic elements of writing — purpose, argument, evidence, style — and that these skills are best practiced in shorter, focused assignments. Opt for shorter essays and papers throughout the semester in lieu of long, end-of-semester research papers. Build opportunities for revision and refinement into your assignments and lesson plans.
For each assignment, there are steps you can take to help students produce better writing . First, use strategies for making sure students understand the assignment. Use individual meetings, short, in-class writing exercises or small-group activities to make sure students can articulate what their paper will accomplish (describe, compare/contrast, explain, argue) and to what standard.
Second, guide students in selecting and analyzing primary and secondary source material. Use in-class activities to teach students: the difference between types of sources and their uses; strategies for evaluating a source and its value in a given argument; and examples of how to incorporate source material into an argument or other text with proper citation .
Finally, teach them to construct strong thesis statements and support their arguments with evidence. Use model documents to introduce students to strong, arguable statements. Give students practice developing statements from scratch and refining statements that lack importance or clarity . Ask students to analyze the relationship between thesis statements and supporting evidence in short essays. Teach them to use the active voice .
Students who have never gone through a thorough revision process are used to handing in and receiving poor grades on first drafts. These students will lack confidence in their ability to produce good writing. Do all you can to let your students experience good writing through revision. Require drafts of papers, or parts of papers, so students can learn to apply the standards of good writing to make their papers better. Have students read and comment on each other’s papers to give them practice reading for clarity, style, persuasiveness, etc.
By focusing on the process of writing, not just the product, you will help students write better papers and gain confidence along the way.
For those of you who work with teaching fellows, we also include an agenda for teaching these skills to others and a workshop evaluation form .
Downloads
YOU MAY BE INTERESTED IN

Reserve a Room
The Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning partners with departments and groups on-campus throughout the year to share its space. Please review the reservation form and submit a request.

Writing Consultations
For graduate students looking for expert advice on planning, drafting, and revising their research paper, dissertation, presentation, or any other writing project.

The Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning routinely supports members of the Yale community with individual instructional consultations and classroom observations.
- How to Teach Essay Writing
Don't just throw your homeschooled-student intoformal essay crafting. Focus on sentence structure and basic paragraph composition before movingto more complicated formal essay composition.
Are you a competent essay writer? Even if you know how to write an essay , chances are you are dreading the coming years of teaching homeschool writing just as much as your novice writer could be dreading learning how to write . Writing comes naturally for very few, but most view writing as an insurmountable abstract mountain. The Write Foundation writing curriculum is a divide and conquer method of teaching writing. Focusing on small portions of writing paragraphs and later five-paragraph college level essays, eventually you and your students will be able to use all the necessary writing skills to easily compose wonderfully crafted formal essays .
Start with a good foundation
That is, of course, what The Write Foundation teaches. Don’t just throw your homeschooled-child into the middle of essay crafting. Focus on sentence structure and basic paragraph composition before moving to more complicated formal essay composition . Learn to write essays one bite at a time. This helps students develop writing skills by using writing tools which helps them gain confidence and enables parents who are insecure about their own writing skills learn with their students.
Hold their hand as much as they need you hold their hand.
An abstract assignment with limited instructions can appear quite daunting to a reluctant, struggling, or new writer; tiny decisions can become writing blocks in a new writer’s mind.
Share the experience with your homeschooler. Discuss writing blocks and ways to overcome them. Discuss the planning process and experience how it helps flesh out an essay. Walk them through each lesson making sure they complete each step successfully before attempting to move on in the writing process. Working side by side with your student also helps you become a better instructor by solidifying the lesson for yourself. As students gain confidence with their new skills they will need your help less and less so they will shoo you away as they learn writing is much easier using the complete writing process.
Use concrete assignments
Creative writing is very subjective, and it is also very abstract for a new writer. You need a writing curriculum which focuses on concrete assignments and provides a variety of writing topics that fit the type of writing being taught in that assignment. Give your students a structure to work into a paragraph using their creative information. Leaving several factors to the unknown, such as type of writing, structure, and so on, leaves more decisions that the novice writer is not ready to determine. An abstract assignment with limited instructions can appear quite daunting to a reluctant, struggling, or just new writer; tiny decisions can become writing blocks in a new writer’s mind. Even experienced writers face writer’s block. Students need to be given tools and taught skills that overcome “But, what do I write about?”
Know your audience
Let your child select from a list of possible writing topics that may be interesting to them. Your child may enjoy the experience more if he is writing about his favorite pastime instead of writing about your favorite pastime. Choosing topics about things that directly influence your child, such as different views about their favorite sport, the influence of network TV or political topics that hit close to home may open the doors for lively discussion and insight into your child’s mind.
Writing is a necessary life skill. When teaching writing remember you are not alone. If you are worried about teaching formal writing to your homeschooler, use the support system of The Write Foundation for any questions you may have through the process, and know that you are not alone. Look into a homeschool writing co-op in your area to lighten the burden and give new perspective on your child’s essay writing development. Use The Write Foundation and use a proven writing system.
Questions or Comments?
Recent articles.
- Correcting Run-on Sentences
- How Does Skipping the Writing Process Affect your Writing?
- Graduating Homeschooling
- Is My Child Ready for Formal Writing?
- Teaching Spelling
- Evaluating Homeschool Writing Curriculums
- Why Most Writing Curriculums Fail (and How to Make Sure your Homeschooler Doesn't!)
- Top Five Reasons Students Hate to Write (and How You can Help!)
- College Preparation for Homeschooled Students
H e is like a man building a house, who dug deep and laid the foundation on the rock. Luke 6:48

View, Print, and Practice the Sample Lessons
(We're here to help you teach!)
Now Available!
Free Reading Lists Get your copy today!
Have a struggling writer? Maybe he hates writing? Does your student just need to learn how to write? Long for teacher-friendly lesson plans you can quickly prepare and teach? Desire a writing curriculum your children will enjoy while learning creatively?
- Complete Lesson Plans
- Free Assessment Tests
- Free Reading Lists
- Organization for Writing
- Checklists & Guidelines
- Brainstorm & Outline Forms
Open doors to writing success!
Contact Rebecca . Rebecca Celsor will answer your questions regarding how to easily teach your child to write.
" Generally speaking, level 1 does not require your child to come up with content out of thin air or make the assumption that she has tons of ideas she can’t wait to get on paper. One example: Lesson 20 will have your child rewriting fables by taking well-known fables and changing aspects about them to make new stories. (Imitation is a worthwhile way of improving one’s own writing, by the way.) The "

- Course Selection Assistance
- Suggested Age Levels for Homeschool Writing
- Entry Level I - Prepare to Write
- Entry Level II - Creating Sentences
- Level 1 - Sentence to Paragraph
- Level 2 - Paragraph
- Level 3 - Essay
- Free Curriculum Writing Samples
- Example Teaching Videos
- Online Grading Service
- Writing Skills Reference Folder
- How to Present a Lesson
- Grading Writing
- Key Points for Grading Writing
- MindBenders®
- Order Curriculum Packages
- Order Worksheets Only
- Refund/Return Policy
- Selecting Home School Curriculum
- Writing Preparation
- Writing Development
- High School and Beyond
- Homeschool Co-ops
- Homeschool How To
- The Story Behind TWF
- Why Another Writing Curriculum?
- Copyright Information

He is like a man building a house, who dug deep and laid the foundation on the rock . Luke 6:48
Dedicated to equipping God's children with the ability to communicate His Truth to the world.
- Teaching Tools
- Curriculum Ordering
- homeschool writing curriculum
- home school writing samples
- Mind Benders®
- Online Grading
Copyright © 2021 TheWriteFoundation.org
web site design - evolvethebrand.com
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
10 Ways to Teach Argument-Writing With The New York Times

By Katherine Schulten
- Oct. 5, 2017
Updated, Feb. 2020
How can writing change people’s understanding of the world? How can it influence public opinion? How can it lead to meaningful action?
Below, we round up the best pieces we’ve published over the years about how to use the riches of The Times’s Opinion section p to teach and learn.
We’ve sorted the ideas — many of them from teachers — into two sections. The first helps students do close-readings of editorials and Op-Eds, as well as Times Op-Docs, Op-Art and editorial cartoons. The second suggests ways for students to discover their own voices on the issues they care about. We believe they, too, can “write to change the world.”
Ideas for Reading Opinion Pieces
1. Explore the role of a newspaper opinion section.
How would your students describe the differences between the news sections of a newspaper and the opinion section? What do they have in common? How do they differ? Where else in newspapers are opinions — for instance, in the form of reviews or personal essays — often published?
Bring in a few print copies of a newspaper, whether The Times or a local or school paper, and have your students work in small groups to contrast a news page with an opinion page and see what they discover.
Though this piece, “ And Now a Word From Op-Ed ,” is from 2004, it still provides a useful and quick overview of The Times’s Opinion section, even if the section then was mostly a print product. It begins this way:
Here at the Op-Ed page, there are certain questions that are as constant as the seasons. How does one get published? Who chooses the articles? Does The Times have an agenda? And, of course, why was my submission rejected? Now that I’ve been Op-Ed editor for a year, let me try to offer a few answers.
This 2013 article, “ Op-Ed and You ,” also helps both readers of the section, and potential writers for it, understand how Times Opinion works:
Anything can be an Op-Ed. We’re not only interested in policy, politics or government. We’re interested in everything, if it’s opinionated and we believe our readers will find it worth reading. We are especially interested in finding points of view that are different from those expressed in Times editorials. If you read the editorials, you know that they present a pretty consistent liberal point of view. There are lots of other ways of looking at the world, to the left and right of that position, and we are particularly interested in presenting those points of view.
After students have read one or both of these overviews, invite them to explore the Times’s Opinion section , noting what they find and raising questions as they go. You might ask:
• What pieces look most interesting to you? Why?
• What subsections are featured in the links across the top of the section (“Columnists”; “Series”; “Editorials”; “Op-Ed”; “Letters”; etc.) and what do you find in each? How do they seem to work together?
• How do you think the editors of this section decide what to publish?
• What role does this section seem to play in The Times as a whole?
• Would you ever want to write an Op-Ed or a letter to the editor? What might you write about?
If your students are confused about where and how news and opinion can sometimes bleed together, our lesson plan, News and ‘News Analysis’: Navigating Fact and Opinion in The Times , can help.
And to go even deeper, this lesson plan from 2010 focuses on a special section produced that year, “ Op-Ed at 40: Four Decades of Argument and Illustration .” It helps students understand the role the Op-Ed page has played at The Times since 1970, and links to many classic pieces.
2. Know the difference between fact and opinion.
In our lesson plan Distinguishing Between Fact and Opinion , you’ll find activities students can use with any day’s Times to practice.
For instance, you might invite them to read an Op-Ed and underline the facts and circle the opinion statements they find, then compare their work in small groups.
Or, read a news report and an opinion piece on the same topic and look for the differences. For example, which of the first paragraphs below about the shooting in Las Vegas is from a news article and which is from an opinion piece? How can they tell?
Paragraph A: After the horrific mass shooting in Las Vegas, the impulse of politicians will be to lower flags, offer moments of silence, and lead a national mourning. Yet what we need most of all isn’t mourning, but action to lower the toll of guns in America. (From “ Preventing Mass Shootings Like the Vegas Strip Attack ”) Paragraph B: A gunman on a high floor of a Las Vegas hotel rained a rapid-fire barrage on an outdoor concert festival on Sunday night, leaving at least 59 people dead, injuring 527 others, and sending thousands of terrified survivors fleeing for cover, in one of the deadliest mass shootings in American history. (From “ Multiple Weapons Found in Las Vegas Gunman’s Hotel Room ”)
3. Analyze the use of rhetorical strategies like ethos , pathos and logos.
Do your students know what ethos , pathos and logos mean? The video above, “ What Aristotle and Joshua Bell Can Teach Us About Persuasion ,” can help. We use it in this lesson plan , in which students explore the use of these rhetorical devices via the Op-Ed “ Rap Lyrics on Trial ” and more. The lesson also helps students try out their own use of rhetoric to make a persuasive argument.
In the post, we quote a New Yorker article, “The Six Things That Make Stories Go Viral Will Amaze, and Maybe Infuriate, You,” that explains the strategies in a way that students may readily understand:
In 350 B.C., Aristotle was already wondering what could make content — in his case, a speech — persuasive and memorable, so that its ideas would pass from person to person. The answer, he argued, was three principles: ethos, pathos, and logos. Content should have an ethical appeal, an emotional appeal, or a logical appeal. A rhetorician strong on all three was likely to leave behind a persuaded audience. Replace rhetorician with online content creator, and Aristotle’s insights seem entirely modern. Ethics, emotion, logic — it’s credible and worthy, it appeals to me, it makes sense. If you look at the last few links you shared on your Facebook page or Twitter stream, or the last article you e-mailed or recommended to a friend, chances are good that they’ll fit into those categories.
Take the New Yorker’s advice and invite them to choose viral content from their social networks and identify ethos , pathos and logos at work.
Or, use the handouts and ideas in our post An Argument-Writing Unit: Crafting Student Editorials , in which Kayleen Everitt, an eighth-grade English teacher, has her students take on advertising the same way.
Finally, if you’d like a recommendation for a specific Op-Ed that will richly reward student analysis of these elements, Kabby Hong, a teacher at Verona Area High School in Wisconsin, who will be our guest on our “Write to Change the World” webinar, recommends Nicholas Kristof’s column “ If Americans Love Moms, Why Do We Let Them Die? “
4. Identify claims and evidence.
The Common Core Standards put argument front and center in American education, and even young readers are now expected to be able to identify claims in opinion pieces and find the evidence to support them.
We have a number of lesson plans that can help.
First, Constructing Arguments: “Room for Debate” and the Common Core Standards , uses an Opinion feature that, though now defunct, can still be a great resource for teachers. Use the archives of Room for Debate , which featured succinct arguments on interesting topics from a number of points of view, to introduce students to perspectives on everything from complex geopolitical or theological topics to whether people are giving Too Much Information in today’s Facebook world .
We also have two comprehensive lesson plans — For the Sake of Argument: Writing Persuasively to Craft Short, Evidence-Based Editorials and I Don’t Think So: Writing Effective Counterarguments — that were written to support students in crafting their own editorials for our annual contest . In both, we first introduce readers to “mentor texts,” from The Times and elsewhere, that help them see how effective claims, evidence and counterclaims function in making a strong argument.
Finally, if you’re looking for a fun way to practice, we often hear from teachers that our What’s Going On in This Picture? feature works well. To participate, students must make a claim about what they believe is “going on” in a work of Times photojournalism stripped of its caption, then come up with evidence to support what they say.
5. Adopt a columnist.
This Is What a Refugee Looks Like
If elena, 14, is sent back to her country, she may be murdered..
VISUAL AUDIO Nick debarks plane B-roll streets of Mexico, B-roll rural Mexico, on truck, train passing Nick [VO]: We’re in Southern Mexico on the Guatemala-Mexico border, an area where you have hundreds of thousands of Central Americans, in many cases aiming to get to the US. B-roll people getting on bus Nick [VO]: These are not economic migrants. These are people who are fleeing gangs and sexual violence. Nick talking to women outside refugee agency INTV Nick B-roll Tapachula sky Nick [VO]:The homicide rates in Central America are some of the highest in the world. If you or I were there, we would be fleeing this as well. INSERT TITLE CARD Nick greeting Brenda Nick walks up steps to apartment Nick: Hola Brenda, Buenos dias. Brenda: Buenos dia, que tal? Nick [VO]: One of the people we met, Brenda, has applied for refugee status for her and for her daughters and she’s waiting. Nick meets Brenda’s children Translator: Hello. What’s your name? Kimberly: Kimberly. Nick: Kimberly, okay. Translator: She’s Kimberly. Brenda: Nestor Nick: Nestor! How are you? Inside Brenda’s apartment Nick talking to Elena Brenda: She’s Zoila Elena Nick: Elena, you are 14? Is that right? Translator: You’re 14 years old, right? Elena: Si. Nick: Kimberly… once? Elena: Doce. Nick: Doce! Translator: It’s twelve now. Nick: Okay. ElenaB-roll washing up in apartment, preparing chicken feet Her mother joins her INTV Elena on stairs Elena: My family calls me Elena. The house where I lived was in Honduras. Before, in our neighborhood, you could go out at whatever time you wanted, you could go out to play. But now these gangs arrived, the men from the 18th Street Gang, they started to establish rules. Everything was different, and that’s when our mother brought us here. Nick interviewing Elena inside house CU Brenda crying Nick: There’s special dangers for girls growing up from the maras . Did you have any girlfriends who were attacked by boys, did you worry about that happening to you? Elena: Yes I know someone. She was dating someone from the 18th Street Gang. They forced her by saying that if she didn’t join them… they would kill her whole family. So that nothing would happen to her family she had to do it. So they arranged to meet at the river. And she went to the river. She ended up getting raped. And when she left the river. she came out with a bullet in here and had to walk naked to her house. Well from then on we didn’t hear from her again. Nick: So you saw her coming from the river, naked, bleeding from a gunshot wound in the stomach? Elena: I was just like this, and I was shocked. But I couldn’t do anything because the gangsters were there and… if they would see us helping her, something could have happened to us. Nick: Did the gang members ever pay attention to you in ways that made you feel dangerous, that they might do the same thing to you? Elena: And there was one that told me that if I didn’t go out with him, he was going to kill my mom and dad. So I sent him a text message saying yes, agreeing to it. Nick: And how old were you when he wanted you to be his girlfriend? Elena: Eleven and a half years old. Translator: Eleven years. Nick: And you were able to say no to him then? Elena: No... because if I didn’t agree... he would have killed my family. Because he forced me.... even though I did not want to. So, I had to say yes... in order to protect my family. B-roll border checkpoint INTV Nick Nick [VO]: The United States and Mexico together have sent back 800,000 adults over the last 5 years, and 40,000 children to just those 3 countries of Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras. Brenda and her kids inside apartment Brenda: I think I’m moving forward, whether or not I have to go through, what I already went through. I don’t have anywhere else to go. Nick [VO]: If they’re sent back, her daughters will be perhaps killed and preyed upon by the gangs. Nick in taxi Brenda’s family in apartment Nick [VO]: What would you do if you were Elena? Stay in Honduras and be forced into a relationship with a gang member? I doubt it. Elena in apartment with family INTV Elena Elena: And now we are moving from one place to another, and people think we are less important because we are immigrants. But they don’t know what we are running from.

We have heard from many teachers over the years that a favorite assignment is to have students each “adopt” a different newspaper columnist, and follow him or her over weeks or months, noting the issues they focus on and the rhetorical strategies they use to make their cases. Throughout, students can compare what they find — and, of course, apply what they learn to their own writing.
One teacher, Charles Costello, wrote up the details of his yearlong “Follow a Columnist” project for us. If you would like to try it with The Times, here are the current Op-Ed columnists:
Charles M. Blow
Jamelle Bouie
David Brooks
Frank Bruni
Roger Cohen
Gail Collins
Ross Douthat
Maureen Dowd
Thomas L. Friedman
Michelle Goldberg
Nicholas Kristof
Paul Krugman
David Leonhardt
Farhad Manjoo
Jennifer Senior
Bret Stephens
6. Explore visual argument-making via Times Op-Art, editorial cartoons and Op-Docs.
The New York Times regularly commissions artists and cartoonists to create work to accompany Opinion pieces. How do illustrations like the one above add meaning to a text, while grabbing readers’ attention at the same time? What can students infer about the argument being made in an Op-Ed article by looking at the illustration alone?
In this lesson plan , students investigate how art works together with text to emphasize a point of view. They then create their own original illustrations to go with a Times editorial, Op-Ed article or letter to the editor. We also suggest that they can illustrate an Opinion piece or letter to the editor that does not have an illustration associated with it.
Recently, Clara Lieu, a teacher at the Rhode Island School of Design, told us how she uses that very idea to help her student-artists to create their own pieces. To see some of their work, check out “ Finding Artistic Inspiration in The New York Times’s Opinion Section .”
If your students would like to go further and create their own editorial cartoons, we offer an annual student contest . Invite your students to check out the work of this year’s winners for inspiration. We also have a lesson plan, Drawing for Change: Analyzing and Making Political Cartoons , to go with it.
Another way to use visual journalism to teach argument-making? Use Op-Docs , The Times’s short documentary series (most under 15 minutes), that touches on issues like race and gender identity, technology and society, civil rights, criminal justice, ethics, and artistic and scientific exploration — issues that both matter to teenagers and complement classroom content.
Every Friday during the school year, we host a Film Club in which we select short Op-Docs we think will inspire powerful conversations — and then invite teenagers and teachers from around the world to have those conversations here, on our site.
And for a great classroom example of how this might work in practice, check out Using an Op-Doc Video to Teach Argumentative Writing , a Reader Idea from Allison Marchetti, an English teacher at Trinity Episcopal School in Richmond, Va. She details how her students analyzed the seven-minute film “China’s Web Junkies” to see how the filmmakers used evidence to support an argument, including expert testimony, facts, interview, imagery, statistics and anecdotes.
Ideas for Writing Opinion Pieces
7. Use our student writing prompts to practice making arguments for a real audience.
Does Technology Make Us More Alone?
Is It Ethical to Eat Meat?
Is It O.K. for Men and Boys to Comment on Women and Girls on the Street?
Are Some Youth Sports Too Intense?
Does Reality TV Promote Dangerous Stereotypes?
When Do You Become an Adult?
Is America Headed in the Right Direction?
Every day during the school year we invite teenagers to share their opinions about questions like these, and hundreds do, posting arguments, reflections and anecdotes to our Student Opinion feature. We have also curated a list drawn from this feature of 401 Prompts for Argumentative Writing on an array of topics like technology, politics, sports, education, health, parenting, science and pop culture.
Teachers tell us they use our writing prompts because they offer an opportunity for students to write for an “authentic audience.” But we also consider our daily questions to be a chance for the kind of “low-stakes” writing that can help students practice thinking through thorny questions informally.
We also call out our favorite comments weekly via our Current Events Conversation feature. Will your students’ posts be next?
8. Participate in our annual Student Editorial Contest.
What issues matter most to your students?
Every year, we invite teenagers to channel their passions into formal pieces : short, evidence-based persuasive essays like the editorials The New York Times publishes every day.
The challenge is pretty straightforward. Choose a topic you care about, gather evidence from sources both within and outside of The New York Times, and write a concise editorial (450 words or less) to convince readers of your point of view.
Our judges use this rubric (PDF) for selecting winners to publish on The Learning Network.
And at a time when breaking out of one’s “filter bubble” is more important than ever, we hope this contest also encourages students to broaden their news diets by using multiple sources, ideally ones that offer a range of perspectives on their chosen issue.
This school year, as you can see from our 2019-20 Student Contest Calendar , the challenge will run from Feb. 13 to March 31, 2020. You can find the submission form and all the details here .
To help guide this contest, we have published two additional ideas from teachers:
• In “ A New Research and Argument-Writing Approach Helps Students Break Out of the Echo Chamber, ” Jacqueline Hesse and Christine McCartney describe methods for helping students examine multiple viewpoints and make thoughtful, nuanced claims about a range of hot-button issues.
• In “ Helping Students Discover and Write About the Issues that Matter to Them ,” Beth Pandolpho describes how she takes her students through the process of finding a topic for our annual Student Editorial Contest, then writing, revising and submitting their final drafts.
9. Take advice from writers and editors at the Times’s Opinion section.

How can you write a powerful Op-Ed or editorial?
Well, over the years, many Times editors and writers have given the aspiring opiners advice. In the video above, for instance, Andrew Rosenthal, in his previous role as Editorial Page editor, detailed seven pointers for the students who participate in our annual Editorial Contest.
In 2017 Times Op-Ed columnist Bret Stephens wrote his own Tips for Aspiring Op-Ed Writers .
And on our 2017 webinar , Op-Ed columnist Nicholas Kristof suggested his own ten ideas. (Scroll down to see what they are, as well as to find related Op-Ed columns.)
Finally, if you’d like to get a letter to the editor published, here is what Tom Feyer, the longtime head of that section, recommends. Until Feb. 16, 2020, that section is offering a special letter-writing challenge for high school students . Submit a letter to the editor in response to a recent news article, editorial, column or Op-Ed essay, and they will pick a selection of the best entries and publish them.
10. Use the published work of young people as mentor texts.
In 2017, five students of Kabby Hong, the teacher who joined us for our Oct. 10 webinar, were either winners, runners-up or honorable mentions in our Student Editorial Contest.
How did he do it? First, he helps his students brainstorm by asking them the questions on this sheet . (The first page shows his own sample answers since he models them for his students.)
Then, he uses the work of previous student winners alongside famous pieces like “ Letter from Birmingham Jail ” to show his class what effective persuasive writing looks like. Here is a PDF of the handout Mr. Hong gave out last year, which he calls “Layering in Brushstrokes,” and which analyzes aspects of each of these winning essays:
•“ In Three and a Half Hours, an Alarm Will Go Off ”
•“ Redefining Ladylike ”
•“ Why I, a Heterosexual Teenage Boy, Want to See More Men in Speedos ”
Another great source of published opinion writing by young people? The Times series “ On Campus .” Though it is now discontinued, you can stil read essays by college students on everything from “ The Looming Uncertainty for Dreamers Like Me ” to “ Dropping Out of College Into Life .”
Update: Links from Our 2017 Webinar
On our 2017 webinar (still available on-demand), Nicholas Kristof talked teachers through ten ways anyone can make their persuasive writing stronger. Here is a list of his tips, along with the columns that relate to each — though you’ll need to watch the full webinar to hear the stories and examples that illustrate them.
Nicholas Kristof’s Ten Tips for Writing Op-Eds
1. Start out with a very clear idea in your own mind about the point you want to make.
Related: Preventing Mass Shootings Like the Vegas Strip Attack
2. Don’t choose a topic, choose an argument.
Related: On Death Row, but Is He Innocent?
3. Start with a bang.
Related: If Americans Love Moms, Why Do We Let Them Die?
4. Personal stories are often very powerful to make a point.
Related: This is What a Refugee Looks Like
5. If the platform allows it, use photos or video or music or whatever.
Related: The Photos the U.S. and Saudi Arabia Don’t Want You to See
6. Don’t feel the need to be formal and stodgy.
Related: Meet the World’s Leaders, in Hypocrisy
7. Acknowledge shortcomings in your arguments if the readers are likely to be aware of them, and address them openly.
Related: A Solution When a Nation’s Schools Fail
8. It’s often useful to cite an example of what you’re criticizing, or quote from an antagonist, because it clarifies what you’re against.
Related: Anne Frank Today Is a Syrian Girl
9. If you’re really trying to persuade people who are on the fence, remember that their way of thinking may not be yours.
Related: We Don’t Deny Harvey, So Why Deny Climate Change?
10. When your work is published, spread the word through social media or emails or any other avenue you can think of.
Related: You can find Nicholas Kristof on Twitter , Facebook , Instagram , his Times blog , and via his free newsletter .
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
- Headphones for Schools
- Customer cases
- Become a reseller
Language education , Tips for Language Teachers
How to teach essay writing skills.
More about us

Learning any new language is a challenging task. Whether that’s quickly coming up with an answer during a conversation or reading through some text to extract key information, the journey to second language fluency takes time and hard work. This is particularly true when it comes to writing lengthy pieces of text or essays – it’s a massive leap up from translating or writing short sentences.
This skill is particularly important for university students or adult language learners, who are usually trying to develop professional writing skills for international business roles or academic studies. Yet the ability to construct compelling written text is a key, albeit difficult, skill to acquire. This blog post outlines six tips for language teachers to use to help and support their students to write clearer and better structured essays.
6 tips to build your students’ essay writing skills
1. Get the basics right
It is clearly unrealistic to expect students to suddenly be able to write an essay in the target language without support. Build up their confidence over time so that they become familiar with writing increasingly long pieces of text. A key part of this will be to ensure that they understand sentence connectors and know how to write simple, compound and complex sentences – these are the foundations on which more advanced skills can then be developed.
2. Don’t jump straight in
Even in a timed exam situation, it is vital that students take the time to plan their writing and to work out the key points that they wish to communicate. This is also an opportunity for them to identify specific vocabulary or phrases that they might want to include.
Depending on their ability, some of this work can be scaffolded by the teacher to support and encourage progress. Perhaps your students could begin by following an essay structure / word bank you’ve provided or working through a set of questions you’ve prepared? They could then progress to working collaboratively in pairs or groups before tackling a long writing task on their own.
Mind mapping can also be a useful tool to help students organise their ideas and articulate their thoughts before putting pen to paper. It also helps provide a clear reference point for students to revisit whilst writing to ensure that they are still answering the question set!
3. Follow a structure
For most students being asked to write a 1,000 word essay will, at first, feel like a huge ask. So help them to make it feel less of a challenge by breaking it down into manageable chunks. The 5-paragraph essay structure is widely used for second language writers and provides a clear road-map for students to follow.
- Paragraph 1: This is meant to grab the reader’s attention, give them a clear idea of what’s to come and generally sets the tone for the rest of the piece.
- Paragraphs 2 to 4 form the core of the essay’s content. These make specific points that are then backed up by a variety of evidence.
- Paragraph 5 delivers the conclusion, pulling together all of the arguments along with a summary of the key points.
Students may also find the acronym P.E.E useful when writing paragraphs 2 to 4. This stands for Point, Explanation and Evidence. Paragraphs should contain clear points or arguments that support (or reject) the overall theme. This is then followed by a brief explanation and relevant evidence to reinforce the point.
Focusing on these structures can be a big help in building students’ confidence. Their attention can be focused on getting the content and language correct rather than worrying about the essay structure.
4. Share examples of great writing
When writing in their target language it can be very difficult for students to imagine or know what good writing actually looks and sounds like. So share examples with them – from books, the internet or magazines on topics that will engage and interest them.
Whilst it’s important to read them and pick up new words / phrases to include, your students may also find it useful to carefully dissect the examples in detail. Help them to identify what makes a piece of writing entertaining or persuasive and help them build the skills to try it themselves (either individually or as a group)
5. Practice, Practice, Practice
Of course, the very best way to do this is to practice. Writing more often remains the most effective way for students to improve their writing skills. Of course, some of these tasks should be done as homework, but setting small writing tasks in class reduces grade pressure and ensures that educators are on hand to answer any questions and provide constructive feedback.
Pairing students to write practice essays can also be highly effective, particularly when students of mixed ability come together. The weaker student learns from their peers and the stronger student reinforces their understanding by explaining it to their classmate.
It’s also important that educators make the time to review the outputs from writing tasks with students. Highlight the areas where students did well, show them where improvement can be made and get them to look again at grammar / words that they frequently get wrong. This process is vital – it inspires their confidence and encourages students to keep writing and to keep trying to get better.
6. More than words
Every educator will have their own view on the accuracy vs. fluency debate and how they judge the quality of written work students produce will be based on that . Of course, it’s important that students pay attention to using correct grammar, spelling etc, but it’s also vital that the aim of the piece of writing is achieved. More specifically, does it convince? Does it persuade? Does it encourage me to change my behaviour or think again about a topic?
It’s imperative therefore for educators strive to create and deliver writing lessons that cover the core writing skills but which also encourage students to expand their creativity and critical thinking. Helping students to understand the importance of how to plan and structure an argument is also, of course, valuable beyond just language learning. Ultimately these tips aim to help you ensure that students find writing a more fulfilling experience.
How can Sanako help you to teach essay writing skills?
Tools like Sanako Connect can make a big difference in helping students practice and improve their writing skills. It has been specifically designed to help language educators to do this in asynchronous or asynchronous settings. It enables teachers to easily set students tasks that test their writing skills. Connect’s flexibility also allows teachers to upload stimulus material to which students can respond with detailed written answers of any length.
Whatever approach you use to improve your students’ writing skills, Sanako’s market-leading tools include a wealth of unique features that help language educators teach languages more efficiently and more successfully. It’s why the world’s leading educational institutions choose Sanako as their preferred supplier to support online and in-person lesson delivery.
If you are interested in learning more about how Sanako products support language teachers and students and would like to see how they could benefit your institution, book a FREE remote demo now to see them in action.
Block "feature-request-pop-up" not found
Become a partner
MAKE WAVES WITH THIS FREE WEEKLONG VOCABULARY UNIT!

10 Steps to Teach Persuasive Writing

Kids are natural-born persuaders. They do it all the time. The trick as a teacher is to take their set of skills and help them use their power for good. And by good, I mean to channel these skills into writing effective persuasive pieces.
So, what exactly do we need to do to teach persuasive writing? I won’t lie to you…it’s not an easy task, but I’ll try to break it down here and simplify the steps to hopefully make this something that you can use in your classroom.
1. Teach Paragraph Writing FIRST
Before I even begin to think about teaching students to create an opinion piece, I make sure that my class has learned the basics of writing a good paragraph. We spend a lot of time with each component, and after they’ve mastered one paragraph, we move on to the five-paragraph essay.
Since I teach 4th/5th, this is one of the standards we need to reach. Once I know that students can write a reasonably good essay, then they can learn an opinion essay a little more easily.

2. Use Mentor Texts to Introduce Opinion Writing
I am a big fan of mentor texts. I just love how picture books easily capture the attention of my “big” kids, while quickly teaching them so many lessons.
When I teach opinion writing, I like to gather several of these persuasive mentor texts and share them with my class. We talk about how the character used persuasive techniques well, or how he/she didn’t.

3. Start With the Big Picture
Before we start to officially write, we talk about what an opinion essay is and isn’t. I like to give students three choices with similar topics and ask them which one is the opinion essay. For example, they might choose between these titles: The Magical Elephant, Elephants and Their Families, and How to Save the Elephants. Next, I have a handout that shows the structure of an opinion essay. Since we’ve written five-paragraph essays before, they have a good handle on the basic essay structure. Then I guide them step by step through each component. We absolutely do not write a single opinion essay until we’ve had the opportunity to have lots of mini-lessons, see many examples, and practice all parts of the essay in a very low-stakes environment.
4. The Introduction Paragraph is First
A. introduce hooks.
Now we spend some time focusing on how to start the essay. We start by using a hook (also called a lead).
I like to describe a writing “hook” using a fishing analogy. The fisherman puts a nice pink, juicy worm on the hook, hoping to attract the attention of the fish. If the fish bites, the fisherman’s happy. If the fish doesn’t bite, that means that it wasn’t interested in the hook, and there won’t be any fish caught.
Our goal as a writer is to get the reader interested by “hooking” them into reading our essay, from the very first sentence.
We go over six different types of hooks and practice these. I also love using opinion writing posters as I introduce each new opinion essay concept. They’re a great reference for students on the wall or printed in miniature for writing notebooks.
B. Review Topic Sentences
For an opinion essay, the topic sentence is the opinion sentence. It is the author’s viewpoint. We do a lesson reviewing the five types of topic sentences we use for paragraph and essay writing, and I show students how to tweak these into opinion statements.
C. Time to Add the Three Reasons
The last part of the introduction lists the three reasons for our opinion. I teach students that these can be listed as a single sentence with commas between them, or we can write three separate sentences, one for each reason.
For the first lesson on reasons, I give students a topic (cell phones or vending machines at school or which season is the best, etc.) and then ask students to write three bullet points on their whiteboards. Next to each one, they write a word to describe a reason they like/dislike this idea.
For example, if the topic was school uniforms, the child might write lack of individuality, gets boring, uncomfortable… I can quickly glance at their lists while we discuss a few of them, and then we’re ready to practice with the next topic.
Without writing a whole essay, this is teaching students to think about organization and how reasons help support their opinions. I think this kind of practice is great!
When we transition this activity to a full essay, these reasons would turn into the topic sentences for each body paragraph of a five-paragraph opinion essay!
Btw.. if you don’t have whiteboards for your class, this is something you’ll really want to consider. They’re great for writing practice and so many things. I actually purchased shower boards at Home Depot for about $15 to make into whiteboards. They cut them into 12 x 12-inch squares for me for free!
5. Review, Review, Review
After we spend some time on each main section of the opinion essay (the introduction, the body paragraphs, and the conclusion), I like to give my students activities to really reinforce what they’ve learned. Besides review worksheets, we do games (like Stump the Expert), sorts, and color coding.

I really like to have students color code already-made paragraphs so they can see examples of quality writing, and they can master the structure of the paragraph . Once we’ve reviewed the introduction, it’s time to move on to the body paragraphs.
6. The Three Body Paragraphs are Next
There are three parts of each body paragraph, and I teach each part separately, one by one. The parts include a topic sentence that starts with a transition, three to five details to describe and explain the author’s reason for his/her viewpoint, and a conclusion sentence.
These three paragraphs are the meat of the essay. This is where students explain why they support or don’t support something.
We spend time doing activities like looking at three sentences and identifying which one is the topic sentence, which one is a detail, and which one is a conclusion sentence.
We look at pre-made topic sentences and related conclusion sentences and rate them as part of a great class discussion and then in pairs or independently. Then, we review with more color coding, games, and sorts.


7. Focus on the Conclusion Paragraph
Conclusions can be a little intimidating for some students. Maybe it’s because they’re tired from the heavy lifting of the other four paragraphs, but with practice, you can help take away some of their apprehension and replace it with confidence!
The conclusion paragraph is a shorter paragraph (in 3rd – 5th grade) than a body paragraph. It has three distinct parts, an opinion sentence that starts with a transition, the three reasons, and a final thought or call to action.
A. The Opinion Sentence Starting with a Transition
The opinion sentence is really a topic sentence. It reinforces the same idea presented in the introduction paragraph but uses synonyms and usually a different type of topic sentence than the introduction to add variety.
We go over specific transitions that can be used for conclusions. While students may not always use a transition for their conclusion later on, I think it gives students structure and helps them break the ice of crafting a strong conclusion paragraph.
B. The Three Reasons (again!)
Just like the introduction paragraph, the conclusion paragraph lists the three reasons, usually in a single sentence with commas. Like always, you’ll want students to reword the sentence using synonyms to add variety.
C. The Conclusion, The Ending, The VERY LAST SENTENCE!
This last sentence is another place students may feel apprehensive to write at first. We go over the difference between a final thought and a call to action and practice by seeing lots of exemplars and then creating our own.
By the time we’re finished, most students understand how to gracefully and effectively add the conclusion sentence to finish the opinion essay.
Just like we usually do, once we finish a section, we review that section carefully using handouts, sorts, color coding, games, and reviews.
8. Share an Opinion Essay Example
It’s one thing to talk about an opinion essay’s components and to even practice them. It’s another thing to see a really good example of an essay and to get to go through it and discuss what makes it work and why.
I have several great examples I’ve saved over the years (and I have two that I wrote and included in my opinion essay unit). We take time to color code the essay and then create a reverse outline for it. They save this essay as an example.
9. Make an Outline and an Essay as a Whole Class (Eeek!)
Okay, here’s where your perseverance has to kick in.
Trying to complete an essay as a whole class will drive even the most saintly of teachers to want to pull their hair out at times, but this hard part is crucial. There, I said it. It is that important that this is a step you shouldn’t miss.
Here’s how I do it. I break it down into two to four days. On the first day, we created an outline together. I have students write this outline in their Writer’s Notebooks as a model to refer to when they need to make their own outline later.
We always do school uniforms, because I find it to be a great topic and one that my students feel strongly about.

I tell them for the sake of continuity, we need to take a stand as a class for the essay, whether they really agree with that stand or not. We take a class vote and then stick with it, whether it’s for or against the uniform idea.
On the second day, when we have the outline in place, I make a deal with the kids…I tell them if they stick with me, stay on task, and participate…I’ll do the writing (this time), and they can just tell me what to write.
If they don’t stay focused, then they’ll have to write it themselves. This works like magic. I’ve never had a class that lost out on this “deal.”
So, using yesterday’s outline, we go step by step and write each paragraph together. Students feed me sentences (I write these on the SmartBoard), which I try to use or gently guide them a bit where needed.
Usually, we do about 2 paragraphs in one day. The attention spans of 8 – 11-year-olds can be a killer, so I find that breaking it into several days helps.
10. Before Students Write – Go over Expectations Using a Rubric
I really like to use rubrics for lots of assignments. It breaks down the activity into its components, and it also serves as a road map for students to know what is expected of them. I think the more we can explain to students exactly what we’re looking for, the more they can meet and sometimes exceed (hallelujah) our expectations.
There’s never a reason to hide what we want from students, in my opinion. So, we go over the rubric together, and it’s a kind of review for all the lessons leading up to this. You can three-hole punch it so they can store it in their binders, or you can print it in a smaller size to fit their Writer’s Notebooks if you wish.
BONUS #11. Practice Writing Opinion Essays…Over and Over and…
Once your students have practiced each part of the opinion essay and are very familiar with its structure, it’s their turn to write independently. I choose several different topics for them over the next few weeks, and we do about an essay a week in class. The students get better as time goes by, and usually, I let them choose a topic for the last essay or two. It’s interesting to see what they come up with.
Whew…such a huge unit and so many skills to fit in, but in my mind, it is an awesome unit. I love teaching it because of the great number of discussions it provides and because I see it as an important set of tools for them to have in their writing toolboxes.

If you’d like some resources for opinion writing , I love this unit I created. It’s a bundle with over 100 printable pages and includes a digital format too. It will take you through the entire process with teaching pages, and detailed teaching notes, student practice pages, activities, and posters for 3rd – 5th grade.
Sarah is a 4th Grade Teacher and uses this unit and process in her classroom. This is what she had to say.

CLICK HERE TO FIND THE OPINION WRITING BUNDLE ON TPT!

- Read more about: Writing & Grammar
You might also like...

Unlocking Student Writing Success: The Power of Explicit Writing Instruction
As upper elementary teachers, our goal is to create strong writers. However, the lack of Explicit Writing Instruction has caused students in the US to

The Major Problem with Writing Instruction and How to Fix It
Writing instruction at the elementary level needs an overhaul. The last time the National Assessment of Education Progress (NAEP) measured 8th-grade students’ writing proficiency in

How to Optimize Grammar Instruction in 15 Minutes a Day
As elementary school teachers, we are always thinking about how to integrate subjects. History content and nonfiction text features. A science equation and a math
Hi, I’m Jenn, CEO and owner of The Teacher Next Door!
I know that you strive to be an effective upper elementary teacher while maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
In order to do that, you need resources that are impactful, yet simple .
The problem is that most resources and curriculums out there are far from simple. The pages upon pages of daily lesson plans are just plain overwhelming .
At TTND, we believe teachers should be living their lives outside of the classroom, and not spend hours lesson planning and searching for resources.
We understand that now, more than ever, teachers need space to be themselves which is why we create and support teachers with timesaving tips and standards-aligned resources.
Want access to TTND's Free Resource Library? Sign up for our newsletter and we'll email you the exclusive password!
Trending posts.

SEARCH BY TOPIC
- Classroom Ideas
- Holidays and Seasonal
- Mentor Texts
- Reading Block
- Uncategorized
- Writing & Grammar
POPULAR RESOURCES

Facebook Group
Teachers Pay Teachers
Free Resource Library
💌 Contact Us
Disclosures
Privacy Policy
Refund Policy
Purchase Orders
Your Downloads
Reward Points
© The Teacher Next Door, LLC. All rights reserved.
* Please note: If your school has strong email filters, you may wish to use your personal email to ensure access.

A Guide to Teaching Essay Structure

Prevent students from 'telling a story' in their essays by helping them understand how arguments work
Essays are an important assessment type in subjects like History, and the skills required to succeed in essay writing are also foundational to other assessment pieces as well. As a result, both students and teachers need to invest significant time in understanding how to craft them.
When you first teach essay writing to students, it is important to demonstrate the core elements of structure first. Since the structure of History essays is foundational to the success of the argument and, by definition, the success of the essay itself, it is the most obvious place to start.
Here are the crucial ideas that students need to grasp about the argumentative structure of History essays:
- An essay’s hypothesis must be a 'genuine argument'
- The topic sentences of each body paragraph must be drawn from the hypothesis
- Each body paragraph needs to be supported by good evidence

In order to teach these ideas, I find that it is best not to use a historical topic as your first example. Most students struggle to understand the contestability of historical arguments, so using one as your first example could only confuse students more as they will already be working hard to understand essay structure.
Therefore, I tend to find that more ‘real world’ examples work best when teaching essays for the first time. These ‘real world’ examples can be based upon your students’ own interests. For example, create an example argument about who the best sports team is, or who the most influential global personality is, or whether homework is important to academic success. The more interesting the topic, the more the students will care about the argument.
Alternatively, you could prepare a number of these example topics for your class and even get them to choose which one they would like to use.
Once decided, use it to proceed through the following steps.
1. An essay’s hypothesis is a 'genuine argument'
One of the most common mistakes that students make when writing essays is that they simply present a ‘story’ about a historical event or person. As a result, they fail to understand the purpose of a hypothesis .
A hypothesis is a statement about what the entire essay is arguing .
When an essay is nothing more than a narrative story, there is no argument.
Crucially, then, the first concept that needs to be understood is that each essay needs a hypothesis that is a 'genuine argument'. A ‘genuine argument’ means that what the essay is trying to prove could be challenged by someone else, or that the opposite of the hypothesis could be used in a different essay.
For example, a student could argue that:
“Homework is detrimental to the social, emotional and physical wellbeing of students”
If this is a genuine argument, the opposite of it could easily be used by someone else for their own argument. For example, another student could argue that:
“Homework is beneficial to the social, emotional and physical wellbeing of students”
This is one of the reasons that a ‘narrative’ essay fails to create good hypotheses: it doesn’t create a genuine argument. For example, a simple ‘story’ essay could say that “World War One saw a tragic loss of life as millions of soldiers from many countries died between 1914 and 1918”. Clearly, there is no argument here: it is just telling a story. One way of demonstrating the lack of an argument is to show that there is no way to argue the opposite of this.
2. Topic sentences of each body paragraph must be drawn from the hypothesis
The second key concept helps build upon the first. As a hypothesis presents the argument that the entire essay is going to prove, then students must make sure that they’re proving it throughout their body paragraphs .
Students can easily get lost in writing their body paragraphs and forget that they are supposed to be proving the argument they presented in their hypothesis.
To highlight that there is a direct relationship between their hypothesis and each of their body paragraphs, it is worth showing students that a good hypothesis can be ‘sliced’ into three parts that each of their body paragraphs will prove.
For example, the hypothesis that “ Homework is detrimental to the social, emotional and physical wellbeing of students ” has three clear elements that need to be proven: the social , emotional and physical impacts. As a result, each will become a topic sentence for their body paragraphs.
Be aware that once students notice the three elements, they will try to take the ‘path of least resistance’ in making their topic sentences. So, using the example above, they might try to make the following topic sentences:
- Homework is detrimental to the social wellbeing of students
- Homework is detrimental to the emotional wellbeing of students
- Homework is detrimental to the physical wellbeing of students
It is important to stress that each topic sentence needs to be expanded to provide a specific reason. Most of the time, students will need to know what evidence they’re using in order to successfully provide specific justifications. For the sake of the above example, here are three improved versions of the topic sentences:
- Due to the extra time required that could otherwise be spent developing friendships, homework is detrimental to the social development of students
- Homework is detrimental to the emotional wellbeing of students because of the additional daily stress it adds to students who are already overloaded with assessment pieces.
- Homework is detrimental to the physical health of students because it requires extended periods of student inactivity.
If the students find that they cannot identify three separate components from their hypothesis to prove in each body paragraph, it may indicate that their hypothesis was not developed enough. However, if you are introducing essays to your students for the first time, ensure that you provide example hypotheses that have three clear elements in order to help students grasp this step easily.
3. Each body paragraph needs to be supported by good evidence
Another common mistake made by students is that they feel the need to fill their body paragraphs with as much historical knowledge as possible. Consequently, students often fall back into the ‘tell a story’ mode which provides a series of people and events about the topic, rather than using the paragraph to present information that helps prove their argument.
The crucial step for students to understand is that whatever they said in their topic sentence needs to be shown in the sources from which they quote in their body paragraphs. While students will have to demonstrate historical knowledge of people, places, dates and event in their work, it should only be used as a way to help show how their sources prove their topic sentences.
If you’re doing your example essay which was based upon a ‘real world’ argument, this can be a great time to let students conduct research to find their own evidence. For example, if students are arguing for their favourite sporting team or their most inspiring personality, they can find facts and figures to justify their argument. (Also, this might be a great time to teach referencing of their sources, if you have time).
Once students then have their sources, they can begin crafting their body paragraphs in order to use their chosen evidence to prove their topic sentences. (You can read more about how to write essay paragraphs here , as I don't have the space to expand upon this part of essay writing in this blog post).
The end result
By the end of their example essay, students should have a better understanding of what makes a good hypothesis, how each topic sentence is drawn from the argument and how evidence is used by body paragraphs to help prove the argument.
Once you have built the example essay as a class (about a sports team or homework, etc.), working as a class to deconstruct a pre-written History essay to identify each element can be enormously beneficial for the students. Furthermore, if time allows, following the same steps to then begin writing their own History essay will often be the moment when the ‘lightbulb moment’ occurs for many of your students.
The entire process I have outlined may take as much as three or four lessons. If you have this amount of time, here is a potential approach:
- Lesson 1: Example ‘real world’ essay construction
- Lesson 2: Deconstruct a pre-written History essay
- Lesson 3-4: Plan and write a class History essay
Also, if you're looking for a more detailed guide to academic essay writing, particularly for senior students, I cannot recommend the book A Short Guide to Writing About History enough (pictured to the right).

Final thoughts
Essay writing is an art that can only truly be mastered by continual practice. Don’t expect students to produce academically sophisticated essays straight away. However, if they can master the key structural elements of how an argument works through the hypothesis, topic sentences and evidence, they can avoid the simplistic errors found in the ‘narrative’ essay.
I hope that this has helped spark some new ideas for your own teaching of History essays. I would be very interested to hear from other teachers about what they have found works for them. Please feel free to add your thoughts below so that we can all benefit from the accumulated wisdom of other professionals.
Write a comment
What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
Brockton Public Schools
How To Teach Essay Writing: Top 5 Tips For Young Teachers
The art of essay writing is an important aspect of the grades and helps your students boost their creativity and express their ideas and notions fluently. Nonetheless, as surprising as it sounds, writing an essay is not a walk in the park and requires proper preparation and effort to establish good writing skills.
The challenge is especially heavier for young teachers seeking to establish rapport with their students while also encouraging them to hone their writing skills. Ideally, even in the finest learning institutions worldwide, it is not uncommon to find students who need to enhance their essay writing skills. But how do you teach essay writing to your students, and ensure they perfect this so important skill?
Luckily, this post has everything every young teacher should know about how to teach essay writing. Here are useful tips you can use to help your students transform into better essay writers!
1. Start By Teaching The Basics Of Good Essay Writing.
The first and most important step to helping your students understand how to write an essay is introducing them to the basics of essay writing. Besides defining essay writing, you must help your students comprehend the proper structure of writing sentences and paragraphs. Once they have this understanding, they can focus on word choice and ideas, among other crucial elements of a good essay. This is often quite similar to reading-you can’t teach your students comprehension before teaching them fluency and decoding, can you?
2. Establish Strong And Regular Writing Routines
As you already know, Practice makes perfect, and this statement is true, especially so with essay writing. Incorporating regular and solid writing routines in your class creates a strong writing culture and promotes creativity.
Ideally, while it is easy for you only to mandate your students to write essays during the normal writing times without offering any extra activities, it
is best to push your students to write through the entire curriculum, especially if you want them to improve their writing skills faster.
It is best to extend writing into every subject area (math included!) by having your students compare, summarize, and contrast journal concepts and ideas. Better yet, incorporating writing into science with multiple activities and research projects allows students to be engaged with current events and even get better at other subjects.
In essence, your students need to see writing-essay writing in virtually everything to allow them to feel comfortable with writing. Oh, and if writing becomes too overwhelming, you can talk about writing in class and get your students engaged in answering questions and floating ideas.
3. Show Your Students Exemplary Essay Samples And Writings To Emulate
For your students to produce better quality essays, they must see a good essay, study how it is established, emulate it, and eventually compare their writings to the necessary standards-rinse and repeat!
You can offer your students two distinct essay writing samples, one weak and the other of superb quality. Initiate an appropriate discussion where the class highlights claims, assess to identify if the topic sentences aptly reinforce the claim and subsequently highlight the key areas of strong argumentation.
Once you grade the samples, your students can then compare their essays to the analyzed samples. The goal you should establish is for your class to make their essays as much as the best sample as possible.
4. Analyze Various Essays Highlighting Both Their Merits And Flaws
On establishing a rapport with your students, you can start offering them various writing pieces regularly for your students to analyze. Depending on their level of understanding, you can twist it, either starting with only a paragraph or offering them a full piece. The best way you can do this is by separating them into various groups ranging from ‘need improvement’ to ‘very good.
Here, you should require your students to justify their reasoning, and when you identify a ‘needs improvement classification,’ ask them to rewrite until it is a good essay.
5. Offer Student-specific And Timely Feedback.
Finally, another crucial aspect you should grasp as a young teacher to help your students create better essays is ensuring you provide them with timely and specific feedback. Once all your students have it, you can spend an entire classroom period analyzing the feedback.
Starting with a mini-lesson is the most effective approach and then divide the classroom into pods, specifically focusing on different essay aspects where your students struggled. What’s more, experts recommend that you pair weak and string writers together to discuss various ways they approach their essay writing process.
With your students having timely feedback regularly, you can spend much of your time planning on re-instruction and better ways to write better essays.
Eventually, with a little desire, effort, and the right guidance from you, every student turns into a better writer. It is upon you to invest both your time and resources in establishing conducive learning and writing culture while offering the necessary guidance to promote their growth and development in the area of essay writing. Using these five easy tips is only a matter of time before your students achieve essay writing success.
Happy Writing!
A Step-by-Step Plan for Teaching Narrative Writing
July 29, 2018
Can't find what you are looking for? Contact Us

Listen to this post as a podcast:
Sponsored by Peergrade and Microsoft Class Notebook
This post contains Amazon Affiliate links. When you make a purchase through these links, Cult of Pedagogy gets a small percentage of the sale at no extra cost to you.
“Those who tell the stories rule the world.” This proverb, attributed to the Hopi Indians, is one I wish I’d known a long time ago, because I would have used it when teaching my students the craft of storytelling. With a well-told story we can help a person see things in an entirely new way. We can forge new relationships and strengthen the ones we already have. We can change a law, inspire a movement, make people care fiercely about things they’d never given a passing thought.
But when we study storytelling with our students, we forget all that. Or at least I did. When my students asked why we read novels and stories, and why we wrote personal narratives and fiction, my defense was pretty lame: I probably said something about the importance of having a shared body of knowledge, or about the enjoyment of losing yourself in a book, or about the benefits of having writing skills in general.
I forgot to talk about the power of story. I didn’t bother to tell them that the ability to tell a captivating story is one of the things that makes human beings extraordinary. It’s how we connect to each other. It’s something to celebrate, to study, to perfect. If we’re going to talk about how to teach students to write stories, we should start by thinking about why we tell stories at all . If we can pass that on to our students, then we will be going beyond a school assignment; we will be doing something transcendent.
Now. How do we get them to write those stories? I’m going to share the process I used for teaching narrative writing. I used this process with middle school students, but it would work with most age groups.
A Note About Form: Personal Narrative or Short Story?
When teaching narrative writing, many teachers separate personal narratives from short stories. In my own classroom, I tended to avoid having my students write short stories because personal narratives were more accessible. I could usually get students to write about something that really happened, while it was more challenging to get them to make something up from scratch.
In the “real” world of writers, though, the main thing that separates memoir from fiction is labeling: A writer might base a novel heavily on personal experiences, but write it all in third person and change the names of characters to protect the identities of people in real life. Another writer might create a short story in first person that reads like a personal narrative, but is entirely fictional. Just last weekend my husband and I watched the movie Lion and were glued to the screen the whole time, knowing it was based on a true story. James Frey’s book A Million Little Pieces sold millions of copies as a memoir but was later found to contain more than a little bit of fiction. Then there are unique books like Curtis Sittenfeld’s brilliant novel American Wife , based heavily on the early life of Laura Bush but written in first person, with fictional names and settings, and labeled as a work of fiction. The line between fact and fiction has always been really, really blurry, but the common thread running through all of it is good storytelling.
With that in mind, the process for teaching narrative writing can be exactly the same for writing personal narratives or short stories; it’s the same skill set. So if you think your students can handle the freedom, you might decide to let them choose personal narrative or fiction for a narrative writing assignment, or simply tell them that whether the story is true doesn’t matter, as long as they are telling a good story and they are not trying to pass off a fictional story as fact.
Here are some examples of what that kind of flexibility could allow:
- A student might tell a true story from their own experience, but write it as if it were a fiction piece, with fictional characters, in third person.
- A student might create a completely fictional story, but tell it in first person, which would give it the same feel as a personal narrative.
- A student might tell a true story that happened to someone else, but write it in first person, as if they were that person. For example, I could write about my grandmother’s experience of getting lost as a child, but I might write it in her voice.
If we aren’t too restrictive about what we call these pieces, and we talk about different possibilities with our students, we can end up with lots of interesting outcomes. Meanwhile, we’re still teaching students the craft of narrative writing.
A Note About Process: Write With Your Students
One of the most powerful techniques I used as a writing teacher was to do my students’ writing assignments with them. I would start my own draft at the same time as they did, composing “live” on the classroom projector, and doing a lot of thinking out loud so they could see all the decisions a writer has to make.
The most helpful parts for them to observe were the early drafting stage, where I just scratched out whatever came to me in messy, run-on sentences, and the revision stage, where I crossed things out, rearranged, and made tons of notes on my writing. I have seen over and over again how witnessing that process can really help to unlock a student’s understanding of how writing actually gets made.
A Narrative Writing Unit Plan
Before I get into these steps, I should note that there is no one right way to teach narrative writing, and plenty of accomplished teachers are doing it differently and getting great results. This just happens to be a process that has worked for me.
Step 1: Show Students That Stories Are Everywhere
Getting our students to tell stories should be easy. They hear and tell stories all the time. But when they actually have to put words on paper, they forget their storytelling abilities: They can’t think of a topic. They omit relevant details, but go on and on about irrelevant ones. Their dialogue is bland. They can’t figure out how to start. They can’t figure out how to end.
So the first step in getting good narrative writing from students is to help them see that they are already telling stories every day . They gather at lockers to talk about that thing that happened over the weekend. They sit at lunch and describe an argument they had with a sibling. Without even thinking about it, they begin sentences with “This one time…” and launch into stories about their earlier childhood experiences. Students are natural storytellers; learning how to do it well on paper is simply a matter of studying good models, then imitating what those writers do.
So start off the unit by getting students to tell their stories. In journal quick-writes, think-pair-shares, or by playing a game like Concentric Circles , prompt them to tell some of their own brief stories: A time they were embarrassed. A time they lost something. A time they didn’t get to do something they really wanted to do. By telling their own short anecdotes, they will grow more comfortable and confident in their storytelling abilities. They will also be generating a list of topic ideas. And by listening to the stories of their classmates, they will be adding onto that list and remembering more of their own stories.
And remember to tell some of your own. Besides being a good way to bond with students, sharing your stories will help them see more possibilities for the ones they can tell.
Step 2: Study the Structure of a Story
Now that students have a good library of their own personal stories pulled into short-term memory, shift your focus to a more formal study of what a story looks like.
Use a diagram to show students a typical story arc like the one below. Then, using a simple story (try a video like The Present or Room ), fill out the story arc with the components from that story. Once students have seen this story mapped out, have them try it with another one, like a story you’ve read in class, a whole novel, or another short video.
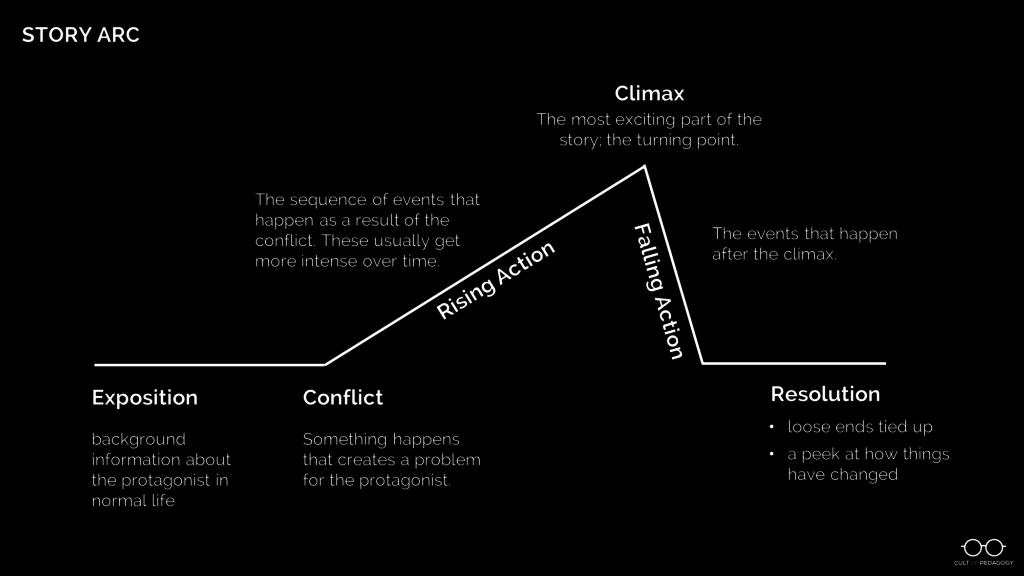
Step 3: Introduce the Assignment
Up to this point, students have been immersed in storytelling. Now give them specific instructions for what they are going to do. Share your assignment rubric so they understand the criteria that will be used to evaluate them; it should be ready and transparent right from the beginning of the unit. As always, I recommend using a single point rubric for this.
Step 4: Read Models
Once the parameters of the assignment have been explained, have students read at least one model story, a mentor text that exemplifies the qualities you’re looking for. This should be a story on a topic your students can kind of relate to, something they could see themselves writing. For my narrative writing unit (see the end of this post), I wrote a story called “Frog” about a 13-year-old girl who finally gets to stay home alone, then finds a frog in her house and gets completely freaked out, which basically ruins the fun she was planning for the night.
They will be reading this model as writers, looking at how the author shaped the text for a purpose, so that they can use those same strategies in their own writing. Have them look at your rubric and find places in the model that illustrate the qualities listed in the rubric. Then have them complete a story arc for the model so they can see the underlying structure.
Ideally, your students will have already read lots of different stories to look to as models. If that isn’t the case, this list of narrative texts recommended by Cult of Pedagogy followers on Twitter would be a good place to browse for titles that might be right for your students. Keep in mind that we have not read most of these stories, so be sure to read them first before adopting them for classroom use.
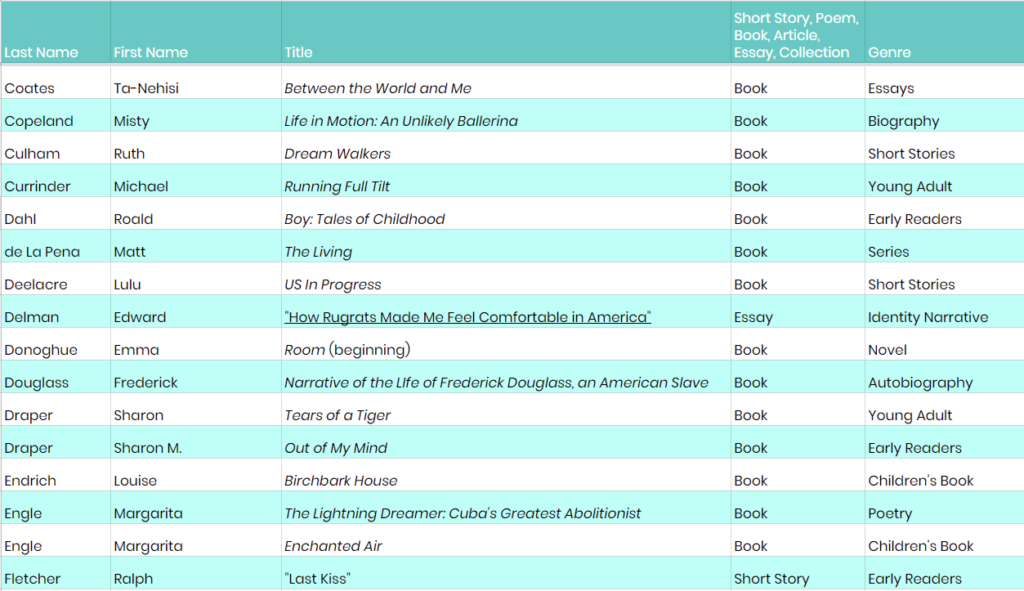
Step 5: Story Mapping
At this point, students will need to decide what they are going to write about. If they are stuck for a topic, have them just pick something they can write about, even if it’s not the most captivating story in the world. A skilled writer could tell a great story about deciding what to have for lunch. If they are using the skills of narrative writing, the topic isn’t as important as the execution.
Have students complete a basic story arc for their chosen topic using a diagram like the one below. This will help them make sure that they actually have a story to tell, with an identifiable problem, a sequence of events that build to a climax, and some kind of resolution, where something is different by the end. Again, if you are writing with your students, this would be an important step to model for them with your own story-in-progress.
Step 6: Quick Drafts
Now, have students get their chosen story down on paper as quickly as possible: This could be basically a long paragraph that would read almost like a summary, but it would contain all the major parts of the story. Model this step with your own story, so they can see that you are not shooting for perfection in any way. What you want is a working draft, a starting point, something to build on for later, rather than a blank page (or screen) to stare at.
Step 7: Plan the Pacing
Now that the story has been born in raw form, students can begin to shape it. This would be a good time for a lesson on pacing, where students look at how writers expand some moments to create drama and shrink other moments so that the story doesn’t drag. Creating a diagram like the one below forces a writer to decide how much space to devote to all of the events in the story.

Step 8: Long Drafts
With a good plan in hand, students can now slow down and write a proper draft, expanding the sections of their story that they plan to really draw out and adding in more of the details that they left out in the quick draft.
Step 9: Workshop
Once students have a decent rough draft—something that has a basic beginning, middle, and end, with some discernible rising action, a climax of some kind, and a resolution, you’re ready to shift into full-on workshop mode. I would do this for at least a week: Start class with a short mini-lesson on some aspect of narrative writing craft, then give students the rest of the period to write, conference with you, and collaborate with their peers. During that time, they should focus some of their attention on applying the skill they learned in the mini-lesson to their drafts, so they will improve a little bit every day.
Topics for mini-lessons can include:
- How to weave exposition into your story so you don’t give readers an “information dump”
- How to carefully select dialogue to create good scenes, rather than quoting everything in a conversation
- How to punctuate and format dialogue so that it imitates the natural flow of a conversation
- How to describe things using sensory details and figurative language; also, what to describe…students too often give lots of irrelevant detail
- How to choose precise nouns and vivid verbs, use a variety of sentence lengths and structures, and add transitional words, phrases, and features to help the reader follow along
- How to start, end, and title a story
Step 10: Final Revisions and Edits
As the unit nears its end, students should be shifting away from revision , in which they alter the content of a piece, toward editing , where they make smaller changes to the mechanics of the writing. Make sure students understand the difference between the two: They should not be correcting each other’s spelling and punctuation in the early stages of this process, when the focus should be on shaping a better story.
One of the most effective strategies for revision and editing is to have students read their stories out loud. In the early stages, this will reveal places where information is missing or things get confusing. Later, more read-alouds will help them immediately find missing words, unintentional repetitions, and sentences that just “sound weird.” So get your students to read their work out loud frequently. It also helps to print stories on paper: For some reason, seeing the words in print helps us notice things we didn’t see on the screen.
To get the most from peer review, where students read and comment on each other’s work, more modeling from you is essential: Pull up a sample piece of writing and show students how to give specific feedback that helps, rather than simply writing “good detail” or “needs more detail,” the two comments I saw exchanged most often on students’ peer-reviewed papers.
Step 11: Final Copies and Publication
Once revision and peer review are done, students will hand in their final copies. If you don’t want to get stuck with 100-plus papers to grade, consider using Catlin Tucker’s station rotation model , which keeps all the grading in class. And when you do return stories with your own feedback, try using Kristy Louden’s delayed grade strategy , where students don’t see their final grade until they have read your written feedback.
Beyond the standard hand-in-for-a-grade, consider other ways to have students publish their stories. Here are some options:
- Stories could be published as individual pages on a collaborative website or blog.
- Students could create illustrated e-books out of their stories.
- Students could create a slideshow to accompany their stories and record them as digital storytelling videos. This could be done with a tool like Screencastify or Screencast-O-Matic .
So this is what worked for me. If you’ve struggled to get good stories from your students, try some or all of these techniques next time. I think you’ll find that all of your students have some pretty interesting stories to tell. Helping them tell their stories well is a gift that will serve them for many years after they leave your classroom. ♦
Want this unit ready-made?
If you’re a writing teacher in grades 7-12 and you’d like a classroom-ready unit like the one described above, including slideshow mini-lessons on 14 areas of narrative craft, a sample narrative piece, editable rubrics, and other supplemental materials to guide students through every stage of the process, take a look at my Narrative Writing unit . Just click on the image below and you’ll be taken to a page where you can read more and see a detailed preview of what’s included.

What to Read Next

Categories: Instruction , Podcast
Tags: English language arts , Grades 6-8 , Grades 9-12 , teaching strategies
52 Comments
Wow, this is a wonderful guide! If my English teachers had taught this way, I’m sure I would have enjoyed narrative writing instead of dreading it. I’ll be able to use many of these suggestions when writing my blog! BrP
Lst year I was so discouraged because the short stories looked like the quick drafts described in this article. I thought I had totally failed until I read this and realized I did not fai,l I just needed to complete the process. Thank you!
I feel like you jumped in my head and connected my thoughts. I appreciate the time you took to stop and look closely at form. I really believe that student-writers should see all dimensions of narrative writing and be able to live in whichever style and voice they want for their work.
Can’t thank you enough for this. So well curated that one can just follow it blindly and ace at teaching it. Thanks again!
Great post! I especially liked your comments about reminding kids about the power of storytelling. My favourite podcasts and posts from you are always about how to do things in the classroom and I appreciate the research you do.
On a side note, the ice breakers are really handy. My kids know each other really well (rural community), and can tune out pretty quickly if there is nothing new to learn about their peers, but they like the games (and can remember where we stopped last time weeks later). I’ve started changing them up with ‘life questions’, so the editable version is great!
I love writing with my students and loved this podcast! A fun extension to this narrative is to challenge students to write another story about the same event, but use the perspective of another “character” from the story. Books like Wonder (R.J. Palacio) and Wanderer (Sharon Creech) can model the concept for students.
Thank you for your great efforts to reveal the practical writing strategies in layered details. As English is not my first language, I need listen to your podcast and read the text repeatedly so to fully understand. It’s worthy of the time for some great post like yours. I love sharing so I send the link to my English practice group that it can benefit more. I hope I could be able to give you some feedback later on.
Thank you for helping me get to know better especially the techniques in writing narrative text. Im an English teacher for 5years but have little knowledge on writing. I hope you could feature techniques in writing news and fearute story. God bless and more power!
Thank you for this! I am very interested in teaching a unit on personal narrative and this was an extremely helpful breakdown. As a current student teacher I am still unsure how to approach breaking down the structures of different genres of writing in a way that is helpful for me students but not too restrictive. The story mapping tools you provided really allowed me to think about this in a new way. Writing is such a powerful way to experience the world and more than anything I want my students to realize its power. Stories are how we make sense of the world and as an English teacher I feel obligated to give my students access to this particular skill.
The power of story is unfathomable. There’s this NGO in India doing some great work in harnessing the power of storytelling and plots to brighten children’s lives and enlighten them with true knowledge. Check out Katha India here: http://bit.ly/KathaIndia
Thank you so much for this. I did not go to college to become a writing professor, but due to restructuring in my department, I indeed am! This is a wonderful guide that I will use when teaching the narrative essay. I wonder if you have a similar guide for other modes such as descriptive, process, argument, etc.?
Hey Melanie, Jenn does have another guide on writing! Check out A Step-by-Step Plan for Teaching Argumentative Writing .
Hi, I am also wondering if there is a similar guide for descriptive writing in particular?
Hey Melanie, unfortunately Jenn doesn’t currently have a guide for descriptive writing. She’s always working on projects though, so she may get around to writing a unit like this in the future. You can always check her Teachers Pay Teachers page for an up-to-date list of materials she has available. Thanks!
I want to write about the new character in my area
That’s great! Let us know if you need any supports during your writing process!
I absolutely adore this unit plan. I teach freshmen English at a low-income high school and wanted to find something to help my students find their voice. It is not often that I borrow material, but I borrowed and adapted all of it in the order that it is presented! It is cohesive, understandable, and fun. Thank you!!
So glad to hear this, Nicole!
Thanks sharing this post. My students often get confused between personal narratives and short stories. Whenever I ask them to write a short story, she share their own experiences and add a bit of fiction in it to make it interesting.
Thank you! My students have loved this so far. I do have a question as to where the “Frog” story mentioned in Step 4 is. I could really use it! Thanks again.
This is great to hear, Emily! In Step 4, Jenn mentions that she wrote the “Frog” story for her narrative writing unit . Just scroll down the bottom of the post and you’ll see a link to the unit.
I also cannot find the link to the short story “Frog”– any chance someone can send it or we can repost it?
This story was written for Jenn’s narrative writing unit. You can find a link to this unit in Step 4 or at the bottom of the article. Hope this helps.
I cannot find the frog story mentioned. Could you please send the link.? Thank you
Hi Michelle,
The Frog story was written for Jenn’s narrative writing unit. There’s a link to this unit in Step 4 and at the bottom of the article.
Debbie- thanks for you reply… but there is no link to the story in step 4 or at the bottom of the page….
Hey Shawn, the frog story is part of Jenn’s narrative writing unit, which is available on her Teachers Pay Teachers site. The link Debbie is referring to at the bottom of this post will take you to her narrative writing unit and you would have to purchase that to gain access to the frog story. I hope this clears things up.
Thank you so much for this resource! I’m a high school English teacher, and am currently teaching creative writing for the first time. I really do value your blog, podcast, and other resources, so I’m excited to use this unit. I’m a cyber school teacher, so clear, organized layout is important; and I spend a lot of time making sure my content is visually accessible for my students to process. Thanks for creating resources that are easy for us teachers to process and use.
Do you have a lesson for Informative writing?
Hey Cari, Jenn has another unit on argumentative writing , but doesn’t have one yet on informative writing. She may develop one in the future so check back in sometime.
I had the same question. Informational writing is so difficult to have a good strong unit in when you have so many different text structures to meet and need text-dependent writing tasks.
Creating an informational writing unit is still on Jenn’s long list of projects to get to, but in the meantime, if you haven’t already, check out When We All Teach Text Structures, Everyone Wins . It might help you out!
This is a great lesson! It would be helpful to see a finished draft of the frog narrative arc. Students’ greatest challenge is transferring their ideas from the planner to a full draft. To see a full sample of how this arc was transformed into a complete narrative draft would be a powerful learning tool.
Hi Stacey! Jenn goes into more depth with the “Frog” lesson in her narrative writing unit – this is where you can find a sample of what a completed story arc might look. Also included is a draft of the narrative. If interested in checking out the unit and seeing a preview, just scroll down to the bottom of the post and click on the image. Hope this helps!
Helped me learn for an entrance exam thanks very much
Is the narrative writing lesson you talk about in https://www.cultofpedagogy.com/narrative-writing/
Also doable for elementary students you think, and if to what levels?
Love your work, Sincerely, Zanyar
Hey Zanyar,
It’s possible the unit would work with 4th and 5th graders, but Jenn definitely wouldn’t recommend going any younger. The main reason for this is that some of the mini-lessons in the unit could be challenging for students who are still concrete thinkers. You’d likely need to do some adjusting and scaffolding which could extend the unit beyond the 3 weeks. Having said that, I taught 1st grade and found the steps of the writing process, as described in the post, to be very similar. Of course learning targets/standards were different, but the process itself can be applied to any grade level (modeling writing, using mentor texts to study how stories work, planning the structure of the story, drafting, elaborating, etc.) Hope this helps!
This has made my life so much easier. After teaching in different schools systems, from the American, to British to IB, one needs to identify the anchor standards and concepts, that are common between all these systems, to build well balanced thematic units. Just reading these steps gave me the guidance I needed to satisfy both the conceptual framework the schools ask for and the standards-based practice. Thank you Thank you.
Would this work for teaching a first grader about narrative writing? I am also looking for a great book to use as a model for narrative writing. Veggie Monster is being used by his teacher and he isn’t connecting with this book in the least bit, so it isn’t having a positive impact. My fear is he will associate this with writing and I don’t want a negative association connected to such a beautiful process and experience. Any suggestions would be helpful.
Thank you for any information you can provide!
Although I think the materials in the actual narrative writing unit are really too advanced for a first grader, the general process that’s described in the blog post can still work really well.
I’m sorry your child isn’t connecting with The Night of the Veggie Monster. Try to keep in mind that the main reason this is used as a mentor text is because it models how a small moment story can be told in a big way. It’s filled with all kinds of wonderful text features that impact the meaning of the story – dialogue, description, bold text, speech bubbles, changes in text size, ellipses, zoomed in images, text placement, text shape, etc. All of these things will become mini-lessons throughout the unit. But there are lots of other wonderful mentor texts that your child might enjoy. My suggestion for an early writer, is to look for a small moment text, similar in structure, that zooms in on a problem that a first grader can relate to. In addition to the mentor texts that I found in this article , you might also want to check out Knuffle Bunny, Kitten’s First Full Moon, When Sophie Gets Angry Really Really Angry, and Whistle for Willie. Hope this helps!
I saw this on Pinterest the other day while searching for examples of narritives units/lessons. I clicked on it because I always click on C.o.P stuff 🙂 And I wasn’t disapointed. I was intrigued by the connection of narratives to humanity–even if a student doesn’t identify as a writer, he/she certainly is human, right? I really liked this. THIS clicked with me.
A few days after I read the P.o.C post, I ventured on to YouTube for more ideas to help guide me with my 8th graders’ narrative writing this coming spring. And there was a TEDx video titled, “The Power of Personal Narrative” by J. Christan Jensen. I immediately remembered the line from the article above that associated storytelling with “power” and how it sets humans apart and if introduced and taught as such, it can be “extraordinary.”
I watched the video and to the suprise of my expectations, it was FANTASTIC. Between Jennifer’s post and the TEDx video ignited within me some major motivation and excitement to begin this unit.
Thanks for sharing this with us! So glad that Jenn’s post paired with another text gave you some motivation and excitement. I’ll be sure to pass this on to Jenn!
Thank you very much for this really helpful post! I really love the idea of helping our students understand that storytelling is powerful and then go on to teach them how to harness that power. That is the essence of teaching literature or writing at any level. However, I’m a little worried about telling students that whether a piece of writing is fact or fiction does not matter. It in fact matters a lot precisely because storytelling is powerful. Narratives can shape people’s views and get their emotions involved which would, in turn, motivate them to act on a certain matter, whether for good or for bad. A fictional narrative that is passed as factual could cause a lot of damage in the real world. I believe we should. I can see how helping students focus on writing the story rather than the truth of it all could help refine the needed skills without distractions. Nevertheless, would it not be prudent to teach our students to not just harness the power of storytelling but refrain from misusing it by pushing false narratives as factual? It is true that in reality, memoirs pass as factual while novels do as fictional while the opposite may be true for both cases. I am not too worried about novels passing as fictional. On the other hand, fictional narratives masquerading as factual are disconcerting and part of a phenomenon that needs to be fought against, not enhanced or condoned in education. This is especially true because memoirs are often used by powerful people to write/re-write history. I would really like to hear your opinion on this. Thanks a lot for a great post and a lot of helpful resources!
Thank you so much for this. Jenn and I had a chance to chat and we can see where you’re coming from. Jenn never meant to suggest that a person should pass off a piece of fictional writing as a true story. Good stories can be true, completely fictional, or based on a true story that’s mixed with some fiction – that part doesn’t really matter. However, what does matter is how a student labels their story. We think that could have been stated more clearly in the post , so Jenn decided to add a bit about this at the end of the 3rd paragraph in the section “A Note About Form: Personal Narrative or Short Story?” Thanks again for bringing this to our attention!
You have no idea how much your page has helped me in so many ways. I am currently in my teaching credential program and there are times that I feel lost due to a lack of experience in the classroom. I’m so glad I came across your page! Thank you for sharing!
Thanks so much for letting us know-this means a whole lot!
No, we’re sorry. Jenn actually gets this question fairly often. It’s something she considered doing at one point, but because she has so many other projects she’s working on, she’s just not gotten to it.
I couldn’t find the story
Hi, Duraiya. The “Frog” story is part of Jenn’s narrative writing unit, which is available on her Teachers Pay Teachers site. The link at the bottom of this post will take you to her narrative writing unit, which you can purchase to gain access to the story. I hope this helps!
I am using this step-by-step plan to help me teach personal narrative story writing. I wanted to show the Coca-Cola story, but the link says the video is not available. Do you have a new link or can you tell me the name of the story so I can find it?
Thank you for putting this together.
Hi Corri, sorry about that. The Coca-Cola commercial disappeared, so Jenn just updated the post with links to two videos with good stories. Hope this helps!
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.

How to Teach Argument Writing: 3 Simple Steps to Improve Instruction

Teaching students how to write argumentative papers can be a challenging task. From teaching students how to include and refute the counterclaim to ensure students find the most relevant evidence to support their claims, teachers have their work cut out for them. This blog post will go over exactly how to teach argument writing in the secondary ELA classroom.
When I teach students how to write argument essays , I like to introduce challenging concepts to my students using ideas and topics they are familiar with. By doing this, I help them understand more complex ideas in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
How to Teach Argument Writing: 3 Steps for Success
Teaching argument essay writing step 1: develop the claim.
One of the first steps in helping students write an argument essay is developing the claim. Students need to understand that a claim is a debatable statement that they can back up and support using evidence and reasoning. Once students have a good idea about their essay’s claim, they can start writing their essay.
To teach students what a claim is, I’ll write a series of statements on the board, and we will have a quick discussion about fact vs. opinion. When I do this, I like to use topics that my students are interested in. Some topics I use frequently include food, Disney movies, and superheroes.
To illustrate this exercise, I might write these two statements on the board. I’ll have students identify which one is a fact and which one is a statement. The ultimate goal of this exercise is to get my students talking.
Let’s use superheroes as an example:
- Captain Marvel is a superhero.
- Captain Marvel is the most powerful superhero in the Marvel Cinematic Universe.
Immediately, when I reveal these statements on the board, my students are engaged. Not only are they engaged, but they might even be debating in class about their favorite Avenger.
Once students see the debatable aspect of a claim versus a fact, they are ready to move on and find supporting evidence for their claim. With the Captain Marvel example above, students will either agree or disagree with that statement.
Teaching Argument Essay Writing Step 2: Support the Claim
Once students understand what a debatable claim is, they are ready to support their claim with reasons and examples. This is where a quick four-corners type of classroom exercise comes into play. I divide my class up into the north side of the classroom and the south side of the classroom. If students agree with the claim, they must go to one side, and if they disagree, they go to the other side.
Once students stake their claim and choose a side, I give them a couple of moments to discuss their reasons with their like-minded peers. Students will then share their reasons either aloud or on the whiteboard or chart paper.
During this exercise, I teach students about the importance of why it is so important to have relevant supporting reasons and evidence.
Teaching Argument Essay Writing Step 3: Use Relevant Evidence
After students learn how to find related and supporting reasons, it is time to incorporate supporting evidence. By scaffolding the instruction with topics in which students are familiar, they should have a pretty good understanding of finding evidence that is related. However, this is still a tricky concept for high school and middle school students to master.
To help students keep their evidence related to the prompt, claim, and topic sentence, I suggest these teaching strategies.
- Write the prompt on the whiteboard and refer to it throughout the class period.
- Have students write their claim at the top of the paper
- Encourage students to get in the habit of rephrasing parts of the essay prompt and claim in their body paragraphs, especially their commentary.
With these three teaching strategies and ideas, students will have an easier time writing their augment essays. You might also be interested in my blog post about 50 argumentative essay prompts .
Begin your argument unit today
Help your students master the art of argumentative writing with this argument writing teaching unit ! I created this argumentative essay writing teaching unit with secondary ELA students in mind, and it includes step-by-step and engaging writing instructional materials. This argument essay writing unit includes everything you need for a complete argumentative writing instructional unit, including the print & digital materials.
This essay writing instructional unit includes an editable instructional presentation for direct instruction and student resources to help you and your students work through an argument essay. With a focus on argument writing and informational text, this unit fuses together key ELA standards as it covers the differences between persuasive and argumentative writing. Thus unit also teaches purpose, audience, tone, diction, and the rhetorical triangle.
Fellow teachers say…
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ Extremely satisfied
“ This is another excellently developed writing unit fromThe Daring English Teacher. It is basically print and teach lessons which are designed to keep students engaged! I used this in conjunction with a film study and my students actually loved completing it!”
“ I loved using this with my 7th graders when we did the argumentative unit! It was a big help on me as a teacher to have all of this in one area. 10/10 would get again!”
“ This is an excellent resource for teaching argumentative writing to my 11th-grade students. I especially liked using it for remediation purposes. It helps the student break down the writing process into manageable pieces. They were then able to see how everything comes together like a puzzle. I am extremely happy with this resource!”

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

SUBSCRIBE NOW
- Learning Portal
- Support Center
- Store Account

Read this blog online at https://www.collaborativeclassroom.org/blog/teaching-writing-process/
In Praise of the Writing Process
By Jennifer Evans | Categories: Expert Voices , Writing
How Explicitly Teaching the Writing Process Empowers Young Writers
“I’m not good at writing. I don’t know where to start. I don’t know how to make my writing better.”
Every K–5 teacher of writing has heard these remarks. To our young students, authors seem to possess magical abilities, effortlessly producing writing of all sorts, from captivating stories to compelling essays. As educators, it’s our responsibility to demystify the act of writing and share some empowering truths:
There is a clear process to writing.
The writing process is accessible to all of us, and it helps us create pieces of writing that successfully inform, persuade, and delight our readers.
The more deeply we engage in the writing process, the greater the rewards.
The Power of the Writing Process
Writing in the age of ai.
The recent explosion of AI language learning models has strengthened the notion, even among some adults, that the act of writing involves magic. You put in a prompt and (ta-da!) you get writing.
The reality is, even with access to helpful AI tools, great writing doesn’t appear out of thin air. As writers we must have:
- strong critical thinking skills
- background knowledge about our chosen topic and the skills to research it further
- knowledge of writing genres and author’s craft
- the skills to structure and organize ideas effectively
- understanding of grammar and conventions
- methods for finding and fixing the parts of our writing that aren’t working
- confidence in our own voice as a writer
- trusted readers who give us feedback
The Reality of Writing Assistance from AI
In my early drafts of this blog, I did benefit from AI tools to help generate ideas and suggest ways to organize the content. While revising, I used AI to assist me in recognizing words I overuse.
These AI tools were useful. Nonetheless we must acknowledge the limitations of AI in helping writers—especially student writers—navigate the writing process, produce strong work, and see themselves as writers.
The Limitations of AI Writing Tools
The use of AI tools did not enable me to fast-forward my way through the writing process. Nor did it magically drop a complete and polished piece of writing into my lap.
In fact I rejected quite a few of the AI-generated suggestions, instead trusting my knowledge of the topic and my discernment as a writer, as well as insightful feedback from colleagues.
I also said “no thanks” to AI suggestions that would have erased my own unique voice as a writer.
Why the Writing Process Remains Vital
Perhaps most importantly, I leaned into the writing process in order to refine my ideas —something the AI tool couldn’t do for me.
In other words, I used the act of writing itself (and rewriting and revising) to help me interrogate my own thinking and deeply examine the ideas I wanted to share.
I used the act of writing itself (and rewriting and revising) to help me interrogate my own thinking and deeply examine the ideas I wanted to share.
In short, this piece was not created with a wave of an AI wand. I went through the entire writing process, repeating several steps two or even three times. This published blog is better for having gone through the process.
The Joy of the Writing Process
If my journey through the writing process sounds onerous, well, it wasn’t.
As a former educator who knows the writing process well, I enjoyed every step along the way—including the messy parts and the moments of writer’s block.
That knowledge of and joyful trust in the writing process is something that we should strive to develop in all of our young writers.
So, how do we achieve that?
Writing Instruction Should Be Process-Focused, Not Product-Focused
It can be tempting to focus on writing as a product—the final pieces that our students publish. But we know that successful writing instruction is actually process-focused (NCTE, 2022). As the saying goes, it’s about the journey, not the destination.
That’s why it is so important to explicitly teach the writing process, step by step, and center that process in our instruction.
Unpacking the Writing Process
The journey begins with prewriting. Writers brainstorm ideas, ask themselves questions, consider what they already know about their topic, do research, and organize their thoughts. They might sketch an outline or use a planning tool.
Writers are also examining their initial ideas in the context of the genre, their intended audience, and the purpose they want to fulfill via their writing. Younger writers may want to rush through prewriting and just start drafting, but as educators, it’s our job to show them the value of spending time in this stage.
Younger writers may want to rush through prewriting and just start drafting.
During prewriting, students may also have the opportunity to work in pairs or small groups as they brainstorm and share ideas with peers. The value of nurturing a strong classroom writing community is obvious; this collaborative work will be most fruitful when all writers feel supported and valued.
The first draft is akin to laying a foundation. It’s rough, imperfect, disjointed, and probably doesn’t resemble the final product, but it’s a necessary step on the road to literary creation.
When teaching K–5 writers, it’s important to emphasize that messiness is a completely normal part of drafting.
When teaching K–5 writers, it’s important to emphasize that messiness is a completely normal part of drafting. Students should concentrate on writing as freely as possible and getting their ideas on paper. If writers focus too much on editing themselves as they draft, it can often slow them down.
Writers refine their work through revision. They polish sentences, improve word choice, and add color and interest to their writing. Other revisions go deeper as writers review and evaluate the ideas in their writing.
When supporting young writers, invite them to reflect on questions such as: “Did I actually accomplish what I envisioned in the prewriting stage? Are there places in my writing where I might want to rethink my original ideas or structures?”
Young writers may initially approach revision with a deficit mindset: “Here are all the things that are wrong with my draft and now I have to fix them.” However, we can help them reframe revision as one of the most exciting and rewarding parts of the writing process.
Revision is often the time when writers suddenly get new insights, discover more engaging ways to present ideas, and tease out a key point that clinches their argument.
Revision is often the time when writers suddenly get new insights, discover more engaging ways to present ideas, and tease out a key point that clinches their argument.

Feedback from peers and the teacher also plays a vital part during revision. So much depends on how feedback is given and received. Students need regular practice to learn how to ask for, give, and receive helpful feedback through peer and teacher conferring.
So much depends on how feedback is given and received.
As in the prewriting stage, having a safe, supportive writing community is a prerequisite for students to consistently give and receive helpful feedback.
Editing and Proofreading
Editing and proofreading are necessary skills for every writer to develop. Ideally our instruction integrates spelling, grammar, and conventions directly into the writing process and emphasizes the interconnectedness of reading, spelling, and writing. Young writers also benefit from applying this instruction directly to their own writing.
At the same time, we as educators need to be mindful of our blind spots around what “good writing” is, especially during this stage of the process. Every writer brings their own distinct cultural richness and linguistic assets to their work.
Publishing
Publishing is the final stage, when writers launch their finished work into the world. This is a joyful part of the process, as writers savor their accomplishments and recognize themselves as authors.
Publishing is also a valuable opportunity for learning. Young writers gain so much when they see their writing being read and experienced by actual readers.
Writers can find out how well their published writing accomplished its purpose. What moment of the story got the biggest laugh? What part of the argument won readers’ hearts and minds?
And by interacting with readers—hearing their reactions and answering their questions—writers can reflect authentically on the writing process they went through.
K–5 writers often share their published work with the classroom community via an Author’s Chair. You might also post student writing where it can be read and enjoyed by a wider audience.
In my own classroom, I encouraged my students to share their work in a variety of ways such as giving poetry readings and creating books. One student, without prompting, even recorded a movie of his short screenplay with friends over a weekend!
The Writing Process Is Not Linear
As we engage in the writing process with our students, we also want them to learn that the process is flexible and highly adaptable. According to Flower and Hayes, writing is a recursive process; it can (and should!) repeat and circle back around itself (Flower & Hayes, 1981).
In other words, skilled writers do not necessarily move through the writing process in a linear way. They feel empowered to revisit different parts of the process as needed.
Sometimes writers circle back to drafting to get a fresh start, sometimes reworking just a small piece—an opening or closing, perhaps—to make a stronger statement. Other times they are fine-tuning word choice or revising a tricky passage multiple times.
Explicitly Teaching the Writing Process: Practical Examples
Modeling the writing process in the classroom.
How can we explicitly teach the writing process in the classroom? One practical way to do so is through modeling the process ourselves. This has the added benefit of further strengthening the classroom writing community.
“Getting hands-on with writing alongside my students, I joined our class as a fellow writer.” Marine Freibrun
As my colleague Marine Freibrun explained in her recent blog , “I modeled the writing process to my students, sharing my own ups and downs to make it clear that we were all in it together. Getting hands-on with writing alongside my students, I joined our class as a fellow writer.”
Creative Teaching with Play-Doh: A Hands-On Approach
Taking an example from my own time as a middle school teacher, I always began the school year by using Play-Doh to teach the writing process.
Using a script shared in the Ideas Plus Book 15 (NCTE, 1997) as my initial guidance, I walked 150 of my brand-new sixth graders through the process of creating a pencil holder using the Play-Doh I’d provided to them. And they got to watch me as I created my own alongside them.
Through this act of tearing down and starting over, students learned that in prewriting, we have an infinite number of ideas to choose from, limited only by our imagination.
Every year there would be a collective gasp when I told them to mash up their first idea. “Why, Ms. Evans? This one works just fine!” students would say. Through this act of tearing down and starting over, students learned that in prewriting, we have an infinite number of ideas to choose from, limited only by our imagination.
Later steps showed the students how the writer, like a sculptor, goes through a creative and refining process to produce a final piece.
This hands-on activity served both as an opportunity for our classroom to get to know each other and start becoming a true writing community, as well as a very concrete reminder for them as to what the writing process looked like.
From Play-Doh to Pen and Paper: Transitioning Tools in Teaching
When we moved on from Play-Doh to pen and paper, my students felt safe, embracing the inherent messiness of the writing process with newfound confidence.
They were no longer afraid to take risks, acknowledging imperfections as part of the journey, and eagerly diving into revisions to refine and enhance their drafts.
Continuous Modeling Throughout the School Year
For the remainder of the school year, I continued to model writing frequently, showing everything from my brainstorming a creative story to identifying important research for a persuasive article, from how I’d draft a message to my best friend to how I’d craft a letter to the district superintendent.
My students saw how the writing process played a role in drafting any piece, no matter the context.

Writing well doesn’t require magic, AI tools, or rare talent. As educators, it’s our job to demystify the act of writing for our young writers.
Let’s empower students with the knowledge that at its heart, writing is a process … and if any magic exists, it lives within the process itself.
Every writer can access the writing process and, with time and practice, take full ownership of it and reap its rewards.
Flower, L. & Hayes J.R. (1981). A Cognitive Process Theory of Writing. College Composition and Communication , 32 (4), 365–387. https://www.jstor.org/stable/356600 .
National Council of Teachers of English (NCTE). (1997). IDEAS Plus: A Collection of Practical Teaching Ideas , Book Fifteen.
National Council of Teachers of English (NCTE). (2022). Position Statement on Writing Instruction in School. Accessed from https://ncte.org/statement/statement-on-writing-instruction-in-school/ .
Learn more about Being a Writer
Read a recent interview with Joan Sedita
- Our Mission
Strategies for Teaching Argument Writing
Three simple ways a ninth-grade teacher scaffolds argument writing for students.

My ninth-grade students love to argue. They enjoy pushing back against authority, sharing their opinions, and having those opinions validated by their classmates. That’s no surprise—it’s invigorating to feel right about a hot-button topic. But through the teaching of argument writing, we can show our students that argumentation isn’t just about convincing someone of your viewpoint—it’s also about researching the issues, gathering evidence, and forming a nuanced claim.
Argument writing is a crucial skill for the real world, no matter what future lies ahead of a student. The Common Core State Standards support the teaching of argument writing , and students in the elementary grades on up who know how to support their claims with evidence will reap long-term benefits.
Argument Writing as Bell Work
One of the ways I teach argument writing is by making it part of our bell work routine, done in addition to our core lessons. This is a useful way to implement argument writing in class because there’s no need to carve out two weeks for a new unit.
Instead, at the bell, I provide students with an article to read that is relevant to our coursework and that expresses a clear opinion on an issue. They fill out the first section of the graphic organizer I’ve included here, which helps them identify the claim, supporting evidence, and hypothetical counterclaims. After three days of reading nonfiction texts from different perspectives, their graphic organizer becomes a useful resource for forming their own claim with supporting evidence in a short piece of writing.
The graphic organizer I use was inspired by the resources on argument writing provided by the National Writing Project through the College, Career, and Community Writers Program . They have resources for elementary and secondary teachers interested in argument writing instruction. I also like to check Kelly Gallagher’s Article of the Week for current nonfiction texts.
Moves of Argument Writing
Another way to practice argument writing is by teaching students to be aware of, and to use effectively, common moves found in argument writing. Joseph Harris’s book Rewriting: How to Do Things With Texts outlines some common moves:
- Illustrating: Using examples, usually from other sources, to explain your point.
- Authorizing: Calling upon the credibility of a source to help support to your argument.
- Borrowing: Using the terminology of other writers to help add legitimacy to a point.
- Extending: Adding commentary to the conversation on the issue at hand.
- Countering: Addressing opposing arguments with valid solutions.
Teaching students to identify these moves in writing is an effective way to improve reading comprehension, especially of nonfiction articles. Furthermore, teaching students to use these moves in their own writing will make for more intentional choices and, subsequently, better writing.
Argument Writing With Templates
Students who purposefully read arguments with the mindset of a writer can be taught to recognize the moves identified above and more. Knowing how to identify when and why authors use certain sentence starters, transitions, and other syntactic strategies can help students learn how to make their own point effectively.
To supplement our students’ knowledge of these syntactic strategies, Gerald Graff and Cathy Birkenstein recommend writing with templates in their book They Say, I Say: The Moves That Matter in Academic Writing . Graff and Birkenstein provide copious templates for students to use in specific argument writing scenarios. For example, consider these phrases that appear commonly in argument writing:
- On the one hand...
- On the other hand...
- I agree that...
- This is not to say that...
If you’re wary of having your students write using a template, I once felt the same way. But when I had my students purposefully integrate these words into their writing, I saw a significant improvement in their argument writing. Providing students with phrases like these helps them organize their thoughts in a way that better suits the format of their argument writing.
When we teach students the language of arguing, we are helping them gain traction in the real world. Throughout their lives, they’ll need to convince others to support their goals. In this way, argument writing is one of the most important tools we can teach our students to use.
The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
PeopleImages / Getty Images
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
A five-paragraph essay is a prose composition that follows a prescribed format of an introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph, and is typically taught during primary English education and applied on standardized testing throughout schooling.
Learning to write a high-quality five-paragraph essay is an essential skill for students in early English classes as it allows them to express certain ideas, claims, or concepts in an organized manner, complete with evidence that supports each of these notions. Later, though, students may decide to stray from the standard five-paragraph format and venture into writing an exploratory essay instead.
Still, teaching students to organize essays into the five-paragraph format is an easy way to introduce them to writing literary criticism, which will be tested time and again throughout their primary, secondary, and further education.
Writing a Good Introduction
The introduction is the first paragraph in your essay, and it should accomplish a few specific goals: capture the reader's interest, introduce the topic, and make a claim or express an opinion in a thesis statement.
It's a good idea to start your essay with a hook (fascinating statement) to pique the reader's interest, though this can also be accomplished by using descriptive words, an anecdote, an intriguing question, or an interesting fact. Students can practice with creative writing prompts to get some ideas for interesting ways to start an essay.
The next few sentences should explain your first statement, and prepare the reader for your thesis statement, which is typically the last sentence in the introduction. Your thesis sentence should provide your specific assertion and convey a clear point of view, which is typically divided into three distinct arguments that support this assertation, which will each serve as central themes for the body paragraphs.
Writing Body Paragraphs
The body of the essay will include three body paragraphs in a five-paragraph essay format, each limited to one main idea that supports your thesis.
To correctly write each of these three body paragraphs, you should state your supporting idea, your topic sentence, then back it up with two or three sentences of evidence. Use examples that validate the claim before concluding the paragraph and using transition words to lead to the paragraph that follows — meaning that all of your body paragraphs should follow the pattern of "statement, supporting ideas, transition statement."
Words to use as you transition from one paragraph to another include: moreover, in fact, on the whole, furthermore, as a result, simply put, for this reason, similarly, likewise, it follows that, naturally, by comparison, surely, and yet.
Writing a Conclusion
The final paragraph will summarize your main points and re-assert your main claim (from your thesis sentence). It should point out your main points, but should not repeat specific examples, and should, as always, leave a lasting impression on the reader.
The first sentence of the conclusion, therefore, should be used to restate the supporting claims argued in the body paragraphs as they relate to the thesis statement, then the next few sentences should be used to explain how the essay's main points can lead outward, perhaps to further thought on the topic. Ending the conclusion with a question, anecdote, or final pondering is a great way to leave a lasting impact.
Once you complete the first draft of your essay, it's a good idea to re-visit the thesis statement in your first paragraph. Read your essay to see if it flows well, and you might find that the supporting paragraphs are strong, but they don't address the exact focus of your thesis. Simply re-write your thesis sentence to fit your body and summary more exactly, and adjust the conclusion to wrap it all up nicely.
Practice Writing a Five-Paragraph Essay
Students can use the following steps to write a standard essay on any given topic. First, choose a topic, or ask your students to choose their topic, then allow them to form a basic five-paragraph by following these steps:
- Decide on your basic thesis , your idea of a topic to discuss.
- Decide on three pieces of supporting evidence you will use to prove your thesis.
- Write an introductory paragraph, including your thesis and evidence (in order of strength).
- Write your first body paragraph, starting with restating your thesis and focusing on your first piece of supporting evidence.
- End your first paragraph with a transitional sentence that leads to the next body paragraph.
- Write paragraph two of the body focussing on your second piece of evidence. Once again make the connection between your thesis and this piece of evidence.
- End your second paragraph with a transitional sentence that leads to paragraph number three.
- Repeat step 6 using your third piece of evidence.
- Begin your concluding paragraph by restating your thesis. Include the three points you've used to prove your thesis.
- End with a punch, a question, an anecdote, or an entertaining thought that will stay with the reader.
Once a student can master these 10 simple steps, writing a basic five-paragraph essay will be a piece of cake, so long as the student does so correctly and includes enough supporting information in each paragraph that all relate to the same centralized main idea, the thesis of the essay.
Limitations of the Five-Paragraph Essay
The five-paragraph essay is merely a starting point for students hoping to express their ideas in academic writing; there are some other forms and styles of writing that students should use to express their vocabulary in the written form.
According to Tory Young's "Studying English Literature: A Practical Guide":
"Although school students in the U.S. are examined on their ability to write a five-paragraph essay , its raison d'être is purportedly to give practice in basic writing skills that will lead to future success in more varied forms. Detractors feel, however, that writing to rule in this way is more likely to discourage imaginative writing and thinking than enable it. . . . The five-paragraph essay is less aware of its audience and sets out only to present information, an account or a kind of story rather than explicitly to persuade the reader."
Students should instead be asked to write other forms, such as journal entries, blog posts, reviews of goods or services, multi-paragraph research papers, and freeform expository writing around a central theme. Although five-paragraph essays are the golden rule when writing for standardized tests, experimentation with expression should be encouraged throughout primary schooling to bolster students' abilities to utilize the English language fully.
- How To Write an Essay
- How to Write a Great Essay for the TOEFL or TOEIC
- How to Write and Format an MBA Essay
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- How to Structure an Essay
- How to Help Your 4th Grader Write a Biography
- Paragraph Writing
- Definition and Examples of Body Paragraphs in Composition
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- What Is Expository Writing?
- 3 Changes That Will Take Your Essay From Good To Great
- An Introduction to Academic Writing
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
- The Five Steps of Writing an Essay
How to Teach Essay Writing to ESL Students Better
23 December 2020 Guest posts

Teaching essay writing to ESL students is no easy feat. There's a lot of things to consider, such as making sure the language is correct, of course, as well things like structure, accurate covering of the topic, the context of the essay, and how well the points are represented.
Throughout this guide, I'm going to detail some of the ways you can make every essay writing task as beneficial as possible. Your students can take on board these tips with the aim of making their essays better than ever before.
There are lots of tips and advice I could share, but today I'm going to focus on the most important, hopefully giving you a great place to get started when it comes to improving your students essay writing abilities
Start with the Basics
The absolute first place you want to start is with improving your student's sentence structure since sentences, after all, are what go into making an essay what it is. You'll want to start with teaching your students about basic sentences and then move onto compound and then complex.
Build it up slowly and highlight the key differences between each sentence type and why they would be used and what effect each sentence type has.
There's plenty of information online on how you can approach the basics of essay writing, such as on websites like Revieweal , Boomessays , Studydemic , Ukservicesreviews , and Assignment writing service , or you can simply ask a question you may have in your preferred search engine.
Understanding the Topic
A student will not be able to write a proper essay if they don't truly understand the topic they're writing about. Whether your students get to choose their topics or not, it's important that you explain that they should take their time to research and have a proper grasp on the topic they're writing about.
"It's important to remember that you can also suggest topics if the students are struggling to think of their own, ones that you believe will play to their strengths. Remember, essay writing within the ESL community is all about building confidence. If the students believe they can do a task, then they will be able to do it," explains Fergie Marie, a writer at Ukwritings and Custom Writing .
It's all about overcoming that first hurdle.
Break the Essay Down
Most essays are written in the same way, very similar to how stories are written. They have a start, a middle, and an end, and highlighting this structure form is a great way to make essays seem a little less daunting.
After all, being tasked with a 1,000-word essay can feel overwhelming at first, but when you break it down into three main sections that can be focused on individually, the task seems a little more manageable.
Of course, each section of the essay has a specific purpose. The introduction is meant to grab the reader, hook them into the writing, and sets the tone for the essay ahead. The middle is for laying down and explaining the points that would answer the question of whatever the essay topic is about.
Finally, you have the conclusion, which wraps everything up, answers any questions that were asked, and rounds off the essay nicely. Focusing on these points can help massively when it comes to writing an essay because there's less thought needed on what you need to write and more focus on what the actual writing will be.
Practice, Practice, Practice
"It might seem a bit mean to set regular essays all the time, and you don't want to be that kind of teacher, but the best way to get better at essay writing, as with everything else in life, is to practice. This means giving your students essay tasks to complete, and then reviewing the mistakes and highlighting what they did well," shares Duncan Turner, an educator at Assignment Help and Essayroo .
And that's the important bit. Not only do you want to highlight the areas where your students can improve or perhaps correcting mistakes they made, you always want to make sure you're showcasing what they did well and congratulating them on the bits they got right.
This inspires confidence and will encourage your students to keep trying, keep writing, and keep getting better.
Katherine Rundell is a book writer at Essay Writing Service and BigAssignments . She writes about teaching and helping ESL students make the most of their educational efforts. Also, she is a proof-reader at Essay writing services reviews .
Previous post: 7 Debunked Myths On Teaching English
- Features (34)
- Guest posts (37)
- Argentina (10)
- Colombia (6)
- Ecuador (2)
- Hong Kong (5)
- Thailand (15)
- Vietnam (5)
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
ESL Essay Writing: 7 Important Tips to Teach Students Plus Resources for Writing Lessons
“Every good story has a beginning, a middle and an end.”
This is true for a good essay, too.
An essay needs a coherent structure to successfully articulate its arguments. Strong preparation and planning is crucial to providing that structure.
Of course, essay writing can be challenging for ESL students. They must order their thoughts and construct their arguments—all in their second language.
So, here are seven ESL essay writing tips that will allow your students to weave together a coherent and persuasive essay, plus teacher resources for writing activities, prompts and lessons!
1. Build the Essay Around a Central Question
2. use the traditional 5-paragraph essay structure, 3. plan the essay carefully before writing, 4. encourage research and rewriting, 5. practice utilizing repetition, 6. aim to write a “full circle” essay, 7. edit the essay to the end, esl essay writing resources.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Encourage your students to build all their writing around one central question.
That central question is the engine of the writing—it should drive everything!
If a word or sentence is not assisting that forward motion toward the explication of that question and its possible answers, then it needs to be reworded, rephrased or just plain cut out and discarded.
Lean writing is merciless. Focusing on a central question throughout the prewriting, writing and rewriting stages helps develop the critical faculties required to discern what to keep and what to throw away.
Providing a clear structure for the student to approach essay writing can do a lot to build their confidence. The 5-paragraph essay, or “hamburger” essay, provides that clear structure for ESL writers.
Generally, this structure employs five separate paragraphs for the entire essay. Each paragraph serves a specific purpose, melding together to form a coherent whole:
- Paragraph 1: The introductory paragraph. This includes the thesis statement, orientating the reader to the purpose of the essay.
- Paragraphs 2 to 4: The body paragraphs. These make individual points that are further backed up by various forms of evidence.
- Paragraph 5: The conclusion paragraph. This provides a summation of the arguments and a final statement of the thesis.
While students do not need to rigidly follow this format forever, the simple structure outlined above can serve as excellent training wheels for your writers.
Using the 5-paragraph structure as outlined above makes planning clear cut.
Once they have their theses and are planning their paragraphs, share with the students the ridiculously useful acronym P.E.E. This stands for Point, Explanation and Evidence.
Each body paragraph should make a point or argument in favor of the central thesis, followed by an explanation of this point and relevant evidence to back it up.
Students can make note of all their points, explanations and evidence before they start writing them in essay form. This helps take away some of the pressure ESL writers feel when faced with a blank page.
Extol the necessity for students to constantly refer to their planning. The mind-mapping techniques popularized by Tony Buzan can be useful at the planning stage and make for easy reference points to ensure focus is maintained throughout the essay.
Having a visual reference such as this can help ensure that your student-writers see each piece of the whole as well as that elusive “bigger picture,” so it becomes a case of seeing the forest and the trees!
Just as planning is crucial, so too is research.
Often ideas or connections do not occur until the writing process has begun. This is a good thing! Essay writing is a creative act, so students can have more ideas along the way and work them in as they go.
The key is to always be able to back up these ideas. Students who have done their research on their subject will be much more confident and articulate in expressing their arguments in their writing.
One way you can help students with context and research is to show relevant video content via FluentU . This language learning program uses authentic videos made by and for native speakers to help students learn English.
You can watch videos as a class or assign them directly to students for individual viewing. Videos come equipped with interactive bilingual subtitles and other learning tools such as multimedia flashcards and personalized quizzes so you can see how each student is doing.
No matter how your students do their research, the important thing is that they explore and understand their topic area before beginning the big task of writing their essay.
Even with thorough planning and research, writing oneself into a linguistic cul-de-sac is a common error. Especially with higher-level students, unforeseen currents can pull the student-writer off course.
Sometimes abandoning such a sentence helps. Going back to the drawing board and rewriting it is often best.
Students can be creative with their sentence structures when expressing simpler ideas and arguments. However, when it comes to more complex concepts, help them learn to use shorter sentences to break their arguments into smaller, more digestible chunks.
Essay writing falls firmly in the camp of non-fiction. However, that doesn’t mean that essay writers can’t use some of the techniques more traditionally associated with fiction, poetry and drama .
One technique that’s particularly useful in essay writing is repetition. Just as poetry relies heavily on rhythm, so too does argument. Repetition can provide that sense of rhythm.
This is because written language has its origins in oral language. Think of the great orators and demagogues and their use of repetition. Speechwriters, too, are well aware of the power of repetition.
The writing principle of the “rule of 3” states that ideas expressed in these terms are more convincing and memorable. This is true of both spoken and written words and the ideas they express. Teach your students to use this method in their essay writing.
The very structure of the 5-paragraph essay lends itself to planning for this repetition, in fact. Each idea that is explored in a body paragraph should be outlined first in the introductory paragraph.
Then, the single body paragraph devoted to the idea will explore it at greater length, supported by evidence. And the third rap of the hammer occurs in the summation of the concluding paragraph, driving the point securely and convincingly home.
As mentioned at the start of this post, every good essay has a beginning, a middle and an end.
Each point made, explained and supported by evidence is a step toward what the writing teacher Roy Peter Clark calls “closing the circle of meaning.”
In planning for the conclusion of the essay, the students should take the opportunity to reaffirm their position. By referring to the points outlined in the introduction and driving them home one last time, the student-writer is bringing the essay to a satisfying full circle.
This may be accomplished by employing various strategies: an apt quotation, referring to future consequences or attempting to inspire and mobilize the reader.
Ending with a succinct quotation has the double benefit of lending some authoritative weight to the argument while also allowing the student to select a well-written, distilled expression of their central thesis. This can make for a strong ending, particularly for ESL students.
Often the essay thesis will suggest its own ending. If the essay is structured around a problem, it’s frequently appropriate to end the essay by offering solutions to the problem and outlining potential consequences if those solutions are not followed.
In the more polemical type of essay, the student may end with a call to arms, a plea for action on the part of the reader.
The strategy chosen by the student will depend largely on what fits the central thesis of their essay best.
For the ESL student, the final edit is especially important.
It offers a final chance to check form and meaning. For all writers, this process can be daunting, but more so for language students.
Often, ESL students will use the same words over and over again due to a limited vocabulary. Encourage your students to employ a thesaurus in the final draft before submission. This will freshen up their work, making it more readable, and will also increase their active vocabulary in the long run!
Another useful strategy at this stage is to encourage students to read their work aloud before handing it in.
This can be good pronunciation practice , but it also provides an opportunity to listen for grammatical errors. Further, it helps students hear where punctuation is required in the text, helping the overall rhythm and readability of the writing.
To really help your students become master essay writers, you’ll want to provide them with plenty of opportunities to test and flex their skills.
Writing prompts and exercises are a good place to start:
Descriptive writing activities encourage students to get creative and use their five senses, literary devices and diverse vocabulary. Read on for eight descriptive writing…
https://www.fluentu.com/blog/educator-english/esl-writing-projects/ https://www.fluentu.com/blog/educator-english/esl-picture-description/
Giving good ESL writing prompts is important because inspiring prompts inspire students to write more and writing more is how they improve. Read this post to learn 50…
You’ll likely also want to teach them more about the mechanics of writing :
Are you looking for ESL writing skills to share with your ESL students? In this guide, you’ll find different ESL writing techniques, such as helping students understand…
Would you like to introduce journal writing into your ESL classes? Fantastic idea! Here are 9 essential tips to make it creative, engaging and fun.
https://www.fluentu.com/blog/educator-english/esl-writing-lessons/
Essays are a great way not only for students to learn how the language works, but also to learn about themselves.
Formulating thoughts and arguments about various subjects is good exercise for not only the students’ linguistic faculties, but also for understanding who they are and how they see the world.
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Whether writing a particular academic essay (such as persuasive, narrative, descriptive, or expository) or a timed exam essay, the key to getting good at writing is to write. Creating opportunities for our students to engage in extended writing activities will go a long way to helping them improve their skills as scribes.
Try having students post a weekly response to a writing prompt or question that you assign. You may also want to create a separate discussion board where students can post ideas about their essay and get feedback from you and their classmates. 6. Give students homework to help them develop their essays.
The Harvard Writing Project publishes resource guides for faculty and teaching fellows that help them integrate writing into their courses more effectively — for example, by providing ideas about effective assignment design and strategies for responding to student writing.. A list of current HWP publications for faculty and teaching fellows is provided below.
'Four Square' Michele Morgan has been writing IEPs and behavior plans to help students be more successful for 17 years. She is a national-board-certified teacher, Utah Teacher Fellow with Hope ...
Outline. The last thing to do before starting to write an essay is to make its outline. Choose some topic and make a list of points your students would need to mention if they wrote an essay on it. Such a technique will give them a better understanding of what and essay is, and how it should be written. Make sure that all students perfectly ...
Harvard College Writing Center 5 Asking Analytical Questions When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a
Step 1: Start with Casual Augmentation. Engage your students in a low-stakes debate before formally teaching argumentative essay writing. This approach will help get students in the right mindset as you begin to lay the foundation for effective argumentation. Don't even mention the word essay at this point.
Once students have their introduction and body paragraphs complete, I then have them move on to writing the conclusion. At this step, I teach conclusion writing to my students and have them restate the thesis and add a general thought to the end of the paragraph. At this point, I emphasize that students should not be adding in any new information.
There are several steps TFs and faculty can take to prepare students to write good papers. If you are responsible for making writing assignments, remember that most students need to practice the basic elements of writing — purpose, argument, evidence, style — and that these skills are best practiced in shorter, focused assignments. Opt for shorter essays and papers throughout the semester ...
Discuss writing blocks and ways to overcome them. Discuss the planning process and experience how it helps flesh out an essay. Walk them through each lesson making sure they complete each step successfully before attempting to move on in the writing process. Working side by side with your student also helps you become a better instructor by ...
4. Identify claims and evidence. Related Article Tim Lahan. The Common Core Standards put argument front and center in American education, and even young readers are now expected to be able to ...
Effective writing is a vital component of students' literacy achievement, and writing is a critical communication tool for students to convey thoughts and opinions, describe ideas and events, and analyze information. Indeed, writing is a life-long skill that plays a key role in post-secondary success across academic and vocational disciplines.1
1. Help students understand the different purposes of writing. Students should understand the purpose of each genre (to describe, to narrate, to inform, or to persuade/analyze) so that they can select the genre best suited to their writing task. 2. Expand students' concept of audience.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
1. Get the basics right. It is clearly unrealistic to expect students to suddenly be able to write an essay in the target language without support. Build up their confidence over time so that they become familiar with writing increasingly long pieces of text. A key part of this will be to ensure that they understand sentence connectors and know ...
1. Teach Paragraph Writing FIRST. Before I even begin to think about teaching students to create an opinion piece, I make sure that my class has learned the basics of writing a good paragraph. We spend a lot of time with each component, and after they've mastered one paragraph, we move on to the five-paragraph essay.
The entire process I have outlined may take as much as three or four lessons. If you have this amount of time, here is a potential approach: Lesson 1: Example 'real world' essay construction. Lesson 2: Deconstruct a pre-written History essay. Lesson 3-4: Plan and write a class History essay.
5. Offer Student-specific And Timely Feedback. Finally, another crucial aspect you should grasp as a young teacher to help your students create better essays is ensuring you provide them with timely and specific feedback. Once all your students have it, you can spend an entire classroom period analyzing the feedback.
Start by modeling clear writing at the sentence level. The best way to approach essay writing skills is to start at the sentence level. Once students have learned to compose simple, compound, and complex sentences, they will have the tools necessary to write longer documents such as essays, business reports, formal emails, and so on.
Writing assignments are rooted in the texts that students are reading, and texts connect important topics like history, science, or art. I'm grateful that my school went on to adopt this kind of knowledge-building approach. What a difference it made. To give you a sense of the change, in a fourth-grade class, students studied the American ...
Before I get into these steps, I should note that there is no one right way to teach narrative writing, and plenty of accomplished teachers are doing it differently and getting great results. This just happens to be a process that has worked for me. Step 1: Show Students That Stories Are Everywhere. Getting our students to tell stories should ...
Teaching Argument Essay Writing Step 1: Develop the Claim. One of the first steps in helping students write an argument essay is developing the claim. Students need to understand that a claim is a debatable statement that they can back up and support using evidence and reasoning. Once students have a good idea about their essay's claim, they ...
There is a clear process to writing. The writing process is accessible to all of us, and it helps us create pieces of writing that successfully inform, persuade, and delight our readers. The more deeply we engage in the writing process, the greater the rewards. The Power of the Writing Process Writing in the Age of AI
Extending: Adding commentary to the conversation on the issue at hand. Countering: Addressing opposing arguments with valid solutions. Teaching students to identify these moves in writing is an effective way to improve reading comprehension, especially of nonfiction articles. Furthermore, teaching students to use these moves in their own ...
Students can use the following steps to write a standard essay on any given topic. First, choose a topic, or ask your students to choose their topic, then allow them to form a basic five-paragraph by following these steps: Decide on your basic thesis, your idea of a topic to discuss. Decide on three pieces of supporting evidence you will use to ...
Practice, Practice, Practice. "It might seem a bit mean to set regular essays all the time, and you don't want to be that kind of teacher, but the best way to get better at essay writing, as with everything else in life, is to practice. This means giving your students essay tasks to complete, and then reviewing the mistakes and highlighting ...
Ideas- The main idea, supporting details, evidence, and explanation. Ideas are the heart of any good paper. This is where you get the argument, the main idea, or the details that really bring the paper to life. Ideas should be the first thing discussed and brainstormed in the writing process.
So, here are seven ESL essay writing tips that will allow your students to weave together a coherent and persuasive essay, plus teacher resources for writing activities, prompts and lessons! Contents. 1. Build the Essay Around a Central Question; 2. Use the Traditional 5-paragraph Essay Structure; 3. Plan the Essay Carefully Before Writing; 4.