Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

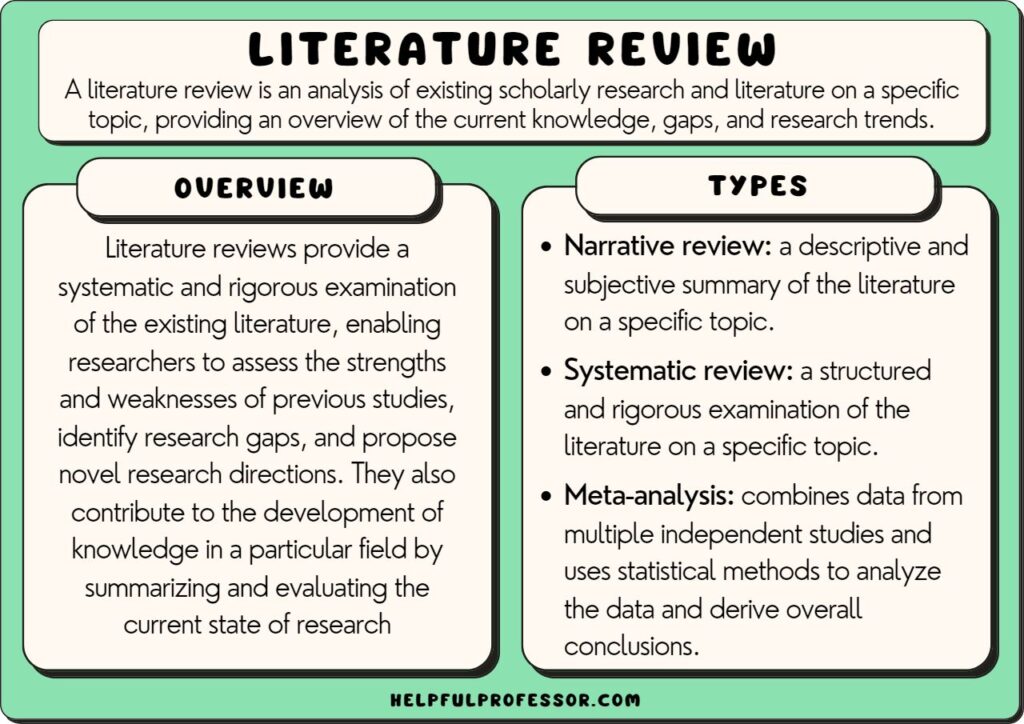
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, what is academic writing: tips for students.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

Literature Review Guide: Examples of Literature Reviews
- What is a Literature Review?
- How to start?
- Search strategies and Databases
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- How to organise the review
- Library summary
- Emerald Infographic
All good quality journal articles will include a small Literature Review after the Introduction paragraph. It may not be called a Literature Review but gives you an idea of how one is created in miniature.
Sample Literature Reviews as part of a articles or Theses
- Sample Literature Review on Critical Thinking (Gwendolyn Reece, American University Library)
- Hackett, G and Melia, D . The hotel as the holiday/stay destination:trends and innovations. Presented at TRIC Conference, Belfast, Ireland- June 2012 and EuroCHRIE Conference
Links to sample Literature Reviews from other libraries
- Sample literature reviews from University of West Florida
Standalone Literature Reviews
- Attitudes towards the Disability in Ireland
- Martin, A., O'Connor-Fenelon, M. and Lyons, R. (2010). Non-verbal communication between nurses and people with an intellectual disability: A review of the literature. Journal of Intellectual Diabilities, 14(4), 303-314.
Irish Theses
- Phillips, Martin (2015) European airline performance: a data envelopment analysis with extrapolations based on model outputs. Master of Business Studies thesis, Dublin City University.
- The customers’ perception of servicescape’s influence on their behaviours, in the food retail industry : Dublin Business School 2015
- Coughlan, Ray (2015) What was the role of leadership in the transformation of a failing Irish Insurance business. Masters thesis, Dublin, National College of Ireland.
- << Previous: Search strategies and Databases
- Next: Tutorials >>
- Last Updated: Feb 27, 2024 4:07 PM
- URL: https://ait.libguides.com/literaturereview
The Sheridan Libraries
- Write a Literature Review
- Sheridan Libraries
- Find This link opens in a new window
- Evaluate This link opens in a new window

Not every source you found should be included in your annotated bibliography or lit review. Only include the most relevant and most important sources.
BOOKS (sorted by title)
Organizing Your Review
Your lit review should not be a summary and evaluation of each article, one after the other. Your sources must be integrated together to create a narrative on your topic. Consider the following ways to organize your review:
- By themes, variables, issues.
- By varying perspectives regarding a topic of controversy.
- Chronologically, to show how the topic and research have developed over time.
Main Components of a Literature Review
Introduction.
- Describe the topic and provide a basic definition.
- Parameters of the topic. (What does the topic include and exclude?)
- Why did you select the literature you did?
- Historical background.
- Definitions in use.
- Mainstream ideas vs. alternative theoretical or ideological views.
- Principle questions being asked.
- Current research studies and discoveries.
- Methodologies.
- General conclusions.
- Summary of agreements and disagreements from the literature.
- How does your thesis fit in?
- << Previous: Synthesize
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 10:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/lit-review
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

I’m worried I’ve been contacted by a predatory publisher — how do I find out?
Career Feature 15 MAY 24

How I fled bombed Aleppo to continue my career in science
Career Feature 08 MAY 24

Illuminating ‘the ugly side of science’: fresh incentives for reporting negative results

US halts funding to controversial virus-hunting group: what researchers think
News 16 MAY 24
Japan can embrace open science — but flexible approaches are key
Correspondence 07 MAY 24

US funders to tighten oversight of controversial ‘gain of function’ research
News 07 MAY 24

Mount Etna’s spectacular smoke rings and more — April’s best science images
News 03 MAY 24
Faculty Positions& Postdoctoral Research Fellow, School of Optical and Electronic Information, HUST
Job Opportunities: Leading talents, young talents, overseas outstanding young scholars, postdoctoral researchers.
Wuhan, Hubei, China
School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology
Postdoc in CRISPR Meta-Analytics and AI for Therapeutic Target Discovery and Priotisation (OT Grant)
APPLICATION CLOSING DATE: 14/06/2024 Human Technopole (HT) is a new interdisciplinary life science research institute created and supported by the...
Human Technopole
Research Associate - Metabolism
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Postdoc Fellowships
Train with world-renowned cancer researchers at NIH? Consider joining the Center for Cancer Research (CCR) at the National Cancer Institute
Bethesda, Maryland
NIH National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Faculty Recruitment, Westlake University School of Medicine
Faculty positions are open at four distinct ranks: Assistant Professor, Associate Professor, Full Professor, and Chair Professor.
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Westlake University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

How to Write a Literature Review - A Self-Guided Tutorial
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the question
- 2. Review discipline styles
- Searching article databases - video
- Finding the article full-text
- Citation trails
- When to stop searching
- Citation Managers
- 5. Critically analyze and evaluate
- 6. Synthesize
- 7. Write literature review
- Additional Resources
You can meet with a librarian to talk about your literature review, or other library-related topics.

You can sort the literature in various ways, for example:

Synthesis Vizualization
Four examples of student writing.
In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D . For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.

Long description of "Four Examples of Student Writing" for web accessibility
- Download a copy of the "Four Examples of Student Writing" chart

Synthesis Matrix Example

From Jennifer Lim
Synthesis Templates
Synthesis grids are organizational tools used to record the main concepts of your sources and can help you make connections about how your sources relate to one another.
- Source Template Basic Literature Review Source Template from Walden University Writing Center to help record the main findings and concepts from different articles.
- Sample Literature Review Grids This spreadsheet contains multiple tabs with different grid templates. Download or create your own copy to begin recording notes.
- << Previous: 5. Critically analyze and evaluate
- Next: 7. Write literature review >>
- Last Updated: Apr 22, 2024 5:17 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ucmerced.edu/literature-review


Literature Reviews
- Types of reviews
- Getting started
Types of reviews and examples
Choosing a review type.
- 1. Define your research question
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
- Meta-analysis
- Systematized
Definition:
"A term used to describe a conventional overview of the literature, particularly when contrasted with a systematic review (Booth et al., 2012, p. 265).
Characteristics:
- Provides examination of recent or current literature on a wide range of subjects
- Varying levels of completeness / comprehensiveness, non-standardized methodology
- May or may not include comprehensive searching, quality assessment or critical appraisal
Mitchell, L. E., & Zajchowski, C. A. (2022). The history of air quality in Utah: A narrative review. Sustainability , 14 (15), 9653. doi.org/10.3390/su14159653
Booth, A., Papaioannou, D., & Sutton, A. (2012). Systematic approaches to a successful literature review. London: SAGE Publications Ltd.
"An assessment of what is already known about a policy or practice issue...using systematic review methods to search and critically appraise existing research" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 100).
- Assessment of what is already known about an issue
- Similar to a systematic review but within a time-constrained setting
- Typically employs methodological shortcuts, increasing risk of introducing bias, includes basic level of quality assessment
- Best suited for issues needing quick decisions and solutions (i.e., policy recommendations)
Learn more about the method:
Khangura, S., Konnyu, K., Cushman, R., Grimshaw, J., & Moher, D. (2012). Evidence summaries: the evolution of a rapid review approach. Systematic reviews, 1 (1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-1-10
Virginia Commonwealth University Libraries. (2021). Rapid Review Protocol .
Quarmby, S., Santos, G., & Mathias, M. (2019). Air quality strategies and technologies: A rapid review of the international evidence. Sustainability, 11 (10), 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102757
Grant, M.J. & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of the 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal , 26(2), 91-108. https://www.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
Developed and refined by the Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating Centre (EPPI-Centre), this review "map[s] out and categorize[s] existing literature on a particular topic, identifying gaps in research literature from which to commission further reviews and/or primary research" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 97).
Although mapping reviews are sometimes called scoping reviews, the key difference is that mapping reviews focus on a review question, rather than a topic
Mapping reviews are "best used where a clear target for a more focused evidence product has not yet been identified" (Booth, 2016, p. 14)
Mapping review searches are often quick and are intended to provide a broad overview
Mapping reviews can take different approaches in what types of literature is focused on in the search
Cooper I. D. (2016). What is a "mapping study?". Journal of the Medical Library Association: JMLA , 104 (1), 76–78. https://doi.org/10.3163/1536-5050.104.1.013
Miake-Lye, I. M., Hempel, S., Shanman, R., & Shekelle, P. G. (2016). What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products. Systematic reviews, 5 (1), 1-21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0204-x
Tainio, M., Andersen, Z. J., Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J., Hu, L., De Nazelle, A., An, R., ... & de Sá, T. H. (2021). Air pollution, physical activity and health: A mapping review of the evidence. Environment international , 147 , 105954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105954
Booth, A. (2016). EVIDENT Guidance for Reviewing the Evidence: a compendium of methodological literature and websites . ResearchGate. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.1562.9842 .
Grant, M.J. & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of the 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal , 26(2), 91-108. https://www.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
"A type of review that has as its primary objective the identification of the size and quality of research in a topic area in order to inform subsequent review" (Booth et al., 2012, p. 269).
- Main purpose is to map out and categorize existing literature, identify gaps in literature—great for informing policy-making
- Search comprehensiveness determined by time/scope constraints, could take longer than a systematic review
- No formal quality assessment or critical appraisal
Learn more about the methods :
Arksey, H., & O'Malley, L. (2005) Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology , 8 (1), 19-32. https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000119616
Levac, D., Colquhoun, H., & O’Brien, K. K. (2010). Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implementation Science: IS, 5, 69. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-5-69
Example :
Rahman, A., Sarkar, A., Yadav, O. P., Achari, G., & Slobodnik, J. (2021). Potential human health risks due to environmental exposure to nano-and microplastics and knowledge gaps: A scoping review. Science of the Total Environment, 757 , 143872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143872
A review that "[compiles] evidence from multiple...reviews into one accessible and usable document" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 103). While originally intended to be a compilation of Cochrane reviews, it now generally refers to any kind of evidence synthesis.
- Compiles evidence from multiple reviews into one document
- Often defines a broader question than is typical of a traditional systematic review
Choi, G. J., & Kang, H. (2022). The umbrella review: a useful strategy in the rain of evidence. The Korean Journal of Pain , 35 (2), 127–128. https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.127
Aromataris, E., Fernandez, R., Godfrey, C. M., Holly, C., Khalil, H., & Tungpunkom, P. (2015). Summarizing systematic reviews: Methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. International Journal of Evidence-Based Healthcare , 13(3), 132–140. https://doi.org/10.1097/XEB.0000000000000055
Rojas-Rueda, D., Morales-Zamora, E., Alsufyani, W. A., Herbst, C. H., Al Balawi, S. M., Alsukait, R., & Alomran, M. (2021). Environmental risk factors and health: An umbrella review of meta-analyses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Dealth , 18 (2), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020704
A meta-analysis is a "technique that statistically combines the results of quantitative studies to provide a more precise effect of the result" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 98).
- Statistical technique for combining results of quantitative studies to provide more precise effect of results
- Aims for exhaustive, comprehensive searching
- Quality assessment may determine inclusion/exclusion criteria
- May be conducted independently or as part of a systematic review
Berman, N. G., & Parker, R. A. (2002). Meta-analysis: Neither quick nor easy. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 2(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-2-10
Hites R. A. (2004). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the environment and in people: a meta-analysis of concentrations. Environmental Science & Technology , 38 (4), 945–956. https://doi.org/10.1021/es035082g
A systematic review "seeks to systematically search for, appraise, and [synthesize] research evidence, often adhering to the guidelines on the conduct of a review" provided by discipline-specific organizations, such as the Cochrane Collaboration (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 102).
- Aims to compile and synthesize all known knowledge on a given topic
- Adheres to strict guidelines, protocols, and frameworks
- Time-intensive and often takes months to a year or more to complete
- The most commonly referred to type of evidence synthesis. Sometimes confused as a blanket term for other types of reviews
Gascon, M., Triguero-Mas, M., Martínez, D., Dadvand, P., Forns, J., Plasència, A., & Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J. (2015). Mental health benefits of long-term exposure to residential green and blue spaces: a systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 12 (4), 4354–4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120404354
"Systematized reviews attempt to include one or more elements of the systematic review process while stopping short of claiming that the resultant output is a systematic review" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 102). When a systematic review approach is adapted to produce a more manageable scope, while still retaining the rigor of a systematic review such as risk of bias assessment and the use of a protocol, this is often referred to as a structured review (Huelin et al., 2015).
- Typically conducted by postgraduate or graduate students
- Often assigned by instructors to students who don't have the resources to conduct a full systematic review
Salvo, G., Lashewicz, B. M., Doyle-Baker, P. K., & McCormack, G. R. (2018). Neighbourhood built environment influences on physical activity among adults: A systematized review of qualitative evidence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 15 (5), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050897
Huelin, R., Iheanacho, I., Payne, K., & Sandman, K. (2015). What’s in a name? Systematic and non-systematic literature reviews, and why the distinction matters. https://www.evidera.com/resource/whats-in-a-name-systematic-and-non-systematic-literature-reviews-and-why-the-distinction-matters/

- Review Decision Tree - Cornell University For more information, check out Cornell's review methodology decision tree.
- LitR-Ex.com - Eight literature review methodologies Learn more about 8 different review types (incl. Systematic Reviews and Scoping Reviews) with practical tips about strengths and weaknesses of different methods.
- << Previous: Getting started
- Next: 1. Define your research question >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/litreviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries

- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview
15 Literature Review Examples
Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal . They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed.
Ideally, once you have completed your literature review, you will be able to identify how your research project can build upon and extend existing knowledge in your area of study.
Generally, for my undergraduate research students, I recommend a narrative review, where themes can be generated in order for the students to develop sufficient understanding of the topic so they can build upon the themes using unique methods or novel research questions.
If you’re in the process of writing a literature review, I have developed a literature review template for you to use – it’s a huge time-saver and walks you through how to write a literature review step-by-step:
Get your time-saving templates here to write your own literature review.
Literature Review Examples
For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics.
1. Narrative Review Examples
Also known as a traditional literature review, the narrative review provides a broad overview of the studies done on a particular topic.
It often includes both qualitative and quantitative studies and may cover a wide range of years.
The narrative review’s purpose is to identify commonalities, gaps, and contradictions in the literature .
I recommend to my students that they should gather their studies together, take notes on each study, then try to group them by themes that form the basis for the review (see my step-by-step instructions at the end of the article).
Example Study
Title: Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations
Citation: Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.12686
Overview: This narrative review analyzed themes emerging from 69 articles about communication in healthcare contexts. Five key themes were found in the literature: poor communication can lead to various negative outcomes, discontinuity of care, compromise of patient safety, patient dissatisfaction, and inefficient use of resources. After presenting the key themes, the authors recommend that practitioners need to approach healthcare communication in a more structured way, such as by ensuring there is a clear understanding of who is in charge of ensuring effective communication in clinical settings.
Other Examples
- Burnout in United States Healthcare Professionals: A Narrative Review (Reith, 2018) – read here
- Examining the Presence, Consequences, and Reduction of Implicit Bias in Health Care: A Narrative Review (Zestcott, Blair & Stone, 2016) – read here
- A Narrative Review of School-Based Physical Activity for Enhancing Cognition and Learning (Mavilidi et al., 2018) – read here
- A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents (Dyrbye & Shanafelt, 2015) – read here
2. Systematic Review Examples
This type of literature review is more structured and rigorous than a narrative review. It involves a detailed and comprehensive plan and search strategy derived from a set of specified research questions.
The key way you’d know a systematic review compared to a narrative review is in the methodology: the systematic review will likely have a very clear criteria for how the studies were collected, and clear explanations of exclusion/inclusion criteria.
The goal is to gather the maximum amount of valid literature on the topic, filter out invalid or low-quality reviews, and minimize bias. Ideally, this will provide more reliable findings, leading to higher-quality conclusions and recommendations for further research.
You may note from the examples below that the ‘method’ sections in systematic reviews tend to be much more explicit, often noting rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria and exact keywords used in searches.
Title: The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review
Citation: Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092422441730122X
Overview: This systematic review included 72 studies of food naturalness to explore trends in the literature about its importance for consumers. Keywords used in the data search included: food, naturalness, natural content, and natural ingredients. Studies were included if they examined consumers’ preference for food naturalness and contained empirical data. The authors found that the literature lacks clarity about how naturalness is defined and measured, but also found that food consumption is significantly influenced by perceived naturalness of goods.
- A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018 (Martin, Sun & Westine, 2020) – read here
- Where Is Current Research on Blockchain Technology? (Yli-Huumo et al., 2016) – read here
- Universities—industry collaboration: A systematic review (Ankrah & Al-Tabbaa, 2015) – read here
- Internet of Things Applications: A Systematic Review (Asghari, Rahmani & Javadi, 2019) – read here
3. Meta-analysis
This is a type of systematic review that uses statistical methods to combine and summarize the results of several studies.
Due to its robust methodology, a meta-analysis is often considered the ‘gold standard’ of secondary research , as it provides a more precise estimate of a treatment effect than any individual study contributing to the pooled analysis.
Furthermore, by aggregating data from a range of studies, a meta-analysis can identify patterns, disagreements, or other interesting relationships that may have been hidden in individual studies.
This helps to enhance the generalizability of findings, making the conclusions drawn from a meta-analysis particularly powerful and informative for policy and practice.
Title: Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Meta-Meta-Analysis
Citation: Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Source: https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060386
O verview: This study examines the relationship between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Researchers conducted a systematic search of meta-analyses and reviewed several databases, collecting 100 primary studies and five meta-analyses to analyze the connection between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. They find that the literature compellingly demonstrates that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels significantly influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
- The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research (Wisniewski, Zierer & Hattie, 2020) – read here
- How Much Does Education Improve Intelligence? A Meta-Analysis (Ritchie & Tucker-Drob, 2018) – read here
- A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling (Geiger et al., 2019) – read here
- Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits (Patterson, Chung & Swan, 2014) – read here
Other Types of Reviews
- Scoping Review: This type of review is used to map the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It can be undertaken as stand-alone projects in their own right, or as a precursor to a systematic review.
- Rapid Review: This type of review accelerates the systematic review process in order to produce information in a timely manner. This is achieved by simplifying or omitting stages of the systematic review process.
- Integrative Review: This review method is more inclusive than others, allowing for the simultaneous inclusion of experimental and non-experimental research. The goal is to more comprehensively understand a particular phenomenon.
- Critical Review: This is similar to a narrative review but requires a robust understanding of both the subject and the existing literature. In a critical review, the reviewer not only summarizes the existing literature, but also evaluates its strengths and weaknesses. This is common in the social sciences and humanities .
- State-of-the-Art Review: This considers the current level of advancement in a field or topic and makes recommendations for future research directions. This type of review is common in technological and scientific fields but can be applied to any discipline.
How to Write a Narrative Review (Tips for Undergrad Students)
Most undergraduate students conducting a capstone research project will be writing narrative reviews. Below is a five-step process for conducting a simple review of the literature for your project.
- Search for Relevant Literature: Use scholarly databases related to your field of study, provided by your university library, along with appropriate search terms to identify key scholarly articles that have been published on your topic.
- Evaluate and Select Sources: Filter the source list by selecting studies that are directly relevant and of sufficient quality, considering factors like credibility , objectivity, accuracy, and validity.
- Analyze and Synthesize: Review each source and summarize the main arguments in one paragraph (or more, for postgrad). Keep these summaries in a table.
- Identify Themes: With all studies summarized, group studies that share common themes, such as studies that have similar findings or methodologies.
- Write the Review: Write your review based upon the themes or subtopics you have identified. Give a thorough overview of each theme, integrating source data, and conclude with a summary of the current state of knowledge then suggestions for future research based upon your evaluation of what is lacking in the literature.
Literature reviews don’t have to be as scary as they seem. Yes, they are difficult and require a strong degree of comprehension of academic studies. But it can be feasibly done through following a structured approach to data collection and analysis. With my undergraduate research students (who tend to conduct small-scale qualitative studies ), I encourage them to conduct a narrative literature review whereby they can identify key themes in the literature. Within each theme, students can critique key studies and their strengths and limitations , in order to get a lay of the land and come to a point where they can identify ways to contribute new insights to the existing academic conversation on their topic.
Ankrah, S., & Omar, A. T. (2015). Universities–industry collaboration: A systematic review. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 31(3), 387-408.
Asghari, P., Rahmani, A. M., & Javadi, H. H. S. (2019). Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Computer Networks , 148 , 241-261.
Dyrbye, L., & Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Medical education , 50 (1), 132-149.
Geiger, J. L., Steg, L., Van Der Werff, E., & Ünal, A. B. (2019). A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. Journal of environmental psychology , 64 , 78-97.
Martin, F., Sun, T., & Westine, C. D. (2020). A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018. Computers & education , 159 , 104009.
Mavilidi, M. F., Ruiter, M., Schmidt, M., Okely, A. D., Loyens, S., Chandler, P., & Paas, F. (2018). A narrative review of school-based physical activity for enhancing cognition and learning: The importance of relevancy and integration. Frontiers in psychology , 2079.
Patterson, G. T., Chung, I. W., & Swan, P. W. (2014). Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits: A meta-analysis. Journal of experimental criminology , 10 , 487-513.
Reith, T. P. (2018). Burnout in United States healthcare professionals: a narrative review. Cureus , 10 (12).
Ritchie, S. J., & Tucker-Drob, E. M. (2018). How much does education improve intelligence? A meta-analysis. Psychological science , 29 (8), 1358-1369.
Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., & Hattie, J. (2020). The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 3087.
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., Park, S., & Smolander, K. (2016). Where is current research on blockchain technology?—a systematic review. PloS one , 11 (10), e0163477.
Zestcott, C. A., Blair, I. V., & Stone, J. (2016). Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations , 19 (4), 528-542

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.
Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.
Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
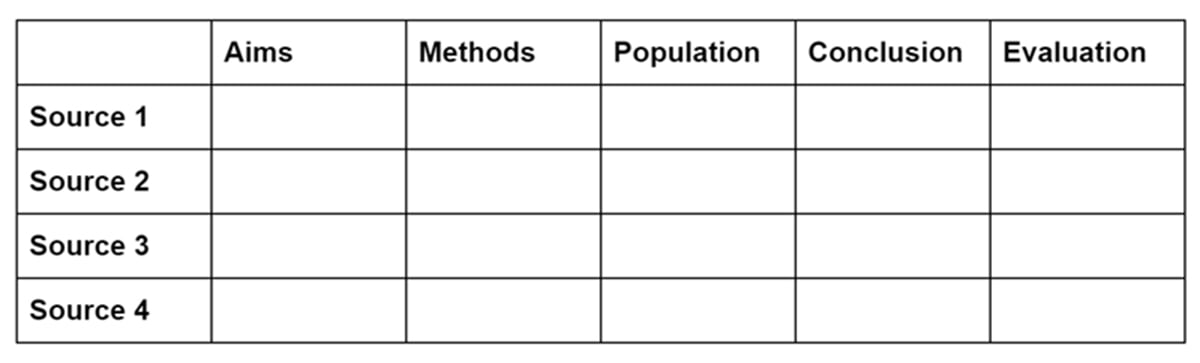
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.
Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
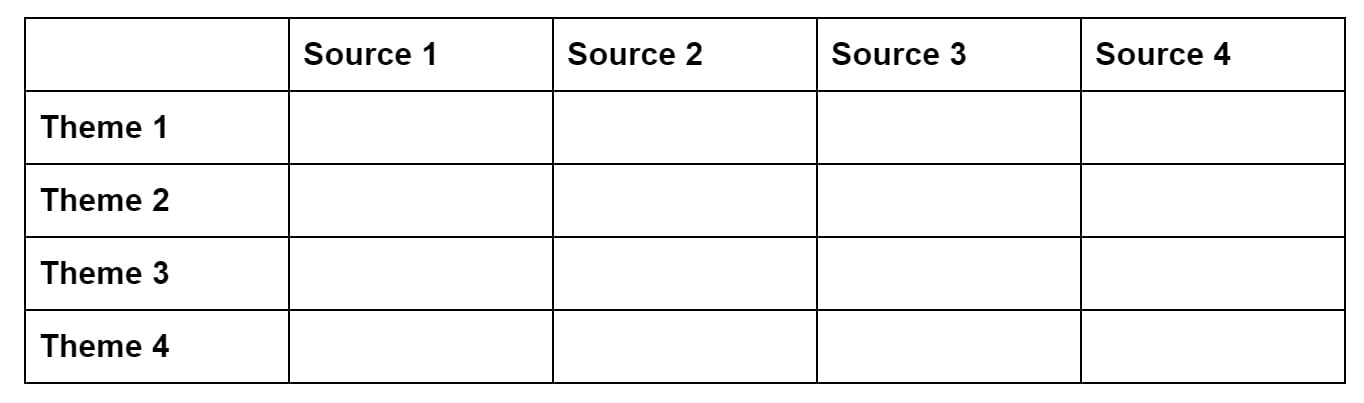
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
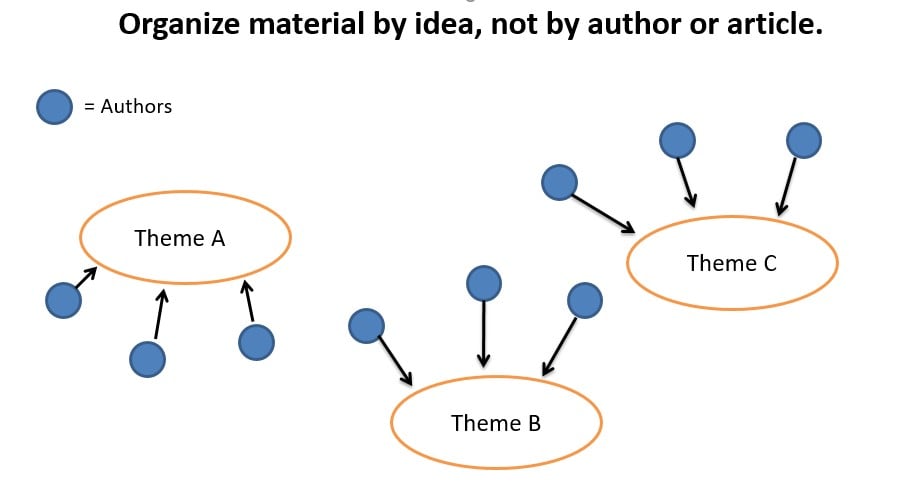
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay
Related Articles

Student Resources
How To Cite A YouTube Video In APA Style – With Examples

How to Write an Abstract APA Format

APA References Page Formatting and Example

APA Title Page (Cover Page) Format, Example, & Templates

How do I Cite a Source with Multiple Authors in APA Style?
How to Write a Psychology Essay
Literature Review Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Literature Review Template
If you’re working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a strong literature review chapter , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through an A-grade literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction . We start off by discussing the five core sections of a literature review chapter by unpacking our free literature review template . This includes:
- The literature review opening/ introduction section
- The theoretical framework (or foundation of theory)
- The empirical research
- The research gap
- The closing section
We then progress to the sample literature review (from an A-grade Master’s-level dissertation) to show how these concepts are applied in the literature review chapter. You can access the free resources mentioned in this video below.
PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Literature Review Example
Literature review example: frequently asked questions, is the sample literature review real.
Yes. The literature review example is an extract from a Master’s-level dissertation for an MBA program. It has not been edited in any way.
Can I replicate this literature review for my dissertation?
As we discuss in the video, every literature review will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your literature review to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a literature review here .
Where can I find more examples of literature reviews?
The best place to find more examples of literature review chapters would be within dissertation/thesis databases. These databases include dissertations, theses and research projects that have successfully passed the assessment criteria for the respective university, meaning that you have at least some sort of quality assurance.
The Open Access Thesis Database (OATD) is a good starting point.
How do I get the literature review template?
You can access our free literature review chapter template here .
Is the template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the template and you are free to use it as you wish.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

What will it take for you to guide me in my Ph.D research work?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Undergraduate courses
- Postgraduate courses
- Foundation courses
- Apprenticeships
- Part-time and short courses
- Apply undergraduate
- Apply postgraduate
Search for a course
Search by course name, subject, and more
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- (suspended) - Available in Clearing Not available in Clearing location-sign UCAS
Fees and funding
- Tuition fees
- Scholarships
- Funding your studies
- Student finance
- Cost of living support
Why study at Kent
Student life.
- Careers and employability
- Student support and wellbeing
- Our locations
- Placements and internships
- Year abroad
- Student stories
- Schools and colleges
- International
- International students
- Your country
- Applicant FAQs
- International scholarships
- University of Kent International College
- Campus Tours
- Applicant Events
- Postgraduate events
- Maps and directions
- Research strengths
- Research centres
- Research impact
Research institutes
- Durrell Institute of Conservation and Ecology
- Institute of Cyber Security for Society
- Institute of Cultural and Creative Industries
- Institute of Health, Social Care and Wellbeing
Research students
- Graduate and Researcher College
- Research degrees
- Find a supervisor
- How to apply
Popular searches
- Visits and Open Days
- Jobs and vacancies
- Accommodation
- Student guide
- Library and IT
- Partner with us
- Student Guide
- Student Help
- Health & wellbeing
- Student voice
- Living at Kent
- Careers & volunteering
- Diversity at Kent
- Finance & funding
- Life after graduation
Literature reviews
Writing a literature review.
The following guide has been created for you by the Student Learning Advisory Service . For more detailed guidance and to speak to one of our advisers, please book an appointment or join one of our workshops . Alternatively, have a look at our SkillBuilder skills videos.
Preparing a literature review involves:
- Searching for reliable, accurate and up-to-date material on a topic or subject
- Reading and summarising the key points from this literature
- Synthesising these key ideas, theories and concepts into a summary of what is known
- Discussing and evaluating these ideas, theories and concepts
- Identifying particular areas of debate or controversy
- Preparing the ground for the application of these ideas to new research
Finding and choosing material
Ensure you are clear on what you are looking for. ask yourself:.
- What is the specific question, topic or focus of my assignment?
- What kind of material do I need (e.g. theory, policy, empirical data)?
- What type of literature is available (e.g. journals, books, government documents)?
What kind of literature is particularly authoritative in this academic discipline (e.g. psychology, sociology, pharmacy)?
How much do you need?
This will depend on the length of the dissertation, the nature of the subject, and the level of study (undergraduate, Masters, PhD). As a very rough rule of thumb – you may choose 8-10 significant pieces (books and/or articles) for an 8,000 word dissertation, up to 20 major pieces of work for 12-15,000 words, and so on. Bear in mind that if your dissertation is based mainly around an interaction with existing scholarship you will need a longer literature review than if it is there as a prelude to new empirical research. Use your judgement or ask your supervisor for guidance.
Where to find suitable material
Your literature review should include a balance between substantial academic books, journal articles and other scholarly publications. All these sources should be as up-to-date as possible, with the exception of ‘classic texts’ such as major works written by leading scholars setting out formative ideas and theories central to your subject. There are several ways to locate suitable material:
Module bibliography: for undergraduate dissertations, look first at the bibliography provided with the module documentation. Choose one or two likely looking books or articles and then scan through the bibliographies provided by these authors. Skim read some of this material looking for clues: can you use these leads to identify key theories and authors or track down other appropriate material?
Library catalogue search engine: enter a few key words to capture a range of items, but avoid over-generalisations; if you type in something as broad as ‘social theory’ you are likely to get several thousand results. Be more specific: for example, ‘Heidegger, existentialism’. Ideally, you should narrow the field to obtain just a few dozen results. Skim through these quickly to identity texts which are most likely to contribute to your study.
Library bookshelves: browse the library shelves in the relevant subject area and examine the books that catch your eye. Check the contents and index pages, or skim through the introductions (or abstracts, in the case of journal articles) to see if they contain relevant material, and replace them if not. Don’t be afraid to ask one of the subject librarians for further help. Your supervisor may also be able to point you in the direction of some of the important literature , but remember this is your literature search, not theirs.
Online: for recent journal articles you will almost certainly need to use one of the online search engines. These can be found on the ‘Indexing Services’ button on the Templeman Library website. Kent students based at Medway still need to use the Templeman pages to access online journals, although you can get to these pages through the Drill Hall Library catalogue. Take a look as well at the Subject Guides on both the Templeman and DHL websites.
Check that you have made the right selection by asking:
- Has my search been wide enough to ensure that I have identified all the relevant material, but narrow enough to exclude irrelevant material?
- Is there a good enough sample of literature for the level (PhD, Masters, undergraduate) of my dissertation or thesis?
- Have I considered as many alternative points of view as possible?
- Will the reader find my literature review relevant and useful?
Assessing the literature
Read the material you have chosen carefully, considering the following:
- The key point discussed by the author: is this clearly defined
- What evidence has the author produced to support this central idea?
- How convincing are the reasons given for the author’s point of view?
- Could the evidence be interpreted in other ways?
- What is the author's research method (e.g. qualitative, quantitative, experimental, etc.)?
- What is the author's theoretical framework (e.g. psychological, developmental, feminist)?
- What is the relationship assumed by the author between theory and practice?
- Has the author critically evaluated the other literature in the field?
- Does the author include literature opposing their point of view?
- Is the research data based on a reliable method and accurate information?
- Can you ‘deconstruct’ the argument – identify the gaps or jumps in the logic?
- What are the strengths and limitations of this study?
- What does this book or article contribute to the field or topic?
- What does this book or article contribute to my own topic or thesis?
As you note down the key content of each book or journal article (together with the reference details of each source) record your responses to these questions. You will then be able to summarise each piece of material from two perspectives:
Content: a brief description of the content of the book or article. Remember, an author will often make just one key point; so, what is the point they are making, and how does it relate to your own research project or assignment?
Critical analysis: an assessment of the relative strengths and weaknesses of the evidence used, and the arguments presented. Has anything conveniently been left out or skated over? Is there a counter-argument, and has the author dealt with this adequately? Can the evidence presented be interpreted another way? Does the author demonstrate any obvious bias which could affect their reliability? Overall, based on the above analysis of the author’s work, how do you evaluate its contribution to the scholarly understanding and knowledge surrounding the topic?
Structuring the literature review
In a PhD thesis, the literature review typically comprises one chapter (perhaps 8-10,000 words), for a Masters dissertation it may be around 2-3,000 words, and for an undergraduate dissertation it may be no more than 2,000 words. In each case the word count can vary depending on a range of factors and it is always best, if in doubt, to ask your supervisor.
The overall structure of the section or chapter should be like any other: it should have a beginning, middle and end. You will need to guide the reader through the literature review, outlining the strategy you have adopted for selecting the books or articles, presenting the topic theme for the review, then using most of the word limit to analyse the chosen books or articles thoroughly before pulling everything together briefly in the conclusion.
Some people prefer a less linear approach. Instead of simply working through a list of 8-20 items on your book review list, you might want to try a thematic approach, grouping key ideas, facts, concepts or approaches together and then bouncing the ideas off each other. This is a slightly more creative (and interesting) way of producing the review, but a little more risky as it is harder to establish coherence and logical sequencing.
Whichever approach you adopt, make sure everything flows smoothly – that one idea or book leads neatly to the next. Take your reader effortlessly through a sequence of thought that is clear, accurate, precise and interesting.
Writing up your literature review
As with essays generally, only attempt to write up the literature review when you have completed all the reading and note-taking, and carefully planned its content and structure. Find an appropriate way of introducing the review, then guide the reader through the material clearly and directly, bearing in mind the following:
- Be selective in the number of points you draw out from each piece of literature; remember that one of your objectives is to demonstrate that you can use your judgement to identify what is central and what is secondary.
- Summarise and synthesise – use your own words to sum up what you think is important or controversial about the book or article.
- Never claim more than the evidence will support. Too many dissertations and theses are let down by sweeping generalisations. Be tentative and careful in the way you interpret the evidence.
- Keep your own voice – you are entitled to your own point of view provided it is based on evidence and clear argument.
- At the same time, aim to project an objective and tentative tone by using the 3rd person, (for example, ‘this tends to suggest’, ‘it could be argued’ and so on).
- Even with a literature review you should avoid using too many, or overlong, quotes. Summarise material in your own words as much as possible. Save the quotes for ‘punch-lines’ to drive a particular point home.
- Revise, revise, revise: refine and edit the draft as much as you can. Check for fluency, structure, evidence, criticality and referencing, and don’t forget the basics of good grammar, punctuation and spelling.
- Library Hours
- Strategic Plan
- Giving to the Libraries
- Jobs at the Libraries
- Find Your Librarian
- View All →
- Google Scholar
- Research Guides
- Textbook/Reserves
- Government Documents
- Get It For Me
- Print/Copy/Scan
- Renew Materials
- Study Rooms
- Use a Computer
- Borrow Tech Gear
- Student Services
- Faculty Services
- Users with Disabilities
- Visitors & Alumni
- Special Collections
- Find Information
Basics of Systematic Reviews
- About Systematic Review

Types of Reviews
Literature review.
Collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other
- Standard for research articles in most disciplines
- Tells the reader what is known, or not known, about a particular issue, topic, or subject
- Demonstrates knowledge and understanding of a topic
- Establishes context or background for a case or argument
- Helps develop the author’s ideas and perspective
Rapid Review
Thorough methodology but with process limitations in place to expeditethe completion of a review.
- For questions that require timely answers
- 3-4 months vs. 12-24 months
- Limitations - scope, comprehensiveness bias, and quality of appraisal
- Discusses potential effects that the limited methods may have had on results
Scoping Review
Determine the scope or coverage of a body of literature on a given topic and give clear indication of the volume of literature and studies available as well as an overview of its focus.
- Identify types of available evidence in a given field
- Clarify key concepts/definitions in the literature
- Examine how research is conducted on a certain topic or field
- Identify key factors related to a concept
- Key difference is focus
- Identify and analyze knowledge gaps
Systematic Review
Attempts to identify, appraise, and summarize all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria to answer a specific research question.
- clearly defined question with inclusion/exclusion criteria
- rigorous and systematic search of the literature
- thorough screening of results
- data extraction and management
- analysis and interpretation of results
- risk of bias assessment of included studies
Meta-Analysis
Used to systematically synthesize or merge the findings of single, independent studies, using statistical methods to calculate an overall or ‘absolute’ effect.
- Combines results from multiple empirical studies
- Requires systematic review first
- Use well recognized, systematic methods to account for differences in sample size, variability (heterogeneity) in study approach and findings (treatment effects)
- Test how sensitive their results are to their own systematic review protocol
For additional types of reviews please see these articles:
- Sutton, A., Clowes, M., Preston, L. and Booth, A. (2019), Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements. Health Info Libr J, 36: 202-222. https://doi.org/10.1111/hir.12276
- Grant, M.J. and Booth, A. (2009), A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal, 26: 91-108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
- << Previous: About Systematic Review
- Next: Sources >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 10:04 AM
- URL: https://libguides.utsa.edu/systematicreview
- Library Locations
- Staff Directory
- 508 Compliance
- Site Search
- © The University of Texas at San Antonio
- Information: 210-458-4011
- Campus Alerts
- Required Links
- UTSA Policies
- Report Fraud
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.

Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet].
Chapter 9 methods for literature reviews.
Guy Paré and Spyros Kitsiou .
9.1. Introduction
Literature reviews play a critical role in scholarship because science remains, first and foremost, a cumulative endeavour ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). As in any academic discipline, rigorous knowledge syntheses are becoming indispensable in keeping up with an exponentially growing eHealth literature, assisting practitioners, academics, and graduate students in finding, evaluating, and synthesizing the contents of many empirical and conceptual papers. Among other methods, literature reviews are essential for: (a) identifying what has been written on a subject or topic; (b) determining the extent to which a specific research area reveals any interpretable trends or patterns; (c) aggregating empirical findings related to a narrow research question to support evidence-based practice; (d) generating new frameworks and theories; and (e) identifying topics or questions requiring more investigation ( Paré, Trudel, Jaana, & Kitsiou, 2015 ).
Literature reviews can take two major forms. The most prevalent one is the “literature review” or “background” section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. This section synthesizes the extant literature and usually identifies the gaps in knowledge that the empirical study addresses ( Sylvester, Tate, & Johnstone, 2013 ). It may also provide a theoretical foundation for the proposed study, substantiate the presence of the research problem, justify the research as one that contributes something new to the cumulated knowledge, or validate the methods and approaches for the proposed study ( Hart, 1998 ; Levy & Ellis, 2006 ).
The second form of literature review, which is the focus of this chapter, constitutes an original and valuable work of research in and of itself ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Rather than providing a base for a researcher’s own work, it creates a solid starting point for all members of the community interested in a particular area or topic ( Mulrow, 1987 ). The so-called “review article” is a journal-length paper which has an overarching purpose to synthesize the literature in a field, without collecting or analyzing any primary data ( Green, Johnson, & Adams, 2006 ).
When appropriately conducted, review articles represent powerful information sources for practitioners looking for state-of-the art evidence to guide their decision-making and work practices ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, high-quality reviews become frequently cited pieces of work which researchers seek out as a first clear outline of the literature when undertaking empirical studies ( Cooper, 1988 ; Rowe, 2014 ). Scholars who track and gauge the impact of articles have found that review papers are cited and downloaded more often than any other type of published article ( Cronin, Ryan, & Coughlan, 2008 ; Montori, Wilczynski, Morgan, Haynes, & Hedges, 2003 ; Patsopoulos, Analatos, & Ioannidis, 2005 ). The reason for their popularity may be the fact that reading the review enables one to have an overview, if not a detailed knowledge of the area in question, as well as references to the most useful primary sources ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Although they are not easy to conduct, the commitment to complete a review article provides a tremendous service to one’s academic community ( Paré et al., 2015 ; Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Most, if not all, peer-reviewed journals in the fields of medical informatics publish review articles of some type.
The main objectives of this chapter are fourfold: (a) to provide an overview of the major steps and activities involved in conducting a stand-alone literature review; (b) to describe and contrast the different types of review articles that can contribute to the eHealth knowledge base; (c) to illustrate each review type with one or two examples from the eHealth literature; and (d) to provide a series of recommendations for prospective authors of review articles in this domain.
9.2. Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
As explained in Templier and Paré (2015) , there are six generic steps involved in conducting a review article:
- formulating the research question(s) and objective(s),
- searching the extant literature,
- screening for inclusion,
- assessing the quality of primary studies,
- extracting data, and
- analyzing data.
Although these steps are presented here in sequential order, one must keep in mind that the review process can be iterative and that many activities can be initiated during the planning stage and later refined during subsequent phases ( Finfgeld-Connett & Johnson, 2013 ; Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ).
Formulating the research question(s) and objective(s): As a first step, members of the review team must appropriately justify the need for the review itself ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ), identify the review’s main objective(s) ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ), and define the concepts or variables at the heart of their synthesis ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ; Webster & Watson, 2002 ). Importantly, they also need to articulate the research question(s) they propose to investigate ( Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ). In this regard, we concur with Jesson, Matheson, and Lacey (2011) that clearly articulated research questions are key ingredients that guide the entire review methodology; they underscore the type of information that is needed, inform the search for and selection of relevant literature, and guide or orient the subsequent analysis. Searching the extant literature: The next step consists of searching the literature and making decisions about the suitability of material to be considered in the review ( Cooper, 1988 ). There exist three main coverage strategies. First, exhaustive coverage means an effort is made to be as comprehensive as possible in order to ensure that all relevant studies, published and unpublished, are included in the review and, thus, conclusions are based on this all-inclusive knowledge base. The second type of coverage consists of presenting materials that are representative of most other works in a given field or area. Often authors who adopt this strategy will search for relevant articles in a small number of top-tier journals in a field ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In the third strategy, the review team concentrates on prior works that have been central or pivotal to a particular topic. This may include empirical studies or conceptual papers that initiated a line of investigation, changed how problems or questions were framed, introduced new methods or concepts, or engendered important debate ( Cooper, 1988 ). Screening for inclusion: The following step consists of evaluating the applicability of the material identified in the preceding step ( Levy & Ellis, 2006 ; vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). Once a group of potential studies has been identified, members of the review team must screen them to determine their relevance ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). A set of predetermined rules provides a basis for including or excluding certain studies. This exercise requires a significant investment on the part of researchers, who must ensure enhanced objectivity and avoid biases or mistakes. As discussed later in this chapter, for certain types of reviews there must be at least two independent reviewers involved in the screening process and a procedure to resolve disagreements must also be in place ( Liberati et al., 2009 ; Shea et al., 2009 ). Assessing the quality of primary studies: In addition to screening material for inclusion, members of the review team may need to assess the scientific quality of the selected studies, that is, appraise the rigour of the research design and methods. Such formal assessment, which is usually conducted independently by at least two coders, helps members of the review team refine which studies to include in the final sample, determine whether or not the differences in quality may affect their conclusions, or guide how they analyze the data and interpret the findings ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Ascribing quality scores to each primary study or considering through domain-based evaluations which study components have or have not been designed and executed appropriately makes it possible to reflect on the extent to which the selected study addresses possible biases and maximizes validity ( Shea et al., 2009 ). Extracting data: The following step involves gathering or extracting applicable information from each primary study included in the sample and deciding what is relevant to the problem of interest ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Indeed, the type of data that should be recorded mainly depends on the initial research questions ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ). However, important information may also be gathered about how, when, where and by whom the primary study was conducted, the research design and methods, or qualitative/quantitative results ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Analyzing and synthesizing data : As a final step, members of the review team must collate, summarize, aggregate, organize, and compare the evidence extracted from the included studies. The extracted data must be presented in a meaningful way that suggests a new contribution to the extant literature ( Jesson et al., 2011 ). Webster and Watson (2002) warn researchers that literature reviews should be much more than lists of papers and should provide a coherent lens to make sense of extant knowledge on a given topic. There exist several methods and techniques for synthesizing quantitative (e.g., frequency analysis, meta-analysis) and qualitative (e.g., grounded theory, narrative analysis, meta-ethnography) evidence ( Dixon-Woods, Agarwal, Jones, Young, & Sutton, 2005 ; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic. Our classification scheme is largely inspired from Paré and colleagues’ (2015) typology. Below we present and illustrate those review types that we feel are central to the growth and development of the eHealth domain.
9.3.1. Narrative Reviews
The narrative review is the “traditional” way of reviewing the extant literature and is skewed towards a qualitative interpretation of prior knowledge ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). Put simply, a narrative review attempts to summarize or synthesize what has been written on a particular topic but does not seek generalization or cumulative knowledge from what is reviewed ( Davies, 2000 ; Green et al., 2006 ). Instead, the review team often undertakes the task of accumulating and synthesizing the literature to demonstrate the value of a particular point of view ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ). As such, reviewers may selectively ignore or limit the attention paid to certain studies in order to make a point. In this rather unsystematic approach, the selection of information from primary articles is subjective, lacks explicit criteria for inclusion and can lead to biased interpretations or inferences ( Green et al., 2006 ). There are several narrative reviews in the particular eHealth domain, as in all fields, which follow such an unstructured approach ( Silva et al., 2015 ; Paul et al., 2015 ).
Despite these criticisms, this type of review can be very useful in gathering together a volume of literature in a specific subject area and synthesizing it. As mentioned above, its primary purpose is to provide the reader with a comprehensive background for understanding current knowledge and highlighting the significance of new research ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Faculty like to use narrative reviews in the classroom because they are often more up to date than textbooks, provide a single source for students to reference, and expose students to peer-reviewed literature ( Green et al., 2006 ). For researchers, narrative reviews can inspire research ideas by identifying gaps or inconsistencies in a body of knowledge, thus helping researchers to determine research questions or formulate hypotheses. Importantly, narrative reviews can also be used as educational articles to bring practitioners up to date with certain topics of issues ( Green et al., 2006 ).
Recently, there have been several efforts to introduce more rigour in narrative reviews that will elucidate common pitfalls and bring changes into their publication standards. Information systems researchers, among others, have contributed to advancing knowledge on how to structure a “traditional” review. For instance, Levy and Ellis (2006) proposed a generic framework for conducting such reviews. Their model follows the systematic data processing approach comprised of three steps, namely: (a) literature search and screening; (b) data extraction and analysis; and (c) writing the literature review. They provide detailed and very helpful instructions on how to conduct each step of the review process. As another methodological contribution, vom Brocke et al. (2009) offered a series of guidelines for conducting literature reviews, with a particular focus on how to search and extract the relevant body of knowledge. Last, Bandara, Miskon, and Fielt (2011) proposed a structured, predefined and tool-supported method to identify primary studies within a feasible scope, extract relevant content from identified articles, synthesize and analyze the findings, and effectively write and present the results of the literature review. We highly recommend that prospective authors of narrative reviews consult these useful sources before embarking on their work.
Darlow and Wen (2015) provide a good example of a highly structured narrative review in the eHealth field. These authors synthesized published articles that describe the development process of mobile health ( m-health ) interventions for patients’ cancer care self-management. As in most narrative reviews, the scope of the research questions being investigated is broad: (a) how development of these systems are carried out; (b) which methods are used to investigate these systems; and (c) what conclusions can be drawn as a result of the development of these systems. To provide clear answers to these questions, a literature search was conducted on six electronic databases and Google Scholar . The search was performed using several terms and free text words, combining them in an appropriate manner. Four inclusion and three exclusion criteria were utilized during the screening process. Both authors independently reviewed each of the identified articles to determine eligibility and extract study information. A flow diagram shows the number of studies identified, screened, and included or excluded at each stage of study selection. In terms of contributions, this review provides a series of practical recommendations for m-health intervention development.
9.3.2. Descriptive or Mapping Reviews
The primary goal of a descriptive review is to determine the extent to which a body of knowledge in a particular research topic reveals any interpretable pattern or trend with respect to pre-existing propositions, theories, methodologies or findings ( King & He, 2005 ; Paré et al., 2015 ). In contrast with narrative reviews, descriptive reviews follow a systematic and transparent procedure, including searching, screening and classifying studies ( Petersen, Vakkalanka, & Kuzniarz, 2015 ). Indeed, structured search methods are used to form a representative sample of a larger group of published works ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, authors of descriptive reviews extract from each study certain characteristics of interest, such as publication year, research methods, data collection techniques, and direction or strength of research outcomes (e.g., positive, negative, or non-significant) in the form of frequency analysis to produce quantitative results ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). In essence, each study included in a descriptive review is treated as the unit of analysis and the published literature as a whole provides a database from which the authors attempt to identify any interpretable trends or draw overall conclusions about the merits of existing conceptualizations, propositions, methods or findings ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In doing so, a descriptive review may claim that its findings represent the state of the art in a particular domain ( King & He, 2005 ).
In the fields of health sciences and medical informatics, reviews that focus on examining the range, nature and evolution of a topic area are described by Anderson, Allen, Peckham, and Goodwin (2008) as mapping reviews . Like descriptive reviews, the research questions are generic and usually relate to publication patterns and trends. There is no preconceived plan to systematically review all of the literature although this can be done. Instead, researchers often present studies that are representative of most works published in a particular area and they consider a specific time frame to be mapped.
An example of this approach in the eHealth domain is offered by DeShazo, Lavallie, and Wolf (2009). The purpose of this descriptive or mapping review was to characterize publication trends in the medical informatics literature over a 20-year period (1987 to 2006). To achieve this ambitious objective, the authors performed a bibliometric analysis of medical informatics citations indexed in medline using publication trends, journal frequencies, impact factors, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) term frequencies, and characteristics of citations. Findings revealed that there were over 77,000 medical informatics articles published during the covered period in numerous journals and that the average annual growth rate was 12%. The MeSH term analysis also suggested a strong interdisciplinary trend. Finally, average impact scores increased over time with two notable growth periods. Overall, patterns in research outputs that seem to characterize the historic trends and current components of the field of medical informatics suggest it may be a maturing discipline (DeShazo et al., 2009).
9.3.3. Scoping Reviews
Scoping reviews attempt to provide an initial indication of the potential size and nature of the extant literature on an emergent topic (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Daudt, van Mossel, & Scott, 2013 ; Levac, Colquhoun, & O’Brien, 2010). A scoping review may be conducted to examine the extent, range and nature of research activities in a particular area, determine the value of undertaking a full systematic review (discussed next), or identify research gaps in the extant literature ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In line with their main objective, scoping reviews usually conclude with the presentation of a detailed research agenda for future works along with potential implications for both practice and research.
Unlike narrative and descriptive reviews, the whole point of scoping the field is to be as comprehensive as possible, including grey literature (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005). Inclusion and exclusion criteria must be established to help researchers eliminate studies that are not aligned with the research questions. It is also recommended that at least two independent coders review abstracts yielded from the search strategy and then the full articles for study selection ( Daudt et al., 2013 ). The synthesized evidence from content or thematic analysis is relatively easy to present in tabular form (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
One of the most highly cited scoping reviews in the eHealth domain was published by Archer, Fevrier-Thomas, Lokker, McKibbon, and Straus (2011) . These authors reviewed the existing literature on personal health record ( phr ) systems including design, functionality, implementation, applications, outcomes, and benefits. Seven databases were searched from 1985 to March 2010. Several search terms relating to phr s were used during this process. Two authors independently screened titles and abstracts to determine inclusion status. A second screen of full-text articles, again by two independent members of the research team, ensured that the studies described phr s. All in all, 130 articles met the criteria and their data were extracted manually into a database. The authors concluded that although there is a large amount of survey, observational, cohort/panel, and anecdotal evidence of phr benefits and satisfaction for patients, more research is needed to evaluate the results of phr implementations. Their in-depth analysis of the literature signalled that there is little solid evidence from randomized controlled trials or other studies through the use of phr s. Hence, they suggested that more research is needed that addresses the current lack of understanding of optimal functionality and usability of these systems, and how they can play a beneficial role in supporting patient self-management ( Archer et al., 2011 ).
9.3.4. Forms of Aggregative Reviews
Healthcare providers, practitioners, and policy-makers are nowadays overwhelmed with large volumes of information, including research-based evidence from numerous clinical trials and evaluation studies, assessing the effectiveness of health information technologies and interventions ( Ammenwerth & de Keizer, 2004 ; Deshazo et al., 2009 ). It is unrealistic to expect that all these disparate actors will have the time, skills, and necessary resources to identify the available evidence in the area of their expertise and consider it when making decisions. Systematic reviews that involve the rigorous application of scientific strategies aimed at limiting subjectivity and bias (i.e., systematic and random errors) can respond to this challenge.
Systematic reviews attempt to aggregate, appraise, and synthesize in a single source all empirical evidence that meet a set of previously specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a clearly formulated and often narrow research question on a particular topic of interest to support evidence-based practice ( Liberati et al., 2009 ). They adhere closely to explicit scientific principles ( Liberati et al., 2009 ) and rigorous methodological guidelines (Higgins & Green, 2008) aimed at reducing random and systematic errors that can lead to deviations from the truth in results or inferences. The use of explicit methods allows systematic reviews to aggregate a large body of research evidence, assess whether effects or relationships are in the same direction and of the same general magnitude, explain possible inconsistencies between study results, and determine the strength of the overall evidence for every outcome of interest based on the quality of included studies and the general consistency among them ( Cook, Mulrow, & Haynes, 1997 ). The main procedures of a systematic review involve:
- Formulating a review question and developing a search strategy based on explicit inclusion criteria for the identification of eligible studies (usually described in the context of a detailed review protocol).
- Searching for eligible studies using multiple databases and information sources, including grey literature sources, without any language restrictions.
- Selecting studies, extracting data, and assessing risk of bias in a duplicate manner using two independent reviewers to avoid random or systematic errors in the process.
- Analyzing data using quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Presenting results in summary of findings tables.
- Interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
Many systematic reviews, but not all, use statistical methods to combine the results of independent studies into a single quantitative estimate or summary effect size. Known as meta-analyses , these reviews use specific data extraction and statistical techniques (e.g., network, frequentist, or Bayesian meta-analyses) to calculate from each study by outcome of interest an effect size along with a confidence interval that reflects the degree of uncertainty behind the point estimate of effect ( Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins, & Rothstein, 2009 ; Deeks, Higgins, & Altman, 2008 ). Subsequently, they use fixed or random-effects analysis models to combine the results of the included studies, assess statistical heterogeneity, and calculate a weighted average of the effect estimates from the different studies, taking into account their sample sizes. The summary effect size is a value that reflects the average magnitude of the intervention effect for a particular outcome of interest or, more generally, the strength of a relationship between two variables across all studies included in the systematic review. By statistically combining data from multiple studies, meta-analyses can create more precise and reliable estimates of intervention effects than those derived from individual studies alone, when these are examined independently as discrete sources of information.
The review by Gurol-Urganci, de Jongh, Vodopivec-Jamsek, Atun, and Car (2013) on the effects of mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments is an illustrative example of a high-quality systematic review with meta-analysis. Missed appointments are a major cause of inefficiency in healthcare delivery with substantial monetary costs to health systems. These authors sought to assess whether mobile phone-based appointment reminders delivered through Short Message Service ( sms ) or Multimedia Messaging Service ( mms ) are effective in improving rates of patient attendance and reducing overall costs. To this end, they conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases using highly sensitive search strategies without language or publication-type restrictions to identify all rct s that are eligible for inclusion. In order to minimize the risk of omitting eligible studies not captured by the original search, they supplemented all electronic searches with manual screening of trial registers and references contained in the included studies. Study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments were performed independently by two coders using standardized methods to ensure consistency and to eliminate potential errors. Findings from eight rct s involving 6,615 participants were pooled into meta-analyses to calculate the magnitude of effects that mobile text message reminders have on the rate of attendance at healthcare appointments compared to no reminders and phone call reminders.
Meta-analyses are regarded as powerful tools for deriving meaningful conclusions. However, there are situations in which it is neither reasonable nor appropriate to pool studies together using meta-analytic methods simply because there is extensive clinical heterogeneity between the included studies or variation in measurement tools, comparisons, or outcomes of interest. In these cases, systematic reviews can use qualitative synthesis methods such as vote counting, content analysis, classification schemes and tabulations, as an alternative approach to narratively synthesize the results of the independent studies included in the review. This form of review is known as qualitative systematic review.
A rigorous example of one such review in the eHealth domain is presented by Mickan, Atherton, Roberts, Heneghan, and Tilson (2014) on the use of handheld computers by healthcare professionals and their impact on access to information and clinical decision-making. In line with the methodological guidelines for systematic reviews, these authors: (a) developed and registered with prospero ( www.crd.york.ac.uk/ prospero / ) an a priori review protocol; (b) conducted comprehensive searches for eligible studies using multiple databases and other supplementary strategies (e.g., forward searches); and (c) subsequently carried out study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments in a duplicate manner to eliminate potential errors in the review process. Heterogeneity between the included studies in terms of reported outcomes and measures precluded the use of meta-analytic methods. To this end, the authors resorted to using narrative analysis and synthesis to describe the effectiveness of handheld computers on accessing information for clinical knowledge, adherence to safety and clinical quality guidelines, and diagnostic decision-making.
In recent years, the number of systematic reviews in the field of health informatics has increased considerably. Systematic reviews with discordant findings can cause great confusion and make it difficult for decision-makers to interpret the review-level evidence ( Moher, 2013 ). Therefore, there is a growing need for appraisal and synthesis of prior systematic reviews to ensure that decision-making is constantly informed by the best available accumulated evidence. Umbrella reviews , also known as overviews of systematic reviews, are tertiary types of evidence synthesis that aim to accomplish this; that is, they aim to compare and contrast findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Umbrella reviews generally adhere to the same principles and rigorous methodological guidelines used in systematic reviews. However, the unit of analysis in umbrella reviews is the systematic review rather than the primary study ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Unlike systematic reviews that have a narrow focus of inquiry, umbrella reviews focus on broader research topics for which there are several potential interventions ( Smith, Devane, Begley, & Clarke, 2011 ). A recent umbrella review on the effects of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with heart failure critically appraised, compared, and synthesized evidence from 15 systematic reviews to investigate which types of home telemonitoring technologies and forms of interventions are more effective in reducing mortality and hospital admissions ( Kitsiou, Paré, & Jaana, 2015 ).
9.3.5. Realist Reviews
Realist reviews are theory-driven interpretative reviews developed to inform, enhance, or supplement conventional systematic reviews by making sense of heterogeneous evidence about complex interventions applied in diverse contexts in a way that informs policy decision-making ( Greenhalgh, Wong, Westhorp, & Pawson, 2011 ). They originated from criticisms of positivist systematic reviews which centre on their “simplistic” underlying assumptions ( Oates, 2011 ). As explained above, systematic reviews seek to identify causation. Such logic is appropriate for fields like medicine and education where findings of randomized controlled trials can be aggregated to see whether a new treatment or intervention does improve outcomes. However, many argue that it is not possible to establish such direct causal links between interventions and outcomes in fields such as social policy, management, and information systems where for any intervention there is unlikely to be a regular or consistent outcome ( Oates, 2011 ; Pawson, 2006 ; Rousseau, Manning, & Denyer, 2008 ).
To circumvent these limitations, Pawson, Greenhalgh, Harvey, and Walshe (2005) have proposed a new approach for synthesizing knowledge that seeks to unpack the mechanism of how “complex interventions” work in particular contexts. The basic research question — what works? — which is usually associated with systematic reviews changes to: what is it about this intervention that works, for whom, in what circumstances, in what respects and why? Realist reviews have no particular preference for either quantitative or qualitative evidence. As a theory-building approach, a realist review usually starts by articulating likely underlying mechanisms and then scrutinizes available evidence to find out whether and where these mechanisms are applicable ( Shepperd et al., 2009 ). Primary studies found in the extant literature are viewed as case studies which can test and modify the initial theories ( Rousseau et al., 2008 ).
The main objective pursued in the realist review conducted by Otte-Trojel, de Bont, Rundall, and van de Klundert (2014) was to examine how patient portals contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The specific goals were to investigate how outcomes are produced and, most importantly, how variations in outcomes can be explained. The research team started with an exploratory review of background documents and research studies to identify ways in which patient portals may contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The authors identified six main ways which represent “educated guesses” to be tested against the data in the evaluation studies. These studies were identified through a formal and systematic search in four databases between 2003 and 2013. Two members of the research team selected the articles using a pre-established list of inclusion and exclusion criteria and following a two-step procedure. The authors then extracted data from the selected articles and created several tables, one for each outcome category. They organized information to bring forward those mechanisms where patient portals contribute to outcomes and the variation in outcomes across different contexts.
9.3.6. Critical Reviews
Lastly, critical reviews aim to provide a critical evaluation and interpretive analysis of existing literature on a particular topic of interest to reveal strengths, weaknesses, contradictions, controversies, inconsistencies, and/or other important issues with respect to theories, hypotheses, research methods or results ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ; Kirkevold, 1997 ). Unlike other review types, critical reviews attempt to take a reflective account of the research that has been done in a particular area of interest, and assess its credibility by using appraisal instruments or critical interpretive methods. In this way, critical reviews attempt to constructively inform other scholars about the weaknesses of prior research and strengthen knowledge development by giving focus and direction to studies for further improvement ( Kirkevold, 1997 ).
Kitsiou, Paré, and Jaana (2013) provide an example of a critical review that assessed the methodological quality of prior systematic reviews of home telemonitoring studies for chronic patients. The authors conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases to identify eligible reviews and subsequently used a validated instrument to conduct an in-depth quality appraisal. Results indicate that the majority of systematic reviews in this particular area suffer from important methodological flaws and biases that impair their internal validity and limit their usefulness for clinical and decision-making purposes. To this end, they provide a number of recommendations to strengthen knowledge development towards improving the design and execution of future reviews on home telemonitoring.
9.4. Summary
Table 9.1 outlines the main types of literature reviews that were described in the previous sub-sections and summarizes the main characteristics that distinguish one review type from another. It also includes key references to methodological guidelines and useful sources that can be used by eHealth scholars and researchers for planning and developing reviews.
Typology of Literature Reviews (adapted from Paré et al., 2015).
As shown in Table 9.1 , each review type addresses different kinds of research questions or objectives, which subsequently define and dictate the methods and approaches that need to be used to achieve the overarching goal(s) of the review. For example, in the case of narrative reviews, there is greater flexibility in searching and synthesizing articles ( Green et al., 2006 ). Researchers are often relatively free to use a diversity of approaches to search, identify, and select relevant scientific articles, describe their operational characteristics, present how the individual studies fit together, and formulate conclusions. On the other hand, systematic reviews are characterized by their high level of systematicity, rigour, and use of explicit methods, based on an “a priori” review plan that aims to minimize bias in the analysis and synthesis process (Higgins & Green, 2008). Some reviews are exploratory in nature (e.g., scoping/mapping reviews), whereas others may be conducted to discover patterns (e.g., descriptive reviews) or involve a synthesis approach that may include the critical analysis of prior research ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Hence, in order to select the most appropriate type of review, it is critical to know before embarking on a review project, why the research synthesis is conducted and what type of methods are best aligned with the pursued goals.
9.5. Concluding Remarks
In light of the increased use of evidence-based practice and research generating stronger evidence ( Grady et al., 2011 ; Lyden et al., 2013 ), review articles have become essential tools for summarizing, synthesizing, integrating or critically appraising prior knowledge in the eHealth field. As mentioned earlier, when rigorously conducted review articles represent powerful information sources for eHealth scholars and practitioners looking for state-of-the-art evidence. The typology of literature reviews we used herein will allow eHealth researchers, graduate students and practitioners to gain a better understanding of the similarities and differences between review types.
We must stress that this classification scheme does not privilege any specific type of review as being of higher quality than another ( Paré et al., 2015 ). As explained above, each type of review has its own strengths and limitations. Having said that, we realize that the methodological rigour of any review — be it qualitative, quantitative or mixed — is a critical aspect that should be considered seriously by prospective authors. In the present context, the notion of rigour refers to the reliability and validity of the review process described in section 9.2. For one thing, reliability is related to the reproducibility of the review process and steps, which is facilitated by a comprehensive documentation of the literature search process, extraction, coding and analysis performed in the review. Whether the search is comprehensive or not, whether it involves a methodical approach for data extraction and synthesis or not, it is important that the review documents in an explicit and transparent manner the steps and approach that were used in the process of its development. Next, validity characterizes the degree to which the review process was conducted appropriately. It goes beyond documentation and reflects decisions related to the selection of the sources, the search terms used, the period of time covered, the articles selected in the search, and the application of backward and forward searches ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). In short, the rigour of any review article is reflected by the explicitness of its methods (i.e., transparency) and the soundness of the approach used. We refer those interested in the concepts of rigour and quality to the work of Templier and Paré (2015) which offers a detailed set of methodological guidelines for conducting and evaluating various types of review articles.
To conclude, our main objective in this chapter was to demystify the various types of literature reviews that are central to the continuous development of the eHealth field. It is our hope that our descriptive account will serve as a valuable source for those conducting, evaluating or using reviews in this important and growing domain.
- Ammenwerth E., de Keizer N. An inventory of evaluation studies of information technology in health care. Trends in evaluation research, 1982-2002. International Journal of Medical Informatics. 2004; 44 (1):44–56. [ PubMed : 15778794 ]
- Anderson S., Allen P., Peckham S., Goodwin N. Asking the right questions: scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2008; 6 (7):1–12. [ PMC free article : PMC2500008 ] [ PubMed : 18613961 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Archer N., Fevrier-Thomas U., Lokker C., McKibbon K. A., Straus S.E. Personal health records: a scoping review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2011; 18 (4):515–522. [ PMC free article : PMC3128401 ] [ PubMed : 21672914 ]
- Arksey H., O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2005; 8 (1):19–32.
- A systematic, tool-supported method for conducting literature reviews in information systems. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 19th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2011); June 9 to 11; Helsinki, Finland. 2011.
- Baumeister R. F., Leary M.R. Writing narrative literature reviews. Review of General Psychology. 1997; 1 (3):311–320.
- Becker L. A., Oxman A.D. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Overviews of reviews; pp. 607–631.
- Borenstein M., Hedges L., Higgins J., Rothstein H. Introduction to meta-analysis. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2009.
- Cook D. J., Mulrow C. D., Haynes B. Systematic reviews: Synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 126 (5):376–380. [ PubMed : 9054282 ]
- Cooper H., Hedges L.V. In: The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis. 2nd ed. Cooper H., Hedges L. V., Valentine J. C., editors. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2009. Research synthesis as a scientific process; pp. 3–17.
- Cooper H. M. Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowledge in Society. 1988; 1 (1):104–126.
- Cronin P., Ryan F., Coughlan M. Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing. 2008; 17 (1):38–43. [ PubMed : 18399395 ]
- Darlow S., Wen K.Y. Development testing of mobile health interventions for cancer patient self-management: A review. Health Informatics Journal. 2015 (online before print). [ PubMed : 25916831 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Daudt H. M., van Mossel C., Scott S.J. Enhancing the scoping study methodology: a large, inter-professional team’s experience with Arksey and O’Malley’s framework. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2013; 13 :48. [ PMC free article : PMC3614526 ] [ PubMed : 23522333 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Davies P. The relevance of systematic reviews to educational policy and practice. Oxford Review of Education. 2000; 26 (3-4):365–378.
- Deeks J. J., Higgins J. P. T., Altman D.G. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses; pp. 243–296.
- Deshazo J. P., Lavallie D. L., Wolf F.M. Publication trends in the medical informatics literature: 20 years of “Medical Informatics” in mesh . bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2009; 9 :7. [ PMC free article : PMC2652453 ] [ PubMed : 19159472 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dixon-Woods M., Agarwal S., Jones D., Young B., Sutton A. Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. Journal of Health Services Research and Policy. 2005; 10 (1):45–53. [ PubMed : 15667704 ]
- Finfgeld-Connett D., Johnson E.D. Literature search strategies for conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2013; 69 (1):194–204. [ PMC free article : PMC3424349 ] [ PubMed : 22591030 ]
- Grady B., Myers K. M., Nelson E. L., Belz N., Bennett L., Carnahan L. … Guidelines Working Group. Evidence-based practice for telemental health. Telemedicine Journal and E Health. 2011; 17 (2):131–148. [ PubMed : 21385026 ]
- Green B. N., Johnson C. D., Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine. 2006; 5 (3):101–117. [ PMC free article : PMC2647067 ] [ PubMed : 19674681 ]
- Greenhalgh T., Wong G., Westhorp G., Pawson R. Protocol–realist and meta-narrative evidence synthesis: evolving standards ( rameses ). bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 :115. [ PMC free article : PMC3173389 ] [ PubMed : 21843376 ]
- Gurol-Urganci I., de Jongh T., Vodopivec-Jamsek V., Atun R., Car J. Mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments. Cochrane Database System Review. 2013; 12 cd 007458. [ PMC free article : PMC6485985 ] [ PubMed : 24310741 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hart C. Doing a literature review: Releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE Publications; 1998.
- Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Cochrane book series. Hoboken, nj : Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
- Jesson J., Matheson L., Lacey F.M. Doing your literature review: traditional and systematic techniques. Los Angeles & London: SAGE Publications; 2011.
- King W. R., He J. Understanding the role and methods of meta-analysis in IS research. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2005; 16 :1.
- Kirkevold M. Integrative nursing research — an important strategy to further the development of nursing science and nursing practice. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1997; 25 (5):977–984. [ PubMed : 9147203 ]
- Kitchenham B., Charters S. ebse Technical Report Version 2.3. Keele & Durham. uk : Keele University & University of Durham; 2007. Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering.
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with chronic diseases: a critical assessment of their methodological quality. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2013; 15 (7):e150. [ PMC free article : PMC3785977 ] [ PubMed : 23880072 ]
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Effects of home telemonitoring interventions on patients with chronic heart failure: an overview of systematic reviews. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2015; 17 (3):e63. [ PMC free article : PMC4376138 ] [ PubMed : 25768664 ]
- Levac D., Colquhoun H., O’Brien K. K. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implementation Science. 2010; 5 (1):69. [ PMC free article : PMC2954944 ] [ PubMed : 20854677 ]
- Levy Y., Ellis T.J. A systems approach to conduct an effective literature review in support of information systems research. Informing Science. 2006; 9 :181–211.
- Liberati A., Altman D. G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gøtzsche P. C., Ioannidis J. P. A. et al. Moher D. The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2009; 151 (4):W-65. [ PubMed : 19622512 ]
- Lyden J. R., Zickmund S. L., Bhargava T. D., Bryce C. L., Conroy M. B., Fischer G. S. et al. McTigue K. M. Implementing health information technology in a patient-centered manner: Patient experiences with an online evidence-based lifestyle intervention. Journal for Healthcare Quality. 2013; 35 (5):47–57. [ PubMed : 24004039 ]
- Mickan S., Atherton H., Roberts N. W., Heneghan C., Tilson J.K. Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: a systematic review. bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2014; 14 :56. [ PMC free article : PMC4099138 ] [ PubMed : 24998515 ]
- Moher D. The problem of duplicate systematic reviews. British Medical Journal. 2013; 347 (5040) [ PubMed : 23945367 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Montori V. M., Wilczynski N. L., Morgan D., Haynes R. B., Hedges T. Systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study of location and citation counts. bmc Medicine. 2003; 1 :2. [ PMC free article : PMC281591 ] [ PubMed : 14633274 ]
- Mulrow C. D. The medical review article: state of the science. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1987; 106 (3):485–488. [ PubMed : 3813259 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Evidence-based information systems: A decade later. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems ; 2011. Retrieved from http://aisel .aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent .cgi?article =1221&context =ecis2011 .
- Okoli C., Schabram K. A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research. ssrn Electronic Journal. 2010
- Otte-Trojel T., de Bont A., Rundall T. G., van de Klundert J. How outcomes are achieved through patient portals: a realist review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2014; 21 (4):751–757. [ PMC free article : PMC4078283 ] [ PubMed : 24503882 ]
- Paré G., Trudel M.-C., Jaana M., Kitsiou S. Synthesizing information systems knowledge: A typology of literature reviews. Information & Management. 2015; 52 (2):183–199.
- Patsopoulos N. A., Analatos A. A., Ioannidis J.P. A. Relative citation impact of various study designs in the health sciences. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2005; 293 (19):2362–2366. [ PubMed : 15900006 ]
- Paul M. M., Greene C. M., Newton-Dame R., Thorpe L. E., Perlman S. E., McVeigh K. H., Gourevitch M.N. The state of population health surveillance using electronic health records: A narrative review. Population Health Management. 2015; 18 (3):209–216. [ PubMed : 25608033 ]
- Pawson R. Evidence-based policy: a realist perspective. London: SAGE Publications; 2006.
- Pawson R., Greenhalgh T., Harvey G., Walshe K. Realist review—a new method of systematic review designed for complex policy interventions. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy. 2005; 10 (Suppl 1):21–34. [ PubMed : 16053581 ]
- Petersen K., Vakkalanka S., Kuzniarz L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Information and Software Technology. 2015; 64 :1–18.
- Petticrew M., Roberts H. Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide. Malden, ma : Blackwell Publishing Co; 2006.
- Rousseau D. M., Manning J., Denyer D. Evidence in management and organizational science: Assembling the field’s full weight of scientific knowledge through syntheses. The Academy of Management Annals. 2008; 2 (1):475–515.
- Rowe F. What literature review is not: diversity, boundaries and recommendations. European Journal of Information Systems. 2014; 23 (3):241–255.
- Shea B. J., Hamel C., Wells G. A., Bouter L. M., Kristjansson E., Grimshaw J. et al. Boers M. amstar is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2009; 62 (10):1013–1020. [ PubMed : 19230606 ]
- Shepperd S., Lewin S., Straus S., Clarke M., Eccles M. P., Fitzpatrick R. et al. Sheikh A. Can we systematically review studies that evaluate complex interventions? PLoS Medicine. 2009; 6 (8):e1000086. [ PMC free article : PMC2717209 ] [ PubMed : 19668360 ]
- Silva B. M., Rodrigues J. J., de la Torre Díez I., López-Coronado M., Saleem K. Mobile-health: A review of current state in 2015. Journal of Biomedical Informatics. 2015; 56 :265–272. [ PubMed : 26071682 ]
- Smith V., Devane D., Begley C., Clarke M. Methodology in conducting a systematic review of systematic reviews of healthcare interventions. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 (1):15. [ PMC free article : PMC3039637 ] [ PubMed : 21291558 ]
- Sylvester A., Tate M., Johnstone D. Beyond synthesis: re-presenting heterogeneous research literature. Behaviour & Information Technology. 2013; 32 (12):1199–1215.
- Templier M., Paré G. A framework for guiding and evaluating literature reviews. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2015; 37 (6):112–137.
- Thomas J., Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2008; 8 (1):45. [ PMC free article : PMC2478656 ] [ PubMed : 18616818 ]
- Reconstructing the giant: on the importance of rigour in documenting the literature search process. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2009); Verona, Italy. 2009.
- Webster J., Watson R.T. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. Management Information Systems Quarterly. 2002; 26 (2):11.
- Whitlock E. P., Lin J. S., Chou R., Shekelle P., Robinson K.A. Using existing systematic reviews in complex systematic reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2008; 148 (10):776–782. [ PubMed : 18490690 ]
This publication is licensed under a Creative Commons License, Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0): see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- Cite this Page Paré G, Kitsiou S. Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews. In: Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.
- PDF version of this title (4.5M)
- Disable Glossary Links
In this Page
- Introduction
- Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
- Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
- Concluding Remarks
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Recent Activity
- Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Ev... Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
- Open access
- Published: 14 May 2024
Protocol for a scoping review study on learning plan use in undergraduate medical education
- Anna Romanova ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1118-1604 1 ,
- Claire Touchie 1 ,
- Sydney Ruller 2 ,
- Victoria Cole 3 &
- Susan Humphrey-Murto 4
Systematic Reviews volume 13 , Article number: 131 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
The current paradigm of competency-based medical education and learner-centredness requires learners to take an active role in their training. However, deliberate and planned continual assessment and performance improvement is hindered by the fragmented nature of many medical training programs. Attempts to bridge this continuity gap between supervision and feedback through learner handover have been controversial. Learning plans are an alternate educational tool that helps trainees identify their learning needs and facilitate longitudinal assessment by providing supervisors with a roadmap of their goals. Informed by self-regulated learning theory, learning plans may be the answer to track trainees’ progress along their learning trajectory. The purpose of this study is to summarise the literature regarding learning plan use specifically in undergraduate medical education and explore the student’s role in all stages of learning plan development and implementation.
Following Arksey and O’Malley’s framework, a scoping review will be conducted to explore the use of learning plans in undergraduate medical education. Literature searches will be conducted using multiple databases by a librarian with expertise in scoping reviews. Through an iterative process, inclusion and exclusion criteria will be developed and a data extraction form refined. Data will be analysed using quantitative and qualitative content analyses.
By summarising the literature on learning plan use in undergraduate medical education, this study aims to better understand how to support self-regulated learning in undergraduate medical education. The results from this project will inform future scholarly work in competency-based medical education at the undergraduate level and have implications for improving feedback and supporting learners at all levels of competence.
Scoping review registration:
Open Science Framework osf.io/wvzbx.
Peer Review reports
Competency-based medical education (CBME) has transformed the approach to medical education to focus on demonstration of acquired competencies rather than time-based completion of rotations [ 1 ]. As a result, undergraduate and graduate medical training programs worldwide have adopted outcomes-based assessments in the form of entrustable professional activities (EPAs) comprised of competencies to be met [ 2 ]. These assessments are completed longitudinally by multiple different evaluators to generate an overall impression of a learner’s competency.
In CBME, trainees will progress along their learning trajectory at individual speeds and some may excel while others struggle to achieve the required knowledge, skills or attitudes. Therefore, deliberate and planned continual assessment and performance improvement is required. However, due to the fragmented nature of many medical training programs where learners rotate through different rotations and work with many supervisors, longitudinal observation is similarly fragmented. This makes it difficult to determine where trainees are on their learning trajectories and can affect the quality of feedback provided to them, which is a known major influencer of academic achievement [ 3 ]. As a result, struggling learners may not be identified until late in their training and the growth of high-performing learners may be stifled [ 4 , 5 , 6 ].
Bridging this continuity gap between supervision and feedback through some form of learner handover or forward feeding has been debated since the 1970s and continues to this day [ 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ]. The goal of learner handover is to improve trainee assessment and feedback by sharing their performance and learning needs between supervisors or across rotations. However, several concerns have been raised about this approach including that it could inappropriately bias subsequent assessments of the learner’s abilities [ 9 , 11 , 12 ]. A different approach to keeping track of trainees’ learning goals and progress along their learning trajectories is required. Learning plans (LPs) informed by self-regulated learning (SRL) theory may be the answer.
SRL has been defined as a cyclical process where learners actively control their thoughts, actions and motivation to achieve their goals [ 13 ]. Several models of SRL exist but all entail that the trainee is responsible for setting, planning, executing, monitoring and reflecting on their learning goals [ 13 ]. According to Zimmerman’s SRL model, this process occurs in three stages: forethought phase before an activity, performance phase during an activity and self-reflection phase after an activity [ 13 ]. Since each trainee leads their own learning process and has an individual trajectory towards competence, this theory relates well to the CBME paradigm which is grounded in learner-centredness [ 1 ]. However, we know that medical students and residents have difficulty identifying their own learning goals and therefore need guidance to effectively partake in SRL [ 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ]. Motivation has also emerged as a key component of SRL, and numerous studies have explored factors that influence student engagement in learning [ 18 , 19 ]. In addition to meeting their basic psychological needs of autonomy, relatedness and competence, perceived learning relevance through meaningful learning activities has been shown to increase trainee engagement in their learning [ 19 ].
LPs are a well-known tool across many educational fields including CBME that can provide trainees with meaningful learning activities since they help them direct their own learning goals in a guided fashion [ 20 ]. Also known as personal learning plans, learning contracts, personal action plans, personal development plans, and learning goals, LPs are documents that outline the learner’s roadmap to achieve their learning goals. They require the learner to self-identify what they need to learn and why, how they are going to do it, how they will know when they are finished, define the timeframe for goal achievement and assess the impact of their learning [ 20 ]. In so doing, LPs give more autonomy to the learner and facilitate objective and targeted feedback from supervisors. This approach has been described as “most congruent with the assumptions we make about adults as learners” [ 21 ].
LP use has been explored across various clinical settings and at all levels of medical education; however, most of the experience lies in postgraduate medical education [ 22 ]. Medical students are a unique learner population with learning needs that appear to be very well suited for using LPs for two main reasons. First, their education is often divided between classroom and clinical settings. During clinical training, students need to be more independent in setting learning goals to meet desired competencies as their education is no longer outlined for them in a detailed fashion by the medical school curriculum [ 23 ]. SRL in the workplace is also different than in the classroom due to additional complexities of clinical care that can impact students’ ability to self-regulate their learning [ 24 ]. Second, although most medical trainees have difficulty with goal setting, medical students in particular need more guidance compared to residents due to their relative lack of experience upon which they can build within the SRL framework [ 25 ]. LPs can therefore provide much-needed structure to their learning but should be guided by an experienced tutor to be effective [ 15 , 24 ].
LPs fit well within the learner-centred educational framework of CBME by helping trainees identify their learning needs and facilitating longitudinal assessment by providing supervisors with a roadmap of their goals. In so doing, they can address current issues with learner handover and identification as well as remediation of struggling learners. Moreover, they have the potential to help trainees develop lifelong skills with respect to continuing professional development after graduation which is required by many medical licensing bodies.
An initial search of the JBI Database, Cochrane Database, MEDLINE (PubMed) and Google Scholar conducted in July–August 2022 revealed a paucity of research on LP use in undergraduate medical education (UGME). A related systematic review by van Houten–Schat et al. [ 24 ] on SRL in the clinical setting identified three interventions used by medical students and residents in SRL—coaching, LPs and supportive tools. However, only a couple of the included studies looked specifically at medical students’ use of LPs, so this remains an area in need of more exploration. A scoping review would provide an excellent starting point to map the body of literature on this topic.
The objective of this scoping review will therefore be to explore LP use in UGME. In doing so, it will address a gap in knowledge and help determine additional areas for research.
This study will follow Arksey and O’Malley’s [ 26 ] five-step framework for scoping review methodology. It will not include the optional sixth step which entails stakeholder consultation as relevant stakeholders will be intentionally included in the research team (a member of UGME leadership, a medical student and a first-year resident).
Step 1—Identifying the research question
The overarching purpose of this study is to “explore the use of LPs in UGME”. More specifically we seek to achieve the following:
Summarise the literature regarding the use of LPs in UGME (including context, students targeted, frameworks used)
Explore the role of the student in all stages of the LP development and implementation
Determine existing research gaps
Step 2—Identifying relevant studies
An experienced health sciences librarian (VC) will conduct all searches and develop the initial search strategy. The preliminary search strategy is shown in Appendix A (see Additional file 2). Articles will be included if they meet the following criteria [ 27 ]:
Participants
Medical students enrolled at a medical school at the undergraduate level.
Any use of LPs by medical students. LPs are defined as a document, usually presented in a table format, that outlines the learner’s roadmap to achieve their learning goals [ 20 ].
Any stage of UGME in any geographic setting.
Types of evidence sources
We will search existing published and unpublished (grey) literature. This may include research studies, reviews, or expert opinion pieces.
Search strategy
With the assistance of an experienced librarian (VC), a pilot search will be conducted to inform the final search strategy. A search will be conducted in the following electronic databases: MEDLINE, Embase, Education Source, APA PsycInfo and Web of Science. The search terms will be developed in consultation with the research team and librarian. The search strategy will proceed according to the JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis three-step search strategy for reviews [ 27 ]. First, we will conduct a limited search in two appropriate online databases and analyse text words from the title, abstracts and index terms of relevant papers. Next, we will conduct a second search using all identified key words in all databases. Third, we will review reference lists of all included studies to identify further relevant studies to include in the review. We will also contact the authors of relevant papers for further information if required. This will be an iterative process as the research team becomes more familiar with the literature and will be guided by the librarian. Any modifications to the search strategy as it evolves will be described in the scoping review report. As a measure of rigour, the search strategy will be peer-reviewed by another librarian using the PRESS checklist [ 28 ]. No language or date limits will be applied.
Step 3—Study selection
The screening process will consist of a two-step approach: screening titles/abstracts and, if they meet inclusion criteria, this will be followed by a full-text review. All screening will be done by two members of the research team and any disagreements will be resolved by an independent third member of the team. Based on preliminary inclusion criteria, the whole research team will first pilot the screening process by reviewing a random sample of 25 titles/abstracts. The search strategy, eligibility criteria and study objectives will be refined in an iterative process. We anticipate several meetings as the topic is not well described in the literature. A flowchart of the review process will be generated. Any modifications to the study selection process will be described in the scoping review report. The papers will be excluded if a full text is not available. The search results will be managed using Covidence software.
Step 4—Charting the data
A preliminary data extraction tool is shown in Appendix B (see Additional file 3 ). Data will be extracted into Excel and will include demographic information and specific details about the population, concept, context, study methods and outcomes as they relate to the scoping review objectives. The whole research team will pilot the data extraction tool on ten articles selected for full-text review. Through an iterative process, the final data extraction form will be refined. Subsequently, two members of the team will independently extract data from all articles included for full-text review using this tool. Charting disagreements will be resolved by the principal and senior investigators. Google Translate will be used for any included articles that are not in the English language.
Step 5—Collating, summarising and reporting the results
Quantitative and qualitative analyses will be used to summarise the results. Quantitative analysis will capture descriptive statistics with details about the population, concept, context, study methods and outcomes being examined in this scoping review. Qualitative content analysis will enable interpretation of text data through the systematic classification process of coding and identifying themes and patterns [ 29 ]. Several team meetings will be held to review potential themes to ensure an accurate representation of the data. The PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) will be used to guide the reporting of review findings [ 30 ]. Data will be presented in tables and/or diagrams as applicable. A descriptive summary will explain the presented results and how they relate to the scoping review objectives.
By summarising the literature on LP use in UGME, this study will contribute to a better understanding of how to support SRL amongst medical students. The results from this project will also inform future scholarly work in CBME at the undergraduate level and have implications for improving feedback as well as supporting learners at all levels of competence. In doing so, this study may have practical applications by informing learning plan incorporation into CBME-based curricula.
We do not anticipate any practical or operational issues at this time. We assembled a team with the necessary expertise and tools to complete this project.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study will be included in the published scoping review article.
Abbreviations
- Competency-based medical education
Entrustable professional activity
- Learning plan
- Self-regulated learning
- Undergraduate medical education
Frank JR, Snell LS, Cate OT, et al. Competency-based medical education: theory to practice. Med Teach. 2010;32(8):638–45.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Shorey S, Lau TC, Lau ST, Ang E. Entrustable professional activities in health care education: a scoping review. Med Educ. 2019;53(8):766–77.
Hattie J, Timperley H. The power of feedback. Rev Educ Res. 2007;77(1):81–112.
Article Google Scholar
Dudek NL, Marks MB, Regehr G. Failure to fail: the perspectives of clinical supervisors. Acad Med. 2005;80(10 Suppl):S84–7.
Warm EJ, Englander R, Pereira A, Barach P. Improving learner handovers in medical education. Acad Med. 2017;92(7):927–31.
Spooner M, Duane C, Uygur J, et al. Self-regulatory learning theory as a lens on how undergraduate and postgraduate learners respond to feedback: a BEME scoping review : BEME Guide No. 66. Med Teach. 2022;44(1):3–18.
Frellsen SL, Baker EA, Papp KK, Durning SJ. Medical school policies regarding struggling medical students during the internal medicine clerkships: results of a National Survey. Acad Med. 2008;83(9):876–81.
Humphrey-Murto S, LeBlanc A, Touchie C, et al. The influence of prior performance information on ratings of current performance and implications for learner handover: a scoping review. Acad Med. 2019;94(7):1050–7.
Morgan HK, Mejicano GC, Skochelak S, et al. A responsible educational handover: improving communication to improve learning. Acad Med. 2020;95(2):194–9.
Dory V, Danoff D, Plotnick LH, et al. Does educational handover influence subsequent assessment? Acad Med. 2021;96(1):118–25.
Humphrey-Murto S, Lingard L, Varpio L, et al. Learner handover: who is it really for? Acad Med. 2021;96(4):592–8.
Shaw T, Wood TJ, Touchie T, Pugh D, Humphrey-Murto S. How biased are you? The effect of prior performance information on attending physician ratings and implications for learner handover. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2021;26(1):199–214.
Artino AR, Brydges R, Gruppen LD. Chapter 14: Self-regulated learning in health professional education: theoretical perspectives and research methods. In: Cleland J, Duning SJ, editors. Researching Medical Education. 1st ed. John Wiley & Sons; 2015. p. 155–66.
Chapter Google Scholar
Cleland J, Arnold R, Chesser A. Failing finals is often a surprise for the student but not the teacher: identifying difficulties and supporting students with academic difficulties. Med Teach. 2005;27(6):504–8.
Reed S, Lockspeiser TM, Burke A, et al. Practical suggestions for the creation and use of meaningful learning goals in graduate medical education. Acad Pediatr. 2016;16(1):20–4.
Wolff M, Stojan J, Cranford J, et al. The impact of informed self-assessment on the development of medical students’ learning goals. Med Teach. 2018;40(3):296–301.
Sawatsky AP, Halvorsen AJ, Daniels PR, et al. Characteristics and quality of rotation-specific resident learning goals: a prospective study. Med Educ Online. 2020;25(1):1714198.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pintrich PR. Chapter 14: The role of goal orientation in self-regulated learning. In: Boekaerts M, Pintrich PR, Zeidner M, editors. Handbook of self-regulation. 1st ed. Academic Press; 2000. p. 451–502.
Kassab SE, El-Sayed W, Hamdy H. Student engagement in undergraduate medical education: a scoping review. Med Educ. 2022;56(7):703–15.
Challis M. AMEE medical education guide No. 19: Personal learning plans. Med Teach. 2000;22(3):225–36.
Knowles MS. Using learning contracts. 1 st ed. San Francisco: Jossey Bass; 1986.
Parsell G, Bligh J. Contract learning, clinical learning and clinicians. Postgrad Med J. 1996;72(847):284–9.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Teunissen PW, Scheele F, Scherpbier AJJA, et al. How residents learn: qualitative evidence for the pivotal role of clinical activities. Med Educ. 2007;41(8):763–70.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
van Houten-Schat MA, Berkhout JJ, van Dijk N, Endedijk MD, Jaarsma ADC, Diemers AD. Self-regulated learning in the clinical context: a systematic review. Med Educ. 2018;52(10):1008–15.
Taylor DCM, Hamdy H. Adult learning theories: Implications for learning and teaching in medical education: AMEE Guide No. 83. Med Teach. 2013;35(11):e1561–72.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Peters MDJ, Godfrey C, McInerney P, Munn Z, Tricco AC, Khalol H. Chapter 11: Scoping reviews. In: Aromataris E, Munn Z, eds. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. JBI; 2020. https://synthesismanual.jbi.global. . Accessed 30 Aug 2022.
McGowan J, Sampson M, Salzwedel DM, Cogo E, Foerster V, Lefebvre C. PRESS Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies: 2015 Guideline Statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;75:40–6.
Hsieh HF, Shannon SE. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual Health Res. 2005;15(9):1277–88.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Venables M, Larocque A, Sikora L, Archibald D, Grudniewicz A. Understanding indigenous health education and exploring indigenous anti-racism approaches in undergraduate medical education: a scoping review protocol. OSF; 2022. https://osf.io/umwgr/ . Accessed 26 Oct 2022.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This study will be supported through grants from the Department of Medicine at the Ottawa Hospital and the University of Ottawa. The funding bodies had no role in the study design and will not have any role in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data or writing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Ottawa Hospital – General Campus, 501 Smyth Rd, PO Box 209, Ottawa, ON, K1H 8L6, Canada
Anna Romanova & Claire Touchie
The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, Ottawa, Canada
Sydney Ruller
The University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada
Victoria Cole
The Ottawa Hospital – Riverside Campus, Ottawa, Canada
Susan Humphrey-Murto
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AR designed and drafted the protocol. CT and SH contributed to the refinement of the research question, study methods and editing of the manuscript. VC designed the initial search strategy. All authors reviewed the manuscript for final approval. The review guarantors are CT and SH. The corresponding author is AR.
Authors’ information
AR is a clinician teacher and Assistant Professor with the Division of General Internal Medicine at the University of Ottawa. She is also the Associate Director for the internal medicine clerkship rotation at the General campus of the Ottawa Hospital.
CT is a Professor of Medicine with the Divisions of General Internal Medicine and Infectious Diseases at the University of Ottawa. She is also a member of the UGME Competence Committee at the University of Ottawa and an advisor for the development of a new school of medicine at Toronto Metropolitan University.
SH is an Associate Professor with the Department of Medicine at the University of Ottawa and holds a Tier 2 Research Chair in Medical Education. She is also the Interim Director for the Research Support Unit within the Department of Innovation in Medical Education at the University of Ottawa.
CT and SH have extensive experience with medical education research and have numerous publications in this field.
SR is a Research Assistant with the Division of General Internal Medicine at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute.
VC is a Health Sciences Research Librarian at the University of Ottawa.
SR and VC have extensive experience in systematic and scoping reviews.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Anna Romanova .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. prisma-p 2015 checklist., 13643_2024_2553_moesm2_esm.docx.
Additional file 2: Appendix A. Preliminary search strategy [ 31 ].
Additional file 3: Appendix B. Preliminary data extraction tool.
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Romanova, A., Touchie, C., Ruller, S. et al. Protocol for a scoping review study on learning plan use in undergraduate medical education. Syst Rev 13 , 131 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-024-02553-w
Download citation
Received : 29 November 2022
Accepted : 03 May 2024
Published : 14 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-024-02553-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Case report
- Open access
- Published: 19 May 2024
Fistulising skin metastases in Crohn’s disease: a case report and review of the literature
- Tanja Elger 1 ,
- Johanna Loibl 1 ,
- Christa Buechler 1 ,
- Sebastian Haferkamp 3 ,
- Jens Werner 2 ,
- Konstantin Drexler 3 ,
- Ulrich Hohenleutner 3 ,
- Karsten Guelow 1 ,
- Claudia Kunst 1 ,
- Arne Kandulski 1 ,
- Pia Goeggelmann 1 ,
- Martina Mueller 1 &
- Hauke Christian Tews 1
Journal of Medical Case Reports volume 18 , Article number: 252 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Metastatic Crohn’s disease is a rare disorder characterized by various granulomatous skin lesions that occur independently of gastrointestinal tract involvement. However, currently there is no standardized care or specific treatment. Therapeutic approaches include immunosuppressive agents, such as corticosteroids, azathioprine, and monoclonal antibodies targeting inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor (TNF).
Case presentation
We present a case of a 29-year-old western European woman with significant blind ending abdominal subcutaneous fistulas and abscesses, who sought evaluation in the dermatology department. Histological examination revealed multiple epithelioid cell granulomas. There was no evidence of infectious or rheumatologic diseases such as sarcoidosis. The tentative diagnosis was metastatic Crohn’s disease, which was not related to an intestinal manifestation of the disease. The patient responded to infliximab but had to discontinue it due to an allergic reaction. Subsequent adalimumab treatment failed to induce clinical remission; thus, therapy was switched to ustekinumab, resulting in a positive response. Written informed consent for publication of their clinical details and clinical images was obtained from the patient.
For our study more than 1600 publications were screened for cases of metastatic Crohn’s disease on PubMed database. 59 case reports with 171 patients were included in the analysis and evaluated for localization, diagnostic and therapeutic approaches, and complications and were summarized in this review.
The successful ustekinumab treatment of a patient with metastatic Crohn's disease underscores the potential of this minimally investigated therapeutic option, highlighting the need for future treatment guidelines given the increasing prevalence of such cases.
Peer Review reports
Metastatic Crohn`s disease is a rare disease that primarily affects patients diagnosed with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). In rare cases, cutaneous manifestations precede gastrointestinal involvement. It most commonly occurs in the genital region, but can also affect every other part of the body. The lesions present as plaques, ulcers, fissures or papules [ 1 ] and, in rare cases, as fistulas. They are often asymptomatic but may also cause pain or itching. Despite the misleading wording, metastatic Crohn’s disease is not considered an oncologic entity. Instead, the term “metastatic” refers to the involvement of sites with no physical connection to the GI-tract. Metastatic Crohn’s disease must not be mixed up with extraintestinal manifestations of Crohn´s disease. Whereas extraintestinal manifestations such as pyoderma gangraenosum and erythema nodosum represent distinct immunologic phenomena, metastatic Crohn’s disease exhibits the same histological findings as intestinal Crohn’s disease, but on other organ sites.
Usually, a biopsy from the involved site is required for the diagnosis of metastatic Crohn’s disease. Histological findings show non-caseating, sarcoid-like granulomas, Langerhans giant cells and foreign body giant cells surrounded by inflammatory histiocytes, plasma cells and lymphocytes [ 2 ]. For a confirmed diagnosis of metastatic Crohn’s disease, other causes for granulomatous disorders have to be excluded, especially cutaneous sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, syphilis, mycobacterial infections, actinomycosis, deep fungal infections, lymphogranuloma venereum and granuloma inguinale. Also non-granulomatous skin lesions such as hidradenitis suppurativa, pyoderma gangrenosum, impetigo, erythema nodosum, factitial dermatitis from factitial injection of foreign substances, schistosomiasis, chronic lymphedema resulting from obstruction, erysipelas, chronic cellulitis and foreign body reaction need to be ruled out [ 3 ].
To objectively assess intestinal involvement, endoscopy of the upper and lower GI tract along with an abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan should be performed.
Currently, there is no standardized treatment of metastatic Crohn’s disease and no German or European guideline, especially for cases without GI involvement. Only individual case reports exist regarding the therapeutic use of approved medication for intestinal Crohn’s disease in metastatic conditions, including steroids, anti-TNF antibodies, azathioprine, and antibiotic therapy [ 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ].
Ustekinumab is a human monoclonal IgG1κ-antibody, which binds specifically to the p40-subunit of interleucin 12 (IL-12) and interleucin 23 (IL-23). The bioactivity of IL-12 and IL-23 is inhibited by ustekinumab by preventing the p40 subunit from binding to IL-12Rß1-receptorprotein on the surface of immune cells. It is assumed that hereby the cytokine pathways of Th1- and Th17-cells are interrupted, which both play an important role in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease [ 8 ].
We here report a case of metastatic Crohn’s disease successfully treated with ustekinumab at our university hospital and provide a literature review on the current therapeutic options for metastatic Crohn’s disease.
In 2020, a 29-year-old western European woman presented to the dermatology department of our university hospital with pronounced abdominal blind-ending fistulas. The initial patient contact was documented in 2019 when she sought care at the emergency department with multiple recurrent abscesses of the abdominal skin that first appeared after a tick bite a few weeks prior.
Between January 2019 and July 2020, multiple incisions of recurrent abscesses were performed in combination with antibiotic treatment. However, complete healing was not achieved. Instead, the abscess cavities expanded beneath the skin, subsequently forming a system of connected fistulas (Fig. 1 ), as visualized in MRI enterography (Fig. 2 ).
Large subcutaneous fistula, 2020
MRI enterography of the large subcutaneous abdominal fistula (red circle), April 2021
When the patient presented to the dermatology department in 2020, the fistulas showed active inflammation with secretion and were almost 2 cm in diameter. In addition, a blind ending subcutaneous fistula of the thigh could be detected, which also showed active inflammation and secretion.
Histologic examination revealed a granulomatous infiltrate with histiocytes and multinuclear giant cells, forming granulomas. In addition, lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils, and eosinophils, and a granulomatous perivasculitis were observed (Fig. 3 ). Differential diagnoses of granulomatous diseases such as sarcoidosis, tuberculosis and immunodeficiencies were ruled out, confirming the diagnosis of metastatic Crohn’s disease.
Histologic examination of a fistula biopsy showing granulomas with histiocytes and multinuclear giant cells, July 2020
To investigate intestinal involvement, abdominal MRI, gastroscopy, and colonoscopy were performed. However, these examinations did not reveal any gastrointestinal involvement at this time. Moreover, fecal calprotectin levels were normal. There was no history of inflammatory bowel disease in the patient’s family.
Antibiotic therapy had failed in the past, but the Patient responded well to prednisolone. As maintenance therapy for metastatic Crohn’s disease, the patient initially received infliximab at a dosage of 5 mg/kg. The patient responded well to this therapy, leading to the cessation of fluid secretion by the fistulas. However, an allergic reaction with dyspnea and rash occurred after the 10th dose of infliximab in October 2021, necessitating the discontinuation of treatment.
To evaluate further treatment options, the patient was referred to the department of Gastroenterology in November 2021. Meanwhile, she had developed diarrhea and abdominal pain. MRI revealed a mild ileitis, which, however, could not be validated by colonoscopy.
Therapy was switched to adalimumab in December 2021, to which the patient did not respond. Instead, a new fistula ostium developed.
Despite the lack of evidence for ustekinumab therapy in metastatic Crohn’s disease, and given its established efficacy only for intestinal manifestation, treatment with ustekinumab was initiated in May 2022 with an initial dose of 390 mg intravenous, followed by 90 mg subcutaneous every 8 weeks. This decision was based on the suspicion that the inflammatory processes in the abdominal fistula mirrored those seen in intestinal inflammation. The patient responded well and inflammation decreased within a few weeks. However, fistulas persisted, albeit with reduced secretion.
In June 2022, the blind-ending subcutaneous fistula of the thigh could be successfully treated by surgery after the active inflammation resolved. In April 2023, the abdominal fistula also showed no remaining inflammation, so a complete excision of the abdominal fistulas was performed. At the patients last visit in August 2023, no new fistula or abscesses were detected, but ustekinumab was continued due to the long and complicated clinical history. Written informed consent for publication of their clinical details and clinical images was obtained from the patient.
Review of the current literature
Material and methods.
A data base literature search was performed using the keywords “metastatic” and “Crohn’s” and “disease”. 1,875 reports published from January 2012 to November 2023 were found. The number of papers meeting the search criteria steadily increased, highlighting the clinical relevance of this topic.
So far, 59 case reports including 171 patients and 12 reviews about clinical presentation, diagnostic approach and therapeutic options have been published. However, no statistical analysis of patient characteristics and treatments is available. Therefore, our aim was to objectively assess these items. Moreover, we intended to discuss ustekinumab as a novel but successful therapeutic approach for metastatic Crohn’s disease.
Of the patients with metastatic Crohn’s disease, 74% were female, and 38% of the cases involved individuals under 18 years old. From this cohort, we assessed diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for metastatic Crohn’s disease.
80% of the patients were diagnosed with intestinal Crohn’s disease before or at the time skin lesions appearance, while 10% exhibited gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea or abdominal pain without IBD [ 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. 7% had isolated extraintestinal manifestations as illustrated in our presented case. Fistulas were described in 13% of all cases [ 4 , 20 , 21 , 22 ], highlighting the rarity of this condition. However, fistula presence or absence was not explicitly mentioned in 58% of all published cases.
At the time of diagnosing metastatic Crohn’s disease, usually skin biopsies are taken and examined. Granulomas were present in 58% of all cases [ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 ], with some studies not commenting on histological findings.
(Fig. 4 ).
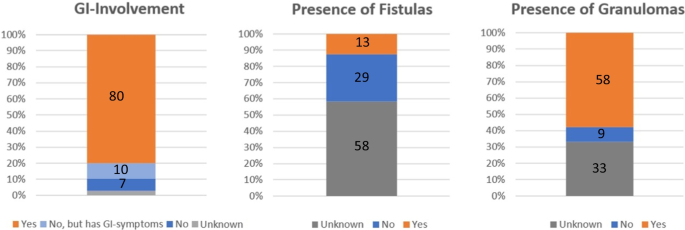
Proportion of patients with GI-Involvement, granuloma and fistula ( n = 171)
The most common localization of metastatic Crohn’s disease was the genital region, including groin, vulva and penis/scrotum (Fig. 5 ). Notably, our case report highlights that metastatic Crohn’s disease can affect almost every part of the body. This is in accordance with other reports describing affected skin at various sites of the body including extremities, trunk or head/face [ 4 , 5 , 16 , 22 , 25 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 41 , 44 , 47 , 48 ].
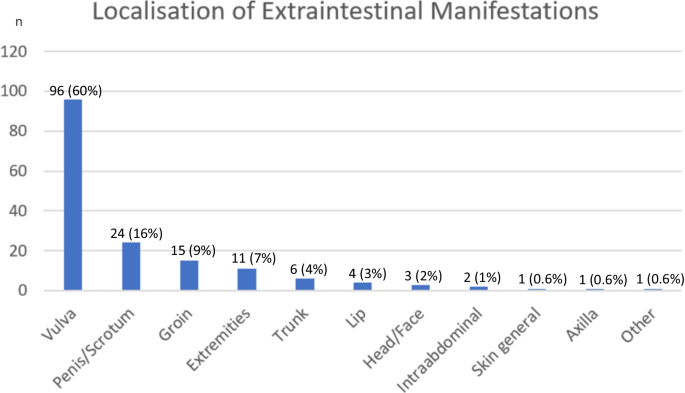
Localisation of lesions in patients with metastatic Crohn’s disease ( n = 159)
Less common sites of involvement included intraabdominal abscesses [ 31 , 49 ] and necrotizing endocarditis of the aortic valve with granuloma formation [ 26 ]. Some patients also exhibited lesions on more than one site. They were counted for each site in Fig. 5 . For 12 patients, the site of involvement was not mentioned.
There are no general recommendations for the treatment of metastatic Crohn’s disease, but similar pathophysiological processes are suspected. Hence, established therapeutic regimens for the treatment of intestinal Crohn’s disease are employed. The most common therapeutic approach involves corticosteroid admission (Figure 6 ), often resulting in a lesion reduction. Anti-TNF, especially infliximab, was effective and utilized in 41.6% of cases. Some patients received multiple therapies and were counted accordingly (Fig. 6 ).
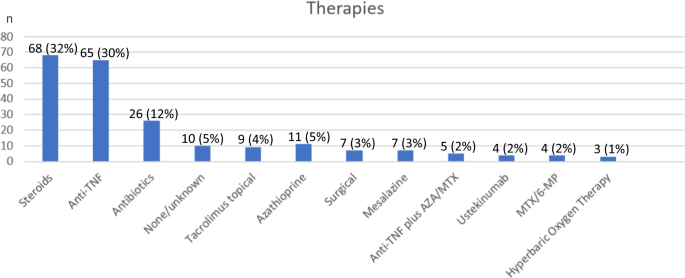
Therapeutic approaches for metastatic Crohn’s disease ( n = 219)
Steroid treatment led to remission or improvement in 30.8% of all described cases (Table 1 ). Excluding unknown cases, steroids induced remission (17.2%) or improvement (55.2%) in 72.4% of patients.
Anti-TNF, especially infliximab, less common also adalimumab and certolizumab, only had an effect (improvement or remission) in 15.6% of the cases. However, excluding unknown cases, remission was induced in 13.3% and improvement in 53.3% of patients (Table 1 ).
Antibiotics, azathioprine and topical tacrolimus also showed positive effects, although azathioprine did not induce remission in any patient. Data regarding surgical interventions, mesalazine, anti-TNF plus azathioprine, MTX/6-MP, ustekinumab, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy are limited and inconclusive based on the literature. Notably and in line with the presented case, two out of three patients achieved remission after treatment with ustekinumab.
Our examination summarizes patient characteristics in metastatic Crohn’s disease and outlines therapeutic options based on the presented case. However, there are some limitations.
We established the diagnosis of metastatic Crohn’s diseases based on clinical and histological findings. Other granulomatous diseases such as sarcoidosis, tuberculosis and immunodeficiencies were ruled out, and histological findings were typical for Crohn’s lesions despite there was no intestinal involvement at the time of diagnosis. However, there is no possibility of completely ruling out any other underlying immunological condition causing similar symptoms. The analyzed case reports mostly also based their diagnosis on histological findings fitting Crohn’s criteria, and often on a known underlying intestinal Crohn’s disease, but in some publications, diagnostic criteria were not discussed in detail.
Our analysis is a summary of published cases and no randomized trial, making it impossible to compare the efficiencies of different therapies. This article outlines various treatment approaches and their success rates according to literature data. However, assessing the patient's condition before and after treatment from literature data can be challenging.
Several patients responded well to antibiotic treatment (see Table 1 ). This was also effective in some patients with GI involvement. Nevertheless, it remains unclear if lesions described as metastatic Crohn’s disease are infectious or a manifestation of Crohn’s disease.
Despite these limitations, treatments for metastatic Crohn`s disease could be evaluated. The most effective treatments, according to the current literature, include steroids and anti-TNF-antibodies. Despite the small number of cases, also azathioprine showed good clinical results. Mesalazine also appeared to positively impact skin lesions in patients with metastatic Crohn’s disease (see Table 1 ).
Conclusively, mesalazine, azathioprine, steroids, and anti-TNF antibodies should be considered as first line therapy for metastatic Crohn´s disease.
In case of treatment failure, there are less common therapeutic options such as ustekinumab, surgical intervention or hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which can be offered to the patient. Although the efficacy cannot be evaluated based on the limited amount of available data, the existing literature as well as our case report suggests a positive effect of ustekinumab in patients with metastatic Crohn’s disease.
Topical tacrolimus can improve the lesions, but there is no case report where topical tacrolimus could induce remission [ 3 , 5 , 9 , 24 , 39 , 57 , 61 ], and can currently not be recommended as a single therapeutic option. It might be useful to support other therapies.
Metastatic Crohn’s disease can affect patients with or without GI involvement. Diagnostics include anamnesis, inspection and biopsies of the involved site as well as endoscopy and MRI.
Currently, with no German, European or American guidelines available, approved therapies for intestinal Crohn’s disease are employed, based on the suspected similar inflammatory pathophysiology in intestinal and extraintestinal sites: Steroids, anti-TNF antibodies, and antibiotics were the primary and most potent agents. Mesalazine and azathioprine as well as less common treatment options such as surgical intervention or hyperbaric oxygen therapy may also be considered in case of treatment failure.
With the increasing number of reported cases of metastatic Crohn’s disease, the need for future guidelines for treating these patients becomes apparent. Our case demonstrates successful ustekinumab treatment for metastatic Crohn’s disease, suggesting a potential new therapeutic option.
Availability of data and materials
Laboratory results, histological findings, imaging and other diagnostic results are available if necessary.
Ickrath F, Stoevesandt J, Schulmeyer L, Glatzel C, Goebeler M, Kerstan A. Metastatic Crohn’s disease: an underestimated entity. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2021;19(7):973–82.
PubMed Google Scholar
Kurtzman DJB, Jones T, Lian F, Peng LS. Metastatic Crohn’s disease: a review and approach to therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71(4):804–13.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Aberumand B, Howard J, Howard J. Metastatic Crohn’s disease: an approach to an uncommon but important cutaneous disorder. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:8192150.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ballester Sánchez R, Sanchís Sánchez C, Rodrigo Nicolás B, Valcuende CF. Enfermedad de Crohn metastásica tratada con ustekinumab. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;112(2):182–3.
Blasco Alonso J, Girón Fernández-Crehuet F, Lendínez Ramírez MA, Gallego Gutiérrez S, Luque Pérez S, Serrano Nieto J, et al . Metastatic Crohn’s disease in pediatrics. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2016;108(9):598–603.
Kapur SV, Oswal JS, Viswanathan V. Vulval edema as a manifestation of childhood metastatic Crohn’s disease. Indian J Pediatr. 2021;88(2):182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-020-03419-4.pdf .
Kyriakou G, Gkermpesi M, Thomopoulos K, Marangos M, Georgiou S. Metastatic vulvar Crohn’s disease preceding intestinal manifestations: a case report and short review. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2019;28(3):131–3.
Janssen Cilag International, editor. Fachinformation Ustekinumab. 2023.
Barrick BJ, Tollefson MM, Schoch JJ, McEvoy MT, Hand JL, Wieland CN, et al . Penile and scrotal swelling: an underrecognized presentation of Crohn’s disease. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33(2):172–7.
Gulseren D, Ersoy-Evans S. Metastatic Crohn disease with groin localization in an adult patient. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2022;12(2): e2022056.
Kim SSY, Flannigan RK, Samarasekera D, Terry J, Macneily AE. Case: metastatic Crohn’s disease of the genitalia in a prepubescent male: an illustrative case of an uncommon diagnosis. Can Urol Assoc J. 2017;11(9):E379–81.
Kim S, Won YB, Seo SK, Cho S, Choi YS, Lee BS, et al . Vulvar Crohn’s disease in an adolescent diagnosed after unsuccessful surgical treatment. BMC Womens Health. 2021;21(1):316.
Lanka P, Lanka LR, Sylvester N, Lakshmi MD, Ethirajan N. Metastatic Crohn’s disease. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5(1):41–3.
Mazzoni D, Bodapati S, Mortimore R, Davies J, Wheller L. Metastatic Crohn’s disease in a boy presenting with genital swelling. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37(6):1165–6.
Mirheydar HS, Friedlander SF, Kaplan GW. Prepubertal male genitourinary metastatic Crohn’s disease: report of a case and review of literature. Urology. 2014;83(5):1165–9.
Pérez-Santiago L, García-Vázquez A, Martín-Arévalo J. A diagnostic challenge: chronic cutaneous ulcers as an isolated clinical finding in metastatic Crohn’s disease. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2022. https://doi.org/10.17235/reed.2022.8995/2022 .
Article Google Scholar
Saito K, Iwata Y, Nakajima Y, Numata S, Sugiura K. Metastatic Crohn’s disease in childhood: a case report. J Dermatol. 2018;45(7):e199–200.
Schneider SL, Foster K, Patel D, Shwayder T. Cutaneous manifestations of metastatic Crohn’s disease. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/pde.13565 .
Vahabi-Amlashi S, Molkara S, Shahrokhi Y. Cutaneous Crohn disease without intestinal manifestations. Adv Biomed Res. 2021;10:39.
Rani U, Russell A, Tanaka S, Correa H, Nicholson MR. Urogenital manifestations of metastatic Crohn’s disease in children: case series and review of the literature. Urology. 2016;92:117–21.
Batra J, Goraya SK, Grewal S, Singh A. Metastatic Crohn’s Disease of the Vulva: A Rare Presentation. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2020;11(3):416–8.
Farkas K, Nagy F, Kovács L, Wittmann T, Molnár T. Anti-tumor necrosis factor-α induced systemic lupus erythematosus in a patient with metastatic Crohn’s disease–what is the role of anti-TNF antibody? J Crohns Colitis. 2013;7(4):e143–5.
Adachi A, Komine M, Murata S, Ohtsuki M. Japanese case of metastatic cutaneous Crohn’s disease of the groin. J Dermatol. 2015;42(2):224–5.
AlAsmari A, AlEssa R, AlAjroush W, AlKhodair R, AlHaddad S. Novel association of metastatic Crohn’s disease and Wolman disease. JAAD Case Rep. 2022;20:40–3.
Campos S, Coutinho I, Cardoso JC, Portela F. Metastatic Crohn’s disease despite infliximab therapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92(5 Suppl 1):104–6.
Gettigan NM, Sheehan M, Slattery E. Metastatic Crohn’s disease of the aortic valve resulting in severe aortic insufficiency, non-infective endocarditis, and pericarditis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019;25(10):e117–8.
Guglielmetti A, Gompertz M, Jahr C, Silva T, González S. Remission of refractory metastatic Crohn’s disease achieved with dapsone. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57(4):467–9.
Hogan N, Byrnes V, Hussey A, Joyce M. Surgical management of gluteal metastatic cutaneous Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2012;6(5):617–20.
Ishida M, Iwai M, Yoshida K, Kagotani A, Okabe H. Metastatic Crohn’s disease accompanying granulomatous vasculitis and lymphangitis in the vulva. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6(10):2263–6.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kiuru M, Camp B, Adhami K, Jacob V, Magro C, Wildman H. Treatment of metastatic cutaneous Crohn disease with certolizumab. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21(11):4.
Labidi A, Karoui S, Ben Mustapha N, Serghini M, Azzouz H, Allouche W, et al . Cutaneous metastatic Crohn’s disease of the abdominal wall: an exceptional location. Tunis Med. 2013;91(6):424–5.
Lang N, Hartschuh W, Enk A, Toberer F. Metastatic Crohn’s disease: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2015;13(6):571–4.
Lansdorp CA, Buskens CJ, Gecse KB, D’Haens GR, van Hulst RA. Wound healing of metastatic perineal Crohn’s disease using hyperbaric oxygen therapy: a case series. United Eur Gastroenterol J. 2020;8(7):820–7.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Lim Y, Singh M. Metastatic vulval crohn’s disease with good outcome on Ustekinumab. Cureus. 2021;13(7): e16252.
Math CJ, George A. Vegetating plaques in the groin: a manifestation of metastatic Crohn’s disease. Indian J Dermatol. 2018;63(4):338–41.
Misago N, Narisawa Y. Erythema induratum (nodular vasculitis) associated with Crohn’s disease: a rare type of metastatic Crohn’s disease. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34(3):325–9.
Park HC, Kim HW, Park CG, Ko JY. Metastatic Crohn disease clinically reminiscent of erythema nodosum on the right leg. Cutis. 2016;98(3):E11–5.
Patel AV, Jones DM, Hill JC, MacDermott RP. Development of metastatic Crohn’s disease of the skin while on anti-TNF biologics. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18(6):1188–90.
Pérez-Belmonte LM, Gómez-Moyano E. Metastatic Crohn’s disease. Indian J Med Res. 2015;142(4):497.
Pousa-Martínez M, Alfageme F, de Domingo González MA, Suárez-Masa D, Calvo M, Roustán G. Vulvar metastatic Crohn disease: clinical, histopathological and ultrasonographic findings. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23(11):21.
Ruiz-Villaverde R, Sánchez-Cano D, Perez-Lopez I, Aneiros-Fernández J. Enfermedad de Crohn metastásica. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017;108(2):171–2.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Sabbadini C, Banzato C, Schena D, Peroni D, Girolomoni G. Metastatic Crohn’s disease in childhood. J Deutsche Derma Gesell. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddg.12861 .
Sackett DD, Meshekow JS, Figueroa TE, Napoli JA. Isolated penile lymphedema in an adolescent male: a case of metastatic Crohn’s disease. J Pediatr Urol. 2012;8(5):e55–8.
Streight KL, Braun TL, Lowe N, Kim SJ. A rare clinical presentation of metastatic Crohn’s disease. Cureus. 2020;12(5): e8285.
Vint R, Husain E, Hussain F, McClinton S, Ormerod A. Metastatic Crohn’s disease of the penis: two cases. Int Urol Nephrol. 2012;44(1):45–9.
Wylomanski S, Bouquin R, Dréno B, Quéreux G. Spectacular response of metastatic vulval Crohn’s disease to infliximab treatment. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55(10):1146–8.
Gontijo JRV, Leidenz FAB, de Sousa MSLA. Case for diagnosis. Metastatic Crohn’s disease. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91(4):531–3.
Her Y, Park SE, Kim SS, Kim CW. Metastatic cutaneous Crohn’s disease in a child. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25(1):74–5.
Amarapurkar DN, Sonavane A, Amarapurkar AD. Metastatic Crohn’s Disease. J Assoc Phys India. 2017;65(4):86–8.
Google Scholar
Alotaibi HM, Fathaddin AA, AlMutairi HM, Barakeh MM. Metastatic Crohn’s disease in external genitalia with good outcome on adalimumab: a rare case of a Saudi female and a short review. Cureus. 2023;15(8): e43380.
Bhoyrul B, Lyon C. Crohn’s disease of the vulva: a prospective study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;33(12):1969–74.
Chatterjee D, Bhattacharjee R, Khullar G, Kumaran S, De D, Saikia UN, et al . Metastatic Crohn disease: a clinicohistological appraisal from a tertiary care center in India. Am J Dermatopathol. 2020;42(7):506–12.
Costa Blasco M, McFeely O, Doyle C, Wolinska A, Andrawis M, Murphy L, et al . Metastatic Crohn disease improving with vedolizumab. Br J Dermatol. 2023;189(2): e35.
Das D, Gupta B, Saha M. Metastatic vulvar Crohn’s disease-a rare case report and short review of literature. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61(1):70–4.
Dederichs F, Iesalnieks I, Sladek M, Tzivinikos C, Hansen R, Muñoz C, et al . Genital granulomatosis in male and female patients with Crohn’s disease: clinical presentation and treatment outcomes. J Crohns Colitis. 2018;12(2):197–203.
Ferreira de Castro L, Gomes R, Sá DC, Fernandes E, Lima R, Tavares M. Metastatic Crohn’s disease in paediatrics: Vulvar lesions as the first clinical presentation. J Paediatr Child Health. 2023;59(9):1092–4.
García-Delgado R, Escario-Travesedo E, Sánchez-Romero A. Absorción sistémica de tacrolimus tópico en enfermedad de Crohn metastásica con úlceras cutáneas. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2016;107(10):866–7.
Pampín A, Gamo R, Andreu-Barasoain M, Pinedo F, La Gómez-de FE, López-Estebaranz JL. Metastatic Crohn’s disease in genital and perianal area preceding 11 years intestinal Crohn’s disease. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53(3):e176–7.
Pereira AS, Coutinho I. A challenging case of metastatic Crohn’s disease without gastrointestinal manifestations. Cureus. 2023;15(9): e45791.
Raman LG, AbdullGaffar B. Metastatic Crohn disease revealing vascular embolization: report of two cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2023;50(11):929–32.
Shields BE, Richardson C, Arkin L, Kornik R. Vulvar Crohn disease: diagnostic challenges and approach to therapy. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6(5):390–4.
Xiao TL, Ezenwa E, Ruiz de Luzuriaga A, Hoffman MD. Refractory metastatic Crohn’s disease responsive to ustekinumab dose intensification. JAAD Case Rep. 2023;32:65–7.
Woody MM, Holliday AC, Gavino ACP, McReynolds A, Soldano AC. Metastatic vulvovaginal Crohn disease in the setting of well-controlled intestinal disease. Cutis. 2018;102(2):E16–8.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. This study received no funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Internal Medicine I, Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Endocrinology, Rheumatology and Infectious Diseases, University Hospital Regensburg, Franz-Josef-Strauß-Allee 11, 93053, Regensburg, Germany
Tanja Elger, Johanna Loibl, Christa Buechler, Karsten Guelow, Claudia Kunst, Arne Kandulski, Pia Goeggelmann, Martina Mueller & Hauke Christian Tews
Department of Visceral Surgery, University Hospital Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany
Jens Werner
Department of Dermatology, University Hospital Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany
Sebastian Haferkamp, Konstantin Drexler & Ulrich Hohenleutner
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
HCT initiated the project and designed the work; TE and HCT were responsible for case preparation; TE drafted the manuscript; TE, JL, CB, SH, JW, KD, UH, AK, PG, and HCT analyzed results; TE performed literature search; TE prepared figures; TE, CK, KG, MMS, and HCT wrote and edited the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Tanja Elger .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate.
See section below.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication of their clinical details and clinical images was obtained from the patient. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
All authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Elger, T., Loibl, J., Buechler, C. et al. Fistulising skin metastases in Crohn’s disease: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Reports 18 , 252 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-024-04569-1
Download citation
Received : 02 February 2024
Accepted : 10 April 2024
Published : 19 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-024-04569-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Metastatic Crohn’s disease
- Skin fistulae
- Ustekinumab
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Extraintestinal manifestation
Journal of Medical Case Reports
ISSN: 1752-1947
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
An apple a day keeps the doctor away: pediatric scurvy case report and mini review
- Case Report
- Published: 16 May 2024
Cite this article

- Talia Mia Bitonti ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0002-6392-3630 1 &
- Albert Tu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8238-9202 2
1 Altmetric
Scurvy is a rare nutritional disorder caused by deficiency of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). It is often under-diagnosed in clinical settings, especially in North America where population statistics are unavailable. However, scurvy is more common than previously thought and appears to be re-emerging in children with developmental delays. Here, we review the pertinent literature and present a case of a previously healthy, 5-year-old, non-verbal boy who presented with multiple, acute, and subacute spontaneous epidural hemorrhages managed by neurosurgical intervention. He remained in hospital for 17 days and was seen in follow-up 3 weeks post-operatively having returned to his neurological baseline. Our case suggests the importance of considering scurvy in patients who have developmental delays and poor nutritional status.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Neurology of Nutritional Deficiencies
Shaken baby syndrome: what certainty do we have.

Neurodisability
Data availability.
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Agarwal A, Shaharyar A, Kumar A, Bhat MS, Mishra M (2015) Scurvy in pediatric age group – a disease often forgotten? J Clin Orthop Trauma 6(2):101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcot.2014.12.003
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
de Boer HC, Sawhney JS (2024) Pediatric Scurvy case report: a novel presentation with deep vein thrombosis secondary to large bilateral spontaneous iliac subperiosteal hematomas. BMC Pediatr 24(1):126. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-024-04579-4
Ganske A, Kolbe AB, Thomas K, Hull N (2021) Pediatric scurvy MRI appearance. Radiol Case Rep 16(5):1148–1152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radcr.2021.02.045
Pan T, Hennrikus EF, Hennrikus WL (2021) Modern day scurvy in pediatric orthopaedics: a forgotten illness. J Pediatr Orthop 41(3):e279–e284. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000001731
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Rubino C, Mastrangelo G, Bartolini E, Indolfi G, Trapani S (2021) The pitfall in differential diagnosis of musculoskeletal symptoms in children: a case series of pediatric scurvy. J Clin Rheumatol 27(8S):S362–S367. https://doi.org/10.1097/RHU.0000000000001562
Brambilla A, Pizza C, Lasagni D, Lachina L, Resti M, Trapani S (2018) Pediatric scurvy: when contemporary eating habits bring back the past. Front Pead 6:126. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2018.00126
Article Google Scholar
Burhop J, Gibson J, de Boer J, Heydarian C (2020) Do you C what IC: emergency department evaluation and diagnosis of pediatric scurvy in an autistic child with a restricted diet. Pediatr Emerg Care 36(1):e1–e3. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000001412
Fain O (2005) Musculoskeletal manifestations of scurvy. Joint bone Spine 72(2):124–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2004.01.007
Kothari P, Tate A, Adewumi A, Kinlin LM, Ritwik P (2020) The risk for scurvy in children with neurodevelopmental disorders. Spec Care Dentist 40(3):251–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/scd.12459
Musa H, Ismail II, Abdul Rashid NH (2021) Paediatric scurvy: frequently misdiagnosed. Paediatrics Int Child Health 41(2):158–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/20469047.2020.1816285
Trapani S, Rubino C, Indolfi G, Lionetti P (2022) A narrative review on pediatric scurvy: the last twenty years. Nutrients 14(3):684. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030684
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Longo U, Giuseppe Denaro V (2023) Textbook of musculoskeletal disorders. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20987-1
Book Google Scholar
Zessis NR, Peters SW, Samet JD, Parzen-Johnson S, Russo LT, Samady W, Stephen R (2023) Unusual presentation of pediatric scurvy: a necrotic gastrostomy tube site in a 14-year-old boy. Am J Case Rep 24:e940770–e940771. https://doi.org/10.12659/AJCR.940770
Patel N, Bessler S, Howard J, Cohen R, Doshi B (2022) Bifrontal epidural hemorrhage secondary to scurvy in a 10-year-old boy. Clin Pediatr 61(11):745–748. https://doi.org/10.1177/00099228221103975
Verma S, Sivanandan S, Aneesh MK, Gupta V, Seth R, Kabra S (2007) Unilateral proptosis and extradural hematoma in a child with scurvy. Pediatr Radiol 37(9):937–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0543-9
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Ottawa Hospital, Ottawa, ON, Canada
Talia Mia Bitonti
Division of Neurosurgery, Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, Ottawa, ON, Canada
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
TMB wrote the main manuscript and extracted highlighted figures.AT edited the main manuscript, and all authors reviewed the final version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Albert Tu .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Consent from patient guardians was received on March 11, 2024.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Bitonti, T.M., Tu, A. An apple a day keeps the doctor away: pediatric scurvy case report and mini review. Childs Nerv Syst (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-024-06454-0
Download citation
Received : 30 March 2024
Accepted : 10 May 2024
Published : 16 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-024-06454-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Ascorbic acid
- Case report
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 12 May 2024
Association between problematic social networking use and anxiety symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Mingxuan Du 1 ,
- Chengjia Zhao 2 ,
- Haiyan Hu 1 ,
- Ningning Ding 1 ,
- Jiankang He 1 ,
- Wenwen Tian 1 ,
- Wenqian Zhao 1 ,
- Xiujian Lin 1 ,
- Gaoyang Liu 1 ,
- Wendan Chen 1 ,
- ShuangLiu Wang 1 ,
- Pengcheng Wang 3 ,
- Dongwu Xu 1 ,
- Xinhua Shen 4 &
- Guohua Zhang 1
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 263 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
186 Accesses
Metrics details
A growing number of studies have reported that problematic social networking use (PSNU) is strongly associated with anxiety symptoms. However, due to the presence of multiple anxiety subtypes, existing research findings on the extent of this association vary widely, leading to a lack of consensus. The current meta-analysis aimed to summarize studies exploring the relationship between PSNU levels and anxiety symptoms, including generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out. 209 studies with a total of 172 articles were included in the meta-analysis, involving 252,337 participants from 28 countries. The results showed a moderately positive association between PSNU and generalized anxiety (GA), social anxiety (SA), attachment anxiety (AA), and fear of missing out (FoMO) respectively (GA: r = 0.388, 95% CI [0.362, 0.413]; SA: r = 0.437, 95% CI [0.395, 0.478]; AA: r = 0.345, 95% CI [0.286, 0.402]; FoMO: r = 0.496, 95% CI [0.461, 0.529]), and there were different regulatory factors between PSNU and different anxiety subtypes. This study provides the first comprehensive estimate of the association of PSNU with multiple anxiety subtypes, which vary by time of measurement, region, gender, and measurement tool.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Social network refers to online platforms that allow users to create, share, and exchange information, encompassing text, images, audio, and video [ 1 ]. The use of social network, a term encompassing various activities on these platforms, has been measured from angles such as frequency, duration, intensity, and addictive behavior, all indicative of the extent of social networking usage [ 2 ]. As of April 2023, there are 4.8 billion social network users globally, representing 59.9% of the world’s population [ 3 ]. The usage of social network is considered a normal behavior and a part of everyday life [ 4 , 5 ]. Although social network offers convenience in daily life, excessive use can lead to PSNU [ 6 , 7 ], posing potential threats to mental health, particularly anxiety symptoms (Rasmussen et al., 2020). Empirical research has shown that anxiety symptoms, including generalized anxiety (GA), social anxiety (SA), attachment anxiety (AA), and fear of missing out (FoMO), are closely related to PSNU [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ]. While some empirical studies have explored the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms, their conclusions are not consistent. Some studies have found a significant positive correlation [ 13 , 14 , 15 ], while others have found no significant correlation [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Furthermore, the degree of correlation varies widely in existing research, with reported r-values ranging from 0.12 to 0.80 [ 20 , 21 ]. Therefore, a systematic meta-analysis is necessary to clarify the impact of PSNU on individual anxiety symptoms.
Previous research lacks a unified concept of PSNU, primarily due to differing theoretical interpretations by various authors, and the use of varied standards and diagnostic tools. Currently, this phenomenon is referred to by several terms, including compulsive social networking use, problematic social networking use, excessive social networking use, social networking dependency, and social networking addiction [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]. These conceptual differences hinder the development of a cohesive and systematic research framework, as it remains unclear whether these definitions and tools capture the same underlying construct [ 27 ]. To address this lack of uniformity, this paper will use the term “problematic use” to encompass all the aforementioned nomenclatures (i.e., compulsive, excessive, dependent, and addictive use).
Regarding the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms, two main perspectives exist: the first suggests a positive correlation, while the second proposes a U-shaped relationship. The former perspective, advocating a positive correlation, aligns with the social cognitive theory of mass communication. It posits that PSNU can reinforce certain cognitions, emotions, attitudes, and behaviors [ 28 , 29 ], potentially elevating individuals’ anxiety levels [ 30 ]. Additionally, the cognitive-behavioral model of pathological use, a primary framework for explaining factors related to internet-based addictions, indicates that psychiatric symptoms like depression or anxiety may precede internet addiction, implying that individuals experiencing anxiety may turn to social networking platforms as a coping mechanism [ 31 ]. Empirical research also suggests that highly anxious individuals prefer computer-mediated communication due to the control and social liberation it offers and are more likely to have maladaptive emotional regulation, potentially leading to problematic social network service use [ 32 ]. Turning to the alternate perspective, it proposes a U-shaped relationship as per the digital Goldilocks hypothesis. In this view, moderate social networking usage is considered beneficial for psychosocial adaptation, providing individuals with opportunities for social connection and support. Conversely, both excessive use and abstinence can negatively impact psychosocial adaptation [ 33 ]. In summary, both perspectives offer plausible explanations.
Incorporating findings from previous meta-analyses, we identified seven systematic reviews and two meta-analyses that investigated the association between PSNU and anxiety. The results of these meta-analyses indicated a significant positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety (ranging from 0.33 to 0.38). However, it is evident that these previous meta-analyses had certain limitations. Firstly, they focused only on specific subtypes of anxiety; secondly, they were limited to adolescents and emerging adults in terms of age. In summary, this systematic review aims to ascertain which theoretical perspective more effectively explains the relationship between PSNU and anxiety, addressing the gaps in previous meta-analyses. Additionally, the association between PSNU and anxiety could be moderated by various factors. Drawing from a broad research perspective, any individual study is influenced by researcher-specific designs and associated sample estimates. These may lead to bias compared to the broader population. Considering the selection criteria for moderating variables in empirical studies and meta-analyses [ 34 , 35 ], the heterogeneity of findings on problematic social network usage and anxiety symptoms could be driven by divergence in sample characteristics (e.g., gender, age, region) and research characteristics (measurement instrument of study variables). Since the 2019 coronavirus pandemic, heightened public anxiety may be attributed to the fear of the virus or heightened real life stress. The increased use of electronic devices, particularly smartphones during the pandemic, also instigates the prevalence of problematic social networking. Thus, our analysis focuses on three moderators: sample characteristics (participants’ gender, age, region), measurement tools (for PSNU and anxiety symptoms) and the time of measurement (before COVID-19 vs. during COVID-19).
The present study was conducted in accordance with the 2020 statement on Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [ 36 ]. To facilitate transparency and to avoid unnecessary duplication of research, this study was registered on PROSPERO, and the number is CRD42022350902.
Literature search
Studies on the relationship between the PSNU and anxiety symptoms from 2000 to 2023 were retrieved from seven databases. These databases included China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Data, Chongqing VIP Information Co. Ltd. (VIP), Web of Science, ScienceDirect, PubMed, and PsycARTICLES. The search strings consisted of (a) anxiety symptoms, (b) social network, and (c) Problematic use. As shown in Table 1 , the keywords for anxiety are as follows: anxiety, generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, fear of missing out, and FoMO. The keywords for social network are as follows: social network, social media, social networking site, Instagram, and Facebook. The keywords for addiction are as follows: addiction, dependence, problem/problematic use, excessive use. The search deadline was March 19, 2023. A total of 2078 studies were initially retrieved and all were identified ultimately.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Retrieved studies were eligible for the present meta-analysis if they met the following inclusion criteria: (a) the study provided Pearson correlation coefficients used to measure the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms; (b) the study reported the sample size and the measurement instruments for the variables; (c) the study was written in English and Chinese; (d) the study provided sufficient statistics to calculate the effect sizes; (e) effect sizes were extracted from independent samples. If multiple independent samples were investigated in the same study, they were coded separately; if the study was a longitudinal study, they were coded by the first measurement. In addition, studies were excluded if they: (a) examined non-problematic social network use; (b) had an abnormal sample population; (c) the results of the same sample were included in another study and (d) were case reports or review articles. Two evaluators with master’s degrees independently assessed the eligibility of the articles. A third evaluator with a PhD examined the results and resolved dissenting views.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two evaluators independently coded the selected articles according to the following characteristics: literature information, time of measurement (before the COVID-19 vs. during the COVID-19), sample source (developed country vs. developing country), sample size, proportion of males, mean age, type of anxiety, and measurement instruments for PSNU and anxiety symptoms. The following principles needed to be adhered to in the coding process: (a) effect sizes were extracted from independent samples. If multiple independent samples were investigated in the same study, they were coded separately; if the study was a longitudinal study, it was coded by the first measurement; (b) if multiple studies used the same data, the one with the most complete information was selected; (c) If studies reported t or F values rather than r , the following formula \( r=\sqrt{\frac{{t}^{2}}{{t}^{2}+df}}\) ; \( r=\sqrt{\frac{F}{F+d{f}_{e}}}\) was used to convert them into r values [ 37 , 38 ]. Additionally, if some studies only reported the correlation matrix between each dimension of PSNU and anxiety symptoms, the following formula \( {r}_{xy}=\frac{\sum {r}_{xi}{r}_{yj}}{\sqrt{n+n(n-1){r}_{xixj}}\sqrt{m+m(m-1){r}_{yiyj}}}\) was used to synthesize the r values [ 39 ], where n or m is the number of dimensions of variable x or variable y, respectively, and \( {r}_{xixj} \) or \( {r}_{yiyj}\) represents the mean of the correlation coefficients between the dimensions of variable x or variable y, respectively.
Literature quality was determined according to the meta-analysis quality evaluation scale developed [ 40 ]. The quality of the post-screening studies was assessed by five dimensions: sampling method, efficiency of sample collection, level of publication, and reliability of PSNU and anxiety symptom measurement instruments. The total score of the scale ranged from 0 to 10; higher scores indicated better quality of the literature.
Data analysis
All data were performed using Comprehensive Meta Analysis 3.3 (CMA 3.3). Pearson’s product-moment coefficient r was selected as the effect size index in this meta-analysis. Firstly, \( {\text{F}\text{i}\text{s}\text{h}\text{e}\text{r}}^{{\prime }}\text{s} Z=\frac{1}{2}\times \text{ln}\left(\frac{1+r}{1-r}\right)\) was used to convert the correlation coefficient to Fisher Z . Then the formula \( SE=\sqrt{\frac{1}{n-3}}\) was used to calculate the standard error ( SE ). Finally, the summary of r was obtained from the formula \( r=\frac{{e}^{2z}-1}{{e}^{2z}+1}\) for a comprehensive measure of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms [ 37 , 41 ].
Although the effect sizes estimated by the included studies may be similar, considering the actual differences between studies (e.g., region and gender), the random effects model was a better choice for data analysis for the current meta-analysis. The heterogeneity of the included study effect sizes was measured for significance by Cochran’s Q test and estimated quantitatively by the I 2 statistic [ 42 ]. If the results indicate there is a significant heterogeneity (the Q test: p -value < 0.05, I 2 > 75) and the results of different studies are significantly different from the overall effect size. Conversely, it indicates there are no differences between the studies and the overall effect size. And significant heterogeneity tends to indicate the possible presence of potential moderating variables. Subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis were used to examine the moderating effect of categorical and continuous variables, respectively.
Funnel plots, fail-safe number (Nfs) and Egger linear regression were utilized to evaluate the publication bias [ 43 , 44 , 45 ]. The likelihood of publication bias was considered low if the intercept obtained from Egger linear regression was not significant. A larger Nfs indicated a lower risk of publication bias, and if Nfs < 5k + 10 (k representing the original number of studies), publication bias should be a concern [ 46 ]. When Egger’s linear regression was significant, the Duval and Tweedie’s trim-and-fill was performed to correct the effect size. If there was no significant change in the effect size, it was assumed that there was no serious publication bias [ 47 ].
A significance level of P < 0.05 was deemed applicable in this study.
Sample characteristics
The PRISMA search process is depicted in Fig. 1 . The database search yielded 2078 records. After removing duplicate records and screening the title and abstract, the full text was subject to further evaluation. Ultimately, 172 records fit the inclusion criteria, including 209 independent effect sizes. The present meta-analysis included 68 studies on generalized anxiety, 44 on social anxiety, 22 on attachment anxiety, and 75 on fear of missing out. The characteristics of the selected studies are summarized in Table 2 . The majority of the sample group were adults. Quality scores for selected studies ranged from 0 to 10, with only 34 effect sizes below the theoretical mean, indicating high quality for the included studies. The literature included utilized BSMAS as the primary tool to measure PSNU, DASS-21-A to measure GA, IAS to measure SA, ECR to measure AA, and FoMOS to measure FoMO.
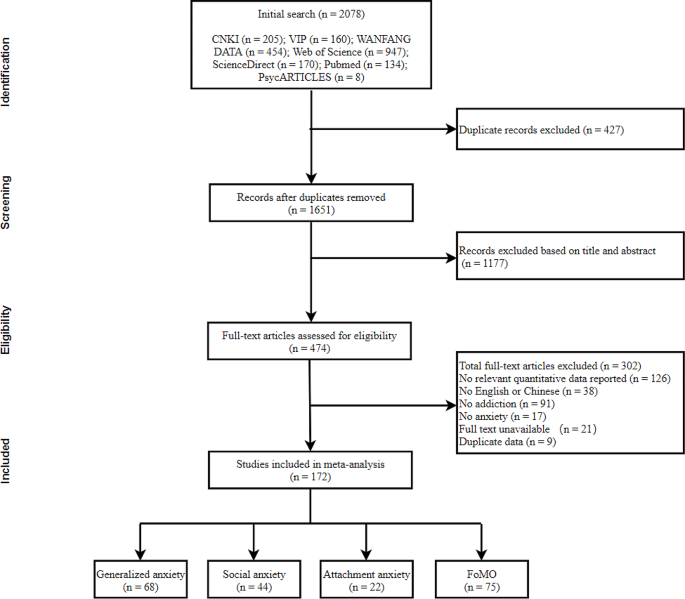
Flow chart of the search and selection strategy
Overall analysis, homogeneity tests and publication bias
As shown in Table 3 , there was significant heterogeneity between PSNU and all four anxiety symptoms (GA: Q = 1623.090, I 2 = 95.872%; SA: Q = 1396.828, I 2 = 96.922%; AA: Q = 264.899, I 2 = 92.072%; FoMO: Q = 1847.110, I 2 = 95.994%), so a random effects model was chosen. The results of the random effects model indicate a moderate positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety symptoms (GA: r = 0.350, 95% CI [0.323, 0.378]; SA: r = 0.390, 95% CI [0.347, 0.431]; AA: r = 0.345, 95% CI [0.286, 0.402]; FoMO: r = 0.496, 95% CI [0.461, 0.529]).
Figure 2 shows the funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms. No significant symmetry was seen in the funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and GA and between PSNU and SA. And the Egger’s regression results also indicated that there might be publication bias ( t = 3.775, p < 0.001; t = 2.309, p < 0.05). Therefore, it was necessary to use fail-safe number (Nfs) and the trim and fill method for further examination and correction. The Nfs for PSNU and GA as well as PSNU and SA are 4591 and 7568, respectively. Both Nfs were much larger than the standard 5 k + 10. After performing the trim and fill method, 14 effect sizes were added to the right side of the funnel plat (Fig. 2 .a), the correlation coefficient between PSNU and GA changed to ( r = 0.388, 95% CI [0.362, 0.413]); 10 effect sizes were added to the right side of the funnel plat (Fig. 2 .b), the correlation coefficient between PSNU and SA changed to ( r = 0.437, 95% CI [0.395, 0.478]). The correlation coefficients did not change significantly, indicating that there was no significant publication bias associated with the relationship between PSNU and these two anxiety symptoms (GA and SA).
Funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms. Note: Black dots indicated additional studies after using trim and fill method; ( a ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and GA; ( b ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and SA; ( c ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and AA; ( d ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and FoMO
Sensitivity analyses
Initially, the findings obtained through the one-study-removed approach indicated that the heterogeneities in the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms were not attributed to any individual study. Nevertheless, it is important to note that sensitivity analysis should be performed based on literature quality [ 223 ] since low-quality literature could potentially impact result stability. In the relationship between PSNU and GA, the 10 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.402, 95% CI [0.375, 0.428]); In the relationship between PSNU and SA, the 8 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.431, 95% CI [0.387, 0.472]); In the relationship between PSNU and AA, the 5 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.367, 95% CI [0.298, 0.433]); In the relationship between PSNU and FoMO, the 11 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.508, 95% CI [0.470, 0.544]). The revised estimates indicate that meta-analysis results were stable.
Moderator analysis
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between psnu and ga.
The results of subgroup analysis and meta-regression are shown in Table 4 , the time of measurement significantly moderated the correlation between PSNU and GA ( Q between = 19.268, df = 2, p < 0.001). The relation between the two variables was significantly higher during the COVID-19 ( r = 0.392, 95% CI [0.357, 0.425]) than before the COVID-19 ( r = 0.270, 95% CI [0.227, 0.313]) or measurement time uncertain ( r = 0.352, 95% CI [0.285, 0.415]).
The moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 6.852, df = 1, p = 0.009). The relation was significantly higher when PSNU was measured with the BSMAS ( r = 0.373, 95% CI [0.341, 0.404]) compared to others ( r = 0.301, 95% CI [0.256, 0.344]).
The moderating effect of the GA measurement was significant ( Q between = 60.061, df = 5, p < 0.001). Specifically, when GA measured by the GAD ( r = 0.398, 95% CI [0.356, 0.438]) and the DASS-21-A ( r = 0.433, 95% CI [0.389, 0.475]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the STAI ( r = 0.232, 95% CI [0.187, 0.276]).
For the relation between PSNU and GA, the moderating effect of region, gender and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and SA
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and SA were shown in Table 5 . The results revealed a gender-moderated variances between the two variables (b = 0.601, 95% CI [ 0.041, 1.161], Q model (1, k = 41) = 4.705, p = 0.036).
For the relation between PSNU and SA, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, measurement of PSNU and SA, and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and AA
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and AA were shown in Table 6 , region significantly moderated the correlation between PSNU and AA ( Q between = 6.410, df = 2, p = 0.041). The correlation between the two variables was significantly higher in developing country ( r = 0.378, 95% CI [0.304, 0.448]) than in developed country ( r = 0.242, 95% CI [0.162, 0.319]).
The moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 6.852, df = 1, p = 0.009). Specifically, when AA was measured by the GPIUS-2 ( r = 0.484, 95% CI [0.200, 0.692]) and the PMSMUAQ ( r = 0.443, 95% CI [0.381, 0.501]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the BSMAS ( r = 0.248, 95% CI [0.161, 0.331]) and others ( r = 0.313, 95% CI [0.250, 0.372]).
The moderating effect of the AA measurement was significant ( Q between = 17.283, df = 2, p < 0.001). The correlation was significantly higher when measured using the ECR ( r = 0.386, 95% CI [0.338, 0.432]) compared to the RQ ( r = 0.200, 95% CI [0.123, 0.275]).
For the relation between PSNU and AA, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, gender, and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and FoMO
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and FoMO were shown in Table 7 , the moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 8.170, df = 2, p = 0.017). Among the sub-dimensions, the others was excluded because there was only one sample. Specifically, when measured using the FoMOS-MSME ( r = 0.630, 95% CI [0.513, 0.725]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the FoMOS ( r = 0.472, 95% CI [0.432, 0.509]) and the T-S FoMOS ( r = 0.557, 95% CI [0.463, 0.639]).
For the relationship between PSNU and FoMO, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, measurement of PSNU, gender and age were not significant.
Through systematic review and meta-analysis, this study established a positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety symptoms (i.e., generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out), confirming a linear relationship and partially supporting the Social Cognitive Theory of Mass Communication [ 28 ] and the Cognitive Behavioral Model of Pathological Use [ 31 ]. Specifically, a significant positive correlation between PSNU and GA was observed, implying that GA sufferers might resort to social network for validation or as an escape from reality, potentially alleviating their anxiety. Similarly, the meta-analysis demonstrated a strong positive correlation between PSNU and SA, suggesting a preference for computer-mediated communication among those with high social anxiety due to perceived control and liberation offered by social network. This preference is often accompanied by maladaptive emotional regulation, predisposing them to problematic use. In AA, a robust positive correlation was found with PSNU, indicating a higher propensity for such use among individuals with attachment anxiety. Notably, the study identified the strongest correlation in the context of FoMO. FoMO’s significant association with PSNU is multifaceted, stemming from the real-time nature of social networks that engenders a continuous concern about missing crucial updates or events. This drives frequent engagement with social network, thereby establishing a direct link to problematic usage patterns. Additionally, social network’s feedback loops amplify this effect, intensifying FoMO. The culture of social comparison on these platforms further exacerbates FoMO, as users frequently compare their lives with others’ selectively curated portrayals, enhancing both their social networking usage frequency and the pursuit for social validation. Furthermore, the integral role of social network in modern life broadens FoMO’s scope, encompassing anxieties about staying informed and connected.
The notable correlation between FoMO and PSNU can be comprehensively understood through various perspectives. FoMO is inherently linked to the real-time nature of social networks, which cultivates an ongoing concern about missing significant updates or events in one’s social circle [ 221 ]. This anxiety prompts frequent engagement with social network, leading to patterns of problematic use. Moreover, the feedback loops in social network algorithms, designed to enhance user engagement, further intensify this fear [ 224 ]. Additionally, social comparison, a common phenomenon on these platforms, exacerbates FoMO as users continuously compare their lives with the idealized representations of others, amplifying feelings of missing out on key social experiences [ 225 ]. This behavior not only increases social networking usage but also is closely linked to the quest for social validation and identity construction on these platforms. The extensive role of social network in modern life further amplifies FoMO, as these platforms are crucial for information exchange and maintaining social ties. FoMO thus encompasses more than social concerns, extending to anxieties about staying informed with trends and dynamics within social networks [ 226 ]. The multifaceted nature of FoMO in relation to social network underscores its pronounced correlation with problematic social networking usage. In essence, the combination of social network’s intrinsic characteristics, psychological drivers of user behavior, the culture of social comparison, and the pervasiveness of social network in everyday life collectively make FoMO the most pronouncedly correlated anxiety type with PSNU.
Additionally, we conducted subgroup analyses on the timing of measurement (before COVID-19 vs. during COVID-19), measurement tools (for PSNU and anxiety symptoms), sample characteristics (participants’ region), and performed a meta-regression analysis on gender and age in the context of PSNU and anxiety symptoms. It was found that the timing of measurement, tools used for assessing PSNU and anxiety, region, and gender had a moderating effect, whereas age did not show a significant moderating impact.
Firstly, the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms was significantly higher during the COVID-19 period than before, especially between PSNU and GA. However, the moderating effect of measurement timing was not significant in the relationship between PSNU and other types of anxiety. This could be attributed to the increased uncertainty and stress during the pandemic, leading to heightened levels of general anxiety [ 227 ]. The overuse of social network for information seeking and anxiety alleviation might have paradoxically exacerbated anxiety symptoms, particularly among individuals with broad future-related worries [ 228 ]. While the COVID-19 pandemic altered the relationship between PSNU and GA, its impact on other types of anxiety (such as SA and AA) may not have been significant, likely due to these anxiety types being more influenced by other factors like social skills and attachment styles, which were minimally impacted by the epidemic.
Secondly, the observed variance in the relationship between PSNU and AA across different economic contexts, notably between developing and developed countries, underscores the multifaceted influence of socio-economic, cultural, and technological factors on this dynamic. The amplified connection in developing countries may be attributed to greater socio-economic challenges, distinct cultural norms regarding social support and interaction, rising social network penetration, especially among younger demographics, and technological disparities influencing accessibility and user experience [ 229 , 230 ]. Moreover, the role of social network as a coping mechanism for emotional distress, potentially fostering insecure attachment patterns, is more pronounced in these settings [ 231 ]. These findings highlight the necessity of considering contextual variations in assessing the psychological impacts of social network, advocating for a nuanced understanding of how socio-economic and cultural backgrounds mediate the relationship between PSNU and mental health outcomes [ 232 ]. Additionally, the relationship between PSNU and other types of anxiety (such as GA and SA) presents uniform characteristics across different economic contexts.
Thirdly, the significant moderating effects of measurement tools in the context of PSNU and its correlation with various forms of anxiety, including GA, and AA, are crucial in interpreting the research findings. Specifically, the study reveals that the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale (BSMAS) demonstrates a stronger correlation between PSNU and GA, compared to other tools. Similarly, for AA, the Griffiths’ Problematic Internet Use Scale 2 (GPIUS2) and the Problematic Media Social Media Use Assessment Questionnaire (PMSMUAQ) show a more pronounced correlation with AA than the BSMAS or other instruments, but for SA and FoMO, the PSNU instrument doesn’t significantly moderate the correlation. The PSNU measurement tool typically contains an emotional change dimension. SA and FoMO, due to their specific conditional stimuli triggers and correlation with social networks [ 233 , 234 ], are likely to yield more consistent scores in this dimension, while GA and AA may be less reliable due to their lesser sensitivity to specific conditional stimuli. Consequently, the adjustment effects of PSNU measurements vary across anxiety symptoms. Regarding the measurement tools for anxiety, different scales exhibit varying degrees of sensitivity in detecting the relationship with PSNU. The Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD) and the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales 21 (DASS-21) are more effective in illustrating a strong relationship between GA and PSNU than the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI). In the case of AA, the Experiences in Close Relationships-21 (ECR-21) provides a more substantial correlation than the Relationship Questionnaire (RQ). Furthermore, for FoMO, the Fear of Missing Out Scale - Multi-Social Media Environment (FoMOS-MSME) is more indicative of a strong relationship with PSNU compared to the standard FoMOS or the T-S FoMOS. These findings underscore the importance of the selection of appropriate measurement tools in research. Different tools, due to their unique design, focus, and sensitivity, can reveal varying degrees of correlation between PSNU and anxiety disorders. This highlights the need for careful consideration of tool characteristics and their potential impact on research outcomes. It also cautions against drawing direct comparisons between studies without acknowledging the possible variances introduced by the use of different measurement instruments.
Fourthly, the significant moderating role of gender in the relationship between PSNU and SA, particularly pronounced in samples with a higher proportion of females. Women tend to engage more actively and emotionally with social network, potentially leading to an increased dependency on these platforms when confronting social anxiety [ 235 ]. This intensified use might amplify the association between PSNU and SA. Societal and cultural pressures, especially those related to appearance and social status, are known to disproportionately affect women, possibly exacerbating their experience of social anxiety and prompting a greater reliance on social network for validation and support [ 236 ]. Furthermore, women’s propensity to seek emotional support and express themselves on social network platforms [ 237 ] could strengthen this link, particularly in the context of managing social anxiety. Consequently, the observed gender differences in the relationship between PSNU and SA underscore the importance of considering gender-specific dynamics and cultural influences in psychological research related to social network use. In addition, gender consistency was observed in the association between PSNU and other types of anxiety, indicating no significant gender disparities.
Fifthly, the absence of a significant moderating effect of age on the relationship between PSNU and various forms of anxiety suggests a pervasive influence of social network across different age groups. This finding indicates that the impact of PSNU on anxiety is relatively consistent, irrespective of age, highlighting the universal nature of social network’s psychological implications [ 238 ]. Furthermore, this uniformity suggests that other factors, such as individual psychological traits or socio-cultural influences, might play a more crucial role in the development of anxiety related to social networking usage than age [ 239 ]. The non-significant role of age also points towards a potential generational overlap in social networking usage patterns and their psychological effects, challenging the notion that younger individuals are uniquely susceptible to the adverse effects of social network on mental health [ 240 ]. Therefore, this insight necessitates a broader perspective in understanding the dynamics of social network and mental health, one that transcends age-based assumptions.
Limitations
There are some limitations in this research. First, most of the studies were cross-sectional surveys, resulting in difficulties in inferring causality of variables, longitudinal study data will be needed to evaluate causal interactions in the future. Second, considerable heterogeneity was found in the estimated results, although heterogeneity can be partially explained by differences in study design (e.g., Time of measurement, region, gender, and measurement tools), but this can introduce some uncertainty in the aggregation and generalization of the estimated results. Third, most studies were based on Asian samples, which limits the generality of the results. Fourth, to minimize potential sources of heterogeneity, some less frequently used measurement tools were not included in the classification of measurement tools, which may have some impact on the results of heterogeneity interpretation. Finally, since most of the included studies used self-reported scales, it is possible to get results that deviate from the actual situation to some extent.
This meta-analysis aims to quantifies the correlations between PSNU and four specific types of anxiety symptoms (i.e., generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out). The results revealed a significant moderate positive association between PSNU and each of these anxiety symptoms. Furthermore, Subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis indicated that gender, region, time of measurement, and instrument of measurement significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and specific anxiety symptoms. Specifically, the measurement time and GA measurement tools significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and GA. Gender significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and SA. Region, PSNU measurement tools, and AA measurement tools all significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and AA. The FoMO measurement tool significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and FoMO. Regarding these findings, prevention interventions for PSNU and anxiety symptoms are important.
Data availability
The datasets are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Problematic social networking use
- Generalized anxiety
- Social anxiety
- Attachment anxiety
Fear of miss out
Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale
Facebook Addiction Scale
Facebook Intrusion Questionnaire
Generalized Problematic Internet Use Scale 2
Problematic Mobile Social Media Usage Assessment Questionnaire
Social Network Addiction Tendency Scale
Brief Symptom Inventory
The anxiety subscale of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
The anxiety subscale of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale
State-Trait Anxiety Inventory
Interaction Anxiousness Scale
Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale
Social Anxiety Scale for Social Media Users
Social Anxiety for Adolescents
Social Anxiety Subscale of the Self-Consciousness Scale
Social Interaction Anxiety Scale
Experiences in Close Relationship Scale
Relationship questionnaire
Fear of Missing Out Scale
FoMO Measurement Scale in the Mobile Social Media Environment
Trait-State Fear of missing Out Scale
Rozgonjuk D, Sindermann C, Elhai JD, Montag C. Fear of missing out (FoMO) and social media’s impact on daily-life and productivity at work: do WhatsApp, Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat Use disorders mediate that association? Addict Behav. 2020;110:106487.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Mieczkowski H, Lee AY, Hancock JT. Priming effects of social media use scales on well-being outcomes: the influence of intensity and addiction scales on self-reported depression. Social Media + Soc. 2020;6(4):2056305120961784.
Article Google Scholar
Global digital population as of April. 2023 [ https://www.statista.com/statistics/617136/digital-population-worldwide/ ].
Marengo D, Settanni M, Fabris MA, Longobardi C. Alone, together: fear of missing out mediates the link between peer exclusion in WhatsApp classmate groups and psychological adjustment in early-adolescent teens. J Social Personal Relationships. 2021;38(4):1371–9.
Marengo D, Fabris MA, Longobardi C, Settanni M. Smartphone and social media use contributed to individual tendencies towards social media addiction in Italian adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic. Addict Behav. 2022;126:107204.
Müller SM, Wegmann E, Stolze D, Brand M. Maximizing social outcomes? Social zapping and fear of missing out mediate the effects of maximization and procrastination on problematic social networks use. Comput Hum Behav. 2020;107:106296.
Sun Y, Zhang Y. A review of theories and models applied in studies of social media addiction and implications for future research. Addict Behav. 2021;114:106699.
Boustead R, Flack M. Moderated-mediation analysis of problematic social networking use: the role of anxious attachment orientation, fear of missing out and satisfaction with life. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Hussain Z, Griffiths MD. The associations between problematic social networking Site Use and Sleep Quality, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, Depression, anxiety and stress. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2021;19(3):686–700.
Gori A, Topino E, Griffiths MD. The associations between attachment, self-esteem, fear of missing out, daily time expenditure, and problematic social media use: a path analysis model. Addict Behav. 2023;141:107633.
Marino C, Manari T, Vieno A, Imperato C, Spada MM, Franceschini C, Musetti A. Problematic social networking sites use and online social anxiety: the role of attachment, emotion dysregulation and motives. Addict Behav. 2023;138:107572.
Tobin SJ, Graham S. Feedback sensitivity as a mediator of the relationship between attachment anxiety and problematic Facebook Use. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2020;23(8):562–6.
Brailovskaia J, Rohmann E, Bierhoff H-W, Margraf J. The anxious addictive narcissist: the relationship between grandiose and vulnerable narcissism, anxiety symptoms and Facebook Addiction. PLoS ONE 2020, 15(11).
Kim S-S, Bae S-M. Social Anxiety and Social Networking Service Addiction Proneness in University students: the Mediating effects of Experiential Avoidance and interpersonal problems. Psychiatry Invest. 2022;19(8):702–702.
Zhao J, Ye B, Yu L, Xia F. Effects of Stressors of COVID-19 on Chinese College Students’ Problematic Social Media Use: A Mediated Moderation Model. Front Psychiatry 2022, 13.
Astolfi Cury GS, Takannune DM, Prates Herrerias GS, Rivera-Sequeiros A, de Barros JR, Baima JP, Saad-Hossne R, Sassaki LY. Clinical and Psychological Factors Associated with Addiction and Compensatory Use of Facebook among patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a cross-sectional study. Int J Gen Med. 2022;15:1447–57.
Balta S, Emirtekin E, Kircaburun K, Griffiths MD. Neuroticism, trait fear of missing out, and Phubbing: the mediating role of state fear of missing out and problematic Instagram Use. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2020;18(3):628–39.
Boursier V, Gioia F, Griffiths MD. Do selfie-expectancies and social appearance anxiety predict adolescents’ problematic social media use? Comput Hum Behav. 2020;110:106395.
Worsley JD, McIntyre JC, Bentall RP, Corcoran R. Childhood maltreatment and problematic social media use: the role of attachment and depression. Psychiatry Res. 2018;267:88–93.
de Bérail P, Guillon M, Bungener C. The relations between YouTube addiction, social anxiety and parasocial relationships with YouTubers: a moderated-mediation model based on a cognitive-behavioral framework. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;99:190–204.
Naidu S, Chand A, Pandaram A, Patel A. Problematic internet and social network site use in young adults: the role of emotional intelligence and fear of negative evaluation. Pers Indiv Differ. 2023;200:111915.
Apaolaza V, Hartmann P, D’Souza C, Gilsanz A. Mindfulness, compulsive Mobile Social Media Use, and derived stress: the mediating roles of self-esteem and social anxiety. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2019;22(6):388–96.
Demircioglu ZI, Goncu-Kose A. Antecedents of problematic social media use and cyberbullying among adolescents: attachment, the dark triad and rejection sensitivity. Curr Psychol (New Brunsw NJ) 2022:1–19.
Gao Q, Li Y, Zhu Z, Fu E, Bu X, Peng S, Xiang Y. What links to psychological needs satisfaction and excessive WeChat use? The mediating role of anxiety, depression and WeChat use intensity. BMC Psychol. 2021;9(1):105–105.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Malak MZ, Shuhaiber AH, Al-amer RM, Abuadas MH, Aburoomi RJ. Correlation between psychological factors, academic performance and social media addiction: model-based testing. Behav Inform Technol. 2022;41(8):1583–95.
Song C. The effect of the need to belong on mobile phone social media dependence of middle school students: Chain mediating roles of fear of missing out and maladaptive cognition. Sichuan Normal University; 2022.
Tokunaga RS, Rains SA. A review and meta-analysis examining conceptual and operational definitions of problematic internet use. Hum Commun Res. 2016;42(2):165–99.
Bandura A. Social cognitive theory of mass communication. Media effects. edn.: Routledge; 2009. pp. 110–40.
Valkenburg PM, Peter J, Walther JB. Media effects: theory and research. Ann Rev Psychol. 2016;67:315–38.
Slater MD. Reinforcing spirals: the mutual influence of media selectivity and media effects and their impact on individual behavior and social identity. Communication Theory. 2007;17(3):281–303.
Ahmed E, Vaghefi I. Social media addiction: A systematic review through cognitive-behavior model of pathological use. 2021.
She R, han Mo PK, Li J, Liu X, Jiang H, Chen Y, Ma L, fai Lau JT. The double-edged sword effect of social networking use intensity on problematic social networking use among college students: the role of social skills and social anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;140:107555.
Przybylski AK, Weinstein N. A large-scale test of the goldilocks hypothesis: quantifying the relations between digital-screen use and the mental well-being of adolescents. Psychol Sci. 2017;28(2):204–15.
Ran G, Li J, Zhang Q, Niu X. The association between social anxiety and mobile phone addiction: a three-level meta-analysis. Comput Hum Behav. 2022;130:107198.
Fioravanti G, Casale S, Benucci SB, Prostamo A, Falone A, Ricca V, Rotella F. Fear of missing out and social networking sites use and abuse: a meta-analysis. Comput Hum Behav. 2021;122:106839.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group* P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264–9.
Card NA. Applied meta-analysis for social science research. Guilford; 2015.
Peterson RA, Brown SP. On the use of beta coefficients in meta-analysis. J Appl Psychol. 2005;90(1):175.
Hunter JE, Schmidt FL. Methods of meta-analysis: correcting error and bias in research findings. Sage; 2004.
Zhang Y, Li S, Yu G. The relationship between self-esteem and social anxiety: a meta-analysis with Chinese students. Adv Psychol Sci. 2019;27(6):1005–18.
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JP, Rothstein HR. Introduction to meta-analysis. Wiley; 2021.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629–34.
Light RJ, Pillemer DB. Summing up: the science of reviewing research. Harvard University Press; 1984.
Rosenthal R. Meta-Analytic Procedures for Social Science Research Sage Publications: Beverly Hills, 1984, 148 pp. Educational Researcher 1986;15(8):18–20.
Rothstein HR, Sutton AJ, Borenstein M. Publication bias in meta-analysis. Publication bias meta‐analysis: Prev Assess Adjustments 2005:1–7.
Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot–based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta‐analysis. Biometrics. 2000;56(2):455–63.
Al-Mamun F, Hosen I, Griffiths MD, Mamun MA. Facebook use and its predictive factors among students: evidence from a lower- and middle-income country, Bangladesh. Front Psychiatry 2022, 13.
Schou Andreassen C, Billieux J, Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z, Mazzoni E, Pallesen S. The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol Addict Behaviors: J Soc Psychologists Addict Behav. 2016;30(2):252–62.
Arikan G, Acar IH, Ustundag-Budak AM. A two-generation study: The transmission of attachment and young adults’ depression, anxiety, and social media addiction. Addict Behav 2022, 124.
Arpaci I, Karatas K, Kiran F, Kusci I, Topcu A. Mediating role of positivity in the relationship between state anxiety and problematic social media use during the COVID-19 pandemic. Death Stud. 2022;46(10):2287–97.
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. Facebook Addiction Disorder (FAD) among German students-A longitudinal approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12(12).
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. The relationship between burden caused by coronavirus (Covid-19), addictive social media use, sense of control and anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2021;119:106720–106720.
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. Addictive social media use during Covid-19 outbreak: validation of the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale (BSMAS) and investigation of protective factors in nine countries. Curr Psychol (New Brunsw NJ) 2022:1–19.
Brailovskaia J, Krasavtseva Y, Kochetkov Y, Tour P, Margraf J. Social media use, mental health, and suicide-related outcomes in Russian women: a cross-sectional comparison between two age groups. Women’s Health (London England). 2022;18:17455057221141292–17455057221141292.
PubMed Google Scholar
Chang C-W, Huang R-Y, Strong C, Lin Y-C, Tsai M-C, Chen IH, Lin C-Y, Pakpour AHH, Griffiths MDD. Reciprocal relationships between Problematic Social Media Use, problematic gaming, and psychological distress among University students: a 9-Month Longitudinal Study. Front Public Health 2022, 10.
Charzynska E, Sussman S, Atroszko PA. Profiles of potential behavioral addictions’ severity and their associations with gender, personality, and well-being: A person-centered approach. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Chen C-Y, Chen IH, Pakpour AH, Lin C-Y, Griffiths MD. Internet-related behaviors and psychological distress among Schoolchildren during the COVID-19 School Hiatus. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2021;24(10):654–63.
Da Veiga GF, Sotero L, Pontes HM, Cunha D, Portugal A, Relvas AP. Emerging adults and Facebook Use: the validation of the Bergen Facebook Addiction Scale (BFAS). Int J Mental Health Addict. 2019;17(2):279–94.
Dadiotis A, Bacopoulou F, Kokka I, Vlachakis D, Chrousos GP, Darviri C, Roussos P. Validation of the Greek version of the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale in Undergraduate Students. EMBnetjournal 2021, 26.
Fekih-Romdhane F, Jahrami H, Away R, Trabelsi K, Pandi-Perumal SR, Seeman MV, Hallit S, Cheour M. The relationship between technology addictions and schizotypal traits: mediating roles of depression, anxiety, and stress. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23(1).
Flynn S, Noone C, Sarma KM. An exploration of the link between adult attachment and problematic Facebook use. BMC Psychol. 2018;6(1):34–34.
Fung XCC, Siu AMH, Potenza MN, O’Brien KS, Latner JD, Chen C-Y, Chen IH, Lin C-Y. Problematic use of internet-related activities and Perceived Weight Stigma in Schoolchildren: a longitudinal study across different epidemic periods of COVID-19 in China. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Gonzalez-Nuevo C, Cuesta M, Muniz J, Postigo A, Menendez-Aller A, Kuss DJ. Problematic Use of Social Networks during the First Lockdown: User Profiles and the Protective Effect of Resilience and Optimism. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, 11(24).
Hou X-L, Wang H-Z, Hu T-Q, Gentile DA, Gaskin J, Wang J-L. The relationship between perceived stress and problematic social networking site use among Chinese college students. J Behav Addictions. 2019;8(2):306–17.
Hussain Z, Wegmann E. Problematic social networking site use and associations with anxiety, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and resilience. Computers Hum Behav Rep. 2021;4:100125.
Imani V, Ahorsu DK, Taghizadeh N, Parsapour Z, Nejati B, Chen H-P, Pakpour AH. The mediating roles of anxiety, Depression, Sleepiness, Insomnia, and Sleep Quality in the Association between Problematic Social Media Use and Quality of Life among patients with Cancer. Healthcare 2022, 10(9).
Islam MS, Sujan MSH, Tasnim R, Mohona RA, Ferdous MZ, Kamruzzaman S, Toma TY, Sakib MN, Pinky KN, Islam MR et al. Problematic smartphone and Social Media Use among Bangladeshi College and University students amid COVID-19: the role of Psychological Well-Being and Pandemic related factors. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Islam MS, Jahan I, Dewan MAA, Pontes HM, Koly KN, Sikder MT, Rahman M. Psychometric properties of three online-related addictive behavior instruments among Bangladeshi school-going adolescents. PLoS ONE 2022, 17(12).
Jahan I, Hosen I, Al Mamun F, Kaggwa MM, Griffiths MD, Mamun MA. How has the COVID-19 pandemic impacted Internet Use behaviors and facilitated problematic internet use? A Bangladeshi study. Psychol Res Behav Manage. 2021;14:1127–38.
Jiang Y. Problematic social media usage and anxiety among University Students during the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating role of Psychological Capital and the moderating role of academic burnout. Front Psychol. 2021;12:612007–612007.
Kim M-R, Oh J-W, Huh B-Y. Analysis of factors related to Social Network Service Addiction among Korean High School Students. J Addictions Nurs. 2020;31(3):203–12.
Koc M, Gulyagci S. Facebook addiction among Turkish college students: the role of psychological health, demographic, and usage characteristics. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2013;16(4):279–84.
Lin C-Y, Namdar P, Griffiths MD, Pakpour AH. Mediated roles of generalized trust and perceived social support in the effects of problematic social media use on mental health: a cross-sectional study. Health Expect. 2021;24(1):165–73.
Lin C-Y, Imani V, Griffiths MD, Brostrom A, Nygardh A, Demetrovics Z, Pakpour AH. Temporal associations between morningness/eveningness, problematic social media use, psychological distress and daytime sleepiness: mediated roles of sleep quality and insomnia among young adults. J Sleep Res 2021, 30(1).
Lozano Blasco R, Latorre Cosculluela C, Quilez Robres A. Social Network Addiction and its impact on anxiety level among University students. Sustainability 2020, 12(13).
Marino C, Musetti A, Vieno A, Manari T, Franceschini C. Is psychological distress the key factor in the association between problematic social networking sites and poor sleep quality? Addict Behav 2022, 133.
Meshi D, Ellithorpe ME. Problematic social media use and social support received in real-life versus on social media: associations with depression, anxiety and social isolation. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Mitropoulou EM, Karagianni M, Thomadakis C. Social Media Addiction, Self-Compassion, and Psychological Well-Being: a structural equation Model. Alpha Psychiatry. 2022;23(6):298–304.
Ozimek P, Brailovskaia J, Bierhoff H-W. Active and passive behavior in social media: validating the Social Media Activity Questionnaire (SMAQ). Telematics Inf Rep. 2023;10:100048.
Phillips WJ, Wisniewski AT. Self-compassion moderates the predictive effects of social media use profiles on depression and anxiety. Computers Hum Behav Rep. 2021;4:100128.
Reer F, Festl R, Quandt T. Investigating problematic social media and game use in a nationally representative sample of adolescents and younger adults. Behav Inform Technol. 2021;40(8):776–89.
Satici B, Kayis AR, Griffiths MD. Exploring the Association between Social Media Addiction and relationship satisfaction: psychological distress as a Mediator. Int J Mental Health Addict 2021.
Sediri S, Zgueb Y, Ouanes S, Ouali U, Bourgou S, Jomli R, Nacef F. Women’s mental health: acute impact of COVID-19 pandemic on domestic violence. Archives Womens Mental Health. 2020;23(6):749–56.
Shabahang R, Shim H, Aruguete MS, Zsila A. Oversharing on Social Media: anxiety, Attention-Seeking, and Social Media Addiction Predict the breadth and depth of sharing. Psychol Rep 2022:332941221122861–332941221122861.
Sotero L, Ferreira Da Veiga G, Carreira D, Portugal A, Relvas AP. Facebook Addiction and emerging adults: the influence of sociodemographic variables, family communication, and differentiation of self. Escritos De Psicología - Psychol Writings. 2019;12(2):81–92.
Stockdale LA, Coyne SM. Bored and online: reasons for using social media, problematic social networking site use, and behavioral outcomes across the transition from adolescence to emerging adulthood. J Adolesc. 2020;79:173–83.
Wang Z, Yang H, Elhai JD. Are there gender differences in comorbidity symptoms networks of problematic social media use, anxiety and depression symptoms? Evidence from network analysis. Pers Indiv Differ. 2022;195:111705.
White-Gosselin C-E, Poulin F. Associations Between Young Adults’ Social Media Addiction, Relationship Quality With Parents, and Internalizing Problems: A Path Analysis Model. 2022.
Wong HY, Mo HY, Potenza MN, Chan MNM, Lau WM, Chui TK, Pakpour AH, Lin C-Y. Relationships between Severity of Internet Gaming Disorder, Severity of Problematic Social Media Use, Sleep Quality and Psychological Distress. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17(6).
Yam C-W, Pakpour AH, Griffiths MD, Yau W-Y, Lo C-LM, Ng JMT, Lin C-Y, Leung H. Psychometric testing of three Chinese online-related addictive Behavior instruments among Hong Kong University students. Psychiatr Q. 2019;90(1):117–28.
Yuan Y, Zhong Y. A survey on the use of social networks and mental health of college students during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Campus Life Mental Health\. 2021;19(3):209–12.
Google Scholar
Yurdagul C, Kircaburun K, Emirtekin E, Wang P, Griffiths MD. Psychopathological consequences related to problematic Instagram Use among adolescents: the mediating role of body image dissatisfaction and moderating role of gender. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2021;19(5):1385–97.
Zhang W, Pu J, He R, Yu M, Xu L, He X, Chen Z, Gan Z, Liu K, Tan Y, et al. Demographic characteristics, family environment and psychosocial factors affecting internet addiction in Chinese adolescents. J Affect Disord. 2022;315:130–8.
Zhang L, Wu Y, Jin T, Jia Y. Revision and validation of the Chinese short version of social media disorder. Mod Prev Med. 2021;48(8):1350–3.
Zhang X, Fan L. The influence of anxiety on colleges’ life satisfaction. Chin J Health Educ. 2021;37(5):469–72.
Zhao M, Wang H, Dong Y, Niu Y, Fang Y. The relationship between self-esteem and wechat addiction among undergraduate students: the multiple mediating roles of state anxiety and online interpersonal trust. J Psychol Sci. 2021;44(1):104–10.
Zhao J, Zhou Z, Sun B, Zhang X, Zhang L, Fu S. Attentional Bias is Associated with negative emotions in problematic users of Social Media as measured by a dot-probe Task. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(24).
Atroszko PA, Balcerowska JM, Bereznowski P, Biernatowska A, Pallesen S, Schou Andreassen C. Facebook addiction among Polish undergraduate students: validity of measurement and relationship with personality and well-being. Comput Hum Behav. 2018;85:329–38.
Chen Y, Li R, Zhang P, Liu X. The moderating role of state attachment anxiety and avoidance between social anxiety and social networking sites Addiction. Psychol Rep. 2020;123(3):633–47.
Chen B, Zheng X, Sun X. The relationship between problematic social media use and online social anxiety: the roles of social media cognitive overload and dispositional mindfulness. Psychol Dev Educ. 2023;39(5):743–51.
Chentsova VO, Bravo AJ, Mezquita L, Pilatti A, Hogarth L, Cross-Cultural AS. Internalizing symptoms, rumination, and problematic social networking site use: a cross national examination among young adults in seven countries. Addict Behav 2023, 136.
Chu X, Ji S, Wang X, Yu J, Chen Y, Lei L. Peer phubbing and social networking site addiction: the mediating role of social anxiety and the moderating role of Family Financial Difficulty. Front Psychol. 2021;12:670065–670065.
Dempsey AE, O’Brien KD, Tiamiyu MF, Elhai JD. Fear of missing out (FoMO) and rumination mediate relations between social anxiety and problematic Facebook use. Addict Behav Rep. 2019;9:100150–100150.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yildiz Durak H, Seferoglu SS. Modeling of variables related to problematic social media usage: Social desirability tendency example. Scand J Psychol. 2019;60(3):277–88.
Ekinci N, Akat M. The relationship between anxious-ambivalent attachment and social appearance anxiety in adolescents: the serial mediation of positive Youth Development and Instagram Addiction. Psychol Rep 2023:332941231159600–332941231159600.
Foroughi B, Griffiths MD, Iranmanesh M, Salamzadeh Y. Associations between Instagram Addiction, academic performance, social anxiety, Depression, and life satisfaction among University students. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2022;20(4):2221–42.
He L. Influence mechanism and intervention suggestions on addiction of social network addiction. Gannan Normal University; 2021.
Hu Y. The influencing mechanism of type D personality on problematic social networking sites use among adolescents and intervention research. Central China Normal University; 2020.
Jia L. A study of the relationship between neuroticism, perceived social support, social anxiety and problematic social network use in high school students. Harbin Normal University; 2022.
Lee-Won RJ, Herzog L, Park SG. Hooked on Facebook: the role of social anxiety and need for Social Assurance in Problematic Use of Facebook. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2015;18(10):567–74.
Li H. Social anxiety and internet interpersonal addiction in adolescents and countermeasures. Central China Normal University; 2022.
Lin W-S, Chen H-R, Lee TS-H, Feng JY. Role of social anxiety on high engagement and addictive behavior in the context of social networking sites. Data Technol Appl. 2019;53(2):156–70.
Liu Y. The influence of family function on social media addiction in adolescents: the chain mediation effect of social anxiety and resilience. Hunan Normal University; 2021.
Lyvers M, Salviani A, Costan S, Thorberg FA. Alexithymia, narcissism and social anxiety in relation to social media and internet addiction symptoms. Int J Psychology: J Int De Psychologie. 2022;57(5):606–12.
Majid A, Yasir M, Javed A, Ali P. From envy to social anxiety and rumination: how social media site addiction triggers task distraction amongst nurses. J Nurs Adm Manag. 2020;28(3):504–13.
Mou Q, Zhuang J, Gao Y, Zhong Y, Lu Q, Gao F, Zhao M. The relationship between social anxiety and academic engagement among Chinese college students: a serial mediation model. J Affect Disord. 2022;311:247–53.
Ruggieri S, Santoro G, Pace U, Passanisi A, Schimmenti A. Problematic Facebook use and anxiety concerning use of social media in mothers and their offspring: an actor-partner interdependence model. Addict Behav Rep. 2020;11:100256–100256.
Ruiz MJ, Saez G, Villanueva-Moya L, Exposito F. Adolescent sexting: the role of body shame, Social Physique anxiety, and social networking site addiction. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2021;24(12):799–805.
She R, Kit Han Mo P, Li J, Liu X, Jiang H, Chen Y, Ma L, Tak Fai Lau J. The double-edged sword effect of social networking use intensity on problematic social networking use among college students: the role of social skills and social anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;140:107555.
Stănculescu E. The Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale Validity in a Romanian sample using item response theory and network analysis. Int J Mental Health Addict 2022.
Teng X, Lei H, Li J, Wen Z. The influence of social anxiety on social network site addiction of college students: the moderator of intentional self-regulation. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(3):514–7.
Tong W. Influence of boredom on the problematic mobile social networks usage in adolescents: multiple chain mediator. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(5):932–6.
Tu W, Jiang H, Liu Q. Peer victimization and adolescent Mobile Social Addiction: mediation of social anxiety and gender differences. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(17).
Wang S. The influence of college students self-esteem, social anxiety and fear of missing out on the problematic mobile social networks usage. Huaibei Normal University; 2021.
Wang X. The impact of peer relationship and social anxiety on secondary vocational school students’ problematic social network use and intervention study. Huaibei Normal University; 2022.
Wegmann E, Stodt B, Brand M. Addictive use of social networking sites can be explained by the interaction of internet use expectancies, internet literacy, and psychopathological symptoms. J Behav Addictions. 2015;4(3):155–62.
Yang W. The relationship between the type of internet addiction and the personality traits in college students. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2004.
Yang Z. The relationship between social variables and social networking usage among shanghai working population. East China Normal University; 2013.
Zhang C. The relationship between perceived social support and problematic social network use among junior high school students: a chain mediation model and an intervention study. Hebei University; 2022.
Zhang J, Chang F, Huang D, Wen X. The relationship between neuroticism and the problematic mobile social networks use in adolescents: the mediating role of anxiety and positive self-presentation. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(3):598–602.
Zhang Z. College students’ loneliness and problematic social networking use: Chain mediation of social self-efficacy and social anxiety. Shanghai Normal University; 2019.
Zhu B. Discussion on mechanism of social networking addiction——Social anxiety, craving and excitability. Liaoning Normal University; 2017.
Blackwell D, Leaman C, Tramposch R, Osborne C, Liss M. Extraversion, neuroticism, attachment style and fear of missing out as predictors of social media use and addiction. Pers Indiv Differ. 2017;116:69–72.
Chen A. From attachment to addiction: the mediating role of need satisfaction on social networking sites. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;98:80–92.
Chen Y, Zhong S, Dai L, Deng Y, Liu X. Attachment anxiety and social networking sites addiction in college students: a moderated mediating model. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(3):497–500.
Li J. The relations among problematic social networks usage behavior, Childhood Trauma and adult attachment in University students. Hunan Agricultural University; 2020.
Liu C, Ma J-L. Adult attachment orientations and social networking site addiction: the Mediating effects of Online Social Support and the fear of missing out. Front Psychol. 2019;10:2629–2629.
Mo S, Huang W, Xu Y, Tang Z, Nie G. The impact of medical students’ attachment anxiety on the use of problematic social networking sites during the epidemic. Psychol Monthly. 2022;17(9):1–4.
Teng X. The effect of attachment anxiety on problematic mobile social network use: the role of loneliness and self-control. Harbin Normal University; 2021.
Worsley JD, Mansfield R, Corcoran R. Attachment anxiety and problematic social media use: the Mediating Role of Well-Being. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2018;21(9):563–8.
Wu Z. The effect of adult attachment on problematic social network use: the chain mediating effect of loneliness and fear of missing out. Jilin University; 2022.
Xia N. The impact of attachment anxiety on adolescent problem social networking site use: a moderated mediation model. Shihezi University; 2022.
Young L, Kolubinski DC, Frings D. Attachment style moderates the relationship between social media use and user mental health and wellbeing. Heliyon 2020, 6(6).
Bakioglu F, Deniz M, Griffiths MD, Pakpour AH. Adaptation and validation of the online-fear of missing out inventory into Turkish and the association with social media addiction, smartphone addiction, and life satisfaction. BMC Psychol. 2022;10(1):154–154.
Bendayan R, Blanca MJ. Spanish version of the Facebook Intrusion Questionnaire (FIQ-S). Psicothema. 2019;31(2):204–9.
Blachnio A, Przepiorka A. Facebook intrusion, fear of missing out, narcissism, and life satisfaction: a cross-sectional study. Psychiatry Res. 2018;259:514–9.
Casale S, Rugai L, Fioravanti G. Exploring the role of positive metacognitions in explaining the association between the fear of missing out and social media addiction. Addict Behav. 2018;85:83–7.
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Wang K. Effect of fear of’ missing out on college students negative social adaptation: Chain¬ - mediating effect of rumination and problematic social media use. China J Health Psychol. 2022;30(4):581–6.
Cheng S, Zhang X, Han Y. Relationship between fear of missing out and phubbing on college students: the chain intermediary effect of intolerance of uncertainty and problematic social media use. China J Health Psychol. 2022;30(9):1296–300.
Cui Q, Wang J, Zhang J, Li W, Li Q. The relationship between loneliness and negative emotion in college students: the chain-mediating role of fear of missing out and social network sites addiction. J Jining Med Univ. 2022;45(4):248–51.
Ding Q, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Zhou Z. The more gossip, the more addicted: the relationship between interpersonal curiosity and social networking sites addiction tendencies in college students. Psychol Dev Educ. 2022;38(1):118–25.
Fabris MA, Marengo D, Longobardi C, Settanni M. Investigating the links between fear of missing out, social media addiction, and emotional symptoms in adolescence: the role of stress associated with neglect and negative reactions on social media. Addict Behav. 2020;106:106364.
Fang J, Wang X, Wen Z, Zhou J. Fear of missing out and problematic social media use as mediators between emotional support from social media and phubbing behavior. Addict Behav. 2020;107:106430.
Gao Z. The study on the relationship and intervention among fear of missing out self-differentiation and problematic social media use of college students. Yunnan Normal University; 2021.
Gioia F, Fioravanti G, Casale S, Boursier V. The Effects of the Fear of Missing Out on People’s Social Networking Sites Use During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Mediating Role of Online Relational Closeness and Individuals’ Online Communication Attitude. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Gu X. Study on the Inhibitory Effect of Mindfulness Training on Social Media Addiction of College Students. Wuhan University; 2020.
Gugushvili N, Taht K, Schruff-Lim EM, Ruiter RA, Verduyn P. The Association between Neuroticism and problematic social networking sites Use: the role of fear of missing out and Self-Control. Psychol Rep 2022:332941221142003–332941221142003.
Hou J. The study on FoMO and content social media addiction among young people. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Hu R, Zhang B, Yang Y, Mao H, Peng Y, Xiong S. Relationship between college students’ fear of missing and wechat addiction: a cross-lagged analysis. J Bio-education. 2022;10(5):369–73.
Hu G. The relationship between basic psychological needs satisfaction and the use of problematic social networks by college students: a moderated mediation model and online intervention studies. Jiangxi Normal University; 2020.
Jiang Y, Jin T. The relationship between adolescents’ narcissistic personality and their use of problematic mobile social networks: the effects of fear of missing out and positive self-presentation. Chin J Special Educ 2018(11):64–70.
Li J. The effect of positive self-presentation on social networking sites on problematic use of social networking sites: a moderated mediation model. Henan University; 2020.
Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang X. The impact of Freshmen Social Exclusion on problematic Social Network Use: a Moderated Mediation Model. J Heilongjiang Vocat Inst Ecol Eng. 2023;36(1):118–22.
Li M. The relationship between fear of missing out and social media addiction among middle school students——The moderating role of self-control. Kashi University; 2022.
Li R, Dong X, Wang M, Wang R. A study on the relationship between fear of missing out and social network addiction. New Educ Era 2021(52):122–3.
Li Y. Fear of missing out or social avoidance? The influence of peer exclusion on problematic social media use among adolescents in Guangdong Province and Macao. Guangzhou University; 2020.
Ma J, Liu C. The effect of fear of missing out on social networking sites addiction among college students: the mediating roles of social networking site integration use and social support. Psychol Dev Educ. 2019;35(5):605–14.
Mao H. A follow-up study on the mechanism of the influence of university students’ Qi deficiency quality on WeChat addiction. Hunan University of Chinese Medicine; 2021.
Mao Y. The effect of dual filial piety to the college students ’internet social dependence: the mediation of maladaptive cognition and fear of missing out. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Moore K, Craciun G. Fear of missing out and personality as predictors of Social networking sites usage: the Instagram Case. Psychol Rep. 2021;124(4):1761–87.
Niu J. The relationship of college students’ basic psychological needs and social media dependence: the mediating role of fear of missing out. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Pi L, Li X. Research on the relationship between loneliness and problematic mobile social media usage: evidence from variable-oriented and person-oriented analyses. China J Health Psychol. 2023;31(6):936–42.
Pontes HM, Taylor M, Stavropoulos V. Beyond Facebook Addiction: the role of cognitive-related factors and Psychiatric Distress in Social networking site addiction. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2018;21(4):240–7.
Quaglieri A, Biondi S, Roma P, Varchetta M, Fraschetti A, Burrai J, Lausi G, Marti-Vilar M, Gonzalez-Sala F, Di Domenico A et al. From Emotional (Dys) Regulation to Internet Addiction: A Mediation Model of Problematic Social Media Use among Italian Young Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, 11(1).
Servidio R, Koronczai B, Griffiths MD, Demetrovics Z. Problematic smartphone Use and Problematic Social Media Use: the predictive role of Self-Construal and the Mediating Effect of Fear Missing Out. Front Public Health 2022, 10.
Sheldon P, Antony MG, Sykes B. Predictors of problematic social media use: personality and life-position indicators. Psychol Rep. 2021;124(3):1110–33.
Sun C, Li Y, Kwok SYCL, Mu W. The relationship between intolerance of uncertainty and problematic Social Media Use during the COVID-19 pandemic: a serial mediation model. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(22).
Tang Z. The relationship between loneliness and problematic social networks use among college students: the mediation of fear of missing out and the moderation of social support. Jilin University; 2022.
Tomczyk Ł, Selmanagic-Lizde E. Fear of missing out (FOMO) among youth in Bosnia and Herzegovina — Scale and selected mechanisms. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2018;88:541–9.
Unal-Aydin P, Ozkan Y, Ozturk M, Aydin O, Spada MM. The role of metacognitions in cyberbullying and cybervictimization among adolescents diagnosed with major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders: a case-control study. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy; 2023.
Uram P, Skalski S. Still logged in? The Link between Facebook Addiction, FoMO, Self-Esteem, Life satisfaction and loneliness in social media users. Psychol Rep. 2022;125(1):218–31.
Varchetta M, Fraschetti A, Mari E, Giannini AM. Social Media Addiction, fear of missing out (FoMO) and online vulnerability in university students. Revista Digit De Investigación en Docencia Universitaria. 2020;14(1):e1187.
Wang H. Study on the relationship and intervention between fear of missing and social network addiction in college students. Yunnan Normal University; 2021.
Wang M, Yin Z, Xu Q, Niu G. The relationship between shyness and adolescents’ social network sites addiction: Moderated mediation model. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2020;28(5):906–9.
Wegmann E, Oberst U, Stodt B, Brand M. Online-specific fear of missing out and internet-use expectancies contribute to symptoms of internet-communication disorder. Addict Behav Rep. 2017;5:33–42.
Wegmann E, Brandtner A, Brand M. Perceived strain due to COVID-19-Related restrictions mediates the Effect of Social needs and fear of missing out on the risk of a problematic use of Social Networks. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Wei Q. Negative emotions and problematic social network sites usage: the mediating role of fear of missing out and the moderating role of gender. Central China Normal University; 2018.
Xiong L. Effect of social network site use on college students’ social network site addiction: A moderated mediation model and attention bias training intervention study. Jiangxi Normal University; 2022.
Yan H. The influence of college students’ basic psychological needs on social network addiction: The intermediary role of fear of missing out. Wuhan University; 2020.
Yan H. The status and factors associated with social media addiction among young people——Evidence from WeChat. Chongqing University; 2021.
Yang L. Research on the relationship of fear of missing out, excessive use of Wechat and life satisfaction. Beijing Forestry University; 2020.
Yin Y, Cai X, Ouyang M, Li S, Li X, Wang P. FoMO and the brain: loneliness and problematic social networking site use mediate the association between the topology of the resting-state EEG brain network and fear of missing out. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;141:107624.
Zhang C. The parental rejection and problematic social network sites with adolescents: the chain mediating effect of basic psychological needs and fear of missing out. Central China Normal University; 2022.
Zhang J. The influence of basic psychological needs on problematic mobile social networks usage of adolescent: a moderated mediation model. Liaocheng University; 2020.
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Jin J, Yu G. The relationship between fear of missing out and social media addiction: a cross-lagged analysis. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(5):1082–5.
Zhang Y, Jiang W, Ding Q, Hong M. Social comparison orientation and social network sites addiction in college students: the mediating role of fear of missing out. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(5):928–31.
Zhou J, Fang J. Social network sites support and addiction among college students: a moderated mediation model. Psychology: Techniques Appl. 2021;9(5):293–9.
Andreassen CS, Torsheim T, Brunborg GS, Pallesen S. Development of a Facebook addiction scale. Psychol Rep. 2012;110(2):501–17.
Andreassen CS, Billieux J, Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z, Mazzoni E, Pallesen S. The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol Addict Behav. 2016;30(2):252.
Elphinston RA, Noller P. Time to face it! Facebook intrusion and the implications for romantic jealousy and relationship satisfaction. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2011;14(11):631–5.
Caplan SE. Theory and measurement of generalized problematic internet use: a two-step approach. Comput Hum Behav. 2010;26(5):1089–97.
Jiang Y. Development of problematic mobile social media usage assessment questionnaire for adolescents. Psychology: Techniques Appl. 2018;6(10):613–21.
Wang X. College students’ social network addiction tendency: Questionnaire construction and correlation research. Master’s thesis Southwest University; 2016.
Derogatis LR. Brief symptom inventory 18. Johns Hopkins University Baltimore; 2001.
Lovibond PF, Lovibond SH. The structure of negative emotional states: comparison of the Depression anxiety stress scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression and anxiety inventories. Behav Res Ther. 1995;33(3):335–43.
Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, Löwe B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(10):1092–7.
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 1983;67(6):361–70.
Spielberger CD, Gonzalez-Reigosa F, Martinez-Urrutia A, Natalicio LF, Natalicio DS. The state-trait anxiety inventory. Revista Interamericana de Psicologia/Interamerican Journal of Psychology 1971, 5(3&4).
Marteau TM, Bekker H. The development of a six-item short‐form of the state scale of the Spielberger State—trait anxiety inventory (STAI). Br J Clin Psychol. 1992;31(3):301–6.
Leary MR. Social anxiousness: the construct and its measurement. J Pers Assess. 1983;47(1):66–75.
Liebowitz MR. Social phobia. Modern problems of pharmacopsychiatry 1987.
Alkis Y, Kadirhan Z, Sat M. Development and validation of social anxiety scale for social media users. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;72:296–303.
La Greca AM, Stone WL. Social anxiety scale for children-revised: factor structure and concurrent validity. J Clin Child Psychol. 1993;22(1):17–27.
Fenigstein A, Scheier MF, Buss AH. Public and private self-consciousness: Assessment and theory. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1975;43(4):522.
Mattick RP, Clarke JC. Development and validation of measures of social phobia scrutiny fear and social interaction anxiety. Behav Res Ther. 1998;36(4):455–70.
Peters L, Sunderland M, Andrews G, Rapee RM, Mattick RP. Development of a short form Social Interaction anxiety (SIAS) and Social Phobia Scale (SPS) using nonparametric item response theory: the SIAS-6 and the SPS-6. Psychol Assess. 2012;24(1):66.
Brennan KA, Clark CL, Shaver PR. Self-report measurement of adult attachment: an integrative overview. Attachment Theory Close Relationships. 1998;46:76.
Wei M, Russell DW, Mallinckrodt B, Vogel DL. The experiences in Close Relationship Scale (ECR)-short form: reliability, validity, and factor structure. J Pers Assess. 2007;88(2):187–204.
Bartholomew K, Horowitz LM. Attachment styles among young adults: a test of a four-category model. J Personal Soc Psychol. 1991;61(2):226.
Przybylski AK, Murayama K, DeHaan CR, Gladwell V. Motivational, emotional, and behavioral correlates of fear of missing out. Comput Hum Behav. 2013;29(4):1841–8.
Xiaokang S, Yuxiang Z, Xuanhui Z. Developing a fear of missing out (FoMO) measurement scale in the mobile social media environment. Libr Inform Service. 2017;61(11):96.
Bown M, Sutton A. Quality control in systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2010;40(5):669–77.
Turel O, Qahri-Saremi H. Problematic use of social networking sites: antecedents and consequence from a dual-system theory perspective. J Manage Inform Syst. 2016;33(4):1087–116.
Chou H-TG, Edge N. They are happier and having better lives than I am: the impact of using Facebook on perceptions of others’ lives. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2012;15(2):117–21.
Beyens I, Frison E, Eggermont S. I don’t want to miss a thing: adolescents’ fear of missing out and its relationship to adolescents’ social needs, Facebook use, and Facebook related stress. Comput Hum Behav. 2016;64:1–8.
Di Blasi M, Gullo S, Mancinelli E, Freda MF, Esposito G, Gelo OCG, Lagetto G, Giordano C, Mazzeschi C, Pazzagli C. Psychological distress associated with the COVID-19 lockdown: a two-wave network analysis. J Affect Disord. 2021;284:18–26.
Yang X, Hu H, Zhao C, Xu H, Tu X, Zhang G. A longitudinal study of changes in smart phone addiction and depressive symptoms and potential risk factors among Chinese college students. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):252.
Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD. Social networking sites and addiction: ten lessons learned. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017;14(3):311.
Ryan T, Chester A, Reece J, Xenos S. The uses and abuses of Facebook: a review of Facebook addiction. J Behav Addictions. 2014;3(3):133–48.
Elhai JD, Levine JC, Dvorak RD, Hall BJ. Non-social features of smartphone use are most related to depression, anxiety and problematic smartphone use. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;69:75–82.
Jackson LA, Wang J-L. Cultural differences in social networking site use: a comparative study of China and the United States. Comput Hum Behav. 2013;29(3):910–21.
Ahrens LM, Mühlberger A, Pauli P, Wieser MJ. Impaired visuocortical discrimination learning of socially conditioned stimuli in social anxiety. Soc Cognit Affect Neurosci. 2014;10(7):929–37.
Elhai JD, Yang H, Montag C. Fear of missing out (FOMO): overview, theoretical underpinnings, and literature review on relations with severity of negative affectivity and problematic technology use. Brazilian J Psychiatry. 2020;43:203–9.
Barker V. Older adolescents’ motivations for social network site use: the influence of gender, group identity, and collective self-esteem. Cyberpsychology Behav. 2009;12(2):209–13.
Krasnova H, Veltri NF, Eling N, Buxmann P. Why men and women continue to use social networking sites: the role of gender differences. J Strateg Inf Syst. 2017;26(4):261–84.
Palmer J. The role of gender on social network websites. Stylus Knights Write Showc 2012:35–46.
Vannucci A, Flannery KM, Ohannessian CM. Social media use and anxiety in emerging adults. J Affect Disord. 2017;207:163–6.
Primack BA, Shensa A, Sidani JE, Whaite EO, yi Lin L, Rosen D, Colditz JB, Radovic A, Miller E. Social media use and perceived social isolation among young adults in the US. Am J Prev Med. 2017;53(1):1–8.
Twenge JM, Campbell WK. Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: evidence from a population-based study. Prev Med Rep. 2018;12:271–83.
Download references
This research was supported by the Social Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 23BSH135).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Mental Health, Wenzhou Medical University, 325035, Wenzhou, China
Mingxuan Du, Haiyan Hu, Ningning Ding, Jiankang He, Wenwen Tian, Wenqian Zhao, Xiujian Lin, Gaoyang Liu, Wendan Chen, ShuangLiu Wang, Dongwu Xu & Guohua Zhang
School of Education, Renmin University of China, 100872, Beijing, China
Chengjia Zhao
School of Media and Communication, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Dongchuan Road 800, 200240, Shanghai, China
Pengcheng Wang
Department of Neurosis and Psychosomatic Diseases, Huzhou Third Municipal Hospital, 313002, Huzhou, China
Xinhua Shen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
GZ, XS, XL and MD prepared the study design, writing - review and editing. MD and CZ wrote the main manuscript text. MD and HH analyzed data and edited the draft. ND, JH, WT, WZ, GL, WC, SW, PW and DX conducted resources and data curation. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Xinhua Shen or Guohua Zhang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Du, M., Zhao, C., Hu, H. et al. Association between problematic social networking use and anxiety symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychol 12 , 263 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01705-w
Download citation
Received : 25 January 2024
Accepted : 03 April 2024
Published : 12 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01705-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Fear of missing out
- Meta-analysis
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
It may not be called a Literature Review but gives you an idea of how one is created in miniature. Sample Literature Reviews as part of a articles or Theses Building Customer Loyalty: A Customer Experience Based Approach in a Tourism Context Detailed one for Masters see chapters two and three
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
Okay - with the why out the way, let's move on to the how. As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter.
Organizing Your Review. Your lit review should not be a summary and evaluation of each article, one after the other. Your sources must be integrated together to create a narrative on your topic. Consider the following ways to organize your review: By themes, variables, issues. By varying perspectives regarding a topic of controversy.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
When writing a literature review it is important to start with a brief introduction, followed by the text broken up into subsections and conclude with a summary to bring everything together. A summary table including title, author, publication date and key findings is a useful feature to present in your review (see Table 1 for an example).
The first example is an early draft of the literature review. The second example is a revised version. Notice how the student's revision makes better use of synthesis at both the paragraph and sentence level. The revised example is also more accurate in its portrayal of the literature. Unrevised Paragraph: Much of the literature agrees that ...
Basic Literature Review Source Template from Walden University Writing Center to help record the main findings and concepts from different articles. Sample Literature Review Grids. This spreadsheet contains multiple tabs with different grid templates. Download or create your own copy to begin recording notes.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
Types of reviews and examples. Definition: "A term used to describe a conventional overview of the literature, particularly when contrasted with a systematic review (Booth et al., 2012, p. 265). Characteristics: Example: Mitchell, L. E., & Zajchowski, C. A. (2022). The history of air quality in Utah: A narrative review.
Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews. Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts; Have an exemplary literature review? Get Help!
15 Literature Review Examples. By Chris Drew (PhD) / December 6, 2023. Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal. They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed.
Step 1 Organize your sources. Step 2 Outline your structure. Step 3 Write paragraphs with topic sentences. Step 4 Revise, edit and proofread. When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you've read - you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own ...
2. MOTIVATE YOUR RESEARCH in addition to providing useful information about your topic, your literature review must tell a story about how your project relates to existing literature. popular literature review narratives include: ¡ plugging a gap / filling a hole within an incomplete literature ¡ building a bridge between two "siloed" literatures, putting literatures "in conversation"
We start off by discussing the five core sections of a literature review chapter by unpacking our free literature review template. This includes: The literature review opening/ introduction section. The theoretical framework (or foundation of theory) The empirical research. The research gap.
Preparing a literature review involves: Searching for reliable, accurate and up-to-date material on a topic or subject. Reading and summarising the key points from this literature. Synthesising these key ideas, theories and concepts into a summary of what is known. Discussing and evaluating these ideas, theories and concepts.
Literature Review Comment: 1. A literature review can be challenging to write because it should not be a source-by-source summary, but instead it should synthesize or bring multiple sources together. Each paragraphs within a literature review should contain at least two sources that speak to the same sociological factor. Your goal is to discover if
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
Systematic Review. Attempts to identify, appraise, and summarize all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria to answer a specific research question. clearly defined question with inclusion/exclusion criteria. rigorous and systematic search of the literature. thorough screening of results. data extraction and management.
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations. EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic.
Purpose The primary goal of this scoping review was to summarize the literature published after the 2018 National Cancer Institute think tank, "Measuring Aging and Identifying Aging Phenotypes in Cancer Survivors," on physical and cognitive functional outcomes among cancer survivors treated with chemotherapy. We focused on the influence of chemotherapy on aging-related outcomes (i.e ...
Background The current paradigm of competency-based medical education and learner-centredness requires learners to take an active role in their training. However, deliberate and planned continual assessment and performance improvement is hindered by the fragmented nature of many medical training programs. Attempts to bridge this continuity gap between supervision and feedback through learner ...
Background Metastatic Crohn's disease is a rare disorder characterized by various granulomatous skin lesions that occur independently of gastrointestinal tract involvement. However, currently there is no standardized care or specific treatment. Therapeutic approaches include immunosuppressive agents, such as corticosteroids, azathioprine, and monoclonal antibodies targeting inflammatory ...
Here, we review the pertinent literature and present a case of a previously healthy, 5-year-old, non-verbal boy who presented with multiple, acute, and subacute spontaneous epidural hemorrhages managed by neurosurgical intervention. He remained in hospital for 17 days and was seen in follow-up 3 weeks post-operatively having returned to his ...
A growing number of studies have reported that problematic social networking use (PSNU) is strongly associated with anxiety symptoms. However, due to the presence of multiple anxiety subtypes, existing research findings on the extent of this association vary widely, leading to a lack of consensus. The current meta-analysis aimed to summarize studies exploring the relationship between PSNU ...