

Dr. vs. PhD: Was ist der Unterschied?

Das Wichtigste auf einen Blick
- Während in Deutschland am Ende eines Promotionsstudiums der Doktortitel verliehen wird, ist es in englischsprachigen Ländern meistens der PhD.
- Beide Grade berechtigen zum Lehren an einer Universität und werden international anerkannt.
- Die Systeme der beiden Titel haben jedoch einige Unterschiede.
Dr. oder PhD?
Wenn Du Deinen Bachelor und Master bereits hinter Dir hast, die Universität aber nicht verlassen möchtest, bietet es sich an, in der Forschung und Entwicklung zu arbeiten . Dazu benötigst Du einen Promotionsplatz – und von denen gibt es immer mehr. Das ist die Reaktion auf die Nachfrage der wachsenden Zahl an Studenten in Deutschland. Wissenschaft und Forschung werden aber auch international immer wichtiger . So bietet sich Dir vielleicht sogar die Chance, die Promotion mit einem Auslandsaufenthalt zu verknüpfen.
Was bringt ein Dr. oder PhD?
Wer denkt, der Doktortitel sorgt nur für Anerkennung oder schmückt den eigenen Namen, liegt falsch. Ein Doktortitel öffnet nicht nur Türen in Medizinberufen oder im naturwissenschaftlichen Sektor. Auch Juristen und Wirtschaftswissenschaftler verdienen mit einem Titel spürbar mehr oder bekommen sogar erst dadurch Zugang zu höheren Positionen . Für Geisteswissenschaftler bedeutet der Titel leider kaum Zuwachs beim Gehalt, dafür kannst Du in einem Sektor forschen, der Dich interessiert, oder auch am Lehrstuhl arbeiten.
Begriffliche Unterscheidung
Während der klassische Grad des Doktors in Deutschland verbreitet ist, wird in englischsprachigen Ländern vor allem vom PhD , also vom Philosophical doctorate, gesprochen. Das leitet sich vom lateinischen philosophiae doctor ab, der aus der antiken Wissenschaftstradition kommt, heute aber nichts mehr mit dem Fach Philosophie zu tun hat . Stattdessen berechtigt der Titel zum selbstständigen und alleinverantwortlichen Lehren an einer Universität. Gleichzustellen ist der PhD im Englischsprachigen jedoch nicht mit einer Promotion in medizinischen Fächern. Hierbei handelt es sich um einen MD-PhD, der nur an Schools of Medicine verliehen wird. Der PhD hat meistens noch den Zusatz ‚in’, der angibt, in welchem Fach man den Titel erlangt hat.
Die wichtigsten Unterschiede
Dr. vs. PhD
4–6 Jahre (ausgenommen Mediziner)
Viel Eigenarbeit
Ausrichtung
Starke Bindung an Professor und Lehrstuhl
Angestrebtes Karriereziel
Strukturiert; Vorlesungen & Kurse gehören zum Programm
Betreuung und Austausch; Keine feste Bindung an einen Lehrstuhl oder einen Professor
Der Hauptunterschied zwischen Dr. und PhD ist also, dass man beim PhD nicht an einen bestimmten Lehrstuhl gebunden ist. Damit kannst Du beim PhD auch leichter den Betreuer wechseln. Beim Dr. ist das in der Regel schwer bis gar nicht möglich. Zusätzlich musst Du beim PhD im Schnitt eine größere Anzahl an Kursen belegen - also im Endeffekt mehr ECTS Credits sammeln. Der Umfang und die erwartete Qualität Deiner Doktorarbeit bzw. Deiner PhD-Thesis unterscheiden sich jedoch nicht voneinander. In jedem Fall ist sehr viel Eigenarbeit gefragt.
Achtung: Dr. nicht in PhD übersetzen
Auch wenn der deutsche Doktortitel im Ausland genauso anerkannt wird wie der PhD, solltest Du ihn auf gar keinen Fall übersetzen. Das ist sogar illegal . Grund dafür ist der Unterschied der beiden Systeme – vor allem die wissenschaftliche Forschung in PhD-Programmen ist intensiver als im Promotionsstudium.
Weitere Artikel

PhD oder Doktortitel - Was passt zu Dir?
Auch wenn der PhD im Ausland für Arbeiten auf Augenhöhe mit den Professoren steht, darfst Du das natürlich nicht verallgemeinern. Es kann sowohl im Ausland als auch an deutschen Universitäten große Unterschiede im Promotionsstudium geben. Falls Du die Wahl zwischen beiden Optionen hast, ist es wichtig, dass Du Dir Gedanken über Deine Zukunft machst. Dazu gehört zum Beispiel auch die Frage danach, wo Du später arbeiten möchtest. Du solltest Dich außerdem fragen, ob Du für diese Zeit ins Ausland gehen willst .
Falls Du das mit Nein beantwortest, der PhD aber trotzdem besser zu Dir passt, kannst Du nach geeigneten Programmen in Deutschland suchen, die es mittlerweile auch schon gibt.
Wo finde ich Doktorandenstellen?
- Finanzberatung
- Investitionsmanagement
- Risikomanagement
- Aushilfs- & Vertretungslehrer
- Beurteilung
- Kindertagesstätte
- Lehrassistenz
- Schulleitung
- Sekretariat
- Berufsschule
- Erwachsenenbildung
- Kindergarten, KiTa, Vorschule
- Sozialarbeit
- Universität, Fachhochschule
- Unterricht: Grundschule
- Unterricht: Sekundarstufe
- Weitere: Bildung und Soziales
- Buchführung
- Kreditkontrolle
- Lohnabrechnung
- Architektur
- Fotografie, Video
- Grafik- und Kommunikationsdesign
- Medien-, Screen-, Webdesign
- Modedesign, Schmuckdesign
- Produktdesign, Industriedesign
- Theater, Schauspiel, Musik, Tanz
- Weitere: Design, Gestaltung und Architektur
- Wohltätigkeit
- Audiologie, Hörakustik, HNO
- Ernährungswissenschaften
- Gynäkologie
- Hair & Beauty
- Kardiologie
- Kinder- und Jugendmedizin
- Medizinischer Vertrieb
- Pflegepersonal
- Psychische Gesundheit
- Unfall- und Notfallmedizin
- Filialleitung
- Merchandising
- Verkaufspersonal
- Bestattungsdienst
- Garten- und Landschaftsbau
- Gartenarbeit
- Hilfsarbeiten
- Malerei und Dekoration
- Montage und Bearbeitung
- Schreinerei
- Servicetechnik
- Arbeitssicherheit
- Bauwesen, Montage
- Beauty, Wellness
- Elektrik, Sanitär, Heizung, Klima
- Kontrollsysteme
- Lebensmittelindustrie
- Qualität & Sicherheit
- Abteilungsköche
- Barista-Management
- Barista-Personal
- Catering Management
- Eventmanagement
- Eventpersonal
- Freizeit- und Wellnessmanagement
- Freizeit- und Wellnesspersonal
- Hauswirtschafspersonal
- Hauswirtschaftsleitung
- Hotelleitung
- Hotelpersonal
- Kreuzfahrtmanagement
- Küchenchefs
- Küchenmanagement
- Parkservice
- Portierdienst
- Restaurantleitung
- Restaurantpersonal
- Service- und Barmanagement
- Service- und Barpersonal
- Servicepersonal
- Speisen und Getränke - Management
- Speisen und Getränke - Personal
- Holzhandwerk
- Maler, Lackierer
- Metallhandwerk
- Nahrungsmittelherstellung, -verarbeitung
- Raumgestaltung
- Reiseverkehr, Touristik
- Sicherheitsdienste, Schutzdienste
- Weitere: Handwerk, Dienstleistung und Fertigung
- Gebäudemanagement
- Immobilienagentur
- Immobilienverwaltung
- Verhandlung
- Vermietungen
- Vermögensbewertung
- Elektrotechnik
- Luft- und Raumfahrt
- Keine Disziplin
- Glücksspiel
- Kunstgewerbe
- Museum und Bibliothek
- Unterhaltung
- Distributionslogistik
- Packpersonal
- Post, Paketdienste
- Vendor Assurance
- Versorgungskette
- Assistant Management
- Gebietsleitung
- Geschäftsführung
- Geschäftsleitung
- Kaufmännische Leitung
- Brand Management
- Category Management
- Channel Management
- Marktforschung
- Verlagswesen
- (Bundes-)Polizei, Justizvollzug
- Angestellte, Beamte auf Bundesebene
- Angestellte, Beamte auf Landes-, kommunaler Ebene
- Angestellte, Beamte im auswärtigen Dienst
- Bundeswehr, Wehrverwaltung
- Steuerverwaltung, Finanzverwaltung
- Verbände, Vereine
- Weitere: Öffentlicher Dienst
- Lokalverwaltung
- Sicherheitsüberprüfung
- Zentralregierung
- Anwaltschaft
- Anwaltsgehilfen
- Arbeitsrecht
- Einwanderung
- Geistiges Eigentum
- Gerichtsverfahren
- Handelsrecht
- Justiziariat, Rechtsabteilung
- Körperverletzung
- Notar-, Justizfachangestellter, Anwaltsfachgehilfe
- Privatrecht
- Richter, Justizbeamte
- Sachenrecht
- Schlichtung/Schiedsgericht
- Weitere: Recht
- Fachreinigung
- Gebäudereinigung
- Geschäftsreisen
- Reiseberatung
- Reservation
- Heim-, Hausleitung
- Pflege, Betreung
- Unterbringung
- Fitness und Freizeit
- Haustierpflege
- Forderungen
- Versicherungsgeschäft
- Versicherungsmathematik
- Account-Management
- Angebotserstellung
- Außendienst
- Gebietsverkauf
- Immobilienmakler
- Innendienst, Sachbearbeitung
- Abholservice
- Call-Center
- Front Office
- Kundendienst
- Reklamation
- Leadgenerierung
- Leitung, Teamleitung
- Mittelbeschaffung
- Pharmaberater, Pharmareferent
- Tele-Marketing
- Verkauf (Handel)
- Verkaufsberatung
- Vertriebsassistenz
- Weitere: Vertrieb und Verkauf
- Landwirtschaft
- Data Science
- Forschung und Entwicklung
- Technologie
- Affalterbach
- Ahlden (Aller)
- Ahrensfelde
- Aichstetten
- Albershausen
- Alfeld (Leine)
- Allershausen
- Alsbach-Hähnlein
- Alsenbrück-Langmeil
- Altenkirchen
- Altenmarkt an der Alz
- Altentreptow
- Althengstett
- Altleiningen
- Altstrimmig
- Alzenau in Unterfranken
- Annaberg-Buchholz
- Annweiler am Trifels
- Asbach-Bäumenheim
- Aschaffenburg
- Aschau am Inn
- Aschersleben
- Aschersleben Aschersleben
- Aurich Haxtum
- Australien/Neuseeland
- Babenhausen
- Bad Aibling
- Bad Arolsen
- Bad Bentheim
- Bad Berleburg
- Bad Berleburg Bad Berleburg
- Bad Bevensen
- Bad Bramstedt
- Bad Brückenau
- Bad Camberg
- Bad Doberan
- Bad Driburg
- Bad Dürkheim
- Bad Dürrenberg
- Bad Dürrheim
- Bad Feilnbach
- Bad Frankenhausen
- Bad Freienwalde
- Bad Friedrichshall
- Bad Füssing
- Bad Harzburg
- Bad Harzburg Bad Harzburg
- Bad Hersfeld
- Bad Homburg vor der Höhe
- Bad Kissingen
- Bad Kleinen
- Bad Kreuznach
- Bad Krozingen
- Bad Laasphe
- Bad Langensalza
- Bad Lausick
- Bad Mergentheim
- Bad Münder am Deister
- Bad Nauheim
- Bad Nenndorf
- Bad Nenndorf Bad Nenndorf
- Bad Neuenahr-Ahrweiler
- Bad Neustadt an der Saale
- Bad Oeynhausen
- Bad Oldesloe
- Bad Pyrmont
- Bad Rappenau
- Bad Reichenhall
- Bad Saarow Bad Saarow
- Bad Säckingen
- Bad Salzuflen
- Bad Salzungen
- Bad Saulgau
- Bad Schönborn
- Bad Schussenried
- Bad Schwalbach
- Bad Schwartau
- Bad Segeberg
- Bad Sobernheim
- Bad Soden am Taunus
- Bad Soden-Salmünster
- Bad Staffelstein
- Bad Waldsee
- Bad Wildungen
- Bad Wörishofen
- Bad Wünnenberg
- Bad Wurzach
- Bad Zwischenahn
- Baden-Baden
- Baden-Württemberg
- Bahlingen am Kaiserstuhl
- Baiersbronn
- Bargteheide
- Barleben Barleben
- Barsinghausen
- Bayerischer Wald
- Beetzendorf
- Beindersheim
- Bempflingen
- Berchtesgaden
- Berchtesgadener Land
- Berg (Pfalz)
- Bergisch Gladbach
- Bergisches Land
- Bergkirchen
- Bergneustadt
- Berka/Werra
- Berlin Friedrichshain
- Berlin Kreuzberg
- Bernau am Chiemsee
- Bernkastel-Kues
- Bernstadt auf dem Eigen
- Bersenbrück
- Betzenstein
- Beutelsbach
- Biberach an der Riß
- Biebesheim am Rhein
- Bietigheim-Bissingen
- Bingen am Rhein
- Birkenwerder
- Bischofsheim
- Bischofswerda
- Blankenburg
- Blankenfelde
- Blaubeuren Seißen
- Bobenheim-Roxheim
- Bodelshausen
- Bodensee-Oberschwaben
- Bodman-Ludwigshafen
- Böhmenkirch
- Borgholzhausen
- Bosnien-Herzegowina
- Brackenheim
- Brandenburg
- Brandenburg an der Havel
- Braunfels Braunfels
- Braunschweig
- Breisach am Rhein
- Breitenbach
- Breitenfeld
- Bremerhaven
- Bremervörde
- Bretzenheim
- Bromskirchen
- Brunsbüttel
- Buchholz in der Nordheide
- Bückeburg Bückeburg
- Burg Stargard
- Burgkunstadt
- Büsingen am Hochrhein
- Buttenwiesen
- Castrop-Rauxel
- Cloppenburg
- Crimmitschau
- Crossen an der Elster
- Crottendorf
- D-PLZ &*
- D-PLZ &a
- D-PLZ 1&
- D-PLZ 3&
- D-PLZ 6&
- Dachsenhausen
- Dahlwitz-Hoppegarten
- Dallgow-Döberitz
- Delmenhorst
- Dettenhausen
- Dettingen an der Erms
- Dettingen unter Teck
- Deutschland
- Deutschland gesamt
- Dietmannsried
- Dietzenbach
- Dillingen an der Donau
- Dinkelsbühl
- Dinkelscherben
- Dippoldiswalde
- Dissen am Teutoburger Wald
- Doberlug-Kirchhain
- Donaueschingen
- Donnersdorf
- Dorf Mecklenburg
- Dörfles-Esbach
- Drensteinfurt
- Dresden Gompitz, Steinbach
- Durchhausen
- Durmersheim
- Ebersbach/Sachsen
- Ebsdorfergrund
- Eckernförde
- Edingen-Neckarhausen
- Efringen-Kirchen
- Eggenfelden
- Eggenstein-Leopoldshafen
- Ehingen an der Donau
- Ehringshausen
- Eigeltingen
- Eisenhüttenstadt
- Eislingen/Fils
- Ellwangen (Jagst)
- Elmenhorst-Lichtenhagen
- Elsterwerda
- Eltville am Rhein
- Emmelshausen
- Emmendingen
- Endingen am Kaiserstuhl
- Engelskirchen
- Eningen unter Achalm
- Enkenbach-Alsenborn
- Eppertshausen
- Erbes-Büdesheim
- Ergoldsbach
- Erndtebrück
- Essen (Oldenburg)
- Esslingen am Neckar
- Estorf Estorf
- Eutingen im Gäu
- Everswinkel
- Falkenberg/Elster
- Falkenstein/Vogtland
- Fallingbostel
- Feldkirchen
- Feldkirchen-Westerham
- Feuchtwangen
- Filderstadt
- Finsterwalde
- Fischen im Allgäu
- Flechtingen
- Fluorn-Winzeln
- Forchtenberg
- Forstinning
- Frammersbach
- Frankenberg (Eder)
- Frankenthal
- Frankenthal (Pfalz)
- Frankfurt (Oder)
- Frankfurt am Main
- Freiberg am Neckar
- Freiburg (Elbe)
- Freiburg im Breisgau
- Freilassing
- Freudenstadt
- Frickenhausen
- Fridingen an der Donau
- Friedeburg Friedeburg
- Friedrichsdorf
- Friedrichshafen
- Friesenhagen
- Fröndenberg
- Fürstenfeldbruck
- Fürstenwalde/Spree
- Furth im Wald
- Furtwangen im Schwarzwald
- Gaimersheim
- Gammelshausen
- Gammertingen
- Ganderkesee
- Garching bei München
- Garmisch-Partenkirchen
- Gatersleben
- Gau-Bischofsheim
- Geilenkirchen
- Geiselhöring
- Geislingen an der Steige
- Geislingen an der Steige Türkheim
- Gelsenkirchen
- Gemünden am Main
- Georgensgmünd
- Georgsmarienhütte
- Germersheim
- Geroldshausen
- Gerolzhofen
- Giebelstadt
- Giengen an der Brenz
- Ginsheim-Gustavsburg
- Gmund am Tegernsee
- Goldkronach
- Gondelsheim
- Gorleben Gorleben
- Goslar Goslar
- Gottmadingen
- Graben-Neudorf
- Grafenrheinfeld
- Grafing bei München
- Graitschen bei Bürgel
- Grävenwiesbach
- Greifenstein
- Grenzach-Wyhlen
- Greußenheim
- Grevenbroich
- Grevesmühlen
- Griechenland
- Gronau (Westfalen)
- Groß Gaglow
- Groß Kienitz
- Groß-Bieberau
- Groß-Umstadt
- Großbritannien
- Großenlüder
- Großhansdorf
- Großheide Berumerfehn
- Großheide Großheide
- Großkorbetha
- Großkrotzenburg
- Großmehring
- Großmühlingen
- Großostheim
- Großschirma
- Großthiemig
- Großwallstadt
- Großziethen
- Grünheide (Mark)
- Grünheide (Mark) Grünheide
- Gummersbach
- Gundremmingen
- Gunzenhausen
- Haag in Oberbayern
- Hagen am Teutoburger Wald
- Halberstadt
- Haldensleben
- Hall in Tirol
- Hallbergmoos
- Haltern am See
- Hamburg Allermöhe
- Hamburg Altenwerder
- Hamburg Bahrenfeld
- Hamburg Bergedorf
- Hamburg Bergstedt
- Hamburg Billbrook
- Hamburg Billstedt
- Hamburg Blankenese
- Hamburg Bramfeld
- Hamburg Eidelstedt
- Hamburg Eilbek
- Hamburg Eimsbüttel
- Hamburg Eppendorf
- Hamburg Finkenwerder
- Hamburg Fuhlsbüttel
- Hamburg Hamm-Mitte
- Hamburg Hammerbrook
- Hamburg Harburg
- Hamburg Harvestehude
- Hamburg Hausbruch
- Hamburg Hoheluft-Ost
- Hamburg Jenfeld
- Hamburg Kleiner Grasbrook
- Hamburg Klostertor
- Hamburg Langenhorn
- Hamburg Lokstedt
- Hamburg Lurup
- Hamburg Neustadt
- Hamburg Niendorf
- Hamburg Ohlsdorf
- Hamburg Osdorf
- Hamburg Othmarschen
- Hamburg Rahlstedt
- Hamburg Rotherbaum
- Hamburg Sankt Georg
- Hamburg Sankt Pauli
- Hamburg Sasel
- Hamburg Schnelsen
- Hamburg Steinwerder
- Hamburg Stellingen
- Hamburg Tonndorf
- Hamburg Volksdorf
- Hamburg Waltershof
- Hamburg Wandsbek
- Hamburg Wilhelmsburg
- Hammersbach
- Hannoversch Münden
- Harsewinkel
- Hartenstein
- Hartenstein Thierfeld
- Harthausen (Igersheim)
- Haslach im Kinzigtal
- Haßmersheim
- Hattersheim
- Hausen (Wied)
- Heidenheim an der Brenz
- Heidesheim am Rhein
- Heiligengrabe
- Heimenkirch
- Helpsen Helpsen
- Hemmingstedt
- Hengersberg
- Hennigsdorf
- Henstedt-Ulzburg
- Heppenheim (Bergstraße)
- Herbolzheim
- Herbrechtingen
- Herdwangen-Schönach
- Hergensweiler
- Heringen (Werra)
- Heringsdorf
- Herleshausen
- Hermaringen
- Heroldsberg
- Herrsching am Ammersee
- Herxheim bei Landau/Pfalz
- Herzberg (Elster)
- Herzberg am Harz
- Herzebrock-Clarholz
- Herzogenaurach
- Herzogenrath
- Hessisch Oldendorf
- Heusenstamm
- Hiddenhausen
- Hilchenbach
- Hildburghausen
- Hilpoltstein
- Hilter am Teutoburger Wald
- Hirschberg an der Bergstraße
- Hirschfelde
- Hirschfelde Dittelsdorf
- Hitzacker Hitzacker
- Hochheim am Main
- Höchst im Odenwald
- Höchstadt an der Aisch
- Hofheim am Taunus
- Höheischweiler
- Hohen Neuendorf
- Hohenkammer
- Hohenlinden
- Hohenlockstedt
- Hohenwarsleben
- Hohenwestedt
- Höhr-Grenzhausen
- Holzgerlingen
- Holzkirchen
- Holzwickede
- Homberg (Efze)
- Homberg (Ohm)
- Horb am Neckar
- Horst (Holstein)
- Hötensleben
- Hoyerswerda
- Hückelhoven
- Ichtershausen
- Idar-Oberstein
- Illerkirchberg
- Illertissen
- Immenstadt im Allgäu
- Ingelfingen
- Ingelheim am Rhein
- Inning am Ammersee
- Isny im Allgäu
- Jagsthausen
- Jandelsbrunn
- Jänschwalde
- Jessen (Elster)
- Jessen (Elster) Jessen (Elster)
- Jettingen-Scheppach
- Jever Jever
- Kaisersbach
- Kaiserslautern
- Kaltenkirchen
- Kammerstein
- Kamp-Lintfort
- Karlsdorf-Neuthard
- Karlstein am Main
- Katharinenberg
- Kelkheim (Taunus)
- Kelsterbach
- Kernen im Remstal
- Kiefersfelden
- Kirchentellinsfurt
- Kirchheim bei München
- Kirchheim unter Teck
- Kirchheimbolanden
- Kirchlengern
- Kirchweidach
- Kirchzarten
- Klein-Winternheim
- Kleinaitingen
- Kleinblittersdorf
- Kleinheubach
- Kleinmachnow
- Kleinostheim
- Kleinwallstadt
- Kloster Lehnin
- Klosterfelde
- Knittlingen
- Kölln-Reisiek
- Königs Wusterhausen
- Königsbach-Stein
- Königsbrück
- Königsbrunn
- Königstein im Taunus
- Königstein im Taunus Mammolshain
- Königswinter
- Korntal-Münchingen
- Kornwestheim
- Korschenbroich
- Kottgeisering
- Kranichfeld
- Kressbronn am Bodensee
- Kreuzlingen
- Kronberg im Taunus
- Krottelbach
- Kusterdingen
- Lahr/Schwarzwald
- Laichingen Machtolsheim
- Lampertheim
- Lampertswalde
- Landau in der Pfalz
- Landesbergen
- Landesbergen Landesbergen
- Landsberg am Lech
- Langelsheim
- Langenhagen
- Langenselbold
- Langewiesen
- Lappersdorf
- Lauchhammer
- Lauchringen
- Lauda-Königshofen
- Lauenburg/Elbe
- Lauf an der Pegnitz
- Lebus Lebus
- Leer (Ostfriesland)
- Leichlingen
- Leinfelden-Echterdingen
- Leopoldshagen
- Leopoldshöhe
- Leutkirch im Allgäu
- Lichtenfels
- Lichtenstein
- Lichtenwald
- Lichterfelde
- Liebenwalde
- Liechtenstein
- Liederbach am Taunus
- Limbach-Oberfrohna
- Limburg an der Lahn
- Limburgerhof
- Lindau (Bodensee)
- Lindhorst Lindhorst
- Linz am Rhein
- Lohne (Oldenburg)
- Lohr am Main
- Losheim am See
- Lübbenau/Spreewald
- Luckenwalde
- Lüdenscheid
- Lüdinghausen
- Ludwigsburg
- Ludwigsfelde
- Ludwigshafen am Rhein
- Ludwigslust
- Lüneburger Heide
- Lutherstadt Eisleben
- Lutherstadt Wittenberg
- Luxemburg (Land)
- Mainaschaff
- Markgröningen
- Markkleeberg
- Markranstädt
- Markt Bibart
- Markt Indersdorf
- Markt Schwaben
- Marktheidenfeld
- Marktoberdorf
- Marktredwitz
- Maxhütte-Haidhof
- Meckenbeuren
- Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- Meinerzhagen
- Memmingerberg
- Michelstadt
- Mittel - und Südamerika
- Mittelbiberach
- Mitteldeutschland
- Mittelfranken
- Mittenwalde
- Mönchengladbach
- Monheim am Rhein
- Monheim am Rhein Baumberg
- Mörfelden-Walldorf
- Muggensturm
- Mühldorf am Inn
- Mulda/Sachsen
- Mülheim an der Ruhr
- Mülheim-Kärlich
- Münchhausen
- Mundelsheim
- Munderkingen
- Münsterland
- Münstermaifeld
- Muri bei Bern
- Murnau am Staffelsee
- Müschenbach
- Mutterschied
- Mutterstadt
- Nachterstedt
- Naher Osten
- Nebelschütz
- Neckargemünd
- Neckarwestheim
- Neu Fahrland
- Neu Wulmstorf
- Neu-Anspach
- Neu-Bamberg
- Neu-Isenburg
- Neubrandenburg
- Neuburg an der Donau
- Neuenburg am Rhein
- Neuendettelsau
- Neuenhagen bei Berlin
- Neuenkirchen
- Neuenkirchen-Vörden
- Neuenstadt am Kocher
- Neufahrn bei Freising
- Neugersdorf
- Neuhardenberg
- Neuhardenberg Neuhardenberg
- Neuhausen auf den Fildern
- Neukieritzsch
- Neukirchen-Vluyn
- Neukirchen/Erzgebirge
- Neumarkt in der Oberpfalz
- Neumarkt-Sankt Veit
- Neundorf (bei Lobenstein)
- Neunkirchen
- Neunkirchen/Saar
- Neustadt (Dosse)
- Neustadt (Hessen)
- Neustadt (Wied)
- Neustadt am Rübenberge
- Neustadt an der Aisch
- Neustadt an der Donau
- Neustadt an der Orla
- Neustadt an der Waldnaab
- Neustadt an der Weinstraße
- Neustadt bei Coburg
- Neustadt in Holstein
- Neustadt in Sachsen
- Neustadt, Bremen
- Neustadt-Glewe
- Neustrelitz
- Neutraubling
- Niederaichbach
- Niederalteich
- Niederbayern
- Niederdorfelden
- Niederdorla
- Niederfischbach
- Niederfrohna
- Niederlande
- Niederlehme
- Niedernhall
- Niederrhein
- Niedersachsen
- Niederstetten
- Niederstotzingen
- Niefern-Öschelbronn
- Nienburg (Weser)
- Nienburg (Weser) Holtorf
- Nienburg (Weser) Nienburg (Weser)
- Norddeutschland
- Norden Norden
- Norden Westermarsch II
- Norderstedt
- Nordkirchen
- Nordrhein-Westfalen
- Nörten-Hardenberg
- Nörtershausen
- Nuthe-Urstromtal
- Ober-Ramstadt
- Oberammergau
- Oberderdingen
- Oberfranken
- Obergünzburg
- Oberhaching
- Oberleichtersbach
- Oberlungwitz
- Oberndorf am Neckar
- Obernkirchen
- Obernkirchen Obernkirchen
- Oberroßbach
- Oberschleißheim
- Obersontheim
- Obertraubling
- Obertshausen
- Oberviechtach
- Ochsenhausen
- Odelzhausen
- Oer-Erkenschwick
- Oerlinghausen
- Oestrich-Winkel
- Oettingen in Bayern
- Offenbach an der Queich
- Offenhausen
- Ölbronn-Dürrn
- Oldenburg (Oldenburg)
- Oldenburg in Holstein
- Oranienbaum
- Oranienburg
- Oschersleben
- Ostdeutschland
- Osterburken
- Osterholz-Scharmbeck
- Österreich gesamt
- Osterrönfeld
- Ostfriesland
- Oststeinbek
- Ostwestfalen-Lippe
- Ottendorf-Okrilla
- Ottenhöfen im Schwarzwald
- Ottersweier
- Oy-Mittelberg
- Paaren im Glien
- Petersaurach
- Petershagen
- Petershagen-Eggersdorf
- Petershausen
- Pfaffenhofen an der Ilm
- Pfarrkirchen
- Pfullendorf
- Philadelphia
- Philippsburg
- Plau am See
- Pleckhausen
- Pleidelsheim
- Plettenberg
- Pliezhausen
- Plüderhausen
- Porta Westfalica
- Postbauer-Heng
- Prichsenstadt
- Prien am Chiemsee
- Pullach im Isartal
- Quakenbrück
- Quedlinburg
- Radevormwald
- Radolfzell am Bodensee
- Ramstein-Miesenbach
- Rangendingen
- Ransbach-Baumbach
- Rechberghausen
- Recklinghausen
- Reichelsheim
- Reichenbach an der Fils
- Reichenschwand
- Reichertshofen
- Reinfeld (Holstein)
- Reinhardshagen
- Reit im Winkl
- Remseck am Neckar
- Rheda-Wiedenbrück
- Rhein-Erft-Kreis
- Rhein-Main-Gebiet
- Rhein-Neckar
- Rhein-Neckar-Kreis
- Rhein-Pfalz-Kreis
- Rheinböllen
- Rheinbreitbach
- Rheinfelden
- Rheinhausen
- Rheinland-Pfalz
- Rheinmünster
- Rheinstetten
- Rheinzabern
- Ribnitz-Damgarten
- Rielasingen-Worblingen
- Rinteln Rinteln
- Rittersdorf
- Rodenberg Rodenberg
- Rödinghausen
- Römerstein Donnstetten
- Rommerskirchen
- Rosbach vor der Höhe
- Rosbach vor der Höhe Nieder-Rosbach
- Rosengarten
- Rot an der Rot
- Rotenburg (Wümme)
- Rotenburg an der Fulda
- Röthenbach an der Pegnitz
- Rothenburg ob der Tauber
- Rothenstein
- Rottach-Egern
- Rottenburg am Neckar
- Rottleberode
- Rövershagen
- Rückersdorf
- Rüdesheim am Rhein
- Rüsselsheim
- Russische Föderation
- Saalburg-Ebersdorf
- Saalfeld/Saale
- Saarbrücken
- Saarwellingen
- Sachsen-Anhalt
- Sachsenhausen
- Sachsenheim
- Salzgitter Barum
- Salzgitter Calbecht
- Salzgitter Engelnstedt
- Salzgitter Engenrode
- Salzgitter Gebhardshagen
- Salzgitter Hallendorf
- Salzgitter Heerte
- Salzgitter Lebenstedt
- Salzgitter Salder
- Sandersdorf
- Sandersdorf Sandersdorf
- Sandesneben
- Sangerhausen
- Sankt Augustin
- Sankt Blasien
- Sankt Egidien
- Sankt Georgen im Schwarzwald
- Sankt Ingbert
- Sankt Johann
- Sankt Katharinen
- Sankt Leon-Rot
- Sankt Peter-Ording
- Sankt Wendel
- Sankt Wolfgang
- Schaffhausen
- Schalksmühle
- Schauenburg
- Schellerten
- Schenkenberg
- Schkopau Döllnitz
- Schkopau Schkopau
- Schlangenbad
- Schleswig Holstein
- Schleusingen
- Schlierbach
- Schloß Holte-Stukenbrock
- Schlüchtern
- Schmalkalden
- Schmidgaden
- Schmiedefeld
- Schmiedefeld am Rennsteig
- Schnaittenbach
- Schönau am Königssee
- Schönberg (Holstein)
- Schöneck/Vogtland
- Schönerlinde
- Schönkirchen
- Schöppingen
- Schortens Schortens
- Schriesheim
- Schrobenhausen
- Schuttertal
- Schutterwald
- Schwäbisch Gmünd
- Schwäbisch Hall
- Schwabmünchen
- Schwaikheim
- Schwalbach am Taunus
- Schwallungen
- Schwalmstadt
- Schwanewede
- Schwarzenbach an der Saale
- Schwarzenbek
- Schwarzenbruck
- Schwarzenfeld
- Schwarzheide
- Schwarzwald
- Schwedt/Oder
- Schweinfurt
- Schweitenkirchen
- Schweiz gesamt
- Schwenningen
- Schwentinental
- Schwetzingen
- Schwieberdingen
- Schwielowsee
- Seddiner See
- Seeheim-Jugenheim
- Seeon-Seebruck
- Seeth-Ekholt
- Seifhennersdorf
- Seligenstadt
- Senftenberg
- Sigmaringen
- Simbach am Inn
- Sindelfingen
- Sondershausen
- Spittal an der Drau
- Sprendlingen
- Sprockhövel
- Stadtallendorf
- Stadthagen Stadthagen
- Stadtlengsfeld
- Steinau an der Straße
- Steinbach (Taunus)
- Steinheim an der Murr
- Stephanskirchen
- Stetten am kalten Markt
- Stockstadt am Main
- Stockstadt am Rhein
- Stolberg (Rheinland)
- Stollberg/Erzgebirge
- Stolzenau Stolzenau
- Storkow (Mark)
- Storkow (Mark) Storkow
- Straßkirchen
- Straubenhardt
- Stuttgart Bad Cannstatt
- Stuttgart Birkach
- Stuttgart Büsnau
- Stuttgart Degerloch
- Stuttgart Feuerbach
- Stuttgart Hausen
- Stuttgart Hedelfingen
- Stuttgart Heumaden
- Stuttgart Hohenheim
- Stuttgart Möhringen
- Stuttgart Plieningen
- Stuttgart Stammheim
- Stuttgart Stuttgart-Mitte
- Stuttgart Stuttgart-Nord
- Stuttgart Stuttgart-Ost
- Stuttgart Stuttgart-Süd
- Stuttgart Stuttgart-West
- Stuttgart Untertürkheim
- Stuttgart Vaihingen
- Stuttgart Wangen
- Stuttgart Weilimdorf
- Stuttgart Zuffenhausen
- Süddeutschland
- Südwestdeutschland
- Sulz am Neckar
- Sulzbach-Laufen
- Sulzbach-Rosenberg
- Sulzbach/Saar
- Tauberbischofsheim
- Tauberrettersheim
- Taufkirchen
- Taufkirchen (Vils)
- Taunusstein
- Tennenbronn
- Teutschenthal
- Thalmässing
- Thüringer Wald
- Timmendorfer Strand
- Titisee-Neustadt
- Trebsen/Mulde
- Treuchtlingen
- Trochtelfingen
- Trollenhagen
- Tschechische Republik
- Tümlauer Koog
- Übach-Palenberg
- Ubstadt-Weiher
- Uhldingen-Mühlhofen
- Ulm Jungingen
- Unterdießen
- Unterensingen
- Unterföhring
- Unterfranken
- Untergruppenbach
- Unterhaching
- Untermerzbach
- Unterschleißheim
- Unterstadion
- Ursensollen
- Vaihingen an der Enz
- Varel Varel
- Vaterstetten
- Veitshöchheim
- Verden (Aller)
- Vestenbergsgreuth
- Vettelschoß
- Vierkirchen
- Villingen-Schwenningen
- Visselhövede
- Vogtsburg im Kaiserstuhl
- Vohburg an der Donau
- Volkenschwand
- Wachtendonk
- Wächtersbach
- Waigandshain
- Wakendorf II
- Waldbreitbach
- Waldkraiburg
- Waldlaubersheim
- Waldmünchen
- Waldshut-Tiengen
- Waldstetten
- Wallersdorf
- Waltenhofen
- Walterschen
- Waltershausen
- Wangen im Allgäu
- Wasserburg am Inn
- Wasserlosen
- Wefensleben
- Weferlingen
- Weikersheim
- Weil am Rhein
- Weil der Stadt
- Weil im Schönbuch
- Weilerswist
- Weilheim an der Teck
- Weilheim in Oberbayern
- Weißenburg in Bayern
- Weißensberg
- Weißrussland
- Weiterstadt
- Weltweit (außer Europa)
- Wendelstein
- Wendlingen am Neckar
- Wenningstedt
- Wentorf bei Hamburg
- Werder (Havel)
- Wermelskirchen
- Wernigerode
- Westdeutschland
- Westerkappeln
- Westerstede
- Westliches Europa
- Wetter (Ruhr)
- Wetterzeube
- Wiefelstede
- Wiemersdorf
- Wiesengrund
- Wiesentheid
- Wiesmoor Wiesmoor
- Wietmarschen
- Wildenbruch
- Wildenfels Wildenfels
- Wildeshausen
- Wildflecken
- Wildpoldsried
- Wilhelmsdorf
- Wilhelmshaven
- Wilmersdorf
- Winsen (Aller)
- Winsen (Luhe)
- Wipperfürth
- Wittenberge
- Wittighausen
- Wittislingen
- Wittmund Wittmund
- Wittstock/Dosse
- Wolfenbüttel
- Wolfratshausen
- Wolfschlugen
- Wolkenstein
- Wolmirstedt
- Woltersdorf
- WorkingFromHome
- Wörth am Rhein
- Wörth an der Isar
- Wyk auf Föhr
- Zella-Mehlis
- Zimmern ob Rottweil
- Zschornewitz
- Zusmarshausen
- Zuzenhausen
- Zweibrücken
- Zwingenberg
- [Die ganze Welt]
- Agentur, Werbung, Marketing & PR
- Armed Forces
- Art, Culture, Entertainment & Sport
- Auditing/Accounting
- Automotive Industry
- Banking, Financial Services & Insurance
- Baugewerbe/-industrie
- Bildung & Training
- Building & Construction
- Chemie- und Erdölverarbeitende Industrie
- Conservation & Environment
- Druck-, Papier- und Verpackungsindustrie
- Elektrotechnik, Feinmechanik & Optik
- Energie- und Wasserversorgung & Entsorgung
- Fahrzeugbau/-zulieferer
- Finanzdienstleister
- Freizeit, Touristik, Kultur & Sport
- Gesundheit & soziale Dienste
- Glas-, Keramik-Herstellung & -verarbeitung
- Groß- & Einzelhandel
- Holz- und Möbelindustrie
- Hotel, Gastronomie & Catering
- IT & Internet
- Konsumgüter/Gebrauchsgüter
- Land-, Forst- und Fischwirtschaft, Gartenbau
- Leisure & Tourism
- Manufacture of chemical products
- Manufacturing
- Maschinen- und Anlagenbau
- Medien (Film, Funk, TV, Verlage)
- Medizintechnik
- Metallindustrie
- Nahrungs- & Genussmittel
- Öffentlicher Dienst & Verbände
- Personaldienstleistungen
- Pharmaindustrie
- Public Administration
- Public Services
- Sonstige Branchen
- Sonstige Dienstleistungen
- Sonstiges produzierendes Gewerbe
- Telekommunikation
- Textilien, Bekleidung & Lederwaren
- Transport & Logistik
- Unternehmensberatg., Wirtschaftsprüfg., Recht
- Versicherungen
- Wissenschaft & Forschung
- Arbeitnehmerüberlassung
- Ausbildung, Studium
- Bachelor-/Master-/Diplom-Arbeiten
- Befristeter Vertrag
- Berufseinstieg/Trainee
- Feste Anstellung
- Freie Mitarbeit/Projektmitarbeit
- Handelsvertreter
- Promotion/Habilitation
- Referendariat
- Studentenjobs, Werkstudent
- Mit Berufserfahrung
- Mit Personalverantwortung
- Ohne Berufserfahrung
Detailsuche


Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
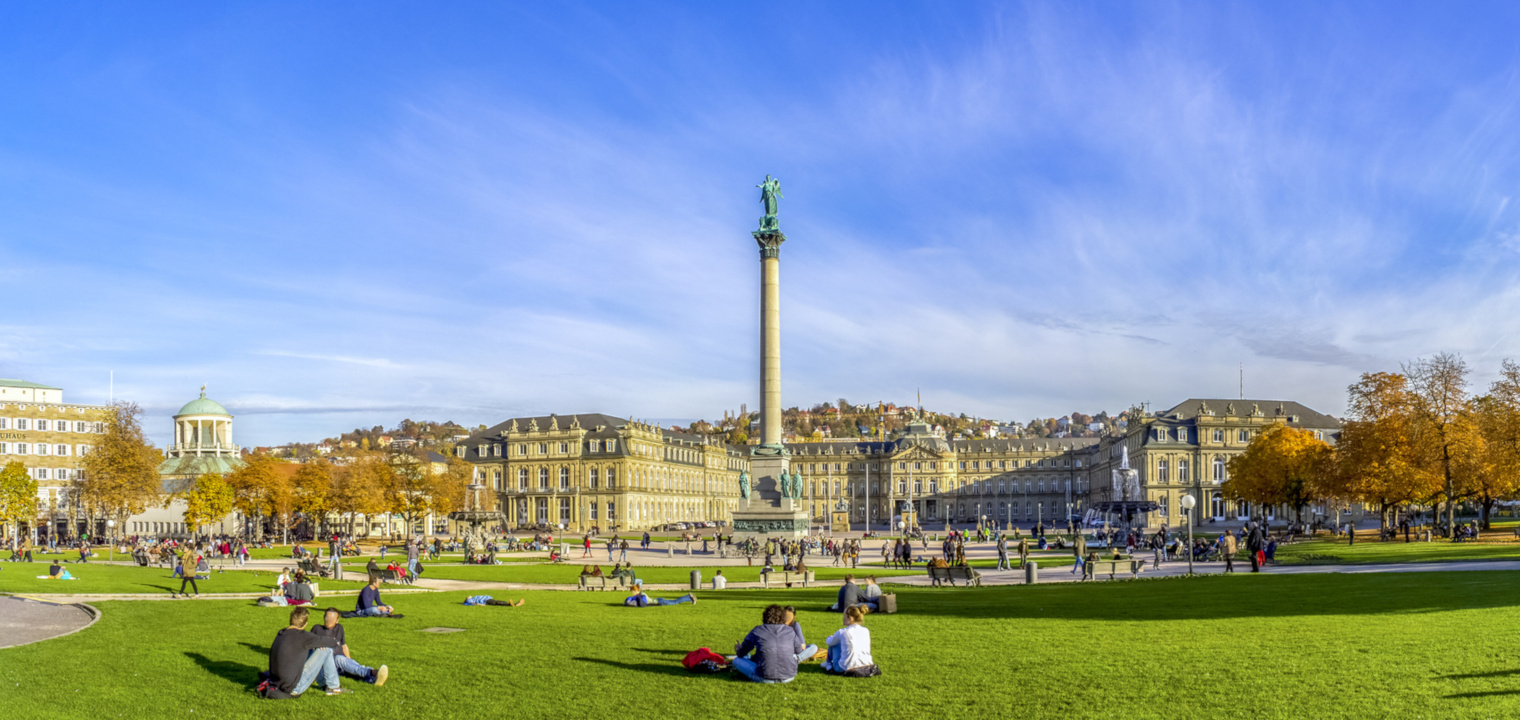
What is the Difference Between a PhD Candidate and a PhD Student?
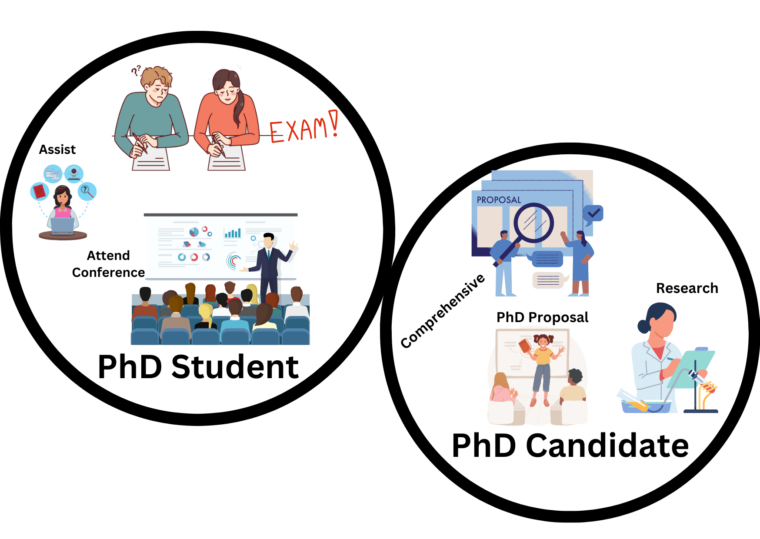
Pursuing a doctoral degree is a significant academic achievement that requires years of dedicated study, research, and intellectual rigour. Within the realm of doctoral studies, the terms ‘PhD candidate’ and ‘PhD student’ are commonly used, often interchangeably. However, a closer examination reveals that there are nuanced differences between these two designations. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for both prospective doctoral students and those seeking to comprehend the various stages of the doctoral journey.
In this article, we delve into the disparity between a PhD candidate and a PhD student, shedding light on the roles, responsibilities, and progression associated with each stage. We explore the specific criteria that differentiate a student from a candidate and the various milestones marking the transition. Additionally, we delve into the responsibilities and expectations that accompany each designation, illuminating the unique experiences and commitments faced by PhD candidates and students.
Furthermore, we acknowledge the variability in terminology across international boundaries, academic institutions, and disciplinary fields, providing insights into how different contexts might influence the usage of these terms. By the end, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the contrasting aspects between a PhD candidate and a PhD student, facilitating informed conversations and a deeper appreciation for the intricate nature of doctoral education.
Introduction
Who is a phd student, when phd student attains status of phd candidate, variation in terminology.
Pursuing a PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) degree involves conducting original research in a specific field of study, making a significant contribution to knowledge, and demonstrating a high level of expertise. It is the highest academic qualification one can attain and is highly valued in academia, research institutions, and certain industries. A PhD signifies a deep understanding of a subject area, advanced analytical and critical thinking skills, and the ability to conduct independent research.
While the terms “PhD candidate” and “PhD student” are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences between the two.
A PhD student typically refers to an individual who has been admitted to a doctoral program, actively engaging in coursework and other program requirements. They are in the early stages of their doctoral journey and are working towards completing the necessary academic components of their degree. On the other hand, a PhD candidate is typically someone who has progressed beyond the coursework stage and has advanced to the research phase of their program. They have usually completed comprehensive exams, passed a research proposal defense, and are actively engaged in independent research for their dissertation or thesis.
The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the distinction between a PhD candidate and a PhD student. By exploring the criteria, milestones, and responsibilities associated with each designation, this article aims to clarify the unique experiences and progression of doctoral students. It also seeks to address the varying terminology used across different contexts and disciplines, enabling readers to grasp the intricacies of the doctoral journey and fostering informed discussions around this topic.
Through this article, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of the journey from being a PhD student to becoming a PhD candidate and the distinct roles and responsibilities associated with each stage.
A PhD student is an individual who has been admitted to a doctoral program and is actively engaged in pursuing their doctoral studies. They are at the initial stages of their doctoral journey, seeking to expand their knowledge, skills, and expertise in a specific field of study. PhD students play a vital role in academic research communities as they contribute to the generation of new knowledge and the advancement of their discipline.
PhD students are required to complete a set of coursework specific to their field of study. These courses are designed to provide a foundation in the discipline, enhance research skills, and broaden the student’s understanding of relevant theories and methodologies. Coursework may include seminars, advanced classes, and specialized topics. The specific coursework requirements can vary between programs and disciplines.
Example: Imagine a student named Alex who has just been accepted into a doctoral program in psychology. At this stage, Alex is considered a PhD student as they begin taking relevant coursework, attending seminars, and collaborating with faculty members. They are laying the foundation for their research and acquiring the necessary knowledge in their field.
Who is a PhD Candidate?
Advancement from being a PhD student to a PhD candidate typically involves meeting specific requirements set by the doctoral program. These requirements may vary depending on the institution and field of study but often include successful completion of coursework, exams, and other program-specific milestones.
One of the primary requirements for transitioning to a PhD candidate is the successful completion of coursework and exams. PhD students are expected to complete a designated set of courses, which provide a broad understanding of their field and research methodologies. They are also required to pass comprehensive exams, which assess their comprehensive knowledge and understanding of their research area.
As part of the transition to becoming a PhD candidate, students typically prepare and defend a research proposal. The research proposal outlines the scope, objectives, methodology, and significance of the intended research. The proposal defense may involve presenting the proposal to a committee of faculty members, who evaluate its feasibility, rigour, and contribution to the field. Additionally, PhD students often have to pass comprehensive exams, which test their knowledge of their research area and related disciplines.
If you are not familiar with writing PhD proposal and making PhD proposal presentation, then visit my articles on “ How to Write PhD Proposal Presentation to the University ” and ” How to Make a PhD Proposal Presentation to the University Panel” . These articles will guide you through the process of preparation and presentation of PhD proposal to the University panel.
Upon successful completion of the requirements, PhD students are often granted candidacy status. Advancement to candidacy signifies that the student has demonstrated the necessary knowledge, skills, and potential to conduct independent research and contribute to their field. This status allows students to focus more exclusively on their research and dissertation work.
Once students become PhD candidates, there is a shift towards an increased emphasis on independent research. They are expected to dedicate a significant portion of their time and effort to conducting original research, collecting data, analyzing results, and making novel contributions to their field. The focus is primarily on their dissertation or thesis work, which serves as the culmination of their doctoral studies.
Example: Let’s consider a PhD student named Alex in the field of computer science. After completing their coursework and passing comprehensive exams, Alex develops a research proposal outlining their intention to investigate the applications of machine learning in cybersecurity. They present the proposal to a committee of faculty members, who assess the feasibility and potential impact of the research.
Alex successfully defends their research proposal and is granted candidacy status, transitioning from a PhD student to a PhD candidate. With candidacy status, Alex’s focus shifts towards conducting independent research. They spend considerable time collecting and analyzing cybersecurity datasets, developing and refining machine learning algorithms, and testing their effectiveness in detecting and preventing cyber threats.
As a PhD candidate, Alex works closely with their advisor, regularly discussing research progress, seeking guidance, and receiving feedback. They collaborate with other researchers in the field, attend conferences to present their findings and contribute to the scholarly community through publications. The focus is now on producing an original and significant contribution to the field of computer science through their dissertation.
The transition to PhD candidacy marks a critical stage in the doctoral journey, as it signifies the ability to independently drive research and make scholarly contributions. PhD candidates like Alex are immersed in the world of research, expanding knowledge, and pushing the boundaries of their field.
Terminology related to PhD candidates and PhD students can vary internationally and among different academic institutions. In some countries, the terms “PhD candidate” and “PhD student” may be used interchangeably, while in others, there may be specific distinctions. For example, in the United States, “PhD student” is commonly used, while in the United Kingdom, “PhD candidate” is more frequently employed. Additionally, different universities or institutions may have their own terminology preferences, which can create further variation.
Terminology can also vary based on the disciplinary field of study. Different academic disciplines have their own conventions and terminology for referring to individuals pursuing a doctoral degree. For instance, in the sciences, one might encounter terms like “graduate researcher” or “doctoral candidate.” In the humanities and social sciences, the terms “PhD candidate” and “PhD student” are often used. This variation reflects the specific linguistic and cultural norms within different academic domains.
In Canada, for instance, doctoral students are commonly referred to as “PhD candidates,” regardless of their stage in the program. In Australia, “PhD candidate” is the preferred term for those who have completed the required coursework and have advanced to the research phase. In contrast, in the United States, “PhD student” is frequently used to refer to individuals at all stages of their doctoral studies.
Disciplinary variations can also be observed. In engineering, individuals pursuing a doctoral degree are often referred to as “PhD students” or “doctoral students.” In contrast, in the field of education, the term “PhD candidate” is commonly used to denote those who have advanced to the research and dissertation stage.
It is important to note that these examples represent general trends, and there can still be variation within specific institutions and programs. The usage of terminology can evolve over time and may be influenced by regional or institutional preferences.
The distinction between a PhD candidate and a PhD student holds significant importance in the realm of doctoral education.
While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent different stages and responsibilities within the doctoral journey. A PhD student is in the initial stages of their program, actively engaging in coursework, research, and academic requirements.
On the other hand, a PhD candidate has advanced beyond coursework, passed comprehensive exams, and is focused primarily on independent research and the completion of their dissertation.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- 04 Reasons for Outsourcing Academic Conference Management
- How to Put Research Grants on Your CV ?
- How to Request for Journal Publishing Charge (APC) Discount or Waiver?
- Do Review Papers Count for the Award of a PhD Degree?
- Vinay Kabadi, University of Melbourne, Interview on Award-Winning Research
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

- Ratgeber nach Positionen
- Promovieren
- Postdoc-Ratgeber
- Habilitation
- HAW-Professur
- Branchen-Ratgeber
- Geisteswissenschaften
- Ingenieurwissenschaften
- Naturwissenschaften
- Öffentlicher Dienst
- NGO, Stiftung & Co.
- Wirtschafts- und Rechtswissenschaften
- Informatik & IT
- Themen-Ratgeber
- Frauen in der Wissenschaft
- Arbeit & Gesundheit
- Service-Angebot
- Karriereberatung
- Promotions-Test
- Booklet: Arbeiten im öffentlichen Dienst
- Nachwuchspreis
- Arbeitgeber
- Graduiertenschulen
Ph.D. in Deutschland machen Ph.D. oder Dr.? Unterschiede des internationalen und deutschen Doktortitels
Der Ph.D. gewinnt in Deutschland neben dem klassischen Doktortitel immer mehr an Bedeutung. Doch was macht den Abschluss aus und wann ist der Ph.D. im Vergleich zum Doktortitel sinnvoll?

Was ist ein Ph.D.? Bedeutung und Relevanz
Dr. vs. ph.d.: welche unterschiede gibt es, ph.d.-studium in deutschland: wo und wie, ph.d. in deutschland: voraussetzungen, promotion als ph.d. berufsbegleitend oder im fernstudium.
Ph.D. ist die Abkürzung für den lateinischen Ausdruck „Philosophiae Doctor“. Damit bezeichnet der Titel wörtlich den Doktor der Philosophie. Faktisch handelt es sich beim Ph.D. jedoch um einen der höchsten allgemeinen akademischen Grade in verschiedensten Fachrichtungen , den beispielsweise US-amerikanische Universitäten vergeben. Die Erklärung für die Benennung liegt in der Geschichte begründet: Die Philosophie gilt als Mutter aller Wissenschaften.
Der Titel ist vor allem im englischsprachigen Raum sehr verbreitet . Inzwischen gibt es jedoch auch immer mehr Hochschulen in Deutschland, die den Ph.D. anbieten. Von Sprachwissenschaften über Biologie bis hin zum Ingenieurwesen: Promotionen mit dem Ziel Ph.D. gibt es hierzulande bereits in diversen Fachbereichen.
Wissenschaftliche*r Mitarbeiter*in (m/w/d) (Postdoc oder Doktorand*in) in der Informatik / Algorithmische Chemieinformatik

PhD candidates (m/f/d)

Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter (m/w/d) für die Bereiche "Grüner Wasserstoff International", "Kühlung und Abwärmenutzung von Rechenzentren" und "Smart Energy Lab"

Der Ph.D. ist prinzipiell vergleichbar mit dem deutschen Doktortitel . Jedoch unterscheiden sich die beiden akademischen Grade deutlich im Hinblick auf die spezifischen Voraussetzungen, den Prozess zum Erwerb des Titels sowie die Dauer. Einige der wichtigsten Unterschiede zwischen den beiden Abschlüssen zeigt die folgende Übersicht.
Mit unserer Job-Mail erhalten Sie wöchentlich passende Stellen sowie interessante Inhalte zu Ihrem Suchprofil.
Diese deutlichen Unterschiede zeigen, dass sich Ph.D. und Doktortitel nicht unbedingt gleichsetzen lassen . Bei einer internationalen Bewerbung etwa ist es daher unzulässig, den Dr. mit Ph.D. zu übersetzen . Und wie ist es mit der Anerkennung des Ph.D. in Deutschland? In sehr vielen Fällen ist es erlaubt, einen im Ausland erworbenen Ph.D. in Deutschland als Dr. zu führen. Welche dies sind, definiert ein Beschluss der Kultusministerkonferenz (KMK) .
Gibt es noch mehr Unterschiede? In den USA ist es üblicher als in Deutschland, dass ein Ph.D. bereits mit dem Abschluss eines Bachelorstudiums angestrebt werden kann. Das Programm umfasst in solchen Fällen häufig eine Kombination aus einem Master- und einem Ph.D.-Studium, das mit dem Abschluss Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) endet. In Deutschland ist diese sogenannte Fast-Track-Promotion herausragend guten Studierenden vorbehalten und somit selten.
Die Voraussetzungen wie auch die Inhalte des Ph.D.-Studiums können sich allerdings nicht nur in den einzelnen Fachgebieten, sondern auch von Programm zu Programm deutlich unterscheiden. Eine Vereinheitlichung gibt es also weder in den USA noch in Deutschland.
Hat der Ph.D. Vorteile gegenüber dem Doktortitel?
Der Ph.D. ist als Abschluss internationaler als der deutsche Doktortitel . Wer plant, in einem internationalen Umfeld oder beispielsweise im englischsprachigen Ausland zu arbeiten , ist unter Umständen mit dem Ph.D. besser beraten.
Auch wer eine Stelle in der Forschung anstrebt, verfügt mit dem Ph.D. eventuell über Vorteile. Denn der Aufbau des Ph.D.-Studiums beinhaltet einen starken allgemeinen Forschungsansatz, während der deutsche Doktortitel eher die persönlichen wissenschaftlichen Ziele verfolg t.
In der Wirtschaft sowie in bestimmten Fachbereichen der Medizin kann dagegen der klassische Doktortitel hilfreicher sein. Gerade in Deutschland hat der Dr. für manche Berufe noch einen hohen Stellenwert. Allerdings lässt sich das unter Umständen umgehen, da Inhaber eines Ph.D. in vielen Fällen auch den Doktortitel verwenden dürfen.
Wer beides zur Wahl hat, sollte jedoch nicht nur auf den Titel selbst, sondern vor allem auf die Ausrichtung des jeweiligen Programms achten . Die Qualität von Ph.D. und Doktortitel kann sich je nach Lehrstuhl unterscheiden. Angehende Promovend:innen sollten daher die spezifischen Inhalte genau prüfen, bevor sie sich für eines der angebotenen Programme entscheiden.
Wer sich für einen Ph.D. entscheidet, für den gilt es, entsprechende Promotionsmöglichkeiten zu finden. Auch in Deutschland werden immer mehr Ph.D.-Programme angeboten.
Ph.D.-Programme in Deutschland
Entsprechende Programme mit dem Ziel Ph.D. gibt es in vielen großen deutschen Städten, unter anderem hier:
- Graduate School Life Science Munich
- Graduate School of Quantitative Biosciences Munich
- Munich Business School
- Max Planck School of Photonics (verschiedene Standorte: München, Erlangen, Jena, Karlsruhe, Göttingen, Aachen, Paderborn, Hamburg)
- Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg
- Berlin School of Business and Innovation
- DIW Berlin – German Institute for Economic Research
- Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf (verschiedene Standorte: Düsseldorf, Köln, Jülich)
- Hector Fellow Academy (Karlsruhe)
- International Max Planck Research School on Cellular Biophysics (verschiedene Standorte: Frankfurt, Mainz)
- Max-Planck-Institut für Hirnforschung (Frankfurt)
- European Molecular Biology Laboratory (Heidelberg)
- Allensbach Hochschule (Konstanz)
- Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften Kempten
Für wen wird in Deutschland ein Ph.D. angeboten?
Die Zahl der Ph.D.-Programme in Deutschland steigt stetig an. Der klassische Doktortitel bekommt damit mehr und mehr Konkurrenz. Unter den Ph.D.-Programmen sind hierzulande bereits diverse Fachbereiche wie Naturwissenschaften oder auch Geisteswissenschaften vertreten. Absolvent:innen von Bachelor-, Master- und Magisterstudiengängen sowie Studienabgänger:innen mit vergleichbaren Abschlüssen finden passende Promotionsangebote unter anderen an Universitäten, privaten Hochschulen und Graduiertenschulen .
Unter den Studiengängen, in denen Graduierte den Ph.D. erwerben können, sind beispielsweise:
- Agrarwissenschaft
- Bildungsforschung
- Computerwissenschaften
- Elektrotechnik
- Maschinenbau
- Philosophie
- Politikwissenschaft
- Psychologie
- Public Management
- Volkswirtschaft
- Wirtschaftswissenschaften
Eine Übersicht zu diesen und weiteren Ph.D.-Studiengängen in Deutschland und weltweit bietet etwa das Netzwerk phdstudies.de .
Ph.D.-Abschluss in Deutschland: Ablauf und Dauer
Der genaue Ablauf der Promotionsprogramme ist individuell – ebenso wie deren dezidierte Inhalte. Meist wird zu Beginn ein Forschungsthema eingereicht, das in den Jahren des Studiums dann bearbeitet wird.
Viele Programme bieten ihren Studierenden folgende Möglichkeiten und Inhalte:
- Seminare zu fachlichen Methodologien
- ggf. internationale Module mit Partnerschulen
- Vorbereitung auf eine Laufbahn als Akademikerin
- Präsentationen
- Doktorandenworkshops
- Journal Clubs
- Zugang zu Netzwerken (national wie international)
- regelmäßige Kollegwochenenden
- mündliche Prüfung(en)
Die Dauer des Ph.D.-Promotionsstudiums, dessen Unterrichtssprache meist Englisch ist, beträgt in Deutschland – ähnlich wie in vielen anderen Ländern auch – häufig drei bis fünf Jahre . Je nach Bundesland, Einrichtung und Fachgebiet kann der für den Ph.D. angesetzte Zeitraum jedoch ebenso davon abweichen. Im Vergleich zum Doktortitel ist der Ph.D. damit häufig schneller zu erreichen , denn ein klassisches Doktorat dauert in Deutschland in der Regel vier bis sechs Jahre.
Die Voraussetzungen für einen Ph.D. können sehr unterschiedlich ausfallen. Viele Einrichtungen vergeben Plätze für Ph.D.-Programme in Deutschland lediglich an Studienabgängerinnen, die ihren Master-, Diplom- oder Magisterabschluss mindestens mit der Note „gut“ erworben haben, in einigen Fällen ist sogar ein „sehr guter“ Abschluss erforderlich.
Es gibt jedoch auch Ausnahmen. Unter bestimmten Voraussetzungen lassen Institutionen Absolvent:innen bereits mit einem Bachelorabschluss zu einem Ph.D.-Studium zu. Allerdings müssen diese in der Regel weitere Voraussetzungen erfüllen. Zum Beispiel können zusätzliches Engagement oder ein Abschluss mit besonderer Auszeichnung gefordert sein.
Die meisten Ph.D.-Studiengänge sind campusgebundene Vollzeitprogramme . Heißt: Es wird vor Ort studiert – und zwar als Fulltime-Job. Einige wenige Angebote können auch in Teilzeit absolviert werden, richten sich dann aber meist an leitende Angestellte oder Manager:innen, die Job und Weiterbildung sowie Forschungsarbeit oder Job und Familie gern miteinander verbinden möchten. Präsenztermine gibt es in der Regel trotzdem. Darüber hinaus werden diese Programme in erster Linie von privaten Hochschulen angeboten. Die Kosten für eine nebenberufliche Ph.D.-Promotion sind daher vergleichsweise hoch und können sich auf etwa 20.000 bis 30.000 Euro belaufen.
Wer für einen Ph.D.-Titel nicht extra umziehen möchte oder gern von zuhause arbeitet, hat auch die Möglichkeit, ein Onlinestudium zu absolvieren. Vorteil: Der Ph.D. kann auch an einer ausländischen Institution erworben werden – an einer Universität in London, in Vancouver oder in der Schweiz beispielsweise. In Deutschland werden gelegentlich Kombinationen aus Campus- und Onlineprogrammen angeboten, reine Ph.D.-Onlinestudiengänge finden sich jedoch nicht. Für wen also nur ein Ph.D.-Fernstudium infrage kommt, sollte sich international orientieren.
Weitere Ratgeber zum Thema Promotion

Ab wann und unter welchen Voraussetzungen dürfen Promovierte sich „Doktor“ nennen – und gibt es eine Pflicht, den Titel zu führen?

Sie sind aus dem Unialltag nicht wegzudenken: Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter und Mitarbeiterinnen unterstützen in Lehre, Forschung und Verwaltung.

Dr. phil., Ph.D. oder Dr. rer. nat: Doktortitel ist nicht gleich Doktortitel. Worin sich die akademischen Grade unterscheiden und die wichtigsten Titel im Überblick.

Obwohl viele Akademiker mit einer Beeinträchtigung leben, ist die Promotion mit Behinderung noch immer keine Selbstverständlichkeit. Vielfältige Unterstützungsangebote wollen hier Abhilfe schaffen.

What is a PhD?
- Types of Doctorates
- A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is the highest globally recognized postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award.
- PhDs are awarded to candidates who undertake original and extensive research in a particular field of study.
- Full time PhD programmes typically last three to four years, whilst part time PhD programmes typically last six to seven years.
- A PhD can lead to an academia teaching role or a career in research. A PhD can also equip you with skills suitable for a wide range of jobs unrelated to your research topic or academia.
Definition of a PhD – A Doctor of Philosophy (commonly abbreviated to PhD , Ph.D or a DPhil ) is a university research degree awarded from across a broad range of academic disciplines; in most countries, it is a terminal degree, i.e. the highest academic degree possible.
PhDs differ from undergraduate and master’s degrees in that PhDs are entirely research-based rather than involving taught modules (although doctoral training centres (DTCs) offer programmes that start with a year of lecture-based teaching to help develop your research skills prior to starting your project).
In most English-speaking countries, those that complete a PhD use the title “Doctor” (typically abbreviated to Dr) in front of their names and are referred to as such within academic and/or research settings. Those that work in fields outside of academia may decide not to use the formal doctor title but use post-nominal letters (e.g. John Smith PhD); it’s unusual though for someone to use both the Doctor title and post-nominal letters in their name.
PhD vs Doctorate
A PhD and a professional doctorate are both research-based terminal degrees.
However, where a PhD focuses on original research mostly around theoretical concepts, a professional doctorate focuses on examining existing knowledge to solve real-life, practical problems.
While there is much crossover between the two, a PhD is generally better suited for an individual to wants to advance the knowledge and understanding in their field, and a professional doctorate degree is better suited to a working professional who wants to better be able to apply knowledge and understanding to their field.
What Are the Entry Requirements for a PhD?
To be accepted on to a PhD programme, students usually need to hold at least a high ( 2:1 and above ) undergraduate degree that is related to the field of research that they want to pursue. A PhD candidate may also be expected to hold a Master’s degree , however, this does not mean you must have one, as it is still possible to enrol into a PhD without a Master’s .
Self-funded courses may sometimes be more relaxed in relation to entry requirements. It may be possible to be accepted onto a self-funded PhD programme with lower grades, though these students typically demonstrate their suitability for the role through professional work experience.
Whilst a distance learning project is possible , most PhD candidates will carry out their research over at least three years based at their university, with regular contact with two academic supervisors (primary and secondary). This is particularly the case for lab-based projects, however, some PhD projects require spending time on-site away from university (e.g. at a specialist research lab or at a collaborating institution abroad).
How Long Does a PhD Take?
Typically, full-time PhDs last 3-4 years and part-time PhDs last 6-7 years. However, at the discretion of the university, the thesis writing-up period can be extended by up to four years.
Although most doctoral programmes start in September or October, they are generally much more flexible than taught-courses and can start at any time of the year.
How Much Does a PhD Cost?
Tuition fees for UK and EU students vary between £3,000 and £6,000 per year, with the average tuition fee of £4,712 per year for 2023/24 programmes.
Tuition fees increase considerably for international students, varying between £16,000 to £25,000 per year, with an average tuition fee of £19,600 per year .
Nonetheless, most students will secure PhD funding in the form of studentships, scholarships and bursaries to help pay for these fees. These funding opportunities can either be partial, which cover tuition fees only, or full, which cover both tuition fees and living expenses.
UK national students can also apply for Doctoral Loans from Student Finance England if they are unable to secure funding.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
What Does a PhD Involve?
To be awarded a PhD, a doctoral student is required to produce a substantial body of work that adds new knowledge to their chosen field.
A PhD programme will typically involve four key stages:
Stage 1: Literature Review
The first year of a PhD involves attending regular meetings with your supervisors and carrying out a search on previously published work in your subject area. This search will be used to produce a literature review which should set the context of the project by explaining the foundation of what is currently known within the field of research, what recent developments have occurred, and where the gaps in knowledge are. In most cases, this will be an extension of your research proposal should you have produced one as part of your application. The literature review should conclude by outlining the overarching aims and objectives of the research project. This stage of setting achievable goals which are original and contribute to the field of research is an essential first step in a successful PhD.
The supervisor is the main point of contact through the duration of a PhD – but remember: they are there to mentor, not to teach, or do it for you . It will be your responsibility to plan, execute and monitor your own work as well as to identify gaps in your own knowledge and address them.
Stage 2: Research
The second year (and prehapse some of your third year) is when you work on your research. Having identified novel research questions from your review of the literature, this is where you collect your data to help answer these questions. How you do this will depend on the nature of your doctoral research: for example, you may design and run experiments in a lab alongside other PhD students or visit excavation sites in remote regions of the world. You should check in regularly with your supervisors to update them and run any ideas or issues past them.
Have the structure and chapters of your thesis in mind as you develop and tackle your research questions. Working with a view of publishing your work will be very valuable later on.
Stage 3: Write up of Thesis
The next key stage of a PhD is writing a doctoral thesis , which typically takes from anywhere between three months to one year. A thesis is a substantial body of work that describes the work and outcomes of the research over the previous two to three years. It should tell a detailed story of the PhD project – focusing on:
- The motivations for the research questions identified from the literature review.
- The methodologies used, results obtained, and a comprehensive analysis and discussion of the findings.
- A detailed discussion of the key findings with an emphasis on the original contributions made to your field of research and how this has been impactful.
There is no universal rule for the length of a PhD thesis, but general guidelines set the word count between 80,000 to 100,000 words.
For your thesis to be successful, it needs to adequately defend your argument and provide a unique or increased insight into your field that was not previously available.
Stage 4: Attending the Viva
A viva voce , most commonly referred to as just a ‘ viva ‘, is an interview-style examination where the PhD student is required to engage in a critical appraisal of their work and defend their thesis against at least two examiners. The examiners will ask questions to check the PhD student has an in-depth understanding of the ideas and theories proposed in their thesis, and whether they have developed the research skills that would be expected of them.
The viva is one of the final steps in achieving a PhD, and typically lasts at least two hours, but this duration can vary depending on the examiners, the university and the PhD project itself.
Once you have done the viva – you’re on the home stretch. You will typically be asked to make some amendments to your thesis based on the examiner’s feedback. You are then ready to submit your final thesis for either:
- PhD – If you pass the requirements you will be awarded a PhD degree (most common outcome),
- MPhil – If you failed to meet requirements for a PhD, you may be downgraded to an MPhil degree (uncommon outcome),
- Fail – No award is given, typically for cases of plagiarism (extremely uncommon outcome).
What Is It Like to Undertake a PhD?
We’re often asked what it is like to undertake a PhD study. Unfortunately, this isn’t a simple answer to this question as every research project is different.
To help give insight into the life of a PhD student, we’ve interviewed PhD students at various stages of their programmes and put together a series of PhD Student Interviews . Check out the link to find out what a PhD is like and what advice they have to offer you.
What Are the Benefits of A PhD?
A PhD is the highest globally recognised postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award. The degree, which is awarded to candidates who demonstrate original and independent research in a particular field of study, is not only invaluable in itself, but sets you up with invaluable skills and traits.
Career Opportunities
First, a PhD prepares you for a career in academia if you wish to continue in this area. This takes form as a career in the Higher Education sector, typically as a lecturer working their way to becoming a professor leading research on the subject you’ve studied and trained in.
Second, a PhD also enables the opportunity for landing a job in a research & development role outside of the academic environment. Examples of this include laboratory work for a private or third sector company, a governmental role and research for commercial and industrial applications.
Transferable Skills
Finally, in possessing a PhD degree, you can show to employers that you have vital skills that make you an asset to any company. Three examples of the transferable skills that you gain through a PhD are effective communication, time management, and report writing.
- Communication – presenting your work in written and oral forms using journal papers and podium presentations, shows your ability to share complex ideas effectively and to those with less background knowledge than you. Communication is key in the professional environment, regardless of the job.
- Time management – The ability to prioritise and organise tasks is a tremendous asset in the professional industry. A PhD holder can use their qualification to demonstrate that they are able to manage their time, arrange and follow a plan, and stick to deadlines.
- Report writing – Condensing three years of work into a thesis demonstrates your ability to filter through massive amounts of information, identify the key points, and get these points across to the reader. The ability to ‘cut out the waffle’ or ‘get to the point’ is a huge asset in the professional industry.
Aside from the above, you also get to refer to yourself as a Doctor and add fancy initials after your name!
What Can I Do After a PhD?
One of the most desirable postdoctoral fields is working within independent Research and Development (R&D) labs and new emerging companies. Both industries, especially R&D labs, have dedicated groups of PhD graduates who lead research activities, design new products and take part in crucial strategic meetings. Not only is this a stimulating line of work, but the average salaries in R&D labs and emerging start-ups are lucrative. In comparison, an undergraduate with five years of experience within their given field will, on average, likely earn less than a new PhD graduate taking on a R&D position.
It’s a common misunderstanding that PhDs only opens the door for an academic career such as university lecturers and training providers. Although obtaining a PhD opens these doors, the opportunities extend far beyond educational roles. In fact, recent data from the UK’s Higher Education Statistics Agency (HESA) indicates only 23% of PhD graduates take a position in educational roles . This low percentage is primarily because PhD graduates have a wide range of skills that make them suitable for a broad spectrum of roles. This is being seen first hand by the increasing number of PhD graduates who are entering alternative roles such as research, writing, law and investment banking.
How Do I Find a PhD?
We appreciate that finding a PhD programme to undertake can be a relatively daunting process. According to Higher Education Student Statistics , over 22,000 PhDs were awarded in 2016/17 within the United Kingdom alone. Clearly there are a huge number of PhD programmes available. This can sometimes be confusing for prospective doctorates, particularly when different programmes are advertised in different places. Often, it is difficult to know where to look or where to even start. We’ve put together a list of useful sources to find the latest PhD programmes:
- A great place to start is with our comprehensive and up-to-date database of available PhD positions .
- Assuming you are still at university, speak to an existing PhD supervisor within your department.
- Attend as many postgraduate open days as you can. Whilst there, speak to current PhD students and career advisors to get an awareness of what PhDs are on offer.
- Visit the postgraduate section of university websites and the PhD Research Council section of the UKRI website.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Home »
- Advice »
- Studying For A PhD
find your perfect postgrad program Search our Database of 30,000 Courses
What is a phd.
A PhD is the highest postgraduate qualification level that can be awarded in academic study. This is usually completed over three to four years of full-time study, and involves research into an original contribution in your chosen field.
PhD is an acronym that stands for Doctor of Philosophy. The name for PhD comes from the Latin term “Philosophiae Doctor”, which roughly translates to “Lover of wisdom”.
Whether you’re finishing up from an undergraduate degree, on a masters course or even just looking to get back into education, you’ll have seen people talking about getting a PhD .
Most people know vaguely what a PhD is – it’s a university course that means you can call yourself ‘Doctor’ without having to do medicine, right? Whilst that is surprisingly close to the truth, we’re here to answer the oft-asked question of ‘what is a PhD?’.
This guide covers everything you need to know about a PhD.
What does a PhD involve?
A PhD will typically take three years to complete. If taken part time, then it will be separated into three different stages:
Year 1: This will involve you speaking with your advisor about your research ideas, finishing your research proposal and beginning to put deadlines in place for your research. You’ll also complete your literature review in this stage. During this, you’ll review the existing research done on the topic that you’re planning to research to help you determine the gaps in the research that you can target
Year 2: During this stage, you’ll begin to conduct your research to gather data. You’ll document this whole process for your thesis and begin to attend conferences where you will have the opportunity to present your current research to other professionals and researchers in the field. You can take this further and take steps to educate the public on the benefits of your research.
Year 3: The final stage of a PhD involves using the data you’ve collected and the documentation of your research to write your thesis. You may still be conducting research at this point, and that’s OK. Once you’ve finished your thesis, you’ll justify your research and decisions in a viva .
How long is a PhD?
A typical PhD will take three to four years to complete when studying full time. Studying part time can take up to six years. The good news is that the thesis can be extended by up to four years. This means that if you haven’t gotten anywhere near finishing your research by the end of the second year, you can apply to extend your thesis and continue your research for up to four more years. Many PhD students will complete their thesis in the 4th year.
How is a PhD different from other degrees?

To start with, describing a PhD as a university course can be a bit misleading. Whilst it is a course offered by a university, it’s incredibly different to most courses. Unlike the undergraduate level, you won’t be covering your subject broadly you’ll be focused on one very particular area. Whilst a masters degree, especially a research one, may be focused, it won’t be nearly as focused as a PhD.
That said – don’t expect this focused level of research to necessarily be groundbreaking! Though part of doing a PhD is the intent to produce original research, it’s also primarily there to train your research skills and to prove yourself as a capable researcher.
A PhD is research focused
One of the main differences between PhDs and other types of postgraduate degree is that PhDs are heavily research based. PhDs involve a lot of independent research time, where you'll study your topic in detail using academic resources – such as the university's online library and online materials. This format is different to taught postgraduate degrees, which involve a lot more taught aspects such as lectures and seminars.
Do you need a masters to study a PhD?
In order to study a PhD, you’ll need to have a masters degree and a bachelors degree with a 2:1 or higher. Though self-funded students and students with professional experience in the field may be admitted with lower grades
Some students may begin with a MPhil (Masters of philosophy) or a Mres ( Master of research) and upgrade to a PhD by the end of their studies.
Where can I study a PhD?
Most universities offer PhD programs across a variety of disciplines. It is possible to study a PhD at almost any university and in almost any subject. Since a PhD is an independent research-based program, there is a lot of flexibility in regard to what you’ll study.
PhD students often choose their own study topics and carry out independent research into that topic. This makes it possible to study your intended PhD at almost any university.
Although, it is important to check which specific subject areas the university specialises in. For instance, if a university specialises in linguistics, then it would be a good idea to complete a linguistics PhD at that university as opposed to one that specialises in another subject.
It can be difficult to find the perfect course at the right university. That’s why we’ve put together advice on how to find a PhD .
It’s important to remember that a PhD is different from a typical university course. Rather than going to lectures, you’ll be conducting independent research, and so the application process will be quite different. Learn how to apply for a PhD with our expert guide.
A PhD means attending ‘optional’ lectures and conferences
PhDs do involve some aspects of taught study, including lectures and conferences, although these are often optional and take place less often than on lower level courses.
Now of course, the university doesn’t just accept you, your project and tell you to have fun. You’ll work with a supervisor, and there will be conferences, lectures, and other such things that you can attend. Unlike lower level courses, however, although you won’t necessarily be examined on these things that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t go! Conferences are a great way to meet people, get your name out and network . For any career, but especially one in academia, networking is well worth it.
A PhD is a high standard qualification
But what does having a PhD show, other than the fact you spent three to four years working on research and can now call yourself Dr [Your surname here]?
A PhD is a globally recognised, high standard qualification. This means that if you choose to move elsewhere in the world, your PhD will be recognised as a credible postgraduate qualification.
In addition, a PhD can open up a whole world of new job opportunities! This includes academic roles , such as postdoctoral research posts, or even possibly fellowships.
Regardless of which career path you choose to take, a PhD is regarded as the highest level postgraduate qualification – reflecting your impressive work ethic, knowledge, and workplace skills.
How to get a PhD
Getting a PhD is not easy by any means. But, if it’s something you truly want to do, it’s well worth it. So let’s take a look at just how to get a PhD!
Choose your research area
Before getting started with your PhD, you want to make sure you know what area you’d like to do it in. Don’t just pick something on a whim – this is something you’re going to be studying for the next four years of your life, and something that, once you finished your PhD, you’ll have your name attached to. So, for arts and humanities students, find an area of your subject that fascinates you enough that you’ll want to spend the next few years writing about it. For scientists, find an area you’d be happy to be working on in a team, and wouldn’t mind moving into as a career!
Find a good supervisor
Once you’ve selected your topic, it’s time to start looking for a supervisor . Depending on what you’re currently doing, asking tutors for contacts or recommendations can be well worthwhile, but if you can’t do this, check out what research your potential supervisor has done.
In addition, try and arrange an in-person meeting – or at least, a phone conversation. Email can make communication difficult and given this is the person you’ll be working under for the foreseeable future, you want to ensure you get on.
Then, assuming you’re accepted and have appropriate funding, you’ll be considered a probationary PhD student . At the end of your first year, you’ll be expected to prove you’re capable of the full course, so you’ll be tested in the form of writing a report. Once you pass this, you’re good to go!
Your next few years will be spent attending conferences, working on the research and your thesis. Your thesis will talk about what you’ve spent your time doing, how you dealt with any difficulties that arose, and generally show what your contribution to your subject is! Once that’s out the way, you get the fun job of having a viva – that is, talking about your thesis to a bunch of academics.
Pass the viva? Then you’ve succeeded.
So that’s how to get a PhD!
UK Research Councils
There are a selection of UK Research Councils, each of whom are part of the UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) organisation. Collectively, these UK research councils provide an average of £380 million in PhD studentship funding every year – acting as the largest PhD funding body in the UK.
Here’s an overview of UK research councils:
- Science and Technology Facilities Council
- Arts and Humanities Research Council
- Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council
- Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council
- Economic and Social Research Council
- Medical Research Council
- Natural Environment Research Council
Related articles
Dos And Don'ts Of A PhD Interview
Are You Ready For A PhD?
How To Get The Most From Your PhD Supervisor
Common PhD Myths
Alphabet Of PhD Study
What Is A Postgraduate Degree? A Definition
Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries

Exclusive bursaries Open day alerts Funding advice Application tips Latest PG news
Sign up now!

Take 2 minutes to sign up to PGS student services and reap the benefits…
- The chance to apply for one of our 5 PGS Bursaries worth £2,000 each
- Fantastic scholarship updates
- Latest PG news sent directly to you.
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
What Is a PhD?
A PhD is often the highest possible academic degree you can get in a subject. Learn more about whether earning a PhD could benefit your career.
![phd student bedeutung [Featured image] Two PhD students in caps and gowns celebrate their new degrees on a video call.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/6s5qn9Bv4nySJetkmsaOGj/baea54b21625b8601d4debf8589775cb/GettyImages-1307766599.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
A Doctor of Philosophy, often known as a PhD, is a terminal degree —or the highest possible academic degree you can earn in a subject. While PhD programs (or doctorate programs) are often structured to take between four and five years , some graduate students may take longer as they balance the responsibilities of coursework, original research, and other degree requirements with raising families or working full time.
With a PhD, you may find opportunities to work as a university professor, a researcher in a commercial or government laboratory, a consultant, or a subject matter expert (SME). If you have the intellectual curiosity and dedication, earning a PhD can be a rewarding experience. In this article, we’ll go over what it takes to earn a PhD, the requirements to apply for a PhD program, and other factors worth considering.
Learn more: What Does ‘PhD’ Stand For?
PhD: Key facts
Generally, students begin their PhD after earning a bachelor’s degree and a master’s degree . However, some doctoral programs may offer you the chance to earn your master’s while pursuing your PhD, so that may not be an admissions requirement.
What can you get a PhD in?
It’s possible to earn your PhD in a number of academic disciplines, including the natural sciences , humanities , arts, and social sciences . The 2021 Survey of Earned Doctorates, from the National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics, offers a numerical breakdown of actual degrees earned in broad academic fields [ 1 ]:
Engineering: 10,240
Biological and biomedical sciences: 8,149
Social sciences: 4,878
Physical sciences: 4,693
Psychology: 3,797
Computer and information sciences: 2,361
Health sciences: 2,331
Mathematics and statistics: 2,012
Agricultural sciences and natural resources: 1,334
Geosciences, atmospheric sciences, and ocean sciences: 1,064
Education: 4,252
Humanities and arts: 4,137
Business: 1,392
Other fields: 1,610
Depending on the university you attend, you may find that the broad academic fields above break down into more specific disciplines. For example, within a physical science department, you might get a PhD in physics or chemistry. Within an engineering department, you might get a PhD in electrical or mechanical engineering. Philosophy, theology, history, or English might fall within a humanities department, while economics or social work could fall within a social sciences department. Marketing could be a specific PhD major within a business department.
In terms of your PhD coursework and research, you will likely be expected to concentrate in some area of your larger subject. For example, PhDs in biology may focus on biochemistry or biostatistics, whereas a PhD in English may concentrate on twentieth-century American literature.
Requirements to get a PhD
PhD programs typically require at least two years of advanced coursework, as well as comprehensive exams, and the successful completion of a dissertation. Let’s break that down on a year-by-year basis:
Years 1 and 2: Take classes to develop advanced knowledge in your subject area.
Year 3: Study for and successfully pass your comprehensive exams.
Years 4 and 5: Research, write, and defend your dissertation.
Once you have successfully passed your comprehensive exams, you’re typically considered “All But Dissertation” or ABD, which signals that you’ve finished everything in your doctoral program except your dissertation.
Research supervisor
PhD students often choose a faculty member who specializes in their area of interest to serve as the research supervisor. It can help to identify professors or programs that will support your research endeavors before applying, so you can establish a relationship with your potential research advisor early.
The average cost of a PhD program in the US is $106,860, though that figure can differ based on the type of institution you attend and what you study [ 2 ].
Reasons to get a PhD
Earning your PhD can be an immensely rewarding experience, but the degree can be a big commitment, requiring significant time, money, and work.
Here are some more reasons you may want to pursue a PhD:
Become a subject matter expert in a particular field.
Conduct the research you are passionate about.
Develop transferable skills that can help in your professional life.
Make a difference in the world with new research.
Make connections with scholars in your academic community.
Open up career avenues in academic and research work.
Completing a PhD can reveal to employers that you possess a wide range of competencies that are valued in both academic and non-academic settings.
PhD salaries
PhD holders earn a median weekly income of $1,909 compared to master’s degree holders, who earn a median weekly income of $1,574, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) [ 3 ]. They may also experience lower percentages of unemployment. The unemployment rate for PhD graduates is 1.5 percent compared to master’s degree holders at 2.6 percent [ 3 ].
Requirements to apply to a PhD program
PhD programs expect you to meet several requirements before enrolling. Here are some examples of common requirements:
Have an undergraduate degree, usually with at least a 3.0 overall GPA.
Have a master's degree, though some programs may not require it.
Take the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) and achieve a minimum score.
Submit a sample of your academic writing.
Submit your CV .
Provide letters of recommendation , which should ideally come from academic faculty members who can speak to your research or intellectual abilities.
Requirements differ by program and school, so take time to become familiar with the entry requirements of universities where you’re interested in applying. Admissions staff or departmental staff should be able to give you specific information about their admissions requirements.
If a program is interested in you, based on your application, you may have to complete an interview. The university representatives that interview you will look at your motivation, how prepared you are, and how suitable you are for acceptance into the doctoral degree program.
PhD vs. other terminal degrees
Terminal degrees are the highest degree available in a field of study. While the PhD is the highest academic degree you can earn in a field of study, a Juris Doctor (JD) is the highest degree you can earn in law, and a professional degree , such as a Doctor of Medicine (MD) or a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) , is the highest degree you can earn in these medical professions.
Learn more: What is a Terminal Degree and Do You Need One?
Professional doctorates are a different category of doctorate degree. They are usually intended for professionals already working in a field who want to pursue advanced training in their area. The main difference between a professional doctorate and an academic doctorate has to do with subject matter and research. While PhDs are interested in conducting new research, professional degree students take existing models and knowledge and apply them to solve problems. Professional doctorates are also designed to prepare learners for careers in a certain industry rather than academia.
Examples of professional doctorates include:
DBA (Doctor of Business Administration)
DNP (Doctor of Nursing Practice)
EdD (Doctor of Education)
DPH (Doctor of Public Health)
Is someone with a PhD a doctor?
You can use the salutation "Dr" to address people who hold doctorates, including PhDs and other professional degrees. The word "doctor" comes from the Latin word for "teacher," and PhDs are often professors at universities. While it has become more common to refer to medical doctors as “Dr,” some professors use the honorific when addressing students and in professional settings.

Explore career and education options with Coursera
Learning online can be a great way to explore a field you're interested in, discover career paths , and even decide whether a PhD is for you. Consider one of Coursera's Professional Certificates , available from Google, Meta, IBM, Salesforce, and other industry leaders, and gain job-ready skills that employers are looking for.
Ready to get a Master's degree ? Coursera partners with universities to offer online Master's degrees in a range of fields like data science, public health, and business.
Article sources
NCSES. " 2021 Survey of Earned Doctorates , https://ncses.nsf.gov/pubs/nsf23300/report/field-of-doctorate." Accessed August 1, 2023.
Education Data Initiative. “Average Cost of a Doctorate Degree , https://educationdata.org/average-cost-of-a-doctorate-degree.” Accessed August 1, 2023.
US Bureau of Labor Statistics. “Earnings and Unemployment rates by educational attainment, 2021 , https://www.bls.gov/emp/chart-unemployment-earnings-education.htm." Accessed August 1, 2023.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.

- Majors & Careers
- Online Grad School
- Preparing For Grad School
- Student Life
PhD Candidate vs Student: What’s the Difference?

Many people use the terms “PhD student” and “PhD candidate” interchangeably. However, these terms actually mean something quite different, including a different status level at universities.
We’re here to define the differences between a PhD candidate vs student, as well as other essential information, before you continue your educational journey.
Table of Contents
What I s a PhD student?
A doctoral student is anyone who is enrolled in a doctorate degree, also referred to as a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) program. PhD students are typically required to complete a certain number of course credits and sit qualifying exams. Next, they can move on to conduct research and present it in the form of a dissertation.
A PhD is centered around self-directed research and possibly teaching/running tutorials, but they typically also involve a substantial amount of coursework and require attending classes, either online or in person.
Unlike candidates, PhD students are in the process of completing the required coursework for the degree. They haven’t passed the relevant qualifying exams yet.
What Is a PhD Candidate?
A PhD candidate has completed the required coursework and passed the qualifying exams for their doctorate program. They are currently working on their dissertation.
Most PhD students need to go through an application process and show they meet certain requirements such as a relevant master’s degree . To become a PhD candidate, doctoral students need to pass an internal application process, typically involving a set of exams.
This stage involves significant research usually in innovative areas and incorporating this into a dissertation (this stage is sometimes referred to as “all but dissertation” [ABD]), as they’ve completed all other aspects of the program and satisfied these requirements. To complete their doctoral journey, a PhD candidate must defend their dissertation. Once they’ve successfully done this, they will be awarded their degree and move from PhD candidate to doctor of their chosen field.
PhD Candidate vs Student: 6 Key Differences

There are a number of key differences between a PhD student vs PhD candidate, from their status to the structure and nature of study.
Note: Some universities have recently started adopting hybrid approaches (where there is no clear difference between PhD students and PhD candidates). These programs don’t involve any qualifying exams and students typically begin the dissertation as part of their coursework. Most schools, however, continue with the traditional distinction between a PhD candidate and PhD student.
1. Program Stage
A PhD student could be at any stage of the doctoral program . Coursework still needs to be completed and qualifying exams must be passed. Students may be in the initial stage of the program or about to complete the coursework (before beginning their research).
On the other hand, a PhD candidate has completed all coursework and has at least started their research. They may have completed their dissertation and are preparing to defend it.
2. Research Progress
A PhD student may not have selected their research topic or settled on a particular research question. A candidate’s research is in progress and they should already have a clear research question.
3. Relationship with Advisors
A PhD student may not yet have an advisor. A candidate has an established working relationship with their advisor and works closely with them to complete their research and dissertation.
4. Level of Support
Although they work closely with an advisor, a PhD candidate is generally expected to work more independently than a student enrolled in a doctoral student. Once candidates reach this stage of their doctorate, they typically won’t receive as much direction or supervision.
5. Flexibility and Structure
Understandably, PhD candidates have more freedom and flexibility in their work. Most candidates choose their area of research, as well as the methods used to conduct their work. As part of their coursework, PhD students usually have to work within a set structure (e.g., completing core subjects, meeting deadlines).
Being a PhD candidate comes with a certain degree of status. If they’ve demonstrated a degree of expertise through completing qualifying exams, candidates can put the letters PhD(c) after their name.
Tips for PhD Candidates

A PhD is an advanced degree designed to demonstrate expertise in a given field, as well as high-level skills and abilities in various areas (including research and writing). As such, earning a doctorate can be a challenging process.
The following tips for doctoral candidates will help you put your best foot forward and set yourself up for success.
Stay Organized
Because PhD candidates have to balance many competing priorities, organization is essential. Using organizational tools such as calendars, note-taking apps , and project management software can help you keep track of deadlines and meet your targets.
Focus on Your Research
PhD candidates likely have busy schedules with plenty of demands (such as teaching commitments and crafting a dissertation). As it’s the backbone of any doctoral program, be sure to prioritize this part of your work and monitor progress to stay on track.
Actively Seek Out Feedback
Because PhD candidates often work independently, there’s a risk of feeling isolated. Ask your advisors, mentors, and fellow candidates for feedback and advice. This will help ensure that you’re considering all aspects of your research question and multiple solutions, rather than focusing too intensely on a single area.
Take Advantage of Networking Opportunities
Networking is one of the biggest benefits for PhD candidates, so take full advantage of these events. Use this time to build a strong network of professors, advisors, fellow candidates, and other professionals you meet at conferences and events.
Take Care of Yourself
A PhD program can be taxing, and it’s easy for your mental and physical health to take a backseat. Make sure you exercise, eat well, and get enough sleep . Remember: Resting and recharging is crucial for working on your dissertation.
How Long Is a Typical PhD Candidacy?

Most PhD students require 1-2 years to complete their coursework and pass their qualifying exams. However, the length of a PhD candidacy is much more open. In most cases, programs take between two and five years, depending on:
- the complexity of the field of research
- the candidate’s other commitments, such as teaching load
- other abilities, such as a candidate’s level of organization.
Once a PhD candidate has completed their dissertation, they have to defend it successfully before a panel of faculty members before they can earn their doctorate degree. This process of defending a PhD dissertation can take several months.
Some universities specify a maximum length for PhD candidacy duration. For example, Carnegie Mellon University limits this to six years .
Benefits of Being a PhD Candidate
Being a PhD candidate can be rewarding for several reasons:
1. Research Opportunities
You’ll be exposed to vast research opportunities in your field. You may contribute to valuable discoveries while developing advanced knowledge and skills.
2. Networking
Through your PhD candidacy, you’ll also be in a great position to build gain a stronger network of fellow professionals.
3. Critical Thinking
A PhD candidacy can help you develop high intellectual independence and critical thinking skills.
4. Career Opportunitie s
A PhD is an advanced degree that allows you to build a rewarding career in the academic, government, and private sectors. PhD-holders can also expect to earn more than other graduates and are most likely to find a job.
5. Salaries
According to Northeastern University , professionals with a doctorate degree earn an average annual salary of $99,290 on average (and much more for the highest-paid PhDs ) and have a 1.5% unemployment rate. For master’s degree holders, the average annual salary is $81,867 average annual salary and a 2.6% unemployment rate.
6. Personal Fulfillment
Being a PhD candidate can help you pursue your passions. This advanced qualification will allow you to become a specialist in your chosen field, allowing you to hone in on the exact subject thatl fulfills you the most.
Qualifying Exams to Become a PhD Candidate

While requirements vary by program, to become a PhD candidate, most students will need to pass a set of exams. These will test students’ knowledge in the field, measure their research skills, and ensure they’re ready to start their dissertation research.
Traditionally, qualifying exams for PhD candidates involved a written test and an oral exam. These will cover a range of topics related to your field of study, with the oral component designed to demonstrate your level of understanding.
Some universities have recently started to issue doctoral students with a set of questions and have them submit the answers within a set timeframe (usually around two weeks). Other schools ask prospective doctoral candidates to submit a dissertation proposal instead of an exam.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a phd candidate be called a doctor.
In most cases, a doctoral candidate cannot be called a doctor until after they successfully defend their dissertation and receive their doctorate.
Can I Put ‘PhD Candidate’ after My Name?
Once you’ve passed qualifying exams and embarked on dissertation research, you’re technically entitled to put “PhD candidate” or “PhD (c)” after your name. However, this is uncommon and not always recommended. It is generally more acceptable to mention that you are pursuing a doctorate (along with the field of research and university) or that you expect to complete your PhD in a certain year (on your CV and online profiles).
How Long Can You Be a PhD Candidate?
There isn’t a set length of time that a person can be a PhD candidate. The length of candidacy depends on a range of factors, including the subject of research and program requirements. Most PhD candidates complete this phase in around 3-5 years (where some university programs have set limits).
Do PhD Students Take Classes?
Yes, most PhD students must take classes and complete coursework as part of the first 1-2 years of their doctorate program. Once they’ve completed this coursework and passed qualifying exams, they move on to work on their research dissertation. At this stage, they’ll be considered a PhD candidate.
Key Takeaways
Now that you know the differences between PhD candidates vs. students, you’ve got a deeper understanding of how to obtain a doctorate. However you slice it, both will help you build your knowledge and skills to become an expert in your field.
However the program is structured, a PhD is a highly valuable degree that allows you to become a high-level professional and build a successful career.
If you know a PhD candidate who’s celebrating their accomplishments soon? Take a look at this guide to the best PhD graduation gifts .
- 10 Best PhD Programs in Pennsylvania
- Top 10 Best PhD in Cybersecurity Online Programs
- 10 Top PhD Programs in Chemistry
- The Top 10 Easiest PhDs: Tuition, Duration, and Financial Aid
- Top 10 Fully Funded PhD Programs and Universities
- Top 10 Best PhD in Medicine Programs

Lisa Marlin
Lisa is a full-time writer specializing in career advice, further education, and personal development. She works from all over the world, and when not writing you'll find her hiking, practicing yoga, or enjoying a glass of Malbec.
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ ACBSP Vs AACSB: Which Business Program Accreditations is Better?
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ BA vs BS: What You Need to Know [2024 Guide]
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ The 19 Best MBA Scholarships to Apply for [2024-2025]
- Lisa Marlin https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/lisa-marlin/ 25 Best Gifts for Law Students for 2024
Should You Take Work Advice From TikTok?
Today’s graduates are in a “perkcession” – here’s what that means, related posts.

- Is a Master’s Degree Worth It? [2024 Guide]
![phd student bedeutung Graduate Certificate vs Degree: What’s the Difference? [2024 Guide]](https://blog.thegradcafe.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/GradCafe-Featured-Images-4-350x250.png)
- Graduate Certificate vs Degree: What’s the Difference? [2024 Guide]

- What is a Good GRE Score?

BA vs BS: What You Need to Know [2024 Guide]

Harvard GPA Requirements: What GPA Do You Need to Get In?

Dissertation vs Thesis: Your 2024 Guide

Today's Graduates Are In A "Perkcession" - Here's What That Means
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
- 73% of job seekers believe a degree is needed for a well-paying role–but is it?
- ACBSP Vs AACSB: Which Business Program Accreditations is Better?

© 2024 TheGradCafe.com All rights reserved
- Partner With Us
- Results Search
- Submit Your Results
- Write For Us
- International website
- Find courses
- Find research
- Find organisation

Doctoral studies
Doctoral studies are an important part of the University’s mission and responsibility and, as a doctoral student, you will be making important contributions to research at the University of Gothenburg. Doctoral studies allow you to develop a deeper understanding of a scientific field of study and are provided free of charge in Sweden.
Doctoral studies comprise of 240 credits, equivalent to four years of full-time studies, and leads to a Degree of Doctor. It is also possible to finish your studies with a Degree of Licentiate (120 credits) after two years of full-time studies. Doctoral studies are divided into two parts: doctoral courses and an individual research project. The structure of your doctoral studies depends on the general syllabus for the subject you are admitted to and by your individual study plan that you establish together with your supervisor and your doctoral examiner.
How to apply to doctoral studies

Doctoral student at the University of Gothenburg
Study support for students with disabilities.
Doctoral students with documented permanent disabilities are eligible for different forms of study support. Examples of this are note-taking support, adapted course literature, adjusted assessments, mentoring, and software that can make reading and writing easier.

Doctoral studies at the faculties
- The Faculty of Science
- School of Business, Economics and Law
- Faculty of Humanities
- The Artistic Faculty
- The Sahlgrenska Academy
- Faculty of Social Science
- Faculty of Education

Welcome to the University of Gothenburg
Cookie Consent
To improve the website, the DAAD and third parties set cookies and process usage data . In doing so, the DAAD and third parties transfer usage data to third countries in which there is no level of data protection comparable to that under EU law. By clicking the "Accept all" button, you consent to this processing. You can also find selection options and explanations of these cookies and processing at the end of this page under "Cookies". There you can withdraw consent at any time with effect for the future.
- Privacy Policy
Jump to content

84 PhD programmes
- Standard sorting (Publication)
- Similarity to search term
- Promotion (A-Z)
- Promotion (Z-A)
- Institution (A-Z)
- Institution (Z-A)
- Application deadline (closest first)
- Beginning (closest first)
Technische Universität Dresden School of Embedded Composite AI (SECAI) Research Associate / PhD Student (m/f/x)
- Application deadline: 31.05.2024
- Working language: English
- Beginning: 01.09.2024
- Required degree: Diplom, Master
Last changed: 09.04.2024 (Published: 09.04.2024)
more More about Research Associate / PhD Student (m/f/x) - Technische Universität Dresden School of Embedded Composite AI (SECAI)
Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry International Max Planck Research School for Translational Psychiatry Fully funded PhD positions in Psychiatric, Translational Research and Basic Neuroscience
- Application deadline: 31.10.2024
- Beginning: 01.06.2025
- Required degree: Master
more More about Fully funded PhD positions in Psychiatric, Translational Research and Basic Neuroscience - Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry International Max Planck Research School for Translational Psychiatry
German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) DKFZ International PhD Program PhD Positions in Cancer Research at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ)
- Application deadline: 15.05.2024
more More about PhD Positions in Cancer Research at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) - German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) DKFZ International PhD Program
Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf Institute of Radiopharmaceutical Cancer Research PhD Student (f/m/d) Pre-clinical development and validation of Adapter-RevCAR‐T-cell-system for immunotherapy of melanoma
- Application deadline: 16.04.2024
- Working language: English, German
- Beginning: 01.06.2024
more More about PhD Student (f/m/d) Pre-clinical development and validation of Adapter-RevCAR‐T-cell-system for immunotherapy of melanoma - Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf Institute of Radiopharmaceutical Cancer Research
Technische Universität Dresden Faculty of Environmental Sciences, Department of Forest Sciences, Institute of Forest Utilization and Forest Technology, Chair of Forest Utilization Research Associate / PhD Student (m/f/x)
- Application deadline: 30.04.2024
- Working language: German, English
- Beginning: 01.07.2024
more More about Research Associate / PhD Student (m/f/x) - Technische Universität Dresden Faculty of Environmental Sciences, Department of Forest Sciences, Institute of Forest Utilization and Forest Technology, Chair of Forest Utilization
Georg-August-Universität Göttingen RTG 2756 CYTAC 12 PhD Positions at the RTG 2756 “Cytoskeletal elements of active matter - CYTAC"
- Application deadline: 20.05.2024
- Beginning: 01.01.2025
Last changed: 05.04.2024 (Published: 05.04.2024)
more More about 12 PhD Positions at the RTG 2756 “Cytoskeletal elements of active matter - CYTAC" - Georg-August-Universität Göttingen RTG 2756 CYTAC
European XFEL GmbH c/o Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf PhD Student (f/m/d) high energy density physics with focus on XFEL applications
- Application deadline: 18.04.2024
- Required degree: Master, Diplom
more More about PhD Student (f/m/d) high energy density physics with focus on XFEL applications - European XFEL GmbH c/o Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf
Leipzig University Research Training Group 2721: Hydrogen Isotopes, ¹²³H 14 Doctoral researchers (d/f/m) in chemistry or physics for RTG 2721: Hydrogen Isotopes, ¹·²·³H (67% E13 TV-L)
- Beginning: 01.10.2024
Last changed: 03.04.2024 (Published: 03.04.2024)
more More about 14 Doctoral researchers (d/f/m) in chemistry or physics for RTG 2721: Hydrogen Isotopes, ¹·²·³H (67% E13 TV-L) - Leipzig University Research Training Group 2721: Hydrogen Isotopes, ¹²³H
Universität des Saarlandes Biosciences (Naturwissenschaftlich-Technische Fakultät) Academic research assistants (m/f/x)
- Beginning: as soon as possible
- Saarbrücken
more More about Academic research assistants (m/f/x) - Universität des Saarlandes Biosciences (Naturwissenschaftlich-Technische Fakultät)
Bonn-Rhein-Sieg University of Applied Sciences (Hochschule Bonn-Rhein-Sieg) Department of Natural Sciences & Institute for Functional Gene Analytics (IFGA) Research Associate/PhD Student (d/f/m) for Research on the Transport of Ketone Bodies
- Application deadline: 28.04.2024
- Required degree: State Examination, Master, Diplom
more More about Research Associate/PhD Student (d/f/m) for Research on the Transport of Ketone Bodies - Bonn-Rhein-Sieg University of Applied Sciences (Hochschule Bonn-Rhein-Sieg) Department of Natural Sciences & Institute for Functional Gene Analytics (IFGA)
Registration / Login for German universities and research institutions Subscribe to RSS Legal notice: The information on this website is provided to the DAAD by third parties. Despite careful checking, the DAAD cannot guarantee the accuracy and completeness.
Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst e.V. Kennedyallee 50 53175 Bonn
All addresses in the DAAD Network
DAAD Newsletters
Receive regular up-to-date information about our work and organisation.
Newsletter - DAAD
Useful Links
- Find Scholarships
- DAAD offices worldwide
Jump to top of page
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Teaching Staff
- Lifelong learning
- All Degree Programs
- ALMA Portal
- Excellence Strategy
- Staff Search (EPV)
- Student Administration
- University Library
- Online Course Catalogue
- Webmail Uni Tübingen
- Advice for International Students
Important information about closing days
The PhD office is closed from May 21, 2024 to May 24, 2024. Please note that displaying periods cannot be started and registrations for oral exams will not be processed. Displaying periods will be extended accordingly. Registrations for oral exams during this closing period must be submitted until May 13, 2024 the latest.
Doctoral Studies at the Faculty of Science
Office hours.
Dr. Sarah Müller Monday - Thursday, 10.00 a.m. - 12.00 p.m. (no appointment neccessary) (Auf der Morgenstelle 8, B-Building, 10th floor, room 10A38) and by appointment (29- 75955 ).
Dr. Elaine Huggenberger Monday - Thursday, 10.00 a.m. - 12.00 p.m. (no appointment neccessary) (Auf der Morgenstelle 8, B-Building, 10th floor, room 10A23) and by appointment (29- 72751 ).
Sebastian Schlemender Monday - Thursday, 10.00 a.m. - 12.00 p.m. (no appointment neccessary) (Auf der Morgenstelle 8, B-Building, 10th floor, room 10R38) and by appointment (29- 76853 ) .
Feel free to contact us, if you have any further questions. However, we recommend reading the information sheet first, as it usually resolves most of the questions.
Areas of Responsibilities
Dr. Sarah Müller
Applications for acceptance as a doctoral student
Ongoing doctoral procedures (Chemistry, Pharmaceutics, Biochemistry, Psychology)
Verification and confirmation of doctoral degrees
Information about doctoral guidelines of the Faculty of Science
Cotutelle agreements
Dr. Elaine Huggenberger
Ongoing doctoral procedures (Computer Science, Bioinformatics, Mathematics, Physics)
State Postgraduate Fellowship Programme (Landesgraduiertenförderung)
Sebastian Schlemender
Submission/Acceptance of doctoral dissertations
Doctoral procedures (Biology and Geosciences)
Annette Goller
PhD Certificates
Doctoral Subjects
At the Faculty of Science, you can pursue a doctoral degree (Dr. rer. nat.) in the following fields:
Archaeological Sciences and Human Evolution
Biochemistry
Bioinformatics
Cognitive Science
Computer Science
Environmental Sciences
Geosciences
Mathematics
Medical Informatics
Pharmaceutics
Prehistory and Early History
Supervision of Doctoral Candidates
In general, all persons with professorship and all persons with a Habilitation are allowed to supervise doctoral candidates at the Faculty of Science.
Scientists without professorship and Habilitation have the possibility to apply for the supervision of doctoral candidates provided the funding of these candidates is provided by the scientists themselves.
Please submit the following application at the PhD office:
- Application for supervision (German) word | pdf
- Application for supervision (English) word | pdf
Scientists from abroad are allowed to supervise doctoral candidates at the Faculty of Science provided they have this right at the relevant university abroad.
Code of Conduct for the Doctoral Phase
Advice and Help
The ombudsperson assists the doctoral students in settling conflicts or solving problems. All matters are treated as strictly confidential and neutral. Ombudsperson is the Dean of the Faculty, the Vice Dean for Research and the Dean of Studies ( Contact).
First Points of Contact within each Department
Confidental Representatives - Good Scientific Practice
Psychosocial Counseling Service for University Employees
Psychotherapeutic Counselling of the Studierendenwerk Tübingen-Hohenheim
Legal Advice of the Studierendenwerks Tübingen-Hohenheim
Family Office - Advice Concerning Work/Life Balance
Advice on sexual harassment/mobbing
Downloads and Information
Information.
Information Sheet for Doctoral Candidates: pdf
PromO-Rules and Guidelines for Doctoral Studies 2015: pdf (This is a courtesy translation. The sole legally binding regulations are the Promotionsordnung der Mathematisch Naturwissenschaftlichen Fakultät der Universität Tübingen, in der Fassung vom 24. April 2015 pdf )
Recommendations for Cumulative Dissertations: pdf
Recommendations for Dissertations including Scientific Manuscripts with Co-Authors pdf
Information on "systematic reviews" pdf
Guidelines for Safeguarding Good Scientific Practice
Library Info Sheet Concerning Online Publication pdf
Postgraduate Affairs Board
Forms and Policies
Application for acceptance.
Application for Acceptance as Doctoral Candidate and Supervision Agreement: pdf
Please be aware that incomplete applications cannot be processed. We need all required certificates and documents, the filled out supervision agreement, and the signatures of the docotral candidate and both supervisors.
According to German university law (LHG §38 (5)) PhD candidates must be enrolled as students (until date of oral exam). You can register as student at the Student Administration with the acceptance letter of the PhD Office.
Exceptions:
- Doctoral students accepted by their faculty prior to 30 March 2018 may enroll but are not compelled to do so.
- Employees of the university of Tübingen can apply for an exception of this compulsory duty (application on webpage of Student Administration).
Admission to the Doctoral Examination Procedure
Application for Admission to the Doctoral Examination Procedure: pdf
Declaration Colaborative Publications: word | pdf
Please be aware that incomplete applications cannot be processed.
Registration Form Oral Exam: word | pdf
Abstract (Please hand in pdf file): word | pdf
Information on online exam: pdf
Self certification for online exam: word | pdf
Publishing Procedure
Declaration of Changes: pdf
- Oral Exams from April 1st, 2021: word | pdf
- Oral Exams before April 1st, 2021 and after August 19th, 2020 : word | pdf
Oral Exams before August 19th, 2020: word | pdf
Remark: In case of English titles, please capitalize the first word and all the principal words, i.e. not the articles, prepositions and conjuctions.
Please do not use double titles. Language of title should correspond to language of thesis.
Please do not use the university logo on the title page. For more information check the webpages of the Corporate Design .
Supervisors' Approval for Online Publication: pdf
Link to Dissertation Center of the University Library
Checking plagiarism
The ZDV offers the possiblity of conduction a similarity analysis for free by the software "Turnitiin". We recommend to make use of this offer before submitting the thesis. More information can be found under Link .
Please contact your supervisor if you do not have the authorization for using "Turnitin" yourself.
Dissertation Center of the University Library
Doctoral Studies at the Universit yof Tuebingen
Welcome Center for Visiting Researches & Scholars
International Doctoral Candidates
Career Service: Consulting and Coaching on Career Entry

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Der Ph.D. [piː‿eɪtʃ diː] (auch PhD, englisch Doctor of Philosophy, neulateinisch philosophiae doctor) ist in englischsprachigen Ländern der wissenschaftliche Doktorgrad in fast allen Fächern und der höchste Abschluss des Postgraduiertenstudiums.In diesen Ländern ist der Ph.D.-Abschluss in aller Regel mit der Berechtigung verbunden, an einer Universität selbstständig und ...
Der Dr. ist ein deutscher Doktortitel, der in Deutschland verliehen wird und meistens für den Lehren an einer Universität berechtigt. Der PhD ist ein internationaler Titel, der in englischsprachigen Ländern verliehen wird und meistens für die Forschung berechtigt. Die beiden Systeme haben jedoch einige Unterschiede in Dauer, Ausrichtung, Bindung und Qualität. Erfahre mehr über die wichtigsten Unterschiede und Tipps für Deine Promotionskarriere.
Introduction. Pursuing a PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) degree involves conducting original research in a specific field of study, making a significant contribution to knowledge, and demonstrating a high level of expertise. It is the highest academic qualification one can attain and is highly valued in academia, research institutions, and certain industries.
Ph.D. ist die Abkürzung für den lateinischen Ausdruck „Philosophiae Doctor". Damit bezeichnet der Titel wörtlich den Doktor der Philosophie. Faktisch handelt es sich beim Ph.D. jedoch um einen der höchsten allgemeinen akademischen Grade in verschiedensten Fachrichtungen, den beispielsweise US-amerikanische Universitäten vergeben.
PhD students are all mature students, as they have already completed undergraduate and postgraduate degrees already. Most PhD students will have done a masters in preparation for starting a PhD , this is often an MPhil or a Masters by Research. All of this previous study means that PhD students have strong study skills and have spent time ...
A PhD is a terminal academic degree students typically pursue when they're interested in an academic or research career. A PhD is the highest possible academic degree a student can obtain. PhD stands for "Doctor of Philosophy," which refers to the immense knowledge a student gains when earning the degree. While you can actually get a PhD in ...
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: philosophiae doctor or doctor philosophiae) is the most common degree at the highest academic level, awarded following a course of study and research. The degree is abbreviated PhD and sometimes, especially in the U.S., as Ph.D. It is derived from the Latin Philosophiae Doctor, pronounced as three separate letters (/ p iː eɪ tʃ ˈ d iː ...
Definition of a PhD - A Doctor of Philosophy (commonly abbreviated to PhD, Ph.D or a DPhil) is a university research degree awarded from across a broad range of academic disciplines; in most countries, it is a terminal degree, i.e. the highest academic degree possible. PhDs differ from undergraduate and master's degrees in that PhDs are ...
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. This is one of the highest level academic degrees that can be awarded. PhD is an abbreviation of the Latin term (Ph)ilosophiae (D)octor. Traditionally the term 'philosophy' does not refer to the subject but its original Greek meaning which roughly translates to 'lover of wisdom'.
Zur mobilen Version wechseln. Lernen Sie die Übersetzung für 'Ph.D. student' in LEOs Englisch ⇔ Deutsch Wörterbuch. Mit Flexionstabellen der verschiedenen Fälle und Zeiten Aussprache und relevante Diskussionen Kostenloser Vokabeltrainer .
PhD Studies & Research. Science and research in Germany are characterised by a distinguished infrastructure, a wide variety of disciplines, well-equipped research facilities and competent staff. Germany offers various career opportunities for international PhD students and researchers. Discover Germany's top-tier PhD programs and research scene ...
What is a PhD? A PhD is the highest postgraduate qualification level that can be awarded in academic study. This is usually completed over three to four years of full-time study, and involves research into an original contribution in your chosen field. PhD is an acronym that stands for Doctor of Philosophy. The name for PhD comes from the Latin ...
A Doctor of Philosophy, often known as a PhD, is a terminal degree—or the highest possible academic degree you can earn in a subject. While PhD programs (or doctorate programs) are often structured to take between four and five years, some graduate students may take longer as they balance the responsibilities of coursework, original research, and other degree requirements with raising ...
A PhD student is different from a PhD candidate in that the student is still working through the coursework. They have not yet begun the dissertation process or passed the qualifying exams. A PhD student may also be in the process of taking the qualifying exams, but not yet finished with them. Many people believe that earning a doctorate degree ...
Discover your best route to a PhD in Germany, including financing options and advice on how to prepare for your research stay. Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst e.V. Kennedyallee 50. 53175 Bonn. Germany. Receive regular up-to-date information about our work and organisation. Information about doing a PhD in Germany.
Here in the U.S., a "Ph.D. Candidate" is a student who has completed all of the academic requirements for their degree, except their dissertation. So this works in the USA and Canada I presume, because they have structured PhD programs where you attend courses as part of your PhD.
PhD Study in Germany - 2024. Germany's historic and highly-ranked universities make it an excellent choice for studying abroad. Having offered the PhD since the nineteenth century, they know a thing or two about delivering innovative, high-quality postgraduate programmes.
Students may be in the initial stage of the program or about to complete the coursework (before beginning their research). On the other hand, a PhD candidate has completed all coursework and has at least started their research. They may have completed their dissertation and are preparing to defend it. 2.
Doctoral studies are an important part of the University's mission and responsibility and, as a doctoral student, you will be making important contributions to research at the University of Gothenburg. Doctoral studies allow you to develop a deeper understanding of a scientific field of study and are provided free of charge in Sweden.
Georg-August-Universität Göttingen. RTG 2756 CYTAC 12 PhD Positions at the RTG 2756 "Cytoskeletal elements of active matter - CYTAC". Full PhD. Application deadline: 20.05.2024. Working language: English. Beginning: 01.01.2025. Required degree: Master. Göttingen. Last changed: 05.04.2024 (Published: 05.04.2024)
A Graduate student is usually enrolled with the objective of doing a PhD, many Graduate students, provided they have the coursework and thesis, might get a Masters degree in the middle of the program along with the PhD. Usually for postgraduate students I also think is for post docs, but I'm not sure. In Mexico (and maybe France, because we ...
According to German university law (LHG §38 (5)) PhD candidates must be enrolled as students (until date of oral exam). You can register as student at the Student Administration with the acceptance letter of the PhD Office. Exceptions: Doctoral students accepted by their faculty prior to 30 March 2018 may enroll but are not compelled to do so.
PhD student - Wörterbuch Englisch-Deutsch. 90.000 Stichwörter und Wendungen sowie 120.000 Übersetzungen.