- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies

Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Ferdinand de Saussure
Introduction.
- Introductory Works
- In-Depth Studies
- Reference Works
- Anthologies
- Bibliographies
- Journals and Website
- Cours de linguistique générale and Its Sources
- Other Writings by Saussure
- The Mémoire and Other Work in Historical Linguistics
- The Anagram Research and Other Unpublished Work
- Cours de linguistique générale
- Later Extensions of Saussure’s Work
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Analogy in Language and Linguistics
- Comparative-Historical Linguistics
- Georg von der Gabelentz
- History of Linguistics
- Jan Baudouin de Courtenay
- Linguistic Prescriptivism
- Literature and Linguistics
- Sign Language Linguistics
- Sound Change
- The Prague Linguistic Circle
- William Dwight Whitney
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Cognitive Grammar
- Edward Sapir
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Ferdinand de Saussure by John E. Joseph LAST REVIEWED: 27 November 2023 LAST MODIFIED: 27 November 2023 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199772810-0003
Ferdinand de Saussure (b. 1857–d. 1913) is acknowledged as the founder of modern linguistics and semiology, and as having laid the groundwork for structuralism and post-structuralism. Born and educated in Geneva, in 1876 he went to the University of Leipzig, where he received a doctorate in 1881. While a student there he published the Mémoire sur le système primitif des voyelles dans les langues indo-européennes (1879), which radically reimagined how the original Indo-European vowel system might be reconstructed. During the 1880s Saussure was lecturer in Gothic and Old High German at the École Pratique des Hautes Études in Paris, and he served as adjunct secretary of the Société de Linguistique de Paris and was responsible for the Société’s publications in which a number of his own papers appeared. He also began, but abandoned, several more ambitious projects. In 1891 he returned to Geneva to take up a chair in Sanskrit and comparative Indo-European philology. He began another project on the “double essence” of language that was never completed. His papers on Lithuanian accentuation from this period would earn recognition for “Saussure’s Law,” which applies to historical accent shifts in a particular category of Lithuanian words. The next decade saw him devote his attention to various topics, including local toponyms around Geneva, legends of the Germanic peoples who had settled in the area, and finally the search for anagrams in Greek and Latin poetry, but no publications resulted. In 1907 he was given responsibility for the university’s course in general linguistics, a course meant for students who lacked sufficient grounding in any ancient or medieval language to do in-depth textual study. Saussure had no experience in teaching a course in general linguistics, nor indeed had he ever taken one. Restructuring the course each of the three times he gave it, he brought in sign theory and other aspects of the grammaire générale tradition in which he himself had been taught (see John E. Joseph, Saussure [Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2012]) but that linguists had laid aside and forgotten in the intervening decades. Soon after his death in 1913, his colleagues Charles Bally and Albert Sechehaye, appreciating the extraordinary nature of his lectures, began gathering his manuscript notes and the notebooks of his students. From these they fashioned the Cours de linguistique générale (Course in general linguistics), published in 1916. It would become one of the most influential books of the twentieth century, not just for linguistics but also across many realms of intellectual endeavor. Many previously unpublished texts by Saussure have been appearing in recent years, principally in the volumes of the Cahiers Ferdinand de Saussure . Various projects are underway for making photographic reproductions of the manuscript material online.
General Overviews
Because Saussure did not actually write the book that he is most famous for and that had the most direct impact on later linguistics, it is especially useful to approach his work in its broader context, rather than to focus exclusively on the Cours . Indeed, some Saussure scholars (most notably Simon Bouquet) maintain that the published Cours badly misrepresents Saussure’s ideas about language as recorded in his students’ notebooks, although others, probably a majority, consider such misrepresentations to be few in number and rarely to amount to serious distortion. The studies in this section are divided between those aimed at an audience looking for an initial introduction to Saussure and those that analyze his linguistic theories in depth. In both cases, the ones published before 1980 rarely take serious account of the manuscripts available up to that time, while those from the 1980s and 1990s do tend to look at the full scope of the material then available, and those from the 2000s and after are able to draw on new manuscripts that have come to light since 1996.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Linguistics »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Acceptability Judgments
- Accessibility Theory in Linguistics
- Acquisition, Second Language, and Bilingualism, Psycholin...
- Adpositions
- African Linguistics
- Afroasiatic Languages
- Algonquian Linguistics
- Altaic Languages
- Ambiguity, Lexical
- Animal Communication
- Applicatives
- Applied Linguistics, Critical
- Arawak Languages
- Argument Structure
- Artificial Languages
- Australian Languages
- Austronesian Linguistics
- Auxiliaries
- Balkans, The Languages of the
- Baudouin de Courtenay, Jan
- Berber Languages and Linguistics
- Bilingualism and Multilingualism
- Biology of Language
- Borrowing, Structural
- Caddoan Languages
- Caucasian Languages
- Celtic Languages
- Celtic Mutations
- Chomsky, Noam
- Chumashan Languages
- Classifiers
- Clauses, Relative
- Clinical Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Colonial Place Names
- Comparative Reconstruction in Linguistics
- Complementation
- Complexity, Linguistic
- Compositionality
- Compounding
- Computational Linguistics
- Conditionals
- Conjunctions
- Connectionism
- Consonant Epenthesis
- Constructions, Verb-Particle
- Contrastive Analysis in Linguistics
- Conversation Analysis
- Conversation, Maxims of
- Conversational Implicature
- Cooperative Principle
- Coordination
- Creoles, Grammatical Categories in
- Critical Periods
- Cross-Language Speech Perception and Production
- Cyberpragmatics
- Default Semantics
- Definiteness
- Dementia and Language
- Dene (Athabaskan) Languages
- Dené-Yeniseian Hypothesis, The
- Dependencies
- Dependencies, Long Distance
- Derivational Morphology
- Determiners
- Dialectology
- Distinctive Features
- Dravidian Languages
- Endangered Languages
- English as a Lingua Franca
- English, Early Modern
- English, Old
- Eskimo-Aleut
- Euphemisms and Dysphemisms
- Evidentials
- Exemplar-Based Models in Linguistics
- Existential
- Existential Wh-Constructions
- Experimental Linguistics
- Fieldwork, Sociolinguistic
- Finite State Languages
- First Language Attrition
- Formulaic Language
- Francoprovençal
- French Grammars
- Gabelentz, Georg von der
- Genealogical Classification
- Generative Syntax
- Genetics and Language
- Grammar, Categorial
- Grammar, Construction
- Grammar, Descriptive
- Grammar, Functional Discourse
- Grammars, Phrase Structure
- Grammaticalization
- Harris, Zellig
- Heritage Languages
- History of the English Language
- Hmong-Mien Languages
- Hokan Languages
- Humor in Language
- Hungarian Vowel Harmony
- Idiom and Phraseology
- Imperatives
- Indefiniteness
- Indo-European Etymology
- Inflected Infinitives
- Information Structure
- Interface Between Phonology and Phonetics
- Interjections
- Iroquoian Languages
- Isolates, Language
- Jakobson, Roman
- Japanese Word Accent
- Jones, Daniel
- Juncture and Boundary
- Khoisan Languages
- Kiowa-Tanoan Languages
- Kra-Dai Languages
- Labov, William
- Language Acquisition
- Language and Law
- Language Contact
- Language Documentation
- Language, Embodiment and
- Language for Specific Purposes/Specialized Communication
- Language, Gender, and Sexuality
- Language Geography
- Language Ideologies and Language Attitudes
- Language in Autism Spectrum Disorders
- Language Nests
- Language Revitalization
- Language Shift
- Language Standardization
- Language, Synesthesia and
- Languages of Africa
- Languages of the Americas, Indigenous
- Languages of the World
- Learnability
- Lexical Access, Cognitive Mechanisms for
- Lexical Semantics
- Lexical-Functional Grammar
- Lexicography
- Lexicography, Bilingual
- Linguistic Accommodation
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Areas
- Linguistic Landscapes
- Linguistic Profiling and Language-Based Discrimination
- Linguistic Relativity
- Linguistics, Educational
- Listening, Second Language
- Machine Translation
- Maintenance, Language
- Mande Languages
- Mass-Count Distinction
- Mathematical Linguistics
- Mayan Languages
- Mental Health Disorders, Language in
- Mental Lexicon, The
- Mesoamerican Languages
- Minority Languages
- Mixed Languages
- Mixe-Zoquean Languages
- Modification
- Mon-Khmer Languages
- Morphological Change
- Morphology, Blending in
- Morphology, Subtractive
- Munda Languages
- Muskogean Languages
- Nasals and Nasalization
- Niger-Congo Languages
- Non-Pama-Nyungan Languages
- Northeast Caucasian Languages
- Oceanic Languages
- Papuan Languages
- Penutian Languages
- Philosophy of Language
- Phonetics, Acoustic
- Phonetics, Articulatory
- Phonological Research, Psycholinguistic Methodology in
- Phonology, Computational
- Phonology, Early Child
- Policy and Planning, Language
- Politeness in Language
- Positive Discourse Analysis
- Possessives, Acquisition of
- Pragmatics, Acquisition of
- Pragmatics, Cognitive
- Pragmatics, Computational
- Pragmatics, Cross-Cultural
- Pragmatics, Developmental
- Pragmatics, Experimental
- Pragmatics, Game Theory in
- Pragmatics, Historical
- Pragmatics, Institutional
- Pragmatics, Second Language
- Pragmatics, Teaching
- Prague Linguistic Circle, The
- Presupposition
- Psycholinguistics
- Quechuan and Aymaran Languages
- Reading, Second-Language
- Reciprocals
- Reduplication
- Reflexives and Reflexivity
- Register and Register Variation
- Relevance Theory
- Representation and Processing of Multi-Word Expressions in...
- Salish Languages
- Sapir, Edward
- Saussure, Ferdinand de
- Second Language Acquisition, Anaphora Resolution in
- Semantic Maps
- Semantic Roles
- Semantic-Pragmatic Change
- Semantics, Cognitive
- Sentence Processing in Monolingual and Bilingual Speakers
- Sociolinguistics
- Sociolinguistics, Variationist
- Sociopragmatics
- South American Indian Languages
- Specific Language Impairment
- Speech, Deceptive
- Speech Perception
- Speech Production
- Speech Synthesis
- Switch-Reference
- Syntactic Change
- Syntactic Knowledge, Children’s Acquisition of
- Tense, Aspect, and Mood
- Text Mining
- Tone Sandhi
- Transcription
- Transitivity and Voice
- Translanguaging
- Translation
- Trubetzkoy, Nikolai
- Tucanoan Languages
- Tupian Languages
- Usage-Based Linguistics
- Uto-Aztecan Languages
- Valency Theory
- Verbs, Serial
- Vocabulary, Second Language
- Voice and Voice Quality
- Vowel Harmony
- Whitney, William Dwight
- Word Classes
- Word Formation in Japanese
- Word Recognition, Spoken
- Word Recognition, Visual
- Word Stress
- Writing, Second Language
- Writing Systems
- Zapotecan Languages
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|45.133.227.243]
- 45.133.227.243
- Bangla Blog

- Select Honours Year
- Bangla Summary (Bangla Site)
- Lectures (Channel)
- English Speaking
Saussure's contribution in linguistics | Langue and Parole | Syntagmatic and Paradigmatic relationships | Try.Fulfill
Discuss saussure's contribution to the study of language | difference between langue and parole | saussure's contribution in linguistics | difference between syntagmatic and paradigmatic relationships | syntagmatic and paradigmatic relationships with diagram | sign signifier signified diagram | try.fulfill, saussure's contribution in linguistics:.
- · Saussure’s introduction.
- · Sign= signifier + signified .
- · Synchronic and diachronic axis .
- · Syntagmatic and paradigmatic relationships .
- · L angue and parole .
Ferdinand De Saussure , the founder of modern linguistics was born in 1857 and breathed for last in 1913. He was a Swiss linguist as well as semiotician. He contributed to the field of linguistics and semiotics. He is titled as the founder of structuralism . His famous book written on linguistics is ‘course in General Linguistics’ . Saussure’s contribution in linguistics circulated over several branches. His contribution on Sign, Synchronic and diachronic axis and Langue and parole is prominent.
Saussure improved the idea of sign which is further classified as the summation of signifier and signified . Signifier is the sound, word or image or the physical existence of the concept and signified is the mental concept. For example: An apple.
While a person see the image of an apple or written word ‘Apple`, he identifies a concept of a thing in his mind. Then he get the sign of the apple.
Difference between syntagmatic and paradigmatic relationships :
Saussure’s contribution in linguistics is also specified in the development of syntagmatic and paradigmatic relationships . In syntagmatic relationships , signs occur in sequence and they operate together. On the other side, in paradigmatic relationships , signs can be replaced by one another. Syntagmatic and Paradigmatic relationships with diagram :
Difference between Synchronic and Diachronic Axes:
Saussure also contributed by improving the concept of synchronic and diachronic axes . Synchronic axis is the measurement of a language based on a particular time and a specific speech community. Rather, diachronic axis judges a language researching historical development of the language over different periods. Synchronic axis studies grammar, classification or arrangement of language while diachronic axis studies comparative linguistics and etymology.
- La langue ( The language system )
- La parole (The act of speaking )
You may like these posts
Post a comment.

Download Our App

Select Year
- Honours 1st Year
- Honours 2nd Year
- Honours 3rd Year
- Honours 4th Year
- Suggestions
Select Subject
- Linguistics
- History of English Literature
- Literary Criticism
- ELT - Approaches and Methods of Language Teaching
- Elizabethan and Jecobean Drama
- IELTS Preparation
- Creative Writings
- Life of Authors/Poets
- Social Awareness
- Writing Skills
- 20th Century Novel
- Classics in Translation
- English Grammar
- Reading and Writing

12 handnotes of History of English Literature - Notes for honours 2nd year
Hand notes of History of English literature
Highest Read
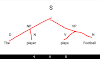
IC analysis through tree diagram | IC analysis diagram | IC analysis examples.

Importance of Teaching Aids | Teaching Aids Examples | Try.Fulfil

Organs of Speech with diagram | Classification of Organs of speech | Try.Fulfil.

Dialogues for kids / Short Dialogues / Short Conversations / Try.Fulfil

Roles of a teacher in a Language Teaching Classroom | Roles of a Teacher | Try Dot Fulfill.

Syntax definition | Syntactic process with diagram | Try.Fulfil

Different varieties of sociolinguistics | Varieties of language in sociolinguistics | Try.Fulfil

Education and morality; Compatibility, variations.

The Metaphysical Poets Summary | The Metaphysical Poets by T S Eliot – Summary | Try Dot Fulfil

Set Suggestion 1st Year 2021 pdf | English Department | Try Dot Fulfill
Most popular (7 days).

‘The Study of Poetry’ Summary | The Study of Poetry by Matthew Arnold | Try.Fulfill

The Duchess of Malfi as a portrait of a corrupt society / We are in a world of intense evil.

Set suggestion 4th year 2021 English Department | Set Suggestion 4th year 2020 pdf English Department | Try.Fulfil
Don't copy or screenshot., about try dot fulfil.

Other Sites.
- Our FACEBOOK GROUP
- Bangla Summary, HandNotes
- Learn about Entire Entity tech

- Linguistics 30
- History of English Literature 15
- Suggestions 13
- Literary Criticism 10
- ELT - Approaches and Methods of Language Teaching 7
- English Speaking 6
- Elizabethan and Jecobean Drama 5
- Life of Authors/Poets 2
- Social Awareness 2
- Writing Skills 2
- 20th Century Novel 1
- Classics in Translation 1
- English Grammar 1
- Exam Routine 1
- Reading and Writing 1
Menu Footer Widget
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Acquisition
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music and Religion
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Law and Politics
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Games
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business Strategy
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Systems
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Politics and Law
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >
1 The signifier and the signified
- Published: January 2015
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This chapter takes on the classic signifier/signified distinction, which supports the structuralist view of language as a closed and autonomous system of signs. It considers the presentation of linguistic arbitrariness in relation to an individual sign in the Course in light of materials from the Nachlass, to suggest a possible editorial confusion between Saussure’s critique of the received view of language with its focus on individual names and his own conception of language as a relational system. It then explains that the view of language as a sign system is made more concrete when Saussure defines it as a set of historically sedimented conventions shared by a speaking community. Contrary to the structuralist view, language is shaped by reality: the reality of social conventions as they are transmitted, sedimented, and revised over time. Linguistic arbitrariness is a counterpart of this sociohistorical understanding.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]

Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Constructed scripts
- Multilingual Pages
Saussure's Basic Principles of Structural Linguistics
By Julia Kinsley
Ferdinand de Saussure (1857-1913), was a Swiss Linguist who laid the great foundation of the field of Linguistics in 20tth century. The book Cours de Linguistiques Générale , written by his disciples published posthumously in 1916, is a compilation of his lectures given at University of Geneva around 1901 or 1906. It has become an essential text in the literary canon of linguistics as the book documents his research, ideas, and analysis of the nature of language that gives us a great insight into the basics of structural linguistics.
For anyone new to the linguistics, it becomes necessarily important to be thoroughly familiar with the major dichotomies or concepts that Saussure came up with in his Cours de Linguistiques Generale (1916). Through these principles or concepts, we can trace back the origins of the Structural Linguistics.
Langue & Parole
The language is constituted of two parts: langue and parole. And the linguistic communication is just not possible if these two work independently and individually. The Langue represents the system of language having signs, rules, and patterns devised by a particular social group for communication. The parole meaning the utterance of that Langue and thus, it varies from community to community and region to region. (However, this dichotomy is now overshadowed by Chomsky's distinction between competence and performance.)
For example, in English, an apple is called an apple whereas it is called яблоко (yabloko) in Russian. Hence, the langue in English has rules and patterns of letters which allows the parole to utter an apple as an apple. The same goes with the latter.
Paradigm & Syntagm
Saussure named the relation between the words corresponding to our the operation of our brain. A syntagmatic relation between words is when the words either spoken or written have different grammatical roles in the sentence. The syntagmatic structures the words in the sequence to form a meaningful whole. For example,
Rachael drinks juice a lot for keeping her body healthy.
On the contrary, a paradigmatic relation between the words will be when these two words can substitute each other in a sentence without affecting the meaning of the sentence. A paradigmatic
John likes to drink water a lot for keeping his body healthy.
Here are few more examples:
If you look closely at the table, you can see that horizontally when words are sequenced in order; it creates a meaningful whole that something is being eaten by someone whereas you may see that vertically, the words can be replaced without changing this meaning. This opposition of paradigmatic and syntagmatic relationship is a dichotomy in linguistics.
Synchrony & Diachrony
Saussure analysed the nature of language through the two different and opposed perspectives: one he called synchronic and the other diachronic. Where synchrony studies the language existing in a particular point of time, diachronic studies the language concerning its historic development.
For example, you study the Old English in England, you are using a synchronic approach where you are limiting your study to a particular period of time.
But if you are researching on the evolution of English language and its use from Middle English to Modern English, it would be called a diachronic study or historical linguistics.
Arbitrariness of the Sign
Signs are the basic elements of the linguistic communication which Saussure called arbitrary. He believed that signs are understood best on the basis of what is signified (mental image) and what signifies (signifier). He argued that a word in any language is given the meaning through the functioning of signs which forms the relationship between signifier and signified. And this relationship he called purely arbitrary which has no logical meaning. Let us understand this through this example:
The word cat has no logic why it refers to a cat, and hence there are different names for the cat in various languages.
- Cat : The Signifier
A small mammal with four legs: The Signified
However, if we can name a cat as Meow, it can be said to be logical because the cat actually makes this sound.
- Meow : The Signifier
A small mammal with four legs which makes the sound meow : The Signified
Hence, Saussure concluded that the relationship between signifier and signified is arbitrary.
These were the central concepts of Saussure that made his successors study the use and function of language in a different perspective.
About the writer
Julia Kinsley is pursuing PhD from Leicester University. Her area of specialisation is historical linguistics and is currently working with Geoff and Francis as a professional proofreader.
Writing systems | Language and languages | Language learning | Pronunciation | Learning vocabulary | Language acquisition | Motivation and reasons to learn languages | Arabic | Basque | Celtic languages | Chinese | English | Esperanto | French | German | Greek | Hebrew | Indonesian | Italian | Japanese | Korean | Latin | Portuguese | Russian | Sign Languages | Spanish | Swedish | Other languages | Minority and endangered languages | Constructed languages (conlangs) | Reviews of language courses and books | Language learning apps | Teaching languages | Languages and careers | Being and becoming bilingual | Language and culture | Language development and disorders | Translation and interpreting | Multilingual websites, databases and coding | History | Travel | Food | Other topics | Spoof articles | How to submit an article
Saussurean Linguistics and Bakhtin’s Critique
- Howard Mancing 5 &
- Jennifer Marston William 6
- First Online: 28 January 2022
361 Accesses
Part of the book series: Cognitive Studies in Literature and Performance ((CSLP))
This chapter briefly reviews the important contributions to the study of linguistics by Ferdinand de Saussure, followed by a critique of these theories, particularly outlining the role of Russian philosopher and theorist Mikhail Bakhtin in pointing out the shortcomings of Saussure’s work, namely its lack of regard for linguistic aspects such as change over time, syntax, and, most importantly for the purposes of this book, context.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Aronowitz, Stanley. 1994. Dead Artists, Live Theories, and Other Cultural Problems . New York: Routledge.
Google Scholar
Bakhtin, Mikhail M. 1986. Speech Genres and Other Late Essays . Ed. Caryl Emerson and Michael Holquist. Trans. Vern W. McGee. Austin: U of Texas P.
Bouchard, Denis. 2014. The Nature and Origin of Language . Oxford: Oxford UP.
Brown, Donald E. 1991. Human Universals . New York: McGraw-Hill.
Chomsky, Noam. 1972 (1968). Language and Mind . New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich.
Cook, Guy. 1994. “Contradictory Voices: A Dialogue Between Russian and Western European Linguists.” In Literature and the New Interdisciplinarity: Poetics, Linguistics, History . Ed. Roger D. Sell and Peter Verdonk. Amsterdam: Rodopi. 151–61.
Halmøy, Madeleine. 2016. The Norwegian Nominal System: A Neo-Saussurean Perspective . Berlin: de Gruyter.
Harland, Richard. 1993. Beyond Superstructuralism: The Syntagmatic Side of Language . London: Routledge.
Harris, Roy. 1987. Reading Saussure: A Critical Commentary on the Cours de linguistique générale. La Salle: Open Court.
Holland, Norman N. 1992. The Critical I . New York: Columbia UP.
Jackson, Leonard. 1991. The Poverty of Structuralism: Literature and Structuralist Theory . London: Longman.
Newmeyer, Frederick J. 2017. “Two Challenges for ‘Neo-Sassurean’ Approaches to Morphosyntax.” In Formal Models in the Study of Language . Ed. Joanna Blochowiak, et al. Cham: Springer. 49–64.
Saussure, Ferdinand de. 1986 (1916). Course in General Linguistics . Ed. Charles Bally and Albert Sechehaye, with Albert Riedlinger. Trans. and annotated by Roy Harris. La Salle: Open Court.
Spariosu, Mihai. 2004. Global Intelligence and Human Development: Toward an Ecology of Global Learning . Cambridge: MIT P.
Taylor, John R. 1995 (1989). Linguistic Categorization: Prototypes in Linguistic Theory . Oxford: Clarendon P.
Voloshinov, V. N. 1986 (1929). Marxism and the Philosophy of Language . Trans. Ladislav Matejika and I. R. Titunik. Cambridge: Harvard UP.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA
Howard Mancing
Jennifer Marston William
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Howard Mancing .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Mancing, H., Marston William, J. (2022). Saussurean Linguistics and Bakhtin’s Critique. In: Restoring the Human Context to Literary and Performance Studies. Cognitive Studies in Literature and Performance. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89078-0_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89078-0_2
Published : 28 January 2022
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-89077-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-89078-0
eBook Packages : Literature, Cultural and Media Studies Literature, Cultural and Media Studies (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Literary Theory and Criticism
Home › Saussurean Structuralism
Saussurean Structuralism
By NASRULLAH MAMBROL on March 20, 2016 • ( 7 )

As Jacques Derrida pointed out, Saussure’s theory is based on binary oppositions or dyads, i.e., defining a unit in terms of what it is not, which give rise to oppositional pairs in which one is always superior to the other. The most fundamental binary opposition is related to the concept of sign, the basic unit of signification. In Saussure, the previously undivided sign gets divided into the signifier (the sound image) and the signified (the concept). Saussure stressed that the relationship between the signifier and the signified is conventional and arbitrary, and that both terms are psychological in nature. There is no one-to-one relation between the signifier and the signified. For instance the sound image “tree” may refer to different kinds of trees or it may even be a metaphor for forest. Therefore, it is inferred that meaning is arbitrary and unstable.
The second binary opposition is-that of the langue and parole, where langue refers to language as a structural system based on certain rules, while parole refers to an individual expression of language. The terms langue and parole are parallel to the terms competence and performance formulated by Chomsky. The binary opposition of synchronic and diachronic refers to the study of the structure and functions of language at a particular point of time, and over a period of time respectively. Paradigmatic and Syntagmatic axes refer to the axes of selection and combination respectively, where syntagmatic denotes the relationship of units/words in a linear pattern, while ‘paradigmatic, axis constitutes of the interchangeable units in a language.
The most significant of the binary oppositions that has been criticized by Derrida is that of speech and writing. Saussure privileged speech over writing owing to the subjectivity, authority and presence of the speaker. Derrida called this phonocentrism, a manifestation of the logocentrism, which literally means the centrality of the logos. “Logos” etymologically and historically means the “Word of God” and by extension, rationality, wisdom, law – all synonymous with power. Derrida describes logocentrism as the metaphysics of presence, and is opposed to the concept of the centrality of presence, because presence contains within itself, traces of absence, thereby deconstructing its very centrality. In connection to and in opposition to logocentrism, Derrida introduces “ecriture”, a French term roughly translated as writing – which exists beyond the logos and is characterised by absence and differance, where meaning is constantly under erasure, and does not have the authority of the logos, and is hence anti-logocentric. A related word, archi ecriture, refers to writing as an ultimate principle than as a derivative of logos. According to Derrida, even speech can be considered as a form of writing — writing on air waves, or into the memory of the listener. Thus the concept of ecriture subverts the superiority of speech over writing.
Saussure’s Course in General Linguistics proved to be of seminal influence in various fields such as Anthropology (Levi-Strauss), Semiology (Roland Barthes), the literary and philosophical concepts of Derrida, Marxist analysis of ideology by Althusser, psychoanalytical theories of Lacan, and analysis of language conducted by Feminists like Kristeva, Cixous, Irigaray.
Share this:
Categories: Uncategorized
Tags: 8.25 Geneva to Paris Express , Course in General Linguistics , derrida , diachronic , ecriture , Linguistics , Literary Criticism , Literary Theory , Roland Barthes , Saussure. , Structuralism , synchronic
Related Articles

I liked this explanation, it helps to understand the binarity of structuralist linguistics.
- Key Theories of Jacques Derrida – Literary Theory and Criticism Notes
- Anthropological Criticism: An Essay – Literary Theory and Criticism Notes
- Binarism in Post-colonial Theory – Literary Theory and Criticism Notes
- Structuralism – Literary Theory and Criticism Notes
- Key Theories of Ferdinand de Saussure – Literary Theory and Criticism Notes
- Structuralism | Literary Theory and Criticism
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Architecture and Design
- Asian and Pacific Studies
- Business and Economics
- Classical and Ancient Near Eastern Studies
- Computer Sciences
- Cultural Studies
- Engineering
- General Interest
- Geosciences
- Industrial Chemistry
- Islamic and Middle Eastern Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Library and Information Science, Book Studies
- Life Sciences
- Linguistics and Semiotics
- Literary Studies
- Materials Sciences
- Mathematics
- Social Sciences
- Sports and Recreation
- Theology and Religion
- Publish your article
- The role of authors
- Promoting your article
- Abstracting & indexing
- Publishing Ethics
- Why publish with De Gruyter
- How to publish with De Gruyter
- Our book series
- Our subject areas
- Your digital product at De Gruyter
- Contribute to our reference works
- Product information
- Tools & resources
- Product Information
- Promotional Materials
- Orders and Inquiries
- FAQ for Library Suppliers and Book Sellers
- Repository Policy
- Free access policy
- Open Access agreements
- Database portals
- For Authors
- Customer service
- People + Culture
- Journal Management
- How to join us
- Working at De Gruyter
- Mission & Vision
- De Gruyter Foundation
- De Gruyter Ebound
- Our Responsibility
- Partner publishers

Your purchase has been completed. Your documents are now available to view.
Ferdinand de Saussure (1857-1913) and Structural Linguistics
From the book introducing literary theories.
- Kenneth Womack
- X / Twitter
Supplementary Materials
Please login or register with De Gruyter to order this product.
Chapters in this book (112)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Ferdinand de Saussure (born Nov. 26, 1857, Geneva, Switz.—died Feb. 22, 1913, Vufflens-le-Château) was a Swiss linguist whose ideas on structure in language laid the foundation for much of the approach to and progress of the linguistic sciences in the 20th century.. While still a student, Saussure established his reputation with a brilliant contribution to comparative linguistics, Mémoire ...
Ferdinand de Saussure (/ s oʊ ˈ sj ʊər /; French: [fɛʁdinɑ̃ də sosyʁ]; 26 November 1857 - 22 February 1913) was a Swiss linguist, semiotician and philosopher.His ideas laid a foundation for many significant developments in both linguistics and semiotics in the 20th century. He is widely considered one of the founders of 20th-century linguistics and one of two major founders ...
General Overviews. Because Saussure did not actually write the book that he is most famous for and that had the most direct impact on later linguistics, it is especially useful to approach his work in its broader context, rather than to focus exclusively on the Cours.Indeed, some Saussure scholars (most notably Simon Bouquet) maintain that the published Cours badly misrepresents Saussure's ...
1. Introduction. Ferdinand de Saussure (1857-1913), though a universally known figure in and outside modern linguistics, has remained an enigmatic source of controversy and confusion ever since the posthumous publication, in 1916, of his now world-famous Cours de linguistique générale (henceforth Cours), published by Payot in Paris/Lausanne.This book was, though published under his name ...
Ferdinand de Saussure's thoughts on language came to light in 1916 with the publication of Cours de linguistique générale by his students. A hundred years on, the influence of his thoughts on modern linguistics is still being pinpointed. This paper reviews Saussure's influence on the cognitive approaches to meaning and grammar.
Summary. That the work of Saussure, a Swiss linguist, should be the subject of a book in a series called Modern European Thought should occasion little surprise, for his subject was one to which he made a seminal contribution. What is notable is that he is an important figure not only in the development of twentieth-century linguistics, but ...
Ferdinand De Saussure, the founder of modern linguistics was born in 1857 and breathed for last in 1913. He was a Swiss linguist as well as semiotician. He contributed to the field of linguistics and semiotics. He is titled as the founder of structuralism.His famous book written on linguistics is 'course in General Linguistics'. Saussure's contribution in linguistics circulated over ...
Berne. He wrote proliÞcally on Saussure, making frequent contributions to the Cahiers Ferdinand de Saussure, including bibliographical lists up to the 1980s. He is known in particular for his monumental comparative critical edition of the student notes for SaussureÕs lectures on general linguistics,
Abstract. This entry provides an introduction to the work of Ferdinand de Saussure, who is widely regarded as one of the founding figures of modern linguistics, notably of structural linguistics, and whose work has had - and continues to have - a significant impact upon the development of the humanities and social sciences, especially in ...
T he received structuralist view of Saussure's general linguistics foregrounds the signifier/signified distinction as the single most important contribution made by the Course.The terminological complex sign, signifier, and signified has been described as "perhaps Saussure's most influential gift to Structuralism" (Sturrock, 2003, p. 35); this distinction—"once it has been ...
Paradigm & Syntagm. Saussure named the relation between the words corresponding to our the operation of our brain. A syntagmatic relation between words is when the words either spoken or written have different grammatical roles in the sentence. The syntagmatic structures the words in the sequence to form a meaningful whole.
Key Theories of Ferdinand de Saussure By NASRULLAH MAMBROL on March 12, 2018 • ( 8). Before 1960, few people in academic circles or outside had heard the name of Ferdinand de Saussure (1857-1913). But after 1968, European intellectual life was a-buzz with references to the father of both linguistics and structuralism.That Saussure was as much a catalyst as an intellectual innovator is ...
Structuralism started with the linguistic work of Ferdinand de Saussure and the Prague and Moscow schools of linguistics. The basic thought of this approach to linguistics was not to study the use ...
This is the first English-language guidebook geared at an interdisciplinary audience that reflects relevant scholarly developments related to the legacy and legitimacy of Ferdinand de Saussure's Course in General Linguistics (1916) today. It critically assesses the relation between materials from the Course and from the linguist's Nachlass (works unpublished or even unknown at Saussure's ...
Structuralism owes its origin to Ferdinand Saussure (26 November 1857 - 22 February 19 13). He is. renowned for his revolutionary ideas about the fields of linguistics and semiology. His ...
De Mauro, 1968:283-334). De Mauro's study, it should be noted, represents the first serious attempt to evaluate Saussure's life in the light of his educational background and the prevailing intellectual activities of his time, in particular those which concern the investigation of linguistic phenomena.
I. Theme, Audience, and Approach. Stawarska has done a great service for those of us interested in these issues, but who may not have had the time (as in my case) to read her much larger, 250-page work on this topic, Saussure's Philosophy of Language as Phenomenology: Undoing the Doctrine of the Course in General Linguistics (Oxford ...
Abstract. This chapter briefly reviews the important contributions to the study of linguistics by Ferdinand de Saussure, followed by a critique of these theories, particularly outlining the role of Russian philosopher and theorist Mikhail Bakhtin in pointing out the shortcomings of Saussure's work, namely its lack of regard for linguistic ...
Saussure introduced Structuralism in Linguistics, marking a revolutionary break in the study of language, which had till then been historical and philological. In his Course in General Linguistics (1916), Saussure saw language as a system of signs constructed by convention. Understanding meaning to be relational, being produced by the interaction between various signifiers and signifieds,…
Chinese and Saussure's conception of writing in the Cours. One of the first lessons of the Cours is that linguistics deals with language as it is spoken and does not limit itself with the written word. However, the written word is so 'intimately bound' to the spoken word that it 'usurps' its role as the main object of study (CGL 23-24):
Ferdinand de Saussure (1857-1913) and Structural Linguistics was published in Introducing Literary Theories on page 70. ... Critical Fictions: Experiments in Writing from Le Nouveau Roman to the Oulipo. Tel Quel(1960-1982) Other French Feminisms: Sarah Kofman (1934-1994), Monique Wittig (1935-), Michèle Le Doeuff (1948-) ...
The emergence of semiology in post-war France coincided with renewed interest in the work of Ferdinand de Saussure and his 1916 Course in General Linguistics (henceforth Course).This interest extended beyond linguists, to include anthropologists, philosophers, literary critics and others associated with the rise of structuralism in France between the late 1940s and the mid 1960s.
pieces. Saussure made very valuable contribution to linguistics. His contribution to linguistics helped it to form a separate independent branch of language study. We can summarize Saussure's contribution to linguistics as follows. 1] Langue and Parole:- 1] Langue:- Saussure has introduced these two terms to distinguish the sense of the word ...