

8 Effective Strategies to Write Argumentative Essays
In a bustling university town, there lived a student named Alex. Popular for creativity and wit, one challenge seemed insurmountable for Alex– the dreaded argumentative essay!
One gloomy afternoon, as the rain tapped against the window pane, Alex sat at his cluttered desk, staring at a blank document on the computer screen. The assignment loomed large: a 350-600-word argumentative essay on a topic of their choice . With a sigh, he decided to seek help of mentor, Professor Mitchell, who was known for his passion for writing.
Entering Professor Mitchell’s office was like stepping into a treasure of knowledge. Bookshelves lined every wall, faint aroma of old manuscripts in the air and sticky notes over the wall. Alex took a deep breath and knocked on his door.
“Ah, Alex,” Professor Mitchell greeted with a warm smile. “What brings you here today?”
Alex confessed his struggles with the argumentative essay. After hearing his concerns, Professor Mitchell said, “Ah, the argumentative essay! Don’t worry, Let’s take a look at it together.” As he guided Alex to the corner shelf, Alex asked,
Table of Contents
“What is an Argumentative Essay?”
The professor replied, “An argumentative essay is a type of academic writing that presents a clear argument or a firm position on a contentious issue. Unlike other forms of essays, such as descriptive or narrative essays, these essays require you to take a stance, present evidence, and convince your audience of the validity of your viewpoint with supporting evidence. A well-crafted argumentative essay relies on concrete facts and supporting evidence rather than merely expressing the author’s personal opinions . Furthermore, these essays demand comprehensive research on the chosen topic and typically follows a structured format consisting of three primary sections: an introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph.”
He continued, “Argumentative essays are written in a wide range of subject areas, reflecting their applicability across disciplines. They are written in different subject areas like literature and philosophy, history, science and technology, political science, psychology, economics and so on.
Alex asked,
“When is an Argumentative Essay Written?”
The professor answered, “Argumentative essays are often assigned in academic settings, but they can also be written for various other purposes, such as editorials, opinion pieces, or blog posts. Some situations to write argumentative essays include:
1. Academic assignments
In school or college, teachers may assign argumentative essays as part of coursework. It help students to develop critical thinking and persuasive writing skills .
2. Debates and discussions
Argumentative essays can serve as the basis for debates or discussions in academic or competitive settings. Moreover, they provide a structured way to present and defend your viewpoint.
3. Opinion pieces
Newspapers, magazines, and online publications often feature opinion pieces that present an argument on a current issue or topic to influence public opinion.
4. Policy proposals
In government and policy-related fields, argumentative essays are used to propose and defend specific policy changes or solutions to societal problems.
5. Persuasive speeches
Before delivering a persuasive speech, it’s common to prepare an argumentative essay as a foundation for your presentation.
Regardless of the context, an argumentative essay should present a clear thesis statement , provide evidence and reasoning to support your position, address counterarguments, and conclude with a compelling summary of your main points. The goal is to persuade readers or listeners to accept your viewpoint or at least consider it seriously.”
Handing over a book, the professor continued, “Take a look on the elements or structure of an argumentative essay.”
Elements of an Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components:
Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
2. Evidence
Evidence must consist of factual information, data, examples, or expert opinions that support the claim. Also, it lends credibility by strengthening the writer’s position.
3. Counterarguments
Presenting a counterclaim demonstrates fairness and awareness of alternative perspectives.
4. Rebuttal
After presenting the counterclaim, the writer refutes it by offering counterarguments or providing evidence that weakens the opposing viewpoint. It shows that the writer has considered multiple perspectives and is prepared to defend their position.
The format of an argumentative essay typically follows the structure to ensure clarity and effectiveness in presenting an argument.
How to Write An Argumentative Essay
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an argumentative essay:
1. Introduction
- Begin with a compelling sentence or question to grab the reader’s attention.
- Provide context for the issue, including relevant facts, statistics, or historical background.
- Provide a concise thesis statement to present your position on the topic.
2. Body Paragraphs (usually three or more)
- Start each paragraph with a clear and focused topic sentence that relates to your thesis statement.
- Furthermore, provide evidence and explain the facts, statistics, examples, expert opinions, and quotations from credible sources that supports your thesis.
- Use transition sentences to smoothly move from one point to the next.
3. Counterargument and Rebuttal
- Acknowledge opposing viewpoints or potential objections to your argument.
- Also, address these counterarguments with evidence and explain why they do not weaken your position.
4. Conclusion
- Restate your thesis statement and summarize the key points you’ve made in the body of the essay.
- Leave the reader with a final thought, call to action, or broader implication related to the topic.
5. Citations and References
- Properly cite all the sources you use in your essay using a consistent citation style.
- Also, include a bibliography or works cited at the end of your essay.
6. Formatting and Style
- Follow any specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or institution.
- Use a professional and academic tone in your writing and edit your essay to avoid content, spelling and grammar mistakes .
Remember that the specific requirements for formatting an argumentative essay may vary depending on your instructor’s guidelines or the citation style you’re using (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Always check the assignment instructions or style guide for any additional requirements or variations in formatting.
Did you understand what Prof. Mitchell explained Alex? Check it now!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

Prof. Mitchell continued, “An argumentative essay can adopt various approaches when dealing with opposing perspectives. It may offer a balanced presentation of both sides, providing equal weight to each, or it may advocate more strongly for one side while still acknowledging the existence of opposing views.” As Alex listened carefully to the Professor’s thoughts, his eyes fell on a page with examples of argumentative essay.
Example of an Argumentative Essay
Alex picked the book and read the example. It helped him to understand the concept. Furthermore, he could now connect better to the elements and steps of the essay which Prof. Mitchell had mentioned earlier. Aren’t you keen to know how an argumentative essay should be like? Here is an example of a well-crafted argumentative essay , which was read by Alex. After Alex finished reading the example, the professor turned the page and continued, “Check this page to know the importance of writing an argumentative essay in developing skills of an individual.”
Importance of an Argumentative Essay
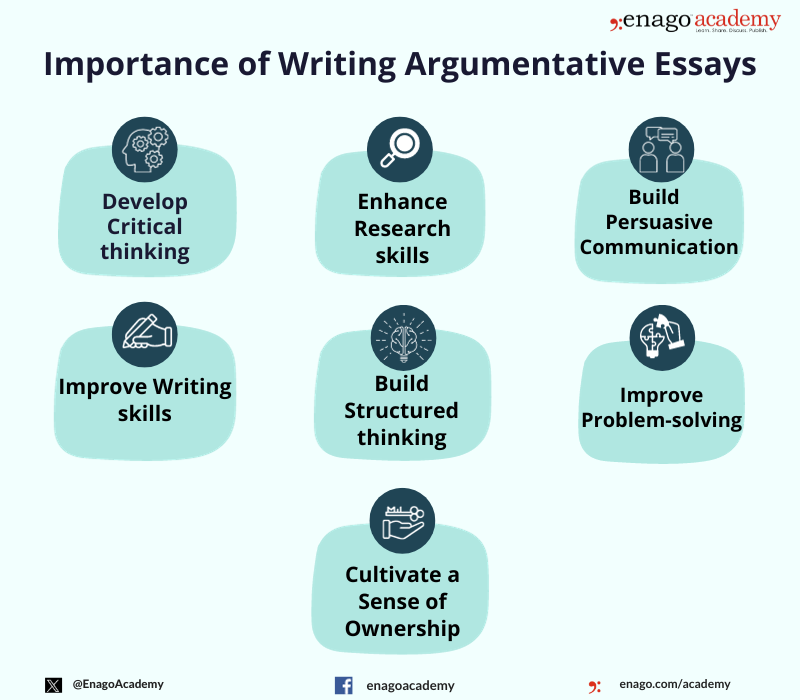
After understanding the benefits, Alex was convinced by the ability of the argumentative essays in advocating one’s beliefs and favor the author’s position. Alex asked,
“How are argumentative essays different from the other types?”
Prof. Mitchell answered, “Argumentative essays differ from other types of essays primarily in their purpose, structure, and approach in presenting information. Unlike expository essays, argumentative essays persuade the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action on a controversial issue. Furthermore, they differ from descriptive essays by not focusing vividly on describing a topic. Also, they are less engaging through storytelling as compared to the narrative essays.
Alex said, “Given the direct and persuasive nature of argumentative essays, can you suggest some strategies to write an effective argumentative essay?
Turning the pages of the book, Prof. Mitchell replied, “Sure! You can check this infographic to get some tips for writing an argumentative essay.”
Effective Strategies to Write an Argumentative Essay

As days turned into weeks, Alex diligently worked on his essay. He researched, gathered evidence, and refined his thesis. It was a long and challenging journey, filled with countless drafts and revisions.
Finally, the day arrived when Alex submitted their essay. As he clicked the “Submit” button, a sense of accomplishment washed over him. He realized that the argumentative essay, while challenging, had improved his critical thinking and transformed him into a more confident writer. Furthermore, Alex received feedback from his professor, a mix of praise and constructive criticism. It was a humbling experience, a reminder that every journey has its obstacles and opportunities for growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
An argumentative essay can be written as follows- 1. Choose a Topic 2. Research and Collect Evidences 3. Develop a Clear Thesis Statement 4. Outline Your Essay- Introduction, Body Paragraphs and Conclusion 5. Revise and Edit 6. Format and Cite Sources 7. Final Review
One must choose a clear, concise and specific statement as a claim. It must be debatable and establish your position. Avoid using ambiguous or unclear while making a claim. To strengthen your claim, address potential counterarguments or opposing viewpoints. Additionally, use persuasive language and rhetoric to make your claim more compelling
Starting an argument essay effectively is crucial to engage your readers and establish the context for your argument. Here’s how you can start an argument essay are: 1. Begin With an Engaging Hook 2. Provide Background Information 3. Present Your Thesis Statement 4. Briefly Outline Your Main 5. Establish Your Credibility
The key features of an argumentative essay are: 1. Clear and Specific Thesis Statement 2. Credible Evidence 3. Counterarguments 4. Structured Body Paragraph 5. Logical Flow 6. Use of Persuasive Techniques 7. Formal Language
An argumentative essay typically consists of the following main parts or sections: 1. Introduction 2. Body Paragraphs 3. Counterargument and Rebuttal 4. Conclusion 5. References (if applicable)
The main purpose of an argumentative essay is to persuade the reader to accept or agree with a particular viewpoint or position on a controversial or debatable topic. In other words, the primary goal of an argumentative essay is to convince the audience that the author's argument or thesis statement is valid, logical, and well-supported by evidence and reasoning.
Great article! The topic is simplified well! Keep up the good work
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Using AI for Journal Selection — Simplifying your academic publishing journey in the smart way
Strategic journal selection plays a pivotal role in maximizing the impact of one’s scholarly work.…

- Career Corner
Recognizing the signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Reassessing the Lab Environment to Create an Equitable and Inclusive Space
The pursuit of scientific discovery has long been fueled by diverse minds and perspectives. Yet…

Simplifying the Literature Review Journey — A comparative analysis of 6 AI summarization tools
Imagine having to skim through and read mountains of research papers and books, only to…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…
How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without…
Digital Citations: A comprehensive guide to citing of websites in APA, MLA, and CMOS…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay

4-minute read
- 30th April 2022
An argumentative essay is a structured, compelling piece of writing where an author clearly defines their stance on a specific topic. This is a very popular style of writing assigned to students at schools, colleges, and universities. Learn the steps to researching, structuring, and writing an effective argumentative essay below.
Requirements of an Argumentative Essay
To effectively achieve its purpose, an argumentative essay must contain:
● A concise thesis statement that introduces readers to the central argument of the essay
● A clear, logical, argument that engages readers
● Ample research and evidence that supports your argument
Approaches to Use in Your Argumentative Essay
1. classical.
● Clearly present the central argument.
● Outline your opinion.
● Provide enough evidence to support your theory.
2. Toulmin
● State your claim.
● Supply the evidence for your stance.
● Explain how these findings support the argument.
● Include and discuss any limitations of your belief.
3. Rogerian
● Explain the opposing stance of your argument.
● Discuss the problems with adopting this viewpoint.
● Offer your position on the matter.
● Provide reasons for why yours is the more beneficial stance.
● Include a potential compromise for the topic at hand.
Tips for Writing a Well-Written Argumentative Essay
● Introduce your topic in a bold, direct, and engaging manner to captivate your readers and encourage them to keep reading.
● Provide sufficient evidence to justify your argument and convince readers to adopt this point of view.
● Consider, include, and fairly present all sides of the topic.
● Structure your argument in a clear, logical manner that helps your readers to understand your thought process.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
● Discuss any counterarguments that might be posed.
● Use persuasive writing that’s appropriate for your target audience and motivates them to agree with you.
Steps to Write an Argumentative Essay
Follow these basic steps to write a powerful and meaningful argumentative essay :
Step 1: Choose a topic that you’re passionate about
If you’ve already been given a topic to write about, pick a stance that resonates deeply with you. This will shine through in your writing, make the research process easier, and positively influence the outcome of your argument.
Step 2: Conduct ample research to prove the validity of your argument
To write an emotive argumentative essay , finding enough research to support your theory is a must. You’ll need solid evidence to convince readers to agree with your take on the matter. You’ll also need to logically organize the research so that it naturally convinces readers of your viewpoint and leaves no room for questioning.
Step 3: Follow a simple, easy-to-follow structure and compile your essay
A good structure to ensure a well-written and effective argumentative essay includes:
Introduction
● Introduce your topic.
● Offer background information on the claim.
● Discuss the evidence you’ll present to support your argument.
● State your thesis statement, a one-to-two sentence summary of your claim.
● This is the section where you’ll develop and expand on your argument.
● It should be split into three or four coherent paragraphs, with each one presenting its own idea.
● Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that indicates why readers should adopt your belief or stance.
● Include your research, statistics, citations, and other supporting evidence.
● Discuss opposing viewpoints and why they’re invalid.
● This part typically consists of one paragraph.
● Summarize your research and the findings that were presented.
● Emphasize your initial thesis statement.
● Persuade readers to agree with your stance.
We certainly hope that you feel inspired to use these tips when writing your next argumentative essay . And, if you’re currently elbow-deep in writing one, consider submitting a free sample to us once it’s completed. Our expert team of editors can help ensure that it’s concise, error-free, and effective!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Praxis Core Writing
Course: praxis core writing > unit 1, argumentative essay | quick guide.
- Source-based essay | Quick guide
- Revision in context | Quick guide
- Within-sentence punctuation | Quick guide
- Subordination and coordination | Quick guide
- Independent and dependent Clauses | Video lesson
- Parallel structure | Quick guide
- Modifier placement | Quick guide
- Shifts in verb tense | Quick guide
- Pronoun clarity | Quick guide
- Pronoun agreement | Quick guide
- Subject-verb agreement | Quick guide
- Noun agreement | Quick guide
- Frequently confused words | Quick guide
- Conventional expressions | Quick guide
- Logical comparison | Quick guide
- Concision | Quick guide
- Adjective/adverb confusion | Quick guide
- Negation | Quick guide
- Capitalization | Quick guide
- Apostrophe use | Quick guide
- Research skills | Quick guide
Argumentative essay (30 minutes)
- states or clearly implies the writer’s position or thesis
- organizes and develops ideas logically, making insightful connections between them
- clearly explains key ideas, supporting them with well-chosen reasons, examples, or details
- displays effective sentence variety
- clearly displays facility in the use of language
- is generally free from errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics
- organizes and develops ideas clearly, making connections between them
- explains key ideas, supporting them with relevant reasons, examples, or details
- displays some sentence variety
- displays facility in the use of language
- states or implies the writer’s position or thesis
- shows control in the organization and development of ideas
- explains some key ideas, supporting them with adequate reasons, examples, or details
- displays adequate use of language
- shows control of grammar, usage, and mechanics, but may display errors
- limited in stating or implying a position or thesis
- limited control in the organization and development of ideas
- inadequate reasons, examples, or details to explain key ideas
- an accumulation of errors in the use of language
- an accumulation of errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics
- no clear position or thesis
- weak organization or very little development
- few or no relevant reasons, examples, or details
- frequent serious errors in the use of language
- frequent serious errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics
- contains serious and persistent writing errors or
- is incoherent or
- is undeveloped or
- is off-topic
How should I build a thesis?
- (Choice A) Kids should find role models that are worthier than celebrities because celebrities may be famous for reasons that aren't admirable. A Kids should find role models that are worthier than celebrities because celebrities may be famous for reasons that aren't admirable.
- (Choice B) Because they profit from the admiration of youths, celebrities have a moral responsibility for the reactions their behaviors provoke in fans. B Because they profit from the admiration of youths, celebrities have a moral responsibility for the reactions their behaviors provoke in fans.
- (Choice C) Celebrities may have more imitators than most people, but they hold no more responsibility over the example they set than the average person. C Celebrities may have more imitators than most people, but they hold no more responsibility over the example they set than the average person.
- (Choice D) Notoriety is not always a choice, and some celebrities may not want to be role models. D Notoriety is not always a choice, and some celebrities may not want to be role models.
- (Choice E) Parents have a moral responsibility to serve as immediate role models for their children. E Parents have a moral responsibility to serve as immediate role models for their children.
How should I support my thesis?
- (Choice A) As basketball star Charles Barkley stated in a famous advertising campaign for Nike, he was paid to dominate on the basketball court, not to raise your kids. A As basketball star Charles Barkley stated in a famous advertising campaign for Nike, he was paid to dominate on the basketball court, not to raise your kids.
- (Choice B) Many celebrities do consider themselves responsible for setting a good example and create non-profit organizations through which they can benefit youths. B Many celebrities do consider themselves responsible for setting a good example and create non-profit organizations through which they can benefit youths.
- (Choice C) Many celebrities, like Kylie Jenner with her billion-dollar cosmetics company, profit directly from being imitated by fans who purchase sponsored products. C Many celebrities, like Kylie Jenner with her billion-dollar cosmetics company, profit directly from being imitated by fans who purchase sponsored products.
- (Choice D) My ten-year-old nephew may love Drake's music, but his behaviors are more similar to those of the adults he interacts with on a daily basis, like his parents and teachers. D My ten-year-old nephew may love Drake's music, but his behaviors are more similar to those of the adults he interacts with on a daily basis, like his parents and teachers.
- (Choice E) It's very common for young people to wear fashions similar to those of their favorite celebrities. E It's very common for young people to wear fashions similar to those of their favorite celebrities.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write an a+ argumentative essay.
Miscellaneous

You'll no doubt have to write a number of argumentative essays in both high school and college, but what, exactly, is an argumentative essay and how do you write the best one possible? Let's take a look.
A great argumentative essay always combines the same basic elements: approaching an argument from a rational perspective, researching sources, supporting your claims using facts rather than opinion, and articulating your reasoning into the most cogent and reasoned points. Argumentative essays are great building blocks for all sorts of research and rhetoric, so your teachers will expect you to master the technique before long.
But if this sounds daunting, never fear! We'll show how an argumentative essay differs from other kinds of papers, how to research and write them, how to pick an argumentative essay topic, and where to find example essays. So let's get started.
What Is an Argumentative Essay? How Is it Different from Other Kinds of Essays?
There are two basic requirements for any and all essays: to state a claim (a thesis statement) and to support that claim with evidence.
Though every essay is founded on these two ideas, there are several different types of essays, differentiated by the style of the writing, how the writer presents the thesis, and the types of evidence used to support the thesis statement.
Essays can be roughly divided into four different types:
#1: Argumentative #2: Persuasive #3: Expository #4: Analytical
So let's look at each type and what the differences are between them before we focus the rest of our time to argumentative essays.
Argumentative Essay
Argumentative essays are what this article is all about, so let's talk about them first.
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance.
An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the factually and logically correct one. This means that an argumentative essay must use only evidence-based support to back up a claim , rather than emotional or philosophical reasoning (which is often allowed in other types of essays). Thus, an argumentative essay has a burden of substantiated proof and sources , whereas some other types of essays (namely persuasive essays) do not.
You can write an argumentative essay on any topic, so long as there's room for argument. Generally, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one, so long as you support the argumentative essay with hard evidence.
Example topics of an argumentative essay:
- "Should farmers be allowed to shoot wolves if those wolves injure or kill farm animals?"
- "Should the drinking age be lowered in the United States?"
- "Are alternatives to democracy effective and/or feasible to implement?"
The next three types of essays are not argumentative essays, but you may have written them in school. We're going to cover them so you know what not to do for your argumentative essay.
Persuasive Essay
Persuasive essays are similar to argumentative essays, so it can be easy to get them confused. But knowing what makes an argumentative essay different than a persuasive essay can often mean the difference between an excellent grade and an average one.
Persuasive essays seek to persuade a reader to agree with the point of view of the writer, whether that point of view is based on factual evidence or not. The writer has much more flexibility in the evidence they can use, with the ability to use moral, cultural, or opinion-based reasoning as well as factual reasoning to persuade the reader to agree the writer's side of a given issue.
Instead of being forced to use "pure" reason as one would in an argumentative essay, the writer of a persuasive essay can manipulate or appeal to the reader's emotions. So long as the writer attempts to steer the readers into agreeing with the thesis statement, the writer doesn't necessarily need hard evidence in favor of the argument.
Often, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one—the difference is all in the approach and the evidence you present.
Example topics of a persuasive essay:
- "Should children be responsible for their parents' debts?"
- "Should cheating on a test be automatic grounds for expulsion?"
- "How much should sports leagues be held accountable for player injuries and the long-term consequences of those injuries?"
Expository Essay
An expository essay is typically a short essay in which the writer explains an idea, issue, or theme , or discusses the history of a person, place, or idea.
This is typically a fact-forward essay with little argument or opinion one way or the other.
Example topics of an expository essay:
- "The History of the Philadelphia Liberty Bell"
- "The Reasons I Always Wanted to be a Doctor"
- "The Meaning Behind the Colloquialism ‘People in Glass Houses Shouldn't Throw Stones'"
Analytical Essay
An analytical essay seeks to delve into the deeper meaning of a text or work of art, or unpack a complicated idea . These kinds of essays closely interpret a source and look into its meaning by analyzing it at both a macro and micro level.
This type of analysis can be augmented by historical context or other expert or widely-regarded opinions on the subject, but is mainly supported directly through the original source (the piece or art or text being analyzed) .
Example topics of an analytical essay:
- "Victory Gin in Place of Water: The Symbolism Behind Gin as the Only Potable Substance in George Orwell's 1984"
- "Amarna Period Art: The Meaning Behind the Shift from Rigid to Fluid Poses"
- "Adultery During WWII, as Told Through a Series of Letters to and from Soldiers"

There are many different types of essay and, over time, you'll be able to master them all.
A Typical Argumentative Essay Assignment
The average argumentative essay is between three to five pages, and will require at least three or four separate sources with which to back your claims . As for the essay topic , you'll most often be asked to write an argumentative essay in an English class on a "general" topic of your choice, ranging the gamut from science, to history, to literature.
But while the topics of an argumentative essay can span several different fields, the structure of an argumentative essay is always the same: you must support a claim—a claim that can reasonably have multiple sides—using multiple sources and using a standard essay format (which we'll talk about later on).
This is why many argumentative essay topics begin with the word "should," as in:
- "Should all students be required to learn chemistry in high school?"
- "Should children be required to learn a second language?"
- "Should schools or governments be allowed to ban books?"
These topics all have at least two sides of the argument: Yes or no. And you must support the side you choose with evidence as to why your side is the correct one.
But there are also plenty of other ways to frame an argumentative essay as well:
- "Does using social media do more to benefit or harm people?"
- "Does the legal status of artwork or its creators—graffiti and vandalism, pirated media, a creator who's in jail—have an impact on the art itself?"
- "Is or should anyone ever be ‘above the law?'"
Though these are worded differently than the first three, you're still essentially forced to pick between two sides of an issue: yes or no, for or against, benefit or detriment. Though your argument might not fall entirely into one side of the divide or another—for instance, you could claim that social media has positively impacted some aspects of modern life while being a detriment to others—your essay should still support one side of the argument above all. Your final stance would be that overall , social media is beneficial or overall , social media is harmful.
If your argument is one that is mostly text-based or backed by a single source (e.g., "How does Salinger show that Holden Caulfield is an unreliable narrator?" or "Does Gatsby personify the American Dream?"), then it's an analytical essay, rather than an argumentative essay. An argumentative essay will always be focused on more general topics so that you can use multiple sources to back up your claims.
Good Argumentative Essay Topics
So you know the basic idea behind an argumentative essay, but what topic should you write about?
Again, almost always, you'll be asked to write an argumentative essay on a free topic of your choice, or you'll be asked to select between a few given topics . If you're given complete free reign of topics, then it'll be up to you to find an essay topic that no only appeals to you, but that you can turn into an A+ argumentative essay.
What makes a "good" argumentative essay topic depends on both the subject matter and your personal interest —it can be hard to give your best effort on something that bores you to tears! But it can also be near impossible to write an argumentative essay on a topic that has no room for debate.
As we said earlier, a good argumentative essay topic will be one that has the potential to reasonably go in at least two directions—for or against, yes or no, and why . For example, it's pretty hard to write an argumentative essay on whether or not people should be allowed to murder one another—not a whole lot of debate there for most people!—but writing an essay for or against the death penalty has a lot more wiggle room for evidence and argument.
A good topic is also one that can be substantiated through hard evidence and relevant sources . So be sure to pick a topic that other people have studied (or at least studied elements of) so that you can use their data in your argument. For example, if you're arguing that it should be mandatory for all middle school children to play a sport, you might have to apply smaller scientific data points to the larger picture you're trying to justify. There are probably several studies you could cite on the benefits of physical activity and the positive effect structure and teamwork has on young minds, but there's probably no study you could use where a group of scientists put all middle-schoolers in one jurisdiction into a mandatory sports program (since that's probably never happened). So long as your evidence is relevant to your point and you can extrapolate from it to form a larger whole, you can use it as a part of your resource material.
And if you need ideas on where to get started, or just want to see sample argumentative essay topics, then check out these links for hundreds of potential argumentative essay topics.
101 Persuasive (or Argumentative) Essay and Speech Topics
301 Prompts for Argumentative Writing
Top 50 Ideas for Argumentative/Persuasive Essay Writing
[Note: some of these say "persuasive essay topics," but just remember that the same topic can often be used for both a persuasive essay and an argumentative essay; the difference is in your writing style and the evidence you use to support your claims.]

KO! Find that one argumentative essay topic you can absolutely conquer.
Argumentative Essay Format
Argumentative Essays are composed of four main elements:
- A position (your argument)
- Your reasons
- Supporting evidence for those reasons (from reliable sources)
- Counterargument(s) (possible opposing arguments and reasons why those arguments are incorrect)
If you're familiar with essay writing in general, then you're also probably familiar with the five paragraph essay structure . This structure is a simple tool to show how one outlines an essay and breaks it down into its component parts, although it can be expanded into as many paragraphs as you want beyond the core five.
The standard argumentative essay is often 3-5 pages, which will usually mean a lot more than five paragraphs, but your overall structure will look the same as a much shorter essay.
An argumentative essay at its simplest structure will look like:
Paragraph 1: Intro
- Set up the story/problem/issue
- Thesis/claim
Paragraph 2: Support
- Reason #1 claim is correct
- Supporting evidence with sources
Paragraph 3: Support
- Reason #2 claim is correct
Paragraph 4: Counterargument
- Explanation of argument for the other side
- Refutation of opposing argument with supporting evidence
Paragraph 5: Conclusion
- Re-state claim
- Sum up reasons and support of claim from the essay to prove claim is correct
Now let's unpack each of these paragraph types to see how they work (with examples!), what goes into them, and why.
Paragraph 1—Set Up and Claim
Your first task is to introduce the reader to the topic at hand so they'll be prepared for your claim. Give a little background information, set the scene, and give the reader some stakes so that they care about the issue you're going to discuss.
Next, you absolutely must have a position on an argument and make that position clear to the readers. It's not an argumentative essay unless you're arguing for a specific claim, and this claim will be your thesis statement.
Your thesis CANNOT be a mere statement of fact (e.g., "Washington DC is the capital of the United States"). Your thesis must instead be an opinion which can be backed up with evidence and has the potential to be argued against (e.g., "New York should be the capital of the United States").
Paragraphs 2 and 3—Your Evidence
These are your body paragraphs in which you give the reasons why your argument is the best one and back up this reasoning with concrete evidence .
The argument supporting the thesis of an argumentative essay should be one that can be supported by facts and evidence, rather than personal opinion or cultural or religious mores.
For example, if you're arguing that New York should be the new capital of the US, you would have to back up that fact by discussing the factual contrasts between New York and DC in terms of location, population, revenue, and laws. You would then have to talk about the precedents for what makes for a good capital city and why New York fits the bill more than DC does.
Your argument can't simply be that a lot of people think New York is the best city ever and that you agree.
In addition to using concrete evidence, you always want to keep the tone of your essay passionate, but impersonal . Even though you're writing your argument from a single opinion, don't use first person language—"I think," "I feel," "I believe,"—to present your claims. Doing so is repetitive, since by writing the essay you're already telling the audience what you feel, and using first person language weakens your writing voice.
For example,
"I think that Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
"Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
The second statement sounds far stronger and more analytical.
Paragraph 4—Argument for the Other Side and Refutation
Even without a counter argument, you can make a pretty persuasive claim, but a counterargument will round out your essay into one that is much more persuasive and substantial.
By anticipating an argument against your claim and taking the initiative to counter it, you're allowing yourself to get ahead of the game. This way, you show that you've given great thought to all sides of the issue before choosing your position, and you demonstrate in multiple ways how yours is the more reasoned and supported side.
Paragraph 5—Conclusion
This paragraph is where you re-state your argument and summarize why it's the best claim.
Briefly touch on your supporting evidence and voila! A finished argumentative essay.
Your essay should have just as awesome a skeleton as this plesiosaur does. (In other words: a ridiculously awesome skeleton)
Argumentative Essay Example: 5-Paragraph Style
It always helps to have an example to learn from. I've written a full 5-paragraph argumentative essay here. Look at how I state my thesis in paragraph 1, give supporting evidence in paragraphs 2 and 3, address a counterargument in paragraph 4, and conclude in paragraph 5.
Topic: Is it possible to maintain conflicting loyalties?
Paragraph 1
It is almost impossible to go through life without encountering a situation where your loyalties to different people or causes come into conflict with each other. Maybe you have a loving relationship with your sister, but she disagrees with your decision to join the army, or you find yourself torn between your cultural beliefs and your scientific ones. These conflicting loyalties can often be maintained for a time, but as examples from both history and psychological theory illustrate, sooner or later, people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever.
The first two sentences set the scene and give some hypothetical examples and stakes for the reader to care about.
The third sentence finishes off the intro with the thesis statement, making very clear how the author stands on the issue ("people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever." )
Paragraphs 2 and 3
Psychological theory states that human beings are not equipped to maintain conflicting loyalties indefinitely and that attempting to do so leads to a state called "cognitive dissonance." Cognitive dissonance theory is the psychological idea that people undergo tremendous mental stress or anxiety when holding contradictory beliefs, values, or loyalties (Festinger, 1957). Even if human beings initially hold a conflicting loyalty, they will do their best to find a mental equilibrium by making a choice between those loyalties—stay stalwart to a belief system or change their beliefs. One of the earliest formal examples of cognitive dissonance theory comes from Leon Festinger's When Prophesy Fails . Members of an apocalyptic cult are told that the end of the world will occur on a specific date and that they alone will be spared the Earth's destruction. When that day comes and goes with no apocalypse, the cult members face a cognitive dissonance between what they see and what they've been led to believe (Festinger, 1956). Some choose to believe that the cult's beliefs are still correct, but that the Earth was simply spared from destruction by mercy, while others choose to believe that they were lied to and that the cult was fraudulent all along. Both beliefs cannot be correct at the same time, and so the cult members are forced to make their choice.
But even when conflicting loyalties can lead to potentially physical, rather than just mental, consequences, people will always make a choice to fall on one side or other of a dividing line. Take, for instance, Nicolaus Copernicus, a man born and raised in Catholic Poland (and educated in Catholic Italy). Though the Catholic church dictated specific scientific teachings, Copernicus' loyalty to his own observations and scientific evidence won out over his loyalty to his country's government and belief system. When he published his heliocentric model of the solar system--in opposition to the geocentric model that had been widely accepted for hundreds of years (Hannam, 2011)-- Copernicus was making a choice between his loyalties. In an attempt t o maintain his fealty both to the established system and to what he believed, h e sat on his findings for a number of years (Fantoli, 1994). But, ultimately, Copernicus made the choice to side with his beliefs and observations above all and published his work for the world to see (even though, in doing so, he risked both his reputation and personal freedoms).
These two paragraphs provide the reasons why the author supports the main argument and uses substantiated sources to back those reasons.
The paragraph on cognitive dissonance theory gives both broad supporting evidence and more narrow, detailed supporting evidence to show why the thesis statement is correct not just anecdotally but also scientifically and psychologically. First, we see why people in general have a difficult time accepting conflicting loyalties and desires and then how this applies to individuals through the example of the cult members from the Dr. Festinger's research.
The next paragraph continues to use more detailed examples from history to provide further evidence of why the thesis that people cannot indefinitely maintain conflicting loyalties is true.
Paragraph 4
Some will claim that it is possible to maintain conflicting beliefs or loyalties permanently, but this is often more a matter of people deluding themselves and still making a choice for one side or the other, rather than truly maintaining loyalty to both sides equally. For example, Lancelot du Lac typifies a person who claims to maintain a balanced loyalty between to two parties, but his attempt to do so fails (as all attempts to permanently maintain conflicting loyalties must). Lancelot tells himself and others that he is equally devoted to both King Arthur and his court and to being Queen Guinevere's knight (Malory, 2008). But he can neither be in two places at once to protect both the king and queen, nor can he help but let his romantic feelings for the queen to interfere with his duties to the king and the kingdom. Ultimately, he and Queen Guinevere give into their feelings for one another and Lancelot—though he denies it—chooses his loyalty to her over his loyalty to Arthur. This decision plunges the kingdom into a civil war, ages Lancelot prematurely, and ultimately leads to Camelot's ruin (Raabe, 1987). Though Lancelot claimed to have been loyal to both the king and the queen, this loyalty was ultimately in conflict, and he could not maintain it.
Here we have the acknowledgement of a potential counter-argument and the evidence as to why it isn't true.
The argument is that some people (or literary characters) have asserted that they give equal weight to their conflicting loyalties. The refutation is that, though some may claim to be able to maintain conflicting loyalties, they're either lying to others or deceiving themselves. The paragraph shows why this is true by providing an example of this in action.
Paragraph 5
Whether it be through literature or history, time and time again, people demonstrate the challenges of trying to manage conflicting loyalties and the inevitable consequences of doing so. Though belief systems are malleable and will often change over time, it is not possible to maintain two mutually exclusive loyalties or beliefs at once. In the end, people always make a choice, and loyalty for one party or one side of an issue will always trump loyalty to the other.
The concluding paragraph summarizes the essay, touches on the evidence presented, and re-states the thesis statement.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 8 Steps
Writing the best argumentative essay is all about the preparation, so let's talk steps:
#1: Preliminary Research
If you have the option to pick your own argumentative essay topic (which you most likely will), then choose one or two topics you find the most intriguing or that you have a vested interest in and do some preliminary research on both sides of the debate.
Do an open internet search just to see what the general chatter is on the topic and what the research trends are.
Did your preliminary reading influence you to pick a side or change your side? Without diving into all the scholarly articles at length, do you believe there's enough evidence to support your claim? Have there been scientific studies? Experiments? Does a noted scholar in the field agree with you? If not, you may need to pick another topic or side of the argument to support.
#2: Pick Your Side and Form Your Thesis
Now's the time to pick the side of the argument you feel you can support the best and summarize your main point into your thesis statement.
Your thesis will be the basis of your entire essay, so make sure you know which side you're on, that you've stated it clearly, and that you stick by your argument throughout the entire essay .
#3: Heavy-Duty Research Time
You've taken a gander at what the internet at large has to say on your argument, but now's the time to actually read those sources and take notes.
Check scholarly journals online at Google Scholar , the Directory of Open Access Journals , or JStor . You can also search individual university or school libraries and websites to see what kinds of academic articles you can access for free. Keep track of your important quotes and page numbers and put them somewhere that's easy to find later.
And don't forget to check your school or local libraries as well!
#4: Outline
Follow the five-paragraph outline structure from the previous section.
Fill in your topic, your reasons, and your supporting evidence into each of the categories.
Before you begin to flesh out the essay, take a look at what you've got. Is your thesis statement in the first paragraph? Is it clear? Is your argument logical? Does your supporting evidence support your reasoning?
By outlining your essay, you streamline your process and take care of any logic gaps before you dive headfirst into the writing. This will save you a lot of grief later on if you need to change your sources or your structure, so don't get too trigger-happy and skip this step.
Now that you've laid out exactly what you'll need for your essay and where, it's time to fill in all the gaps by writing it out.
Take it one step at a time and expand your ideas into complete sentences and substantiated claims. It may feel daunting to turn an outline into a complete draft, but just remember that you've already laid out all the groundwork; now you're just filling in the gaps.
If you have the time before deadline, give yourself a day or two (or even just an hour!) away from your essay . Looking it over with fresh eyes will allow you to see errors, both minor and major, that you likely would have missed had you tried to edit when it was still raw.
Take a first pass over the entire essay and try your best to ignore any minor spelling or grammar mistakes—you're just looking at the big picture right now. Does it make sense as a whole? Did the essay succeed in making an argument and backing that argument up logically? (Do you feel persuaded?)
If not, go back and make notes so that you can fix it for your final draft.
Once you've made your revisions to the overall structure, mark all your small errors and grammar problems so you can fix them in the next draft.
#7: Final Draft
Use the notes you made on the rough draft and go in and hack and smooth away until you're satisfied with the final result.
A checklist for your final draft:
- Formatting is correct according to your teacher's standards
- No errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation
- Essay is the right length and size for the assignment
- The argument is present, consistent, and concise
- Each reason is supported by relevant evidence
- The essay makes sense overall
#8: Celebrate!
Once you've brought that final draft to a perfect polish and turned in your assignment, you're done! Go you!

Be prepared and ♪ you'll never go hungry again ♪, *cough*, or struggle with your argumentative essay-writing again. (Walt Disney Studios)
Good Examples of Argumentative Essays Online
Theory is all well and good, but examples are key. Just to get you started on what a fully-fleshed out argumentative essay looks like, let's see some examples in action.
Check out these two argumentative essay examples on the use of landmines and freons (and note the excellent use of concrete sources to back up their arguments!).
The Use of Landmines
A Shattered Sky
The Take-Aways: Keys to Writing an Argumentative Essay
At first, writing an argumentative essay may seem like a monstrous hurdle to overcome, but with the proper preparation and understanding, you'll be able to knock yours out of the park.
Remember the differences between a persuasive essay and an argumentative one, make sure your thesis is clear, and double-check that your supporting evidence is both relevant to your point and well-sourced . Pick your topic, do your research, make your outline, and fill in the gaps. Before you know it, you'll have yourself an A+ argumentative essay there, my friend.
What's Next?
Now you know the ins and outs of an argumentative essay, but how comfortable are you writing in other styles? Learn more about the four writing styles and when it makes sense to use each .
Understand how to make an argument, but still having trouble organizing your thoughts? Check out our guide to three popular essay formats and choose which one is right for you.
Ready to make your case, but not sure what to write about? We've created a list of 50 potential argumentative essay topics to spark your imagination.
Courtney scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT in high school and went on to graduate from Stanford University with a degree in Cultural and Social Anthropology. She is passionate about bringing education and the tools to succeed to students from all backgrounds and walks of life, as she believes open education is one of the great societal equalizers. She has years of tutoring experience and writes creative works in her free time.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

What this handout is about
This handout will define what an argument is and explain why you need one in most of your academic essays.
Arguments are everywhere
You may be surprised to hear that the word “argument” does not have to be written anywhere in your assignment for it to be an important part of your task. In fact, making an argument—expressing a point of view on a subject and supporting it with evidence—is often the aim of academic writing. Your instructors may assume that you know this and thus may not explain the importance of arguments in class.
Most material you learn in college is or has been debated by someone, somewhere, at some time. Even when the material you read or hear is presented as a simple fact, it may actually be one person’s interpretation of a set of information. Instructors may call on you to examine that interpretation and defend it, refute it, or offer some new view of your own. In writing assignments, you will almost always need to do more than just summarize information that you have gathered or regurgitate facts that have been discussed in class. You will need to develop a point of view on or interpretation of that material and provide evidence for your position.
Consider an example. For nearly 2000 years, educated people in many Western cultures believed that bloodletting—deliberately causing a sick person to lose blood—was the most effective treatment for a variety of illnesses. The claim that bloodletting is beneficial to human health was not widely questioned until the 1800s, and some physicians continued to recommend bloodletting as late as the 1920s. Medical practices have now changed because some people began to doubt the effectiveness of bloodletting; these people argued against it and provided convincing evidence. Human knowledge grows out of such differences of opinion, and scholars like your instructors spend their lives engaged in debate over what claims may be counted as accurate in their fields. In their courses, they want you to engage in similar kinds of critical thinking and debate.
Argumentation is not just what your instructors do. We all use argumentation on a daily basis, and you probably already have some skill at crafting an argument. The more you improve your skills in this area, the better you will be at thinking critically, reasoning, making choices, and weighing evidence.
Making a claim
What is an argument? In academic writing, an argument is usually a main idea, often called a “claim” or “thesis statement,” backed up with evidence that supports the idea. In the majority of college papers, you will need to make some sort of claim and use evidence to support it, and your ability to do this well will separate your papers from those of students who see assignments as mere accumulations of fact and detail. In other words, gone are the happy days of being given a “topic” about which you can write anything. It is time to stake out a position and prove why it is a good position for a thinking person to hold. See our handout on thesis statements .
Claims can be as simple as “Protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged,” with evidence such as, “In this experiment, protons and electrons acted in such and such a way.” Claims can also be as complex as “Genre is the most important element to the contract of expectations between filmmaker and audience,” using reasoning and evidence such as, “defying genre expectations can create a complete apocalypse of story form and content, leaving us stranded in a sort of genre-less abyss.” In either case, the rest of your paper will detail the reasoning and evidence that have led you to believe that your position is best.
When beginning to write a paper, ask yourself, “What is my point?” For example, the point of this handout is to help you become a better writer, and we are arguing that an important step in the process of writing effective arguments is understanding the concept of argumentation. If your papers do not have a main point, they cannot be arguing for anything. Asking yourself what your point is can help you avoid a mere “information dump.” Consider this: your instructors probably know a lot more than you do about your subject matter. Why, then, would you want to provide them with material they already know? Instructors are usually looking for two things:
- Proof that you understand the material
- A demonstration of your ability to use or apply the material in ways that go beyond what you have read or heard.
This second part can be done in many ways: you can critique the material, apply it to something else, or even just explain it in a different way. In order to succeed at this second step, though, you must have a particular point to argue.
Arguments in academic writing are usually complex and take time to develop. Your argument will need to be more than a simple or obvious statement such as “Frank Lloyd Wright was a great architect.” Such a statement might capture your initial impressions of Wright as you have studied him in class; however, you need to look deeper and express specifically what caused that “greatness.” Your instructor will probably expect something more complicated, such as “Frank Lloyd Wright’s architecture combines elements of European modernism, Asian aesthetic form, and locally found materials to create a unique new style,” or “There are many strong similarities between Wright’s building designs and those of his mother, which suggests that he may have borrowed some of her ideas.” To develop your argument, you would then define your terms and prove your claim with evidence from Wright’s drawings and buildings and those of the other architects you mentioned.
Do not stop with having a point. You have to back up your point with evidence. The strength of your evidence, and your use of it, can make or break your argument. See our handout on evidence . You already have the natural inclination for this type of thinking, if not in an academic setting. Think about how you talked your parents into letting you borrow the family car. Did you present them with lots of instances of your past trustworthiness? Did you make them feel guilty because your friends’ parents all let them drive? Did you whine until they just wanted you to shut up? Did you look up statistics on teen driving and use them to show how you didn’t fit the dangerous-driver profile? These are all types of argumentation, and they exist in academia in similar forms.
Every field has slightly different requirements for acceptable evidence, so familiarize yourself with some arguments from within that field instead of just applying whatever evidence you like best. Pay attention to your textbooks and your instructor’s lectures. What types of argument and evidence are they using? The type of evidence that sways an English instructor may not work to convince a sociology instructor. Find out what counts as proof that something is true in that field. Is it statistics, a logical development of points, something from the object being discussed (art work, text, culture, or atom), the way something works, or some combination of more than one of these things?
Be consistent with your evidence. Unlike negotiating for the use of your parents’ car, a college paper is not the place for an all-out blitz of every type of argument. You can often use more than one type of evidence within a paper, but make sure that within each section you are providing the reader with evidence appropriate to each claim. So, if you start a paragraph or section with a statement like “Putting the student seating area closer to the basketball court will raise player performance,” do not follow with your evidence on how much more money the university could raise by letting more students go to games for free. Information about how fan support raises player morale, which then results in better play, would be a better follow-up. Your next section could offer clear reasons why undergraduates have as much or more right to attend an undergraduate event as wealthy alumni—but this information would not go in the same section as the fan support stuff. You cannot convince a confused person, so keep things tidy and ordered.
Counterargument
One way to strengthen your argument and show that you have a deep understanding of the issue you are discussing is to anticipate and address counterarguments or objections. By considering what someone who disagrees with your position might have to say about your argument, you show that you have thought things through, and you dispose of some of the reasons your audience might have for not accepting your argument. Recall our discussion of student seating in the Dean Dome. To make the most effective argument possible, you should consider not only what students would say about seating but also what alumni who have paid a lot to get good seats might say.
You can generate counterarguments by asking yourself how someone who disagrees with you might respond to each of the points you’ve made or your position as a whole. If you can’t immediately imagine another position, here are some strategies to try:
- Do some research. It may seem to you that no one could possibly disagree with the position you are arguing, but someone probably has. For example, some people argue that a hotdog is a sandwich. If you are making an argument concerning, for example, the characteristics of an exceptional sandwich, you might want to see what some of these people have to say.
- Talk with a friend or with your teacher. Another person may be able to imagine counterarguments that haven’t occurred to you.
- Consider your conclusion or claim and the premises of your argument and imagine someone who denies each of them. For example, if you argued, “Cats make the best pets. This is because they are clean and independent,” you might imagine someone saying, “Cats do not make the best pets. They are dirty and needy.”
Once you have thought up some counterarguments, consider how you will respond to them—will you concede that your opponent has a point but explain why your audience should nonetheless accept your argument? Will you reject the counterargument and explain why it is mistaken? Either way, you will want to leave your reader with a sense that your argument is stronger than opposing arguments.
When you are summarizing opposing arguments, be charitable. Present each argument fairly and objectively, rather than trying to make it look foolish. You want to show that you have considered the many sides of the issue. If you simply attack or caricature your opponent (also referred to as presenting a “straw man”), you suggest that your argument is only capable of defeating an extremely weak adversary, which may undermine your argument rather than enhance it.
It is usually better to consider one or two serious counterarguments in some depth, rather than to give a long but superficial list of many different counterarguments and replies.
Be sure that your reply is consistent with your original argument. If considering a counterargument changes your position, you will need to go back and revise your original argument accordingly.
Audience is a very important consideration in argument. Take a look at our handout on audience . A lifetime of dealing with your family members has helped you figure out which arguments work best to persuade each of them. Maybe whining works with one parent, but the other will only accept cold, hard statistics. Your kid brother may listen only to the sound of money in his palm. It’s usually wise to think of your audience in an academic setting as someone who is perfectly smart but who doesn’t necessarily agree with you. You are not just expressing your opinion in an argument (“It’s true because I said so”), and in most cases your audience will know something about the subject at hand—so you will need sturdy proof. At the same time, do not think of your audience as capable of reading your mind. You have to come out and state both your claim and your evidence clearly. Do not assume that because the instructor knows the material, he or she understands what part of it you are using, what you think about it, and why you have taken the position you’ve chosen.
Critical reading
Critical reading is a big part of understanding argument. Although some of the material you read will be very persuasive, do not fall under the spell of the printed word as authority. Very few of your instructors think of the texts they assign as the last word on the subject. Remember that the author of every text has an agenda, something that he or she wants you to believe. This is OK—everything is written from someone’s perspective—but it’s a good thing to be aware of. For more information on objectivity and bias and on reading sources carefully, read our handouts on evaluating print sources and reading to write .
Take notes either in the margins of your source (if you are using a photocopy or your own book) or on a separate sheet as you read. Put away that highlighter! Simply highlighting a text is good for memorizing the main ideas in that text—it does not encourage critical reading. Part of your goal as a reader should be to put the author’s ideas in your own words. Then you can stop thinking of these ideas as facts and start thinking of them as arguments.
When you read, ask yourself questions like “What is the author trying to prove?” and “What is the author assuming I will agree with?” Do you agree with the author? Does the author adequately defend her argument? What kind of proof does she use? Is there something she leaves out that you would put in? Does putting it in hurt her argument? As you get used to reading critically, you will start to see the sometimes hidden agendas of other writers, and you can use this skill to improve your own ability to craft effective arguments.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Booth, Wayne C., Gregory G. Colomb, Joseph M. Williams, Joseph Bizup, and William T. FitzGerald. 2016. The Craft of Research , 4th ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Ede, Lisa. 2004. Work in Progress: A Guide to Academic Writing and Revising , 6th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Gage, John T. 2005. The Shape of Reason: Argumentative Writing in College , 4th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A., and John J. Ruszkiewicz. 2016. Everything’s an Argument , 7th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- SAT BootCamp
- SAT MasterClass
- SAT Private Tutoring
- SAT Proctored Practice Test
- ACT Private Tutoring
- Academic Subjects
- College Essay Workshop
- Academic Writing Workshop
- AP English FRQ BootCamp
- 1:1 College Essay Help
- Online Instruction
- Free Resources
12 Essential Steps for Writing an Argumentative Essay (with 10 example essays)
Bonus Material: 10 complete example essays
Writing an essay can often feel like a Herculean task. How do you go from a prompt… to pages of beautifully-written and clearly-supported writing?
This 12-step method is for students who want to write a great essay that makes a clear argument.
In fact, using the strategies from this post, in just 88 minutes, one of our students revised her C+ draft to an A.
If you’re interested in learning how to write awesome argumentative essays and improve your writing grades, this post will teach you exactly how to do it.
First, grab our download so you can follow along with the complete examples.
Then keep reading to see all 12 essential steps to writing a great essay.
Download 10 example essays

Why you need to have a plan
One of the most common mistakes that students make when writing is to just dive in haphazardly without a plan.
Writing is a bit like cooking. If you’re making a meal, would you start throwing ingredients at random into a pot? Probably not!
Instead, you’d probably start by thinking about what you want to cook. Then you’d gather the ingredients, and go to the store if you don’t already have them in your kitchen. Then you’d follow a recipe, step by step, to make your meal.

Here’s our 12-step recipe for writing a great argumentative essay:
- Pick a topic
- Choose your research sources
- Read your sources and take notes
- Create a thesis statement
- Choose three main arguments to support your thesis statement —now you have a skeleton outline
- Populate your outline with the research that supports each argument
- Do more research if necessary
- Add your own analysis
- Add transitions and concluding sentences to each paragraph
- Write an introduction and conclusion for your essay
- Add citations and bibliography
Grab our download to see the complete example at every stage, along with 9 great student essays. Then let’s go through the steps together and write an A+ essay!
1. Pick a topic
Sometimes you might be assigned a topic by your instructor, but often you’ll have to come up with your own idea!
If you don’t pick the right topic, you can be setting yourself up for failure.
Be careful that your topic is something that’s actually arguable —it has more than one side. Check out our carefully-vetted list of 99 topic ideas .
Let’s pick the topic of laboratory animals . Our question is should animals be used for testing and research ?

Download our set of 10 great example essays to jump to the finished version of this essay.
2. Choose your research sources
One of the big differences between the way an academic argumentative essay and the version of the assignment that you may have done in elementary school is that for an academic argumentative essay, we need to support our arguments with evidence .
Where do we get that evidence?
Let’s be honest, we all are likely to start with Google and Wikipedia.
Now, Wikipedia can be a useful starting place if you don’t know very much about a topic, but don’t use Wikipedia as your main source of evidence for your essay.
Instead, look for reputable sources that you can show to your readers as proof of your arguments. It can be helpful to read some sources from either side of your issue.
Look for recently-published sources (within the last 20 years), unless there’s a specific reason to do otherwise.

Good places to look for sources are:
- Books published by academic presses
- Academic journals
- Academic databases like JSTOR and EBSCO
- Nationally-published newspapers and magazines like The New York Times or The Atlantic
- Websites and publications of national institutions like the NIH
- Websites and publications of universities
Some of these sources are typically behind a paywall. This can be frustrating when you’re a middle-school or high-school student.
However, there are often ways to get access to these sources. Librarians (at your school library or local public library) can be fantastic resources, and they can often help you find a copy of the article or book you want to read. In particular, librarians can help you use Interlibrary Loan to order books or journals to your local library!
More and more scientists and other researchers are trying to publish their articles for free online, in order to encourage the free exchange of knowledge. Check out respected open-access platforms like arxiv.org and PLOS ONE .
How do you find these sources?
If you have access to an academic database like JSTOR or EBSCO , that’s a great place to start.
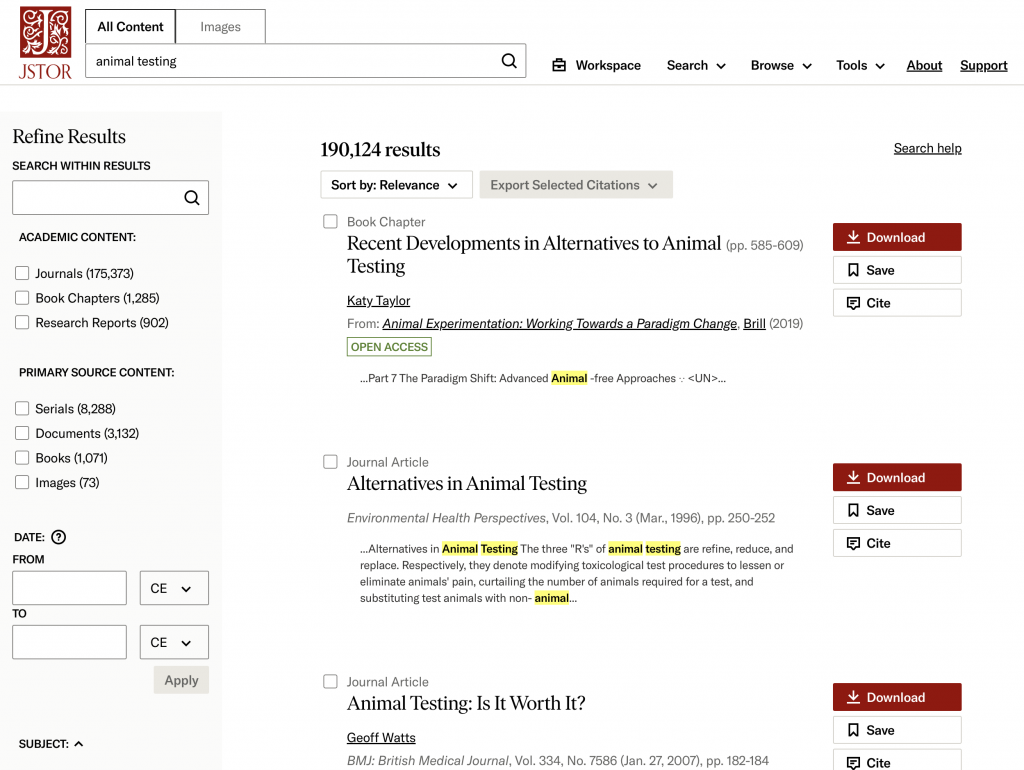
Everyone can use Google Scholar to search for articles. This is a powerful tool and highly recommended!

Of course, if there’s a term you come across that you don’t recognize, you can always just Google it!
How many sources do you need? That depends on the length of your essay and on the assignment. If your instructor doesn’t give you any other guidance, assume that you should have at least three good sources.
For our topic of animal research, here’s a few sources that we could assemble:
Geoff Watts. “Animal Testing: Is It Worth It?” BMJ: British Medical Journal , Jan. 27, 2007, Vol. 334, No. 7586 (Jan. 27, 2007), pp. 182-184.
Kim Bartel Sheehan and Joonghwa Lee. “What’s Cruel About Cruelty Free: An Exploration of Consumers, Moral Heuristics, and Public Policy.” Journal of Animal Ethics , Vol. 4, No. 2 (Fall 2014), pp. 1-15.
Justin Goodman, Alka Chandna and Katherine Roe. “Trends in animal use at US research facilities.” Journal of Medical Ethics , July 2015, Vol. 41, No. 7 (July 2015), pp. 567-569.
Katy Taylor. “Recent Developments in Alternatives to Animal Testing.” In Animal Experimentation: Working Towards a Paradigm Change . Brill 2019.
Thomas Hartung. “Research and Testing Without Animals: Where Are We Now and Where Are We Heading?” In Animal Experimentation: Working Towards a Paradigm Change . Brill 2019.
Bonus: download 10 example essays now .
3. Read your sources and take notes
Once you have a nice pile of sources, it’s time to read them!
As we read, we want to take notes that will be useful to us later as we write our essay.
We want to be careful to keep the source’s ideas separate from our own ideas . Come up with a system to clearly mark the difference as you’re taking notes: use different colors, or use little arrows to represent the ideas that are yours and not the source’s ideas.
We can use this structure to keep notes in an organized way:
Download a template for these research notes here .

For our topic of animal research, our notes might look something like this:
Grab our download to read the rest of the notes and see more examples of how to do thoughtful research!

4. Create a thesis
What major themes did you find in your reading? What did you find most interesting or convincing?
Now is the point when you need to pick a side on your topic, if you haven’t already done so. Now that you’ve read more about the issue, what do you think? Write down your position on the issue:
Animal testing is necessary but should be reduced.
Next, it’s time to add more detail to your thesis. What reasons do you have to support that position? Add those to your sentence.
Animal testing is necessary but should be reduced by eliminating testing for cosmetics, ensuring that any testing is scientifically sound, and replacing animal models with other methods as much as possible.
Add qualifiers to refine your position. Are there situations in which your position would not apply? Or are there other conditions that need to be met?
For our topic of animal research, our final thesis statement (with lead-in) might look something like this:
The argument: Animal testing and research should not be abolished, as doing so would upend important medical research and substance testing. However, scientific advances mean that in many situations animal testing can be replaced by other methods that not only avoid the ethical problems of animal testing, but also are less costly and more accurate. Governments and other regulatory bodies should further regulate animal testing to outlaw testing for cosmetics and other recreational products, ensure that the tests conducted are both necessary and scientifically rigorous, and encourage the replacement of animal use with other methods whenever possible.
The highlighted bit at the end is the thesis statement, but the lead-in is useful to help us set up the argument—and having it there already will make writing our introduction easier!
The thesis statement is the single most important sentence of your essay. Without a strong thesis, there’s no chance of writing a great essay. Read more about it here .
See how nine real students wrote great thesis statements in 9 example essays now.
5. Create three supporting arguments
Think of three good arguments why your position is true. We’re going to make each one into a body paragraph of your essay.
For now, write them out as 1–2 sentences. These will be topic sentences for each body paragraph.

For our essay about animal testing, it might look like this:
Supporting argument #1: For ethical reasons, animal testing should not be allowed for cosmetics and recreational products.
Supporting argument #2: The tests that are conducted with animals should be both necessary (for the greater good) and scientifically rigorous—which isn’t always the case currently. This should be regulated by governments and institutions.
Supporting argument #3: Governments and institutions should do more to encourage the replacement of animal testing with other methods.
Optional: Find a counterargument and respond to it
Think of a potential counterargument to your position. Consider writing a fourth paragraph anticipating this counterargument, or find a way to include it in your other body paragraphs.

For our essay, that might be:
Possible counterargument: Animal testing is unethical and should not be used in any circumstances.
Response to the counterargument: Animal testing is deeply entrenched in many research projects and medical procedures. Abruptly ceasing animal testing would upend the scientific and medical communities. But there are many ways that animal testing could be reduced.
With these three arguments, a counterargument, and a thesis, we now have a skeleton outline! See each step of this essay in full in our handy download .
6. Start populating your outline with the evidence you found in your research
Look through your research. What did you find that would support each of your three arguments?
Copy and paste those quotes or paraphrases into the outline. Make sure that each one is annotated so that you know which source it came from!
Ideally you already started thinking about these sources when you were doing your research—that’s the ideas in the rightmost column of our research template. Use this stuff too!
A good rule of thumb would be to use at least three pieces of evidence per body paragraph.
Think about in what order it would make most sense to present your points. Rearrange your quotes accordingly! As you reorder them, feel free to start adding short sentences indicating the flow of ideas .

For our essay about animal testing, part of our populated outline might look something like:
Argument #1: For ethical reasons, animal testing should not be allowed for cosmetics and recreational products.
Lots of animals are used for testing and research.
In the US, about 22 million animals were used annually in the early 1990s, mostly rodents (BMJ 1993, 1020).
But there are ethical problems with using animals in laboratory settings. Opinions about the divide between humans and animals might be shifting.
McIsaac refers to “the essential moral dilemma: how to balance the welfare of humans with the welfare of other species” (Hubel, McIsaac 29).
The fundamental legal texts used to justify animal use in biomedical research were created after WWII, and drew a clear line between experiments on animals and on humans. The Nuremburg Code states that “the experiment should be so designed and based on the results of animal experimentation and a knowledge of the natural history of the disease or other problem under study that the anticipated results will justify the performance of the experiment” (Ferrari, 197). The 1964 Declaration of the World Medical Association on the Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects (known as the Helsinki Declaration) states that “Medical research involving human subjects must conform to generally accepted scientific principles, be based on a thorough knowledge of the scientific literature, other relevant sources of information, and adequate laboratory and, as appropriate, animal experimentation. The welfare of animals used for research must be respected” (Ferrari, 197).
→ Context? The Nuremberg Code is a set of ethical research principles, developed in 1947 in the wake of Nazi atrocities during WWII, specifically the inhumane and often fatal experimentation on human subjects without consent.
“Since the 1970s, the animal-rights movement has challenged the use of animals in modern Western society by rejecting the idea of dominion of human beings over nature and animals and stressing the intrinsic value and rights of individual animals” (van Roten, 539, referencing works by Singer, Clark, Regan, and Jasper and Nelkin).
“The old (animal) model simply does not fully meet the needs of scientific and economic progress; it fails in cost, speed, level of detail of understanding, and human relevance. On top of this, animal experimentation lacks acceptance by an ethically evolving society” (Hartung, 682).
Knight’s article summarizes negative impacts on laboratory animals—invasive procedures, stress, pain, and death (Knight, 333). These aren’t very widely or clearly reported (Knight, 333). → Reading about these definitely produces an emotional reaction—they sound bad.
Given this context, it makes sense to ban animal testing in situations where it’s just for recreational products like cosmetics.
Fortunately, animal testing for cosmetics is less common than we might think.
A Gallup poll published in 1990 found that 14% of people thought that the most frequent reason for using animals to test cosmetics for safety—but figures from the UK Home Office in 1991 found that less than 1% of animals were used for tests for cosmetics and toiletries (BMJ 1993, 1019). → So in the early 1990s there was a big difference between what people thought was happening and what actually was happening!
But it still happens, and there are very few regulations of it (apart from in the EU).
Because there are many definitions of the phrase “cruelty-free,” many companies “can (and do) use the term when the product or its ingredients were indeed tested on animals” (Sheehan and Lee, 1).
The authors compare “cruelty-free” to the term “fair trade.” There is an independent inspection and certification group (Flo-Cert) that reviews products labeled as “fair trade,” but there’s no analogous process for “cruelty-free” (Sheehan and Lee, 2). → So anyone can just put that label on a product? Apparently, apart from in the European Union. That seems really easy to abuse for marketing purposes.
Companies can also hire outside firms to test products and ingredients on animals (Sheehan and Lee, 3).
Animal testing for recreational, non-medical purposes should be banned, like it is in the EU.
Download the full example outline here .

7. Do more research if necessary
Occasionally you might realize that there’s a hole in your research, and you don’t have enough evidence to support one of your points.
In this situation, either change your argument to fit the evidence that you do have, or do a bit more research to fill the hole!
For example, looking at our outline for argument #1 for our essay on animal testing, it’s clear that this paragraph is missing a small but crucial bit of evidence—a reference to this specific ban on animal testing for cosmetics in Europe. Time for a bit more research!
A visit to the official website of the European Commission yields a copy of the law, which we can add to our populated outline:
“The cosmetics directive provides the regulatory framework for the phasing out of animal testing for cosmetics purposes. Specifically, it establishes (1) a testing ban – prohibition to test finished cosmetic products and cosmetic ingredients on animals, and (2) a marketing ban – prohibition to market finished cosmetic products and ingredients in the EU which were tested on animals. The same provisions are contained in the cosmetics regulation , which replaced the cosmetics directive as of 11 July 2013. The testing ban on finished cosmetic products applies since 11 September 2004. The testing ban on ingredients or combination of ingredients applies since 11 March 2009. The marketing ban applies since 11 March 2009 for all human health effects with the exception of repeated-dose toxicity, reproductive toxicity, and toxicokinetics. For these specific health effects, the marketing ban applies since 11 March 2013, irrespective of the availability of alternative non-animal tests.” (website of the European Commission, “Ban on animal testing”)
Alright, now this supporting argument has the necessary ingredients!
You don’t need to use all of the evidence that you found in your research. In fact, you probably won’t use all of it!
This part of the writing process requires you to think critically about your arguments and what evidence is relevant to your points .

8. Add your own analysis and synthesis of these points
Once you’ve organized your evidence and decided what you want to use for your essay, now you get to start adding your own analysis!
You may have already started synthesizing and evaluating your sources when you were doing your research (the stuff on the right-hand side of our template). This gives you a great starting place!
For each piece of evidence, follow this formula:
- Context and transitions: introduce your piece of evidence and any relevant background info and signal the logical flow of ideas
- Reproduce the paraphrase or direct quote (with citation )
- Explanation : explain what the quote/paraphrase means in your own words
- Analysis : analyze how this piece of evidence proves your thesis
- Relate it back to the thesis: don’t forget to relate this point back to your overarching thesis!
If you follow this fool-proof formula as you write, you will create clear, well-evidenced arguments.
As you get more experienced, you might stray a bit from the formula—but a good essay will always intermix evidence with explanation and analysis, and will always contain signposts back to the thesis throughout.
For our essay about animal testing, our first body paragraph might look like:
Every year, millions of animals—mostly rodents—are used for testing and research (BMJ 1993, 1020) . This testing poses an ethical dilemma: “how to balance the welfare of humans with the welfare of other species” (Hubel, McIsaac 29) . Many of the fundamental legal tests that are used to justify animal use in biomedical research were created in wake of the horrors of World War II, when the Nazi regime engaged in terrible experimentation on their human prisoners. In response to these atrocities, philosophers and lawmakers drew a clear line between experimenting on humans without consent and experimenting on (non-human) animals. For example, the 1947 Nuremberg Code stated that “the experiment should be so designed and based on the results of animal experimentation and a knowledge of the natural history of the disease or other problem under study that the anticipated results will justify the performance of the experiment” (Ferrari, 197) . Created two years after the war, the code established a set of ethical research principles to demarcate ethical differences between animals and humans, clarifying differences between Nazi atrocities and more everyday research practices. However, in the following decades, the animal-rights movement has challenged the philosophical boundaries between humans and animals and questioned humanity’s right to exert dominion over animals (van Roten, 539, referencing works by Singer, Clark, Regan, and Jasper and Nelkin) . These concerns are not without justification, as animals used in laboratories are subject to invasive procedures, stress, pain, and death (Knight, 333) . Indeed, reading detailed descriptions of this research can be difficult to stomach . In light of this, while some animal testing that contributes to vital medical research and ultimately saves millions of lives may be ethically justified, animal testing that is purely for recreational purposes like cosmetics cannot be ethically justified . Fortunately, animal testing for cosmetics is less common than we might think . In 1990, a poll found that 14% of people in the UK thought that the most frequent reason for using animals to test cosmetics for safety—but actual figures were less than 1% (BMJ 1993, 1019) . Unfortunately, animal testing for cosmetics is not subject to very much regulation . In particular, companies can use the phrase “cruelty-free” to mean just about anything, and many companies “can (and do) use the term when the product or its ingredients were indeed tested on animals” (Sheehan and Lee, 1) . Unlike the term “fair trade,” which has an independent inspection and certification group (Flo-Cert) that reviews products using the label, there’s no analogous process for “cruelty-free” (Sheehan and Lee, 2) . Without regulation, the term is regularly abused by marketers . Companies can also hire outside firms to test products and ingredients on animals and thereby pass the blame (Sheehan and Lee, 3) . Consumers trying to avoid products tested on animals are frequently tricked . Greater regulation of terms would help, but the only way to end this kind of deceit will be to ban animal testing for recreational, non-medical purposes . The European Union is the only governmental body yet to accomplish this . In a series of regulations, the EU first banned testing finished cosmetic products (2004), then testing ingredients or marketing products which were tested on animals (2009); exceptions for specific health effects ended in 2013 (website of the European Commission, “Ban on animal testing”) . The result is that the EU bans testing cosmetic ingredients or finished cosmetic products on animals, as well as marketing any cosmetic ingredients and products which were tested on animals elsewhere (Regulation 1223/2009/EU, known as the “Cosmetics Regulation”) . The rest of the world should follow this example and ban animal testing on cosmetic ingredients and products, which do not contribute significantly to the greater good and therefore cannot outweigh the cost to animal lives .
Edit down the quotes/paraphrases as you go. In many cases, you might copy out a great long quote from a source…but only end up using a few words of it as a direct quote, or you might only paraphrase it!
There were several good quotes in our previous step that just didn’t end up fitting here. That’s fine!
Take a look at the words and phrases highlighted in red. Notice how sometimes a single word can help to provide necessary context and create a logical transition for a new idea. Don’t forget the transitions! These words and phrases are essential to good writing.
The end of the paragraph should very clearly tie back to the thesis statement.
As you write, consider your audience
If it’s not specified in your assignment prompt, it’s always appropriate to ask your instructor who the intended audience of your essay or paper might be. (Your instructor will usually be impressed by this question!)
If you don’t get any specific guidance, imagine that your audience is the typical readership of a newspaper like the New York Times —people who are generally educated, but who don’t have any specialized knowledge of the specific subject, especially if it’s more technical.
That means that you should explain any words or phrases that aren’t everyday terminology!
Equally important, you don’t want to leave logical leaps for your readers to make. Connect all of the dots for them!
See the other body paragraphs of this essay, along with 9 student essays, here .
9. Add paragraph transitions and concluding sentences to each body paragraph
By now you should have at least three strong body paragraphs, each one with 3–5 pieces of evidence plus your own analysis and synthesis of the evidence.
Each paragraph has a main topic sentence, which we wrote back when we made the outline. This is a good time to check that the topic sentences still match what the rest of the paragraph says!
Think about how these arguments relate to each other. What is the most logical order for them? Re-order your paragraphs if necessary.
Then add a few sentences at the end of each paragraph and/or the beginning of the next paragraph to connect these ideas. This step is often the difference between an okay essay and a really great one!
You want your essay to have a great flow. We didn’t worry about this at the beginning of our writing, but now is the time to start improving the flow of ideas!
10. The final additions: write an introduction and a conclusion
Follow this formula to write a great introduction:
- It begins with some kind of “hook”: this can be an anecdote, quote, statistic, provocative statement, question, etc.
(Pro tip: don’t use phrases like “throughout history,” “since the dawn of humankind,” etc. It’s good to think broadly, but you don’t have to make generalizations for all of history.)
- It gives some background information that is relevant to understand the ethical dilemma or debate
- It has a lead-up to the thesis
- At the end of the introduction, the thesis is clearly stated
This makes a smooth funnel that starts more broadly and smoothly zeroes in on the specific argument.

Your conclusion is kind of like your introduction, but in reverse. It starts with your thesis and ends a little more broadly.
For the conclusion, try and summarize your entire argument without being redundant. Start by restating your thesis but with slightly different wording . Then summarize each of your main points.
If you can, it’s nice to point to the larger significance of the issue. What are the potential consequences of this issue? What are some future directions for it to go in? What remains to be explored?
See how nine students wrote introductions in different styles here .
11. Add citations and bibliography
Check what bibliographic style your instructor wants you to use. If this isn’t clearly stated, it’s a good question to ask them!
Typically the instructions will say something like “Chicago style,” “APA,” etc., or they’ll give you their own rules.
These rules will dictate how exactly you’ll write your citations in the body of your essay (either in parentheses after the quote/paraphrase or else with a footnote or endnote) and how you’ll write your “works cited” with the full bibliographic information at the end.
Follow these rules! The most important thing is to be consistent and clear.
Pro tip: if you’re struggling with this step, your librarians can often help! They’re literally pros at this. 🙂
Now you have a complete draft!
Read it from beginning to end. Does it make sense? Are there any orphan quotes or paraphrases that aren’t clearly explained? Are there any abrupt changes of topic? Fix it!
Are there any problems with grammar or spelling ? Fix them!
Edit for clarity.

Ideally, you’ll finish your draft at least a few days before it’s due to be submitted. Give it a break for a day or two, and then come back to it. Things to be revised are more likely to jump out after a little break!
Try reading your essay out loud. Are there any sentences that don’t sound quite right? Rewrite them!
Double-check your thesis statement. This is the make-or-break moment of your essay, and without a clear thesis it’s pretty impossible for an essay to be a great one. Is it:
- Arguable: it’s not just the facts—someone could disagree with this position
- Narrow & specific: don’t pick a position that’s so broad you could never back it up
- Complex: show that you are thinking deeply—one way to do this is to consider objections/qualifiers in your thesis
Try giving your essay to a friend or family member to read. Sometimes (if you’re lucky) your instructors will offer to read a draft if you turn it in early. What feedback do they have? Edit accordingly!
See the result of this process with 10 example essays now .
You’re done!
You did it! Feel proud of yourself 🙂
We regularly help students work through all of these steps to write great academic essays in our Academic Writing Workshop or our one-on-one writing tutoring . We’re happy to chat more about what’s challenging for you and provide you customized guidance to help you write better papers and improve your grades on writing assignments!
Want to see what this looks like when it’s all pulled together? We compiled nine examples of great student essays, plus all of the steps used to create this model essay, in this handy resource. Download it here !

Emily graduated summa cum laude from Princeton University and holds an MA from the University of Notre Dame. She was a National Merit Scholar and has won numerous academic prizes and fellowships. A veteran of the publishing industry, she has helped professors at Harvard, Yale, and Princeton revise their books and articles. Over the last decade, Emily has successfully mentored hundreds of students in all aspects of the college admissions process, including the SAT, ACT, and college application essay.
Privacy Preference Center
Privacy preferences.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay with Impact

When it comes to persuading others, legal professionals are masters. They use persuasive skills, like crafting compelling stories, to win cases in court. This shows how important it is to argue effectively, especially when the stakes are high. In our journey into argumentative essays, we'll learn how to structure our writing well, predict counterarguments, and tell a convincing story.
With help of our argumentative essay writer , you'll learn how to organize your ideas, support your arguments, and see examples that make it all clearer. Whether you're new to writing an argumentative essay or have some experience, come along to become better at arguing your point.
What Is an Argumentative Essay
Argumentative essays deal with topics that spark different opinions. Here, writers take a stand on an issue and back it up with evidence and reasons. The topic should be something people can have different views on. The goal isn't just to share an opinion but to persuade others to agree with the writer.
In these essays, writers use strong and convincing language, similar to when learning how to write persuasive essay . They try to make readers see their point of view. For example, in an essay about online education, the writer might say:
'Online education offers more flexibility and access compared to traditional classrooms.'
This statement sets up the essay to discuss reasons, evidence, and examples supporting this view. These essays rely on facts, stats, research, and examples to prove the writer's points.
If you find writing such essays daunting, don't worry. There are skilled writers who can help. If you feel like saying, ' Write essay for me !' let experienced writers handle it with their expertise.
Argumentative Essay Examples
Let's check out some example essays where convincing arguments, backed by facts and clear language, have made a big difference. These stories not only inspire us but also teach us valuable lessons on how to effectively sway opinions and create compelling narratives that resonate with others.
Argumentative Essay Example
Want to Spice Up Your Arguments with Our Sizzling Prose?
Order a paper on any argumentative essay prompts – because eloquence is the ultimate mic drop in the world of words.
Argumentative Essay Outline
Understanding how to structure an argumentative essay goes beyond having strong opinions. It involves creating a clear framework that helps both the writer and the reader follow a logical flow of ideas. In this part, we'll look closely at three different ways to outline an argumentative essay: the Aristotelian (Classic) method, the Toulmin model, and the Rogerian strategy. Each method has its own structure, giving writers various tools to craft convincing and well-organized arguments.
.webp)
Aristotelian (Classic)
The Aristotelian approach, also known as the Classic method, pays homage to the ancient wisdom of Aristotle's rhetorical principles. This argumentative essay structure is composed of three distinct movements: introduction, body, and conclusion.
Introduction :
- Initiate with a captivating hook to captivate the reader's attention.
- Offer background context to illuminate the significance of the topic at hand.
- Articulate a clear and concise thesis statement that unequivocally states your position.
- Deploy the power of logos (logical appeal) by presenting concrete evidence, factual information, and cogent reasoning.
- Establish ethos (ethical appeal) by integrating reputable sources to bolster your credibility and authority.
- Evoke pathos (emotional appeal) to resonate with the reader's emotions and forge a deeper connection.
Conclusion :
- Synthesize the main arguments and insights discussed throughout the essay.
- Reiterate the thesis to leave a lasting impression on the reader.
- Conclude with a poignant and thought-provoking closing statement that lingers in the reader's mind.
Crafted by philosopher Stephen Toulmin, this model zooms in on the pieces of an argument puzzle and how they fit together. Here's the breakdown, tailor-made by our team at dissertation writing services :
Claim : Clearly state your main argument or point.
Grounds : Back up your claim with evidence and support.
Warrant : Connect the dots between your claim and the evidence provided.
Backing : Give more backup for your reasoning.
Qualifier : Recognize any limitations or boundaries to your argument.
Rebuttal : Take on opposing views and arguments head-on.
Inspired by psychologist Carl Rogers, the Rogerian method for writing an argumentative essay prioritizes building bridges and fostering empathy.
- Set a neutral tone to encourage open-mindedness.
- Acknowledge the complexity of the topic to show understanding.
- Introduce the issue from various viewpoints to provide a broader understanding.
- Clearly state your stance while acknowledging opposing viewpoints to demonstrate fairness.
- Explore common ground and areas of agreement to foster understanding.
- Present your perspective with empathy, respecting differing opinions.
- Highlight shared objectives and potential areas for compromise to promote cooperation.
- Encourage ongoing dialogue to continue exploring solutions.
Argumentative Essay Structure
Understanding how to write an argumentative essay requires a structured approach that leads both writer and reader through a compelling narrative. Let's break it down into key parts: introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
- Capture attention with a striking opener. 'In a world driven by environmental concerns, the debate over renewable energy sources becomes increasingly critical.'
- Offer a brief context to the topic. 'With the looming threat of climate change, society grapples with the urgent need for sustainable energy solutions.'
- Clearly state your stance. 'This essay argues that investing in solar energy is imperative for combating climate change and securing a greener future.'
Thesis Statement:
- Example: 'Investing in solar energy infrastructure is not only environmentally responsible but also economically advantageous.'
Body Paragraphs:
- Introduce the main idea. 'Solar energy presents a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.'
- Provide supporting facts or examples. 'Research shows that solar power installations have steadily increased over the past decade, demonstrating growing global interest in renewable energy.'
- Explain the significance of the evidence. 'This trend indicates a shifting mindset towards clean energy, driven by concerns over climate change and dwindling fossil fuel reserves.'
- Recap key arguments. 'In summary, investing in solar energy offers a viable solution to mitigate climate change and reduce dependence on non-renewable resources.'
- Restate your thesis. 'Embracing solar energy not only addresses environmental challenges but also promotes sustainable economic development.'
- End with a compelling thought. 'By harnessing the power of the sun, we can pave the way for a brighter, cleaner future for generations to come.'

Building a Compelling Argumentative Essay Thesis
Crafting a strong thesis statement is essential for a persuasive argumentative essay. Let's dive into a guide that will help you create a thesis statement that grabs attention and sets the stage for your essay.
Ask a Provocative Question and Answer It
Start by igniting curiosity with a thought-provoking question that directly connects to your topic. Then, provide a clear and insightful response that not only sets the stage for your argument but also hints at the complexities and nuances surrounding the issue.
Example: 'Is the use of smartphones beneficial for children's development? This essay argues that while smartphones offer educational opportunities, excessive screen time may hinder social skills.'
Introduce Your Argument and Address Contrary Views
A good argumentative essay should begin with a bold assertion of your main claim. However, to truly enrich your position, it's important to delve deeper by acknowledging and addressing opposing perspectives. This not only showcases a nuanced understanding of the topic but also reinforces the validity of your argument.
Example: 'While many believe that technology improves productivity, it's crucial to consider its potential drawbacks. This essay asserts that while technology enhances efficiency, it can also lead to information overload and burnout.'
Outline Your Main Points for Clarity
Provide a brief overview of the key points you'll explore in your essay. This helps clarify your direction and prepares your reader for the arguments ahead.
Example: 'In examining the impact of technology on work-life balance, we'll explore the benefits of remote work, the challenges of constant connectivity, and strategies for achieving harmony between work and personal life.'
By adding these steps from our experts in research paper help to your thesis-building process, you establish a base that not only clearly expresses your standpoint but also captivates readers with interesting questions, challenges, and key points that will unfold in your essay.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay with Quick Steps
Let's break down each part of your writing process step by step. By embracing these steps, you'll sail through the challenges of argumentative writing, crafting a piece that not only shares your thoughts clearly but also grabs the attention and persuades your readers along the way.
.webp)
Generating Ideas
Before you start writing, take some time to brainstorm ideas. Research different viewpoints and gather information about your topic. Try techniques like freewriting or mind mapping to explore various angles and gather a range of perspectives. This phase is all about gathering a pool of ideas so that you can choose the strongest arguments to support your essay later on.
Getting Ready
Preparation is key before diving into the writing process. Organize your thoughts and argumentative essay topics into a coherent structure. Develop a focused thesis statement that not only communicates your main point but also sets the tone for your entire essay. This stage is crucial for refining your focus and ensuring that each part of your essay supports your central argument effectively.
Putting Pen to Paper
Now it's time to start writing! Maintain a logical progression in your essay as you draft your ideas. Begin with an engaging introduction that introduces your topic and presents your thesis statement. In the body paragraphs, explore each argument thoroughly, providing supporting evidence and examples. Don't forget to address potential counterarguments to demonstrate a well-rounded understanding of the topic. This step is all about fleshing out your ideas and constructing a compelling narrative.
Perfecting Your Work
Once you've finished drafting, it's time to refine your essay. Review your arguments to ensure they flow logically and contribute effectively to your thesis. Pay attention to the clarity of your language and the strength of your evidence. This stage allows you to fine-tune the persuasiveness of your essay, transforming it from a draft into a polished piece of writing.
Polishing the Final Product
Now it's time for the finishing touches! Meticulously proofread your essay to ensure it's polished and impactful. Check for grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure errors. Make sure your writing style remains consistent throughout and clarify any parts that may be unclear. In the conclusion, revisit your thesis statement and leave your reader with a thought-provoking statement that lingers in their mind. This attention to detail ensures that your argumentative essay not only captivates but also showcases your writing skills effectively.
Essential Argumentative Essay Tips
Our tips on writing an argumentative essay work just as effectively as they do for any other type of essay. So, if you're in need of additional guidance, here are some specific tips that can help you craft persuasive arguments:
Strengthen Your Case with Solid Facts
Ensure your argument is supported by reliable facts and evidence. Utilize research, data, and examples to reinforce your points. You can also use our essay writing help helping you ground your argument in verifiable information, demonstrate credibility and strengthen your position.
Example: Drawing from recent studies by leading environmental organizations, it's clear that deforestation has reached alarming levels, with devastating consequences for ecosystems worldwide. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Environmental Science found that deforestation contributes to biodiversity loss, soil erosion, and disruptions in the water cycle, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts.
Take Charge with Language
While learning how to write an argumentative essay, remember to choose your words carefully to convey your argument persuasively. Adopt a tone that is confident yet respectful, and craft your sentences to engage and convince your audience. The language you use can influence how your argument is perceived, so wield it skillfully to make a compelling case.
Example: Without a doubt, the urgency of addressing climate change demands immediate action and concerted efforts from policymakers and individuals alike. As evidenced by recent climate reports, the consequences of inaction are dire, with rising global temperatures leading to more frequent and severe weather events, loss of biodiversity, and threats to food security.
Employ Tools for Effective Writing
Similar to learning how to write an explanatory essay , structure your arguments logically, with a clear introduction, well-developed body paragraphs, and a concise conclusion. Use transition words to guide your reader smoothly through your argument. Incorporate rhetorical devices to add depth and resonance to your writing, making your arguments more impactful and memorable.
Example: Transitioning from the causes of environmental degradation to potential solutions, the essay navigates a range of approaches, each offering a unique perspective on balancing ecological preservation with human needs. For instance, implementing reforestation projects and promoting sustainable land management practices are crucial steps in mitigating the effects of deforestation and preserving natural habitats for future generations.
In this guide, we've covered the basics of crafting great argumentative essays. We've looked at everything from coming up with ideas to refining your final draft, sharing helpful strategies and tips along the way. With these insights into language, facts, and writing techniques, you're all set to create essays that really grab attention and persuade your readers. Consider this your starting point for smooth and confident argumentative writing.
Got Excellent Ideas?
Let's make your thoughts shine so bright they'll need sunglasses.
What’s a Good Starter for an Argumentative Essay?
Related articles.
.webp)
How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 101 Guide [+ Examples]
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing that investigates different sides of a particular issue. Its central purpose is to inform the readers rather than expressively persuade them. Thus, it is crucial to differentiate between argumentative and persuasive essays.
While composing an argumentative essay, the students have to demonstrate their research and analytical skills. The secret of a successful paper lies behind strong arguments and counterarguments. So, the writer should focus on facts and data rather than personal values and beliefs.
Besides, a good argumentative essay should be structured appropriately:
- The introduction and conclusion have to create a frame for the entire essay.
- The body paragraphs are supposed to cover the essential points.
- Supporting evidence should make a paper more professional and reputable.
Are you still wondering what an argumentative essay is and how to write it? Check out the sections below prepared by our experts . Here, you can find the most valuable info, helpful tips, and useful examples.
📜 Classic Strategy
📋 toulmin strategy, 🗣️ rogerian strategy, ✒️ fill in the blanks, 🔍 edit and proofread, 🔗 references, 📌 argumentative essay in a nutshell.
Are you trying to figure out what an argumentative essay is? It’s a type of academic paper that covers both sides of a given issue. An author can decide whether they aim to present both sides equally or support one side more dynamically.
One of the mistakes among students is the confusion of argumentative and persuasive essays . Do you want to figure out the differences? Take a look at the following table.
Before writing an argument essay, it would be helpful to choose an appropriate model to rely on. There are three strategies to consider: Classical, Toulmin, and Rogerian.
Look at the following sections and choose the most suitable one for you.
Are you wondering how to write an argumentative essay? Consider using the classical approach. It is the most popular way of composing an argumentative paper.
Under the classical strategy, the author has to follow these rules:
- research the issue;
- present both sides;
- express own opinion;
- prove the reader the validity of the conclusion.
It is up to the audience to decide whether your position is right or wrong. Yet, you should try to convince the readers of the effectiveness of your opinion.
Usually, the classical argument paper is structured in the following way:
- Introduction . Use the hook to catch the readers’ attention. State the problem and explain why your topic is relatable to the audience.
- General background. Introduce the general info and several facts about your issue.
- Thesis statement . State your position clearly and concisely.
- The central argument. Provide valid evidence and appropriate examples to support your position. Refer only to reliable sources.
- Rebuttal . Include a counter paragraph in your essay, presenting the opposing arguments. Provide specific examples to make the reader understand your position. Also, explain to the audience why the counterclaims are incorrect.
- Conclusion . Synthesize your arguments and counterarguments. Give the readers a question for further investigation of your problem. To make your essay more impressive, compose a memorable concluding sentence.
Toulmin strategy is the most suitable for the discussion of controversial issues. This model aims to find common ground through clear logic and valid evidence. Besides, the Toulmin strategy eliminates unnecessary things and limits the points to agree upon.
An argumentative essay written by the Toulmin model includes the following elements:
- Claim . A viewpoint that the author aims to prove.
- Evidence . Supportive facts from reliable resources that highlight the significance of the claim.
- Warrant . An element that connects the claim and that evidence.
- Backing . Additional reasoning that underlines the warrant’s validity.
- Rebuttal . Counterarguments that contradict the author’s position.
- Qualifier . An additional element (usually, a word or a short phrase) that narrows the claim’s capacity. Several examples of qualifiers: “typically,” “usually,” “occasionally,” etc.
- Exceptions . Specific limitations that indicate the cases where that claim may not be valid.
Like the Toulmin approach, Rogerian strategy attempts to find common ground between two sides of one issue. However, the technique is slightly different.
The Rogerian model is often used in highly controversial debates when the parties do not accept each other’s position. Thus, the given strategy focuses on finding the agreement by proving the validity of the opposing arguments.
Below, you can find the primary outline for the Rogerian argumentative essay:
- Introduce the problem. Present the issue clearly and explain why it is worth the readers’ attention.
- Summarize and analyze the counterarguments. Take into consideration all the possible counterpoints and look at them from different perspectives. Discuss the cases in which the opposing claims could be valid. Demonstrate your open-mindedness. This will make the opposite party more loyal to you.
- Present your position. After discussing the counterpoints, state your opinion. Convince the audience about the validity of your points.
- Prove the advantages of your position. Explain to the opposite party how the acceptance and adoption of your points will benefit them.
🧐 How to Write an Argumentative Essay
Before working on your essay, carefully read the assignment. Make sure you understand all the instructor’s requirements and the purpose of the paper.
- Pay enough attention to the task. Did your professor assign you a topic? Or do you need to choose it yourself ? Make sure you have an idea that will turn into an outstanding essay.
- Select the strategy you are going to apply. An argumentative essay format will depend on the model you choose to compose your paper. Analyze the issue you will arise and decide what strategy is the most suitable. Is it the Classical model, the Toulmin, or the Rogerian one?
After that, start composing your argumentative essay. Check out the following sections. We have a lot of insightful info to share with you!
📚 Research the Topic
The first step of writing an argumentative paper is an in-depth investigation of the topic. To validate your arguments, you have to refer to credible resources. The essay will look more professional if you use reliable sources in it.

To research like a professional , do the following:
- Use only credible sources. You can refer to the books, research articles, materials from academic databases, or Google Scholar. Webpages registered as governmental or educational institutions (.gov, .edu.) and widely-known news websites (New York Times, BBC, CNBC) are also considered appropriate. Avoid using blog posts, outdated materials, and any other data from unreliable sources. You may get into huge trouble, taking information from random websites, since it may be invalid.
- Pay attention to the publishing date . You may be required to use the sources released no later than five years ago. Yet, it is not always the case, especially when you’re dealing with historical documents. Thus, double-check your instructions regarding recommended sources.
- Keep your topic in mind. Concentrate on what you are writing about and select the sources for your exact issue. Avoid sources that provide too general information and look for more limited ones. If your idea is World War II’s economic consequences, the history book from ancient times to modern days will not be the best option.
- Become an expert. Take enough time to investigate the issue you are writing about. Read numerous articles, compare and contrast the scientists’ opinions. Prove your reader that you are a reliable person who selected the best sources.
📝 Outline Your Essay
The majority of students tend to underestimate the power of outlining. Don’t do this! An argumentative essay outline is a helpful tool for planning, structuring, and composing.
Firstly , a well-developed outline helps the writer to put all their thoughts in an appropriate order. None of the essential points will be lost if the student plans the essay before writing.
Secondly , it lets the writer figure out what evidence suits what argument most. Before writing, draft your essay first. Put examples, facts, etc. in the right parts of the paper. Then, write the entire text.
Thirdly , an outline provides a perfect opportunity to change the essay’s parts without rewriting the paper. Are you unsure of specific details? Not a problem. Change them in the outline without ruining the text.
There are essential elements that your outline should contain. Check out the following section to see them.
Introduction
How to start an argumentative essay? First and foremost, include an argumentative essay introduction in your outline.
This part should grab the readers’ attention from the first words. Thus, put enough effort into composing a compelling hook . What can it be? An impressive statistic or an exciting fact? Be creative – decide yourself! But make sure that your intro is catchy enough.
After the hook, introduce your topic’s general background . Prove the readers the significance of your issue and gradually come to the thesis statement .
The concept of studying abroad is becoming increasingly popular in both developed and developing countries. Students around the globe strive to explore the world and broaden their minds, and studying in a foreign country is an excellent opportunity to do so. Such experience may be extremely beneficial because meeting new people and discovering foreign cultures help students to gain valuable knowledge and see the world from a new perspective. However, while presenting significant opportunities for personal growth, it may also bring about some challenges.
Thesis Statement
A thesis is an essential part of your argumentative essay. It should state your position regarding the issue clearly and concisely. Avoid general statements, vague words, and be as specific and possible. Your thesis statement should guide the readers throughout the main points of the paper.
The location of the thesis in the essay plays a crucial role. The most appropriate place for it is the last sentence of the introductory paragraph.
Although students face difficulties such as loneliness while studying abroad, it is a worthy experience to introduce them to new knowledge, people, and culture and promote their independence.
Body Paragraphs
The body of your paper is supposed to develop your position, provide valid evidence and examples. Each paragraph has to focus only on one idea. This will ensure the logical structure of your argumentative essay.
A body paragraph should start from the topic sentence and end with the concluding sentence . Such a frame around every section will make your readers stay concentrated on your ideas and get your opinion.
- The topic sentence is the first sentence of the passage. It should reflect its point and correspond to the thesis statement.
- The concluding sentence aims to wrap up the author’s thoughts. Thus, make sure that the last sentence of a paragraph is insightful enough.
Each body paragraph should include an argument (or a counterargument) with supporting evidence. Get your proof from credible sources and ensure that it directly corresponds to the point.
An example of a topic sentence :
The benefits of education abroad are almost innumerable, prominent examples being gaining new knowledge, making friends with people who have different mindsets, and discovering new cultures.
An example of a concluding sentence:
Participants of student exchange programs usually return more driven and eager to develop both themselves and their country.
A conclusion plays a critical role in understanding the entire paper. It summarizes the body and leaves the final impression. Besides, it may push the readers on further investigation of the issue.
- To make your argumentative essay conclusion powerful, it is not enough just to summarize the arguments. It has to synthesize your ideas and show the connection between them. In other words, your points should be summarized and analyzed.
- Moreover, a conclusion refers to the thesis statement . A mere restatement of the central idea is not the most successful way of finishing your paper. You should try to develop it to demonstrate the reason you’ve written the previous paragraphs.
One more tip:
- Give the audience an incentive to explore the topic more in-depth. Insert the questions for further investigation at the end of your essay. It would play a significant role in making an impressive conclusion.
To sum up, studying abroad is beneficial as it helps a person evolve and perceive a world from new perspectives. It is an opportunity for a participant to explore the world, meet new people, gain valuable knowledge and experience, and broaden their horizons. Education abroad might pose problems like homesickness, loneliness, and trouble with getting accustomed to a new environment. However, all of them can be easily overcome if a student is flexible and eager to become autonomous and independent.
The list of references is a crucial part of any argumentative essay. It should contain all the sources the writer uses in the paper.
Before organizing your reference list , double-check your argumentative essay format. Is it written in MLA, APA, or maybe in Chicago style? How many references does the professor expect you to include? What kind of sources are you required to use?
After figuring out these issues, move to the format requirements of the writing style you use for your paper. The most popular ones are APA (7th edition), MLA, and ChicagoAD (author-date) styles. Below, you can find the examples of a reference for the same book in different formatting styles.
Did you develop a good outline? Congratulations! You are almost done with the essay. Now, you need to fill in the blanks and create a final version of your paper. Here is where you need to demonstrate a high level of your writing skills.
- Make sure your paper has no logical fallacies. Information from an untrustworthy source, a hasty generalization, or a false conclusion may put your reliability as an author under threat. So double-check all the data you include in your essay. Moreover, make sure all your statements are well-developed and supported by valid evidence.
- Check your argumentative essay structure . All the arguments should refer to the thesis statement and must be presented in the logical sequence. The supporting evidence and examples have to be inserted in the text logically, according to the arguments.
- Pay enough attention to the citations. References and in-text citations are incredibly tricky. Always check every detail according to your essay format. If you are unsure of specific issues, refer to a citation guide and make your paper free of formatting mistakes.
- Ensure the coherence of your argumentative essay. Often, the paper’s material seems raw only because it is presented without a logical connection. To ensure a smooth connection between the ideas, use transitions between the paragraphs and linking words inside them. Insert them in the text to connect the points. As a result, you will have a coherent essay with the logical flow of the arguments.

The final step of your writing process is editing and proofreading. Although it is not that energy and time consuming, it still plays a critical role in the work’s success.
While writing your argumentative paper, plan your time accordingly. This will provide you with an opportunity to polish your essay before submitting it. And take a look at our checklist and always use it to improve your papers:
- NO first and second person. Use only the third person in your argumentative essay. It is a general requirement for any kind of academic paper.
- NO slang. The word choice is an essential part of the essay writing process. Ensure you use only formal vocabulary and avoid using informal language (jargon, slang, etc.).
- NO unchecked words. Sometimes, words can raise questions and lead to misunderstandings. If you are unsure whether the term is used appropriately, double-check its meaning or replace it with another.
- NO plagiarism. While proofreading, make sure your citations are either properly paraphrased or taken in quotation marks. You can change the sentence structure to avoid plagiarism.
- NO minor mistakes. Grammar, spelling, punctuation play a crucial role. Want to make your paper look professional? Make sure it is free of minor mistakes then.
Argumentative Essay Topics
- Should student-athletes benefit from sports?
- Do celebrities really have influence on people behavior?
- Will decriminalization of drugs increase drug menace?
- Does social and environmental reporting promote organizations’ financial success?
- Should online learning be promoted?
- Can space exploration resolve human problems?
- Is success really the outcome of hard work?
- Is there discrimination against women in sports?
- Will banning tobacco sales promote public health?
- Is euthanasia a clemency?
- Should college education be free and accessible for every student?
- Should football be banned for being too dangerous?
- Is it time to change social norms ?
- Should public servants’ strikes be prohibited?
- Does media create a negative image of ageing and older people?
- Is capitalism the best economic system?
- Can children under 18 make an appropriate decision on getting tattoo ?
- Should net neutrality be protected?
- Can an improper use of social media provoke a family crisis?
- Is it right to use animals in biomedical research ?
- Does the climate change affect our indoor environment?
- Are children’s crimes a result of poor parenting?
- Should health care be universal?
- Does the increased use of technology hurt students’ efficiency?
- Is transformative education a key to the system modernization?
- Why should patients have access to truthful information?
- How does language barrier affect health care access?
- Would allowing adoption by same-sex couples benefit the country’s child welfare system?
- Is spanking children a proper way to improve their behavior?
- Does gun control law lowers crime rates?
- Will ban on spamming improve users’ internet experience?
- Should behavior be made illegal because it’s immoral?
- Is globalization really a progress?
- Does aid to developing countries bring more harm than good?
- Can parents improve children mental health by restricting internet use ?
- Is trusting our senses the best way to get the truth?
- Why parents should not have the right to choose their children based on genetics.
- Is college education really worth it?
- Will wearing a body camera by police officer enhance public trust?
- Immigration : a benefit or a threat?
- Is it a duty of adult children to take care of their elderly parents?
- Should abortions be legal?
- Are agents an integral part of professional sports?
- Will ban of cellphones while driving decrease the car accident rates?
- Should marijuana be legal for medical use?
- Is veganism diet universally beneficial?
- Should museums return artefacts?
- Is water birth beneficial for women’s health?
- Will paying people to stay healthy benefit the nation in the long-term perspective?
- Is obesity a disease or a choice?
It is up to you to decide how many parts to include in your essay. However, the 5 paragraph structure is the most appropriate model for an argumentative paper. So, write an introduction, a conclusion, and three body paragraphs.
The pronoun “you” is acceptable for informal writing. Yet, in academic papers, avoid using the second person. The same situation is with the first person. Generally, academic papers require the use of the third person.
A hook aims to grab the readers’ attention. Thus, you could start your essay with an interesting fact about your issue. Another way to create a catchy hook is to prove the audience the relatability of your topic. Make the readers want to explore your essay by demonstrating the significance of your issue.
Yes, you can. A question might become a compelling hook. Just make sure that it is profound, thought-provocative, and concise. A too broad or complicated question will only confuse your readers.
A title is an essential part of the essay since it causes the first impression. While selecting a heading, take into consideration the following points:
1. The title must be catchy.
2. It has to be not too long (5-12 words).
3. The title has to reflect the topic of the paper.
4. It should not be too complicated: the simpler – the better.
Thank you for visiting our page! We hope the information was helpful and insightful. Do you have friends who seek help with writing an argumentative essay? Share our article with them. And don’t forget to leave your comments!
- Sample Argument Essays: Mesa Community College
- Argument: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay: Grace Fleming, ThoughtCo
- Tips for Organizing an Argumentative Essay: Judith L., Beumer Writing Center, Valparaiso University
- Argumentative Essay: Oya Ozagac, Bogazici University, Online Writing Lab
- Argumentative Essays: Purdue Online Writing Lab, College of Liberal Arts, Purdue University
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay Step by Step: Virginia Kearney, Owlcation
- Counterargument: Gordon Harvey for the Writing Center at Harvard University
- Basic Steps in the Research Process: North Hennepin Community College, Minnesota
- How to Recognize Plagiarism, Overview: School of Education, Indiana University Bloomington
- 15 Steps to Good Research: Georgetown University Library
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email
![writing skills argument essay How to Title an Essay: Guide with Creative Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-woman-making-greeting-card-new-year-christmas-2021-friends-family-scrap-booking-diy-writing-letter-with-best-wishes-design-her-homemade-card-holidays-celebration-284x153.jpg)
It’s not a secret that the reader notices an essay title first. No catchy hook or colorful examples attract more attention from a quick glance. Composing a creative title for your essay is essential if you strive to succeed, as it: Thus, how you name your paper is of the...

The conclusion is the last paragraph in your paper that draws the ideas and reasoning together. However, its purpose does not end there. A definite essay conclusion accomplishes several goals: Therefore, a conclusion usually consists of: Our experts prepared this guide, where you will find great tips on how to...
![writing skills argument essay How to Write a Good Introduction: Examples & Tips [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/closeup-shot-woman-working-studying-from-home-with-red-coffee-cup-nearby-284x153.jpg)
A five-paragraph essay is one of the most common academic assignments a student may face. It has a well-defined structure: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Writing an introduction can be the most challenging part of the entire piece. It aims to introduce the main ideas and present...

Exemplification essays, also called illustration essays, are one of the easiest papers to write. However, even the simplest tasks require experience and practice. It is a good idea to find and analyze free exemplification essay examples. You can also ask your teacher to give you some sample exemplification essays from...
![writing skills argument essay How to Write about a Topic You Lack Interest in [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Frustrated-exhausted-young-woman-blogger-284x153.jpg)
During their school years, students may not always have the opportunity to select a topic for their essay or research paper. Instructors tend to assign one or offer a list of ideas that might not seem engaging. Moreover, even the topic that you choose yourself can sometimes end up being...

Sorry to disappoint you, but if you think that your high scores and grades would be enough to get accepted into the university of your dreams, you’re wrong… The best colleges worldwide, such as the Ivy League schools receive applications from thousands and thousands of talented students. You gotta stand...

Often when you’re completing academic writing, especially essays, you need to use pronouns. In academic writing, the use of the word you is unacceptable. You can find yourself in a sticky situation, deciding upon gender-neutral pronouns in your academic writing. How can students deal with it? In most situations today,...

A divorce is a life-changing experience that affects spouses and their children (if there are any). Since divorce rates are relatively high in modern society, more and more people face this problem nowadays. When you are assigned to compose an argumentative essay about divorce, you should be as careful as...
![writing skills argument essay How to Stop Corruption Essay: Guide & Topics [+4 Samples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/close-up-two-hands-while-paying-money-284x153.jpeg)
Corruption is an abuse of power that was entrusted to a person or group of people for personal gain. It can appear in various settings and affect different social classes, leading to unemployment and other economic issues. This is why writing an essay on corruption can become a challenge. One...

Do you have to write an essay for the first time? Or maybe you’ve only written essays with less than 1000 words? Someone might think that writing a 1000-word essay is a rather complicated and time-consuming assignment. Others have no idea how difficult thousand-word essays can be. Well, we have...

To write an engaging “If I Could Change the World” essay, you have to get a few crucial elements: The questions that define this paper type: What? How? Whom? When? Where? The essay structure that determines where each answer should be; Some tips that can make your writing unique and original. Let us...
![writing skills argument essay Why I Want to be a Pharmacist Essay: How to Write [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/cut-out-medicament-drug-doctor-medical-1-284x153.jpg)
Why do you want to be a pharmacist? An essay on this topic can be challenging, even when you know the answer. The most popular reasons to pursue this profession are the following:

Essay and dissertation writing skills
Planning your essay
Writing your introduction
Structuring your essay
- Writing essays in science subjects
- Brief video guides to support essay planning and writing
- Writing extended essays and dissertations
- Planning your dissertation writing time
Structuring your dissertation
- Top tips for writing longer pieces of work
Advice on planning and writing essays and dissertations
University essays differ from school essays in that they are less concerned with what you know and more concerned with how you construct an argument to answer the question. This means that the starting point for writing a strong essay is to first unpick the question and to then use this to plan your essay before you start putting pen to paper (or finger to keyboard).
A really good starting point for you are these short, downloadable Tips for Successful Essay Writing and Answering the Question resources. Both resources will help you to plan your essay, as well as giving you guidance on how to distinguish between different sorts of essay questions.
You may find it helpful to watch this seven-minute video on six tips for essay writing which outlines how to interpret essay questions, as well as giving advice on planning and structuring your writing:
Different disciplines will have different expectations for essay structure and you should always refer to your Faculty or Department student handbook or course Canvas site for more specific guidance.
However, broadly speaking, all essays share the following features:
Essays need an introduction to establish and focus the parameters of the discussion that will follow. You may find it helpful to divide the introduction into areas to demonstrate your breadth and engagement with the essay question. You might define specific terms in the introduction to show your engagement with the essay question; for example, ‘This is a large topic which has been variously discussed by many scientists and commentators. The principle tension is between the views of X and Y who define the main issues as…’ Breadth might be demonstrated by showing the range of viewpoints from which the essay question could be considered; for example, ‘A variety of factors including economic, social and political, influence A and B. This essay will focus on the social and economic aspects, with particular emphasis on…..’
Watch this two-minute video to learn more about how to plan and structure an introduction:
The main body of the essay should elaborate on the issues raised in the introduction and develop an argument(s) that answers the question. It should consist of a number of self-contained paragraphs each of which makes a specific point and provides some form of evidence to support the argument being made. Remember that a clear argument requires that each paragraph explicitly relates back to the essay question or the developing argument.
- Conclusion: An essay should end with a conclusion that reiterates the argument in light of the evidence you have provided; you shouldn’t use the conclusion to introduce new information.
- References: You need to include references to the materials you’ve used to write your essay. These might be in the form of footnotes, in-text citations, or a bibliography at the end. Different systems exist for citing references and different disciplines will use various approaches to citation. Ask your tutor which method(s) you should be using for your essay and also consult your Department or Faculty webpages for specific guidance in your discipline.
Essay writing in science subjects
If you are writing an essay for a science subject you may need to consider additional areas, such as how to present data or diagrams. This five-minute video gives you some advice on how to approach your reading list, planning which information to include in your answer and how to write for your scientific audience – the video is available here:
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.
Short videos to support your essay writing skills
There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing, including:
- Approaching different types of essay questions
- Structuring your essay
- Writing an introduction
- Making use of evidence in your essay writing
- Writing your conclusion
Extended essays and dissertations
Longer pieces of writing like extended essays and dissertations may seem like quite a challenge from your regular essay writing. The important point is to start with a plan and to focus on what the question is asking. A PDF providing further guidance on planning Humanities and Social Science dissertations is available to download.
Planning your time effectively
Try not to leave the writing until close to your deadline, instead start as soon as you have some ideas to put down onto paper. Your early drafts may never end up in the final work, but the work of committing your ideas to paper helps to formulate not only your ideas, but the method of structuring your writing to read well and conclude firmly.
Although many students and tutors will say that the introduction is often written last, it is a good idea to begin to think about what will go into it early on. For example, the first draft of your introduction should set out your argument, the information you have, and your methods, and it should give a structure to the chapters and sections you will write. Your introduction will probably change as time goes on but it will stand as a guide to your entire extended essay or dissertation and it will help you to keep focused.
The structure of extended essays or dissertations will vary depending on the question and discipline, but may include some or all of the following:
- The background information to - and context for - your research. This often takes the form of a literature review.
- Explanation of the focus of your work.
- Explanation of the value of this work to scholarship on the topic.
- List of the aims and objectives of the work and also the issues which will not be covered because they are outside its scope.
The main body of your extended essay or dissertation will probably include your methodology, the results of research, and your argument(s) based on your findings.
The conclusion is to summarise the value your research has added to the topic, and any further lines of research you would undertake given more time or resources.
Tips on writing longer pieces of work
Approaching each chapter of a dissertation as a shorter essay can make the task of writing a dissertation seem less overwhelming. Each chapter will have an introduction, a main body where the argument is developed and substantiated with evidence, and a conclusion to tie things together. Unlike in a regular essay, chapter conclusions may also introduce the chapter that will follow, indicating how the chapters are connected to one another and how the argument will develop through your dissertation.
For further guidance, watch this two-minute video on writing longer pieces of work .
Systems & Services
Access Student Self Service
- Student Self Service
- Self Service guide
- Registration guide
- Libraries search
- OXCORT - see TMS
- GSS - see Student Self Service
- The Careers Service
- Oxford University Sport
- Online store
- Gardens, Libraries and Museums
- Researchers Skills Toolkit
- LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com)
- Access Guide
- Lecture Lists
- Exam Papers (OXAM)
- Oxford Talks
Latest student news
CAN'T FIND WHAT YOU'RE LOOKING FOR?
Try our extensive database of FAQs or submit your own question...
Ask a question
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that develops an idea or argument using evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
There are many types of essays you might write as a student. The content and length of an essay depends on your level, subject of study, and course requirements. However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages:
- Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
- Writing : Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion.
- Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay writing process, preparation for writing an essay, writing the introduction, writing the main body, writing the conclusion, essay checklist, lecture slides, frequently asked questions about writing an essay.
The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay .
For example, if you’ve been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you’ll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay , on the other hand, you’ll need to spend more time researching your topic and developing an original argument before you start writing.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Before you start writing, you should make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to say and how you’re going to say it. There are a few key steps you can follow to make sure you’re prepared:
- Understand your assignment: What is the goal of this essay? What is the length and deadline of the assignment? Is there anything you need to clarify with your teacher or professor?
- Define a topic: If you’re allowed to choose your own topic , try to pick something that you already know a bit about and that will hold your interest.
- Do your research: Read primary and secondary sources and take notes to help you work out your position and angle on the topic. You’ll use these as evidence for your points.
- Come up with a thesis: The thesis is the central point or argument that you want to make. A clear thesis is essential for a focused essay—you should keep referring back to it as you write.
- Create an outline: Map out the rough structure of your essay in an outline . This makes it easier to start writing and keeps you on track as you go.
Once you’ve got a clear idea of what you want to discuss, in what order, and what evidence you’ll use, you’re ready to start writing.
The introduction sets the tone for your essay. It should grab the reader’s interest and inform them of what to expect. The introduction generally comprises 10–20% of the text.
1. Hook your reader
The first sentence of the introduction should pique your reader’s interest and curiosity. This sentence is sometimes called the hook. It might be an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement emphasizing the relevance of the topic.
Let’s say we’re writing an essay about the development of Braille (the raised-dot reading and writing system used by visually impaired people). Our hook can make a strong statement about the topic:
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
2. Provide background on your topic
Next, it’s important to give context that will help your reader understand your argument. This might involve providing background information, giving an overview of important academic work or debates on the topic, and explaining difficult terms. Don’t provide too much detail in the introduction—you can elaborate in the body of your essay.
3. Present the thesis statement
Next, you should formulate your thesis statement— the central argument you’re going to make. The thesis statement provides focus and signals your position on the topic. It is usually one or two sentences long. The thesis statement for our essay on Braille could look like this:
As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness.
4. Map the structure
In longer essays, you can end the introduction by briefly describing what will be covered in each part of the essay. This guides the reader through your structure and gives a preview of how your argument will develop.
The invention of Braille marked a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by blind and visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Write your essay introduction
The body of your essay is where you make arguments supporting your thesis, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. Its purpose is to present, interpret, and analyze the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
Length of the body text
The length of the body depends on the type of essay. On average, the body comprises 60–80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8–10 pages.
Paragraph structure
To give your essay a clear structure , it is important to organize it into paragraphs . Each paragraph should be centered around one main point or idea.
That idea is introduced in a topic sentence . The topic sentence should generally lead on from the previous paragraph and introduce the point to be made in this paragraph. Transition words can be used to create clear connections between sentences.
After the topic sentence, present evidence such as data, examples, or quotes from relevant sources. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how it helps develop your overall argument.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
See the full essay example
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The conclusion is the final paragraph of an essay. It should generally take up no more than 10–15% of the text . A strong essay conclusion :
- Returns to your thesis
- Ties together your main points
- Shows why your argument matters
A great conclusion should finish with a memorable or impactful sentence that leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What not to include in a conclusion
To make your essay’s conclusion as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid. The most common mistakes are:
- Including new arguments or evidence
- Undermining your arguments (e.g. “This is just one approach of many”)
- Using concluding phrases like “To sum up…” or “In conclusion…”
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Write your essay conclusion
Checklist: Essay
My essay follows the requirements of the assignment (topic and length ).
My introduction sparks the reader’s interest and provides any necessary background information on the topic.
My introduction contains a thesis statement that states the focus and position of the essay.
I use paragraphs to structure the essay.
I use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph.
Each paragraph has a single focus and a clear connection to the thesis statement.
I make clear transitions between paragraphs and ideas.
My conclusion doesn’t just repeat my points, but draws connections between arguments.
I don’t introduce new arguments or evidence in the conclusion.
I have given an in-text citation for every quote or piece of information I got from another source.
I have included a reference page at the end of my essay, listing full details of all my sources.
My citations and references are correctly formatted according to the required citation style .
My essay has an interesting and informative title.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (e.g. font, page numbers, line spacing).
Your essay meets all the most important requirements. Our editors can give it a final check to help you submit with confidence.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
More interesting articles
- Checklist for academic essays | Is your essay ready to submit?
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
- Generate topic ideas for an essay or paper | Tips & techniques
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
- How to write a descriptive essay | Example & tips
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
- How to write an expository essay
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
- Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
- Organizational tips for academic essays
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
What is your plagiarism score?

10 Argumentative Skills and How To Improve Them
Discover 10 Argumentative skills along with some of the best tips to help you improve these abilities.

Argumentative skills are important for many reasons. They can help you win debates, persuade others to see your point of view, and even just better understand the world around you. In this guide, we’ll discuss what argumentative skills are, why they’re important, and how you can improve your own argumentative skills.
Critical Thinking
Problem solving, organizational skills, time management, public speaking.
Critical thinking is the ability to think about a topic in a logical way and to make judgments based on facts and evidence. When we think critically, we are able to consider different points of view, to make decisions based on our own values and to make arguments that are supported by evidence.
Critical thinking is an important skill for argumentative writing because it allows you to make well-supported arguments and to counter arguments made by others. When you can think critically, you are better able to see both sides of an issue, to understand the facts and to make a decision based on your own values.
Research is an important argumentative skill because it allows you to support your claims with evidence. When you are making an argument, you will need to back up your claims with evidence. This evidence can come from research that you have done yourself or from other sources.
When you are doing research, you will need to be sure to use reliable sources. You will also need to be able to critically evaluate the sources you are using. This means that you will need to be able to determine whether the sources are credible and whether they actually support your claims.
Analysis is the process of breaking down a complex idea or object into smaller parts in order to better understand it. When you analyze something, you’re looking at it critically and breaking it down into its component parts. This can be done with a text, a speech, a piece of legislation, a data set or any other complex idea.
When you’re analyzing something, you’re looking at the parts and how they fit together to make up the whole. You’re also looking at the relationships between the parts and the whole. For example, if you were analyzing a data set, you might look at the different variables and how they relate to each other. If you were analyzing a piece of legislation, you might look at the different clauses and how they fit together to make up the whole.
Analysis is an important skill for argumentative writing because it allows you to better understand the topic you’re writing about and the arguments on both sides. When you can understand the arguments on both sides, you can better formulate your own argument and support it with evidence.
Problem solving is an important argumentative skill because it allows you to identify and solve problems. When you can identify and solve problems, you can improve the quality of your argument and make a stronger case. Problem solving also requires you to be flexible and open to new ideas. You need to be able to see all sides of the problem and consider different solutions before you can choose the best option.
Explain why Listening is an important Argumentative skill. Listening is an important argumentative skill because it allows you to understand the other person’s point of view. When you can understand the other person’s point of view, you can better understand the problem and find the best solution. Listening also requires you to be flexible and open to new ideas. You need to be able to see all sides of the problem and consider different solutions before you can choose the best option.
Organizational skills are important in argumentative writing because they help you structure your argument and support it with evidence. Good organization can make your argument more persuasive and easier to follow.
Some ways to improve your organizational skills include:
-Using an outline to structure your argument -Using headings to break up your argument -Using transitions to connect your points -Using punctuation to clarify your organization -Practicing your argument out loud to see if it flows -Using visuals like charts and graphs to help your audience follow your argument
Time management is the ability to use your time wisely and efficiently. It involves planning, prioritizing and scheduling your time to achieve your goals. Good time management skills can help you in every aspect of your life, from your work life to your personal life.
Time management is an important skill for argumentative writing because it can help you organize your thoughts and arguments. When you’re writing an argument, you need to be able to support your position with evidence. Time management can help you make sure you have all the evidence you need and that you’re presenting it in the most effective way.
Writing is an important argumentative skill because it is the foundation of every argument. An argument is made up of three parts: the claim, the evidence and the support. The claim is the main point that you are trying to prove. The evidence is the facts, statistics or examples that you use to support your claim. The support is the way that you connect the evidence to the claim.
The way that you write your argument can make a big difference in how convincing it is. Good writers use clear, concise language and organize their arguments in a way that is easy for the reader to follow.
Editing is an important argumentative skill because it allows you to improve the quality of your argument by removing any unnecessary information and ensuring that your argument is clear and concise. When you edit your argument, you should also edit your supporting evidence to make sure that it is relevant and that it supports your argument.
Editing your argumentative essay can be a difficult process, but it is important to remember that your argument should always come first. You can always add more supporting evidence later, but you can’t take away what is already there.
Public speaking is an important argumentative skill because it allows you to present your argument to a large group of people. When you are able to deliver your argument in a clear and concise way, you are more likely to convince your audience that your argument is valid. Public speaking also allows you to see how your argument holds up when you are challenged by other people.
Practicing your public speaking skills can help you become more comfortable with arguing and better at defending your position. It can also help you become more aware of the weaknesses in your argument and how to fix them.
Debate is an important argumentative skill because it allows you to present your argument to an audience and defend your position against opposing arguments. In a debate, you will need to be able to present your argument in a clear and concise way, understand and respond to opposing arguments, and use evidence to support your position.
Being able to debate effectively requires practice and experience. You can start by participating in mock debates with your classmates or friends, or by attending local or national debate competitions. As you gain experience, you will be able to develop your argumentative skills and become a more effective debater.
How to Improve Your Argumentative Skills
1. Understand the basics of argument Before you can start improving your argumentative skills, you need to understand the basics of argument. This includes understanding the different types of arguments, the components of an argument and how to identify fallacies.
2. Research your topic Once you have a basic understanding of argument, you need to start researching your topic. This includes finding reliable sources, taking notes and brainstorming your own ideas.
3. Develop your thesis After you have done your research, you need to develop a thesis. This is the main point of your argument. It should be clear, concise and supported by your research.
4. Write your essay Once you have developed your thesis, you need to start writing your essay. This includes developing an introduction, body and conclusion. Make sure to support your thesis with evidence from your research.
5. Edit your essay After you have written your essay, you need to edit it. This includes proofreading for grammar and spelling mistakes, as well as ensuring that your argument is clear and concise.
6. Practice your argumentative skills The best way to improve your argumentative skills is to practice. This includes practicing writing essays, as well as participating in debates and public speaking.
10 Relationship Building Skills and How To Improve Them
10 analytical and quantitative skills and how to improve them, you may also be interested in..., what does an infosys technology architect do, 16 real time analyst skills for your career and resume, what does a veterinary office manager do, what does an office depot sales advisor do.

Tips on essay planning and writing
What is an essay, brainstorm your topic by creating a mind map, check you understand what your essay question is asking you, academic writing style, signposting, building an argument and summarising other people's ideas, what is paraphrasing, essay structure, useful links.

Traditional academic essays are pieces of writing which are designed to demonstrate the following points:
- that you understand a particular subject
- that you have undertaken some kind of research
- that you can produce a clear and coherent argument
This means that you have to combine important ideas, examples, and interpretations from other writers with your own. All of these have to be put together in a linear, written format (making one point, then moving on to the next), which persuades the reader that your line of argument is a convincing one.
Note : There may be variations in the approach you need to take depending on the discipline you are studying. Check with your tutor/department for discipline specific guidelines.
When you choose, or are assigned, an essay question, you are asked to focus on something very specific. It's not just a case of writing down everything you know about the subject. An essay question instructs you to do something with the knowledge you have, and to put it into a certain context, which will allow you to demonstrate the range of your critical thinking.
Essay questions therefore have instructional verbs to determine what your approach should be. These are words such as: discuss, analyse, argue, compare, review, evaluate, examine, outline, illustrate .... These tell you how to answer the question and what your essay should do. It is important that you understand exactly what these words mean so that you don’t misinterpret a question.

- For more examples check 'Terms that may be used in essays or examinations'
You will usually be expected to write using academic language and specialist vocabulary from your subject area. Academic writing normally contains these features:
- Formal writing in an impersonal or objective style and often takes the 'passive' voice. Passive constructions can be used to avoid using 'I' in essays, e.g. 'It can be argued...'
- Vocabulary appropriate for particular academic contexts is used which may include technical and specialist words.
- Contains references to other writers’ publications which are used to support the arguments in the text
- You may notice that cautious language is frequently used in reporting research and making claims. 'Cautious language' indicates reservations or tentativeness about the conclusions that may be drawn from the evidence presented. Useful phrases are: 'it may be concluded', and 'we can assume'.

Major Signposting
Major signposting is used to signal the introduction of key sections or aspects of the work. These might include the aim, purpose, or structure.
In the introduction:
- This essay will…
- The aim of this essay is to…
- The major issue being discussed is…
- This essay will define and describe…
- This essay will critically examine…
- This essay will first define…then discuss…before making recommendations for…
- This essay is organised in the following way;
In the conclusion:
- To conclude,
- In conclusion,
- To summarise,
- It is evident that
Minor Signposting
Minor signposting are linking words and phrases that make connections for your reader and move them through the text.
- They may be as simple as: First, second, third, next, then, last, lastly, finally
- To offer a counterpoint: However, although, though, yet, alternatively, nevertheless
- To indicate an example: For example, notably, for instance, in this case
Linking words and phrases help give your writing more fluidity. Linking words and phrases will help the flow of your academic writing.
Linking words are particularly useful for use in comparing and contrasting ideas and to move from one idea to another.
Check these resources for examples of linking words and phrases:
- Examples of linking words and phrases (University of Reading via Future Learn)
- Transitional devices (Purdue University)
- Signposting (Queen's University Belfast)
Source: Academic Writing Skills by Patricia Williamson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0
Illustrations vector created by stories - www.freepik.com

Often the clearest way to combine different points of view and to show that you have understood those points of view is to summarise them. Each summary of a different viewpoint can include direct and indirect quotations of key points, plus your understanding of what they mean and a comment on the weaknesses and strengths of the idea or viewpoint. Having described, interpreted and analysed other people's ideas, you can then go on to describe your own point of view and explain why you have chosen it.
Writing which ignores any of the parts described above, can become unbalanced. For example, if there are none of your own ideas, the piece becomes a review of everyone else's work. In these circumstances you could be accused of being uncritical. If the writing does not refer to other people's ideas (directly or indirectly), there is a problem of being too personal and non-academic (this partly depends on your subject). Neither of these would be persuasive arguments.
Paraphrasing is expressing someone else’s writing in your own choice of words, while keeping the same essential meaning. As Pears and Shields (2019, p. 15) explain, it is ‘an alternative way of referring to an author’s ideas or arguments without using direct quotations from their text’.
Paraphrasing is generally more highly valued by academics than direct quoting because it allows you to demonstrate a greater understanding of your source and helps you to maintain your personal writing style and the smooth flow of your essay.
Don’t forget to include in-text citations (author and date) in the text of your assignment and full references at the end of your assignment every time you paraphrase someone else’s words or ideas.
- Paraphrasing - an overview A guide on paraphrasing, academic writing, citing and referencing
- Introduction
- The main body
- Bibliography
The introduction is the official start of the essay and it usually includes some or all of the following:
- a statement introducing the topic
- an explanation of why it is important
- a brief mention of work on the same topic written by other writers
- a gap or problem in previous related work which will be solved or answered in this essay
- an outline of the structure of the essay
- definitions of key terms
- an anecdote or vignette (short story) which highlights the main point of the essay
The body is the largest part of your writing and this is where you guide your reader through your main ideas and arguments. These ideas and arguments come from your brainstorming and research. It is therefore a mixture of other people’s ideas and your own. These points should be organised into a logical order which allows your reader to follow your train of thought.
The balance of discussion between your own ideas and information and those from external sources is crucial to the development of your argument. Without this balance, the writing can become either a summary of other people's ideas and theories, or a description of your personal ideas and experiences with no evidence of research. Both of these would lack analysis, a core component of a good essay. It is therefore vitally important to ensure that a mixture of positions are presented.
Each main point will be described, supported and analysed using examples from your own experiences, and information and theories from external sources (books, journals, websites, lectures, etc.). The main points should be clearly organised by using paragraphs.
In short pieces of writing (< 3,000 words), there will be groups of paragraphs which together form one part of your argument. Usually these sections in "short" essays do not have specific headings. However, they can be clearly identified by using linking phrases which show for example:
- how many elements the section consists of:
There are four main reasons why ...
- the connection of additional points:
Another important point to consider is ... A further issue of importance is ... Moving on the the issue of ...
- or the introduction of a contrasting point:
On the other hand, ... In contrast to the above, ... An alternative understanding of the issue is ...
Longer pieces of writing and dissertations
In long pieces of writing (> 3,000 words) it is sometimes useful to identify clear sections by using sub-headings. Each section (or chapter of a dissertation or thesis) with a sub-heading is like a short essay which could stand alone. The sub-headings may come from your brainstorm and/or your research. However, the best order for the sections in long essays may only become clear after you have started writing them. When the best order becomes clear, chapter introductions and conclusions can be written in each section.
A short chapter introduction should briefly outline the contents of each section and where possible, should also refer back to the sections before and explain how they are related. Similarly, each section needs a conclusion. This should summarise what has been written in this part and should again make connections to other sections. In particular, it should describe the relationship between this part and the next. These are crucial in order to tell the reader what each part is about and how it fits with the other sections. It is like tying knots between separate pieces of string in order to make a single, stronger cord: your argument.
The conclusion is the closing part of the essay and, like the i ntroduction, connects the body of the essay to the title. However, whereas the introduction often starts generally, becomes more focussed and often includes an outline of the main points; the conclusion attempts to summarise the main ideas and arguments, then leads to a final statement.
It should not include new ideas which have not been mentioned before, although you can join ideas you have mentioned in a new way. You may also want to restate questions which you could not answer in your essay, but which you think deserve further study. As the final part of the essay, the conclusion is the last thing which the reader sees. Therefore, it should tie together the different points you have made.
Conclusions often include the following elements:
- language 'markers' showing that this is the conclusion (e.g. to conclude, in summary, this essay has given an account of...)
- a summary of the ideas in the main body
- a comment about the limitations of the scope of the essay / study
- a glance to the future: a prediction, recommendations for action, suggestions for further research, implications for future policy
A bibliography (or reference list) comes after the conclusion (or appendices and final figures) and includes all the information about the sources you have mentioned in the essay. For more information on referencing please see the Write it Right guide.
- Academic Writing Basics (Author: Megan Robertson)
- Academic Writing Essays in English (© 2021 UEfAP)
- Academic Writing Handbook
- OWL Purdue Online Writing Lab
- The Writing Process by English Language Studies group at the MIT Understanding and using the information on this site should make writing not only less anxiety-provoking and more efficient and effective for you, but ultimately it should also help you feel more creative and more satisfied with the products of your writing efforts and learn more in your classes as well.
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 10:13 AM
- URL: https://lit.libguides.com/tips-writing-essays
The Library, Technological University of the Shannon: Midwest
- Memberships
- Institutional Members
- Teacher Members

Argument Essays – the basics
Terms & Conditions of Use
An argument essay
Should parents educate their children at home.
In Britain some parents are now choosing to educate their children at home. This is often because some children find it difficult to fit into the school system because they are especially gifted or have problems of some kind. However, despite the various arguments that have been put forward for home tutoring, this essay will argue that it is better for a child to be educated at school.
Teaching children at home has a number of advantages. Firstly, parents feel that their children will be able to realise their potential better if they can work at their own rate and concentrate on specific subjects. For example, there have been cases of children who have gone to university as young as twelve or thirteen because they are especially gifted and have opted out of the school system. Parents feel that they will also be able to protect their children from harmful influences they may encounter at school if they keep them at home. Problems such as truancy and drugs are common and adolescents particularly can be led astray by their peers. Thus, school can prevent learning from taking place effectively.
However, there are also arguments in support of sending children to school rather than educating them at home. First of all, children are isolated at home. At school, on the other hand, they are able to socialise and meet people of different ages and so become increasingly independent. Children also need their peers to do subjects like sports and drama. Another important point is that schools have more resources and equipment than can be provided at home such as libraries, sports equipment and laboratories for science experiments. A final argument is that school can offer a much wider range of subjects and expertise than parents can provide on their own. Parents would need to have a whole range of professional knowledge in science subjects like physics and chemistry to English literature and economics. It is also questionable whether parents could keep a disciplined study atmosphere at home because of the friendly family atmosphere. In sum, home tuition can affect social independence and fail to provide the correct resources and professional teaching.
To sum up, it seems that education at school is preferable to learning at home. Although home education aids concentration and protection, it limits socialising, availability of resources and professional teaching. There may be particular cases where home tutoring would be advantageous, such as for severely disabled children; however, for the vast majority of children there are greater benefits from going to school.
[440 words]
COPYRIGHT of ACADEMIC ENGLISH – please contact us for permission to use.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Free download
Argument essay: home education.
Question: ‘Should parents educate their children at home?’ This is the full lesson from the images above. The essay can be used in a number of different ways – see the lesson plan. Words: 440 Level ** *** [B1/B2 C1]
Free Download
Argument Essays
Argument essays on a variety of topics and divided into two types; general and academic. These essays are block-type arguments of 500-700 words long, divided into four paragraphs with three clear arguments for and against.
online resources

Medical English

New for 2024

DropBox Files
Members only

Instant Lessons

OneDrive Files

Topic-lessons

Feedback Forms

6-Week Course

SPSE Essays

Free Resources

Charts and graphs

AEUK The Blog

12-Week Course
Search form
A for and against essay.
Look at the essay and do the exercises to improve your writing skills.
Instructions
Do the preparation exercise first. Then do the other exercises.
Preparation

Check your understanding: multiple selection
Check your writing: reordering - essay structure, check your writing: typing - linking words, worksheets and downloads.
What are your views on reality TV? Are these types of shows popular in your country?

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 12 April 2024
Feedback sources in essay writing: peer-generated or AI-generated feedback?
- Seyyed Kazem Banihashem 1 , 2 ,
- Nafiseh Taghizadeh Kerman 3 ,
- Omid Noroozi 2 ,
- Jewoong Moon 4 &
- Hendrik Drachsler 1 , 5
International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education volume 21 , Article number: 23 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Peer feedback is introduced as an effective learning strategy, especially in large-size classes where teachers face high workloads. However, for complex tasks such as writing an argumentative essay, without support peers may not provide high-quality feedback since it requires a high level of cognitive processing, critical thinking skills, and a deep understanding of the subject. With the promising developments in Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly after the emergence of ChatGPT, there is a global argument that whether AI tools can be seen as a new source of feedback or not for complex tasks. The answer to this question is not completely clear yet as there are limited studies and our understanding remains constrained. In this study, we used ChatGPT as a source of feedback for students’ argumentative essay writing tasks and we compared the quality of ChatGPT-generated feedback with peer feedback. The participant pool consisted of 74 graduate students from a Dutch university. The study unfolded in two phases: firstly, students’ essay data were collected as they composed essays on one of the given topics; subsequently, peer feedback and ChatGPT-generated feedback data were collected through engaging peers in a feedback process and using ChatGPT as a feedback source. Two coding schemes including coding schemes for essay analysis and coding schemes for feedback analysis were used to measure the quality of essays and feedback. Then, a MANOVA analysis was employed to determine any distinctions between the feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT. Additionally, Spearman’s correlation was utilized to explore potential links between the essay quality and the feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT. The results showed a significant difference between feedback generated by ChatGPT and peers. While ChatGPT provided more descriptive feedback including information about how the essay is written, peers provided feedback including information about identification of the problem in the essay. The overarching look at the results suggests a potential complementary role for ChatGPT and students in the feedback process. Regarding the relationship between the quality of essays and the quality of the feedback provided by ChatGPT and peers, we found no overall significant relationship. These findings imply that the quality of the essays does not impact both ChatGPT and peer feedback quality. The implications of this study are valuable, shedding light on the prospective use of ChatGPT as a feedback source, particularly for complex tasks like argumentative essay writing. We discussed the findings and delved into the implications for future research and practical applications in educational contexts.
Introduction
Feedback is acknowledged as one of the most crucial tools for enhancing learning (Banihashem et al., 2022 ). The general and well-accepted definition of feedback conceptualizes it as information provided by an agent (e.g., teacher, peer, self, AI, technology) regarding aspects of one’s performance or understanding (e.g., Hattie & Timplerely, 2007 ). Feedback serves to heighten students’ self-awareness concerning their strengths and areas warranting improvement, through providing actionable steps required to enhance performance (Ramson, 2003 ). The literature abounds with numerous studies that illuminate the positive impact of feedback on diverse dimensions of students’ learning journey including increasing motivation (Amiryousefi & Geld, 2021 ), fostering active engagement (Zhang & Hyland, 2022 ), promoting self-regulation and metacognitive skills (Callender et al., 2016 ; Labuhn et al., 2010 ), and enriching the depth of learning outcomes (Gan et al., 2021 ).
Normally, teachers have primarily assumed the role of delivering feedback, providing insights into students’ performance on specific tasks or their grasp of particular subjects (Konold et al., 2004 ). This responsibility has naturally fallen upon teachers owing to their expertise in the subject matter and their competence to offer constructive input (Diezmann & Watters, 2015 ; Holt-Reynolds, 1999 ; Valero Haro et al., 2023 ). However, teachers’ role as feedback providers has been challenged in recent years as we have witnessed a growth in class sizes due to the rapid advances in technology and the widespread use of digital technologies that resulted in flexible and accessible education (Shi et al., 2019 ). The growth in class sizes has translated into an increased workload for teachers, leading to a pertinent predicament. This situation has directly impacted their capacity to provide personalized and timely feedback to each student, a capability that has encountered limitations (Er et al., 2021 ).
In response to this challenge, various solutions have emerged, among which peer feedback has arisen as a promising alternative instructional approach (Er et al., 2021 ; Gao et al., 2024 ; Noroozi et al., 2023 ; Kerman et al., 2024 ). Peer feedback entails a process wherein students assume the role of feedback providers instead of teachers (Liu & Carless, 2006 ). Involving students in feedback can add value to education in several ways. First and foremost, research indicates that students delve into deeper and more effective learning when they take on the role of assessors, critically evaluating and analyzing their peers’ assignments (Gielen & De Wever, 2015 ; Li et al., 2010 ). Moreover, involving students in the feedback process can augment their self-regulatory awareness, active engagement, and motivation for learning (e.g., Arguedas et al., 2016 ). Lastly, the incorporation of peer feedback not only holds the potential to significantly alleviate teachers’ workload by shifting their responsibilities from feedback provision to the facilitation of peer feedback processes but also nurtures a dynamic learning environment wherein students are actively immersed in the learning journey (e.g., Valero Haro et al., 2023 ).
Despite the advantages of peer feedback, furnishing high-quality feedback to peers remains a challenge. Several factors contribute to this challenge. Primarily, generating effective feedback necessitates a solid understanding of feedback principles, an element that peers often lack (Latifi et al., 2023 ; Noroozi et al., 2016 ). Moreover, offering high-quality feedback is inherently a complex task, demanding substantial cognitive processing to meticulously evaluate peers’ assignments, identify issues, and propose constructive remedies (King, 2002 ; Noroozi et al., 2022 ). Furthermore, the provision of valuable feedback calls for a significant level of domain-specific expertise, which is not consistently possessed by students (Alqassab et al., 2018 ; Kerman et al., 2022 ).
In recent times, advancements in technology, coupled with the emergence of fields like Learning Analytics (LA), have presented promising avenues to elevate feedback practices through the facilitation of scalable, timely, and personalized feedback (Banihashem et al., 2023 ; Deeva et al., 2021 ; Drachsler, 2023 ; Drachsler & Kalz, 2016 ; Pardo et al., 2019 ; Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019 ; Rüdian et al., 2020 ). Yet, a striking stride forward in the field of educational technology has been the advent of a novel Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool known as “ChatGPT,” which has sparked a global discourse on its potential to significantly impact the current education system (Ray, 2023 ). This tool’s introduction has initiated discussions on the considerable ways AI can support educational endeavors (Bond et al., 2024 ; Darvishi et al., 2024 ).
In the context of feedback, AI-powered ChatGPT introduces what is referred to as AI-generated feedback (Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ). While the literature suggests that ChatGPT has the potential to facilitate feedback practices (Dai et al., 2023 ; Katz et al., 2023 ), this literature is very limited and mostly not empirical leading us to realize that our current comprehension of its capabilities in this regard is quite restricted. Therefore, we lack a comprehensive understanding of how ChatGPT can effectively support feedback practices and to what degree it can improve the timeliness, impact, and personalization of feedback, which remains notably limited at this time.
More importantly, considering the challenges we raised for peer feedback, the question is whether AI-generated feedback and more specifically feedback provided by ChatGPT has the potential to provide quality feedback. Taking this into account, there is a scarcity of knowledge and research gaps regarding the extent to which AI tools, specifically ChatGPT, can effectively enhance feedback quality compared to traditional peer feedback. Hence, our research aims to investigate the quality of feedback generated by ChatGPT within the context of essay writing and to juxtapose its quality with that of feedback generated by students.
This study carries the potential to make a substantial contribution to the existing body of recent literature on the potential of AI and in particular ChatGPT in education. It can cast a spotlight on the quality of AI-generated feedback in contrast to peer-generated feedback, while also showcasing the viability of AI tools like ChatGPT as effective automated feedback mechanisms. Furthermore, the outcomes of this study could offer insights into mitigating the feedback-related workload experienced by teachers through the intelligent utilization of AI tools (e.g., Banihashem et al., 2022 ; Er et al., 2021 ; Pardo et al., 2019 ).
However, there might be an argument regarding the rationale for conducting this study within the specific context of essay writing. Addressing this potential query, it is crucial to highlight that essay writing stands as one of the most prevalent yet complex tasks for students (Liunokas, 2020 ). This task is not without its challenges, as evidenced by the extensive body of literature that indicates students often struggle to meet desired standards in their essay composition (e.g., Bulqiyah et al., 2021 ; Noroozi et al., 2016 ;, 2022 ; Latifi et al., 2023 ).
Furthermore, teachers frequently express dissatisfaction with the depth and overall quality of students’ essay writing (Latifi et al., 2023 ). Often, these teachers lament that their feedback on essays remains superficial due to the substantial time and effort required for critical assessment and individualized feedback provision (Noroozi et al., 2016 ;, 2022 ). Regrettably, these constraints prevent them from delving deeper into the evaluation process (Kerman et al., 2022 ).
Hence, directing attention towards the comparison of peer-generated feedback quality and AI-generated feedback quality within the realm of essay writing bestows substantial value upon both research and practical application. This study enriches the academic discourse and informs practical approaches by delivering insights into the adequacy of feedback quality offered by both peers and AI for the domain of essay writing. This investigation serves as a critical step in determining whether the feedback imparted by peers and AI holds the necessary caliber to enhance the craft of essay writing.
The ramifications of addressing this query are noteworthy. Firstly, it stands to significantly alleviate the workload carried by teachers in the process of essay evaluation. By ascertaining the viability of feedback from peers and AI, teachers can potentially reduce the time and effort expended in reviewing essays. Furthermore, this study has the potential to advance the quality of essay compositions. The collaboration between students providing feedback to peers and the integration of AI-powered feedback tools can foster an environment where essays are not only better evaluated but also refined in their content and structure.With this in mind, we aim to tackle the following key questions within the scope of this study:
RQ1. To what extent does the quality of peer-generated and ChatGPT-generated feedback differ in the context of essay writing?
Rq2. does a relationship exist between the quality of essay writing performance and the quality of feedback generated by peers and chatgpt, context and participant.
This study was conducted in the academic year of 2022–2023 at a Dutch university specializing in life sciences. In total, 74 graduate students from food sciences participated in this study in which 77% of students were female ( N = 57) and 23% were male ( N = 17).
Study design and procedure
This empirical study has an exploratory nature and it was conducted in two phases. An online module called “ Argumentative Essay Writing ” (AEW) was designed to be followed by students within the Brightspace platform. The purpose of the AEW module was to improve students’ essay writing skills by engaging them in a peer learning process where students were invited to provide feedback on each other’s essays. After designing the module, the study was implemented in two weeks and followed in two phases.
In week one (phase one), students were asked to write an essay on given topics. The topics for the essay were controversial and included “ Scientists with affiliations to the food industry should abstain from participating in risk assessment processes ”, “ powdered infant formula must adhere to strict sterility standards ”, and “ safe food consumption is the responsibility of the consumer ”. The given controversial topics were directly related to the course content and students’ area of study. Students had time for one week to write their essays individually and submit them to the Brightspace platform.
In week two (phase two), students were randomly invited to provide two sets of written/asynchronous feedback on their peers’ submitted essays. We gave a prompt to students to be used for giving feedback ( Please provide feedback to your peer and explain the extent to which she/he has presented/elaborated/justified various elements of an argumentative essay. What are the problems and what are your suggestions to improve each element of the essay? Your feedback must be between 250 and 350 words ). To be able to engage students in the online peer feedback activity, we used the FeedbackFruits app embedded in the Brightspace platform. FeedbackFruits functions as an external educational technology tool seamlessly integrated into Brightspace, aimed at enhancing student engagement via diverse peer collaboration approaches. Among its features are peer feedback, assignment evaluation, skill assessment, automated feedback, interactive videos, dynamic documents, discussion tasks, and engaging presentations (Noroozi et al., 2022 ). In this research, our focus was on the peer feedback feature of the FeedbackFruits app, which empowers teachers to design tasks that enable students to offer feedback to their peers.
In addition, we used ChatGPT as another feedback source on peers’ essays. To be consistent with the criteria for peer feedback, we gave the same feedback prompt question with a minor modification to ChatGPT and asked it to give feedback on the peers’ essays ( Please read and provide feedback on the following essay and explain the extent to which she/he has presented/elaborated/justified various elements of an argumentative essay. What are the problems and what are your suggestions to improve each element of the essay? Your feedback must be between 250 and 350 words ).
Following this design, we were able to collect students’ essay data, peer feedback data, and feedback data generated by ChatGPT. In the next step, we used two coding schemes to analyze the quality of the essays and feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT.
Measurements
Coding scheme to assess the quality of essay writing.
In this study, a coding scheme proposed by Noroozi et al. ( 2016 ) was employed to assess students’ essay quality. This coding system was constructed based on the key components of high-quality essay composition, encompassing eight elements: introduction pertaining to the subject, taking a clear stance on the subject, presenting arguments in favor of the chosen position, providing justifications for the arguments supporting the position, counter-arguments, justifications for counter-arguments, responses to counter-arguments, and concluding with implications. Each element in the coding system is assigned a score ranging from zero (indicating the lowest quality level) to three (representing the highest quality level). The cumulative scores across all these elements were aggregated to determine the overall quality score of the student’s written essays. Two experienced coders in the field of education collaborated to assess the quality of the written essays, and their agreement level was measured at 75% (Cohen’s Kappa = 0.75 [95% confidence interval: 0.70–0.81]; z = 25.05; p < 0.001), signifying a significant level of consensus between the coders.
Coding scheme to assess the quality of feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT
To assess the quality of feedback provided by both peers and ChatGPT, we employed a coding scheme developed by Noroozi et al. ( 2022 ). This coding framework dissects the characteristics of feedback, encompassing three key elements: the affective component, which considers the inclusion of emotional elements such as positive sentiments like praise or compliments, as well as negative emotions such as anger or disappointment; the cognitive component, which includes description (a concise summary of the essay), identification (pinpointing and specifying issues within the essay), and justification (providing explanations and justifications for the identified issues); and the constructive component, which involves offering recommendations, albeit not detailed action plans for further enhancements. Ratings within this coding framework range from zero, indicating poor quality, to two, signifying good quality. The cumulative scores were tallied to determine the overall quality of the feedback provided to the students. In this research, as each essay received feedback from both peers and ChatGPT, we calculated the average score from the two sets of feedback to establish the overall quality score for the feedback received, whether from peers or ChatGPT. The same two evaluators were involved in the assessment. The inter-rater reliability between the evaluators was determined to be 75% (Cohen’s Kappa = 0.75 [95% confidence interval: 0.66–0.84]; z = 17.52; p < 0.001), showing a significant level of agreement between them.
The logic behind choosing these coding schemes was as follows: Firstly, from a theoretical standpoint, both coding schemes were developed based on robust and well-established theories. The coding scheme for evaluating essay quality draws on Toulmin’s argumentation model ( 1958 ), a respected framework for essay writing. It encompasses all elements essential for high-quality essay composition and aligns well with the structure of essays assigned in the chosen course for this study. Similarly, the feedback coding scheme is grounded in prominent works on identifying feedback features (e.g., Nelson & Schunn, 2009 ; Patchan et al., 2016 ; Wu & Schunn, 2020 ), enabling the identification of key features of high-quality feedback (Noroozi et al., 2022 ). Secondly, from a methodological perspective, both coding schemes feature a transparent scoring method, mitigating coder bias and bolstering the tool’s credibility.
To ensure the data’s validity and reliability for statistical analysis, two tests were implemented. Initially, the Levene test assessed group homogeneity, followed by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to evaluate data normality. The results confirmed both group homogeneity and data normality. For the first research question, gender was considered as a control variable, and the MANCOVA test was employed to compare the variations in feedback quality between peer feedback and ChatGPT-generated feedback. Addressing the second research question involved using Spearman’s correlation to examine the relationships among original argumentative essays, peer feedback, and ChatGPT-generated feedback.
The results showed a significant difference in feedback quality between peer feedback and ChatGPT-generated feedback. Peers provided feedback of higher quality compared to ChatGPT. This difference was mainly due to the descriptive and identification of the problem features of feedback. ChatGPT tended to produce more extensive descriptive feedback including a summary statement such as the description of the essay or taken action, while students performed better in pinpointing and identifying the issues in the feedback provided (see Table 1 ).
A comprehensive list featuring selected examples of feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT is presented in Fig 1 . This table additionally outlines examples of how the generated feedback was coded based on the coding scheme to assess the quality of feedback.
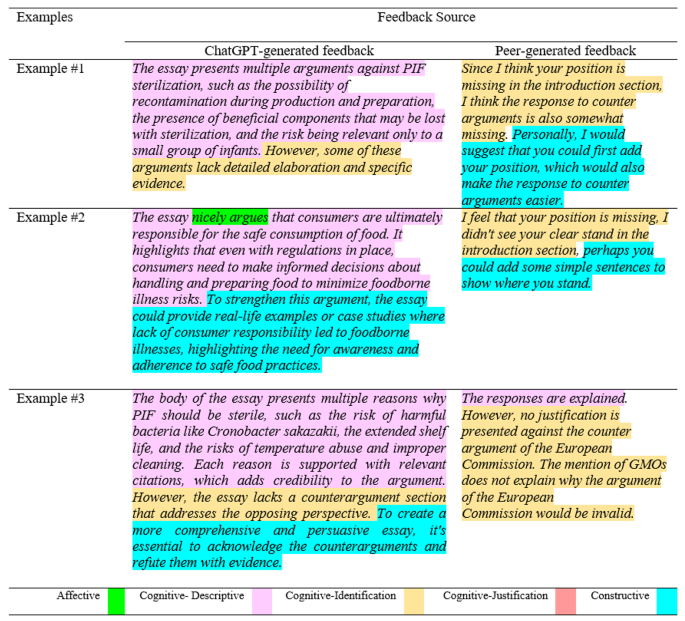
A comparative list of selected examples of peer-generated and ChatGPT-generated feedback
Overall, the results indicated that there was no significant relationship between the quality of essay writing and the feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT. However, a positive correlation was observed between the quality of the essay and the affective feature of feedback generated by ChatGPT, while a negative relationship was observed between the quality of the essay and the affective feature of feedback generated by peers. This finding means that as the quality of the essay improves, ChatGPT tends to provide more affective feedback, while peers tend to provide less affective feedback (see Table 2 ).
This study was an initial effort to explore the potential of ChatGPT as a feedback source in the context of essay writing and to compare the extent to which the quality of feedback generated by ChatGPT differs from the feedback provided by peers. Below we discuss our findings for each research question.
Discussion on the results of RQ1
For the first research question, the results revealed a disparity in feedback quality when comparing peer-generated feedback to feedback generated by ChatGPT. Peer feedback demonstrated higher quality compared to ChatGPT-generated feedback. This discrepancy is attributed primarily to variations in the descriptive and problem-identification features of the feedback.
ChatGPT tended to provide more descriptive feedback, often including elements such as summarizing the content of the essay. This inclination towards descriptive feedback could be related to ChatGPT’s capacity to analyze and synthesize textual information effectively. Research on ChatGPT further supports this notion, demonstrating the AI tool’s capacity to offer a comprehensive overview of the provided content, therefore potentially providing insights and a holistic perspective on the content (Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ; Ray, 2023 ).
ChatGPT’s proficiency in providing extensive descriptive feedback could be seen as a strength. It might be particularly valuable for summarizing complex arguments or providing comprehensive overviews, which could aid students in understanding the overall structure and coherence of their essays.
In contrast, students’ feedback content entailed high quality regarding identifying specific issues and areas for improvement. Peers outperformance compared to ChatGPT in identifying problems within the essays could be related to humans’ potential in cognitive skills, critical thinking abilities, and contextual understanding (e.g., Korteling et al., 2021 ; Lamb et al., 2019 ). This means that students, with their contextual knowledge and critical thinking skills, may be better equipped to identify issues within the essays that ChatGPT may overlook.
Furthermore, a detailed look at the findings of the first research question discloses that the feedback generated by ChatGPT comprehensively encompassed all essential components characterizing high-quality feedback, including affective, cognitive, and constructive dimensions (Kerman et al., 2022 ; Patchan et al., 2016 ). This comprehensive observation could be an indication of the fact that ChatGPT-generated feedback could potentially serve as a viable source of feedback. This observation is supported by previous studies where a positive role for AI-generated feedback and automated feedback in enhancing educational outcomes has been recognized (e.g., Bellhäuser et al., 2023 ; Gombert et al., 2024 ; Huang et al., 2023 ; Xia et al., 2022 ).
Finally, an overarching look at the results of the first research question suggests a potential complementary role for ChatGPT and students in the feedback process. This means that using these two feedback sources together creates a synergistic relationship that could result in better feedback outcomes.
Discussion on the results of RQ2
Results for the second research question revealed no observations of a significant correlation between the quality of the essays and the quality of the feedback generated by both peers and ChatGPT. These findings carry a consequential implication, suggesting that the inherent quality of the essays under scrutiny exerts negligible influence over the quality of feedback furnished by both students and the ChatGPT.
In essence, these results point to a notable degree of independence between the writing prowess exhibited in the essays and the efficacy of the feedback received from either source. This disassociation implies that the ability to produce high-quality essays does not inherently translate into a corresponding ability to provide equally insightful feedback, neither for peers nor for ChatGPT. This decoupling of essay quality from feedback quality highlighted the multifaceted nature of these evaluative processes, where proficiency in constructing a coherent essay does not necessarily guarantee an equally adept capacity for evaluating and articulating constructive commentary on peers’ work.
The implications of these findings are both intriguing and defy conventional expectations, as they deviate somewhat from the prevailing literature’s stance. The existing body of scholarly work generally posits a direct relationship between the quality of an essay and the subsequent quality of generated feedback (Noroozi et al., 2016 ;, 2022 ; Kerman et al., 2022 ; Vale Haro et al., 2023 ). This line of thought contends that essays of inferior quality might serve as a catalyst for more pronounced error detection among students, encompassing grammatical intricacies, depth of content, clarity, and coherence, as well as the application of evidence and support. Conversely, when essays are skillfully crafted, the act of pinpointing areas for enhancement becomes a more complex task, potentially necessitating a heightened level of subject comprehension and nuanced evaluation.
However, the present study’s findings challenge this conventional wisdom. The observed decoupling of essay quality from feedback quality suggests a more nuanced interplay between the two facets of assessment. Rather than adhering to the anticipated pattern, wherein weaker essays prompt clearer identification of deficiencies, and superior essays potentially render the feedback process more challenging, the study suggests that the process might be more complex than previously thought. It hints at a dynamic in which the act of evaluating essays and providing constructive feedback transcends a simple linear connection with essay quality.
These findings, while potentially unexpected, are an indication of the complex nature of essay assignments and feedback provision highlighting the complexity of cognitive processes that underlie both tasks, and suggesting that the relationship between essay quality and feedback quality is not purely linear but influenced by a multitude of factors, including the evaluator’s cognitive framework, familiarity with the subject matter, and critical analysis skills.
Despite this general observation, a closer examination of the affective features within the feedback reveals a different pattern. The positive correlation between essay quality and the affective features present in ChatGPT-generated feedback could be related to ChatGPT’s capacity to recognize and appreciate students’ good work. As the quality of the essay increases, ChatGPT might be programmed to offer more positive and motivational feedback to acknowledge students’ progress (e.g., Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ; Ray, 2023 ). In contrast, the negative relationship between essay quality and the affective features in peer feedback may be attributed to the evolving nature of feedback from peers (e.g., Patchan et al., 2016 ). This suggests that as students witness improvements in their peers’ essay-writing skills and knowledge, their feedback priorities may naturally evolve. For instance, students may transition from emphasizing emotional and affective comments to focusing on cognitive and constructive feedback, with the goal of further enhancing the overall quality of the essays.
Limitations and implications for future research and practice
We acknowledge the limitations of this study. Primarily, the data underpinning this investigation was drawn exclusively from a singular institution and a solitary course, featuring a relatively modest participant pool. This confined scope inevitably introduces certain constraints that need to be taken into consideration when interpreting the study’s outcomes and generalizing them to broader educational contexts. Under this constrained sampling, the findings might exhibit a degree of contextual specificity, potentially limiting their applicability to diverse institutional settings and courses with distinct curricular foci. The diverse array of academic environments, student demographics, and subject matter variations existing across educational institutions could potentially yield divergent patterns of results. Therefore, while the current study’s outcomes provide insights within the confines of the studied institution and course, they should be interpreted and generalized with prudence. Recognizing these limitations, for future studies, we recommend considering a large-scale participant pool with a diverse range of variables, including individuals from various programs and demographics. This approach would enrich the depth and breadth of understanding in this domain, fostering a more comprehensive comprehension of the complex dynamics at play.
In addition, this study omitted an exploration into the degree to which students utilize feedback provided by peers and ChatGPT. That is to say that we did not investigate the effects of such feedback on essay enhancements in the revision phase. This omission inherently introduces a dimension of uncertainty and places a constraint on the study’s holistic understanding of the feedback loop. By not addressing these aspects, the study’s insights are somewhat partial, limiting the comprehensive grasp of the potential influences that these varied feedback sources wield on students’ writing enhancement processes. An analysis of the feedback assimilation patterns and their subsequent effects on essay refinement would have unveiled insights into the practical utility and impact of the feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT.
To address this limitation, future investigations could be structured to encompass a more thorough examination of students’ feedback utilization strategies and the resulting implications for the essay revision process. By shedding light on the complex interconnection between feedback reception, its integration into the revision process, and the ultimate outcomes in terms of essay improvement, a more comprehensive understanding of the dynamics involved could be attained.
Furthermore, in this study, we employed identical question prompts for both peers and ChatGPT. However, there is evidence indicating that ChatGPT is sensitive to how prompts are presented to it (e.g., Cao et al., 2023 ; White et al., 2023 ; Zuccon & Koopman, 2023 ). This suggests that variations in the wording, structure, or context of prompts might influence the responses generated by ChatGPT, potentially impacting the comparability of its outputs with those of peers. Therefore, it is essential to carefully consider and control for prompt-related factors in future research when assessing ChatGPT’s performance and capabilities in various tasks and contexts.
In addition, We acknowledge that ChatGPT can potentially generate inaccurate results. Nevertheless, in the context of this study, our examination of the results generated by ChatGPT did not reveal a significant inaccuracies that would warrant inclusion in our findings.
From a methodological perspective, we reported the interrater reliability between the coders to be 75%. While this level of agreement was statistically significant, signifying the reliability of our coders’ analyses, it did not reach the desired level of precision. We acknowledge this as a limitation of the study and suggest enhancing interrater reliability through additional coder training.
In addition, it is worth noting that the advancement of Generative AI like ChatGPT, opens new avenues in educational feedback mechanisms. Beyond just generating feedback, these AI models have the potential to redefine how feedback is presented and assimilated. In the realm of research on adaptive learning systems, the findings of this study also echo the importance of adaptive learning support empowered by AI and ChatGPT (Rummel et al., 2016 ). It can pave the way for tailored educational experiences that respond dynamically to individual student needs. This is not just about the feedback’s content but its delivery, timing, and adaptability. Further exploratory data analyses, such as sequential analysis and data mining, may offer insights into the nuanced ways different adaptive learning supports can foster student discussions (Papamitsiou & Economides, 2014 ). This involves dissecting the feedback dynamics, understanding how varied feedback types stimulate discourse, and identifying patterns that lead to enhanced student engagement.
Ensuring the reliability and validity of AI-empowered feedback is also crucial. The goal is to ascertain that technology-empowered learning support genuinely enhances students’ learning process in a consistent and unbiased manner. Given ChatGPT’s complex nature of generating varied responses based on myriad prompts, the call for enhancing methodological rigor through future validation studies becomes both timely and essential. For example, in-depth prompt validation and blind feedback assessment studies could be employed to meticulously probe the consistency and quality of ChatGPT’s responses. Also, comparative analysis with different AI models can be useful.
From an educational standpoint, our research findings advocate for the integration of ChatGPT as a feedback resource with peer feedback within higher education environments for essay writing tasks since there is a complementary role potential for pee-generated and ChatGPT-generated feedback. This approach holds the potential to alleviate the workload burden on teachers, particularly in the context of online courses with a significant number of students.
This study contributes to and adds value to the young existing but rapidly growing literature in two distinct ways. From a research perspective, this study addresses a significant void in the current literature by responding to the lack of research on AI-generated feedback for complex tasks like essay writing in higher education. The research bridges this gap by analyzing the effectiveness of ChatGPT-generated feedback compared to peer-generated feedback, thereby establishing a foundation for further exploration in this field. From a practical perspective of higher education, the study’s findings offer insights into the potential integration of ChatGPT as a feedback source within higher education contexts. The discovery that ChatGPT’s feedback quality could potentially complement peer feedback highlights its applicability for enhancing feedback practices in higher education. This holds particular promise for courses with substantial enrolments and essay-writing components, providing teachers with a feasible alternative for delivering constructive feedback to a larger number of students.
Data availability
The data is available upon a reasonable request.
Alqassab, M., Strijbos, J. W., & Ufer, S. (2018). Training peer-feedback skills on geometric construction tasks: Role of domain knowledge and peer-feedback levels. European Journal of Psychology of Education , 33 (1), 11–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-017-0342-0 .
Article Google Scholar
Amiryousefi, M., & Geld, R. (2021). The role of redressing teachers’ instructional feedback interventions in EFL learners’ motivation and achievement in distance education. Innovation in Language Learning and Teaching , 15 (1), 13–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/17501229.2019.1654482 .
Arguedas, M., Daradoumis, A., & Xhafa Xhafa, F. (2016). Analyzing how emotion awareness influences students’ motivation, engagement, self-regulation and learning outcome. Educational Technology and Society , 19 (2), 87–103. https://www.jstor.org/stable/jeductechsoci.19.2.87 .
Google Scholar
Banihashem, S. K., Noroozi, O., van Ginkel, S., Macfadyen, L. P., & Biemans, H. J. (2022). A systematic review of the role of learning analytics in enhancing feedback practices in higher education. Educational Research Review , 100489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2022.100489 .
Banihashem, S. K., Dehghanzadeh, H., Clark, D., Noroozi, O., & Biemans, H. J. (2023). Learning analytics for online game-based learning: A systematic literature review. Behaviour & Information Technology , 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2023.2255301 .
Bellhäuser, H., Dignath, C., & Theobald, M. (2023). Daily automated feedback enhances self-regulated learning: A longitudinal randomized field experiment. Frontiers in Psychology , 14 , 1125873. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1125873 .
Bond, M., Khosravi, H., De Laat, M., Bergdahl, N., Negrea, V., Oxley, E., & Siemens, G. (2024). A meta systematic review of artificial intelligence in higher education: A call for increased ethics, collaboration, and rigour. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education , 21 (4), 1–41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00436-z .
Bulqiyah, S., Mahbub, M., & Nugraheni, D. A. (2021). Investigating writing difficulties in Essay writing: Tertiary Students’ perspectives. English Language Teaching Educational Journal , 4 (1), 61–73. https://doi.org/10.12928/eltej.v4i1.2371 .
Callender, A. A., Franco-Watkins, A. M., & Roberts, A. S. (2016). Improving metacognition in the classroom through instruction, training, and feedback. Metacognition and Learning , 11 (2), 215–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-015-9142-6 .
Cao, J., Li, M., Wen, M., & Cheung, S. C. (2023). A study on prompt design, advantages and limitations of chatgpt for deep learning program repair. arXiv Preprint arXiv:2304 08191 . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2304.08191 .
Dai, W., Lin, J., Jin, F., Li, T., Tsai, Y. S., Gasevic, D., & Chen, G. (2023). Can large language models provide feedback to students? A case study on ChatGPT. https://doi.org/10.35542/osf.io/hcgzj .
Darvishi, A., Khosravi, H., Sadiq, S., Gašević, D., & Siemens, G. (2024). Impact of AI assistance on student agency. Computers & Education , 210 , 104967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2023.104967 .
Deeva, G., Bogdanova, D., Serral, E., Snoeck, M., & De Weerdt, J. (2021). A review of automated feedback systems for learners: Classification framework, challenges and opportunities. Computers & Education , 162 , 104094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.104094 .
Diezmann, C. M., & Watters, J. J. (2015). The knowledge base of subject matter experts in teaching: A case study of a professional scientist as a beginning teacher. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education , 13 , 1517–1537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-014-9561-x .
Drachsler, H. (2023). Towards highly informative learning analytics . Open Universiteit. https://doi.org/10.25656/01:26787 .
Drachsler, H., & Kalz, M. (2016). The MOOC and learning analytics innovation cycle (MOLAC): A reflective summary of ongoing research and its challenges. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning , 32 (3), 281–290. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12135 .
Er, E., Dimitriadis, Y., & Gašević, D. (2021). Collaborative peer feedback and learning analytics: Theory-oriented design for supporting class-wide interventions. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , 46 (2), 169–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2020.1764490 .
Farrokhnia, M., Banihashem, S. K., Noroozi, O., & Wals, A. (2023). A SWOT analysis of ChatGPT: Implications for educational practice and research. Innovations in Education and Teaching International , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2195846 .
Gan, Z., An, Z., & Liu, F. (2021). Teacher feedback practices, student feedback motivation, and feedback behavior: How are they associated with learning outcomes? Frontiers in Psychology , 12 , 697045. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.697045 .
Gao, X., Noroozi, O., Gulikers, J. T. M., Biemans, H. J., & Banihashem, S. K. (2024). A systematic review of the key components of online peer feedback practices in higher education. Educational Research Review , 100588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2023.100588 .
Gielen, M., & De Wever, B. (2015). Scripting the role of assessor and assessee in peer assessment in a wiki environment: Impact on peer feedback quality and product improvement. Computers & Education , 88 , 370–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.07.012 .
Gombert, S., Fink, A., Giorgashvili, T., Jivet, I., Di Mitri, D., Yau, J., & Drachsler, H. (2024). From the Automated Assessment of Student Essay Content to highly informative feedback: A case study. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education , 1–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-023-00387-6 .
Hattie, J., & Timperley, H. (2007). The power of feedback. Review of Educational Research , 77 (1), 81–112. https://doi.org/10.3102/003465430298487 .
Holt-Reynolds, D. (1999). Good readers, good teachers? Subject matter expertise as a challenge in learning to teach. Harvard Educational Review , 69 (1), 29–51. https://doi.org/10.17763/haer.69.1.pl5m5083286l77t2 .
Huang, A. Y., Lu, O. H., & Yang, S. J. (2023). Effects of artificial intelligence–enabled personalized recommendations on learners’ learning engagement, motivation, and outcomes in a flipped classroom. Computers & Education , 194 , 104684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104684 .
Katz, A., Wei, S., Nanda, G., Brinton, C., & Ohland, M. (2023). Exploring the efficacy of ChatGPT in analyzing Student Teamwork Feedback with an existing taxonomy. arXiv Preprint arXiv . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.11882 .
Kerman, N. T., Noroozi, O., Banihashem, S. K., Karami, M., & Biemans, H. J. (2022). Online peer feedback patterns of success and failure in argumentative essay writing. Interactive Learning Environments , 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2022.2093914 .
Kerman, N. T., Banihashem, S. K., Karami, M., Er, E., Van Ginkel, S., & Noroozi, O. (2024). Online peer feedback in higher education: A synthesis of the literature. Education and Information Technologies , 29 (1), 763–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12273-8 .
King, A. (2002). Structuring peer interaction to promote high-level cognitive processing. Theory into Practice , 41 (1), 33–39. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15430421tip4101_6 .
Konold, K. E., Miller, S. P., & Konold, K. B. (2004). Using teacher feedback to enhance student learning. Teaching Exceptional Children , 36 (6), 64–69. https://doi.org/10.1177/004005990403600608 .
Korteling, J. H., van de Boer-Visschedijk, G. C., Blankendaal, R. A., Boonekamp, R. C., & Eikelboom, A. R. (2021). Human-versus artificial intelligence. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence , 4 , 622364. https://doi.org/10.3389/frai.2021.622364 .
Labuhn, A. S., Zimmerman, B. J., & Hasselhorn, M. (2010). Enhancing students’ self-regulation and mathematics performance: The influence of feedback and self-evaluative standards. Metacognition and Learning , 5 , 173–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-010-9056-2 .
Lamb, R., Firestone, J., Schmitter-Edgecombe, M., & Hand, B. (2019). A computational model of student cognitive processes while solving a critical thinking problem in science. The Journal of Educational Research , 112 (2), 243–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2018.1514357 .
Latifi, S., Noroozi, O., & Talaee, E. (2023). Worked example or scripting? Fostering students’ online argumentative peer feedback, essay writing and learning. Interactive Learning Environments , 31 (2), 655–669. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2020.1799032 .
Li, L., & Liu, X. (2010). Steckelberg. Assessor or assessee: How student learning improves by giving and receiving peer feedback. British Journal of Educational Technology , 41 (3), 525–536. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2009.00968.x .
Liu, N. F., & Carless, D. (2006). Peer feedback: The learning element of peer assessment. Teaching in Higher Education , 11 (3), 279–290. https://doi.org/10.1080/13562510600680582 .
Liunokas, Y. (2020). Assessing students’ ability in writing argumentative essay at an Indonesian senior high school. IDEAS: Journal on English language teaching and learning. Linguistics and Literature , 8 (1), 184–196. https://doi.org/10.24256/ideas.v8i1.1344 .
Nelson, M. M., & Schunn, C. D. (2009). The nature of feedback: How different types of peer feedback affect writing performance. Instructional Science , 37 , 375–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-008-9053-x .
Noroozi, O., Banihashem, S. K., Taghizadeh Kerman, N., Parvaneh Akhteh Khaneh, M., Babayi, M., Ashrafi, H., & Biemans, H. J. (2022). Gender differences in students’ argumentative essay writing, peer review performance and uptake in online learning environments. Interactive Learning Environments , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2022.2034887 .
Noroozi, O., Biemans, H., & Mulder, M. (2016). Relations between scripted online peer feedback processes and quality of written argumentative essay. The Internet and Higher Education , 31, 20-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2016.05.002
Noroozi, O., Banihashem, S. K., Biemans, H. J., Smits, M., Vervoort, M. T., & Verbaan, C. L. (2023). Design, implementation, and evaluation of an online supported peer feedback module to enhance students’ argumentative essay quality. Education and Information Technologies , 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11683-y .
Papamitsiou, Z., & Economides, A. A. (2014). Learning analytics and educational data mining in practice: A systematic literature review of empirical evidence. Journal of Educational Technology & Society , 17 (4), 49–64. https://doi.org/10.2307/jeductechsoci.17.4.49 . https://www.jstor.org/stable/ .
Pardo, A., Jovanovic, J., Dawson, S., Gašević, D., & Mirriahi, N. (2019). Using learning analytics to scale the provision of personalised feedback. British Journal of Educational Technology , 50 (1), 128–138. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12592 .
Patchan, M. M., Schunn, C. D., & Correnti, R. J. (2016). The nature of feedback: How peer feedback features affect students’ implementation rate and quality of revisions. Journal of Educational Psychology , 108 (8), 1098. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000103 .
Ramsden, P. (2003). Learning to teach in higher education . Routledge.
Ray, P. P. (2023). ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems , 3 , 121–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iotcps.2023.04.003 .
Rüdian, S., Heuts, A., & Pinkwart, N. (2020). Educational Text Summarizer: Which sentences are worth asking for? In DELFI 2020 - The 18th Conference on Educational Technologies of the German Informatics Society (pp. 277–288). Bonn, Germany.
Rummel, N., Walker, E., & Aleven, V. (2016). Different futures of adaptive collaborative learning support. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education , 26 , 784–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-016-0102-3 .
Shi, M. (2019). The effects of class size and instructional technology on student learning performance. The International Journal of Management Education , 17 (1), 130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2019.01.004 .
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Toulmin, S. (1958). The uses of argument . Cambridge University Press.
Valero Haro, A., Noroozi, O., Biemans, H. J., Mulder, M., & Banihashem, S. K. (2023). How does the type of online peer feedback influence feedback quality, argumentative essay writing quality, and domain-specific learning? Interactive Learning Environments , 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2023.2215822 .
White, J., Fu, Q., Hays, S., Sandborn, M., Olea, C., Gilbert, H., & Schmidt, D. C. (2023). A prompt pattern catalog to enhance prompt engineering with chatgpt. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.11382 . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2302.11382 .
Wu, Y., & Schunn, C. D. (2020). From feedback to revisions: Effects of feedback features and perceptions. Contemporary Educational Psychology , 60 , 101826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2019.101826 .
Xia, Q., Chiu, T. K., Zhou, X., Chai, C. S., & Cheng, M. (2022). Systematic literature review on opportunities, challenges, and future research recommendations of artificial intelligence in education. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence , 100118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2022.100118 .
Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V. I., Bond, M., & Gouverneur, F. (2019). Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education–where are the educators? International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education , 16 (1), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0171-0 .
Zhang, Z. V., & Hyland, K. (2022). Fostering student engagement with feedback: An integrated approach. Assessing Writing , 51 , 100586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asw.2021.100586 .
Zuccon, G., & Koopman, B. (2023). Dr ChatGPT, tell me what I want to hear: How prompt knowledge impacts health answer correctness. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302 .13793. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2302.13793 .
Download references
No funding has been received for this research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Open Universiteit, Heerlen, The Netherlands
Seyyed Kazem Banihashem & Hendrik Drachsler
Wageningen University and Research, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Seyyed Kazem Banihashem & Omid Noroozi
Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran
Nafiseh Taghizadeh Kerman
The University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, USA
Jewoong Moon
DIPE Leibniz Institute, Goethe University, Frankfurt, Germany
Hendrik Drachsler
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S. K. Banihashem led this research experiment. N. T. Kerman contributed to the data analysis and writing. O. Noroozi contributed to the designing, writing, and reviewing the manuscript. J. Moon contributed to the writing and revising the manuscript. H. Drachsler contributed to the writing and revising the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Seyyed Kazem Banihashem .
Ethics declarations
Declaration of ai-assisted technologies in the writing process.
The authors used generative AI for language editing and took full responsibility.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Banihashem, S.K., Kerman, N.T., Noroozi, O. et al. Feedback sources in essay writing: peer-generated or AI-generated feedback?. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 21 , 23 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-024-00455-4
Download citation
Received : 20 November 2023
Accepted : 18 March 2024
Published : 12 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-024-00455-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- AI-generated feedback
- Essay writing
- Feedback sources
- Higher education
- Peer feedback

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components: 1. Claim. Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
Tips for Writing a Well-Written Argumentative Essay. Introduce your topic in a bold, direct, and engaging manner to captivate your readers and encourage them to keep reading. Provide sufficient evidence to justify your argument and convince readers to adopt this point of view. Consider, include, and fairly present all sides of the topic.
What is the argumentative essay? ... A 1 essay demonstrates fundamental deficiencies in writing skills. An essay in this category: contains serious and persistent writing errors or; ... take a minute to choose 3-4 examples that directly support your argument. If you start writing before outlining your support, the resulting essay may be ...
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance. An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the ...
In order to succeed at this second step, though, you must have a particular point to argue. Arguments in academic writing are usually complex and take time to develop. Your argument will need to be more than a simple or obvious statement such as "Frank Lloyd Wright was a great architect.". Such a statement might capture your initial ...
The argument you are making should be clearly stated within your thesis statement. You should have several reasons or points of discussion that help you to support your argument. You will explain and support these reasons and points of discussion within the body paragraphs of your paper. As with all academic writing, you'll need to cite any ...
Here's our 12-step recipe for writing a great argumentative essay: Pick a topic. Choose your research sources. Read your sources and take notes. Create a thesis statement. Choose three main arguments to support your thesis statement —now you have a skeleton outline.
Crafted by philosopher Stephen Toulmin, this model zooms in on the pieces of an argument puzzle and how they fit together. Here's the breakdown, tailor-made by our team at dissertation writing services: Claim: Clearly state your main argument or point. Grounds: Back up your claim with evidence and support.
Secondly, it lets the writer figure out what evidence suits what argument most. Before writing, draft your essay first. Put examples, facts, etc. in the right parts of the paper. Then, write the entire text. Thirdly, an outline provides a perfect opportunity to change the essay's parts without rewriting the paper.
4. Write a rough draft. Now at last you are ready to start writing your paper. Start with a short introduction paragraph and then use your outline to draft the body and conclusion. Don't forget to begin each paragraph in the body with a topic sentence that conveys the main argument of that paragraph.
Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore needs
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.. Short videos to support your essay writing skills. There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing ...
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
Edit your essay. After you have written your essay, you need to edit it. This includes proofreading for grammar and spelling mistakes, as well as ensuring that your argument is clear and concise. 6. Practice your argumentative skills. The best way to improve your argumentative skills is to practice.
WORD CHOICE. When students are ready to revise, word choice lessons can make a big difference! I like to cover formal vocabulary options throughout the research unit so that students have an opportunity to use the new words they are learning in writing.. Each day, students learn two formal word options that can replace common cliches in writing.
But many developing writers struggle to write clear and compelling arguments. You can help them succeed by teaching the following strategies. 1. Distinguishing Argumentation from Persuasion. National writing standards and the tests that assess them focus on argumentation rather than persuasion.
Essays. In short pieces of writing (< 3,000 words), there will be groups of paragraphs which together form one part of your argument. Usually these sections in "short" essays do not have specific headings. However, they can be clearly identified by using linking phrases which show for example: how many elements the section consists of:
"Writing" is usually understood as the expression of thought. This book redefines "writing" as the thought process itself. Writing is not what you do with thought. Writing is thinking. Better living through interpretation: that's the promise of academic writing, which is a foundational course in most schools because it's a
Argument Essay Lessons. The argument essay lesson can be used in a number of different ways: A reading to highlight key arguments. A writing where students use a blank outline to plan a writing and then compare with a model essay. A guided writing where the tutor provides the completed outline and the students write an essay using these ideas.
Second, follow these steps on how to write an argumentative essay: Brainstorm: research, free-write, and read samples to choose a debatable topic. Prepare: organize thoughts, craft a thesis, decide on arguments and evidence. Draft: outline an essay, start with an engaging introduction, delve into arguments, and conclude like a boss.
Worksheets and downloads. A for and against essay - exercises 945.25 KB. A for and against essay - answers 293.66 KB. A for and against essay - essay 786.07 KB. A for and against essay - writing practice 497.45 KB.
An online module called "Argumentative Essay Writing" (AEW) was designed to be followed by students within the Brightspace platform. The purpose of the AEW module was to improve students' essay writing skills by engaging them in a peer learning process where students were invited to provide feedback on each other's essays.