
- Master Your Homework
- Do My Homework

What’s the Difference: Research Paper vs. Journal?
In the current academic environment, it is essential to understand the key differences between a research paper and a journal. Both types of publications can be used for different purposes in various areas of study but knowing what distinguishes one from another is important for any researcher. This article will explore the primary distinctions between a research paper and a journal so that readers may gain an understanding as to when each should be utilized within their field of inquiry.
I. Introduction
Ii. definition of research paper and journal, iii. similarities between a research paper and a journal, iv. differences between a research paper and a journal, v. purpose for writing different types of academic texts, vi. distinguishing characteristics in content, formatting, & tone, vii. conclusion.
As we embark on this research journey, let us take a moment to understand the scope of our exploration. Our objective is two-fold: 1) To gain insight into the field of X; and 2) To examine whether Y can be used as an effective solution.
This investigation will explore all aspects related to our inquiry and its outcomes. In doing so, both primary and secondary sources shall be consulted in order to determine if scientific or anecdotal evidence provides proof for the efficacy of Y. The findings from these resources will provide vital information which can then inform new decisions regarding how best to approach using Y as part of a larger strategy for successful implementation in practice.
Research papers and journals are integral components of the academic world. Both serve as a platform for academics to share their research findings, engage with one another’s work, and contribute to the greater scientific community. But they have distinct definitions that must be understood in order to effectively use them.
A research paper is typically used for reporting on an individual study or investigation. It should provide details such as a hypothesis being tested, results obtained from experiments/surveys conducted, and analysis of those results. Research papers will often take into account previous studies related to the topic discussed so it can build off existing knowledge within the field. Furthermore, while citing other works is important when creating a research paper its primary focus is usually centered around your own original ideas surrounding the particular subject matter you studied.
- This form of writing primarily acts as both an exploration tool and means by which new information can be shared.
On the other hand, journals are created for scholars in specific fields who need access to articles written about current topics in their discipline. This type of publication offers regular publications where authors submit their works covering various aspects relating directly back to whatever field it focuses on . Journals do not solely act as reference sources but also functions as outlets where active discussions between experts occur regarding issues impacting that area. Additionally when submitting work most publications require authors adhere strictly follow standard formats so content remains organized making journaling easier source material more accessible
- As opposed questions answered through experiments like withresearchpapers journallings main objectiveis providing scholarly insightinto pertinent matters facingthe targeted field
. Is research paper a journal? The answer would be no since each serves distinctly different purposes when published academically
Comparison of Features When comparing a research paper and a journal, it is evident that they both have certain similarities. Though their purpose may differ slightly, there are aspects which they share in common.
One similarity between the two lies in their structure; each follows an orderly progression from introduction to conclusion. In addition, the content must be well researched and properly cited when needed. The writing style for both should also adhere to accepted academic standards.
- Research Paper: Uses third-person point of view.
- Journal: Utilizes first-person perspective.
Another connection between the two is present in their goals; regardless if one produces either work type, they seek to provide new knowledge or insight on a particular subject matter within its given field. Furthermore, both look into complex topics with critical thinking skills at play while striving towards accuracy throughout all stages.
- Research Paper: Content should include evidence supporting conclusions made.
A key difference however stands out as research papers typically focus more deeply on specific concepts while journals often make use of broad theoretical frameworks — though this is not always necessarily true for every example presented here. Is research paper a journal? No – Research papers are designed as an empirical investigation whereas Journals involve creative writing processes such as reflective essays or stories about life experiences.
A research paper and a journal differ in many ways. Here, we will explore the key distinctions between these two types of scholarly writing.
A research paper is used to convey original thought regarding a particular subject or topic. It can be presented as part of an assignment or for publication; it typically involves detailed analyses and comprehensive synthesis from multiple sources. On the other hand, journals are generally periodicals that have been published regularly over time, featuring content which has undergone formal peer review process before being accepted for publishing. Additionally, they often contain abstracts summarizing their contents written by expert researchers within the respective field.
- Formatting & Style:
Different academic texts have different purposes, which range from the informative to the persuasive. Writing a research paper requires an in-depth understanding of how scholarly inquiry works and why it is important. A research paper aims to discover new information, present original ideas or theories, analyze existing material on a given topic, or apply current knowledge to a novel situation.
- Informative: Research papers
- Persuasive: Journals
The English language is filled with subtle nuances in both content and formatting. When it comes to distinguishing between an academic research paper, a journal article, or any other type of writing style, there are certain characteristics that help differentiate them.
To start off with content, the scope of each type can vary greatly depending on what genre you’re dealing with. Generally speaking though, research papers have more detailed information than journals because they usually cover a single topic in-depth while journals focus on broad issues within their field; this means that research papers will go into far greater detail concerning evidence found for their claims when compared to journal articles which often make sweeping generalizations instead. Additionally, formats used by researchers tend to be more structured since they must adhere to specific guidelines set forth by scholarly institutions such as having citations at the end of each section rather than throughout the text like one would find in a newspaper report or blog post.
In terms of tone and language usage however these two types may not differ too drastically from one another as most academics write using sophisticated words regardless if it’s for publication or personal use so readers should expect complex vocabulary being utilized either way; however some authors do have differing styles where one might use scientific terminology whereas another might prefer colloquial phrases even when discussing similar topics so paying attention to author preferences can help discern between different forms of literature easily enough.
In summary, this paper has demonstrated that research on journaling can provide meaningful insights into the human condition. Through an examination of relevant literature and key findings from our own research study, we have highlighted a number of beneficial outcomes associated with journaling – including improved emotional wellbeing and increased self-awareness.
It is clear that further studies are needed to more thoroughly investigate the impact of journaling on different populations in various contexts; however, for now it appears likely that there is much potential benefit to be found through regularly engaging in reflective writing practices.
The differences between a research paper and journal are clear. In summary, the main difference is that research papers build upon existing knowledge with an original purpose in mind while journals record events from everyday life or provide commentary on current topics of interest. Each type has its place in academia; both have value as useful tools for disseminating information and sparking further study. Ultimately, how each source material is used will depend largely on individual circumstances and preferences when it comes to gaining insight into relevant subject matter.

- UNO Criss Library
Social Work Research Guide
What is a research journal.
- Find Articles
- Find E-Books and Books
Reading an Academic Article
- Free Online Resources
- Reference and Writing
- Citation Help This link opens in a new window
Anatomy of a Scholarly Article
TIP: When possible, keep your research question(s) in mind when reading scholarly articles. It will help you to focus your reading.
Title : Generally are straightforward and describe what the article is about. Titles often include relevant key words.
Abstract : A summary of the author(s)'s research findings and tells what to expect when you read the full article. It is often a good idea to read the abstract first, in order to determine if you should even bother reading the whole article.
Discussion and Conclusion : Read these after the Abstract (even though they come at the end of the article). These sections can help you see if this article will meet your research needs. If you don’t think that it will, set it aside.
Introduction : Describes the topic or problem researched. The authors will present the thesis of their argument or the goal of their research.
Literature Review : May be included in the introduction or as its own separate section. Here you see where the author(s) enter the conversation on this topic. That is to say, what related research has come before, and how do they hope to advance the discussion with their current research?
Methods : This section explains how the study worked. In this section, you often learn who and how many participated in the study and what they were asked to do. You will need to think critically about the methods and whether or not they make sense given the research question.
Results : Here you will often find numbers and tables. If you aren't an expert at statistics this section may be difficult to grasp. However you should attempt to understand if the results seem reasonable given the methods.
Works Cited (also be called References or Bibliography ): This section comprises the author(s)’s sources. Always be sure to scroll through them. Good research usually cites many different kinds of sources (books, journal articles, etc.). As you read the Works Cited page, be sure to look for sources that look like they will help you to answer your own research question.
Adapted from http://library.hunter.cuny.edu/research-toolkit/how-do-i-read-stuff/anatomy-of-a-scholarly-article
A research journal is a periodical that contains articles written by experts in a particular field of study who report the results of research in that field. The articles are intended to be read by other experts or students of the field, and they are typically much more sophisticated and advanced than the articles found in general magazines. This guide offers some tips to help distinguish scholarly journals from other periodicals.
CHARACTERISTICS OF RESEARCH JOURNALS
PURPOSE : Research journals communicate the results of research in the field of study covered by the journal. Research articles reflect a systematic and thorough study of a single topic, often involving experiments or surveys. Research journals may also publish review articles and book reviews that summarize the current state of knowledge on a topic.
APPEARANCE : Research journals lack the slick advertising, classified ads, coupons, etc., found in popular magazines. Articles are often printed one column to a page, as in books, and there are often graphs, tables, or charts referring to specific points in the articles.
AUTHORITY : Research articles are written by the person(s) who did the research being reported. When more than two authors are listed for a single article, the first author listed is often the primary researcher who coordinated or supervised the work done by the other authors. The most highly‑regarded scholarly journals are typically those sponsored by professional associations, such as the American Psychological Association or the American Chemical Society.
VALIDITY AND RELIABILITY : Articles submitted to research journals are evaluated by an editorial board and other experts before they are accepted for publication. This evaluation, called peer review, is designed to ensure that the articles published are based on solid research that meets the normal standards of the field of study covered by the journal. Professors sometimes use the term "refereed" to describe peer-reviewed journals.
WRITING STYLE : Articles in research journals usually contain an advanced vocabulary, since the authors use the technical language or jargon of their field of study. The authors assume that the reader already possesses a basic understanding of the field of study.
REFERENCES : The authors of research articles always indicate the sources of their information. These references are usually listed at the end of an article, but they may appear in the form of footnotes, endnotes, or a bibliography.
PERIODICALS THAT ARE NOT RESEARCH JOURNALS
POPULAR MAGAZINES : These are periodicals that one typically finds at grocery stores, airport newsstands, or bookstores at a shopping mall. Popular magazines are designed to appeal to a broad audience, and they usually contain relatively brief articles written in a readable, non‑technical language.
Examples include: Car and Driver , Cosmopolitan , Esquire , Essence , Gourmet , Life , People Weekly , Readers' Digest , Rolling Stone , Sports Illustrated , Vanity Fair , and Vogue .
NEWS MAGAZINES : These periodicals, which are usually issued weekly, provide information on topics of current interest, but their articles seldom have the depth or authority of scholarly articles.
Examples include: Newsweek , Time , U.S. News and World Report .
OPINION MAGAZINES : These periodicals contain articles aimed at an educated audience interested in keeping up with current events or ideas, especially those pertaining to topical issues. Very often their articles are written from a particular political, economic, or social point of view.
Examples include: Catholic World , Christianity Today , Commentary , Ms. , The Militant , Mother Jones , The Nation , National Review , The New Republic , The Progressive , and World Marxist Review .
TRADE MAGAZINES : People who need to keep up with developments in a particular industry or occupation read these magazines. Many trade magazines publish one or more special issues each year that focus on industry statistics, directory lists, or new product announcements.
Examples include: Beverage World , Progressive Grocer , Quick Frozen Foods International , Rubber World , Sales and Marketing Management , Skiing Trade News , and Stores .
Literature Reviews
- Literature Review Guide General information on how to organize and write a literature review.
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It Contains two sets of questions to help students review articles, and to review their own literature reviews.
- << Previous: Find E-Books and Books
- Next: Statistics >>
- Last Updated: Mar 8, 2024 11:27 AM
- URL: https://libguides.unomaha.edu/social_work
- Skip to global menu .
- Skip to primary navigation .
- Skip to secondary navigation .
- Skip to page content .
- Return to global menu .

- Search Library site
- Search UVic
- Search for people
- Search for departments
- Search for experts
- Search for news
- Search for resources
- tips and tutorials
- what's a journal?
What's a journal?
A journal is a scholarly publication containing articles written by researchers, professors and other experts. Journals focus on a specific discipline or field of study. Unlike newspapers and magazines, journals are intended for an academic or technical audience, not general readers.
Most journal articles...
- Are peer reviewed
- Have original research
- Focus on current developments
- Cite other works and have bibliographies
- Can be in print, online or both
Journals are published on a regular basis (monthly, quarterly, etc.) and are sequentially numbered.
Each copy is an issue ; a set of issues makes a volume (usually each year is a separate volume). Like newspapers and magazines, journals are also called periodicals or serials.
Take the Peer Review Tutorial here
Email [email protected]
What's new?
- Return to primary navigation .
- Return to secondary navigation .
- Return to page content .
- SpringerLink shop
Types of journal articles
It is helpful to familiarise yourself with the different types of articles published by journals. Although it may appear there are a large number of types of articles published due to the wide variety of names they are published under, most articles published are one of the following types; Original Research, Review Articles, Short reports or Letters, Case Studies, Methodologies.
Original Research:
This is the most common type of journal manuscript used to publish full reports of data from research. It may be called an Original Article, Research Article, Research, or just Article, depending on the journal. The Original Research format is suitable for many different fields and different types of studies. It includes full Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion sections.
Short reports or Letters:
These papers communicate brief reports of data from original research that editors believe will be interesting to many researchers, and that will likely stimulate further research in the field. As they are relatively short the format is useful for scientists with results that are time sensitive (for example, those in highly competitive or quickly-changing disciplines). This format often has strict length limits, so some experimental details may not be published until the authors write a full Original Research manuscript. These papers are also sometimes called Brief communications .
Review Articles:
Review Articles provide a comprehensive summary of research on a certain topic, and a perspective on the state of the field and where it is heading. They are often written by leaders in a particular discipline after invitation from the editors of a journal. Reviews are often widely read (for example, by researchers looking for a full introduction to a field) and highly cited. Reviews commonly cite approximately 100 primary research articles.
TIP: If you would like to write a Review but have not been invited by a journal, be sure to check the journal website as some journals to not consider unsolicited Reviews. If the website does not mention whether Reviews are commissioned it is wise to send a pre-submission enquiry letter to the journal editor to propose your Review manuscript before you spend time writing it.
Case Studies:
These articles report specific instances of interesting phenomena. A goal of Case Studies is to make other researchers aware of the possibility that a specific phenomenon might occur. This type of study is often used in medicine to report the occurrence of previously unknown or emerging pathologies.
Methodologies or Methods
These articles present a new experimental method, test or procedure. The method described may either be completely new, or may offer a better version of an existing method. The article should describe a demonstrable advance on what is currently available.
Back │ Next

Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.

International Journal of Research (IJR)
IJR Journal is Multidisciplinary, high impact and indexed journal for research publication. IJR is a monthly journal for research publication.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN RESEARCH PAPER AND JOURNAL ARTICLE
Difference between research paper and journal article.

Research Paper

Argumentative Research Paper
Analytical research paper, journal article, the differences, research paper:, journal article:.
- Share on Tumblr

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

200 million monthly downloads
24 million monthly readers
3 million authors submit annually
SpringerLink - Home for all research
Discover open access.

- Publish with us

- Track your research

Featured articles and journals
Browse by subject, about springerlink.

Calls for papers
Log in for personalised recommendations.
Ageing in Place
The world’s population is ageing, and with ageing comes an increased risk of disability, multimorbidity and dementia, and an increased need for support. Older people are motivated to stay in their own homes as they age as an alternative to intramural care that is cost-beneficial and often provides...
Urban Lifelines and Supply Chains: Enhancing Resilience and Sustainability with Foundational Technologies
An urban community is an intricate network connected by a myriad of functional systems and subsystems, including civil structures, underground spaces, multi-modal transportation, telecom, energy grids, retail facilities, food systems, and healthcare facilities, all operating with unique spatial and...
Photons to Fuels: Recent Progress of Photocatalytic For CO2 Reduction and H2 Production
To address the detrimental effects of climate change, innovative and timely approaches in renewable energy and environmental chemistry are essential. Photocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide has garnered significant attention as a viable method for carbon capture and utilization, offering the...

Trending research
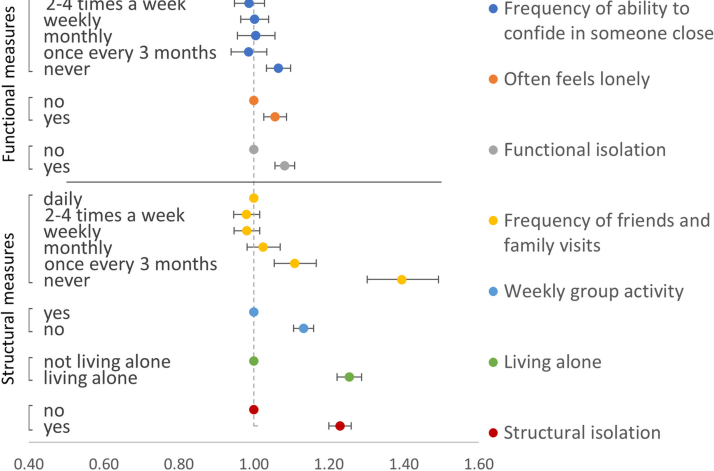
Social connection and mortality in UK Biobank: a prospective cohort analysis
From clicks to consequences: a multi-method review of online grocery shopping
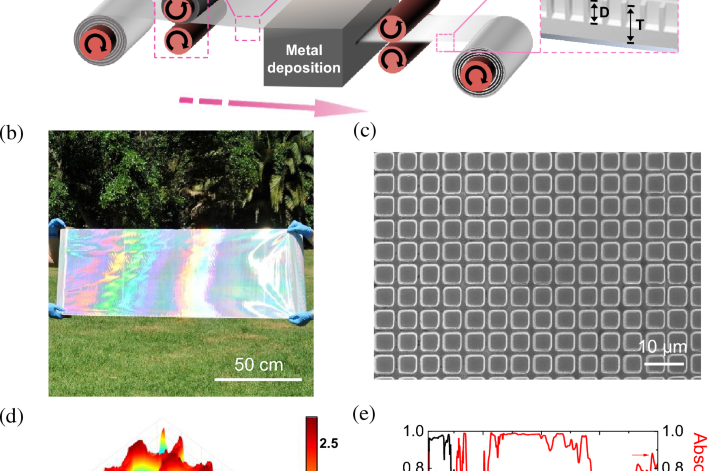
Highly efficient flexible structured metasurface by roll-to-roll printing for diurnal radiative cooling
Persistent cognitive slowing in post-covid patients: longitudinal study over 6 months.
Blame it on my youth: the origins of attitudes towards immigration
Creating the ICU of the future: patient-centred design to optimise recovery

Featured journals

SN Applied Sciences is now Discover Applied Sciences! We are excited to announce that SN Applied Sciences moved into our fully OA Discover journal...

Discover Sustainability is an open access journal publishing research across all fields relevant to sustainability. Average number of article...

The Journal of Epidemiology and Global Healthis an international peer reviewed journal which aims to impact global epidemiology and international...

Featured books

As part of Springer Nature, SpringerLink delivers fast access to the depth and breadth of our online collection of journals, eBooks, reference works and protocols across a vast range of subject disciplines.
SpringerLink is the reading platform of choice for hundreds of thousands of researchers worldwide. Find out how to publish your research with Springer Nature .
- Find a journal
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.

Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
How to find the right journal for your research (using actual data)

Joanna Wilkinson
Want to help your research flourish? We share tips for using publisher-neutral data and statistics to find the right journal for your research paper.
The right journal helps your research flourish. It puts you in the best position to reach a relevant and engaged audience, and can extend the impact of your paper through a high-quality publishing process.
Unfortunately, finding the right journal is a particular pain point for inexperienced authors and those who publish on interdisciplinary topics. The sheer number of journals published today is one reason for this. More than 42,000 active scholarly peer-reviewed journals were published in 2018 alone, and there’s been accelerated growth of more than 5% in recent years.
The overwhelming growth in journals has left many researchers struggling to find the best home for their manuscripts which can be a daunting prospect after several long months producing research. Submitting to the wrong journal can hinder the impact of your manuscript. It could even result in a series of rejections, stalling both your research and career. Conversely, the right journal can help you showcase your research to the world in an environment consistent with your values.
Keep reading to learn how solutions like Journal Citation Reports ™ (JCR) and Master Journal List can help you find the right journal for your research in the fastest possible time.
What to look for in a journal and why
To find the right journal for your research paper, it’s important to consider what you need and want out of the publishing process.
The goal for many researchers is to find a prestigious, peer-reviewed journal to publish in. This might be one that can support an application for tenure, promotion or future funding. It’s not always that simple, however. If your research is in a specialized field, you may want to avoid a journal with a multidisciplinary focus. And if you have ground-breaking results, you may want to pay attention to journals with a speedy review process and frequent publication schedule. Moreover, you may want to publish your paper as open access so that it’s accessible to everyone—and your institution or funder may also require this.
With so many points to consider, it’s good practice to have a journal in mind before you start writing. We published an earlier post to help you with this: Find top journals in a research field, step-by-step guide . Check it out to discover where the top researchers in your field are publishing.
Already written your manuscript? No problem: this blog will help you use publisher-neutral data and statistics to choose the right journal for your paper.
First stop: Manuscript Matcher in the Master Journal List
Master Journal List Manuscript Matcher is the ultimate place to begin your search for journals. It is a free tool that helps you narrow down your journal options based on your research topic and goals.

Pairing your research with a journal
Manuscript Matcher, also available via EndNote™ , provides a list of relevant journals indexed in the Web of Science™ . First, you’ll want to input your title and abstract (or keywords, if you prefer). You can then filter your results using the options shown on the left-hand sidebar, or simply click on the profile page of any journal listed.
Each journal page details the journal’s coverage in the Web of Science. Where available, it may also display a wealth of information, including:
- open access information (including whether a journal is Gold OA)
- the journal’s aims and scope
- download statistics
- average number of weeks from submission to publication, and
- peer review information (including type and policy)
Ready to try Manuscript Matcher? Follow this link .
Identify the journals that are a good topical fit for your research using Manuscript Matcher. You can then move to Journal Citation Reports to understand their citation impact, audience and open access statistics.
Find the right journal with Journal Citation Reports
Journal Citation Reports is the most powerful solution for journal intelligence. It uses transparent, publisher-neutral data and statistics to provide unique insight into a journal’s role and influence. This will help you produce a definitive list of journals best-placed to publish your findings, and more.
Three data points exist on every journal page to help you assess a journal as a home for your research. These are: citation metrics, article relevance and audience.
Citation Metrics
The Journal Impact Factor™ (JIF) is included as part of the rich array of citation metrics offered on each journal page. It shows how often a journal’s recently published material is cited on average.
Learn how the JIF is calculated in this guide .
It’s important to note that the JIF has its limitations and no researcher should depend on the impact factor alone when assessing the usefulness or prestige of a journal. Journal Citation Reports helps you understand the context of a journal’s JIF and how to use the metric responsibly.
The JCR Trend Graph, for example, places the JIF in the context of time and subject category performance. Citation behavior varies across disciplines, and journals in JCR may be placed across multiple subject categories depending on the scope of their content. The Trend Graph shows you how the journal performs against others in the same subject category. It also gives you an understanding of how stable that performance is year-on-year.
You can learn more about this here .
The 2021 JCR release introduced a new, field-normalized metric for measuring the citation impact of a journal’s recent publications. By normalizing for different fields of research and their widely varying rates of publication and citation, the Journal Citation Indicator provides a single journal-level metric that can be easily interpreted and compared across disciplines. Learn more about the Journal Citation Indicator here .
Article relevance
The Contributing Items section in JCR demonstrates whether the journal is a good match for your paper. It can also validate the information you found in the Manuscript Matcher. You can view the full list in the Web of Science by selecting “Show all.”
JCR helps you understand the scholarly community engaging with a journal on both a country and an institutional level. This information provides insight on where in the world your own paper might have an impact if published in that particular journal. It also gives you a sense of general readership, and who you might be talking to if you choose that journal.
Start using Journal Citation Reports today .
Ready to find the right journal for your paper?
The expansion of scholarly journals in previous years has made it difficult for researchers to choose the right journal for their research. This isn’t a good position to be in when you’ve spent many long months preparing your research for the world. Journal Citation Reports , Manuscript Matcher by Master Journal List and the Web of Science are all products dedicated to helping you find the right home for your paper. Try them out today and help your research flourish.
Stay connected
Want to learn more? You can also read related articles in our Research Smarter series, with guidance on finding the relevant papers for your research and how you can save hundreds of hours in the writing process . You can also read about the 2022 JCR release here . Finally, subscribe to receive our latest news, resources and events to help make your research journey a smart one.
Subscribe to receive regular updates on how to research smarter
Related posts
Reimagining research impact: introducing web of science research intelligence.

Beyond discovery: AI and the future of the Web of Science

Clarivate welcomes the Barcelona Declaration on Open Research Information


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

The State of Development Journals 2024: Quality, Acceptance Rates, Review Times, and What’s New
David mckenzie.

This is the eighth in my annual series of efforts to put together data on development economics journals that is not otherwise publicly available or easy to access (see 2017 , 2018 , 2019 , 2020 , 2021 , 2022 , 2023 for the previous editions). I once again thank all the journal editors and editorial staff who graciously shared their statistics with me.
Journal Quality
The most well-known metric of journal quality is its impact factor . The standard impact factor is the mean number of citations in the last year of papers published in the journal in the past 2 years, while the 5-year is the mean number of cites in the last year of papers published in the last 5. As noted in previous years, the distribution of citations are highly skewed, and while the mean number of citations differs across journals, there is substantial overlap in the distributions – most of the variation in citations is within, rather than across journals. We continue to see growth in these impact factors at many journals. The big news this year is that they have decided that you really don’t need three decimal places any more in the impact factors. I compliment these stats with RePec’s journal rankings which take into account article downloads and abstract views in addition to citations.

Table 3 then shows two additional metrics, taken from Scimago , which uses information from the Scopus database. The first is the SJR (SCImago Journal Rank), which is a prestige-weighted citation metric – which works like Google PageRank, giving more weight to citations in sources with a relatively high SJR. I’ve included some of the top general journals in economics for comparison. Scimago also provides an H-index which is the number of papers published by a journal in any year that were cited at least h times in the reference year – so this captures how many papers continue to be influential but as a result, favors more established journals, and ones that publish more articles, that have a larger body of articles to draw upon.

How many submissions are received, and what are the chances of getting accepted?
Table 4 shows the number of submissions received each year. See previous years posts for statistics before 2019. The total submissions in the 11 journals tracked is almost 10,000 papers (note I received no data from the Review of Development Economics this year so have excluded it). Total submissions in these journals are up 7.7% over last year, although not quite at the 2020 peak.

At most journals the number of submissions has either leveled off or fallen since a peak in 2020-21. World Development had the largest 2020 peak when they had a special call for a variety of short papers on COVID-19, but perhaps the combination of people sending off lots of papers during the pandemic and then being a little slower to start new projects has halted the rapid growth somewhat.
· The newish World Development Perspectives already received 532 submissions last year, more than many long established development journals.
· The Review of Development Economics has seen very rapid growth in submissions. I only started collecting stats for it last year, but the editors note that in 2015 they received about 450 submissions, and this has now grown to more than 1,500 last year.
Table 5 shows the total number of papers published in each journal. 782 papers were published in 2023, so that’s a lot of development research (even though less than 1 in 10 of the submitted papers and down slightly on the 811 papers published in 2022). I’ve noted in previous years that some of the journals have been able to flexibly increase the number of articles published as their submission numbers have risen, reducing publication lags as well.

The ratio of the number of papers published to those submitted is approximately the acceptance rate. Of course papers are often published in a different year from when they are submitted, and so journals calculate acceptance rates by trying to match up the timing. Each journal does this in somewhat different ways. Hence Economia-Lacea reports a 0% acceptance rate for 2023 since none of the papers submitted in 2023 have yet been accepted, although some are still under review. Table 6 shows the acceptance rates at different journals as reported by these journals. Of course the number and quality of submissions varies across journals, and so comparing acceptance rates across journals does not tell you what the chances are of your particular paper getting accepted is at these different journals.

How long does it take papers to get refereed?
In addition to wanting to publish in a high quality outlet, and having a decent chance of publication, authors also care a lot about how efficient the process is. Table 7 provides data on the review process (see the previous years’ posts for historic data). The first column shows the desk rejection rate, which averages 73%. Column 2 uses the desk rejection rates and acceptance rates to estimate the acceptance rate conditional on you making it past the desk rejection stage. On average, about one in three papers that gets sent to referees gets accepted, with this varying from 12% to 63% across journals.
The remaining columns give some numbers on how long it takes to get a first-round decision. The statistics “Unconditional on going to referees” includes all the desk rejections, which typically don’t take that many days. The average conditional on going to referees is in the 3-5 month range. The last two columns then show that at most journals, almost all papers have a decision within 6 months – so in my opinion, you should feel free to send an enquiry if your paper takes longer than that.

Do revisions typically get sent back to the referees or handled by the editor?
Another factor that can make a big difference in how long it takes to publish a paper is whether editors send revised papers back to referees, or instead reads the response letter and revision themselves and just makes a decision on this basis. This is something that the AER and AEJ Applied have been trying to do more and more, with only 25% of revisions at the AEJ Applied going back to referees. In my own editing at WBE, I send fewer than 5% of revisions back to referees. This year I asked the different journals what their approaches were. Many do not systematically track this, but offered some approximations:
· Journal of Development Economics: approximately 60% of revisions go back to referees, although 0% for the short papers (see below)
· Development Policy Review: only 10% of revisions go back to referees.
· Journal of Development Effectiveness: 7.7% were sent back to referees
· Journal of Development Studies: not tracked, but less than 20% go back to referees
· Journal of African Economies: 52% are sent back to referees
· Economia: 70% go back to referees.
· EDCC: does not track this, but first revisions are usually sent back to referees.
· World Development, World Development Perspectives, WBRO, and WBER do not track this, and results may vary a lot by editor.
Updates on the JDE Short Paper and Registered Report Tracks
The Journal of Development Economics has two other categories of papers that differ from other development journals:
· The short paper format has proved popular. There were 148 submissions in 2023 (about 8% of total submissions), and 21 short papers were accepted. These papers follow the model of AER Insights, ReStat, etc in which papers are either conditionally accepted or rejected, and so any revisions are minor and are not sent back to referees.
· The JDE registered reports had 19 stage 1 acceptances in 2023, and 1 stage 2 acceptance, reflecting a lag from COVID when there were not many new submissions. They have a website jdepreresults.org which tracks the stage 1 and stage 2 registered reports, but some of the data was lost when transitioning the website, so if you have a registered report accepted that is not listed there, please let the journal know.
Other Development Journal News
Finally, I asked the journals if they had any other major news or changes to report. Here are what they wanted to share:
· At EDCC, Prashant Bharadwaj has replaced Marcel Fafchamps as editor. Thanks to Marcel for 10 years at the helm. The journal is one of the few development journals with a submission fee ($50), but offers a fee waiver to referees who have submitted a timely report in the year prior to submission.
· Other editorial changes are Ganeshan Wignaraja replacing Colin Kirkpatrick as co-editor at Development Policy Review, and Marie Gardner and Ashu Handa taking over from Manny Jimenez at the Journal of Development Effectiveness.
· The Journal of Development Effectiveness notes they are implementing a set of actions to raise awareness about transparency, ethics and equity in research, and to address power imbalances among HIC-L&MIC research teams. The editors note they are particularly concerned with research involving primary data collection in an L&MIC where there is no author from an institution in that country. For articles submitted to JDEff that fall into this category, they will require the authors to complete a short author reflexivity statement that will be published along with the article. The statement will explain the contribution of each author per Taylor & Francis authorship criteria, which are consistent with the criteria established by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Authors will be asked to explain why there is no contributing author from the study location, specifically, whether any team member based in the study location made a ’significant contribution to conception, study design, execution or acquisition of data,’ and if so, why they were not subsequently invited to review the manuscript and take responsibility for its contents. And for work involving randomized controlled trials or interviews with vulnerable groups, authors will also be asked to answer a set of questions about research ethics. Final manuscript acceptance and publication in JDEff will be based on the scientific quality of the work as well as an assessment of whether the work was conducted in an equitable, inclusive and ethical manner.
Finally, thanks again to all the editors for all the time and effort they devote to improving the quality and visibility of development research. As you can see, they have a lot to deal with!

Lead Economist, Development Research Group, World Bank
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 14 May 2024
2023 summer warmth unparalleled over the past 2,000 years
- Jan Esper ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3919-014X 1 , 2 ,
- Max Torbenson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2720-2238 1 &
- Ulf Büntgen 2 , 3 , 4
Nature ( 2024 ) Cite this article
912 Accesses
3320 Altmetric
Metrics details
We are providing an unedited version of this manuscript to give early access to its findings. Before final publication, the manuscript will undergo further editing. Please note there may be errors present which affect the content, and all legal disclaimers apply.
- Climate change
- Palaeoclimate
Including an exceptionally warm Northern Hemisphere (NH) summer 1 ,2 , 2023 has been reported as the hottest year on record 3-5 . Contextualizing recent anthropogenic warming against past natural variability is nontrivial, however, because the sparse 19 th century meteorological records tend to be too warm 6 . Here, we combine observed and reconstructed June-August (JJA) surface air temperatures to show that 2023 was the warmest NH extra-tropical summer over the past 2000 years exceeding the 95% confidence range of natural climate variability by more than half a degree Celsius. Comparison of the 2023 JJA warming against the coldest reconstructed summer in 536 CE reveals a maximum range of pre-Anthropocene-to-2023 temperatures of 3.93°C. Although 2023 is consistent with a greenhouse gases-induced warming trend 7 that is amplified by an unfolding El Niño event 8 , this extreme emphasizes the urgency to implement international agreements for carbon emission reduction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
The economic commitment of climate change
Climate extremes likely to drive land mammal extinction during next supercontinent assembly

Climate damage projections beyond annual temperature
Author information, authors and affiliations.
Department of Geography, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz, Germany
Jan Esper & Max Torbenson
Global Change Research Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Brno, Czech Republic
Jan Esper & Ulf Büntgen
Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom
Ulf Büntgen
Department of Geography, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jan Esper .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Esper, J., Torbenson, M. & Büntgen, U. 2023 summer warmth unparalleled over the past 2,000 years. Nature (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07512-y
Download citation
Received : 16 January 2024
Accepted : 02 May 2024
Published : 14 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07512-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research Paper: Uses third-person point of view. Journal: Utilizes first-person perspective. Another connection between the two is present in their goals; regardless if one produces either work type, they seek to provide new knowledge or insight on a particular subject matter within its given field.
A research journal is a periodical that contains articles written by experts in a particular field of study who report the results of research in that field. The articles are intended to be read by other experts or students of the field, and they are typically much more sophisticated and advanced than the articles found in general magazines. ...
A journal is a scholarly publication containing articles written by researchers, professors and other experts. Journals focus on a specific discipline or field of study. Unlike newspapers and magazines, journals are intended for an academic or technical audience, not general readers. Journal examples:
This article provides an overview of writing for publication in peer-reviewed journals. While the main focus is on writing a research article, it also provides guidance on factors influencing journal selection, including journal scope, intended audience for the findings, open access requirements, and journal citation metrics.
Original Research: This is the most common type of journal manuscript used to publish full reports of data from research. It may be called an Original Article, Research Article, Research, or just Article, depending on the journal. The Original Research format is suitable for many different fields and different types of studies.
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and scholars. JSTOR is a digital library of academic journals ...
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common ...
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1. Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper.
Elsevier journals offer the latest peer-reviewed research papers on climate change, biodiversity, renewable energy and other topics addressing our planet's climate emergency. Join us in working towards a sustainable future with our editorially independent report on creating a Net Zero future.
Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist. Free lecture slides.
1. Where is the article published? The journal (academic publication) where the article is published says something about the quality of the article. Journals are ranked in the Journal Quality List (JQL). If the journal you used is ranked at the top of your professional field in the JQL, then you can assume that the quality of the article is high.
First published in 1869, Nature is the world's leading multidisciplinary science journal. Nature publishes the finest peer-reviewed research that drives ground-breaking discovery, and is read by ...
The key difference is the use of each. One is for practice in writing, and the other is a certain practice for fellow practitioners. That said, one (research paper) is used more as a way to educate a student on how to write clearly and effectively about a topic, while the other (journal article) is written to educate the reader on a subject or ...
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature. As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question.More specifically, that's called a research question, and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What's important to understand though is that you'll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources - for ...
As part of Springer Nature, SpringerLink delivers fast access to the depth and breadth of our online collection of journals, eBooks, reference works and protocols across a vast range of subject disciplines. SpringerLink is the reading platform of choice for hundreds of thousands of researchers worldwide. Find out how to publish your research ...
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research. ... T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398. Appendix: The survey used in this ...
To find the right journal for your research paper, it's important to consider what you need and want out of the publishing process. The goal for many researchers is to find a prestigious, peer-reviewed journal to publish in. This might be one that can support an application for tenure, promotion or future funding.
Elsevier Journal Finder helps you find journals that could be best suited for publishing your scientific article. Journal Finder uses smart search technology and field-of-research specific vocabularies to match your paper's abstract to scientific journals.
When you write a thesis, dissertation, or research paper, you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to: Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context; Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 "Section Headings", but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to ...
The title and abstracts are the only sections of the research paper that are often freely available to the readers on the journal websites, search engines, and in many abstracting agencies/databases, whereas the full paper may attract a payment per view or a fee for downloading the pdf copy.[1,2,3,7,8,10,11,13,14] The abstract is an independent ...
Formatting your research paper according to journal guidelines can be a daunting task. You must pay close attention to margins, font sizes, headings, and spacing, which may differ significantly ...
Table 5 shows the total number of papers published in each journal. 782 papers were published in 2023, so that's a lot of development research (even though less than 1 in 10 of the submitted papers and down slightly on the 811 papers published in 2022). I've noted in previous years that some of the journals have been able to flexibly ...
The biggest hit has come to Wiley, a 217-year-old publisher based in Hoboken, N.J., which Tuesday will announce that it is closing 19 journals, some of which were infected by large-scale research ...
Global Change Research Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Brno, Czech Republic. Jan Esper & Ulf Büntgen. Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom. Ulf ...
In this double issue of the Journal of New Music Research, we have gathered together seven papers on a broad range of topics, including music information retrieval, instrumental acoustics, instrument design and luthiery, sound synthesis, music and language, scales and modes, and aesthetics.This range of subject areas nicely illustrates the uniquely broad, multi- and trans-disciplinarity of the ...
Geophysical Research Letters is a gold open access journal that publishes high-impact, innovative, and timely communications-length articles on major advances spanning all of the major geoscience disciplines. Papers should have broad and immediate implications meriting rapid decisions and high visibility.
Data and materials availability: All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper and/or the Supplementary Materials. Hi-net seismic data required in the paper are available from the National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention (NIED; www.hinet.bosai.go.jp).