

How To Write an Autobiography 2024 (Tips, Templates, & Guide)
Your life story has value, merit, and significance. You want to share it with the world, but maybe you don’t know how .
Here’s how to write an autobiography:
Write an autobiography by creating a list of the most important moments, people, and places in your life. Gather photos, videos, letters, and notes about these experiences. Then, use an outline, templates, sentence starters, and questions to help you write your autobiography .
In this article, you are going to learn the fastest method for writing your autobiography.
We are going to cover everything you need to know with examples and a free, downloadable, done-for-you template.
What Is an Autobiography?

Table of Contents
Before you can write an autobiography, you must first know the definition.
An autobiography is the story of your life, written by you. It covers the full span of your life (at least, up until now), hitting on the most significant moments, people and events.
When you write your autobiography, you write an intimate account of your life.
What Should I Include In an Autobiography?
If you are scratching your head, baffled about what to include in your autobiography, you are not alone.
After all, a big part of how to write an autobiography is knowing what to put in and what to leave out of your life story. Do you focus on every detail?
Every person? Won’t your autobiography be too long?
A good way to think about how to write an autobiography is to use the Movie Trailer Method.
What do movie trailers include?
- High emotional moments
- The big events
- The most important characters
When you plan, organize, and write your autobiography, keep the Movie Trailer Method in mind. You can even watch a bunch of free movie trailers on YouTube for examples of how to write an autobiography using the Movie Trailer Method.
When wondering what to include in your autobiography, focus on what would make the cut for a movie trailer of your life:
- Most important people (like family, friends, mentors, coaches, etc.)
- Significant events (like your origin story, vacations, graduations, life turning points, life lessons)
- Emotional moments (When you were homeless, when you battled a life-threatening condition, or when you fell in love)
- Drama or suspense (Did you make it into Harvard? Did your first surgery go well? Did your baby survive?)
Autobiography Structure Secrets
Like any compelling story, a well-structured autobiography often follows a pattern that creates a logical flow and captures readers’ attention.
Traditionally, autobiographies begin with early memories, detailing the writer’s childhood, family background, and the events or people that shaped their formative years.
From here, the narrative typically progresses chronologically, covering major life events like schooling, friendships, challenges, achievements, career milestones, and personal relationships.
It’s essential to weave these events with introspective insights.
This allows readers to understand not just the what, but also the why behind the author’s choices and experiences.
Towards the end, an effective autobiography often includes reflections on lessons learned, changes in perspective over time, and the wisdom acquired along life’s journey.
Example of the Structure:
- Introduction: A gripping event or anecdote that gives readers a hint of what to expect. It could be a pivotal moment or challenge that defines the essence of the story.
- Childhood and Early Memories: Recounting family dynamics, birthplace, cultural background, and memorable incidents from early years.
- Adolescence and Discovering Identity: Experiences during teenage years, challenges faced, friendships formed, and personal evolutions.
- Pursuits and Passions: Describing education, early career choices, or any particular hobby or skill that played a significant role in the author’s life.
- Major Life Events and Challenges: Chronicles of marriage, parenthood, career shifts, or any significant setbacks and how they were overcome.
- Achievements and Milestones: Celebrating major accomplishments and recounting the journey to achieving them.
- Reflections and Wisdom: Sharing life lessons, changes in beliefs or values over time, and offering insights gained from lived experiences.
- Conclusion: Summarizing the journey, contemplating on the present state, and sharing hopes or aspirations for the future.
How To Write an Autobiography Quickly: Strategies & Templates
Want the quickest way to organize and write your autobiography in record time? You can literally write your autobiography in 7 days or less with this method.
The secret is to use done-for-you templates.
I have personally designed and collected a series of templates to take you from a blank page to a fully complete Autobiography. I call this the How to Write an Autobiography Blueprint.
And it’s completely free to download right from this article. 🙂
In the How to Write an Autobiography Blueprint, you get:
- The Autobiography Questions Template
- The Autobiography Brainstorm Templates
- The Autobiography Outline Template
Here is an image of it so that you know exactly what you get when you download it:

How To Write an Autobiography: Step-by-Step
When you sit down to write an autobiography, it’s helpful to have a step-by-step blueprint to follow.
You already have the done-for-you templates that you can use to organize and write an autobiography faster than ever before. Now here’s a complete step-by-step guide on how to maximize your template.
- Brainstorm Ideas
- Order your sections (from medium to high interest)
- Order the ideas in each section (from medium to high interest)
- Write three questions to answer in each section
- Choose a starter sentence
- Complete a title template
- Write each section of your by completing the starter sentence and answering all three questions
Brainstorm Your Autobiography
The first step in writing your autobiography is to brainstorm.
Give yourself time and space to write down the most significant people, events, lessons, and experiences in your life. The templates in the How to Write an Autobiography Blueprint provide sections for you to write down your brainstormed ideas.

This will help you organize your ideas into what will become the major sections of your book.
These will be:
- Y our most significant events and experiences.
- The people who impacted you the most.
- The challenges you have overcome.
- Your achievements and successes.
- The lessons you have learned.
The “other” sections on the second page of the Brainstorm template is for creating your own sections or to give you more space for the sections I provided in case you run out of space.
As I brainstorm, I find asking myself specific questions really activates my imagination.
So I have compiled a list of compelling questions to help you get ideas down on paper or on your screen.

Order Your Sections (From Medium to High Interest)
The next step is to order your main sections.
The main sections are the five (or more) sections from your Brainstorm templates (Significant events, significant people, life lessons, challenges, successes, other, etc). This order will become the outline and chapters for your book.
How do you decide what comes first, second or third?
I recommend placing the sections in order of interest. Ask yourself, “What’s the most fascinating part of my life?”
If it’s a person, then write the name of that section (Significant People) on the last line in the How to Write an Autobiography Outline Template. If it’s an experience, place the name of that section (Significant Events) on the last line.
For example, if you met the Pope, you might want to end with that nugget from your life. If you spent three weeks lost at sea and survived on a desert island by spearfishing, that is your ending point.
Then complete the Outline by placing the remaining sections in order of interest. You can work your way backward from high interest to medium interest.
If you are wondering why I say “medium to high interest” instead of “low to high interest” it is because there should be no “low interest” parts of your autobiography.
But wait, what if you met the Pope AND spent three weeks lost at sea? How do you choose which one comes first or last?
First of all, I want to read this book! Second, when in doubt, default to chronological order. Whatever event happened first, start there.
Here is an example of how it might look:

Order The Ideas in Each Section (From Medium To High Interest)
Now, organize the ideas inside of each section. Again, order the ideas from medium to high interest).
Within your “Significant People” section, decide who you want to talk about first, second, third, etc. You can organize by chronological order (who you met first) but I recommend building to the most interesting or most significant person.
This creates a more compelling read.
Keep in mind that the most significant person might not be the most well-known, most famous, or most popular. The most significant person might be your family member, friend, partner, or child.
It comes down to who shaped your life the most.
So, if your “significant people list” includes your dad, a famous social media influencer, and Mike Tyson, your dad might come last because he had the biggest significance in your life.
Write Three Questions to Answer in Each Section
Ok, you’ve done the heavy lifting already. You have the major sections organized and outlined.
Next on your autobiography to-do list is to choose and write down three questions you are going to answer in each section. You can write your questions down in the provided “boxes” for each section on the template outline (or on another piece of paper.
This is easier than it might seem.
Simply choose one of the sample autobiography questions below or create your own:
- Why did I choose this person/event?
- What does this person/event mean to me?
- How did I meet this person?
- Where did it happen?
- When did it happen?
- Why did it happen?
- How did it happen?
- What is the most interesting part?
- How did I feel about this person or event?
- How do I feel now?
- Why does this person or event matters to me?
- How did this person or event change my life?
- What is the most challenging part?
- How did I fail?
- How did I succeed?
- What did I learn?
Questions are the perfect way to write quickly and clearly. I LOVE writing to questions. It’s how I write these blog posts and articles.
Choose a Starter Sentence
Sometimes the hardest part of any project is knowing how to start.
Even though we know we can always go back and edit our beginnings, so many of us become paralyzed with indecision at the starting gate.
That’s why I provided sample starter sentences in your How to Write an Autobiography Blueprint.
Here are the story starters:
- I began writing this book when…
- Of all the experiences in my life, this one was the most…
- I’ve been a…
- My name is…
- Growing up in…
- It wasn’t even a…
- It all started when…
- I first…
- I was born…
Keep in mind that you do not need to begin your book with one of these story starters. I provide them simply to get you going.
The key is to not get bogged down in this, or any, part of writing your autobiography. Get organized and then get writing.
Complete a Title Template
At the top of the How to Write an Autobiography Outline is a place for you to write your book title.
Some authors struggle forever with a title. And that’s ok. What’s not ok is getting stuck. What’s not ok is if coming up with your title prevents you from finishing your book.
So, I provided a few title templates to help juice your creativity.
Just like the story starters, you do not need to use these title templates, but you certainly can. All you need to do is fill in the title templates below and then write your favorite one (for now) at the top of your outline. Presto! You have your working title.
You can always go back and change it later.
How to Write an Autobiography Title templates:
- [Your Name]: [Phrase or Tag Line]
- The [Your Last Name] Files
- Born [Activity]: A [Career]’s Life
- The Perfect [Noun]: The Remarkable Life of [Your Name]
Examples using the Templates:
- Christopher Kokoski: Blog Until You Drop
- The Kokoski Files
- Born Writing: A Blogger’s Life
- The Perfect Freelancer: The Remarkable Life of Christopher Kokoski
Write Your Autobiography
You have your outline. You have your title, templates, and sentence starters. All that is left to do is write your autobiography.
However, you can use tools like Jasper AI and a few other cool tricks to craft the most riveting book possible.
This is the easy way to remarkable writing.
Check out this short video that goes over the basics of how to write an autobiography:
How To Write an Autobiography (All the Best Tips)
Now that you are poised and ready to dash out your first draft, keep the following pro tips in mind:
- Be vulnerable. The best autobiographies share flaws, faults, foibles, and faux pas. Let readers in on the real you.
- Skip the boring parts. There is no need to detail every meal, car ride, or a gripping trip to the grocery store. Unless you ran into the Russian Mafia near the vegetables or the grocery store is perched on the side of a mountain above the jungles of Brazil.
- Keep your autobiography character-driven . This is the story of YOU!
- Be kind to others (or don’t). When writing about others in your story, keep in mind that there may be fallout or backlash from your book.
- Consider a theme: Many autobiographies are organized by theme. A perfect example is Becoming . Each section of the book includes “becoming” in the title. Themes connect and elevate each part of the autobiography.
- Write your story in vignettes (or scenes). Each vignette is a mini-story with a beginning, middle, and end. Each vignette builds. Each vignette should be described in rich sensory language that shows the reader the experience instead of telling the reader about the experience. Each vignette is immersive, immediate, and intimate.
- Include snippets of dialogue. Use quotation marks just like in fiction. Show the dialogue in brief back-and-forth tennis matches of conversation. Remember to leave the boring parts out!
- Choose a consistent tone. Some autobiographies are funny like Bossy Pants by Tina Fey. Others are serious such as Open by Andre Agassi. Your story (like most stories) will likely include a mix of emotions but choose an overall tone and stick with it.
- Don’t chronicle, captivate . Always think about how to make each section, each chapter, each page, each paragraph, and each sentence more compelling. You want to tell the truth, but HOW you tell the truth is up to you. Create suspense, conflict, and mystery. Let drama linger until it becomes uncomfortable. Don’t solve problems quickly or take away tension right away.
How Do I Format an Autobiography?
Most autobiographies are written in the first person (using the pronouns I, me, we, and us).
Your autobiography is written about you so write as yourself instead of pretending to be writing about someone else.
Most autobiographies are also written in chronological order, from birth right up to your current age, with all the boring parts left out. That doesn’t mean you can’t play around with the timeline.
Sometimes it’s more interesting to start at a high moment, backtrack to the beginning and show how you got to that high moment.
Whatever format you choose, be intentional, and make the choice based on making the most compelling experience possible for your readers.
How Long Should an Autobiography Be?
There are no rules to how long an autobiography should be but a rough guideline is to aim for between 200 and 400 pages.
This will keep your book in line with what most readers expect for books in general, and will help get your book traditionally published or help with marketing your self-published book.
How To Write a Short Autobiography
You write a short autobiography the same way that you write a long autobiography.
You simply leave more out of the story.
You cut everything down to the bones. Or you choose a slice of your life as you do in a memoir. This often means limiting the people in your book, reducing the events and experiences, and shrinking your story to a few pivotal moments in your life.
How To Start an Autobiography
The truth is that you can start your autobiography in any number of ways.
Here are four common ways to begin an autobiography.
- Start at the beginning (of your life, career or relationship, etc.)
- Start at a high moment of drama or interest.
- Start at the end of the story and work backward
- Start with why you wrote the book.
Good Autobiography Titles
If you are still stuck on titling your autobiography, consider going to Amazon to browse published works. You can even just Google “autobiographies.”
When you read the titles of 10, 20, or 50 other autobiographies, you will start to see patterns or get ideas for your own titles. (HINT: the title templates in the Autobiography Blueprint were reverse-engineered from popular published books.
Also, check out the titles of the full autobiography examples below that I have included right here in this article.
Types of Autobiographies
There are several different kinds of autobiographies.
Each one requires a similar but slightly nuanced approach to write effectively. The lessons in this article will serve as a great starting point.
Autobiography Types:
- Autobiography for School
- Autobiography Novel
- Autobiography for a Job
- Short Autobiography
- Autobiography for Kids
Therefore, there is actually not just one way to write an autobiography.
Memoir vs. Autobiography: Are They The Same?
It’s common to feel confused about a memoir and an autobiography. I used to think they were the same thing.
But, nope, they’re not.
They are pretty similar, which is the reason for all the confusion. A memoir is the story of one part of your life. An autobiography is the story of your full life (up until now).
What Is the Difference Between an Autobiography and a Biography?
An autobiography is when you write about your own life. A biography, on the other hand, is when you write the story of someone else’s life.
So, if I write a book about the life of the President, that’s a biography.
If the President writes a story about his or her own life, that’s an autobiography.
What Not To Include In an Autobiography
Autobiographies are meant to be a snapshot of our lives that we can share with others, but there are some things that are best left out.
Here are three things you should avoid including in your autobiography:
1) Anything That Readers Will Skip
Your life may not be filled with non-stop excitement, but that doesn’t mean you need to include every mundane detail in your autobiography.
Stick to the highlights and leave out the low points.
2) Character Attacks on Others
It’s okay to discuss conflicts you’ve had with others, but don’t use your autobiography as a platform to attack someone’s character.
Keep it civil and focus on your own experiences and how they’ve affected you.
3) Skipping Highlights
Just because something embarrassing or painful happened to you doesn’t mean you should gloss over it in your autobiography.
These are the moments that shape us and make us who we are today, so don’t skip past them just because they’re uncomfortable.
By following these simple tips, you can ensure that your autobiography is interesting, honest, and engaging.
How To Write an Autobiography: Autobiography Examples
I have always found examples to be extremely instructive. Especially complete examples of finished products. In this case, books.
Below you will find examples of published autobiographies for adults and for kids. These examples will guide you, motivate you and inspire you to complete your own life story.
They are listed here as examples, not as endorsements, although I think they are all very good.
The point is that you don’t have to agree with anything written in the books to learn from them.
Autobiography Examples for Adults
- A Promised Land (Autobiography of Barack Obama)
- If You Ask Me: (And of Course You Won’t) (Betty White)
- It’s a Long Story: My Life (Willie Nelson)
- Stories I Only Tell My Friends: An Autobiography (Rob Lowe)
- Becoming (Michelle Obama)
Autobiography Examples for Kids
- This Kid Can Fly: It’s About Ability (NOT Disability) (Aaron Philips)
- Bee Fearless: Dream Like a Kid (Mikaila Ulmer)
Final Thoughts: How To Write An Autobiography
Thank you for reading my article on How to Write an Autobiography.
Now that you know all of the secrets to write your book, you may want to get it published, market it, and continue to upskill yourself as an author.
In that case, read these posts next:
- Can Anyone Write A Book And Get It Published?
- The Best Writing Books For Beginners 2022 (My 10 Favorites)
- Why Do Writers Hate Adverbs? (The Final Answer)
- How To Write a Manifesto: 20 Ultimate Game-Changing Tips
2 thoughts on “How To Write an Autobiography 2024 (Tips, Templates, & Guide)”
Pingback: How To Write Like Danielle Steel - CHRISTOPHER KOKOSKI
Pingback: How Many Characters Should A Book Have? - CHRISTOPHER KOKOSKI
Comments are closed.
Autobiography
Definition of autobiography.
Autobiography is one type of biography , which tells the life story of its author, meaning it is a written record of the author’s life. Rather than being written by somebody else, an autobiography comes through the person’s own pen, in his own words. Some autobiographies are written in the form of a fictional tale; as novels or stories that closely mirror events from the author’s real life. Such stories include Charles Dickens ’ David Copperfield and J.D Salinger’s The Catcher in The Rye . In writing about personal experience, one discovers himself. Therefore, it is not merely a collection of anecdotes – it is a revelation to the readers about the author’s self-discovery.
Difference between Autobiography and Memoir
In an autobiography, the author attempts to capture important elements of his life. He not only deals with his career, and growth as a person, he also uses emotions and facts related to family life, relationships, education, travels, sexuality, and any types of inner struggles. A memoir is a record of memories and particular events that have taken place in the author’s life. In fact, it is the telling of a story or an event from his life; an account that does not tell the full record of a life.
Six Types of Autobiography
There are six types of autobiographies:
- Autobiography: A personal account that a person writes himself/herself.
- Memoir : An account of one’s memory.
- Reflective Essay : One’s thoughts about something.
- Confession: An account of one’s wrong or right doings.
- Monologue : An address of one’s thoughts to some audience or interlocuters.
- Biography : An account of the life of other persons written by someone else.
Importance of Autobiography
Autobiography is a significant genre in literature. Its significance or importance lies in authenticity, veracity, and personal testimonies. The reason is that people write about challenges they encounter in their life and the ways to tackle them. This shows the veracity and authenticity that is required of a piece of writing to make it eloquent, persuasive, and convincing.
Examples of Autobiography in Literature
Example #1: the box: tales from the darkroom by gunter grass.
A noble laureate and novelist, Gunter Grass , has shown a new perspective of self-examination by mixing up his quilt of fictionalized approach in his autobiographical book, “The Box: Tales from the Darkroom.” Adopting the individual point of view of each of his children, Grass narrates what his children think about him as their father and a writer. Though it is really an experimental approach, due to Grass’ linguistic creativity and dexterity, it gains an enthralling momentum.
Example #2: The Story of My Life by Helen Keller
In her autobiography, The Story of My Life , Helen Keller recounts her first twenty years, beginning with the events of the childhood illness that left her deaf and blind. In her childhood, a writer sent her a letter and prophesied, “Someday you will write a great story out of your own head that will be a comfort and help to many.”
In this book, Keller mentions prominent historical personalities, such as Alexander Graham Bell, whom she met at the age of six, and with whom she remained friends for several years. Keller paid a visit to John Greenleaf Whittier , a famous American poet, and shared correspondence with other eminent figures, including Oliver Wendell Holmes, and Mrs. Grover Cleveland. Generally, Keller’s autobiography is about overcoming great obstacles through hard work and pain.
Example #3: Self Portraits: Fictions by Frederic Tuten
In his autobiography, “Self Portraits: Fictions ,” Frederic Tuten has combined the fringes of romantic life with reality. Like postmodern writers, such as Jorge Luis Borges, and Italo Calvino, the stories of Tuten skip between truth and imagination, time and place, without warning. He has done the same with his autobiography, where readers are eager to move through fanciful stories about train rides, circus bears, and secrets to a happy marriage; all of which give readers glimpses of the real man.
Example #4: My Prizes by Thomas Bernhard
Reliving the success of his literary career through the lens of the many prizes he has received, Thomas Bernhard presents a sarcastic commentary in his autobiography, “My Prizes.” Bernhard, in fact, has taken a few things too seriously. Rather, he has viewed his life as a farcical theatrical drama unfolding around him. Although Bernhard is happy with the lifestyle and prestige of being an author, his blasé attitude and scathing wit make this recollection more charmingly dissident and hilarious.
Example #5: The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin by Benjamin Franklin
“The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin ” is written by one of the founding fathers of the United States. This book reveals Franklin’s youth, his ideas, and his days of adversity and prosperity. He is one of the best examples of living the American dream – sharing the idea that one can gain financial independence, and reach a prosperous life through hard work.
Through autobiography, authors can speak directly to their readers, and to their descendants. The function of the autobiography is to leave a legacy for its readers. By writing an autobiography, the individual shares his triumphs and defeats, and lessons learned, allowing readers to relate and feel motivated by inspirational stories. Life stories bridge the gap between peoples of differing ages and backgrounds, forging connections between old and new generations.
Synonyms of Autobiography
The following words are close synonyms of autobiography such as life story, personal account, personal history, diary, journal, biography, or memoir.
Related posts:
- The Autobiography of Malcolm X
Post navigation
How to Write an Autobiography Fast

Writing your autobiography is like exploring a treasure trove of memories that make up your life. But starting can feel overwhelming. Where do you begin? How do you turn your experiences into a compelling story? Don't worry – this guide is here to help. Whether you're a seasoned writer or a total beginner, we'll break down the process of how to write your autobiography into easy-to-follow steps. Together, we'll uncover the magic of storytelling and turn your life into a captivating reflective essay that's uniquely yours. Get ready to start this adventure of self-discovery and creativity!
What Is an Autobiography
The autobiography definition explains it is a written account of a person's life penned by the individual who has lived those experiences. It is a personal narrative that chronicles significant events, reflections, and emotions throughout various stages of the author's life. Unlike a biography, which is typically written by someone else, an autobiography provides a firsthand perspective, allowing the author to share their thoughts, memories, and insights. It is a cogent medium for self-expression, enabling students to convey the essence of their unique journey, impart lessons learned, and leave a lasting record of their lives for themselves and others to explore.
Need Help With Writing an AUTOBIOGRAPHY?
All you have to do to get professional help is to us send your paper requirements and set the deadline.
Autobiography vs. Biography: What’s the Difference
The key distinction between an autobiography and a biography lies in the authorship and perspective. An autobiography is a personal account of one's own life written by the subject themselves. It offers an intimate insight into the author's experiences, emotions, and reflections. For instance, in "The Diary of a Young Girl," Anne Frank provides a poignant autobiographical account of her life hiding from the Nazis during World War II. On the other hand, a biography is a narrative of someone's life written by another person. It often involves extensive research and interviews to present a comprehensive and objective view. A notable example is "Steve Jobs" by Walter Isaacson, a biography offering an in-depth portrayal of the Apple co-founder, drawing on interviews with Jobs himself and those who knew him. While both genres illuminate lives, the crucial difference lies in the source of the narrative – whether it emanates directly from the subject or is crafted by an external observer.
A biography vs autobiography offers distinct perspectives on individuals' lives, shaping narratives through either personal reflections or external observations. Maya Angelou's "I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings" is a powerful autobiography chronicling her tumultuous childhood and journey toward self-discovery. In contrast, a notable biography like "Leonardo da Vinci" by Walter Isaacson delves into the life of the Renaissance polymath, painting a vivid picture through meticulous research and analysis. Autobiographies often provide a deeply personal lens, as seen in "The Glass Castle" by Jeannette Walls, where Walls recounts her unconventional upbringing. In contrast, biographies such as "Unbroken" by Laura Hillenbrand meticulously document the extraordinary life of Louis Zamperini, offering a comprehensive view shaped by the author's investigative work. These examples underscore the unique storytelling approaches each genre employs, either from the firsthand perspective of the subject or the external perspective of an author.
Autobiography Example
Ready to explore autobiography examples? We've got a cool section coming up where we'll check out two awesome examples. Autobiographies are like personal tours into someone's life, and we'll be looking at the stories of Alex Sterling and Trevor Noah. They've poured their experiences onto the pages, and we're going to see what we can learn from their journeys. Get ready to be inspired and maybe even think about telling your own story down the line. Let's dive in!
.webp)
Example 1: “Wanderer's Odyssey: The Uncharted Life of Alex Sterling”
This autobiography recounts the life of a character born in a bustling city who, driven by a thirst for adventure, leaves behind urban life to explore the open road. The narrative explores the protagonist's experiences of hitchhiking, forming connections, and finding self-discovery in the midst of the unpredictable journey. The story emphasizes the lessons learned from the road, the challenges faced, and the ultimate embrace of authenticity. The epilogue reflects on the character's life as a well-lived odyssey, highlighting themes of resilience, connection, and the pursuit of one's true identity.
Example 2: “Echoes of Eternity: The Memoirs of Amelia Reed”
This autobiography follows a character from a countryside village who harbors expansive dreams of adventure. The narrative unfolds as the protagonist sets out to pursue these dreams, facing trials and triumphs that shape their character and lead to self-discovery. The story emphasizes the transformative power of embracing the unknown, with the epilogue reflecting on a life well-lived, highlighting the legacy of fulfilled dreams and the enduring impact on future generations. In addition to examples, we have samples of narrative essay topics that might be useful for you as well.
Tell your story with EssayPro . Our skilled writers can help you craft an autobiography that truly reflects your journey. Share your unique experiences and life lessons in a way that resonates with readers.

Autobiography Elements Explained
Writing an autobiography provides a personal account of one's experiences, achievements, challenges, and personal growth. While each autobiography is unique, certain common elements are often found in this genre:
Introduction
- Autobiographies typically begin with an introduction where the author sets the stage for their life story.
- It may include background information such as birthplace, family, and early experiences.
Birth and Early Years
- Authors often include details about their birth, childhood, and family background.
- Early influences, relationships, and experiences that shaped the individual may be highlighted.
Significant Life Events
- Autobiographies focus on key events and milestones that have had a significant impact on the author's life.
- This could include achievements, failures, relationships, and other impactful experiences.
Challenges and Obstacles
- Autobiographies explore the challenges and obstacles the author faced throughout their life.
- This can include personal struggles, professional setbacks, or other difficulties.
Personal Growth and Development
- Authors reflect on their personal growth and development over the years.
- This may involve self-discovery, learning from experiences, and evolving perspectives.
Achievements and Milestones
- Autobiographies highlight the author's achievements, whether personal, professional, or both.
- Major milestones and successes are often detailed to showcase the individual's journey.
Influential Relationships
- Autobiographies frequently discuss relationships with family, friends, mentors, and significant others.
- The impact of these relationships on the author's life is explored.
Reflection and Insight
- Authors often reflect on their lives, offering insights into their beliefs, values, and lessons learned.
- This section may also include the author's perspective on the world and society.
Themes and Motifs
- Autobiographies may explore recurring themes or motifs that run throughout the individual's life.
- Common themes include resilience, determination, love, loss, and personal identity.
- Autobiographies typically conclude with a summary or reflection on the author's life.
- The author may share their current perspective and future aspirations.
Writing Style
- The writing style can vary, ranging from a formal tone to a more conversational and reflective approach.
- Authors may use literary devices and storytelling techniques to engage readers.
Remember that autobiographies are highly personal, and the structure and emphasis on different elements can vary widely depending on the author's preferences and purpose for writing.
Autobiographical Essay Structure
Autobiographies typically follow a chronological order, beginning with the author's early life and progressing towards the present or a significant moment. The introduction sets the stage, introducing the author and offering insight into the main themes. As you can see in an autobiography example, the narrative then unfolds, exploring the author's significant life events, challenges faced, and personal growth. Achievements and milestones are highlighted, and the impact of influential relationships is examined. Throughout, recurring themes and motifs add depth to the narrative. In the reflection and insight section, the author shares personal lessons learned and beliefs. The conclusion summarizes the autobiography, reflecting on the author's life and future aspirations.
.webp)
Learning how to start an autobiography involves captivating the reader's attention while providing context. Authors often employ engaging anecdotes, vivid descriptions, or thought-provoking statements related to the overarching theme of their lives. The goal is to draw readers in from the beginning and establish a connection between the author and the audience. In the introduction, authors can introduce themselves to the reader. This can be done by sharing a captivating snapshot of their life or posing a question that intrigues the audience. The autobiography introduction sets the tone for the entire narrative, providing a glimpse into the themes and events that will be explored in the autobiography.
The autobiography conclusion offers the culmination of the author's life story. Here, authors often summarize the key points and experiences shared throughout the narrative. It is a moment of reflection, where the author can offer insights into the significance of their journey and the lessons learned along the way. The conclusion may also touch on the author's current perspective, providing a sense of closure to the narrative while leaving room for future aspirations and growth.
Literary Forms of Autobiography
Autobiographies, while generally a non-fiction genre, can take on various literary forms and styles. Here are some literary forms commonly found in autobiographical works:
Traditional Autobiography
- The straightforward narrative of an individual's life, which is usually written by the person themselves. It follows a chronological order, covering significant events and experiences.
- Similar to an autobiography but often focusing on specific themes, periods, or aspects of the author's life rather than a comprehensive account. Memoirs often delve into personal reflections and emotions.
Diary or Journal Form
- Some autobiographies adopt the form of a diary or journal, presenting the author's life through dated entries. This format provides a more immediate and personal perspective.
Epistolary Autobiography
- Written in the form of letters, an epistolary autobiography may consist of the author addressing themselves or others. This style adds an intimate and conversational tone to the narrative.
Graphic Novel or Comic Memoir
- Autobiographical stories are presented in a graphic novel or comic format. Visual elements complement the written narrative, providing a unique and engaging way to convey personal experiences.
Experimental or Nonlinear Autobiography
- Some authors choose to play with the chronological order, presenting their life story non-linearly. This experimental approach can create a more artistic and challenging reading experience.
Biographical Fiction
- While not entirely autobiographical, some authors write fictionalized versions of their own lives. It allows for creative exploration and artistic liberties while drawing inspiration from real experiences.
Travelogue Autobiography
- Autobiographies that take on the form of a travelogue often focus on the author's journeys, both physical and metaphorical. The narrative is shaped by the places visited and the impact of these experiences on personal growth.
Essayistic Autobiography
- Autobiographies that incorporate elements of essays, exploring themes, ideas, and reflections on the author's life. This form allows for a more contemplative and philosophical approach.
Collaborative Autobiography
- Co-written autobiographies involve collaboration between the autobiographical subject and a professional writer. It is common when the subject may not be a writer but has a compelling story to share.
These literary forms highlight the versatility of autobiographical writing, showcasing how authors can creatively shape their life stories to engage readers in various ways. Are you working on other academic assignments? Use our term paper writing services to put your finger on any pending task at hand quickly and for a reasonable price.
How to Write an Autobiography in 5 Steps
Writing an autobiography can be a rewarding and reflective process. Here's a simplified guide in 5 steps to help you get started:
Step 1: Reflection and Brainstorming
Begin by reflecting on your life, considering important events, challenges, and moments of growth. Make a mental inventory of key experiences and people who have influenced you.
Step 2: Establish a Focus
Choose a central theme or focus for your autobiography. This could be a specific period of your life, a significant achievement, or a recurring theme that ties your experiences together. Having a clear focus will guide your writing.
Step 3: Create a Chronological Outline
Develop a rough chronological outline of your life story, starting from your early years and progressing through significant events to the present or another crucial point. Identify key moments and experiences to include in each section.
Step 4: Write with Detail and Emotion
An important aspect of how to write an autobiography for college is appealing to emotion. As you delve into each body paragraph, share your story with vivid details. Use descriptive language to bring your experiences to life for the reader. Infuse your writing with emotion, allowing readers to connect with the depth of your personal journey.
Step 5: Conclude Reflectively
In the concluding section, summarize the key aspects of your life story. Reflect on the significance of your journey, the lessons you've learned, and how you've grown. Provide insights into your current perspective and aspirations for the future, bringing your autobiography to a thoughtful conclusion.
Writing Techniques to Use in an Autobiography
When you write an autobiography, the process involves employing various techniques to make the narrative engaging, evocative, and compelling. Here are some tips for writing autobiography commonly used in autobiographies:
Descriptive Language
- Use vivid and descriptive language to paint a detailed picture of events, people, and settings. Engage the reader's senses to create a more immersive experience.
- Incorporate dialogue to bring conversations to life. Direct quotes can provide authenticity and convey the personalities of the people involved.
Show, Don't Tell
- Instead of merely stating facts, show the emotions and experiences through actions, reactions, and sensory details.
Flashbacks and Foreshadowing
- Employ flashbacks to delve into past events and foreshadowing to create anticipation about future developments.
Metaphors and Similes
- Use metaphors and similes to enhance descriptions and convey complex emotions. Comparisons can make abstract concepts more relatable.
- Integrate symbols and motifs that hold personal significance. This adds depth to the narrative and can be a thematic thread throughout the autobiography.
Humor and Wit
- Infuse your writing with humor and wit when appropriate.
- Introduce suspense by strategically withholding information or revealing key details at crucial moments.
First-Person Perspective
- Utilize the first-person point of view to offer a direct and personal connection between the author and the reader.
Dramatic Irony
- Introduce dramatic irony by revealing information to the reader that the author may not have known at the time.
Parallelism
- Create parallel structures within the narrative, drawing connections between different periods, events, or themes in your life.
Experimenting with different styles can make your story more engaging and memorable for readers. If you haven’t used these techniques in your paper, simply say, ‘ edit my essay ,’ and our experts will imbue stylistic and creative devices in your document to increase its scholarly value.
Benefits of Writing an Autobiography
Working on an autobiography can be incredibly beneficial on a personal level. When you take the time to reflect on your life and put it into words, you gain a deeper understanding of yourself. It's like a journey of self-discovery where you uncover patterns, values, and beliefs that have shaped who you are. This process not only promotes self-awareness but can also help you grow and bounce back from tough times. Writing about challenging moments can be a therapeutic release, allowing you to confront and make sense of your experiences, leading to emotional healing.
On a broader scale, sharing your life story through an autobiography has its impact. It becomes a piece of history, offering insights into the times you've lived through, the culture around you, and societal changes. Your personal narrative connects you with others, creating empathy and understanding. Autobiographies often inspire people by showing that it's possible to overcome challenges, find purpose, and navigate the ups and downs of life. By sharing your story, you become a part of the larger human experience, contributing to a rich tapestry of diverse stories that help us better understand the shared journey of being human. Order an essay or any other type of task to streamline your educational progress is only a few clicks.
Best Piece of Advice for Making Your Autobiography Spot-on
The most valuable advice on how to write an autobiography is to infuse authenticity into every word. Be genuine, raw, and honest about your experiences, emotions, and growth. Readers connect deeply with authenticity, and it's what makes your story uniquely yours. Don't shy away from expressing vulnerability, as it adds a human touch and makes your narrative relatable. Share the highs and lows, the triumphs and struggles, with sincerity, and let your true self shine through. This honesty not only enhances the impact of your autobiography but also contributes to a more profound connection between you and your readers, creating an authentic and memorable narrative. Here are additional tips for bringing your autobiography assignment up to par:
- Essential Details. Focus on key moments that significantly contribute to your story, avoiding unnecessary details.
- Thematic Cohesion. Introduce and explore recurring themes to add depth and coherence to your narrative.
- Authentic Expression. Embrace your unique voice, personality, and storytelling style to create an authentic connection with readers.
- Dialogue and Monologue. Use genuine dialogue and inner monologue to provide insights into your thoughts and emotions during pivotal moments.
- Symbolic Elements. Incorporate symbolic imagery or metaphors to convey deeper meanings and emotions.
- Strategic Foreshadowing. Use foreshadowing purposefully, providing subtle hints that contribute meaningfully to the overall narrative.
- Reflective Closure. Conclude your autobiography with a reflective summary that offers insights into the broader significance of your journey.
Our essay writers know many more tips regarding all possible types of academic tasks. If you ever find yourself in writer’s block, not knowing how to tackle any particular assignment, let us know!
Final Words
If you want to understand how to write a good autobiography, think of it as painting a vivid picture of your life for others to see. It's about being real, digging deep into your memories, and choosing the moments that really matter. Let your personality shine through in your writing – be yourself because that's what makes your story unique. Weave in themes that tie everything together, and use storytelling techniques like dialogue and symbolism to make your narrative come alive. And as you reach the end, leave your readers with some food for thought – a reflection on the bigger lessons learned from your journey. If you ever need assistance with this or any other college assignment, use our research paper services without hesitation.
Do You Need Some Help With Your AUTOBIOGRAPHY?
Address to out professional writers to get your paper done asap
How to Write an Autobiography?
How to start an autobiography essay, what is the difference between autobiography and biography, related articles.
.webp)
How to Define Autobiography
Glossary of Grammatical and Rhetorical Terms
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
An autobiography is an account of a person's life written or otherwise recorded by that person. Adjective: autobiographical .
Many scholars regard the Confessions (c. 398) by Augustine of Hippo (354–430) as the first autobiography.
The term fictional autobiography (or pseudoautobiography ) refers to novels that employ first-person narrators who recount the events of their lives as if they actually happened. Well-known examples include David Copperfield (1850) by Charles Dickens and Salinger's The Catcher in the Rye (1951).
Some critics believe that all autobiographies are in some ways fictional. Patricia Meyer Spacks has observed that "people do make themselves up. . . . To read an autobiography is to encounter a self as an imaginative being" ( The Female Imagination , 1975).
For the distinction between a memoir and an autobiographical composition, see memoir as well as the examples and observations below.
From the Greek, "self" + "life" + "write"
Examples of Autobiographical Prose
- Imitating the Style of the Spectator , by Benjamin Franklin
- Langston Hughes on Harlem
- On the Street, by Emma Goldman
- Ritual in Maya Angelou's Caged Bird
- The Turbid Ebb and Flow of Misery, by Margaret Sanger
- Two Ways of Seeing a River, by Mark Twain
Examples and Observations of Autobiographical Compositions
- "An autobiography is an obituary in serial form with the last installment missing." (Quentin Crisp, The Naked Civil Servant , 1968)
- "Putting a life into words rescues it from confusion even when the words declare the omnipresence of confusion, since the art of declaring implies dominance." (Patricia Meyer Spacks, Imagining a Self: Autobiography and Novel in Eighteenth-Century England . Harvard University Press, 1976)
- The Opening Lines of Zora Neale Hurston's Autobiography - "Like the dead-seeming, cold rocks, I have memories within that came out of the material that went to make me. Time and place have had their say. "So you will have to know something about the time and place where I came from, in order that you may interpret the incidents and directions of my life. "I was born in a Negro town. I do not mean by that the black back-side of an average town. Eatonville, Florida, is, and was at the time of my birth, a pure Negro town--charter, mayor, council, town marshal and all. It was not the first Negro community in America, but it was the first to be incorporated, the first attempt at organized self-government on the part of Negroes in America. "Eatonville is what you might call hitting a straight lick with a crooked stick. The town was not in the original plan. It is a by-product of something else. . . ." (Zora Neale Hurston, Dust Tracks on a Road . J.B. Lippincott, 1942) - "There is a saying in the Black community that advises: 'If a person asks you where you're going, you tell him where you've been. That way you neither lie nor reveal your secrets.' Hurston had called herself the 'Queen of the Niggerati.' She also said, 'I like myself when I'm laughing.' Dust Tracks on a Road is written with royal humor and an imperious creativity. But then all creativity is imperious, and Zora Neale Hurston was certainly creative." (Maya Angelou, Foreword to Dust Tracks on a Road , rpt. HarperCollins, 1996)
- Autobiography and Truth "All autobiographies are lies. I do not mean unconscious, unintentional lies; I mean deliberate lies. No man is bad enough to tell the truth about himself during his lifetime, involving, as it must, the truth about his family and friends and colleagues. And no man is good enough to tell the truth in a document which he suppresses until there is nobody left alive to contradict him." (George Bernard Shaw, Sixteen Self Sketches , 1898)" " Autobiography is an unrivaled vehicle for telling the truth about other people." (attributed to Thomas Carlyle, Philip Guedalla, and others)
- Autobiography and Memoir - "An autobiography is the story of a life : the name implies that the writer will somehow attempt to capture all the essential elements of that life. A writer's autobiography, for example, is not expected to deal merely with the author's growth and career as a writer but also with the facts and emotions connected to family life, education, relationships, sexuality, travels, and inner struggles of all kinds. An autobiography is sometimes limited by dates (as in Under My Skin: Volume One of My Autobiography to 1949 by Doris Lessing), but not obviously by theme. "Memoir, on the other hand, is a story from a life . It makes no pretense of replicating a whole life." (Judith Barrington, Writing the Memoir: From Truth to Art . Eighth Mountain Press, 2002) - "Unlike autobiography , which moves in a dutiful line from birth to fame, memoir narrows the lens, focusing on a time in the writer's life that was unusually vivid, such as childhood or adolescence, or that was framed by war or travel or public service or some other special circumstance." (William Zinsser, "Introduction," Inventing the Truth: The Art and Craft of Memoir . Mariner Books, 1998)
- An "Epidemical Rage for Auto-Biography" "[I]f the populace of writers become thus querulous after fame (to which they have no pretensions) we shall expect to see an epidemical rage for auto-biography break out, more wide in its influence and more pernicious in its tendency than the strange madness of the Abderites, so accurately described by Lucian. London, like Abdera, will be peopled solely by 'men of genius'; and as the frosty season, the grand specific for such evils, is over, we tremble for the consequences. Symptoms of this dreadful malady (though somewhat less violent) have appeared amongst us before . . .." (Isaac D'Israeli, "Review of "The Memoirs of Percival Stockdale," 1809)|
- The Lighter Side of Autobiography - "The Confessions of St. Augustine are the first autobiography , and they have this to distinguish them from all other autobiographies, that they are addressed directly to God." (Arthur Symons, Figures of Several Centuries , 1916) - "I write fiction and I'm told it's autobiography , I write autobiography and I'm told it's fiction, so since I'm so dim and they're so smart, let them decide what it is or isn't." (Philip Roth, Deception , 1990) - "I'm writing an unauthorized autobiography ." (Steven Wright)
Pronunciation: o-toe-bi-OG-ra-fee
- 6 Revealing Autobiographies by African American Thinkers
- Biographies: The Stories of Humanity
- 5 Writers of the Harlem Renaissance
- 42 Must-Read Feminist Female Authors
- Zora Neale Hurston
- 35 Zora Neale Hurston Quotes
- How It Feels to Be Colored Me, by Zora Neale Hurston
- Point of View in Grammar and Composition
- What Is a Personal Essay (Personal Statement)?
- Harlem Renaissance Women
- 5 Leaders of the Harlem Renaissance
- Quotes From Women in Black History
- 4 Publications of the Harlem Renaissance
- Men of the Harlem Renaissance
- Five African American Women Writers
Become a Bestseller
Follow our 5-step publishing path.
Fundantals of Fiction & Story
Bring your story to life with a proven plan.
Market Your Book
Learn how to sell more copies.
Edit Your Book
Get professional editing support.
Author Advantage Accelerator Nonfiction
Grow your business, authority, and income.
Author Advantage Accelerator Fiction
Become a full-time fiction author.
Author Accelerator Elite
Take the fast-track to publishing success.
Take the Quiz
Let us pair you with the right fit.
Free Copy of Published.
Book title generator, nonfiction outline template, writing software quiz, book royalties calculator.
Learn how to write your book
Learn how to edit your book
Learn how to self-publish your book
Learn how to sell more books
Learn how to grow your business
Learn about self-help books
Learn about nonfiction writing
Learn about fiction writing
How to Get An ISBN Number
A Beginner’s Guide to Self-Publishing
How Much Do Self-Published Authors Make on Amazon?
Book Template: 9 Free Layouts
How to Write a Book in 12 Steps
The 15 Best Book Writing Software Tools
The Only (FREE) Autobiography Template You Need – 4 Simple Steps
POSTED ON Nov 22, 2023

Written by Shannon Clark
Are you looking for an autobiography template?
First things first.
What is your story? Not the shiny, air-brushed one you edit before posting on Instagram or the one you politely share during a writer’s chat on Zoom.
By your story, I mean the one with the cracks in it caused by childhood insecurities or the deep craters forged by unexpected collisions with life—the triumphs and tragedies that are forever etched into your DNA.
Yes, that story.
When you’re truly ready to write an autobiography, you’ll know it because you’ve come to a point in your life where the beauty of sharing your story has nothing to do with perfection. It’s knowing that despite the roller coaster ride that started at birth, you’ve found the courage to stay on it—sometimes holding on for dear life and other times riding with your hands up and screaming at the top of your lungs.
Get your autobiography template here:
Need A Nonfiction Book Outline?
You’ve lived thoroughly and learned to embrace who you’ve become in the process, scars and all.
This post will show you the format for writing an autobiography and the best way to package your story so you can provide the best reader experience possible.
This blog gives you a free autobiography template and more…
What is an autobiography.
The basic definition of an autobiography is that it’s a first-person account of your life. It differs from a memoir , which usually focuses on a single event or group of events that lead you to a discovery about yourself, your life, or some other revelation. An autobiography is a look at the total sum of your life from birth (early childhood) to the time of your book’s writing that highlights the key points that shaped who you’ve become.

Ready to start writing your autobiography? Let's get into it…
What is the format for an autobiography?
Just like any good story, every autobiography has a beginning, middle, and end. But before you begin filling in the sections, you want to come up with a theme for your book . Most people have too much life content to fit into one book. Selecting the parts that fit under the umbrella of a theme will make the book easier to follow.
When coming up with a theme, think about what you want the key takeaway to be for the reader. You don’t want to give them some boring slog through your life history. If you want them to feel something, your book needs direction. That’s where your theme takes the lead. By keeping it in the back of your mind while writing, you’ll give your readers a track to stay on. Otherwise, they may lose interest and stop reading.
Once you have your theme, right down the events in your life that are related to your book’s focus. You’ll plug these into the outline as you develop it.
Some examples of autobiography book themes are:
- Overcoming challenges
- Creating your own destiny
- The unbreakable bonds of family
- A faith journey
- Perseverance
Your theme can be whatever you want it to be, but keep your audience in mind when selecting one. Below you’ll find an autobiography template. It includes an outline with writing prompts in each section.
Whether you are an “outliner” (someone who outlines) or a “pantser” (someone who writes by the seat of their pants), the outline has enough structure and flexibility to make both writer types happy.
Autobiography Template: An Outline
I've laid out what a traditional autobiography might look like below. But to really help you get the most out of the blog post, I recommend downloading our nonfiction book outline to use alongside this guide.
1. Introduction
Before you share your life story, prepare your readers for what is to follow by introducing yourself and telling them what they can expect. You can cover some or all of the following:
- Why you are writing your autobiography?
- What do you hope the reader will take away from the experience?
- Any pertinent information that’s not covered in your book but that is needed for context.
2. The beginning – the early years
Since autobiographies are a condensed view of your life, you want to focus on the significant events that will move your story forward.
- Where do you want to begin your story?
- Where does your book’s theme first show up when you look back over your life? You want the opening of your book to have an impact, so choose something that will hook your readers and bring them into your world.
- How did your formative years influence how you viewed yourself? What we experience during our childhood can affect us for a lifetime. Consider how the early events of your life developed your character.
- Who influenced you the most during your childhood?
- What defining moments do you remember?
Where (on your timeline) and how you start your story is up to you. You want it to be something strong and significant to have the most impact on your reader. Here are the first few sentences of some autobiographies for inspiration .

“Some would say the McEntires are a very set-in-their-ways, stubborn, hardheaded bunch of people. But I think that hardheadedness is what got Daddy to where he was, Grandpap to where he was, and his father, Pap, to where he was. Some might say it wasn't all that far- but it was much further than where they started!”
– Not That Fancy: Simple Lessons on Living, Loving, Eating, and Dusting Off Your Boots by Reba McEntire
(Nostalgia / Specific Event)

“My grandmother Nanny and I were at the picture show. I hadn't reached two digits yet in age because I distinctly remember my feet couldn't touch the floor of the movie house. Nanny and I were still living in San Antonio, Texas. My mama and daddy had gone ahead to California, where Nanny and I would later wind up.” – This Time Together: Laughter and Reflection by Carol Burnett
(From Birth)

“ If you know my music, you almost certainly know me as Craig Morgan. But I was actually born Craig Morgan Greer. Craig Morgan came along many years later.” – God, Family, Country: A Memoir by Craig Morgan
- 31 Best Autobiographies
- 30 Celebrity Autobiographies
3. The middle- halfway between the early years and where you are today.
If you are using a timeline to divide your story, the period that you cover during the “middle” of your autobiography depends on how old you are at the writing of your book. If you are in your golden years, your midpoint might be in your 30s or 40s. For someone like Malala Yousafzai , who wrote her autobiography at age 15, her “middle” looked very different.
Whichever “middle” you choose consider the following:
- What are the defining moments during this time of your life?
- Did they change how you viewed yourself?
- Did they change the trajectory of what you initially thought you’d do with your life?
- Who had the most influence on your life during this time?
- What are some of the challenges you faced? How did you overcome them?
- Did your worldview change during this time? If so, in what ways?
If your “middle” doesn’t fit neatly into a timeline, consider grouping your autobiography into themed sections.
The autobiography Cash by Johnny Cash groups his story into sections based on places that had special meaning to him: Cinnamon Hill, The Road, Port Rickey, Bon Aqua, and The Road Again.
4. The end—wrap-up
The end of your autobiography is the climax. It’s what you’ve been leading your reader to since the first sentence of your book.
- Where are you in your life now? What have you learned? How has your journey impacted who you’ve become?
- How do you want the reader to feel when they read the last sentence of your book? Inspired? Hopeful? Full? Enlightened? Satisfied? All of the above?
- Is there any part of your life that feels unfinished or incomplete?
- Looking back over your life, what is the greatest lesson you learned?
- Don’t forget your audience, especially at the beginning of your book. You want to hook your readers early and bring them along for the ride.
- Write an eye-catching autobiography title for your book.
- Leave out the minutia. If it doesn’t move your story along, drop it.
- Tone matters. A good rule of thumb is to write your story like you were talking to a friend. Your story doesn’t have to be a monotone race to the finish line. Spice it up. Add some sparkle. Make sure your personality shines through.
- It’s always about the story. Buyers pick up your book to be entertained. Regardless of how serious your story is, it should be presented in a way that makes the reader want to keep turning the page.
- Every good story has a resolution. Good or bad, offer a resolution for each life conflict you introduce.
- As you share the final pieces of your story, use the end of your story to reflect on where you’ve been, what you’ve learned, and where you plan to go from there. Every relationship that ends can benefit from closure, and if the end of your story is not the end of your relationship with your reader, tell them where they can go to continue getting to know you.
Writing your autobiography is a courageous move, but who better to write your life story than you? If you have experiences that others will find interesting, share! You never know how your journey will impact someone else.
If you’re serious about getting your story published, Selfpublishing.com has a team of publishing experts who can walk you through the book development process.
FREE BOOK OUTLINE TEMPLATE
100% Customizable For Your Manuscript.
Related posts
Non-Fiction
Need Some Memorable Memoir Titles? Use These Tips
Business, Non-Fiction
How to Get More Patients With a Book & Brand
How to write a biography: 10 step guide + book template.
autobiography
What is autobiography definition, usage, and literary examples, autobiography definition.
An autobiography (awe-tow-bye-AWE-gruh-fee) is a self-written biography . The author writes about all or a portion of their own life to share their experience, frame it in a larger cultural or historical context, and/or inform and entertain the reader.
Autobiographies have been a popular literary genre for centuries. The first Western autobiography is attributed to Saint Augustine of Hippo for his 13-book work titled Confessions , written between 397 and 400 CE. Some autobiographies are a straightforward narrative that recollects a linear chain of events as they unfolded. The genre has expanded and evolved to include different approaches to the form.
The word autobiography comes from the Ancient Greek auto (“self”) + bios (“life”) + graphein (“to write”) = “a self-written life.” It is also known as autography .

The History of Autobiography
Scholars regard Augustine’s Confessions as the first Western autobiography. Other autobiographical works from antiquity include Jewish historian Flavius Josephus’s Vita (circa 99 CE) and Greek scholar Libanius’s Oration I (374 CE). Works of this kind were called apologias, which essentially means “in my defense.” Writers approached these works not as acts of self-documentation but as self-defense. They represented a way to explain and provide rationale for their life, work, and escapades. There was also less focus on their emotional lives.
The Book of Margery Kempe , written in 1438 by an English Christian mystic, is the earliest known autobiography in English. (Though it didn’t see full publication until the 20th century.) Other early English-language biographies of note include:
- Lord Herbert of Cherbury’s 1764 memoirs
- John Bunyan’s Grace Abounding to the Chief of Sinners in 1666
- Jarena Lee’s The Life and Religious Experience of Jarena Lee (the first autobiography of an African American woman)
Philosopher Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s Confessions was published in 1782. It paved the way for the more thoughtful, emotionally centered autobiographies seen today. Autobiography as a literary genre emerged a few years later, when British scholar William Taylor first used the term to describe a self-written biography. He did so disparagingly, suggesting the form was pedantic . In 1809, English Romantic poet Robert Southey used the term more seriously to describe self-written biographies.
Starting in the 20th century, more young people started writing autobiographies. Perhaps the most famous example is Anne Frank’s The Diary of a Young Girl , about her time hiding from the Nazis in an Amsterdam attic. The 21st century saw an increase in autobiographical essay collections and memoirs by younger celebrities, including:
- Anna Kendrick
- Mindy Kaling
- Gabourey Sidibe
- Mike Birbiglia
- Lena Dunham
- Chelsea Handler
Autobiographies are not immune to controversy. One notable scandal involved author James Frey’s A Million Little Pieces . Originally billed as a memoir, evidence later emerged that Frey invented key parts of the story. This example underscores how easily authors can cross over into autofiction—fictional autobiography—and how seriously readers take authors’ responsibility to accurately and honestly market their books.
Types of Autobiographies
There are a few different types of self-written works that qualify as autobiography.
Standard Autobiographies
In the most traditional form, authors recount their life or specific formative events from their life. This approach often utilizes a chronological format of events, but it doesn’t necessarily have to. An author’s approach might include a framing device such as flashbacks, in which they move from the present to the past as they remember their lives. For example, Broadway star Patti LuPone’s self-titled autobiography begins on the opening night of Gypsy in 2004 before moving back in time to LuPone’s childhood. An author could take a more stream-of-consciousness style, in which one memory links to another by a common theme. Irish writer Seán O’Casey narrates his six-volume Autobiographies in this manner
This is a type of autobiography that is narrower in scope and focus. It places greater emphasis on particular memories, thoughts, and feelings. A standard autobiography can certainly cover some of this same ground—most do—but the memoir is more interested in individual events or defined portions of the author’s life and the emotions and lessons behind them.
Henry David Thoreau is a notable memoirist. In Walden , he reflects on his time spent living in solitude in the woods of Massachusetts and what he learned about life and nature throughout this experience. Another example is The Year of Magical Thinking by Joan Didion, which relates the death of her husband and its impact on her life and work. Another is Wild by Cheryl Strayed, wherein Strayed remembers her time hiking the Pacific Crest Trail during a period of great change in her life.
Autofiction
The fictionalized autobiography, or autofiction, is another type of autobiography. The author presents their story not as fact but as fiction. This method gives them considerable space to take creative license with events and characters, thereby blurring the lines between reality and fiction. The overall goal is less about the author wanting to obscure facts and make things up and more a matter of taking another tactic to delve into their experiences in service of self-discovery. Taipei by Tao Lin is a work of autofiction. The central character, Paul, mirrors Lin’s own life and experiences, from the literary world of New York City to his ancestral roots in Taiwan.
Spiritual Autobiographies
These autobiographies center on the author’s religious or spiritual awakening and the subsequent journey their faith has taken them on. Common elements include struggles and doubt, a life-altering conversion, periods of regression, and sharing the “message.” These all act as endorsements of the author’s faith. Augustine’s Confessions , Paramahansa Yogananda’s Autobiography of a Yogi , and Augusten Burroughs’s Toil & Trouble: A Memoir are all spiritual autobiographies.
Autobiography vs. Biography
Both autobiographies and biographies are records of real lives, but there is one major distinction. A person other than the book’s subject writes a biography, while the subject themselves writes an autobiography. In this way, an autobiography is essentially a biography of the self. The biographer’s job is typically more involved, entailing detailed research into the life of the subject. The autobiographer, however, is usually not burdened by this because they lived through the events they write about. They may need only to confirm dates and stories to accurately relate the pertinent details.
The Function of Autobiography
An autobiography allows the author to tell the true story of their own life. This is the reason why autobiographies have always been written by famous people. History tends to remember notable individuals for just one significant contribution or event and, even then, the public’s perception of it may be inaccurate. Writing an autobiography allows the author to share the real story and put it into the larger context of their life and times.
Most readers pick up an autobiography expecting some degree of subjectivity from the author. After all, the events chronicled happened to the author, so the writing will of course have a biased perspective . There are advantages to this subjectivity, though. The reader gets the real story directly from the person who lived it, unvarnished by others’ opinions or erroneous historical data.
One way this subjectivity is problematic is that the author may not possess the ability to see the story they’re telling from other perspectives. For example, they may not acknowledge any hurt they caused others, dangerous behaviors they engaged in, or the “other side” of a controversial event in which there are equally valid opposing viewpoints and experiences. Any of these deficiencies can result in a somewhat skewed narrative.
Writers Known for Autobiography & Autobiography Books
- Maya Angelou, I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings , Gather Together in My Name
- Jung Chang, Wild Swans: Three Daughters of China
- Isak Dinesen, Out of Africa , Shadows on the Grass
- Carrie Fisher, Wishful Drinking , Shockaholic
- Anne Frank, The Diary of a Young Girl
- Ernest Hemingway, A Moveable Feast
- Karl Ove Knausgård, My Struggle
- Frank McCourt, Angela’s Ashes
- Anaïs Nin, The Diaries of Anaïs Nin
- Marcel Proust, Remembrance of Things Past
- Patti Smith, Just Kids , M Train
- Mark Twain, The Autobiography of Mark Twain
- Benjamin Franklin, The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin
- Malcolm X, The Autobiography of Malcolm X
- Agatha Christie, Agatha Christie: An Autobiography
- Nelson Mandela, Long Walk to Freedom
- Mahatma Gandhi, Gandhi: An Autobiography
Examples of Autobiographies
1. Maya Angelou, I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings
Angelou’s autobiography is the first installment in a seven-volume series chronicling the life of the legendary poet, teacher, actress, director, dancer, and civil rights activist. Given all those roles, it’s easy to see why Angelou’s life story makes for interesting reading.
This volume centers primarily on her early life in Stamps, Arkansas, and the devastating effects of a childhood rape. It also explores racism in the American South. It discuses the important role reading plays in helping young Maya deal with the sexual assault and pervasive prejudice in her environment.
2. Helen Keller, The Story of My Life
Keller’s autobiography details her first 20 years, starting with the childhood illness that caused her blindness and deafness. She discusses the obstacles she had to overcome and the life-changing relationship she shared with her teacher, Anne Sullivan, who helped her learn to read and write. Keller also documents her friendships with several famous figures of her day, including Alexander Graham Bell, John Greenleaf Whittier, Oliver Wendell Holmes, and First Lady Frances Cleveland.
3. Vinh Chung, Where the Wind Leads
Chung’s autobiography recalls the harrowing story of a Vietnamese refugee and his journey to make the American Dream his own. Born in South Vietnam, Chung comes of age in a changing political climate that eventually compels his family to flee the country. Their voyage takes them through the South China Sea, run-ins with pirates, resettlement in Arkansas, and Chung’s graduation from Harvard Medical School.
How to Write an Autobiography
Autobiography is a truly universal art form and is accessible to anyone, whether you're in high school or 100 years old. Exploring the process of writing an autobiography deserves an article in itself, but the process should include these steps:
- Determine your "why." What lessons do you want to impart via your story, and why are they worth sharing with a broader audience?
- Draft an autobiographical outline. It should include information about your upbringing, impactful moments throughout your life, stories of failure and success, and meaningful mentors.
- Begin with the easiest sections. Getting started is often the greatest hurdle, so begin by writing the chapters that feel most accessible or enjoyable.
- Write your first draft. Once you write the first chapters, it will feel easier to write the rest. Capitalize on your momentum and write a full draft.
- Step away. As with anything, stepping away from your work will help foster fresh perspectives when you return.
- Edit and re-write your draft. Your first draft will probably benefit from thorough revisions, as will your second draft, and maybe your third. Continue to edit and revise until it feels right.
- Ask for help. Bring in a trusted family member or friend or professional editor to help with final edits.
Further Resources on Autobiography
ThoughtCo. shares some important points to consider before writing an autobiography .
The Living Handbook of Narratology delves into the history of the autobiography .
MasterClass breaks autobiography writing down into eight basic steps .
Pen & the Pad looks at the advantages and disadvantages of the autobiography .
Lifehack has a list of 15 autobiographies everyone should read at least once .
Related Terms
- Frame Story
- Point of View
- Literary Terms
- Autobiography
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write Autobiography
I. What is Autobiography?
An autobiography is a self-written life story.
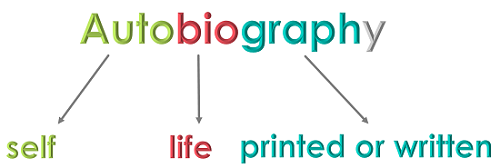
It is different from a biography , which is the life story of a person written by someone else. Some people may have their life story written by another person because they don’t believe they can write well, but they are still considered an author because they are providing the information. Reading autobiographies may be more interesting than biographies because you are reading the thoughts of the person instead of someone else’s interpretation.
II. Examples of Autobiography
One of the United States’ forefathers wrote prolifically (that means a lot!) about news, life, and common sense. His readings, quotes, and advice are still used today, and his face is on the $100 bill. Benjamin Franklin’s good advice is still used through his sayings, such as “We are all born ignorant, but one must work hard to remain stupid.” He’s also the one who penned the saying that’s seen all over many schools: “Tell me and I forget. Teach me and I remember. Involve me and I learn.” His autobiography is full of his adventures , philosophy about life, and his wisdom. His autobiography shows us how much he valued education through his anecdotes (stories) of his constant attempts to learn and improve himself. He also covers his many ideas on his inventions and his thoughts as he worked with others in helping the United States become free from England.
III. Types of Autobiography
There are many types of autobiographies. Authors must decide what purpose they have for writing about their lives, and then they can choose the format that would best tell their story. Most of these types all share common goals: helping themselves face an issue by writing it down, helping others overcome similar events, or simply telling their story.
a. Full autobiography (traditional):
This would be the complete life story, starting from birth through childhood, young adulthood, and up to the present time at which the book is being written. Authors might choose this if their whole lives were very different from others and could be considered interesting.
There are many types of memoirs – place, time, philosophic (their theory on life), occupational, etc. A memoir is a snapshot of a person’s life. It focuses on one specific part that stands out as a learning experience or worth sharing.
c. Psychological illness
People who have suffered mental illness of any kind find it therapeutic to write down their thoughts. Therapists are specialists who listen to people’s problems and help them feel better, but many people find writing down their story is also helpful.
d. Confession
Just as people share a psychological illness, people who have done something very wrong may find it helps to write down and share their story. Sharing the story may make one feel he or she is making amends (making things right), or perhaps hopes that others will learn and avoid the same mistake.
e. Spiritual
Spiritual and religious experiences are very personal . However, many people feel that it’s their duty and honor to share these stories. They may hope to pull others into their beliefs or simply improve others’ lives.
f. Overcoming adversity
Unfortunately, many people do not have happy, shining lives. Terrible events such as robberies, assaults, kidnappings, murders, horrific accidents, and life-threatening illnesses are common in some lives. Sharing the story can inspire others while also helping the person express deep emotions to heal.
IV. The Importance of Autobiography
Autobiographies are an important part of history. Being able to read the person’s own ideas and life stories is getting the first-person story versus the third-person (he-said/she-said) version. In journalism, reporters go to the source to get an accurate account of an event. The same is true when it comes to life stories. Reading the story from a second or third source will not be as reliable. The writer may be incorrectly explaining and describing the person’s life events.
Autobiographies are also important because they allow other people in similar circumstances realize that they are not alone. They can be inspiring for those who are facing problems in their lives. For the author, writing the autobiography allows them to heal as they express their feelings and opinions. Autobiographies are also an important part of history.
V. Examples of Autobiography in Literature
A popular autobiography that has lasted almost 100 years is that of Helen Keller. Her life story has been made into numerous movies and plays. Her teacher, Anne Sullivan, has also had her life story written and televised multiple times. Students today still read and learn about this young girl who went blind and deaf at 19 months of age, causing her to also lose her ability to learn to speak. Sullivan’s entrance into Helen’s life when the girl was seven was the turning point. She learned braille and soon became an activist for helping blind and deaf people across the nation. She died in 1968, but her autobiography is still helping others.
Even in the days before my teacher came, I used to feel along the square stiff boxwood hedges, and, guided by the sense of smell, would find the first violets and lilies. There, too, after a fit of temper, I went to find comfort and to hide my hot face in the cool leaves and grass. What joy it was to lose myself in that garden of flowers, to wander happily from spot to spot, until, coming suddenly upon a beautiful vine, I recognized it by its leaves and blossoms, and knew it was the vine which covered the tumble-down summer-house at the farther end of the garden! (Keller).
An autobiography that many middle and high school students read every year is “Night” by Elie Wiesel. His story is also a memoir, covering his teen years as he and his family went from the comfort of their own home to being forced into a Jewish ghetto with other families, before ending up in a Nazi prison camp. His book is not that long, but the details and description he uses brings to life the horrors of Hitler’s reign of terror in Germany during World War II. Students also read “The Diary of Anne Frank,” another type of autobiography that shows a young Jewish girl’s daily life while hiding from the Nazis to her eventual capture and death in a German camp. Both books are meant to remind us to not be indifferent to the world’s suffering and to not allow hate to take over.
“The people were saying, “The Red Army is advancing with giant strides…Hitler will not be able to harm us, even if he wants to…” Yes, we even doubted his resolve to exterminate us. Annihilate an entire people? Wipe out a population dispersed throughout so many nations? So many millions of people! By what means? In the middle of the twentieth century! And thus my elders concerned themselves with all manner of things—strategy, diplomacy, politics, and Zionism—but not with their own fate. Even Moishe the Beadle had fallen silent. He was weary of talking. He would drift through synagogue or through the streets, hunched over, eyes cast down, avoiding people’s gaze. In those days it was still possible to buy emigration certificates to Palestine. I had asked my father to sell everything, to liquidate everything, and to leave” (Wiesel 8).
VI. Examples of Autobiography in Pop Culture
One example of an autobiography that was a hit in the movie theaters is “American Sniper,” the story of Navy SEAL Chris Kyle. According to an article in the Dallas, Texas, magazine D, Kyle donated all the proceeds from the film to veterans and their families. He had a story to tell, and he used it to help others. His story is a memoir, focusing on a specific time period of his life when he was overseas in the military.
An autobiography by a young Olympian is “Grace, Gold and Glory: My Leap of Faith” by Gabrielle (Gabby) Douglas. She had a writer, Michelle Burford, help her in writing her autobiography. This is common for those who have a story to tell but may not have the words to express it well. Gabby was the darling of the 2012 Olympics, winning gold medals for the U.S. in gymnastics along with being the All-Around Gold Medal winner, the first African-American to do so. Many young athletes see her as an inspiration. Her story also became a television movie, “The Gabby Douglas Story.”
VII. Related Terms
The life story of one person written by another. The purpose may to be highlight an event or person in a way to help the public learn a lesson, feel inspired, or to realize that they are not alone in their circumstance. Biographies are also a way to share history. Historic and famous people may have their biographies written by many authors who research their lives years after they have died.
VIII. Conclusion
Autobiographies are a way for people to share stories that may educate, inform, persuade, or inspire others. Many people find writing their stories to be therapeutic, healing them beyond what any counseling might do or as a part of the counseling. Autobiographies are also a way to keep history alive by allowing people in the present learn about those who lived in the past. In the future, people can learn a lot about our present culture by reading autobiographies by people of today.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
What Is an Autobiography? Definition & 50+ Examples
Have you ever wondered what goes on behind the scenes in the lives of your favorite icons? Autobiographies offer us an intimate glimpse into the minds and hearts of those who’ve walked extraordinary paths.
These firsthand accounts of personal triumphs, challenges, and wisdom acquired along the way, illuminate the human experience in a profound and often surprising manner.
Join us as we journey through the pages of these literary treasures, unearthing the secrets that make them so compelling.
Table of Contents
Definition of Autobiography
An autobiography is a type of non-fiction writing that provides a firsthand account of a person’s life. The author recounts their own experiences, thoughts, emotions, and insights, often focusing on how these events have shaped their life. Typically structured around a chronological narrative, an autobiography provides a window into the author’s world
While autobiographies may be written for various reasons, including preserving personal history or sharing an inspiring story with others, they all aim to provide a genuine account of the author’s life.
Autobiographies can include stories of personal growth, challenges overcome, successes achieved, and important relationships. They often cover topics such as childhood, family life, education, career, personal struggles, and life-changing experiences.
It can portray both ordinary and extraordinary lives, allowing readers to connect with the author’s experiences and gain insights into their personal journeys.
Historical Overview
Autobiographies have a rich history, stemming from ancient times to the present day.
Early Examples
One of the earliest known examples of an autobiography is Augustine of Hippo’s “Confessions,” written in the 4th century AD. This seminal work is not only an important milestone in the development of the genre but also a deeply introspective and spiritual account of Augustine’s life and faith.
Born in 354 AD in Thagaste, Roman North Africa (modern-day Algeria), Augustine of Hippo was a Christian theologian and philosopher who became one of the most influential figures in the development of Western Christianity.
His “Confessions” were written between 397 and 400 AD, primarily as a testimony of his own personal conversion and growth in faith. The work is considered to be both a literary masterpiece and a foundational text in Christian theology.
Divided into thirteen books, the “Confessions” follows Augustine’s life chronologically, beginning with his childhood and progressing through his adolescence, early adulthood, and eventual conversion to Christianity.
The “Confessions” has been widely regarded as a groundbreaking work that laid the foundation for the autobiographical genre in Western literature. Its introspective and self-reflective style has influenced countless authors over the centuries, including Jean-Jacques Rousseau, John Henry Newman, and Thomas Merton.
Development Through the Centuries
By the early modern period, autobiographies became more widespread, with some of the best-known examples including:
- Saint Teresa of Avila’s “The Life of Saint Teresa of Avila by Herself” chronicling the 15th-century Spanish mystic and Carmelite nun’s spiritual relationship with God.
- “The True Travels, Adventures, and Observations of Captain John Smith” of John Smith in 16th-century, which recounts his experiences in the early days of the Virginia Colony and his encounters with Native Americans.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, the genre continued to develop, with unique works such as:
- Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s “Confessions”
- Mary Wollstonecraft’s “Letters Written During a Short Residence in Sweden “
- Frederick Douglass’ “Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave”
These important texts highlighted personal experiences, struggles, and social issues, shaping the autobiographical genre into what we recognize today.
In the 20th and 21st centuries, autobiographies span a wide range of themes and voices, including globally renowned works such as:
- Anne Frank’s “The Diary of a Young Girl”
- Nelson Mandela’s “Long Walk to Freedom”
These works demonstrate how the genre has evolved to encompass diverse perspectives and life experiences.
Elements of an Autobiography
An autobiography contains several key elements that help readers understand the life story of the author.
Chronological Order
Chronological order is a common structure used in autobiographies as it allows readers to follow the author’s life events in a linear sequence. This format provides a clear and organized presentation of the author’s experiences and life stages, making it easier for the reader to follow and understand.
One of the primary benefits of using a chronological structure in an autobiography is that it mirrors the natural progression of a person’s life.
As readers move through the narrative, they can witness the author’s growth, the various influences that shaped them, and the crucial turning points that led to significant changes in their lives. This progression allows for a comprehensive understanding of the author’s personal journey and evolution.
Moreover, a chronological order in autobiographies can help to contextualize the author’s experiences within broader historical and cultural events.
By situating their lives within a specific time frame, authors can provide readers with a deeper understanding of the social, political, and cultural forces that influenced their experiences and decisions. This context helps to illuminate the unique circumstances and challenges faced by the author, as well as the ways in which their lives intersected with larger societal trends and issues.
First-Person Perspective
Autobiographies are written in first-person perspective, using “I” statements, as a means of conveying the author’s personal journey through their own eyes. This technique allows the author to provide personal insights, emotions, and opinions, creating a stronger connection between the reader and the author’s personal experiences.
One of the primary benefits of the first-person perspective in autobiographies is the immediacy it lends to the narrative. When authors share their experiences and emotions directly, they draw readers into their world, allowing them to experience events as the author did. This immersive quality can evoke empathy, curiosity, and a sense of connection between the reader and the author.
Furthermore, the use of “I” statements in autobiographies facilitates an authentic portrayal of the author’s voice and personality.
As readers encounter the author’s unique perspective, they gain insight into the author’s individual character, including their values, beliefs, and aspirations. This authenticity can help to establish credibility and trust, as readers come to understand the author’s experiences on a more personal level.
The first-person perspective in autobiographies also enables authors to reflect on their experiences and draw connections between past events and their present understanding.
Self-Reflection
A key aspect of autobiographies is self-reflection, which involves the author’s analysis of their experiences and growth throughout their life. This self-examination can reveal profound insights and lessons learned, offering value and inspiration to readers.
Self-reflection in autobiographies allows authors to delve deeper into their personal experiences and emotions, exploring the impact of those events on their character and worldview.
By examining their past actions, decisions, and relationships, authors can uncover patterns and recurring themes, shedding light on the factors that have shaped their identity and personal growth. This introspective process adds depth and nuance to the narrative, making it more relatable and engaging for readers.
Self-reflection can also contribute to the development of broader themes and life lessons within an autobiography. As authors analyze their experiences and the consequences of their choices, they often identify universal truths or insights that can resonate with readers from diverse backgrounds.
These themes may include the importance of perseverance , the value of self-discovery, or the transformative power of forgiveness, among others. By sharing these lessons, authors can offer readers valuable wisdom and guidance for their own lives.
Intimate Details
Intimate details are important in an autobiography, as they shed light on the author’s personality and emotions. These personal aspects of an individual’s life can provide readers with a deeper understanding and empathy towards the author’s journey.
By sharing the intricacies of their daily lives, relationships, and innermost thoughts, authors can create a more vivid and relatable portrayal of their experiences, allowing readers to connect with their story on a more personal level.
One reason intimate details are significant in an autobiography is that they humanize the author. By providing glimpses into their private lives, authors reveal their vulnerabilities, fears, desires, and joys.
This openness can help break down barriers between the author and the reader, fostering a sense of connection and empathy. As readers recognize shared emotions and experiences, they are more likely to develop a deeper understanding of the author’s life and perspective.
Types of Autobiographies
Traditional autobiographies.
Traditional autobiographies aim to provide an in-depth and personal view of the author’s life experiences, emotions, and thoughts. They are often structured in a chronological order, starting from the author’s childhood and progressing through various stages of their life, ultimately reaching the present day.
The author usually shares anecdotes, lessons learned, and personal growth experiences, which can inspire and educate readers.
Examples of traditional autobiographies:
The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin by Benjamin Franklin (1791)
The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin is a classic piece of American literature written by one of the founding fathers of the United States, Benjamin Franklin.
It was composed in four distinct parts over a period of nearly two decades, beginning in 1771 and ending in 1790, shortly before Franklin’s death. The autobiography provides a unique insight into the life, character, and values of one of the most influential figures in American history.
The autobiography is divided into four parts, each with its own focus and purpose:
- Part One This section, written in 1771, covers Franklin’s early life, from his birth in 1706 to his early career as a printer in Philadelphia. He details his family background, childhood, and early experiences in the printing trade. He also includes some of his initial forays into writing and his early experiments with electricity.
- Part Two Written in 1784, this section focuses on Franklin’s famous list of thirteen virtues, which he devised as a means of achieving moral perfection. These virtues are temperance, silence, order, resolution, frugality, industry, sincerity, justice, moderation, cleanliness, tranquility, chastity, and humility. Franklin also discusses the Junto, a mutual improvement society he founded, and his efforts to establish public services and institutions in Philadelphia, such as the first public library and the American Philosophical Society.
- Part Three Penned in 1788, this part of the autobiography provides an account of Franklin’s role in the founding of the United States. It covers his involvement in the drafting of the Declaration of Independence and the U.S. Constitution, his diplomatic missions to France during the Revolutionary War, and his eventual return to America.
- Part Four In this brief, final section, written in 1790, Franklin reflects on his life and the writing of his autobiography. He expresses his hope that his story will inspire others and serve as a useful guide to future generations.
Long Walk to Freedom by Nelson Mandela (1994)
“Long Walk to Freedom” is an autobiography written by Nelson Mandela, a prominent anti-apartheid revolutionary, political leader, and philanthropist who served as the first black president of South Africa from 1994 to 1999. The book was published in 1994, the same year Mandela was elected president.
The autobiography chronicles Mandela’s life from his early childhood in a small rural village in the Eastern Cape of South Africa, through his education and political awakening, to his 27 years in prison, and ultimately to his release and the establishment of a new democratic South Africa.
The book provides a detailed account of Mandela’s early life, including his family background and his experiences growing up in a traditional African setting.
It also delves into his education and professional life, during which he became increasingly involved in politics and the struggle against apartheid, a racially discriminatory system that segregated and oppressed the non-white population of South Africa.
Born a Crime: Stories from a South African Childhood by Trevor Noah (2016)
“Born a Crime: Stories from a South African Childhood” is an autobiographical comedy book written by Trevor Noah, a South African comedian and the host of The Daily Show, an American satirical news program.
The book, published in 2016, shares Noah’s life story growing up during the last years of apartheid and the turbulent times that followed as South Africa transitioned into a post-apartheid society.
The title “Born a Crime” refers to Noah’s own birth, as he was born to a black South African mother and a white Swiss father. At the time, his parents’ interracial relationship was considered illegal under the apartheid-era racial classification system, making Noah’s very existence a crime.
The book is a collection of 18 personal essays that delve into various aspects of Noah’s life. It explores his childhood experiences, such as growing up in Soweto, a South African township, learning to navigate the complexities of racial identity, and the challenges he faced due to his mixed heritage.
It also delves into Noah’s relationship with his strong-willed, fiercely independent mother, Patricia Nombuyiselo Noah, who played a pivotal role in shaping his life.
A memoir is a sub-type of autobiography that focuses on a specific aspect or period of a person’s life. It is usually more introspective and character-driven than traditional autobiographies, allowing authors to explore their experiences, emotions, and relationships in greater depth.
Memoirs often emphasize personal growth, self-discovery, and the lessons learned from the author’s unique experiences. Some examples of well-known memoirs include:
The Glass Castle by Jeannette Walls (2005)
In “The Glass Castle,” Jeannette Walls recounts her extraordinary and often chaotic upbringing as the second oldest of four children in a highly unconventional family. Her parents, Rex and Rose Mary Walls, were unapologetically free-spirited, opting for a nomadic lifestyle that frequently left the family in poverty and uncertainty.
The memoir is an honest and poignant exploration of the impact of such a lifestyle on the family, touching on the importance of self-reliance, love, and forgiveness.
As they moved from town to town across America, the Walls family faced a plethora of challenges, including homelessness, hunger, and a lack of stability.
Throughout the memoir, Jeannette and her siblings develop an incredible resilience, learning to navigate their unpredictable world with resourcefulness and tenacity. They scavenge for food, devise ways to make money, and adapt to their ever-changing circumstances.
As the children grow older, they begin to question their parents’ choices and recognize the dysfunction within their family. Ultimately, they find the strength to break free and forge their paths in life.
Wild by Cheryl Strayed (2012)
In “Wild: From Lost to Found on the Pacific Crest Trail,” Cheryl Strayed takes readers on a breathtaking and emotional journey as she embarks on a solo hike across the rugged Pacific Crest Trail (PCT).
Span miles from the Mojave Desert in California to the Bridge of the Gods on the border of Oregon and Washington, Strayed’s trek was a quest for healing and redemption following the death of her mother and the subsequent collapse of her marriage.
Throughout the memoir, Strayed shares her raw, honest reflections on the pain and grief she experienced, as well as the life choices that led her to the PCT. With each step on the trail, she grapples with the harsh realities of her past and the emotional baggage she carries with her.
As Strayed confronts the physical challenges of the trail, such as blistered feet, grueling climbs, and encounters with wildlife, she also faces an emotional and spiritual transformation that ultimately leads to profound self-discovery and growth.
I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings by Maya Angelou (1969)
In “I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings,” Maya Angelou shares the powerful story of her childhood and adolescence, growing up in the racially segregated South during the 1930s and 1940s.
The narrative follows young Maya and her brother, Bailey, as they navigate life in Stamps, Arkansas, raised by their strong-willed and loving grandmother, Momma, and their disabled Uncle Willie.
Throughout the memoir, Angelou confronts the harsh realities of racial prejudice and the limitations imposed on her and her community due to their skin color. Her experiences with discrimination, sexual assault, and the subsequent muteness that resulted from her trauma shed light on the challenges faced by Black individuals in a deeply divided society.
As Angelou grows older, she begins to question the injustices around her and develops a deep appreciation for literature and language. Through reading works by Black authors and immersing herself in the world of poetry, she gradually finds her voice and the strength to overcome her past traumas.
Angelou’s love for the written word not only empowers her but also sparks her passion for activism and the fight for civil rights.
I’m Glad My Mom Died by Jennette McCurdy (2022)
“I’m Glad My Mom Died” is an autobiography written by Jennette McCurdy, published in 2022. The book offers a candid and honest account of the life and experiences of the former Nickelodeon star, who is best known for her roles in popular TV shows like “iCarly” and “Sam & Cat.”
In the autobiography, McCurdy delves into her tumultuous relationship with her mother, Debra, who passed away in 2013 after battling cancer. The title of the book, while provocative, reflects the complicated emotions that McCurdy experienced throughout her life, as her mother’s death ultimately allowed her to break free from the control and manipulation she had experienced growing up.
Throughout the book, McCurdy explores her upbringing and the ways in which her mother’s controlling nature impacted her mental health, self-esteem, and overall well-being. She shares her struggles with anorexia, which she developed at a young age as a result of her mother’s fixation on her appearance and weight.
Additionally, McCurdy delves into her experiences as a child actor and the immense pressure she faced to succeed in the entertainment industry.
Educated by Tara Westover (2018)
In “Educated: A Memoir,” Tara Westover recounts her harrowing and inspiring journey from a life of isolation and abuse in rural Idaho to the halls of Cambridge University, where she ultimately earned a Ph.D. Born to a strict and domineering father with a mistrust of formal education and government institutions, Westover grew up in a household where schooling was forbidden and paranoia reigned.
Despite these seemingly insurmountable obstacles, she embarked on a courageous path to self-education and personal liberation.
The memoir provides a vivid portrayal of Westover’s childhood, marked by dangerous work in her family’s junkyard, physical and emotional abuse from her father and brother, and a near-total absence of formal education.
With unwavering determination, she taught herself enough mathematics, grammar, and science to gain admission to Brigham Young University. Her pursuit of education exposed her to a world far beyond the confines of her family’s mountain home, leading her to question the beliefs and values she had been raised with.
Westover’s journey took her from Brigham Young University to Harvard and finally to Cambridge, where she earned a Ph.D. in history. Along the way, she faced the challenges of adjusting to unfamiliar social norms, reconciling her past with her newfound knowledge, and navigating the emotional turmoil of gradually breaking away from her family.
Psychological Illness
Autobiographies dealing with psychological illness delve into the challenges faced by individuals suffering from mental health disorders. These accounts offer a unique perspective on the daily struggles and triumphs of people dealing with such conditions, providing readers with valuable insights into the realities of living with mental illness.
By sharing their personal experiences, authors help to destigmatize mental health issues, raise awareness, and promote empathy and understanding. Some examples of autobiographies that focus on psychological illness include:
An Unquiet Mind: A Memoir of Moods and Madness by Kay Redfield Jamison
An Unquiet Mind is a deeply personal and powerful memoir by Kay Redfield Jamison, who is not only a renowned clinical psychologist specializing in mood disorders, but also someone who has personally experienced the tumultuous journey of living with bipolar disorder.
Through her candid narrative, Jamison provides a rare, first-hand account of the struggles, triumphs, and complexities of this mental illness.
Jamison shares her story from the early onset of her symptoms in adolescence to her eventual diagnosis and the long road to finding an effective treatment. As a medical professional, she offers a unique perspective on the disorder, blending her clinical knowledge with her own intimate experiences.
Readers are given an inside look at the emotional rollercoaster of mania and depression, as well as the challenges faced in her personal relationships and professional life.
Jamison’s memoir also delves into the stigma surrounding mental illness, and the difficulties she faced in accepting her diagnosis and seeking help. By openly discussing her struggles, she aims to foster understanding and empathy for those who are affected by bipolar disorder, as well as their friends, families, and healthcare providers.
Darkness Visible: A Memoir of Madness by William Styron (1989)
Darkness Visible is a powerful and deeply personal memoir by Pulitzer Prize-winning author William Styron, who chronicles his harrowing descent into the depths of clinical depression and his subsequent near-fatal suicide attempt.
Through this unflinching narrative, Styron sheds light on the often misunderstood and underestimated nature of depression, providing readers with an intimate understanding of the devastating effects it can have on an individual’s life.
In this poignant and raw account, Styron vividly details the insidious onset of his depression, the growing sense of despair and hopelessness that enveloped him, and his struggle to make sense of what was happening to him.
He also explores the various factors that may have contributed to his illness, including the loss of his mother, the stress of his literary career, and the side effects of medications he was taking.
Styron’s memoir serves as a powerful reminder of the importance of seeking help and support when grappling with mental illness. He recounts his journey through the mental health care system, his encounters with various professionals, and the eventual intervention of friends that ultimately saved his life.
The Center Cannot Hold: My Journey Through Madness by Elyn R. Saks (2007)
“The Center Cannot Hold: My Journey Through Madness” is a memoir written by Elyn R. Saks, a prominent legal scholar, professor, and mental health advocate. Published in 2007, the book offers an insightful and candid account of Saks’ life as she navigates her struggles with schizophrenia, a chronic and severe mental disorder characterized by disordered thoughts, hallucinations, and delusions.
The title of the memoir is inspired by the poem “The Second Coming” by W.B. Yeats, which contains the line “Things fall apart; the center cannot hold.” This line reflects Saks’ experience with her illness, as it often felt like her life was falling apart and her sense of self was slipping away.
Throughout the book, Saks shares her journey from the onset of her symptoms during her teenage years, to her time at Oxford University and Yale Law School, and her eventual career as a law professor at the University of Southern California.
She provides a firsthand account of her struggles with psychosis, hospitalizations, and the impact of her illness on her relationships, career, and sense of self.
It has been widely praised for its honest portrayal of schizophrenia and for helping to reduce the stigma associated with mental illness. The book offers a unique perspective into the mind of someone living with schizophrenia, and serves as a source of inspiration and hope for those who face similar challenges.
Confessional autobiographies are a form of literature where authors intimately share their personal experiences, including their mistakes, transgressions, and the consequences they faced as a result.
This type of writing often serves as a means for the author to achieve self-reflection, growth, and a sense of redemption. At the same time, it allows readers to empathize with the author’s journey and gain insights into the human condition.
Confessional autobiographies can be raw, honest, and sometimes shocking, but they often resonate deeply with readers due to their authenticity.
Examples of confessional autobiographies include:
The Autobiography of Malcolm X by Malcolm X and Alex Haley (1965)
The Autobiography of Malcolm X is a 1965 autobiography that recounts the life of Malcolm X, a prominent African American leader, human rights activist, and one of the most influential figures in the Civil Rights Movement in the United States.
The book was co-authored by journalist and writer Alex Haley, who conducted a series of interviews with Malcolm X over a two-year period before his assassination in 1965.
The book provides a detailed account of Malcolm X’s life, including his early years, criminal past, conversion to Islam, and rise as a prominent leader within the Nation of Islam. It chronicles his evolving political and philosophical beliefs, his eventual disillusionment with the Nation of Islam, and his conversion to Sunni Islam after a transformative pilgrimage to Mecca.
The autobiography also delves into Malcolm X’s international travels, encounters with various world leaders, and his efforts to build a global human rights movement.
The Autobiography of Malcolm X is an important work for several reasons:
- It provides a unique and personal insight into the life and thoughts of a highly influential figure in American history.
- It serves as a powerful account of the racial and social injustices faced by African Americans during the mid-20th century.
- It explores themes of personal transformation, redemption, and the power of education to change one’s life.
The book has been highly regarded since its publication, and it has had a significant impact on the understanding of Malcolm X’s life and work, as well as on the broader Civil Rights Movement.
A Heartbreaking Work of Staggering Genius by Dave Eggers (2000)
“A Heartbreaking Work of Staggering Genius” is a memoir by American author Dave Eggers, published in 2000. The book is a blend of autobiography, fiction, and metafiction, recounting Eggers’ experiences after the death of both his parents from cancer within a span of five weeks.
In the wake of their deaths, the then-21-year-old Eggers is left to care for his 8-year-old brother, Toph. The memoir follows their journey together as they navigate grief, responsibility, and the challenges of creating a new life.
The narrative is characterized by Eggers’ innovative and unconventional writing style. He employs self-awareness, humor, and irony to explore themes of loss, family, and the search for identity. The book’s metafictional elements often break the fourth wall, as Eggers directly addresses the reader and critiques his own writing.
Spiritual Autobiographies
Spiritual autobiographies are unique in that they delve deeply into an individual’s spiritual life, exploring their encounters with the divine, struggles with doubt, and moments of profound insight. They often document the author’s transformative experiences and the lessons they’ve learned as they grow spiritually.
Here are two examples of spiritual autobiographies, each of which illustrates a different aspect of spiritual growth:
The Seven Storey Mountain by Thomas Merton (1948)
“The Seven Storey Mountain” is an autobiography written by Thomas Merton, published in 1948. The book chronicles Merton’s life, spiritual journey, and eventual conversion to Roman Catholicism and entrance into the Trappist monastic order at the Abbey of Our Lady of Gethsemani in Kentucky.
The title is inspired by “The Dark Night of the Soul,” a poem by 16th-century Spanish mystic St. John of the Cross, which uses the metaphor of a seven storey mountain to describe the soul’s ascent to union with God.
In the book, Merton recounts his early life, including his childhood and education in France, England, and the United States, as well as the deaths of both of his parents. He details his search for meaning and purpose, which initially led him to a hedonistic lifestyle and pursuit of worldly pleasures.
Merton’s life took a turn when he started studying at Columbia University, where he encountered influential figures, such as the Catholic writer and professor Dan Walsh, who introduced him to the works of prominent Catholic thinkers and mystics.
As Merton delved deeper into Catholicism, he experienced a profound spiritual awakening and felt a strong calling to the monastic life. He eventually entered the Abbey of Gethsemani, where he found peace and a sense of belonging.
The Autobiography of a Yogi by Paramahansa Yogananda (1946)
“The Autobiography of a Yogi” is a spiritual classic written by Paramahansa Yogananda, an Indian yogi and guru who introduced millions of Westerners to the teachings of meditation and Kriya Yoga through his book.
First published in 1946, the autobiography is an account of Yogananda’s life, his search for enlightenment, and his encounters with various saints and spiritual masters in India and beyond.
The book begins with Yogananda’s childhood in India, where he was born in 1893 as Mukunda Lal Ghosh. Early in life, he was drawn to spirituality and had mystical experiences that fueled his quest for spiritual truth.
As he grew older, he met his guru, Swami Sri Yukteswar Giri, who guided him in the practice of Kriya Yoga—a sacred meditation technique that accelerates spiritual growth by cleansing the body and mind of negative energy.
In the book, Yogananda recounts the teachings and wisdom he received from various spiritual figures such as his guru, Sri Yukteswar; the saintly Mahavatar Babaji, who is said to have revived Kriya Yoga; and Lahiri Mahasaya, who was a direct disciple of Babaji.
Yogananda also shares stories of other saints and spiritually advanced individuals he encountered, both in India and during his travels to the West.
Overcoming Adversities
Autobiographies centered around overcoming adversities provide readers with inspirational and motivational stories of individuals who have faced significant challenges in their lives. These memoirs often emphasize the themes of resilience, personal growth, and transformation as the authors share their personal journeys of overcoming various obstacles.
A Man Named Dave by Dave Pelzer (1999)
“A Man Named Dave: A Story of Triumph and Forgiveness” is a memoir written by Dave Pelzer, published in 1999. It is the third and final installment in his autobiographical trilogy, following “A Child Called ‘It'” (1995) and “The Lost Boy” (1997).
The series chronicles the author’s journey through a horrifically abusive childhood, his time in foster care, and ultimately his path to healing, redemption, and forgiveness.
“A Man Named Dave” picks up where “The Lost Boy” leaves off, as Dave Pelzer enters adulthood. The memoir details his life in the U.S. Air Force, his search for love, his struggles with trust and relationship issues, and his efforts to break the cycle of abuse that plagued his upbringing.
The book also delves into Dave’s attempts to reconcile with his abusive mother and the importance of forgiveness in the healing process.
Throughout the memoir, Dave shares his experiences and insights, highlighting the power of resilience, perseverance, and self-discovery. The book serves as an inspiration for those who have faced adversity and a reminder that forgiveness and personal growth are essential for healing from trauma.
The Pursuit of Happyness by Chris Gardner
“The Pursuit of Happyness” is a memoir written by Chris Gardner, published in 2006. The book tells the inspiring story of Gardner’s journey from homelessness and severe financial struggles to becoming a successful stockbroker and entrepreneur.
The memoir highlights the importance of determination, resilience, and the pursuit of happiness amidst life’s adversities.
In the book, Chris Gardner recounts his difficult childhood, marked by poverty, domestic violence, and sexual abuse. As an adult, Gardner finds himself struggling to provide for his son as a single father while also dealing with homelessness. Despite these challenges, he refuses to give up and remains determined to secure a better life for himself and his son.
Gardner’s journey takes a turn for the better when he secures an unpaid internship at the brokerage firm Dean Witter Reynolds. He faces numerous obstacles, including balancing his demanding work with caring for his son, finding shelter, and meeting their basic needs.
However, his hard work and perseverance eventually pay off, as he becomes a full-time employee and later starts his own brokerage firm, Gardner Rich & Co.
The book was adapted into a critically acclaimed film of the same name in 2006, starring Will Smith as Chris Gardner and Jaden Smith as his son. The film brought widespread attention to Gardner’s story, inspiring and motivating many people around the world.
Famous Examples
The world of autobiographies offers a plethora of captivating stories from various walks of life. In this section, we explore famous examples from historical figures, political figures, literary figures, and celebrities.
Historical Figures
Autobiographies of historical figures provide a glimpse into their personal lives and the events that shaped their legacies. Some standout examples include:
- The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass by Frederick Douglass
- The Story of My Life by Helen Keller
- My Experiments with Truth by Mahatma Gandhi
- Up From Slavery by Booker T. Washington
- My Life by Golda Meir
Political Figures
Politicians often share their experiences, challenges, and accomplishments through autobiographies, offering a look into their minds and ideologies. Noteworthy examples are:
- The Downing Street Years by Margaret Thatcher
- The Audacity of Hope: Thoughts on Reclaiming the American Dream by Barack Obama
- Hard Choices by Hillary Rodham Clinton
- My Life by Bill Clinton
- The Courage to Act: A Memoir of a Crisis and Its Aftermath by Ben S. Bernanke
Literary Figures
As masters of words, literary figures have created autobiographies filled with compelling insights and vivid details. Some distinguished examples include:
- The Confessions of Jean-Jacques Rousseau by Jean-Jacques Rousseau
- Surprised by Joy by C.S. Lewis
- Black Boy by Richard Wright
- Speak, Memory by Vladimir Nabokov
- The Autobiography of Mark Twain by Mark Twain (Samuel Langhorne Clemens)
- A Moveable Feast by Ernest Hemingway
- Out of Africa by Isak Dinesen (Karen Blixen)
- Hunger: A Memoir of (My) Body by Roxane Gay
Celebrities
Autobiographies of celebrities offer a unique perspective on fame, art, and the weight of societal expectations. Some popular examples are:
- Bossypants by Tina Fey
- Open by Andre Agassi
- Yes Please by Amy Poehler
- My Life So Far by Jane Fonda
- Is Everyone Hanging Out Without Me (And Other Concerns) by Mindy Kaling
- The Last Black Unicorn by Tiffany Haddish
- The Princess Diarist by Carrie Fisher
- Scar Tissue by Anthony Kiedis and Larry Sloman
- Paddle Your Own Canoe: One Man’s Fundamentals for Delicious Living by Nick Offerman
- Total Recall: My Unbelievably True Life Story by Arnold Schwarzenegger
- Me by Elton John
Purpose and Impact
The autobiography as a literary form has several purposes and impacts on both the author and the reader. Some of these purposes and impacts include self-reflection, sharing personal experiences, and influencing society and culture.
One of the primary purposes of writing an autobiography is self-reflection. Through the process of narrating their own lives, authors can reflect on their experiences and emotions, gaining insight into their personal development and growth. This self-reflection can lead to both greater self-awareness and ultimately, self-improvement.
Sharing Personal Experience
Another important aspect of autobiographies is the sharing of personal experiences. The authors use the written word as a means to share their unique perspectives, triumphs, and difficulties with a wider audience.
These personal narratives can offer valuable lessons and insights to readers, allowing them to empathize with the author’s experiences and potentially apply these insights to their own lives.
Influencing Society and Culture
Autobiographies can also have a profound impact on society and culture. By sharing their personal stories, authors can spark change, raise awareness of certain issues, or challenge societal norms and beliefs.
This influence on society and culture allows autobiographies to have a lasting impact beyond the individual lives depicted within their pages.
Challenges and Criticisms
Reliability.
One challenge often faced by autobiographies is the issue of reliability. Since the author is the subject of the story, there may be a tendency to portray themselves in a more favorable light or to omit certain details that could be perceived as negative.
For example, in the autobiography “The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin,” Franklin may have omitted certain aspects of his life to maintain a positive public image.
Another challenge faced by autobiographies is the concept of truth. Autobiographical narratives can sometimes blur the lines between fact and fiction, making it difficult for readers to discern the accuracy of the story. A notable example of this is James Frey’s “A Million Little Pieces,” which was later revealed to contain fabricated information.
Writing Your Own Autobiography
Writing an autobiography can be a rewarding and insightful experience, capturing your life’s journey and creating a record for future generations.
Finding Your Focus
Before you begin writing, it’s essential to identify the defining moments and themes in your life that you want to highlight. Reflect on your experiences and identify the most significant events that shaped who you are today.
Creating an Outline
An outline will provide structure to your autobiography, making it easier to navigate through your life’s chronology. Organize your outline by dividing it into sections such as childhood, adolescence, and adulthood, or by thematic categories specific to your life. This will help you present your story in a logical and coherent manner.
Developing Your Voice
Your voice as an autobiographer is essential, as it will set the tone and atmosphere of your narrative. Strive for a confident, knowledgeable, and neutral tone that authentically represents your experiences.
Revising and Editing
Revise and edit your autobiography carefully, ensuring that your writing is clear, concise, and engaging. This process not only includes checking for grammatical errors and factual inaccuracies but also enhancing the narrative flow and readability of your story.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can i write an autobiography about someone else.
If you are writing about someone else’s life, the work would be considered a biography rather than an autobiography. A biography is a narrative account of someone’s life written by someone other than the subject.
To write a biography, you’ll need to conduct thorough research, including interviews with the subject (if possible), their friends and family, and any relevant documents, such as letters, diaries, or published works.
Like an autobiography, a biography should be engaging and well-structured, offering readers insight into the subject’s life and experiences.
Can I collaborate with someone to write my autobiography?
Yes, collaborating with another writer or a professional ghostwriter is a common approach to writing an autobiography.
This process typically involves the subject sharing their life story through a series of interviews, conversations, or written correspondence, which the collaborator then uses as the basis for crafting the narrative.
Collaborating with a skilled writer can help ensure that your autobiography is well-structured, engaging, and professionally written, while still maintaining your personal voice and perspective.
Are there any legal or ethical considerations when writing an autobiography?
When writing an autobiography, it’s important to be aware of potential legal and ethical considerations, such as privacy and defamation.
Sharing personal information about others, especially if it could potentially harm their reputation or violate their privacy, can lead to legal issues. To avoid potential problems, it’s wise to:
– Seek permission from individuals whose stories you plan to include, especially if they involve sensitive or private information. – Use discretion when discussing the lives and experiences of others, considering the potential impact on their lives and relationships. – Ensure that your accounts of events and experiences are truthful and accurate, avoiding exaggeration or fabrication that could be construed as defamation.
Being mindful of these considerations will help you write a responsible and respectful autobiography that shares your story while minimizing potential risks.
Autobiographies provide a captivating glimpse into the lives of their authors, offering readers an intimate and authentic account of personal experiences, growth, and challenges.
From historical figures to everyday people, these self-written narratives reveal the human spirit’s resilience and the transformative power of personal reflection. By exploring the rich world of autobiographies, we can broaden our understanding of the diverse tapestry of human experiences, ultimately deepening our empathy and connection with others.
Whether you’re an aspiring writer or a curious reader, delving into the realm of autobiographies promises an enriching and enlightening journey.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
As you found this post useful...
Share it on social media!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?


5 Key Differences between Autobiography and Biography [with Examples]
Last Updated on July 20, 2022 by Dr Sharon Baisil MD
Introduction
Many people define autobiography as a story about themselves, written by themselves. But what about biography? Is that a story about someone, written by someone who is not themselves? And if not, how do these two categories differ? This article will unveil the answers to these questions and give you some examples to help you understand the key differences. So scroll on to read more about the different types of biography!
What is an Autobiography?
An autobiography is a book that a person writes about their own life. As a result, an autobiography encompasses all the features of biography but is written or narrated by the author himself. They may compose on their own or outsource the composition to ghostwriters.
The narrator’s character sketch, as well as information about his birthplace and upbringing, education, employment, life difficulties, and accomplishments, are described in the autobiography. Events from his childhood, adolescence, and adulthood may all be included.
What is a Biography?
An in-depth account of a person’s life produced or written by another person is a biography, also known as a “bio.” It provides detailed information about their birthplace, educational history, employment, connections, and death. It looks at the highs and lows of a person’s life, analyzes their entire personality, and reveals the subject’s secrets.
It’s when another person puts words together to replicate a particular person’s life. To captivate the readers in the tale, the author collects all of the information on the topic and presents it in a relevant and fascinating biography.
5 Key Differences Between an Autobiography and Biography
In the following points, I go into detail about the difference between biography and autobiography:
The distinction between an autobiography and a biography is who writes the book. The person the book is about always writes their autobiography. Other than the book’s subject is almost always the author of a biography.
For instance, famous people who have already lived a long life span can write life stories that are sometimes known as biographies, autobiographical novels, and memoirs.
The individual discussed in the story writes their autobiography. On the other hand, biographies may be written by anybody and about anybody, and Biographies may offer less realistic portrayals of a person’s personal experiences, explaining this.
Narrative Voice/Point of View
The narrative voice is another aspect that distinguishes biography from autobiography writing. First-person stories (using I and me) are used in autobiography writings. Third-person narratives are used to write biographies, and this is a much less intimate third-person narrative.
The first person point of view (I, me, my) gives the experience and thoughts of one person or an entity in a certain situation.
In the third-person point of view you have “he” was born on Tuesday 30th September 1948 in Liverpool he has been married three times but divorced twice his first wife died after giving birth to their son by her death Robert suffered a mental breakdown he moved into the house with his father who later committed suicide.
Level of Objectivity
In comparison to an autobiography, a biography is more objective. Biography writers normally investigate data via a journalistic study effort that may include investigating archives of occurrences and speaking with the book’s subject and others.
Rather than including input from other sources, an autobiography writer usually bases the content on their recollections of events. Biographies are written to introduce and educate the reader about the individual, whereas autobiographies are authored to express, through words, the narrator’s life experiences and accomplishments.
Unauthorized vs. Authorized
The book is written with the collaboration and permission of the person it refers to if that person is authorized. If not, it is written without their permission. An autobiography is always authorized, even if it is unauthorized.
There is no rule against self-authored autobiographies. But, when a writer creates a biography about someone else, the situation becomes more complicated. Autobiographies, on the other hand, need no permission to be written!
Timeline: Both forms of writing are most commonly written in chronological order, and this means that they write events from birth to death or the present day.
Purpose: although different people may write memoirs and biographies, both share the same purpose: telling a story about an individual’s life and experiences.
Kind of Information
Biographies give readers a different perspective since they contain information obtained from many sources over a long period. On the other hand, autobiographies are authored by the individual himself, and the author portrays events and his philosophy, giving readers an overall restricted and biased viewpoint.
Some Famous Examples of Autobiographies & Biographies for Better Understanding
Biography and autobiography are the most basic non-fiction genres. A biography is a non-fiction account of the life of an individual or group, while an autobiography is similar but focuses on telling events in a person’s lifetime. Both can write accurate stories about their subjects without bias: biographer David McCullough said he wanted his book “1776” to tell “the story as it happened.”
The book is not precisely the same as an autobiography, even though it is written by the individual. Memoirs, unlike autobiographies, focus on a specific incident or aspect of a person’s life rather than the whole narrative. The tone of a memoir is usually informal and emotional.
Autobiography Examples
Our Anne Frank Reading Comprehension, ideal for students interested in autobiographical writing, will introduce them to this form of writing by focusing on one of the most well-known examples .
I am Malala
Malala Yousafzai tells the narrative of her remarkable life in I Am Malala : The Girl Who Stood Up for Education and Was Shot by the Taliban. At a very early age, she was an outspoken supporter of education as a youngster in Pakistan. Consequently, she was shot in the head by Taliban members when she was 15 years old. She spoke about her experiences at the UN after recovering from her trauma and returning to school.
Many autobiographies worth mentioning include Helen Keller’s “The Story of My Life,” Jawaharlal Nehru’s “My Autobiography,” Anne Frank’s “Diary of a Young Girl,” and Winston Churchill’s “Memoirs of the Second World War.” P. is an actor born in Australia and moved to England in the early 2000s. J. is the final letter in the alphabet. Abdul Kalam, among others, is mentioned.
Biography Examples
In his biography of Steve Jobs , journalist and author Walter Isaacson tell one of the most important persons in the technology business. Isaacson spent over two years researching Jobs’ life and spoke with more than 100 individuals who knew him to tell this tale. The author has narrated the story of Jobs’ life in biography form by piecing together accounts from those who lived, loved, worked with, competed with, and were influenced by him.
And other famous biographies include Florence Nightingale, Snow White, Mary Mackillop, and more.
Memoir Example
Born a crime.
In Born a Crime , Trevor Noah discusses another aspect of his life as a stand-up comedian and host of The Daily Show. Noah’s early years as a multiracial kid in South Africa during apartheid are the subject of this memoir, which he wrote with his white father and black mother. Noah’s existence was unlawful because interracial relationships were prohibited in his country. This book gives fresh insights into the author’s upbringing in difficult times under extraordinary circumstances and is written in a light storytelling style that is both touching and funny.
Final Words
All autobiographies, biographies, and memoirs accomplish one thing: they tell a person’s non-fictional life story. Each, however, is distinctive in its way, as you can see.
Most Read Articles in 2023:

Hi, I am a doctor by profession, but I love writing and publishing ebooks. I have self-published 3 ebooks which have sold over 100,000 copies. I am featured in Healthline, Entrepreneur, and in the Massachusetts Institute of Technology blog.
Whether you’re a busy professional or an aspiring author with a day job, there’s no time like now to start publishing your ebook! If you are new to this world or if you are seeking help because your book isn’t selling as well as it should be – don’t worry! You can find here resources, tips, and tricks on what works best and what doesn’t work at all.
In this blog, I will help you to pick up the right tools and resources to make your ebook a best seller.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
How To Write An Autobiography
Autobiography Examples

Top Autobiography Examples & Samples For Your Help
Published on: Sep 10, 2021
Last updated on: Feb 12, 2024

People also read
How to Write an Autobiography - A Step-by-Step Guide
How To Write A Memoir - A Beginner's Guide
Autobiography vs. Biography - Learn the Differences
Autobiography Format - Forms and Elements
6 Types of Autobiography and their Comparison
Share this article
An autobiography is a story of a person's life written down or told. They are interesting to read, but they can be even more interesting to write.
An autobiography is different from a biography. A biography is someone else's story about a person's life. But, an autobiography is the person's own story about their life.
This may make autobiographies more interesting to read than biographies. Also, they give the thoughts and feelings of the person rather than someone else's interpretation.
There are many different stories in the world. Uniquely telling your story is not easy. You need to describe what is happening to make the reader feel like they are right there with you.
In this blog, you will learn about some amazing examples of autobiographies. So, start reading now.
Your first order with us is FREE!

On This Page On This Page -->
Autobiography Examples For Students
An autobiography is the story of someone's life written by them. They might write about their hardships or success. Here are some examples of autobiographies that might inspire you to write your own.
Short Autobiography Examples
This is a good example of a creative and interesting autobiography to read. It will teach you how to write your own great autobiography.
Autobiography Examples For Class 6
Autobiography essays are not easy to write. They are different from other essays because they tell the story of a person's life experiences. Every person has a lot of interesting experiences, so it can be hard to choose which ones to write about.
For your help, we compiled an example that you can use for your help and make your writing process easy.
Autobiography Examples For Grade 7
Only you know yourself best. Writing an autobiography is a great way to share your life with others. Everyone has a story to tell, and writing an autobiography is one way to leave your mark on history.
Here is an example that gives you a better idea of sharing your life story with others.
Autobiography Examples For College Students
An autobiography is a text that tells your life story. It can be in the form of a memoir , which is more informal or more formal. Autobiographies can be written for different reasons:
- To introduce yourself to the world.
- To get into a program at school, for a job, volunteering, etc.
You can find more ideas for an autobiography from this example.
Note: As a college student, you might encounter confusion distinguishing between an autobiography and a statement of purpose . While both involve personal narratives, autobiographies provide a comprehensive life story, while statements of purpose focus on specific goals and qualifications for academic or professional opportunities. Understanding their distinct purposes and structures can help streamline your application processes effectively.
Autobiography Examples For High School Students
An autobiography is a self-written biography that someone writes about themselves. They might write about all of their life or just some parts. They do this to share their experiences, put them in a larger cultural or historical context, and entertain the reader.
Take a look at the below example and create a well-written one without any mistakes.
Spiritual Autobiography Examples
A spiritual autobiography is your life story. In it, you write about how God has been present in your life. This includes your journey in and out of organized religion and everything spiritual.
Writing your spiritual autobiography is a chance for you to identify specific experiences with God. You will then reflect on how those experiences have impacted you.
Below is an example for your ease.
Autobiography Examples in Literature
An autobiography is a book written by somebody about their own life. It tells the story of the authorâs life, accomplishments, things they have done, etc.
The following is an example that can help you better understand how to write an autobiography.
Cultural Autobiography Examples
A cultural autobiography is more than just telling your life story. Your cultural identity reveals your beliefs and ideas about culture. It also shows how culture affects different cultural groups that make up who you are.
You may want to write a cultural autobiography better to understand yourself and your culture's role in your life. It is important to be aware of your own cultural identity in a multicultural world and be open to other cultures.
An example of a perfect cultural autobiography is below for your help.
Educational Autobiography Examples
The educational autobiography is a way to tell your life story. This type of autobiography includes what you did in school and how it affected other parts of your life.
Take a look at this example to see how to write a good educational autobiography.
Social Class Autobiography Examples
In most sociology classes, students are assigned to write a socio-autobiography. This assignment helps them understand that the subject is relevant to their daily lives. Your interactions with society have a big impact on who you become as a person.
Writing your social class autobiography is a great way to show people how you fit into society. The following example will show what kind of social autobiography looks like.
Autobiography Examples For Kids
Children are often encouraged to write an autobiography, but few people recognize the importance of this task. Everyone has something special from their childhood that they should remember and reflect on. Writing about your life is a good way to do this.
There are many different ways to write an autobiography. If you are writing about yourself, it is best to start by writing about your early life and work experience.
You can also mention your school experiences. After that, you can write about other topics that may be of interest to readers, like your hobbies or interests.
Here is an example that will help in starting an autobiography.
We all have the opportunity to write our own story, but it doesn't always come easy. If writing about yourself seems difficult, then follow the examples mentioned above.
However, if you want a professional writer to write it for you, just say ' write an essay for me ' and consult a professional at CollegeEssay.org .
We have expert writers who will help you write an autobiography, personal narrative, college essay, and any academic assignment.
AI essay writing tools are also readily available to provide you with additional assistance and support.
Nova A. (Literature, Marketing)
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A memoir is a type of autobiography that focuses on a particular period in the author's life rather than their whole life. The strict definition of autobiography is a first-person account of its author's entire life. A memoir does not document the memoirist's full life story but rather a selected era or a specific multi-era journey within ...
Order your sections (from medium to high interest) Order the ideas in each section (from medium to high interest) Write three questions to answer in each section. Choose a starter sentence. Complete a title template. Write each section of your by completing the starter sentence and answering all three questions.
6. Living for Change: An Autobiography by Grace Lee Boggs (1998) We listed the dual biography of Grace Lee Boggs and her husband James Boggs on our best biographies list, but even if you've read ...
This presidential biography is an example of a biography with a living subject. ... Examples & Essays; Non-Fiction as Literary Form: Definition and Examples; Literary Device Types, Use & Examples;
One of the best-known autobiographies, The Diary of a Young Girl, is an excellent example of a journal-style layout. Featuring the story of a young girl who is hiding during the Holocaust, aspiring writers will find inspiration in Frank's raw emotions and candor. 2. Autobiography of a Yogi by Paramahansa Yogananda.
There are six types of autobiographies: Autobiography: A personal account that a person writes himself/herself. Memoir: An account of one's memory. Reflective Essay: One's thoughts about something. Confession: An account of one's wrong or right doings. Monologue: An address of one's thoughts to some audience or interlocuters.
The emergence of autobiography. There are but few and scattered examples of autobiographical literature in antiquity and the Middle Ages. In the 2nd century bce the Chinese classical historian Sima Qian included a brief account of himself in the Shiji ("Historical Records"). It may be stretching a point to include, from the 1st century bce, the letters of Cicero (or, in the early Christian ...
Step 4: Write with Detail and Emotion. An important aspect of how to write an autobiography for college is appealing to emotion. As you delve into each body paragraph, share your story with vivid details. Use descriptive language to bring your experiences to life for the reader.
A personal perspective: An autobiography is written from the author's unique point of view. A strong conclusion: The ending of the book should reflect on the author's current state or outlook. Famous Autobiography Examples. Now that you know what an autobiography is, let's look at some famous autobiography examples.
The term fictional autobiography (or pseudoautobiography) refers to novels that employ first-person narrators who recount the events of their lives as if they actually happened. Well-known examples include David Copperfield (1850) by Charles Dickens and Salinger's The Catcher in the Rye (1951). Some critics believe that all autobiographies are ...
The autobiography Cash by Johnny Cash groups his story into sections based on places that had special meaning to him: Cinnamon Hill, The Road, Port Rickey, Bon Aqua, and The Road Again. 4. The end—wrap-up. The end of your autobiography is the climax. It's what you've been leading your reader to since the first sentence of your book.
Autobiography Definition. An autobiography (awe-tow-bye-AWE-gruh-fee) is a self-written biography. The author writes about all or a portion of their own life to share their experience, frame it in a larger cultural or historical context, and/or inform and entertain the reader. Autobiographies have been a popular literary genre for centuries.
Examples of Autobiography in Pop Culture Example 1. One example of an autobiography that was a hit in the movie theaters is "American Sniper," the story of Navy SEAL Chris Kyle. According to an article in the Dallas, Texas, magazine D, Kyle donated all the proceeds from the film to veterans and their families. He had a story to tell, and he ...
An autobiography is a type of non-fiction writing that provides a firsthand account of a person's life. The author recounts their own experiences, thoughts, emotions, and insights, often focusing on how these events have shaped their life. Typically structured around a chronological narrative, an autobiography provides a window into the ...
autobiography, Biography of oneself narrated by oneself. Little autobiographical literature exists from antiquity and the Middle Ages; with a handful of exceptions, the form begins to appear only in the 15th century. Autobiographical works take many forms, from intimate writings made during life that are not necessarily intended for publication ...
Spiritual autobiography. Spiritual autobiography is an account of an author's struggle or journey towards God, followed by conversion a religious conversion, often interrupted by moments of regression. The author re-frames their life as a demonstration of divine intention through encounters with the Divine. The earliest example of a spiritual ...
4.1 Map out your whole life. 4.2 Creating your narrative. 5 Autobiographical Essay Templates. 6 Creating and publishing your autobiography. 6.1 Edit your information first. 6.2 Publishing your autobiography. Fortunately, there are plenty of innovative and well-thought-out autobiography samples that are available.
An autobiography is a kind of literary nonfiction, which means it is a factual story that features real people and events. It also has features like plot, character, and setting that are common in ...
Memoir - This autobiography talks about certain themes or moments in your life such as history, religion, philosophy, sexuality, etc. Script or Drama - This format uses stage or film dialogues to tell a personal story. Traditional Autobiography - This one covers the author's life from birth till date. Graphic Novels - This format ...
Biographies and autobiographies are both types of non-fiction stories about someone's life. ... Watch: Rosa Parks autobiography example The life of Rosa Parks, in her own words. ...
avg rating 3.96 — 2,015 ratings — published 1990. Books shelved as nonfiction-autobiography: The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank, When Breath Becomes Air by Paul Kalanithi, Born a Crime: Stories From...
Some Famous Examples of Autobiographies & Biographies for Better Understanding. Biography and autobiography are the most basic non-fiction genres. A biography is a non-fiction account of the life of an individual or group, while an autobiography is similar but focuses on telling events in a person's lifetime.
A cultural autobiography is more than just telling your life story. Your cultural identity reveals your beliefs and ideas about culture. It also shows how culture affects different cultural groups that make up who you are. You may want to write a cultural autobiography better to understand yourself and your culture's role in your life.