- No category

Jollibee - An In-Depth Analysis of Operational Excellence, Supply Chain Management, E-commerce Strategies, and Future Trends

Related documents

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer

Jollibee #ChickenSad – An IT Management Case Study

Editor’s note: Calen discusses the system migration issues Jollibee faced that allegedly led to inventory issues for the fast food giant. Here’s his take on what went wrong and what could’ve been done right.
Last week, a system migration caused problems in inventory deliveries to Jollibee stores, and even outright shutdown of 72 stores. According to this article, Jollibee suffered a sales loss of 6% for at least the first seven days of August. Calculating using Jollibee’s 2013 revenue, this loss amounts to at least a whopping Php 92 million! And considering that the project reportedly already costs Php 500 million, this whole debacle looks like it will cost Jollibee Php 600 million, not including the cost of all the man-days that Jollibee’s management and staff are probably devoting to fixing this problem.
I asked some of my friends in the industry (who shall not be named) on their take on what happened. Below is the information I got so far, and I’ll update this post as I get more information. I’ve also reached out to some friends in Jollibee hoping to get some inside information.
Please note that none of these are from official statements. If anyone wants to provide me with more accurate information on this, or better yet, official statements from the parties concerned, please send me a message and I will gladly incorporate it into the article. My objective here is to provide lessons to the IT and business community so that we can hopefully avoid the all-too-often costly mistakes of IT projects in the future.
1. Rip and Replace
Jollibee had originally been using an Oracle product for managing its supply chain – including deliveries of supplies to stores. Because of a dispute with Oracle, Jollibee decided to move its entire supply chain over to Oracle’s rival in this space, SAP.
Now, supply chain software isn’t just out-of-the-box products that you can just install and run. These need to be customized heavily in order to fit a company’s business processes, which usually takes months if not over a year of programming and configuration just to get started. The Oracle system had been running in Jollibee for years, and most certainly had a huge amount of complex programming and configuration from continuous modifications over time. These programs and configurations would have had a lot of fragile interrelationships between them, that made it a huge and risky task to migrate over to the SAP system
2. Staffing and Expertise
The project was outsourced to a large multinational IT service provider. Upon my interviews with members of the Philippine SAP community, they expressed doubt that the Philippine office of the service provider had a sizable local SAP team, if any. They have never heard of that vendor taking on Philippine projects using SAP before, which is why they concluded that the vendor did not have a significant local SAP practice.
My friends further reported that last year there was a large flurry of recruiting activity for SAP professionals from recruiters for that vendor. One of my friends considered this a “red flag”, meaning that the vendor seemed to be having trouble filling the positions required for the project, which is not surprising considering how high the demand for SAP skills are, and how small the supply. Eventually, the vendor allegedly brought in people from India and other countries to staff the project. Based on when the flurry of recruitment activity subsided, my friends estimate that the project was only properly staffed late last year.

Assembling a large team of outsiders quickly is troublesome. They have not worked under a common methodology and culture. They don’t have a common understanding of standards and processes. Any leaders in the group would be overwhelmed from the tasks of understanding the client’s business and designing solutions for the client’s requirements, working with other leaders to agree to common standards and processes, and then organizing and training teams to adhere to those common standards and processes, and then explaining client requirements and overseeing the quality of work.
3. Schedule and Size
This is a half-a-billion-peso project, yet it seems that the project is only operating on schedule of just a little over a year, based on when the recruitment activity started, and when the production issue broke out. Just to give this some perspective, many of the projects I’ve seen costing just 1/20 of this one usually have a two-year timetable. I’d expect that a project of this size would require three to five years to properly implement, from inception to transition.
Maybe this was just a first phase, but unfortunately for Jollibee it has already been a costly first phase. Let’s hope some methodology changes have already taken place to avoid costly mistakes in the future.
Ok, my notes here are not specifically about this project, but about ERP projects in general. As one of my friends pointed out, “You’d be surprised at what passes for unit / functional / integration testing in Oracle and SAP projects.”
Granted, testing is still a terrible area even in Java or .Net projects, but the practices have slowly been gaining ground and maturity over the last ten years. Successful projects often plan and implement tests from the beginning of the project and throughout, not just at the end, with the majority of the tests automated. Testing is elevated to a core part of part of the project, not just auxiliary to programming.
Recommendations
1. start small.
I’ve been in the situation where I have been asked by existing clients or potential clients to accept large fixed-scope projects, often on compressed schedules. In such situations, we usually respond by proposing only a smaller-scoped project, one that can be accomplished in around six months, by a team of five people or less. The only exception is if the large project is similar to a project we’ve done before, for the same client.
This is an extremely risky move on our part, since normally, clients are dead set on a large scope, and will only consider vendors that meet the complete scope. However, we do this because it is in the best interest of the client and us as the vendor.

First of all, requirements are never right. Almost all fixed-scope projects go through a series of change requests after the project. It is just impossible to correctly imagine upfront all the requirements needed for a project, even for small projects. The only time people realize what they really need is when they actually see the product, or get to use it.
A small initial project would allow the clients to better understand what they really need, and then specify succeeding scope based on something they can see and use. This is similar to the Singaporean government’s “Call for Collaboration” approach , where they invite multiple vendors to build paid prototypes in response to specific problems, which becomes the basis for the full project scope.
Second, it allows the vendor to field a seasoned team. Instead of scrambling to staff a large project, the vendor can source existing people within the company, led by one or more senior people, and having a common methodology. This allows the team to focus on the project concerns instead of having to deal with culture and process issues.
Third, scaling becomes easier later on. After the first project with a small seasoned team, both client and vendor learn about how each other works and how to best work with each other. This allows them to take on larger projects together in an efficient manner. The members of the initial team can be the seed members of new teams, to take on succeeding projects. Those that participated on the first project on both sides can pass on their learnings to others to improve the chances of success of succeeding projects.
2. Testing is Core & Automated
The approach of Test-Driven Development has its origins in 1999, and since then the open-source community has produced a rich set of tools to deal with the various aspects of test specification and automation – from functional testing, to user-interface, to data and integration, to performance.
The most effective teams have testing as part of the core of their methodology. Teams start the project by defining tests, and then define and run tests throughout the project, not just towards the end. Testing is not relegated to just “testers” or QA personnel, but is an activity done by all practices in their own ways – developers, for example, build numerous automated tests around each significant unit of logic, modeling various scenarios.
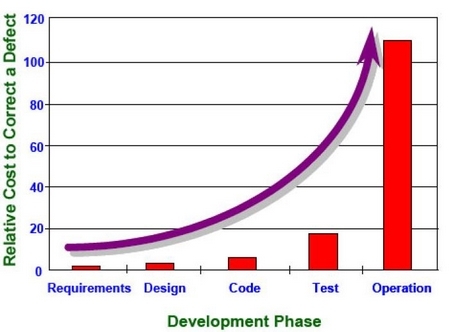
The benefit of this is that as the project moves along, the team builds up a large and rich set of automated tests, that are able to catch bugs early and often, when they are still easy and cheap to fix. Because the majority of these tests are automated, they can be run several times a day and give the team instant feedback.
Let me repeat this fact – defects are cheaper to find and fix if they are found sooner rather than later . Certainly, the defects in the current Jollibee project would have been cheaper had they been found during development, rather than during production, where they are now costing Jollibee millions of pesos a day.
After the system is built, it would naturally go through further enhancements and modifications. These changes can introduce defects. However, the robust suite of automated tests that were created with the system would improve the chances of catching these defects, making it safer and cheaper to maintain the system in the future.
3. Continuous Delivery
One of the riskiest things I see organizations do time and time again, is a big cut-over to a new system. They have a big announcement that, “System X will go live by __ !” When that day does come around (usually delayed), it’s invariably a mess! People are unable to get their work done with the new system. If they’re lucky, the old system is still around for them to fall back to, while the new system undergoes bug-fixing. If they’re not lucky, the old system is no longer available either.
Compare this to how Google or Facebook roll out their changes. Notice that your GMail or Facebook has new features that come out every few weeks or months. If you don’t like the feature, there’s a button that allows you to roll back to the old way of doing things. This button is Google’s and Facebook’s way of getting feedback from their users. They roll out the new features to just a partial set of users. If the users opt to roll back, then Facebook and Google know they still need to improve the feature. Then they roll it out again to another set of users. When they hit the point when few users opt to roll back, then they know they’ve got the feature right and make it a permanent part of their systems.
You can apply this to corporate systems. Don’t roll out your systems in big bangs, rather have a lot of frequent rollouts every few weeks or months, to initially a partial set of users, and then gather feedback. It will be easier and safer to roll back small increments of change rather than large ones. Even the deployment and roll back can be automated. This will certainly be less costly to the productivity of your people and the operations of the company.
4. Visibility Through Process & Tools
My final piece of advice sort of puts everything together so that clients can monitor the progress of a project, and catch problems earlier rather than later. A good, responsible team provides visibility to its client. And this visibility is provided via concrete evidence, not status reports that can be faked.
Regular Demos. A good team can provide their client with working software, as often as every one or two weeks. These aren’t PowerPoint presentations. Instead, they’re demos of new features to the software that clients can try out and give feedback on.
Test Reports. Automated tests can and should be run multiple times a day, usually using centralized systems called “Continuous Integration Servers”. These systems can provide clients several times a day with reports on the various tests, and whether they pass or fail. Some of these tests, known as “Acceptance Tests”, are readable by non-technical users, so you can see what behavior is being added to the system, and whether the system already complies with the behavior.
Quality Metrics. Aside from test reports, various tools can be added to the Continuous Integration Server to generate other reports. Among these reports are metrics on quality – For example, in Java there are various tools that can check if the code contains violations of coding standards, or contains logic that is too convoluted, or contains code that often leads to bugs.
Big Visible Charts. If the team works onsite, various charts in the team work area can give the rest of the organization an idea of the progress of the team. Two of the more popular charts are Task Boards and Burndown Charts.
The worst part about this case is, this is normal. Huge projects blow up all the time, in fact the bigger the project, the more likely that it will fail. The only difference here is that this one hit the public eye, which is good, since now we get to talk about what causes success and failure in IT projects. I hope the Filipino IT community moves forward with continued discourse and reflection, so that in the future IT projects deliver value to its stakeholders, instead of frustration and waste.

Further Reading

Women Who Code: Transforming the Tech Landscape with Diversity and Skill

Embracing EQ in UX: A New Era for the Philippines National Skills Framework

Transforming Tech Talent: Philippines Introduces Game-Changing National Skills Framework for IT Excellence

Intern @ O&B
Grow with us and make a difference.

- Banking & Financial Services
- Real Estate & Development
- Corporate Finance
- Digital Strategy
- Sustainability & Social Impact
- Governance Transformation
- Risk Assessment
- Cybersecurity
- Business Continuity
- Data Privacy
- Disaster Recovery
- Managed Security Operations (MSOC)
- Business Transformation
- Additional Services
- Sustainable Agility
- Change Management
- Security & Compliance
- Legacy Asset Digitalisation
- ESG Metrics & Monitoring
- Smart Buildings
- Smart Offices
- Smart Cities
- Smart Agriculture
- Industrial & Manufacturing
- Best Java Developers
- Enterprise Software Engineering
- Infrastructure As Code
- Agile / XP Coaching
- Design Thinking
- UX Design & Testing
- Featured Insights
- Great Place to Work
- Hybrid Workplace
- Our Commitments
- Our Leaders
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- ASEAN Business Award
- PSIA Seminars
- JAVA Users Group PH
- Media Center
Don't have an account? Sign up now
Already have an account login, get 10% off on your next order.
Subscribe now to get your discount coupon *Only correct email will be accepted
(Approximately ~ 0.0 Page)
Total Price
Thank you for your email subscription. Check your email to get Coupon Code.
Jollibee Foods Corporation Case Analysis and Case Solution
Posted by Peter Williams on Aug-09-2018
Introduction of Jollibee Foods Corporation Case Solution
The Jollibee Foods Corporation case study is a Harvard Business Review case study, which presents a simulated practical experience to the reader allowing them to learn about real life problems in the business world. The Jollibee Foods Corporation case consisted of a central issue to the organization, which had to be identified, analysed and creative solutions had to be drawn to tackle the issue. This paper presents the solved Jollibee Foods Corporation case analysis and case solution. The method through which the analysis is done is mentioned, followed by the relevant tools used in finding the solution.
The case solution first identifies the central issue to the Jollibee Foods Corporation case study, and the relevant stakeholders affected by this issue. This is known as the problem identification stage. After this, the relevant tools and models are used, which help in the case study analysis and case study solution. The tools used in identifying the solution consist of the SWOT Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, PESTEL Analysis, VRIO analysis, Value Chain Analysis, BCG Matrix analysis, Ansoff Matrix analysis, and the Marketing Mix analysis. The solution consists of recommended strategies to overcome this central issue. It is a good idea to also propose alternative case study solutions, because if the main solution is not found feasible, then the alternative solutions could be implemented. Lastly, a good case study solution also includes an implementation plan for the recommendation strategies. This shows how through a step-by-step procedure as to how the central issue can be resolved.
Problem Identification of Jollibee Foods Corporation Case Solution
Harvard Business Review cases involve a central problem that is being faced by the organization and these problems affect a number of stakeholders. In the problem identification stage, the problem faced by Jollibee Foods Corporation is identified through reading of the case. This could be mentioned at the start of the reading, the middle or the end. At times in a case analysis, the problem may be clearly evident in the reading of the HBR case. At other times, finding the issue is the job of the person analysing the case. It is also important to understand what stakeholders are affected by the problem and how. The goals of the stakeholders and are the organization are also identified to ensure that the case study analysis are consistent with these.
Analysis of the Jollibee Foods Corporation HBR Case Study
The objective of the case should be focused on. This is doing the Jollibee Foods Corporation Case Solution. This analysis can be proceeded in a step-by-step procedure to ensure that effective solutions are found.
- In the first step, a growth path of the company can be formulated that lays down its vision, mission and strategic aims. These can usually be developed using the company history is provided in the case. Company history is helpful in a Business Case study as it helps one understand what the scope of the solutions will be for the case study.
- The next step is of understanding the company; its people, their priorities and the overall culture. This can be done by using company history. It can also be done by looking at anecdotal instances of managers or employees that are usually included in an HBR case study description to give the reader a real feel of the situation.
- Lastly, a timeline of the issues and events in the case needs to be made. Arranging events in a timeline allows one to predict the next few events that are likely to take place. It also helps one in developing the case study solutions. The timeline also helps in understanding the continuous challenges that are being faced by the organisation.
SWOT analysis of Jollibee Foods Corporation
An important tool that helps in addressing the central issue of the case and coming up with Jollibee Foods Corporation HBR case solution is the SWOT analysis.
- The SWOT analysis is a strategic management tool that lists down in the form of a matrix, an organisation's internal strengths and weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats. It helps in the strategic analysis of Jollibee Foods Corporation.
- Once this listing has been done, a clearer picture can be developed in regards to how strategies will be formed to address the main problem. For example, strengths will be used as an advantage in solving the issue.
Therefore, the SWOT analysis is a helpful tool in coming up with the Jollibee Foods Corporation Case Study answers. One does not need to remain restricted to using the traditional SWOT analysis, but the advanced TOWS matrix or weighted average SWOT analysis can also be used.
Porter Five Forces Analysis for Jollibee Foods Corporation
Another helpful tool in finding the case solutions is of Porter's Five Forces analysis. This is also a strategic tool that is used to analyse the competitive environment of the industry in which Jollibee Foods Corporation operates in. Analysis of the industry is important as businesses do not work in isolation in real life, but are affected by the business environment of the industry that they operate in. Harvard Business case studies represent real-life situations, and therefore, an analysis of the industry's competitive environment needs to be carried out to come up with more holistic case study solutions. In Porter's Five Forces analysis, the industry is analysed along 5 dimensions.
- These are the threats that the industry faces due to new entrants.
- It includes the threat of substitute products.
- It includes the bargaining power of buyers in the industry.
- It includes the bargaining power of suppliers in an industry.
- Lastly, the overall rivalry or competition within the industry is analysed.
This tool helps one understand the relative powers of the major players in the industry and its overall competitive dynamics. Actionable and practical solutions can then be developed by keeping these factors into perspective.
PESTEL Analysis of Jollibee Foods Corporation
Another helpful tool that should be used in finding the case study solutions is the PESTEL analysis. This also looks at the external business environment of the organisation helps in finding case study Analysis to real-life business issues as in HBR cases.
- The PESTEL analysis particularly looks at the macro environmental factors that affect the industry. These are the political, environmental, social, technological, environmental and legal (regulatory) factors affecting the industry.
- Factors within each of these 6 should be listed down, and analysis should be made as to how these affect the organisation under question.
- These factors are also responsible for the future growth and challenges within the industry. Hence, they should be taken into consideration when coming up with the Jollibee Foods Corporation case solution.
VRIO Analysis of Jollibee Foods Corporation
This is an analysis carried out to know about the internal strengths and capabilities of Jollibee Foods Corporation. Under the VRIO analysis, the following steps are carried out:
- The internal resources of Jollibee Foods Corporation are listed down.
- Each of these resources are assessed in terms of the value it brings to the organization.
- Each resource is assessed in terms of how rare it is. A rare resource is one that is not commonly used by competitors.
- Each resource is assessed whether it could be imitated by competition easily or not.
- Lastly, each resource is assessed in terms of whether the organization can use it to an advantage or not.
The analysis done on the 4 dimensions; Value, Rareness, Imitability, and Organization. If a resource is high on all of these 4, then it brings long-term competitive advantage. If a resource is high on Value, Rareness, and Imitability, then it brings an unused competitive advantage. If a resource is high on Value and Rareness, then it only brings temporary competitive advantage. If a resource is only valuable, then it’s a competitive parity. If it’s none, then it can be regarded as a competitive disadvantage.
Value Chain Analysis of Jollibee Foods Corporation
The Value chain analysis of Jollibee Foods Corporation helps in identifying the activities of an organization, and how these add value in terms of cost reduction and differentiation. This tool is used in the case study analysis as follows:
- The firm’s primary and support activities are listed down.
- Identifying the importance of these activities in the cost of the product and the differentiation they produce.
- Lastly, differentiation or cost reduction strategies are to be used for each of these activities to increase the overall value provided by these activities.
Recognizing value creating activities and enhancing the value that they create allow Jollibee Foods Corporation to increase its competitive advantage.
BCG Matrix of Jollibee Foods Corporation
The BCG Matrix is an important tool in deciding whether an organization should invest or divest in its strategic business units. The matrix involves placing the strategic business units of a business in one of four categories; question marks, stars, dogs and cash cows. The placement in these categories depends on the relative market share of the organization and the market growth of these strategic business units. The steps to be followed in this analysis is as follows:
- Identify the relative market share of each strategic business unit.
- Identify the market growth of each strategic business unit.
- Place these strategic business units in one of four categories. Question Marks are those strategic business units with high market share and low market growth rate. Stars are those strategic business units with high market share and high market growth rate. Cash Cows are those strategic business units with high market share and low market growth rate. Dogs are those strategic business units with low market share and low growth rate.
- Relevant strategies should be implemented for each strategic business unit depending on its position in the matrix.
The strategies identified from the Jollibee Foods Corporation BCG matrix and included in the case pdf. These are either to further develop the product, penetrate the market, develop the market, diversification, investing or divesting.
Ansoff Matrix of Jollibee Foods Corporation
Ansoff Matrix is an important strategic tool to come up with future strategies for Jollibee Foods Corporation in the case solution. It helps decide whether an organization should pursue future expansion in new markets and products or should it focus on existing markets and products.
- The organization can penetrate into existing markets with its existing products. This is known as market penetration strategy.
- The organization can develop new products for the existing market. This is known as product development strategy.
- The organization can enter new markets with its existing products. This is known as market development strategy.
- The organization can enter into new markets with new products. This is known as a diversification strategy.
The choice of strategy depends on the analysis of the previous tools used and the level of risk the organization is willing to take.
Marketing Mix of Jollibee Foods Corporation
Jollibee Foods Corporation needs to bring out certain responses from the market that it targets. To do so, it will need to use the marketing mix, which serves as a tool in helping bring out responses from the market. The 4 elements of the marketing mix are Product, Price, Place and Promotions. The following steps are required to carry out a marketing mix analysis and include this in the case study analysis.
- Analyse the company’s products and devise strategies to improve the product offering of the company.
- Analyse the company’s price points and devise strategies that could be based on competition, value or cost.
- Analyse the company’s promotion mix. This includes the advertisement, public relations, personal selling, sales promotion, and direct marketing. Strategies will be devised which makes use of a few or all of these elements.
- Analyse the company’s distribution and reach. Strategies can be devised to improve the availability of the company’s products.
Jollibee Foods Corporation Blue Ocean Strategy
The strategies devised and included in the Jollibee Foods Corporation case memo should have a blue ocean strategy. A blue ocean strategy is a strategy that involves firms seeking uncontested market spaces, which makes the competition of the company irrelevant. It involves coming up with new and unique products or ideas through innovation. This gives the organization a competitive advantage over other firms, unlike a red ocean strategy.
Competitors analysis of Jollibee Foods Corporation
The PESTEL analysis discussed previously looked at the macro environmental factors affecting business, but not the microenvironmental factors. One of the microenvironmental factors are competitors, which are addressed by a competitor analysis. The Competitors analysis of Jollibee Foods Corporation looks at the direct and indirect competitors within the industry that it operates in.
- This involves a detailed analysis of their actions and how these would affect the future strategies of Jollibee Foods Corporation.
- It involves looking at the current market share of the company and its competitors.
- It should compare the marketing mix elements of competitors, their supply chain, human resources, financial strength etc.
- It also should look at the potential opportunities and threats that these competitors pose on the company.
Organisation of the Analysis into Jollibee Foods Corporation Case Study Solution
Once various tools have been used to analyse the case, the findings of this analysis need to be incorporated into practical and actionable solutions. These solutions will also be the Jollibee Foods Corporation case answers. These are usually in the form of strategies that the organisation can adopt. The following step-by-step procedure can be used to organise the Harvard Business case solution and recommendations:
- The first step of the solution is to come up with a corporate level strategy for the organisation. This part consists of solutions that address issues faced by the organisation on a strategic level. This could include suggestions, changes or recommendations to the company's vision, mission and its strategic objectives. It can include recommendations on how the organisation can work towards achieving these strategic objectives. Furthermore, it needs to be explained how the stated recommendations will help in solving the main issue mentioned in the case and where the company will stand in the future as a result of these.
- The second step of the solution is to come up with a business level strategy. The HBR case studies may present issues faced by a part of the organisation. For example, the issues may be stated for marketing and the role of a marketing manager needs to be assumed. So, recommendations and suggestions need to address the strategy of the marketing department in this case. Therefore, the strategic objectives of this business unit (Marketing) will be laid down in the solutions and recommendations will be made as to how to achieve these objectives. Similar would be the case for any other business unit or department such as human resources, finance, IT etc. The important thing to note here is that the business level strategy needs to be aligned with the overall corporate strategy of the organisation. For example, if one suggests the organisation to focus on differentiation for competitive advantage as a corporate level strategy, then it can't be recommended for the Jollibee Foods Corporation Case Study Solution that the business unit should focus on costs.
- The third step is not compulsory but depends from case to case. In some HBR case studies, one may be required to analyse an issue at a department. This issue may be analysed for a manager or employee as well. In these cases, recommendations need to be made for these people. The solution may state that objectives that these people need to achieve and how these objectives would be achieved.
The case study analysis and solution, and Jollibee Foods Corporation case answers should be written down in the Jollibee Foods Corporation case memo, clearly identifying which part shows what. The Jollibee Foods Corporation case should be in a professional format, presenting points clearly that are well understood by the reader.
Alternate solution to the Jollibee Foods Corporation HBR case study
It is important to have more than one solution to the case study. This is the alternate solution that would be implemented if the original proposed solution is found infeasible or impossible due to a change in circumstances. The alternate solution for Jollibee Foods Corporation is presented in the same way as the original solution, where it consists of a corporate level strategy, business level strategy and other recommendations.

Implementation of Jollibee Foods Corporation Case Solution
The case study does not end at just providing recommendations to the issues at hand. One is also required to provide how these recommendations would be implemented. This is shown through a proper implementation framework. A detailed implementation framework helps in distinguishing between an average and an above average case study answer. A good implementation framework shows the proposed plan and how the organisations' resources would be used to achieve the objectives. It also lays down the changes needed to be made as well as the assumptions in the process.
- A proper implementation framework shows that one has clearly understood the case study and the main issue within it.
- It shows that one has been clarified with the HBR fundamentals on the topic.
- It shows that the details provided in the case have been properly analysed.
- It shows that one has developed an ability to prioritise recommendations and how these could be successfully implemented.
- The implementation framework also helps by removing out any recommendations that are not practical or actionable as these could not be implemented. Therefore, the implementation framework ensures that the solution to the Jollibee Foods Corporation Harvard case is complete and properly answered.
Recommendations and Action Plan for Jollibee Foods Corporation case analysis
For Jollibee Foods Corporation, based on the SWOT Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, PESTEL Analysis, VRIO analysis, Value Chain Analysis, BCG Matrix analysis, Ansoff Matrix analysis, and the Marketing Mix analysis, the recommendations and action plan are as follows:
- Jollibee Foods Corporation should focus on making use of its strengths identified from the VRIO analysis to make the most of the opportunities identified from the PESTEL.
- Jollibee Foods Corporation should enhance the value creating activities within its value chain.
- Jollibee Foods Corporation should invest in its stars and cash cows, while getting rid of the dogs identified from the BCG Matrix analysis.
- To achieve its overall corporate and business level objectives, it should make use of the marketing mix tools to obtain desired results from its target market.
Baron, E. (2015). How They Teach the Case Method At Harvard Business School. Retrieved from https://poetsandquants.com/2015/09/29/how-they-teach-the-case-method-at-harvard-business-school/
Bartol. K, & Martin, D. (1998). Management, 3rd edition. Boston: Irwin McGrawHill.
Free Management E-Books. (2013a). PESTLE Analysis. Retrieved from http://www.free-management-ebooks.com/dldebk-pdf/fme-pestle-analysis.pdf
Gupta, A. (2013). Environment & PEST analysis: an approach to the external business environment. International Journal of Modern Social Sciences, 2(1), 34-43.
Hambrick, D. C., MacMillan, I. C., & Day, D. L. (1982). Strategic attributes and performance in the BCG matrix—A PIMS-based analysis of industrial product businesses. Academy of Management Journal, 25(3), 510-531.
Hill, C., & Jones, G. (2010). Strategic Management Theory: An Integrated Approach, Ninth Ed. Mason, OH: South-Western, Cengage Learning.
Hussain, S., Khattak, J., Rizwan, A., & Latif, M. A. (2013). ANSOFF matrix, environment, and growth-an interactive triangle. Management and Administrative Sciences Review, 2(2), 196-206.
IIBMS. (2015). 7 Effective Steps to Solve Case Study. Retrieved from http://www.iibms.org/c-7-effective-steps-to-solve-case-study/
Kim, W. C., & Mauborgne, R. (2004). Blue ocean strategy. If you read nothing else on strategy, read thesebest-selling articles., 71.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (2010). Principles of marketing. Pearson education.
Kulkarni, N. (2018). 8 Tips to Help You Prepare for the Case Method. Retrieved from https://www.hbs.edu/mba/blog/post/8-tips-to-help-you-prepare-for-the-case-method
Lin, C., Tsai, H. L., Wu, Y. J., & Kiang, M. (2012). A fuzzy quantitative VRIO-based framework for evaluating organizational activities. Management Decision, 50(8), 1396-1411.
Nixon, J., & Helms, M. M. (2010). Exploring SWOT analysis – where are we now?: A review of academic research from the last decade. Journal of Strategy and Management, 3(3), 215-251.
Panagiotou, G. (2003). Bringing SWOT into Focus. Business Strategy Review, 14(2), 8-10.
Pickton, D. W., & Wright, S. (1998). What's swot in strategic analysis? Strategic Change, 7(2), 101-109.
Porter, M. E. (2001). The value chain and competitive advantage. Understanding Business Processes, 50-66.
Porter, M. E. (1985). Competitive advantage: creating and sustaining superior performance (Vol. 2). New York: Free Press.
Porter, M.E. (1979, March). Harvard Business Review: Strategic Planning, How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy. Retrieved July 7, 2016, from https://hbr.org/1979/03/how-competitive-forces-shape-strategy
Rastogi, N., & Trivedi, M. K. (2016). PESTLE Technique–a Tool to Identify External Risks in Construction Projects. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 3(1), 384-388.
Rauch, P. (2007). SWOT analyses and SWOT strategy formulation for forest owner cooperations in Austria. European Journal of Forest Research, 126(3), 413-420.
Warning! This article is only an example and cannot be used for research or reference purposes. If you need help with something similar, please submit your details here .
9414 Students can’t be wrong
PhD Experts
Eimiely George
Checked the paper through Turnitin and it was 4% plagiarised, so no issue. Hope to get good marks!
Finally, I’m not under worries because prices of these services are not as high as the other services argue for.
I always order here and am happy with this service. Convenient, quick and right quality. Recommended!
Matteo Zayron
My topic was very complicated but they did a great job. The result was very good. I’m satisfied with this paper writing service!
Calculate the Price
(approx ~ 0.0 page), total price $0, next articles.
- Earls Restaurants Ltd.: The Importance Of A Communication Plan Case Analysis
- Hari Krishna Exports: Transforming Employees Case Analysis
- Faber Castell Case Analysis
- MD Solutions: Working From Home Case Analysis
- Fei Ni Mo Shu (You Are The One) And The Chinese Employment Market Case Analysis
- IGATE Corporation: Toxic Talent And Organizational Resilience Case Analysis
- The National Geographic Society (B) Case Analysis
- Deltecs InfoTech: Scaling An Indian Start Up Case Analysis
- Expatica Communications: Leading Through Tragedy Case Analysis
- Managing Up (A): Grace Case Analysis
Previous Articles
- MacEwan Residence Services: A Risky Accommodation? Case Analysis
- AW Ltd.: Managing Change Case Analysis
- London Health Sciences Centre: Talent Development (B) Case Analysis
- Allergan South Africa's Merger: Contextual Leadership Sustaining Culture Case Analysis
- London Health Sciences Centre: Talent Development (A) Case Analysis
- Valley Health (B) Case Analysis
- Valley Health (A) Case Analysis
- Alameda Health System Case Analysis
- HealthCare.gov: The Crash And The Fix (A) Case Analysis
- HealthCare.gov: The Crash And The Fix (B) Case Analysis
Be a great writer or hire a greater one!
Academic writing has no room for errors and mistakes. If you have BIG dreams to score BIG, think out of the box and hire Case48 with BIG enough reputation.

Our Guarantees
Zero plagiarism, best quality, qualified writers, absolute privacy, timely delivery.
Interesting Fact
Most recent surveys suggest that around 76 % students try professional academic writing services at least once in their lifetime!
Allow Our Skilled Essay Writers to Proficiently Finish Your Paper.
We are here to help. Chat with us on WhatsApp for any queries.
Customer Representative

- < Previous
Home > ETD > ETD_BACHELORS > 7591
Bachelor's Theses
A system study on jollibee foods corporation - manila city plaza branch.
Mary Andrea T. Bacani Rachelle P. Red Michelle M. Sze
Date of Publication
Document type.
Bachelor's Thesis
Degree Name
Bachelor of Science in Industrial Engineering
Gokongwei College of Engineering
Department/Unit
Industrial and Systems Engineering
Thesis Adviser
Bryan Gobaco
Defense Panel Member
Debbie Nacu
Abstract/Summary
Jollibee Foods Corporation, being a large-scale fast food business, is expected to deliver fast and quality service at all times. This study then takes the view of the customer on how they perceive the service of Jollibee. Data respondents and observations are gathered in a specific high-volume store of Jollibee which is the Manila City Plaza Branch in Quiapo, Manila.
This system study, focusing on service quality, is employed by using the different service management tools in the appraisal and problem analysis of the study. First aspect of the study is to determine the expectation and perception of the customers through the service quality survey. The results of the survey are used in the Quality Function Deployment. Also, Gap Analysis and Hypothesis Testing are verification tools to identify the weaknesses and problems of the study.
Based from these, the main problem of the study is the resulting average satisfaction level (3.36 out of 5) with the service responsiveness dimension of service quality.
Service responsiveness is specifically attributed to the problems of queuing and long turn around times. Both have very low satisfaction ratings, 2.649 for queuing time and 2.856 for waiting time at counter or turn around time. Specific and significant factors or causes are identified through cause and effect analysis and regression analysis. Furthermore, the critical fail points in the overall service process is identified with the use of the service blueprint.
At present, the standard turn around time is set at 90 seconds during peak periods. Observations and analysis were done to test the validity of this standard in terms of the demand and quantity of the products ordered by the customers. This is done to establish the problem of long turn around time that exceeds the standard even if it is proven to be achievable. But then again, actual observations indicate an average turn around time of only 132.67 seconds, thus having a deviation of 32% from standard.
Meanwhile, the queuing time is considered based from the customer requirements. Through a survey, it is found out that at five minutes about 60% of the customers are still willing to wait in line. Since majority of the respondents, have a positive response until five minutes, this is the set customer requirement for queuing time. However, the actual queuing time observed is 355.67 seconds, having a deviation of 16% from the customer requirements.
The identified factors for queuing and turn around time are made-to-order products, soft serve items, pending, voiding, discounting and personnel. Based from these specific causes, the alternative solutions are generated. These alternatives are subjected to the Kepner-Tregoe Decision Analysis.
Based from these alternatives, the proposed solutions are discussed. These solutions are integrated to one proposed system which is described as a technological service innovation. This proposal includes a proper implementation of pending policy, designation of soda, fries and soft serve person and also assignment of head cashier for voiding and discounting orders. The technological advancement involve is the use of a duplicate receipt printer to ensure simultaneity of activities and to accommodate more customer transactions. Simulation of the counter service transaction is also included to show estimated improvements when the significant factors of delay are solved.
The objectives of reducing the deviations are reached and even exceeded, as reducing the preparation time of food items alone through the designation of soda person, fries person and soft serve person lead to a 43% reduced in turn around time. Lesser queuing time is a direct effect of a faster turn around time. Basically, there are more benefits realized with the solutions to these objectives, particularly the reduction of number of customers experiencing delay in turn around time and TAT benefits which is translated to sales benefits.
Abstract Format
Accession number, shelf location.
Archives, The Learning Commons, 12F, Henry Sy Sr. Hall
Physical Description
xx, 385 leaves : col. ill. ; 28 cm.
Fast food restaurants--Philippines--Management; Jollibee Foods Corporation
Recommended Citation
Bacani, M. T., Red, R. P., & Sze, M. M. (2006). A system study on Jollibee Foods Corporation - Manila City Plaza Branch. Retrieved from https://animorepository.dlsu.edu.ph/etd_bachelors/7591
This document is currently not available here.
Since July 27, 2021
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Collections
- Disciplines
- Colleges and Units
- Submission Consent Form
- Animo Repository Policies
- Animo Repository Guide
- AnimoSearch
- DLSU Libraries
- DLSU Website
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
- : Food & Beverage
Jollibee Foods Builds Conversational Skills, Instills a Coaching Culture Across the Organization

Jollibee Foods Corporation (JFC) is one of the largest global food companies with 16 brands operating in 33 countries. The organization was seeking to establish a One JFC Coaching Culture that would empower employees and teams and reinforce a cohesive organizational culture as it continued to expand internationally.
The unique challenges brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic also led to an increased need for approaches and tools that could help JFC leaders navigate uncertainty with more self-awareness and resilience. In addition to needing to build a cohesive coaching culture, JFC needed a leadership development solution that would enable employees to communicate and engage with one another more effectively in a virtual environment and successfully adjust to the new world of work.

Jollibee Foods Corporation chose to partner with the Center for Creative Leadership (CCL)® out of a desire to form a trusting relationship with a solution provider. JFC wanted a partner that would work closely to understand the company’s unique needs and develop a solution that would deliver results.
The journey began with a custom face-to-face coaching skills program, Coaching for Greater Effectiveness, provided to 200 top leaders at JFC. Starting with senior leaders allowed for buy-in and support of the initiative, and ultimately led to increased traction as the larger-scale conversational skills program , Better Conversations Every Day (BCE)™ , was rolled out to all managers through a train-the-trainer model.
The program was pivoted to a live online virtual format in 2020 to nimbly adapt to the COVID-19 situation and continue the momentum of the initiative.
The CCL team worked closely with JFC to co-create the journey and program design, making adjustments along the way to maximize the impact in both the face-to-face and virtual environments. The journey included learning modules, assessments, online digital tools, and post-program pulse checks.
Involvement of JFC leaders throughout the process was a critical success factor. In addition to participating as sponsors and key stakeholders, a number of JFC leaders were trained as virtual breakout room hosts and led the small group discussions. The approach further increased the level of coaching capability within the organization and created comfort as participants were able to speak their local language.
Incorporating learnings from initial sessions into future iterations was key to maximizing the ROI for the initiative. With accumulated exposure to virtual coaching and training, it became apparent that facilitators and coaches needed to adopt additional tools and techniques to maintain high levels of engagement with participants. More interactive activities, such as polling, annotation, and quizzes were utilized in the program design as a result.
So far, the One JFC Coaching Culture has resulted in notable positive outcomes for the company, including significant improvement in managers’ ability to:
- Engage in difficult conversations
- Provide feedback for development
- Support colleagues to be the best version of themselves
Data from hundreds of leaders within JFC confirms that virtual BCE sessions have been equally impactful compared to face-to-face BCE sessions. When asked to rate overall satisfaction with the program, participants of both face-to-face and virtual programs have given an average of 4.8 out of 5 . A recent pulse check that measures behaviors and outcomes from the perspective of direct reports shows virtual sessions receiving even higher scores on leadership effectiveness compared to face-to-face.
Overall, employees across store brands report that their direct managers are challenging and supporting them more effectively, which has led to positive transformation across the organization.
Participants Say
“With the use of BCE techniques, we were able to pinpoint the exact problem and as a result, as of today, our store has ‘zero’ complaints pertaining to delivery.”
“I immediately put [new skills] into practice after the course and saw improvement on the performance of the person I was coaching.”
“I felt psychologically safe in practicing and making mistakes while doing the activities.”
“It was so much more than what I was expecting. It was fun and engaging and I learned so much that I can actually apply in both my professional and personal life.”
Partner With Us
We can work with you to create a customized solution that will help to build coaching and conversational skills, leading to a stronger coaching culture across your organization.
| What to Explore Next

SGX Group Partners With CCL to Boost Remote Worker Engagement by Building Internal Coaching Skills & Capacity

A Coaching Culture’s Foundation Is Better Conversations
| related solutions.

Better Conversations Every Day™

Conversational Skills Training
Sign Up for Newsletters
Don’t miss a single insight! Get our latest cutting-edge, research-based leadership content sent directly to your inbox.
Related Content

Andi Williams, Director of the Nonprofit and Population Health Leadership practices for Societal Impact at CCL, has been awarded the 2024 Shirley Chater Enduring Leadership Award by NurseTRUST.

CCL has partnered with The Financial Academy to further develop leadership effectiveness in the financial sector of Saudi Arabia.

We’ve once again been named a top provider of leadership training on Training Industry.com’s global Top 20 Leadership Training Companies list.


Corporate Governance
Risk management, enterprise risk management.
The Company and its subsidiaries, in global growth and expansion, require a comprehensive approach to corporate risk management that promotes extensive strategic thinking and analysis, while fundamentally integrating and maintaining highest ethical standards in the Company’s core values and beliefs. Risk management will provide the organization with the superior capabilities to identify, assess and manage the risks and enable the organization and its employees, at all levels, to better understand and manage risks.
The Company and its subsidiaries are all in the quick-service restaurant sector. Quick-service restaurants like those maintained by the Company are expected to maintain high quality in terms of food, service and cleanliness (“ FSC ”). The Company responds by observing stringent guidelines, processes and procedures in its FSC, and conducting regular and spot audits to ensure that FSC standards are maintained not only in stores but also in commissaries. The Company has likewise instituted a system of incentives to reward excellent performance in terms of FSC by stores.
The Company’s directors and management periodically review the effectiveness of the Company’s risk management system.
Financial Risk Management
The Company’s principal financial instruments comprise cash and cash equivalents and receivables. The main purpose of these financial instruments is to obtain financing for its operations. The Company has other financial assets and liabilities such as other noncurrent assets and trade payables and other current liabilities which arise directly from its operations.
The main risks arising from these financial instruments are credit risk and liquidity risk. The Company does not engage in any long-term debt and foreign currency-denominated transactions that may cause exposure to interest rate risk and foreign currency risk, respectively. The policies for managing each of these risks are summarized as follows:
Equity Price Risk
The Company is not exposed to significant equity price risk on its investment in quoted equity securities consisting of investment in club shares and shares of public utility companies.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk arises from the possibility that the fair value or future cash flows of financial instruments will fluctuate because of changes in market interest rates.
The Company’s interest rate exposure management policy centers on reducing the Company’s overall interest expense and exposure to changes in the interest rates.
To manage the interest rate risk related to the Company’s long-term debt, the Company uses a derivative instrument to fix the interest rate over the term of the debt.
There is minimal exposure on the other sources of Company’s interest rate risk. These other sources are from its cash in bank, short-term deposits, refundable deposits and employees’ car plan receivables.
Foreign Currency Risk
The Company’s exposure to foreign currency risk arises from the Parent Company’s investments outside the Philippines, which are mainly in People’s Republic of China and United States of America. While the foreign businesses have been rapidly growing, the net assets of foreign businesses account for only 10.84% and 15.57% of the consolidated net assets of the Company as at December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Therefore, the total exposure to foreign exchange risk of the Company is still not significant.
The Company also has transactional foreign currency exposures. Such exposure arises from its Philippine operations’cash and cash equivalents, receivables and long-term debt in foreign currencies.
Credit Risk
Credit risk is the risk that a customer or counterparty fails to fulfill its contractual obligations to the Company. This includes risk of non-payment by borrowers and issuers, failed settlement of transactions and default on outstanding contracts.
The Company has a strict credit policy. Its credit transactions are with franchisees that have gone through rigorous screening before granting them the franchise. The credit terms are very short, while deposits and advance payments are also required before rendering the service or delivering the goods, thus, mitigating the possibility of non-collection. In cases of non-collection, defaults of the debtors are not tolerated; the exposure is contained the moment a default occurs and transactions that will increase the Company’s exposure are not permitted.
The Company has no significant concentration of credit risk with counterparty. Its franchisee profile is such that no single franchisee accounts for more than 5% of its total system wide sales.
Liquidity Risk
The Company’s exposure to liquidity risk refers to the risk that its financial liabilities are not serviced in a timely manner and that its working capital requirements and planned capital expenditures are not met. To manage this exposure and to ensure sufficient liquidity levels, the Company closely monitors its cash flows.
On a weekly basis, the Company’s Cash and Banking Team monitors its collections, expenditures and any excess/deficiency in the working capital requirements, by preparing cash position reports that present actual and projected cash flows for the subsequent week. Cash outflows resulting from major expenditures are planned so that money market placements are available in time with the planned major expenditure. In addition, the Company has short-term cash deposits and has available credit lines with accredited banking institutions, in case there is a sudden deficiency. The Company maintains a level of cash and cash equivalents deemed sufficient to finance the operations.
Capital Management
Capital includes equity attributable to equity holders of the Parent Company.
The primary objective of the Company’s capital management is to ensure that it maintains a strong credit rating and healthy capital ratios in order to support its business and maximize shareholder value. The Company has sufficient capitalization.
The Company generates cash flows from operations sufficient to finance its organic growth. It declares cash dividends representing about one-third of its consolidated net income, a ratio that would still leave some additional cash for future acquisitions. If needed, the Company would borrow money for acquisitions of new businesses.

- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Coconut sugar
- Horticulture
- Capacity building
- Chemical inputs
- Climate smart agriculture
- Demonstration plots
- Environmental sustainability
- Extension services/field schools
- Farmer engagement
- Farmer organizations
- Greenhouse gas emissions
- Impact assessment
- Information access
- Land rights
- Land security/title
- Market access
- Mobile/digital solutions
- Monitoring and evaluation
- Partnership
- Performance measurement
- Productivity
- Profitability
- Project design
- Public-private partnerships
- Seeds/nurseries
- Standards/certification
- Women/gender
You are here
Jollibee foods corporation: a case study on responsible investment into farmer entrepreneurship in the philippines.
This case study outlines the journey of Jollibee Food Corporation's in their investment in Jollibee Group Foundation’s Farmer Entrepreneurship Program (FEP) that supports multiple groups of smallholder farmers who are producing high-value crops including white onions, salad tomatoes, bell peppers, Philippine lemon, and hot pepper.
Watch the video summary.
Smallholder farmers in the Philippines rely on multiple layers of intermediaries to consolidate and transport their products to market. Many farmers lack the knowledge and capacity to make their products marketready to reach end consumers. Farmers relying on intermediaries earn less for the price of their products compared to those that are able to supply and sell directly to the end market. With the goal to create social and economic impact on the Philippines’ agricultural sector, the Jollibee Group Foundation, with support from an annual investment by the Jollibee Group, initiated the Farmer Entrepreneurship Program (FEP) which has proven to address economic challenges by empowering smallholder farmers and transforming them to become entrepreneurs more than being producers.
Read the full case study to learn more about how Jollibee Foods Corporation impacts the lives of smallholder farmers through their investment, following principles of the ASEAN Guidelines on Promoting Responsible Investment in Food, Agriculture and Forestry.
This case study is part of a four-part series that showcases how recent agribusiness investments in food, agriculture and forestry sectors retroactively align with the ASEAN Guidelines on Promoting Responsible Investment in Food, Agriculture and Forestry (ASEAN Guidelines). Critically, these case studies showcase:
- Social, environmental and financial results of these investments
- Business case for responsibly investing in supply chain projects
- How agribusinesses ensure long-term sustainability and viability of their investments
- Key policy recommendations and learnings for the future
Copyright © 2020 Grow Asia Terms of Use Privacy Policy Contact Us
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Jollibee Food Corporation Mini Case Study
Jollibee Foods Corporation currently owns several food service businesses in its portfolio including Chowking, Greenwich, Red Ribbon, Burger King, and Mang Inasal. What other food service business opportunities do you think should Jollibee pursue? Why? How do you propose JFC should pursue them? An opportunity that JFC can look into would be entering the health-centric and sectarian market. It is widely reported consumers are trending toward more health-conscious eating and that the fastest growing religion in the world is Islam. JFC has barely reached a largely untapped market of vegans, vegetarians, halal and kosher observers— a market which had avoided QSRs or fast food chains for the reason that fast food equal to unhealthy or impermissible in their chosen denomination. This is the case for most fast food chains, even for bigger players. There is, however, a plethora of foods that can be prepared in a QSR manner but is considered vegan, halal and kosher. To be particular, I would suggest that JFC look into the possibility of acquiring a falafel joint. Falafel is a Middle East dish that is popular to vegans and vegetarians as it is plant-based and considered healthy. It also follows the strict standards of halal and kosher rules. The manner falafel is prepared is very much like fast food menus, quick and easy. This way, the new acquisition will still stay true to the JFC branding. If JFC considers acquiring a falafel joint, we can now set an objective for such move. A long-term objective that is applicable would be to grow and capture a customer base for the health-conscious and sectarian market. Using product differentiation, they can focus on this market segment and position the new acquisition as a way to have economic and physical access to nutritious food that meet dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life. It will be a food establishment that is both healthy and aligned with the customer's values. Since the penetration of health-centric establishments in the Philippines (and worldwide) is limited, it is important for JFC to consider acquiring a falafel joint that has a solid following or brand promoters. One that comes to mind is Beni's Falafel which currently has locations in Makati and SM MOA. The menu of Beni's Falafel is limited and can be prepared quickly. Sourcing of the ingredients is also fairly easy. This establishment also has a significant number of repeat customers and could be considered
Related Papers
Fauzia Jabeen
International Conference for Tourism and Business
RYAN T LIBA
The purpose of this study is to determine the issues, challenges and prospects of halal food industry focusing on halal restaurants in three key cities in the Metro Manila which serves as basis for a proposed competitive marketing strategy. This study focused on the issues in terms of halal logo and certification, challenges in terms of product strategy, pricing strategy, place strategy and promotion strategy encountered by halal restaurant owners and prospects in terms of future expansion and customer patronage. This research utilized descriptive research design. To address the problem sought, survey questionnaire was distributed to gather data from the owner of halal restaurants. The sampling frame of the study is composed of all the halal restaurants located in the three key cities of Metro Manila such as Manila, Makati and Quezon City. The study found out that halal restaurant owners strongly agreed on the significance of uniform halal logo. The restaurant owners agreed that they encounter challenges related to the marketing mix. They experienced problem in hiring well-qualified chef, providing sufficient training for the chef, preparing the menu, verifying the halal ingredients and finding credible supplier, finding strategic place and paying for the high rental cost and promoting halal food. Halal restaurant owners want to open a company owned branch within and outside Metro Manila and opening a new company owned halal restaurant with new concept. They strongly agreed that there is a greater patronage of Muslim and non-Muslim customers for halal restaurants. The researcher concluded that the issues related to the halal restaurants include the absence of uniform halal logo. The challenges encountered by halal restaurants when implementing the 4Ps of marketing strategy includes hiring well-qualified chef, providing sufficient training for the chef, preparing the menu, verifying the halal ingredients, finding credible supplier, finding strategic place, paying for the high rental cost, sustaining the type of promotional strategy and promoting halal food. The prospects are opening company owned halal restaurants within and outside Metro Manila and greater customer patronage from both Muslim and non-Muslim customers. It was also concluded that halal restaurant owners from the City of Manila, Makati City and Quezon City encountered the same challenges in terms of product, price, place and promotion strategy.
Australasian Marketing Journal (AMJ)
Paul Patterson
Farida Komalasari
Increasing number of fast food restaurant encourages entrepreneurs to compose a suitable strategy in developing their business. Entrepreneurs should know well about the customers satisfaction factors of fast food restaurant and its impact on customers’ purchase intention. Knowing the influence of dineserve’s variables (food.quality, atmosphere, servicesquality,.convenicence.and.price) on customers’.satisfaction and purchase intention in fast food restaurant is needed. Therefore, this research’s objectives are to indentify the influence of dineserve on.customer satisfaction and to identify the influence of customers’.satisfaction on purchase intention of FK Chicken products. A quantitative analysis is carried out through circulating an online questionnaire, which consists of 37 statements.There are 250respondents which are choosen using purposive sampling and snowball sampling from its population. The population are people who have ever purchase of FK Chicken products in Indonesia. A...
International Journal of Science and Management Studies (IJSMS)
Mark Abadiano
In general, fast-food organizations typically have distinctive ways of managing their business operations and achieving their corporate goals and objectives. The companies used marketing strategies to bring the organization’s mission and vision to life. Because these were influenced by the expanding population, trends, consumer behavior, internal and external factors in various situations, such as the most recent pandemic impact in 2020 continuing until 2021, many business models were introduced, adjusted, or replicated over the course of years. This study focuses on various business techniques and tactics that are crucial for the survival and sustainability of the fast-food industry and for competing against recently introduced rivals in the expanding food chain sector. This investigation will serve as a Quantitative Documentary Analysis through Data Mining. To sum it up, this research will offer suggestions on how to sell fast-food chains domestically, develop internationally, and...
iRAPA International Journal of Business Studies
Jordan Cabaguing
Diversification is one of the main problems faced by every organization. It is considered challenging to handle; hence it caters to diversified attitudes, personality, characteristics, cultural background, perceptions, and values. This study explored the main diversity issue in fast-food chains in Eastern Visayas, Philippines, and its management. A mixed-method research design was used in the study, utilizing a survey questionnaire and an interview guide to gather the data. The results showed that gender inequality is a widespread diversity issue in fast-food chains. A relevant, suitable, and responsive diversity program must be developed to continuously educate employees on the importance of diversity in attaining organizational success. Management commitment is necessary for managing diversity.
maninder singh
International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal
Bassem Nasri
The IMC Sourcebook Book: Readings and Cases in Integrated Marketing Communications
Bela Florenthal , Manar Awad
In this study, we consider the owners of two Burger King franchise establishments that have been struggling financially over the past three years. The owners are looking to grow the revenue of their two struggling locations and remain competitive in the changing fast food landscape. They realize that their competitors are not only other fast food brands but also the growing number of fast casual chains, ethnic cuisine restaurants, and convenience store establishments. They notice that their target segment, Millennials, has become more health conscious and exhibit an increasing desire to diversify their palates. As a result, the franchisees struggle to meet Millennials’ expectations in terms of their menu items. In addition, they do not keep up with innovative technology, such as mobile apps for ordering and delivering fast food items, that has been gradually adopted by competitors. Thus, the owners of the two Burger King locations are faced with two key challenges: (a) how to stay competitive and (b) how to be more attractive to Millennials.
RELATED PAPERS
Journal of Zoology
Robert Timm
Federica Boraldi
Bruno Neves
International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE)
Sunil Kuntawar
Journal of Theoretical Biology
Fourth Annual IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PERCOMW'06)
Roberta Fracchia
Revue des affaires européennes (submitted)
Araceli Turmo
Nguyễn Hoàng
Transformative Approaches to New Technologies and Student Diversity in Futures Oriented Classrooms
Chris Bigum
Dávid Simon
Ciência Rural
vanessa sousa viera
Seminars in Liver Disease
Andres Cardenas
The Open Marine Biology Journal
Monia TRABELSI
JAMA Health Forum
Sarah Wetter
Geological Behavior
MUHD NUR ISMAIL ABDUL RAHMAN
Celine Chanson
Journal of the American Chemical Society
Valerie Walters
Franciscanum
Pablo Román Rodriguez
Lab on a Chip
Nursing Outlook
Patricia Marck
International Journal of Legal Medicine
Herman Bernitz
Cell Death and Disease
Miryam Cadenas
Sustainability
Agata Cabanek
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The case study of Jollibee's response to the COVID-19 pandemic exemplifies how these e-commerce initiatives not only sustain customer engagement but also open up new avenues for growth. In embracing sustainability, Jollibee has turned to transparent sourcing practices, using blockchain technology to provide customers with end-to-end ...
Precedence diagram is used. together with process map to illustrate the cycle time and methods of the different processes. ANALYSIS. Performance Objectives. Workf orce: Jollibee crew works per ...
Jollibee #ChickenSad - An IT Management Case Study. Editor's note: Calen discusses the system migration issues Jollibee faced that allegedly led to inventory issues for the fast food giant. Here's his take on what went wrong and what could've been done right. Last week, a system migration caused problems in inventory deliveries to ...
To evaluate the business performance incorporating inventory management procedures. 3. To provide an analysis of the current inventory system of Jollibee Foods Corporation for further improvement. 4. To determine the advantages and disadvantages of the current inventory system of Jollibee Foods Corporation. 5.
An Analysis of the Inventory Management System (Case study).pptx - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Jollibee, the largest fast food chain in the Philippines, faced issues with its inventory management system in 2014 when migrating to a new SAP system from Oracle.
Case Studies C24.1. Joll ibee Food s Corpora tion. Leonar do R. Garci a Jr., Chr istopher Lovelock, and Jo chen Wirtz. A Philippine fast food company has achieved market dominance in three ...
Case Study Choi recognized that for Jollibee to scale their US operations, the company needed to cut ties with their legacy MSP and partner with a forward-thinking, agile provider to help them transform their operations from the ground up. The Solution After a comprehensive search, Jollibee selected SMPL to streamline IT
Jollibee is one of the world's largest chains of fast-food restaurants. Originating in Philippines, it owns a total of ~1,200 outlets all over the world. In order to keep up with the service level, the fast-food giant has been working on improvement on its operations and inventory management systems. Altai Super WiFi has
Case Studies C24.1 Jollibee Foods Corporation Leonardo R. Garcia Jr., Christopher Lovelock, and Jochen Wirtz ... However, Jollibee's management team decided to see this as an opportunity that would
Home Research & Knowledge Strategy Jollibee: Bringing Filipino fast food to the world. The case deals with the international expansion of Jollibee across Asia, USA and Europe along various dimensions (in particular its brands portfolio) Josh Wei-Jun Hsueh Alfredo De Massis. Arnaud Chevallier Frédéric Dalsace Jean-Louis Barsoux.
An Analysis of the Inventory Management System (Case study).pptx - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Jollibee, the largest fast food chain in the Philippines, faced issues with its inventory management system in 2014 when migrating to a new SAP system from Oracle.
JOLLIBEE FOODS CORPORATION: INTERNATIONAL EXPANSION A Case Study by Group 4. Jollibee Foods Corporation (JFC) is the most successful fast food chain in the Philippines. It started out as an ice cream parlor owned by the Tan family, headed by Tony Tan Caktiong (TTC) as President. Brought about by oil crisis which doubled the.
Since Jollibee franchised to expand their business and achieve market penetration, it affects the political issues based on the policies governing tax, licenses, regulation and employment. Economic - Based on the case study, Mr. Artiaga wants to invest a Jollibee franchise in order to attract more customers to his gas station which will ...
Jollibee Foods Corporation is the largest fast food chain operator in the Philippines. SSI Schaefer installed a 3-tier picking module with Pallet Live Storage and Carton Live Storage (KDR) the goods are picked, bar-coded and tagged before it is transported through Conveyor System. The first-in-first-out (FIFO) design ensures that supplies leave the warehouse in optimal condition.
The case solution first identifies the central issue to the Jollibee Foods Corporation case study, and the relevant stakeholders affected by this issue. This is known as the problem identification stage. After this, the relevant tools and models are used, which help in the case study analysis and case study solution.
Jollibee Foods Corporation, being a large-scale fast food business, is expected to deliver fast and quality service at all times. This study then takes the view of the customer on how they perceive the service of Jollibee. Data respondents and observations are gathered in a specific high-volume store of Jollibee which is the Manila City Plaza Branch in Quiapo, Manila.
This paper aims to study the financial performance of Jollibee from 2010 - 2014. Specifically, this paper. delves on the computed financial ratios based on the available data (a udited fi ...
Jollibee Foods Corporation chose to partner with the Center for Creative Leadership (CCL)® out of a desire to form a trusting relationship with a solution provider. JFC wanted a partner that would work closely to understand the company's unique needs and develop a solution that would deliver results. The journey began with a custom face-to ...
Enterprise Risk Management. The Company and its subsidiaries, in global growth and expansion, require a comprehensive approach to corporate risk. management that promotes extensive strategic thinking and analysis, while fundamentally integrating and maintaining. highest ethical standards in the Company's core values and beliefs.
This case study outlines the journey of Jollibee Food Corporation's in their investment in Jollibee Group Foundation's Farmer Entrepreneurship Program (FEP) that supports multiple groups of smallholder farmers who are producing high-value crops including white onions, salad tomatoes, bell peppers, Philippine lemon, and hot pepper.
from 1998 to 2003. Exhibit 3 reproduces the company' s. values, vision, and mission. T wenty nine years a er J ollibee was founded, Jollibee. Foods Corporation controlled abo ut 55% of the quick ...
JFC case study - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Case Study
This study explored the main diversity issue in fast-food chains in Eastern Visayas, Philippines, and its management. A mixed-method research design was used in the study, utilizing a survey questionnaire and an interview guide to gather the data. The results showed that gender inequality is a widespread diversity issue in fast-food chains.