

The Real Roots of Student Cheating
Let's address the mixed messages we are sending to young people..
Updated September 28, 2023 | Reviewed by Ray Parker
- Why Education Is Important
- Find a Child Therapist
- Cheating is rampant, yet young people consistently affirm honesty and the belief that cheating is wrong.
- This discrepancy arises, in part, from the tension students perceive between honesty and the terms of success.
- In an integrated environment, achievement and the real world are not seen as at odds with honesty.

The release of ChatGPT has high school and college teachers wringing their hands. A Columbia University undergraduate rubbed it in our face last May with an opinion piece in the Chronicle of Higher Education titled I’m a Student. You Have No Idea How Much We’re Using ChatGPT.
He goes on to detail how students use the program to “do the lion’s share of the thinking,” while passing off the work as their own. Catching the deception , he insists, is impossible.
As if students needed more ways to cheat. Every survey of students, whether high school or college, has found that cheating is “rampant,” “epidemic,” “commonplace, and practically expected,” to use a few of the terms with which researchers have described the scope of academic dishonesty.
In a 2010 study by the Josephson Institute, for example, 59 percent of the 43,000 high school students admitted to cheating on a test in the past year. According to a 2012 white paper, Cheat or Be Cheated? prepared by Challenge Success, 80 percent admitted to copying another student’s homework. The other studies summarized in the paper found self-reports of past-year cheating by high school students in the 70 percent to 80 percent range and higher.
At colleges, the situation is only marginally better. Studies consistently put the level of self-reported cheating among undergraduates between 50 percent and 70 percent depending in part on what behaviors are included. 1
The sad fact is that cheating is widespread.
Commitment to Honesty
Yet, when asked, most young people affirm the moral value of honesty and the belief that cheating is wrong. For example, in a survey of more than 3,000 teens conducted by my colleagues at the University of Virginia, the great majority (83 percent) indicated that to become “honest—someone who doesn’t lie or cheat,” was very important, if not essential to them.
On a long list of traits and qualities, they ranked honesty just below “hard-working” and “reliable and dependent,” and far ahead of traits like being “ambitious,” “a leader ,” and “popular.” When asked directly about cheating, only 6 percent thought it was rarely or never wrong.
Other studies find similar commitments, as do experimental studies by psychologists. In experiments, researchers manipulate the salience of moral beliefs concerning cheating by, for example, inserting moral reminders into the test situation to gauge their effect. Although students often regard some forms of cheating, such as doing homework together when they are expected to do it alone, as trivial, the studies find that young people view cheating in general, along with specific forms of dishonesty, such as copying off another person’s test, as wrong.
They find that young people strongly care to think of themselves as honest and temper their cheating behavior accordingly. 2
The Discrepancy Between Belief and Behavior
Bottom line: Kids whose ideal is to be honest and who know cheating is wrong also routinely cheat in school.
What accounts for this discrepancy? In the psychological and educational literature, researchers typically focus on personal and situational factors that work to override students’ commitment to do the right thing.
These factors include the force of different motives to cheat, such as the desire to avoid failure, and the self-serving rationalizations that students use to excuse their behavior, like minimizing responsibility—“everyone is doing it”—or dismissing their actions because “no one is hurt.”
While these explanations have obvious merit—we all know the gap between our ideals and our actions—I want to suggest another possibility: Perhaps the inconsistency also reflects the mixed messages to which young people (all of us, in fact) are constantly subjected.
Mixed Messages
Consider the story that young people hear about success. What student hasn’t been told doing well includes such things as getting good grades, going to a good college, living up to their potential, aiming high, and letting go of “limiting beliefs” that stand in their way? Schools, not to mention parents, media, and employers, all, in various ways, communicate these expectations and portray them as integral to the good in life.
They tell young people that these are the standards they should meet, the yardsticks by which they should measure themselves.
In my interviews and discussions with young people, it is clear they have absorbed these powerful messages and feel held to answer, to themselves and others, for how they are measuring up. Falling short, as they understand and feel it, is highly distressful.
At the same time, they are regularly exposed to the idea that success involves a trade-off with honesty and that cheating behavior, though regrettable, is “real life.” These words are from a student on a survey administered at an elite high school. “People,” he continued, “who are rich and successful lie and cheat every day.”

In this thinking, he is far from alone. In a 2012 Josephson Institute survey of 23,000 high school students, 57 percent agreed that “in the real world, successful people do what they have to do to win, even if others consider it cheating.” 3
Putting these together, another high school student told a researcher: “Grades are everything. You have to realize it’s the only possible way to get into a good college and you resort to any means necessary.”
In a 2021 survey of college students by College Pulse, the single biggest reason given for cheating, endorsed by 72 percent of the respondents, was “pressure to do well.”
What we see here are two goods—educational success and honesty—pitted against each other. When the two collide, the call to be successful is likely to be the far more immediate and tangible imperative.
A young person’s very future appears to hang in the balance. And, when asked in surveys , youths often perceive both their parents’ and teachers’ priorities to be more focused on getting “good grades in my classes,” than on character qualities, such as being a “caring community member.”
In noting the mixed messages, my point is not to offer another excuse for bad behavior. But some of the messages just don’t mix, placing young people in a difficult bind. Answering the expectations placed on them can be at odds with being an honest person. In the trade-off, cheating takes on a certain logic.
The proposed remedies to academic dishonesty typically focus on parents and schools. One commonly recommended strategy is to do more to promote student integrity. That seems obvious. Yet, as we saw, students already believe in honesty and the wrongness of (most) cheating. It’s not clear how more teaching on that point would make much of a difference.
Integrity, though, has another meaning, in addition to the personal qualities of being honest and of strong moral principles. Integrity is also the “quality or state of being whole or undivided.” In this second sense, we can speak of social life itself as having integrity.
It is “whole or undivided” when the different contexts of everyday life are integrated in such a way that norms, values, and expectations are fairly consistent and tend to reinforce each other—and when messages about what it means to be a good, accomplished person are not mixed but harmonious.
While social integrity rooted in ethical principles does not guarantee personal integrity, it is not hard to see how that foundation would make a major difference. Rather than confronting students with trade-offs that incentivize “any means necessary,” they would receive positive, consistent reinforcement to speak and act truthfully.
Talk of personal integrity is all for the good. But as pervasive cheating suggests, more is needed. We must also work to shape an integrated environment in which achievement and the “real world” are not set in opposition to honesty.
1. Liora Pedhazur Schmelkin, et al. “A Multidimensional Scaling of College Students’ Perceptions of Academic Dishonesty.” The Journal of Higher Education 79 (2008): 587–607.
2. See, for example, the studies in Christian B. Miller, Character and Moral Psychology. New York: Oxford University Press, 2014, Ch. 3.
3. Josephson Institute. The 2012 Report Card on the Ethics of American Youth (Installment 1: Honesty and Integrity). Josephson Institute of Ethics, 2012.

Joseph E. Davis is Research Professor of Sociology and Director of the Picturing the Human Colloquy of the Institute for Advanced Studies in Culture at the University of Virginia.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Effective Classroom Management
Collaboration or Cheating: What Are the Distinctions?
- January 11, 2017
- Maryellen Weimer, PhD
The line between collaboration and cheating is fuzzy. It’s still clear at the edges, but messy in the middle. When students are working in groups, searching for a solution to a problem, looking through possible answers for the best one, or sorting out material to include in a presentation, that’s collaboration. When one student in the group solves the problem and everyone else copies the answer, that’s cheating. When one student fails to deliver material she or he’s been assigned and the rest of the group covers, that’s cheating.
Collaboration on exams or quizzes further highlights the messiness of the distinctions. If a student admits to a group working on quiz questions that he doesn’t know an answer and someone else in group identifies the right answer, explains what makes it right, and that explanation enables the first student to understand, has cheating occurred? For exams, must a student discover all answers working alone? The question can be framed more globally, when does collaboration cross the line and become cheating?
Teachers have the responsibility to assess individual mastery of the material. Grades provide a measure of how well an individual knows something. When students collaborate, when they produce work collectively, that makes it much more difficult to determine who knows what and how well they know it. Promoting collaboration and preventing cheating can feel like one of those spots between a rock and hard place.
The distinctions matter because collaboration is an expectation in most professional settings. Professionals “cheat,” as we usually define it. If they don’t know an answer, they look it up. If they don’t know how to do something, they ask someone to show them. Most decisions are group decisions. Who contributed what is of little concern; it’s the quality of the decision that matters.
Are we conveying mixed messages if we put a problem on the board and tell students to work on it with someone seated nearby, but then silently expect all homework to be completed independently? Do they see what differentiates in-class collaboration from the individual work we require that they do for grades? As far as that goes, how clear is our own thinking about what makes them different?
If we don’t understand the distinctions, then we don’t have much hope of clarifying them for students. Students already have permissive attitudes about cheating—so many of them do it, despite our efforts to prevent it. If we’re teaching students in that traditional 18-23-year-old cohort, then there’s the added power of peer pressure. If the student asking for your answer is a friend, can you say no without doing damage to the friendship?
Unfortunately, it’s also possible for groups to collaborate with the intent of cheating—the giving and taking of answers without any attempt at learning. We focus our efforts on the person who’s cheated—the one who’s gotten the answer from somebody else. We don’t pay much attention to those who enabled the cheating—the ones giving away the solutions and facing no consequences when they are in fact co-conspirators.
Finally, are we so focused on preventing cheating that we’re neglecting to teach the skills of collaboration? I’m wondering if the place to start is by exploring with students what it means to work collaboratively, how everyone has the responsibility to contribute, and why it’s everyone’s responsibility to prevent the undeserved taking of ideas and information from others. That doesn’t mean everyone must always know the answer, but everyone ought to have ideas about the possible answers or at least some thoughts about how to probe the problem further. Handing out an answer to somebody who hasn’t done any work is different from trying to help someone who’s struggling but still working to understand the content. Effort on the part of the receiver is key.
Please share your thoughts. Writing this post has stimulated a lot of thinking (and rewriting). I’m not sure I’ve gotten us to good answers yet.
© Magna Publications. All rights reserved.
Stay Updated with Faculty Focus!
Get exclusive access to programs, reports, podcast episodes, articles, and more!
- Opens in a new tab
Welcome Back
Username or Email
Remember Me
Already a subscriber? log in here.
Advertisement
Academic dishonesty when doing homework: How digital technologies are put to bad use in secondary schools
- Open access
- Published: 23 July 2022
- Volume 28 , pages 1251–1271, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Juliette C. Désiron ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3074-9018 1 &
- Dominik Petko ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1569-1302 1
6015 Accesses
4 Citations
4 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The growth in digital technologies in recent decades has offered many opportunities to support students’ learning and homework completion. However, it has also contributed to expanding the field of possibilities concerning homework avoidance. Although studies have investigated the factors of academic dishonesty, the focus has often been on college students and formal assessments. The present study aimed to determine what predicts homework avoidance using digital resources and whether engaging in these practices is another predictor of test performance. To address these questions, we analyzed data from the Program for International Student Assessment 2018 survey, which contained additional questionnaires addressing this issue, for the Swiss students. The results showed that about half of the students engaged in one kind or another of digitally-supported practices for homework avoidance at least once or twice a week. Students who were more likely to use digital resources to engage in dishonest practices were males who did not put much effort into their homework and were enrolled in non-higher education-oriented school programs. Further, we found that digitally-supported homework avoidance was a significant negative predictor of test performance when considering information and communication technology predictors. Thus, the present study not only expands the knowledge regarding the predictors of academic dishonesty with digital resources, but also confirms the negative impact of such practices on learning.
Similar content being viewed by others
The impact of smartphone use on learning effectiveness: A case study of primary school students
Jen Chun Wang, Chia-Yen Hsieh & Shih-Hao Kung

Adoption of online mathematics learning in Ugandan government universities during the COVID-19 pandemic: pre-service teachers’ behavioural intention and challenges
Geofrey Kansiime & Marjorie Sarah Kabuye Batiibwe

Generative AI and the future of higher education: a threat to academic integrity or reformation? Evidence from multicultural perspectives
Abdullahi Yusuf, Nasrin Pervin & Marcos Román-González
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Academic dishonesty is a widespread and perpetual issue for teachers made even more easier to perpetrate with the rise of digital technologies (Blau & Eshet-Alkalai, 2017 ; Ma et al., 2008 ). Definitions vary but overall an academically dishonest practices correspond to learners engaging in unauthorized practice such as cheating and plagiarism. Differences in engaging in those two types of practices mainly resides in students’ perception that plagiarism is worse than cheating (Evering & Moorman, 2012 ; McCabe, 2005 ). Plagiarism is usually defined as the unethical act of copying part or all of someone else’s work, with or without editing it, while cheating is more about sharing practices (Krou et al., 2021 ). As a result, most students do report cheating in an exam or for homework (Ma et al., 2008 ). To note, other research follow a different distinction for those practices and consider that plagiarism is a specific – and common – type of cheating (Waltzer & Dahl, 2022 ). Digital technologies have contributed to opening possibilities of homework avoidance and technology-related distraction (Ma et al., 2008 ; Xu, 2015 ).
The question of whether the use of digital resources hinders or enhances homework has often been investigated in large-scale studies, such as the Program for International Student Assessment (PISA), the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS), and the Progress in International Reading Literacy Study (PIRLS). While most of the early large-scale studies showed positive overall correlations between the use of digital technologies for learning at home and test scores in language, mathematics, and science (e.g., OECD, 2015 ; Petko et al., 2017 ; Skryabin et al., 2015 ), there have been more recent studies reporting negative associations as well (Agasisti et al., 2020 ; Odell et al., 2020 ). One reason for these inconclusive findings is certainly the complex interplay of related factors, which include diverse ways of measuring homework, gender, socioeconomic status, personality traits, learning goals, academic abilities, learning strategies, motivation, and effort, as well as support from teachers and parents. Despite this complexity, it needs to be acknowledged that doing homework digitally does not automatically lead to productive learning activities, and it might even be associated with counter-productive practices such as digital distraction or academic dishonesty. Digitally enhanced academic dishonesty has mostly been investigated regarding formal assessment-related examinations (Evering & Moorman, 2012 ; Ma et al., 2008 ); however, it might be equally important to investigate its effects regarding learning-related assignments such as homework. Although a large body of research exists on digital academic dishonesty regarding assignments in higher education, relatively few studies have investigated this topic on K12 homework. To investigate this issue, we integrated questionnaire items on homework engagement and digital homework avoidance in a national add-on to PISA 2018 in Switzerland. Data from the Swiss sample can serve as a case study for further research with a wider cultural background. This study provides an overview of the descriptive results and tries to identify predictors of the use of digital technology for academic dishonesty when completing homework.
1.1 Prevalence and factors of digital academic dishonesty in schools
According to Pavela’s ( 1997 ) framework, four different types of academic dishonesty can be distinguished: cheating by using unauthorized materials, plagiarism by copying the work of others, fabrication of invented evidence, and facilitation by helping others in their attempts at academic dishonesty. Academic dishonesty can happen in assessment situations, as well as in learning situations. In formal assessments, academic dishonesty usually serves the purpose of passing a test or getting a better grade despite lacking the proper abilities or knowledge. In learning-related situations such as homework, where assignments are mandatory, cheating practices equally qualify as academic dishonesty. For perpetrators, these practices can be seen as shortcuts in which the willingness to invest the proper time and effort into learning is missing (Chow, 2021; Waltzer & Dahl, 2022 ). The interviews by Waltzer & Dahl ( 2022 ) reveal that students do perceive cheating as being wrong but this does not prevent them from engaging in at least one type of dishonest practice. While academic dishonesty is not a new phenomenon, it has been changing together with the development of new digital technologies (Anderman & Koenka, 2017 ; Ercegovac & Richardson, 2004 ). With the rapid growth in technologies, new forms of homework avoidance, such as copying and plagiarism, are developing (Evering & Moorman, 2012 ; Ma et al., 2008 ) summarized the findings of the 2006 U.S. surveys of the Josephson Institute of Ethics with the conclusion that the internet has led to a deterioration of ethics among students. In 2006, one-third of high school students had copied an internet document in the past 12 months, and 60% had cheated on a test. In 2012, these numbers were updated to 32% and 51%, respectively (Josephson Institute of Ethics, 2012 ). Further, 75% reported having copied another’s homework. Surprisingly, only a few studies have provided more recent evidence on the prevalence of academic dishonesty in middle and high schools. The results from colleges and universities are hardly comparable, and until now, this topic has not been addressed in international large-scale studies on schooling and school performance.
Despite the lack of representative studies, research has identified many factors in smaller and non-representative samples that might explain why some students engage in dishonest practices and others do not. These include male gender (Whitley et al., 1999 ), the “dark triad” of personality traits in contrast to conscientiousness and agreeableness (e.g., Cuadrado et al., 2021 ; Giluk & Postlethwaite, 2015 ), extrinsic motivation and performance/avoidance goals in contrast to intrinsic motivation and mastery goals (e.g., Anderman & Koenka, 2017 ; Krou et al., 2021 ), self-efficacy and achievement scores (e.g., Nora & Zhang, 2010 ; Yaniv et al., 2017 ), unethical attitudes, and low fear of being caught (e.g., Cheng et al., 2021 ; Kam et al., 2018 ), influenced by the moral norms of peers and the conditions of the educational context (e.g., Isakov & Tripathy, 2017 ; Kapoor & Kaufman, 2021 ). Similar factors have been reported regarding research on the causes of plagiarism (Husain et al., 2017 ; Moss et al., 2018 ). Further, the systematic review from Chiang et al. ( 2022 ) focused on factors of academic dishonesty in online learning environments. The analyses, based on the six-components behavior engineering, showed that the most prominent factors were environmental (effect of incentives) and individual (effect of motivation). Despite these intensive research efforts, there is still no overarching model that can comprehensively explain the interplay of these factors.
1.2 Effects of homework engagement and digital dishonesty on school performance
In meta-analyses of schools, small but significant positive effects of homework have been found regarding learning and achievement (e.g., Baş et al., 2017 ; Chen & Chen, 2014 ; Fan et al., 2017 ). In their review, Fan et al. ( 2017 ) found lower effect sizes for studies focusing on the time or frequency of homework than for studies investigating homework completion, homework grades, or homework effort. In large surveys, such as PISA, homework measurement by estimating after-school working hours has been customary practice. However, this measure could hide some other variables, such as whether teachers even give homework, whether there are school or state policies regarding homework, where the homework is done, whether it is done alone, etc. (e.g., Fernández-Alonso et al., 2015 , 2017 ). Trautwein ( 2007 ) and Trautwein et al. ( 2009 ) repeatedly showed that homework effort rather than the frequency or the time spent on homework can be considered a better predictor for academic achievement Effort and engagement can be seen as closely interrelated. Martin et al. ( 2017 ) defined engagement as the expressed behavior corresponding to students’ motivation. This has been more recently expanded by the notion of the quality of homework completion (Rosário et al., 2018 ; Xu et al., 2021 ). Therefore, it is a plausible assumption that academic dishonesty when doing homework is closely related to low homework effort and a low quality of homework completion, which in turn affects academic achievement. However, almost no studies exist on the effects of homework avoidance or academic dishonesty on academic achievement. Studies investigating the relationship between academic dishonesty and academic achievement typically use academic achievement as a predictor of academic dishonesty, not the other way around (e.g., Cuadrado et al., 2019 ; McCabe et al., 2001 ). The results of these studies show that low-performing students tend to engage in dishonest practices more often. However, high-performing students also seem to be prone to cheating in highly competitive situations (Yaniv et al., 2017 ).
1.3 Present study and hypotheses
The present study serves three combined purposes.
First, based on the additional questionnaires integrated into the Program for International Student Assessment 2018 (PISA 2018) data collection in Switzerland, we provide descriptive figures on the frequency of homework effort and the various forms of digitally-supported homework avoidance practices.
Second, the data were used to identify possible factors that explain higher levels of digitally-supported homework avoidance practices. Based on our review of the literature presented in Section 1.1 , we hypothesized (Hypothesis 1 – H1) that these factors include homework effort, age, gender, socio-economic status, and study program.
Finally, we tested whether digitally-supported homework avoidance practices were a significant predictor of test score performance. We expected (Hypothesis 2 – H2) that technology-related factors influencing test scores include not only those reported by Petko et al. ( 2017 ) but also self-reported engagement in digital dishonesty practices. .
2.1 Participants
Our analyses were based on data collected for PISA 2018 in Switzerland, made available in June 2021 (Erzinger et al., 2021 ). The target sample of PISA was 15-year-old students, with a two-phase sampling: schools and then students (Erzinger et al., 2019 , p.7–8, OECD, 2019a ). A total of 228 schools were selected for Switzerland, with an original sample of 5822 students. Based on the PISA 2018 technical report (OECD, 2019a ), only participants with a minimum of three valid responses to each scale used in the statistical analyses were included (see Section 2.2 ). A final sample of 4771 responses (48% female) was used for statistical analyses. The mean age was 15 years and 9 months ( SD = 3 months). As Switzerland is a multilingual country, 60% of the respondents completed the questionnaires in German, 23% in French, and 17% in Italian.
2.2 Measures
2.2.1 digital dishonesty in homework scale.
This six-item digital dishonesty for homework scale assesses the use of digital technology for homework avoidance and copying (IC801 C01 to C06), is intended to work as a single overall scale for digital homework dishonesty practice constructed to include items corresponding to two types of dishonest practices from Pavela ( 1997 ), namely cheating and plagiarism (see Table 1 ). Three items target individual digital practices to avoid homework, which can be referred to as plagiarism (items 1, 2 and 5). Two focus more on social digital practices, for which students are cheating together with peers (items 4 and 6). One item target cheating as peer authorized plagiarism. Response options are based on questions on the productive use of digital technologies for homework in the common PISA survey (IC010), with an additional distinction for the lowest frequency option (6-point Likert scale). The scale was not tested prior to its integration into the PISA questionnaire, as it was newly developed for the purposes of this study.
2.2.2 Homework engagement scale
The scale, originally developed by Trautwein et al. (Trautwein, 2007 ; Trautwein et al., 2006 ), measures homework engagement (IC800 C01 to C06) and can be subdivided into two sub-scales: homework compliance and homework effort. The reliability of the scale was tested and established in different variants, both in Germany (Trautwein et al., 2006 ; Trautwein & Köller, 2003 ) and in Switzerland (Schnyder et al., 2008 ; Schynder Godel, 2015 ). In the adaptation used in the PISA 2018 survey, four items were positively poled (items 1, 2, 4, and 6), and two items were negatively poled (items 3 and 5) and presented with a 4-point Likert scale ranging from “Does not apply at all” to “Applies absolutely.” This adaptation showed acceptable reliability in previous studies in Switzerland (α = 0.73 and α = 0.78). The present study focused on homework effort, and thus only data from the corresponding sub-scale was analyzed (items 2 [I always try to do all of my homework], 4 [When it comes to homework, I do my best], and 6 [On the whole, I think I do my homework more conscientiously than my classmates]).
2.2.3 Demographics
Previous studies showed that demographic characteristics, such as age, gender, and socioeconomic status, could impact learning outcomes (Jacobs et al., 2002 ) and intention to use digital tools for learning (Tarhini et al., 2014 ). Gender is a dummy variable (ST004), with 1 for female and 2 for male. Socioeconomic status was analyzed based on the PISA 2018 index of economic, social, and cultural status (ESCS). It is computed from three other indices (OECD, 2019b , Annex A1): parents’ highest level of education (PARED), parents’ highest occupational status (HISEI), and home possessions (HOMEPOS). The final ESCS score is transformed so that 0 corresponds to an average OECD student. More details can be found in Annex A1 from PISA 2018 Results Volume 3 (OECD, 2019b ).
2.2.4 Study program
Although large-scale studies on schools have accounted for the differences between schools, the study program can also be a factor that directly affects digital homework dishonesty practices. In Switzerland, 15-year-old students from the PISA sampling pool can be part of at least six main study programs, which greatly differ in terms of learning content. In this study, study programs distinguished both level and type of study: lower secondary education (gymnasial – n = 798, basic requirements – n = 897, advanced requirements – n = 1235), vocational education (classic – n = 571, with baccalaureate – n = 275), and university entrance preparation ( n = 745). An “other” category was also included ( n = 250). This 6-level ordinal variable was dummy coded based on the available CNTSCHID variable.
2.2.5 Technologies and schools
The PISA 2015 ICT (Information and Communication Technology) familiarity questionnaire included most of the technology-related variables tested by Petko et al. ( 2017 ): ENTUSE (frequency of computer use at home for entertainment purposes), HOMESCH (frequency of computer use for school-related purposes at home), and USESCH (frequency of computer use at school). However, the measure of student’s attitudes toward ICT in the 2015 survey was different from that of the 2012 dataset. Based on previous studies (Arpacı et al., 2021 ; Kunina-Habenicht & Goldhammer, 2020 ), we thus included INICT (Student’s ICT interest), COMPICT (Students’ perceived ICT competence), AUTICT (Students’ perceived autonomy related to ICT use), and SOIACICT (Students’ ICT as a topic in social interaction) instead of the variable ICTATTPOS of the 2012 survey.
2.2.6 Test scores
The PISA science, mathematics, and reading test scores were used as dependent variables to test our second hypothesis. Following Aparicio et al. ( 2021 ), the mean scores from plausible values were computed for each test score and used in the test score analysis.
2.3 Data analyses
Our hypotheses aim to assess the factors explaining student digital homework dishonesty practices (H1) and test score performance (H2). At the student level, we used multilevel regression analyses to decompose the variance and estimate associations. As we used data for Switzerland, in which differences between school systems exist at the level of provinces (within and between), we also considered differences across schools (based on the variable CNTSCHID).
Data were downloaded from the main PISA repository, and additional data for Switzerland were available on forscenter.ch (Erzinger et al., 2021 ). Analyses were computed with Jamovi (v.1.8 for Microsoft Windows) statistics and R packages (GAMLj, lavaan).
3.1 Additional scales for Switzerland
3.1.1 digital dishonesty in homework practices.
The digital homework dishonesty scale (6 items), computed with the six items IC801, was found to be of very good reliability overall (α = 0.91, ω = 0.91). After checking for reliability, a mean score was computed for the overall scale. The confirmatory factor analysis for the one-dimensional model reached an adequate fit, with three modifications using residual covariances between single items χ 2 (6) = 220, p < 0.001, TLI = 0.969, CFI = 0.988, RMSEA (Root Mean Square Error of Approximation) = 0.086, SRMR = 0.016).
On the one hand, the practice that was the least reported was copying something from the internet and presenting it as their own (51% never did). On the other hand, students were more likely to partially copy content from the internet and modify it to present as their own (47% did it at least once a month). Copying answers shared by friends was rather common, with 62% of the students reporting that they engaged in such practices at least once a month.
When all surveyed practices were taken together, 7.6% of the students reported that they had never engaged in digitally dishonest practices for homework, while 30.6% reported cheating once or twice a week, 12.1% almost every day, and 6.9% every day (Table 1 ).
3.1.2 Homework effort
The overall homework engagement scale consisted of six items (IC800), and it was found to be acceptably reliable (α = 0.76, ω = 0.79). Items 3 and 5 were reversed for this analysis. The homework compliance sub-scale had a low reliability (α = 0.58, ω = 0.64), whereas the homework effort sub-scale had an acceptable reliability (α = 0.78, ω = 0.79). Based on our rationale, the following statistical analyses used only the homework effort sub-scale. Furthermore, this focus is justified by the fact that the homework compliance scale might be statistically confounded with the digital dishonesty in homework scale.
Descriptive weighted statistics per item (Table 2 ) showed that while most students (80%) tried to complete all of their homework, only half of the students reported doing those diligently (53.3%). Most students also reported that they believed they put more effort into their homework than their peers (77.7%). The overall mean score of the composite scale was 2.81 ( SD = 0.69).
3.2 Multilevel regression analysis: Predictors of digital dishonesty in homework (H1)
Mixed multilevel modeling was used to analyze predictors of digital homework avoidance while considering the effect of school (random component). Based on our first hypothesis, we compared several models by progressively including the following fixed effects: homework effort and personal traits (age, gender) (Model 2), then socio-economic status (Model 3), and finally, study program (Model 4). The results are presented in Table 3 . Except for the digital homework dishonesty and homework efforts scales, all other scales were based upon the scores computed according to the PISA technical report (OECD, 2019a ).
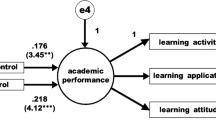
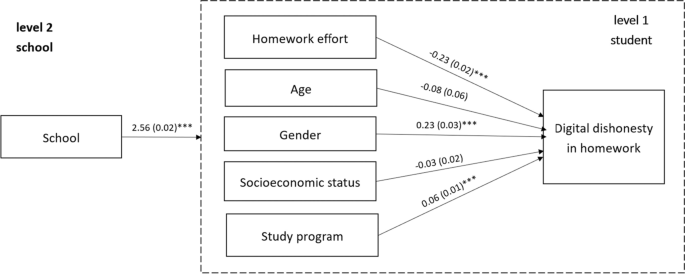
We first compared variance components. Variance was decomposed into student and school levels. Model 1 provides estimates of the variance component without any covariates. The intraclass coefficient (ICC) indicated that about 6.6% of the total variance was associated with schools. The parameter (b = 2.56, SE b = 0.025 ) falls within the 95% confidence interval. Further, CI is above 0 and thus we can reject the null hypothesis. Comparing the empty model to models with covariates, we found that Models 2, 3 and 4 showed an increase in total explained variance to 10%. Variance explained by the covariates was about 3% in Models 2 and 3, and about 4% in Model 4. Interestingly, in our models, student socio-economic status, measured by the PISA index, never accounted for variance in digitally-supported dishonest practices to complete homework.
Summary of the two-steps Model 4 (estimates - β, with standard errors and significance levels, *** p < 0.001)
Further, model comparison based on AIC indicates that Model 4, including homework effort, personal traits, socio-economic status, and study program, was the better fit for the data. In Model 4 (Table 3 ; Fig. 1 ), we observed that homework effort and gender were negatively associated with digital dishonesty. Male students who invested less effort in their homework were more prone to engage in digital dishonesty. The study program was positively but weakly associated with digital dishonesty. Students in programs that target higher education were less likely to engage in digital dishonesty when completing homework.
3.3 Multilevel regression analysis: Cheating and test scores (H2)
Our first hypothesis aimed to provide insights into characteristics of students reporting that they regularly use digital resources dishonestly when completing homework. Our second hypothesis focused on whether digitally-supported homework avoidance practices was linked to results of test scores. Mixed multilevel modeling was used to analyze predictors of test scores while considering the effect of school (random component). Based on the study by Petko et al. ( 2017 ), we compared several models by progressively including the following fixed effects ICT use (three measures) (Model 2), then attitude toward ICT (four measures) (Model 3), and finally, digital dishonesty in homework (single measure) (Model 4). The results are presented in Table 4 for science, Table 5 for mathematics, and Table 6 for reading.
Variance components were decomposed into student and school level. ICC for Model 1 indicated that 37.9% of the variance component without covariates was associated with schools.
Taking Model 1 as a reference, we observed an increase in total explained variance to 40.5% with factors related to ICT use (Model 2), to 40.8% with factors related to attitude toward ICT (Model 3), and to 41.1% with the single digital dishonesty factor. It is interesting to note that we obtained different results from those reported by Petko et al. ( 2017 ). In their study, they found significant effects on the explained variances of ENTUSE, USESCH, and ICTATTPOS but not of HOMESCH for Switzerland. In the present study (Model 3), HOMESCH and USESCH were significant predictors but not ENTUSE, and for attitude toward ICT, all but INTICT were significant predictors of the variance. However, factors corresponding to ICT use were negatively associated with test performance, as in the study by Petko et al. ( 2017 ). Similarly, all components of attitude toward ICT positively affected science test scores, except for students’ ICT as a topic in social interaction.
Based on the AIC values, Model 4, including ICT use, attitude toward ICT, and digital dishonesty, was the better fit for the data. The parameter ( b = 498.00, SE b = 3.550) shows that our sample falls within the 95% confidence interval and that we can reject the null hypothesis. In this model, all factors except the use of ICT outside of school for leisure were significant predictors of explained variance in science test scores. These results are consistent with those reported by Petko et al. ( 2017 ), in which more frequent use of ICT negatively affected science test scores, with an overall positive effect of positive attitude toward ICT. Further, we observed that homework avoidance with digital resources strongly negatively affected performance, with lower performance associated with students reporting a higher frequency of engagement in digital dishonesty practices.
For mathematics test scores, results from Models 2 and 3 showed a similar pattern than those for science, and Model 4 also explained the highest variance (41.2%). The results from Model 4 contrast with those found by Petko et al. ( 2017 ), as in this study, HOMESCH was the only significant variable of ICT use. Regarding attitudes toward ICT, only two measures (COMPICT and AUTICT) were significant positive factors in Model 4. As for science test scores, digital dishonesty practices were a significantly strong negative predictor. Students who reported cheating more frequently were more likely to perform poorly on mathematics tests.
The analyses of PISA test scores for reading in Model 2 was similar to that of science and mathematics, with ENTUSE being a non-significant predictor when we included only measures of ICT use as predictors. In Model 3, contrary to the science and mathematics test scores models, in which INICT was non-significant, all measures of attitude toward ICT were positively significant predictors. Nevertheless, as for science and mathematics, Model 4, which included digital dishonesty, explained the greater variance in reading test scores (42.2%). We observed that for reading, all predictors were significant in Model 4, with an overall negative effect of ICT use, a positive effect of attitude toward ICT—except for SOIAICT, and a negative effect of digital dishonesty on test scores. Interestingly, the detrimental effect of using digital resources to engage in dishonest homework completion was the strongest in reading test scores.
4 Discussion
In this study, we were able to provide descriptive statistics on the prevalence of digital dishonesty among secondary students in the Swiss sample of PISA 2018. Students from this country were selected because they received additional questions targeting both homework effort and the frequency with which they engaged in digital dishonesty when doing homework. Descriptive statistics indicated that fairly high numbers of students engage in dishonest homework practices, with 49.6% reporting digital dishonesty at least once or twice a week. The most frequently reported practice was copying answers from friends, which was undertaken at least once a month by more than two-thirds of respondents. Interestingly, the most infamous form of digital dishonesty, that is plagiarism by copy-pasting something from the internet (Evering & Moorman, 2012 ), was admitted to by close to half of the students (49%). These results for homework avoidance are close to those obtained by previous research on digital academic plagiarism (e.g., McCabe et al., 2001 ).
We then investigated what makes a cheater, based on students’ demographics and effort put in doing their homework (H1), before looking at digital dishonesty as an additional ICT predictor of PISA test scores (mathematics, reading, and science) (H2).
The goal of our first research hypothesis was to determine student-related factors that may predict digital homework avoidance practices. Here, we focused on factors linked to students’ personal characteristics and study programs. Our multilevel model explained about 10% of the variance overall. Our analysis of which students are more likely to digital resources to avoid homework revealed an increased probability for male students who did not put much effort into doing their homework and who were studying in a program that was not oriented toward higher education. Thus, our findings tend to support results from previous research that stresses the importance of gender and motivational factors for academic dishonesty (e.g., Anderman & Koenka, 2017 ; Krou et al., 2021 ). Yet, as our model only explained little variance and more research is needed to provide an accurate representation of the factors that lead to digital dishonesty. Future research could include more aspects that are linked to learning, such as peer-related or teaching-related factors. Possibly, how closely homework is embedded in the teaching and learning culture may play a key role in digital dishonesty. Additional factors might be linked to the overall availability and use of digital tools. For example, the report combining factors from the PISA 2018 school and student questionnaires showed that the higher the computer–student ratio, the lower students scored in the general tests (OECD, 2020b ). A positive association with reading disappeared when socio-economic background was considered. This is even more interesting when considering previous research indicating that while internet access is not a source of divide among youths, the quality of use is still different based on gender or socioeconomic status (Livingstone & Helsper, 2007 ). Thus, investigating the usage-related “digital divide” as a potential source of digital dishonesty is an interesting avenue for future research (Dolan, 2016 ).
Our second hypothesis considered that digital dishonesty in homework completion can be regarded as an additional ICT-related trait and thus could be included in models targeting the influence of traditional ICT on PISA test scores, such as Petko et al. ( 2017 ) study. Overall, our results on the influence of ICT use and attitudes toward ICT on test scores are in line with those reported by Petko et al. ( 2017 ). Digital dishonesty was found to negatively influence test scores, with a higher frequency of cheating leading to lower performance in all major PISA test domains, and particularly so for reading. For each subject, the combined models explained about 40% of the total variance.
4.1 Conclusions and recommendations
Our results have several practical implications. First, the amount of cheating on homework observed calls for new strategies for raising homework engagement, as this was found to be a clear predictor of digital dishonesty. This can be achieved by better explaining the goals and benefits of homework, the adverse effects of cheating on homework, and by providing adequate feedback on homework that was done properly. Second, teachers might consider new forms of homework that are less prone to cheating, such as doing homework in non-digital formats that are less easy to copy digitally or in proctored digital formats that allow for the monitoring of the process of homework completion, or by using plagiarism software to check homework. Sometimes, it might even be possible to give homework and explicitly encourage strategies that might be considered cheating, for example, by working together or using internet sources. As collaboration is one of the 21st century skills that students are expected to develop (Bray et al., 2020 ), this can be used to turn cheating into positive practice. There is already research showing the beneficial impact of computer-supported collaborative learning (e.g., Janssen et al., 2012 ). Zhang et al. ( 2011 ) compared three homework assignment (creation of a homepage) conditions: individually, in groups with specific instructions, and in groups with general instructions. Their results showed that computer supported collaborative homework led to better performance than individual settings, only when the instructions were general. Thus, promoting digital collaborative homework could support the development of students’ digital and collaborative skills.
Further, digital dishonesty in homework needs to be considered different from cheating in assessments. In research on assessment-related dishonesty, cheating is perceived as a reprehensible practice because grades obtained are a misrepresentation of student knowledge, and cheating “implies that efficient cheaters are good students, since they get good grades” (Bouville, 2010 , p. 69). However, regarding homework, this view is too restrictive. Indeed, not all homework is graded, and we cannot know for sure whether students answered this questionnaire while considering homework as a whole or only graded homework (assessments). Our study did not include questions about whether students displayed the same attitudes and practices toward assessments (graded) and practice exercises (non-graded), nor did it include questions on how assessments and homework were related. By cheating on ungraded practice exercises, students will primarily hamper their own learning process. Future research could investigate in more depth the kinds of homework students cheat on and why.
Finally, the question of how to foster engaging homework with digital tools becomes even more important in pandemic situations. Numerous studies following the switch to home schooling at the beginning of the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic have investigated the difficulties for parents in supporting their children (Bol, 2020 ; Parczewska, 2021 ); however, the question of digital homework has not been specifically addressed. It is unknown whether the increase in digital schooling paired with discrepancies in access to digital tools has led to an increase in digital dishonesty practices. Data from the PISA 2018 student questionnaires (OECD, 2020a ) indicated that about 90% of students have a computer for schoolwork (OECD average), but the availability per student remains unknown. Digital homework can be perceived as yet another factor of social differences (see for example Auxier & Anderson, 2020 ; Thorn & Vincent-Lancrin, 2022 ).
4.2 Limitations and directions
The limitations of the study include the format of the data collected, with the accuracy of self-reports to mirror actual practices restricted, as these measures are particularly likely to trigger response bias, such as social desirability. More objective data on digital dishonesty in homework-related purposes could, for example, be obtained by analyzing students’ homework with plagiarism software. Further, additional measures that provide a more complete landscape of contributing factors are necessary. For example, in considering digital homework as an alternative to traditional homework, parents’ involvement in homework and their attitudes toward ICT are factors that have not been considered in this study (Amzalag, 2021 ). Although our results are in line with studies on academic digital dishonesty, their scope is limited to the Swiss context. Moreover, our analyses focused on secondary students. Results might be different with a sample of younger students. As an example, Kiss and Teller ( 2022 ) measured primary students cheating practices and found that individual characteristics were not a stable predictor of cheating between age groups. Further, our models included school as a random component, yet other group variables, such as class and peer groups, may well affect digital homework avoidance strategies.
The findings of this study suggest that academic dishonesty when doing homework needs to be addressed in schools. One way, as suggested by Chow et al. ( 2021 ) and Djokovic et al. ( 2022 ), is to build on students’ practices to explain which need to be considered cheating. This recommendation for institutions to take preventive actions and explicit to students the punishment faced in case of digital academic behavior was also raised by Chiang et al. ( 2022 ). Another is that teachers may consider developing homework formats that discourage cheating and shortcuts (e.g., creating multimedia documents instead of text-based documents, using platforms where answers cannot be copied and pasted, or using advanced forms of online proctoring). It may also be possible to change homework formats toward more open formats, where today’s cheating practices are allowed when they are made transparent (open-book homework, collaborative homework). Further, experiences from the COVID-19 pandemic have stressed the importance of understanding the factors related to the successful integration of digital homework and the need to minimize the digital “homework gap” (Auxier & Anderson, 2020 ; Donnelly & Patrinos, 2021 ). Given that homework engagement is a core predictor of academic dishonesty, students should receive meaningful homework in preparation for upcoming lessons or for practicing what was learned in past lessons. Raising student’s awareness of the meaning and significance of homework might be an important piece of the puzzle to honesty in learning.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in SISS base at https://doi.org/10.23662/FORS-DS-1285-1 , reference number 1285.
Agasisti, T., Gil-Izquierdo, M., & Han, S. W. (2020). ICT Use at home for school-related tasks: What is the effect on a student’s achievement? Empirical evidence from OECD PISA data. Education Economics, 28 (6), 601–620. https://doi.org/10.1080/09645292.2020.1822787
Article Google Scholar
Amzalag, M. (2021). Parent attitudes towards the integration of digital learning games as an alternative to traditional homework. International Journal of Information and Communication Technology Education, 17 (3), 151–167. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJICTE.20210701.oa10
Anderman, E. M., & Koenka, A. C. (2017). The relation between academic motivation and cheating. Theory into Practice, 56 (2), 95–102. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405841.2017.1308172
Aparicio, J., Cordero, J. M., & Ortiz, L. (2021). Efficiency analysis with educational data: How to deal with plausible values from international large-scale assessments. Mathematics, 9 (13), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9131579
Arpacı, S., Mercan, F., & Arıkan, S. (2021). The differential relationships between PISA 2015 science performance and, ICT availability, ICT use and attitudes toward ICT across regions: evidence from 35 countries. Education and Information Technologies, 26 (5), 6299–6318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10576-2
Auxier, B., & Anderson, M. (2020, March 16). As schools close due to the coronavirus, some U.S. students face a digital “homework gap”. Pew Research Center, 1–8. http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2018/10/19/5-charts-on-global-views-of-china/ . Retrieved November 29th, 2021
Baş, G., Şentürk, C., & Ciğerci, F. M. (2017). Homework and academic achievement: A meta-analytic review of research. Issues in Educational Research, 27 (1), 31–50.
Google Scholar
Blau, I., & Eshet-Alkalai, Y. (2017). The ethical dissonance in digital and non-digital learning environments: Does technology promotes cheating among middle school students? Computers in Human Behavior, 73, 629–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.03.074
Bol, T. (2020). Inequality in homeschooling during the Corona crisis in the Netherlands. First results from the LISS Panel. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/hf32q
Bouville, M. (2010). Why is cheating wrong? Studies in Philosophy and Education, 29 (1), 67–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11217-009-9148-0
Bray, A., Byrne, P., & O’Kelly, M. (2020). A short instrument for measuring students’ confidence with ‘key skills’ (SICKS): Development, validation and initial results. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 37 (June), 100700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2020.100700
Chen, C. M., & Chen, F. Y. (2014). Enhancing digital reading performance with a collaborative reading annotation system. Computers and Education, 77, 67–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2014.04.010
Cheng, Y. C., Hung, F. C., & Hsu, H. M. (2021). The relationship between academic dishonesty, ethical attitude and ethical climate: The evidence from Taiwan. Sustainability (Switzerland), 13 (21), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132111615
Chiang, F. K., Zhu, D., & Yu, W. (2022). A systematic review of academic dishonesty in online learning environments. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning , 907–928. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12656
Chow, H. P. H., Jurdi-Hage, R., & Hage, H. S. (2021). Justifying academic dishonesty: A survey of Canadian university students. International Journal of Academic Research in Education , December. https://doi.org/10.17985/ijare.951714
Cuadrado, D., Salgado, J. F., & Moscoso, S. (2019). Prevalence and correlates of academic dishonesty: Towards a sustainable university. Sustainability (Switzerland) , 11 (21). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11216062
Cuadrado, D., Salgado, J. F., & Moscoso, S. (2021). Personality, intelligence, and counterproductive academic behaviors: A meta-analysis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 120 (2), 504–537. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspp0000285
Djokovic, R., Janinovic, J., Pekovic, S., Vuckovic, D., & Blecic, M. (2022). Relying on technology for countering academic dishonesty: the impact of online tutorial on students’ perception of academic misconduct. Sustainability (Switzerland) , 14 (3). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031756
Dolan, J. E. (2016). Splicing the divide: A review of research on the evolving digital divide among K–12 students. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 48 (1), 16–37.
Donnelly, R., & Patrinos, H. A. (2021). Learning loss during Covid-19: An early systematic review. Prospects , 0123456789 . https://doi.org/10.1007/s11125-021-09582-6
Ercegovac, Z., & Richardson, J. V. (2004). Academic dishonesty, plagiarism included, in the digital age: A literature review. College & Research Libraries, 65 (4), 301–318. https://doi.org/10.5860/crl.65.4.301
Erzinger, A. B., Verner, M., König, N., Petrucci, F., Nidegger, C., Roos, E., & Salvisberg, M. (2019). PISA 2018: Les élèves de Suisse en comparaison internationale . SEFRI/CDIP et Consortium PISA.ch.
Erzinger, A. B., Verner, M., Salvisberg, M., Nidegger, C., & Seiler, S. (2021). PISA 2018 in Switzerland, add-on to the international dataset: Swiss specific variables [Dataset] . FORS. https://doi.org/10.23662/FORS-DS-1285-1
Evering, L. C., & Moorman, G. (2012). Rethinking plagiarism in the digital age. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 56 (1), 35–44.
Fan, H., Xu, J., Cai, Z., He, J., & Fan, X. (2017). Homework and students’ achievement in math and science: A 30-year meta-analysis, 1986–2015. Educational Research Review, 20, 35–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2016.11.003
Fernández-Alonso, R., álvarez-Díaz, M., Suárez-álvarez, J., & Muñiz, J. (2017). Students’ achievement and homework assignment strategies. Frontiers in Psychology, 8 (MAR), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00286
Fernández-Alonso, R., Suárez-Álvarez, J., & Muñiz, J. (2015). Adolescents’ homework performance in mathematics and science: Personal factors and teaching practices. Journal of Educational Psychology, 107 (4), 1075–1085. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000032
Giluk, T. L., & Postlethwaite, B. E. (2015). Big Five personality and academic dishonesty: A meta-analytic review. Personality and Individual Differences, 72, 59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2014.08.027
Husain, F. M., Al-Shaibani, G. K. S., & Mahfoodh, O. H. A. (2017). Perceptions of and attitudes toward plagiarism and factors contributing to plagiarism: A review of studies. Journal of Academic Ethics, 15 (2), 167–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10805-017-9274-1
Isakov, M., & Tripathy, A. (2017). Behavioral correlates of cheating: Environmental specificity and reward expectation. PLoS One1, 12 (10), 6–11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186054
Jacobs, J. E., Lanza, S., Osgood, D. W., Eccles, J. S., & Wigfield, A. (2002). Changes in children’s self-competence and values: Gender and domain differences across grades one through twelve. Child Development, 73 (2), 509–527. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00421
Janssen, J., Erkens, G., Kirschner, P., & Kanselaar, G. (2012). Task-related and social regulation during online collaborative learning. Metacognition and Learning, 7 (1), 25–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-010-9061-5
Josephson Institute of Ethics (2012). 2012 Report card on the ethics of American youth . https://charactercounts.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/ReportCard-2012-DataTables.pdf . Retrieved January 24th, 2022
Kam, C. C. S., Hue, M. T., & Cheung, H. Y. (2018). Academic dishonesty among Hong Kong secondary school students: Application of theory of planned behavior. Educational Psychology, 38 (7), 945–963. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2018.1454588
Kapoor, H., & Kaufman, J. C. (2021). Are cheaters common or creative?: Person-situation interactions of resistance in learning contexts. Journal of Academic Ethics, 19 (2), 157–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10805-020-09379-w
Kiss, H. J., & Keller, T. J. (2022). Individual characteristics do (not) matter in cheating. Available at SSRN 4001278. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4001278
Krou, M. R., Fong, C. J., & Hoff, M. A. (2021). Achievement motivation and academic dishonesty: A meta-analytic investigation. Educational Psychology Review, 33 (2), 427–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-020-09557-7
Kunina-Habenicht, O., & Goldhammer, F. (2020). ICT engagement: A new construct and its assessment in PISA 2015. Large-Scale Assessments in Education , 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40536-020-00084-z
Livingstone, S., & Helsper, E. (2007). Gradations in digital inclusion: Children, young people and the digital divide. New Media and Society, 9 (4), 671–696. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444807080335
Ma, H. J., Wan, G., & Lu, E. Y. (2008). Digital cheating and plagiarism in schools. Theory into Practice, 47 (3), 197–203. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405840802153809
Martin, A. J., Ginns, P., & Papworth, B. (2017). Motivation and engagement: Same or different? Does it matter? Learning and Individual Differences, 55, 150–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2017.03.013
McCabe, D. L. (2005). It takes a village: Academic dishonesty & educational opportunity. Liberal Education, 91 (3), 26–31.
McCabe, D. L., Treviño, L. K., & Butterfield, K. D. (2001). Cheating in academic institutions: A decade of research. Ethics and Behavior, 11 (3), 219–232. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327019EB1103_2
Moss, S. A., White, B., & Lee, J. (2018). A systematic review into the psychological causes and correlates of plagiarism. Ethics and Behavior, 28 (4), 261–283. https://doi.org/10.1080/10508422.2017.1341837
Nora, W. L. Y., & Zhang, K. C. (2010). Motives of cheating among secondary students: The role of self-efficacy and peer influence. Asia Pacific Education Review, 11 (4), 573–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12564-010-9104-2
Odell, B., Cutumisu, M., & Gierl, M. (2020). A scoping review of the relationship between students’ ICT and performance in mathematics and science in the PISA data. Social Psychology of Education , 23 (6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11218-020-09591-x
OECD, & Publishing, O. E. C. D. (2015). Students, computers and learning: Making the connection . PISA. https://doi.org/10.1787/factbook-2015-68-en
OECD (2019a). Chapter 16. Scaling procedures and construct validation of context questionnaire data. In PISA 2018 Technical Report . OECD.
OECD (2019b). PISA 2018 Results - What school life means for students’ life (Vol. III). OECD Publishing. https://www.oecd.org/pisa/publications/PISA2018_CN_IDN.pdf . Retrieved October 20th, 2021
OECD (2020a). Learning remotely when schools close . 1–13. https://read.oecd-ilibrary.org/view/?ref=127_127063-iiwm328658&title=Learning-remotely-when-schools-close . Retrieved November 29th, 2021
OECD (2020b). PISA 2018 Results: Effective policies, successful schools (Vol. V). PISA, OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/ca768d40-en
Parczewska, T. (2021). Difficult situations and ways of coping with them in the experiences of parents homeschooling their children during the COVID-19 pandemic in Poland. Education 3–13 , 49 (7), 889–900. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004279.2020.1812689
Pavela, G. (1997). Applying the power of association on campus: A model code of academic integrity. Law and Policy, 24 (1), 1–22.
Petko, D., Cantieni, A., & Prasse, D. (2017). Perceived quality of educational technology matters: A secondary analysis of students ICT use, ICTRelated attitudes, and PISA 2012 test scores. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 54 (8), 1070–1091. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633116649373
Rosário, P., Carlos Núñez, J., Vallejo, G., Nunes, T., Cunha, J., Fuentes, S., & Valle, A. (2018). Homework purposes, homework behaviors, and academic achievement. Examining the mediating role of students’ perceived homework quality. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 53 (April), 168–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2018.04.001
Schnyder, I., Niggli, A., & Trautwein, U. (2008). Hausaufgabenqualität im Französischunterricht aus der Sicht von Schülern, Lehrkräften und Experten und die Entwicklung von Leistung, Hausaufgabensorgfalt und Bewertung der Hausaufgaben. Zeitschrift Fur Padagogische Psychologie, 22 (3–4), 233–246. https://doi.org/10.1024/1010-0652.22.34.233
Schynder Godel, I. (2015). Die Hausaufgaben unter der Lupe. Eine empirische Untersuchung im Fach Französisch als Fremdsprache.
Skryabin, M., Zhang, J., Liu, L., & Zhang, D. (2015). How the ICT development level and usage influence student achievement in reading, mathematics, and science. Computers and Education, 85, 49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.02.004
Tarhini, A., Hone, K., & Liu, X. (2014). Measuring the moderating effect of gender and age on e-learning acceptance in England: A structural equation modeling approach for an extended technology acceptance model. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 51 (2), 163–184. https://doi.org/10.2190/EC.51.2.b
Thorn, W., & Vincent-Lancrin, S. (2022). Education in the time of COVID-19 in France, Ireland, the Unites Kingdom and the United States: The nature and impact of remote learning. In F. M. Reimers (Ed.), Primary and secondary education during Covid-19 (pp. 383–420). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2632-5_2
Trautwein, U. (2007). The homework-achievement relation reconsidered: Differentiating homework time, homework frequency, and homework effort. Learning and Instruction, 17 (3), 372–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2007.02.009
Trautwein, U., & Köller, O. (2003). Was lange währt, wird nicht immer gut: Zur Rolle selbstregulativer Strategien bei der Hausaufgabenerledigung. Zeitschrift Für Pädagogische Psychologie German Journal of Educational Psychology, 17 (3–4), 199–209.
Trautwein, U., Lüdtke, O., Schnyder, I., & Niggli, A. (2006). Predicting homework effort: Support for a domain-specific, multilevel homework model. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98 (2), 438–456. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.98.2.438
Trautwein, U., Schnyder, I., Niggli, A., Neumann, M., & Lüdtke, O. (2009). Chameleon effects in homework research: The homework-achievement association depends on the measures used and the level of analysis chosen. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 34 (1), 77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2008.09.001
Waltzer, T., & Dahl, A. (2022). Why do students cheat? Perceptions, evaluations, and motivations. Ethics and Behavior , 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/10508422.2022.2026775
Whitley, B. E., Nelson, A. B., & Jones, C. J. (1999). Gender differences in cheating attitudes and classroom cheating behavior: A meta-analysis. Sex Roles, 41 (9–10), 657–680. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018863909149
Xu, J. (2015). Investigating factors that influence conventional distraction and tech-related distraction in math homework. Computers and Education, 81, 304–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2014.10.024
Xu, J., Du, J., Cunha, J., & Rosário, P. (2021). Student perceptions of homework quality, autonomy support, effort, and math achievement: Testing models of reciprocal effects. Teaching and Teacher Education , 108 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2021.103508
Yaniv, G., Siniver, E., & Tobol, Y. (2017). Do higher achievers cheat less? An experiment of self-revealing individual cheating. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Economics, 68, 91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2017.04.005
Zhang, L., Ayres, P., & Chan, K. (2011). Examining different types of collaborative learning in a complex computer-based environment: A cognitive load approach. Computers in Human Behavior, 27 (1), 94–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.03.038
Download references
Open access funding provided by University of Zurich
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Education, University of Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland
Juliette C. Désiron & Dominik Petko
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Juliette C. Désiron: Formal analysis, Writing (Original, Review and Editing), Dominik Petko: Conceptualization, Writing (Original, Review and Editing), Supervision.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Juliette C. Désiron .
Ethics declarations
Competing of interests, additional information, publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
List of abbreviations related to PISA datasets
students’ perceived autonomy related to ICT use
students’ perceived ICT competence
frequency of computer use at home for entertainment purposes
index of economic, social, and cultural status (computed from PARED, HISEI and HOMEPOS)
parents’ highest occupational status
home possessions
frequency of computer use for school-related purposes at home
digital cheating for homework items for Switzerland
homework engagement items for Switzerland
positive attitude towards ICT as a learning tool
student’s ICT interest
parents’ highest level of education
students’ ICT as a topic in social interaction
frequency of computer use at school
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Désiron, J.C., Petko, D. Academic dishonesty when doing homework: How digital technologies are put to bad use in secondary schools. Educ Inf Technol 28 , 1251–1271 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11225-y
Download citation
Received : 11 May 2022
Accepted : 05 July 2022
Published : 23 July 2022
Issue Date : February 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11225-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Academic dishonesty
- Digitally-supported cheating
- Secondary education
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Office of Student Support and Judicial Affairs
collaboration: when you can and when you can’t work with others, collaboration:, when you can and when you can’t work with others.
Collaboration is working with another or receiving assistance from someone (a classmate, friend, or parent, whether in person or electronically) to complete course work for a grade. Sometimes collaboration may be permitted, other times it is not. Collaboration can include:
- Jointly calculating homework problems
- Working in a group on a lab assignment
- Having another help one rewrite a paper
- Checking homework answers with others
- Sharing sources for a take-home exam
- “Debugging” another’s computer program

What is unauthorized collaboration ?
“Unauthorized collaboration” means working with others, without the specific permission of the instructor, on assignments that will be submitted for a grade. This rule applies to in-class or take-home tests, papers, labs, or homework assignments. Students may not collaborate without faculty authorization.
What are the ground rules?
Under the Code of Academic Conduct , all work submitted for a grade must be the student’s own original, independent work, unless the instructor permits collaboration, use of sources, or outside assistance.
- If working with others or receiving assistance is allowed, any help or collaboration must be given credit and cited.
- Students must comply with the course rules, and may only work together, or receive help, to the extent allowed by the instructor.
- If unsure about the limits, students must seek the instructor’s permission before working with one another.
- Even if the instructor permits collaboration, it is never ethical to copy someone’s work or let them copy yours.
- If your instructor asks whether you worked with anyone on an assignment, always tell the truth.
What about studying together?
The rules about unauthorized collaboration do not mean that students can't study together or help each other learn. Students are encouraged to do this. Having study partners and explaining concepts and ideas to one another is valuable in the learning process. If in doubt, ask your instructor.
1. In a computer science class, students are allowed to discuss “general concepts,” but all computer code submitted must be “individual work.” Four students assume they can work in a group, since each of them writes part of the code. Is this unauthorized collaboration?
Yes. “Individual work” means that students must work alone. Even if they didn’t copy, portions of the code submitted by each student were written by the other students – none of these four wrote all their own code as assigned. “General concepts” do not include specific solutions, answers, or code.
2. An instructor prohibits all collaboration, and tells students not to discuss homework, solve problems together, or compare answers. During office hours, a student asks about a homework assignment and the TA explains the question. Seeing this, two students work on the homework together. Have they violated the professor's rule?
Yes. Assistance provided by those who teach the course (whether in class, at discussion sections, or during office hours) does not imply or give permission for students to work together on assignments. Students may not exceed the limits set by the instructor, and may only work together as specified.
3. Students are assigned to do a lab experiment as partners because the apparatus needs two operators. Partners are allowed to discuss the concepts involved in the experiment and the lab report format, but calculations and write-ups (procedures and equipment used, results, graphs, and conclusions) are to be completed by each student, working alone, in the student's own words. Two student partners discuss their analysis of the data and work together to create a joint data table and graphs. Each paraphrases the joint work and submits the same table and graphs, formatted with different fonts and spacing. Did they break the rules?
Yes. Analyzing data, preparing graphs, and writing the report are important parts of the learning process; each student was required to do them alone. Even if neither copied, and they worked together only on the graphs, they still broke the rule.
Can the rules change from one course to the next? From one assignment to the next?
Yes. Collaboration may be permitted in one class and forbidden in another, because faculty have varying teaching strategies and goals. Different subjects (English, computer science, microbiology, and drama) require different approaches. Some assignments may be designed for individual work, and others for groups. Important lessons are learned from working individually, while group work develops other abilities. Working alone builds a student’s individual skills, knowledge, and self-confidence. This permits a more accurate and individually tailored evaluation of each student’s strengths and weaknesses, achievements and needs for improvement. When allowed, collaboration gives students experience working on a team, and they can learn from solving problems together, discussing questions, sharing strategies, and giving mutual encouragement. Students need both experiences – working alone and collaborating – to prepare for their chosen fields.
How can you know which rules apply?
- Read the syllabus, review the course website, and follow assignment instructions.
- If you’re not sure, ask the instructor. Or call OSSJA for help with understanding the rules.
- Don’t guess or assume – if you’re confused, others probably are too. You can help by raising the issue with the instructor.
- When in doubt, remember the Code of Academic Conduct requires students to work alone unless they have permission to work together.
- Students may consult tutors about pending work, as long as the tutor only identifies errors or demonstrates sample problems that are NOT part of the assignment. The tutor may not fix mistakes, re-write papers, or do homework for the student.
- Students may study together for tests, and may discuss concepts, readings, and notes to help each other learn the material before the test.
Why limit or prohibit collaboration?
- Unauthorized collaboration misrepresents joint work as the work of an individual.
- Unauthorized collaboration gives those who break the rules an unjust advantage and creates unfair competition.
- Those who always work with others are unaware of gaps in their own knowledge and skills, and do not learn all they can or should from their assignments.
Students are held accountable for understanding and following class rules, and must ask questions if they are unsure.
Although new technologies and communications media make unauthorized collaboration easier than ever, it can be detected. Some students who break the rules might not get caught this time – but next time they will. Unauthorized collaboration is unfair and undermines the educational goals of the University. If you have questions about course rules, talk to your instructor. For assistance regarding these issues, please visit the OSSJA website or call our office (530-752-1128).
Collaboration (Updated October 2022)

When does getting help on an assignment turn into cheating?
Policy Fellow, Mitchell Institute, Victoria University
Disclosure statement
Peter Hurley is affiliated with the Mitchell Institute for Education and Health Policy at Victoria University.
Victoria University provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
Students – whether at university or school – can get help from many places. They can go to a tutor, parent, teacher, a friend or consult a textbook.
But at which point does getting help cross the line into cheating?
Sometimes it’s clear. If you use a spy camera or smartwatch in an exam, you’re clearly cheating. And you’re cheating if you get a friend to sit an exam for you or write your assignment.
At other times the line is blurry. When it’s crossed, it constitutes academic misconduct. Academic misconduct is any action or attempted action that may result in creating an unfair academic advantage for yourself or others.
What about getting someone else to read a draft of your essay? What if they do more than proofread and they alter sections of an assignment? Does that constitute academic misconduct?
Learning, teaching or cheating?
There are a wide range of activities that constitute academic misconduct. These can include:
fabrication, which is just making things up. I could say “90 % of people admit to fabricating their assignments”, when this is not a fact but a statement I just invented
falsification, which is manipulating data to inaccurately portray results. This can occur by taking research results out of context and drawing conclusions not supported by data
misrepresentation, which is falsely representing yourself. Did you know I have a master’s degree from the University of Oxford on this topic? (Actually, I don’t)
plagiarism, which is when you use other people’s ideas or words without appropriate attribution. For instance, this list came from other people’s research and it is important to reference the source.
Sometimes students and teachers have different ideas of academic misconduct. One study found around 45% of academics thought getting someone else to correct a draft could constitute academic misconduct. But only 32% of students thought the same thing.
Read more: Assessment design won’t stop cheating, but our relationships with students might
In the same survey, most academics and students agreed having someone else like a parent or friend identify errors in a draft assignment, as opposed to correcting them, was fine.

Generally when a lecturer, teacher or another marker is assessing an assignment they need to establish the authenticity of the work. Authenticity means having confidence the work actually relates to the performance of the person being assessed, and not of another person.
The Australian government’s vocational education and training sector’s quality watchdog, for instance, considers authenticity as one of four so-called rules of evidence for an “effective assessment”.
The rules are:
validity, which is when the assessor is confident the student has the skills and knowledge required by the module or unit
sufficiency, which is when the quality, quantity and relevance of the assessment evidence is enough for the assessor to make a judgement
authenticity, where the assessor is confident the evidence presented for assessment is the learner’s own work
currency, where the assessor is confident the evidence relates to what the student can do now instead of some time in the past.
Generally speaking, if the assessor is confident the work is the product of a student’s thoughts and where help has been provided there is proper acknowledgement, it should be fine.
Why is cheating a problem?
It’s difficult to get a handle on how big the cheating problem is. Nearly 30% of students who responded to a 2012 UK survey agreed they had “submitted work taken wholly from an internet source” as their own.
In Australia, 6% of students in a survey of 14,000 reported they had engaged in “outsourcing behaviours” such as submitting someone else’s assignment as their own, and 15% of students had bought, sold or traded notes.
Getting someone to help with your assignment might seem harmless but it can hinder the learning process. The teacher needs to understand where the student is at with their learning, and too much help from others can get in the way.
Read more: Children learn from stress and failure: all the more reason you shouldn't do their homework
Some research describes formal education as a type of “ signal ”. This means educational attainment communicates important information about an individual to a third party such as an employer, a customer, or to an authority like a licensing body or government department. Academic misconduct interferes with that process.

How to deal with cheating
It appears fewer cheaters are getting away with it than before. Some of the world’s leading academic institutions have reported a 40% increase in academic misconduct cases over a three year period.
Technological advances mean online essay mills and “ contract cheating ” have become a bigger problem. This type of cheating involves outsourcing work to third parties and is concerning because it is difficult to detect .
Read more: 15% of students admit to buying essays. What can universities do about it?
But while technology has made cheating easier, it has also offered sophisticated systems for educators to verify the work is a person’s own. Software programs such as Turnitin can check if a student has plagiarised their assignment.
Institutions can also verify the evidence they are assessing relates to a student’s actual performance by using a range of assessment methods such as exams, oral presentations, and group assignments.
Academic misconduct can be a learning and cultural issue . Many students, particularly when they are new to higher education, are simply not aware what constitutes academic misconduct. Students can often be under enormous pressure that leads them to make poor decisions.
It is possible to deal with these issues in a constructive manner that help students learn and get the support they need. This can include providing training to students when they first enrol, offering support to assist students who may struggle, and when academic misconduct does occur, taking appropriate steps to ensure it does not happen again.
- Exam cheating
- Contract cheating
- University cheating
- Academic misconduct

Senior Lecturer - Earth System Science

Associate Director, Operational Planning

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Deputy Social Media Producer

Associate Professor, Occupational Therapy
Search form
- Impact and Prevention of Technology Concerning Student Cheating
BY ANNABEL MONAGHAN
The vast majority of Americans – 95 percent – today own a mobile phone. In 2015, 64 percent of American adults owned a smartphone and that percentage has grown to almost 77 percent in recent years. For adults aged 18 to 29, a whopping 94 percent own smartphones, according to Pew Research Center.
While the growing popularity of smartphones is often seen as “progress”, it is also having a monumentally negative impact on the tertiary education sector. The increased use of technology has contributed to the simplification and ease of copying homework assignments – and cheating in general – across schools and tertiary institutions around the world. Despite the fact that repercussions for cheating are severe, involving possible suspension or expulsion, 62% of U.S. students have reported seeing or hearing of another student using a connected device to cheat on an exam, quiz or project. In the U.K., there has been a 42% rise in cheating cases involving gadgets such as mobile phones and hidden earpieces since 2012, and in Australia cheating via technology is also on the rise at universities, with engineering and international students the most likely offenders. In one study across eight national universities and four colleges in Australia, it was found that a “widespread tolerance for cheating” existed among students and staff, with 68 percent of university staff admitting they had found “suspected contract cheaters” among their students in the past.
“Contract cheating” is perhaps the most serious form of academic dishonesty, involving students putting out a tender for others to complete their homework, coursework and assessments. But most students are cheating in a far simpler way: by switching on their mobile devices and snapping a photo of a classmate’s work, enabling them to copy that homework almost word for word in order to avoid doing it themselves. Students are also using mobile phones or earpieces during exams, by activating their device’s infrared, Bluetooth, or texting applications to share exam information with other test takers.
With the rise of technology, academic cheating is becoming more and more prolific, with hundreds of thousands of websites now offering custom-written papers, selling cheat aids and publishing how-to-cheat videos, teaching students anything from how to load programmable calculators with exam responses to how to replace a water bottle’s nutrition information with mathematics notes. Students are cheating in extremely advanced ways – with some even resorting to the use of a virtual private network to protect their activities.
But teachers are catching up, quickly.
The learning center Happy Numbers notes, “using new technologies, including text-matching software and plagiarism websites, webcams, biometric equipment, as well as drawing on strategies such as virtual students and cheat-proof tests, it is ever so slowly becoming harder to plagiarize other students work”. Surprisingly, teachers often find they have the most success in identifying plagiarism by simply Googling phrases they find in students’ papers. But more tech-savvy professors and teachers set up web “honey pots” – phony Web pages that answer specific questions allocated by them for homework with blatantly out-of-date or inaccurate information. Innovative technologies like Computerized Adaptive Testing (CAT) provide a way of improving the accuracy of assessment by addressing cheating concerns, by using an algorithm to choose test items based on students’ strengths and weaknesses. Using this method, every student takes a different test. As a result of new “anti-cheat” innovations like these, the U.S. has seen the percentage of students who admit to cheating – which rose from 20 percent in the mid-1900s to over 50 percent in 2002 – drop down to around 10 percent in recent years.
But the reality is, advances in technology will continue allowing for easy, accessible sharing unless significant steps are taken to address the problem.
Some attribute the rise in student cheating to an ever-increasing workload, others see it as a changing work ethic seen in the Millenial and Gen Z groups. Some see a direct correlation between the rise of standardized testing and cheating. Others hold accountability policies responsible: they have pressured educators to raise test scores. Whatever the cause, it’s evident the education sector needs to address the phenomenon soon before cheating becomes the status quo, as opposed to a rare lapse in judgment.
To ensure you don’t find yourself falling for the same traps other students have and “accidentally” plagiarizing your next assessment, try to implement the following measures. Develop a more efficient weekly schedule so that you can spend more time on each subject – and assessment – so that when deadlines approach you aren’t tempted to find a “quick solution” to completing your work. If in doubt, don’t copy and paste a piece of work found online but if you must, ensure it is correctly referenced. Don’t give in to peer pressure and share your work with others, because developing a habit of cheating – either for yourself or for others – creates a poor work ethic that can damage your future. And lastly, always remember your ethics. They will get a lot further than an A+ will.
Annabel Monaghan is a writer with a passion for education and edtech. She writes education and career articles for The College Puzzle with the aim of providing useful information for students and young professionals. If you have any questions, please feel free to email her at [email protected].
Leave a Reply
Download Michael Kirst “Autobiographical Reflections”

- About Dr. Michael W. Kirst
RECENT POSTS
- How Microlearning is Stopping Student Burnout Syndrome
- Is Lack Of Sleep The New College Normal?
- Can a Private Tutor Help You Get Better Grades?
- Students Learning While Working: Adapting to the Business Environment
RECENT COMMENTS
Leave a comment.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Search form
Academic honesty: cheating & plagiarism, academic honesty: cheating & plagiarism, what is academic misconduct.
You are guilty of cheating whenever you present as your own work something that you did not do. You are also guilty of cheating if you help someone else to cheat.
One of the most common forms of cheating is plagiarism, using another's words or ideas without proper citation. When students plagiarize, they usually do so in one of the following six ways:
- Using another writer's words without proper citation. If you use another writer's words, you must place quotation marks around the quoted material and include a footnote or other indication of the source of the quotation.
- Using another writer's ideas without proper citation. When you use another author's ideas, you must indicate with footnotes or other means where this information can be found. Your instructors want to know which ideas and judgments are yours and which you arrived at by consulting other sources. Even if you arrived at the same judgment on your own, you need to acknowledge that the writer you consulted also came up with the idea.
- Citing your source but reproducing the exact words of a printed source without quotation marks. This makes it appear that you have paraphrased rather than borrowed the author's exact words.
- Original: If the existence of a signing ape was unsettling for linguists, it was also startling news for animal behaviorists.
- Unacceptable borrowing of words: An ape who knew sign language unsettled linguists and startled animal behaviorists.
- Unacceptable borrowing of sentence structure: If the presence of a sign-language-using chimp was disturbing for scientists studying language, it was also surprising to scientists studying animal behavior.
- Acceptable paraphrase: When they learned of an ape's ability to use sign language, both linguists and animal behaviorists were taken by surprise.
- Borrowing all or part of another student's paper or using someone else's outline to write your own paper.
- Using a paper writing "service" or having a friend write the paper for you. Regardless of whether you pay a stranger or have a friend do it, it is a breach of academic honesty to hand in work that is not your own or to use parts of another student's paper.
- In computer programming classes, borrowing computer code from another student and presenting it as your own. When original computer code is a requirement for a class, it is a violation of the University's policy if students submit work they themselves did not create.
Note: The guidelines that define plagiarism also apply to information secured on internet websites. Internet references must specify precisely where the information was obtained and where it can be found.
You may think that citing another author's work will lower your grade. In some unusual cases this may be true, if your instructor has indicated that you must write your paper without reading additional material. But in fact, as you progress in your studies, you will be expected to show that you are familiar with important work in your field and can use this work to further your own thinking. Your professors write this kind of paper all the time. The key to avoiding plagiarism is that you show clearly where your own thinking ends and someone else's begins.
Multiple submissions
Multiple submissions is the practice of submitting a single paper for credit in two different classes (in the same quarter or in different quarters). The UW does not have a general policy prohibiting this practice. However, because an individual professor may not permit the practice in their class, a student wishing to make a multiple submission must clear it with both professors involved. Non-compliance will result in a violation of the University's standard of conduct.
Another common form of cheating involves exams. Copying from someone else's paper, using notes (unless expressly allowed by the teacher), altering an exam for re-grading, getting an advance copy of the examination, or hiring a surrogate test-taker are all flagrant violations of University policy.
Collaboration
Educators recognize the value of collaborative learning; students are often encouraged to form study groups and assigned group projects. Group study often results in accelerated learning, but only when each student takes responsibility for mastering all the material before the group. For example, suppose a calculus study group is working on a set of homework problems. Little would be learned if each student worked only one or two problems and merely copied answers for the rest. A more beneficial approach would be for each member to work all problems and be assigned the task of explaining a few problems to the group. Illegal collaboration often occurs on homework in computer programming courses. A common case is when two students outline a program in detail together, and then type it into the computer separately, perhaps making minor modifications or corrections as they type. To a grader's trained eye, the structure of the programs is identical and the students are guilty of cheating because they haven't turned in separate, original work.
Illegal collaboration also occurs on writing assignments in liberal arts courses. Typically, students will create a detailed outline together, then write separate papers from the outline. The final papers may have different wording but share structure and important ideas. This is cheating because the students have failed to hand in something that is substantially their own work, and because they haven't cited the ideas that they've borrowed from each other.
Group projects require careful division of responsibility and careful coordination to control the quality of the final product. Collective work quickly degenerates when some students see it as a way to get through an assignment with the least amount of effort. Group work calls for a different kind of effort, not less of it. When group projects are assigned, the instructor is usually interested in your mastery of group process as well as the subject. Ask the instructor to clarify individual responsibilities and suggest a method of proceeding.
In summary, when a professor says, "Go ahead and work together," don't assume that anything goes. Professors often don't state the limits of collaboration explicitly. It is your responsibility to avoid crossing the line that turns collaboration into cheating. If you're not sure, ask.
Become an Insider
Sign up today to receive premium content.

EdTech Goes Undercover: An Insider’s View of What Students Post on Contract Cheating Sites

Amelia Pang is a journalist and an editor at EdTech: Focus on Higher Education. Her work has appeared in the New Republic, Mother Jones, and The New York Times Sunday Review, among other publications.
Editor’s Note: This is part 1 of a 2-part investigation. Part 2 covers how IT departments can detect and prevent contract cheating in higher education.
“Please complete my assignment,” a student posts on a microtutoring website that universities say facilitates contract cheating . The assignment is on the history of public health. APA format. Three sources. At least 750 words. In less than 15 minutes, EdTech sees a university ghostwriter accepting the assignment for $20.
There are hundreds of “homework help” websites that have seen an exponential increase in customers since the start of the pandemic. The services offered on sites like these typically run the gamut of legitimate tutoring to selling exam documents and answers. Some flat out offer to take an entire online course or exam for students.
The shadow industry of contract cheating falls into a legal gray area. When students and tutors make an account on a homework help site, they must sign a terms-of-service agreement and honor code that forbids academic cheating. But an undercover EdTech investigation found this agreement appears to be rarely enforced.
“I have definitely seen an increase in customers since the pandemic began,” Alex, an academic ghostwriter who currently works for a homework help site, tells EdTech. “Specifically, there has been an increase in the number of students posting that they want full online classes done for them. Most of the time, students have no problem finding a contractor.”

What Is Contract Cheating, and How Does It Work?
To avoid legal liability, some homework help sites are using automation tools to edit the language of posts. Whenever students submit a post, the first line always says something like “I need help understanding the assignment,” or “Help me learn.”
But EdTech saw this as mostly a cursory statement. Many students will also directly say, “Please complete my assignment.” Some even go so far as to request that the “tutor” be available at a certain date and time to take an online exam for them.
“I would say that 30 percent of the requests are for ‘help’ versus completing assignments,” a tutor for one of these sites told BRIGHT Magazine in 2016. “It is largely a place for students to cheat.”
When EdTech created a tutor account at a homework help site earlier this year, we found that not much has changed since the BRIGHT Magazine article came out five years ago.
An insider's view of what students post on contract cheating sites.
Although students are blatantly asking for “tutors” to complete assignments and exams for them, EdTech saw academic ghostwriters making bids and accepting the work — often within minutes.
Students Hire Academic Ghostwriters to Take Online Courses for Them
Former and current academic ghostwriters also say that taking an entire online course for students is a common practice in the industry — a practice that has existed since the inception of online education. “That was always standard operating procedure,” says Dave Tomar, a former academic ghostwriter who started his decade-long career in contract cheating in 2000. He is currently the managing editor of Academic Influence , where he shares his insights on how educators can counter the surge of contract cheating during the pandemic.
“When I started doing this, I would frequently get these full online modules at the beginning of a rolling semester," Tomar says. “I got the full syllabus, and everything that I was expected to do over the next couple of months. Now, with countless students forced into remote learning, you have a whole new customer pool that is growing.”
As for how much students are willing to pay, the contractors charge “anywhere from $300 to $700 for a full class depending on the student, the subject and the difficulty,” says Alex, who currently works for a homework help site.
INSIDER EXCLUSIVE: Read Part 2 – What can universities do about contract cheating?
Fake Tutors Entice Unknowing Students to Engage in Contract Cheating
Academic cheating sites also strongly encourage students to sell their coursework— an act that may be illegal in 17 states.
“Distributing any post-secondary assignment for a profit with reasonable knowledge that it will be submitted by another person for academic credit is a crime in many US states,” Citron Research, an investment research firm that investigates overvalued fraudulent companies, stated in a report.
It’s a big problem for many institutions. According to Douglas Harrison, vice president and dean of the school of cybersecurity and information technology at the University of Maryland Global Campus , some of these contract cheating websites are “facilitating massive transfers of institutional proprietary material into their file-sharing systems.”
Harrison says many students may not even realize they are cheating when they download a university’s copyrighted classroom assessment materials because these websites reframe downloading answers to tests as a form of studying or tutoring. “They reframe file-sharing as educational, even though these are behaviors that conventional norms of academic integrity would consider misconduct,” he says.

Dave Tomar former academic ghostwriter.
To make matters worse, these websites have mastered sophisticated techniques to lure unsuspecting students. Several of these prominent homework tutoring sites will offer to give students a discount if they let their academic ghostwriter have access to the online course. This often results in the contract cheater stealing other students’ personal information.
“So the contract cheater then reaches out to other students and says, ‘I’m a tutor in your course. And I’ve helped another student in your class with their assignments. Would you like a little help?’” Harrison says, describing how the contract cheater pitches cheating “services” to other students.
This can be especially confusing for students, who may not know how to tell the difference between a contract cheater and a legitimate tutor who is affiliated with the university.
“Most of the students who we find in academic misconduct settings after inappropriately using materials on these sites, they did not set out to be malicious cheaters. Now that doesn’t mean we don’t hold them accountable, but we have to hold them accountable in proportion to the root cause of the situation,” Harrison says.
Who Is Using Academic Ghostwriters?
According to the ghostwriters who are contracted to help students cheat, their customers are usually underserved students who need access to remedial courses, and nontraditional students who struggle to balance coursework with full-time employment.
“I would argue that what is facilitating the surge of contract cheating is the fact that students are increasingly desperate and lacking support,” says Tomar.
During Tomar’s time as an academic ghostwriter, he caught glimpses into their personal circumstances. “Some would tell you they are a parent working full time. And they just can’t deal with this challenge right now. Some say, ‘I’ve invested X number of dollars into this education, and I cannot afford to fail this class. But I don’t know how to do this assignment.’”

Alex mentions that many are also English language learners. “As I noted, some students are asking for whole classes to be done, and a lot of those are English or writing-intensive courses,” he says. “That does not mean that they are ESL, but [my sense is] most of them are.”
To fundamentally address the cheating pandemic, universities and colleges may need to invest in more resources for vulnerable student populations.
“It begins with figuring out who’s struggling, why they’re struggling and what we can do to help them before they end up as contract cheating customers,” Tomar says.

- Blended Learning
- Distance Learning
- Online Learning
- IT Governance
Related Articles

Unlock white papers, personalized recommendations and other premium content for an in-depth look at evolving IT
Copyright © 2024 CDW LLC 200 N. Milwaukee Avenue , Vernon Hills, IL 60061 Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Ethics Home Page
- Business Ethics
- Campus Ethics
- Character Education
- Government Ethics
- Leadership Ethics
- Ethics Articles
- Ethics Cases
- Ethical Decision Making
- Ethics Blogs
- Center News
- E-letter/Subscribe
- Make a Gift

Featured Materials
- Ethics Home
- About the Center
- © 2014 Markkula Center for Applied Ethics
Trending Post : 12 Powerful Discussion Strategies to Engage Students
Why Students Cheat on Homework and How to Prevent It
One of the most frustrating aspects of teaching in today’s world is the cheating epidemic. There’s nothing more irritating than getting halfway through grading a large stack of papers only to realize some students cheated on the assignment. There’s really not much point in teachers grading work that has a high likelihood of having been copied or otherwise unethically completed. So. What is a teacher to do? We need to be able to assess students. Why do students cheat on homework, and how can we address it?
Like most new teachers, I learned the hard way over the course of many years of teaching that it is possible to reduce cheating on homework, if not completely prevent it. Here are six suggestions to keep your students honest and to keep yourself sane.
ASSIGN LESS HOMEWORK
One of the reasons students cheat on homework is because they are overwhelmed. I remember vividly what it felt like to be a high school student in honors classes with multiple extracurricular activities on my plate. Other teens have after school jobs to help support their families, and some don’t have a home environment that is conducive to studying.
While cheating is never excusable under any circumstances, it does help to walk a mile in our students’ shoes. If they are consistently making the decision to cheat, it might be time to reduce the amount of homework we are assigning.
I used to give homework every night – especially to my advanced students. I wanted to push them. Instead, I stressed them out. They wanted so badly to be in the Top 10 at graduation that they would do whatever they needed to do in order to complete their assignments on time – even if that meant cheating.
When assigning homework, consider the at-home support, maturity, and outside-of-school commitments involved. Think about the kind of school and home balance you would want for your own children. Go with that.
PROVIDE CLASS TIME
Allowing students time in class to get started on their assignments seems to curb cheating to some extent. When students have class time, they are able to knock out part of the assignment, which leaves less to fret over later. Additionally, it gives them an opportunity to ask questions.
When students are confused while completing assignments at home, they often seek “help” from a friend instead of going in early the next morning to request guidance from the teacher. Often, completing a portion of a homework assignment in class gives students the confidence that they can do it successfully on their own. Plus, it provides the social aspect of learning that many students crave. Instead of fighting cheating outside of class , we can allow students to work in pairs or small groups in class to learn from each other.
Plus, to prevent students from wanting to cheat on homework, we can extend the time we allow them to complete it. Maybe students would work better if they have multiple nights to choose among options on a choice board. Home schedules can be busy, so building in some flexibility to the timeline can help reduce pressure to finish work in a hurry.
GIVE MEANINGFUL WORK
If you find students cheat on homework, they probably lack the vision for how the work is beneficial. It’s important to consider the meaningfulness and valuable of the assignment from students’ perspectives. They need to see how it is relevant to them.
In my class, I’ve learned to assign work that cannot be copied. I’ve never had luck assigning worksheets as homework because even though worksheets have value, it’s generally not obvious to teenagers. It’s nearly impossible to catch cheating on worksheets that have “right or wrong” answers. That’s not to say I don’t use worksheets. I do! But. I use them as in-class station, competition, and practice activities, not homework.
So what are examples of more effective and meaningful types of homework to assign?
- Ask students to complete a reading assignment and respond in writing .
- Have students watch a video clip and answer an oral entrance question.
- Require that students contribute to an online discussion post.
- Assign them a reflection on the day’s lesson in the form of a short project, like a one-pager or a mind map.
As you can see, these options require unique, valuable responses, thereby reducing the opportunity for students to cheat on them. The more open-ended an assignment is, the more invested students need to be to complete it well.
DIFFERENTIATE
Part of giving meaningful work involves accounting for readiness levels. Whenever we can tier assignments or build in choice, the better. A huge cause of cheating is when work is either too easy (and students are bored) or too hard (and they are frustrated). Getting to know our students as learners can help us to provide meaningful differentiation options. Plus, we can ask them!
This is what you need to be able to demonstrate the ability to do. How would you like to show me you can do it?

REDUCE THE POINT VALUE
If you’re sincerely concerned about students cheating on assignments, consider reducing the point value. Reflect on your grading system.
Are homework grades carrying so much weight that students feel the need to cheat in order to maintain an A? In a standards-based system, will the assignment be a key determining factor in whether or not students are proficient with a skill?
Each teacher has to do what works for him or her. In my classroom, homework is worth the least amount out of any category. If I assign something for which I plan on giving completion credit, the point value is even less than it typically would be. Projects, essays, and formal assessments count for much more.
CREATE AN ETHICAL CULTURE
To some extent, this part is out of educators’ hands. Much of the ethical and moral training a student receives comes from home. Still, we can do our best to create a classroom culture in which we continually talk about integrity, responsibility, honor, and the benefits of working hard. What are some specific ways can we do this?
Building Community and Honestly
- Talk to students about what it means to cheat on homework. Explain to them that there are different kinds. Many students are unaware, for instance, that the “divide and conquer (you do the first half, I’ll do the second half, and then we will trade answers)” is cheating.
- As a class, develop expectations and consequences for students who decide to take short cuts.
- Decorate your room with motivational quotes that relate to honesty and doing the right thing.
- Discuss how making a poor decision doesn’t make you a bad person. It is an opportunity to grow.
- Share with students that you care about them and their futures. The assignments you give them are intended to prepare them for success.
- Offer them many different ways to seek help from you if and when they are confused.
- Provide revision opportunities for homework assignments.
- Explain that you partner with their parents and that guardians will be notified if cheating occurs.
- Explore hypothetical situations. What if you have a late night? Let’s pretend you don’t get home until after orchestra and Lego practices. You have three hours of homework to do. You know you can call your friend, Bob, who always has his homework done. How do you handle this situation?
EDUCATE ABOUT PLAGIARISM
Many students don’t realize that plagiarism applies to more than just essays. At the beginning of the school year, teachers have an energized group of students, fresh off of summer break. I’ve always found it’s easiest to motivate my students at this time. I capitalize on this opportunity by beginning with a plagiarism mini unit .
While much of the information we discuss is about writing, I always make sure my students know that homework can be plagiarized. Speeches can be plagiarized. Videos can be plagiarized. Anything can be plagiarized, and the repercussions for stealing someone else’s ideas (even in the form of a simple worksheet) are never worth the time saved by doing so.
In an ideal world, no one would cheat. However, teaching and learning in the 21st century is much different than it was fifty years ago. Cheating? It’s increased. Maybe because of the digital age… the differences in morals and values of our culture… people are busier. Maybe because students don’t see how the school work they are completing relates to their lives.
No matter what the root cause, teachers need to be proactive. We need to know why students feel compelled to cheat on homework and what we can do to help them make learning for beneficial. Personally, I don’t advocate for completely eliminating homework with older students. To me, it has the potential to teach students many lessons both related to school and life. Still, the “right” answer to this issue will be different for each teacher, depending on her community, students, and culture.
STRATEGIES FOR ADDRESSING CHALLENGING BEHAVIORS IN SECONDARY
You are so right about communicating the purpose of the assignment and giving students time in class to do homework. I also use an article of the week on plagiarism. I give students points for the learning – not the doing. It makes all the difference. I tell my students why they need to learn how to do “—” for high school or college or even in life experiences. Since, they get an A or F for the effort, my students are more motivated to give it a try. No effort and they sit in my class to work with me on the assignment. Showing me the effort to learn it — asking me questions about the assignment, getting help from a peer or me, helping a peer are all ways to get full credit for the homework- even if it’s not complete. I also choose one thing from each assignment for the test which is a motivator for learning the material – not just “doing it.” Also, no one is permitted to earn a D or F on a test. Any student earning an F or D on a test is then required to do a project over the weekend or at lunch or after school with me. All of this reinforces the idea – learning is what is the goal. Giving students options to show their learning is also important. Cheating is greatly reduced when the goal is to learn and not simply earn the grade.
Thanks for sharing your unique approaches, Sandra! Learning is definitely the goal, and getting students to own their learning is key.
Comments are closed.
Get the latest in your inbox!
- Latest Latest
- The West The West
- Sports Sports
- Opinion Opinion
- Magazine Magazine
Is it cheating for students to use homework apps?

By Amy Iverson
Apps now exist in our digital world that can take nearly any homework question or problem and solve it instantly, leaving parents and students with the decision whether or not to use these apps. Some call it cheating; others call it learning.
Parents, think back to when you were in high school doing homework. I recall having complicated calculus assignments that my mom wouldn’t even attempt and that stumped my father, who was an engineer. He would spend the evening reading through my book to remember how to do the equations and then try to teach me.
Even now with my teenagers, I have to study before I can help them with their math homework. And I’ll admit that most often, I send them to my husband who has a better mind for such things. I can help them with any literature, English, or language, but math was never my forte. So, I started getting help for teaching my kids from an app I featured on my radio show years ago.
The photomath app is a simple and genius concept. You point your phone’s camera at any math problem and the app gives you detailed instructions on how to solve it. And it’s free. So if students use this to do their homework, is that considered cheating?
It definitely could be. But it could also be a wonderful teaching tool, especially for students who are good independent learners. Apps like this could also be amazing for a student who doesn’t mesh well with a certain educator’s teaching style. Students can visualize how to solve the problems on their own timeline and terms.
Students have a teacher to answer questions while at school, but what are they supposed to do when they are at home? Sure, a parent may be able to help, but there's also the possibility that their parents never finished high school.
Recently, the app Socratic sat atop the list of the App Store’s Free Education apps. It works a lot like photomath, but for many different subjects. Again, you scan any question with your phone and the app gives you the answer.
The question may be from English class, “How is antithesis different from paradox?” Socratic will give you the perfect answer. That example may not be much different than just Googling the question. But the creators of this app took hundreds of thousands of student-submitted questions and had teachers break them down into core concepts.
After months of refining the algorithms, Socratic’s artificial intelligence can predict which ones a student needs to learn to solve the problem. The app’s website has this example of an organic chemistry question, “How is acetophenone phenylhydrazone catalyzed into 2-phenylindole?”
Now, if my child came to me with that homework question, I would likely fall on the floor laughing. But besides artificial intelligence, this app has carefully chosen real life Socratic Heroes like Ernest Z. to answer questions.
He’s a retired professor from Acadia University who taught organic chemistry for two decades. Ernest Z. has been with Socratic for three years and in this case gives a perfectly explained solution to that question with step-by-step instructions.
Cheating? I say learning. Professor Christopher Boyle, a psychologist and teacher based at Exeter University, agrees, saying this app could be an excellent tool .
The app’s co-founder, Shreyans Bhansali, believes kids are asking Google all their homework questions anyway . He says at least Socratic goes a step further by teaching students what they need to know to answer the questions.
A final example of homework helper apps is Brainly . This website and app uses crowdsourcing to answer homework questions. It’s like a gigantic worldwide study group. Brainly believes students are smarter together and uses the tagline, “No one knows everything, but everyone knows something.”
Students can post questions about assignments and a fellow student will answer within minutes. You can also search millions of previous questions and answers. Moderators make sure all the questions are school related and that answers aren’t copied from other websites.
Like most technology, parents will need to monitor their kids using these apps. Students could definitely just use them to copy down correct answers for their homework. But everyone would know the truth once test time rolled around. If students use these apps to learn concepts and problem-solving — ideally with help from parents — they could be a huge asset in a student’s path to a diploma.
Amy Iverson is a graduate of the University of Utah. She has worked as a broadcast journalist in Dallas, Seattle, Italy, and Salt Lake City. Amy, her husband, and three kids live in Summit County, Utah. Contact Amy on Facebook.com/theamyiverson
Customer Reviews
You are free to order a full plagiarism PDF report while placing the order or afterwards by contacting our Customer Support Team.
If you can’t write your essay, then the best solution is to hire an essay helper. Since you need a 100% original paper to hand in without a hitch, then a copy-pasted stuff from the internet won’t cut it. To get a top score and avoid trouble, it’s necessary to submit a fully authentic essay. Can you do it on your own? No, I don’t have time and intention to write my essay now! In such a case, step on a straight road of becoming a customer of our academic helping platform where every student can count on efficient, timely, and cheap assistance with your research papers, namely the essays.
Gombos Zoran
Original Drafts
Margurite J. Perez

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Although students often regard some forms of cheating, such as doing homework together when they are expected to do it alone, as trivial, the studies find that young people view cheating in ...
The distinctions matter because collaboration is an expectation in most professional settings. Professionals "cheat," as we usually define it. If they don't know an answer, they look it up. If they don't know how to do something, they ask someone to show them. Most decisions are group decisions. Who contributed what is of little concern ...
David Koltick, a professor of physics, said he encourages students to work together on homework assignments, but he can tell when students have been copying other students' assignments by ...
Sometimes, it might even be possible to give homework and explicitly encourage strategies that might be considered cheating, for example, by working together or using internet sources. As collaboration is one of the 21st century skills that students are expected to develop (Bray et al., 2020 ), this can be used to turn cheating into positive ...
Excessive homework can also lead to cheating: 90% of middle school students and 67% of high school students admit to copying someone else's homework, and 43% of college students engaged in "unauthorized collaboration" on out-of-class assignments. ... Valerie Strauss, "Does Homework Work When Kids Are Learning All Day at Home ...
2. An instructor prohibits all collaboration, and tells students not to discuss homework, solve problems together, or compare answers. During office hours, a student asks about a homework assignment and the TA explains the question. Seeing this, two students work on the homework together. Have they violated the professor's rule? Yes.
Students and academics agree having someone else identify errors in your assignment is OK. Correcting them is another story. from shutterstock.com. Read more: Fewer cheaters are getting away with ...
Then there are professors who are "tired of students cheating" and will seemingly "do anything to find something to report," she says. When Hofstra put its Honor Code in place, one goal was to increase the number of reports, Frisina says, adding that the goal was realized early on. Still, many professors want to manage the situation ...
"Contract cheating" is perhaps the most serious form of academic dishonesty, involving students putting out a tender for others to complete their homework, coursework and assessments. But most students are cheating in a far simpler way: by switching on their mobile devices and snapping a photo of a classmate's work, enabling them to copy ...
Plagiarism. One of the most common forms of cheating is plagiarism, using another's words or ideas without proper citation. When students plagiarize, they usually do so in one of the following six ways: Using another writer's words without proper citation. If you use another writer's words, you must place quotation marks around the quoted ...
The shadow industry of contract cheating falls into a legal gray area. When students and tutors make an account on a homework help site, they must sign a terms-of-service agreement and honor code that forbids academic cheating. But an undercover EdTech investigation found this agreement appears to be rarely enforced.
Yes. I help students all over the country fight accusations of unauthorized collaboration and cheating. By working together to craft the best defense possible, you will be given the greatest chance at success. I also attend hearings with students to support them during this very stressful event. Typically, a panel of students and staff will ...
Unless specifically permitted or required by the instructor, collaboration will usually be viewed by the university as cheating. Each student, therefore, is responsible for understanding the policies of the department offering any course as they refer to the amount of help and collaboration permitted in preparation of assignments. --Honor Code ...
If you find students cheat on homework, they probably lack the vision for how the work is beneficial. It's important to consider the meaningfulness and valuable of the assignment from students' perspectives. They need to see how it is relevant to them. In my class, I've learned to assign work that cannot be copied.
This is the point to heavily underscore as you move forward. If students want to work together or need help, encourage them to collaborate or come to you. Don't worry about cheating, but make it clear that the point of the homework is to help students gauge their level of personal comfort with the material prior to the exam.
Copying homework wasn't seen as a big deal, because you were usually allowed to work together on it anyway. Cheating on tests and quizzes was a big deal. Some kids did it, and you knew they did it, but as long as they weren't caught, you just considered them sort of dumb, because they couldn't do the work themselves.
If you don't do your own homework, you're mostly cheating yourself out of the benefit of the homework. ... if I were you, is instead of helping with homework, study independently of the homework, before doing the homework. Go over the concepts together from class, make sure you understand all of the instructor's examples. ... as others have ...
Sometimes students are seated tight together so policing cheating is harder, and you have logistic problems like the students who finish first bothering the rest when they pass through. ... But most importantly of all (I think), you should admit in your question that you're working on a homework problem. That way people will try to help you ...
At most, I'd split the points between the two of them. If you did this together, then each of you gets five of the ten points. Quiz them on the work. If they cheated, they won't be able to answer questions on a quiz. I call this cheating. Someone did the work and someone else did not do the work and just copied.
Website Screenshot. Apps now exist in our digital world that can take nearly any homework question or problem and solve it instantly, leaving parents and students with the decision whether or not to use these apps. Some call it cheating; others call it learning. Parents, think back to when you were in high school doing homework.
The best online essay services have large groups of authors with diverse backgrounds. They can complete any type of homework or coursework, regardless of field of study, complexity, and urgency. When you contact the company Essayswriting, the support service immediately explains the terms of cooperation to you.