We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!

Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
Research methods for law
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
32 Previews
4 Favorites
Better World Books
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
PDF access not available for this item.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by station20.cebu on April 22, 2023
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)
- Architecture and Design
- Asian and Pacific Studies
- Business and Economics
- Classical and Ancient Near Eastern Studies
- Computer Sciences
- Cultural Studies
- Engineering
- General Interest
- Geosciences
- Industrial Chemistry
- Islamic and Middle Eastern Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Library and Information Science, Book Studies
- Life Sciences
- Linguistics and Semiotics
- Literary Studies
- Materials Sciences
- Mathematics
- Social Sciences
- Sports and Recreation
- Theology and Religion
- Publish your article
- The role of authors
- Promoting your article
- Abstracting & indexing
- Publishing Ethics
- Why publish with De Gruyter
- How to publish with De Gruyter
- Our book series
- Our subject areas
- Your digital product at De Gruyter
- Contribute to our reference works
- Product information
- Tools & resources
- Product Information
- Promotional Materials
- Orders and Inquiries
- FAQ for Library Suppliers and Book Sellers
- Repository Policy
- Free access policy
- Open Access agreements
- Database portals
- For Authors
- Customer service
- People + Culture
- Journal Management
- How to join us
- Working at De Gruyter
- Mission & Vision
- De Gruyter Foundation
- De Gruyter Ebound
- Our Responsibility
- Partner publishers

Your purchase has been completed. Your documents are now available to view.
Research methods for law
Available online, at the library.

Law Library (Crown)
More options.
- Find it at other libraries via WorldCat
- Contributors
Description
Creators/contributors, contents/summary.
- ch. 1. Qualitative legal research / Ian Dobinson and Francis Johns
- ch. 2. Quantative legal research / Wing Hong Chui
- ch. 3. Doing ethnographic research : lessons from a case study / Satnam Choongh
- ch. 4. Comparative legal scholarship / Geoffrey Wilson
- ch. 5. Integrating theory and method in the comparative contextual analysis of trial process / Mark Findlay and Ralph Henman
- ch. 6. Researching the landless movement in Brazil / George Meszaros
- ch. 7. Non-empirical discovery in legal scholarship : choosing, researching and writing a traditional scholarly article / Michael Pendleton
- ch. 8. Researching international law / Stephen Hall
- ch. 9. Development of empirical techniques and theory / Mike McConville.
Bibliographic information
Browse related items.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Legal Research Strategy
Preliminary analysis, organization, secondary sources, primary sources, updating research, identifying an end point, getting help, about this guide.
This guide will walk a beginning researcher though the legal research process step-by-step. These materials are created with the 1L Legal Research & Writing course in mind. However, these resources will also assist upper-level students engaged in any legal research project.
How to Strategize
Legal research must be comprehensive and precise. One contrary source that you miss may invalidate other sources you plan to rely on. Sticking to a strategy will save you time, ensure completeness, and improve your work product.
Follow These Steps
Running Time: 3 minutes, 13 seconds.
Make sure that you don't miss any steps by using our:
- Legal Research Strategy Checklist
If you get stuck at any time during the process, check this out:
- Ten Tips for Moving Beyond the Brick Wall in the Legal Research Process, by Marsha L. Baum
Understanding the Legal Questions
A legal question often originates as a problem or story about a series of events. In law school, these stories are called fact patterns. In practice, facts may arise from a manager or an interview with a potential client. Start by doing the following:

- Read anything you have been given
- Analyze the facts and frame the legal issues
- Assess what you know and need to learn
- Note the jurisdiction and any primary law you have been given
- Generate potential search terms
Jurisdiction
Legal rules will vary depending on where geographically your legal question will be answered. You must determine the jurisdiction in which your claim will be heard. These resources can help you learn more about jurisdiction and how it is determined:
- Legal Treatises on Jurisdiction
- LII Wex Entry on Jurisdiction
This map indicates which states are in each federal appellate circuit:

Getting Started
Once you have begun your research, you will need to keep track of your work. Logging your research will help you to avoid missing sources and explain your research strategy. You will likely be asked to explain your research process when in practice. Researchers can keep paper logs, folders on Westlaw or Lexis, or online citation management platforms.
Organizational Methods
Tracking with paper or excel.
Many researchers create their own tracking charts. Be sure to include:
- Search Date
- Topics/Keywords/Search Strategy
- Citation to Relevant Source Found
- Save Locations
- Follow Up Needed
Consider using the following research log as a starting place:
- Sample Research Log
Tracking with Folders
Westlaw and Lexis offer options to create folders, then save and organize your materials there.
- Lexis Advance Folders
- Westlaw Edge Folders
Tracking with Citation Management Software
For long term projects, platforms such as Zotero, EndNote, Mendeley, or Refworks might be useful. These are good tools to keep your research well organized. Note, however, that none of these platforms substitute for doing your own proper Bluebook citations. Learn more about citation management software on our other research guides:
- Guide to Zotero for Harvard Law Students by Harvard Law School Library Research Services Last Updated Sep 12, 2023 246 views this year
Types of Sources
There are three different types of sources: Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary. When doing legal research you will be using mostly primary and secondary sources. We will explore these different types of sources in the sections below.

Secondary sources often explain legal principles more thoroughly than a single case or statute. Starting with them can help you save time.
Secondary sources are particularly useful for:
- Learning the basics of a particular area of law
- Understanding key terms of art in an area
- Identifying essential cases and statutes
Consider the following when deciding which type of secondary source is right for you:
- Scope/Breadth
- Depth of Treatment
- Currentness/Reliability

For a deep dive into secondary sources visit:
- Secondary Sources: ALRs, Encyclopedias, Law Reviews, Restatements, & Treatises by Catherine Biondo Last Updated Apr 12, 2024 4260 views this year
Legal Dictionaries & Encyclopedias
Legal dictionaries.
Legal dictionaries are similar to other dictionaries that you have likely used before.
- Black's Law Dictionary
- Ballentine's Law Dictionary
Legal Encyclopedias
Legal encyclopedias contain brief, broad summaries of legal topics, providing introductions and explaining terms of art. They also provide citations to primary law and relevant major law review articles.

Here are the two major national encyclopedias:
- American Jurisprudence (AmJur) This resource is also available in Westlaw & Lexis .
- Corpus Juris Secundum (CJS)
Treatises are books on legal topics. These books are a good place to begin your research. They provide explanation, analysis, and citations to the most relevant primary sources. Treatises range from single subject overviews to deep treatments of broad subject areas.

It is important to check the date when the treatise was published. Many are either not updated, or are updated through the release of newer editions.
To find a relevant treatise explore:
- Legal Treatises by Subject by Catherine Biondo Last Updated Apr 12, 2024 3204 views this year
American Law Reports (ALR)
American Law Reports (ALR) contains in-depth articles on narrow topics of the law. ALR articles, are often called annotations. They provide background, analysis, and citations to relevant cases, statutes, articles, and other annotations. ALR annotations are invaluable tools to quickly find primary law on narrow legal questions.

This resource is available in both Westlaw and Lexis:
- American Law Reports on Westlaw (includes index)
- American Law Reports on Lexis
Law Reviews & Journals
Law reviews are scholarly publications, usually edited by law students in conjunction with faculty members. They contain both lengthy articles and shorter essays by professors and lawyers. They also contain comments, notes, or developments in the law written by law students. Articles often focus on new or emerging areas of law and may offer critical commentary. Some law reviews are dedicated to a particular topic while others are general. Occasionally, law reviews will include issues devoted to proceedings of panels and symposia.

Law review and journal articles are extremely narrow and deep with extensive references.
To find law review articles visit:
- Law Journal Library on HeinOnline
- Law Reviews & Journals on LexisNexis
- Law Reviews & Journals on Westlaw
Restatements
Restatements are highly regarded distillations of common law, prepared by the American Law Institute (ALI). ALI is a prestigious organization comprised of judges, professors, and lawyers. They distill the "black letter law" from cases to indicate trends in common law. Resulting in a “restatement” of existing common law into a series of principles or rules. Occasionally, they make recommendations on what a rule of law should be.
Restatements are not primary law. However, they are considered persuasive authority by many courts.

Restatements are organized into chapters, titles, and sections. Sections contain the following:
- a concisely stated rule of law,
- comments to clarify the rule,
- hypothetical examples,
- explanation of purpose, and
- exceptions to the rule
To access restatements visit:
- American Law Institute Library on HeinOnline
- Restatements & Principles of the Law on LexisNexis
- Restatements & Principles of Law on Westlaw
Primary Authority
Primary authority is "authority that issues directly from a law-making body." Authority , Black's Law Dictionary (11th ed. 2019). Sources of primary authority include:
- Constitutions
- Statutes
Regulations
Access to primary legal sources is available through:
- Bloomberg Law
- Free & Low Cost Alternatives
Statutes (also called legislation) are "laws enacted by legislative bodies", such as Congress and state legislatures. Statute , Black's Law Dictionary (11th ed. 2019).
We typically start primary law research here. If there is a controlling statute, cases you look for later will interpret that law. There are two types of statutes, annotated and unannotated.
Annotated codes are a great place to start your research. They combine statutory language with citations to cases, regulations, secondary sources, and other relevant statutes. This can quickly connect you to the most relevant cases related to a particular law. Unannotated Codes provide only the text of the statute without editorial additions. Unannotated codes, however, are more often considered official and used for citation purposes.
For a deep dive on federal and state statutes, visit:
- Statutes: US and State Codes by Mindy Kent Last Updated Apr 12, 2024 2603 views this year
- 50 State Surveys
Want to learn more about the history or legislative intent of a law? Learn how to get started here:
- Legislative History Get an introduction to legislative histories in less than 5 minutes.
- Federal Legislative History Research Guide
Regulations are rules made by executive departments and agencies. Not every legal question will require you to search regulations. However, many areas of law are affected by regulations. So make sure not to skip this step if they are relevant to your question.
To learn more about working with regulations, visit:
- Administrative Law Research by AJ Blechner Last Updated Apr 12, 2024 535 views this year
Case Basics
In many areas, finding relevant caselaw will comprise a significant part of your research. This Is particularly true in legal areas that rely heavily on common law principles.
Running Time: 3 minutes, 10 seconds.
Unpublished Cases
Up to 86% of federal case opinions are unpublished. You must determine whether your jurisdiction will consider these unpublished cases as persuasive authority. The Federal Rules of Appellate Procedure have an overarching rule, Rule 32.1 Each circuit also has local rules regarding citations to unpublished opinions. You must understand both the Federal Rule and the rule in your jurisdiction.
- Federal and Local Rules of Appellate Procedure 32.1 (Dec. 2021).
- Type of Opinion or Order Filed in Cases Terminated on the Merits, by Circuit (Sept. 2021).
Each state also has its own local rules which can often be accessed through:
- State Bar Associations
- State Courts Websites
First Circuit
- First Circuit Court Rule 32.1.0
Second Circuit
- Second Circuit Court Rule 32.1.1
Third Circuit
- Third Circuit Court Rule 5.7
Fourth Circuit
- Fourth Circuit Court Rule 32.1
Fifth Circuit
- Fifth Circuit Court Rule 47.5
Sixth Circuit
- Sixth Circuit Court Rule 32.1
Seventh Circuit
- Seventh Circuit Court Rule 32.1
Eighth Circuit
- Eighth Circuit Court Rule 32.1A
Ninth Circuit
- Ninth Circuit Court Rule 36-3
Tenth Circuit
- Tenth Circuit Court Rule 32.1
Eleventh Circuit
- Eleventh Circuit Court Rule 32.1
D.C. Circuit
- D.C. Circuit Court Rule 32.1
Federal Circuit
- Federal Circuit Court Rule 32.1
Finding Cases

Headnotes show the key legal points in a case. Legal databases use these headnotes to guide researchers to other cases on the same topic. They also use them to organize concepts explored in cases by subject. Publishers, like Westlaw and Lexis, create headnotes, so they are not consistent across databases.
Headnotes are organized by subject into an outline that allows you to search by subject. This outline is known as a "digest of cases." By browsing or searching the digest you can retrieve all headnotes covering a particular topic. This can help you identify particularly important cases on the relevant subject.
Running Time: 4 minutes, 43 seconds.
Each major legal database has its own digest:
- Topic Navigator (Lexis)
- Key Digest System (Westlaw)
Start by identifying a relevant topic in a digest. Then you can limit those results to your jurisdiction for more relevant results. Sometimes, you can keyword search within only the results on your topic in your jurisdiction. This is a particularly powerful research method.
One Good Case Method
After following the steps above, you will have identified some relevant cases on your topic. You can use good cases you find to locate other cases addressing the same topic. These other cases often apply similar rules to a range of diverse fact patterns.
- in Lexis click "More Like This Headnote"
- in Westlaw click "Cases that Cite This Headnote"
to focus on the terms of art or key words in a particular headnote. You can use this feature to find more cases with similar language and concepts.
Ways to Use Citators
A citator is "a catalogued list of cases, statutes, and other legal sources showing the subsequent history and current precedential value of those sources. Citators allow researchers to verify the authority of a precedent and to find additional sources relating to a given subject." Citator , Black's Law Dictionary (11th ed. 2019).
Each major legal database has its own citator. The two most popular are Keycite on Westlaw and Shepard's on Lexis.
- Keycite Information Page
- Shepard's Information Page
Making Sure Your Case is Still Good Law
This video answers common questions about citators:
For step-by-step instructions on how to use Keycite and Shepard's see the following:
- Shepard's Video Tutorial
- Shepard's Handout
- Shepard's Editorial Phrase Dictionary
- KeyCite Video Tutorial
- KeyCite Handout
- KeyCite Editorial Phrase Dictionary
Using Citators For
Citators serve three purposes: (1) case validation, (2) better understanding, and (3) additional research.
Case Validation
Is my case or statute good law?
- Parallel citations
- Prior and subsequent history
- Negative treatment suggesting you should no longer cite to holding.
Better Understanding
Has the law in this area changed?
- Later cases on the same point of law
- Positive treatment, explaining or expanding the law.
- Negative Treatment, narrowing or distinguishing the law.
Track Research
Who is citing and writing about my case or statute?
- Secondary sources that discuss your case or statute.
- Cases in other jurisdictions that discuss your case or statute.
Knowing When to Start Writing
For more guidance on when to stop your research see:
- Terminating Research, by Christina L. Kunz
Automated Services
Automated services can check your work and ensure that you are not missing important resources. You can learn more about several automated brief check services. However, these services are not a replacement for conducting your own diligent research .
- Automated Brief Check Instructional Video
Contact Us!
Ask Us! Submit a question or search our knowledge base.
Chat with us! Chat with a librarian (HLS only)
Email: [email protected]
Contact Historical & Special Collections at [email protected]
Meet with Us Schedule an online consult with a Librarian
Hours Library Hours
Classes View Training Calendar or Request an Insta-Class
Text Ask a Librarian, 617-702-2728
Call Reference & Research Services, 617-495-4516
This guide is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 United States License .
You may reproduce any part of it for noncommercial purposes as long as credit is included and it is shared in the same manner.
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2023 2:56 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/law/researchstrategy
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous
- Next chapter >

1 Introduction: Legal Research Methodology, Purposes, and Footsteps
- Published: January 2020
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
The first chapter introduces the subject by explaining key words like research, legal research, method, and methodology. By linking knowledge with research, it brings out the purposive character of knowledge influencing research. It lists various objectives of legal research such as exploration, description, historical explanation, law reform, prediction, and publication, briefly explaining each. It traces the historical development of legal research in India thorugh ancient, medieval, colonial, and modern times. It finds that legal research became systematic and wide spread only along with orderly growth of legal education. Finally, it catalogues diverse methods of legal research under the categories of doctrinal, non-doctrinal, and integrated methods of legal research. Reader gets a basic idea about legal research, its past, present, and future potentiality and a glimpse of its wider canvas.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
- Google Scholar Indexing
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

Legal Dissertation: Research and Writing Guide
About this guide, video on choosing a topic, tools on westlaw, lexis and bloomberg, circuit splits, research methodologies, additional methodology resources, conducting a literature review, beginning research, writing style guides, citation guides, ask a librarian.
Ask a librarian:
Reference Hours:
Monday - Friday: 9am-5pm
(812) 855-2938
Q&A Form
About This Page
Choosing a topic can be one of the most challenging aspects of writing an extensive paper. This page has resources to help you find topics and inspiration, before you get started on the in-depth research process.
Related Guides
Citation and Writing Resources
Legal Research Tutorials
Secondary Sources for Legal Research
Methods of Finding Cases
Methods of Finding Statutes
Current Awareness and Alerting Resources
Compiling State Legislative Histories
Locating International and Foreign Law Journals
This guide contains resources to help students researching and writing a legal dissertation or other upper-level writing project. Some of the resources in this guide are directed at researching and writing in general, not specifically on legal topics, but the strategies and tips can still be applied.
The Law Library maintains a number of other guides on related skills and topics that may be of interest:
The Wells Library also maintains guides. A few that may be helpful for managing research can be found here:
Choosing a Topic
This video discusses tips and strategies for choosing a dissertation topic.
Note: this video is not specific to legal dissertation topics, but it may still be of interest as an overview generally.
The Bloomberg/BNA publication United States Law Week can be a helpful resource for tracking down the major legal stories of the day. Log into Bloomberg Law, in the big search box, start typing United States Law Week and the title will appear in the drop down menu beneath the box. This publication provides coverage of top legal news stories, and in-depth "insight" features.
If you have a general idea of the area of law you wish to write about, check out the Practice Centers on Bloomberg. From the homepage, click the Browse link in the top left-hand corner. Then select Practice Centers and look for your area of law. Practice Centers are helpful because they gather cases, statutes, administrative proceedings, news, and more on the selected legal area.
Bloomberg has other news sources available as well. From the homepage, click the Browse link in the top left-hand corner. Then select News and Analysis, then select News or Analysis, and browse the available topics.
If you know what area of law you'd like to write about, you may find the Browse Topics feature in Lexis Advance helpful for narrowing down your topic.
Log into Lexis Advance, click the Browse Topics tab, and select a topic. If you don't see your topic listed, try using the provided search bar to see whether your topic is categorized as a sub-topic within this list.
Once you click on a topic, a box pops up with several options. If you click on Get Topic Document, you'll see results listed in a number of categories, including Cases, Legislation, and more. The News and Legal News categories at the right end of the list may help you identify current developments of interest for your note. Don't forget about the filtering options on the left that will allow you to search within your results, narrow your jurisdiction, and more.
Similar to Lexis Advance, Westlaw Edge has a Topics tab that may be helpful if you know what area of law you'd like to write about.
Log onto Westlaw Edge, and click on the Topics tab. This time, you won't be able to search within this list, so if you're area is not listed, you should either run a regular search from the main search bar at the top or try out some of the topics listed under this tab - once you click on a topic, you can search within its contents.
What is great about the Topics in Westlaw Edge is the Practitioner Insights page you access by clicking on a topic. This is an information portal that allows you quick access to cases, legislation, top news, and more on your selected topic.
In United States federal courts, a circuit split occurs whenever two or more circuit courts of appeals issue conflicting rulings on the same legal question. Circuit splits are ripe for legal analysis and commentary because they present a situation in which federal law is being applied in different ways in different parts of the country, even if the underlying litigants themselves are otherwise similarly situated. The Supreme Court also frequently accepts cases on appeal that involve these types of conflicted rulings from various sister circuits.
To find a circuit split on a topic of interest to you, try searching on Lexis and Westlaw using this method:
in the search box, enter the following: (circuit or court w/s split) AND [insert terms or phrases to narrow the search]
You can also browse for circuit splits on Bloomberg. On the Bloomberg homepage, in the "Law School Success" box, Circuit Splits Charts appear listed under Secondary Sources.
Other sources for circuit splits are American Law Reports (ALR) and American Jurisprudence (AmJur). These publications provide summaries of the law, point out circuit splits, and provide references for further research.
"Blawgs" or law-related blogs are often written by scholars or practitioners in the legal field. Ordinarily covering current events and developments in law, these posts can provide inspiration for note topics. To help you find blawgs on a specific topic, consider perusing the ABA's Blawg Directory or Justia's Blawg Search .
Research Methodology
Types of research methodologies.
There are different types of research methodologies. Methodology refers to the strategy employed in conducting research. The following methodologies are some of the most commonly used in legal and social science research.
Doctrinal legal research methodology, also called "black letter" methodology, focuses on the letter of the law rather than the law in action. Using this method, a researcher composes a descriptive and detailed analysis of legal rules found in primary sources (cases, statutes, or regulations). The purpose of this method is to gather, organize, and describe the law; provide commentary on the sources used; then, identify and describe the underlying theme or system and how each source of law is connected.
Doctrinal methodology is good for areas of law that are largely black letter law, such as contract or property law. Under this approach, the researcher conducts a critical, qualitative analysis of legal materials to support a hypothesis. The researcher must identify specific legal rules, then discuss the legal meaning of the rule, its underlying principles, and decision-making under the rule (whether cases interpreting the rule fit together in a coherent system or not). The researcher must also identify ambiguities and criticisms of the law, and offer solutions. Sources of data in doctrinal research include the rule itself, cases generated under the rule, legislative history where applicable, and commentaries and literature on the rule.
This approach is beneficial by providing a solid structure for crafting a thesis, organizing the paper, and enabling a thorough definition and explanation of the rule. The drawbacks of this approach are that it may be too formalistic, and may lead to oversimplifying the legal doctrine.
Comparative
Comparative legal research methodology involves critical analysis of different bodies of law to examine how the outcome of a legal issue could be different under each set of laws. Comparisons could be made between different jurisdictions, such as comparing analysis of a legal issue under American law and the laws of another country, or researchers may conduct historical comparisons.
When using a comparative approach be sure to define the reasons for choosing this approach, and identify the benefits of comparing laws from different jurisdictions or time periods, such as finding common ground or determining best practices and solutions. The comparative method can be used by a researcher to better understand their home jurisdiction by analyzing how other jurisdictions handle the same issue. This method can also be used as a critical analytical tool to distinguish particular features of a law. The drawback of this method is that it can be difficult to find material from other jurisdictions. Also, researchers should be sure that the comparisons are relevant to the thesis and not just used for description.
This type of research uses data analysis to study legal systems. A detailed guide on empirical methods can be found here . The process of empirical research involves four steps: design the project, collect and code the data, analyze the data, determine best method of presenting the results. The first step, designing the project, is when researchers define their hypothesis and concepts in concrete terms that can be observed. Next, researchers must collect and code the data by determining the possible sources of information and available collection methods, and then putting the data into a format that can be analyzed. When researchers analyze the data, they are comparing the data to their hypothesis. If the overlap between the two is significant, then their hypothesis is confirmed, but if there is little to no overlap, then their hypothesis is incorrect. Analysis involves summarizing the data and drawing inferences. There are two types of statistical inference in empirical research, descriptive and causal. Descriptive inference is close to summary, but the researcher uses the known data from the sample to draw conclusions about the whole population. Causal inference is the difference between two descriptive inferences.
Two main types of empirical legal research are qualitative and quantitative.
Quantitative, or numerical, empirical legal research involves taking information about cases and courts, translating that information into numbers, and then analyzing those numbers with statistical tools.
Qualitative, or non-numerical, empirical legal research involves extracting information from the text of court documents, then interpreting and organizing the text into categories, and using that information to identify patterns.
Drafting The Methodology Section
This is the part of your paper that describes the research methodology, or methodologies if you used more than one. This section will contain a detailed description of how the research was conducted and why it was conducted in that way. First, draft an outline of what you must include in this section and gather the information needed.
Generally, a methodology section will contain the following:
- Statement of research objectives
- Reasons for the research methodology used
- Description and rationale of the data collection tools, sampling techniques, and data sources used, including a description of how the data collection tools were administered
- Discussion of the limitations
- Discussion of the data analysis tools used
Be sure that you have clearly defined the reasoning behind the chosen methodology and sources.
- Legal Reasoning, Research, and Writing for International Graduate Students Nadia E. Nedzel Aspen (2004) A guide to American legal research and the federal system, written for international students. Includes information on the research process, and tips for writing. Located in the Law Library, 3rd Floor: KF 240 .N43 2004.
- Methodologies of Legal Research: Which Kind of Method for What Kind of Discipline? Mark van Hoecke Oxford (2013) This book examines different methods of legal research including doctrinal, comparative, and interdisciplinary. Located at Lilly Law Library, Indianapolis, 2nd Floor: K 235 .M476 2013. IU students may request item via IUCAT.
- An Introduction to Empirical Legal Research Lee Epstein and Andrew D. Martin Oxford University Press (2014) This book includes information on designing research, collecting and coding data, analyzing data, and drafting the final paper. Located at Lilly Law Library, Indianapolis, 2nd Floor: K 85 .E678 2014. IU students may request item via IUCAT.
- Emplirical Legal Studies Blog The ELS blog was created by several law professors, and focuses on using empirical methods in legal research, theory, and scholarship. Search or browse the blog to find entries on methodology, data sources, software, and other tips and techniques.
Literature Review
The literature review provides an examination of existing pieces of research, and serves as a foundation for further research. It allows the researcher to critically evaluate existing scholarship and research practices, and puts the new thesis in context. When conducting a literature review, one should consider the following: who are the leading scholars in the subject area; what has been published on the subject; what factors or subtopics have these scholars identified as important for further examination; what research methods have others used; what were the pros and cons of using those methods; what other theories have been explored.
The literature review should include a description of coverage. The researcher should describe what material was selected and why, and how those selections are relevant to the thesis. Discuss what has been written on the topic and where the thesis fits in the context of existing scholarship. The researcher should evaluate the sources and methodologies used by other researchers, and describe how the thesis different.
The following video gives an overview of conducting a literature review.
Note: this video is not specific to legal literature, however it may be helpful as a general overview.
Not sure where to start? Here are a few suggestions for digging into sources once you have selected a topic.
Research Guides
Research guides are discovery tools, or gateways of information. They pull together lists of sources on a topic. Some guides even offer brief overviews and additional research steps specifically for that topic. Many law libraries offer guides on a variety of subjects. You can locate guides by visiting library websites, such as this Library's site , the Law Library of Congress , or other schools like Georgetown . Some organizations also compile research guides, such as the American Society of International Law . Utilizing a research guide on your topic to generate an introductory source list can save you valuable time.
Secondary Sources
It is often a good idea to begin research with secondary sources. These resources summarize, explain, and analyze the law. They also provide references to primary sources and other secondary sources. This saves you time and effort, and can help you quickly identify major themes under your topic and help you place your thesis in context.
Encyclopedias provide broad coverage of all areas of the law, but do not go in-depth on narrow topics, or discuss differences by jurisdiction, or include all of the pertinent cases. American Jurisprudence ( AmJur ) and Corpus Juris Secundum ( CJS ) have nationwide coverage, while the Indiana Law Encyclopedia focuses on Indiana state law. A number of other states also have their own state-specific encyclopedias.
American Law Reports ( ALR ) are annotations that synopsize various cases on narrow legal topics. Each annotation covers a different topic, and provides a leading or typical case on the topic, plus cases from different jurisdictions that follow different rules, or cases where different facts applying the same rule led to different outcomes. The annotations also refer to other secondary sources.
Legal periodicals include several different types of publications such as law reviews from academic institutions or organizations, bar journals, and commercial journals/newspapers/newsletters. Legal periodicals feature articles that describe the current state of the law and often explore underlying policies. They also critique laws, court decisions, and policies, and often advocate for changes. Articles also discuss emerging issues and notify the profession of new developments. Law reviews can be useful for in-depth coverage on narrow topics, and references to primary and other secondary sources. However, content can become outdated and researchers must be mindful of biases in articles.
Treatises/Hornbooks/Practice Guides are a type of secondary source that provides comprehensive coverage of a legal subject. It could be broad, such as a treatise covering all of contract law, or very narrow such as a treatise focused only on search and seizure cases. These sources are good when you have some general background on the topic, but you need more in-depth coverage of the legal rules and policies. Treatises are generally well organized, and provide you with finding aids (index, table of contents, etc.) and extensive footnotes or endnotes that will lead you to primary sources like cases, statutes, and regulations. They may also include appendices with supporting material like forms. However, treatises may not be updated as frequently as other sources and may not cover your specific issue or jurisdiction.
Citation and Writing Style
- Legal Writing in Plain English Bryan A. Garner University of Chicago Press, 2001. Call # KF 250 .G373 2001 Location: Law Library, 3rd Floor Provides lawyers, judges, paralegals, law students, and legal scholars with sound advice and practical tools for improving their written work. The leading guide to clear writing in the field, this book offers valuable insights into the writing process: how to organize ideas, create and refine prose, and improve editing skills. This guide uses real-life writing samples that Garner has gathered through decades of teaching experience. Includes sets of basic, intermediate, and advanced exercises in each section.
- The Elements of Legal Style Bryan A. Garner Oxford University Press, 2002. Call # KF 250 .G37 2002 Location: Law Library, 1st Floor, Reference This book explains the full range of what legal writers need to know: mechanics, word choice, structure, and rhetoric, as well as all the special conventions that legal writers should follow in using headings, defined terms, quotations, and many other devices. Garner also provides examples from highly regarded legal writers, including Oliver Wendell Holmes, Clarence Darrow, Frank Easterbrook, and Antonin Scalia.
- Grammarly Blog Blog featuring helpful information about quirks of the English language, for example when to use "affect" or "effect" and other tips. Use the search feature to locate an article relevant to your grammar query.
- Plain English for Lawyers Richard C. Wydick Carolina Academic Press, 2005. Call # KF 250 .W9 2005 Location: Law Library, 3rd Floor Award-winning book that contains guidance to improve the writing of lawyers and law students and to promote the modern trend toward a clear, plain style of legal writing. Includes exercises at the end of each chapter.
- The Chicago Manual of Style University of Chicago Press, 2010. Call # Z 253 .U69 2010 Location: Law Library, 2nd Floor While not addressing legal writing specifically, The Chicago Manual of Style is one of the most widely used and respected style guides in the United States. It focuses on American English and deals with aspects of editorial practice, including grammar and usage, as well as document preparation and formatting.
- The Chicago Manual of Style (Online) Bryan A. Garner and William S. Strong The University of Chicago Press, 2017. Online edition: use the link above to view record in IUCAT, then click the Access link (for IU students only).
- The Bluebook Compiled by the editors of the Columbia Law Review, the Harvard Law Review, the University of Pennsylvania Law Review, and the Yale Law Journal. Harvard Law Review Association, 2015. Call # KF245 .B58 2015 Location: Law Library, 1st Floor, Circulation Desk The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation is a style guide that prescribes the most widely used legal citation system in the United States. The Bluebook is taught and used at a majority of U.S. law schools, law reviews and journals, and used in a majority of U.S. federal courts.
- User's Guide to the Bluebook Alan L. Dworsky William S. Hein & Co., Inc., 2015. Call # KF 245 .D853 2015 Location: Law Library, Circulation Desk "This User's Guide is written for practitioners (law students, law clerks, lawyers, legal secretaries and paralegals), and is designed to make the task of mastering citation form as easy and painless as possible. To help alleviate the obstacles faced when using proper citation form, this text is set up as a how-to manual with a step-by-step approach to learning the basic skills of citation and includes the numbers of the relevant Bluebook rules under most chapter subheadings for easy reference when more information is needed"--Provided by the publisher.
- Legal Citation in a Nutshell Larry L. Teply West Academic Publishing, 2016. Call # KF 245 .T47 2016 Location: Law Library, 1st Floor, Circulation Desk This book is designed to ease the task of learning legal citation. It initially focuses on conventions that underlie all accepted forms and systems of legal citation. Building on that understanding and an explanation of the “process” of using citations in legal writing, the book then discusses and illustrates the basic rules.
- Introduction to Basic Legal Citation (Online) Peter W. Martin Cornell Legal Information Institute, 2017. Free online resource. Includes a thorough review of the relevant rules of appellate practice of federal and state courts. It takes account of the latest edition of The Bluebook, published in 2015, and provides a correlation table between this free online citation guide and the Bluebook.
- Last Updated: Oct 24, 2019 11:00 AM
- URL: https://law.indiana.libguides.com/dissertationguide
Business development
- Billing management software
- Court management software
- Legal calendaring solutions
Practice management & growth
- Project & knowledge management
- Workflow automation software
Corporate & business organization
- Business practice & procedure
Legal forms
- Legal form-building software
Legal data & document management
- Data management
- Data-driven insights
- Document management
- Document storage & retrieval
Drafting software, service & guidance
- Contract services
- Drafting software
- Electronic evidence
Financial management
- Outside counsel spend
Law firm marketing
- Attracting & retaining clients
- Custom legal marketing services
Legal research & guidance
- Anywhere access to reference books
- Due diligence
- Legal research technology
Trial readiness, process & case guidance
- Case management software
- Matter management
Recommended Products
Conduct legal research efficiently and confidently using trusted content, proprietary editorial enhancements, and advanced technology.
Fast track case onboarding and practice with confidence. Tap into a team of experts who create and maintain timely, reliable, and accurate resources so you can jumpstart your work.
A business management tool for legal professionals that automates workflow. Simplify project management, increase profits, and improve client satisfaction.
- All products
Tax & Accounting
Audit & accounting.
- Accounting & financial management
- Audit workflow
- Engagement compilation & review
- Guidance & standards
- Internal audit & controls
- Quality control
Data & document management
- Certificate management
- Data management & mining
- Document storage & organization
Estate planning
- Estate planning & taxation
- Wealth management
Financial planning & analysis
- Financial reporting

Payroll, compensation, pension & benefits
- Payroll & workforce management services
- Healthcare plans
- Billing management
- Client management
- Cost management
- Practice management
- Workflow management
Professional development & education
- Product training & education
- Professional development
Tax planning & preparation
- Financial close
- Income tax compliance
- Tax automation
- Tax compliance
- Tax planning
- Tax preparation
- Sales & use tax
- Transfer pricing
- Fixed asset depreciation
Tax research & guidance
- Federal tax
- State & local tax
- International tax
- Tax laws & regulations
- Partnership taxation
- Research powered by AI
- Specialized industry taxation
- Credits & incentives
- Uncertain tax positions
A powerful tax and accounting research tool. Get more accurate and efficient results with the power of AI, cognitive computing, and machine learning.
Provides a full line of federal, state, and local programs. Save time with tax planning, preparation, and compliance.
Automate workpaper preparation and eliminate data entry
Trade & Supply
Customs & duties management.
- Customs law compliance & administration
Global trade compliance & management
- Global export compliance & management
- Global trade analysis
- Denied party screening
Product & service classification
- Harmonized Tariff System classification
Supply chain & procurement technology
- Foreign-trade zone (FTZ) management
- Supply chain compliance
Software that keeps supply chain data in one central location. Optimize operations, connect with external partners, create reports and keep inventory accurate.
Automate sales and use tax, GST, and VAT compliance. Consolidate multiple country-specific spreadsheets into a single, customizable solution and improve tax filing and return accuracy.
Risk & Fraud
Risk & compliance management.
- Regulatory compliance management
Fraud prevention, detection & investigations
- Fraud prevention technology
Risk management & investigations
- Investigation technology
- Document retrieval & due diligence services
Search volumes of data with intuitive navigation and simple filtering parameters. Prevent, detect, and investigate crime.
Identify patterns of potentially fraudulent behavior with actionable analytics and protect resources and program integrity.
Analyze data to detect, prevent, and mitigate fraud. Focus investigation resources on the highest risks and protect programs by reducing improper payments.
News & Media
Who we serve.
- Broadcasters
- Governments
- Marketers & Advertisers
- Professionals
- Sports Media
- Corporate Communications
- Health & Pharma
- Machine Learning & AI
Content Types
- All Content Types
- Human Interest
- Business & Finance
- Entertainment & Lifestyle
- Reuters Community
- Reuters Plus - Content Studio
- Advertising Solutions
- Sponsorship
- Verification Services
- Action Images
- Reuters Connect
- World News Express
- Reuters Pictures Platform
- API & Feeds
- Reuters.com Platform
Media Solutions
- User Generated Content
- Reuters Ready
- Ready-to-Publish
- Case studies
- Reuters Partners
- Standards & values
- Leadership team
- Reuters Best
- Webinars & online events
Around the globe, with unmatched speed and scale, Reuters Connect gives you the power to serve your audiences in a whole new way.
Reuters Plus, the commercial content studio at the heart of Reuters, builds campaign content that helps you to connect with your audiences in meaningful and hyper-targeted ways.
Reuters.com provides readers with a rich, immersive multimedia experience when accessing the latest fast-moving global news and in-depth reporting.
- Reuters Media Center
- Jurisdiction
- Practice area
- View all legal
- Organization
- View all tax
Featured Products
- Blacks Law Dictionary
- Thomson Reuters ProView
- Recently updated products
- New products
Shop our latest titles
ProView Quickfinder favorite libraries
- Visit legal store
- Visit tax store
APIs by industry
- Risk & Fraud APIs
- Tax & Accounting APIs
- Trade & Supply APIs
Use case library
- Legal API use cases
- Risk & Fraud API use cases
- Tax & Accounting API use cases
- Trade & Supply API use cases
Related sites
United states support.
- Account help & support
- Communities
- Product help & support
- Product training
International support
- Legal UK, Ireland & Europe support
New releases
- Westlaw Precision
- 1040 Quickfinder Handbook
Join a TR community
- ONESOURCE community login
- Checkpoint community login
- CS community login
- TR Community
Free trials & demos
- Westlaw Edge
- Practical Law
- Checkpoint Edge
- Onvio Firm Management
- Proview eReader

How to do legal research in 3 steps
Knowing where to start a difficult legal research project can be a challenge. But if you already understand the basics of legal research, the process can be significantly easier — not to mention quicker.
Solid research skills are crucial to crafting a winning argument. So, whether you are a law school student or a seasoned attorney with years of experience, knowing how to perform legal research is important — including where to start and the steps to follow.
What is legal research, and where do I start?
Black's Law Dictionary defines legal research as “[t]he finding and assembling of authorities that bear on a question of law." But what does that actually mean? It means that legal research is the process you use to identify and find the laws — including statutes, regulations, and court opinions — that apply to the facts of your case.
In most instances, the purpose of legal research is to find support for a specific legal issue or decision. For example, attorneys must conduct legal research if they need court opinions — that is, case law — to back up a legal argument they are making in a motion or brief filed with the court.
Alternatively, lawyers may need legal research to provide clients with accurate legal guidance . In the case of law students, they often use legal research to complete memos and briefs for class. But these are just a few situations in which legal research is necessary.
Why is legal research hard?
Each step — from defining research questions to synthesizing findings — demands critical thinking and rigorous analysis.
1. Identifying the legal issue is not so straightforward. Legal research involves interpreting many legal precedents and theories to justify your questions. Finding the right issue takes time and patience.
2. There's too much to research. Attorneys now face a great deal of case law and statutory material. The sheer volume forces the researcher to be efficient by following a methodology based on a solid foundation of legal knowledge and principles.
3. The law is a fluid doctrine. It changes with time, and staying updated with the latest legal codes, precedents, and statutes means the most resourceful lawyer needs to assess the relevance and importance of new decisions.
Legal research can pose quite a challenge, but professionals can improve it at every stage of the process .
Step 1: Key questions to ask yourself when starting legal research
Before you begin looking for laws and court opinions, you first need to define the scope of your legal research project. There are several key questions you can use to help do this.
What are the facts?
Always gather the essential facts so you know the “who, what, why, when, where, and how” of your case. Take the time to write everything down, especially since you will likely need to include a statement of facts in an eventual filing or brief anyway. Even if you don't think a fact may be relevant now, write it down because it may be relevant later. These facts will also be helpful when identifying your legal issue.
What is the actual legal issue?
You will never know what to research if you don't know what your legal issue is. Does your client need help collecting money from an insurance company following a car accident involving a negligent driver? How about a criminal case involving excluding evidence found during an alleged illegal stop?
No matter the legal research project, you must identify the relevant legal problem and the outcome or relief sought. This information will guide your research so you can stay focused and on topic.
What is the relevant jurisdiction?
Don't cast your net too wide regarding legal research; you should focus on the relevant jurisdiction. For example, does your case deal with federal or state law? If it is state law, which state? You may find a case in California state court that is precisely on point, but it won't be beneficial if your legal project involves New York law.
Where to start legal research: The library, online, or even AI?
In years past, future attorneys were trained in law school to perform research in the library. But now, you can find almost everything from the library — and more — online. While you can certainly still use the library if you want, you will probably be costing yourself valuable time if you do.
When it comes to online research, some people start with free legal research options , including search engines like Google or Bing. But to ensure your legal research is comprehensive, you will want to use an online research service designed specifically for the law, such as Westlaw . Not only do online solutions like Westlaw have all the legal sources you need, but they also include artificial intelligence research features that help make quick work of your research
Step 2: How to find relevant case law and other primary sources of law
Now that you have gathered the facts and know your legal issue, the next step is knowing what to look for. After all, you will need the law to support your legal argument, whether providing guidance to a client or writing an internal memo, brief, or some other legal document.
But what type of law do you need? The answer: primary sources of law. Some of the more important types of primary law include:
- Case law, which are court opinions or decisions issued by federal or state courts
- Statutes, including legislation passed by both the U.S. Congress and state lawmakers
- Regulations, including those issued by either federal or state agencies
- Constitutions, both federal and state
Searching for primary sources of law
So, if it's primary law you want, it makes sense to begin searching there first, right? Not so fast. While you will need primary sources of law to support your case, in many instances, it is much easier — and a more efficient use of your time — to begin your search with secondary sources such as practice guides, treatises, and legal articles.
Why? Because secondary sources provide a thorough overview of legal topics, meaning you don't have to start your research from scratch. After secondary sources, you can move on to primary sources of law.
For example, while no two legal research projects are the same, the order in which you will want to search different types of sources may look something like this:
- Secondary sources . If you are researching a new legal principle or an unfamiliar area of the law, the best place to start is secondary sources, including law journals, practice guides , legal encyclopedias, and treatises. They are a good jumping-off point for legal research since they've already done the work for you. As an added bonus, they can save you additional time since they often identify and cite important statutes and seminal cases.
- Case law . If you have already found some case law in secondary sources, great, you have something to work with. But if not, don't fret. You can still search for relevant case law in a variety of ways, including running a search in a case law research tool.
Once you find a helpful case, you can use it to find others. For example, in Westlaw, most cases contain headnotes that summarize each of the case's important legal issues. These headnotes are also assigned a Key Number based on the topic associated with that legal issue. So, once you find a good case, you can use the headnotes and Key Numbers within it to quickly find more relevant case law.
- Statutes and regulations . In many instances, secondary sources and case law list the statutes and regulations relevant to your legal issue. But if you haven't found anything yet, you can still search for statutes and regs online like you do with cases.
Once you know which statute or reg is pertinent to your case, pull up the annotated version on Westlaw. Why the annotated version? Because the annotations will include vital information, such as a list of important cases that cite your statute or reg. Sometimes, these cases are even organized by topic — just one more way to find the case law you need to support your legal argument.
Keep in mind, though, that legal research isn't always a linear process. You may start out going from source to source as outlined above and then find yourself needing to go back to secondary sources once you have a better grasp of the legal issue. In other instances, you may even find the answer you are looking for in a source not listed above, like a sample brief filed with the court by another attorney. Ultimately, you need to go where the information takes you.
Step 3: Make sure you are using ‘good’ law
One of the most important steps with every legal research project is to verify that you are using “good" law — meaning a court hasn't invalidated it or struck it down in some way. After all, it probably won't look good to a judge if you cite a case that has been overruled or use a statute deemed unconstitutional. It doesn't necessarily mean you can never cite these sources; you just need to take a closer look before you do.
The simplest way to find out if something is still good law is to use a legal tool known as a citator, which will show you subsequent cases that have cited your source as well as any negative history, including if it has been overruled, reversed, questioned, or merely differentiated.
For instance, if a case, statute, or regulation has any negative history — and therefore may no longer be good law — KeyCite, the citator on Westlaw, will warn you. Specifically, KeyCite will show a flag or icon at the top of the document, along with a little blurb about the negative history. This alert system allows you to quickly know if there may be anything you need to worry about.
Some examples of these flags and icons include:
- A red flag on a case warns you it is no longer good for at least one point of law, meaning it may have been overruled or reversed on appeal.
- A yellow flag on a case warns that it has some negative history but is not expressly overruled or reversed, meaning another court may have criticized it or pointed out the holding was limited to a specific fact pattern.
- A blue-striped flag on a case warns you that it has been appealed to the U.S. Supreme Court or the U.S. Court of Appeals.
- The KeyCite Overruling Risk icon on a case warns you that the case may be implicitly undermined because it relies on another case that has been overruled.
Another bonus of using a citator like KeyCite is that it also provides a list of other cases that merely cite your source — it can lead to additional sources you previously didn't know about.
Perseverance is vital when it comes to legal research
Given that legal research is a complex process, it will likely come as no surprise that this guide cannot provide everything you need to know.
There is a reason why there are entire law school courses and countless books focused solely on legal research methodology. In fact, many attorneys will spend their entire careers honing their research skills — and even then, they may not have perfected the process.
So, if you are just beginning, don't get discouraged if you find legal research difficult — almost everyone does at first. With enough time, patience, and dedication, you can master the art of legal research.
Thomson Reuters originally published this article on November 10, 2020.
Related insights

Westlaw tip of the week: Checking cases with KeyCite

Why legislative history matters when crafting a winning argument

Case law research tools: The most useful free and paid offerings

Request a trial and experience the fastest way to find what you need
The Research Method: Law Reform Design
- First Online: 18 October 2019
Cite this chapter

- Kristina Loguinova 4
Part of the book series: Economic and Financial Law & Policy – Shifting Insights & Values ((EFLP,volume 4))
322 Accesses
Due to the criticism of Critical Legal Studies coming down to nothing more than nihilism, the third chapter of the first part of this monograph identifies law reform design as the most appropriate research method for answering research questions from a Critical Legal Studies’ perspective. Namely, law reform design provides for the opportunity to formulate constructive solutions instead of engaging in critique for the sake of critique. Also, this chapter suggest to make a distinction between a micro and macro design of law reform.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Gordon ( 1998 ), p. 87; Williams ( 2011 ), p. 374; Williams (1987), pp. 431–496; Caudill ( 1987 ), pp. 292–292; Kelman ( 1987 ), p. 9; Rabinowitz (1998), p. 681; Hutchinson and Monahan ( 1984 ), p. 236; Schlag (2009), p. 298; Gabel ( 2009 ), p. 519. To set the tone for the following chapter it seems appropriate to quote Freeman on the nihilist allegation. “The goal of trashing, however, is not liberation into nihilist resignation. I am no nihilist. If anything, I might be more justly accused of having utopian tendencies. The point of delegitimation is to expose possibilities more truly expressing reality, possibilities of fashioning a future that might at least partially realize a substantive notion of justice instead of the abstract, rightsy, traditional, bourgeois notions of justice that generate so much of the contradictory scholarship.”: Freeman ( 1981 ), p. 1230.
Hunt ( 1987 ), p. 7. A similar point has been made by Schwartz: Schwartz ( 1984 ), p. 422.
Russell ( 1986 ), p. 3.
Fischl ( 1992 ), pp. 783–805. Indeed, by solely trashing ( unfreezing the world as it now appears) a Crit engages in a liberating and creating activity to encourage imagination and innovation. That is, not a completely worthless and useless activity per se: Hutchinson ( 1989 ), p. 8; Hutchinson and Monahan ( 1984 ), pp. 227–228. Crits are in other words not obsessed with normative questions in concern to what to do next (a form of neurotic projection): Fischl ( 1992 ), pp. 783–805.
Gordon ( 1998 ), p. 83.
Gordon ( 1998 ), p. 83 (personally added underlineation). Zamboni has also spoken encouragingly of Crits engaging in concrete project of reconstruction after they finish with trashing. Namely, “[o]nce free from the traditional formalistic legal barriers erected between the law and politics, CLS legal scholar should then not be indifferent to the type of [ideology] the legal order ought to implement in society. In other words, she should primarily charge her investigation with political indications of the type of [ideology] the law-making should implement.”: Zamboni ( 2008 ), p. 77.
Namely, CLS “has now been around sufficiently long that is must (…) pass beyond the stage of debunking and trashing (…) [it should] grapple with the problems of advancing (…) alternative[s]”: Hunt ( 1987 ), p. 7 (personally added underlineation).
Hutchinson and Monahan ( 1984 ), p. 227 (personally added underlineation).
Hessel ( 2013 ), pp. 30–70.
Silbey and Sarat (2008), p. 502.
Fischl ( 1992 ), pp. 780–820.
The research method represents the central relationship between the main research question of a research and the (overall) strategy that enables the provision of an answer to this question. Moreover, the research method emphasises the function of the research. Taking my main research question into account, it is safe to say that the function of my research (my research method) is design. The research method of design is about proposing a change or solution to solve a problem or to improve a situation. Design is intrinsically linked to the evaluation of a (problematic) situation: Tijssen ( 1961 ), pp. 53–59. Bakshi has remarked that designing proposals for law reform either result as a by-product of the undertaken research or as the manifestation of an intention that has been specified in the beginning the research (the latter being my case): Bakshi (2001), p. 111. When the latter option is opted for, the research “is undertaken with a definite end, namely, making suggestions for improvements in the law on concrete and easily identifiable matters and the formulation of those proposals in precise terms.”: Bakshi (2001), p. 111. This process of conducting a research with the intention to design proposals of law reform generally involves slightly more than just evaluation according to Bakshi. It involves the analysis of the existing law; a historical examination (finding out what the previous law looked like in order to understand how and why it changed); a comparison; a statistical examination (if statistics are available); and a critical examination (finding out the defects or problems in the existing law on the basis of which reforms are suggested: Bakshi (2001), p. 113. The research method of design has been utilized in legal research (see Chap. 4 ) but is gaining more and more prominence outside the legal context. Examples of scholars who have designed alternative ways to structure the current political economy or alternative parts of the current political economy include the Skydelskys, Bregman and Mason: Skidelsky and Skidelsky ( 2013 ), pp. 11–218; Bregman ( 2017 ), pp. 33–72; Mason ( 2016 ), pp. 263–292.
Marano and Siri ( 2017 ), p. 16; Focarelli (2017), p. 354.
Van Hoecke ( 2011 ), p. v . To clarify, “[e]valuative scholarship is in some way providing an assessment of the way the (legal) world is , and, either implicitly or explicitly, subjecting the law to appraisal either from the point of view of coherence with earlier law , other areas of law, or from an external viewpoint and where shortfalls are identified , suggesting how things might be improved .”: Cryer et al. ( 2011 ), p. 9 (personally added underlineation). Cryer et al. ( 2011 ), p. 9.
Wendt ( 2008 ), p. 144.
Wendt ( 2008 ), pp. 132–144.
Gordon (1989), p. 384.
This assumption is shared by the legal method of comparative law. That is, “[c]omparative law is an ‘école de vérité’ which extends and enriches the ‘supply of solutions’ (Zitelmann) and offers the scholar of critical capacity the opportunity of finding the ‘better solution’ for his time and place.”: Zweigert and Kötz ( 1994 ), p. 15 (personally added underlineation).
Tushnet ( 2011 ), p. 299; Kennedy ( 1985 ), p. 1031; Hutchinson ( 1989 ), p. 10.
It needs to be specified that my comparison, borrowing from the legal method of comparative law, is based on the principle of functionality . The principle of functionality dictates that a question to which a comparison is devoted must be posed in functional terms. It must concern a concrete problem without a reference to concepts from either one of the sources that are compared: Zweigert and Kötz ( 1994 ), pp. 30–33. In my case, the concrete problem on which the comparison is based is ideology . I also need to specify that my research is not primarily using the method of comparative law since this method assumes a dimension of internationalism: Zweigert and Kötz ( 1994 ), p. 2. This dimension of internationalism is not the main focus of my comparison that primarily concerns Solvency II and its predecessor, i.e. my comparison takes place in the framework of one legal system (the EU legal system). However, Van Gerven and Lierman have indicated that the requirement of the dimension of internationalism in the method of comparative law is outdated. In the last couple of decades internal comparative law has emerged (as opposed to the comparative law described by Zweigert and Kӧtz which has been labelled as external comparative law by Van Gerven and Lierman) which is concerned with looking beyond the boundaries of a specific field in one legal system (especially in case law): Van Gerven and Lieman ( 2010 ), pp. 137–147.
Indeed, how can one design any alternatives without knowing what the law is and what it was before?: Meyendorff (1933), p. 22.
Fiss ( 1986 ), p. 10. It should be emphasised that my design of an alternative ideology does not aim to claim to be the optimal design of an alternative ideology. It is just one possible option to show that there is nothing natural and inevitable about the existing ideology. Moreover, it is one possible option that should be communicated, debated and pulled apart in society. By emphasising this I am attempting to “be careful to avoid foisting [my] own structure of thought on others”: Hutchinson and Monahan ( 1984 ), p. 229.
Shiffrin ( 2006 ), p. 178. By crafting an alternative decision for Lechmere, Inc. v. NLRB , Shiffrin did not intend to show that the Supreme Court reached the wrong decision. Rather, Shiffrin hoped to show that law should be a conversation about things that matter to us: Shiffrin ( 2006 ), p. 178. In the spirit of methodological trashing, Shiffrin designed an alternative to spark awareness and communication.
Hutchinson and Monahan ( 1984 ), p. 230.
Byttebier ( 2015 ), pp. 5–525. By now this monograph has been translated to English: Byttebier ( 2017 ), pp. vii -501. Now that the English version of this monograph is available, I will refer to it from this point on. Outside of a legal context, the monograph by the Skydelskys about how much is enough is an example of a research employing the method of design of reform. The Skydelskys have namely argued that we have lost touch with the good life and have made propositions (design) to return to it by means of a different social and economic organization. The propositions include the introduction of basic income, the reduction of the pressure to consume and the reduction of advertising: Skidelsky and Skidelsky ( 2013 ), pp. 11–218.
Within the legal method of comparative law such a distinction already exists. Namely, whenever comparative lawyers engage in a comparison of how concrete problems are dealt with in the legal systems of different nations they can do so on a large scale or a on a smaller scale. A comparison on a large is called a macrocomparison whereas a comparison on a smaller scale is called a microcomparison : Zweigert and Kötz ( 1994 ), pp. 4–5.
Hutchinson ( 1989 ), p. 8 (personally added underlineation). Hopeless, in this context seems to signify not “connected in a meaningful way to reality: Austin ( 1998 ), p. 110. Granted that being too abstract is of no use to anyone, being utopian is not necessarily a bad thing. Certainly not if thinking of alternatives and having different visions is utopian. If such is the case, then “CLS should wear the badge of utopianism with pride, for more, not less not-status-quo-oriented thinking is needed.”: Hutchinson ( 1989 ), p. 8. Also, why can’t human beings form a picture of an ideal life or a perfect society and share it with other human beings? Thoughts, debates and dreams are never wasted, especially in today’s information society (see Sect. 3.4.1.4 ): Mason ( 2016 ), pp. xviii–xxi . Moreover, the criticism of utopianism goes either way. Proponents of free markets and TINA can be criticized for being utopian just as much. For those interested in an achievable utopia (and the difference between utopia as a rigid blueprint and utopia as an alternative with the capacity to spark the imagination), see: Bregman ( 2017 ), pp. 1–316.
Schwartz ( 1984 ), p. 428.
Caudill ( 1987 ), p. 355. This vice is particularly dangerous as “the elaboration of grand schemes for future societies runs the danger of simply imposing one more form of ‘alien’ social consciousness.”: Hutchinson ( 1989 ), p. 8. However, there is something to be said for grandiose ideas. According to Bregman, Overton (an American lawyer) asked himself why a lot of good ideas simply don’t get taken seriously in the context of politics. “Overton realized that politicians, provided they want to be reelected, can’t permit themselves viewpoints that are seen as too extreme. In order to hold power, they have to keep their ideas within the margins of what’s acceptable. This window of acceptability is populated by schemes that are rubber-stamped by the experts, tallied up by statistics services, and have good odds of making it into the law books. Anybody who forays outside the ‘Overton window’ faces a rocky road. He or she will quickly be branded as ‘unrealistic’ or ‘unreasonable’ by the media, the fearsome gatekeepers of the window. (…) And yet, despite all this, a society can change completely in a few decades. The Overton Window can shift. A classic strategy for achieving this is to proclaim ideas so shocking and subversive that anything less radical suddenly sounds sensible .”: Bregman ( 2017 ), pp. 254–255 (personally added underlineation). And thus even grandiose ideas have a function. They can pave the way for a better society by making other ideas, more alternative ideologies of how to shape a social order, seem less radical and thus more sensible. A good example of such a strategy within CLS specifically was Kennedy’s proposal to inter alia establish a single salary at the Harvard Law School for everyone (from the janitor to the dean), to implement a rotation system whereby each member of the Harvard Law School would rotate through each job and to implement a system whereby university admission would operate by lot. Kennedy was partly serious about his proposals. The sentiment for the part that he was not serious about revolved around provocation and confounding: Schwartz ( 1984 ), pp. 413–414.
Schwartz ( 1984 ), p. 448.
As such I am trying to be both constructive and concrete. Namely, as Kelman points out, when Crits only trash, they are accused of nihilism. When Crits trash and actually propose alternatives, they are accused of being utopian since they allegedly do not propose concrete steps, i.e. are too vague: Kelman (1989), p. 210. Austin has also mentioned that CLS is either accused of not mentioning solutions (resulting in nihilism) or of being utopian: Austin ( 1998 ), pp. 90–110.
Mason ( 2016 ), p. xiii .
Rickards (2014), p. 292. According to Popper (and Soros, who follows Popper in this matter) it is better to introduce changes on a small (scarcely noticeable) scale rather than to directly propose changes on a large scale as the first assumes graduality which has a larger chance to succeed anything drastic: Rickards (2014), p. 292.
Mason ( 2016 ), p. 277.
Unger (2015), p. 29.
Bibliography
Austin A (1998) The empire strikes back: outsiders and the struggle over legal education. New York University Press, New York
Google Scholar
Bregman R (2017) Utopia for realists: and how we can get there. Bloomsbury, London
Byttebier K (2015) Nu het gouden kalf verdronken is: Van hebzucht naar altruïsme als hoeksteen voor een Nieuwe Monetaire Wereldorde. Maklu, Antwerp
Byttebier K (2017) Towards a new international monetary order. Springer, Sham
Book Google Scholar
Caudill DS (1987) Disclosing tilt: a partial defence of critical legal studies and a comparative introduction to the philosophy of the law-idea. Iowa Law Rev 72:287–359
Cryer R, Hervey T, Sokhi-Bulley B (2011) Research methodologies in EU and international law. Hart, Oxford
Fischl M (1992) The question that killed critical legal studies. Law Soc Inq 17:779–820
Article Google Scholar
Fiss OM (1986) Death of the law. Cornell Law Rev 72:1–16
Freeman AD (1981) Truth and mystification in legal scholarship. Yale Law J 90:1229–1237
Gabel P (2009) Critical legal studies as a spiritual practice. Pepp Law Rev 36:515–534
Gordon RW (1998) Law and ideology. Tikkun 3:14–87
Hessel S (2013) Neem het niet. Van Gennep, Amsterdam
Hunt A (1987) The critique of law: what is ‘critical’ about critical legal theory? J Law Soc 14:5–19
Hutchinson AC (ed) (1989) Critical legal studies. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Totowa
Hutchinson AC, Monahan PJ (1984) Law, politics and the critical legal scholars: the unfolding Drama of American legal thought. Stan Law Rev 36:199–235
Kairys D (ed) (1998) The politics of law: a progressive critique. Basic Books, New York
Katz SN (ed) (2009) The Oxford international Encyclopedia of legal history. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Kelman M (1987) A guide to critical legal studies. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Kennedy D (1985) Afterword. Psycho-social CLS: a comment on the Cardozo Symposium. Cardozo Law Rev 6:1013–1031
London School of Economics and Political Science (ed) (1933) Modern theories of law. Oxford University Press, London
Marano P, Siri M (eds) (2017) Insurance regulation in the European Union: solvency II and beyond. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Mason P (2016) Post capitalism: a guide to our future. Penguin Books, London
Mertz E (ed) (2008) The role of social science in law. Ashgate, Hampshire
Russell JS (1986) The critical legal studies challenge to contemporary mainstream legal philosophy. Ottowa Law 18:1–24
Schwartz LB (1984) With gun and camera through darkest CLS-land. Stan Law Rev 1984(36):413–464
Shiffrin JB (2006) A practical jurisprudence of values: re-writing Lechmere, Inc. v. NLRB. Harv Civ Rights-Civ Libr Law Rev 41:177–217
Skidelsky R, Skidelsky E (2013) How much is enough? Money and the good life. Penguin Books, London
Tijssen HEB (1961) De juridische dissertatie onder de loep: De verantwoording van methodologische keuzes in juridische dissertaties. Dissertation, University of Tilburg
Tushnet M (2011) Some current controversies in critical legal studies. German Law J 12:290–299
Van Gerven W, Lierman S (2010) Algemeen Deel Veertig jaar later: Privaat-en Publiekrecht in een Meergelaagd kader van regelgeving, rechtsvorming en regeltoepassing, I, Beginselen van Belgisch Privaatrecht. Kluwer, Mechelen
Van Hoecke M (ed) (2011) Methodologies of legal research: which kind of method for what kind of discipline? Hart, Oxford
Verma SK, Afzal Wani M (eds) (2001) Legal research and methodology. Indian Law Institute, New Delhi
Wendt JAI (2008) De methode der rechtswetenschap vanuit kritisch-rationeel perspectief. Dissertation, Erasmus University of Rotterdam
Williams J (2011) Is law and art [sic] or a science?: Comments on objectivity, feminism and power. JGSPL 7:355–372
Zamboni M (2008) Law and politics: a dilemma for contemporary legal theory. Springer, Berlin
Zweigert K, Kötz H (1994) An introduction to comparative law. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
ECOR and ETAF, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium
Kristina Loguinova
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Loguinova, K. (2019). The Research Method: Law Reform Design. In: A Critical Legal Study of the Ideology Behind Solvency II. Economic and Financial Law & Policy – Shifting Insights & Values, vol 4. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26357-7_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26357-7_4
Published : 18 October 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-26356-0
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-26357-7
eBook Packages : Law and Criminology Law and Criminology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- Law Practice

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.
Return this item for free
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable
- To view this video download Flash Player
Research Methods for Law
Purchase options and add-ons.
- ISBN-10 139951508X
- ISBN-13 978-1399515085
- Publisher Edinburgh University Press
- Publication date July 31, 2023
- Language English
- Print length 356 pages
- See all details

Editorial Reviews
About the author, product details.
- Publisher : Edinburgh University Press (July 31, 2023)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 356 pages
- ISBN-10 : 139951508X
- ISBN-13 : 978-1399515085
- Item Weight : 1.1 pounds
- #668 in Law Practice Research (Books)
- #2,307 in Legal Self-Help
- #6,510 in Research Reference Books
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
No customer reviews
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
Legal Research Methodology: Types And Approaches of Legal Research

Legal research methodologies explore unsettled legal questions, acquire and analyze relevant information, and apply findings to solve legal problems.
Let’s understand the definition of legal research methodologies and the types and approaches to Legal research methodologies.
Understand Legal Research Methodology
What is legal research methodology.
Legal research methodologies serve three main functions, exploring a legal problem, critically describing facts and legislation, and explaining or interpreting legal issues and concepts.
Why is a methodology needed in the first place?
The methodology is a means of inquiry to achieve these purposes in a meaningful way .
In legal research, the methodology;
- is a systematic inquiry that provides information to guide legal research,
- is the trained and scientific investigation of the principles and facts of any subject,
- helps the readers understand the research methods to discover the truth and evaluate the results’ validity,
- helps the researchers follow a consistent logic in research and prepare them to meet possible challenges,
- is also an important way to jam reliable and valid knowledge and explore the relationship between theory and practice.
Understanding research methods will help students conduct and write up their research monographs, dissertations, or theses systematically.
However, research methodology is different from research methods. ‘Research method’ usually implies all methods and techniques used to collect and process the data.
Thus, the method is a tool or technique such as a qualitative or quantitative method. It also includes interviews, case studies, or surveys.
On the other hand, research methodology refers to the body of methods that guide thinking within a specific field of study.
A methodology is a justification or rationale for the research approach and is concerned with the general strategy or approach of undertaking research.
Legal research methodology is a must.
It is vital for a researcher to know the research methodology and understand the underlying methodologies’ assumptions.
Researchers also need to know the criteria by which they can decide that certain methodologies will apply to certain problems.
Research methodology has been defined as the means of acquiring scientific knowledge. It has also been defined as a means to gather information and data to achieve a valid outcome.
Legal research methodology is simply a way of addressing and exploring unsettled legal questions or issues.
Legal research methodologies are techniques by which one acquires legally relevant information, analyzes, interprets, and applies them to resolve issues and present the findings.
Thus, legal research methodology is a scientific and systematic way to solve any legal question.
Legal research methodology also refers to rules of interpretation of legal problems and issues. It is a systematic effort to make an argument to arrive at a true or accurate account of the subject matter under consideration.
The researcher should explain properly why he uses a particular method to evaluate research results by the researcher himself or others. Adopting a particular methodology should stem from the research objective and purpose.

Types of Legal Research
Two types of Legal research are;
- Qualitative Research for Legal Research.
- Quantitative Research for Legal Research.
The main difference between qualitative and quantitative legal research is that; qualitative legal research is pure and applied research, concerned with the analysis of theories. Whereas quantitative legal research is concerned with testing the theories in the real world.
Depending upon the nature of the research question, legal research is also classified as descriptive and exploratory one.
Descriptive research attempts to describe a situation, problem, phenomenon, or behavior systematically. A description is concerned with making complicated things understandable and simple.
Exploratory research is undertaken to explore areas about which the researcher has little or no knowledge . It involves findings the reason for things, events and situations, showing why and how they have come to be what they are. Exploratory research enables the researcher to formulate problems for more in-depth study, develop hypotheses, and find the best solution.
Another popular distinction is between pure doctrinal research and non-doctrinal or empirical research.
While the former is theoretical work undertaken primarily to acquire new knowledge without a specific application, the latter is original work undertaken to acquire new knowledge with a specific practical application in view.
Doctrinal legal research is concerned with the analysis of legal theories, concepts, rules, and principles.
Most doctrinal legal research is based on the ‘black-letter law’ approach, which focuses on the knowledge of law found in the legal texts, legal theories, statutes, and court judgments with ‘little or no reference to the world outside the law.’
The doctrinal or ‘black-letter’ legal research aims to explain, systemize, and clarify the law on any particular topic by a distinctive mode of analysis.
In recent times, pure doctrinal legal research has been criticized for its rigidity, narrower scope, and inflexibility in addressing diverse contexts m which legal issues or situations arise and operate.
As a result, empirical or inter-disciplinary legal research emerged as a distinct type of legal scholarship in the law schools of western countries to study law in the broader social and political contexts.
This empirical and interdisciplinary legal research employs various social science and humanities methods. According to Epstein and King,
What makes research empirical is that it is based on observations of the world, in other words, data, which is just a term for facts about the world.
These facts may be historical or contemporary or based on legislation or case law, the results of interviews or surveys , or the outcomes of secondary archival research or primary data collection .
Another important classification is between qualitative and quantitative research.
Qualitative Research for Legal Research
Qualitative research is concerned with the explanation, interpretation, and understanding of phenomena or issues, or things. It relies primarily on human perception and understanding. It concerns the subjective assessment of the social or legal problem, situation, and attitude.
Qualitative research is critical in the behavioral sciences, where the aim is to discover the underlying motives of human behavior. A qualitative approach is concerned with the subjective assessment of attitudes, opinions, and behavior.
Quantitative research offers:
- richly descriptive reports of individual perceptions, attitudes, beliefs, views, and feelings,
- the meanings and interpretations are given to events and things, as well as their behavior;
- it displays how these are put together, more or less coherently and consciously,
- into frameworks that make sense of their experiences; and
- illuminates the motivations which connect attitudes and behavior, the discontinuities, or
- even contradictions between attitudes and behavior, or
- how conflicting attitudes and motivations are resolved in particular choices made.
Qualitative research is related to the analysis of some abstract idea, doctrine, or theory. It is generally used to develop new concepts or to reinterpret existing ones.
In qualitative research, researchers use analytical techniques and their views on the subject matter in question.
Qualitative research varifies the old established principles of laws. It may lead to discovering a new theory, refinement, or interpretation of an existing theory, principles, or legal issues.
On the other hand, empirical research relies on experience or observation alone, often without due regard for system and theory.
Qualitative research involves more explicit judgment, interpretation, or critical evaluation of a problem.
As far as legal study is concerned, the qualitative method is applied to analyze legal propositions or legal theories or doctrines and explore existing statutory propositions and cases in light of propositions or doctrines.
Qualitative research of law involves studying general theoretical questions about the nature of laws and legal systems, the relationship of law to justice and morality , and problems of application of law in a given society.
The main advantage of the qualitative method is that qualitative analysis draws on the interpretive skills of the researcher and opens up the possibility of more than one explanation being valid.
The main criticism of qualitative research is that it is too impressionistic and subjective. Qualitative findings rely too much on the researcher’s subjective assessment of views about what is significant.
The qualitative research findings tend to be open-ended, which is difficult to generalize: Many qualitative research works are doctrinal. Observation, interviewing, case study, examination, and analysis are the most common method of qualitative research.
Quantitative Research for Legal Research
Quantitative research for legal research is based on the measurement of quantity or amount. It consists of counting how frequently things happen. It applies to phenomena that can be expressed in terms of quantity. It is also known as the statistical method.
Because in quantitative research, researchers use an array of statistical methods and generalizations to determine the meaning of data.
It has been the dominant strategy for conducting socio-legal research. Quantitative methods often test or verify existing theories or hypotheses.
Quantitative research involves finding a solution to a real-life problem requiring an action or policy decision.
Quantitative research also tests many variables through the generation of primary data. The generalization process from sample to a population is an example of quantitative instead of qualitative research methodology.
Quantitative research can contribute new evidence, challenge old theories, and help conceptual clarification.
Usually, the quantitative approach involves generating data in quantitative form, which can be subjected to rigorous quantitative analysis formally and rigidly. Quantification can make it easier to aggregate, compare and summarise data.
Data can be collected from questionnaire surveys, fact-finding inquiries, and interviews. Data analysis is one of the important components of quantitative research.
The quantitative method is also sometimes termed an empirical approach as data are collected to test the hypothesis or examine the propositions or interpretations of findings.
Advantages of the Quantitative Legal Research Methods
- First, quantitative data are gathered by various forms of statistical techniques based on the principles of mathematics and probability. The analysis appears to be based on objective laws rather than the researcher’s values.
- Second, statistical tests of significance give researchers additional credibility in terms of their interpretations and their confidence in their findings.
- Third, quantitative data analysis provides a solid foundation for description and analysis.
- Fourth, large volumes of quantitative data can be analyzed relatively quickly, provided adequate preparation and planning have occurred in advance.
- Finally, tables and charts effectively organize quantitative data and communicate the findings to others.
The quantitative research method supplements traditional legal research to investigate the complexities of the law, legal actors, and legal activities.
Quantitative legal research is mostly applicable for conducting non-doctrinal, empirical, and socio-legal research . Objectivity remains the main aspect of quantitative research.
A set of rules or procedures should be followed in quantitative research, even though qualitative research tends to be more flexible.
While the researcher’s values and bias influence qualitative research, quantitative research seeks to report the findings objectively, and the role of the researcher is neutral.
Which One is Better – Quantitative or Qualitative Legal Research Methods?
To some extent, it depends on the training of the researcher and the nature of the research questions. But choosing one method in exclusion of others may be counterproductive for advancing legal scholarship.
Rather blending both quantitative and qualitative approaches can be the best way to accomplish the objectives of research work.
It is generally accepted that using more than one method strengthens the validity and credibility of the research.
5 Approaches to Legal Research

Legal research methodology is not particularly different from the research methodology used in other disciplines.
Nonetheless, it has some special attributes regarding source materials and ways of approaching the problems.
Researchers should be clear about the methodology and reasons for choosing a particular methodology.
Effective legal research is hardly possible without a proper understanding of research methodology . A researcher should justify the important methodological choices in their work.
Legal research may be of combination of methods for interpreting and applying legally relevant information. There are no single or universal approaches to legal research methodologies.
There are several approaches to research methodology , such as analytical, inter-disciplinary, comparative, and historical.
A particular type of methodology depends considerably upon the research question formulated and the sources of materials chosen.
Analytical Approach to Legal Research
Interdisciplinary approach to legal research, socio-legal approach to legal research, comparative approach to legal research, historical approach to legal research.

An analytical method is the most important and widely used in legal research. The analysis involves an explanation of the cause and effect of complex phenomena.
Analytical skill is crucial for any legal researcher. The analytical approach requires logical reasoning and interpreting laws to conclude .
Since laws are written in abstract and general terms by their nature, it is the researchers’ and judges’ task to apply those general rules to concrete factual circumstances, for which they apply logic and common sense to analyze and interpret the words in the law.
In most cases, the analytical approach deals with one or more legal concepts or legal theories.
Analytical research uses interpretive methods to examine cases, statutes, and other forms of law to seek out, construct, or reconstruct rules and principles.
An analytical approach is sometimes viewed as doctrinal research.
Doctrinal research of law provides a systematic exposition of the rules governing a particular legal category, analyses the relationship between the rules, explains areas of difficulty, and predicts future developments.
The sources of law have been the primary materials, law doctrines, case law, and legislation. The legal research is largely confined to an analysis of legal doctrine .
The salient characteristic of the analytical approach is its emphasis on the autonomy of law as an independent discipline or science.
Thus, the analytical approach of legal research can lead to ‘close reasoning.’
The analytical method serves the fundamental object of giving effect to the terms of a legislative instrument.
Analytical research is applied to dissect the terms of a provision, draw inferences from them, and apply the conclusions to resolve legal questions.
The most relevant aspects of the analytical approach are:
- what did the law-maker intend to achieve with the legislation under consideration?
- What is the underlying policy rationale of a piece of legislation?
In the analytical approach, the researcher should highlight the positive aspect of the law, e.g., what a legal situation is, and its normative aspect, e.g., what a legal situation should be.
Thus, it not only describes facts and circumstances but also defines parameters and interprets the facts. It involves applying critical judgment and developing one’s view of the situation.
The normative analysis concerns rational criticism and evaluation of legal doctrines and rules. Such judicial interpretation and process should only be a logical application of existing rules of law .
On the other hand, the positivistic approach holds that the conception of law is a coherent and complete system.

It implies a concerted effort to integrate disciplinary insights and apply the integrated insight to the study of problems.
The interdisciplinary approach of legal research advances the proposition that legal research ought not to content itself with the strictly legal but should also explore the interface between law and the other disciplines.
It integrates disciplines such as history, political science, economics and philosophy, and even different methodologies.
The interdisciplinary approach is distinguished from a multidisciplinary approach, which juxtaposes several disciplines without any attempt to integrate or synthesize aspects of their knowledge and perspectives.
The interdisciplinary approach requires looking at various aspects of the subject and viewing it from more than one perspective.
The interdisciplinary approach suggests the accommodation of sociology of law, economics and law, and law and technology within a single discourse to integrate and establish communicative links between disciplines.
The objective of interdisciplinary research is to combine knowledge, skills, and forms of research experience from two or several disciplines to transcend some of the theoretical and methodological limitations of the discipline in question and create a basis for developing a new form of analysis.
This is evident from integration because legal researchers and lawyers need to look at the law from a much broader angle than previously.
Inter-disciplinary research is “research designed to secure a deeper understanding of law as a social phenomenon, including research for the historical, philosophical, linguistic, economic, social or political implications of the law.”
On the other hand, it also seeks to evaluate the influence of other disciplines on legal scholarship. An interdisciplinary approach often produces results relevant to more than one discipline.
This interrelationship of disciplines is often reflected because many reputed law schools have designed their curriculum to include other subjects to explain a problem coherently and logically.
The interdisciplinary approach also suggests that social science methodologies and information are integrated into legal discourse.
The interdisciplinary approach as the interface of law and social science dates back to the Realist movement in the 1930s and 1940s. That movement highlighted the differences between ‘law in the books’ and ‘law in action.’

A sociological approach to law is one of the most characteristic features of modem jurisprudence—the socio-legal approach views law as a means of social control and change.
According to this approach, the law is essentially a social phenomenon.
The sociology of law seeks to explain the nature o law in terms of the empirical conditions within which doctrines and institutions exist in particular societies or social conditions.
Socio-legal research uses the theories and methods of social science to explore the operation of law, legal processes, and legal institutions.
The sociological approach tells us that law is a social phenomenon and works in a social setting instead of a textual approach.
According to the socio-legal approach, analysis of law is directly linked to the analysis of the social situation to which the law applies and should be put into the perspective of that situation.
It contrasts with the textual or ‘ black letter law ‘ approach, which emphasizes the text’s literal meaning. It calls for going beyond the ‘black letter law and investigating the social milieu against which law is enacted and applied.
On the relationship between law and sociology, Roger Cotterrell wrote succinctly.
Both law and sociology are concerned with the whole range of significant forms of social relationships.
And in practice, the criteria determining which relationships are significant are often similar, deriving from the same cultural assumptions or conceptions of policy relevance.
Furthermore, both legal and sociological inquiries typically seek to view these phenomena as part of, or potentially part of, an integrated social structure.
Thus, law and sociology share a fundamentally similar basic subject matter despite their radical differences in method and outlook.
Law is the practical craft of systematic control of social relations and institutions.
Sociology is the scientific enterprise that seeks systematic knowledge of them.
The socio-legal approach helps researchers to realize a closer understanding of the policy objectives of any legal rule.
The sociological views law as an emanation of social elements and depends not on state authority but on social compulsion.
The socio-legal research assesses the impact of legal doctrines upon society.
The sociological approach tries to investigate through empirical data how law and legal institutions affect human attitudes and what impact they create on society; assess the suitability of legal institutions to the needs of society.
It aims to understand legal and social phenomena, whereas the main concern of the traditional approach to jurisprudence is to undertake analytical-linguistic studies.
Using the law as an instrument of government policy requires understanding the socio-economic context in which the law works and what effects are likely to happen.
In socio-legal research, the law is considered one of the social policy tools.
A wide range of strategies is used in socio-legal research, from the statistical analysis of the survey to the interview analysis.
By using these strategies, the socio-legal approach addresses the following questions:
- what are the effects of law and the legal order on the social order?
- What are the effects of the social order on the legal order?
- What are the effects of the law on attitude, behavior, institutions, and organizations in society, maintenance, and change of society?
- What are the effects of attitudes, maintenance, behavior, institutions, and organizations in society, maintenance, and change of society on the law?

Each legal system has its history, fundamental principles and procedures, and forms of legal publication sources.
But in this globalized and interdependent world-the study of the law of other countries is assuming greater significance.
The law of foreign countries is increasingly becoming relevant in national court proceedings involving international transactions.
Interaction between various legal systems is sometimes described as a transnational legal system. The comparative method is advantageous for understanding the transnational legal system.
The comparative approach as a study of legal systems by comp comparison has assumed wider significance due to the ongoing globalization process.
With the growth of international and regional legal orders, understanding the forms and methods of comparative legal study has become essential to all those wishing to understand and engage in current legal debates.
Even one needs a comparative method to understand the law within one’s own country. The comparative method offers how the differences between the law of diverse countries and systems are analyzed.
In this way, a comparative study is appreciated for its benefit to the national legal system.
The comparative method aims to harmonize but not unify the world’s different laws and legal cultures.
Because often, the comparative approach may involve a comparison of two or more national legal systems.
But undoubtedly, comparative study helps to harmonize the laws of different countries.
In this sense, it has an international dimension.
The comparative approach takes the insider’s view on the legal systems studied and helps understand the institutional structure of concepts, thinking, and organizations of the systems in question.
The comparative method denotes different ways of addressing the same issue and finding differences. The comparison may give a fuller view of the subject under investigation.
However, the objective of the comparative method is not to draw mere similarities and dissimilarities.
Instead, it can enable a researcher to suggest a suitable solution to legal problems in light of a set of rules ideal for a given society.
The comparative method may confer the following 3 advantages:
- comparative research can throw doubts on the usefulness or firmly entrenched views;
- it may suggest a suitable solution to legal problems;
- A comparative study tends to aid in assembling which principles, applicable in the field concerned, are fundamental and which are secondary.

The historical approach looks at the evolution and development of a particular system of rules to provide useful contextual background and a fuller understanding of a certain legal discipline both for the researcher and the ultimate reader.
A historical approach examines the relations between law and events, showing how the law has been used at different times for different purposes and how it connects with interests and classes, political ends, and social movements.
The historical approach helps us understand how a particular institution or law evolved and why they need a change in the present context.
It takes the view that history has a significant role in explaining the current state of law, its past development, and likely future direction.
For example, to understand the institutional and jurisdictional aspects of the United Nations , a brief look at the whole concept and history of collective security and that of the League of Nations could be of some help.
The historical approach takes us from the past to the future. The historical approach serves to understand the present situation and shows the general trend of changes in laws.
As the present can not be properly understood without some knowledge about the past, the foremost purpose of the historical approach is to gain a clear perspective of the present.
But historical research can aim at the simply scholarly desire of the researcher to arrive at an accurate account of the past.
The sources of the historical approach include parliamentary debates on any legislative scheme, official reports of inquiry, case reports, newspaper reports, and journals.
The researcher should be careful about the authenticity and integrity of the documents.
In evaluating documents, the researcher should try to determine their completeness by verifying whether there have been additions or deletions to the original text.
The researcher should also maintain objectivity in interpreting historical events and show an adequate historical perspective of the issue under research.
For this purpose, primary sources or historical documents should be used as extensively as possible .
There is “no set legal methodology” that is applicable in all cases. It is not always possible to make clear-cut distinctions among the above ways of approaching the methodology.
A research paper that is concerned essentially with examining a subject may also involve comparison.
The researcher can choose a method best suited to questions and available sources. It depends upon the nature of the research question.

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Browse Subjects
- Legal research.

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Take action
- Report an antitrust violation
- File adjudicative documents
- Find banned debt collectors
- View competition guidance
- Competition Matters Blog
New HSR thresholds and filing fees for 2024
View all Competition Matters Blog posts
We work to advance government policies that protect consumers and promote competition.
View Policy
Search or browse the Legal Library
Find legal resources and guidance to understand your business responsibilities and comply with the law.
Browse legal resources
- Find policy statements
- Submit a public comment

Vision and Priorities
Memo from Chair Lina M. Khan to commission staff and commissioners regarding the vision and priorities for the FTC.
Technology Blog
Consumer facing applications: a quote book from the tech summit on ai.
View all Technology Blog posts
Advice and Guidance
Learn more about your rights as a consumer and how to spot and avoid scams. Find the resources you need to understand how consumer protection law impacts your business.
- Report fraud
- Report identity theft
- Register for Do Not Call
- Sign up for consumer alerts
- Get Business Blog updates
- Get your free credit report
- Find refund cases
- Order bulk publications
- Consumer Advice
- Shopping and Donating
- Credit, Loans, and Debt
- Jobs and Making Money
- Unwanted Calls, Emails, and Texts
- Identity Theft and Online Security
- Business Guidance
- Advertising and Marketing
- Credit and Finance
- Privacy and Security
- By Industry
- For Small Businesses
- Browse Business Guidance Resources
- Business Blog
Servicemembers: Your tool for financial readiness
Visit militaryconsumer.gov
Get consumer protection basics, plain and simple
Visit consumer.gov
Learn how the FTC protects free enterprise and consumers
Visit Competition Counts
Looking for competition guidance?
- Competition Guidance
News and Events
Latest news, ftc to host compliance webinar on rule banning noncompetes.
View News and Events
Upcoming Event
Older adults and fraud: what you need to know.
View more Events
Sign up for the latest news
Follow us on social media
--> --> --> --> -->

Playing it Safe: Explore the FTC's Top Video Game Cases
Learn about the FTC's notable video game cases and what our agency is doing to keep the public safe.
Latest Data Visualization
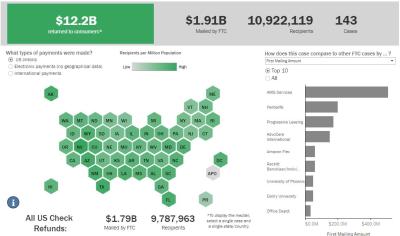
FTC Refunds to Consumers
Explore refund statistics including where refunds were sent and the dollar amounts refunded with this visualization.
About the FTC
Our mission is protecting the public from deceptive or unfair business practices and from unfair methods of competition through law enforcement, advocacy, research, and education.
Learn more about the FTC

Meet the Chair
Lina M. Khan was sworn in as Chair of the Federal Trade Commission on June 15, 2021.
Chair Lina M. Khan
Looking for legal documents or records? Search the Legal Library instead.
- Cases and Proceedings
- Premerger Notification Program
- Merger Review
- Anticompetitive Practices
- Competition and Consumer Protection Guidance Documents
- Warning Letters
- Consumer Sentinel Network
- Criminal Liaison Unit
- FTC Refund Programs
- Notices of Penalty Offenses
- Advocacy and Research
- Advisory Opinions
- Cooperation Agreements
- Federal Register Notices
- Public Comments
- Policy Statements
- International
- Office of Technology Blog
- Military Consumer
- Consumer.gov
- Bulk Publications
- Data and Visualizations
- Stay Connected
- Commissioners and Staff
- Bureaus and Offices
- Budget and Strategy
- Office of Inspector General
- Careers at the FTC
FTC Announces Rule Banning Noncompetes
- Competition
- Office of Policy Planning
- Bureau of Competition
Today, the Federal Trade Commission issued a final rule to promote competition by banning noncompetes nationwide, protecting the fundamental freedom of workers to change jobs, increasing innovation, and fostering new business formation.
“Noncompete clauses keep wages low, suppress new ideas, and rob the American economy of dynamism, including from the more than 8,500 new startups that would be created a year once noncompetes are banned,” said FTC Chair Lina M. Khan. “The FTC’s final rule to ban noncompetes will ensure Americans have the freedom to pursue a new job, start a new business, or bring a new idea to market.”
The FTC estimates that the final rule banning noncompetes will lead to new business formation growing by 2.7% per year, resulting in more than 8,500 additional new businesses created each year. The final rule is expected to result in higher earnings for workers, with estimated earnings increasing for the average worker by an additional $524 per year, and it is expected to lower health care costs by up to $194 billion over the next decade. In addition, the final rule is expected to help drive innovation, leading to an estimated average increase of 17,000 to 29,000 more patents each year for the next 10 years under the final rule.
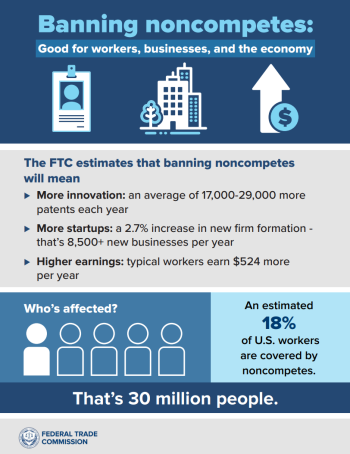
Noncompetes are a widespread and often exploitative practice imposing contractual conditions that prevent workers from taking a new job or starting a new business. Noncompetes often force workers to either stay in a job they want to leave or bear other significant harms and costs, such as being forced to switch to a lower-paying field, being forced to relocate, being forced to leave the workforce altogether, or being forced to defend against expensive litigation. An estimated 30 million workers—nearly one in five Americans—are subject to a noncompete.
Under the FTC’s new rule, existing noncompetes for the vast majority of workers will no longer be enforceable after the rule’s effective date. Existing noncompetes for senior executives - who represent less than 0.75% of workers - can remain in force under the FTC’s final rule, but employers are banned from entering into or attempting to enforce any new noncompetes, even if they involve senior executives. Employers will be required to provide notice to workers other than senior executives who are bound by an existing noncompete that they will not be enforcing any noncompetes against them.
In January 2023, the FTC issued a proposed rule which was subject to a 90-day public comment period. The FTC received more than 26,000 comments on the proposed rule, with over 25,000 comments in support of the FTC’s proposed ban on noncompetes. The comments informed the FTC’s final rulemaking process, with the FTC carefully reviewing each comment and making changes to the proposed rule in response to the public’s feedback.
In the final rule, the Commission has determined that it is an unfair method of competition, and therefore a violation of Section 5 of the FTC Act, for employers to enter into noncompetes with workers and to enforce certain noncompetes.
The Commission found that noncompetes tend to negatively affect competitive conditions in labor markets by inhibiting efficient matching between workers and employers. The Commission also found that noncompetes tend to negatively affect competitive conditions in product and service markets, inhibiting new business formation and innovation. There is also evidence that noncompetes lead to increased market concentration and higher prices for consumers.
Alternatives to Noncompetes
The Commission found that employers have several alternatives to noncompetes that still enable firms to protect their investments without having to enforce a noncompete.
Trade secret laws and non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) both provide employers with well-established means to protect proprietary and other sensitive information. Researchers estimate that over 95% of workers with a noncompete already have an NDA.
The Commission also finds that instead of using noncompetes to lock in workers, employers that wish to retain employees can compete on the merits for the worker’s labor services by improving wages and working conditions.
Changes from the NPRM
Under the final rule, existing noncompetes for senior executives can remain in force. Employers, however, are prohibited from entering into or enforcing new noncompetes with senior executives. The final rule defines senior executives as workers earning more than $151,164 annually and who are in policy-making positions.
Additionally, the Commission has eliminated a provision in the proposed rule that would have required employers to legally modify existing noncompetes by formally rescinding them. That change will help to streamline compliance.
Instead, under the final rule, employers will simply have to provide notice to workers bound to an existing noncompete that the noncompete agreement will not be enforced against them in the future. To aid employers’ compliance with this requirement, the Commission has included model language in the final rule that employers can use to communicate to workers.
The Commission vote to approve the issuance of the final rule was 3-2 with Commissioners Melissa Holyoak and Andrew N. Ferguson voting no. Commissioners Rebecca Kelly Slaughter , Alvaro Bedoya , Melissa Holyoak and Andrew N. Ferguson each issued separate statements. Chair Lina M. Khan will issue a separate statement.
The final rule will become effective 120 days after publication in the Federal Register.
Once the rule is effective, market participants can report information about a suspected violation of the rule to the Bureau of Competition by emailing [email protected] .
The Federal Trade Commission develops policy initiatives on issues that affect competition, consumers, and the U.S. economy. The FTC will never demand money, make threats, tell you to transfer money, or promise you a prize. Follow the FTC on social media , read consumer alerts and the business blog , and sign up to get the latest FTC news and alerts .
Press Release Reference
Contact information, media contacts.
Victoria Graham Office of Public Affairs
The independent source for health policy research, polling, and news.
A New Use for Wegovy Opens the Door to Medicare Coverage for Millions of People with Obesity
Juliette Cubanski , Tricia Neuman , Nolan Sroczynski , and Anthony Damico Published: Apr 24, 2024
The FDA recently approved a new use for Wegovy (semaglutide), the blockbuster anti-obesity drug, to reduce the risk of heart attacks and stroke in people with cardiovascular disease who are overweight or obese. Wegovy belongs to a class of medications called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) agonists that were initially approved to treat type 2 diabetes but are also highly effective anti-obesity drugs. The new FDA-approved indication for Wegovy paves the way for Medicare coverage of this drug and broader coverage by other insurers. Medicare is currently prohibited by law from covering Wegovy and other medications when used specifically for obesity. However, semaglutide is covered by Medicare as a treatment for diabetes, branded as Ozempic.
What does the FDA’s decision mean for Medicare coverage of Wegovy?
The FDA’s decision opens the door to Medicare coverage of Wegovy, which was first approved by the FDA as an anti-obesity medication. Soon after the FDA’s approval of the new use for Wegovy, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) issued a memo indicating that Medicare Part D plans can add Wegovy to their formularies now that it has a medically-accepted indication that is not specifically excluded from Medicare coverage . Because Wegovy is a self-administered injectable drug, coverage will be provided under Part D , Medicare’s outpatient drug benefit offered by private stand-alone drug plans and Medicare Advantage plans, not Part B, which covers physician-administered drugs.
How many Medicare beneficiaries could be eligible for coverage of Wegovy for its new use?
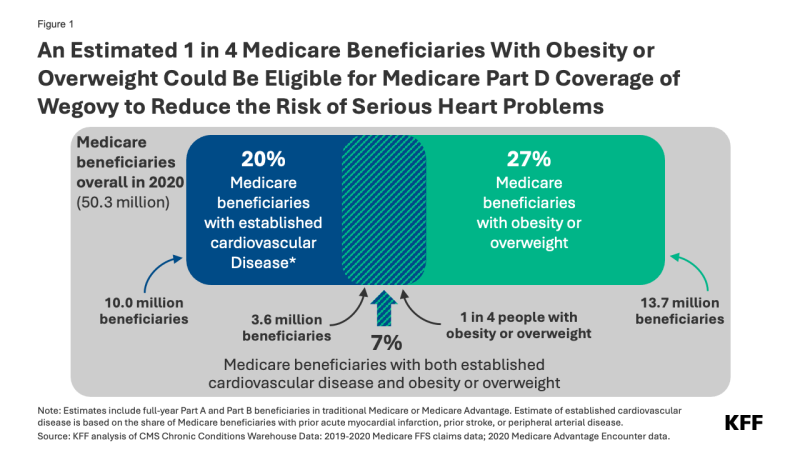
Of these 3.6 million beneficiaries, 1.9 million also had diabetes (other than Type 1) and may already have been eligible for Medicare coverage of GLP-1s as diabetes treatments prior to the FDA’s approval of the new use of Wegovy.
Not all people who are eligible based on the new indication are likely to take Wegovy, however. Some might be dissuaded by the potential side effects and adverse reactions . Out-of-pocket costs could also be a barrier. Based on the list price of $1,300 per month (not including rebates or other discounts negotiated by pharmacy benefit managers), Wegovy could be covered as a specialty tier drug, where Part D plans are allowed to charge coinsurance of 25% to 33%. Because coinsurance amounts are pegged to the list price, Medicare beneficiaries required to pay coinsurance could face monthly costs of $325 to $430 before they reach the new cap on annual out-of-pocket drug spending established by the Inflation Reduction Act – around $3,300 in 2024, based on brand drugs only, and $2,000 in 2025. But even paying $2,000 out of pocket would still be beyond the reach of many people with Medicare who live on modest incomes . Ultimately, how much beneficiaries pay out of pocket will depend on Part D plan coverage and formulary tier placement of Wegovy.
Further, some people may have difficulty accessing Wegovy if Part D plans apply prior authorization and step therapy tools to manage costs and ensure appropriate use. These factors could have a dampening effect on use by Medicare beneficiaries, even among the target population.
When will Medicare Part D plans begin covering Wegovy?
Some Part D plans have already announced that they will begin covering Wegovy this year, although it is not yet clear how widespread coverage will be in 2024. While Medicare drug plans can add new drugs to their formularies during the year to reflect new approvals and expanded indications, plans are not required to cover every new drug that comes to market. Part D plans are required to cover at least two drugs in each category or class and all or substantially all drugs in six protected classes . However, facing a relatively high price and potentially large patient population for Wegovy, many Part D plans might be reluctant to expand coverage now, since they can’t adjust their premiums mid-year to account for higher costs associated with use of this drug. So, broader coverage in 2025 could be more likely.
How might expanded coverage of Wegovy affect Medicare spending?
The impact on Medicare spending associated with expanded coverage of Wegovy will depend in part on how many Part D plans add coverage for it and the extent to which plans apply restrictions on use like prior authorization; how many people who qualify to take the drug use it; and negotiated prices paid by plans. For example, if plans receive a 50% rebate on the list price of $1,300 per month (or $15,600 per year), that could mean annual net costs per person around $7,800. If 10% of the target population (an estimated 360,000 people) uses Wegovy for a full year, that would amount to additional net Medicare Part D spending of $2.8 billion for one year for this one drug alone.
It’s possible that Medicare could select semaglutide for drug price negotiation as early as 2025, based on the earliest FDA approval of Ozempic in late 2017 . For small-molecule drugs like semaglutide, at least seven years must have passed from its FDA approval date to be eligible for selection, and for drugs with multiple FDA approvals, CMS will use the earliest approval date to make this determination. If semaglutide is selected for negotiation next year, a negotiated price would be available beginning in 2027. This could help to lower Medicare and out-of-pocket spending on semaglutide products, including Wegovy as well as Ozempic and Rybelsus, the oral formulation approved for type 2 diabetes. As of 2022, gross Medicare spending on Ozempic alone placed it sixth among the 10 top-selling drugs in Medicare Part D, with annual gross spending of $4.6 billion, based on KFF analysis . This estimate does not include rebates, which Medicare’s actuaries estimated to be 31.5% overall in 2022 but could be as high as 69% for Ozempic, according to one estimate.
What does this mean for Medicare coverage of anti-obesity drugs?
For now, use of GLP-1s specifically for obesity continues to be excluded from Medicare coverage by law. But the FDA’s decision signals a turning point for broader Medicare coverage of GLP-1s since Wegovy can now be used to reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke by people with cardiovascular disease and obesity or overweight, and not only as an anti-obesity drug. And more pathways to Medicare coverage could open up if these drugs gain FDA approval for other uses . For example, Eli Lilly has just reported clinical trial results showing the benefits of its GLP-1, Zepbound (tirzepatide), in reducing the occurrence of sleep apnea events among people with obesity or overweight. Lilly reportedly plans to seek FDA approval for this use and if approved, the drug would be the first pharmaceutical treatment on the market for sleep apnea.
If more Medicare beneficiaries with obesity or overweight gain access to GLP-1s based on other approved uses for these medications, that could reduce the cost of proposed legislation to lift the statutory prohibition on Medicare coverage of anti-obesity drugs. This is because the Congressional Budget Office (CBO), Congress’s official scorekeeper for proposed legislation, would incorporate the cost of coverage for these other uses into its baseline estimates for Medicare spending, which means that the incremental cost of changing the law to allow Medicare coverage for anti-obesity drugs would be lower than it would be without FDA’s approval of these drugs for other uses. Ultimately how widely Medicare Part D coverage of GLP-1s expands could have far-reaching effects on people with obesity and on Medicare spending.
- Medicare Part D
- Chronic Diseases
- Heart Disease
- Medicare Advantage
news release
- An Estimated 1 in 4 Medicare Beneficiaries With Obesity or Overweight Could Be Eligible for Medicare Coverage of Wegovy, an Anti-Obesity Drug, to Reduce Heart Risk
Also of Interest
- An Overview of the Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Benefit
- FAQs about the Inflation Reduction Act’s Medicare Drug Price Negotiation Program
- What Could New Anti-Obesity Drugs Mean for Medicare?
- Medicare Spending on Ozempic and Other GLP-1s Is Skyrocketing

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
GENERAL EDITOR: GABRIELE GRIFFIN Designed to serve postgraduate students and academics teaching research. methods, this series provides discipline-specific volumes which explore the. possibilities and limitations of a range of research methods applicable to the subject in question. A handbook and guide to research methods for students of law ...
Research methods for law ... Legal research as qualitative research / Ian Dobinson and Francis Johns -- Quantitative legal research / Wing Hong Chui -- Doing ethnographic research : lessons from a case study / Satnam Choongh -- Interdisciplinarity in legal research / Paul Roberts -- Integrating theory and method in the comparative contextual ...
Brings existing chapters up to date with the newest thinking in legal research. Drawing on actual research projects, Research Methods for Law discusses how legal research as process impacts on research as product. The author team has a broad range of teaching and research experience in law, criminal justice and socio-legal studies, and give ...
xml. Research Methods for Law introduces undergraduate and postgraduate students to available methods of research - legalistic, empirical, comparative and theoretical - drawing on actual research projects as examples. The book is written by a team of contributors with a broad range of teaching and research experience in law, criminal justice ...
Research Methods for Law introduces undergraduate and postgraduate students to available methods of research - legalistic, empirical, comparative and theoretical - drawing on actual research projects as examples. The book is written by a team of contributors with a broad range of teaching and research experience in law, criminal justice and socio-legal studies.Designed to serve as a handbook ...
Research Methods for Law. Mike McConville. Edinburgh University Press, Jan 18, 2017 - Law - 336 pages. Introduces students to legalistic, theoretical, empirical, comparative and cross-disciplinary research methods, grounded in working examplesNew for this editionNew chapter on inter- and cross-disciplinary research essential reading for ...
Introduces students to legalistic, theoretical, empirical, comparative and cross-disciplinary research methods, grounded in working examples. Drawing on actual research projects, Research Methods for Law discusses how legal research as process impacts on research as product. The author team has a broad range of teaching and research experience in law, criminal justice and socio-legal studies ...
Research Methods for Law. M. McConville, W. Chui. Published 2007. Law. About the Authors Preface and Acknowledgements Introduction and Overview Mike McConville and Wing Hong Chui 1 Qualitative Legal Research Ian Dobinson and Francis Johns 2 Quantitative Legal Research Wing Hong Chui 3 Doing Ethnographic Research: Lessons from a Case Study ...
Research Methods for Law - Ebook written by Mike McConville. Read this book using Google Play Books app on your PC, android, iOS devices. Download for offline reading, highlight, bookmark or take notes while you read Research Methods for Law.
Research Methods for Law introduces undergraduate and postgraduate students to available methods of research -- legalistic, empirical, comparative and theoretical -- drawing on actual research projects as examples. The book is written by a team of contributors with a broad range of teaching and research experience in law, criminal justice and ...
We typically start primary law research here. If there is a controlling statute, cases you look for later will interpret that law. There are two types of statutes, annotated and unannotated. ... This is a particularly powerful research method. One Good Case Method. After following the steps above, you will have identified some relevant cases on ...
16 Action Research in Law: Role and Methods Notes. Notes. 17 Methodology of Feminist Legal Research Notes. Notes. Notes. ... it catalogues diverse methods of legal research under the categories of doctrinal, non-doctrinal, and integrated methods of legal research. Reader gets a basic idea about legal research, its past, present, and future ...
This focus on one main topic allows the reader to draw comparisons between methods with relative ease. The broad range of contributors makes Research Methods in Law well suited to an international audience, and it is ideal reading for PhD students in law, undergraduate dissertation students in law, LL.M Research students and early year researchers.
An Introduction to Empirical Legal Research. Lee Epstein and Andrew D. Martin. Oxford University Press (2014) This book includes information on designing research, collecting and coding data, analyzing data, and drafting the final paper. Located at Lilly Law Library, Indianapolis, 2nd Floor: K 85 .E678 2014.
1. Identifying the legal issue is not so straightforward. Legal research involves interpreting many legal precedents and theories to justify your questions. Finding the right issue takes time and patience. 2. There's too much to research. Attorneys now face a great deal of case law and statutory material.
Abstract. Due to the criticism of Critical Legal Studies coming down to nothing more than nihilism, the third chapter of the first part of this monograph identifies law reform design as the most appropriate research method for answering research questions from a Critical Legal Studies' perspective. Namely, law reform design provides for the ...
This focus on one main topic allows the reader to draw comparisons between methods with relative ease. The broad range of contributors makes Research Methods in Law well suited to an international audience, and it is ideal reading for PhD students in law, undergraduate dissertation students in law, LL.M Research students and early year researchers.
Research Methods for Law introduces undergraduate and postgraduate students to available methods of research - legalistic, empirical, comparative and theoretical - drawing on actual research projects as examples. The book is written by a team of contributors with a broad range of teaching and research experience in law, criminal justice and ...
The quantitative research method supplements traditional legal research to investigate the complexities of the law, legal actors, and legal activities. Quantitative legal research is mostly applicable for conducting non-doctrinal, empirical, and socio-legal research. Objectivity remains the main aspect of quantitative research.
Section 2 is about research questions. It first offers a simplified typology of research question, including a few words on theory and method, and then suggests some thoughts about thinking of and framing your question. Section 3 is about secondary and primary sources in the research of international law.
Title Research methods for law / edited by Mike McConville and Wing Hong Chui. Added Author McConville, Michael, editor. Chui, Wing Hong, editor. Edition Second edition. Imprint Edinburgh : Edinburgh University Press, [2017] Description xi, 316 pages : illustrations ; 24 cm. Series Research methods for the arts and humanities.
Abstract:-. Research methodology is the process for direct approach through mixed types of research. techniques. The research approach supports the researcher to come across the research result ...
the variance in drug use was explained by varia ons in the certainty and severity of punishment. 24 Compare. the message of sta s cal signi cance (something has an impact) with that of the ...
The Texas State Law Library is a public law library that serves the legal research needs of Texas. my account ... For smaller or less complicated estates, simplified probate methods may be available. These alternatives are often faster and cheaper than formal administration. Our guide discusses small estate affidavits, muniments of title ...
The FTC estimates that the final rule banning noncompetes will lead to new business formation growing by 2.7% per year, resulting in more than 8,500 additional new businesses created each year. The final rule is expected to result in higher earnings for workers, with estimated earnings increasing for the average worker by an additional $524 per ...
This means that the FDA's approval of the new use for Wegovy potentially opens up access to this drug for 1 in 4 people on Medicare with obesity or overweight. Of these 3.6 million beneficiaries ...
Access the portal of NASS, the official source of agricultural data and statistics in the US, and explore various reports and products.
The conference was founded in 1987 and is now a multi-track interdisciplinary annual meeting that includes invited talks, demonstrations, symposia, and oral and poster presentations of refereed papers. Along with the conference is a professional exposition focusing on machine learning in practice, a series of tutorials, and topical workshops ...