
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


3.2: Problem Solving Approaches and Interventions
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 43049

- Vera Kennedy
- West Hills College Lemoore
There are six problem solving approaches and interventions most commonly used among practitioners. Each approach examines a different aspect of a social problem. The nature of the problem and people involved determines the most appropriate intervention to apply.
A social systems approach examines the social structure surrounding the problem or issue. This approach requires macro, meso, and micro levels of analysis (see pages 12-13) to help understand the structure of the problem and the arrangement of individuals and social groups involved. Analysis requires comprehension of the entire issue and parts associated, as well as, which components and protocols of the structure are independent or dependent of each other. Application of this approach requires grasp of the complete problem including the hierarchy, order, patterns, and boundaries of individuals and social groups including their interactions, relationships, and processes as a body or structure surrounding the issue (Bruhn and Rebach 2007).

The interventions deployed using a social systems approach focus on establishing and maintaining stability for all parties even while change is occurring. Social system interventions require change agents or leaders such as sociological practitioners to help control and guide inputs (what is put in or taken into the problem) and outputs (what is produced, delivered, or supplied resulting from change) used in problem solving (Bruhn and Rebach 2007). This approach requires the involvement of everyone in the social structure to design or re-design the system and processes around the issue.
The human ecology approach examines the “web of life” or the ecosystem of a social problem or issue. This approach is often visually represented by a spider web to demonstrate how lives are interlinked and interdependent. A human ecology approach focuses on macro and meso levels of analysis to develop knowledge about the social bonds, personal needs, and environmental conditions that impede or support life challenges and opportunities for individuals. Practitioners evaluate and analyze where individuals and groups fit in the social structure or ecosystem and their roles. The purpose of this approach is to identify cognitive and emotional boundaries people experience living in social systems to help confront and remove the obstacles they face.

Interventions applied in a human ecological approach target changes in families, institutions, and small communities. The goal is to confront the stressors and strain created by social situations and settings. Interventions from a human ecology approach help people determine acceptable behaviors within different social environments (Bruhn and Rebach 2007). Practitioners work with social groups to remove collaborative challenges between groups in a social ecosystem and the individuals working and living within them. Change is concentrated on developing a new system and process to support and remove obstacles for individuals effected by a social problem.
- Describe the social systems approach and explain what type of social problems or issues this approach is the most valid method to use.
- Describe the human ecology approach and explain what type of social problem or issues this approach is the most valid method to use.
- A county mental health court
- Gender neutral bathrooms on a college campus
- Anti-bullying campaign in local K-12 schools
A life cycle approach examines the developmental stages and experiences of individuals facing issues or various life crises. Meso and micro levels of analysis are required with this method. Data gathered assists practitioners in understanding the adaption of individuals or groups to change, challenges, and demands at each developmental stage of life (Bruhn and Rebach 2007). Analysis incorporates evaluation of interpersonal connections between a person and the environment, life transitions, and patterns. This approach if applicable when working with individuals, groups, and organizations, which all have and go through a life cycle and stages of development.
Interventions using this approach target changes in social norms and expectations of individuals or groups facing difficulties. Practitioners help identify the context and issues creating anxiety among individuals or groups and facilitate coping strategies to attack their issues. This approach builds on positive personal and social resources and networks to mend, retrain, or enable development and growth.
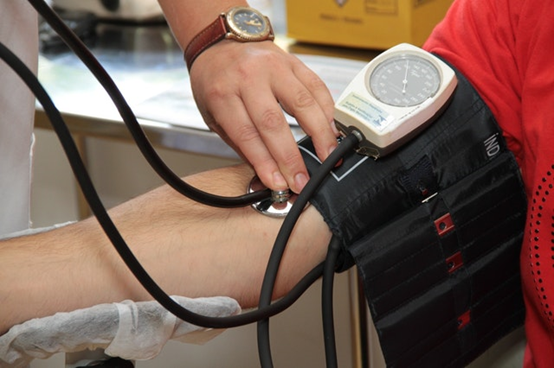
The clinical approach evaluates disease, illness, and distress. Both meso and micro levels of analysis are required for this method. Practitioners assess biological, personal, and environmental connections by surveying the patient or client’s background, and current and recent conditions (Bruhn and Rebach 2007). A Patient Evaluation Grid (PEG) is the most commonly used tool for data collection. This approach requires in-depth interactions with the patient or client to identify themes associated with their condition and the structure of the social system related to their illness and support. When applying this approach in medical practice, the evaluation and analysis leads to a diagnosis.
- Describe the life cycle approach and explain what type of social problems or issues this approach is the most valid method to use.
- Describe the clinical approach and explain what type of social problem or issues this approach is the most valid method to use.
- Policing strategies to reduce crime and improve community relationships
- Reductions in self-injury or cutting among teens
- A community college social work education degree program
Intervention in a clinical approach concentrates on removal of symptoms, condition, or changes in the individual to solve the problem. The overarching goal of this method is to prevent the problem from reoccurring and the solution from interfering with the individual’s functioning. Problem management must minimally disrupt the social system of the patient or client.
A social norms approach focuses on peer influences to provide individuals with accurate information and role models to induce change (Bruhn and Rebach 2007). This approach observes macro, meso, and micro levels of analysis. Intervention centers on providing correct perceptions about thinking and behavior to induce change in one’s thoughts and actions. This technique is a proactive prevention model aimed at addressing something from happening or arising.
There are three levels of intervention when applying a social norms approach (Bruhn and Rebach 2007). Practitioners use interventions independently or together for a comprehensive solution. At the universal level of intervention , all members of a population receive the intervention without identifying which individuals are at risk. A selective level of intervention directs assistance or services to an entire group of at risk individuals. When specific individuals are beyond risk and already show signs of the problem, they receive an indicated level of intervention . A comprehensive intervention requires an integration of all three levels.
Practitioners assist communities in problem solving by applying a community based approach . All three levels of analysis (macro, meso, and micro) are required for this method. The aim of this approach is to plan, develop, and implement community based interventions whereby local institutions and residents participate in problem solving and work towards preventing future issues. Practitioners work with communities on three outcomes, individual empowerment, connecting people, and improving social interactions and cooperation (Bruhn and Rebach 2007). Concentrating on these outcomes builds on community assets while tailoring solutions to local political, economic, and social conditions. By building bridges among individuals and groups in the community, practitioners facilitate connections between services, programs, and policies while attacking the problem from multiple vantage points.

A community based approach helps ensure problem analysis, evaluation, and interventions are culturally and geographically appropriate for local residents, groups, and organizations. To operate effectively, this intervention requires practitioners to help facilitate face-to-face interactions among community members and develop a communication pattern for solving community problems. To build an appropriate intervention, practitioners must develop knowledge and understanding about the purpose, structure, and process of each group, organization, and collaboration within the community (Bruhn and Rebach 2007). Upon implementation, a community based approach endows local residents and organizations to observe and monitor their own progress and solutions directly.
- Describe the social norms approach and explain what type of social problems or issues this approach is the most valid method to use.
- Describe the community based approach and explain what type of social problem or issues this approach is the most valid method to use.
- Human trafficking prevention program
- Reductions in electronic cigarette, vaping, and new tobacco product usage

Encyclopedia of Child Behavior and Development pp 1399–1403 Cite as
Social Problem Solving
- Molly Adrian 3 ,
- Aaron Lyon 4 ,
- Rosalind Oti 5 &
- Jennifer Tininenko 6
- Reference work entry
796 Accesses
4 Altmetric
Interpersonal cognitive problem solving ; Interpersonal problem solving ; Social decision making ; Social information processing
Social problem solving is the process by which individuals identify and enact solutions to social life situations in an effort to alter the problematic nature of the situation, their relation to the situation, or both [ 7 ].
Description
In D’Zurilla and Goldfried’s [ 6 ] seminal article, the authors conceptualized social problem solving as an individuals’ processing and action upon entering interpersonal situations in which no immediately effective response is available. One primary component of social problem solving is the cognitive-behavioral process of generating potential solutions to the social dilemma. The steps in this process were posited to be similar across individuals despite the wide variability of observed behaviors. The revised model [ 7 ] is comprised of two interrelated domains: problem orientation and problem solving style....
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Bowlby, J. (1982). Attachment and loss: Vol 1: Attachment (2nd ed.). New York: Basic Books.
Google Scholar
Chen, X., & French, D. C. (2008). Children’s social competence in cultural context. Annual Review of Psychology, 59 , 591–616.
PubMed Google Scholar
Crick, N. R., & Dodge, K. A. (1994). A review and reformulation of social information processing mechanisms in children’s social adjustment. Psychological Bulletin, 115 , 74–101.
Dodge, K. A., & Coie, J. D. (1987). Social-information-processing factors in reactive and proactive aggression in children’s peer groups. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 53 , 1146–1158.
Downey, G., & Coyne, J. C. (1990). Children of depressed parents: An integrative review. Psychological Bulletin, 108 , 50–76.
D’Zurilla, T. J., & Goldfried, M. R. (1971). Problem solving and behavior modification. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 78 , 107–126.
D’Zurilla, T. J., & Nezu, A. M. (1999). Problem solving therapy: A social competence approach to clinical intervention (2nd ed.). New York: Springer.
Lochman, J. E., & Dodge, K. A. (1994). Social-cognitive processes of severely violent, moderately aggressive, and nonaggressive boys. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 62 , 366–374.
Pettit, G. S., Dodge, K. A., & Brown, M. M. (1988). Early family experience, social problem solving patterns, and children’s social competence. Child Development, 59 , 107–120.
Quiggle, N. L., Garber, J., Panak, W. F., & Dodge, K. A. (1992). Social information processing in aggressive and depressed children. Child Development, 63 , 1305–1320.
Rubin, K. H., & Krasnor, L. R. (1986). Social-cognitive and social behavioral perspectives on problem solving. In M. Perlmutter (Ed.), Cognitive perspectives on children’s social and behavioral development. The Minnesota symposia on child psychology (Vol. 18, pp. 1–68). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Rubin, K. H., & Rose-Krasnor, L. (1992). Interpersonal problem-solving and social competence in children. In V. B. van Hasselt & M. Hersen (Eds.), Handbook of social development: A lifespace perspective . New York: Plenum.
Shure, M. B., & Spivack, G. (1980). Interpersonal problem solving as a mediator of behavioral adjustment in preschool and kindergarten children. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 1 , 29–43.
Spivack, G., & Shure, M. B. (1974). Social adjustment of young children . San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Epidemiology, University of Washington, Box 354920, Seattle, WA, 98195, USA
Molly Adrian
Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Health, Seattle Children's Hospital, 4800 Gand Point way NE, Seattle, WA, 98125, USA
Rosalind Oti
Evidence Based Treatment Center of Seattle, 1200 5th Avenue, Suite 800, Seattle, WA, 98101, USA
Jennifer Tininenko
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Neurology, Learning and Behavior Center, 230 South 500 East, Suite 100, Salt Lake City, Utah, 84102, USA
Sam Goldstein Ph.D.
Department of Psychology MS 2C6, George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, 22030, USA
Jack A. Naglieri Ph.D. ( Professor of Psychology ) ( Professor of Psychology )
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Adrian, M., Lyon, A., Oti, R., Tininenko, J. (2011). Social Problem Solving. In: Goldstein, S., Naglieri, J.A. (eds) Encyclopedia of Child Behavior and Development. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-79061-9_2703
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-79061-9_2703
Publisher Name : Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN : 978-0-387-77579-1
Online ISBN : 978-0-387-79061-9
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Close ×
- ASWB Exam Prep Overview
- LCSW Exam Prep (ASWB Clinical Exam)
- LMSW Exam Prep (ASWB Masters Exam)
- LSW Exam Prep (ASWB Bachelors Exam)
- California Law and Ethics Exam Practice
- Free Practice Test
- Get Started
- Free Study Guide
- Printed Exams
- Testimonials

The social worker's role in the problem-solving process
First, a question: what's that mean exactly?
The Problem-Solving Process
The problem-solving process is a systematic approach used to identify, analyze, and resolve issues or challenges. It typically involves several steps:
Identification of the Problem: The first step is to clearly define and identify the problem or issue that needs to be addressed. This involves understanding the symptoms and root causes of the problem, as well as its impact on individuals, groups, or the community.
Gathering Information: Once the problem is identified, relevant information and data are gathered to gain a deeper understanding of the issue. This may involve conducting research, collecting data, or consulting with stakeholders who are affected by or have expertise in the problem.
Analysis of the Problem: In this step, the information collected is analyzed to identify patterns, underlying causes, and contributing factors to the problem. This helps in developing a comprehensive understanding of the problem and determining possible solutions.
Generation of Solutions: Based on the analysis, a range of potential solutions or strategies is generated to address the problem. Brainstorming, creative thinking techniques, and consultation with others may be used to generate diverse options.
Evaluation of Solutions: Each potential solution is evaluated based on its feasibility, effectiveness, and potential impact. This involves considering factors such as available resources, potential risks, and alignment with goals and values.
Decision-Making: After evaluating the various solutions, a decision is made regarding which solution or combination of solutions to implement. This decision-making process may involve weighing the pros and cons of each option and considering input from stakeholders.
Implementation: Once a decision is made, the chosen solution is put into action. This may involve developing an action plan, allocating resources, and assigning responsibilities to ensure the effective implementation of the solution.
Monitoring and Evaluation: Throughout the implementation process, progress is monitored, and the effectiveness of the solution is evaluated. This allows for adjustments to be made as needed and ensures that the desired outcomes are being achieved.
Reflection and Learning: After the problem-solving process is complete, it's important to reflect on what was learned from the experience. This involves identifying strengths and weaknesses in the process, as well as any lessons learned that can be applied to future challenges.
The Social Worker's Role
Okay, so social worker's assist with all of that. The trickiest part (and the part most likely to show up on the ASWB exam) is decision making. Do social workers make decisions for clients, give advice, gently suggest...? The answer is no, sometimes, and sort-of. Client self-determination is a key component of social work ethics. Problem-solving and decision-making in social work are guided by these general principles:
Client-Centered Approach: Social workers prioritize the autonomy and self-determination of their clients. They empower clients to make informed decisions by providing them with information, options, and support rather than imposing their own opinions or solutions.
Collaborative Problem-Solving: Social workers engage in collaborative problem-solving with their clients. They work together to explore the client's concerns, goals, and available resources, and then develop strategies and plans of action that are mutually agreed upon.
Strengths-Based Perspective: Social workers focus on identifying and building upon the strengths and resources of their clients. They help clients recognize their own abilities and resilience, which can empower them to find solutions to their problems.
Non-Directive Approach: While social workers may offer suggestions or recommendations, they typically do so in a non-directive manner. They encourage clients to explore various options and consequences, and they respect the client's ultimate decisions.
Cultural Sensitivity: Social workers are sensitive to the cultural backgrounds, beliefs, and values of their clients. They recognize that advice-giving may need to be tailored to align with the cultural norms and preferences of the client.
Ethical Considerations: Social workers adhere to ethical principles, including the obligation to do no harm, maintain confidentiality, and respect the dignity and rights of their clients. They avoid giving advice that may potentially harm or exploit their clients.
Professional Boundaries: Social workers maintain professional boundaries when giving advice, ensuring that their recommendations are based on professional expertise and not influenced by personal biases or conflicts of interest.
On the Exam
ASWB exam questions on this material may look like this:
- During which step of the problem-solving process are potential solutions evaluated based on feasibility, effectiveness, and potential impact?
- In the problem-solving process, what is the purpose of gathering information?
- Which ethical principle guides social workers in giving advice during the problem-solving process?
Or may be a vignette in which client self-determination (eg re sleeping outside) is paramount.
Get ready for questions on this topic and many, many others with SWTP's full-length practice tests. Problem: need to prepare for the social work licensing exam. Solution: practice!
Get Started Now .
March 15, 2024.
Right now, get SWTP's online practice exams at a reduced price. Just $39 . Get additional savings when buying more than one exam at a time-- less than $30 per exam!
Keep going till you pass. Extensions are free.
To receive our free study guide and get started!
Social Work Graduate
Resources for social work graduates
Various social work practice approaches
Blogs added to / updated regularly
https://www.facebook.com/socialworkgraduate
https://www.instagram.com/socialworkgraduate/
- Oct 2, 2020
Practice Model: Problem Solving
Perlman’s model, planned change process model, practice approach based on planned change model
This page has three sections:
Background Material that provides the context for the topic
A suggested Practice Approach
A list of Supporting Material / References
Feedback welcome!
Background Material
Different authors look at the problem-solving model in varying ways.
Murdach (2007) suggests the principal stages of Perlman’s problem-solving model are simply:
problem definition,
problem analysis (including the generation and review of alternatives), and
the need for specific decision about a course of action (including methods of monitoring and evaluating the results of such action).
Chenowith and Lehmann (2008) describe a planned change process model:

Chenowith and Lehman also suggest the model outlined in the Practice Approach that follows. It consists of four phases:
The engagement phase involves making contact, exploring needs and setting preliminary goals.
The assessment phase involves collecting information, prioritising issues and agreeing on action.
The intervention phase involves implementing and modifying strategies to achieve goals.
The evaluation phase involves reviewing what has happened, celebrating progress and either concluding the work or negotiating a continued relationship.
Practice Approach

Supporting Material
(available on request)
Chenoweth, L. M. D. (2014). Road to Social Work and Human Service Practice. South Melbourne: Cengage Learning Australia. Retrieved from http://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/une/detail.action?docID=1696405
Coady, N, & Lehmann, P. (2008). The problem-solving model: A framework for integrating science and art of practice. In N. Coady & P. Lehmann, Theoretical Perspectives for Direct Social Work Practice (pp. 67-86). New York: Springer Publishing Company. Retrieved from http://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/une/detail.action?docID=326279
Murdach, A. D. (2007). Helen Harris Perlman and the problem solving method. Retrieved from https://allisonmurdach.wordpress.com/2011/05/05/helen-harris-perlman-and-the-problem-solving-model/
Recent Posts
An Everyday Social Work Approach
Practice Model: Solution-Focused Approach
Practice Model: Task Centred

- Compare CSWE Accredited Online MSW Programs
- Advanced Standing MSW Programs
- Discover HBCU MSW Programs Online & On-Campus
- On-Campus MSW Programs
- Fast Track MSW Programs
- Hybrid MSW Programs
- Full-time online MSW programs
- Part-Time Online MSW Programs
- Online Clinical Social Work Degree Programs (LCSW)
- Doctorate in Social Work (DSW) Programs Online
- Online Military Social Work Programs
- Considering a Major in Social Work?
- Ph.D. in Social Work Online
- Schools By State
- Sponsored: Fordham University
- Sponsored: University of Denver
- Sponsored: Baylor University
- Sponsored: University of Southern California
- Sponsored: Simmons University
- Sponsored: Case Western Reserve University
- Sponsored: Howard University
- Sponsored: University of Southern California – DSW Online
- Sponsored: Simmons University – DSW Online
- How Long Does It Take to Become a Social Worker?
- 2022 Study Guide to the Social Work Licensing Exam
- How to Become a Veterinary Social Worker
- How to Become a LCSW
- How to Become a School Social Worker
- Become a Victim Advocate
- Social Worker Interviews
- Is a Master of Social Work (MSW) worth it?
- Social Work Salaries – How Much Do Social Workers Make?
- Bachelor’s in Psychology Programs Online
- Concentrations in Online MSW Programs
- Social Work: Core Values & Code of Ethics
- Introduction to Social Learning Theory
- Introduction to Systems Theory
- Introduction to Psychosocial Development Theory
- Introduction to Psychodynamic Theory
- Introduction to Social Exchange Theory
- Introduction to Rational Choice Theory
- What is Social Justice?
- What is Social Ecology?
Online MSW Programs / Social Work / 6 Important Theories in Social Work
Six important theories in social work
Social work theories attempt to describe, explain and predict social events based on scientific evidence, studies and research. Social work perspectives draw from psychology, philosophy, economics, education and other fields to attempt to explain what drives and motivates people at various stages of life.
Some social work students studying for a bachelor’s degree in social work or master of social work may wonder, “Why is theory important in social work?” Studying theory ensures that aspiring professionals are both competent and confident when the time comes to apply social work theories to practice.
Why is theory important in social work?
Social work theories help social workers analyze cases, understand clients, create interventions, predict intervention results, and evaluate outcomes. While the theories are constantly evolving as new evidence is produced, referencing social work theories that have been used over time enables social workers to explore causes of behavior and identify potential solutions.
A crucial objective of learning social work theories is to train and encourage social workers to set aside personal assumptions and beliefs when engaging in social work practice. Social workers should use evidence-based theories to investigate issues and drive their decision making.

University of Denver
Graduate school of social work, master of social work (msw).
The University of Denver’s Online MSW Program is delivered by its top-ranked school of social work and offers two programs. Students can earn their degree in as few as 12 months for the Online Advanced-Standing MSW or 27 months for the Online MSW.
- Complete the Online Advanced-Standing MSW in as few as 12 months if you have a BSW; if you do not have a BSW, the Online MSW Program may be completed in as few as 27 months.
- No GRE Required
- Customizable pathway options include Mental Health and Trauma or Health, Equity and Wellness concentrations

Fordham University
Graduate school of social service.
Fordham’s skills-based, online MSW program integrates advanced relevant social work competencies, preparing students to serve individuals and communities while moving the profession forward. This program includes advanced standing and traditional MSW options.
- Traditional and advanced standing online MSW options are available.
- There are four areas of focus: Individuals and Families, Organizations and Community, Evaluation, and Policy Practice and Advocacy.
- Pursue the degree on a full-time or part-time track.
info SPONSORED
Applying social work theory to practice
Social work theory provides a starting point for social workers to address client problems through a research-based lens.
The theories help social workers better understand complex human behaviors and social environments, which influence their clients lives and the challenges they face. A good grasp of theory that is backed by research-based scientific evidence helps guide social workers by providing them with a sense of direction and purpose.
One challenge when applying social work theories to practice is choosing the right theory for the situation. It can be difficult to assign a single theory to complex client issues. Often, it’s more practical to draw upon the knowledge of multiple theories and use that understanding to design multifaceted interventions.
List of important social work theories
The following list of social work theories includes some of the most widely referenced theories used in social work.
1. Social learning theory
Social learning theory , which is also known as social cognitive theory , was developed by psychologist Albert Bandura. This theory posits that learning occurs by observing others and modeling their behavior.
In order for social learning to occur, a person must want to emulate the person they’re watching. The individual pays close attention to the action and retains the action in memory. Then, the individual must experience a situation where the behavior can be repeated and must be motivated to repeat the behavior.
Social workers can use this theory to better understand how role models affect the behaviors and emotions of their clients. Social learning theory can also help social workers form intervention strategies that use positive modeling and reinforcement to encourage their clients to engage in new positive behaviors.
2. Systems theory
Systems theory proposes that people are products of complex systems, rather than individuals who act in isolation. According to this theory, behavior is influenced by a variety of factors that work together as a system. These factors include family, friends, social settings, religious structure, economic class, and home environment.
Systems theory can be used to treat issues like eating disorders, depression, bipolar disorder, anxiety, school trauma, and risky behavior. In ecological systems theory, individuals are observed in multiple environments so that behavior is fully understood. Family systems theory examines the family as a social system influencing behavior and thoughts.
Social workers using systems theory will work to understand how their clients are influenced by the systems they’re a part of. Social workers then identify where systemic breakdowns are affecting behavior.
3. Psychosocial development theory
Psychosocial development theory was introduced by German psychoanalyst Erik Erikson, who believed personality develops in a series of stages. Erikson created an eight-stage theory of psychosocial development . According to the theory, the eight stages of development that people pass through in life are:
- Trust versus mistrust
- Autonomy versus shame and doubt
- Initiative versus guilt
- Industry versus inferiority
- Identity versus confusion
- Intimacy versus isolation
- Generativity versus stagnation
- Integrity versus despair
Psychosocial development theory explains that humans pass through these stages as they age. By identifying which stage of development their clients are experiencing, social workers can better understand the challenges their clients face.
4. Psychodynamic theory
Psychodynamic theory was introduced by the founder of psychoanalysis, Sigmund Freud. This theory is founded on the idea that humans are biologically driven to seek gratification. The theory states that people do this based on processes that have developed outside of conscious awareness, with origins in childhood experiences. This drive influences everyday behavior, leading to actions like aggression, sex and self-preservation.
In social work, psychodynamic theory can help to explain the internal processes individuals use to guide their behavior , some of which may be unconsciously motivated. Social workers may also examine how early childhood experiences have played a role in influencing their clients’ current behavior.
5. Social exchange theory
Social exchange theory suggests that relationships are based on cost-benefit analysis. Each person seeks to maximize their benefits and is expected to reciprocate for the benefits they’ve received. When risks outweigh potential rewards, relationships may be abandoned. When one person in a relationship has greater personal resources than another, that person is predicted to have greater power as well.
Social workers can use social exchange theory to understand their clients’ relationships, including why they continue to maintain certain relationships or abandon them.
Social exchange theory can also be applied to the techniques social workers use to connect with their clients. This theory can influence how social workers position the social worker-client relationship as one that benefits their clients.
6. Rational choice theory
Rational choice theory helps explain why people make the choices they do, by weighing risks, costs and benefits. This theory suggests that all choices are rational because people calculate the costs and benefits before making a decision. Even when a choice seems irrational, there is reasoning behind it.
This theory can help social workers understand the decision-making processes and motivations of their clients.
Six practice models in social work
Social work practice models enable social workers to implement theories in their day-to-day work. Just like a social worker may use various theories to guide their interventions, social workers may also use various practice models depending on the problems their clients encounter.
1. Cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on how thoughts and feelings influence behaviors, which can sometimes lead to psychological problems. Social workers using cognitive behavioral therapy methods help clients identify self-destructive thoughts that influence negative emotions and behaviors.
Cognitive behavioral therapy is often used for individuals who are experiencing mental health issues, mental illness or depression resulting from crisis or trauma. Social workers using cognitive behavioral therapy help their clients eliminate negative thoughts to prevent destructive behaviors and adverse outcomes.
2. Crisis intervention model
The crisis intervention model is used for clients who are experiencing crisis and trauma, such as victims of domestic violence, and for clients who require intervention to prevent physical harm or suicide. Albert R. Roberts, PhD, and Allen J. Ottens, PhD, developed a seven-stage crisis intervention model :
- Take a psychosocial and lethality assessment.
- Rapidly establish rapport.
- Identify the major crisis cause(s).
- Enable the client to express their feelings and emotions.
- Generate and explore safe alternatives for coping.
- Create an action plan.
- Follow up after the intervention.
This social work model can be used for clients who are experiencing thoughts of suicide or self-harm or who have undergone an acute crisis, like rape or violence.
3. Narrative therapy
Narrative therapy is the process of helping the individual recognize that they have the power to change their life story, also known as the narrative. Narrative therapy helps individuals realize that they are separate from their problems and can fix them when they view the narrative from an outside perspective.
Using narrative therapy, a social worker can help an individual create a new narrative with different positive actions. The social worker enables the individual to understand how the broader context is contributing to their narrative, so that they can be aware of pitfalls to avoid and can utilize various strategies to tackle their problems.
4. Problem-solving model
The problem-solving model was created by Helen Harris Perlman , a social worker and author of “Social Casework: A Problem-solving Process.” Using the problem-solving model, a social worker helps an individual identify a problem, create an action plan to solve it, and implement the solution. Together, the social worker and individual discuss the effectiveness of the problem-solving strategy and adjust it as necessary. The problem-solving model enables the social worker and individual to focus on one concrete problem at a time.
5. Solution-focused therapy
Solution-focused therapy involves the social worker and client identifying a problem and creating a solution based on the individual’s strengths. It’s a short-term practice model that focuses on helping clients cope with challenges using specific behaviors. Instead of focusing on changing who a client is, solution-focused therapy attempts to change a client’s actions in certain situations to achieve more favorable outcomes.
Collaborating to create solutions allows the client to play an active role in implementing necessary actions and achieving positive change.
6. Task-centered practice
Using task-centered practice, a social worker breaks down a problem into manageable tasks. The individual has deadlines to complete the tasks and agrees to meet them. Task-centered practice is a goal-setting form of social work that helps individuals make consistent steps toward improving their lives.
Instead of focusing on the past, this type of practice encourages clients to live in the present and think about how completing certain tasks will positively impact their future.
Resources to explore social work theories
Social work theories have been practiced over decades and continually evolve when new research is completed. Learn more about social work theories by exploring the resources below.
- Journal of Evidence-Based Social Work : This journal features research on evidence-based practice in social work and evaluates social work theory, techniques, and strategies.
- Journal of Social Work Practice : This journal focuses on psychodynamic and systemic social work perspectives. It features research on theory and practice and includes articles offering critical analysis of systemic and psychodynamic theory.
- Journal of Social Work : This journal includes social work research and short “think pieces” on social work theoretical understanding, policy, and practice.
- Social Work: This journal is the official journal of the National Association of Social Workers and features articles on social work and social welfare, including new techniques and research.
- Clinical Social Work Journal: This journal features peer-reviewed articles on clinical social work practice with individuals, groups, families, and couples. It also has articles on theory developments, practice and evidence-based clinical research.
Introductory books
- “A Brief Introduction to Social Work Theory” : This textbook by David Howe explains how social work practice is influenced by various social work theories and shows how social work theories have evolved over time.
- “An Introduction to Applying Social Work Theories and Methods”: This book by Barbra Teater explains the most prominent social work theories and how those approaches can be used in practice.
- “Social Work Theory and Practice”: This book by Lesley Deacon and Stephen J. Macdonald explains how social work theory informs practice for various individuals and contexts.
- “Modern Social Work Theory”: This book by Malcolm Payne introduces the major social work practice theories and explains how to apply theory to practice.
- “An Introduction to Using Theory in Social Work Practice”: This book by James A. Forte covers 14 social work theories and explains how to use them from engagement through evaluation.
Note: the links in this section on Social Work Theory all go to Google Books and are solely provided for your information. edX does not receive any form of compensation for these links.

Other online resources
- NASW Clinical Social Work : This section of the National Association of Social Workers website covers clinical social work practice. It features content, publications, and related resources for clinical social workers, like the “ NASW Standards for Clinical Social Work in Social Work Practice (PDF, 135 KB) .”
- Encyclopedia of Social Work: The Encyclopedia of Social Work by the National Association of Social Workers Press and Oxford University Press features tools for applying social work theory to practice. These resources include scholarly articles and bibliographies.
- Social Work Today : This publication features articles on current social work trends in categories like behavioral health, addictions, children and family, aging and professional practice.
Science-based social work theory helps social workers and their clients succeed
Social work theory helps professionals in the field identify and implement effective interventions for clients. An understanding of the most prominent social work theories gives social workers the tools they need to provide evidence-based treatment and help their clients overcome their problems. As social work theories continue to evolve and emerge, social workers can apply their multifaceted knowledge to unique situations and clients.
Are you considering a career in social work? Read more about the field of social work and the steps to becoming a social worker , which can vary by location.
Last updated: November 2023
The University of Chicago School of Social Service Administration
Chicago/SSA/Centennial
Scholarship and service in a changing world.
- Global Navigation
- Page Navigation
In this Section
- Profiles of Distinction Series
- 100 years of solicitude
- An Examination of Gangs and Urban Violence
- SSA Magazine Previews
- America's Twelve Greatest Women
Share this Page
Fill out this simple form to send an email to a friend who might enjoy this page.
- Navigation:
- Participate
- Faculty Research
- Celebrate SSA
SSA Centennial Celebration Profiles of Distinction Series
Helen Harris Perlman
Samuel Deutsch Distinguished Service Professor
Lingering prejudice and discrimination set Helen Harris Perlman on a course to become one of the most influential people in social services in her era. Ms. Perlman graduated from the University of Minnesota in 1926 with high honors and an A.B. in English literature. Advised that, as a Jew, she would never find an appointment as a professor in the humanities, she took a job as a summer caseworker for the Chicago Jewish Social Service Bureau.
“A whole world opened up to me,” she recalled. “I had no idea of the kinds of trouble people had. I got a great deal of satisfaction from being able to help people. I found that in many cases, families faced the same kinds of problems and conflicts that one encountered in the great works of literature.”
She began her career in social work at a particularly advantageous time. There was, she said, “a sudden flood of psychological knowledge.” In 1933, she received one of four Commonwealth Fund scholarships for students at the New York School of Social Work, now a part of Columbia University.
As she finished her studies in New York, she worked as a caseworker, lecturer, and clinical instructor at the New York School of Social Work, Columbia University, and the Bureau of Child Guidance. It was through this range of experience that she began to develop the conceptual framework for direct-work practice. She earned her master’s degree in social work from Columbia University in 1943.
Shortly after joining the SSA faculty in 1945, she began working on Social Casework: A Problem-solving Process . The book, originally published in 1957, has sold nearly 200,000 copies and has been translated into more than ten languages. Ms. Perlman’s work, together with later work by her colleagues, established the “Chicago School” approach to problem-solving, which is still applied in practice today.
Ms. Perlman’s theories stood apart from the leading theories of the day, which typically focused on long-term psychotherapy. She argued that in-depth study wasn’t always necessary and could even impede progress.
The core idea of her approach was that success could be achieved by partializing – or separating into manageable segments - a client’s intertwined problems and focusing on one specific issue the client and social worker agreed needed to be resolved at a given time. “An important feature of partialization,” Ms. Perlman said, “is the fact that the problem-solving process was transferable to other areas of life’s difficulties.”
Ms. Perlman continued to break new ground in social work, writing more than 75 articles and seven other books, including So You Want to Be a Social Worker , Persona: Social Role and Personality and Relationship: The Heart of Helping People , and a memoir entitled Dancing Clock & Other Childhood Memories . She also edited the book Helping: Charlotte Towle on Social Casework . She also kept up with her love of writing fiction, publishing poetry and stories in newspapers and magazines, including the short story “Twelfth Summer,” published in the 1950s in the New Yorker.
Ms. Perlman was active in many professional and educational circles throughout her career, serving for many years on the editorial board of the Journal of American Orthopsychiatry. The society recognized her service with a life membership. She also served on the editorial board of Social Work, the major publication of the National Association of Social Workers (NASW) and on the curriculum development committee of the Council on Social Work Education (CSWE). CSWE named her a Pioneer of Social Work Education. She received honorary degrees from Boston University, the University of Central Florida, and her alma mater, the University of Minnesota.
Many of her highest accolades came from the University of Chicago. She was the first woman and the first SSA faculty member to be named a Distinguished Service Professor by the University in 1969. In 1996, SSA established the Helen Harris Perlman Visiting Professorship in the School of Social Service Administration in honor of her numerous scholarly contributions.
Ms. Perlman was also the first woman elected to the Quadrangle Club Board, the first woman appointed to the Library Board, and, in January, 1970, the first woman to address the annual meeting of the Board of Trustees and faculty.
The Helping / Problem -Solving Process in Social Work
The helping / problem -solving process in social work.
According to John Dewey, the problem-solving behavior is based on reflective thought that begins with a feeling of doubt or confusion.
Steps in SW Helping Process
Initial contact with your client.
The process by which a potential client achieves the status of a client.
Types of Client
- Walk-in client
- Involuntary client
- Reach-out client
A process and a product of understanding on which action in based.
– Max Siporin
Involves the collection of necessary information and its analysis and interpretation in order to reach an understanding of the client, the problem and the social context in which it exist.
Sources of Data/Information
- Primary Source ~ the client
- Secondary Source ~ significant others
- Existing Data ~ information previously collected
- Worker’s Own Observation
Link between Assessment and Intervention. Planning process translates the content of assessment into a goal statement. Guided by the SW values and body of knowledge, it allows the worker, with the client’s participation, to move from problem definition to problem solution.
Implementation
Rendering of all the specific and interrelated services appropriate to the given problem situation in the light of assessment and planning. Refers to the composite of activities or tasks that the Social Worker is expected to undertake in order to accomplish the goals agreed upon with the client.
Interventive Roles in Direct Practice
Resource Provider
Social Broker
Counselor/Therapist
Collection of data about the outcomes of a program of action relative to goals and objectives set in advance of the implementation that program.
In SW it is a continual process (Ongoing evaluation). Social Worker has to undertake also a Terminal evaluation (evaluation undertaken before ending the helping relationship.
Types of Evaluation
Summative Evaluation – concerned with outcomes or effectiveness.
Formative Evaluation – concerned with the process of work.
Termination
SW problem-solving relationship does not go on forever. Consists of disengagement after evaluation and stabilization of change.
Reasons for Terminating the Client-Worker Relationship
- When the goals set by worker and the client have been reached.
- When, after the reasonable period of time, there has been very little movement toward the attainment of the goals formulated, and the prospect for any change in the situation is held unlikely.
- When the client thinks that the worker has provided sufficient help so that it is now possible for the client to pursue problem-solving in his own.
- When an agency does not have the resources needed by the client or the worker does not get her agency’s approval to provide the services needed by the client.
- When the system outside the client make it difficult for the client to continue with the helping relationship or when these systems influence the client to discontinue the relationship.
- When for one reason or another, the worker must leave the agency.
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

- INTERPERSONAL SKILLS
- Problem Solving and Decision Making
- Social Problem Solving
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Interpersonal Skills:
- A - Z List of Interpersonal Skills
- Interpersonal Skills Self-Assessment
- Communication Skills
- Emotional Intelligence
- Conflict Resolution and Mediation Skills
- Customer Service Skills
- Team-Working, Groups and Meetings
- Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
- Effective Decision Making
- Decision-Making Framework
- Introduction to Problem Solving
- Identifying and Structuring Problems
- Investigating Ideas and Solutions
- Implementing a Solution and Feedback
- Creative Problem-Solving
Social Problem-Solving
- Negotiation and Persuasion Skills
- Personal and Romantic Relationship Skills
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
The SkillsYouNeed Guide to Interpersonal Skills

Social problem-solving might also be called ‘ problem-solving in real life ’. In other words, it is a rather academic way of describing the systems and processes that we use to solve the problems that we encounter in our everyday lives.
The word ‘ social ’ does not mean that it only applies to problems that we solve with other people, or, indeed, those that we feel are caused by others. The word is simply used to indicate the ‘ real life ’ nature of the problems, and the way that we approach them.
Social problem-solving is generally considered to apply to four different types of problems:
- Impersonal problems, for example, shortage of money;
- Personal problems, for example, emotional or health problems;
- Interpersonal problems, such as disagreements with other people; and
- Community and wider societal problems, such as litter or crime rate.
A Model of Social Problem-Solving
One of the main models used in academic studies of social problem-solving was put forward by a group led by Thomas D’Zurilla.
This model includes three basic concepts or elements:
Problem-solving
This is defined as the process used by an individual, pair or group to find an effective solution for a particular problem. It is a self-directed process, meaning simply that the individual or group does not have anyone telling them what to do. Parts of this process include generating lots of possible solutions and selecting the best from among them.
A problem is defined as any situation or task that needs some kind of a response if it is to be managed effectively, but to which no obvious response is available. The demands may be external, from the environment, or internal.
A solution is a response or coping mechanism which is specific to the problem or situation. It is the outcome of the problem-solving process.
Once a solution has been identified, it must then be implemented. D’Zurilla’s model distinguishes between problem-solving (the process that identifies a solution) and solution implementation (the process of putting that solution into practice), and notes that the skills required for the two are not necessarily the same. It also distinguishes between two parts of the problem-solving process: problem orientation and actual problem-solving.
Problem Orientation
Problem orientation is the way that people approach problems, and how they set them into the context of their existing knowledge and ways of looking at the world.
Each of us will see problems in a different way, depending on our experience and skills, and this orientation is key to working out which skills we will need to use to solve the problem.
An Example of Orientation
Most people, on seeing a spout of water coming from a loose joint between a tap and a pipe, will probably reach first for a cloth to put round the joint to catch the water, and then a phone, employing their research skills to find a plumber.
A plumber, however, or someone with some experience of plumbing, is more likely to reach for tools to mend the joint and fix the leak. It’s all a question of orientation.
Problem-Solving
Problem-solving includes four key skills:
- Defining the problem,
- Coming up with alternative solutions,
- Making a decision about which solution to use, and
- Implementing that solution.
Based on this split between orientation and problem-solving, D’Zurilla and colleagues defined two scales to measure both abilities.
They defined two orientation dimensions, positive and negative, and three problem-solving styles, rational, impulsive/careless and avoidance.
They noted that people who were good at orientation were not necessarily good at problem-solving and vice versa, although the two might also go together.
It will probably be obvious from these descriptions that the researchers viewed positive orientation and rational problem-solving as functional behaviours, and defined all the others as dysfunctional, leading to psychological distress.
The skills required for positive problem orientation are:
Being able to see problems as ‘challenges’, or opportunities to gain something, rather than insurmountable difficulties at which it is only possible to fail.
For more about this, see our page on The Importance of Mindset ;
Believing that problems are solvable. While this, too, may be considered an aspect of mindset, it is also important to use techniques of Positive Thinking ;
Believing that you personally are able to solve problems successfully, which is at least in part an aspect of self-confidence.
See our page on Building Confidence for more;
Understanding that solving problems successfully will take time and effort, which may require a certain amount of resilience ; and
Motivating yourself to solve problems immediately, rather than putting them off.
See our pages on Self-Motivation and Time Management for more.
Those who find it harder to develop positive problem orientation tend to view problems as insurmountable obstacles, or a threat to their well-being, doubt their own abilities to solve problems, and become frustrated or upset when they encounter problems.
The skills required for rational problem-solving include:
The ability to gather information and facts, through research. There is more about this on our page on defining and identifying problems ;
The ability to set suitable problem-solving goals. You may find our page on personal goal-setting helpful;
The application of rational thinking to generate possible solutions. You may find some of the ideas on our Creative Thinking page helpful, as well as those on investigating ideas and solutions ;
Good decision-making skills to decide which solution is best. See our page on Decision-Making for more; and
Implementation skills, which include the ability to plan, organise and do. You may find our pages on Action Planning , Project Management and Solution Implementation helpful.
There is more about the rational problem-solving process on our page on Problem-Solving .
Potential Difficulties
Those who struggle to manage rational problem-solving tend to either:
- Rush things without thinking them through properly (the impulsive/careless approach), or
- Avoid them through procrastination, ignoring the problem, or trying to persuade someone else to solve the problem (the avoidance mode).
This ‘ avoidance ’ is not the same as actively and appropriately delegating to someone with the necessary skills (see our page on Delegation Skills for more).
Instead, it is simple ‘buck-passing’, usually characterised by a lack of selection of anyone with the appropriate skills, and/or an attempt to avoid responsibility for the problem.
An Academic Term for a Human Process?
You may be thinking that social problem-solving, and the model described here, sounds like an academic attempt to define very normal human processes. This is probably not an unreasonable summary.
However, breaking a complex process down in this way not only helps academics to study it, but also helps us to develop our skills in a more targeted way. By considering each element of the process separately, we can focus on those that we find most difficult: maximum ‘bang for your buck’, as it were.
Continue to: Decision Making Creative Problem-Solving
See also: What is Empathy? Social Skills

The Social Work “Helping Process”- Engagement, Assessment, Planning, Intervention, Evaluation, and Termination ASWB
- Meagan Mitchell
- March 19, 2022

The Social Work Helping Process on the ASWB Exam
This process will be extremely helpful for you to know and understand for the LCSW and LMSW exams, especially for questions that end in FIRST and NEXT.
What is The Helping Process?
- Intervention
- Termination
This six-step process is very helpful to have a mastery of when you are taking your exam.
1) Engagement : You cannot build a therapeutic relationship without engaging the client. Also includes intake, confidentiality, consent, and explaining the risks of treatment. Additionally, you’ll be setting boundaries during this session.
2) Assessment : Assessment is when you are determining the client’s presenting problem. This step is used to collect information that will be helpful in treatment. This may include a biopsychosocial assessment. We need to determine strengths and weaknesses so we can identify areas that will be worked on in treatment.
Example: In this phase, you may determine anxiety is the main problem you will work on treatment.
3) Planning : The planning stage refers to planning for treatment. This includes setting goals and objectives. Treatment modality may also be determined in this stage. In this stage, you are making an action plan for the next steps in treatment.
Example: You have determined that you will address the client’s anxiety through 12 weeks of CBT. The goal will be to utilize coping strategies to decrease negative thinking in 3 out of 5 situations.
4) Intervention : This is where the “bulk” of the clinical work will be done. This is when you are actively working with the client. In this stage, you may be utilizing a variety of techniques to work towards established goals. You may also give clients activities to work on outside of the session. Depending on the type of work you are doing, this phase may be long or short-term in nature.
Example: During the intervention phase you will be utilizing CBT. This may include working on distorted thoughts, practicing muscle relaxation, and mindfulness.
Learn more about different intervention methods in this post: Mastering Clinical Social Work Interventions For The ASWB Exam
5) Evaluation : This is where you are looking at the client’s progress. Are they making progress towards established goals? Are there areas that need to be changed? Is the treatment modality working? This is an ongoing process that should be used to determine if changes need to be made in the treatment process.
Example: Is my client making progress towards a decrease in negative thinking? Are the CBT techniques and strategies helping the client cope with anxiety?
6) Termination : Termination is signaled by the close or ending of the therapeutic relationship. Ideally, termination occurs once the client and therapist agree that the treatment goals have been met and services are no longer needed. However, a client can terminate at any time. Termination should be discussed early and clients should have time to prepare for the end of treatment.
Learn more about the Termination stage in this post: Termination Of Clients On The ASWB Exam
** For some people termination is signaled by joy and pride. For others, it is more challenging and may be signaled by fear and anxiety. Support your client’s through the termination phase.
Want to learn more about the different stages of the helping process? Watch the video below!
Learn more about my course here: https://agentsofchangeprep.com/
A little bit about me: I am a Licensed Clinical Social Worker and I have been providing individualized and group test prep for the ASWB for over three years. From all of this experience helping others pass their exams, I have created a course to help you prepare for and pass the ASWB exam!
Find more from Agents of Change here:
► Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/aswbtestprep
► Podcast: https://anchor.fm/agents-of-change-sw
#socialwork #testprep #aswb #socialworker #socialwork #socialworktest #socialworkexam #exam #socialworktestprep #socialworklicense #socialworklicensing #licsw #lmsw #lcsw #aswbexam #aswb #lcswexam #lmswexam #aswbtestprep #aswbtest #lcswtestprep #lcswtest #lmswtestprep #lmswtest #aswbcourse
Disclaimer: This video content has been made available for informational and educational purposes only. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical or clinical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Share this:
Popular posts.

What is Veterinary Social Work?

Gambling Disorder and the Role of Social Workers

What is Moral Disengagement? The Role of Social Workers

Sport Social Work: Kickstarting Change

Library Social Work: The New Community Hub

Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders and Social Work

Cultural Humility and the ASWB Exam

Analyzing Data and the ASWB Exam
You may also like.

Pass Your Social Work Exam
Try it for free
Agents of Change
Agents of Change will help you prepare to PASS your licensing exam and level up your career.
Quick Links
If you have any questions not covered by our FAQs, please get in touch using the email below
Email: [email protected]
Discover more from Agents of Change Social Work Test Prep
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!
Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
Social casework : a problem-solving process
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
471 Previews
8 Favorites
Better World Books
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
EPUB and PDF access not available for this item.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by station52.cebu on December 4, 2019
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Johnson features the Stages of the Problem-Solving Process: Stage 1 - Preliminary statement of the problem. Stage 2 - Statement of preliminary assumptions about the nature of the problem. Stage 3 - Selection and collection of information. Stage 4 - Analysis of information available. Stage 5 - Development of a plan.
This report outlined specific steps and procedures for the problem-solving process as key components of a proposed unified generic approach to service delivery (Schatz et al. 1990). To some extent, this report laid the groundwork for the development of the social work problem-solving model by Helen Perlman .
In this chapter we (a) review the early development of the problem-solving model for social work practice; (b) discuss the later development of the problem solving model in terms of its extension to and further elaboration by generalist models of social work practice; (c) provide an overview of how the problem-solving model allows for the integration of the scientific and artistic elements of ...
A social systems approach examines the social structure surrounding the problem or issue. This approach requires macro, meso, and micro levels of analysis (see pages 12-13) to help understand the structure of the problem and the arrangement of individuals and social groups involved. Analysis requires comprehension of the entire issue and parts ...
This approach has important implications for moving the profession toward greater accountability in the practice of social work. Unless educators can motivate practitioners to change the way in which they ask questions and make predictions, it is unlikely that practitioners will use scientific information in their problem-solving processes.
the problems to be worked on in treatment, the number of sessions agreed to,and other relevant rules related to being on time,payment,and the can-cellation policies. Many workers have these rules in written form, with the client and the worker signing the contract. 36 SOCIAL PROBLEMS, SOCIAL WELFARE, AND THE SOCIAL WORK PROFESSION
Paper ID: SR21 1111131022. 868. Social Work: A Problem Solving Profession. Iranna Ronad. Abstract: Man can fly like bird in the sky, can swim like fish in the water, can live on the moon as well ...
many writings, in particular S:Jcial Casework: A Problem-Solving Process,4 'The Problem-Solving Model in Social Casework' ,5 and 'Social Case work in Social Work: its Place and Purpose' .6 The main emphasis in this model is on social casework as an extension of the processes of ordinary living. Life consists of
Abstract. An examination of the way in which social workers use knowledge suggests an instrumental approach to knowledge use. This approach has important implications for moving the profession ...
Description. In D'Zurilla and Goldfried's [ 6] seminal article, the authors conceptualized social problem solving as an individuals' processing and action upon entering interpersonal situations in which no immediately effective response is available. One primary component of social problem solving is the cognitive-behavioral process of ...
The problem-solving process social work practitioners use can also be used to tackle one of many problems at a time to help the client get a win before moving on to the next issue. Working on one issue at a time can be more manageable for both the client and the social worker. In the social work problem-solving process one challenge is identified.
Problem-solving and decision-making in social work are guided by these general principles: Client-Centered Approach: Social workers prioritize the autonomy and self-determination of their clients. They empower clients to make informed decisions by providing them with information, options, and support rather than imposing their own opinions or ...
Murdach (2007) suggests the principal stages of Perlman's problem-solving model are simply: the need for specific decision about a course of action (including methods of monitoring and evaluating the results of such action). Chenowith and Lehmann (2008) describe a planned change process model: Chenowith and Lehman also suggest the model ...
The problem-solving model was created by Helen Harris Perlman, a social worker and author of "Social Casework: A Problem-solving Process." Using the problem-solving model, a social worker helps an individual identify a problem, create an action plan to solve it, and implement the solution. Together, the social worker and individual discuss ...
It was through this range of experience that she began to develop the conceptual framework for direct-work practice. She earned her master's degree in social work from Columbia University in 1943. Shortly after joining the SSA faculty in 1945, she began working on Social Casework: A Problem-solving Process. The book, originally published in ...
Social Worker's Role in the Problem-Solving Process. During treatment, a social worker takes on the role of a mentor. They manage the diagnosis and assessment of the client. They are also ...
4.1 Theory for problem solving in social work . We, the social workers have to work with diverse individuals, families, groups, organizations, and communities. So have to follow some steps and processes. Helen Harries Perlman, discussed about the problem solving model in social care work: a problem solving process (Chicago 1957).
Social Casework: A Problem-Solving Process, Volume 10. Helen Harris Perlman. University of Chicago Press, Mar 15, 1957 - Political Science - 268 pages. This is a basic book in social casework. Its thesis is that among all the complexities within the subject matter and operations of casework there are certain constant elements, forces, and ...
The Helping / Problem -Solving Process in Social Work According to John Dewey, the problem-solving behavior is based on reflective thought that begins with a feeling of doubt or confusion. Steps in SW Helping Process Engagement Initial contact with your client. Intake The process by which a potential client achieves the status of a client.…
Social problem-solving is generally considered to apply to four different types of problems: Impersonal problems, for example, shortage of money; Personal problems, for example, emotional or health problems; Interpersonal problems, such as disagreements with other people; and. Community and wider societal problems, such as litter or crime rate.
Chapter 8: Problem Solving in Social Work Practice. 5.0 (1 review) Problem Solving:u000bThe Traditional Model of Social Work. Click the card to flip 👆. - First articulated by Mary Richmond in 1917. - Borrowed from the medical model. - Original elements: Study, Diagnosis, Treatment. Click the card to flip 👆.
The Social Work Helping Process includes Engagement, Assessment, Planning, Intervention, Evaluation, and Termination. Learn more here! ... Example: In this phase, you may determine anxiety is the main problem you will work on treatment. 3) Planning: The planning stage refers to planning for treatment. This includes setting goals and objectives.
Social casework : a problem-solving process by Perlman, Helen Harris. Publication date 1957 Topics ... Openlibrary_work OL4784555W Page_number_confidence 95 Page_number_module_version 1.0.5 Pages 304 Ppi 300 Republisher_date 20191207150639 Republisher_operator [email protected]