Arithmetic Mean
The arithmetic mean in statistics, is nothing but the ratio of all observations to the total number of observations in a data set. Some of the examples include the average rainfall of a place, the average income of employees in an organization. We often come across statements like "the average monthly income of a family is ₹15,000 or the average monthly rainfall of a place is 1000 mm" quite often. Average is typically referred to as arithmetic mean.
The formula for calculating arithmetic mean is (sum of all observations)/(number of observations). For example, the arithmetic mean of a set of numbers {10, 20, 30, 40} is (10 + 20 + 30 + 40)/4 = 25. Let’s understand the meaning of the term "mean", followed by arithmetic with a few solved examples in the end.

What Is Arithmetic Mean?
Arithmetic mean is often referred to as the mean or arithmetic average. It is calculated by adding all the numbers in a given data set and then dividing it by the total number of items within that set. The arithmetic mean (AM) for evenly distributed numbers is equal to the middlemost number. Further, the AM is calculated using numerous methods, which is based on the amount of the data, and the distribution of the data.
For example, the mean of the numbers 6, 8, 10 is 8 since 6 + 8 + 10 = 24 and 24 divided by 3 [there are three numbers] is 8. The arithmetic mean maintains its place in calculating a stock’s average closing price during a particular month. Let's assume there are 24 trading days in a month. How can we calculate the mean? All you need to do is take all the prices, add them up, and divide by 24 to get the AM.
☛Also Check: Difference Between Average and Mean
Arithmetic Mean Formula
The general formula to find the arithmetic mean of a given data is:
Arithmetic mean (x̄) = Sum of all observations / Number of observations
It is denoted by x̄, (read as x bar). Data can be presented in different forms. For example, when we have raw data like the marks of a student in five subjects, we add the marks obtained in the five subjects and divide the sum by 5, since there are 5 subjects in total.
Now consider a case where we have huge data like the heights of 40 students in a class or the number of people visiting an amusement park across each of the seven days of a week.
Will it be convenient to find the arithmetic mean with the above method? The answer is a big NO! So, how can we find the mean? We group the data in a form that is meaningful and easy to comprehend. Let us study more in detail about finding the arithmetic mean for ungrouped and grouped data. The below-given image presents the general formula to find the arithmetic mean:

Properties of Arithmetic Mean
Let us have a look at some of the important properties of the arithmetic mean. Suppose we have n observations denoted by x₁, x₂, x₃, ….,xₙ and x̄ is their arithmetic mean, then:
- If all the observations in the given data set have a value say ‘m’, then their arithmetic mean is also ‘m’. Consider the data having 5 observations: 15,15,15,15,15. So, their total = 15+15+15+15+15= 15 × 5 = 75; n = 5. Now, arithmetic mean = total/n = 75/5 = 15.
- The algebraic sum of deviations of a set of observations from their arithmetic mean is zero. (x₁−x̄)+(x₂−x̄)+(x₃−x̄)+...+(xₙ−x̄) = 0. For discrete data, ∑(x i −x̄) = 0. For grouped frequency distribution, ∑f(x i −∑x̄) = 0
- If each value in the data increases or decreases by a fixed value, then the mean also increases/decreases by the same number. Let the mean of x₁, x₂, x₃ ……xₙ be X̄, then the mean of x₁+k, x₂+k, x₃ +k ……xₙ+k will be X̄+k.
- If each value in the data gets multiplied or divided by a fixed value, then the mean also gets multiplied or divided by the same number. Let the mean of x₁, x₂, x₃ ……xₙ be X̄, then the mean of kx₁, kx₂, kx₃ ……xₙ+k will be kX̄. Similarly, the mean of x₁/k, x₂/k, x₃/k ……xₙ/k will be X̄/k.
Note: While dividing each value by k, it must be a non-zero number as division by 0 is not defined.
Calculating Arithmetic Mean for Ungrouped Data
The arithmetic mean of ungrouped data is calculated using the formula:
Mean x̄ = Sum of all observations / Number of observations
Example: Compute the arithmetic mean of the first 6 odd natural numbers .
Solution: The first 6 odd natural numbers: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11
x̄ = (1+3+5+7+9+11) / 6 = 36/6 = 6.
Thus, the arithmetic mean is 6.
Calculating Arithmetic Mean for Grouped Data
There are three methods (Direct method, Short-cut method, and Step-deviation method) to calculate the arithmetic mean for grouped data. The choice of the method to be used depends on the numerical value of x i (data value) and f i (corresponding frequency). ∑ (sigma) the symbol represents summation. If x i and f i are sufficiently small, the direct method will work. But, if they are numerically large, we use the assumed arithmetic mean method or step-deviation method. In this section, we will be studying all three methods along with examples.
Direct Method
Let x₁, x₂, x₃ ……xₙ be the observations with the frequency f₁, f₂, f₃ ……fₙ.
Then, arithmetic mean is calculated using the formula:
x̄ = (x₁f₁+x₂f₂+......+xₙfₙ) / ∑f i Here, f₁+ f₂ + ....fₙ = ∑f i indicates the sum of all frequencies.
Example I (discrete grouped data): Find the arithmetic mean of the following distribution:
Add up all the (x i f i ) values to obtain ∑x i f i . Add up all the f i values to get ∑f i
Now, use the arithmetic mean formula.
x̄ = ∑x i f i / ∑f i = 2750/50 = 55
Arithmetic mean = 55. The above problem is an example of discrete grouped data.
Let's now consider an example where the data is present in the form of continuous class intervals.
Example II (continuous class intervals): Let's try finding the mean of the following distribution:
When the data is presented in the form of class intervals , the mid-point of each class (also called class mark) is considered for calculating the arithmetic mean.
The formula for mean remains the same as discussed above.
Class Mark = (Upper limit + Lower limit) / 2
x̄ = ∑x i f i / ∑f i = 1390/35 = 39.71. We have, ∑f i = 35 and ∑x i f i = 35
Arithmetic mean = 39.71
Assumed Mean Method
The short-cut method is called as assumed mean method or change of origin method . The following steps describe this method.
Step1: Calculate the class marks (mid-point) of each class (x i ).
Step2: Let A denote the assumed mean of the data.
Step3: Find deviation (di) = x i – A
Step4: Use the formula:
x̄ = A + (∑f i d i /∑f i )
Example: Let's understand this with the help of the following example. Calculate the mean of the following using the short-cut method.
Solution: Let us make the calculation table. Let the assumed mean be A = 62.5
Note: A is chosen from the x i values. Usually, the value which is around the middle is taken.
Now we use the formula,
x̄ = A + (∑f i d i /∑f i ) = 62.5 + (−25/100) = 62.5 − 0.25 = 62.25
∴ Arithmetic mean = 62.25
Step Deviation Method
This is also called the change of origin or scale method. The following steps describe this method:
Step 1: Calculate the class marks of each class (x i ).
Step 2: Let A denote the assumed mean of the data.
Step 3: Find u i = (x i −A)/h, where h is the class size.
Step 4: Use the formula to find arithmetic mean:
x̄ = A + h × (∑f i u i /∑f i )
To learn more about this method, click here .
Example: Consider the following example to understand this method. Find the arithmetic mean of the following using the step-deviation method.
Solution: To find the mean, we first have to find the class marks and decide A (assumed mean). Let A = 35 Here h (class width) = 10
Using arithmetic mean formula:
x̄ = A + h × (∑f i u i /∑f i ) =35 + (16/50) ×10 = 35 + 3.2 = 38.2
Arithmetic mean = 38.
Advantages of Arithmetic Mean
The uses of arithmetic mean are not just limited to statistics and mathematics, but it is also used in experimental science, economics, sociology, and other diverse academic disciplines. Listed below are some of the major advantages of the arithmetic mean.
- As the formula to find the arithmetic mean is rigid, the result doesn’t change. Unlike the median , it doesn’t get affected by the position of the value in the data set.
- It takes into consideration each value of the data set.
- Finding an arithmetic mean is quite simple; even a common man having very little finance and math skills can calculate it.
- It’s also a useful measure of central tendency, as it tends to provide useful results, even with large groupings of numbers.
- It can be further subjected to many algebraic treatments, unlike mode and median. For example, the mean of two or more series can be obtained from the mean of the individual series.
- The arithmetic mean is widely used in geometry as well. For example, the coordinates of the “ centroid” of a triangle (or any other figure bounded by line segments) are the arithmetic mean of the coordinates of the vertices.
After having discussed some of the major advantages of arithmetic mean, let's understand its limitations.
Disadvantages of Arithmetic Mean
Let us now look at some of the disadvantages/demerits of using the arithmetic mean.
- The strongest drawback of arithmetic mean is that it is affected by extreme values in the data set. To understand this, consider the following example. It’s Ryma’s birthday and she is planning to give return gifts to all who attend her party. She wants to consider the mean age to decide what gift she could give everyone. The ages (in years) of the invitees are as follows: 2, 3, 7, 7, 9, 10, 13, 13, 14, 14 Here, n = 10. Sum of the ages = 2+3+7+7+9+10+13+13+14+14 = 92. Thus, mean = 92/10 = 9.2 In this case, we can say that a gift that is desirable to a kid who is 9 years old may not be suitable for a child aged 2 or 14.
- In a distribution containing open-end classes, the value of the mean cannot be computed without making assumptions regarding the size of the class.
We know that to find the arithmetic mean of grouped data, we need the mid-point of every class. As evident from the table, there are two cases (less than 15 and 45 or more) where it is not possible to find the mid-point and hence, arithmetic mean can’t be calculated for such cases.
- It's practically impossible to locate the arithmetic mean by inspection or graphically.
- It cannot be used for qualitative types of data such as honesty, favorite milkshake flavor, most popular product, etc.
- We can't find the arithmetic mean if a single observation is missing or lost.
Tips and tricks on arithmetic mean:
- If the number of classes is less and the data has values with a smaller magnitude, then the direct method is preferred out of the three methods to find the arithmetic mean.
- Step deviation works best when we have a grouped frequency distribution in which the width remains constant for every class interval and we have a considerably large number of class intervals.
☛Related Topics:
- Arithmetic Mean Calculator
- Arithmetic Mean Vs Geometric Mean
Arithmetic Mean Examples
Example 1: The heights of five students are 5 ft, 6 ft, 4.6 ft, 5.5 ft, and, 6.2 ft respectively. Using the arithmetic mean formula, find the average (mean) height of the students.
To find: Average height of the students We have Arithmetic mean = {Sum of Observation}/{Total numbers of Observations} = (5 + 6 + 4.6 + 5.5 + 6.2)/5 = 27.3/5 = 5.46ft.
Answer: The average height of the students is 5.46 ft.
Example 2: If the arithmetic mean of 2m+3, m+2, 3m+4, 4m+5 is m+2, find m.
Solution: The data contains 4 observations : 2m+3,m+2,3m+4,4m+52m+3,m+2,3m+4,4m+5
Sum of 4 observations = [(2m+3)+(m+2)+(3m+4)+(4m+5)]/4 = (10m+14)/4
Mean = (10m + 14)/4
∴ m + 2 = (10m + 14)/4
4 × (m+2) = (10m + 14)
4m+8 = 10m + 14
Answer: ∴ m = -1
Example 3: The mean monthly salary of 10 workers of a group is ₹1445. One more worker whose monthly salary is ₹1500 has joined the group. Find the arithmetic mean of the monthly salary of 11 workers of the group.
Solution: Here, n = 10, x̄=1445
Using formula,
x̄ = ∑x i /n
∴∑x i = x̄ × n
∑x i = 1445 × 10 = 14450
(Total salary of 10 workers = ₹14450)
Total salary of 11 workers = 14450 + 1500 = ₹15950
Average salary of 11 workers = 15950/11 = 1450
Answer: ∴ Average monthly salary of 11 workers = ₹1450
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Arithmetic Mean
go to slide go to slide
FAQs on Arithmetic Mean
What is the definition of arithmetic mean.
The arithmetic mean is the simplest and most widely used measure of a mean, or average. It simply involves taking the sum of a group of numbers, then dividing that sum by the count of the numbers used in the series. For example, take the numbers 34, 44, 56, and 78. The sum is 212. To find the arithmetic mean we will divide the sum 212 by 4 (total numbers), this will give us the mean as 212/4 = 53.
What are Arithmetic Mean Formulas?
Here are the formulas related to arithmetic mean:
- Arithmetic mean of ungrouped data = Sum of all observations / Number of observations.
- Arithmetic mean of grouped data = ∑x i f i / ∑f i .
- Arithmetic mean using assumed mean method = A + (∑f i d i /∑f i ).
- Arithmetic mean using step deviation method = A + h × (∑f i u i /∑f i ).
How to Calculate the Arithmetic Mean?
In statistics , arithmetic mean (AM) is defined as the ratio of the sum of all the given observations to the total number of observations. For example, if the data set consists of 5 observations, the AM can be calculated by adding all the 5 given observations divided by 5.
How to Find the Arithmetic Mean Between 2 Numbers?
Add the two given numbers and then divide the sum by 2. For example, 2 and 6 are the two numbers, the arithmetic mean (which is nothing but AM or mean ) is calculated as follows: AM = (2+6)/2 = 8/2 = 4
What Are the Types of Arithmetic Mean?
In mathematics, we deal with different types of means such as arithmetic mean, harmonic mean, and geometric mean .
What Is the Use of Arithmetic Mean?
The arithmetic mean is a measure of central tendency. It allows us to know the center of the frequency distribution by considering all of the observations.
What Are the Characteristics of Arithmetic Mean?
Some important properties of the arithmetic mean (AM) are as follows:
- The sum of deviations of the items from their AM is always zero, i.e. ∑(x – X) = 0.
- The sum of the squared deviations of the items from AM is minimum, which is less than the sum of the squared deviations of the items from any other values.
- If each item in the arithmetic series is substituted by the mean, then the sum of these replacements will be equal to the sum of the specific items.
- If the individual values are added or subtracted with a constant, then the AM can also be added or subtracted by the same constant value.
- If the individual values are multiplied or divided by a constant value, then the AM is also multiplied or divided by the same value.
What Is the Sum of Deviations from Arithmetic Mean?
The sum of deviations from the arithmetic mean is equal to zero.
How to Find Arithmetic Mean for Grouped Data?
The arithmetic mean for ungrouped data is found using the formula: x̄ = (x₁f₁+x₂f₂+......+xₙfₙ) / ∑f i = ∑fx/n. Here, f₁+ f₂ + ... + fₙ = ∑f i indicates the sum of all frequencies.
What is the Arithmetic Mean Formula Used for Ungrouped Data?
The arithmetic mean for grouped data is calculated using the formula: x̄ = Sum of all observations / Number of observations.
Word Problems on Arithmetic Mean
Here we will learn to solve the three important types of word problems on arithmetic mean (average). The questions are mainly based on average (arithmetic mean), weighted average and average speed.
How to solve average (arithmetic mean) word problems?
To solve various problems we need to follow the uses of the formula for calculating average (arithmetic mean)
Average = (Sums of the observations)/(Number of observations)
Follow the explanation to solve the word problems on arithmetic mean (average):
1. The heights of five runners are 160 cm, 137 cm, 149 cm, 153 cm and 161 cm respectively. Find the mean height per runner.
Mean height = Sum of the heights of the runners/number of runners
= (160 + 137 + 149 + 153 + 161)/5 cm
Hence, the mean height is 152 cm.
2. Find the mean of the first five prime numbers.
The first five prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7 and 11.
Mean = Sum of the first five prime numbers/number of prime numbers
= (2 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 11)/5
Hence, their mean is 5.6
3. Find the mean of the first six multiples of 4.
The first six multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20 and 24.
Mean = Sum of the first six multiples of 4/number of multiples
= (4 + 8 + 12 + 16 + 20 + 24)/6
Hence, their mean is 14.
4. Find the arithmetic mean of the first 7 natural numbers.
The first 7 natural numbers are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7.
Hence, their mean is 4.
5. If the mean of 9, 8, 10, x, 12 is 15, find the value of x.
Mean of the given numbers = (9 + 8 + 10 + x + 12)/5 = (39 + x)/5
According to the problem, mean = 15 (given).
Therefore, (39 + x)/5 = 15
⇒ 39 + x = 15 × 5
⇒ 39 + x = 75
⇒ 39 - 39 + x = 75 - 39
Hence, x = 36.
More examples on the worked-out word problems on arithmetic mean:
6. If the mean of five observations x, x + 4, x + 6, x + 8 and x + 12 is 16, find the value of x.
Solution: Mean of the given observations
= x + (x + 4) + (x + 6) + (x + 8) + (x + 12)/5
= (5x + 30)/5
According to the problem, mean = 16 (given).
Therefore, (5x + 30)/5 = 16
⇒ 5x + 30 = 16 × 5
⇒ 5x + 30 = 80
⇒ 5x + 30 - 30 = 80 - 30
Hence, x = 10.
148 + 153 + 146 + 147 + 154
7. The mean of 40 numbers was found to be 38. Later on, it was detected that a number 56 was misread as 36. Find the correct mean of given numbers.
Calculated mean of 40 numbers = 38.
Therefore, calculated sum of these numbers = (38 × 40) = 1520.
Correct sum of these numbers
= [1520 - (wrong item) + (correct item)]
= (1520 - 36 + 56)
Therefore, the correct mean = 1540/40 = 38.5.
8. The mean of the heights of 6 boys is 152 cm. If the individual heights of five of them are 151 cm, 153 cm, 155 cm, 149 cm and 154 cm, find the height of the sixth boy.
Mean height of 6 boys = 152 cm.
Sum of the heights of 6 boys = (152 × 6) = 912 cm
Sum of the heights of 5 boys = (151 + 153 + 155 + 149 + 154) cm = 762 cm.
Height of the sixth boy
= (sum of the heights of 6 boys) - (sum of the heights of 5 boys)
= (912 - 762) cm = 150 cm.
Arithmetic Mean
Properties of Arithmetic Mean
Problems Based on Average
Properties Questions on Arithmetic Mean
- 9th Grade Math
From Word Problems on Arithmetic Mean to HOME PAGE
New! Comments
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math . Use this Google Search to find what you need.
- Preschool Activities
- Kindergarten Math
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- 10th Grade Math
- 11 & 12 Grade Math
- Concepts of Sets
- Probability
- Boolean Algebra
- Math Coloring Pages
- Multiplication Table
- Cool Maths Games
- Math Flash Cards
- Online Math Quiz
- Math Puzzles
- Binary System
- Math Dictionary
- Conversion Chart
- Homework Sheets
- Math Problem Ans
- Free Math Answers
- Printable Math Sheet
- Funny Math Answers
- Employment Test
- Math Patterns
- Link Partners
- Privacy Policy

Recent Articles
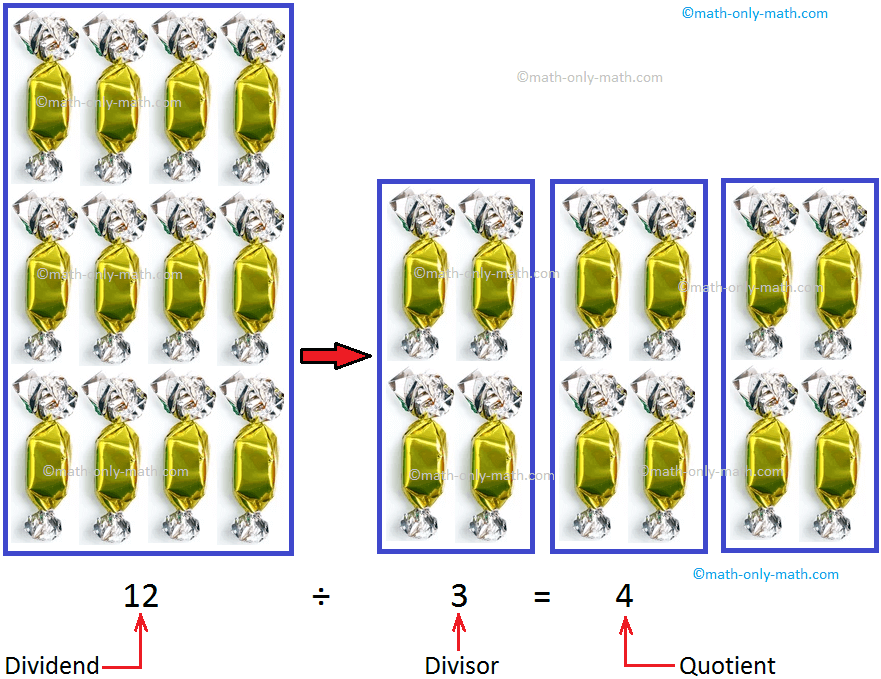
Terms Used in Division | Dividend | Divisor | Quotient | Remainder
Apr 01, 24 05:38 PM
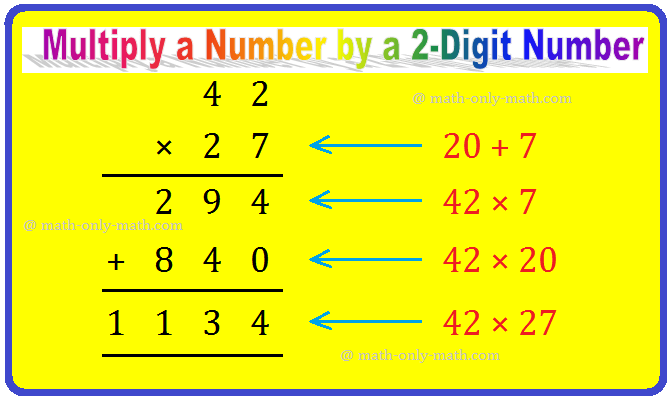
Multiply a Number by a 2-Digit Number | Multiplying 2-Digit by 2-Digit
Apr 01, 24 04:52 PM
Mental Math on Multiplication Worksheet | Multiplication Facts|Answers
Apr 01, 24 04:04 PM
Time Duration |How to Calculate the Time Duration (in Hours & Minutes)
Mar 31, 24 05:49 PM
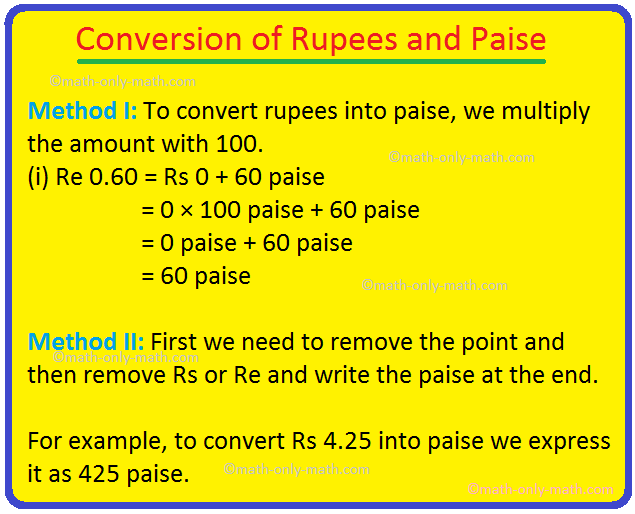
Conversion of Rupees and Paise | How to convert rupees into paise?
Mar 31, 24 05:34 PM
© and ™ math-only-math.com. All Rights Reserved. 2010 - 2024.
[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities Packs
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
- Averages and range
Mean in math
Here you will learn about the mean, including what the mean is and how to find the mean.
Students will first learn about the mean in math as part of statistics and probability in 6 th grade.
What is the mean in math?
The mean in math , specifically the arithmetic mean, is a type of average calculated by finding the total of the values and dividing the total by the number of values.
\text{Mean}=\cfrac{\text{total}}{\text{number of values}}
For example,
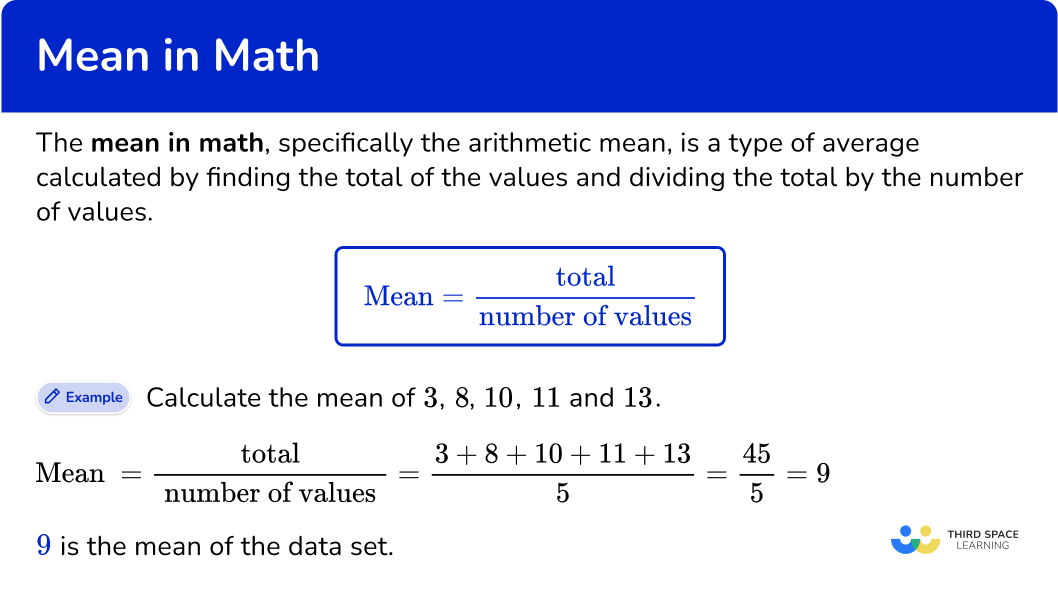
Calculate the mean of 3, \, 8, \, 10, \, 11 and 13.
\text {Mean }=\cfrac{\text { total }}{\text { number of values }}=\cfrac{3+8+10+11+13}{5}=\cfrac{45}{5}=9
9 is the mean of the data set.
This value, also known as the population mean, is a measure of central tendency. It summarizes a data set (population) with a single point. Median and mode are also measures of central tendency.
While all three measure center in some way, they are not the same. Mean can be thought of as sharing equally between all data points.
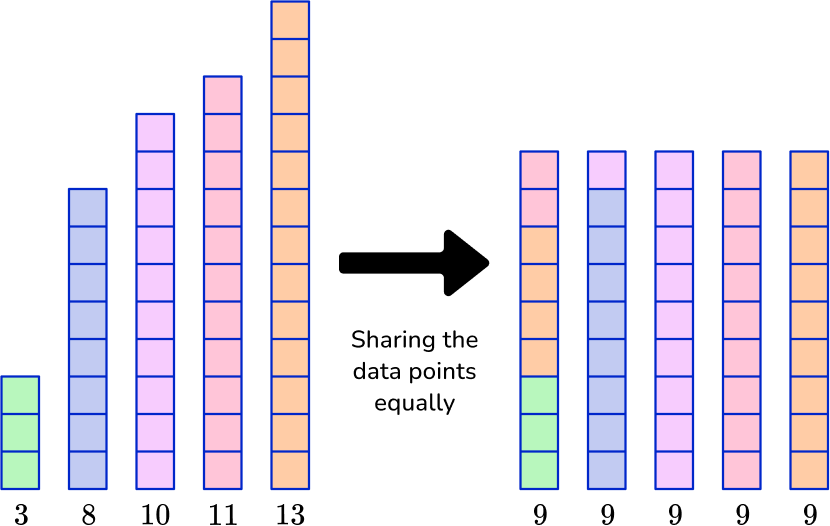
It is also important to consider that the number of observations (number of data points) changes how much each data point affects the mean.
Now add the data point 10 to each data set and recalculate the mean.
Notice that the mean in data set A grew by 1.25, while the mean of data set B grew by 0.7.
Since there are less data points in A , adding (or taking away) a data point impacts the mean more than in a data set with more points, like data set B.
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 6 th grade math?
- Grade 6 – Statistics and Probability (6.SP.A.3) Recognize that a measure of center for a numerical data set summarizes all of its values with a single number, while a measure of variation describes how its values vary with a single number.
How to calculate the mean in math
In order to calculate the mean in math:
Find the sum of the data points.
Divide the sum by the number of data points.
Write down the answer.
![arithmetic mean in problem solving [FREE] Averages and Range Check for Understanding (Grade 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Averages-and-Range-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Averages and Range Check for Understanding (Grade 6)
Use this quiz to check your 6th grade students’ understanding of averages and range. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th grade averages and range topics to identify areas of strength and support!
Mean in math examples
Example 1: finding the mean.
Calculate the mean value of this list of numbers:
2 \quad 7 \quad 9 \quad 10 \quad 12
2+7+9+10+12=40
2 Divide the sum by the number of data points.
There are 5 values in the data set. Divide the total by 5.
\text{Mean}=\cfrac{\text{total}}{\text{number of values}}=\cfrac{40}{5}=8
3 Write down the answer.
The mean is 8.
Example 2: finding the mean
Calculate the mean value of this set of numbers to the nearest tenth.
13 \quad 16 \quad 17 \quad 17 \quad 18 \quad 20
13+16+17+17+18+20=101
There are 6 values in the data set. Divide the total by 6.
\text{Mean}=\cfrac{\text{total}}{\text{number of values}}=\cfrac{101}{6}=16.8333…
16.8333… to the nearest tenth is 16.8.
16.8 is the mean.
Example 3: finding the mean
Calculate the mean value of this set of data to the nearest hundredth.
11 \quad 13 \quad 14 \quad 15 \quad 19 \quad 20 \quad 22
11+13+14+15+19+20+22=114
There are 7 values in the data set. Divide the total by 7.
\text{Mean}=\cfrac{\text{total}}{\text{number of values}}=\cfrac{114}{7}=16.2857…
16.2857… rounded to the nearest hundredth is 16.29.
16.29 is the mean.
Example 4: finding the mean
Calculate the mean value of this list of numbers.
101 \quad 102 \quad 105 \quad 106 \quad 108
101+102+105+106+108=522
\text{Mean}=\cfrac{\text{total}}{\text{number of values}}=\cfrac{522}{5}=104.4
104.4 is the mean.
How to solve a problem involving the mean in math
In order to solve a problem involving the mean in math:
Use the mean and number of values to find the total.
Find the sum of the known data points.
Subtract the sum of the known data points from the first total to find the missing data point.
Problem solving involving mean examples
Example 5: problem solving.
The mean of 4 values is 10.
Here are 3 of the values:
6 \quad 9 \quad 12
Find the 4^{th} value.
The mean of 4 values is 10. Multiply these together to find the total of the 4 numbers.
\text{Total of 4 values}=\text{mean} \times \text{number of values}=10\times 4=40
\text{Total of 3 values}=6+9+12=27
The 4^{th} value is 13.
Alternatively, you could use the equation for finding the mean. You could use x as the missing value.
Then rearrange and solve.
\begin{aligned} \text{Mean} &= \cfrac{\text{total}}{\text{number of values}}\\\\ 10&=\cfrac{6+9+12+x}{4}\\\\ 10 &= \cfrac{27+x}{4}\\\\ 40&=27+x\\\\ 13&=x \end{aligned}
Example 6: problem solving
The mean of 5 values is 14.
Here are 4 of the values:
5 \quad 11 \quad 13 \quad 19
Find the 5^{th} value:
The mean of 5 values is 14. Multiply these together to find the total of the 5 numbers.
\text{Total of 5 values}=\text{mean} \times \text{number of values}=14\times 5=70
\text{Total of 4 values}=5+11+13+19=48
The 5^{th} value is 22.
Alternatively, you could use the equation for finding the mean. You could use x as the missing value. Then rearrange and solve.
\begin{aligned} \text{Mean} &= \cfrac{\text{total}}{\text{number of values}}\\\\ 14&=\cfrac{5+11+13+19+x}{5}\\\\ 14 &= \cfrac{48+x}{5}\\\\ 70&=48+x\\\\ 22&=x\\\\ \end{aligned}
Teaching tips for mean in math
- Introduce mean with countable objects (like counters or connecting cubes). This will allow students to physically add all the data points together and then share them equally – matching the procedure for the mean. Doing a hands-on activity like this helps students make sense of what the mean represents and understand why the procedure to find mean works.
- Worksheets can be useful for teaching mean, but be sure to include a variety of question types – ones with mean missing, ones with a data point missing and a mixture of number types, such as fractions, decimals and integers.
Easy mistakes to make
- Confusing the mean and the median They are both average values, but do not represent the same average and are found in different ways. The median is the middle number (middle value) when the data set is arranged in ascending (or descending) order. The mean is a number that represents the data points equally shared and is found by adding all the values and then dividing by the number of data points.
- Forgetting the mean can be a decimal The mean does not have to be a whole number. It can be a decimal or a fraction. It may be a decimal which needs rounding.
- Thinking the mean has to be a number in the data set While the mean can be a number in the data set, often it is not. Adding the data points together and then dividing them by the number of data points allows for the mean to be a number outside of what is in the data set.
Related averages and range lessons
- Mean median mode
- Mode in math
- Range in math
Practice mean in math questions
1) Find the arithmetic mean of this set of values:
5 \quad 7 \quad 8 \quad 8 \quad 9

First calculate the sum of the numbers in the given set.
5+7+8+8+9=37
Then divide the sum by the number of data points.
\begin{aligned} \text{Mean}&= \cfrac{\text{total}}{\text{number of values}}\\\\ \text{Mean}&=\cfrac{5+7+8+8+9}{5}\\\\ \text{Mean}&= \cfrac{37}{5}\\\\ \text{Mean}&=7.4\\\\ \end{aligned}
2) Find the mean of this list of values:
3 \quad 5 \quad 6 \quad 9
First calculate the sum of the values.
\begin{aligned} \text{Mean}&= \cfrac{\text{total}}{\text{number of values}}\\\\ \text{Mean}&=\cfrac{3+5+6+9}{4}\\\\ \text{Mean}&= \cfrac{23}{4}\\\\ \text{Mean}&=5.75\\\\ \end{aligned}
3) Find the mean of this list of values. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
7 \quad 8 \quad 9 \quad 10 \quad 10 \quad 11
\begin{aligned} \text{Mean}&= \cfrac{\text{total}}{\text{number of values}}\\\\ \text{Mean}&=\cfrac{7+8+9+10+10+11}{6}\\\\ \text{Mean}&= \cfrac{55}{6}\\\\ \text{Mean}&=9.16666…\\\\ \text{Mean}&=9.17\\\\ \end{aligned}
4) Which data set has a mean of 6?
Since each of the given data sets have 6 data points, the total of the data points will be 6 \times 6 (the mean times the number of data points).
\begin{aligned} & 1+15+2+1+17+0=36 \\\\ & \text { Mean }=\cfrac{36}{6} \\\\ & \text { Mean }=6 \end{aligned}
5) The mean of 4 numbers is 9.
Here are 3 of the numbers:
6 \quad 8 \quad 15
What is the 4^{th} number?
The total of 4 numbers is:
\text{Total of 4 values}=\text{mean} \times \text{number of values}=9\times 4=36
The total of 3 numbers is:
The difference between the totals is:
The 4^{th} number is 7.
6) The mean of 6 numbers is 12.
Here are 5 of the numbers:
7 \quad 9 \quad 11 \quad 13 \quad 18
What is the 6^{th} number?
\text{Total of 4 values}=\text{mean} \times \text{number of values}=12\times 6=72
The total of 5 numbers is:
7+9+11+13+18=58
The 6^{th} number is 14.
Mean in math FAQs
No, the context in which the sample was collected may include negative numbers. For example, temperatures or account balances.
Instead of counting all data points equally, the mean of a set is found by counting (or “weighing”) certain data points more than others.
A way to quantify the amount of variation around the mean within a data set or population.
In a normal distribution, all the measures of center are the same and are exactly at the center value. Thinking about the data in percentages, 68\% of the points are within one standard deviation of the mean, median and mode.
Geometric mean and harmonic mean are two other types of means. These are both addressed in upper level mathematics.
The next lessons are
- Frequency table
- Representing data
- Frequency graph
- Cumulative frequency

Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs .
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
Privacy Overview

How do we calculate averages?
- Definition and problems involving the median
- Average pie method
- Interactive activity involving median and mean
Average is the result of adding all numbers in a set then dividing by amount of numbers.
The average of 1 and 5 is 3, because $$ (1+5)/2= 3 $$
The average of 1, 5, and 9 is 5, because $$ (1+5+9)/3=5 $$
Practice Problems
The average (arithmetic mean) of $$3$$ numbers is $$60$$. If two of the numbers are $$50$$ and $$60$$, what is the third number?
$$3*60=180$$, which is the total number of points earned.
The two numbers we do know are $$50$$ and $$60$$ which add up to $$110$$.
The third number is $$180-110=70$$ since all three numbers must add up to $$180$$.
TEST METHOD: AVERAGE PIE
Use the average pie to chart out what you know and simplify this problem.
In the triangles below what is the average (arithmetic mean) of $$a$$, $$b$$, $$c$$, $$x$$, and $$y$$?

$$x+y=90$$ since the other angle is $$90°$$ and a triangle has $$180°$$ in total.
Tip: Total degrees = $$180+180=360$$, the total number of degrees in two triangles.
In a certain game, each of the $$5$$ players received a score between $$0$$ and $$100$$ inclusive. If their average (arithmetic mean) score was $$80$$, what is the greatest possible number of the $$5$$ players who could have received a score of $$50$$?
METHOD: AVERAGE PIE . You know the total $$(5*80=400)$$. You know the number ($$5$$), and you know the average ($$80$$). You also know the answer is between $$0$$-$$4$$. By trial and error you should be able to answer this one.
KEYWORDS: "greatest possible", " inclusive "
If you're clueless, NO MATTER what you should be able to eliminate A and guess. If you couldn't eliminate A, review how to solve average problems.
The average (arithmetic mean) of $$a$$, $$b$$, and $$c$$ is equal to the median of $$a$$, $$b$$, and $$c$$. If $$0 < a < b < c$$, which of the following must be equal to $$b$$?
- $$(a+c)/2$$
- $$(a+c)/3$$
- $$(c-a)/2$$
- $$(c-a)/3$$
A. $$(a+c)/2$$
TEST KEYWORD: "MUST"
Plug in numbers for $$a$$, $$b$$, $$c$$ and see which answer 'must' work.
The average (arithmetic mean) of nine numbers is $$9$$. When a tenth number is added the average of the ten numbers is also $$9$$. What is the tenth number ?
Eliminate some obvious wrong ones B , C , E . Remember to always estimate and have a good rough estimate of where the answers should be which is right around the original average of $$9$$; if you added a new number that was much higher or lower like say $$0$$ or $$1,000$$ the average could never remain $$9$$.
TEST TRAP: D is a trap and since you're not dealing with the first few problems you should not have gone on without really thinking about his one.
Ultimate Math Solver (Free) Free Algebra Solver ... type anything in there!
Popular pages @ mathwarehouse.com.
Weighted Average Problems
In these lessons, we will learn how to solve weighted average problems.
Related Pages Mean, Median, Mode, Range Other Algebra Word Problems
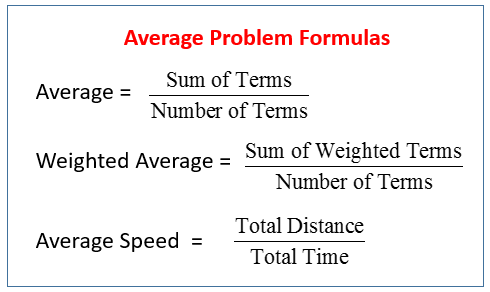
There are three main types of average problems commonly encountered in school algebra: Average (Arithmetic Mean) , Weighted Average and Average Speed .
The following table gives the formulas for average problems: Weighted Average, Mean, and Average Speed. Scroll down the page for examples and solutions.
One type of average problems involves the weighted average - which is the average of two or more terms that do not all have the same number of members. To find the weighted term, multiply each term by its weighting factor, which is the number of times each term occurs.
The formula for weighted average is:
Example: A class of 25 students took a science test. 10 students had an average (arithmetic mean) score of 80. The other students had an average score of 60. What is the average score of the whole class?
Solution: Step 1: To get the sum of weighted terms, multiply each average by the number of students that had that average and then sum them up.
80 × 10 + 60 × 15 = 800 + 900 = 1700
Step 2: Total number of terms = Total number of students = 25
Step 3: Using the formula,
Answer: The average score of the whole class is 68.
Be careful! You will get the wrong answer if you add the two average scores and divide the answer by two.
Example of how to calculate the weighted average
Example: At a health club, 80% of the members are men and 20% of the members are women. If the average age of the men is 30 and the average age of the women is 40, what is the average age of all the members?
How to find the weighted average given a frequency table?
Example: A group of people were surveyed for how many movies they see in a week. The table below shows the result of the survey. (a) How many people took part in the survey? (b) What was the total number of movies seen in a week by all the survey takers? (c) What was the average number of movies seen in a week per person surveyed?
How to solve Weighted Averages and Mixture Problems? Mixture problems are problems in which two or more parts are combined into a whole.
- Premium coffee is $9.50/lb, Supreme coffee is $11.75/lb and Blend coffee is $10.00/lb. How many pounds of Premium coffee beans should be mixed with two pounds of Supreme coffee to make Blend coffee?
- A car’s radiator should contain a solution of 50% antifreeze. Bo has 2 gallons of 35% antifreeze. How many gallons of 100% antifreeze should he add to his solution to produce a solution of 50% antifreeze?
How to solve Weighted Average Word Problems?
- How many pounds of mixed nuts selling for $4.75 per pound should be mixed with 10 pounds of dried fruit selling for $5.50 per pound to obtain a trail mix that sells for $4.95 per pound?
- A chemistry experiment calls for a 30% solution of copper sulfate. Kendra has 40 milliliters of 25% solution. How many milliliters of 60% solution should she add to make a 30% solution?
- A car and an emergency are heading toward each other. The car is traveling at a speed of 30 mph or 44 feet per second. The emergency vehicle is traveling at a speed of 50 mph or about 74 feet per second. If the vehicles are 1000 feet apart and the conditions are ideal, in how many seconds will the drive of the car first hear the siren?

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
GMAT Math : Arithmetic Mean
Study concepts, example questions & explanations for gmat math, all gmat math resources, example questions, example question #2022 : problem solving questions.
Salaries for employees at ABC Company: 1 employee makes $25,000 per year, 4 employees make $40,000 per year, 2 employees make $50,000 per year and 5 employees make $75,000 per year.
What is the average (arithmetic mean) salary for the employees at ABC Company?

Example Question #2023 : Problem Solving Questions
A bowler had an average (arithmetic mean) score of 215 on the first 5 games she bowled. What must she bowl on the 6th game to average 220 overall?

For the first 5 games the bowler has averaged 215. The equation to calculate the answer is

which simplifies to:
After subtracting 1,075 from each side we reach the answer:

Example Question #2021 : Problem Solving Questions
Ashley averaged a score of 87 on her first 5 tests. She scored a 93 on her 6th test. What is her average test score, assuming all 6 tests are weighted equally?

Now combine that with the 6th test to find the overall average.

Example Question #1 : Arithmetic Mean
Sabrina made $3,000 a month for three months, $4,000 the next month, and $5,200 a month for the following two months. What was her average monthly income for the 6 month period?

Luke counts the number of gummy bears he eats every day for 1 week: {39, 18, 24, 51, 40, 15, 23}. On average, how many gummy bears does Luke eat each day?

Example Question #2027 : Problem Solving Questions
The average of 10, 25, and 70 is 10 more than the average of 15, 30, and x. What is the missing number?

So the average of 15, 30, and the unknown number is 25 or, 10 less than the average of 10, 25, and 70 (= 35)

What is the average of 2 x , 3 x + 2, and 7 x +4?
not enough information

Example Question #2029 : Problem Solving Questions
The average high temperature for the week is 85. The first six days of the week have high temperatures of 89, 76, 92, 90, 80, and 84, respectively. What is the high temperature on the seventh day of the week?

Example Question #1 : Calculating Arithmetic Mean
Jimmy's grade in his finance class is based on six equally-weighted tests. If Jimmy scored 98, 64, 82, 90, 70, and 88 on the six tests, what was his grade in the class?

Example Question #2031 : Gmat Quantitative Reasoning
Sandra's grade in economics depends on seven tests - five hourly tests, a midterm, and a final exam. The midterm counts twice as much as an hourly test; the final, three times as much.
Sandra's grades on the five hourly tests are 84, 86, 76, 89, and 93; her grade on the midterm was 72. What score out of 100 must she achieve on the final exam so that her average score at the end of the term is at least 80?

She cannot achieve this average this term

This is a weighted mean, with the hourly tests assigned a weight of 1, the midterm assigned a weight of 2, and the final assigned a weight of 3. The total of the weights will be

Tired of practice problems?
Try live online GMAT prep today.

Report an issue with this question
If you've found an issue with this question, please let us know. With the help of the community we can continue to improve our educational resources.
DMCA Complaint
If you believe that content available by means of the Website (as defined in our Terms of Service) infringes one or more of your copyrights, please notify us by providing a written notice (“Infringement Notice”) containing the information described below to the designated agent listed below. If Varsity Tutors takes action in response to an Infringement Notice, it will make a good faith attempt to contact the party that made such content available by means of the most recent email address, if any, provided by such party to Varsity Tutors.
Your Infringement Notice may be forwarded to the party that made the content available or to third parties such as ChillingEffects.org.
Please be advised that you will be liable for damages (including costs and attorneys’ fees) if you materially misrepresent that a product or activity is infringing your copyrights. Thus, if you are not sure content located on or linked-to by the Website infringes your copyright, you should consider first contacting an attorney.
Please follow these steps to file a notice:
You must include the following:
A physical or electronic signature of the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf; An identification of the copyright claimed to have been infringed; A description of the nature and exact location of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright, in \ sufficient detail to permit Varsity Tutors to find and positively identify that content; for example we require a link to the specific question (not just the name of the question) that contains the content and a description of which specific portion of the question – an image, a link, the text, etc – your complaint refers to; Your name, address, telephone number and email address; and A statement by you: (a) that you believe in good faith that the use of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright is not authorized by law, or by the copyright owner or such owner’s agent; (b) that all of the information contained in your Infringement Notice is accurate, and (c) under penalty of perjury, that you are either the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf.
Send your complaint to our designated agent at:
Charles Cohn Varsity Tutors LLC 101 S. Hanley Rd, Suite 300 St. Louis, MO 63105
Or fill out the form below:
Contact Information
Complaint details.

If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Course: 3rd grade > Unit 8
- Finding patterns in numbers
- Recognizing number patterns
- Math patterns
- Intro to even and odd numbers
- Patterns with multiplying even and odd numbers
- Patterns with even and odd
- Patterns in hundreds chart
- Patterns in multiplication tables
Arithmetic patterns and problem solving: FAQ
What's the difference between a one-step and two-step word problem, what is a 2 -step expression, how do we use estimation in word problems, what are patterns in arithmetic, how do we use the topics from this lesson in the real world, want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
Using the Arithmetic Mean-Geometric Mean Inequality in Problem Solving
A Presentation to the Annual Meeting of School Mathematics and Science Association, Birmingham, November 8, 2012 , was prepared using some parts of this paper. PDF version The Arithmetic Mean-Geometric Mean Inequality (AM-GM Inquality) is a fundamental relationship in mathematics. It is a useful tool for problems solving and building relationships with other mathematics. It should find more use in school mathematics than currently. It what follows I present an introduction to the theorem, some background and generalizations, alternative demonstrations of the proof, and examples of problems that can be explored by using the AM-GM Inquality. I will rely heavily on a collection of problems and essays on my web site: Http://jwilson.coe.uga.edu and the sub-directory for my mathematics problem solving course at the University of Georgia . I will concentrate on the theorem for two positive numbers in my examples, but I mention the generalizations below and occasionally use the case for three positive numbers. Arithmetic Mean - Geometric Mean Inequality For real positive numbers a and b, the AM-GM Inequality for two numbers is: Clearly, the AM-GM Inequality can be generalized for n positive numbers. The link poses the problem of generalizing the proof following the lines of argument advanced by Courant and Robbins (1942). That is, The AM-GM Inequality can also be generalized to its inclusion in relation to other means such as the Harmonic Mean (HM) or the Root Mean Square (RMS -- sometimes called the Quadratic Mean). In particular, for two positive numbers a and b, Geometric demonstration of the RMS-AM-GM-HM Inequality
At a more advanced level (perhaps more fundamental?) all of these means are instances of Power Means where the power parameter p takes on different values for the different means. These may also be called Generalized Means.
What is the Value of this Theorem? An Example.
The AM-GM for two positive numbers can be a useful tool in examining some optimization problems. For example, it is well known that for rectangles with a fixed perimeter, the maximum area is given by a square having that perimeter.
Ed. Comment: The word "minimum" in the second sentence below should be "maximum"
2a + 2b = 10.
The red graph represents the area function of the graph as either of a or b varies from 0 to 5. Let b represent the length of one side and 5 - b the length of the other.
Area = ab = b(5 - b) for 0 < b < 5
Points on the blue curve, Area = 6.25 are always greater than points on the red curve (That is, the area of the rectangle is always less that 6.25) and the blue curve (a horizontal line representing a constant) is tangent to the red curve if and only if b = (5 - b), i.e., b =2.5.
Setting this up with the usual function notation, let the Perimeter of the rectangle equal 10 and let one side be x. The the other side is 5 - x.
The utility of the AM-GM Inequality is that the replacement function after the application of the AM-GM inequality is a constant line tangent to the previous function. The area is always less than the constant AND it is equal to that constant when a = b. In our example for P = 10, a = b = 2.5 when the rectangle is a square.
From my web page, here is a problem posed for students:
The second problem, where ab is a constant rather than a + b, is a nice contrast to the first and it also follows quickly from the AM-GM Inequality:
Alternative Proofs and Demonstrations
Arithmetic mean-geometric mean inequality.
In this section, I will limit the exploration to the simplest case: The arithmetic mean and geometric mean of two positive numbers. In my Problem Solving course I pose AS AN EXPLORATION that the student find a least 5 demonstrations or proofs. Seeing multiple approaches to this relation can help with understanding it, seeing its importance, and finding it useful as a problem solving tool.
Some algebra
A Geometric Demonstration
Another geometric suggestion.
Construct a semicircle with a diameter a + b. The radius will be the Arithmetic Mean of a and b. Construct a perpendicular to the diameter from common endpoint of the segments of length a and b. From the intersection of this perpendicular with the semicircle construct the red segment. This segment will always have a length less than or equal to the radius of the circle and it will be equal only if a = b.
This example is closely related to the well known geometric theorem that the altitude of a right triangle from the 90 degree vertex to the hypothenuse will be the geometric mean of the two segments cut off on the hypotenuse.
Another Geometry Example
Another Algebra Demonstration
This demonstration begins with the identity: Since we have with equality if and only if a = b.
Given two tangent circles of radii a and b. Construct a common external tangent to the two circl3s and draw radii of each circle to the common tangent. Find the length indicatec by ? along the common tanget in terms of a and b.
Solution: by constructing a segment parallel to the one under study, a right triangle with legs of length ? and a-b, and hypotenuse of length a+b. the segment along the common tangent has length twice the geometric mean of a and b.
More Geometry
Consider a circle with chords AB and CD. Let the CD pass through the midpoint M of AB.
Let AM = MB = z and let CM = x, MD = y. The lengths are all positive values.
By an elementary theorem of geometry the products of the parts of the chords are equal.
We know that x + y ≥ 2z with equality only if M is the midpoint of CD.
Something Different
Solving Problems with the AM-GM Inequality
Cost of fencing a field .
Problem : A farmer wants to fence in 60,000 square feet of land in a rectangular plot along a straight highway. The fence he plans to use along the highway costs $2 per foot, while the fence for the other three sides costs $1 per foot. How much of each type of fence will he have to buy in order to keep expenses to a minimum? What is the minimum expense? Solution : (This is a typical calculus problem but no calculus is needed!)
The problem is to find minimum values for this function in the range or 0 < x < π. This one requires some change in the form of the equation in order to apply the AM-GM Inequality. First, however, it is helpful to see a graph and have some sense of the equation. The graph at the right suggests that there may be two minimum values in the range 0 < x < π.
Construct a Square with Same Area as a Given Rectangle
The problem is to construct a square with straightedge and compass that is the same area as a given rectangle. The area will be ab and so the length of the side of the square is the geometric mean. Consider: The red segment is the geometric mean of a and b.
Maximum Area of a Sector of a Circle With Fixed Perimeter
Understanding the problem. A sector of a circle has a perimeter made up of two radii and an arc of the circle connecting the endpoints of the two radii. Compare the areas of three sectors -- each with P = 100 -- central angles of 45 degrees, 90 degrees, and 180 degrees. These are sectors that are an eighth circle, quarter circle, and semicircle. As the angles increas, the radii become shorter because more of the fixed perimeter is in the arc. Note these angles are When these three areas are computed we get Clearly, as the angle increases from 45 to 90 to 180 the area increases and then decreases. Somewhere there is a maximum area. Where? Sector as Fraction of a Circle
Let k be the fraction of a circle represented by the sector. 0 < k < 1. The Perimeter is a constant and so we can represent it as twice the radius plus the fraction of the circumference.
The area of the sector in the fraction notation can be formed as either a function of r or a function of k, depending on a subsitution of r or k from the perimeter equation. Either one can be used with the AM-GM Inequality to reach closure on the problem:
Looking back at the example when P = 100, the maximum area would be when r = 25 and therefore the arc length is 50. The angle is a little less than 120 degrees. Sector in Radian Measure
The parallel of this solution with the one where the square was the maximum area for rectangles with fixed perimeter is worth noting.
Inequalities Problems
Comparison of altitude and median in a right triangle.
Construct segments from the endpoints of the diameter to complete a right triangle.
Maximum and Minimum of
For x > 0, using the arithmetic mean-geometric mean inequality,
Therefore the value of the function is always less than or equal to .5 and it is equal to .5 only when x = 1.
For x < 0, a similar argument leads to finding the minimum of the function at x = -1. Since the Arithmetic Mean -- Geometric Mean Inequality holds only for postitive values, when x < 0 we have to apply the inequality to - x and - 1/x. We know
Keep in mind this is for x< 0 so -x and -1/x are postive. Multiplying each side of the inequality by -1 gives
and equality occurs when x = -1. Therefore the value of the function is always more than or equal to -0.5 and it is equal to -0.5 only when x = -1.
Maximum of f(x) = (1-x)(1+x)(1+x)
We have three factors in the function and we want to know when the function reaches a maximum in the interval [0,1]. In order to take advantage of the AM-GM Inequality, we need the sum of these factors to equal a constant. That is we need -2x rather than -x. We can get that by the following
The function reaches this maximum value for x in [0,1] if and only if
2(1 - x) = 1 + x 2 - 2x = 1 + x 1 = 3x
Minimum Surface Area of a Can of Fixed Volume
In packaging a product in a can the shape of right circular cylinder, various factors such as tradition and supposed customer preferences may enter into decisions about what shape (e.g. short and fat vs. tall and skinny) can might be used for a fixed volume. Note, for example, all 12 oz. soda cans have the same shape -- a height of about 5 inches and a radius of about 1.25 inches. Why? What if the decison was based on minimizing the material used to make the can? This would mean that for a fixed volume V the shape of the can (e.g. the radius and the height) would be determined by the minimum surface area for the can. What is the relationship between the radius and the height in order to minimize the surface area for a fixed volume? What would be the shape of a 12 ounce soda can that minimizes the amount of aluminum in the can? The Volume is fixed.
The Surface area is a function of r and h.
What is the minimum S?
( Note that we have use the AM-GM Inequality for three positive numbers )
Maximum area of a Pen, fixed length of fencing, with Partitions Parallel to a Side
Suppose you have 100 feet of fencing. You want a rectangular pen with a partition parallel to a side. The 100 feet of fencing must enclose the four sides and the partition. What is the shape of the pen and what is the maximum area? Show that the dimensions of the maximum area pen is 25 ft. by 16.67 ft. with maxim area of approximately 417.7 sq. ft.
Prove the Maximum Area of a Triangle with Fixed Perimeter is Equilateral
Minimum distance from (0,0) to.
Find a point on the graph of that is closest to the origin.
(follow the link to the discussion)
Maximum Area of a Triangle with Sides of 9, 40x, and 41x
Given a triangle with one side of length 9 units and the ratio of the other two sides is 40/41. Find the Maximum Area. (use link for discussion)
The Box Problem
Use the Arithmetic Mean-Geometric Mean Inequality to find the maximum volume of a box made from a 25 by 25 square sheet of cardboard by removing a small square from each corner and folding up the sides to form a lidless box.
Theorem: In the Product of n positive numbers is equal to 1 then the sum if the numbers is greater than or equal to n.
Clearly, the proof of 3 implies the first two.
Finding the Square Root
This sets up an efficient process for obtaining successive estimates with a hand calculator, a spreadsheet, or by paper and pencil. On the right is a part of a sqreadsheet showing calculation for . The process quickly converges to a good estimate. Click HERE for the Excel file. Enter in cell A1 the value N for which the square root is wanted.
ARITHMETIC MEAN PROBLEMS
Problem 1 :
John studies for 4 hours, 5 hours and 3 hours respectively on three consecutive days. How many hours does he study daily on an average?
The average study time of John
= Total number of study hours / Number of days for which he studied
= (4 + 5 + 3) / 3
= 12 / 3
= 4 hours
Thus, we can say that John studies for 4 hours daily on an average.
Problem 2 :
A batsman scored the following number of runs in six innings:
36, 35, 50, 46, 60, 55
Calculate the mean runs scored by him in an inning.
To find the mean, we find the sum of all the observations and divide it by the number of observations.
Mean = Total runs / Number of innings
= (36 + 35 + 50 + 46 + 60 + 55) / 6
= 47
Thus, the mean runs scored in an inning are 47.
Problem 3 :
The ages in years of 10 teachers of a school are:
32, 41, 28, 54, 35, 26, 23, 33, 38, 40
What is the mean age of these teachers?
Mean age of the teachers
= Sum of age of teachers / Number of teachers
= (23 + 26 + 28 + 32 + 33 + 35 + 38 + 40 + 41 + 54) /10
= 350 / 10
= 35 years
Problem 4 :
Following table shows the points of each player scored in four games:
Now answer the following questions:
(i) Find the mean to determine A’s average number of points scored per game.
(ii) To find the mean number of points per game for C, would you divide the total points by 3 or by 4? Why?
(iii) B played in all the four games. How would you find the mean?
(iv) Who is the best performer?
(i) Mean score of A = (14 + 16 + 10 + 10) / 4
= 12.5
Mean score of A per game is 12.5
(ii) To find the mean number of points per game for C, we have to divide the total points by 3.
Because he didn't participate in game 3. Total number of games he played is 3.
(iii) Mean score of B = (0 + 8 + 6 + 4) / 4
= 18/4
= 4.5
Mean score of B per game is 4.5
(iv) To choose the best performer, we have to find the mean score of each player.
Mean score of C = (8 + 11 + 13) / 3
= 32/3
= 10.6
Mean score of C per game is 10.6
Hence C is the best performer.

Apart from the stuff given above, if you need any other stuff in math, please use our google custom search here.
Kindly mail your feedback to [email protected]
We always appreciate your feedback.
© All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
- Sat Math Practice
- SAT Math Worksheets
- PEMDAS Rule
- BODMAS rule
- GEMDAS Order of Operations
- Math Calculators
- Transformations of Functions
- Order of rotational symmetry
- Lines of symmetry
- Compound Angles
- Quantitative Aptitude Tricks
- Trigonometric ratio table
- Word Problems
- Times Table Shortcuts
- 10th CBSE solution
- PSAT Math Preparation
- Privacy Policy
- Laws of Exponents
Recent Articles
Honors Algebra 2 Problems on Solving Logarithmic Equations
Apr 01, 24 07:22 PM
Honors Algebra 2 Problems on Solving Exponential Equations
Mar 30, 24 11:45 PM
Properties of Parallelograms Worksheet
Mar 30, 24 09:11 PM

- Math Article
Mean Questions
In mathematics and statistics, the mean is one of the important concepts that can be understood easily without much prior knowledge. Different types of the mean are defined based on the data provided. In this article, you will get questions and solutions for finding the mean of a given data set and grouped data (frequency distribution). These questions will help the students of Classes 9 and 10 to get enough practice for this concept.
What is Mean in Statistics?
Mean is one of the measures of central tendency in statistics. The mean is the average of the given data set, which means it can be calculated by dividing the sum of the given data values by the total number of data values.
Mean for ungrouped data:
Mean (x̄) = ∑x i /n
x i = x 1 , x 2 , x 3 ,…, x n such that i = 1, 2, 3,…n.
Number of observations = n
Mean for grouped data:
Mean (x̄) = ∑f i x i / ∑f i
Here, f i ’s are frequencies of x i ’s.
Mean Questions and Answers
1. Calculate the mean from the data showing marks of students in a class in a test: 40, 50, 55, 78, 58.
Given marks:
40, 50, 55, 78, 58
Here, the number of data values = 5
We know that:
Mean = Sum of data values/Total number of data values
= (40 + 50 + 55 + 78 + 58)/5
Therefore, the mean for the given data is 56.2.
2. A class consists of 50 students, out of which 30 are girls. The mean of marks scored by girls in a test is 73 (out of 100), and that of boys is 71. Determine the mean score of the whole class.
Total number of students in a class = 50
Number of girls in the class = 30
Number of boys in the class = 50 – 30 = 20
Mean marks scored by girls = 73
Mean marks scored by boys = 71
Thus, the total marks scored by girls = 73 × 30 = 2190
Also, the total marks scored by boys = 71 × 20 = 1420
Mean score of the class = (Total marks scored by girls and boys)/Total number of students
= (2190 + 1420)/50
3. The mean of the following distribution is 50.
Find the value of a and hence the frequencies of 30 and 70.
We know that,
Mean for grouped data (x̄) = ∑f i x i /n
(640a + 2800)/ (12a + 60) = 50 {given that mean = 50}
640a + 2800 = 50(12a + 60)
640a + 2800 = 600a + 3000
640a – 600a = 3000 – 2800
Therefore, the frequency for 30 = 5a + 3 = 5(5) + 3 = 28
And the frequency for 70 = 7a – 11 = 7(5) – 11 = 24
4. Find the mean salary of 60 workers of a factory from the following table:
Mean = (305000)/60 = 5083.33.
Therefore, the mean salary = Rs. 5083.33
5. A total of 25 patients admitted to a hospital are tested for levels of blood sugar, (mg/dl) and the results obtained were as follows:
87, 71, 83, 67, 85, 77, 69, 76, 65, 85, 85, 54, 70, 68, 80, 73, 78, 68, 85, 73, 81, 78, 81, 77, 75
Find the mean (mg/dl) of the above data.
Sum of data values = 87 + 71 + 83 + 67 + 85 + 77 + 69 + 76 + 65 + 85 + 85 + 54 + 70 + 68 + 80 + 73 + 78 + 68 + 85 + 73 + 81 + 78 + 81 + 77 + 75
Mean = 1891/25
6. Calculate the mean for the following distribution.
Mean = a + (∑f i d i /∑f i )
= 47.5 + (435/30)
= 47.5 + 14.5
7. The distribution below shows the number of wickets taken by bowlers in one-day cricket matches. Find the mean number of wickets by choosing a suitable method. What does the mean signify?
The given distribution has unequal class heights. So, we can use the direct method for calculating the mean.
Mean = ∑f i x i / ∑f i
Here the mean signifies that, on average, 45 bowlers take 152.89 wickets.
8. A survey was conducted by a group of students as a part of their environment awareness programme, in which they collected the following data regarding the number of plants in 20 houses in a locality. Find the mean number of plants per house.
Which method did you use for finding the mean, and why?
Here, the values of fi and xi are small. Thus, we can use the direct method to calculate the mean.
So, Mean = ∑f i x i / ∑f i
Therefore, the mean number of plants = 8.1
9. The following distribution shows the daily pocket allowance of children of a locality. The mean pocket allowance is Rs 18. Find the missing frequency x.
Mean pocket allowance = a + (∑f i d i / ∑f i )
18 + [(2x – 40)/(44 + x)] = 18 [from the given]
(2x – 40)/(44 + x) = 18 – 18
(2x – 40)/(44 + x) = 0
2x – 40 = 0
Hence, the missing frequency is 20.
10. The following is the cumulative frequency distribution (of less than type) of 1000 persons, each one of age 20 years and above. Determine the mean age.
For the given frequency distribution, we need to write the class intervals and frequencies and then proceed with the necessary calculations for estimating the mean age.
Mean = a + h(∑f i u i /∑f i )
= 55 + 10(-370/1000)
= 55 – 3.7
Therefore, the mean age is 51.3 years.
Practice Questions on Mean
- The points scored by a basketball team in a series of matches are as follows: 17, 2, 7, 27, 25, 5, 14, 18, 10, 24, 48, 10, 8, 7, 10, 28
Find the mean for the data.
- 5 people were asked about the time in a week they spent doing social work in their community. They said 10, 7, 13, 20 and 15 hours, respectively. Find the mean (or average) time in a week devoted by them to social work.
- The following table gives the daily income of ten workers in a factory. Find the arithmetic mean.
- The frequency distribution table of agricultural holdings in a village is given below.
Find the mean agricultural holdings of the village.
- Calculate the mean for the following distribution.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Is Your AI-First Strategy Causing More Problems Than It’s Solving?
- Oguz A. Acar

Consider a more balanced and thoughtful approach to AI transformation.
The problem with an AI-first strategy lies not within the “AI” but with the notion that it should come “first” aspect. An AI-first approach can be myopic, potentially leading us to overlook the true purpose of technology: to serve and enhance human endeavors. Instead, the author recommends following 3Ps during an AI transformation: problem-centric, people-first, and principle-driven.
From technology giants like Google to major management consultants like McKinsey , a rapidly growing number of companies preach an “AI-first” strategy. In essence, this means considering AI as the ultimate strategic priority , one that precedes other alternative directions. At first glance, this strategy seems logical, perhaps even inevitable. The figures speak for themselves: the sheer volume of investment flowing into AI technologies shows the confidence levels in an increasingly AI-driven future.
- Oguz A. Acar is a Chair in Marketing at King’s Business School, King’s College London.
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers (or variables) is the sum of all the numbers, divided by the number of numbers - the average of the set. If we let denote Arithmetic Mean, . is the arithmetic mean of the numbers .. For example, if I wanted to find the average of the numbers 3, 1, 4, 1, and 5, I would compute: Arithmetic means show up frequently in contest problems, often in the AM-GM ...
The arithmetic mean of ungrouped data is calculated using the formula: Mean x̄ = Sum of all observations / Number of observations. Example: Compute the arithmetic mean of the first 6 odd natural numbers. Solution: The first 6 odd natural numbers: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11. x̄ = (1+3+5+7+9+11) / 6 = 36/6 = 6. Thus, the arithmetic mean is 6.
Follow the explanation to solve the word problems on arithmetic mean (average): 1. The heights of five runners are 160 cm, 137 cm, 149 cm, 153 cm and 161 cm respectively. Find the mean height per runner. Solution: Mean height = Sum of the heights of the runners/number of runners. = (160 + 137 + 149 + 153 + 161)/5 cm.
Arithmetic Mean Formula. To find the arithmetic mean of a set of observations, just add them all together and divide the sum by the number of data points. To compute the mean set of observations, use the arithmetic mean formula: Arithmetic mean = Sum of all given values / Total number of values. Also, read: Mean
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KgZ3wn3lfS0&t=261s Finding the Arithmetic Means| Explain in Detailed https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VpWBNiGUWac Solving Lin...
The mean in math, specifically the arithmetic mean, is a type of average calculated by finding the total of the values and dividing the total by the number of values. \text{Mean}=\cfrac{\text{total}}{\text{number of values}} ... Example 5: problem solving. The mean of 4 values is 10. Here are 3 of the values: 6 \quad 9 \quad 12 . Find the 4^{th ...
How to find the arithmetic mean or average? Add up all the numbers. Divide the total by how many there are. Solving Math Problems : Finding the Mean. In math, the mean is found by adding pieces of data together and dividing by the number of pieces of data. Example: Find the mean of 2, 8, 13, 4, 21, 18. Show Video Lesson.
The mean of a set of real numbers usually refers to the arithmetic mean of the set (also known as the average ). For example, the arithmetic mean of the members of the set {3, 5, 10} is. However, there are numerous other kinds of various means used in mathematics and statistics .
For ungrouped data, we can easily find the arithmetic mean by adding all the given values in a data set and dividing it by a number of values. Mean, x̄ = Sum of all values/Number of values. Example: Find the arithmetic mean of 4, 8, 12, 16, 20. Solution: Given, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20 is the set of values. Sum of values = 4+ 8+12+16+20 = 60.
Select amount. $10. $20. $30. $40. Other. Operations and Algebraic Thinking 201-210 2 units · 15 skills. Unit 1 Problem solving with arithmetic. Unit 2 Factors, multiples, and patterns.
A. $$0$$ Eliminate some obvious wrong ones B, C, E.Remember to always estimate and have a good rough estimate of where the answers should be which is right around the original average of $$9$$; if you added a new number that was much higher or lower like say $$0$$ or $$1,000$$ the average could never remain $$9$$.
Step 1: To get the sum of weighted terms, multiply each average by the number of students that had that average and then sum them up. 80 × 10 + 60 × 15 = 800 + 900 = 1700. Step 2: Total number of terms = Total number of students = 25. Step 3: Using the formula, Answer: The average score of the whole class is 68. Be careful!
In algebra, the AM-GM Inequality, also known formally as the Inequality of Arithmetic and Geometric Means or informally as AM-GM, is an inequality that states that any list of nonnegative reals' arithmetic mean is greater than or equal to its geometric mean. Furthermore, the two means are equal if and only if every number in the list is the same. In symbols, the inequality states that for any ...
Find the mean number of raisins. raisins. Show Calculator. Stuck? Do 4 problems. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
GMAT Math Help » Problem-Solving Questions » Arithmetic » Descriptive Statistics » Arithmetic Mean Example Question #2022 : Problem Solving Questions Salaries for employees at ABC Company: 1 employee makes $25,000 per year, 4 employees make $40,000 per year, 2 employees make $50,000 per year and 5 employees make $75,000 per year.
Arithmetic Mean Formula Sum of all of the numbers of a group, when divided by the number of items in that list is known as the Arithmetic Mean or Mean of the group. For example, the mean of the numbers 5, 7, 9 is 4 since 5 + 7 + 9 = 21 and 21 divided by 3 [there are three numbers] is 7.
2. Use the reverse operation to check arithmetic. Example: if you are doing the problem 86-47, check that your answer plus 47 equals 86. 3. Estimate to see if your answer has reasonable size, or if your answer is clearly too big or too small. 4. Find a second method of doing the problem. If you think hard enough, you will see that many math ...
Solution (two solutions - balancing and summing) We know the average is 15. 3, 5, and 7 are, respectively, 12, 10, and 8 below the average. So far then we are -12 - 10 - 8 or 30 below the average. We have to make this up with a and b so on average each is 30/2 = 15 above the average. The average is 15 so each is on average 15+15 = 30, or answer C.
The Arithmetic Mean-Geometric Mean Inequality (AM-GM Inquality) is a fundamental relationship in mathematics. It is a useful tool for problems solving and building relationships with other mathematics. It should find more use in school mathematics than currently.
Problem 2 : A batsman scored the following number of runs in six innings: 36, 35, 50, 46, 60, 55. Calculate the mean runs scored by him in an inning. Solution : To find the mean, we find the sum of all the observations and divide it by the number of observations. Mean = Total runs / Number of innings = (36 + 35 + 50 + 46 + 60 + 55) / 6 = 47
What is Mean in Statistics? Mean is one of the measures of central tendency in statistics. The mean is the average of the given data set, which means it can be calculated by dividing the sum of the given data values by the total number of data values. Mean for ungrouped data: Mean (x̄) = ∑x i /n . x i = x 1, x 2, x 3,…, x n such that i = 1 ...
Problem. The arithmetic mean of two distinct positive integers and is a two-digit integer. The geometric mean of and is obtained by reversing the digits of the arithmetic mean. What is ?. Solution 1. Answer: (D) for some , .. Squaring the first and second equations,
Summary. The problem with an AI-first strategy lies not within the "AI" but with the notion that it should come "first" aspect. An AI-first approach can be myopic, potentially leading us ...
Problem. The sequence satisfies , and, for all , is the arithmetic mean of the first terms. Find . Solution 1. Let be the arithmetic mean of and . We can then write and for some . By definition, . Next, is the mean of , and , which is again . Realizing this, one can easily prove by induction that . It follows that . From we get that . And thus ...