
- Message from SIG Chair
- News & Announcements
- Meetings & Other Events
- Key Initiatives
- Professional Development Opportunities
- Research Connections
- Biographical and Documentary Research (SIG #13)

- Technical Support
- Find My Rep

You are here
Biographical Research Methods
- Marta J. Eichsteller - University College Dublin
- Howard H. Davis - Bangor University, UK
- Description
See what’s new to this edition by selecting the Features tab on this page. Should you need additional information or have questions regarding the HEOA information provided for this title, including what is new to this edition, please email [email protected] . Please include your name, contact information, and the name of the title for which you would like more information. For information on the HEOA, please go to http://ed.gov/policy/highered/leg/hea08/index.html .
For assistance with your order: Please email us at [email protected] or connect with your SAGE representative.
SAGE 2455 Teller Road Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 www.sagepub.com
This book is a practical and thought-provoking account of the use of biographical methods in social science research. The case studies are useful for advanced students and researchers, and for anyone interested in how we tell stories about our lives.
An accessible and lively text, drawing on numerous examples to demonstrate biographical narrative research in action. The fascinating and complex world of biographical research is presented in a highly accessible way. Students and researchers will learn a great deal from reading this before embarking on research projects with any degree of biographical focus.
Anchored in studies drawn from a wide variety of disciplines, Biographical Research Methods fills glaring gaps in the literature through balanced sympathetic consideration of a wide range of methodological approaches and its illumination of both established and innovative research techniques.
Narrative research in social science has come a long way since its urban life heyday. Biographical Research Methods takes this forward, deftly focusing on concepts and techniques for analyzing the contours of personal experience. Outstanding is a view to the context-specific whats and processual hows of biographical construction.
The book of Eichsteller and Davis is an extremely instructive and inviting guide for getting introduced into the social world of biography research. On the one hand, the book is an empirically grounded and unbiased “sociology of knowledge” of distinctive approaches in biography research). It lucidly contrasts different basic assumptions and their implications for concrete methodical guidelines and practical research activities. On the other hand, it is an integrative guideline for the whole arc of work in accomplishing the research act of unravelling the intimate relations between individual and society and for deciphering the features and problems of society and other collective entities as seen and experienced from the perspective of individual members of society and of other collective entities. -The book is written in an elegant and deliberate style of language and presentation; it makes you want to start your own practical research work in biography analysis.
A great, incremental, up-to-date, accessible, comprehensive research methods text for any novice or experienced qualitative researcher contemplating narrative/biographical methods. I personally found this text invaluable for my own PhD - thanks
A supplementary book but a must for those who write their dissertations with the use of Narrative Inquiry.
Preview this book
For instructors, select a purchasing option.

This title is also available on SAGE Research Methods , the ultimate digital methods library. If your library doesn’t have access, ask your librarian to start a trial .
Biographical Resources: A Research Guide: Subject Biographies
- Introduction
- National and International Biographies
- Biographical Indexes
- K. G. Saur Indexes & Microfiche
- Subject Biographies
- Dissertations and Theses
- Research Help
Online Biographies of Disciplines or Subjects
These titles are a few examples of many hundreds of biographical reference titles available for specific fields of study and subjects. A title search in our library catalog on the phrase "biographical dictionary of" yields over 350 items, for example.
- BiografiA: Lexikon österreichischer Frauen Call Number: Olin Stacks HQ 1605 .A3 B56 2016 4 volumes. Biographical dictionary of Austrian women.
- The Biographical Dictionary of American Economists. New York: Oxford University Press, 2010. "...offers in-depth biographies of the most important economic figures in American history from the seventeenth century to the present day. All of the major schools of American economic thought are represented, from the Constitutional school to the Keynesian school, and the dictionary includes in-depth coverage of the many overlooked women who have influenced economic thought in America." [Publisher's description]
- The Biographical Encyclopaedia of Islamic Philosophy. London: Thoemmes Continuum, 2006. Also available in print. Call number: Olin Reference B 741 .B56 2006 2006 Choice Outstanding Academic Title "The notion of philosophy has been interpreted broadly to include a large number of intellectuals who were interested in conceptual issues that either directly relate to philosophy or form part of the background of Islamic philosophy as a whole. Included are details about the lives of significant legal thinkers, theologians, political thinkers and even geographers where their lives are relevant indicators of the progress of philosophy in the Islamic world." [Publisher's description]
- Biographical Encyclopedia of Astronomers 2nd edition. New York: Springer, 2014. 2,357 online biographical articles on astronomers throughout history and worldwide.
- Biographical Resources: An African and African Diaspora Approach A LibGuide created by Eric Acree, Africana Librarian at Cornell, for locating information about people of African descent. Includes online and print resources.
- Biographical Resources: Women. The Biographical Sources section of the Feminism, Gender and Sexuality Studies Research Guide.
- Complete Dictionary of Scientific Biography. Detroit: Scribner, 2008. Lengthy, readable, and signed essays on the major scientists in world history. The standard biographical reference in the history of science. Merges entries from the Dictionary of Scientific Biography (18 volumes, 1970) and the New Dictionary of Scientific Biography (8 volumes, 2008).
- Dictionary of African Biography. New York: Oxford University Press, 2011. Also available in print: Call number: Africana Library Reference CT 1920 .D52 2012.and Library Annex. Edited by Emmanuel K. Akyeampong and Henry Louis Gates, Jr. "From the pharaohs to Frantz Fanon, Dictionary of African Biography provides a comprehensive overview of the lives of the men and women who shaped Africa’s history." [Publisher's description]
- Dictionary of Caribbean and Afro–Latin American Biography. New York: Oxford University Press, 2016. Edited by Franklin W. Knight and Henry Louis Gates, Jr. "[A] comprehensive overview of the lives of Caribbeans and Afro-Latin Americans who are historically significant... covering the entire Caribbean, and the Afro-descended populations throughout Latin America, including people who spoke and wrote Creole, Dutch, English, French, Portuguese, and Spanish." [Publisher's description]
- Dictionary of Literary Biography Gale Group. The major online source of literary biography, these two databases include the content of the Dictionary of Literary Biography and Contemporary Authors .
- A Dictionary of Political Biography. 2nd edition. Oxford University Press, 2013. Describes and assesses the lives of around 870 men and women who have shaped political events across the world. Each entry includes an account of the background, career, and achievements of the individual concerned, balancing fact with critical appraisal. The first edition is also available.
- International Directory of Medievalists Online. Brepols. The International Directory of Medievalists Online is the continuation of the printed editions [Répertoire international des médiévistes. Call Number: Library Annex D 116.5 .R42: 3.ed.-5.ed. (1965-1979) and 7.ed.-8.ed. (1990-1995)] and contains 15,000 names and addresses of specialists from over 70 countries with their fields of study.
- Oxford Art Online. Oxford, 2007- . The major online source of artists' biographies. The database has over 200,000 biographies of artists, architects, and designers, patrons, collectors, and dealers; writers and scholars; and the publishers and printers of art.
- Oxford Music Online. Oxford, 2007- . Over 57,000 online biographies for all manner of people involved in music, from choreographers and instrument makers to composers, arrangers, performers, critics, publishers, curators, collectors, audio engineers, scholars, educators, and more.
Biographies of Disciplines or Subjects, in print format only
- Geographers: Biobibliographical Studies Mansell/Bloomsbury Academic, 1977 to date. Uris Library Stacks Z 6004 .B6 G34 + This annual "biobibliography" consists of lengthy essays on a handful of deceased prominent geographers. Essays end with very substantial bibliographies and a chronology of the subject's work.
- Kürschners deutscher Gelehrten-Kalender . 1925 through 1992 at Library Annex (Z 2230 .K952). 2001 to date in Uris Library Stacks (Z 2230 .K959). Latest volume shelved in Olin Reference. 1996- online . K. G. Saur. German-language biographical and bibliographical encyclopedia of scientists and scholars from the German-speaking part of Europe. [Wikipedia]
Reference Help

- << Previous: K. G. Saur Indexes & Microfiche
- Next: Who's Who >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 4:28 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.cornell.edu/biographyresearch
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of biography
Did you know.
So You've Been Asked to Submit a Biography
In a library, the word biography refers both to a kind of book and to a section where books of that kind are found. Each biography tells the story of a real person's life. A biography may be about someone who lived long ago, recently, or even someone who is still living, though in the last case it must necessarily be incomplete. The term autobiography refers to a biography written by the person it's about. Autobiographies are of course also necessarily incomplete.
Sometimes biographies are significantly shorter than a book—something anyone who's been asked to submit a biography for, say, a conference or a community newsletter will be glad to know. Often the word in these contexts is shortened to bio , a term that can be both a synonym of biography and a term for what is actually a biographical sketch: a brief description of a person's life. These kinds of biographies—bios—vary, but many times they are only a few sentences long. Looking at bios that have been used in the same context can be a useful guide in determining what to put in your own.
Examples of biography in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'biography.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Late Greek biographia , from Greek bi- + -graphia -graphy
1665, in the meaning defined at sense 2
Dictionary Entries Near biography
biographize
Cite this Entry
“Biography.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/biography. Accessed 3 May. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of biography, more from merriam-webster on biography.
Nglish: Translation of biography for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of biography for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about biography
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
What’s the difference between ‘hillbilly’ and ‘redneck’, more commonly misspelled words, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, words of the week - may 3, 9 superb owl words, 'gaslighting,' 'woke,' 'democracy,' and other top lookups, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, your favorite band is in the dictionary, games & quizzes.

- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Faculty of Arts & Sciences Libraries
Library Research Guide for the History of Science: Introduction
- Background and Context/Biography
- Senior Theses 2023
Understanding the History of Science (Background and Context/Biography)
Contemporary subject dictionaries, doing cross-disciplinary research: connecting with other fields, don't forget print, print only resources that were on this page.
- Exploring Your Topic
- Using HOLLIS
- What is a Secondary Source?
- What is a Primary Source?
- Exploring the Special Collections at Harvard
- Citing Sources & Organizing Research
Your History of Science Librarians

Fred Burchsted
History of Science Librarian
Research Librarian
- Fred Burchsted's guides
- History of Science
- Finding Newspaper and Periodical Indexes and Articles
- Finding Archival Materials
Encyclopedias and histories are useful first stops to acquire context and background for your topic. If you have a solid overview of the topic and its history it will be easier to recognize the more in-depth articles, books etc. that will be most helpful to you.
To find one, try searching in HOLLIS for your subject (see the HOLLIS tab in this guide for how to know the proper Subject terms) plus the words encyclopedias or dictionaries.
To find individual encyclopedia articles in HOLLIS - Everything, do a Title search on your topic and then take look at "Refine My Results" on the right side of the page. Find the "Resource Type" section and choose Reference entries .
Major subject encyclopedias and other reference works
Human Biology
Cambridge Histories Online includes Cambridge History of Science :
- Vol. 1: Ancient Science
- Vol. 2: Medieval Science
- Vol. 3: Early Modern Science
- Vol. 4: Eighteenth Century Science
- Vol. 5: Modern Physical and Mathematical Sciences
- Vol. 6: Modern Biological and Earth Sciences
- Vol. 7: Modern Social Sciences
- Vol. 8: Modern Science in National, Transnational and Global Context
The Oxford companion to the history of modern science (Harvard Login) , ed. by J.L. Heilbron et al. NY: Oxford University Press, 2003, 941 p.
The Oxford Encyclopedia of the History of American Science, Medicine, and Technology (Harvard Login) , ed. by Hugh Richard Slotten. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2014.
The Oxford encyclopedia of philosophy, science, and technology in Islam (Harvard Login) , ed. by Ibrahim Kalin. Oxford ; NY: Oxford University Press, 2014.
Science, technology, and society: an encyclopedia (Harvard Login) , ed. by Sal Restivo. NY: Oxford University Press, 2005, 701 p.
Encyclopedia of the history of psychological theories (Harvard Login) , ed. by Robert W. Rieber. NY: Springer, 2012. 2 v.
The Oxford companion to the mind , ed. by Richard L. Gregory. 2nd ed. Oxford ; New York : Oxford University Press, 2004, 1004 p. Internet Archive Full Text
The Oxford handbook of the history of psychology: global perspectives (Harvard Login) , ed. by David B. Baker. Oxford; NY: Oxford University Press, 2012, 645 p.
The Oxford Companion to the body (Harvard Login) , ed. by Colin Blakemore and Sheila Jennett et al. Oxford; NY: Oxford University Press, 2001, 753 p.
The Oxford handbook of the history of eugenics (Harvard Login; print versions also in HOLLIS) , ed. by Alison Bashford, Philippa Levine. NY: Oxford University Press, 2010, 586 p.), ed. by Sarah Toulalan and Kate Fisher. Abingdon, Oxon; NY: Routledge, 2013, 579 p.
Cambridge historical dictionary of disease (Harvard Login) , ed. by Kenneth F. Kiple. Cambridge ; New York : Cambridge University Press, 2003, 412 p.
Cambridge world history of human disease (Harvard Login) ed. by Kenneth F. Kiple et al. Cambridge ; NY: Cambridge University Press, 1993, 1176 p.
Companion encyclopedia of the history of medicine (Harvard Login) , ed. by W.F. Bynum and Roy Porter. London; NY: Routledge, 1993. 2 v. HOLLIS record --This is a useful collection of essays on the History of Science. -- Table of contents of both volumes in Google Books .
Companion to medicine in the twentieth century (Print only) , ed. by Roger Cooter and John Pickstone. London; NY: Routledge, 2003, 756 p. --Articles, with references, especially on social, institutional, political, and policy aspects of medicine. Internet Archive Full Text -- Another copy
Medical research: a midcentury survey Boston, Published for the American Foundation by Little, Brown, 1955, 2 v. --A valuable overview of medical research circa 1940-1955. The first volume covers institutional and policy aspects, the second summarizes the state of research on cancer, infertility, arteriosclerosis, hypertension, rheumatic syndromes, tuberculosis, viruses, alcoholism, and schizophrenia.
Oxford handbook of the history of medicine (Harvard Login) , ed. by Mark Jackson. Oxford ; New York ; Oxford University Press, 2011, 672 p.
American National Biography (Harvard login) is the standard American source for biographies of major figures. Can do searches of occupations and limit by date.
Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (Harvard login) is the standard British source for biographies of major figures. Can do searches of occupations and limit by date: Advanced Search Options: People Search.
Complete Dictionary of Scientific Biography (Harvard login) offers biographical sketches on deceased scientists to 1975, including excellent lists of primary and secondary literature.
- Social .scientists are covered unevenly.
- For more recent sources (post-1975) use History of Science, Technology and Medicine (Harvard login). For new primary works (new editions, etc.) put your person in the author field. For new secondary works, put your person in the Subject field.
Dictionary of American medical biography , ed. by M. Kaufman, S. Galishoff & T. L. Savitt. 2 v. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, 1984. Internet Archive Full Text: Vol. 1 -- Vol. 2
Dictionary of medical biography , ed. by W. F. Bynum and Helen Bynum. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, 2007. 5 v. --Covers 18th century through 1975. Internet Archive Full Text: Vol. 1 -- Vol. 2 -- Vol. 3 -- Vol. 4 -- Vol. 5
A dictionary of scientists (Harvard Login) , Oxford Reference. New York: Oxford University Press, 1999.
Biographical sources for women in science
Biographical sources for American physicians (this guide is still under development)
Additional general sources in Finding Biographical Information
Contemporary subject encyclopedias and dictionaries are useful in interpreting primary sources. They can be found by an Advanced Search in the HOLLIS Catalog with, e.g., <Medicine dictionaries> [Keyword search], limited by year range.
Gould, George M. (George Milbry), 1848-1922. An illustrated dictionary of medicine, biology and allied sciences ... 3d ed. rev. Philadelphia, Blakiston, 1897, c1894.
Subject: Medicine--Dictionaries. Natural history--Dictionaries.
These books are usually shelved toward the beginning of each subject class in the Old Widener system.
History of science topics often explore the relations of scientific work with other fields, such as:
- public policy
- popular media
Primary and secondary sources in other fields may therefore be important to you. You might need to investigate original documents in public policy or film footage in media studies. There are several options for finding this material:
- In the Library Research Guide for History , there is a list of major periodical indexes for other disciplines.
- Research guides by other Harvard librarians on a large variety of subjects .
- To find resources in HOLLIS Databases , choose Subject and browse the resource types..
- Your History of Science librarian is available to help you think about topics and where best sources are likely to be found.
Other Research Guides
- Environmental
- Latin America
- African American
- Area Studies
- Finding Periodical Articles and Book Reviews on Africa
- Asian Studies Research Guides
- Finding Periodical Articles and Book Reviews on Latin America
- Guides for Middle Eastern Studies
- Slavic and Eurasian Studies at Harvard: Library and Archival Resources
- Humanities/Social Sciences
- Inter Libros: Research Guide for Classics, Byzantine, & Medieval Studies
- Rinascimento: Digital Renaissance Studies
- Bioethics sources
- Literary Research in Harvard Libraries
- Philosophy Resources at Harvard

The human subjects of your research didn't read online. Reading linked and related articles online is an entirely different experience from that of browsing the newspaper or an online journal. The medium can be significant.
Don't disregard print indexes and the crucial print resources to which they may lead.
Fall 2020: During the virtual semester our access to print resources is of course limited. During this time you may be able to locate the full text for many normally print-only materials HathiTrust or other digital libraries. (for HathiTrust, this is less common for books published in the last 10 years)
Encyclopedia of American environmental history (Print Only) , ed. by K. A. Brosnan. 4 v. NY: Facts on File, 2011.
Encyclopaedia of the history of science, technology, and medicine in non-western cultures (Print Only) , ed. by Helaine Selin. 2nd ed. Berlin; NY: Springer, 2008. 2 v.
Technology (this was the entire tech section):
An Encyclopaedia of the history of technology , ed. by Ian McNeil. London; New York: Routledge, 1990, 1062 p. (Print only)
The biographical dictionary of scientists (Print Only) , by Roy Porter, Marilyn Ogilvie. NY: Oxford University Press, 3rd. ed., 2000. 2 v.
- A collection of short articles.
- << Previous: Senior Theses 2023
- Next: Exploring Your Topic >>
- Last Updated: Apr 14, 2024 9:25 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/HistSciInfo
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
Definition of Biography
A biography is the non- fiction , written history or account of a person’s life. Biographies are intended to give an objective portrayal of a person, written in the third person. Biographers collect information from the subject (if he/she is available), acquaintances of the subject, or in researching other sources such as reference material, experts, records, diaries, interviews, etc. Most biographers intend to present the life story of a person and establish the context of their story for the reader, whether in terms of history and/or the present day. In turn, the reader can be reasonably assured that the information presented about the biographical subject is as true and authentic as possible.
Biographies can be written about a person at any time, no matter if they are living or dead. However, there are limitations to biography as a literary device. Even if the subject is involved in the biographical process, the biographer is restricted in terms of access to the subject’s thoughts or feelings.
Biographical works typically include details of significant events that shape the life of the subject as well as information about their childhood, education, career, and relationships. Occasionally, a biography is made into another form of art such as a film or dramatic production. The musical production of “Hamilton” is an excellent example of a biographical work that has been turned into one of the most popular musical productions in Broadway history.
Common Examples of Biographical Subjects
Most people assume that the subject of a biography must be a person who is famous in some way. However, that’s not always the case. In general, biographical subjects tend to be interesting people who have pioneered something in their field of expertise or done something extraordinary for humanity. In addition, biographical subjects can be people who have experienced something unusual or heartbreaking, committed terrible acts, or who are especially gifted and/or talented.
As a literary device, biography is important because it allows readers to learn about someone’s story and history. This can be enlightening, inspiring, and meaningful in creating connections. Here are some common examples of biographical subjects:
- political leaders
- entrepreneurs
- historical figures
- serial killers
- notorious people
- political activists
- adventurers/explorers
- religious leaders
- military leaders
- cultural figures
Famous Examples of Biographical Works
The readership for biography tends to be those who enjoy learning about a certain person’s life or overall field related to the person. In addition, some readers enjoy the literary form of biography independent of the subject. Some biographical works become well-known due to either the person’s story or the way the work is written, gaining a readership of people who may not otherwise choose to read biography or are unfamiliar with its form.
Here are some famous examples of biographical works that are familiar to many readers outside of biography fans:
- Alexander Hamilton (Ron Chernow)
- Prairie Fires: The American Dreams of Laura Ingalls Wilder (Caroline Fraser)
- Steve Jobs (Walter Isaacson)
- Churchill: A Life (Martin Gilbert)
- The Professor and the Madman: A Tale of Murder, Insanity, and the Making of the Oxford English Dictionary (Simon Winchester)
- A Beautiful Mind (Sylvia Nasar)
- The Black Rose (Tananarive Due)
- John Adams (David McCullough)
- Into the Wild ( Jon Krakauer )
- John Brown (W.E.B. Du Bois)
- Frida: A Biography of Frida Kahlo (Hayden Herrera)
- The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks (Rebecca Skloot)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham Lincoln (Doris Kearns Goodwin)
- Shirley Jackson : A Rather Haunted Life ( Ruth Franklin)
- the stranger in the Woods: The Extraordinary Story of the Last True Hermit (Michael Finkel)
Difference Between Biography, Autobiography, and Memoir
Biography, autobiography , and memoir are the three main forms used to tell the story of a person’s life. Though there are similarities between these forms, they have distinct differences in terms of the writing, style , and purpose.
A biography is an informational narrative and account of the life history of an individual person, written by someone who is not the subject of the biography. An autobiography is the story of an individual’s life, written by that individual. In general, an autobiography is presented chronologically with a focus on key events in the person’s life. Since the writer is the subject of an autobiography, it’s written in the first person and considered more subjective than objective, like a biography. In addition, autobiographies are often written late in the person’s life to present their life experiences, challenges, achievements, viewpoints, etc., across time.
Memoir refers to a written collection of a person’s significant memories, written by that person. Memoir doesn’t generally include biographical information or chronological events unless it’s relevant to the story being presented. The purpose of memoir is reflection and an intention to share a meaningful story as a means of creating an emotional connection with the reader. Memoirs are often presented in a narrative style that is both entertaining and thought-provoking.
Examples of Biography in Literature
An important subset of biography is literary biography. A literary biography applies biographical study and form to the lives of artists and writers. This poses some complications for writers of literary biographies in that they must balance the representation of the biographical subject, the artist or writer, as well as aspects of the subject’s literary works. This balance can be difficult to achieve in terms of judicious interpretation of biographical elements within an author’s literary work and consideration of the separate spheres of the artist and their art.
Literary biographies of artists and writers are among some of the most interesting biographical works. These biographies can also be very influential for readers, not only in terms of understanding the artist or writer’s personal story but the context of their work or literature as well. Here are some examples of well-known literary biographies:
Example 1: Savage Beauty: The Life of Edna St. Vincent Millay (Nancy Milford)
One of the first things Vincent explained to Norma was that there was a certain freedom of language in the Village that mustn’t shock her. It wasn’t vulgar. ‘So we sat darning socks on Waverly Place and practiced the use of profanity as we stitched. Needle in, . Needle out, piss. Needle in, . Needle out, c. Until we were easy with the words.’
This passage reflects the way in which Milford is able to characterize St. Vincent Millay as a person interacting with her sister. Even avid readers of a writer’s work are often unaware of the artist’s private and personal natures, separate from their literature and art. Milford reflects the balance required on the part of a literary biographer of telling the writer’s life story without undermining or interfering with the meaning and understanding of the literature produced by the writer. Though biographical information can provide some influence and context for a writer’s literary subjects, style, and choices , there is a distinction between the fictional world created by a writer and the writer’s “real” world. However, a literary biographer can illuminate the writer’s story so that the reader of both the biography and the biographical subject’s literature finds greater meaning and significance.
Example 2: The Invisible Woman: The Story of Nelly Ternan and Charles Dickens (Claire Tomalin)
The season of domestic goodwill and festivity must have posed a problem to all good Victorian family men with more than one family to take care of, particularly when there were two lots of children to receive the demonstrations of paternal love.
Tomalin’s literary biography of Charles Dickens reveals the writer’s extramarital relationship with a woman named Nelly Ternan. Tomalin presents the complications that resulted for Dickens from this relationship in terms of his personal and family life as well as his professional writing and literary work. Revealing information such as an extramarital relationship can influence the way a reader may feel about the subject as a person, and in the case of literary biography it can influence the way readers feel about the subject’s literature as well. Artists and writers who are beloved , such as Charles Dickens, are often idealized by their devoted readers and society itself. However, as Tomalin’s biography of Dickens indicates, artists and writers are complicated and as subject to human failings as anyone else.
Example 3: Virginia Woolf (Hermione Lee)
‘A self that goes on changing is a self that goes on living’: so too with the biography of that self. And just as lives don’t stay still, so life-writing can’t be fixed and finalised. Our ideas are shifting about what can be said, our knowledge of human character is changing. The biographer has to pioneer, going ‘ahead of the rest of us, like the miner’s canary, testing the atmosphere , detecting falsity, unreality, and the presence of obsolete conventions’. So, ‘There are some stories which have to be retold by each generation’. She is talking about the story of Shelley, but she could be talking about her own life-story.
In this passage, Lee is able to demonstrate what her biographical subject, Virginia Woolf, felt about biography and a person telling their own or another person’s story. Literary biographies of well-known writers can be especially difficult to navigate in that both the author and biographical subject are writers, but completely separate and different people. As referenced in this passage by Lee, Woolf was aware of the subtleties and fluidity present in a person’s life which can be difficult to judiciously and effectively relay to a reader on the part of a biographer. In addition, Woolf offers insight into the fact that biographers must make choices in terms of what information is presented to the reader and the context in which it is offered, making them a “miner’s canary” as to how history will view and remember the biographical subject.
Post navigation



How to Write a Good Academic Biography (Part 1)
When your journal article gets accepted or you are preparing for a public presentation, you will often be asked for a short academic biography. For many people, these academic bios are more difficult to write than a dissertation. How do you sum up yourself and your work in 3-5 sentences? What do you need to include? What should you leave out?
What You Should Do
- Start with your full name followed by your current position, your general interests, and your current project, keeping them all very brief.
- If you are within a year of receiving a prestigious award, mention that as well.
- Finally, finish with a sentence that’s personal: add a hobby, a pet’s name, the city you live in—whatever you are comfortable with that is personal but not too private.
What You Should Avoid
- Avoid speaking in the first person, i.e., don’t use “I.”
- Don’t divulge details beyond your current position.
- In a longer bio of multiple paragraphs, you may add more awards and information about your master’s and bachelor’s degrees, but not in a short bio. Moreover, don’t add anything that happened before grad school—including your place of birth. For example:
Hi! My name is Scott. I was originally born in Vermont and now I’m a professor at North Yankee University in Fargone, New York (in upstate New York). I study antelopes’ migration patterns and their impact of native grain growth. My interest in antelopes began as a teenager when I first saw one in the wild. I did my undergrad degree in biology at SUNY and my masters and UCLA and my PhD in Forestry at Hunter College.
Related: Finished drafting your academic biography and heading for an international conference? Check out this post now!
The above example is far too casual and Scott’s work and current position are overshadowed by all the other random details. This can be written in a much better way:
Scott Sampson is a professor of Wildlife Biology at North Yankee University. His work focuses specifically on the migration patterns of antelope and their impact on the growth of native grain. His favorite place to do research in his backyard, which opens to the Akron National Forest.
This improvised version is concise, relevant, and makes Scott’s bio appear professional while giving a short description of his personal details.
Longer Bios
For longer bios, follow the same basic rules, but go into a bit more depth about your work, your education, and your future projects or interests. You may also consider adding a line about your immediate family. But as always, leave the personal details for a short and friendly mention at the end of the bio.
Mostly, your bio will be used by someone to introduce you at a conference or public event so if you write your bio using these tips, you will help them give a smooth and accurate introduction. Remember that the bio is the first thing that people know about you so pack it full of the most important things about yourself!
If you would like to know more about different formats of academic biography, read the next article in this series!
Appreciating the dedication you put into your blog and detailed information you provide. It’s good to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same out of date rehashed material. Fantastic read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
Greeting from Enago Academy! Thank you for your positive comment. We are glad to know that you found our resources useful. Your feedback is very valuable to us. Happy reading!
Super helpful! Thank you for writing about this.
wow great article. I got lots of new ideas from this post. Thanks a lot.
Thank you! Really a short and precise description of how to write short biographic sentence.
Excellent! Just what I needed; thank you.
Thanks for sharing this post, It is a very helpful article.
Excellent information…
Comparing to my introduction and yours, there is a huge difference and mine is like grade R?. Thank you so much for developing such content and helping disadvantaged students like me, hence holding Honours. Once again thank you
it is good, i learnt something new
Your articles are so much meaningful and informative.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Manuscripts & Grants
- Reporting Research
How to Write a Good Academic Biography (Part 2)
Writing an academic biography is part of many academic activities. Whether your paper is accepted…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Office: 919.785.1304 | Fax: 919.785.1306

- Donate to SUBR
- Copyright and Privacy Statements
- Why Are Animals Needed in Research?
- What About Using Fewer Animals or No Animals?
- Product and Environmental Safety Research
- What is Biomedical Research?
- Biomedical Research Definitions
- Research Options
- How Animals Help
- Member Organizations
WHAT IS BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH?
Biomedical research is the broad area of science that looks for ways to prevent and treat diseases that cause illness and death in people and in animals. This general field of research includes many areas of both the life and physical sciences.
Utilizing biotechnology techniques, biomedical researchers study biological processes and diseases with the ultimate goal of developing effective treatments and cures. Biomedical research is an evolutionary process requiring careful experimentation by many scientists, including biologists and chemists. Discovery of new medicines and therapies requires careful scientific experimentation, development, and evaluation.
Why are Animals Used in Biomedical Research?
The use of animals in some types of research is essential to the development of new and more effective methods for diagnosing and treating diseases that affect both humans and animals. Scientists use animals to learn more about health problems, and to assure the safety of new medical treatments. Medical researchers need to understand health problems before they can develop ways to treat them. Some diseases and health problems involve processes that can only be studied in living organisms. Animals are necessary to medical research because it is impractical or unethical to use humans.
Animals make good research subjects for a variety of reasons. Animals are biologically similar to humans. They are susceptible to many of the same health problems, and they have short life-cycles so they can easily be studied throughout their whole life-span or across several generations. In addition, scientists can easily control the environment around animals (diet, temperature, lighting), which would be difficult to do with people. Finally, a primary reason why animals are used is that most people feel it would be wrong to deliberately expose human beings to health risks in order to observe the course of a disease.
Animals are used in research to develop drugs and medical procedures to treat diseases. Scientists may discover such drugs and procedures using alternative research methods that do not involve animals. If the new therapy seems promising, it is tested in animals to see whether it seems to be safe and effective. If the results of the animal studies are good, then human volunteers are asked to participate in a clinical trial. The animal studies are conducted first to give medical researchers a better idea of what benefits and complications they are likely to see in humans.
A variety of animals provide very useful models for the study of diseases afflicting both animals and humans. However, approximately 95 percent of research animals in the United States are rats, mice, and other rodents bred specifically for laboratory research. Dogs, cats, and primates account for less than one percent of all the animals used in research.
Those working in the field of biomedical research have a duty to conduct research in a manner that is humane, appropriate, and judicious. CBRA supports adherence to standards of care developed by scientific and professional organizations, and compliance with governmental regulations for the use of animals in research.
Scientists continue to look for ways to reduce the numbers of animals needed to obtain valid results, refine experimental techniques, and replace animals with other research methods whenever feasible.
© California Biomedical Research Association
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Blog • Perfecting your Craft
Posted on Jun 30, 2023
How to Write a Biography: A 7-Step Guide [+Template]
From time to time, nonfiction authors become so captivated by a particular figure from either the present or the past, that they feel compelled to write an entire book about their life. Whether casting them as heroes or villains, there is an interesting quality in their humanity that compels these authors to revisit their life paths and write their story.
However, portraying someone’s life on paper in a comprehensive and engaging way requires solid preparation. If you’re looking to write a biography yourself, in this post we’ll share a step-by-step blueprint that you can follow.
How to write a biography:
1. Seek permission when possible
2. research your subject thoroughly, 3. do interviews and visit locations, 4. organize your findings, 5. identify a central thesis, 6. write it using narrative elements, 7. get feedback and polish the text.

FREE RESOURCE
Biography Outline Template
Craft a satisfying story arc for your biography with our free template.
While you technically don’t need permission to write about public figures (or deceased ones), that doesn't guarantee their legal team won't pursue legal action against you. Author Kitty Kelley was sued by Frank Sinatra before she even started to write His Way , a biography that paints Ol Blue Eyes in a controversial light. (Kelley ended up winning the lawsuit, however).

Whenever feasible, advise the subject’s representatives of your intentions. If all goes according to plan, you’ll get a green light to proceed, or potentially an offer to collaborate. It's a matter of common sense; if someone were to write a book about you, you would likely want to know about it well prior to publication. So, make a sincere effort to reach out to their PR staff to negotiate an agreement or at least a mutual understanding of the scope of your project.
At the same time, make sure that you still retain editorial control over the project, and not end up writing a puff piece that treats its protagonist like a saint or hero. No biography can ever be entirely objective, but you should always strive for a portrayal that closely aligns with facts and reality.
If you can’t get an answer from your subject, or you’re asked not to proceed forward, you can still accept the potential repercussions and write an unauthorized biography . The “rebellious act” of publishing without consent indeed makes for great marketing, though it’ll likely bring more headaches with it too.
✋ Please note that, like other nonfiction books, if you intend to release your biography with a publishing house , you can put together a book proposal to send to them before you even write the book. If they like it enough, they might pay you an advance to write it.

Book Proposal Template
Craft a professional pitch for your nonfiction book with our handy template.
Once you’ve settled (or not) the permission part, it’s time to dive deep into your character’s story.
Deep and thorough research skills are the cornerstone of every biographer worth their salt. To paint a vivid and accurate portrait of someone's life, you’ll have to gather qualitative information from a wide range of reliable sources.
Start with the information already available, from books on your subject to archival documents, then collect new ones firsthand by interviewing people or traveling to locations.
Browse the web and library archives

Put your researcher hat on and start consuming any piece on your subject you can find, from their Wikipedia page to news articles, interviews, TV and radio appearances, YouTube videos, podcasts, books, magazines, and any other media outlets they may have been featured in.
Establish a system to orderly collect the information you find 一 even seemingly insignificant details can prove valuable during the writing process, so be sure to save them.
Depending on their era, you may find most of the information readily available online, or you may need to search through university libraries for older references.

For his landmark biography of Alexander Hamilton, Ron Chernow spent untold hours at Columbia University’s library , reading through the Hamilton family papers, visiting the New York Historical Society, as well as interviewing the archivist of the New York Stock Exchange, and so on. The research process took years, but it certainly paid off. Chernow discovered that Hamilton created the first five securities originally traded on Wall Street. This finding, among others, revealed his significant contributions to shaping the current American financial and political systems, a legacy previously often overshadowed by other founding fathers. Today Alexander Hamilton is one of the best-selling biographies of all time, and it has become a cultural phenomenon with its own dedicated musical.
Besides reading documents about your subject, research can help you understand the world that your subject lived in.
Try to understand their time and social environment
Many biographies show how their protagonists have had a profound impact on society through their philosophical, artistic, or scientific contributions. But at the same time, it’s worth it as a biographer to make an effort to understand how their societal and historical context influenced their life’s path and work.
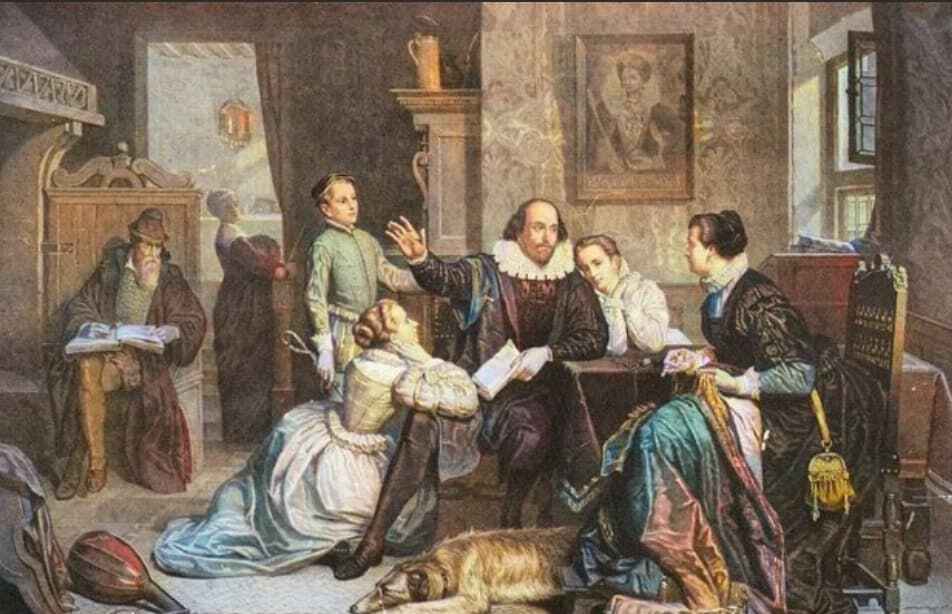
An interesting example is Stephen Greenblatt’s Will in the World . Finding himself limited by a lack of verified detail surrounding William Shakespeare's personal life, Greenblatt, instead, employs literary interpretation and imaginative reenactments to transport readers back to the Elizabethan era. The result is a vivid (though speculative) depiction of the playwright's life, enriching our understanding of his world.

Many readers enjoy biographies that transport them to a time and place, so exploring a historical period through the lens of a character can be entertaining in its own right. The Diary of Samuel Pepys became a classic not because people were enthralled by his life as an administrator, but rather from his meticulous and vivid documentation of everyday existence during the Restoration period.
Once you’ve gotten your hands on as many secondary sources as you can find, you’ll want to go hunting for stories first-hand from people who are (or were) close to your subject.
With all the material you’ve been through, by now you should already have a pretty good picture of your protagonist. But you’ll surely have some curiosities and missing dots in their character arc to figure out, which you can only get by interviewing primary sources.
Interview friends and associates
This part is more relevant if your subject is contemporary, and you can actually meet up or call with relatives, friends, colleagues, business partners, neighbors, or any other person related to them.
In writing the popular biography of Steve Jobs, Walter Isaacson interviewed more than one hundred people, including Jobs’s family, colleagues, former college mates, business rivals, and the man himself.
🔍 Read other biographies to get a sense of what makes a great one. Check out our list of the 30 best biographies of all time , or take our 30-second quiz below for tips on which one you should read next.
Which biography should you read next?
Discover the perfect biography for you. Takes 30 seconds!
When you conduct your interviews, make sure to record them with high quality audio you can revisit later. Then use tools like Otter.ai or Descript to transcribe them 一 it’ll save you countless hours.
You can approach the interview with a specific set of questions, or follow your curiosity blindly, trying to uncover revealing stories and anecdotes about your subject. Whatever your method, author and biography editor Tom Bromley suggests that every interviewer arrives prepared, "Show that you’ve done your work. This will help to put the interviewee at ease, and get their best answers.”
Bromley also places emphasis on the order in which you conduct interviews. “You may want to interview different members of the family or friends first, to get their perspective on something, and then go directly to the main interviewee. You'll be able to use that knowledge to ask sharper, more specific questions.”
Finally, consider how much time you have with each interviewee. If you only have a 30-minute phone call with an important person, make it count by asking directly the most pressing questions you have. And, if you find a reliable source who is also particularly willing to help, conduct several interviews and ask them, if appropriate, to write a foreword as part of the book’s front matter .
Sometimes an important part of the process is packing your bags, getting on a plane, and personally visiting significant places in your character’s journey.
Visit significant places in their life
A place, whether that’s a city, a rural house, or a bodhi tree, can carry a particular energy that you can only truly experience by being there. In putting the pieces together about someone’s life, it may be useful to go visit where they grew up, or where other significant events of their lives happened. It will be easier to imagine what they experienced, and better tell their story.
In researching The Lost City of Z , author David Grann embarked on a trek through the Amazon, retracing the steps of British explorer Percy Fawcett. This led Grann to develop new theories about the circumstances surrounding the explorer's disappearance.
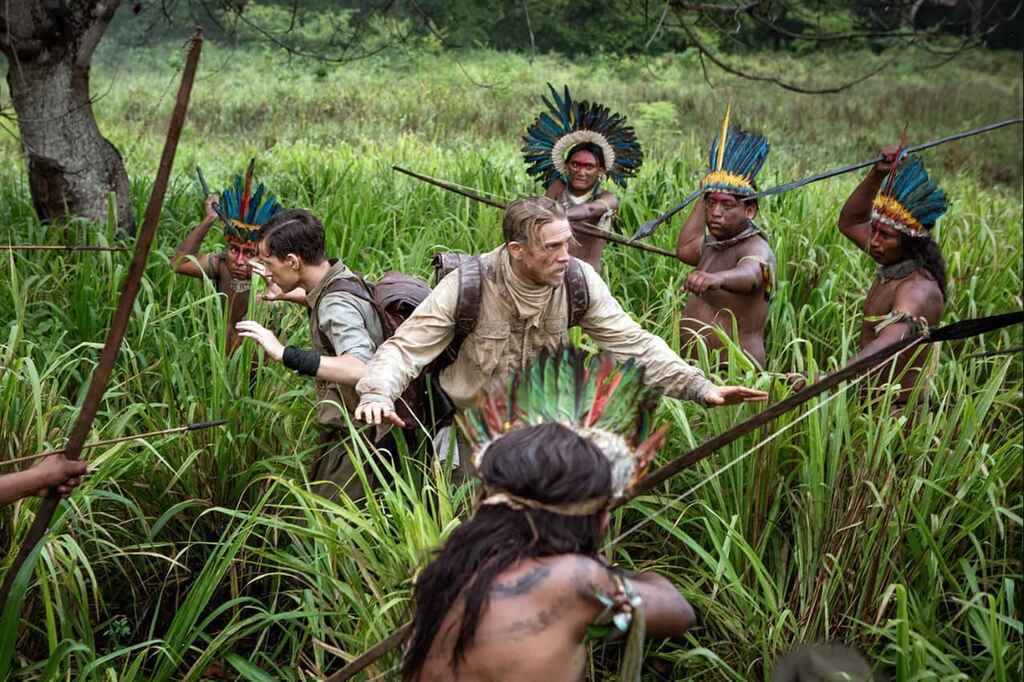

Hopefully, you won’t have to deal with jaguars and anacondas to better understand your subject’s environment, but try to walk into their shoes as much as possible.
Once you’ve researched your character enough, it’s time to put together all the puzzle pieces you collected so far.
Take the bulk of notes, media, and other documents you’ve collected, and start to give them some order and structure. A simple way to do this is by creating a timeline.
Create a chronological timeline
It helps to organize your notes chronologically 一 from childhood to the senior years, line up the most significant events of your subject’s life, including dates, places, names and other relevant bits.
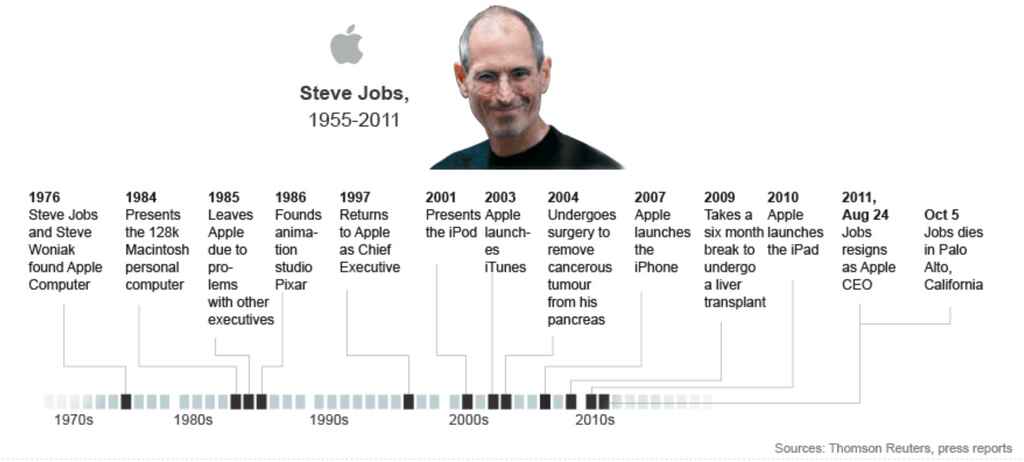
You should be able to divide their life into distinct periods, each with their unique events and significance. Based on that, you can start drafting an outline of the narrative you want to create.
Draft a story outline
Since a biography entails writing about a person’s entire life, it will have a beginning, a middle, and an end. You can pick where you want to end the story, depending on how consequential the last years of your subject were. But the nature of the work will give you a starting character arc to work with.
To outline the story then, you could turn to the popular Three-Act Structure , which divides the narrative in three main parts. In a nutshell, you’ll want to make sure to have the following:
- Act 1. Setup : Introduce the protagonist's background and the turning points that set them on a path to achieve a goal.
- Act 2. Confrontation : Describe the challenges they encounter, both internal and external, and how they rise to them. Then..
- Act 3. Resolution : Reach a climactic point in their story in which they succeed (or fail), showing how they (and the world around them) have changed as a result.
Only one question remains before you begin writing: what will be the main focus of your biography?
Think about why you’re so drawn to your subject to dedicate years of your life to recounting their own. What aspect of their life do you want to highlight? Is it their evil nature, artistic genius, or visionary mindset? And what evidence have you got to back that up? Find a central thesis or focus to weave as the main thread throughout your narrative.

Or find a unique angle
If you don’t have a particular theme to explore, finding a distinct angle on your subject’s story can also help you distinguish your work from other biographies or existing works on the same subject.
Plenty of biographies have been published about The Beatles 一 many of which have different focuses and approaches:
- Philip Norman's Shout is sometimes regarded as leaning more towards a pro-Lennon and anti-McCartney stance, offering insights into the band's inner dynamics.
- Ian McDonald's Revolution in the Head closely examines their music track by track, shifting the focus back to McCartney as a primary creative force.
- Craig Brown's One Two Three Four aims to capture their story through anecdotes, fan letters, diary entries, and interviews.
- Mark Lewisohn's monumental three-volume biography, Tune In , stands as a testament to over a decade of meticulous research, chronicling every intricate detail of the Beatles' journey.
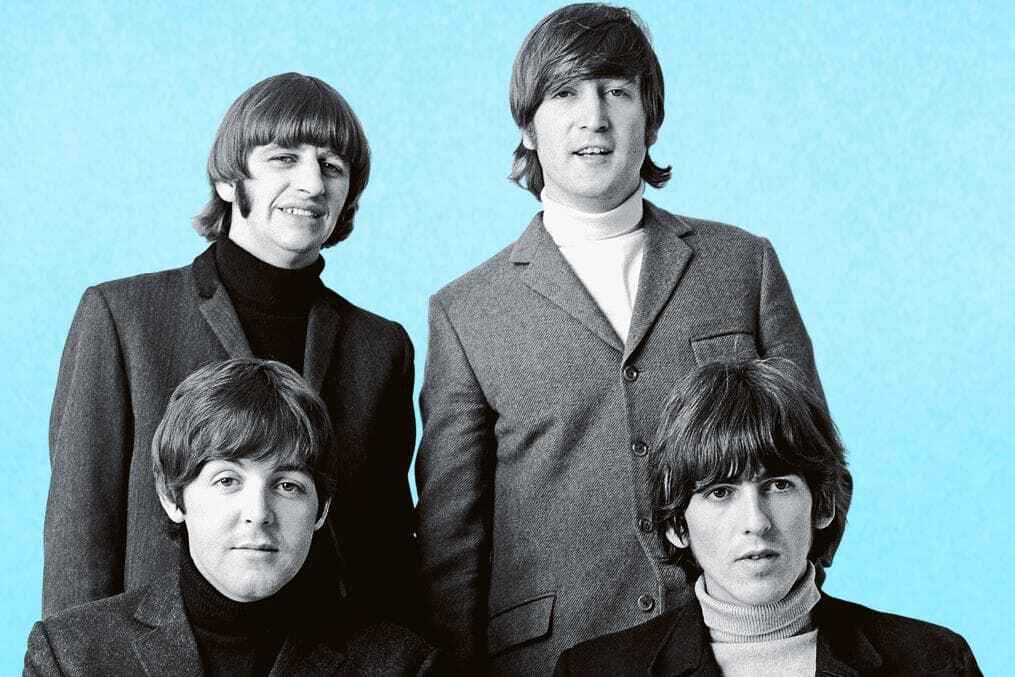

Finally, consider that biographies are often more than recounting the life of a person. Similar to how Dickens’ Great Expectations is not solely about a boy named Pip (but an examination and critique of Britain’s fickle, unforgiving class system), a biography should strive to illuminate a broader truth — be it social, political, or human — beyond the immediate subject of the book.
Once you’ve identified your main focus or angle, it’s time to write a great story.

While biographies are often highly informative, they do not have to be dry and purely expository in nature . You can play with storytelling elements to make it an engaging read.
You could do that by thoroughly detailing the setting of the story , depicting the people involved in the story as fully-fledged characters , or using rising action and building to a climax when describing a particularly significant milestone of the subject’s life.
One common way to make a biography interesting to read is starting on a strong foot…
Hook the reader from the start
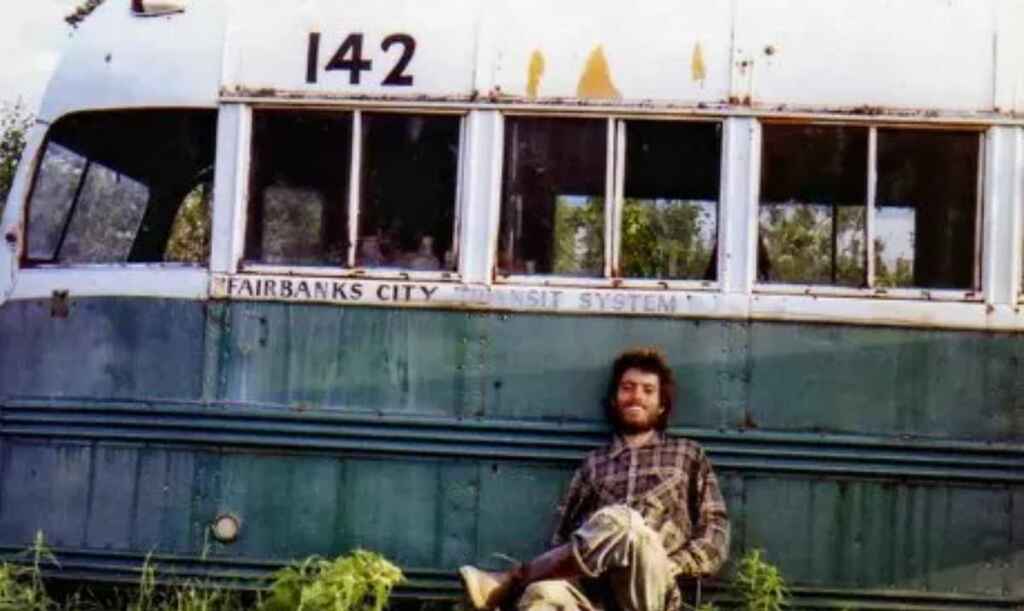
Just because you're honoring your character's whole life doesn't mean you have to begin when they said their first word. Starting from the middle or end of their life can be more captivating as it introduces conflicts and stakes that shaped their journey.
When he wrote about Christopher McCandless in Into the Wild , author Jon Krakauer didn’t open his subject’s childhood and abusive family environment. Instead, the book begins with McCandless hitchhiking his way into the wilderness, and subsequently being discovered dead in an abandoned bus. By starting in medias res , Krakauer hooks the reader’s interest, before tracing back the causes and motivations that led McCandless to die alone in that bus in the first place.

You can bend the timeline to improve the reader’s reading experience throughout the rest of the story too…
Play with flashback
While biographies tend to follow a chronological narrative, you can use flashbacks to tell brief stories or anecdotes when appropriate. For example, if you were telling the story of footballer Lionel Messi, before the climax of winning the World Cup with Argentina, you could recall when he was just 13 years old, giving an interview to a local newspaper, expressing his lifelong dream of playing for the national team.
Used sparsely and intentionally, flashbacks can add more context to the story and keep the narrative interesting. Just like including dialogue does…
Reimagine conversations
Recreating conversations that your subject had with people around them is another effective way to color the story. Dialogue helps the reader imagine the story like a movie, providing a deeper sensory experience.

One thing is trying to articulate the root of Steve Jobs’ obsession with product design, another would be to quote his father , teaching him how to build a fence when he was young: “You've got to make the back of the fence just as good looking as the front of the fence. Even though nobody will see it, you will know. And that will show that you're dedicated to making something perfect.”
Unlike memoirs and autobiographies, in which the author tells the story from their personal viewpoint and enjoys greater freedom to recall conversations, biographies require a commitment to facts. So, when recreating dialogue, try to quote directly from reliable sources like personal diaries, emails, and text messages. You could also use your interview scripts as an alternative to dialogue. As Tom Bromley suggests, “If you talk with a good amount of people, you can try to tell the story from their perspective, interweaving different segments and quoting the interviewees directly.”

FREE COURSE
How to Write Believable Dialogue
Master the art of dialogue in 10 five-minute lessons.
These are just some of the story elements you can use to make your biography more compelling. Once you’ve finished your manuscript, it’s a good idea to ask for feedback.
If you’re going to self-publish your biography, you’ll have to polish it to professional standards. After leaving your work to rest for a while, look at it with fresh eyes and self-edit your manuscript eliminating passive voice, filler words, and redundant adverbs.

Then, have a professional editor give you a general assessment. They’ll look at the structure and shape of your manuscript and tell you which parts need to be expanded on or cut. As someone who edited and commissioned several biographies, Tom Bromley points out that a professional “will look at the sources used and assess whether they back up the points made, or if more are needed. They would also look for context, and whether or not more background information is needed for the reader to understand the story fully. And they might check your facts, too.”
In addition to structural editing, you may want to have someone copy-edit and proofread your work.

MEET EDITORS
Polish your book with expert help
Sign up, meet 1500+ experienced editors, and find your perfect match.
Importantly, make sure to include a bibliography with a list of all the interviews, documents, and sources used in the writing process. You’ll have to compile it according to a manual of style, but you can easily create one by using tools like EasyBib . Once the text is nicely polished and typeset in your writing software , you can prepare for the publication process.
In conclusion, by mixing storytelling elements with diligent research, you’ll be able to breathe life into a powerful biography that immerses readers in another individual’s life experience. Whether that’ll spark inspiration or controversy, remember you could have an important role in shaping their legacy 一 and that’s something not to take lightly.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

Man vs Nature: The Most Compelling Conflict in Writing
What is man vs nature? Learn all about this timeless conflict with examples of man vs nature in books, television, and film.

The Redemption Arc: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
Learn what it takes to redeem a character with these examples and writing tips.

How Many Sentences Are in a Paragraph?
From fiction to nonfiction works, the length of a paragraph varies depending on its purpose. Here's everything you need to know.
Narrative Structure: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
What's the difference between story structure and narrative structure? And how do you choose the right narrative structure for you novel?

What is the Proust Questionnaire? 22 Questions to Write Better Characters
Inspired by Marcel Proust, check out the questionnaire that will help your characters remember things past.

What is Pathos? Definition and Examples in Literature
Pathos is a literary device that uses language to evoke an emotional response, typically to connect readers with the characters in a story.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

We made a writing app for you
Yes, you! Write. Format. Export for ebook and print. 100% free, always.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Biographical research is a qualitative research approach aligned to the social interpretive paradigm of research. The biographical research is concerned with the reconstruction of life histories and the constitution of meaning based on biographical narratives and documents. The material for analysis consists of interview protocols (memorandums), video recordings, photographs, and a diversity ...
Biographical research in education may be conceived in many different ways; however, typically the topic constitutes the study of a single life, focusing primarily upon an individual who in some way is affiliated with the professional field of education, broadly conceived (Garraty, 1957; Oates, 1986). Other research methodologies are often ...
biography, form of literature, commonly considered nonfictional, the subject of which is the life of an individual.One of the oldest forms of literary expression, it seeks to re-create in words the life of a human being—as understood from the historical or personal perspective of the author—by drawing upon all available evidence, including that retained in memory as well as written, oral ...
Introduction. We purchase access to new online versions of major biographical reference sources as they become available. Many important biographical resources are available in print and on microfilm. This guide combines online titles with the selected microform and print biography titles in the Olin and Africana reference collections.
Analysis of the (objective) biographical data. Text and thematic field analysis (structure of self-presentation; reconstruction of the life story; narrated life). Reconstruction of the life history (lived life as experienced). Microanalysis of individual text segments.
A biography, or simply bio, is a detailed description of a person's life. It involves more than just basic facts like education, work, relationships, and death; it portrays a person's experience of these life events. Unlike a profile or curriculum vitae ( résumé ), a biography presents a subject's life story, highlighting various aspects of ...
The life story method is also known as the life history, biographical method and similar, which is a retrospective narrative of an individual about his life or parts of life in either written or ...
Biographical Research Methods. Biographical data provide unique insights into social life, but they also pose some significant challenges for social science researchers. This book offers a systematic, flexible guide to using biographical narrative methods in your research project. Drawing upon the authors' own research, as well as case ...
Reconstructive biographical research is a distinct sociological approach to social analysis. It explores the interrelation between 'biography' and 'society' and thus belongs to those sociological approaches that are linked to the assumption that 'society' is made up of individuals and cannot be conceived independently of their interpretations and actions.
Biography is an important forum for well-considered biographical scholarship. It features stimulating articles that explore the theoretical, generic, historical, and cultural dimensions of life-writing; and the integration of literature, history, the arts, and the social sciences as they relate to biography.
Biography-Research-Methodology. 2. Biography as a literary form. I. Title. II. Series. CT22.R63 2001 808 .06692-dc21 2001021067 ... ated with a precise definition but to indicate various, often interrelated, approaches to the study of individuals. Biographical research is an excit-
Biography is 'an account of someone's life written by someone else.' (Oxford, 2016). Biographical research aids in developing a concept of learning which is context-specific, rather than ...
Google Books (1870, 1874) Hathitrust (1916) (1945); HathiTrust (1930-1973 incomplete) Internet Archive (1911) HOLLIS Record. --Lists diplomats and consuls together with biographies if the recently deceased. Additional sources in Finding Biographical Information. Last Updated: Apr 26, 2024 4:12 PM. URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/history.
2,357 online biographical articles on astronomers throughout history and worldwide. Biographical Resources: An African and African Diaspora Approach. A LibGuide created by Eric Acree, Africana Librarian at Cornell, for locating information about people of African descent. Includes online and print resources.
cal interviewing as a branch of qualitative research assumes, then, that the biographical research interview is interactive, co-constructed, flooded with inter-discursivity, and that it constructs and constitutes local action and mean-ing-making in the rich ecologies of learning and living. 3 Biography and Context: The Ecologies of a Told Life
biography: [noun] a usually written history of a person's life.
Biography . Dive into the world of biography, which is an account of another person's life drawn from available evidence. This evidence might include correspondence, diaries, published articles, recordings, archives, or even the author's personal recollection of the subject of the biographical record.
Biography. American National Biography (Harvard login) is the standard American source for biographies of major figures. Can do searches of occupations and limit by date. ... While you'll need to consider the timing and scope of your research, you will miss opportunities and your research may be incomplete if you use only what's already been ...
<button>Click to continue</button>
Definition of Biography. A biography is the non- fiction, written history or account of a person's life. Biographies are intended to give an objective portrayal of a person, written in the third person. Biographers collect information from the subject (if he/she is available), acquaintances of the subject, or in researching other sources such ...
An academic biography is a concise description of a researcher and his career which is mostly used as an introduction to a conference or public event. This article discusses some important tips on writing an academic bio. ... His favorite place to do research in his backyard, which opens to the Akron National Forest. This improvised version is ...
Biomedical research is the broad area of science that looks for ways to prevent and treat diseases that cause illness and death in people and in animals. This general field of research includes many areas of both the life and physical sciences. Utilizing biotechnology techniques, biomedical researchers study biological processes and diseases ...
Facebook. These are just some of the story elements you can use to make your biography more compelling. Once you've finished your manuscript, it's a good idea to ask for feedback. 7. Get feedback and polish the text. If you're going to self-publish your biography, you'll have to polish it to professional standards.