
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download

Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
- Last modified on: 1 month ago
- Reading Time: 8 Minutes

Table of Contents
[Download] Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
Here we are providing case study or passage-based questions for class 6 science chapter 5 Separation of Substances.
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
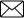
You are asked to add two spoons of solid salt to some liquid water taken in a beaker. On stirring it you find that whole of the salt has disappeared and only liquid can be seen in beaker. 1. After stirring the salt completely disappears and you can see only liquid in the beaker. The liquid in beaker is (a) water (b) solution (c) solute (d) solvent 2 . Which of the following processes will be useful to get salt from this solution? (a) Condensation (b) Evaporation (c) Filtration (d) Sedimentation 3. Which process can you use to get liquid water from the water vapours if you collect them in another container? (a) Sedimentation (b) Condensation (c) Evaporation (d) Filtration
Related Posts
What is case study question for class 6 science.
Case study or passage-based questions in class 6 Science typically require students to read a given scenario or passage and answer questions based on the information provided. These questions assess students’ comprehension, analytical thinking, and application of scientific concepts. Here is an example of case study or passage-based questions for class 6 Science:
Passage: Rahul conducted an experiment to investigate how different liquids affect the rusting of iron nails. He placed four iron nails in four separate beakers containing water, vinegar, oil, and saltwater. After one week, he observed the nails and recorded his observations.
a) What is the purpose of Rahul’s experiment?
b) Compare and contrast the appearance of the iron nails in each beaker after one week.
Best Ways to Prepare for Case Study Questions
To develop a strong command on class 6 Science case study questions, you can follow these steps:
- Read the textbook and study materials: Familiarize yourself with the concepts and topics covered in your class 6 Science curriculum. Read the textbook thoroughly and take notes on important information.
- Practice analyzing case studies: Look for case studies or passages related to class 6 Science topics. Analyze the given information, identify key details, and understand the context of the situation.
- Develop comprehension skills: Focus on improving your reading comprehension skills. Practice reading passages or articles and try to summarize the main points or extract relevant information. Pay attention to details, vocabulary, and the overall structure of the passage.
- Understand scientific concepts: Ensure that you have a solid understanding of the scientific concepts discussed in class. Review the fundamental principles and theories related to each topic.
- Make connections: Try to connect the information provided in the case study to the concepts you have learned in class. Identify any cause-effect relationships, patterns, or relevant scientific principles that apply to the situation.
- Practice critical thinking: Develop your critical thinking skills by analyzing and evaluating the information given in the case study. Think logically, consider multiple perspectives, and draw conclusions based on the evidence provided.
- Solve practice questions: Look for practice questions or sample case study questions specifically designed for class 6 Science. Solve these questions to apply your knowledge, practice your analytical skills, and familiarize yourself with the format of case study questions.
- Seek clarification: If you come across any challenging concepts or have doubts, don’t hesitate to ask your teacher for clarification. Understanding the underlying principles will help you tackle case study questions effectively.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

- Lakhmir Singh
Class 6 Science Case Study Question
Case study question class 6 science (cbse / ncert board).
Class 6 Science Case Study Question and Answer: CBSE / NCERT Board Class 6 Science Case Study Question prepared by expert Science Teacher. Students can learn Case Based Question / Paragraph Type Question for NCERT Class 6 Science.
There are total 16 chapter Food Where Does It Come From, Components of Food, Fibre to Fabric, Sorting Materials Into Groups, Separation of Substances, Changes Around Us, Getting to Know Plants, Body Movements, The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings, Motion and Measurement of Distances, Light Shadows and Reflection, Electricity and Circuits, Fun with Magnets, Water, Air Around Us, Garbage In Garbage Out.
For any problem during learning any Case or any doubts please comment us. We are always ready to help You.
CBSE Class 6 Science Case Study Question
Chapter 1 Food Where Does It come From Case Study Question
Chapter 2 Components of Food Case Study Question
Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric Case Study Question
Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups Case Study Question
Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Case Study Question
Chapter 6 Changes Around Us Case Study Question
Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants Case Study Question
Chapter 8 Body Movements Case Study Question
Chapter 9 The Living Organisms – Characteristics and Habitats Case Study Question
Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances Case Study Question
Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection Case Study Question
Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Case Study Question
Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Case Study Question
Chapter 14 Water Case Study Question
Chapter 15 Air Around Us Case Study Question
Chapter 16 Garbage In Garbage Out Case Study Question
What is Case Study Question?
Ans. At case Study there will one paragraph and on the basis of that concept some question will made. Students have to solve that question.
How many marks will have at case based question?
Most of time 5 questions will made from each case. There will 1 or 2 marks for each question.
Important links:
- Lakhmir Singh Class 6 Book Solution
- NCERT Solution Class 6 Science
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Case Based Questions - Separation of Substances
Case 1: separation of substances in agriculture.
Mr. Patel is a farmer in India, and he's been using traditional methods for separating grains from harvested stalks. He's curious about modern farming equipment. Answer the following questions:
Q1: Explain the traditional method Mr. Patel uses for threshing. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this method? Ans: Mr. Patel uses manual threshing, where small bundles of harvested stalks are thrashed on a hard surface to separate the grains. The advantage is that it's simple and doesn't require machinery. The disadvantage is that it's labor-intensive. Q2: Describe the modern farming equipment called a combine harvester. How does it work, and what are its benefits over traditional methods? Ans: A combine harvester is a modern farming machine that can harvest, thresh, and winnow in a single operation. It works by cutting and collecting crops, separating grains from stalks, and removing husks. Benefits include increased efficiency and reduced labor. Q3: What is the main purpose of threshing in agriculture? (a) Separating grains from harvested stalks (b) Separating stones from rice (c) Separating sand from gravel (d) Separating bran from flour Ans: (a) Q4: What is the purpose of winnowing in agriculture? (a) Separating grains from husk (b) Separating stones from rice (c) Separating sand from gravel (d) Separating bran from flour Ans: (a)
Case 2: Separation of Substances in Filtration
Sophia is a chemistry student conducting an experiment to separate fine insoluble solid particles from a liquid. Answer the following questions:
Q5: Explain the process of filtration that Sophia is using in her experiment. What equipment does she need, and how does it work? Ans: Filtration is a process where a mixture is passed through a filter paper or sieve to separate solid particles from the liquid. Sophia needs a funnel, filter paper, and a container. The liquid passes through the filter paper, leaving solid particles behind. Q6: What are the common applications of filtration in daily life? Provide at least three examples. Ans: Common applications of filtration include purifying drinking water, filtering coffee grounds, and separating impurities from cooking oil. Q7: What does filtration help separate? (a) Soluble solids from liquids (b) Insoluble solids from liquids (c) Gases from liquids (d) Liquids from solids Ans: (b) Q8: In which of the following scenarios would filtration be most suitable? (a) Separating sugar from tea (b) Separating salt from water (c) Separating oxygen from air (d) Separating oil from vinegar Ans: (a)
Case 3: Separation of Substances in Evaporation and Condensation
Lisa wants to separate salt from a solution of salt and water. She decides to use evaporation and condensation. Answer the following questions:
Q9: Explain how Lisa can separate salt from the saltwater solution using evaporation and condensation. What are the steps involved? Ans: Lisa can separate salt from the saltwater solution by evaporating the water, leaving behind salt crystals. Then, she can use condensation to collect the evaporated water vapor and convert it back into liquid water. Q10: Why is it important to use both evaporation and condensation in this process? Ans: Using both evaporation and condensation ensures that only the water is separated from the solution, leaving the salt behind. Q11: What is a saturated solution? (a) A solution with too much solid dissolved in it (b) A solution with too little solid dissolved in it (c) A solution with an equal amount of solid and liquid (d) A solution with no solid dissolved in it Ans: (a) Q12: What is the purpose of condensation in the separation of salt from a saltwater solution? (a) To convert liquid water into vapor (b) To convert water vapor into liquid water (c) To separate salt from water (d) To dissolve salt in water Ans: (b)
Case 4: Separation of Substances in Handpicking and Sieving
John is helping his mother in the kitchen, and she asks him to separate stones from a bowl of rice. Answer the following questions:
Q13: Describe how John can use handpicking to separate stones from rice. What conditions make handpicking suitable for this task? Ans: John can use handpicking to separate stones from rice because the stones have different sizes and colors than the rice. He can simply pick out the stones by hand. Q14: Explain the process of sieving and how it can be used to separate substances. What type of materials can be separated effectively through sieving? Ans: Sieving involves using a sieve with appropriately sized holes to separate substances. It is effective for separating materials like bran from flour, sand from gravel, and pearls of different sizes. Q15: What is the primary condition that makes handpicking effective for separating substances? (a) Differences in size and color (b) Differences in taste (c) Differences in temperature (d) Differences in shape and smell Ans: (a) Q16: What can be effectively separated using sieving? (a) Salt from water (b) Bran from flour (c) Air from gases (d) Liquid from solids Ans: (d)
Case 5: Separation of Substances in Sedimentation and Decantation
Sara is conducting an experiment with muddy water. She wants to separate soil and sand from the water. Answer the following questions:
Q17: Explain the process of sedimentation and how it can be used to separate soil and sand from muddy water. What happens during sedimentation? Ans: Sedimentation involves allowing insoluble particles (soil and sand) to settle at the bottom of the container over time. Sara can use this process to separate soil and sand from muddy water. Q18: What is the purpose of decantation, and when is it used in conjunction with sedimentation? Ans: Decantation is used after sedimentation to carefully pour out the upper layer (water) while leaving the sediment (soil and sand) behind. Q19: What is the outcome of sedimentation in the separation of soil and sand from water? (a) Soil and sand remain suspended in water. (b) Soil and sand settle at the bottom of the container. (c) Water evaporates completely. (d) Soil and sand turn into gas. Ans: (b) Q20: When is decantation typically used in the separation of substances? (a) Before sedimentation (b) After sedimentation (c) Instead of sedimentation (d) During filtration Ans: (b)
Top Courses for Class 6
Faqs on class 6 science chapter 3 case based questions - separation of substances, video lectures, objective type questions, viva questions, practice quizzes, previous year questions with solutions, semester notes, shortcuts and tricks, sample paper, extra questions, mock tests for examination, past year papers, important questions, study material.

Case Based Questions: Separation of Substances Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: separation of substances, case based questions: separation of substances notes, case based questions: separation of substances class 6, study case based questions: separation of substances on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 5 (Free PDF Download)
- Revision Notes

Revision Notes for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5 - Free PDF Download
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 5 are now available online with Vedantu in PDF format to ensure complete exam preparation. Our standard Class 6 Notes in Science on Separation of Substances are compiled by subject experts having years of experience in this field. Such Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes consists of step-by-step chapter explanation as well as short-cut techniques are provided. Apart from Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Notes, we offer revision materials for all subjects that are deemed crucial for your forthcoming exams
Every NCERT Solution is provided to make the study simple and interesting on Vedantu. You can also download NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 6 Science Revision Notes 2023-24 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 6 Science revision notes for All chapters:
Access Class 6 Science Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances
A substance is a piece of matter with certain features and characteristics.
Substances characterised into two types as Pure substance and Impure substance.
Pure Substance:
Many of the substances we come into contact with only have one type of component particle.
Pure substances are elements and compounds.
Iron, copper, water, salt, and other pure substances are examples.
Impure Substance:
Impure substances are those that have multiple types of component particles.
Pond water, milk, and other unclean substances are examples.
Impurities:
Impurities are undesired particles in a substance that cause it to be impure.
Element is a substance made up of the same material's identical particles.
Compound is a substance created by the chemical reaction of two or more elements in a specific ratio.
Mixtures are substances that have more than one component blended in any ratio.
Air, for example, is made up of a variety of gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, dust particles, and so on.
A mixture of two or more components is referred to as a solution.
The solvent is the material with the highest concentration, whereas the solute is the substance with the lowest concentration.
Pure substances are elements and compounds.
Need for Separating Component of a Mixture:
Separation of the components of a mixture or an impure substance for the purposes of:
To get rid of something that isn't beneficial or dangerous.
Obtaining the required component.
To get a pure sample, contaminants must be removed.
Methods of Separation:
The properties of the components in a mixture, such as particle size, density, melting point, boiling temperature, volatility, and so on, remain unchanged.
To separate the components of a mixture, use the differences in any one of these qualities.
The following methods are used for separation, these are as follows;
Threshing
Winnowing
Handpicking
Sieving
Magnetic Separation
Floating and Sinking Method
Sedimentation and Decantation
Loading
Filtration
Separation to Immiscible Liquids
Churning to Separate Cream from Milk
Sublimation
From above Threshing, Winnowing, Handpicking, Sieving and Magnetic Separation methods are used to separate the solid from other solids.
Evaporation and Condensation methods are used to separate water soluble solids or soluble solute in the solvent.
Sedimentation, Decantation, Loading and Filtration methods are used to separate insoluble solids from liquids.
Funnel, Centrifugation and Churning methods are used for separation of immiscible liquids.
Floating and Sinking Method and Sublimation methods are used for removing a non-soluble solute from a solvent.
Separation of Solid From Other Solids:
Threshing is the process of separating grain from husk.
The grains must be separated from the stalks once these crops have been harvested or cut (the dried stems). Threshing is used to accomplish this.
It can be done by hand or with the use of equipment.
Threshing is done manually by grasping a pile of grain and pounding it against a rock or a hard surface.
This loosens the grain and separates it from the stalk.
Bullocks are sometimes used to crush the gathered stalks during threshing.
Threshing can also be done with the assistance of machinery such as the combine harvester.
Seed coverings and small fragments of leaves or stem may still be present in threshed grains (collectively called chaff). Winnowing is used to separate them.

Wind or blowing air is used to separate heavier and lighter components of a combination.
Winnowing is the process used to separate chaff from grain with the help of wind or blowing air.
The farmer places the mixture of chaff and grain in a winnowing basket and stands at a higher level, letting the mixture fall to the ground.
The grain falls practically vertically because it is heavier, whereas the lighter chaff is swept away by the wind and forms a distinct mound from the grain.
Cattle feed is made from the separated chaff.
The direction of the wind is very important factor in the process of winnowing.
Hand-Picking:
Unwanted components are simply picked up by hand in this process.
When the quantity of the combination is tiny, the undesired component is present in lesser quantities, and the size, form, or colour of the unwanted substance differs from that of the useful one, this hand-picking approach is preferable.
The procedure for separating solid parts of a mixture of varying sizes.
The smaller component (stones or husk) passes through the sieve's pores, while the larger component (stones or husk) is left behind. Some people use this approach to remove wheat bran (larger particles) from flour in their homes.
At construction sites, sieving is also used to remove pebbles and stones from sand. The fine sand particles flow through the holes of the sieve, while the stones and pebbles in the combination remain in the sieve.
A sieve is a device having numerous small holes through which smaller particles can pass.
Magnetic Separation:
When a magnet is passed over a magnetic mixture, the magnetic material adheres to it and is removed.
Separation of Water Soluble Particles or Soluble in Solvent Solutes:
Evaporation:
The process of converting a liquid condition to a gaseous state when heated.
Condensation:
On cooling, the process of converting a gaseous state to a liquid state.
Separation of Insoluble Solids From Liquids:
Sedimentation:
Sedimentation is the process of heavier and insoluble components of a mixture sinking down.
Sand and water are two examples.
Decantation:
Decantation is the technique of conveying clean liquid without disturbing the sediment.
The methods for causing finer particles to settle more quickly by dissolving a little amount of alum.
Filtration:
Impurities are passed through a filter in this process. The pores of the filter enable only liquids to flow through, and it may separate suspended particles and solid particles.
The clear liquid recovered is referred to as filtrate, whereas the stuff left on the filter paper is referred to as residue.
Separation of Immiscible Liquids:
In this process, the separation of an insoluble material from a liquid will be done by passing the mixture through a filtering apparatus.
It is used to separate oil and water mixtures.
Centrifugation:
A centrifuge is used to spin a liquid containing suspended particles at a high speed, causing heavier particles to settle down.
It's used to separate milk from cream.
This approach is used to separate lighter solid particles suspended in a liquid.
Butter made from curd is an example.
Separating Solute not Soluble in a Solvent:
Flotation and sinking methods:
This method is employed when one of the components of a mixture is lighter than water and the other is heavier than water and the components are not soluble in water.
Sublimation:
Sublimation is the process of converting a solid to a vapour without first becoming a liquid.
Husk and stones might be extracted from grains by handpicking.
Winnowing separates the husk from the heavier grain seeds.
A saturated solution is one in which no more of a substance can be dissolved.
A solution can be heated to dissolve more of a substance.
Different amounts of soluble compounds dissolve in water.
Class 6 Chapter 5 Science Notes Separation of Substances – Chapter Overview
Science, as a subject is an inevitable addition in the CBSE curriculum of students because it enhances and promotes them with the knowledge how the functioning of everything around us is due to the implementation of various properties of Science.
Similarly, in Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes, students will be able to learn about the fundamental concepts of substances and pure substances, and through which way these elements can be separated if amalgamated in a mixture.
Sound knowledge on these topics at the formative stage will help students to build a stronghold over the subject.
Students can easily lay their hands on our subject, and chapter-specific revision notes, as it comes with a download option. For rounding off their last-minute revision before approaching to their exam hall, students can safely refer to our revision notes and clear the air of vagueness if any.
These standard study sets are curated, keeping in mind the need of students to have access to quality study materials where they can have the maximum retention of chapters. Our Class 6 Notes in Science on Separation of Substances are available online in a PDF format with thus making it easy for everyone to avail it anytime and anywhere.
Class 6 Chapter 5 Science Notes – Pure Substances
In our Class 6 Chapter 5 Science Notes, students will be able to gain a fundamental concept of the most crucial topic of this chapter that is pure substances. According to the clarification stated by our subject experts, it is a substance that contains only pure particles.
Gain access to more such lucid explanation of topics and amp your exam confidence with our Class 6 Notes in Science on Separation of Substances this exam season. Considering that our team of subject experts has drafted such study notes, they are potent enough to fetch subject-best scores!
Class 6 Notes in Science on Separation of Substances – Impure Substances
According to our Class 6 Notes in Science on Separation of Substances, impure substances are those which contains more than one particles separated by their shape colour, size and characteristics.
NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Notes - Element
Our subject experts in our NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Notes have put forth the definition of an element in a highly decipherable way, suitable for children of standard six. It states that elements are substances that are made from identical particles of one material.
Refer to our Class 6 Notes in Science on Separation of Substances for gaining comprehensive knowledge about the topic of elements. Subsequently, attain expertise to handle all sorts of questions centred on this topic.
Class 6 Separation of Substances Notes - Compound
A compound is a substance formed as a result of a chemical combination of two or more elements in a fixed ratio. Students can’t receive a substantial knowledge on this topic from our Class 6 Separation of Substances Notes and achieve a clear perspective on this notion.
Class 6 Science Notes – Need For Separating Component of a Mixture
By following our Class 6 Science Notes, students will learn about the need for separating component of a mixture. The causes are listed below:
Removing harmful or unwanted components
Obtaining a useful component in pure form
Separation of Substances Notes – Methods of Separation
In this section of Separation of Substances Notes, students will learn about the different methods of separation. The lists of the techniques are enumerated below:
Hand-picking
Magnetic separation
Floating and sinking method
Sedimentation and decantation
Students can follow our Class 6 Notes in Science on Separation of Substances to get an elaborative idea about the above-mentioned methods.
Class 6 Science Chapter 5 – Separation of Solids from Other Solids
In this section of Class 6 Science Chapter 5, students will be learning about the various procedures incorporated in the machinery and factories for accomplishing the task of separating solids from the clump of other solids. Given below is the list of several methods taken into account while separating a solid from a solid:
Threshing – The process of removal of grain from husks and chaff is called threshing.
Winnowing – In this process, the heavier and lighter components are separated from each other after the wind blows them off.
Hand-picking – This is a process where the unwanted foreign solid particles are removed by using hands.
Sieving – A sieve is a device that has numerous pores in it, for separating solid constituents of a mixture that are different in sizes.
Our Class 6 Notes in Science on Separation of Substances consists of examples associated with this above-mentioned procedure. It ensures a better understanding of the process for our students.
Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes NCERT – Separation of Insoluble Solids from Liquids
The method of separation of insoluble solids from liquids can be achieved in many ways. Some of them are discussed below:
Sedimentation – It is the practice of settling down heavier and un-dissolvable component from a mixture.
Decantation – It is the process of transferring clean liquid without disturbing the sediment, is called decantation.
Loading - This includes the process of dissolving finer particles in a mixture by adding a small portion of alum in the mixture
Filtration – This process involves the passing of impurities through a filter. These filters have pores which only allow the liquid constituent to pass through. This method can separate suspended particles or solid particles as well.
All the above-mentioned procedures are further elucidated in our Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes NCERT, which students can download from our offline portal and go through the revision notes even when offline.
6th Standard Science Notes – Separating Solute in a Solvent
Separating of solute in a solvent is a crucial mechanism as it occurs when the components are not soluble in water, and one of the elements of a mixture is lighter than water, while the other component is relatively more substantial. Students to give an accurate answer to questions related to this topic, have to peruse the chapter thoroughly without missing the minute details.
Alternatively, to cut off this effort of minute reading students can refer to our 6th Standard Science Notes, and gain access to a comprehensive study material where topics are described broadly, further established with real-life examples.
Chapter 5 Science Class 6 Notes - Sublimation
It is a phenomenon that results in changing of a solid form directly into the state of vapour, without turning into the intermediate liquid state. Sublimation too is a method of separating solute in a solvent.
Few examples cited in our Class 6 Science Notes PDF are mentioned below:
Removal of husks from stones by the simple method hand-picking
Husks from grains can be further removed by employing the process of winnowing.
Students will be able to learn the basics of this chapter comprehensively by referring to our Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Notes and achieve a wholesome exam preparation.
Vedantu – Your Trusted Learning Ally
Vedantu’s revision notes are a comprehensive study aid for students who are still strutting with complex topics of the chapter. We offer online study material for all subjects to help students achieve a foundation cemented with clear ideas and perspective on the chapter content.
Our Class 6 Notes in Science on Separation of Substances are curated with utmost precision by our subject experts to offer students with more straightforward and short-cut techniques required to decipher theories and properties of the chapter without any conundrum.
Make the most of your time and live an unmatched digital learning experience with Vedantu where learning is fun and no longer arduous.
Conclusion
The Class 6 CBSE Science Chapter 5, "Separation of Substances," along with its freely available PDF notes, serves as an indispensable educational asset. These notes demystify the intricate world of separating substances, offering a simplified and structured approach for young learners. They empower students with essential scientific knowledge, fostering an understanding of various separation techniques and their real-world applications. Beyond academics, these notes promote critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and logical reasoning, qualities invaluable for lifelong learning. The availability of these free PDF notes ensures accessibility, democratizing education for all. In essence, these notes contribute to a comprehensive understanding of science, making the subject more engaging and relevant for students.

FAQs on Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes CBSE Science Chapter 5 (Free PDF Download)
1. Give an overview of Chapter 5 of Class 6 Science.
Chapter 5 of Class 6 Science is “Separation of Substances”. This chapter talks about the separation of substances. A majority of substances are a mixture of two or more substances. Separation of substances enables us to separate the various substances that make up a solution. The chapter describes different kinds of methods that can be employed to separate substances depending on the nature of the materials involved. The chapters introduce you to the terms for the various processes that you come across almost daily.
2. What is the separation of substance?
Separation of a substance helps you to remove various impurities from the solution. It also allows you to remove from a solution any material that you do not need. Often, substances also include harmful material that you need to remove so that it is safe to consume. Separation also enables you to separate various materials which then can be used separately. Some of the separation methods are handpicking, sedimentation and sieving. To revise the chapter students can download the NCERT Notes for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 free of cost from the vedantu website (vedantu.com).
3. What is the basis of separation of components of mixture Class 6 Science Chapter 5?
The first step that you have to keep in mind is the nature of the substance that you want to separate into its various constituents. If a substance is visible and can be separated easily, you can use the method of handpicking. But if the substance is too small that it is not visible by naked eyes and the solution is liquid, you can use the method of filtration. If the substance consists of materials that differ in weight, the method that can be used is winnowing. To know more about it, students can download the vedantu app.
4. Why do we separate substances into groups?
Separating the substances into various groups helps us to understand which method of separation will be effective and which method will not work. Considering the nature of the substance one has to select one or more methods to separate it. The separation of substances into different categories enables us to remove the unwanted materials, harmful impurities from the solution. Choosing the right method of separation is dependent on the nature of the constituents of the substance.
5. How to separate mud from water?
The mud in the water usually remains in suspension. Mud is an example of impurity and unwanted material that you have to remove from the water so that it can be consumed. To separate the mud from the water let the water be still. This will allow the mud to settle at the bottom of the container and the clean water will occupy the upper layer. Make sure not to disturb the water. You can remove the water carefully in another container.
NCERT Solutions
Study materials for class 6.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
These NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Questions and Answers are prepared by our highly skilled subject experts to help students while preparing for their exams.
Separation of Substances NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5
Class 6 science chapter 5 separation of substances textbook exercise questions and answers.
Question 1. Why do we need to separate different components of a mixture? Give two examples. Answer: Among different components of mixture there are many substances which are harmful or not useful for us. To remove these harmful or useless components we need to separate them. For example:
- Tea leaves are separated from liquid with a strainer while preparing tea.
- Grain is separated from stalks, while harvesting.

Question 3. How will you separate husk or dirt particles from a given sample of pulses before cooking? Answer: Husk or dirt particles can be separated by winnowing, being lighter they will fly away from pulses. Dirt particles can also be separated by handpicking.
Question 4. What is sieving? Where is it used? Answer: Sieving is a process of separation of particles of different sizes using a sieve. Small and fine sieves are used in the kitchen to separate bran and other impurities from flour. The impurities remain on the sieve and the flour passes through. Bigger sieves are used at construction sites to separate pebbles and stones from sand.
Question 5. How will you separate sand and water from their mixture? Answer: We separate sand and water by sedimentation and decantation method. First we leave this mixture for some time. After sometime, the sand which is heavier is settled down at the bottom. After that we will pour water into another container and the mixture will be separated.
Question 6. Is it possible to separate sugar mixed with wheat flour? If yes, how will you do it? Answer: It is possible to separate sugar mixed with wheat flour. The mixture of sugar and wheat flour can be separated by strainer and sugar being bigger in size remains on the strainer. Thus, sugar can be separated from the mixture of sugar and wheat flour.
Question 7. How would you obtain clear water from a sample of muddy water? Answer: We can separate clear water from muddy water by filtration process. A filter paper is one such filter that has very fine pores in it. A filter paper folded in the form of a cone is fixed in a funnel. The mixture is then poured on the filter paper. Solid particles in the mixture do not pass through it and remain on the filter.
Question 8. Fill in the blanks. a. The method of separating seeds of paddy from its stalks is called …………….. b. When milk, cooled after boiling, is poured onto a piece of cloth the cream (malai) is left behind on it. This process of separating cream from milk is an example of …………….. c. Salt is obtained from seawater by the process of …………….. d. Impurities settled at the bottom when muddy water was kept overnight in a bucket. The clear water was then poured off from the top. The process of separation used in this example is called …………….. Answer: a. threshing b. filtration c. evaporation d. sedimentation and decantation
Question 9. True or False? a. A mixture of milk and water can be separated by filtration. b. A mixture of powdered salt and sugar can be separated by the process of winnowing. c. Separation of sugar from tea can be done with filtration. d. Grain and husk can be separated with the process of decantation. Answer: a. False b. False c. False d. False
Question 10. Lemonade is prepared by mixing lemon juice and sugar in water. You wish to add ice to cool it. Should you add ice to the lemonade before or after dissolving sugar? In which case would it be possible to dissolve more sugar? Answer: We should add ice after dissolving sugar. When the temperature is high, then more sugar can be dissolved. After mixing ice, it gets cool and less sugar will dissolve in it.
NCERT Extended Learning Activities and Projects
Question 1. Visit a nearby dairy and report about the processes used to separate cream from milk. Answer: Do it yourself.
Question 2. You have tried a number of methods to separate impurities like mud from water. Sometimes, the water obtained after employing all these processes could still be a little muddy. Let us see if we can remove even this impurity completely. Take this filtered water in a glass. Tie a thread to a small piece of alum. Suspend the piece of alum in the water and swirl. Did the water become clear? What happened to the mud? This process is called loading. Talk to some elders in your family to find out whether they have seen or used this process. Answer: Do it yourself.
Objective: To prepare a saturated salt solution and study the effect of temperature. Materials Required: Water, glass, salt, spoon. Procedure:
- Dissolve salt in water by continuous stirring.
- After some time, more salt will not be able to dissolve in water. This become a saturated solution.
- Now heat the water and try dissolving more salt.
Observations: More salt can be dissolved in a saturated solution on heating. Conclusion: On increasing temperature, solubility of substances also increase.
Need for Separation: The constituents of mixtures need to be separated for the following reasons: i. To remove undesirable substances: Before we use a substance, we need to separate the harmful substance that may be mixed with it. For example, we need to separate the impurities from ordinary water to make it potable water. ii. To obtain desirable substances: Sometimes, we need to separate even useful components if we need to use them separately. For example, we separate petrol, kerosene and diesel from petroleum (crude oil). iii. To obtain highly pure substances: While producing a medicine, it is essential to remove all harmful impurities from the substance so that it can be used as medicine. But in this case, the impurity has to be removed without any loss or wastage of the substance.
Principle of Separation: The constituents of a mixture do not lose their original properties such as particle size, density, melting point, boiling point, etc. This property is used in separation methods.

v. Magnetic Separation: In this method a magnet is used for picking up iron pieces, nails, pins, etc. from grains or any other commodity. On a larger scale, a powerful magnet is employed for separating scrap iron from non-magnetic waste materials.

The liquid above the sediments is known as the supernatant liquid. The process of pouring out the clear upper liquid without disturbing the sediments is called decantation. The solid particles which are insoluble in a liquid can be separated by decantation. For example, a mixture of sand and water contains sand particles suspended in water. So,sand can be separated from sand-water mixture by the method of sedimentation and decantation.
vii. Filtration: Decantation is not enough for complete separation of a solid-liquid mixture. This can be done better by filtration in which the mixture is dropped on a porous material known as filter.
The liquid passes through the filter and comes down as filtrate. The insoluble solid left behind is known as residue. In this way, a mixture of an insoluble solid in a liquid is separated into the solid residue and clear filtrate.
Objective: To purify a sample of muddy water by the process of filtration. Materials Required: Soil, water, glass, filter paper, funnel, clamp stand and beaker. Procedure:
- Mix some soil with water in a glass.
- Make a filter paper cone and set it in a funnel.
- Arrange the apparatus as shown below.
- Allow water into the funnel through filter paper get collected in the beaker.

viii. Loading: Loading is a method in which a special substance called alum is used to load the suspended particles to make them heavy and increase their sedimentation speed. For example, the particles of clay in muddy water are very fine and their sedimentation takes a very long time.
Alum is used to load suspended clay particles in water. The dissolved particles of alum load the fine particles of clay in water. They become heavier and settle down very fast. The clear water on top is then decanted or filtered.
ix. Centrifugation: All rotating bodies experience centrifugal force. The principle of centrifugal force is applied for separation of solids and liquids. This method is called centrifugation. This method is of great value in case of separating thin pastes from thick pastes, where filtration is not possible.
Cream separating machines are used in dairies. In this machine, milk is rotated at a high speed. Cream being lighter, collects towards the centre. The milk being heavier settles down below the cream layer. The two are then taken out from two separate taps,

Use of more than one method of separation: The method to be used for separating a mixture into its components depends on the nature of components.
Some of the mixtures can be separated by a single method but various mixtures can be separated into individual components by using a combination of various methods. These methods are applied turn by turn. Suppose you are given a mixture of sand, iron fillings, common salt, solid salt and naphthalene. You can separate its components as follows: Iron fillings: by magnetic separation Naphthalene: by sublimation
Salt and sand are dissolved in water. Salt is soluble but sand being insoluble, settles and can be separated by sedimentation, decantation followed by evaporation of salt water.
Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Additional Important Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Name any two methods used for separation of substances. Answer: Threshing and filtration.
Question 2. Which method is used to separate stones from grains on small scale? Answer: Handpicking.
Question 3. How does the farmer separate grain seeds from bundles of stalk? Answer: By threshing, farmer can separate grain seeds from bundles of stalk.
Question 4. Which method is used to separate heavier and lighter components of a mixture by wind or blowing air? Answer: Winnowing.
Question 5. What is decantation? Answer: The process in which water is removed when heavier component of mixture settles is called decantation.
Question 6. Which method of separating tea leaves from prepared tea is better: filtration or decantation? Answer: Filtration.
Question 7. What is evaporation? Answer: The process of conversion of water into its vapour at normal temperature is called evaporation.
Question 8. How can sand be separated from water? Answer: Sand can be separated from water by sedimentation and decantation.
Question 9. We dissolve salt in water. By what way the same amount of water could be made to dissolve more salt before getting saturated? Answer: On heating the water.
Question 10. Define condensation. Answer: The process in which a gas changes into its liquid form is called condensation.
Question 11. What happens when a saturated solution is heated? Answer: It becomes unsaturated.
Question 12. What is the effect of temperature on the solubility of solids in liquids? Answer: The solubility of solids in liquids increases with increase in temperature.
Question 13. Mention one purpose of separating the constituents of a mixture. Answer: To remove the unusual or harmful compound and to obtain the useful component.
Question 14. Name the process by which water is separated from rice and pulses after washing them. Answer: The water is separated from rice and pulses by decantation.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is evaporation? Give one large scale use of the process of evaporation. Answer: The process of conversion of water into vapour is called evaporation. This process takes place continuously where water is present.
The process of evaporation is used on a large scale to obtain common salt from sea water. Sea water is trapped in shallow lakes and allowed to stand there. The heat of sun gradually evaporates water in the shallow lakes and common salt is left behind as a solid.
Question 2. What do you mean by decantation? What is its use? Answer: Decantation is a process by which we can remove a liquid without disturbing the solid settled down in the bottom. This method can be used to separate mixture of sand and water
Question 3. a. State one use of the method of winnowing. b. Give one use of the handpicking method of separating mixtures in daily life. Answer: a. The method of winnowing is used to separate husk from various types of grains like wheat, rice, etc. b. The method of handpicking is usually used to separate undesirable substances, such as small pieces of stones from wheat, rice and pulses.
Question 4. The mixture of a powdered white solid A and a liquid B can be separated by filtration. The solid A is left behind on the filter paper but clear liquid B passes through the filter paper and collects in the beaker kept below. a. Name some solid which could be like A. b. Name the liquid which B could be. c. What name is given to the solid left on the filter paper? d. What name is given to the clear liquid collected in the beaker? Answer: a. Chalk powder b. Water c. Residue d. Filtrate
Question 5. Name the method that should be used to separate the following mixtures: a. Grain from wheat flour b. Grain from the stalks c. Small black pebbles from a plateful of pulses d. Wheat from chaff Answer: a. Sieving b. Threshing c. Handpicking d. Winnowing
Question 6. How will you prepare cheese (paneer)? Answer: For making cheese, a few drops of lemon juice are added to milk as it boils. This gives a mixture of particles of solid cheese and liquid. The cheese is then separated by filtering the mixture through a fine cloth or strainer.
Question 7. What is mixture? Answer: When two or more than two substances are mixed together in any ratio then it is called a mixture.
Question 8. What is a homogeneous mixture? Answer: A mixture in which the various components are uniformly mixed or dissolved and each part of the mixture has the same properties is called a homogenous mixture.
Question 9. What is a heterogeneous mixture? Answer: A mixture whose components are not uniformly mixed or dissolved and hence each part of the mixture does not have the same properties is called a heterogeneous mixture.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is filtration? Give an example. Answer: Decantation is not enough for complete separation of a solid-liquid mixture. This can be done better by filtration, in which the mixture is dropped on a porous material known as filter. The liquid passes through the filter and comes down as filtrate. The insoluble solid left behind is known as residue. When you make tea, you filter it through a strainer having wire gauze. The tea extract comes down as the filtrate and the boiled tea leaves are left behind as the residue.
Question 2. Why is loading used to separate suspended impurities? Explain. Answer: Sometimes water of a river or canal is muddy or turbid due to hanging of very fine particles of clay. They cannot be removed by decantation or filtration. In such a case loading is useful.
Loading: Loading is a method in which a special substance called alum is used to load the suspended particles to make them heavy and increase their sedimentation speed. For example, the particles of clay in muddy water are very fine and their sedimentation takes a very long time.
Question 3. Water is a universal solvent. Give reason. Answer: Water is a universal solvent because it can dissolve a large number of substances in it. Water is essential to our body in the process of digestion. Several waste materials in our body get dissolved in water and are then excreted. A number of chemical reactions occur inside our body. They all occur in the presence of water. Water can dissolve almost all substances, hence is called universal solvent.
Picture-Based Questions

- CBSE Class 10th
CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Main Registration
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- GATE 2024 Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Animation Courses
- Animation Courses in India
- Animation Courses in Bangalore
- Animation Courses in Mumbai
- Animation Courses in Pune
- Animation Courses in Chennai
- Animation Courses in Hyderabad
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Pune
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Hyderabad
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Design Colleges in India
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- DDU Entrance Exam
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET PG Admit Card 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Application Form 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET PG Courses 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Access premium articles, webinars, resources to make the best decisions for career, course, exams, scholarships, study abroad and much more with
Plan, Prepare & Make the Best Career Choices
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances: Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Question Answer is part of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science . In our daily life, there are many instances when we separate a substance from a mixture of materials, like when tea leaves are separated from the liquid with a strainer, the grain is separated from stalks, cotton separates its seeds from the fibre, milk or curd is churned to separate the butter, etc. You will get questions based on such concepts in separation of substances Class 6 solutions. In this article, you will get NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances.
In NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances, you will get many questions related to these separation methods, which will give you more clarity. On the other hand, students must try to complete the NCERT Class 6 Syllabus for Science as soon as possible so that they can refer to the separation of substances Class 6 NCERT solutions and revise well. You can get NCERT Solutions by clicking on the above link. NCERT solutions for Class 6th science chapter 5, provide answers to each question in the NCERT textbook. Students can refer to this link for NCERT Solutions for Class 6 .
According to the latest CBSE syllabus 2023-24, the chapter "separation of substances" has been renumbered as Chapter 3.
Download PDF
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances-Exercises
Question 1: Why do we need to separate different components of a mixture? Give two examples.
Answer: We see that, before we use a substance, we need to separate harmful or useless substances that may be mixed with it. Sometimes, we separate even useful components if we need to use them separately. For examples:
(a)The process that is used to separate the grain from stalks etc. is threshing .
(b) Sieving allows the fine flour particles to pass through the holes of the sieve while the bigger impurities remain on the sieve.
Question 2: What is winnowing? Where is it used?
Answer: This method of separating components of a mixture is called winnowing. Winnowing is used to separate heavier and lighter components of a mixture by wind or by blowing air.
This method is commonly used by farmers to separate lighter husk particles from heavier seeds of grain.
Question 3: How will you separate husk or dirt particles from a given sample of pulses before cooking.
Answer: We will separate husk or dirt particles from a given sample of pulses by the handpicking method.
The handpicking method can be used for separating slightly larger sized impurities like the pieces of dirt, stone, and husk from wheat, rice or pulses.
Question: 4 What is sieving? Where is it used?
Answer: Sieving allows the fine flour particles to pass through the holes of the sieve while the bigger impurities remain on the sieve.
In a flour mill, impurities like husk and stones are removed from wheat before grinding it by sieving.
Question: 5 How will you separate sand and water from their mixture?
Answer: We can separate sand and water from their mixture by the following steps:
- First by sedimentation, when the heavier component that is sand settles down after water is added to it.
- Then by decantation where clear water formed an upper layer is removed carefully to another glass.
Question: 6 Is it possible to separate sugar mixed with wheat flour? If yes, how will you do it?
Answer: Yes, it is possible to separate sugar mixed with wheat flour. We will follow the below steps:
- Add a lot of water to mix wheat flour and sugar both.
- Then filter this mixture using filter paper.
- On the filter paper, we have wheat flour.
- Dry it to get Wheat flour.
- The filtrate has sugar and water mixed so,
- Evaporate the water to get sugar.
Question: 7 How would you obtain clear water from a sample of muddy water?
Answer: We can obtain clear water from a sample of muddy water by the following steps:
- Allow the muddy water to stand for a time.
- You will see that mud settles down at the bottom.
- Upper layer water contains some mud particles.
- Decant it to get that water and filter it to remove traces of mud particles.
Question: 8 Fill up the blanks
(a) The method of separating seeds of paddy from its stalks is called ___________.
(b) When milk, cooled after boiling, is poured onto a piece of cloth the cream (malai) is left behind on it. This process of separating cream from milk is an example of ___________.
(c) Salt is obtained from seawater by the process of ___________.
(d) Impurities settled at the bottom when muddy water was kept overnight in a bucket. The clear water was then poured off from the top. The process of separation used in this example is called ___________.
Answer: (a) The method of separating seeds of paddy from its stalks is called threshing .
(b) When milk, cooled after boiling, is poured onto a piece of cloth the cream (malai) is left behind on it. This process of separating cream from milk is an example of filtration .
(c) Salt is obtained from seawater by the process of evaporation .
(d) Impurities settled at the bottom when muddy water was kept overnight in a bucket. The clear water was then poured off from the top. The process of separation used in this example is called decantation .
Question: 9 True or false?
(a) A mixture of milk and water can be separated by filtration.
(b) A mixture of powdered salt and sugar can be separated by the process of winnowing.
(c) Separation of sugar from tea can be done with filtration.
(d) Grain and husk can be separated with the process of decantation.
Answer: (a) False
Question: 10 Lemonade is prepared by mixing lemon juice and sugar in water. You wish to add ice to cool it. Should you add ice to the lemonade before or after dissolving sugar? In which case would it be possible to dissolve more sugar?
Answer: We should add ice to the lemonade after dissolving the sugar as more sugar will be going to dissolve as solubility is more before adding ice. Because if we add ice before dissolving the sugar, the temperature of the water gets down and the property of dissolving the sugar will decrease.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances
The solution for Class 6 Chapter 5 Science consists of a total of ten questions, including the subjective type of question, true/false, and fill-in-the-blank types of questions. These solutions for NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 5 are prepared by experienced subject matter experts and are available in PDF format, so students can download and use them according to their comfort.
Subtopics of separation of substances Class 6 are given below:
Subtopics of Separation of Substances Class 6 NCERT Science Chapter 5 :
Topics for Chapter 5 Class 6 Science are given below:
- Methods of Separation
- Handpicking
- Sedimentation, Decantation and Filtration
- Evaporation
- Use of more than one method of separation
- Can water dissolve any amount of a substance?
There are Many Methods for Substance Separation from the Mixture of the Materials Which are Listed Below:
- Handpicking:- Husk and stones could be separated from grains by handpicking
- Winnowing:- Husk is separated from heavier seeds of grain by winnowing.
- Sieving:- The difference in the size of particles in a mixture can be separated by sieving.
- Sedimentation:- This method is used to separate impurities when the heavier component in a mixture settles after water is added to it.
- Decantation:- In a mixture of sand and water, the heavier sand particles settle down at the bottom and the water can be separated by decantation.
- Filtration:- This method can be used to separate components of a mixture of an insoluble solid and a liquid.
- Evaporation:- It can be used to separate a solid dissolved in a liquid.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science: Chapter-wise
Ncert solutions for class 6: subject-wise, benefits of ncert solutions for class 6 science chapter 5 separation of substances.
- Separation of substances NCERT solutions are available in very simple language that can be understood by the average student.
- Class 6 Science Chapter 5 NCERT Solutions will provide you with in-depth knowledge of your subject.
- Class 6 Separation of Substances NCERT Solutions will build your fundamental concepts of science, which are required to study science in the upper class.
- You will develop a logical approach and methodology towards science and other subjects, as well as the separation of substances Class 6 solutions.
- You can score good marks in the exam with the help of CBSE NCERT solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances.
- Your homework will be easier as you will get all Class 6 science chapter 5 question answer, including practice questions given after every topic.
- The Class 6 Science Chapter 5 NCERT Solutions PDF is easy to download and use offline
- Separation of substances Class 6 questions and answers are prepared by subject experts as per the latest CBSE syllabus.
Also Check NCERT Books and NCERT Syllabus here
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Syllabus Class 6
- NCERT 6 Science Syllabus
We hope you will ace your 6th grade exam with the help of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
No, CBSE doesn’t provide NCERT solutions for any class or subject
The following are covered in NCERT solution Class 6 Science chapter 5
- Methods of Separation
- Handpicking
- Threshing
- Winnowing
- Sieving
- Sedimentation, Decantation and Filtration
- Evaporation
- Use of more than one method of separation
- Can water dissolve any amount of a substance?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 provide accurate and comprehensive solutions in simplified language, covering the entire syllabus. They aid in exam preparation and enhance problem-solving skills. Furthermore, these solutions are available in PDF format, allowing students to download and utilise them according to their convenience.
Chapter 5 of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science covers important concepts such as methods of separation, including hand-picking, winnowing, threshing, sieving, sedimentation, decantation, and filtration. The chapter also explains the process of evaporation and the use of multiple methods of separation. Additionally, it addresses the question of whether water can dissolve any amount of a substance. To understand these concepts better, students can refer to the NCERT Solutions provided by the Careers360 faculty. These solutions are available in PDF format and can be downloaded by students at their convenience.
Separation of Substances in Class 6 Science refers to dividing a mixture into individual components based on physical properties. It involves learning about various methods such as sedimentation, decantation, filtration, and more.
- Latest Articles
- Popular Articles
Explore Premium
Understand your attachment style and learn how you can reform your relationships, 7 tips to convey your struggles to your loved ones, decision-making: common challenges faced, tips to make good decisions, how stay-at-home parents can care for themselves, teenage relationships: tips to help your teenager deal with a breakup, getting over the pink and blue divide: revising gender roles, artificial rain: concept and techniques, what is lenz’s law in electricity and magnetism and why is it true, cancer treatment: why chemotherapy does not suit all patients, upcoming school exams, national institute of open schooling 12th examination.
Admit Card Date : 28 March,2024 - 22 May,2024
National Institute of Open Schooling 10th examination
Punjab board of secondary education 12th examination.
Exam Date : 05 April,2024 - 27 April,2024
Goa Board Secondary School Certificate Examination
Exam Date : 12 April,2024 - 12 April,2024
Jammu and Kashmir State Board of School Education 10th Examination
Popular questions.
A block of mass 0.50 kg is moving with a speed of 2.00 ms -1 on a smooth surface. It strikes another mass of 1.00 kg and then they move together as a single body. The energy loss during the collision is
A person trying to lose weight by burning fat lifts a mass of 10 kg upto a height of 1 m 1000 times. Assume that the potential energy lost each time he lowers the mass is dissipated. How much fat will he use up considering the work done only when the weight is lifted up ? Fat supplies 3.8×10 7 J of energy per kg which is converted to mechanical energy with a 20% efficiency rate. Take g = 9.8 ms −2 :
An athlete in the olympic games covers a distance of 100 m in 10 s. His kinetic energy can be estimated to be in the range
In the reaction,
If we consider that 1/6, in place of 1/12, mass of carbon atom is taken to be the relative atomic mass unit, the mass of one mole of a substance will
With increase of temperature, which of these changes?
Number of atoms in 558.5 gram Fe (at. wt.of Fe = 55.85 g mol -1 ) is
A pulley of radius 2 m is rotated about its axis by a force F = (20t - 5t 2 ) newton (where t is measured in seconds) applied tangentially. If the moment of inertia of the pulley about its axis of rotation is 10 kg m 2 , the number of rotations made by the pulley before its direction of motion if reversed, is
Colleges After 12th
Popular course after 12th.
- DUET (DU JAT)
- BHU UET,BUMAT,
- MAH CET Law
- JEE Advanced
- COMEDK UGET
- JEE Main Paper 2
- AAT (JEE Advanced)
- ISI Admission Test
Explore Career Options (By Industry)
- Construction
- Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Information Technology
Data Administrator
Database professionals use software to store and organise data such as financial information, and customer shipping records. Individuals who opt for a career as data administrators ensure that data is available for users and secured from unauthorised sales. DB administrators may work in various types of industries. It may involve computer systems design, service firms, insurance companies, banks and hospitals.
Bio Medical Engineer
The field of biomedical engineering opens up a universe of expert chances. An Individual in the biomedical engineering career path work in the field of engineering as well as medicine, in order to find out solutions to common problems of the two fields. The biomedical engineering job opportunities are to collaborate with doctors and researchers to develop medical systems, equipment, or devices that can solve clinical problems. Here we will be discussing jobs after biomedical engineering, how to get a job in biomedical engineering, biomedical engineering scope, and salary.
Ethical Hacker
A career as ethical hacker involves various challenges and provides lucrative opportunities in the digital era where every giant business and startup owns its cyberspace on the world wide web. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path try to find the vulnerabilities in the cyber system to get its authority. If he or she succeeds in it then he or she gets its illegal authority. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path then steal information or delete the file that could affect the business, functioning, or services of the organization.
GIS officer work on various GIS software to conduct a study and gather spatial and non-spatial information. GIS experts update the GIS data and maintain it. The databases include aerial or satellite imagery, latitudinal and longitudinal coordinates, and manually digitized images of maps. In a career as GIS expert, one is responsible for creating online and mobile maps.
Data Analyst
The invention of the database has given fresh breath to the people involved in the data analytics career path. Analysis refers to splitting up a whole into its individual components for individual analysis. Data analysis is a method through which raw data are processed and transformed into information that would be beneficial for user strategic thinking.
Data are collected and examined to respond to questions, evaluate hypotheses or contradict theories. It is a tool for analyzing, transforming, modeling, and arranging data with useful knowledge, to assist in decision-making and methods, encompassing various strategies, and is used in different fields of business, research, and social science.
Geothermal Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as geothermal engineers are the professionals involved in the processing of geothermal energy. The responsibilities of geothermal engineers may vary depending on the workplace location. Those who work in fields design facilities to process and distribute geothermal energy. They oversee the functioning of machinery used in the field.
Database Architect
If you are intrigued by the programming world and are interested in developing communications networks then a career as database architect may be a good option for you. Data architect roles and responsibilities include building design models for data communication networks. Wide Area Networks (WANs), local area networks (LANs), and intranets are included in the database networks. It is expected that database architects will have in-depth knowledge of a company's business to develop a network to fulfil the requirements of the organisation. Stay tuned as we look at the larger picture and give you more information on what is db architecture, why you should pursue database architecture, what to expect from such a degree and what your job opportunities will be after graduation. Here, we will be discussing how to become a data architect. Students can visit NIT Trichy , IIT Kharagpur , JMI New Delhi .
Remote Sensing Technician
Individuals who opt for a career as a remote sensing technician possess unique personalities. Remote sensing analysts seem to be rational human beings, they are strong, independent, persistent, sincere, realistic and resourceful. Some of them are analytical as well, which means they are intelligent, introspective and inquisitive.
Remote sensing scientists use remote sensing technology to support scientists in fields such as community planning, flight planning or the management of natural resources. Analysing data collected from aircraft, satellites or ground-based platforms using statistical analysis software, image analysis software or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a significant part of their work. Do you want to learn how to become remote sensing technician? There's no need to be concerned; we've devised a simple remote sensing technician career path for you. Scroll through the pages and read.
Budget Analyst
Budget analysis, in a nutshell, entails thoroughly analyzing the details of a financial budget. The budget analysis aims to better understand and manage revenue. Budget analysts assist in the achievement of financial targets, the preservation of profitability, and the pursuit of long-term growth for a business. Budget analysts generally have a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, economics, or a closely related field. Knowledge of Financial Management is of prime importance in this career.
Underwriter
An underwriter is a person who assesses and evaluates the risk of insurance in his or her field like mortgage, loan, health policy, investment, and so on and so forth. The underwriter career path does involve risks as analysing the risks means finding out if there is a way for the insurance underwriter jobs to recover the money from its clients. If the risk turns out to be too much for the company then in the future it is an underwriter who will be held accountable for it. Therefore, one must carry out his or her job with a lot of attention and diligence.

Finance Executive
Product manager.
A Product Manager is a professional responsible for product planning and marketing. He or she manages the product throughout the Product Life Cycle, gathering and prioritising the product. A product manager job description includes defining the product vision and working closely with team members of other departments to deliver winning products.
Operations Manager
Individuals in the operations manager jobs are responsible for ensuring the efficiency of each department to acquire its optimal goal. They plan the use of resources and distribution of materials. The operations manager's job description includes managing budgets, negotiating contracts, and performing administrative tasks.
Stock Analyst
Individuals who opt for a career as a stock analyst examine the company's investments makes decisions and keep track of financial securities. The nature of such investments will differ from one business to the next. Individuals in the stock analyst career use data mining to forecast a company's profits and revenues, advise clients on whether to buy or sell, participate in seminars, and discussing financial matters with executives and evaluate annual reports.
A Researcher is a professional who is responsible for collecting data and information by reviewing the literature and conducting experiments and surveys. He or she uses various methodological processes to provide accurate data and information that is utilised by academicians and other industry professionals. Here, we will discuss what is a researcher, the researcher's salary, types of researchers.
Welding Engineer
Welding Engineer Job Description: A Welding Engineer work involves managing welding projects and supervising welding teams. He or she is responsible for reviewing welding procedures, processes and documentation. A career as Welding Engineer involves conducting failure analyses and causes on welding issues.
Transportation Planner
A career as Transportation Planner requires technical application of science and technology in engineering, particularly the concepts, equipment and technologies involved in the production of products and services. In fields like land use, infrastructure review, ecological standards and street design, he or she considers issues of health, environment and performance. A Transportation Planner assigns resources for implementing and designing programmes. He or she is responsible for assessing needs, preparing plans and forecasts and compliance with regulations.
Environmental Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as an environmental engineer are construction professionals who utilise the skills and knowledge of biology, soil science, chemistry and the concept of engineering to design and develop projects that serve as solutions to various environmental problems.
Safety Manager
A Safety Manager is a professional responsible for employee’s safety at work. He or she plans, implements and oversees the company’s employee safety. A Safety Manager ensures compliance and adherence to Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) guidelines.
Conservation Architect
A Conservation Architect is a professional responsible for conserving and restoring buildings or monuments having a historic value. He or she applies techniques to document and stabilise the object’s state without any further damage. A Conservation Architect restores the monuments and heritage buildings to bring them back to their original state.
Structural Engineer
A Structural Engineer designs buildings, bridges, and other related structures. He or she analyzes the structures and makes sure the structures are strong enough to be used by the people. A career as a Structural Engineer requires working in the construction process. It comes under the civil engineering discipline. A Structure Engineer creates structural models with the help of computer-aided design software.
Highway Engineer
Highway Engineer Job Description: A Highway Engineer is a civil engineer who specialises in planning and building thousands of miles of roads that support connectivity and allow transportation across the country. He or she ensures that traffic management schemes are effectively planned concerning economic sustainability and successful implementation.
Field Surveyor
Are you searching for a Field Surveyor Job Description? A Field Surveyor is a professional responsible for conducting field surveys for various places or geographical conditions. He or she collects the required data and information as per the instructions given by senior officials.
Orthotist and Prosthetist
Orthotists and Prosthetists are professionals who provide aid to patients with disabilities. They fix them to artificial limbs (prosthetics) and help them to regain stability. There are times when people lose their limbs in an accident. In some other occasions, they are born without a limb or orthopaedic impairment. Orthotists and prosthetists play a crucial role in their lives with fixing them to assistive devices and provide mobility.
Pathologist
A career in pathology in India is filled with several responsibilities as it is a medical branch and affects human lives. The demand for pathologists has been increasing over the past few years as people are getting more aware of different diseases. Not only that, but an increase in population and lifestyle changes have also contributed to the increase in a pathologist’s demand. The pathology careers provide an extremely huge number of opportunities and if you want to be a part of the medical field you can consider being a pathologist. If you want to know more about a career in pathology in India then continue reading this article.
Veterinary Doctor
Speech therapist, gynaecologist.
Gynaecology can be defined as the study of the female body. The job outlook for gynaecology is excellent since there is evergreen demand for one because of their responsibility of dealing with not only women’s health but also fertility and pregnancy issues. Although most women prefer to have a women obstetrician gynaecologist as their doctor, men also explore a career as a gynaecologist and there are ample amounts of male doctors in the field who are gynaecologists and aid women during delivery and childbirth.
Audiologist
The audiologist career involves audiology professionals who are responsible to treat hearing loss and proactively preventing the relevant damage. Individuals who opt for a career as an audiologist use various testing strategies with the aim to determine if someone has a normal sensitivity to sounds or not. After the identification of hearing loss, a hearing doctor is required to determine which sections of the hearing are affected, to what extent they are affected, and where the wound causing the hearing loss is found. As soon as the hearing loss is identified, the patients are provided with recommendations for interventions and rehabilitation such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and appropriate medical referrals. While audiology is a branch of science that studies and researches hearing, balance, and related disorders.
An oncologist is a specialised doctor responsible for providing medical care to patients diagnosed with cancer. He or she uses several therapies to control the cancer and its effect on the human body such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and biopsy. An oncologist designs a treatment plan based on a pathology report after diagnosing the type of cancer and where it is spreading inside the body.
Are you searching for an ‘Anatomist job description’? An Anatomist is a research professional who applies the laws of biological science to determine the ability of bodies of various living organisms including animals and humans to regenerate the damaged or destroyed organs. If you want to know what does an anatomist do, then read the entire article, where we will answer all your questions.
For an individual who opts for a career as an actor, the primary responsibility is to completely speak to the character he or she is playing and to persuade the crowd that the character is genuine by connecting with them and bringing them into the story. This applies to significant roles and littler parts, as all roles join to make an effective creation. Here in this article, we will discuss how to become an actor in India, actor exams, actor salary in India, and actor jobs.
Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats create and direct original routines for themselves, in addition to developing interpretations of existing routines. The work of circus acrobats can be seen in a variety of performance settings, including circus, reality shows, sports events like the Olympics, movies and commercials. Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats must be prepared to face rejections and intermittent periods of work. The creativity of acrobats may extend to other aspects of the performance. For example, acrobats in the circus may work with gym trainers, celebrities or collaborate with other professionals to enhance such performance elements as costume and or maybe at the teaching end of the career.
Video Game Designer
Career as a video game designer is filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. A video game designer is someone who is involved in the process of creating a game from day one. He or she is responsible for fulfilling duties like designing the character of the game, the several levels involved, plot, art and similar other elements. Individuals who opt for a career as a video game designer may also write the codes for the game using different programming languages.
Depending on the video game designer job description and experience they may also have to lead a team and do the early testing of the game in order to suggest changes and find loopholes.
Radio Jockey
Radio Jockey is an exciting, promising career and a great challenge for music lovers. If you are really interested in a career as radio jockey, then it is very important for an RJ to have an automatic, fun, and friendly personality. If you want to get a job done in this field, a strong command of the language and a good voice are always good things. Apart from this, in order to be a good radio jockey, you will also listen to good radio jockeys so that you can understand their style and later make your own by practicing.
A career as radio jockey has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. If you want to know more about a career as radio jockey, and how to become a radio jockey then continue reading the article.
Choreographer
The word “choreography" actually comes from Greek words that mean “dance writing." Individuals who opt for a career as a choreographer create and direct original dances, in addition to developing interpretations of existing dances. A Choreographer dances and utilises his or her creativity in other aspects of dance performance. For example, he or she may work with the music director to select music or collaborate with other famous choreographers to enhance such performance elements as lighting, costume and set design.
Social Media Manager
A career as social media manager involves implementing the company’s or brand’s marketing plan across all social media channels. Social media managers help in building or improving a brand’s or a company’s website traffic, build brand awareness, create and implement marketing and brand strategy. Social media managers are key to important social communication as well.
Photographer
Photography is considered both a science and an art, an artistic means of expression in which the camera replaces the pen. In a career as a photographer, an individual is hired to capture the moments of public and private events, such as press conferences or weddings, or may also work inside a studio, where people go to get their picture clicked. Photography is divided into many streams each generating numerous career opportunities in photography. With the boom in advertising, media, and the fashion industry, photography has emerged as a lucrative and thrilling career option for many Indian youths.
An individual who is pursuing a career as a producer is responsible for managing the business aspects of production. They are involved in each aspect of production from its inception to deception. Famous movie producers review the script, recommend changes and visualise the story.
They are responsible for overseeing the finance involved in the project and distributing the film for broadcasting on various platforms. A career as a producer is quite fulfilling as well as exhaustive in terms of playing different roles in order for a production to be successful. Famous movie producers are responsible for hiring creative and technical personnel on contract basis.
Copy Writer
In a career as a copywriter, one has to consult with the client and understand the brief well. A career as a copywriter has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. Several new mediums of advertising are opening therefore making it a lucrative career choice. Students can pursue various copywriter courses such as Journalism , Advertising , Marketing Management . Here, we have discussed how to become a freelance copywriter, copywriter career path, how to become a copywriter in India, and copywriting career outlook.
In a career as a vlogger, one generally works for himself or herself. However, once an individual has gained viewership there are several brands and companies that approach them for paid collaboration. It is one of those fields where an individual can earn well while following his or her passion.
Ever since internet costs got reduced the viewership for these types of content has increased on a large scale. Therefore, a career as a vlogger has a lot to offer. If you want to know more about the Vlogger eligibility, roles and responsibilities then continue reading the article.
For publishing books, newspapers, magazines and digital material, editorial and commercial strategies are set by publishers. Individuals in publishing career paths make choices about the markets their businesses will reach and the type of content that their audience will be served. Individuals in book publisher careers collaborate with editorial staff, designers, authors, and freelance contributors who develop and manage the creation of content.
Careers in journalism are filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. One cannot afford to miss out on the details. As it is the small details that provide insights into a story. Depending on those insights a journalist goes about writing a news article. A journalism career can be stressful at times but if you are someone who is passionate about it then it is the right choice for you. If you want to know more about the media field and journalist career then continue reading this article.
Individuals in the editor career path is an unsung hero of the news industry who polishes the language of the news stories provided by stringers, reporters, copywriters and content writers and also news agencies. Individuals who opt for a career as an editor make it more persuasive, concise and clear for readers. In this article, we will discuss the details of the editor's career path such as how to become an editor in India, editor salary in India and editor skills and qualities.
Individuals who opt for a career as a reporter may often be at work on national holidays and festivities. He or she pitches various story ideas and covers news stories in risky situations. Students can pursue a BMC (Bachelor of Mass Communication) , B.M.M. (Bachelor of Mass Media) , or MAJMC (MA in Journalism and Mass Communication) to become a reporter. While we sit at home reporters travel to locations to collect information that carries a news value.
Corporate Executive
Are you searching for a Corporate Executive job description? A Corporate Executive role comes with administrative duties. He or she provides support to the leadership of the organisation. A Corporate Executive fulfils the business purpose and ensures its financial stability. In this article, we are going to discuss how to become corporate executive.
Multimedia Specialist
A multimedia specialist is a media professional who creates, audio, videos, graphic image files, computer animations for multimedia applications. He or she is responsible for planning, producing, and maintaining websites and applications.
Quality Controller
A quality controller plays a crucial role in an organisation. He or she is responsible for performing quality checks on manufactured products. He or she identifies the defects in a product and rejects the product.
A quality controller records detailed information about products with defects and sends it to the supervisor or plant manager to take necessary actions to improve the production process.
Production Manager
A QA Lead is in charge of the QA Team. The role of QA Lead comes with the responsibility of assessing services and products in order to determine that he or she meets the quality standards. He or she develops, implements and manages test plans.
Process Development Engineer
The Process Development Engineers design, implement, manufacture, mine, and other production systems using technical knowledge and expertise in the industry. They use computer modeling software to test technologies and machinery. An individual who is opting career as Process Development Engineer is responsible for developing cost-effective and efficient processes. They also monitor the production process and ensure it functions smoothly and efficiently.
AWS Solution Architect
An AWS Solution Architect is someone who specializes in developing and implementing cloud computing systems. He or she has a good understanding of the various aspects of cloud computing and can confidently deploy and manage their systems. He or she troubleshoots the issues and evaluates the risk from the third party.
Azure Administrator
An Azure Administrator is a professional responsible for implementing, monitoring, and maintaining Azure Solutions. He or she manages cloud infrastructure service instances and various cloud servers as well as sets up public and private cloud systems.
Computer Programmer
Careers in computer programming primarily refer to the systematic act of writing code and moreover include wider computer science areas. The word 'programmer' or 'coder' has entered into practice with the growing number of newly self-taught tech enthusiasts. Computer programming careers involve the use of designs created by software developers and engineers and transforming them into commands that can be implemented by computers. These commands result in regular usage of social media sites, word-processing applications and browsers.
Information Security Manager
Individuals in the information security manager career path involves in overseeing and controlling all aspects of computer security. The IT security manager job description includes planning and carrying out security measures to protect the business data and information from corruption, theft, unauthorised access, and deliberate attack
ITSM Manager
Automation test engineer.
An Automation Test Engineer job involves executing automated test scripts. He or she identifies the project’s problems and troubleshoots them. The role involves documenting the defect using management tools. He or she works with the application team in order to resolve any issues arising during the testing process.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

SAT® | CollegeBoard
Registeration closing on 19th Apr for SAT® | One Test-Many Universities | 90% discount on registrations fee | Free Practice | Multiple Attempts | no penalty for guessing

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

Resonance Coaching
Enroll in Resonance Coaching for success in JEE/NEET exams

TOEFL ® Registrations 2024
Thinking of Studying Abroad? Think the TOEFL® test. Register now & Save 10% on English Proficiency Tests with Gift Cards

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN
Everything about Education
Latest updates, Exclusive Content, Webinars and more.
Explore on Careers360
- Board Exams
- Top Schools
- Navodaya Vidyalaya
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 6
NCERT Exemplars
- NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 10 solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Solutions
- NCERT Books for class 6
- NCERT Books for class 7
- NCERT Books for class 8
- NCERT Books for class 9
- NCERT Books for Class 10
- NCERT Books for Class 11
- NCERT Books for Class 12
- NCERT Notes for Class 9
- NCERT Notes for Class 10
- NCERT Notes for Class 11
- NCERT Notes for Class 12
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 6
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 7
- NCERT Syllabus for class 8
- NCERT Syllabus for class 9
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 10
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 11
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 12
- CBSE Date Sheet
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Admit Card
- CBSE Result
- CBSE Result Name and State Wise
- CBSE Passing Marks
CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Board Class 10th
- CBSE Class 10 Date Sheet
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE 10th Exam Pattern
- CBSE Class 10 Answer Key
- CBSE 10th Admit Card
- CBSE 10th Result
- CBSE 10th Toppers
- CBSE Board Class 12th
- CBSE Class 12 Date Sheet
- CBSE Class 12 Admit Card
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Exam Pattern
- CBSE Class 12 Answer Key
- CBSE 12th Result
- CBSE Class 12 Toppers
CISCE Board 10th
- ICSE 10th time table
- ICSE 10th Syllabus
- ICSE 10th exam pattern
- ICSE 10th Question Papers
- ICSE 10th Result
- ICSE 10th Toppers
- ISC 12th Board
- ISC 12th Time Table
- ISC Syllabus
- ISC 12th Question Papers
- ISC 12th Result
- IMO Syllabus
- IMO Sample Papers
- IMO Answer Key
- IEO Syllabus
- IEO Answer Key
- NSO Syllabus
- NSO Sample Papers
- NSO Answer Key
- NMMS Application form
- NMMS Scholarship
- NMMS Eligibility
- NMMS Exam Pattern
- NMMS Admit Card
- NMMS Question Paper
- NMMS Answer Key
- NMMS Syllabus
- NMMS Result
- NTSE Application Form
- NTSE Eligibility Criteria
- NTSE Exam Pattern
- NTSE Admit Card
- NTSE Syllabus
- NTSE Question Papers
- NTSE Answer Key
- NTSE Cutoff
- NTSE Result
Schools By Medium
- Malayalam Medium Schools in India
- Urdu Medium Schools in India
- Telugu Medium Schools in India
- Karnataka Board PUE Schools in India
- Bengali Medium Schools in India
- Marathi Medium Schools in India
By Ownership
- Central Government Schools in India
- Private Schools in India
- Schools in Delhi
- Schools in Lucknow
- Schools in Kolkata
- Schools in Pune
- Schools in Bangalore
- Schools in Chennai
- Schools in Mumbai
- Schools in Hyderabad
- Schools in Gurgaon
- Schools in Ahmedabad
- Schools in Uttar Pradesh
- Schools in Maharashtra
- Schools in Karnataka
- Schools in Haryana
- Schools in Punjab
- Schools in Andhra Pradesh
- Schools in Madhya Pradesh
- Schools in Rajasthan
- Schools in Tamil Nadu
- NVS Admit Card
- Navodaya Result
- Navodaya Exam Date
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission Class 6
- JNVST admit card for class 6
- JNVST class 6 answer key
- JNVST class 6 Result
- JNVST Class 6 Exam Pattern
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission
- JNVST class 9 exam pattern
- JNVST class 9 answer key
- JNVST class 9 Result
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Cetifications
We Appeared in
- CBSE Notes For Class 6
- Class 6 Science Notes
- Chapter 5: Separation Of Substances
Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes - Chapter 5
According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 3.
We all have seen our parents and grandparents separating small stones or pebbles from the rice grains and pulses, filtering tea leaves before serving tea and a lot more. The practice of separation of substances is usually required to remove or separate the required substances from their mixtures.
A substance can be classified into: Mixture and a pure substance.
A mixture is a material made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically.
To know more about Mixtures, visit the link below;
Separation is the process of separating one or more components from a mixture. For example, distillation, sedimentation, filtration etc.
Handpicking
Handpicking is a method of separation used to separate large-sized impurities like pieces of dirt, stone, and husk from wheat, rice or pulses.
For more information on Handpicking Separation Technique, watch the below video

Threshing is the process of beating stalks to separate the grains from the harvested crop.
- It is done manually by farmers or by threshing machines.
- Method of separation used to separate heavier and lighter components of a mixture by wind or by blowing air.
- Normally, this is used to separate husk from grains.
Sieving is a method of separation in which the mixture is passed through a filter or a sieve.
- The larger particles, usually the impurities, do not pass through the filter and hence collect on the sieve.
- The finer particles flow past the sieve and can be collected below.
For more information on Sieving Separation Technique, watch the below video

Filtration, Sedimentation and Decantation
Filtration is the process of passing the mixture through a filter to remove the solid particles from the fluid components of the mixture.
- For instance, if we pass muddy water through a fine filter, we can notice that the mud gets filtered and the water passes through.
Sedimentation
When the heavier component in the mixture settles when water is added to it, the process is called sedimentation.
- This method is used in separating grains from dust and soil.
Decantation
Decantation is the process after sedimentation that involves removing the water, along with the impurities.
For more information on Separation by Decantation and Loading, watch the below video

Evaporation
Condensation.
The process of conversion of water vapour into its liquid form due to contact with a cooler surface is called condensation.
- Example: Formation of water droplets on a metallic lid while boiling water.
The process of conversion of water into its vapour is called evaporation.
- The process of evaporation takes place continuously wherever water is present.
To know more about “Methods of Separation”, visit the link below;
Methods of Separation
Can Water Dissolve It All
A solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances.
- In such a mixture, a solute is a substance dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent.
Saturated solution
A saturated solution is a chemical solution containing the maximum concentration of a solute dissolved in the solvent.
- For example, a saturated solution of salt in water is one in which no more salt can be dissolved.
- This added salt will just sediment down to the bottom of the vessel.
Churning is the process of shaking up cream or whole milk to make butter. Learn more about separating a pure substance from the topics given below:
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
What is threshing.
Threshing is the process of beating stalks to separate the grains from the harvested crop. It is usually done manually by the farmers.
What is condensation?
Condensation is the process where water vapour becomes liquid. It is the reverse of evaporation.
How can mixtures be separated?
Mixtures can be physically separated by using methods that use differences in physical properties to separate the components of the mixture (evaporation, distillation, filtration and chromatography).
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Separation of Substances
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams
6th Class Science Separation of Substances Question Bank
Done separation of substances total questions - 45.

question_answer 1) X is a separation technique based on the difference in weights of the solids in a solid-solid mixture. What is X?
A) Sieving done clear
B) Handpicking done clear
C) Threshing done clear
D) Winnowing done clear
question_answer 2) What type of a substance is steel?
A) A solid - liquid heterogeneous mixture done clear
B) A solid - solid heterogeneous mixture done clear
C) A solid - solid homogeneous mixture done clear
D) A pure substance done clear
question_answer 3) Vinegar is a solution of acetic acid in water. What kind of mixture is vinegar?
A) A homogeneous mixture of solid and liquid done clear
B) A heterogeneous mixture of liquid and liquid done clear
C) A homogeneous mixture of liquid and liquid done clear
D) A heterogeneous mixture of solid and liquid done clear
question_answer 4) Which of the following separation techniques is used for separating a mixture of two or more gases?
A) Sedimentation done clear
B) Liquification done clear
C) Hand picking done clear
D) Decantation done clear
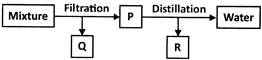
A) Water + sand + glass done clear
B) Oxygen + hydrogen + salt done clear
C) Stones + rice + water done clear
D) Chalk powder + sugar + water done clear
A) Sugar done clear
B) Chalk powder done clear
C) Glass done clear
D) Oxygen done clear
C) Alcohol done clear
D) Oxygen done clear
question_answer 8) How are grain seeds removed from their stalks?
A) Sieving done clear
B) Winnowing done clear
C) Threshing done clear
D) All of the above done clear
question_answer 9) A compound has
A) only one kind of mixture. done clear
B) only one kind of element. done clear
C) a mixture of elements and molecules. done clear
D) only one kind of molecules. done clear
question_answer 10) A Identify the mixture from the following.
A) Oxygen done clear
B) Carbon dioxide done clear
C) Hydrogen done clear
D) Air done clear
question_answer 11) Identify the compound from the following.
question_answer 12) Identify the element from the following.
C) Water done clear
question_answer 13) Which of the following is an example of a solid-in-gas mixture?
A) Soil done clear
B) Smoke done clear
C) Moisture done clear
D) Dew done clear
question_answer 14) Which of the following does NOT belong to the group formed by the others?
A) Brass done clear
B) Water done clear
C) Butter-milk done clear
D) Steel done clear
question_answer 15) A pure substance is made of
A) only one kind of atoms or molecules. done clear
B) two or more kinds of molecules. done clear
C) mixture of homogeneous substances done clear
D) all of the above done clear
question_answer 16) Which of the following statements about a mixture is TRUE?
A) It is a pure substance. done clear
B) Its constituents are not combined chemically. done clear
C) Its constituents do not retain their individual properties. done clear
D) It is always homogeneous. done clear
question_answer 17) In a mixture, constituents exhibit
A) similar properties. done clear
B) only those properties which are characteristic to the mixture. done clear
C) their own properties. done clear
D) no properties. done clear
question_answer 18) What is the process by which a gas changes into a liquid?
A) Decantation done clear
B) Sublimation done clear
C) Condensation done clear
D) Sedimentation done clear
question_answer 19) What kind of mixtures are alloys?
A) Solid-Gas done clear
B) Liquid-Liquid done clear
C) Gas-Gas done clear
D) Solid-Solid done clear
question_answer 20) What kind of mixtures are aerated drinks?
A) Solid-Solid done clear
B) Liquid-Solid done clear
C) Gas-Liquid done clear
D) Liquid-Liquid done clear
question_answer 21) Identify the liquid-in-gas type of mixture from the following.
A) Dissolved carbon dioxide in water done clear
B) Droplets of water in air done clear
C) Dissolved oxygen in water done clear
question_answer 22) A homogeneous mixture
A) is made up of one type of molecules. done clear
B) is the one in which the components can be distinguished. done clear
C) is the one in which the components cannot be distinguished. done clear
D) can be separated into its constituents physically. done clear
question_answer 23) A mixture contains three different substances X, Y and Z. They are of the same size, cubical in shape and yellow in colour. X particles are very heavy, insoluble, non-magnetic and contribute 50% of the mixture. Y particles are very light, insoluble, non-magnetic and contribute 40% of the mixture. And Z particles are iron pieces. Which of the following methods can separate X, Y and Z?
A) Winnowing, Magnetic separation done clear
B) Magnetic separation, Winnowing done clear
C) Sieving, Magnetic separation. Filtration done clear
D) Handpicking, Sublimation, Sieving done clear
question_answer 24) The sky looks clearer and brighter after the rain due to loading by rain drops. Which of the following is similar to the process mentioned above?
A) Separation of butter from curd. done clear
B) Separation of salt from sea water. done clear
C) Sprinkling water on a dusty street before sweeping. done clear
D) Separation of grain seeds from their stalks. done clear
question_answer 25) X is a separation technique used only when the components of a solid-solid mixture have different sizes. Identify X.
A) Winnowing done clear
B) Sieving done clear
C) Threshing done clear
D) Magnetic separation done clear
A) Only X done clear
B) Only Y, Z done clear
C) Only Z, X done clear
D) X, Y and Z done clear
question_answer 27) How is scrap-iron separated from other wastes in the scrap yard?
A) Sublimation done clear
B) Magnetic separation done clear
C) Handpicking done clear
D) Winnowing done clear
A) \[a-2,\text{ }b-3,\text{ }c-4,\text{ }d-1\] done clear
B) \[a-1,\text{ }b-4,\text{ }c-2,\text{ }d-3\] done clear
C) \[a-2,\text{ }b-4,\text{ }c-3,\text{ }d-1\] done clear
D) \[a-2,\text{ }b-4,\text{ }c-1,\text{ }d-3\] done clear
question_answer 29) Which of the following mixtures can be separated by using a filter paper?
A) Vinegar done clear
B) Saltwater done clear
C) Sand and water done clear
D) Sugar water done clear
question_answer 31) Which process is used to separate a pure solid from a solid-liquid solution?
A) Simple distillation done clear
B) Crystallization done clear
C) Filtration done clear
D) Sedimentation and decantation done clear
A) Only (i) and (ii) done clear
B) Only (ii) and (iii) done clear
C) Only (i) and (iii) done clear
D) (i), (ii) and (iii) done clear
question_answer 33) What happens when distilled water is evaporated?
A) Some salt is left behind. done clear
B) Some sand is left behind. done clear
C) Some sugar is left behind. done clear
D) Nothing is left behind. done clear
question_answer 34) Which process is used for separating a mixture of water and sulphur?
A) Filtration done clear
C) Evaporation done clear
D) Distillation done clear
question_answer 35) Which of the following are involved in filtration technique?
A) Hair in our nostrils done clear
B) Oil and air filters in cars done clear
C) Air filters in air conditioners done clear
question_answer 36) What process is used for separating heterogeneous mixtures of insoluble solid-in-liquid?
A) Filtration done clear
C) Sublimation done clear
D) Fractional distillation done clear

A) Salt done clear
B) Flour done clear
C) Sand done clear
D) Iron filings done clear
A) Iodine done clear
B) Calcium done clear
C) Air done clear
D) Sugar done clear
question_answer 39) Which process takes place in a washing machine while clothes are being dried.
A) Magnetic separation done clear
B) Filtration done clear
C) Evaporation done clear
D) Centrifugation done clear
question_answer 41) Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A) No more salt can be dissolved in a saturated solution of salt water without heating. done clear
B) Water dissolves different amounts of soluble substances in it. done clear
C) A mixture of milk and water can be separated by filtration. done clear
D) Salt is separated from sea water by evaporation. done clear
question_answer 42) By which method is wheat flour separated from wheat bran?
A) Handpicking done clear
C) Winnowing done clear
D) Filtration done clear
question_answer 43) Which of the following is NOT a pure substance?
A) Argon done clear
B) Helium done clear
C) Water done clear
D) Air done clear
Study Package

Question - Separation of Substances
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Separation of Substances
- 5th June 2023
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Separation of Substances are available here. These solutions include answers to all exercise questions given in the NCERT textbook. NCERT solutions for class 6 science Chapter 3 contains various type of questions like match the following, fill in the blanks, MCQ and long answer questions.
All these solutions are prepared by expert teachers with detailed explanations of every important topic. It is important for the students to go through these NCERT solutions to get knowledge of the type of question asked in the chapter.
Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Separation of Substances Questions and Answers
Exercise Questions
Question 1: Why do we need to separate different components of a mixture? Give two examples.
Answer: When two or more substances are mixed together they form a mixture. Components of a mixture should be separated because some components may not be useful or may spoil the useful component of the mixture.
For example:
- We used to separate slightly larger sized impurities like the pieces of dirt, stone, and husk from wheat, rice or pulses by handpicking method.
- Rice or pulses are usually washed before cooking. When we add water to these, the impurities like dust and soil particles get separated.
Question 2: What is winnowing? Where is it used?
Answer: Winnowing is the method of separating components of a mixture containing heavier and lighter components by wind or by blowing air. It is used to separate husk particles from seeds of grain.
Question 3: How will you separate husk or dirt particles from a given sample of pulses before Cooking?
Answer: Husk or bigger pieces of dirt particles can be removed from a sample of pulses by handpicking.
Question 4: What is sieving? Where is it used?
Answer: Sieving is the process of filtering components of a mixture of different sizes. Sieving allows fine particles to pass through the holes of the sieve, while the bigger impurities remain on the sieve.
Sieving is used in flour mills to separate broken particles of grains from flour. It is also used at construction sites to separate lumps, smaller stones from the mixture of sand and cement.
Question 5: How will you separate sand and water from their mixture?
Answer: To separate sand and water from their mixture, we follow the following steps:
- Leave mixture to stand undisturbed for some time in a container.
- Sand settles at the bottom of the container. It is called sedimentation.
- Gently pour the water in another container (called decantation).
- We may also use filter paper to remove fine particles of sand (called filtration)
Question 6: Is it possible to separate sugar mixed with wheat flour? If yes, how will you do it?
Answer: Yes it is possible to separate sugar mixed with wheat flour by the following method (a) Mix sugar and wheat flour in water (b) stir the solution to allow sugar to dissolve (c) Now filter the mixture (d) filtrate contains sugar solution and residue will be wheat flour.
Question 7: How would you obtain clear water from a sample of muddy water?
Answer: Following steps are required to obtain clear water from muddy water:
- Allow muddy water to stand undisturbed in a container.
- After sometime, mud settles at the bottom of the container. This process is called sedimentation.
- Upper layer is clear water.
- Pour the clear water gently in another container. This process is called decantation.
- To remove finer impurities we can filter this water again with the help of filter paper. This process is called filtration.
Question 8: Fill up the blanks
(a) The method of separating seeds of paddy from its stalks is called ______ . (b) When milk, cooled after boiling, is poured onto a piece of cloth the cream (malai) is left behind on it. This process of separating cream from milk is an example of ______. (c) Salt is obtained from seawater by the process of ____________ . (d) Impurities settled at the bottom when muddy water was kept overnight in a bucket. The clear water was then poured off from the top. The process of separation used in this example is called ____________.
Answer: (a) threshing (b)filtration (b) evaporation (d) sedimentation and decantation
9. True or false?
(a) A mixture of milk and water can be separated by filtration. (b) A mixture of powdered salt and sugar can be separated by the process of winnowing. (c) Separation of sugar from tea can be done with filtration. (d) Grain and husk can be separated with the process of decantation.
Answer: (a) False (b) False (c) False (d) False
Question 10: Lemonade is prepared by mixing lemon juice and sugar in water. You wish to add ice to cool it. Should you add ice to the lemonade before or after dissolving sugar? In which case would it be possible to dissolve more sugar?
Answer: We should add sugar before adding ice. Sugar dissolves in warm water more quickly than in cold water. We can dissolve more sugar before mixing ice in water.
Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Separation of Substances Extra Questions
Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Separation of Substances From Extra Questions section includes multiple choice questions (MCQs), short and answer type questions etc. All these questions are very important from examination point of view.
Extra Questions
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
(i) Butter is separated from milk by
(a) sedimentation (b) filtration (c) churning (d) decantation
Answer: (c) churning
(ii) Filtration is a method to separate the components of a
(a) solution (b) mixture of a liquid and an insoluble substance (c) both (a) and (b) (d) pure substance
Answer: (b) mixture of a liquid and an insoluble substance
(iii) Threshing is done by
(a) beating (b) bullocks (c) machines (d) all of these
Answer: (d) all of these
(iv) Which method is used to separate pebbles and stones from sand?
(a) Handpicking (b) Winnowing (c) Sieving (d) Any of these
Answer: (c) Sieving
(v) The components of a solution (say sugar in water) can be separated by
(a) filtration (b) evaporation (c) sedimentation (d) decantation
Answer: (b) evaporation
(vi) Sand from water is separated by
(a) sieving (b) evaporation (c) filtration (d) sedimentation and decantation
Answer: (d) sedimentation and decantation
(vii) The process of conversion of water vapours into liquid is called
(a) condensation (b) decantation (c) sedimentation (d) evaporation
Answer: (a) condensation
(viii) The process of conversion of water into its vapours is called
(a) evaporation (b) condensation (c) guttation (d) transpiration
Answer: (a) evaporation
(ix) A mixture of ammonium chloride and sand is separated by
(a) evaporation (b) decantation (c) sublimation (d) filtration
Answer: (c) sublimation
(x) The property which forms the basis of sieving
(a) difference in weight (b) difference in colour (c) difference in shape (d) difference in size
Answer: (d) difference in size
Short Type Questions and Answers
Question 1. When is handpicking used?
Answer: Handpicking is used to separate undesirable component when present in small amount.
Question 2. What is threshing? How is it done?
Answer: The process that is used to separate the grain from stalks is threshing. In this process, the stalks are beaten to free the grain seeds. Sometimes, threshing is done with the help of bullocks. Machines are also used to thresh large quantities of grain.
Question 3. Which type of separation is used in cashew nut factories?
Answer: Sieving.
Question 4. Give one example of sieving used in everyday life.
Answer: Separation of barn (choker) from flour.
Question 5. Name some materials that are used as filters.
Answer: Cotton, ceramic, filter cloth, filter paper.
Question 6. Name the process of separating two immiscible liquids.
Answer: By using separating funnel or by decantation.
Question 7. Which substance is used for loading?
Answer: Alum (phitkari).
Question 8. What is the use of alum in loading?
Answer: Alum is used to make the sedimentation faster. Bv adding alum the clay particles settle down rapidly.
Question 9. Which process is used to separate bacteria from water?
Answer: Filtration, by using special filters, i.e., bacteria proof filter.
Question 10. What is decantation?
Answer: Decantation is a process of separating insoluble solids from liquids. A suspension of solid particles in liquid is allowed to stand for some time. Solid particles settle down at the bottom, due to their weight.
Question 11. What is the use of decantation?
Answer: Decantation is used to separate insoluble solids from liquids. Two immiscible liquids are also separated by this process.
Question 12. What is the drawback of evaporation?
Answer: The liquid in the mixture is evaporated off into the air and is not recovered.
Question 13. Name the process to obtain salt from seawater.
Answer: Evaporation.
Question 14. Which types of mixtures are separated by evaporation?
Answer: Evaporation is used to separate solids dissolved in liquid.
Question 15. Describe the method to obtain pure salt from rock salt.
Answer: First, the mixture is crushed and grinded. Water is then added and filtered. Pure salt is collected as filtrate which is heated for evaporation. Water evaporates off and pure salt is left.
Question 16. How will you separate pure water from a solution of salt in water?
Answer: We can separate pure water from a solution of salt in water, by the process of distillation that is by evaporation and followed by condensation.
Question 17. Write opposite process of condensation.
Question 18. What do you mean by solubility?
Answer: The maximum mass of a solute that can be dissolved in 100 g of the solvent at any specific temperature is called solubility.
Question 19. Why is water a universal solvent?
Answer: Water can dissolve different kinds of substances. That is why water is commonly called as a universal solvent.
Question 20. What is the effect of temperature on solubility?
Answer: Solubility increases when the increase in temperature takes place.
Question 21. Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated solutions.
Answer: Saturated solution: A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature. Unsaturated solution: A solution in which more solute can be dissolved at any temperature.
Question 22. During centrifugation, which particles settle down at the bottom?
Answer: Heavy particles settle down at the bottom and lighter particles float at the top of the liquid.
Question 23. Name the method by which you can separate butter from milk.
Answer: Centrifugation.
Question 24. Name the device by which cream can be separated from milk at home.
Answer: A mixer-grinder is a very important device by which cream can be separated from milk.
Question 25. Why does visibility increase after rains?
Answer: After rains, the objects at a distance are seen more clearly, because the fine dust particles that were present in air settle down due to loading by rain drops.
Question 26. What is strainer?
Answer: Wire mesh is commonly known as strainer. For example, while preparing tea, we separate tea leaves from water by using a filter such as wire mesh. Tea leaves are bigger in size than the holes of the mesh.
Long Type Questions and Answers
Question 1. Name the property of the components used for separating the following mixtures:
- salt and camphor
- wheat and husk
- iron fillings and saw-dust
- coconut oil and water.
- sublimation
- magnetic separation
- separating funnel.
Question 2. Mention the methods that can be used for the separation of the following mixtures:
- wheat, sugar and husk
- rice, gram and iron fillings
- sand, Mack gram (urad) and husk.
Answer: 1. Mixture of wheat, sugar and husk.
- For separating husk from the mixture, we should follow the winnowing method as husk is lighter than other two components.
- Wheat and sugar can be separated by sieving as they have different sizes.
2. Mixture of rice, gram and iron fillings.
- For separating iron fillings, we can use a magnet.
- Rice and gram can be separated either by sieving or by handpicking.
3. Sand, black gram (urad) and husk.
- For separating sand from the mixture, we can sieve the mixture.
- Black gram (urad) and husk can be separated by the method of winnowing.
Question 3. Write various methods of separation of compounds from their mixture.
- Handpicking
- Sedimentation
- Decantation
- Evaporation
- Condensation.
Question 4. How will you Separate a mixture of common salt and chalk powder?
Answer: We know that common salt is soluble in water while chalk is sparingly, soluble. So, on the basis of different solubility, we can separate the common salt and chalk powder as follows:
- First, some water is mixed with the mixture of common salt and chalk powder, stir the solution well. Filter the solution by using filter paper. On filtering, chalk powder is obtained as a residue on the filter paper and salt solution is obtained.
- Now filtrate is evaporated and dry common salt is left behind.
Question 5. Match the following items given in Column A with that in Column B:
Question 6. What is filtration?
Answer: The process by which insoluble substance can be separated from a solution, by passing that solution through a porous paper (filter paper) is called filtration.
When one component of a mixture is soluble in water and other component is insoluble in water, the soluble component gets dissolved and insoluble one is separated by filtering the solution.
During filtration, the solid insoluble substance is retained at the filter paper as residue while the liquid free from any suspended matter passes through the filter paper and is collected as filtrate.
Question 7. How is common salt obtained from seawater?
Answer: When seawater is allowed to evaporate in shallow pits, water gets heated by sunlight and changes into water vapour by the process of evaporation leaving behind impure solid salts. Now, the lumps of impure common salt are crushed to get powdered salt. The powdered common salt is dissolved in water to prepare a solution. Now the solution of common salt is filtered to remove insoluble impurities. The clear solution is evaporated by heating to remove the water content to obtain a concentrated solution of common salt. The hot and concentrated solution is allowed to cool. On cooling, crystallization takes place and crystals of pure common salt are obtained.
Question 8. What is the importance of centrifugation? How is it done?
Answer: Centrifugation is the process of separating suspended particles from a liquid by rotating the liquid at a high speed. The mixture is taken in a closed bottle and rotated at a high speed. The heavy particles settle at the bottom while light particles remain behind. This method is also used to separate cream from milk. Cream collects at the centre and being lighter than milk, it floats at the top of the mixture.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Separation of Substances: Important topics
- Methods of separation
- Hand-picking
- Sedimentation, Decantation and Filtration
- Use of more than one method of separation
- Can water dissolve any amount of a substance?
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 5 Separation of Substances are given below. Our notes are designed by the subject experts and are as per the NCERT guidelines. These notes include all the important points of the chapter in detailed way, so you can refer to this whenever required. Study Path provides CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 5 that are easy to understand and also free downloadable PDF format, so students can practice it for their studies and get good marks in their examinations.
Water Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 5
A substance can be classified into: Mixture and the pure substance.
Pure Substances: Many substances around us contain only one type of constituent particles. Elements and compounds are pure substances. Some of the pure substances are iron, copper, water, salt, etc.
Impure Substances: Substances containing more than one type of constituent particles are called impure substances. Some of the impure substances are pond water, milk, etc.
Mixtures: A mixture is a material made up of two or more different substances, which are mixed but are not combined chemically.
Separation: Separation is the process of separating one or more components from a mixture. Example: distillation, sedimentation, filtration etc.
Need for Separation: We carry out the separation of the components of a mixture or an impure substance with the following purposes:
- To remove the unuseful or harmful component.
- To obtain the useful component.
- To remove impurities for getting a pure sample.
Principle of separation
- The substances present in a mixture retain their original properties like particle size, density, melting point, boiling point, volatility, etc.
- We use the difference in any one of these properties in the components of a mixture to separate them.
Methods of Separation: Handpicking, winnowing, sieving, magnetic separation, sedimentation, decantation, loading, filtration, evaporation, sublimation, distillation, churning, etc., are some common methods of separation.
Handpicking : The simple process of separating slightly bigger sized harmful substances or other useful substances or impurities like small pieces of stones, husk and dirt from grains of wheat, pulses and rice is called handpicking. In situations when the quantity of such impurities is not very large, handpicking turns out to be a time-saving and convenient procedure of separating substances.

Threshing: Threshing is the process of beating stalks to separate the grains from the harvested crop. It is done manually by farmers, or by threshing machines.
After the crop is harvested, stalks are left to dry under the sun. A single stalk has some 100 pieces of grain seeds joined to it. It is manually impossible to pluck each grain seed which is very small in size from the stalk and hence handpicking as a method of separation does not work here. That is why we use a method called threshing to separate these grain seeds.
Thus, Threshing can be defined as the process of separating the edible part i.e., grain seeds from the stalk by either with the help of machines, bullocks or sometimes by beating them.
Winnowing: Winnowing can be used to separate lighter and heavier components of a mixture. For example, to separate husk from grain with the help of air.
Even when threshing is done, husk or chaff is still attached to the grain seed and since the size of the two is quite similar, handpicking does not work and neither does threshing. Hence, a method called winnowing can be used.
Winnowing can be defined as the method of separating lighter husk particles and heavier grain seed components by blowing a current of air through them. The lighter husk particles are carried away by the wind and the grain seeds get separated. This husk can be further used as fodder for the cattle.
Sieving: Sieving is a method of separation in which the mixture is passed through a filter or a sieve.
Sometimes even after the grain seeds have passed through the stages of threshing and winnowing, husk may still be attached to the grain or it may have collected stones and dirt in the earlier stages which need to be removed and this separation is usually done with the help of a sieve.
Sieving is a very simple, convenient and time-saving process through which particles of varying sizes can be separated from each other with the help of a sieve. A sieve is nothing but a simple device with small pores in it which allow finer materials like flour to pass through leaving behind any impurities it might contain.

Filtration: Filtration is the process of passing the mixture through a filter to remove the solid particles from the fluid components of the mixture.
Filtration is the process through which smaller particles like dirt etc. are separated from a solution by making the solution pass through a medium (often a filter paper). This medium is such that only liquids are able to pass through it because of the presence of very tiny pores in it. The filter paper is molded to form a cone and this cone-like structure is then affixed to a funnel through which the dirty solution is allowed to pass. Sometimes, filtration can also be applied to separate pulp and seeds from the juice. It can also be used to separate cottage cheese or paneer from milk.
Sedimentation: When the heavier component in the mixture settles when water is added to it, the process is called sedimentation. This method is used in separating grains from dust and soil.
Sedimentation can be defined as the process through which dirt and other heavier particles in a mixture settle at the bottom of the vessel when water is added to it. When the dust and dirt particles have settled, the clear water which forms the upper layer is moved to a different container and the dirt and dust is done away with. This technique can also be used to separate two liquids which do not mix with each other (also called immiscible liquids) and is called decantation.
Decantation: Decantation is the process after sedimentation that involves removing the water, along with the impurities.
Decantation can be defined as a technique through which immiscible liquids or a liquid and a solid substance are separated. For example, take the case of oil and water. These are two examples of immiscible liquids. Once we pour oil in water, oil forms the upper layer of water and can be easily separated by gently pouring the mixture in another container till all the oil has been removed. Sometimes smaller dirt particles get carried along with the water in the process of decantation which needs to be further removed. This can be achieved through the process of filtration.
Condensation: The process of conversion of water vapour into its liquid form due to contact with a cooler surface is called condensation.
Example: Formation of water droplets on a metallic lid, while boiling water.
Evaporation: The process of conversion of water into its vapour is called evaporation.
Evaporation is the process of converting liquid into gas or vapour by increasing the temperature or pressure of the liquid. This process is often used to separate salt from salt water or salty sea water. Sea water has a number of salts present in it. Shallow pits called evaporation ponds are constructed and salt water is allowed to stand in these. After some time, the water gets evaporated, leaving behind the salts. Common salt is separated from this mixture upon further purification.

Can Water Dissolve Any Amount of a Substance?
Even though water can dissolve a number of substances and solutions in it, it has a limit to how much it can dissolve. After a certain point, it stops dissolving any more of that substance and the substance collects at the bottom of the vessel. We say that the solution has become saturated.
Solution : A solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances.
- In such a mixture, a solute is a substance dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent.
Saturated solution : A saturated solution is a chemical solution containing the maximum concentration of a solute dissolved in the solvent.
- For example, a saturated solution of salt in water is that in which no more salt can be dissolved.
- This added salt will just sediment down to the bottom of the vessel.
A saturated solution is one that contains the maximum possible concentration of a particular solute. For example, if we continue to add increasing amounts of salt to a small quantity of water, there will come a point that the salt will not get mixed with the water and instead deposit at the bottom. At this point, we say that the solution has become saturated i.e. it is now incapable of dissolving any more of the given solute which is in this case, salt.
A salute is defined as a very small element in a solution that is dissolved in a solution.
One way of ensuring that the given amount of water takes more salt even after it has reached its saturation point is by heating the said water. This is because heating the solution helps to increase the solubility of salt or any solute and hence more amount of the same solute can now be dissolved in the same amount of water.
Some Important Definitions
Churning: The process of shaking milk or cream in order to allow lighter particles to come to the surface in order to make butter is called churning.
Pure Substance: This can be defined as a substance composed of only a single type of particle.
Impure Substance: A substance composed of more than one type of particles.
Sublimation: When a solid directly gets converted into vapour, this process is known as sublimation.
Magnetic Separation: This is another method of separation which allows metals (and other articles which are attracted to a magnet) to be separated from a mixture with the help of a magnetic or by applying a magnetic force to it. For example, a mixture of salt and iron filings can be separated with the help of a magnet.
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5 – Free PDF Download
Our Class 6 Revision Notes will provide a quick glimpse of the chapter and improve the learning experience. We have made these revision notes keeping the convenience of students in mind so that it proves more effective. You can easily read these Class 6 notes just by clicking on the chapter names provided above.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances with Answers
We have compiled the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances with Answers Pdf free download covering the entire syllabus. Practice MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science with Answers on a daily basis and score well in exams. Refer to the Separation of Substances Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation.
Separation of Substances Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option.
Question 1. Mixtures need to be separated because (a) to remove undesirable substances (b) to get desirable substances (c) to obtain highly pure substances (d) all of the above
Answer: (d) all of the above

Question 2. The method of separation used to separate stones from rice is (a) handpicking (b) threshing (c) winnowing (d) all of these
Answer: (a) handpicking

Question 3. Butter is separated from milk by (a) sedimentation (b) filtration (c) churning (d) decantation
Answer: (c) churning
Question 4. The separation of grains from husk is done by the process of (a) handpicking (b) sieving (c) winnowing (d) threshing
Answer: (c) winnowing
Question 5. Threshing is done by (a) beating (b) animals (c) machines (d) all of these
Answer: (d) all of these
Question 6. Filtration is a method to separate the components of a (a) solution (b) mixture of a liquid and an insoluble substance (c) both (a) & (b) (d) pure substance
Answer: (b) mixture of a liquid and an insoluble substance
Question 7. A solid is dissolved in water. Which one of the following methods can be used to separate it? (a) Filtration (b) Decantation (c) Distillation (d) Evaporation
Answer: (d) Evaporation
Question 8. Petroleum contains (a) petrol (b) methanol (c) oil (d) water
Answer: (a) petrol
Question 9. Which of the following method is used when there is a difference in size and colour of desirable and undesirable constituents? (a) Handpicking (b) Threshing (c) Filtration (d) Decantation
Answer: (a) Handpicking
Question 10. The components of a solution of sugar in water can be separated by (a) filtration (b) crystallisation (c) decantation (d) sedimentation
Answer: (b) crystallisation
Question 11. At water treatment plants, the river water is filtered by using (a) filter paper (b) porcelain filters (c) cloth filters (d) sand filters
Answer: (d) sand filters
Question 12. The process of separating grains from the stalks is called (a) handpicking (b) threshing (c) decantation (d) evaporation
Answer: (b) threshing
Question 13. Iodine can be recovered from tincture of iodine by the process of (a) filtration (b) distillation (c) evaporation (d) decantation
Answer: (c) evaporation
Question 14. A mesh which is used to separate things on the basis of their difference in size (a) sieve (b) thresher (c) filter paper (d) none of these
Answer: (a) sieve
Question 15. The process of conversion of water into vapour is called (a) condensation (b) evaporation (c) sedimentation (d) decantation
Answer: (b) evaporation
Question 16. The process of separation of tea leaves by strainer is called (a) filtration (b) sedimentation (c) evaporation (d) condensation
Answer: (a) filtration
Question 17. Which of the following mixtures cannot be separated by using water as solvent followed by filtration and evaporation? (a) Sand and sugar (b) Salt and chalk powder (c) Sand and sulphur (d) Blue vitriol and sand
Answer: (c) Sand and sulphur
Question 18. The property which forms the basis of sieving is (a) difference in weight (b) difference in colour (c) difference in shape (d) difference in size
Answer: (d) difference in size
Question 19. When no more salt dissolves in water at a particular temperature, then the solution at that temperature is called (a) unsaturated (b) saturated (c) supersaturated (d) none of these
Answer: (b) saturated
Question 20. The separation of insoluble solids from liquids can be done by (a) sedimentation (b) decantation (c) loading (d) all of these
Answer: (a) sedimentation
Question 21. An example of a heterogeneous mixture is (a) fresh air (b) fresh water (c) sugar solution (d) dirty water
Answer: (d) dirty water
Question 22. ………….. is a convenient method of separation. (a) Handpicking (b) Threshing (c) Winnowing (d) Sieving
Question 23. Thresher machines are also used to thresh large quantities of …………….. (a) grain (b) sugar (c) salt (d) sand
Answer: (a) grain
Question 24. A separation funnel is a ……….. bulb to the stem of which is fitted a stopcock. (a) wooden (b) copper (c) glass (d) steel
Answer: (c) glass
Question 25. Distillation is a method of obtaining pure …………….. from a solution. (a) liquid (b) solid (c) gas (d) all of them
Answer: (a) liquid
Question 26. Water present in …………… is in the form of water vapour. (a) soil (b) moist (c) air (d) dry
Answer: (c) air
Question 27. Common salt is recovered from sea water by the process of (a) filtration (b) evaporation (c) sublimation (d) decantation
Question 28. When no more salt dissolves in water at a particular temperature, then the solution at that temperature is called (a) unsaturated (b) saturated (c) super saturated (d) none of the above
Question 29. The process of conversion of water into vapour is called (a) evaporation (b) condensation (c) sedimentation (d) decantation
Answer: (a) evaporation
Question 30. Tincture of iodine is a weak solution of iodine in alcohol. Iodine can be recovered from tincture of iodine by the process of (a) filtration (b) distillation (c) evaporation (d) decantation
Answer: (b) distillation
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1. Milk is a mixture of ……………., ……………. and …………….
Answer: milk-proteins, water, cream
Question 2. ……………. substance contains particles of only one type.
Answer: Pure
Question 3. ……………. and ……………. are the types of mixtures.
Answer: Heterogeneous, homogeneous
Question 4. Pebbles can be separated from wheat by …………….
Answer: handpicking
Question 5. ……………. is used to separate husk from wheat.
Answer: Winnowing
Question 6. Glass is a …………….
Answer: mixture
Question 7. Common salt is obtained from sea water by …………….
Answer: evaporation
Question 8. Compounds have ……………. melting points.
Answer: fixed
Question 9. Cream is separated from milk by the process of …………….
Answer: churning
Question 10. The method used to separate the components of different sizes in a mixture using a sieve is called …………….
Answer: sieving
Question 11. The process of separating grains from the stalks is called …………….
Answer: Threshing
Question 12. Fine sand can be separated from larger particles by …………….
Question 13. Breaking of stalks from grains is done by a machine called …………….
Answer: threshers
Question 14. Butter is a component of …………….
Answer: buttermilk
Question 15. Mixture may be solid, liquid or …………….
Answer: gas
Question 16. ……………. is used for separating insoluble substances from a liquid.
Answer: Filtration
Question 17. Sedimentation can be done more quickly by adding ……………. into it.
Answer: alum
Question 18. The used tea-leaves are separated from tea by the method of …………….
Answer: filtration
Question 19. The changing of liquid into vapours is called …………….
Question 20. Components retain their properties in a …………….
Question 21. Peanuts can be separated from a mixture of wheat and peanuts by ………………
Question 22. Fine sand can be separated from larger particles by ………………
Question 23. Compounds have ……………… melting points.
Question 24. Mixture may be solid, liquid or ………………
Question 25. Butter is a component of ………………
Answer: milk
Question 26. Sugarcane juice is a mixture of ……………… water and many other substances.
Answer: sugar
Question 27. Separation of components is done to obtain a ……………… substance.
Answer: pure
Question 28. Components retain their properties in a ………………
Question 29. The solid left behind after filtration is called ………………
Answer: residue
Question 30. The component dissolved in a solvent is called ………………
Answer: solute
True or False
Question 1. Milk is a pure substance.
Answer: False
Question 2. Evaporation is a continuous process.
Answer: True
Question 3. Air is a mixture of gases.
Question 4. Filtration can remove any solid substance which are dissolved in a liquid.
Question 5. A mixture of chalk powder and water is separated by sieving.
Question 6. A mixture of oil and water can be separated by decantation.
Question 7. Rocks are pure substances.
Question 8. Ink loses its properties when mixed in water.
Question 9. Common salt is a pure substance.
Question 10. Loading helps the suspended clay particles to settle down.
Question 11. Separating a mixture of two solids by winnowing is based on the difference in their weights.
Question 12. When no more solute can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at a particular temperature, the solution is said to be unsaturated.
Question 13. Grain and husk can be separated by decantation.
Question 14. Handpicking can be used to separate pulses from a mixture of pulsed and pebbles in a plate.
Question 15. Lemonade is a homogeneous mixture.
Question 16. There are a number of useful minerals present in sea water.
Question 17. The tap water is completely pure and fit for drinking.
Question 18. When a mixture consists of heavier and lighter particles, the lighter particles are separated using winnowing.
Question 19. Winnowing and threshing are same processes.
Question 20. Decantation is generally preceded by sedimentation.
Match the following
Hope the information shed above regarding NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 6 Science Separation of Substances MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, feel free to reach us so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
[Download] Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Here we are providing case study or passage-based questions for class 6 science chapter 5 Separation of Substances. Case Study/Passage Based Questions Passage-1 You are asked to add two spoons of solid salt to some liquid water taken in a beaker. On … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 6 ...
Class 6 Science Case Study Question and Answer: CBSE / NCERT Board Class 6 Science Case Study Question prepared by expert Science Teacher. Students can learn Case Based Question / Paragraph Type Question for NCERT Class 6 Science. ... Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Case Study Question. Chapter 6 Changes Around Us Case Study Question.
Separation of barn (choker) from flour. Question 5. Name some materials that are used as filters. Answer: Cotton, ceramic, filter cloth, filter paper. Question 6. Name the process of separating two immiscible liquids. Answer: By using separating funnel or by decantation.
Case 3: Separation of Substances in Evaporation and Condensation. Lisa wants to separate salt from a solution of salt and water. She decides to use evaporation and condensation. Answer the following questions: Q9: Explain how Lisa can separate salt from the saltwater solution using evaporation and condensation.
Answer: The materials having different size and colour can be separated by handpicking. 8. Name the other methods used to separate solid materials of different size. Answer: Sieving. 9. Name the process used to separate heavier and lighter components of a mixture. Answer: Winnowing.
Download Most Important Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter - 5 Separation of Substances. Download Important Questions PDF. The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science are crucial study sources that will help learners clear all the doubts that occur while studying the CBSE syllabus Chapter 5 of Class 6 Science. Fill in the blanks, true or false ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science - All Chapters. Chapter 1 Food Where Does It Come From. Chapter 2 Components of Food. Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric. Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups. Chapter 5 Separation of Substances. Chapter 6 Changes Around Us. Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants. Chapter 8 Body Movements.
Free PDF download of Important Questions with solutions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 5 - Separation of Substances prepared by expert Science teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books.Register Online for NCERT Class 6 Science tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in CBSE board examination. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials ...
5.1 Methods of Separation. The different separation methods of substances Class 6 chapter are simplified in NCERT solution for Class 6 Science Chapter 5. Some of the methods include hand-picking, winnowing, threshing, sieving, evaporation, sedimentation, filtration, etc. Let us discuss each of these methods in detail.
Question 4. Give one example of sieving used in everyday life. Answer: Separation of barn (choker) from flour. Question 5. Name some materials that are used as filters. Answer: Cotton, ceramic, filter cloth, filter paper. Question 6. Name the process of separating two immiscible liquids. Answer: By using separating funnel or by decantation.
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 5 are now available online with Vedantu in PDF format to ensure complete exam preparation. Our standard Class 6 Notes in Science on Separation of Substances are compiled by subject experts having years of experience in this field. Such Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes consists of step-by-step chapter ...
Answer: It is possible to separate sugar mixed with wheat flour. The mixture of sugar and wheat flour can be separated by strainer and sugar being bigger in size remains on the strainer. Thus, sugar can be separated from the mixture of sugar and wheat flour. Question 7.
Chapter 5 of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science covers important concepts such as methods of separation, including hand-picking, winnowing, threshing, sieving, sedimentation, decantation, and filtration. The chapter also explains the process of evaporation and the use of multiple methods of separation. Additionally, it addresses the question ...
Steps for the separation of salt, sand, oil and water. First we will use decantation method to separate oil and water. Water being heavier, forms the lower layer and oil being lighter, forms the upper layer in the beaker. We can decant off the upper layer of oil into another beaker carefully.
Answer: The process of conversion of water into vapour is called evaporation. 12. Name the method by which we get salt from ocean water. Answer: Evaporation. 13. Define condensation. Answer: The process of conversion of water vapour into liquid form is called condensation. 14. Write opposite process of evaporation.
UP Class 6th Science. 17 units · 58 skills. Unit 1. Science in daily life. Unit 2. Substances and groups of substances ... Separation of substances: Unit test; Elements, Compounds and Mixtures ... Practice. Types of mixtures: Homogeneous and Heterogeneous mixtures Get 6 of 8 questions to level up! Common methods of separation. Learn ...
Write the steps involved for the separation of salt, sand and oil from the mixture by giving an activity along with the diagram. Solution: A mixture of salt, sand, oil and water can be separated by following steps. Decant the oil from the mixture which is floating - oil is separated. Filter the mixture.
Separation of Substances Class 6 Notes - Chapter 5. According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 3. We all have seen our parents and grandparents separating small stones or pebbles from the rice grains and pulses, filtering tea leaves before serving tea and a lot more.
Free Question Bank for 6th Class Science Separation of Substances Separation of Substances. Customer Care : 6267349244. Toggle navigation ... Study the information given below. Some substances are made up of two or more elements combined together chemically.
Dipen. 5th June 2023. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Separation of Substances are available here. These solutions include answers to all exercise questions given in the NCERT textbook. NCERT solutions for class 6 science Chapter 3 contains various type of questions like match the following, fill in the blanks, MCQ and long answer ...
Water Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 5. A substance can be classified into: Mixture and the pure substance. Pure Substances: Many substances around us contain only one type of constituent particles. Elements and compounds are pure substances. Some of the pure substances are iron, copper, water, salt, etc. Impure Substances: Substances containing ...
Answer: (a) Shopkeepers add these undesirable substances to increase the quantity of the food materials and thus their profit. (b) Through handpicking. (c) Shopkeepers observing such practices are greedy, self-centred, criminal-minded and soulless. Question 2.
Separation of Substances Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers. Choose the correct option. Question 1. Mixtures need to be separated because. (a) to remove undesirable substances. (b) to get desirable substances. (c) to obtain highly pure substances. (d) all of the above. Answer.