

What is a PhD?
- Types of Doctorates
- A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) is the highest globally recognized postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award.
- PhDs are awarded to candidates who undertake original and extensive research in a particular field of study.
- Full time PhD programmes typically last three to four years, whilst part time PhD programmes typically last six to seven years.
- A PhD can lead to an academia teaching role or a career in research. A PhD can also equip you with skills suitable for a wide range of jobs unrelated to your research topic or academia.
Definition of a PhD – A Doctor of Philosophy (commonly abbreviated to PhD , Ph.D or a DPhil ) is a university research degree awarded from across a broad range of academic disciplines; in most countries, it is a terminal degree, i.e. the highest academic degree possible.
PhDs differ from undergraduate and master’s degrees in that PhDs are entirely research-based rather than involving taught modules (although doctoral training centres (DTCs) offer programmes that start with a year of lecture-based teaching to help develop your research skills prior to starting your project).
In most English-speaking countries, those that complete a PhD use the title “Doctor” (typically abbreviated to Dr) in front of their names and are referred to as such within academic and/or research settings. Those that work in fields outside of academia may decide not to use the formal doctor title but use post-nominal letters (e.g. John Smith PhD); it’s unusual though for someone to use both the Doctor title and post-nominal letters in their name.
PhD vs Doctorate
A PhD and a professional doctorate are both research-based terminal degrees.
However, where a PhD focuses on original research mostly around theoretical concepts, a professional doctorate focuses on examining existing knowledge to solve real-life, practical problems.
While there is much crossover between the two, a PhD is generally better suited for an individual to wants to advance the knowledge and understanding in their field, and a professional doctorate degree is better suited to a working professional who wants to better be able to apply knowledge and understanding to their field.
What Are the Entry Requirements for a PhD?
To be accepted on to a PhD programme, students usually need to hold at least a high ( 2:1 and above ) undergraduate degree that is related to the field of research that they want to pursue. A PhD candidate may also be expected to hold a Master’s degree , however, this does not mean you must have one, as it is still possible to enrol into a PhD without a Master’s .
Self-funded courses may sometimes be more relaxed in relation to entry requirements. It may be possible to be accepted onto a self-funded PhD programme with lower grades, though these students typically demonstrate their suitability for the role through professional work experience.
Whilst a distance learning project is possible , most PhD candidates will carry out their research over at least three years based at their university, with regular contact with two academic supervisors (primary and secondary). This is particularly the case for lab-based projects, however, some PhD projects require spending time on-site away from university (e.g. at a specialist research lab or at a collaborating institution abroad).
How Long Does a PhD Take?
Typically, full-time PhDs last 3-4 years and part-time PhDs last 6-7 years. However, at the discretion of the university, the thesis writing-up period can be extended by up to four years.
Although most doctoral programmes start in September or October, they are generally much more flexible than taught-courses and can start at any time of the year.
How Much Does a PhD Cost?
Tuition fees for UK and EU students vary between £3,000 and £6,000 per year, with the average tuition fee of £4,712 per year for 2023/24 programmes.
Tuition fees increase considerably for international students, varying between £16,000 to £25,000 per year, with an average tuition fee of £19,600 per year .
Nonetheless, most students will secure PhD funding in the form of studentships, scholarships and bursaries to help pay for these fees. These funding opportunities can either be partial, which cover tuition fees only, or full, which cover both tuition fees and living expenses.
UK national students can also apply for Doctoral Loans from Student Finance England if they are unable to secure funding.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
What Does a PhD Involve?
To be awarded a PhD, a doctoral student is required to produce a substantial body of work that adds new knowledge to their chosen field.
A PhD programme will typically involve four key stages:
Stage 1: Literature Review
The first year of a PhD involves attending regular meetings with your supervisors and carrying out a search on previously published work in your subject area. This search will be used to produce a literature review which should set the context of the project by explaining the foundation of what is currently known within the field of research, what recent developments have occurred, and where the gaps in knowledge are. In most cases, this will be an extension of your research proposal should you have produced one as part of your application. The literature review should conclude by outlining the overarching aims and objectives of the research project. This stage of setting achievable goals which are original and contribute to the field of research is an essential first step in a successful PhD.
The supervisor is the main point of contact through the duration of a PhD – but remember: they are there to mentor, not to teach, or do it for you . It will be your responsibility to plan, execute and monitor your own work as well as to identify gaps in your own knowledge and address them.
Stage 2: Research
The second year (and prehapse some of your third year) is when you work on your research. Having identified novel research questions from your review of the literature, this is where you collect your data to help answer these questions. How you do this will depend on the nature of your doctoral research: for example, you may design and run experiments in a lab alongside other PhD students or visit excavation sites in remote regions of the world. You should check in regularly with your supervisors to update them and run any ideas or issues past them.
Have the structure and chapters of your thesis in mind as you develop and tackle your research questions. Working with a view of publishing your work will be very valuable later on.
Stage 3: Write up of Thesis
The next key stage of a PhD is writing a doctoral thesis , which typically takes from anywhere between three months to one year. A thesis is a substantial body of work that describes the work and outcomes of the research over the previous two to three years. It should tell a detailed story of the PhD project – focusing on:
- The motivations for the research questions identified from the literature review.
- The methodologies used, results obtained, and a comprehensive analysis and discussion of the findings.
- A detailed discussion of the key findings with an emphasis on the original contributions made to your field of research and how this has been impactful.
There is no universal rule for the length of a PhD thesis, but general guidelines set the word count between 80,000 to 100,000 words.
For your thesis to be successful, it needs to adequately defend your argument and provide a unique or increased insight into your field that was not previously available.
Stage 4: Attending the Viva
A viva voce , most commonly referred to as just a ‘ viva ‘, is an interview-style examination where the PhD student is required to engage in a critical appraisal of their work and defend their thesis against at least two examiners. The examiners will ask questions to check the PhD student has an in-depth understanding of the ideas and theories proposed in their thesis, and whether they have developed the research skills that would be expected of them.
The viva is one of the final steps in achieving a PhD, and typically lasts at least two hours, but this duration can vary depending on the examiners, the university and the PhD project itself.
Once you have done the viva – you’re on the home stretch. You will typically be asked to make some amendments to your thesis based on the examiner’s feedback. You are then ready to submit your final thesis for either:
- PhD – If you pass the requirements you will be awarded a PhD degree (most common outcome),
- MPhil – If you failed to meet requirements for a PhD, you may be downgraded to an MPhil degree (uncommon outcome),
- Fail – No award is given, typically for cases of plagiarism (extremely uncommon outcome).
What Is It Like to Undertake a PhD?
We’re often asked what it is like to undertake a PhD study. Unfortunately, this isn’t a simple answer to this question as every research project is different.
To help give insight into the life of a PhD student, we’ve interviewed PhD students at various stages of their programmes and put together a series of PhD Student Interviews . Check out the link to find out what a PhD is like and what advice they have to offer you.
What Are the Benefits of A PhD?
A PhD is the highest globally recognised postgraduate degree that higher education institutions can award. The degree, which is awarded to candidates who demonstrate original and independent research in a particular field of study, is not only invaluable in itself, but sets you up with invaluable skills and traits.
Career Opportunities
First, a PhD prepares you for a career in academia if you wish to continue in this area. This takes form as a career in the Higher Education sector, typically as a lecturer working their way to becoming a professor leading research on the subject you’ve studied and trained in.
Second, a PhD also enables the opportunity for landing a job in a research & development role outside of the academic environment. Examples of this include laboratory work for a private or third sector company, a governmental role and research for commercial and industrial applications.
Transferable Skills
Finally, in possessing a PhD degree, you can show to employers that you have vital skills that make you an asset to any company. Three examples of the transferable skills that you gain through a PhD are effective communication, time management, and report writing.
- Communication – presenting your work in written and oral forms using journal papers and podium presentations, shows your ability to share complex ideas effectively and to those with less background knowledge than you. Communication is key in the professional environment, regardless of the job.
- Time management – The ability to prioritise and organise tasks is a tremendous asset in the professional industry. A PhD holder can use their qualification to demonstrate that they are able to manage their time, arrange and follow a plan, and stick to deadlines.
- Report writing – Condensing three years of work into a thesis demonstrates your ability to filter through massive amounts of information, identify the key points, and get these points across to the reader. The ability to ‘cut out the waffle’ or ‘get to the point’ is a huge asset in the professional industry.
Aside from the above, you also get to refer to yourself as a Doctor and add fancy initials after your name!
What Can I Do After a PhD?
One of the most desirable postdoctoral fields is working within independent Research and Development (R&D) labs and new emerging companies. Both industries, especially R&D labs, have dedicated groups of PhD graduates who lead research activities, design new products and take part in crucial strategic meetings. Not only is this a stimulating line of work, but the average salaries in R&D labs and emerging start-ups are lucrative. In comparison, an undergraduate with five years of experience within their given field will, on average, likely earn less than a new PhD graduate taking on a R&D position.
It’s a common misunderstanding that PhDs only opens the door for an academic career such as university lecturers and training providers. Although obtaining a PhD opens these doors, the opportunities extend far beyond educational roles. In fact, recent data from the UK’s Higher Education Statistics Agency (HESA) indicates only 23% of PhD graduates take a position in educational roles . This low percentage is primarily because PhD graduates have a wide range of skills that make them suitable for a broad spectrum of roles. This is being seen first hand by the increasing number of PhD graduates who are entering alternative roles such as research, writing, law and investment banking.
How Do I Find a PhD?
We appreciate that finding a PhD programme to undertake can be a relatively daunting process. According to Higher Education Student Statistics , over 22,000 PhDs were awarded in 2016/17 within the United Kingdom alone. Clearly there are a huge number of PhD programmes available. This can sometimes be confusing for prospective doctorates, particularly when different programmes are advertised in different places. Often, it is difficult to know where to look or where to even start. We’ve put together a list of useful sources to find the latest PhD programmes:
- A great place to start is with our comprehensive and up-to-date database of available PhD positions .
- Assuming you are still at university, speak to an existing PhD supervisor within your department.
- Attend as many postgraduate open days as you can. Whilst there, speak to current PhD students and career advisors to get an awareness of what PhDs are on offer.
- Visit the postgraduate section of university websites and the PhD Research Council section of the UKRI website.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
doctor of philosophy
Definition of doctor of philosophy
Word history.
1651, in the meaning defined above
Dictionary Entries Near doctor of philosophy
doctor of osteopathic medicine
doctors' bills
Cite this Entry
“Doctor of philosophy.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/doctor%20of%20philosophy. Accessed 23 Apr. 2024.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, on 'biweekly' and 'bimonthly', popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 19, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), a great big list of bread words, 9 superb owl words, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, games & quizzes.

- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Grammar Coach ™
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Advertisement
abbreviation for
- Doctor of Philosophy AlsoDPhil
Discover More
Example sentences.
He also bragged about earning a PhD, a point Smerconish did not question.
Even his nametag played up his dweeby nature, labeling him “Mr. Gruber, PhD.”
Throughout her life, she faced public ridicule, legal persecution and, eventually, redemption through a PhD in clinical sexology.
“It is impossible by elections to choose normal people,” argues Yoram Gat, an Israeli software engineer with a PhD in statistics.
The son of Taiwanese immigrants, he grew up in California and earned his PhD in neuroscience at Stanford.
Damn few of them got it from me, I'm happy to say, and those that did, knew more about the subject than most PhD's.
It was a great diversion from the late nights working on my PhD.
[ ak -s uh -lot-l ]
Start each day with the Word of the Day in your inbox!
By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policies.
What is a PhD? Advice for PhD students
How long does it take to get a doctorate degree how do you get into grad school are you qualified to do a phd answers to these questions and more.
What is a PhD?
A PhD, which stands for “doctor of philosophy”, is the most advanced academic degree. It’s earned through extensive research on a specific topic, demonstrating expertise and contributing new knowledge to the field.
What does “PhD” mean?
The term “PhD” is often used as a synonym for any doctoral-level qualification. Doctorate degrees can often be split into two categories: MPhil and PhD.
An MPhil is similar to a PhD as it includes a research element (which is usually shorter and less in-depth than a PhD thesis, and often more akin to a dissertation undertaken at undergraduate or master’s level).
MPhil students focus more on interpreting existing knowledge and theory and critically evaluating other people’s work rather than producing their own research. The precise nature and definition of an MPhil can vary among institutions and countries.
A PhD, meanwhile, follows a more widely known and traditional route and requires students, often referred to as “candidates”, to produce their own work and research on a new area or topic to a high academic standard.
PhD requirements vary significantly among countries and institutions. The PhD, once completed, grants the successful candidate the title of “doctor of philosophy”, also called PhD or DPhil.
What is a professional doctorate?
A professional doctorate is a kind of degree that helps people become experts in their fields. Instead of focusing mainly on theory and research like a regular PhD, a professional doctorate is all about practical skills and knowledge.
This kind of doctorate is great for students who want to get better at their jobs in areas like teaching, healthcare, business, law or psychology. The courses and projects in these programmes are designed to tackle real problems you might face at work.
For example, you might have heard of the doctor of education (EdD), doctor of business administration (DBA), doctor of psychology (PsyD) or doctor of nursing practice (DNP). These programmes combine learning, hands-on projects and sometimes a thesis paper or essay to show you’re skilled at solving on-the-job challenges.
How long does it take to study a PhD?
The time required to complete a PhD can vary significantly based on several factors. Generally, a full-time PhD programme takes around three to six years to finish. However, it’s important to take into account individual circumstances and the nature of the research involved.
1. Full-time vs. part-time: If you’re studying full-time, dedicating most of your time to your studies, it usually takes about three to four years to complete a PhD. However, studying part-time while managing other commitments might extend the duration. Part-time PhDs can take around six to eight years, and sometimes even longer.
2. Nature of research: The complexity of your research proposal can influence the time required. Certain research questions may involve intricate experiments, extensive data collection or in-depth analysis, potentially leading to a longer completion timeline.
3. Field of study: The subject area you’re researching can also affect the necessary time. Some fields, such as sciences or engineering, might involve more hands-on work, while theoretical subjects might require more time for literature review and analysis.
4. Supervision and support: The guidance and availability of your academic supervisor can affect the pace of your research progress. Regular meetings and effective communication can help keep your studies on track.
5. Thesis writing: While the research phase is crucial, the stage of writing your thesis is equally significant. Organising and presenting your research findings in a clear and cohesive manner can take several months.
6. External commitments: Personal commitments, such as work, family or health-related factors, can influence your study time. Some students need to balance these alongside their PhD studies, potentially extending the duration.
7. External Funding: The availability of funding can also affect your study duration. Some funding might be linked to specific project timelines or research objectives.
So, although a PhD usually takes between three and six years of full-time study, with potential variations based on research complexity, enrolment as part-time or full-time, field of study and personal circumstances. It’s vital to have a realistic understanding of these factors when planning your PhD journey.
How long is a PhD in the UK?
In the UK, the length of a PhD programme typically ranges from three to four years of full-time study. As explained above, there are many factors to consider.
How long is a PhD in the US?
Similarly to the UK, in the United States, the duration of a PhD programme can vary widely depending on the field of study, research topic and individual circumstances. On average, a full-time PhD programme in the US typically takes between five and six years to complete.
Why does it take longer to study a PhD in the US?
PhD programmes generally take longer to complete in the US than in the UK due to various factors in the education systems and programme structures of each country:
1. Programme structure: UK PhD programmes often emphasise early, focused research from the first year, leading to shorter completion times. In contrast, US programmes commonly include more initial coursework in your first and second year and broader foundational training, which can extend the overall duration.
2. Course work requirements: Many US PhD programmes require a lot of course work, which can lengthen the time needed to finish. UK programmes tend to have fewer or no course work demands, allowing students to concentrate primarily on research skills.
3. Research funding: In the UK, PhD funding is often awarded with specific timeframes in mind, motivating completion of the research degree in the agreed duration. In the US, funding approaches can vary, requiring students to secure funding from multiple sources, potentially affecting their progress and completion time.
4. Teaching responsibilities: Some US PhD students take on teaching roles as part of their funding, dividing their time and potentially prolonging their studies.
5. Research approach: Differences in research methodologies and project scopes can affect the time needed for data collection, experimentation and analysis.
6. Academic culture: The US education system values a well-rounded education, including coursework and comprehensive exams. This can extend the time before full-time research begins. UK PhD programmes often prioritise independent research early on.
7. Part-time and work commitments: US PhD candidates might have more flexibility for part-time work or other commitments, which can affect research progress.
8. Dissertation requirements: US PhD programmes generally include a longer and more comprehensive dissertation, involving more chapters and a broader exploration of the research topic.
These variations in programme structures, funding models and academic cultures contribute to the differing completion times between the two countries.
What qualifications do you need for a PhD?
To be eligible for a PhD programme, certain educational qualifications are generally expected by universities. These qualifications serve as indicators of your readiness to engage in advanced research and contribute to the academic community.
First, an undergraduate or bachelor’s degree in a relevant field is typically the most common requirement. This degree provides you with a foundational understanding of the subject and introduces you to basic research methodologies. It serves as a starting point for your academic journey.
Do you need a master’s degree to get into a PhD programme?
In addition to an undergraduate degree, many PhD programmes also require candidates to hold postgraduate or master’s degrees, often in fields related to the intended PhD research. A master’s degree offers a deeper exploration of the subject matter and enhances your research skills. Possessing a master’s degree signifies a higher level of expertise and specialisation.
The combination of both undergraduate and postgraduate degrees demonstrates a solid academic background. This background is crucial before you engage in doctoral study because pursuing a PhD involves more than just knowledge; it requires advanced research abilities, critical thinking and the capacity to provide an original contribution and new insights into the chosen field of study.
While these qualifications are usually requested, there are exceptions. Some institutions offer direct-entry programmes that encompass bachelor’s, master’s and PhD degrees in a streamlined structure. This approach is often seen in scientific and engineering disciplines rather than humanities.
In exceptional cases, outstanding performance during undergraduate studies, coupled with a well-defined research proposal, might lead to direct entry into a PhD programme without requiring a master’s degree.
Admission requirements can vary between universities and programmes. Some institutions might have more flexible prerequisites, while others could have more stringent criteria. Make sure that you thoroughly research all admission requirements of the PhD programmes you’re interested in to ensure you provide the right information.
Are PhD entry requirements similar in other countries?
PhD entry requirements in Canada and Australia can be somewhat similar to those in the UK and the US, but there are also some differences. Just like in the UK and the US, having a bachelor’s degree followed by a master’s degree is a common way to qualify for a PhD in Canada and Australia. However, the exact rules can vary, such as how much research experience you need or the grades you should have.
In Canada and Australia, as in the UK and the US, international students usually need to show their English language skills through tests like IELTS or TOEFL. And, like in other places, you might need to give a research proposal to explain what you want to study for your PhD.
But remember, even though there are some similarities, each country has its own rules.
PhD diary: Preparing for a PhD Nine things to know before doing a PhD Women in STEM: undertaking PhD research in cancer Studying for a part-time PhD: the challenges and the benefits Is it possible to do a three-year PhD as an international student? Looking for PhD tips? Why not check Twitter PhD diary: Where do I begin? How to do a PhD on a budget
How much does it cost to study a PhD?
The cost of pursuing a PhD can vary significantly between international and home (domestic) students, and it depends on the country, university and programme you choose.
United Kingdom (UK)
Home students in the UK often pay lower tuition fees compared with international students. Home students might also have access to government funding or subsidised tuition rates.
International students typically pay higher tuition fees, which can vary widely depending on the university and programme. Fees can range from around £10,000 to £25,000 or more per year.
United States (US)
PhD programme costs in the US can be quite high, especially for international students. Public universities often have lower tuition rates for in-state residents compared with out-of-state residents and international students.
Private universities in the US generally have higher tuition fees, and international students might be charged higher rates than domestic students.
Canadian universities often charge higher tuition fees for international students compared with domestic students.
Some universities offer funding packages that include tuition waivers and stipends for both domestic and international doctoral students.
In Australia, domestic students (Australian citizens and permanent residents) usually pay lower tuition fees than international students.
International students in Australia might have higher tuition fees, and costs can vary based on the university and programme.
Apart from tuition fees, other aspects play a role in the overall financial consideration:
PhD studentship: Many universities offer PhD studentships that provide financial support to research students, covering both tuition fees and a stipend for living expenses.
Stipend and housing: Stipends are designed to cover living expenses. Stipend amounts can vary depending on the university and location. If you’re studying in London in the UK, stipends might be higher to account for the higher living costs in the city. Some universities also offer subsidised or affordable housing options for doctoral students.
Tuition and stipend packages: Some PhD programmes provide funding packages that include both tuition waivers and stipends. These packages are to help relieve the financial burden on students during their doctoral studies.
Research the financial support options provided by the universities you’re interested in to make an informed decision about the cost of your PhD journey.
What funding options are available for PhD candidates?
PhD candidates have various funding options available to support their studies and research journeys. Some of these options include:
PhD scholarships: Scholarships are a common form of financial aid for PhD candidates. They are awarded based on academic merit, research potential or other specific criteria. Scholarships can cover tuition fees and provide a stipend for living expenses.
Bursaries: Bursaries are another form of financial assistance offered to students, including PhD candidates, based on financial need. They can help cover tuition fees or provide additional financial support.
In the UK, specific funding options are available:
Regional consortium: Some regions have research consortiums that offer funding opportunities for doctoral candidates. These collaborations can provide financial support for research projects aligned with specific regional needs.
UK research institute: Research councils in the UK often offer stipends to PhD candidates. These stipends cover living expenses and support research work.
University-based studentship: Many UK universities offer studentships. You can read more about these above.
In the USA, there are also funding options available:
Research assistantships (RAs): Many universities offer research assistantships where PhD candidates work on research projects under the guidance of faculty members. In exchange, they receive stipends and often have their tuition waived.
Teaching assistantships (TA): Teaching assistantships involve assisting professors in teaching undergraduate courses. In return, PhD candidates receive stipends and sometimes tuition remission.
Fellowships: Fellowships are competitive awards that provide financial support for PhD candidates. They can come from universities, government agencies, private foundations and other institutions. Fellowships can cover tuition, provide stipends and offer research or travel funds.
Graduate assistantships: Graduate assistantships include a range of roles, from research and teaching to administrative support. These positions often come with stipends and sometimes include tuition benefits.
External grants and fellowships: PhD candidates can apply for grants and fellowships from external organisations and foundations that support research careers in specific fields. Examples include the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Fulbright Programme.
Employer sponsorship: In some cases, employers might sponsor employees to pursue PhDs, especially if the research aligns with the company’s interests.
You can read about the current available scholarships for international students of all education levels on our website .
What does a PhD Involve?
How does a PhD work?
A PhD includes thorough academic research and significant contributions to your chosen field of study. The timeline for completing a PhD can significantly vary based on the country, college or university you attend and the specific subject you study.
The duration of a PhD programme can vary based on factors such as the institution’s requirements and the academic discipline you’re pursuing. For instance, the timeline for a PhD in a science-related field might differ from that of a humanities discipline.
UK PhD timeline example
Looking at a typical PhD degree in a London higher education institution, we can consider this example timeline.
In the initial year of your PhD, you’ll collaborate closely with your designated academic supervisor. This collaboration involves refining and solidifying your research proposal, which lays the foundation for your entire doctoral journey.
This is also the time to establish a comprehensive plan, complete with well-defined milestones and deadlines. A crucial aspect of this year is conducting an extensive literature review, immersing yourself in existing academic works to understand the landscape of your chosen research area. It’s important to make sure that your research idea is original and distinct from prior studies.
As you begin the second year, you’ll actively collect data and gather information related to your research topic. Simultaneously, you’ll initiate the process of crafting your thesis. This involves combining your research findings and analysis into sections of your thesis document.
This is also the phase where you might have opportunities to share your research insights at academic meetings, conferences or workshops. Depending on the programme, you might even engage in teaching activities. Some PhD candidates also begin contributing to academic journals or books, showcasing their findings to a broader audience.
The third year of a PhD programme often marks the final stage of your research efforts. This is when you dedicate substantial time to writing and finalising your complete thesis. Once your thesis is completed to the highest standard, you’ll submit it for thorough evaluation.
A significant milestone in the third year is the viva voce, an oral examination where you’ll defend your thesis before a panel of experts in your field. The viva voce is an opportunity to showcase your deep understanding of your research and defend your findings.
Why should you do a PhD?
For many people, acquiring a doctorate degree is the pinnacle of academic achievement, the culmination of years of commitment to higher education.
However, the act of pursuing a PhD can be a complex, frustrating, expensive and time-consuming exercise. But with the right preparation, some sound advice and a thorough understanding of the task at hand, your years as a doctoral student can be some of the most rewarding of your life.
People choose to work towards a doctorate for many reasons. If you are looking to pursue an academic position, such as university lecturer or researcher, then a PhD is usually required.
Many people obtain a PhD as part of a partnership with an employer, particularly in scientific fields such as engineering, where their research can prove useful for companies.
In some cases, however, PhDs are simply down to an individual’s love of a subject and their desire to learn more about their field.
What are some benefits of studying a PhD?
Pursuing a PhD can have many benefits that extend beyond academic achievement, encompassing personal growth, professional advancement and meaningful contributions to knowledge.
One of the most notable benefits of a PhD is the potential for tenure in academia. Attaining tenure provides a level of job security that allows you to delve into long-term research projects and make enduring contributions to your field. It signifies a stage where you can explore innovative ideas and pursue in-depth research, fostering your academic legacy.
While not obligatory, the opportunity to collaborate on research projects with your supervisor is another valuable aspect of a PhD pursuit. These collaborations might even come with financial compensation, offering real-world experience, skill development and practical applications of your research. Engaging in such collaborations can enrich your research portfolio and refine your research methodologies.
A pivotal aspect of a PhD journey is the chance to publish your original research findings. By disseminating your work in academic journals or presenting it at conferences, you contribute to the expansion of knowledge within your field. These publications establish your expertise and reputation among peers and researchers worldwide, leaving a lasting impact.
The pursuit of a PhD can provide a unique platform to build a diverse network of colleagues, mentors and collaborators. Engaging with fellow researchers, attending conferences and participating in academic events offer opportunities to make valuable connections. This network can lead to collaborations, expose you to a spectrum of perspectives and pave the way for future research endeavours.
What is a PhD thesis? And what is a PhD viva?
A PhD thesis will be produced with help from an academic supervisor, usually one with expertise in your particular field of study. This thesis is the backbone of a PhD, and is the candidate’s opportunity to communicate their original research to others in their field (and a wider audience). PhD students also have to explain their research project and defend their thesis in front of a panel of academics. This part of the process is often the most challenging, since writing a thesis is a major part of many undergraduate or master’s degrees, but having to defend it from criticism in real time is arguably more daunting. This questioning is known as a “viva”, and examiners will pay particular attention to a PhD’s weaknesses either in terms of methodology or findings. Candidates will be expected to have a strong understanding of their subject areas and be able to justify specific elements of their research quickly and succinctly.
In rare cases, students going for a PhD may instead be awarded an MPhil if the academic standard of their work is not considered fully up to par but still strong enough to be deserving of a qualification.
Can you do a PhD part time?
Many PhD and MPhil candidates choose to pursue their qualification part time, in order to allow time to work and earn while studying. This is especially true of older students, who might be returning to academia after working for a few years.
When applying, you should always speak to the admissions team at your university to ensure this is possible and then continue to work with your supervisor to balance all your commitments.
Can I do a PhD through distance learning?
This is something else that you will need to check with your university. Some institutions offer this option, depending on the nature of your research.
You will need to be clear how many times you will need to travel to your university to meet with your supervisor throughout your PhD.
Your PhD supervisor
Choosing the right PhD supervisor is essential if you want to get the most out of your PhD. Do your research into the faculty at the institution and ensure that you meet with your proposed supervisor (either virtually or in person) before fully committing.
You need to know that not only do they have the right expertise and understanding of your research but also that your personalities won’t clash throughout your PhD.
Remember, to complete your PhD, you will need a strong support network in place, and your supervisor is a key part of that network.
Coping with PhD stress
If you do decide to embark on a doctorate, you may well encounter stress and anxiety. The work involved is often carried out alone, the hours can be long and many students can suffer from the pressure they feel is on their shoulders.
Ensuring that you check in regularly with your emotions and your workload is crucial to avoid burnout. If you have other commitments, such as a job or a family, then learning to balance these can feel overwhelming at times.
Give yourself regular breaks, speak to your supervisor and ensure that you know what university resources and support systems are available to you in case you need to access them.
Post-doctorate: what happens after you finish your PhD?
Many PhD graduates pursue a career in academia, while others will work in industry. Some might take time out, if they can afford to, to recover from the efforts of PhD study.
Whatever you choose to do, undertaking a PhD is a huge task that can open up a range of doors professionally. Just remember to take some time out to celebrate your achievement.
How does a PhD affect salary and earning potential?
How much does a professor with a PhD make a year?
Professors with PhDs can earn different amounts depending on where they work and their experience. In the UK, a professor might make around £50,000 to £100,000 or more each year. In the US, it's between about $60,000 and $200,000 or even higher. The exact salary depends on things like the place they work, if they have tenure, and what they teach.
How much does a PhD add to salary?
Having a PhD can make your salary higher than if you had a lower degree. But exactly how much more you earn can change. On average, people with PhDs earn more than those with bachelor’s or master’s degrees. The increase in salary is influenced by many things, such as the job you do, where you work and what field you’re in.
In fields such as research, healthcare, technology and finance, your knowledge and skills from your PhD can potentially help you secure a higher salary position.
In the end, having a PhD can boost your earning potential and open doors to well-paying jobs, including professorships and special roles in different areas. But the exact effect on your salary is influenced by many things, so ensure you weigh the cost against the benefit.
How to choose a PhD programme?
Choosing a PhD programme involves defining your research interest, researching supervisors and programme reputation, evaluating funding options, reviewing programme structure, considering available resources, assessing networking opportunities, factoring in location and career outcomes, visiting the campus if possible and trusting your instincts.
How can I find available PhD programmes?
You can find available PhD programmes by visiting university websites, using online directories such as “FindAPhD”, checking professional associations, networking with professors and students, following universities on social media, attending career fairs and conferences, contacting universities directly and exploring research institutes’ websites.
How to apply for a PhD programme?
To apply for a PhD programme:
Research and select universities aligned with your interests.
Contact potential supervisors, sharing your proposal, CV and references.
Prepare application materials: research proposal, CV, recommendation letters and a writing sample.
Ensure you meet academic and language-proficiency requirements.
Complete an online application through the university’s portal.
Pay any required application fees.
Write a statement of purpose explaining your motivations.
Provide official transcripts of your academic records.
Submit standardised test scores if needed.
Some programmes may require an interview.
The admissions committee reviews applications and decides.
Apply for scholarships or assistantships.
Upon acceptance, review and respond to the offer letter.
Plan travel, accommodation and logistics accordingly.
Remember to research and follow each university’s specific application guidelines and deadlines.
How to apply for a PhD as an international student?
Many stages of the PhD application process are the same for international students as domestic students. However, there are sometimes some additional steps:
International students should apply for a student visa.
Take language proficiency tests such as TOEFL or IELTS if required.
Provide certificates if needed to validate your previous degrees.
Show evidence of sufficient funds for tuition and living expenses.
Check if you need health insurance for your chosen destination.
Translate and authenticate academic transcripts if necessary.
Attend orientation sessions for cultural adaptation.
Apply for university housing or explore off-campus options.
Familiarise yourself with international student support services.
Ben Osborne, the postgraduate student recruitment manager at the University of Sussex explains in detail how to apply for a PhD in the UK .
Giulia Evolvi, a lecturer in media and communication at Erasmus University, Rotterdam explains how to apply for a PhD in the US .
Finally, Samiul Hossain explores the question Is it possible to do a three-year PhD as an international student?
Q. What is a PhD? A. A PhD is the highest level of academic degree awarded by universities, involving in-depth research and a substantial thesis.
Q. What does “PhD” mean? A. “PhD” stands for doctor of philosophy, recognising expertise in a field.
Q. What is a professional doctorate? A. A professional doctorate emphasises practical application in fields such as education or healthcare.
Q. How long does it take to study a PhD? A. It takes between three and six years to study a full-time PhD programme.
Q. How long is a PhD in the UK? A. It takes around three to four years to study a full-time UK PhD.
Q. How long is a PhD in the US? A. It takes approximately five to six years to complete a full-time US PhD.
Q. Why does it take longer to study a PhD in the US? A. US programmes often include more course work and broader training.
Q. What qualifications do you need for a PhD? A. You usually need an undergraduate degree as a minimum requirement, although a master’s might be preferred.
Q. Do you need a master’s degree to get into a PhD programme? A. Master’s degrees are preferred but not always required.
Q. Are PhD entry requirements similar in other countries? A. Entry requirements are similar in many countries, but there may be additional requirements. Make sure to check the university website for specific details.
Q. How much does it cost to study a PhD? A. The cost of PhD programmes vary by country and university.
Q. What funding options are available for PhD candidates? A. Scholarships, assistantships, fellowships, grants, stipends are all funding options for PhD candidates.
Q. What does a PhD involve? A. PhDs involve research, seminars, thesis, literature review, data analysis and a PhD viva.
Q. Why should you do a PhD? A. There are many reasons to study a PhD including personal growth, research skills, contributions to academia and professional development.
Q. What are some benefits of studying a PhD? A. Benefits of graduating with a PhD include achieving tenure, collaborations with colleagues, publication of your work, and networking opportunities.
Q. What is a PhD thesis? A. A PhD thesis is a comprehensive document that showcases the original research conducted by a PhD candidate.
Q. What is a PhD viva? A. A PhD viva, also known as a viva voce or oral examination, is the final evaluation of a PhD candidate’s research and thesis where the panel asks questions, engages in discussions and assesses the depth of the candidate’s understanding and expertise.
Q. Can you do a PhD part-time? A. Yes, part-time options are available for PhDs.
Q. Can I do a PhD through distance learning? A. Some universities offer online PhDs; you can find out more on their websites.
Q. How to choose a PhD programme? A. You can find PhD programmes through research, by contacting faculty, checking resources and considering location.
Q. How can I find available PhD programme? A. You can find available PhD programmes on university sites, through directories and by networking.
Q. How to apply for a PhD programme A. To apply for a PhD programme, research suitable universities and programmes, get in touch with potential supervisors, gather required documents like transcripts and reference letters, complete the online application, pay any necessary fees and submit a statement of purpose and research proposal. If needed, meet language-proficiency criteria and attend interviews. After acceptance, explore funding choices, confirm your spot and get ready for the programme’s start.
Q. How to apply for a PhD as an international student A. To apply for a PhD as an international student, follow similar steps to domestic students, but you need to include securing a student visa and passing language requirements.
Q. What is a PhD dropout rate? A. The dropout rate from PhDs varies but is approximately 30-40 per cent.
Q. How does a PhD affect salary and earning potential? A. A PhD can boost earning potential, especially in research, technology, healthcare and academia. Impact varies by job, industry and location. Experience, skills and demand also influence salary.
Q. How to address a person with a PhD? A. When addressing someone with a PhD, it’s respectful to use “Dr”, followed by their last name, whether they have a PhD in an academic field or a professional doctorate. For instance, “Dr. Smith”.
Q. Is there a difference between a PhD and a doctorate? A. The terms “PhD” and “doctorate” are often used interchangeably, though a PhD is a specific type of doctorate focused on original research. A doctorate can refer more broadly to any doctoral-level degree, including professional doctorates with practical applications.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD and an MD? A. A PhD is a doctor of philosophy, awarded for academic research, while an MD is a doctor of medicine, focusing on medical practice. They lead to different career paths and involve distinct areas of study.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD and a professional doctorate? A. A PhD is an academic research-focused degree, while a professional doctorate emphasises applying research to practical fields such as education or business. PhDs often involve original research, while professional doctorates focus on real-world application.
Q. What is the difference between UK and US PhDs? A. The difference between UK and US PhDs lies mainly in structure and duration. UK PhDs often have shorter durations and a stronger emphasis on independent research from an early stage. US PhDs typically include more initial coursework and broader foundational training before full-time research begins.
Q. What is the difference between a PhD student and a candidate? A. A PhD student is actively studying and researching in a doctoral programme, while a PhD candidate has completed programme requirements except for the dissertation and is close to completion.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an EdD? A. A PhD and an EdD (doctor of education) differ in focus. A PhD emphasises research and academic contributions, while an EdD focuses on applying research to practical educational issues.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and a DBA? A. A PhD and a DBA (doctor of business administration) differ in purpose. A PhD emphasises theoretical research and academia, while a DBA is practice-oriented, aimed at solving real business problems.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and a PsyD? A. A PhD and a PsyD (doctor of psychology) differ in emphasis. A PhD focuses on research and academia, while a PsyD emphasises clinical practice and applying psychological knowledge.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an LLD? A. A PhD and an LLD (doctor of laws or Legum doctor) are distinct. A PhD is awarded in various disciplines, while an LLD is usually an honorary degree for significant contributions to law.
Q. What’s the difference between a PhD and an MD-PhD? A. A PhD and an MD-PhD differ. An MD-PhD is a dual degree combining medical training (MD) with research training (PhD).
Q. What is the Cambridge PhD? A. A Cambridge PhD involves original research guided by a supervisor, resulting in a thesis. It’s offered at the University of Cambridge .
Q. What is the Oxford DPhil? A. An Oxford DPhil is equivalent to a PhD and involves independent research leading to a thesis. The term “DPhil” is unique to the University of Oxford .
Q. What is the PhD programme acceptance rate? A. PhD acceptance rates vary by university, field and competition. Prestigious universities and competitive fields often have lower acceptance rates.
Q. What is a PhD supervisor? A. A PhD supervisor guides and supports a student’s research journey, providing expertise and feedback.
Q. What is a PhD panel? A. A PhD panel evaluates a candidate’s research, thesis and oral defence. It consists of experts in the field.
Q. What is a PhD stipend? A. A PhD stipend is a regular payment supporting living expenses during research, often tied to teaching or research assistant roles.
Q. What is a PhD progression assessment? A. A PhD progression assessment evaluates a student’s progress, often confirming their continuation in the programme.
Q. What is a PhD defence? A. A PhD defence, or viva, is the final oral examination where a candidate presents and defends their research findings and thesis before experts.
You may also like

.css-185owts{overflow:hidden;max-height:54px;text-indent:0px;} Pursuing a PhD in neuroscience
Luis Humberto Eudave Ramos

Why study a PhD in English literature?
John Francis Davies

8 habits to help you get through your PhD
Shabana Khan
Register free and enjoy extra benefits
What Is a Doctorate Degree?
A doctorate is usually the most advanced degree someone can get in an academic discipline, higher education experts say.
What Is a Doctorate?

Getty Images
It's unwise to apply to a doctoral program if you don't have a clear idea of how you might use a doctorate in your career.
In many academic disciplines, the most advanced degree one can earn is a doctorate. Doctorate degree-holders are typically regarded as authorities in their fields, and many note that a major reason for pursuing a doctorate is to increase professional credibility.
"If someone wants to be respected as an expert in their chosen field, and also wants to have a wider array of options in research, writing, publishing, teaching, administration, management, and/or private practice, a doctorate is most definitely worth considering," Don Martin, who has a Ph.D. in higher education administration , wrote in an email.
A doctoral degree is a graduate-level credential typically granted after multiple years of graduate school, with the time-to-degree varying depending on the type of doctoral program, experts say.
Earning a doctorate usually requires at least four years of effort and may entail eight years, depending on the complexity of a program's graduation requirements. It also typically requires a dissertation, a lengthy academic paper based on original research that must be vetted and approved by a panel of professors and later successfully defended before them for the doctorate to be granted.
Some jobs require a doctorate, such as certain college professor positions, says Eric Endlich, founder of Top College Consultants, an admissions consulting firm that helps neurodivergent students navigate undergraduate and graduate school admissions.
Endlich earned a Doctor of Philosophy degree, commonly known as a Ph.D., from Boston University in Massachusetts. He focused on psychology and notes that a doctoral degree is generally required to be a licensed psychologist.
"Since a Ph.D. is a research-focused degree, it can be advantageous to those seeking high-level research positions in scientific fields such as astrophysics or biotechnology," he says.
How Long it Takes to Get a Doctorate Degree
Martin, founder and CEO of Grad School Road Map, an organization that helps grad school applicants navigate the admissions process, says obtaining a doctorate is often a lengthy endeavor.
"Typically it can take between four and six years to complete any doctoral program," he says. "If comprehensive examinations and a dissertation are part of the graduation requirements, it may take a year or two longer. There is no standard amount of time – some students take seven to 10 years to finish."
Endlich says doctoral degree hopefuls should be aware that completing a dissertation may take a long time, especially if unexpected hurdles arise.
"My dissertation, for example, involved recruiting college students to complete questionnaires, and it took much longer than I anticipated to recruit enough subjects for my study," he says.
The standards for a dissertation, which include the proposal and research, are rigorous and usually involve a review and approval by a faculty committee, says Hala Madanat, vice president for research and innovation at San Diego State University in California.
"As part of dissertation requirements, some programs will require publication of the research in high-impact peer-reviewed journals," Madanat wrote in an email.
Types of Doctoral Degree Programs
According to professors and administrators of doctoral programs, there are two types of doctorates.
Doctor of Philosophy
A doctor of philosophy degree is designed to prepare people for research careers at a university or in industry, and teach students how to discover new knowledge within their academic discipline. Ph.D. degrees are offered in a wide range of academic subjects, including highly technical fields like biology , physics, math and engineering; social sciences like sociology and economics; and humanities disciplines like philosophy.
A Ph.D. is the most common degree type among tenure-track college and university faculty, who are typically expected to have a doctorate. But academia is not the only path for someone who pursues a Ph.D. It's common for individuals with biology doctorates to work as researchers in the pharmaceutical industry, and many government expert positions also require a Ph.D.
Professional or clinical doctorates
These are designed to give people the practical skills necessary to be influential leaders within a specific industry or employment setting, such as business, psychology , education or nursing . Examples of professional doctoral degrees include a Doctor of Business Administration degree, typically known as a DBA; a Doctor of Education degree, or Ed.D.; and a Doctor of Nursing Practice degree, or DNP.
A law degree, known as a juris doctor or J.D., as well as a Doctor of Medicine degree, or M.D., are also considered professional doctorates.
How to Get a Doctorate
Getting a doctorate is challenging. It ordinarily requires a series of rigorous classes in a field of study and then passage of a qualification exam in order to begin work on a dissertation, which is the final project.
Dissertations are difficult to write, says David Harpool, vice president of graduate and online programs at Newberry College in South Carolina. Some research indicates that only about half of doctoral students go on to finish their degree, and a main reason is that many never finish and successfully defend their dissertation
"Many of them are in programs that permit them to earn a master’s on the way to a doctorate," Harpool, who earned a Ph.D. from Saint Louis University in Missouri and a J.D. from the University of Missouri , wrote in an email. "The transition from mastering a discipline to creating new knowledge (or at least applying new knowledge in a different way), is difficult, even for outstanding students."
Learn about how M.D.-Ph.D. programs
There is a often a "huge shift in culture" at doctoral programs compared to undergraduate or master's level programs, says Angela Warfield, who earned a Ph.D. in English from the University of Iowa.
Doctoral professors and students have more of a collaborative relationship where they function as colleagues, she says. And there's pressure on each student to produce "significant and original research."
Many full-time doctoral students work for the school as researchers or teaching assistants throughout their program, so time management is crucial to avoid burnout. However, the dissertation "is by far the biggest battle," she says. The goal is to avoid an "ABD," she says, meaning "all but dissertation."
"In my writing group, we had two motivational slogans: 'ABD is not a degree,' and 'a good dissertation is a done dissertation,'" Warfield, now the principal consultant and founder of admissions consulting firm Compass Academics, wrote in an email.
How Are Doctorate Admissions Decisions Made?
Admissions standards for doctoral programs vary depending on the type of doctorate, experts say.
The quality of a candidate's research is a distinguishing factor in admissions decisions, Madanat says. Meanwhile, leaders of clinical and professional doctorate programs say that the quality of a prospective student's work experience matters most.
Doctoral programs typically expect students to have a strong undergraduate transcript , excellent letters of recommendation and, in some cases, high scores on the Graduate Record Examination , or GRE, Endlich says.
"The size of the programs may be relatively small, and universities need to be sure that applicants will be able to handle the demands of their programs," he says.
Because professional doctorates often require students to come up with effective solutions to systemic problems, eligibility for these doctorates is often restricted to applicants with extensive first-hand work experience with these problems, according to recipients of professional doctorates.
In contrast, it's common for Ph.D. students to begin their programs immediately after receiving an undergraduate degree. The admissions criteria at Ph.D. programs emphasize undergraduate grades, standardized test scores and research projects , and these programs don't necessarily require work experience.
Admissions decisions may also depend on available funding, says Madanat, who works with doctoral students to provide funding, workshops and faculty support to help their research.
Who Is a Good Fit for a Doctoral Program?
Doctoral degree hopefuls "should be interested in making a deep impact on their field, open-minded, eager to learn, curious, adaptable and self-motivated," Madanat says. "Doctoral programs are best suited for those whose goals are to transform and change the fields they are studying and want to make a difference in the way the world is."
Someone who loves to study a subject in great depth, can work alone or in teams, is highly motivated and wants to develop research skills may be a good candidate for a doctoral program, Endlich says.
Because of the tremendous effort and time investment involved in earning a doctorate, experts say it's foolish to apply to a doctoral program if it's unclear how you might use a doctorate in your career.
"The students are being trained with depth of knowledge in the discipline to prepare them for critical thinking beyond the current state of the field," Madanat says. "Students should consider the reasons that they are pursuing a doctoral degree and whether or not it aligns with their future professional goals, their family circumstances and finances."
Rachel D. Miller, a licensed marriage and family therapist who completed a Ph.D. degree in couples and family therapy at Adler University in Illinois in 2023, says pursuing a doctorate required her to make significant personal sacrifices because she had to take on large student loans and she needed to devote a lot of time and energy to her program. Miller says balancing work, home life and health issues with the demands of a Ph.D. program was difficult.
For some students, the financial component may be hard to overlook, Warfield notes.
"Student debt is no joke, and students pursuing graduate work are likely only compounding undergraduate debt," she says. "They need to really consider the payoff potential of the time and money sacrifice."
To offset costs, some programs are fully funded, waiving tuition and fees and providing an annual stipend. Some offer health insurance and other benefits. Students can also earn money by teaching at the university or through fellowships, but those adding more to their plate should possess strong time management skills, experts say.
"Graduate school, and higher education in general, can be brutal on your physical and mental health," Miller wrote in an email.
But Miller says the time and effort invested in her doctoral program paid off by allowing her to conduct meaningful research into the best way to provide therapy to children affected by high-conflict divorce and domestic violence. She now owns a therapy practice in Chicago.
Miller urges prospective doctoral students to reflect on whether getting a doctorate is necessary for them to achieve their dream job. "Really know yourself. Know your purpose for pursuing it, because that's what's going to help carry you through."
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
30 Fully Funded Ph.D. Programs

Tags: graduate schools , education , students , academics
You May Also Like
What to ask law students and alumni.
Gabriel Kuris April 22, 2024


Find a Strong Human Rights Law Program
Anayat Durrani April 18, 2024

Environmental Health in Medical School
Zach Grimmett April 16, 2024

How to Choose a Law Career Path
Gabriel Kuris April 15, 2024

Questions Women MBA Hopefuls Should Ask
Haley Bartel April 12, 2024

Law Schools With the Highest LSATs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 11, 2024

MBA Programs That Lead to Good Jobs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 10, 2024

B-Schools With Racial Diversity
Sarah Wood April 10, 2024

Law Schools That Are Hardest to Get Into
Sarah Wood April 9, 2024

Grad School Housing Options
Anayat Durrani April 9, 2024

- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of PhD noun from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
- to do/have/be a PhD
- Anne Thomas, PhD
- acquire/get/lack (an) education/training/ (British English) (some) qualifications
- receive/provide somebody with training/tuition
- develop/design/plan a curriculum/ (especially British English) course/ (North American English) program/syllabus
- give/go to/attend a class/lesson/lecture/seminar
- hold/run/conduct a class/seminar/workshop
- sign up for/take a course/classes/lessons
- go to/start preschool/kindergarten/nursery school
- be in (North American English) the first, second, etc. grade/ (British English) year 1, 2. etc. (at school)
- study/take/drop history/chemistry/German, etc.
- (British English) leave/finish/drop out of/ (North American English) quit school
- (North American English) graduate high school/college
- be the victim/target of bullying
- (British English) play truant from/ (both British English, informal) bunk off/skive off school (= not go to school when you should)
- (both especially North American English) skip/cut class/school
- (British English) cheat in/ (North American English) cheat on an exam/a test
- get/be given a detention (for doing something)
- be expelled from/be suspended from school
- do your homework/ (British English) revision/a project on something
- work on/write/do/submit an essay/a dissertation/a thesis/an assignment/ (North American English) a paper
- finish/complete your dissertation/thesis/studies/coursework
- hand in/ (North American English) turn in your homework/essay/assignment/paper
- study/prepare/ (British English) revise/ (North American English) review/ (North American English, informal) cram for a test/an exam
- take/ (both British English) do/sit a test/an exam
- (especially British English) mark/ (especially North American English) grade homework/a test
- (British English) do well in/ (North American English) do well on/ (especially North American English, informal) ace a test/an exam
- pass/fail/ (especially North American English, informal) flunk a test/an exam/a class/a course/a subject
- apply to/get into/go to/start college/ (British English) university
- leave/graduate from law school/college/ (British English) university (with a degree in computer science)
- study for/take/ (British English) do/complete a law degree/a degree in physics
- (both North American English) major/minor in biology/philosophy
- earn/receive/be awarded/get/have/hold a master’s degree/a bachelor’s degree/a PhD in economics
- dissertation
Want to learn more?
Find out which words work together and produce more natural-sounding English with the Oxford Collocations Dictionary app. Try it for free as part of the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app.

Higher Education News , Tips for Online Students
Is a PhD Degree for Me? This is What it Means
Updated: August 7, 2023
Published: December 26, 2019

Wherever you are in your educational journey, you’ve likely heard of the graduate degree called a PhD degree. You may be wondering what is a PhD degree, what are PhD requirements, and what it means to earn a PhD. At this point, you may be questioning if getting a PhD is the right next step for you.
To receive a PhD, you will add the title “Dr.” to you name, but there is much more to it than that. Here, we will dive into what a PhD means, what it takes to earn one, the different kinds of PhD degrees that exist, and the reasons why you may choose to take the path to graduate with one.
What is a PhD?
First thing’s first, let’s define all the ins and outs of what a PhD means. PhD is an abbreviation for “Doctor of Philosophy.”
A PhD is the ultimate academic degree you can earn in a field of choice. To earn a PhD, you must complete original research and evaluate a theory. More often than not, this includes data analysis. This fact is true no matter where you are in the world.
Unlike undergraduate degrees, a PhD is heavily focused on research. As such, lectures are not all that common when working towards earning the degree, but they do still exist. Rather, students will focus particularly on an aspect of the subject choice to create a dissertation. Along with a written thesis, students must present their work orally (known as a “viva voce”) to a group of examiners.
A PhD is recognized around the world as the highest academic achievement. Therefore, no matter where you go, it bears with it an international standard of understanding and a level of respect. It allows for you to be a professor in academia and work in a highly specialized position within the field.
Requirements and Length of Time
While the payoffs of a PhD may seem enticing, the journey to earn your PhD is not an easy or short one.
More often than not, a PhD comes after a master degree. Yet, that’s not always true. Some institutions allow students to skip the master degree and move straight from a bachelor degree into a PhD program.
The time length of a PhD program can vary, but it generally takes three to four years to complete. If a student chooses to study part-time, it could take upwards of six or seven years to graduate.
In order to be accepted into a PhD program, there are a variety of PhD requirements. The most important requirement tends to be proof of high academic standing from your master degree. Some schools may also factor in your bachelor degree grades.
Grades also play a role in assessing the type of funding you may receive. If you have low grades, but still want to pursue a PhD, you’ll likely have to self-fund.
Along with grades, most institutions will also require the following:
1. Proof of language proficiency in the language you will pursue your PhD.
2. resume of work experience and transcript of academic courses., 3. a personal statement sharing your reasons why you want to pursue a phd in your respective field and perhaps why you are choosing the institution., 4. a phd research proposal, which includes:.
- Your proposed research topic
- Experience regarding the subject matter
- Gaps in current knowledge, your understanding of current findings
- Your research methodology
- How your research and its implications will affect the world

Photo by Wadi Lissa on Unsplash
How to get a phd.
Getting a PhD requires planning, research, and commitment. Some schools vary in their requirements to apply, so it’s best practice to create your list of desired schools and research their needs.
You can choose to get a PhD at any age, but it’s best to start thinking proactively when you are moving along your graduate degree program.
Here are the main steps it takes to get a PhD:
1. Get a bachelor’s degree
2. complete the gre, 3. apply to graduate schools, 4. begin master’s or phd program, 5. if master’s, graduate and then apply again for a phd program, 6. complete phd coursework, 7. start research and write a dissertation, 8. share dissertation and get published, 9. graduate with a phd, types of phd.
There are different categories of PhD degrees. However, students only choose between professional and academic. Higher and honorary PhDs are awarded later in one’s career.
These include:
Granted in traditional subjects by performing academic research (PhD/Doctor of Philosophy/Th.D – Doctor of Theology)
Professional
These contribute directly to a specific vocational field (Doctor of Business Administration, Doctor of Engineering, Doctor of Education, Doctor of Social Science, Doctor of Architecture, etc.)
Higher/Honorary
To honor esteemed researchers and professionals, an honorary PhD may be rewarded (Doctor of Divinity, Doctor of Science – Science, Technology, Engineering and Math, Doctor of Science – Arts and Humanities)
Reasons to Get a PhD
Everyone has their own reasons for why they want to get their PhD. Here are some motivations behind why you may choose to pursue the degree:
1. Intellectual challenge:
As the final degree in academics, a PhD will challenge your intellectual abilities.
2. Career goals:
Your chosen career requires that you have the degree (i.e., becoming a professor).
3. Personal passion:
You enjoy the subject matter and want to be an expert in the field.
4. Research:
You have something to contribute or know how to fill a gap in the current information.

Photo by Abby Chung from Pexels
The bottom line.
Earning a Doctor of Philosophy degree is not only for those who wish to become a professor . Whether your future career requires the degree or not, you may still want to pursue the academic challenge.
The most common trait of a PhD relies on research. As such, a government agency or organization may also want to fund you in performing research if you have something worthwhile to contribute to your field of study.
As the ultimate destination in terms of degrees, the title of PhD next to your name is well-respected and universally acknowledged. However, before enrolling in a program, make sure that you have the time, resources, and personal passion to fulfill all the necessary requirements.
Related Articles
Doctor of Philosophy in Education

Additional Information
- Download the Doctoral Viewbook
- Admissions & Aid
The Harvard Ph.D. in Education trains cutting-edge researchers who work across disciplines to generate knowledge and translate discoveries into transformative policy and practice.
Offered jointly by the Harvard Graduate School of Education and the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, the Ph.D. in Education provides you with full access to the extraordinary resources of Harvard University and prepares you to assume meaningful roles as university faculty, researchers, senior-level education leaders, and policymakers.
As a Ph.D. candidate, you will collaborate with scholars across all Harvard graduate schools on original interdisciplinary research. In the process, you will help forge new fields of inquiry that will impact the way we teach and learn. The program’s required coursework will develop your knowledge of education and your expertise in a range of quantitative and qualitative methods needed to conduct high-quality research. Guided by the goal of making a transformative impact on education research, policy, and practice, you will focus on independent research in various domains, including human development, learning and teaching, policy analysis and evaluation, institutions and society, and instructional practice.
Curriculum Information
The Ph.D. in Education requires five years of full-time study to complete. You will choose your individual coursework and design your original research in close consultation with your HGSE faculty adviser and dissertation committee. The requirements listed below include the three Ph.D. concentrations: Culture, Institutions, and Society; Education Policy and Program Evaluation; and Human Development, Learning and Teaching .
We invite you to review an example course list, which is provided in two formats — one as the full list by course number and one by broad course category . These lists are subject to modification.
Ph.D. Concentrations and Examples
Summary of Ph.D. Program
Doctoral Colloquia In year one and two you are required to attend. The colloquia convenes weekly and features presentations of work-in-progress and completed work by Harvard faculty, faculty and researchers from outside Harvard, and Harvard doctoral students. Ph.D. students present once in the colloquia over the course of their career.
Research Apprenticeship The Research Apprenticeship is designed to provide ongoing training and mentoring to develop your research skills throughout the entire program.
Teaching Fellowships The Teaching Fellowship is an opportunity to enhance students' teaching skills, promote learning consolidation, and provide opportunities to collaborate with faculty on pedagogical development.
Comprehensive Exams The Written Exam (year 2, spring) tests you on both general and concentration-specific knowledge. The Oral Exam (year 3, fall/winter) tests your command of your chosen field of study and your ability to design, develop, and implement an original research project.
Dissertation Based on your original research, the dissertation process consists of three parts: the Dissertation Proposal, the writing, and an oral defense before the members of your dissertation committee.
Culture, Institutions, and Society (CIS) Concentration
In CIS, you will examine the broader cultural, institutional, organizational, and social contexts relevant to education across the lifespan. What is the value and purpose of education? How do cultural, institutional, and social factors shape educational processes and outcomes? How effective are social movements and community action in education reform? How do we measure stratification and institutional inequality? In CIS, your work will be informed by theories and methods from sociology, history, political science, organizational behavior and management, philosophy, and anthropology. You can examine contexts as diverse as classrooms, families, neighborhoods, schools, colleges and universities, religious institutions, nonprofits, government agencies, and more.
Education Policy and Program Evaluation (EPPE) Concentration
In EPPE, you will research the design, implementation, and evaluation of education policy affecting early childhood, K–12, and postsecondary education in the U.S. and internationally. You will evaluate and assess individual programs and policies related to critical issues like access to education, teacher effectiveness, school finance, testing and accountability systems, school choice, financial aid, college enrollment and persistence, and more. Your work will be informed by theories and methods from economics, political science, public policy, and sociology, history, philosophy, and statistics. This concentration shares some themes with CIS, but your work with EPPE will focus on public policy and large-scale reforms.
Human Development, Learning and Teaching (HDLT) Concentration
In HDLT, you will work to advance the role of scientific research in education policy, reform, and practice. New discoveries in the science of learning and development — the integration of biological, cognitive, and social processes; the relationships between technology and learning; or the factors that influence individual variations in learning — are transforming the practice of teaching and learning in both formal and informal settings. Whether studying behavioral, cognitive, or social-emotional development in children or the design of learning technologies to maximize understanding, you will gain a strong background in human development, the science of learning, and sociocultural factors that explain variation in learning and developmental pathways. Your research will be informed by theories and methods from psychology, cognitive science, sociology and linguistics, philosophy, the biological sciences and mathematics, and organizational behavior.
Program Faculty
The most remarkable thing about the Ph.D. in Education is open access to faculty from all Harvard graduate and professional schools, including the Harvard Graduate School of Education, the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, the Harvard Kennedy School, the Harvard Law School, Harvard Medical School, and the Harvard School of Public Health. Learn about the full Ph.D. Faculty.

Jarvis R. Givens
Jarvis Givens studies the history of American education, African American history, and the relationship between race and power in schools.

Paul L. Harris
Paul Harris is interested in the early development of cognition, emotion, and imagination in children.

Meira Levinson
Meira Levinson is a normative political philosopher who works at the intersection of civic education, youth empowerment, racial justice, and educational ethics.

Luke W. Miratrix
Luke Miratrix is a statistician who explores how to best use modern statistical methods in applied social science contexts.

Eric Taylor
Eric Taylor studies the economics of education, with a particular interest in employer-employee interactions between schools and teachers hiring and firing decisions, job design, training, and performance evaluation.

Paola Uccelli
Paola Ucelli studies socio-cultural and individual differences in the language development of multilingual and monolingual students.

View Ph.D. Faculty
Dissertations.
The following is a complete listing of successful Ph.D. in Education dissertations to-date. Dissertations from November 2014 onward are publicly available in the Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard (DASH) , the online repository for Harvard scholarship.
- 2022 Graduate Dissertations (265 KB pdf)
- 2021 Graduate Dissertations (177 KB pdf)
- 2020 Graduate Dissertations (121 KB pdf)
- 2019 Graduate Dissertations (68.3 KB pdf)
Student Directory
An opt-in listing of current Ph.D. students with information about their interests, research, personal web pages, and contact information:
Doctor of Philosophy in Education Student Directory
Introduce Yourself
Tell us about yourself so that we can tailor our communication to best fit your interests and provide you with relevant information about our programs, events, and other opportunities to connect with us.
Program Highlights
Explore examples of the Doctor of Philosophy in Education experience and the impact its community is making on the field:

Reshaping Teacher Licensure: Lessons from the Pandemic
Olivia Chi, Ed.M.'17, Ph.D.'20, discusses the ongoing efforts to ensure the quality and stability of the teaching workforce

Lost in Translation
New comparative study from Ph.D. candidate Maya Alkateb-Chami finds strong correlation between low literacy outcomes for children and schools teaching in different language from home
PHD Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How to Use It?
You’ve likely seen the abbreviation PHD — but what is the meaning of PHD? We’ll tell you. Read on as we explore this common acronym.
Your writing, at its best
Compose bold, clear, mistake-free, writing with Grammarly's AI-powered writing assistant
There are several ways to abbreviate words in the English language — hence why there are so many acronyms and abbreviations found in the dictionary today.
While some terms are pretty self-explanatory, like “Feb,” which stands for “February,” there are some acronyms that could use a bit of explaining — such as Ph.D.
Although Ph.D is an abbreviation with more than one meaning, it commonly refers to a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D): spelled with a capitalized “P,” lowercase “h,” and uppercase “D.”
Interested in learning more? We can help. Read on as we explore the abbreviation Ph.D to uncover its meaning, origin, and more. Are you ready? Let’s dive in.
What Does PhD Mean?
Ph.D — aka Doctor of Philosophy — is defined by Dictionary.com as the highest degree awarded by a school in a field of academic study. A doctorate is typically awarded to an individual who has completed three or more years of graduate study and a dissertation approved by a committee of professors.
Common abbreviations used for the doctor of philosophy include:
- Ph.D.
After completing the Ph.D degree or dissertation, a graduate can use Dr. or Ph.D. For example:
- Dr. Suzie Johnson or
- Suzie Johnson (Ph.D) or
- Dr. Suzie Johnson (Ph.D)
What Is the Origin of Ph.D?
Abbreviated from the Latin term philosophiae doctor meaning “doctor of philosophy,” the Ph.D is the highest degree in most fields, with the notable exceptions of medicine and law that have their own doctorates. The degree originated in 19th century Germany when the word “philosophy” had the much broader meaning of “love of wisdom.”
Though universities have existed in Europe long before the 19th century, the degrees that medieval universities awarded to students had more in common with the MD than with the Ph.D, as they required mastery of already existing knowledge.
In 1861, Yale University became the first institution of higher education in the United States to award the degree, conferring it on three recipients; Arthur W, Wright, James M. Whiton, and Eugene Schuyler. A few decades later, Canada accepted Ph.D as their highest level of honor, and in 1917, the doctoral of philosophy was introduced in all disciplines of the subjects.
How Can I Use Ph.D in a Sentence?
Now that you understand what Ph.D means, let’s take a look at some examples of this acronym in a sentence:
“After telling him I earned an academic degree, he bragged for the rest of the night about having a Ph.D .”
“I can’t decide what academic field to get my Ph.D in.”
“Tom can’t work full-time because he is a Ph.D student and has to work on his thesis.”
“My mom is thinking about going back to school to complete a Ph.D program in psychology.”
“I am in the second year of my Ph.D program.”
“Whether you like physics, chemistry, or psychology, you can find a Ph.D program on campus,”
“Look, I understand that you’re my supervisor, but I am looking to get my Ph.D degree and ultimately become a doctor of medicine; in other words, I have to study and can’t pick up more than one shift per week.”
“Have you taken the exams yet to get your Ph.D ?”
“Did you know that some Ph.D programs accept a portfolio of published papers?”
“To get a Ph.D , it’s important to study hard and get good grades.”
“Gosh, I didn’t realize how many seminars and workshops I’d have to attend to get a Ph.D !”
“A Ph.D comes with a pretty hefty fee, so be sure to apply for scholarships.”
What Is a Doctorate?
Simply put, a doctorate is any qualification that awards a doctoral degree. To qualify for one, you need to produce work at a high level that makes a significant new contribution to knowledge in your academic field. Doing so earns you the title “Doctor.”
Many people believe a doctorate and a Ph.D are the same. However, this is not the case, as a Ph.D is a type of doctorate, such as a Doctor of Philosophy. Other doctoral degrees or types of doctorate include:
- Doctor of Education
- Doctor of Theology
- Doctor of Medicine
- Doctor of Musical Arts
- Doctor of Literature
- Doctor of Divinity
- Doctor of Civil Law
- Doctor of Science
According to the American Psychological Association, the Ph.D is intended for students interested in gaining new knowledge through scientific research, or teaching experience.
Does PHD Stand For Anything Else?
Although the abbreviation PHD is most commonly associated with the Doctorate of Philosophy, it does have a few other meanings:
- Pizza Hut Delivery
- Press Here, Dummy
- Permanent Head Damage
- Pretty Heavy Drinker
- Please Hire Desperate
- Preparing His Disciples
- Player Hating Degree
- Power Hungry Dog
- Premium Hot Dog
- Pretty Heavy Dude
- Poor, Hungry, and Determined
A Final Word
So, what does PHD mean, you ask?
Simply put, PHD is an abbreviation that stands for many words; however, it’s most commonly used to abbreviate “Doctor of Philosophy.”
We hope this guide has provided you with all of the information you need to understand the meaning of PHD fully. To discover more interesting words and strengthen your overall vocabulary, be sure to check out our website , where you’ll find definitions, grammar tips, and more!
- A Brief History of the PhD | NeuWrite West
- Ph.d. Definition & Meaning | Dictionary.com
- The First American Doctor of Philosophy Degree: A Centennial Salute to Yale, 1861-1961 | The Journal of Higher Education
Kevin Miller is a growth marketer with an extensive background in Search Engine Optimization, paid acquisition and email marketing. He is also an online editor and writer based out of Los Angeles, CA. He studied at Georgetown University, worked at Google and became infatuated with English Grammar and for years has been diving into the language, demystifying the do's and don'ts for all who share the same passion! He can be found online here.
Recent Posts

Gentrification Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

Blasphemy Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

AOC Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

333 Angel Number Meaning In Love Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of doctorate in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- associate's degree
- baccalaureate
- bachelor's degree
- first degree
- honors degree
- pass degree
- summa cum laude
Related word
Doctorate | american dictionary, examples of doctorate, translations of doctorate.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
the fact that people or animals do what they are told to do

Binding, nailing, and gluing: talking about fastening things together

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- American Noun
- Translations
- All translations
Add doctorate to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
What’s behind the growing gap between men and women in college completion?

The growing gender gap in higher education – both in enrollment and graduation rates – has been a topic of conversation and debate in recent months. Young women are more likely to be enrolled in college today than young men, and among those ages 25 and older, women are more likely than men to have a four-year college degree. The gap in college completion is even wider among younger adults ages 25 to 34.
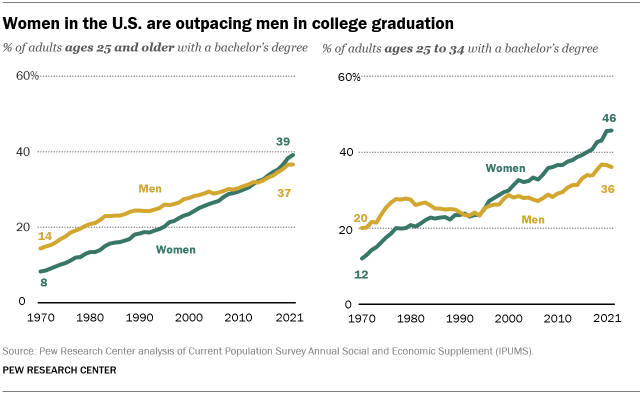
Women’s educational gains have occurred alongside their growing labor force participation as well as structural changes in the economy . The implications of the growing gap in educational attainment for men are significant, as research has shown the strong correlation between college completion and lifetime earnings and wealth accumulation .
To explore the factors contributing to the growing gender gap in college completion, we surveyed 9,676 U.S. adults between Oct. 18-24, 2021. Everyone who took part is a member of Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Data on rates of college completion came from a Center analysis of Current Population Survey Annual Social and Economic Supplement (IPUMS). The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic impacted the data collection for the 2020 ASEC. The response rate for the March 2020 survey was about 10 percentage points lower than in preceding months. Using administrative data, Census Bureau researchers have shown that nonresponding households were less similar to respondents than in earlier years. They also generated entropy balance weights to account for this nonrandom nonresponse. The 2020 ASEC figures presented used these supplementary weights.
Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology .
A majority (62%) of U.S. adults ages 25 and older don’t have a four-year college degree, according to a Pew Research Center analysis of Current Population Survey data. But the reasons for not completing a four-year degree differ for men and women, according to a new Center survey of adults who do not have such a degree and are not currently enrolled in college.
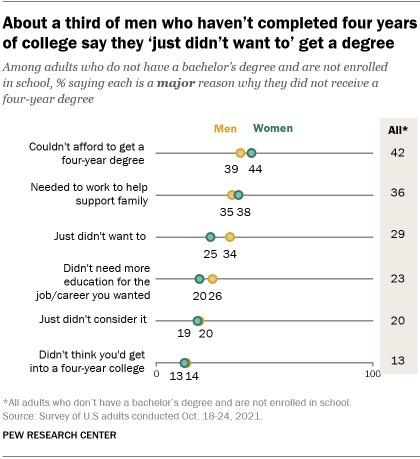
Financial considerations are a key reason why many don’t attend or complete college. Among adults who do not have a bachelor’s degree and are not currently enrolled in school, roughly four-in-ten (42%) say a major reason why they have not received a four-year college degree is that they couldn’t afford college. Some 36% say needing to work to help support their family was a major reason they didn’t get their degree.
Overall, about three-in-ten adults who didn’t complete four years of college (29%) say a major reason for this is that they just didn’t want to, 23% say they didn’t need more education for the job or career they wanted, and 20% say they just didn’t consider getting a four-year degree. Relatively few (13%) adults without a bachelor’s degree say a major reason they didn’t pursue this level of education was that they didn’t think they’d get into a four-year college.
Men are more likely than women to point to factors that have more to do with personal choice. Roughly a third (34%) of men without a bachelor’s degree say a major reason they didn’t complete college is that they just didn’t want to. Only one-in-four women say the same. Non-college-educated men are also more likely than their female counterparts to say a major reason they don’t have a four-year degree is that they didn’t need more education for the job or career they wanted (26% of men say this vs. 20% of women).
Women (44%) are more likely than men (39%) to say not being able to afford college is a major reason they don’t have a bachelor’s degree. Men and women are about equally likely to say needing to work to help support their family was a major impediment.
The shares of men and women saying they didn’t consider going to college or they didn’t think they’d get into a four-year school are not significantly different.
The reasons people give for not completing college also differ across racial and ethnic groups. Among those without a bachelor’s degree, Hispanic adults (52%) are more likely than those who are White (39%) or Black (41%) to say a major reason they didn’t graduate from a four-year college is that they couldn’t afford it. Hispanic and Black adults without a four-year degree are more likely than their White counterparts to say needing to work to support their family was a major reason. There aren’t enough Asian adults without a bachelor’s degree in the sample to analyze this group separately.
While a third of White adults without a four-year degree say not wanting to go to school was a major reason they didn’t complete a four-year degree, smaller shares of Black (22%) and Hispanic (23%) adults say the same. White adults are also more likely to say not needing more education for the job or career they wanted is a major reason why they don’t have a bachelor’s degree.
In some instances, the gender gaps in the reasons for not completing college are more pronounced among White adults than among Black or Hispanic adults. About four-in-ten White men who didn’t complete four years of college (39%) say a major reason for this is that they just didn’t want to. This compares with 27% of White women without a degree. Views on this don’t differ significantly by gender for Black or Hispanic adults.
Similarly, while three-in-ten White men without a college degree say a major reason they didn’t complete college is that they didn’t need more education for the job or career they wanted, only 24% of White women say the same. Among Black and Hispanic non-college graduates, roughly similar shares of men and women say this was a major reason.
Among college graduates, men and women have similar views on the value of their degree
Looking at those who have graduated from college, men and women are equally likely to see value in the experience. Overall, 49% of four-year college graduates say their college education was extremely useful in terms of helping them grow personally and intellectually. Roughly equal shares of men (47%) and women (50%) express this view.
Some 44% of college graduates – including 45% of men and 43% of women – say their college education was extremely useful to them in opening doors to job opportunities. A somewhat smaller share of bachelor’s degree holders (38%) say college was extremely useful in helping them develop specific skills and knowledge that could be used in the workplace (38% of men and 40% of women say this).
There are differences by age on each of these items, as younger college graduates are less likely than older ones to see value in their college education. For example, only a third of college graduates younger than 50, compared with 45% of those 50 and older, say their college experience was extremely useful in helping them develop skills and knowledge that could be used in the workplace.
Note: Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology .
- Education & Gender
- Educational Attainment
- Higher Education
- Hispanics/Latinos & Education

Race and LGBTQ Issues in K-12 Schools
Fewer young men are in college, especially at 4-year schools, women have gained ground in the nation’s highest-paying occupations, but still lag behind men, most americans who are familiar with title ix say it’s had a positive impact on gender equality, how the political typology groups compare, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
Graduate College
Cole denisen, neurodivergent experiences of othering, self-definition, & belonging on a college campus.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: philosophiae doctor or doctor philosophiae) is the most common degree at the highest academic level, awarded following a course of study and research. The degree is abbreviated PhD and sometimes, especially in the U.S., as Ph.D. It is derived from the Latin Philosophiae Doctor, pronounced as three separate letters (/ p iː eɪ tʃ ˈ d iː ...
The meaning of PHD is the academic degree, title, or rank of doctor of philosophy; also : a person who has earned the academic degree of doctor of philosophy. How to use PhD in a sentence.
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. This is one of the highest level academic degrees that can be awarded. PhD is an abbreviation of the Latin term (Ph)ilosophiae (D)octor. Traditionally the term 'philosophy' does not refer to the subject but its original Greek meaning which roughly translates to 'lover of wisdom'.
A PhD is a terminal academic degree students typically pursue when they're interested in an academic or research career. A PhD is the highest possible academic degree a student can obtain. PhD stands for "Doctor of Philosophy," which refers to the immense knowledge a student gains when earning the degree. While you can actually get a PhD in ...
Definition of a PhD - A Doctor of Philosophy (commonly abbreviated to PhD, Ph.D or a DPhil) is a university research degree awarded from across a broad range of academic disciplines; in most countries, it is a terminal degree, i.e. the highest academic degree possible. PhDs differ from undergraduate and master's degrees in that PhDs are ...
The meaning of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY is the highest degree awarded in many academic disciplines; also : a person who has earned the academic degree of doctor of philosophy —abbreviation PhD, Ph.D.. How to use doctor of philosophy in a sentence.
A Doctor of Philosophy, often known as a PhD, is a terminal degree —or the highest possible academic degree you can earn in a subject. While PhD programs (or doctorate programs) are often structured to take between four and five years, some graduate students may take longer as they balance the responsibilities of coursework, original research ...
PhD definition: the highest degree, a doctorate, awarded by a graduate school in a field of academic study, usually to a person who has completed at least three years of graduate study and a dissertation approved by a committee of professors.. See examples of PHD used in a sentence.
PhD is short for Doctor of Philosophy. This is an academic or professional degree that, in most countries, qualifies the degree holder to teach their chosen subject at university level or to work in a specialized position in their chosen field. The word 'philosophy' comes from the Ancient Greek philosophia, literally translated as 'love ...
PhD definition: 1. abbreviation for doctor of philosophy: the highest college or university degree, or someone who…. Learn more.
Doctorate. A doctoral diploma awarded by the State University of New York at Buffalo. A doctorate (from Latin doctor, meaning "teacher") or doctoral degree is a postgraduate academic degree awarded by universities and some other educational institutions, derived from the ancient formalism licentia docendi ("licence to teach").
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3-5 years writing a dissertation, which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge. A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher ...
The Definition of a PhD. Extract from: How to get a PhD. (Open University Press) by Estelle Phillips & Derek Pugh. A bachelor's degree traditionally meant that the recipient had obtained a general education (specializing at this level is a relatively recent nineteenth-century development). A master's degree is a licence to practise.
The precise nature and definition of an MPhil can vary among institutions and countries. A PhD, meanwhile, follows a more widely known and traditional route and requires students, often referred to as "candidates", to produce their own work and research on a new area or topic to a high academic standard.
A doctoral degree is a graduate-level credential typically granted after multiple years of graduate school, with the time-to-degree varying depending on the type of doctoral program, experts say ...
Definition of PhD noun in Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. Meaning, pronunciation, picture, example sentences, grammar, usage notes, synonyms and more.
PhD is an abbreviation for "Doctor of Philosophy.". A PhD is the ultimate academic degree you can earn in a field of choice. To earn a PhD, you must complete original research and evaluate a theory. More often than not, this includes data analysis. This fact is true no matter where you are in the world.
PhD meaning: an advanced university qualification, or a person who has this qualification: . Learn more.
PhD meaning: 1. abbreviation for doctor of philosophy: the highest college or university degree, or someone who…. Learn more.
Academic doctorate. An academic doctorate, often called a PhD (short for Doctor of Philosophy), is a research degree that typically requires completing a dissertation. Students enrolled in a PhD program may be interested in working in academia as a professor or conducting research in their field. However, a growing number of PhD students go on ...
Offered jointly by the Harvard Graduate School of Education and the Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, the Ph.D. in Education provides you with full access to the extraordinary resources of Harvard University and prepares you to assume meaningful roles as university faculty, researchers, senior-level education leaders, and policymakers.
Abbreviated from the Latin term philosophiae doctor meaning "doctor of philosophy," the Ph.D is the highest degree in most fields, with the notable exceptions of medicine and law that have their own doctorates. The degree originated in 19th century Germany when the word "philosophy" had the much broader meaning of "love of wisdom.".
Preparing to graduate. Cronin, although cancer-free since July 2021, still had constant pain while her bones and muscles regrew. It took more than seven months to receive medical clearance to walk. In fall 2022, she returned to CMSRU to complete her third and fourth years of medical school.
DOCTORATE definition: 1. the highest degree from a university: 2. the highest degree from a university: 3. one of the…. Learn more.
Women (44%) are more likely than men (39%) to say not being able to afford college is a major reason they don't have a bachelor's degree. Men and women are about equally likely to say needing to work to help support their family was a major impediment. The shares of men and women saying they didn't consider going to college or they didn ...
Office of the Dean 201 Gilmore Hall 319-335-2143 Office of Academic Affairs 205 Gilmore Hall 319-335-2144 Iowa City, IA 52242-1320 Contact Us Website Feedback