Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples

How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
Published on August 30, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation . You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order. Don’t include subjective interpretations of why you found these results or what they mean—any evaluation should be saved for the discussion section .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to write a results section, reporting quantitative research results, reporting qualitative research results, results vs. discussion vs. conclusion, checklist: research results, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about results sections.
When conducting research, it’s important to report the results of your study prior to discussing your interpretations of it. This gives your reader a clear idea of exactly what you found and keeps the data itself separate from your subjective analysis.
Here are a few best practices:
- Your results should always be written in the past tense.
- While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analyzed, it should be written as concisely as possible.
- Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions . Avoid speculative or interpretative words like “appears” or “implies.”
- If you have other results you’d like to include, consider adding them to an appendix or footnotes.
- Always start out with your broadest results first, and then flow into your more granular (but still relevant) ones. Think of it like a shoe store: first discuss the shoes as a whole, then the sneakers, boots, sandals, etc.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you conducted quantitative research , you’ll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis .
Your results section should report the results of any statistical tests you used to compare groups or assess relationships between variables . It should also state whether or not each hypothesis was supported.
The most logical way to structure quantitative results is to frame them around your research questions or hypotheses. For each question or hypothesis, share:
- A reminder of the type of analysis you used (e.g., a two-sample t test or simple linear regression ). A more detailed description of your analysis should go in your methodology section.
- A concise summary of each relevant result, both positive and negative. This can include any relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., means and standard deviations ) as well as inferential statistics (e.g., t scores, degrees of freedom , and p values ). Remember, these numbers are often placed in parentheses.
- A brief statement of how each result relates to the question, or whether the hypothesis was supported. You can briefly mention any results that didn’t fit with your expectations and assumptions, but save any speculation on their meaning or consequences for your discussion and conclusion.
A note on tables and figures
In quantitative research, it’s often helpful to include visual elements such as graphs, charts, and tables , but only if they are directly relevant to your results. Give these elements clear, descriptive titles and labels so that your reader can easily understand what is being shown. If you want to include any other visual elements that are more tangential in nature, consider adding a figure and table list .
As a rule of thumb:
- Tables are used to communicate exact values, giving a concise overview of various results
- Graphs and charts are used to visualize trends and relationships, giving an at-a-glance illustration of key findings
Don’t forget to also mention any tables and figures you used within the text of your results section. Summarize or elaborate on specific aspects you think your reader should know about rather than merely restating the same numbers already shown.
A two-sample t test was used to test the hypothesis that higher social distance from environmental problems would reduce the intent to donate to environmental organizations, with donation intention (recorded as a score from 1 to 10) as the outcome variable and social distance (categorized as either a low or high level of social distance) as the predictor variable.Social distance was found to be positively correlated with donation intention, t (98) = 12.19, p < .001, with the donation intention of the high social distance group 0.28 points higher, on average, than the low social distance group (see figure 1). This contradicts the initial hypothesis that social distance would decrease donation intention, and in fact suggests a small effect in the opposite direction.
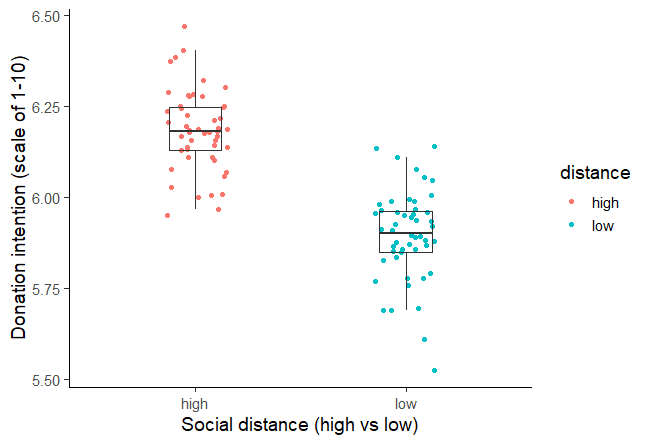
Figure 1: Intention to donate to environmental organizations based on social distance from impact of environmental damage.
In qualitative research , your results might not all be directly related to specific hypotheses. In this case, you can structure your results section around key themes or topics that emerged from your analysis of the data.
For each theme, start with general observations about what the data showed. You can mention:
- Recurring points of agreement or disagreement
- Patterns and trends
- Particularly significant snippets from individual responses
Next, clarify and support these points with direct quotations. Be sure to report any relevant demographic information about participants. Further information (such as full transcripts , if appropriate) can be included in an appendix .
When asked about video games as a form of art, the respondents tended to believe that video games themselves are not an art form, but agreed that creativity is involved in their production. The criteria used to identify artistic video games included design, story, music, and creative teams.One respondent (male, 24) noted a difference in creativity between popular video game genres:
“I think that in role-playing games, there’s more attention to character design, to world design, because the whole story is important and more attention is paid to certain game elements […] so that perhaps you do need bigger teams of creative experts than in an average shooter or something.”
Responses suggest that video game consumers consider some types of games to have more artistic potential than others.
Your results section should objectively report your findings, presenting only brief observations in relation to each question, hypothesis, or theme.
It should not speculate about the meaning of the results or attempt to answer your main research question . Detailed interpretation of your results is more suitable for your discussion section , while synthesis of your results into an overall answer to your main research question is best left for your conclusion .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results.
I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions.
I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics .
I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported or refuted.
I have used tables and figures to illustrate my results where appropriate.
All tables and figures are correctly labelled and referred to in the text.
There is no subjective interpretation or speculation on the meaning of the results.
You've finished writing up your results! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively.
In quantitative research , for each question or hypothesis , state:
- The type of analysis used
- Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics
- Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
In qualitative research , for each question or theme, describe:
- Recurring patterns
- Significant or representative individual responses
- Relevant quotations from the data
Don’t interpret or speculate in the results chapter.
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/results/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

11 Tips For Writing a Dissertation Data Analysis
Since the evolution of the fourth industrial revolution – the Digital World; lots of data have surrounded us. There are terabytes of data around us or in data centers that need to be processed and used. The data needs to be appropriately analyzed to process it, and Dissertation data analysis forms its basis. If data analysis is valid and free from errors, the research outcomes will be reliable and lead to a successful dissertation.
Considering the complexity of many data analysis projects, it becomes challenging to get precise results if analysts are not familiar with data analysis tools and tests properly. The analysis is a time-taking process that starts with collecting valid and relevant data and ends with the demonstration of error-free results.
So, in today’s topic, we will cover the need to analyze data, dissertation data analysis, and mainly the tips for writing an outstanding data analysis dissertation. If you are a doctoral student and plan to perform dissertation data analysis on your data, make sure that you give this article a thorough read for the best tips!
What is Data Analysis in Dissertation?
Dissertation Data Analysis is the process of understanding, gathering, compiling, and processing a large amount of data. Then identifying common patterns in responses and critically examining facts and figures to find the rationale behind those outcomes.
Even f you have the data collected and compiled in the form of facts and figures, it is not enough for proving your research outcomes. There is still a need to apply dissertation data analysis on your data; to use it in the dissertation. It provides scientific support to the thesis and conclusion of the research.
Data Analysis Tools
There are plenty of indicative tests used to analyze data and infer relevant results for the discussion part. Following are some tests used to perform analysis of data leading to a scientific conclusion:
11 Most Useful Tips for Dissertation Data Analysis
Doctoral students need to perform dissertation data analysis and then dissertation to receive their degree. Many Ph.D. students find it hard to do dissertation data analysis because they are not trained in it.
1. Dissertation Data Analysis Services
The first tip applies to those students who can afford to look for help with their dissertation data analysis work. It’s a viable option, and it can help with time management and with building the other elements of the dissertation with much detail.
Dissertation Analysis services are professional services that help doctoral students with all the basics of their dissertation work, from planning, research and clarification, methodology, dissertation data analysis and review, literature review, and final powerpoint presentation.
One great reference for dissertation data analysis professional services is Statistics Solutions , they’ve been around for over 22 years helping students succeed in their dissertation work. You can find the link to their website here .
For a proper dissertation data analysis, the student should have a clear understanding and statistical knowledge. Through this knowledge and experience, a student can perform dissertation analysis on their own.
Following are some helpful tips for writing a splendid dissertation data analysis:
2. Relevance of Collected Data
If the data is irrelevant and not appropriate, you might get distracted from the point of focus. To show the reader that you can critically solve the problem, make sure that you write a theoretical proposition regarding the selection and analysis of data.
3. Data Analysis
For analysis, it is crucial to use such methods that fit best with the types of data collected and the research objectives. Elaborate on these methods and the ones that justify your data collection methods thoroughly. Make sure to make the reader believe that you did not choose your method randomly. Instead, you arrived at it after critical analysis and prolonged research.
On the other hand, quantitative analysis refers to the analysis and interpretation of facts and figures – to build reasoning behind the advent of primary findings. An assessment of the main results and the literature review plays a pivotal role in qualitative and quantitative analysis.
The overall objective of data analysis is to detect patterns and inclinations in data and then present the outcomes implicitly. It helps in providing a solid foundation for critical conclusions and assisting the researcher to complete the dissertation proposal.
4. Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data refers to data that does not involve numbers. You are required to carry out an analysis of the data collected through experiments, focus groups, and interviews. This can be a time-taking process because it requires iterative examination and sometimes demanding the application of hermeneutics. Note that using qualitative technique doesn’t only mean generating good outcomes but to unveil more profound knowledge that can be transferrable.
Presenting qualitative data analysis in a dissertation can also be a challenging task. It contains longer and more detailed responses. Placing such comprehensive data coherently in one chapter of the dissertation can be difficult due to two reasons. Firstly, we cannot figure out clearly which data to include and which one to exclude. Secondly, unlike quantitative data, it becomes problematic to present data in figures and tables. Making information condensed into a visual representation is not possible. As a writer, it is of essence to address both of these challenges.
Qualitative Data Analysis Methods
Following are the methods used to perform quantitative data analysis.
- Deductive Method
This method involves analyzing qualitative data based on an argument that a researcher already defines. It’s a comparatively easy approach to analyze data. It is suitable for the researcher with a fair idea about the responses they are likely to receive from the questionnaires.
- Inductive Method
In this method, the researcher analyzes the data not based on any predefined rules. It is a time-taking process used by students who have very little knowledge of the research phenomenon.
5. Quantitative Data Analysis
Quantitative data contains facts and figures obtained from scientific research and requires extensive statistical analysis. After collection and analysis, you will be able to conclude. Generic outcomes can be accepted beyond the sample by assuming that it is representative – one of the preliminary checkpoints to carry out in your analysis to a larger group. This method is also referred to as the “scientific method”, gaining its roots from natural sciences.
The Presentation of quantitative data depends on the domain to which it is being presented. It is beneficial to consider your audience while writing your findings. Quantitative data for hard sciences might require numeric inputs and statistics. As for natural sciences , such comprehensive analysis is not required.
Quantitative Analysis Methods
Following are some of the methods used to perform quantitative data analysis.
- Trend analysis: This corresponds to a statistical analysis approach to look at the trend of quantitative data collected over a considerable period.
- Cross-tabulation: This method uses a tabula way to draw readings among data sets in research.
- Conjoint analysis : Quantitative data analysis method that can collect and analyze advanced measures. These measures provide a thorough vision about purchasing decisions and the most importantly, marked parameters.
- TURF analysis: This approach assesses the total market reach of a service or product or a mix of both.
- Gap analysis: It utilizes the side-by-side matrix to portray quantitative data, which captures the difference between the actual and expected performance.
- Text analysis: In this method, innovative tools enumerate open-ended data into easily understandable data.
6. Data Presentation Tools
Since large volumes of data need to be represented, it becomes a difficult task to present such an amount of data in coherent ways. To resolve this issue, consider all the available choices you have, such as tables, charts, diagrams, and graphs.
Tables help in presenting both qualitative and quantitative data concisely. While presenting data, always keep your reader in mind. Anything clear to you may not be apparent to your reader. So, constantly rethink whether your data presentation method is understandable to someone less conversant with your research and findings. If the answer is “No”, you may need to rethink your Presentation.
7. Include Appendix or Addendum
After presenting a large amount of data, your dissertation analysis part might get messy and look disorganized. Also, you would not be cutting down or excluding the data you spent days and months collecting. To avoid this, you should include an appendix part.
The data you find hard to arrange within the text, include that in the appendix part of a dissertation . And place questionnaires, copies of focus groups and interviews, and data sheets in the appendix. On the other hand, one must put the statistical analysis and sayings quoted by interviewees within the dissertation.
8. Thoroughness of Data
It is a common misconception that the data presented is self-explanatory. Most of the students provide the data and quotes and think that it is enough and explaining everything. It is not sufficient. Rather than just quoting everything, you should analyze and identify which data you will use to approve or disapprove your standpoints.
Thoroughly demonstrate the ideas and critically analyze each perspective taking care of the points where errors can occur. Always make sure to discuss the anomalies and strengths of your data to add credibility to your research.
9. Discussing Data
Discussion of data involves elaborating the dimensions to classify patterns, themes, and trends in presented data. In addition, to balancing, also take theoretical interpretations into account. Discuss the reliability of your data by assessing their effect and significance. Do not hide the anomalies. While using interviews to discuss the data, make sure you use relevant quotes to develop a strong rationale.
It also involves answering what you are trying to do with the data and how you have structured your findings. Once you have presented the results, the reader will be looking for interpretation. Hence, it is essential to deliver the understanding as soon as you have submitted your data.
10. Findings and Results
Findings refer to the facts derived after the analysis of collected data. These outcomes should be stated; clearly, their statements should tightly support your objective and provide logical reasoning and scientific backing to your point. This part comprises of majority part of the dissertation.
In the finding part, you should tell the reader what they are looking for. There should be no suspense for the reader as it would divert their attention. State your findings clearly and concisely so that they can get the idea of what is more to come in your dissertation.
11. Connection with Literature Review
At the ending of your data analysis in the dissertation, make sure to compare your data with other published research. In this way, you can identify the points of differences and agreements. Check the consistency of your findings if they meet your expectations—lookup for bottleneck position. Analyze and discuss the reasons behind it. Identify the key themes, gaps, and the relation of your findings with the literature review. In short, you should link your data with your research question, and the questions should form a basis for literature.
The Role of Data Analytics at The Senior Management Level

From small and medium-sized businesses to Fortune 500 conglomerates, the success of a modern business is now increasingly tied to how the company implements its data infrastructure and data-based decision-making. According
The Decision-Making Model Explained (In Plain Terms)

Any form of the systematic decision-making process is better enhanced with data. But making sense of big data or even small data analysis when venturing into a decision-making process might
13 Reasons Why Data Is Important in Decision Making

Wrapping Up
Writing data analysis in the dissertation involves dedication, and its implementations demand sound knowledge and proper planning. Choosing your topic, gathering relevant data, analyzing it, presenting your data and findings correctly, discussing the results, connecting with the literature and conclusions are milestones in it. Among these checkpoints, the Data analysis stage is most important and requires a lot of keenness.
In this article, we thoroughly looked at the tips that prove valuable for writing a data analysis in a dissertation. Make sure to give this article a thorough read before you write data analysis in the dissertation leading to the successful future of your research.
Oxbridge Essays. Top 10 Tips for Writing a Dissertation Data Analysis.
Emidio Amadebai
As an IT Engineer, who is passionate about learning and sharing. I have worked and learned quite a bit from Data Engineers, Data Analysts, Business Analysts, and Key Decision Makers almost for the past 5 years. Interested in learning more about Data Science and How to leverage it for better decision-making in my business and hopefully help you do the same in yours.
Recent Posts
Causal vs Evidential Decision-making (How to Make Businesses More Effective)
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, it is crucial to make informed decisions to stay in the competition which makes it important to understand the concept of the different characteristics and...
Bootstrapping vs. Boosting
Over the past decade, the field of machine learning has witnessed remarkable advancements in predictive techniques and ensemble learning methods. Ensemble techniques are very popular in machine...

- Cookies & Privacy
- GETTING STARTED
- Introduction
- FUNDAMENTALS
Getting to the main article
Choosing your route
Setting research questions/ hypotheses
Assessment point
Building the theoretical case
Setting your research strategy
Data collection
Data analysis
Data analysis techniques
In STAGE NINE: Data analysis , we discuss the data you will have collected during STAGE EIGHT: Data collection . However, before you collect your data, having followed the research strategy you set out in this STAGE SIX , it is useful to think about the data analysis techniques you may apply to your data when it is collected.
The statistical tests that are appropriate for your dissertation will depend on (a) the research questions/hypotheses you have set, (b) the research design you are using, and (c) the nature of your data. You should already been clear about your research questions/hypotheses from STAGE THREE: Setting research questions and/or hypotheses , as well as knowing the goal of your research design from STEP TWO: Research design in this STAGE SIX: Setting your research strategy . These two pieces of information - your research questions/hypotheses and research design - will let you know, in principle , the statistical tests that may be appropriate to run on your data in order to answer your research questions.
We highlight the words in principle and may because the most appropriate statistical test to run on your data not only depend on your research questions/hypotheses and research design, but also the nature of your data . As you should have identified in STEP THREE: Research methods , and in the article, Types of variables , in the Fundamentals part of Lærd Dissertation, (a) not all data is the same, and (b) not all variables are measured in the same way (i.e., variables can be dichotomous, ordinal or continuous). In addition, not all data is normal , nor is the data when comparing groups necessarily equal , terms we explain in the Data Analysis section in the Fundamentals part of Lærd Dissertation. As a result, you might think that running a particular statistical test is correct at this point of setting your research strategy (e.g., a statistical test called a dependent t-test ), based on the research questions/hypotheses you have set, but when you collect your data (i.e., during STAGE EIGHT: Data collection ), the data may fail certain assumptions that are important to such a statistical test (i.e., normality and homogeneity of variance ). As a result, you have to run another statistical test (e.g., a Wilcoxon signed-rank test instead of a dependent t-test ).
At this stage in the dissertation process, it is important, or at the very least, useful to think about the data analysis techniques you may apply to your data when it is collected. We suggest that you do this for two reasons:
REASON A Supervisors sometimes expect you to know what statistical analysis you will perform at this stage of the dissertation process
This is not always the case, but if you have had to write a Dissertation Proposal or Ethics Proposal , there is sometimes an expectation that you explain the type of data analysis that you plan to carry out. An understanding of the data analysis that you will carry out on your data can also be an expected component of the Research Strategy chapter of your dissertation write-up (i.e., usually Chapter Three: Research Strategy ). Therefore, it is a good time to think about the data analysis process if you plan to start writing up this chapter at this stage.
REASON B It takes time to get your head around data analysis
When you come to analyse your data in STAGE NINE: Data analysis , you will need to think about (a) selecting the correct statistical tests to perform on your data, (b) running these tests on your data using a statistics package such as SPSS, and (c) learning how to interpret the output from such statistical tests so that you can answer your research questions or hypotheses. Whilst we show you how to do this for a wide range of scenarios in the in the Data Analysis section in the Fundamentals part of Lærd Dissertation, it can be a time consuming process. Unless you took an advanced statistics module/option as part of your degree (i.e., not just an introductory course to statistics, which are often taught in undergraduate and master?s degrees), it can take time to get your head around data analysis. Starting this process at this stage (i.e., STAGE SIX: Research strategy ), rather than waiting until you finish collecting your data (i.e., STAGE EIGHT: Data collection ) is a sensible approach.
Final thoughts...
Setting the research strategy for your dissertation required you to describe, explain and justify the research paradigm, quantitative research design, research method(s), sampling strategy, and approach towards research ethics and data analysis that you plan to follow, as well as determine how you will ensure the research quality of your findings so that you can effectively answer your research questions/hypotheses. However, from a practical perspective, just remember that the main goal of STAGE SIX: Research strategy is to have a clear research strategy that you can implement (i.e., operationalize ). After all, if you are unable to clearly follow your plan and carry out your research in the field, you will struggle to answer your research questions/hypotheses. Once you are sure that you have a clear plan, it is a good idea to take a step back, speak with your supervisor, and assess where you are before moving on to collect data. Therefore, when you are ready, proceed to STAGE SEVEN: Assessment point .

Library Guides
Dissertations 2: structure: thematic.
In the humanities, a thematic dissertation is often structured like a long essay. It can contain:
Title page
Abstract
Table of contents
Introduction
Literature review (which can be included in the introduction rather than as a separate chapter. Check with your supervisor if you are unsure).
Theme 1
Theme 2
Theme 3
Conclusion
Bibliography
Appendices
Abstracts are used by other researchers to establish the relevance of the study to their own work. Therefore, they should contain the what, why, who, where and how of your project.
They are typically between 250 – 300 words long, offer a summary of the main findings and present the conclusions, so you should attempt to write an abstract (if requested), after you have finished writing the dissertation.
A typical abstract summarises:
What the study aimed to achieve
The methodology used
Why the research was conducted
Why the research is important
Who/what was researched
Table of Contents
The table of contents should list all the items included in your dissertation.
It is a good idea to use the electronic table of contents feature in Word to automatically link it to your chapter headings and page numbers. Attempting to manually create a table of contents means that you will have to adjust your page numbers every time you edit your work before submission, which may waste valuable time!
This useful video will walk you through the formatting of longer documents using the electronic table of contents feature.
Introduction
The introduction explains the how, what, where, when, why and who of the research. It introduces the reader to your dissertation and should act as a clear guide as to what it will cover.
The introduction may include the following content:
Introduce the topic of the dissertation
- State why the topic is of interest
- Give background information on the subject.
- Refer to the main debates in the field
Identify the scope of your research
- Highlight what hasn't already been said by the literature
- Demonstrate what you seek to investigate, and why
- Present the aim of the dissertation.
- Mention your research question or hypothesis
Indicate your approach
- Introduce your main argument (especially if you have a research question, rather than hypothesis).
- Mention your methods/research design.
- Outline the dissertation structure (introduce the main points that you will discuss in the order they will be presented).
Normally, the introduction is roughly 10% of a dissertation word count.
Literature Review
The term “literature” in “literature review” comprises scholarly articles, books, and other sources (e.g. reports) relevant to a particular issue, area of research or theory. In a dissertation, the literature review illustrates what the literature already says on your research subject, providing summary and synthesis of such literature.
It is generally structured by topic, starting from general background and concepts, and then addressing what can be found - and cannot be found - on the specific focus of your dissertation. Indeed, the literature review should identify gaps in the literature, that your research aims to fill. This requires you to engage critically with the literature, not merely reproduce the critical understanding of others.
In sum, literature reviews should demonstrate how your research question can be located in a wider field of inquiry. Therefore, a literature review needs to address the connections between your work and the work of others by highlighting links between them. In doing so, you will demonstrate the foundations of your project and show how you are taking the line of inquiry forwards.
By the end of your literature review, your reader should be able to see:
The gap in knowledge and understanding which you say exists in the field.
How your research question will work within that gap.
The work other researchers have carried out and the issues debated in the field.
That you have a good understanding of the field and that you are critically engaged with the debates (Burnett, 2009).
For more detailed guidance on how to write literature reviews, check out the Literature Review Guide.
Theme Chapters
In a thematic structure, the core chapters present analysis and discussion of different themes relevant to answer the research question and support the overall argument of the dissertation. The chapters will include analysis of texts/ research material. They can explore and connect academic theories/research to develop an argument. Stella Cottrell offers some good guidance on how to structure your theme chapters. Each chapter should have the following elements (Cottrell, 2014, p183):
Theme: What is the theme of this chapter? Sequence your themes logically (e.g. from general to specific).
Argument: What argument does this chapter present?
Material: What material you will be using for this chapter?
Clustering: What are the main points you want to make? Deal with one point at a time, and don't jum around? Dedicate your points to sub-headings and paragraphs.
Sequence: In what order are you going to present the points you want to make in this chapter? Draw an outline of the chapter before starting writing it.
Introduction and Conclusion: Each chapter should have a short introduction and conclusion.
The conclusion is the final chapter of your dissertation. It should flow logically from the previously presented text; therefore, you should avoid introducing new ideas, new data, or a new direction.
Ideally, the conclusion should leave the reader with a clear understanding of the discovery or argument you have advanced.
This can be done by:
Summarising and synthesising your main findings and how they relate to your research question or hypotheses
Demonstrating the relevance and importance of your work in the wider context of your field. For example, what recommendations would you make for future research? What do we know now that we didn’t know before?
Link your conclusion to your introduction as both frame your dissertation.
A conclusion is roughly five to ten percent of the word count of the dissertation.
Avoid excessive detail. Decide what your reader needs to know.
Don’t introduce any new information such as theories, data or ideas.
Sum up the main points of your research.
Bibliography
While writing your dissertation, you would have referred to the works and research of many different authors and editors in your field of study. These works should be acknowledged in the bibliography where you will list writers alphabetically by surname.
For example:
Poloian, L.R. (2013). Retailing principles: global, multichannel, and managerial viewpoints. New York: Fairchild. Biggs, J. and Tang, C. (2011). Teaching for quality learning at university . Maidenhead: Open University Press. Ramsay, P., Maier, P. and Price, G. (2010). Study skills for business and management students . Harlow: Longman.
Unless otherwise specified by your module leader, the University uses the Harvard (author-date) style of citing and referencing. For more guidance and support on how to reference effectively check out the Referencing Guide . You can also book an appointment with an Academic Engagement Librarian for extra help with referencing.
While the main results of your study should be placed in the body of your dissertation, any extra information can be placed in the appendices chapter. This supplementary information, for instance, can consist of graphs, charts, or tables that demonstrate less significant results or interview transcripts that would disrupt the flow of the main text if they were included within it.
You can create one long appendix section or divide it into smaller sections to make it easier to navigate. For example, you might want to have an appendix for images, an appendix for transcripts, and an appendix for graphs. Each appendix (each graph or chart, etc.) should have its own number and title. Further, the sources for all appendices should be acknowledged through referencing and listed in the bibliography.
Don’t forget to mention each appendix at least once during your dissertation! This can be done using brackets in the following way: (see appendix 1).
- << Previous: Standard
- Last Updated: Nov 23, 2021 3:47 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/c.php?g=692395
CONNECT WITH US
- How it works
A Step-By-Step Guide to Write the Perfect Dissertation
“A dissertation or a thesis is a long piece of academic writing based on comprehensive research.”
The significance of dissertation writing in the world of academia is unparalleled. A good dissertation paper needs months of research and marks the end of your respected academic journey. It is considered the most effective form of writing in academia and perhaps the longest piece of academic writing you will ever have to complete.
This thorough step-by-step guide on how to write a dissertation will serve as a tool to help you with the task at hand, whether you are an undergraduate student or a Masters or PhD student working on your dissertation project. This guide provides detailed information about how to write the different chapters of a dissertation, such as a problem statement , conceptual framework , introduction , literature review, methodology , discussion , findings , conclusion , title page , acknowledgements , etc.
What is a Dissertation? – Definition
Before we list the stages of writing a dissertation, we should look at what a dissertation is.
The Cambridge dictionary states that a dissertation is a long piece of writing on a particular subject, especially one that is done to receive a degree at college or university, but that is just the tip of the iceberg because a dissertation project has a lot more meaning and context.
To understand a dissertation’s definition, one must have the capability to understand what an essay is. A dissertation is like an extended essay that includes research and information at a much deeper level. Despite the few similarities, there are many differences between an essay and a dissertation.
Another term that people confuse with a dissertation is a thesis. Let's look at the differences between the two terms.
What is the Difference Between a Dissertation and a Thesis?
Dissertation and thesis are used interchangeably worldwide (and may vary between universities and regions), but the key difference is when they are completed. The thesis is a project that marks the end of a degree program, whereas the dissertation project can occur during the degree. Hanno Krieger (Researchgate, 2014) explained the difference between a dissertation and a thesis as follows:
“Thesis is the written form of research work to claim an academic degree, like PhD thesis, postgraduate thesis, and undergraduate thesis. On the other hand, a dissertation is only another expression of the written research work, similar to an essay. So the thesis is the more general expression.
In the end, it does not matter whether it is a bachelor's, master or PhD dissertation one is working on because the structure and the steps of conducting research are pretty much identical. However, doctoral-level dissertation papers are much more complicated and detailed.
Problems Students Face When Writing a Dissertation
You can expect to encounter some troubles if you don’t yet know the steps to write a dissertation. Even the smartest students are overwhelmed by the complexity of writing a dissertation.
A dissertation project is different from any essay paper you have ever committed to because of the details of planning, research and writing it involves. One can expect rewarding results at the end of the process if the correct guidelines are followed. Still, as indicated previously, there will be multiple challenges to deal with before reaching that milestone.
The three most significant problems students face when working on a dissertation project are the following.
Poor Project Planning
Delaying to start working on the dissertation project is the most common problem. Students think they have sufficient time to complete the paper and are finding ways to write a dissertation in a week, delaying the start to the point where they start stressing out about the looming deadline. When the planning is poor, students are always looking for ways to write their dissertations in the last few days. Although it is possible, it does have effects on the quality of the paper.
Inadequate Research Skills
The writing process becomes a huge problem if one has the required academic research experience. Professional dissertation writing goes well beyond collecting a few relevant reference resources.
You need to do both primary and secondary research for your paper. Depending on the dissertation’s topic and the academic qualification you are a candidate for, you may be required to base your dissertation paper on primary research.
In addition to secondary data, you will also need to collect data from the specified participants and test the hypothesis . The practice of primary collection is time-consuming since all the data must be analysed in detail before results can be withdrawn.
Failure to Meet the Strict Academic Writing Standards
Research is a crucial business everywhere. Failure to follow the language, style, structure, and formatting guidelines provided by your department or institution when writing the dissertation paper can worsen matters. It is recommended to read the dissertation handbook before starting the write-up thoroughly.
Steps of Writing a Dissertation
For those stressing out about developing an extensive paper capable of filling a gap in research whilst adding value to the existing academic literature—conducting exhaustive research and analysis—and professionally using the knowledge gained throughout their degree program, there is still good news in all the chaos.
We have put together a guide that will show you how to start your dissertation and complete it carefully from one stage to the next.
Find an Interesting and Manageable Dissertation Topic
A clearly defined topic is a prerequisite for any successful independent research project. An engaging yet manageable research topic can produce an original piece of research that results in a higher academic score.
Unlike essays or assignments, when working on their thesis or dissertation project, students get to choose their topic of research.
You should follow the tips to choose the correct topic for your research to avoid problems later. Your chosen dissertation topic should be narrow enough, allowing you to collect the required secondary and primary data relatively quickly.
Understandably, many people take a lot of time to search for the topic, and a significant amount of research time is spent on it. You should talk to your supervisor or check out the intriguing database of ResearchProspect’s free topics for your dissertation.
Alternatively, consider reading newspapers, academic journals, articles, course materials, and other media to identify relevant issues to your study area and find some inspiration to get going.
You should work closely with your supervisor to agree to a narrowed but clear research plan.Here is what Michelle Schneider, learning adviser at the University of Leeds, had to say about picking the research topics,
“Picking something you’re genuinely interested in will keep you motivated. Consider why it’s important to tackle your chosen topic," Michelle added.
Develop a First-Class Dissertation Proposal.
Once the research topic has been selected, you can develop a solid dissertation proposal . The research proposal allows you to convince your supervisor or the committee members of the significance of your dissertation.
Through the proposal, you will be expected to prove that your work will significantly value the academic and scientific communities by addressing complex and provocative research questions .
Dissertation proposals are much shorter but follow a similar structure to an extensive dissertation paper. If the proposal is optional in your university, you should still create one outline of the critical points that the actual dissertation paper will cover. To get a better understanding of dissertation proposals, you can also check the publicly available samples of dissertation proposals .
Typical contents of the dissertation paper are as follows;
- A brief rationale for the problem your dissertation paper will investigate.
- The hypothesis you will be testing.
- Research objectives you wish to address.
- How will you contribute to the knowledge of the scientific and academic community?
- How will you find answers to the critical research question(s)?
- What research approach will you adopt?
- What kind of population of interest would you like to generalise your result(s) to (especially in the case of quantitative research)?
- What sampling technique(s) would you employ, and why would you not use other methods?
- What ethical considerations have you taken to gather data?
- Who are the stakeholders in your research are/might be?
- What are the future implications and limitations you see in your research?
Let’s review the structure of the dissertation. Keep the format of your proposal simple. Keeping it simple keeps your readers will remain engaged. The following are the fundamental focal points that must be included:
Title of your dissertation: Dissertation titles should be 12 words in length. The focus of your research should be identifiable from your research topic.
Research aim: The overall purpose of your study should be clearly stated in terms of the broad statements of the desired outcomes in the Research aim. Try and paint the picture of your research, emphasising what you wish to achieve as a researcher.
Research objectives: The key research questions you wish to address as part of the project should be listed. Narrow down the focus of your research and aim for at most four objectives. Your research objectives should be linked with the aim of the study or a hypothesis.
Literature review: Consult with your supervisor to check if you are required to use any specific academic sources as part of the literature review process. If that is not the case, find out the most relevant theories, journals, books, schools of thought, and publications that will be used to construct arguments in your literature research.Remember that the literature review is all about giving credit to other authors’ works on a similar topic
Research methods and techniques: Depending on your dissertation topic, you might be required to conduct empirical research to satisfy the study’s objectives. Empirical research uses primary data such as questionnaires, interview data, and surveys to collect.
On the other hand, if your dissertation is based on secondary (non-empirical) data, you can stick to the existing literature in your area of study. Clearly state the merits of your chosen research methods under the methodology section.
Expected results: As you explore the research topic and analyse the data in the previously published papers, you will begin to build your expectations around the study’s potential outcomes. List those expectations here.
Project timeline: Let the readers know exactly how you plan to complete all the dissertation project parts within the timeframe allowed. You should learn more about Microsoft Project and Gantt Charts to create easy-to-follow and high-level project timelines and schedules.
References: The academic sources used to gather information for the proposed paper will be listed under this section using the appropriate referencing style. Ask your supervisor which referencing style you are supposed to follow.
The proposals we write have:
- Precision and Clarity
- Zero Plagiarism
- High-level Encryption
- Authentic Sources

Investigation, Research and Data Collection
This is the most critical stage of the dissertation writing process. One should use up-to-date and relevant academic sources that are likely to jeopardise hard work.
Finding relevant and highly authentic reference resources is the key to succeeding in the dissertation project, so it is advised to take your time with this process. Here are some of the things that should be considered when conducting research.
dissertation project, so it is advised to take your time with this process. Here are some of the things that should be considered when conducting research.
You cannot read everything related to your topic. Although the practice of reading as much material as possible during this stage is rewarding, it is also imperative to understand that it is impossible to read everything that concerns your research.
This is true, especially for undergraduate and master’s level dissertations that must be delivered within a specific timeframe. So, it is important to know when to stop! Once the previous research and the associated limitations are well understood, it is time to move on.
However, review at least the salient research and work done in your area. By salient, we mean research done by pioneers of your field. For instance, if your topic relates to linguistics and you haven’t familiarised yourself with relevant research conducted by, say, Chomsky (the father of linguistics), your readers may find your lack of knowledge disconcerting.
So, to come off as genuinely knowledgeable in your own field, at least don’t forget to read essential works in the field/topic!
Use an Authentic Research database to Find References.
Most students start the reference material-finding process with desk-based research. However, this research method has its own limitation because it is a well-known fact that the internet is full of bogus information and fake information spreads fasters on the internet than truth does .
So, it is important to pick your reference material from reliable resources such as Google Scholar , Researchgate, Ibibio and Bartleby . Wikipedia is not considered a reliable academic source in the academic world, so it is recommended to refrain from citing Wikipedia content.Never underrate the importance of the actual library. The supporting staff at a university library can be of great help when it comes to finding exciting and reliable publications.
Record as you learn
All information and impressions should be recorded as notes using online tools such as Evernote to make sure everything is clear. You want to retain an important piece of information you had planned to present as an argument in the dissertation paper.
Write a Flawless Dissertation
Start to write a fantastic dissertation immediately once your proposal has been accepted and all the necessary desk-based research has been conducted. Now we will look at the different chapters of a dissertation in detail. You can also check out the samples of dissertation chapters to fully understand the format and structures of the various chapters.
Dissertation Introduction Chapter
The introduction chapter of the dissertation paper provides the background, problem statement and research questions. Here, you will inform the readers why it was important for this research to be conducted and which key research question(s) you expect to answer at the end of the study.
Definitions of all the terms and phrases in the project are provided in this first chapter of the dissertation paper. The research aim and objectives remain unchanged from the proposal paper and are expected to be listed under this section.
Dissertation Literature Review Chapter
This chapter allows you to demonstrate to your readers that you have done sufficient research on the chosen topic and understand previous similar studies’ findings. Any research limitations that your research incorporates are expected to be discussed in this section.
And make sure to summarise the viewpoints and findings of other researchers in the dissertation literature review chapter. Show the readers that there is a research gap in the existing work and your job is relevant to it to justify your research value.
Dissertation Methodology
The methodology chapter of the dissertation provides insight into the methods employed to collect data from various resources and flows naturally from the literature review chapter.Simply put, you will be expected to explain what you did and how you did it, helping the readers understand that your research is valid and reliable. When writing the methodology chapter for the dissertation, make sure to emphasise the following points:
- The type of research performed by the researcher
- Methods employed to gather and filter information
- Techniques that were chosen for analysis
- Materials, tools and resources used to conduct research (typically for empirical research dissertations)
- Limitations of your chosen methods
- Reliability and validity of your measuring tools and instruments (e.g. a survey questionnaire) are also typically mentioned within the mythology section. If you used a pre-existing data collection tool, cite its reliability/validity estimates here, too.Make use of the past tense when writing the methodology chapter.
Dissertation Findings
The key results of your research are presented in the dissertation findings chapter . It gives authors the ability to validate their own intellectual and analytical skills
Dissertation Conclusion
Cap off your dissertation paper with a study summary and a brief report of the findings. In the concluding chapter , you will be expected to demonstrate how your research will provide value to other academics in your area of study and its implications.It is recommended to include a short ‘recommendations’ section that will elaborate on the purpose and need for future research to elucidate the topic further.
Follow the referencing style following the requirements of your academic degree or field of study. Make sure to list every academic source used with a proper in-text citation. It is important to give credit to other authors’ ideas and concepts.
Note: Keep in mind whether you are creating a reference list or a bibliography. The former includes information about all the various sources you referred to, read from or took inspiration from for your own study. However, the latter contains things you used and those you only read but didn’t cite in your dissertation.
Proofread, Edit and Improve – Don’t Risk Months of Hard Work.
Experts recommend completing the total dissertation before starting to proofread and edit your work. You need to refresh your focus and reboot your creative brain before returning to another critical stage.
Leave space of at least a few days between the writing and the editing steps so when you get back to the desk, you can recognise your grammar, spelling and factual errors when you get back to the desk.
It is crucial to consider this period to ensure the final work is polished, coherent, well-structured and free of any structural or factual flaws. Daniel Higginbotham from Prospects UK states that:
“Leave yourself sufficient time to engage with your writing at several levels – from reassessing the logic of the whole piece to proofreading to checking you’ve paid attention to aspects such as the correct spelling of names and theories and the required referencing format.”
What is the Difference Between Editing and Proofreading?
Editing means that you are focusing on the essence of your dissertation paper. In contrast, proofreading is the process of reviewing the final draft piece to ensure accuracy and consistency in formatting, spelling, facts, punctuation, and grammar.
Editing: Prepare your work for submission by condensing, correcting and modifying (where necessary). When reviewing the paper, make sure that there are coherence and consistency between the arguments you presented.
If an information gap has been identified, fill that with an appropriate piece of information gathered during the research process. It is easy to lose sight of the original purpose if you become over-involved when writing.
Cut out the unwanted text and refine it, so your paper’s content is to the point and concise.Proofreading: Start proofreading your paper to identify formatting, structural, grammar, punctuation and referencing flaws. Read every single sentence of the paper no matter how tired you are because a few puerile mistakes can compromise your months of hard work.
Many students struggle with the editing and proofreading stages due to their lack of attention to detail. Consult a skilled dissertation editor if you are unable to find your flaws. You may want to invest in a professional dissertation editing and proofreading service to improve the piece’s quality to First Class.
Tips for Writing a Dissertation
Communication with supervisor – get feedback.
Communicate regularly with your supervisor to produce a first-class dissertation paper. Request them to comprehensively review the contents of your dissertation paper before final submission.
Their constructive criticism and feedback concerning different study areas will help you improve your piece’s overall quality. Keep your supervisor updated about your research progress and discuss any problems that you come up against.

Organising your Time
A dissertation is a lengthy project spanning over a period of months to years, and therefore it is important to avoid procrastination. Stay focused, and manage your time efficiently. Here are some time management tips for writing your dissertation to help you make the most of your time as you research and write.
- Don’t be discouraged by the inherently slow nature of dissertation work, particularly in the initial stages.
- Set clear goals and work out your research and write up a plan accordingly.
- Allow sufficient time to incorporate feedback from your supervisor.
- Leave enough time for editing, improving, proofreading, and formatting the paper according to your school’s guidelines. This is where you break or make your grade.
- Work a certain number of hours on your paper daily.
- Create a worksheet for your week.
- Work on your dissertation for time periods as brief as 45 minutes or less.
- Stick to the strategic dissertation timeline, so you don’t have to do the catchup work.
- Meet your goals by prioritising your dissertation work.
- Strike a balance between being overly organised and needing to be more organised.
- Limit activities other than dissertation writing and your most necessary obligations.
- Keep ‘tangent’ and ‘for the book’ files.
- Create lists to help you manage your tasks.
- Have ‘filler’ tasks to do when you feel burned out or in need of intellectual rest.
- Keep a dissertation journal.
- Pretend that you are working in a more structured work world.
- Limit your usage of email and personal electronic devices.
- Utilise and build on your past work when you write your dissertation.
- Break large tasks into small manageable ones.
- Seek advice from others, and do not be afraid to ask for help.
Dissertation Examples
Here are some samples of a dissertation to inspire you to write mind-blowing dissertations and to help bring all the above-mentioned guidelines home.
DE MONTFORT University Leicester – Examples of recent dissertations
Dissertation Research in Education: Dissertations (Examples)
How Long is a Dissertation?
The entire dissertation writing process is complicated and spans over a period of months to years, depending on whether you are an undergraduate, master’s, or PhD candidate. Marcus Beck, a PhD candidate, conducted fundamental research a few years ago, research that didn’t have much to do with his research but returned answers to some niggling questions every student has about the average length of a dissertation.
A software program specifically designed for this purpose helped Beck to access the university’s electronic database to uncover facts on dissertation length.
The above illustration shows how the results of his small study were a little unsurprising. Social sciences and humanities disciplines such as anthropology, politics, and literature had the longest dissertations, with some PhD dissertations comprising 150,000 words or more.Engineering and scientific disciplines, on the other hand, were considerably shorter. PhD-level dissertations generally don’t have a predefined length as they will vary with your research topic. Ask your school about this requirement if you are unsure about it from the start.
Focus more on the quality of content rather than the number of pages.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

Phrases to Avoid
No matter the style or structure you follow, it is best to keep your language simple. Avoid the use of buzzwords and jargon.
A Word on Stealing Content (Plagiarism)
Very straightforward advice to all students, DO NOT PLAGIARISE. Plagiarism is a serious offence. You will be penalised heavily if you are caught plagiarising. Don’t risk years of hard work, as many students in the past have lost their degrees for plagiarising. Here are some tips to help you make sure you don’t get caught.
- Copying and pasting from an academic source is an unforgivable sin. Rephrasing text retrieved from another source also falls under plagiarism; it’s called paraphrasing. Summarising another’s idea(s) word-to-word, paraphrasing, and copy-pasting are the three primary forms plagiarism can take.
- If you must directly copy full sentences from another source because they fill the bill, always enclose them inside quotation marks and acknowledge the writer’s work with in-text citations.
Are you struggling to find inspiration to get going? Still, trying to figure out where to begin? Is the deadline getting closer? Don’t be overwhelmed! ResearchProspect dissertation writing services have helped thousands of students achieve desired outcomes. Click here to get help from writers holding either a master's or PhD degree from a reputed UK university.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a dissertation include.
A dissertation has main chapters and parts that support them. The main parts are:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Research Methodology
- Your conclusion
Other parts are the abstract, references, appendices etc. We can supply a full dissertation or specific parts of one.
What is the difference between research and a dissertation?
A research paper is a sort of academic writing that consists of the study, source assessment, critical thinking, organisation, and composition, as opposed to a thesis or dissertation, which is a lengthy academic document that often serves as the final project for a university degree.
Can I edit and proofread my dissertation myself?
Of course, you can do proofreading and editing of your dissertation. There are certain rules to follow that have been discussed above. However, finding mistakes in something that you have written yourself can be complicated for some people. It is advisable to take professional help in the matter.
What If I only have difficulty writing a specific chapter of the dissertation?
ResearchProspect ensures customer satisfaction by addressing all relevant issues. We provide dissertation chapter-writing services to students if they need help completing a specific chapter. It could be any chapter from the introduction, literature review, and methodology to the discussion and conclusion.
You May Also Like
Are you looking for intriguing and trending dissertation topics? Get inspired by our list of free dissertation topics on all subjects.
Looking for an easy guide to follow to write your essay? Here is our detailed essay guide explaining how to write an essay and examples and types of an essay.
Learn about the steps required to successfully complete their research project. Make sure to follow these steps in their respective order.
More Interesting Articles
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
How To Write The Discussion Chapter
The what, why & how explained simply (with examples).
By: Jenna Crossley (PhD Cand). Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | August 2021
If you’re reading this, chances are you’ve reached the discussion chapter of your thesis or dissertation and are looking for a bit of guidance. Well, you’ve come to the right place ! In this post, we’ll unpack and demystify the typical discussion chapter in straightforward, easy to understand language, with loads of examples .
Overview: Dissertation Discussion Chapter
- What (exactly) the discussion chapter is
- What to include in your discussion chapter
- How to write up your discussion chapter
- A few tips and tricks to help you along the way
What exactly is the discussion chapter?
The discussion chapter is where you interpret and explain your results within your thesis or dissertation. This contrasts with the results chapter, where you merely present and describe the analysis findings (whether qualitative or quantitative ). In the discussion chapter, you elaborate on and evaluate your research findings, and discuss the significance and implications of your results.
In this chapter, you’ll situate your research findings in terms of your research questions or hypotheses and tie them back to previous studies and literature (which you would have covered in your literature review chapter). You’ll also have a look at how relevant and/or significant your findings are to your field of research, and you’ll argue for the conclusions that you draw from your analysis. Simply put, the discussion chapter is there for you to interact with and explain your research findings in a thorough and coherent manner.

What should I include in the discussion chapter?
First things first: in some studies, the results and discussion chapter are combined into one chapter . This depends on the type of study you conducted (i.e., the nature of the study and methodology adopted), as well as the standards set by the university. So, check in with your university regarding their norms and expectations before getting started. In this post, we’ll treat the two chapters as separate, as this is most common.
Basically, your discussion chapter should analyse , explore the meaning and identify the importance of the data you presented in your results chapter. In the discussion chapter, you’ll give your results some form of meaning by evaluating and interpreting them. This will help answer your research questions, achieve your research aims and support your overall conclusion (s). Therefore, you discussion chapter should focus on findings that are directly connected to your research aims and questions. Don’t waste precious time and word count on findings that are not central to the purpose of your research project.
As this chapter is a reflection of your results chapter, it’s vital that you don’t report any new findings . In other words, you can’t present claims here if you didn’t present the relevant data in the results chapter first. So, make sure that for every discussion point you raise in this chapter, you’ve covered the respective data analysis in the results chapter. If you haven’t, you’ll need to go back and adjust your results chapter accordingly.
If you’re struggling to get started, try writing down a bullet point list everything you found in your results chapter. From this, you can make a list of everything you need to cover in your discussion chapter. Also, make sure you revisit your research questions or hypotheses and incorporate the relevant discussion to address these. This will also help you to see how you can structure your chapter logically.
Need a helping hand?
How to write the discussion chapter
Now that you’ve got a clear idea of what the discussion chapter is and what it needs to include, let’s look at how you can go about structuring this critically important chapter. Broadly speaking, there are six core components that need to be included, and these can be treated as steps in the chapter writing process.
Step 1: Restate your research problem and research questions
The first step in writing up your discussion chapter is to remind your reader of your research problem , as well as your research aim(s) and research questions . If you have hypotheses, you can also briefly mention these. This “reminder” is very important because, after reading dozens of pages, the reader may have forgotten the original point of your research or been swayed in another direction. It’s also likely that some readers skip straight to your discussion chapter from the introduction chapter , so make sure that your research aims and research questions are clear.
Step 2: Summarise your key findings
Next, you’ll want to summarise your key findings from your results chapter. This may look different for qualitative and quantitative research , where qualitative research may report on themes and relationships, whereas quantitative research may touch on correlations and causal relationships. Regardless of the methodology, in this section you need to highlight the overall key findings in relation to your research questions.
Typically, this section only requires one or two paragraphs , depending on how many research questions you have. Aim to be concise here, as you will unpack these findings in more detail later in the chapter. For now, a few lines that directly address your research questions are all that you need.
Some examples of the kind of language you’d use here include:
- The data suggest that…
- The data support/oppose the theory that…
- The analysis identifies…
These are purely examples. What you present here will be completely dependent on your original research questions, so make sure that you are led by them .

Step 3: Interpret your results
Once you’ve restated your research problem and research question(s) and briefly presented your key findings, you can unpack your findings by interpreting your results. Remember: only include what you reported in your results section – don’t introduce new information.
From a structural perspective, it can be a wise approach to follow a similar structure in this chapter as you did in your results chapter. This would help improve readability and make it easier for your reader to follow your arguments. For example, if you structured you results discussion by qualitative themes, it may make sense to do the same here.
Alternatively, you may structure this chapter by research questions, or based on an overarching theoretical framework that your study revolved around. Every study is different, so you’ll need to assess what structure works best for you.
When interpreting your results, you’ll want to assess how your findings compare to those of the existing research (from your literature review chapter). Even if your findings contrast with the existing research, you need to include these in your discussion. In fact, those contrasts are often the most interesting findings . In this case, you’d want to think about why you didn’t find what you were expecting in your data and what the significance of this contrast is.
Here are a few questions to help guide your discussion:
- How do your results relate with those of previous studies ?
- If you get results that differ from those of previous studies, why may this be the case?
- What do your results contribute to your field of research?
- What other explanations could there be for your findings?
When interpreting your findings, be careful not to draw conclusions that aren’t substantiated . Every claim you make needs to be backed up with evidence or findings from the data (and that data needs to be presented in the previous chapter – results). This can look different for different studies; qualitative data may require quotes as evidence, whereas quantitative data would use statistical methods and tests. Whatever the case, every claim you make needs to be strongly backed up.

Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations of your study
The fourth step in writing up your discussion chapter is to acknowledge the limitations of the study. These limitations can cover any part of your study , from the scope or theoretical basis to the analysis method(s) or sample. For example, you may find that you collected data from a very small sample with unique characteristics, which would mean that you are unable to generalise your results to the broader population.
For some students, discussing the limitations of their work can feel a little bit self-defeating . This is a misconception, as a core indicator of high-quality research is its ability to accurately identify its weaknesses. In other words, accurately stating the limitations of your work is a strength, not a weakness . All that said, be careful not to undermine your own research. Tell the reader what limitations exist and what improvements could be made, but also remind them of the value of your study despite its limitations.
Step 5: Make recommendations for implementation and future research
Now that you’ve unpacked your findings and acknowledge the limitations thereof, the next thing you’ll need to do is reflect on your study in terms of two factors:
- The practical application of your findings
- Suggestions for future research
The first thing to discuss is how your findings can be used in the real world – in other words, what contribution can they make to the field or industry? Where are these contributions applicable, how and why? For example, if your research is on communication in health settings, in what ways can your findings be applied to the context of a hospital or medical clinic? Make sure that you spell this out for your reader in practical terms, but also be realistic and make sure that any applications are feasible.
The next discussion point is the opportunity for future research . In other words, how can other studies build on what you’ve found and also improve the findings by overcoming some of the limitations in your study (which you discussed a little earlier). In doing this, you’ll want to investigate whether your results fit in with findings of previous research, and if not, why this may be the case. For example, are there any factors that you didn’t consider in your study? What future research can be done to remedy this? When you write up your suggestions, make sure that you don’t just say that more research is needed on the topic, also comment on how the research can build on your study.
Step 6: Provide a concluding summary
Finally, you’ve reached your final stretch. In this section, you’ll want to provide a brief recap of the key findings – in other words, the findings that directly address your research questions . Basically, your conclusion should tell the reader what your study has found, and what they need to take away from reading your report.
When writing up your concluding summary, bear in mind that some readers may skip straight to this section from the beginning of the chapter. So, make sure that this section flows well from and has a strong connection to the opening section of the chapter.
Tips and tricks for an A-grade discussion chapter
Now that you know what the discussion chapter is , what to include and exclude , and how to structure it , here are some tips and suggestions to help you craft a quality discussion chapter.
- When you write up your discussion chapter, make sure that you keep it consistent with your introduction chapter , as some readers will skip from the introduction chapter directly to the discussion chapter. Your discussion should use the same tense as your introduction, and it should also make use of the same key terms.
- Don’t make assumptions about your readers. As a writer, you have hands-on experience with the data and so it can be easy to present it in an over-simplified manner. Make sure that you spell out your findings and interpretations for the intelligent layman.
- Have a look at other theses and dissertations from your institution, especially the discussion sections. This will help you to understand the standards and conventions of your university, and you’ll also get a good idea of how others have structured their discussion chapters. You can also check out our chapter template .
- Avoid using absolute terms such as “These results prove that…”, rather make use of terms such as “suggest” or “indicate”, where you could say, “These results suggest that…” or “These results indicate…”. It is highly unlikely that a dissertation or thesis will scientifically prove something (due to a variety of resource constraints), so be humble in your language.
- Use well-structured and consistently formatted headings to ensure that your reader can easily navigate between sections, and so that your chapter flows logically and coherently.
If you have any questions or thoughts regarding this post, feel free to leave a comment below. Also, if you’re looking for one-on-one help with your discussion chapter (or thesis in general), consider booking a free consultation with one of our highly experienced Grad Coaches to discuss how we can help you.

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

33 Comments
Thank you this is helpful!
This is very helpful to me… Thanks a lot for sharing this with us 😊
This has been very helpful indeed. Thank you.
This is actually really helpful, I just stumbled upon it. Very happy that I found it, thank you.
Me too! I was kinda lost on how to approach my discussion chapter. How helpful! Thanks a lot!
This is really good and explicit. Thanks
Thank you, this blog has been such a help.
Thank you. This is very helpful.
Dear sir/madame
Thanks a lot for this helpful blog. Really, it supported me in writing my discussion chapter while I was totally unaware about its structure and method of writing.
With regards
Syed Firoz Ahmad PhD, Research Scholar
I agree so much. This blog was god sent. It assisted me so much while I was totally clueless about the context and the know-how. Now I am fully aware of what I am to do and how I am to do it.
Thanks! This is helpful!
thanks alot for this informative website
Dear Sir/Madam,
Truly, your article was much benefited when i structured my discussion chapter.
Thank you very much!!!
This is helpful for me in writing my research discussion component. I have to copy this text on Microsoft word cause of my weakness that I cannot be able to read the text on screen a long time. So many thanks for this articles.
This was helpful
Thanks Jenna, well explained.
Thank you! This is super helpful.
Thanks very much. I have appreciated the six steps on writing the Discussion chapter which are (i) Restating the research problem and questions (ii) Summarising the key findings (iii) Interpreting the results linked to relating to previous results in positive and negative ways; explaining whay different or same and contribution to field of research and expalnation of findings (iv) Acknowledgeing limitations (v) Recommendations for implementation and future resaerch and finally (vi) Providing a conscluding summary
My two questions are: 1. On step 1 and 2 can it be the overall or you restate and sumamrise on each findings based on the reaerch question? 2. On 4 and 5 do you do the acknowlledgement , recommendations on each research finding or overall. This is not clear from your expalanattion.
Please respond.
This post is very useful. I’m wondering whether practical implications must be introduced in the Discussion section or in the Conclusion section?
Sigh, I never knew a 20 min video could have literally save my life like this. I found this at the right time!!!! Everything I need to know in one video thanks a mil ! OMGG and that 6 step!!!!!! was the cherry on top the cake!!!!!!!!!
Thanks alot.., I have gained much
This piece is very helpful on how to go about my discussion section. I can always recommend GradCoach research guides for colleagues.
Many thanks for this resource. It has been very helpful to me. I was finding it hard to even write the first sentence. Much appreciated.
Thanks so much. Very helpful to know what is included in the discussion section
this was a very helpful and useful information
This is very helpful. Very very helpful. Thanks for sharing this online!
it is very helpfull article, and i will recommend it to my fellow students. Thank you.
Superlative! More grease to your elbows.
Powerful, thank you for sharing.
Wow! Just wow! God bless the day I stumbled upon you guys’ YouTube videos! It’s been truly life changing and anxiety about my report that is due in less than a month has subsided significantly!
Simplified explanation. Well done.
The presentation is enlightening. Thank you very much.
Thanks for the support and guidance
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
Published on 21 August 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 25 October 2022.

The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results .
It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review , and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion . It should not be a second results section .
There are different ways to write this section, but you can focus your writing around these key elements:
- Summary: A brief recap of your key results
- Interpretations: What do your results mean?
- Implications: Why do your results matter?
- Limitations: What can’t your results tell us?
- Recommendations: Avenues for further studies or analyses
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What not to include in your discussion section, step 1: summarise your key findings, step 2: give your interpretations, step 3: discuss the implications, step 4: acknowledge the limitations, step 5: share your recommendations, discussion section example.
There are a few common mistakes to avoid when writing the discussion section of your paper.
- Don’t introduce new results: You should only discuss the data that you have already reported in your results section .
- Don’t make inflated claims: Avoid overinterpretation and speculation that isn’t directly supported by your data.
- Don’t undermine your research: The discussion of limitations should aim to strengthen your credibility, not emphasise weaknesses or failures.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Start this section by reiterating your research problem and concisely summarising your major findings. Don’t just repeat all the data you have already reported – aim for a clear statement of the overall result that directly answers your main research question . This should be no more than one paragraph.
Many students struggle with the differences between a discussion section and a results section . The crux of the matter is that your results sections should present your results, and your discussion section should subjectively evaluate them. Try not to blend elements of these two sections, in order to keep your paper sharp.
- The results indicate that …
- The study demonstrates a correlation between …
- This analysis supports the theory that …
- The data suggest that …
The meaning of your results may seem obvious to you, but it’s important to spell out their significance for your reader, showing exactly how they answer your research question.
The form of your interpretations will depend on the type of research, but some typical approaches to interpreting the data include:
- Identifying correlations , patterns, and relationships among the data
- Discussing whether the results met your expectations or supported your hypotheses
- Contextualising your findings within previous research and theory
- Explaining unexpected results and evaluating their significance
- Considering possible alternative explanations and making an argument for your position
You can organise your discussion around key themes, hypotheses, or research questions, following the same structure as your results section. Alternatively, you can also begin by highlighting the most significant or unexpected results.
- In line with the hypothesis …
- Contrary to the hypothesised association …
- The results contradict the claims of Smith (2007) that …
- The results might suggest that x . However, based on the findings of similar studies, a more plausible explanation is x .
As well as giving your own interpretations, make sure to relate your results back to the scholarly work that you surveyed in the literature review . The discussion should show how your findings fit with existing knowledge, what new insights they contribute, and what consequences they have for theory or practice.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Do your results support or challenge existing theories? If they support existing theories, what new information do they contribute? If they challenge existing theories, why do you think that is?
- Are there any practical implications?
Your overall aim is to show the reader exactly what your research has contributed, and why they should care.
- These results build on existing evidence of …
- The results do not fit with the theory that …
- The experiment provides a new insight into the relationship between …
- These results should be taken into account when considering how to …
- The data contribute a clearer understanding of …
- While previous research has focused on x , these results demonstrate that y .
Even the best research has its limitations. Acknowledging these is important to demonstrate your credibility. Limitations aren’t about listing your errors, but about providing an accurate picture of what can and cannot be concluded from your study.
Limitations might be due to your overall research design, specific methodological choices , or unanticipated obstacles that emerged during your research process.
Here are a few common possibilities:
- If your sample size was small or limited to a specific group of people, explain how generalisability is limited.
- If you encountered problems when gathering or analysing data, explain how these influenced the results.
- If there are potential confounding variables that you were unable to control, acknowledge the effect these may have had.
After noting the limitations, you can reiterate why the results are nonetheless valid for the purpose of answering your research question.
- The generalisability of the results is limited by …
- The reliability of these data is impacted by …
- Due to the lack of data on x , the results cannot confirm …
- The methodological choices were constrained by …
- It is beyond the scope of this study to …
Based on the discussion of your results, you can make recommendations for practical implementation or further research. Sometimes, the recommendations are saved for the conclusion .
Suggestions for further research can lead directly from the limitations. Don’t just state that more studies should be done – give concrete ideas for how future work can build on areas that your own research was unable to address.
- Further research is needed to establish …
- Future studies should take into account …
- Avenues for future research include …

Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 25). How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/discussion/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a results section | tips & examples, research paper appendix | example & templates, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Dissertation – Format, Example and Template
Dissertation – Format, Example and Template
Table of Contents

Dissertation
Definition:
Dissertation is a lengthy and detailed academic document that presents the results of original research on a specific topic or question. It is usually required as a final project for a doctoral degree or a master’s degree.
Dissertation Meaning in Research
In Research , a dissertation refers to a substantial research project that students undertake in order to obtain an advanced degree such as a Ph.D. or a Master’s degree.
Dissertation typically involves the exploration of a particular research question or topic in-depth, and it requires students to conduct original research, analyze data, and present their findings in a scholarly manner. It is often the culmination of years of study and represents a significant contribution to the academic field.
Types of Dissertation
Types of Dissertation are as follows:
Empirical Dissertation
An empirical dissertation is a research study that uses primary data collected through surveys, experiments, or observations. It typically follows a quantitative research approach and uses statistical methods to analyze the data.
Non-Empirical Dissertation
A non-empirical dissertation is based on secondary sources, such as books, articles, and online resources. It typically follows a qualitative research approach and uses methods such as content analysis or discourse analysis.
Narrative Dissertation
A narrative dissertation is a personal account of the researcher’s experience or journey. It typically follows a qualitative research approach and uses methods such as interviews, focus groups, or ethnography.
Systematic Literature Review
A systematic literature review is a comprehensive analysis of existing research on a specific topic. It typically follows a qualitative research approach and uses methods such as meta-analysis or thematic analysis.
Case Study Dissertation
A case study dissertation is an in-depth analysis of a specific individual, group, or organization. It typically follows a qualitative research approach and uses methods such as interviews, observations, or document analysis.
Mixed-Methods Dissertation
A mixed-methods dissertation combines both quantitative and qualitative research approaches to gather and analyze data. It typically uses methods such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups, as well as statistical analysis.
How to Write a Dissertation
Here are some general steps to help guide you through the process of writing a dissertation:
- Choose a topic : Select a topic that you are passionate about and that is relevant to your field of study. It should be specific enough to allow for in-depth research but broad enough to be interesting and engaging.
- Conduct research : Conduct thorough research on your chosen topic, utilizing a variety of sources, including books, academic journals, and online databases. Take detailed notes and organize your information in a way that makes sense to you.
- Create an outline : Develop an outline that will serve as a roadmap for your dissertation. The outline should include the introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- Write the introduction: The introduction should provide a brief overview of your topic, the research questions, and the significance of the study. It should also include a clear thesis statement that states your main argument.
- Write the literature review: The literature review should provide a comprehensive analysis of existing research on your topic. It should identify gaps in the research and explain how your study will fill those gaps.
- Write the methodology: The methodology section should explain the research methods you used to collect and analyze data. It should also include a discussion of any limitations or weaknesses in your approach.
- Write the results: The results section should present the findings of your research in a clear and organized manner. Use charts, graphs, and tables to help illustrate your data.
- Write the discussion: The discussion section should interpret your results and explain their significance. It should also address any limitations of the study and suggest areas for future research.
- Write the conclusion: The conclusion should summarize your main findings and restate your thesis statement. It should also provide recommendations for future research.
- Edit and revise: Once you have completed a draft of your dissertation, review it carefully to ensure that it is well-organized, clear, and free of errors. Make any necessary revisions and edits before submitting it to your advisor for review.
Dissertation Format
The format of a dissertation may vary depending on the institution and field of study, but generally, it follows a similar structure:
- Title Page: This includes the title of the dissertation, the author’s name, and the date of submission.
- Abstract : A brief summary of the dissertation’s purpose, methods, and findings.
- Table of Contents: A list of the main sections and subsections of the dissertation, along with their page numbers.
- Introduction : A statement of the problem or research question, a brief overview of the literature, and an explanation of the significance of the study.
- Literature Review : A comprehensive review of the literature relevant to the research question or problem.
- Methodology : A description of the methods used to conduct the research, including data collection and analysis procedures.
- Results : A presentation of the findings of the research, including tables, charts, and graphs.
- Discussion : A discussion of the implications of the findings, their significance in the context of the literature, and limitations of the study.
- Conclusion : A summary of the main points of the study and their implications for future research.
- References : A list of all sources cited in the dissertation.
- Appendices : Additional materials that support the research, such as data tables, charts, or transcripts.
Dissertation Outline
Dissertation Outline is as follows:
Title Page:
- Title of dissertation
- Author name
- Institutional affiliation
- Date of submission
- Brief summary of the dissertation’s research problem, objectives, methods, findings, and implications
- Usually around 250-300 words
Table of Contents:
- List of chapters and sections in the dissertation, with page numbers for each
I. Introduction
- Background and context of the research
- Research problem and objectives
- Significance of the research
II. Literature Review
- Overview of existing literature on the research topic
- Identification of gaps in the literature
- Theoretical framework and concepts
III. Methodology
- Research design and methods used
- Data collection and analysis techniques
- Ethical considerations
IV. Results
- Presentation and analysis of data collected
- Findings and outcomes of the research
- Interpretation of the results
V. Discussion
- Discussion of the results in relation to the research problem and objectives
- Evaluation of the research outcomes and implications
- Suggestions for future research
VI. Conclusion
- Summary of the research findings and outcomes
- Implications for the research topic and field
- Limitations and recommendations for future research
VII. References
- List of sources cited in the dissertation
VIII. Appendices
- Additional materials that support the research, such as tables, figures, or questionnaires.
Example of Dissertation
Here is an example Dissertation for students:
Title : Exploring the Effects of Mindfulness Meditation on Academic Achievement and Well-being among College Students
This dissertation aims to investigate the impact of mindfulness meditation on the academic achievement and well-being of college students. Mindfulness meditation has gained popularity as a technique for reducing stress and enhancing mental health, but its effects on academic performance have not been extensively studied. Using a randomized controlled trial design, the study will compare the academic performance and well-being of college students who practice mindfulness meditation with those who do not. The study will also examine the moderating role of personality traits and demographic factors on the effects of mindfulness meditation.
Chapter Outline:
Chapter 1: Introduction
- Background and rationale for the study
- Research questions and objectives
- Significance of the study
- Overview of the dissertation structure
Chapter 2: Literature Review
- Definition and conceptualization of mindfulness meditation
- Theoretical framework of mindfulness meditation
- Empirical research on mindfulness meditation and academic achievement
- Empirical research on mindfulness meditation and well-being
- The role of personality and demographic factors in the effects of mindfulness meditation
Chapter 3: Methodology
- Research design and hypothesis
- Participants and sampling method
- Intervention and procedure
- Measures and instruments
- Data analysis method
Chapter 4: Results
- Descriptive statistics and data screening
- Analysis of main effects
- Analysis of moderating effects
- Post-hoc analyses and sensitivity tests
Chapter 5: Discussion
- Summary of findings
- Implications for theory and practice
- Limitations and directions for future research
- Conclusion and contribution to the literature
Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Recap of the research questions and objectives
- Summary of the key findings
- Contribution to the literature and practice
- Implications for policy and practice
- Final thoughts and recommendations.
References :
List of all the sources cited in the dissertation
Appendices :
Additional materials such as the survey questionnaire, interview guide, and consent forms.
Note : This is just an example and the structure of a dissertation may vary depending on the specific requirements and guidelines provided by the institution or the supervisor.
How Long is a Dissertation
The length of a dissertation can vary depending on the field of study, the level of degree being pursued, and the specific requirements of the institution. Generally, a dissertation for a doctoral degree can range from 80,000 to 100,000 words, while a dissertation for a master’s degree may be shorter, typically ranging from 20,000 to 50,000 words. However, it is important to note that these are general guidelines and the actual length of a dissertation can vary widely depending on the specific requirements of the program and the research topic being studied. It is always best to consult with your academic advisor or the guidelines provided by your institution for more specific information on dissertation length.
Applications of Dissertation
Here are some applications of a dissertation:
- Advancing the Field: Dissertations often include new research or a new perspective on existing research, which can help to advance the field. The results of a dissertation can be used by other researchers to build upon or challenge existing knowledge, leading to further advancements in the field.
- Career Advancement: Completing a dissertation demonstrates a high level of expertise in a particular field, which can lead to career advancement opportunities. For example, having a PhD can open doors to higher-paying jobs in academia, research institutions, or the private sector.
- Publishing Opportunities: Dissertations can be published as books or journal articles, which can help to increase the visibility and credibility of the author’s research.
- Personal Growth: The process of writing a dissertation involves a significant amount of research, analysis, and critical thinking. This can help students to develop important skills, such as time management, problem-solving, and communication, which can be valuable in both their personal and professional lives.
- Policy Implications: The findings of a dissertation can have policy implications, particularly in fields such as public health, education, and social sciences. Policymakers can use the research to inform decision-making and improve outcomes for the population.
When to Write a Dissertation
Here are some situations where writing a dissertation may be necessary:
- Pursuing a Doctoral Degree: Writing a dissertation is usually a requirement for earning a doctoral degree, so if you are interested in pursuing a doctorate, you will likely need to write a dissertation.
- Conducting Original Research : Dissertations require students to conduct original research on a specific topic. If you are interested in conducting original research on a topic, writing a dissertation may be the best way to do so.
- Advancing Your Career: Some professions, such as academia and research, may require individuals to have a doctoral degree. Writing a dissertation can help you advance your career by demonstrating your expertise in a particular area.
- Contributing to Knowledge: Dissertations are often based on original research that can contribute to the knowledge base of a field. If you are passionate about advancing knowledge in a particular area, writing a dissertation can help you achieve that goal.
- Meeting Academic Requirements : If you are a graduate student, writing a dissertation may be a requirement for completing your program. Be sure to check with your academic advisor to determine if this is the case for you.
Purpose of Dissertation
some common purposes of a dissertation include:
- To contribute to the knowledge in a particular field : A dissertation is often the culmination of years of research and study, and it should make a significant contribution to the existing body of knowledge in a particular field.
- To demonstrate mastery of a subject: A dissertation requires extensive research, analysis, and writing, and completing one demonstrates a student’s mastery of their subject area.
- To develop critical thinking and research skills : A dissertation requires students to think critically about their research question, analyze data, and draw conclusions based on evidence. These skills are valuable not only in academia but also in many professional fields.
- To demonstrate academic integrity: A dissertation must be conducted and written in accordance with rigorous academic standards, including ethical considerations such as obtaining informed consent, protecting the privacy of participants, and avoiding plagiarism.
- To prepare for an academic career: Completing a dissertation is often a requirement for obtaining a PhD and pursuing a career in academia. It can demonstrate to potential employers that the student has the necessary skills and experience to conduct original research and make meaningful contributions to their field.
- To develop writing and communication skills: A dissertation requires a significant amount of writing and communication skills to convey complex ideas and research findings in a clear and concise manner. This skill set can be valuable in various professional fields.
- To demonstrate independence and initiative: A dissertation requires students to work independently and take initiative in developing their research question, designing their study, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing conclusions. This demonstrates to potential employers or academic institutions that the student is capable of independent research and taking initiative in their work.
- To contribute to policy or practice: Some dissertations may have a practical application, such as informing policy decisions or improving practices in a particular field. These dissertations can have a significant impact on society, and their findings may be used to improve the lives of individuals or communities.
- To pursue personal interests: Some students may choose to pursue a dissertation topic that aligns with their personal interests or passions, providing them with the opportunity to delve deeper into a topic that they find personally meaningful.
Advantage of Dissertation
Some advantages of writing a dissertation include:
- Developing research and analytical skills: The process of writing a dissertation involves conducting extensive research, analyzing data, and presenting findings in a clear and coherent manner. This process can help students develop important research and analytical skills that can be useful in their future careers.
- Demonstrating expertise in a subject: Writing a dissertation allows students to demonstrate their expertise in a particular subject area. It can help establish their credibility as a knowledgeable and competent professional in their field.
- Contributing to the academic community: A well-written dissertation can contribute new knowledge to the academic community and potentially inform future research in the field.
- Improving writing and communication skills : Writing a dissertation requires students to write and present their research in a clear and concise manner. This can help improve their writing and communication skills, which are essential for success in many professions.
- Increasing job opportunities: Completing a dissertation can increase job opportunities in certain fields, particularly in academia and research-based positions.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Published on August 30, 2022 by Tegan George. Revised on July 18, 2023. A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation. You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order.
The results chapter (also referred to as the findings or analysis chapter) is one of the most important chapters of your dissertation or thesis because it shows the reader what you've found in terms of the quantitative data you've collected. It presents the data using a clear text narrative, supported by tables, graphs and charts.
Data Analysis: Explain how you intend to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, thematic analysis, content analysis, etc., depending on the nature of your study. ... Writing a dissertation methodology requires you to be clear and precise about the way you've carried out your research. It's an opportunity to ...
Time to recap…. And there you have it - the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows: Title page. Acknowledgments page. Abstract (or executive summary) Table of contents, list of figures and tables.
The results chapter in a dissertation or thesis (or any formal academic research piece) is where you objectively and neutrally present the findings of your qualitative analysis (or analyses if you used multiple qualitative analysis methods ). This chapter can sometimes be combined with the discussion chapter (where you interpret the data and ...
Revised on 10 October 2022. Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
The structure of a dissertation depends on your field, but it is usually divided into at least four or five chapters (including an introduction and conclusion chapter). The most common dissertation structure in the sciences and social sciences includes: An introduction to your topic. A literature review that surveys relevant sources.
And place questionnaires, copies of focus groups and interviews, and data sheets in the appendix. On the other hand, one must put the statistical analysis and sayings quoted by interviewees within the dissertation. 8. Thoroughness of Data. It is a common misconception that the data presented is self-explanatory.
dissertation. Reason The introduction sets the stage for the study and directs readers to the purpose and context of the dissertation. Quality Markers A quality introduction situates the context and scope of the study and informs the reader, providing a clear and valid representation of what will be found in the remainder of the dissertation.
Revised on 5 May 2022. A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree. The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the ...
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
An understanding of the data analysis that you will carry out on your data can also be an expected component of the Research Strategy chapter of your dissertation write-up (i.e., usually Chapter Three: Research Strategy). Therefore, it is a good time to think about the data analysis process if you plan to start writing up this chapter at this ...
The dissertation will be structured such that it starts with an introduction, develops on the main idea in its main body paragraphs and is then summarised in conclusion. However, if you are basing your dissertation on primary or empirical research, you will be required to include each of the below components.
Table of contents. Step 1: Coming up with an idea. Step 2: Presenting your idea in the introduction. Step 3: Exploring related research in the literature review. Step 4: Describing your methodology. Step 5: Outlining the potential implications of your research. Step 6: Creating a reference list or bibliography.
In a thematic structure, the core chapters present analysis and discussion of different themes relevant to answer the research question and support the overall argument of the dissertation. The chapters will include analysis of texts/ research material. They can explore and connect academic theories/research to develop an argument.
Work a certain number of hours on your paper daily. Create a worksheet for your week. Work on your dissertation for time periods as brief as 45 minutes or less. Stick to the strategic dissertation timeline, so you don't have to do the catchup work. Meet your goals by prioritising your dissertation work.
Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations of your study. The fourth step in writing up your discussion chapter is to acknowledge the limitations of the study. These limitations can cover any part of your study, from the scope or theoretical basis to the analysis method (s) or sample.
Table of contents. What not to include in your discussion section. Step 1: Summarise your key findings. Step 2: Give your interpretations. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations. Step 5: Share your recommendations. Discussion section example.
A mixed-methods dissertation combines both quantitative and qualitative research approaches to gather and analyze data. It typically uses methods such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups, as well as statistical analysis. How to Write a Dissertation. Here are some general steps to help guide you through the process of writing a dissertation:
Semantic Scholar extracted view of "Tips to write the discussion in a thesis: From analysis to synthesis" by Mahalakshmy Thulasingam et al. Skip to search form Skip to main ... @article{Thulasingam2024TipsTW, title={Tips to write the discussion in a thesis: From analysis to synthesis}, author={Mahalakshmy Thulasingam and Kalaiselvy Arikrishnan ...