- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Summary
Definition:
A research summary is a brief and concise overview of a research project or study that highlights its key findings, main points, and conclusions. It typically includes a description of the research problem, the research methods used, the results obtained, and the implications or significance of the findings. It is often used as a tool to quickly communicate the main findings of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or decision-makers.
Structure of Research Summary
The Structure of a Research Summary typically include:
- Introduction : This section provides a brief background of the research problem or question, explains the purpose of the study, and outlines the research objectives.
- Methodology : This section explains the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study. It describes the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Results : This section presents the main findings of the study, including statistical analysis if applicable. It may include tables, charts, or graphs to visually represent the data.
- Discussion : This section interprets the results and explains their implications. It discusses the significance of the findings, compares them to previous research, and identifies any limitations or future directions for research.
- Conclusion : This section summarizes the main points of the research and provides a conclusion based on the findings. It may also suggest implications for future research or practical applications of the results.
- References : This section lists the sources cited in the research summary, following the appropriate citation style.
How to Write Research Summary
Here are the steps you can follow to write a research summary:
- Read the research article or study thoroughly: To write a summary, you must understand the research article or study you are summarizing. Therefore, read the article or study carefully to understand its purpose, research design, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Identify the main points : Once you have read the research article or study, identify the main points, key findings, and research question. You can highlight or take notes of the essential points and findings to use as a reference when writing your summary.
- Write the introduction: Start your summary by introducing the research problem, research question, and purpose of the study. Briefly explain why the research is important and its significance.
- Summarize the methodology : In this section, summarize the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study. Explain the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Present the results: Summarize the main findings of the study. Use tables, charts, or graphs to visually represent the data if necessary.
- Interpret the results: In this section, interpret the results and explain their implications. Discuss the significance of the findings, compare them to previous research, and identify any limitations or future directions for research.
- Conclude the summary : Summarize the main points of the research and provide a conclusion based on the findings. Suggest implications for future research or practical applications of the results.
- Revise and edit : Once you have written the summary, revise and edit it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors. Make sure that your summary accurately represents the research article or study.
- Add references: Include a list of references cited in the research summary, following the appropriate citation style.
Example of Research Summary
Here is an example of a research summary:
Title: The Effects of Yoga on Mental Health: A Meta-Analysis
Introduction: This meta-analysis examines the effects of yoga on mental health. The study aimed to investigate whether yoga practice can improve mental health outcomes such as anxiety, depression, stress, and quality of life.
Methodology : The study analyzed data from 14 randomized controlled trials that investigated the effects of yoga on mental health outcomes. The sample included a total of 862 participants. The yoga interventions varied in length and frequency, ranging from four to twelve weeks, with sessions lasting from 45 to 90 minutes.
Results : The meta-analysis found that yoga practice significantly improved mental health outcomes. Participants who practiced yoga showed a significant reduction in anxiety and depression symptoms, as well as stress levels. Quality of life also improved in those who practiced yoga.
Discussion : The findings of this study suggest that yoga can be an effective intervention for improving mental health outcomes. The study supports the growing body of evidence that suggests that yoga can have a positive impact on mental health. Limitations of the study include the variability of the yoga interventions, which may affect the generalizability of the findings.
Conclusion : Overall, the findings of this meta-analysis support the use of yoga as an effective intervention for improving mental health outcomes. Further research is needed to determine the optimal length and frequency of yoga interventions for different populations.
References :
- Cramer, H., Lauche, R., Langhorst, J., Dobos, G., & Berger, B. (2013). Yoga for depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Depression and anxiety, 30(11), 1068-1083.
- Khalsa, S. B. (2004). Yoga as a therapeutic intervention: a bibliometric analysis of published research studies. Indian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 48(3), 269-285.
- Ross, A., & Thomas, S. (2010). The health benefits of yoga and exercise: a review of comparison studies. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 16(1), 3-12.
Purpose of Research Summary
The purpose of a research summary is to provide a brief overview of a research project or study, including its main points, findings, and conclusions. The summary allows readers to quickly understand the essential aspects of the research without having to read the entire article or study.
Research summaries serve several purposes, including:
- Facilitating comprehension: A research summary allows readers to quickly understand the main points and findings of a research project or study without having to read the entire article or study. This makes it easier for readers to comprehend the research and its significance.
- Communicating research findings: Research summaries are often used to communicate research findings to a wider audience, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the general public. The summary presents the essential aspects of the research in a clear and concise manner, making it easier for non-experts to understand.
- Supporting decision-making: Research summaries can be used to support decision-making processes by providing a summary of the research evidence on a particular topic. This information can be used by policymakers or practitioners to make informed decisions about interventions, programs, or policies.
- Saving time: Research summaries save time for researchers, practitioners, policymakers, and other stakeholders who need to review multiple research studies. Rather than having to read the entire article or study, they can quickly review the summary to determine whether the research is relevant to their needs.
Characteristics of Research Summary
The following are some of the key characteristics of a research summary:
- Concise : A research summary should be brief and to the point, providing a clear and concise overview of the main points of the research.
- Objective : A research summary should be written in an objective tone, presenting the research findings without bias or personal opinion.
- Comprehensive : A research summary should cover all the essential aspects of the research, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research summary should accurately reflect the key findings and conclusions of the research.
- Clear and well-organized: A research summary should be easy to read and understand, with a clear structure and logical flow.
- Relevant : A research summary should focus on the most important and relevant aspects of the research, highlighting the key findings and their implications.
- Audience-specific: A research summary should be tailored to the intended audience, using language and terminology that is appropriate and accessible to the reader.
- Citations : A research summary should include citations to the original research articles or studies, allowing readers to access the full text of the research if desired.
When to write Research Summary
Here are some situations when it may be appropriate to write a research summary:
- Proposal stage: A research summary can be included in a research proposal to provide a brief overview of the research aims, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
- Conference presentation: A research summary can be prepared for a conference presentation to summarize the main findings of a study or research project.
- Journal submission: Many academic journals require authors to submit a research summary along with their research article or study. The summary provides a brief overview of the study’s main points, findings, and conclusions and helps readers quickly understand the research.
- Funding application: A research summary can be included in a funding application to provide a brief summary of the research aims, objectives, and expected outcomes.
- Policy brief: A research summary can be prepared as a policy brief to communicate research findings to policymakers or stakeholders in a concise and accessible manner.
Advantages of Research Summary
Research summaries offer several advantages, including:
- Time-saving: A research summary saves time for readers who need to understand the key findings and conclusions of a research project quickly. Rather than reading the entire research article or study, readers can quickly review the summary to determine whether the research is relevant to their needs.
- Clarity and accessibility: A research summary provides a clear and accessible overview of the research project’s main points, making it easier for readers to understand the research without having to be experts in the field.
- Improved comprehension: A research summary helps readers comprehend the research by providing a brief and focused overview of the key findings and conclusions, making it easier to understand the research and its significance.
- Enhanced communication: Research summaries can be used to communicate research findings to a wider audience, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the general public, in a concise and accessible manner.
- Facilitated decision-making: Research summaries can support decision-making processes by providing a summary of the research evidence on a particular topic. Policymakers or practitioners can use this information to make informed decisions about interventions, programs, or policies.
- Increased dissemination: Research summaries can be easily shared and disseminated, allowing research findings to reach a wider audience.
Limitations of Research Summary
Limitations of the Research Summary are as follows:
- Limited scope: Research summaries provide a brief overview of the research project’s main points, findings, and conclusions, which can be limiting. They may not include all the details, nuances, and complexities of the research that readers may need to fully understand the study’s implications.
- Risk of oversimplification: Research summaries can be oversimplified, reducing the complexity of the research and potentially distorting the findings or conclusions.
- Lack of context: Research summaries may not provide sufficient context to fully understand the research findings, such as the research background, methodology, or limitations. This may lead to misunderstandings or misinterpretations of the research.
- Possible bias: Research summaries may be biased if they selectively emphasize certain findings or conclusions over others, potentially distorting the overall picture of the research.
- Format limitations: Research summaries may be constrained by the format or length requirements, making it challenging to fully convey the research’s main points, findings, and conclusions.
- Accessibility: Research summaries may not be accessible to all readers, particularly those with limited literacy skills, visual impairments, or language barriers.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- All eBooks & Audiobooks
- Academic eBook Collection
- Home Grown eBook Collection
- Off-Campus Access
- Literature Resource Center
- Opposing Viewpoints
- ProQuest Central
- Course Guides
- Citing Sources
- Library Research
- Websites by Topic
- Book-a-Librarian
- Research Tutorials
- Use the Catalog
- Use Databases
- Use Films on Demand
- Use Home Grown eBooks
- Use NC LIVE
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Scholarly vs. Popular
- Make an Appointment
- Writing Tools
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing Center
Service Alert

Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
Writing an article summary.
- Writing an article REVIEW
- Writing an article CRITIQUE
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- About RCC Library
Text: 336-308-8801
Email: [email protected]
Call: 336-633-0204
Schedule: Book-a-Librarian
Like us on Facebook
Links on this guide may go to external web sites not connected with Randolph Community College. Their inclusion is not an endorsement by Randolph Community College and the College is not responsible for the accuracy of their content or the security of their site.
When writing a summary, the goal is to compose a concise and objective overview of the original article. The summary should focus only on the article's main ideas and important details that support those ideas.
Guidelines for summarizing an article:
- State the main ideas.
- Identify the most important details that support the main ideas.
- Summarize in your own words.
- Do not copy phrases or sentences unless they are being used as direct quotations.
- Express the underlying meaning of the article, but do not critique or analyze.
- The summary should be about one third the length of the original article.
Your summary should include:
- Give an overview of the article, including the title and the name of the author.
- Provide a thesis statement that states the main idea of the article.
- Use the body paragraphs to explain the supporting ideas of your thesis statement.
- One-paragraph summary - one sentence per supporting detail, providing 1-2 examples for each.
- Multi-paragraph summary - one paragraph per supporting detail, providing 2-3 examples for each.
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence.
- Use transitional words and phrases to connect ideas.
- Summarize your thesis statement and the underlying meaning of the article.
Adapted from "Guidelines for Using In-Text Citations in a Summary (or Research Paper)" by Christine Bauer-Ramazani, 2020
Additional Resources
All links open in a new window.
How to Write a Summary - Guide & Examples (from Scribbr.com)
Writing a Summary (from The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center)
- Next: Writing an article REVIEW >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.randolph.edu/summaries
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How to Write a Summary — Researcher's Guide

Table of Contents
Writing a summary can be a bit challenging if you're not familiar with the process. Thankfully, by following a few key steps, you can master the art of writing a summary effectively. In this article, we will explore the essential elements of summary writing, from understanding the basics to editing and proofreading your work. So, let's dive in and learn how to write a summary that captures the essence of your source material while keeping it concise and readable.
What is a Summary in research?
A summary is a condensed version of a longer text that captures its main points and ideas. It should provide a clear overview without getting into excessive detail. By understanding this foundational concept, you can effectively navigate the process of summary writing.
Now, there are several strategies you can follow to get an effective summary. Let’s dive into some of them.
Identify the Key Points of Your Source Material
To create an accurate summary, you must identify and extract the key points from your source material. This involves thorough reading or reviewing the text and highlighting the most important information. By doing so, you'll be able to effectively convey the main ideas and arguments in your summary.
One effective way to identify the key points is to read the source material multiple times. As you read, make sure to highlight or underline the sentences or paragraphs that stand out to you. These are likely to contain the most significant information. You can use AI research assistants to read and understand your source materials which saves plenty of your reading time.
Another helpful strategy is to take notes while reading. Jot down the main ideas and arguments as you encounter them. This not only helps you remember the key points but also allows you to organize your thoughts and structure your summary effectively.
Additionally, pay attention to any headings or subheadings in the source material. These can often indicate important sections or topics that should be included in your summary.
It's important to remember that summarizing is not about copying and pasting sentences from the source material. Instead, it involves condensing the information and presenting it in your own words. This requires a thorough understanding of the key points and the ability to express them concisely. Once you have identified the key points, you can begin crafting your summary.
Choose Your Words Carefully
When writing a summary, every word counts. It is essential to choose your words carefully to convey the message accurately. Aim for concise and clear language without sacrificing important details. By utilizing precise vocabulary and avoiding unnecessary jargon, you can ensure that your summary accurately represents the original text.
One important aspect to consider when choosing your words is the intended audience . Are you summarizing a scientific article for a group of experts in the field, or are you summarizing a news article for a general audience? Tailoring your language to suit the needs and understanding of your readers is crucial in effectively conveying your message.
Another factor to keep in mind is the tone of the original text. Is it formal and academic, or is it more conversational and informal? Adapting your language to match the tone of the original text can help maintain the intended meaning and style.
Furthermore, it is essential to pay attention to the context of the original text. Understanding the background and purpose of the work can provide valuable insights into how to summarize it effectively. By considering the broader context, you can ensure that your summary captures the main ideas and key points without omitting crucial information.
Additionally, when choosing your words, it is crucial to avoid personal biases or interpretations. A summary should present an objective overview of the original text, focusing on the author's ideas rather than your own opinions. By remaining impartial and objective, you can provide a fair and accurate representation of the message. While brevity is important, it is equally crucial to include enough information.
Moreover, a well-crafted summary should include the most significant details and ideas to provide a comprehensive understanding of your research work. Selecting the most relevant and impactful details will help readers grasp the main points without getting lost in unnecessary information.
Create an Outline Before Writing
Organizing your thoughts before you begin writing can significantly enhance the quality of your summary. Create a clear outline that follows the structure of your source material. By logically dividing your summary into sections, you'll ensure a coherent flow and make it easier for your readers to follow along.
Keep Your Summary Concise
A summary should capture the essence of the original text without unnecessary elaboration. Aim to condense the information into its most crucial points, omitting extraneous details. Keep your sentences clear and to the point, maintaining a concise and focused writing style.
Use the Right Tone and Voice
The tone and voice of your summary should match the original source material. Take note of the style from the source and reflect it in your writing. Whether the source material is formal or informal, academic or creative, ensuring consistency in tone and voice is key to an effective summary.
Check for Clarity and Readability
After completing your summary, take the time to review it for clarity and readability. Ensure that your sentences flow smoothly, providing a seamless reading experience. Pay attention to grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure, as these elements contribute to the overall clarity of your summary.
Make Sure You Include All the Important Points
While summarizing, it's vital to include all the necessary information. Double-check your summary against the source material to ensure that you haven't overlooked any important points. By capturing the essence of the original text accurately, you'll provide your readers with a comprehensive overview.
Edit and Proofread Your Summary
Before finalizing your summary, always take the time to edit and proofread. Trim down any unnecessary words or phrases and refine your sentences for clarity and conciseness. Additionally, check for spelling and grammatical errors. By investing effort into this final step, you'll ensure your summary is polished and professional.
Tips for Writing an Effective Summary
Lastly, here are some essential tips to keep in mind as you embark on your summary-writing journey:
- Focus on conveying the central theme and main points.
- Avoid personal opinions or interpretations.
- Use your own words while faithfully representing the source material.
- Read aloud your summary to ensure clarity and coherence.
- Seek feedback from peers or mentors to improve your summarizing skills.
By incorporating these tips into your summary-writing process, you'll be well-equipped to create an effective summary that captures the essence of your source material.
In conclusion
Writing a summary requires an understanding of the basics, careful word choice, and a concise writing style. By following the steps outlined in this article and utilizing the provided tips, you can develop the necessary skills to write a good research summary.
You might also like

AI for Meta-Analysis — A Comprehensive Guide

How To Write An Argumentative Essay

Beyond Google Scholar: Why SciSpace is the best alternative
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Surveys Academic Research
Research Summary: What is it & how to write one

The Research Summary is used to report facts about a study clearly. You will almost certainly be required to prepare a research summary during your academic research or while on a research project for your organization.
If it is the first time you have to write one, the writing requirements may confuse you. The instructors generally assign someone to write a summary of the research work. Research summaries require the writer to have a thorough understanding of the issue.
This article will discuss the definition of a research summary and how to write one.
What is a research summary?
A research summary is a piece of writing that summarizes your research on a specific topic. Its primary goal is to offer the reader a detailed overview of the study with the key findings. A research summary generally contains the article’s structure in which it is written.
You must know the goal of your analysis before you launch a project. A research overview summarizes the detailed response and highlights particular issues raised in it. Writing it might be somewhat troublesome. To write a good overview, you want to start with a structure in mind. Read on for our guide.
Why is an analysis recap so important?
Your summary or analysis is going to tell readers everything about your research project. This is the critical piece that your stakeholders will read to identify your findings and valuable insights. Having a good and concise research summary that presents facts and comes with no research biases is the critical deliverable of any research project.
We’ve put together a cheat sheet to help you write a good research summary below.
Research Summary Guide
- Why was this research done? – You want to give a clear description of why this research study was done. What hypothesis was being tested?
- Who was surveyed? – The what and why or your research decides who you’re going to interview/survey. Your research summary has a detailed note on who participated in the study and why they were selected.
- What was the methodology? – Talk about the methodology. Did you do face-to-face interviews? Was it a short or long survey or a focus group setting? Your research methodology is key to the results you’re going to get.
- What were the key findings? – This can be the most critical part of the process. What did we find out after testing the hypothesis? This section, like all others, should be just facts, facts facts. You’re not sharing how you feel about the findings. Keep it bias-free.
- Conclusion – What are the conclusions that were drawn from the findings. A good example of a conclusion. Surprisingly, most people interviewed did not watch the lunar eclipse in 2022, which is unexpected given that 100% of those interviewed knew about it before it happened.
- Takeaways and action points – This is where you bring in your suggestion. Given the data you now have from the research, what are the takeaways and action points? If you’re a researcher running this research project for your company, you’ll use this part to shed light on your recommended action plans for the business.
LEARN ABOUT: Action Research
If you’re doing any research, you will write a summary, which will be the most viewed and more important part of the project. So keep a guideline in mind before you start. Focus on the content first and then worry about the length. Use the cheat sheet/checklist in this article to organize your summary, and that’s all you need to write a great research summary!
But once your summary is ready, where is it stored? Most teams have multiple documents in their google drives, and it’s a nightmare to find projects that were done in the past. Your research data should be democratized and easy to use.
We at QuestionPro launched a research repository for research teams, and our clients love it. All your data is in one place, and everything is searchable, including your research summaries!
Authors: Prachi, Anas
MORE LIKE THIS

QuestionPro BI: From Research Data to Actionable Dashboards
Apr 22, 2024

21 Best Customer Advocacy Software for Customers in 2024
Apr 19, 2024

10 Quantitative Data Analysis Software for Every Data Scientist
Apr 18, 2024

11 Best Enterprise Feedback Management Software in 2024
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 4. The Introduction
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly the methodological approach used to examine the research problem, highlighting the potential outcomes your study can reveal, and outlining the remaining structure and organization of the paper.
Key Elements of the Research Proposal. Prepared under the direction of the Superintendent and by the 2010 Curriculum Design and Writing Team. Baltimore County Public Schools.
Importance of a Good Introduction
Think of the introduction as a mental road map that must answer for the reader these four questions:
- What was I studying?
- Why was this topic important to investigate?
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study?
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding?
According to Reyes, there are three overarching goals of a good introduction: 1) ensure that you summarize prior studies about the topic in a manner that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem; 2) explain how your study specifically addresses gaps in the literature, insufficient consideration of the topic, or other deficiency in the literature; and, 3) note the broader theoretical, empirical, and/or policy contributions and implications of your research.
A well-written introduction is important because, quite simply, you never get a second chance to make a good first impression. The opening paragraphs of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions about the logic of your argument, your writing style, the overall quality of your research, and, ultimately, the validity of your findings and conclusions. A vague, disorganized, or error-filled introduction will create a negative impression, whereas, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will lead your readers to think highly of your analytical skills, your writing style, and your research approach. All introductions should conclude with a brief paragraph that describes the organization of the rest of the paper.
Hirano, Eliana. “Research Article Introductions in English for Specific Purposes: A Comparison between Brazilian, Portuguese, and English.” English for Specific Purposes 28 (October 2009): 240-250; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide. Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article. Inside Higher Education.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Structure and Approach
The introduction is the broad beginning of the paper that answers three important questions for the reader:
- What is this?
- Why should I read it?
- What do you want me to think about / consider doing / react to?
Think of the structure of the introduction as an inverted triangle of information that lays a foundation for understanding the research problem. Organize the information so as to present the more general aspects of the topic early in the introduction, then narrow your analysis to more specific topical information that provides context, finally arriving at your research problem and the rationale for studying it [often written as a series of key questions to be addressed or framed as a hypothesis or set of assumptions to be tested] and, whenever possible, a description of the potential outcomes your study can reveal.
These are general phases associated with writing an introduction: 1. Establish an area to research by:
- Highlighting the importance of the topic, and/or
- Making general statements about the topic, and/or
- Presenting an overview on current research on the subject.
2. Identify a research niche by:
- Opposing an existing assumption, and/or
- Revealing a gap in existing research, and/or
- Formulating a research question or problem, and/or
- Continuing a disciplinary tradition.
3. Place your research within the research niche by:
- Stating the intent of your study,
- Outlining the key characteristics of your study,
- Describing important results, and
- Giving a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
NOTE: It is often useful to review the introduction late in the writing process. This is appropriate because outcomes are unknown until you've completed the study. After you complete writing the body of the paper, go back and review introductory descriptions of the structure of the paper, the method of data gathering, the reporting and analysis of results, and the conclusion. Reviewing and, if necessary, rewriting the introduction ensures that it correctly matches the overall structure of your final paper.
II. Delimitations of the Study
Delimitations refer to those characteristics that limit the scope and define the conceptual boundaries of your research . This is determined by the conscious exclusionary and inclusionary decisions you make about how to investigate the research problem. In other words, not only should you tell the reader what it is you are studying and why, but you must also acknowledge why you rejected alternative approaches that could have been used to examine the topic.
Obviously, the first limiting step was the choice of research problem itself. However, implicit are other, related problems that could have been chosen but were rejected. These should be noted in the conclusion of your introduction. For example, a delimitating statement could read, "Although many factors can be understood to impact the likelihood young people will vote, this study will focus on socioeconomic factors related to the need to work full-time while in school." The point is not to document every possible delimiting factor, but to highlight why previously researched issues related to the topic were not addressed.
Examples of delimitating choices would be:
- The key aims and objectives of your study,
- The research questions that you address,
- The variables of interest [i.e., the various factors and features of the phenomenon being studied],
- The method(s) of investigation,
- The time period your study covers, and
- Any relevant alternative theoretical frameworks that could have been adopted.
Review each of these decisions. Not only do you clearly establish what you intend to accomplish in your research, but you should also include a declaration of what the study does not intend to cover. In the latter case, your exclusionary decisions should be based upon criteria understood as, "not interesting"; "not directly relevant"; “too problematic because..."; "not feasible," and the like. Make this reasoning explicit!
NOTE: Delimitations refer to the initial choices made about the broader, overall design of your study and should not be confused with documenting the limitations of your study discovered after the research has been completed.
ANOTHER NOTE : Do not view delimitating statements as admitting to an inherent failing or shortcoming in your research. They are an accepted element of academic writing intended to keep the reader focused on the research problem by explicitly defining the conceptual boundaries and scope of your study. It addresses any critical questions in the reader's mind of, "Why the hell didn't the author examine this?"
III. The Narrative Flow
Issues to keep in mind that will help the narrative flow in your introduction :
- Your introduction should clearly identify the subject area of interest . A simple strategy to follow is to use key words from your title in the first few sentences of the introduction. This will help focus the introduction on the topic at the appropriate level and ensures that you get to the subject matter quickly without losing focus, or discussing information that is too general.
- Establish context by providing a brief and balanced review of the pertinent published literature that is available on the subject. The key is to summarize for the reader what is known about the specific research problem before you did your analysis. This part of your introduction should not represent a comprehensive literature review--that comes next. It consists of a general review of the important, foundational research literature [with citations] that establishes a foundation for understanding key elements of the research problem. See the drop-down menu under this tab for " Background Information " regarding types of contexts.
- Clearly state the hypothesis that you investigated . When you are first learning to write in this format it is okay, and actually preferable, to use a past statement like, "The purpose of this study was to...." or "We investigated three possible mechanisms to explain the...."
- Why did you choose this kind of research study or design? Provide a clear statement of the rationale for your approach to the problem studied. This will usually follow your statement of purpose in the last paragraph of the introduction.
IV. Engaging the Reader
A research problem in the social sciences can come across as dry and uninteresting to anyone unfamiliar with the topic . Therefore, one of the goals of your introduction is to make readers want to read your paper. Here are several strategies you can use to grab the reader's attention:
- Open with a compelling story . Almost all research problems in the social sciences, no matter how obscure or esoteric , are really about the lives of people. Telling a story that humanizes an issue can help illuminate the significance of the problem and help the reader empathize with those affected by the condition being studied.
- Include a strong quotation or a vivid, perhaps unexpected, anecdote . During your review of the literature, make note of any quotes or anecdotes that grab your attention because they can used in your introduction to highlight the research problem in a captivating way.
- Pose a provocative or thought-provoking question . Your research problem should be framed by a set of questions to be addressed or hypotheses to be tested. However, a provocative question can be presented in the beginning of your introduction that challenges an existing assumption or compels the reader to consider an alternative viewpoint that helps establish the significance of your study.
- Describe a puzzling scenario or incongruity . This involves highlighting an interesting quandary concerning the research problem or describing contradictory findings from prior studies about a topic. Posing what is essentially an unresolved intellectual riddle about the problem can engage the reader's interest in the study.
- Cite a stirring example or case study that illustrates why the research problem is important . Draw upon the findings of others to demonstrate the significance of the problem and to describe how your study builds upon or offers alternatives ways of investigating this prior research.
NOTE: It is important that you choose only one of the suggested strategies for engaging your readers. This avoids giving an impression that your paper is more flash than substance and does not distract from the substance of your study.
Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Introduction. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Introductions. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Introductions, Body Paragraphs, and Conclusions for an Argument Paper. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70; Resources for Writers: Introduction Strategies. Program in Writing and Humanistic Studies. Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Sharpling, Gerald. Writing an Introduction. Centre for Applied Linguistics, University of Warwick; Samraj, B. “Introductions in Research Articles: Variations Across Disciplines.” English for Specific Purposes 21 (2002): 1–17; Swales, John and Christine B. Feak. Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Skills and Tasks . 2nd edition. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2004 ; Writing Your Introduction. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University.
Writing Tip
Avoid the "Dictionary" Introduction
Giving the dictionary definition of words related to the research problem may appear appropriate because it is important to define specific terminology that readers may be unfamiliar with. However, anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and a general dictionary is not a particularly authoritative source because it doesn't take into account the context of your topic and doesn't offer particularly detailed information. Also, placed in the context of a particular discipline, a term or concept may have a different meaning than what is found in a general dictionary. If you feel that you must seek out an authoritative definition, use a subject specific dictionary or encyclopedia [e.g., if you are a sociology student, search for dictionaries of sociology]. A good database for obtaining definitive definitions of concepts or terms is Credo Reference .
Saba, Robert. The College Research Paper. Florida International University; Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
Another Writing Tip
When Do I Begin?
A common question asked at the start of any paper is, "Where should I begin?" An equally important question to ask yourself is, "When do I begin?" Research problems in the social sciences rarely rest in isolation from history. Therefore, it is important to lay a foundation for understanding the historical context underpinning the research problem. However, this information should be brief and succinct and begin at a point in time that illustrates the study's overall importance. For example, a study that investigates coffee cultivation and export in West Africa as a key stimulus for local economic growth needs to describe the beginning of exporting coffee in the region and establishing why economic growth is important. You do not need to give a long historical explanation about coffee exports in Africa. If a research problem requires a substantial exploration of the historical context, do this in the literature review section. In your introduction, make note of this as part of the "roadmap" [see below] that you use to describe the organization of your paper.
Introductions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; “Writing Introductions.” In Good Essay Writing: A Social Sciences Guide . Peter Redman. 4th edition. (London: Sage, 2011), pp. 63-70.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Always End with a Roadmap
The final paragraph or sentences of your introduction should forecast your main arguments and conclusions and provide a brief description of the rest of the paper [the "roadmap"] that let's the reader know where you are going and what to expect. A roadmap is important because it helps the reader place the research problem within the context of their own perspectives about the topic. In addition, concluding your introduction with an explicit roadmap tells the reader that you have a clear understanding of the structural purpose of your paper. In this way, the roadmap acts as a type of promise to yourself and to your readers that you will follow a consistent and coherent approach to addressing the topic of inquiry. Refer to it often to help keep your writing focused and organized.
Cassuto, Leonard. “On the Dissertation: How to Write the Introduction.” The Chronicle of Higher Education , May 28, 2018; Radich, Michael. A Student's Guide to Writing in East Asian Studies . (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Writing n. d.), pp. 35-37.
- << Previous: Executive Summary
- Next: The C.A.R.S. Model >>
- Last Updated: Apr 22, 2024 9:12 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
How to Write a Peer Review

When you write a peer review for a manuscript, what should you include in your comments? What should you leave out? And how should the review be formatted?
This guide provides quick tips for writing and organizing your reviewer report.
Review Outline
Use an outline for your reviewer report so it’s easy for the editors and author to follow. This will also help you keep your comments organized.
Think about structuring your review like an inverted pyramid. Put the most important information at the top, followed by details and examples in the center, and any additional points at the very bottom.
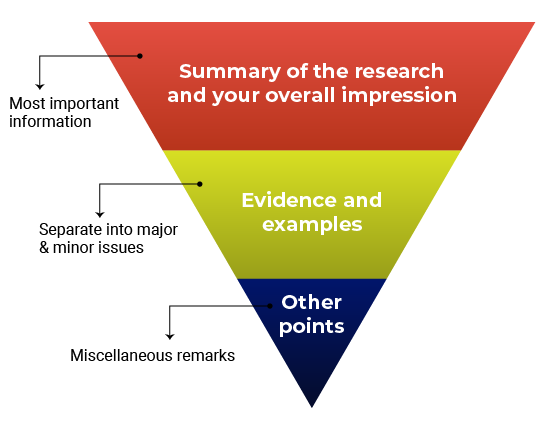
Here’s how your outline might look:
1. Summary of the research and your overall impression
In your own words, summarize what the manuscript claims to report. This shows the editor how you interpreted the manuscript and will highlight any major differences in perspective between you and the other reviewers. Give an overview of the manuscript’s strengths and weaknesses. Think about this as your “take-home” message for the editors. End this section with your recommended course of action.
2. Discussion of specific areas for improvement
It’s helpful to divide this section into two parts: one for major issues and one for minor issues. Within each section, you can talk about the biggest issues first or go systematically figure-by-figure or claim-by-claim. Number each item so that your points are easy to follow (this will also make it easier for the authors to respond to each point). Refer to specific lines, pages, sections, or figure and table numbers so the authors (and editors) know exactly what you’re talking about.
Major vs. minor issues
What’s the difference between a major and minor issue? Major issues should consist of the essential points the authors need to address before the manuscript can proceed. Make sure you focus on what is fundamental for the current study . In other words, it’s not helpful to recommend additional work that would be considered the “next step” in the study. Minor issues are still important but typically will not affect the overall conclusions of the manuscript. Here are some examples of what would might go in the “minor” category:
- Missing references (but depending on what is missing, this could also be a major issue)
- Technical clarifications (e.g., the authors should clarify how a reagent works)
- Data presentation (e.g., the authors should present p-values differently)
- Typos, spelling, grammar, and phrasing issues
3. Any other points
Confidential comments for the editors.
Some journals have a space for reviewers to enter confidential comments about the manuscript. Use this space to mention concerns about the submission that you’d want the editors to consider before sharing your feedback with the authors, such as concerns about ethical guidelines or language quality. Any serious issues should be raised directly and immediately with the journal as well.
This section is also where you will disclose any potentially competing interests, and mention whether you’re willing to look at a revised version of the manuscript.
Do not use this space to critique the manuscript, since comments entered here will not be passed along to the authors. If you’re not sure what should go in the confidential comments, read the reviewer instructions or check with the journal first before submitting your review. If you are reviewing for a journal that does not offer a space for confidential comments, consider writing to the editorial office directly with your concerns.
Get this outline in a template
Giving Feedback
Giving feedback is hard. Giving effective feedback can be even more challenging. Remember that your ultimate goal is to discuss what the authors would need to do in order to qualify for publication. The point is not to nitpick every piece of the manuscript. Your focus should be on providing constructive and critical feedback that the authors can use to improve their study.
If you’ve ever had your own work reviewed, you already know that it’s not always easy to receive feedback. Follow the golden rule: Write the type of review you’d want to receive if you were the author. Even if you decide not to identify yourself in the review, you should write comments that you would be comfortable signing your name to.
In your comments, use phrases like “ the authors’ discussion of X” instead of “ your discussion of X .” This will depersonalize the feedback and keep the focus on the manuscript instead of the authors.
General guidelines for effective feedback

- Justify your recommendation with concrete evidence and specific examples.
- Be specific so the authors know what they need to do to improve.
- Be thorough. This might be the only time you read the manuscript.
- Be professional and respectful. The authors will be reading these comments too.
- Remember to say what you liked about the manuscript!

Don’t
- Recommend additional experiments or unnecessary elements that are out of scope for the study or for the journal criteria.
- Tell the authors exactly how to revise their manuscript—you don’t need to do their work for them.
- Use the review to promote your own research or hypotheses.
- Focus on typos and grammar. If the manuscript needs significant editing for language and writing quality, just mention this in your comments.
- Submit your review without proofreading it and checking everything one more time.
Before and After: Sample Reviewer Comments
Keeping in mind the guidelines above, how do you put your thoughts into words? Here are some sample “before” and “after” reviewer comments
✗ Before
“The authors appear to have no idea what they are talking about. I don’t think they have read any of the literature on this topic.”
✓ After
“The study fails to address how the findings relate to previous research in this area. The authors should rewrite their Introduction and Discussion to reference the related literature, especially recently published work such as Darwin et al.”
“The writing is so bad, it is practically unreadable. I could barely bring myself to finish it.”
“While the study appears to be sound, the language is unclear, making it difficult to follow. I advise the authors work with a writing coach or copyeditor to improve the flow and readability of the text.”
“It’s obvious that this type of experiment should have been included. I have no idea why the authors didn’t use it. This is a big mistake.”
“The authors are off to a good start, however, this study requires additional experiments, particularly [type of experiment]. Alternatively, the authors should include more information that clarifies and justifies their choice of methods.”
Suggested Language for Tricky Situations
You might find yourself in a situation where you’re not sure how to explain the problem or provide feedback in a constructive and respectful way. Here is some suggested language for common issues you might experience.
What you think : The manuscript is fatally flawed. What you could say: “The study does not appear to be sound” or “the authors have missed something crucial”.
What you think : You don’t completely understand the manuscript. What you could say : “The authors should clarify the following sections to avoid confusion…”
What you think : The technical details don’t make sense. What you could say : “The technical details should be expanded and clarified to ensure that readers understand exactly what the researchers studied.”
What you think: The writing is terrible. What you could say : “The authors should revise the language to improve readability.”
What you think : The authors have over-interpreted the findings. What you could say : “The authors aim to demonstrate [XYZ], however, the data does not fully support this conclusion. Specifically…”

What does a good review look like?
Check out the peer review examples at F1000 Research to see how other reviewers write up their reports and give constructive feedback to authors.
Time to Submit the Review!
Be sure you turn in your report on time. Need an extension? Tell the journal so that they know what to expect. If you need a lot of extra time, the journal might need to contact other reviewers or notify the author about the delay.
Tip: Building a relationship with an editor
You’ll be more likely to be asked to review again if you provide high-quality feedback and if you turn in the review on time. Especially if it’s your first review for a journal, it’s important to show that you are reliable. Prove yourself once and you’ll get asked to review again!
- Getting started as a reviewer
- Responding to an invitation
- Reading a manuscript
- Writing a peer review
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
how to write a summary
A step-by-step guide to writing a great summary.
A summary of a literary work isn't just a plain-old synopsis. It's a valuable study tool, a foundational element of all kinds of essays, a common testing mechanism, and one of the basics of literary analysis.
Whether you're in high school or college, developing a deep understanding of how and when to summarize a book or text is a valuable skill. Doing so might require a little more knowledge and effort than you'd think.
That's why we're covering all aspects of summaries, from study tools to plot summaries, below.
What Is a Summary?
A summary is a brief overview of a text (or movie, speech, podcast, etcetera) that succinctly and comprehensively covers the main ideas or plot points.
Sounds simple, right? Well, there are a lot of unique characteristics that differentiate summaries from other commentary, such as analyses, book reviews, or outlines.
Summaries are:
- In your own words. It's important that you don't just copy and paste the writer's words (in fact, that's plagiarizing). Writing the key points of a work in your own words indicates your comprehension and absorption of the material.
- Objective. While a summary should be in your own words, it shouldn't contain your opinions. Instead, you should gather the main points and intentions of the writer and present them impartially. (If you include your opinions, it instead becomes an analysis or review.)
- More than paraphrasing. Many students fall into the trap of simply paraphrasing—plainly restating the ideas or events of the work. (Is our definition starting to sound contradictory? We told you it wasn't straightforward!) Rather than recounting the events or ideas in a work chronologically or in the order they're presented, instead consider the broad scope of how they all contribute to the narrative or argument.
- Short. There are no strict rules regarding length, only that it is concise. It's largely dependent on the length of the text it summarizes: longer texts, longer summaries. It also depends on the assignment or objective. However, most are about one to two paragraphs in length.
- Comprehensive. Yes, it's another seemingly contradictory descriptor, but an important one. Summaries are comprehensive, meaning they cover all of the main plot points or ideas in a work (so they inherently contain "spoilers"). You should present those ideas in a way that condenses them into an inclusive, but not exhaustive, recounting in order to keep it short.
- Straightforward (even if the text isn't). A good summary should be easy to comprehend, presenting the reader with a simple but all-encompassing understanding of the work at hand. With complex texts, summaries can be particularly useful because they distill big, complicated ideas into a bite-sized package.
When to Write a Summary
Like so many elements of literary analysis, summaries are misunderstood. We've already explained why they aren't as simple as most people think, but neither are their uses.
Summary writing is a useful skill in a variety of circumstances, both in and outside the English and Language Arts classrooms.
Readers, writers, teachers, and students can use summaries:
- As a study tactic. The ability to summarize a book or text indicates that you've absorbed and understand the material. Plus, writing down notes (as in a summary) is a great way to retain material. Try summarizing at the end of a book chapter, after each section of an article, or periodically in textbooks. Doing so will help you digest the material you've just read, confirming you understood and retained the information therein. Stopping frequently to summarize is most effective because you're less likely to forget important plot points or ideas.
- As an assignment. Teachers and professors often ask students to summarize a text as a test to confirm they read and understood the material. Before heading into class—especially if you have a test or quiz scheduled—try practicing summarizing the text. Write it down (rather than practicing it out loud or in your head) so that you can review your ideas and ensure you're presenting them succinctly and sensibly.
- As part of an essay. If you're referencing a book or article in your own paper, you might need to summarize the source as the foundation for your argument. In this case, your summary should be particularly short so the reader doesn't lose sight of your own argument and intention. Introduce the name of the work and its author, then use one sentence (two at most) to describe their objective and how it relates to your own.
- As part of a review. Summaries are very useful in an academic setting, but they have their place outside of it too. Whether you're on a book review site or just sharing a recommendation with a friend, being able to succinctly write a book summary (with or without spoilers) will help others to make their own judgements of a book.
Your Step-by-Step Guide for How to Write a Summary
Step 1: read the work .
Summaries are often perceived as a workaround for reading the work itself. That's not a great strategy under most circumstances because you tend to lose a lot of the details and nuance of a work, but it's particularly impractical to do so when writing about the work.
Remember, a summary is supposed to present your perception of the work as a whole. So in order to develop that perception, you have to first read the original text.
Step 2: Take Notes
As you read the work, simultaneously take notes. If you own the book, it might be helpful to add your notes to the margins or highlight passages that are particularly relevant or capture a key idea. If you don't own the book, try taking notes on your computer or in a notebook. You can still notate important passages by writing down the page and paragraph number or writing an abbreviated version of the quotation. Alternatively, try marking key passages with sticky notes or tabs.
It might also be helpful to write out a short outline of the work as you go. While you won't want to use this verbatim (remember, you shouldn't just paraphrase the work), it can help you establish and remember the text's framework.
Step 3: Identify the Author's Thesis Statement, Objective, or Main Point
In some works, such as a journal article, a writer will provide a thesis statement. A thesis statement is a one-sentence synopsis of the author's argument and intention. A thesis statement can be really helpful in forming the backbone of your own summary, just as it forms the backbone of the essay.
However, even when a thesis statement isn't present—like in a novel—the writer always has an objective or main idea. You should always identify this idea and use it to form the foundation of your summary.
The main point might be apparent at the outset of the work. Other times, the author won't present it until the conclusion. Sometimes you might identify multiple objectives throughout the work. That's why it's important, as you read, to note any ideas that might be the main idea. Even those that aren't the most important will likely remain relevant.
Step 4: Note Other Important Elements
If something stands out to you about the work and seems to play an important role in the text's overall narrative or structure, make a note about it. This could be a recurring theme, an incident in the storyline, or a deviation from the overall argument.
As you identify and note important elements and moments in the work, the structure of your summary should begin to fall into place.
Step 5: Prepare to Write Your Summary
Once you've finished reading the work, review your notes and highlight the key points that came to light. Remember, your summary should be objective, so disregard any opinions you might have noted about the work. You should introduce the thesis or objective, briefly encapsulate the important ideas and moments from the work, and end with a conclusion that ties those ideas to the objective. Keep this structure in mind as you begin.
Step 6: Begin by Introducing the Work
As you begin, introduce the work, its author, and, if relevant, the context.
Depending on your situation—for example, if your teacher or professor has asked you to summarize a work as part of an assignment or quiz—this might seem redundant. However, it is standard practice to begin by introducing the work, even if the reader already knows what you're writing about.
Example: In The Great Gatsby , F. Scott Fitzgerald...
Step 7: Present the Thesis, Main Idea, or Central Argument
Once you've introduced the work, your priority is to clearly define the author's thesis, important point, or central argument. As mentioned above, sometimes the author presents this idea clearly and succinctly at the outset of their work; at other times, it's buried deep in the text.
Regardless of how the main idea is presented in the work, it should be front and center in your summary. Some teachers might refer to this as a "topic sentence" or "introductory sentence." This is the central point around which you will construct the rest of your writing. As you progress, you'll highlight other ideas or occurrences that relate or contribute to this main idea, so it's important that your representation of it is easily understood.
Example: In The Great Gatsby , F. Scott Fitzgerald uses the story of Jay Gatsby as a symbol of the social stratification, greed, and indulgence of 1920s America.
Step 8: Briefly Discuss the Important Elements of the Work
After identifying the thesis or central argument, you should provide a brief overview of the work's other elements, ideas, and plot points. For the most part, the information you present throughout this section should bolster the thesis presented previously. Each sentence should serve as a supporting point for the topic sentence. Don't simply list ideas or plot points, but show how they're connected and inform the work as a whole. Of course, there may also be important elements of the work that are not directly tied to the main idea; it's ok to include these if you feel they are vital to understanding the work.
When writing the body, you should consciously and intentionally leave out unnecessary details. They tend to bog down your writing and lose the reader.
Example: The narrator, Nick Carraway, moves to New York's "West Egg," where he reunites with his cousin, Daisy, and her husband, Tom Buchanan. Fitzgerald clearly delineates social lines between West Egg (new money) and East Egg (old money), where Tom and Daisy reside.
Nick attends a lavish party thrown by his neighbor, Jay Gatsby, and learns Jay formerly had a relationship with Daisy. The two reignite their forbidden affair. Tom reveals to Daisy that Gatsby earned his money illegally, through smuggling alcohol, and is actually a man of humble Midwestern origins. Daisy and Gatsby try to run away together, but Daisy accidentally runs over Tom's mistress. Tom, eager to exact revenge, convinces his mistress' husband that Gatsby was to blame in her death, and he murders Gatsby before committing suicide. Few of Gatsby's many friends attend his funeral.
Step 9: Write a Conclusion that Ties It All Together
Much like you introduce the author's major point at the outset of your summary, you should revisit it as you close out your writing. If you presented the author's main idea in the introduction, and then bolstered that main idea by recollecting plot points or important elements from the work, your conclusion should then reiterate how those elements relate to the main idea.
Example: Though Gatsby subscribed to the extravagance of his peers, his efforts to fit into the upper echelon of West and East Egg were negated by his humble origins; always out of place, he was rejected for his social class as much as his perceived crimes.
Step 10: Edit
Before submitting your work, read it in full, and edit out any superfluous and redundant information. It's likely that unnecessary details snuck in as you were writing, and you might find that certain plot points just feel unnecessary within the scope of your finished product.
In addition to editing for content, be sure to edit it closely for grammatical or spelling errors. Even if your summary is well thought out, its expertise is compromised if it's full of errors!
How to Write a Plot Summary
The step-by-step guide to writing an effective summary, outlined above, applies to most summaries. However, each type has its own unique elements outside of those standard requirements.
A plot or book summary, for example, should encapsulate the plot of a short story or novel. When writing one, there are unique strategies to follow.
Dos of Writing a Plot Summary
- Note plot points as the book or story unfolds. Especially in longer novels, it can be difficult to keep track of the twists and turns in the storyline. That's why we recommend taking notes as you read.
- Use online study guides for inspiration. Websites like SuperSummary provide in-depth summaries free of charge. While this is a good starting point when writing your own, it should only be for inspiration. Don't copy examples online (that's plagiarism!).
- Be sure to cover the three main arcs of every story: the exposition, climax, and conclusion. The exposition is the moment when the conflict or driving narrative is introduced. The climax is when that conflict comes to a head, and the narrative reaches its most dramatic moments. The conclusion is when the conflict is resolved or the story comes to an end. You should also include any inciting incidents (the first domino in a plot point).
- Connect the dots. Throughout, you should demonstrate an understanding of how events and characters are related, rather than introducing each element as an independent variable. Remember, you should tie each plot point back to the main idea.
Don'ts of Writing a Plot Summary
- Don't just regurgitate the storyline. Rather than drone through the story plot point by plot point, you should highlight key moments in the narrative and direct them back to the author's objective.
- Avoid repetitive phrases like "then" or "next." A key indication you're just repeating the storyline point by point is utilizing a phrase like "then" or "next." While you should recount the major incidents of the narrative, it shouldn't feel so formulaic.
- Don't let it drag on. Books are long, but summarizing a book should still be short. While it depends on the assignment and the work in question, your summary should be 200 to 600 words, max.
Example : In The Great Gatsby , F. Scott Fitzgerald uses the story of Jay Gatsby as a symbol of the social stratification, greed, and indulgence of 1920s America. The narrator, Nick Carraway, moves to New York's "West Egg," where he reunites with his cousin, Daisy, and her husband, Tom Buchanan. Fitzgerald clearly delineates social lines between West Egg (new money) and East Egg (old money), where Tom and Daisy reside.
Nick attends a lavish party thrown by his neighbor, Jay Gatsby, and learns he formerly had a relationship with Daisy. When the two reignite their forbidden affair, disaster ensues. Tom reveals to Daisy that Gatsby earned his money illegally, through smuggling alcohol, and is actually a man of humble Midwestern origins. Daisy and Gatsby try to run away together, but Daisy accidentally runs over Tom's mistress. Tom, eager to exact revenge, convinces his mistress' husband that Gatsby was to blame in her death, and he murders Gatsby before committing suicide. Few of Gatsby's many friends attend his funeral.
Though Gatsby subscribed to the extravagance of his peers, his efforts to fit into the upper echelon of West and East Egg were negated by his humble origins; always out of place, he was rejected for his social class as much as his perceived crimes.
For an in-depth analysis of The Great Gatsby , check out the our study guide (we have an audio guide, too!).
How to Summarize an Article or Essay
The nature of an article or essay is quite different from a novel or short story, and in many ways, your summary should be too. The outline above remains the same, but the details are different.
Here's what you should and shouldn't do when writing your article summary.
Dos of Writing an Article Summary
- Skim the original article first. To develop a basic understanding of the article and the writer's objectives, skim the content before reading it closely. Doing so will help you to identify some of the key points and then pay attention to the arguments around them when you read the article in full.
- Then read the article closely, marking key passages and ideas. Noting important ideas as you read will help you develop a deeper understanding of the writer's intentions.
- Note headings and subheadings, which likely identify important points. In articles and essays, the author often utilizes subheadings to introduce their most important ideas. These subheadings can help guide your own writing.
- Keep it short. The rule of brevity applies to article summaries too. In fact, because articles are usually short compared to novels or books, your text should be correlatively brief. And if you're utilizing the work as part of your own essay or argument, just a couple sentences will do.
Don'ts of Writing an Article Summary
- Don't ignore the conclusion. When reading a long article or essay, it can be tempting to overlook the conclusion and focus on the body paragraphs of the article. However, the conclusion is often where the author most clearly outlines their findings and why they matter. It can serve as a great foundation for your own writing.
- Don't copy anything from the article directly—always paraphrase. If you copy any passages word-for-word from the article, be sure to identify them as quotations and attribute them to the author. Even this should be done sparingly. Instead, you should encapsulate their ideas within your own, abbreviated words.
- Don't forget to include proper citations. If you do include a direct quotation from the article, be sure to properly cite them. You can learn how to properly cite quotations in our Academic Citation Resource Guide .
Example Summary of "Gatsby as a Drowned Sailor" : In her essay, "Gatsby as a Drowned Sailor," Margaret Lukens posits that a major, and often overlooked, motif in The Great Gatsby is that of the "drowned sailor." The novel, she points out, is immersed in nautical symbols and themes, particularly in the scenes surrounding Jay Gatsby. For example, Gatsby grew up on the shores of Lake Superior, now owns a house on the Long Island Sound, and supposedly spends much of his time on his boat.
Lukens nods to the nautical imagery throughout Gatsby's lavish party, as well as Nick's interactions with Gatsby. Many of these, she argues, foreshadow Gatsby's death in his pool. Even his funeral is a testament to the motif, with the few attendees soaked to the skin with rain. Lukens presents a thorough case for the overarching nautical motif in The Great Gatsby and her argument that though Gatsby hooked a big one, ultimately it was "the one that got away."
FAQs: How to Write a Book Summary
How do you summarize without plagiarizing .
By its very nature, a summary isn't plagiarizing because it should be written in your own words. However, there are cases where it might be difficult to identify an appropriate synonym, and the phrase remains somewhat close to the original. In this scenario, just be sure to differentiate the rest of the phrase as much as possible. And if you need to include a direct quote from the work, be sure to appropriately cite it.
How to write a summary and a reaction?
In some cases, your teacher may ask you to write a summary and a reaction. Whereas a summary is objective, a reaction is a matter of opinion. So in this case, you should present the actions or ideas of the work, then respond to those actions and ideas with your personal thoughts.
Why write a summary?
A summary is a helpful tool many educators use to test their students' comprehension of a text. However, it is also a useful study tactic because recounting what you read can help you organize and retain information.
How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.
Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.
Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.
Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay

- Manuscript Preparation
How to write the results section of a research paper
- 3 minute read
- 58.9K views
Table of Contents
At its core, a research paper aims to fill a gap in the research on a given topic. As a result, the results section of the paper, which describes the key findings of the study, is often considered the core of the paper. This is the section that gets the most attention from reviewers, peers, students, and any news organization reporting on your findings. Writing a clear, concise, and logical results section is, therefore, one of the most important parts of preparing your manuscript.
Difference between results and discussion
Before delving into how to write the results section, it is important to first understand the difference between the results and discussion sections. The results section needs to detail the findings of the study. The aim of this section is not to draw connections between the different findings or to compare it to previous findings in literature—that is the purview of the discussion section. Unlike the discussion section, which can touch upon the hypothetical, the results section needs to focus on the purely factual. In some cases, it may even be preferable to club these two sections together into a single section. For example, while writing a review article, it can be worthwhile to club these two sections together, as the main results in this case are the conclusions that can be drawn from the literature.
Structure of the results section
Although the main purpose of the results section in a research paper is to report the findings, it is necessary to present an introduction and repeat the research question. This establishes a connection to the previous section of the paper and creates a smooth flow of information.
Next, the results section needs to communicate the findings of your research in a systematic manner. The section needs to be organized such that the primary research question is addressed first, then the secondary research questions. If the research addresses multiple questions, the results section must individually connect with each of the questions. This ensures clarity and minimizes confusion while reading.
Consider representing your results visually. For example, graphs, tables, and other figures can help illustrate the findings of your paper, especially if there is a large amount of data in the results.
Remember, an appealing results section can help peer reviewers better understand the merits of your research, thereby increasing your chances of publication.
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper
- Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions.
- The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is best to avoid overinterpreting the results.
- If the research addresses more than one hypothesis, use sub-sections to describe the results. This prevents confusion and promotes understanding.
- Ensure that negative results are included in this section, even if they do not support the research hypothesis.
- Wherever possible, use illustrations like tables, figures, charts, or other visual representations to showcase the results of your research paper. Mention these illustrations in the text, but do not repeat the information that they convey.
- For statistical data, it is adequate to highlight the tests and explain their results. The initial or raw data should not be mentioned in the results section of a research paper.
The results section of a research paper is usually the most impactful section because it draws the greatest attention. Regardless of the subject of your research paper, a well-written results section is capable of generating interest in your research.
For detailed information and assistance on writing the results of a research paper, refer to Elsevier Author Services.

- Research Process
Writing a good review article

Why is data validation important in research?
You may also like.

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②

The Essentials of Writing to Communicate Research in Medicine

Changing Lines: Sentence Patterns in Academic Writing
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Research Synopsis: Template, Examples, & More
Last Updated: February 12, 2024 Fact Checked
Research Synopsis Template
- Organizing & Formatting
- Writing Your Synopsis
- Reviewing & Editing
This article was reviewed by Gerald Posner and by wikiHow staff writer, Raven Minyard, BA . Gerald Posner is an Author & Journalist based in Miami, Florida. With over 35 years of experience, he specializes in investigative journalism, nonfiction books, and editorials. He holds a law degree from UC College of the Law, San Francisco, and a BA in Political Science from the University of California-Berkeley. He’s the author of thirteen books, including several New York Times bestsellers, the winner of the Florida Book Award for General Nonfiction, and has been a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize in History. He was also shortlisted for the Best Business Book of 2020 by the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 229,208 times.
A research synopsis describes the plan for your research project and is typically submitted to professors or department heads so they can approve your project. Most synopses are between 3,000 and 4,000 words and provide your research objectives and methods. While the specific types of information you need to include in your synopsis may vary depending on your department guidelines, most synopses include the same basic sections. In this article, we’ll walk you step-by-step through everything you need to know to write a synopsis for research.
Things You Should Know
- Begin your research synopsis by introducing the question your research will answer and its importance to your field.
- List 2 or 3 specific objectives you hope to achieve and how they will advance your field.
- Discuss your methodology to demonstrate why the study design you chose is appropriate for your research question.

Organizing Your Research Synopsis

- Find out what citation format you’re supposed to use, as well as whether you’re expected to use parenthetical references or footnotes in the body of your synopsis.
- If you have questions about anything in your guidelines, ask your instructor or advisor to ensure you follow them correctly.

- Title: the title of your study
- Abstract: a summary of your research synopsis
- Introduction: identifies and describes your research question
- Literature Review: a review of existing relevant research
- Objectives: goals you hope to accomplish through your study
- Hypotheses: results you expect to find through your research
- Methodology and methods: explains the methods you’ll use to complete your study
- References: a list of any references used in citations
Tip: Your synopsis might have additional sections, depending on your discipline and the type of research you're conducting. Talk to your instructor or advisor about which sections are required for your department.

- Keep in mind that you might not end up using all the sources you initially found. After you've finished your synopsis, go back and delete the ones you didn't use.
Writing Your Research Synopsis

- Your title should be a brief and specific reflection of the main objectives of your study. In general, it should be under 50 words and should avoid unneeded phrases like “an investigation into.”
- On the other hand, avoid a title that’s too short, as well. For example, a title like “A Study of Urban Heating” is too short and doesn’t provide any insight into the specifics of your research.

- The introduction allows you to explain to your reader exactly why the question you’re trying to answer is vital and how your knowledge and experience make you the best researcher to tackle it.
- Support most of the statements in your introduction with other studies in the area that support the importance of your question. For example, you might cite a previous study that mentions your problem as an area where further research needs to be done.
- The length of your introduction will vary depending on the overall length of your synopsis as well as the ultimate length of your eventual paper after you’ve finished your research. Generally, it will cover the first page or two of your synopsis.

- For example, try finding relevant literature through educational journals or bulletins from organizations like WHO and CDC.
- Typically, a thorough literature review discusses 8 to 10 previous studies related to your research problem.
- As with the introduction, the length of your literature review will vary depending on the overall length of your synopsis. Generally, it will be about the same length as your introduction.
- Try to use the most current research available and avoid sources over 5 years old.

- For example, an objective for research on urban heating could be “to compare urban heat modification caused by vegetation of mixed species considering the 5 most common urban trees in an area.”
- Generally, the overall objective doesn’t relate to solving a specific problem or answering a specific question. Rather, it describes how your particular project will advance your field.
- For specific objectives, think in terms of action verbs like “quantify” or “compare.” Here, you’re hoping to gain a better understanding of associations between particular variables.

- Specify the sources you used and the reasons you have arrived at your hypotheses. Typically, these will come from prior studies that have shown similar relationships.
- For example, suppose a prior study showed that children who were home-schooled were less likely to be in fraternities or sororities in college. You might use that study to back up a hypothesis that home-schooled children are more independent and less likely to need strong friendship support networks.

- Expect your methodology to be at least as long as either your introduction or your literature review, if not longer. Include enough detail that your reader can fully understand how you’re going to carry out your study.
- This section of your synopsis may include information about how you plan to collect and analyze your data, the overall design of your study, and your sampling methods, if necessary. Include information about the study setting, like the facilities and equipment that are available to you to carry out your study.
- For example, your research work may take place in a hospital, and you may use cluster sampling to gather data.

- Use between 100 and 200 words to give your readers a basic understanding of your research project.
- Include a clear statement of the problem, the main goals or objectives of your study, the theories or conceptual framework your research relies upon, and the methods you’ll use to reach your goals or objectives.
Tip: Jot down a few notes as you draft your other sections that you can compile for your abstract to keep your writing more efficient.
Reviewing and Editing Your Research Synopsis

- If you don’t have that kind of time because you’re up against a deadline, at least take a few hours away from your synopsis before you go back to edit it. Do something entirely unrelated to your research, like taking a walk or going to a movie.

- Eliminate sentences that don’t add any new information. Even the longest synopsis is a brief document—make sure every word needs to be there and counts for something.
- Get rid of jargon and terms of art in your field that could be better explained in plain language. Even though your likely readers are people who are well-versed in your field, providing plain language descriptions shows you know what you’re talking about. Using jargon can seem like you’re trying to sound like you know more than you actually do.
Tip: Free apps, such as Grammarly and Hemingway App, can help you identify grammatical errors as well as areas where your writing could be clearer. However, you shouldn't rely solely on apps since they can miss things.

- Reference list formatting is very particular. Read your references out loud, with the punctuation and spacing, to pick up on errors you wouldn’t have noticed if you’d just read over them.
- Compare your format to the one in the stylebook you’re using and make sure all of your entries are correct.

- Read your synopsis backward by starting on the last word and reading each word separately from the last to the first. This helps isolate spelling errors. Reading backward sentence by sentence helps you isolate grammatical errors without being distracted by the content.
- Print your synopsis and circle every punctuation mark with a red pen. Then, go through them and focus on whether they’re correct.
- Read your synopsis out loud, including the punctuation, as though you were dictating the synopsis.

- Have at least one person who isn’t familiar with your area of study look over your synopsis. If they can understand your project, you know your writing is clear. If any parts confuse them, then that’s an area where you can improve the clarity of your writing.

Expert Q&A
- If you make significant changes to your synopsis after your first or second round of editing, you may need to proofread it again to make sure you didn’t introduce any new errors. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://admin.umt.edu.pk/Media/Site/iib1/FileManager/FORMAT%20OF%20SYNOPSIS%2012-10-2018.pdf
- ↑ https://www.scientificstyleandformat.org/Tools/SSF-Citation-Quick-Guide.html
- ↑ https://numspak.edu.pk/upload/media/Guidelines%20for%20Synopsis%20Writing1531455748.pdf
- ↑ https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279917593_Research_synopsis_guidelines
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ https://www.cornerstone.edu/blog-post/six-steps-to-really-edit-your-paper/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jul 25, 2022
Did this article help you?
Wave Bubble
Aug 31, 2021

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research Summary. Definition: A research summary is a brief and concise overview of a research project or study that highlights its key findings, main points, and conclusions. It typically includes a description of the research problem, the research methods used, the results obtained, and the implications or significance of the findings.
So, follow the steps below to write a research summary that sticks. 1. Read the parent paper thoroughly. You should go through the research paper thoroughly multiple times to ensure that you have a complete understanding of its contents. A 3-stage reading process helps.
When writing a summary, the goal is to compose a concise and objective overview of the original article. The summary should focus only on the article's main ideas and important details that support those ideas. Guidelines for summarizing an article: State the main ideas. Identify the most important details that support the main ideas.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Use the Right Tone and Voice. The tone and voice of your summary should match the original source material. Take note of the style from the source and reflect it in your writing. Whether the source material is formal or informal, academic or creative, ensuring consistency in tone and voice is key to an effective summary.
An academic summary tells the main points of a source text in brief form. As a condensed version of the source material, it can range anywhere from a couple of sentences to a short summary article, depending on the length of the source and your purposes for writing. In writing a summary, you need to select the most important points of the ...
1. Read The Entire Research Paper. Before you can write an effective summary, you must first read and understand the research paper. This may seem like a time-consuming task, but it is essential to write a good summary. Make sure that you understand all of the main points of the paper before you begin writing. 2.
Like an abstract in a published research article, the purpose of an article summary is to give the reader a brief, structured overview of the study. To write a good summary, identify what information is important and condense that information for your reader. The better you understand a subject, the easier it is to explain it thoroughly and ...
A research summary is a type of paper designed to provide a brief overview of a given study - typically, an article from a peer-reviewed academic journal. It is a frequent type of task encountered in US colleges and universities, both in humanitarian and exact sciences, which is due to how important it is to teach students to properly interact ...
Write objectively. Summaries should not report your opinion on the matter, but should accurately reflect the author's ideas and style. Nevertheless, make note of your evaluative comments and opinions outside of the summary because they may prove useful when writing your paper. 5. Document the publishing information for later reference.
A research summary is a piece of writing that summarizes your research on a specific topic. Its primary goal is to offer the reader a detailed overview of the study with the key findings. A research summary generally contains the article's structure in which it is written. You must know the goal of your analysis before you launch a project.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Summary Paper Find Out the Focus Area of Your Paper. Writing a research report requires you to read the entire article thoroughly. First, skim through the paper and understand the gist of the article. Once you have gone through the contents, you will have a fairly good idea of what the paper is all about.
An abstract summarizes, usually in one paragraph of 300 words or less, the major aspects of the entire paper in a prescribed sequence that includes: 1) the overall purpose of the study and the research problem(s) you investigated; 2) the basic design of the study; 3) major findings or trends found as a result of your analysis; and, 4) a brief summary of your interpretations and conclusions.
The introduction leads the reader from a general subject area to a particular topic of inquiry. It establishes the scope, context, and significance of the research being conducted by summarizing current understanding and background information about the topic, stating the purpose of the work in the form of the research problem supported by a hypothesis or a set of questions, explaining briefly ...
Here's how your outline might look: 1. Summary of the research and your overall impression. In your own words, summarize what the manuscript claims to report. This shows the editor how you interpreted the manuscript and will highlight any major differences in perspective between you and the other reviewers. Give an overview of the manuscript ...
Step 2: Take Notes. As you read the work, simultaneously take notes. If you own the book, it might be helpful to add your notes to the margins or highlight passages that are particularly relevant or capture a key idea. If you don't own the book, try taking notes on your computer or in a notebook.
The executive summary briefly describes the study's key points and suggests changes, actions and implementation strategies for the business. You can use the following steps to write an executive summary for a research paper: 1. Read the entire research paper.
Step 1 Organize your sources. Step 2 Outline your structure. Step 3 Write paragraphs with topic sentences. Step 4 Revise, edit and proofread. When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you've read - you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own ...
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper. Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions. The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is ...
1. Format your title page following your instructor's guidelines. In general, the title page of a research synopsis includes the title of the research project, your name, the degree and discipline for which you're writing the synopsis, and the names of your supervisor, department, institution, and university.
3 or 4 data sets per figure; well-selected scales; appropriate axis label size; symbols clear to read; data sets easily distinguishable. Each photograph must have a scale marker of professional quality in a corner. Use color ONLY when necessary. Color must be visible and distinguishable when printed in black & white.