

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, getting college essay help: important do's and don’ts.
College Essays

If you grow up to be a professional writer, everything you write will first go through an editor before being published. This is because the process of writing is really a process of re-writing —of rethinking and reexamining your work, usually with the help of someone else. So what does this mean for your student writing? And in particular, what does it mean for very important, but nonprofessional writing like your college essay? Should you ask your parents to look at your essay? Pay for an essay service?
If you are wondering what kind of help you can, and should, get with your personal statement, you've come to the right place! In this article, I'll talk about what kind of writing help is useful, ethical, and even expected for your college admission essay . I'll also point out who would make a good editor, what the differences between editing and proofreading are, what to expect from a good editor, and how to spot and stay away from a bad one.
Table of Contents
What Kind of Help for Your Essay Can You Get?
What's Good Editing?
What should an editor do for you, what kind of editing should you avoid, proofreading, what's good proofreading, what kind of proofreading should you avoid.
What Do Colleges Think Of You Getting Help With Your Essay?
Who Can/Should Help You?
Advice for editors.
Should You Pay Money For Essay Editing?
The Bottom Line
What's next, what kind of help with your essay can you get.
Rather than talking in general terms about "help," let's first clarify the two different ways that someone else can improve your writing . There is editing, which is the more intensive kind of assistance that you can use throughout the whole process. And then there's proofreading, which is the last step of really polishing your final product.
Let me go into some more detail about editing and proofreading, and then explain how good editors and proofreaders can help you."
Editing is helping the author (in this case, you) go from a rough draft to a finished work . Editing is the process of asking questions about what you're saying, how you're saying it, and how you're organizing your ideas. But not all editing is good editing . In fact, it's very easy for an editor to cross the line from supportive to overbearing and over-involved.
Ability to clarify assignments. A good editor is usually a good writer, and certainly has to be a good reader. For example, in this case, a good editor should make sure you understand the actual essay prompt you're supposed to be answering.
Open-endedness. Good editing is all about asking questions about your ideas and work, but without providing answers. It's about letting you stick to your story and message, and doesn't alter your point of view.

Think of an editor as a great travel guide. It can show you the many different places your trip could take you. It should explain any parts of the trip that could derail your trip or confuse the traveler. But it never dictates your path, never forces you to go somewhere you don't want to go, and never ignores your interests so that the trip no longer seems like it's your own. So what should good editors do?
Help Brainstorm Topics
Sometimes it's easier to bounce thoughts off of someone else. This doesn't mean that your editor gets to come up with ideas, but they can certainly respond to the various topic options you've come up with. This way, you're less likely to write about the most boring of your ideas, or to write about something that isn't actually important to you.
If you're wondering how to come up with options for your editor to consider, check out our guide to brainstorming topics for your college essay .
Help Revise Your Drafts
Here, your editor can't upset the delicate balance of not intervening too much or too little. It's tricky, but a great way to think about it is to remember: editing is about asking questions, not giving answers .
Revision questions should point out:
- Places where more detail or more description would help the reader connect with your essay
- Places where structure and logic don't flow, losing the reader's attention
- Places where there aren't transitions between paragraphs, confusing the reader
- Moments where your narrative or the arguments you're making are unclear
But pointing to potential problems is not the same as actually rewriting—editors let authors fix the problems themselves.
Bad editing is usually very heavy-handed editing. Instead of helping you find your best voice and ideas, a bad editor changes your writing into their own vision.
You may be dealing with a bad editor if they:
- Add material (examples, descriptions) that doesn't come from you
- Use a thesaurus to make your college essay sound "more mature"
- Add meaning or insight to the essay that doesn't come from you
- Tell you what to say and how to say it
- Write sentences, phrases, and paragraphs for you
- Change your voice in the essay so it no longer sounds like it was written by a teenager
Colleges can tell the difference between a 17-year-old's writing and a 50-year-old's writing. Not only that, they have access to your SAT or ACT Writing section, so they can compare your essay to something else you wrote. Writing that's a little more polished is great and expected. But a totally different voice and style will raise questions.
Where's the Line Between Helpful Editing and Unethical Over-Editing?
Sometimes it's hard to tell whether your college essay editor is doing the right thing. Here are some guidelines for staying on the ethical side of the line.
- An editor should say that the opening paragraph is kind of boring, and explain what exactly is making it drag. But it's overstepping for an editor to tell you exactly how to change it.
- An editor should point out where your prose is unclear or vague. But it's completely inappropriate for the editor to rewrite that section of your essay.
- An editor should let you know that a section is light on detail or description. But giving you similes and metaphors to beef up that description is a no-go.

Proofreading (also called copy-editing) is checking for errors in the last draft of a written work. It happens at the end of the process and is meant as the final polishing touch. Proofreading is meticulous and detail-oriented, focusing on small corrections. It sands off all the surface rough spots that could alienate the reader.
Because proofreading is usually concerned with making fixes on the word or sentence level, this is the only process where someone else can actually add to or take away things from your essay . This is because what they are adding or taking away tends to be one or two misplaced letters.
Laser focus. Proofreading is all about the tiny details, so the ability to really concentrate on finding small slip-ups is a must.
Excellent grammar and spelling skills. Proofreaders need to dot every "i" and cross every "t." Good proofreaders should correct spelling, punctuation, capitalization, and grammar. They should put foreign words in italics and surround quotations with quotation marks. They should check that you used the correct college's name, and that you adhered to any formatting requirements (name and date at the top of the page, uniform font and size, uniform spacing).
Limited interference. A proofreader needs to make sure that you followed any word limits. But if cuts need to be made to shorten the essay, that's your job and not the proofreader's.

A bad proofreader either tries to turn into an editor, or just lacks the skills and knowledge necessary to do the job.
Some signs that you're working with a bad proofreader are:
- If they suggest making major changes to the final draft of your essay. Proofreading happens when editing is already finished.
- If they aren't particularly good at spelling, or don't know grammar, or aren't detail-oriented enough to find someone else's small mistakes.
- If they start swapping out your words for fancier-sounding synonyms, or changing the voice and sound of your essay in other ways. A proofreader is there to check for errors, not to take the 17-year-old out of your writing.

What Do Colleges Think of Your Getting Help With Your Essay?
Admissions officers agree: light editing and proofreading are good—even required ! But they also want to make sure you're the one doing the work on your essay. They want essays with stories, voice, and themes that come from you. They want to see work that reflects your actual writing ability, and that focuses on what you find important.
On the Importance of Editing
Get feedback. Have a fresh pair of eyes give you some feedback. Don't allow someone else to rewrite your essay, but do take advantage of others' edits and opinions when they seem helpful. ( Bates College )
Read your essay aloud to someone. Reading the essay out loud offers a chance to hear how your essay sounds outside your head. This exercise reveals flaws in the essay's flow, highlights grammatical errors and helps you ensure that you are communicating the exact message you intended. ( Dickinson College )
On the Value of Proofreading
Share your essays with at least one or two people who know you well—such as a parent, teacher, counselor, or friend—and ask for feedback. Remember that you ultimately have control over your essays, and your essays should retain your own voice, but others may be able to catch mistakes that you missed and help suggest areas to cut if you are over the word limit. ( Yale University )
Proofread and then ask someone else to proofread for you. Although we want substance, we also want to be able to see that you can write a paper for our professors and avoid careless mistakes that would drive them crazy. ( Oberlin College )
On Watching Out for Too Much Outside Influence
Limit the number of people who review your essay. Too much input usually means your voice is lost in the writing style. ( Carleton College )
Ask for input (but not too much). Your parents, friends, guidance counselors, coaches, and teachers are great people to bounce ideas off of for your essay. They know how unique and spectacular you are, and they can help you decide how to articulate it. Keep in mind, however, that a 45-year-old lawyer writes quite differently from an 18-year-old student, so if your dad ends up writing the bulk of your essay, we're probably going to notice. ( Vanderbilt University )

Now let's talk about some potential people to approach for your college essay editing and proofreading needs. It's best to start close to home and slowly expand outward. Not only are your family and friends more invested in your success than strangers, but they also have a better handle on your interests and personality. This knowledge is key for judging whether your essay is expressing your true self.
Parents or Close Relatives
Your family may be full of potentially excellent editors! Parents are deeply committed to your well-being, and family members know you and your life well enough to offer details or incidents that can be included in your essay. On the other hand, the rewriting process necessarily involves criticism, which is sometimes hard to hear from someone very close to you.
A parent or close family member is a great choice for an editor if you can answer "yes" to the following questions. Is your parent or close relative a good writer or reader? Do you have a relationship where editing your essay won't create conflict? Are you able to constructively listen to criticism and suggestion from the parent?
One suggestion for defusing face-to-face discussions is to try working on the essay over email. Send your parent a draft, have them write you back some comments, and then you can pick which of their suggestions you want to use and which to discard.
Teachers or Tutors
A humanities teacher that you have a good relationship with is a great choice. I am purposefully saying humanities, and not just English, because teachers of Philosophy, History, Anthropology, and any other classes where you do a lot of writing, are all used to reviewing student work.
Moreover, any teacher or tutor that has been working with you for some time, knows you very well and can vet the essay to make sure it "sounds like you."
If your teacher or tutor has some experience with what college essays are supposed to be like, ask them to be your editor. If not, then ask whether they have time to proofread your final draft.
Guidance or College Counselor at Your School
The best thing about asking your counselor to edit your work is that this is their job. This means that they have a very good sense of what colleges are looking for in an application essay.
At the same time, school counselors tend to have relationships with admissions officers in many colleges, which again gives them insight into what works and which college is focused on what aspect of the application.
Unfortunately, in many schools the guidance counselor tends to be way overextended. If your ratio is 300 students to 1 college counselor, you're unlikely to get that person's undivided attention and focus. It is still useful to ask them for general advice about your potential topics, but don't expect them to be able to stay with your essay from first draft to final version.
Friends, Siblings, or Classmates
Although they most likely don't have much experience with what colleges are hoping to see, your peers are excellent sources for checking that your essay is you .
Friends and siblings are perfect for the read-aloud edit. Read your essay to them so they can listen for words and phrases that are stilted, pompous, or phrases that just don't sound like you.
You can even trade essays and give helpful advice on each other's work.

If your editor hasn't worked with college admissions essays very much, no worries! Any astute and attentive reader can still greatly help with your process. But, as in all things, beginners do better with some preparation.
First, your editor should read our advice about how to write a college essay introduction , how to spot and fix a bad college essay , and get a sense of what other students have written by going through some admissions essays that worked .
Then, as they read your essay, they can work through the following series of questions that will help them to guide you.
Introduction Questions
- Is the first sentence a killer opening line? Why or why not?
- Does the introduction hook the reader? Does it have a colorful, detailed, and interesting narrative? Or does it propose a compelling or surprising idea?
- Can you feel the author's voice in the introduction, or is the tone dry, dull, or overly formal? Show the places where the voice comes through.
Essay Body Questions
- Does the essay have a through-line? Is it built around a central argument, thought, idea, or focus? Can you put this idea into your own words?
- How is the essay organized? By logical progression? Chronologically? Do you feel order when you read it, or are there moments where you are confused or lose the thread of the essay?
- Does the essay have both narratives about the author's life and explanations and insight into what these stories reveal about the author's character, personality, goals, or dreams? If not, which is missing?
- Does the essay flow? Are there smooth transitions/clever links between paragraphs? Between the narrative and moments of insight?
Reader Response Questions
- Does the writer's personality come through? Do we know what the speaker cares about? Do we get a sense of "who he or she is"?
- Where did you feel most connected to the essay? Which parts of the essay gave you a "you are there" sensation by invoking your senses? What moments could you picture in your head well?
- Where are the details and examples vague and not specific enough?
- Did you get an "a-ha!" feeling anywhere in the essay? Is there a moment of insight that connected all the dots for you? Is there a good reveal or "twist" anywhere in the essay?
- What are the strengths of this essay? What needs the most improvement?

Should You Pay Money for Essay Editing?
One alternative to asking someone you know to help you with your college essay is the paid editor route. There are two different ways to pay for essay help: a private essay coach or a less personal editing service , like the many proliferating on the internet.
My advice is to think of these options as a last resort rather than your go-to first choice. I'll first go through the reasons why. Then, if you do decide to go with a paid editor, I'll help you decide between a coach and a service.
When to Consider a Paid Editor
In general, I think hiring someone to work on your essay makes a lot of sense if none of the people I discussed above are a possibility for you.
If you can't ask your parents. For example, if your parents aren't good writers, or if English isn't their first language. Or if you think getting your parents to help is going create unnecessary extra conflict in your relationship with them (applying to college is stressful as it is!)
If you can't ask your teacher or tutor. Maybe you don't have a trusted teacher or tutor that has time to look over your essay with focus. Or, for instance, your favorite humanities teacher has very limited experience with college essays and so won't know what admissions officers want to see.
If you can't ask your guidance counselor. This could be because your guidance counselor is way overwhelmed with other students.
If you can't share your essay with those who know you. It might be that your essay is on a very personal topic that you're unwilling to share with parents, teachers, or peers. Just make sure it doesn't fall into one of the bad-idea topics in our article on bad college essays .
If the cost isn't a consideration. Many of these services are quite expensive, and private coaches even more so. If you have finite resources, I'd say that hiring an SAT or ACT tutor (whether it's PrepScholar or someone else) is better way to spend your money . This is because there's no guarantee that a slightly better essay will sufficiently elevate the rest of your application, but a significantly higher SAT score will definitely raise your applicant profile much more.
Should You Hire an Essay Coach?
On the plus side, essay coaches have read dozens or even hundreds of college essays, so they have experience with the format. Also, because you'll be working closely with a specific person, it's more personal than sending your essay to a service, which will know even less about you.
But, on the minus side, you'll still be bouncing ideas off of someone who doesn't know that much about you . In general, if you can adequately get the help from someone you know, there is no advantage to paying someone to help you.
If you do decide to hire a coach, ask your school counselor, or older students that have used the service for recommendations. If you can't afford the coach's fees, ask whether they can work on a sliding scale —many do. And finally, beware those who guarantee admission to your school of choice—essay coaches don't have any special magic that can back up those promises.
Should You Send Your Essay to a Service?
On the plus side, essay editing services provide a similar product to essay coaches, and they cost significantly less . If you have some assurance that you'll be working with a good editor, the lack of face-to-face interaction won't prevent great results.
On the minus side, however, it can be difficult to gauge the quality of the service before working with them . If they are churning through many application essays without getting to know the students they are helping, you could end up with an over-edited essay that sounds just like everyone else's. In the worst case scenario, an unscrupulous service could send you back a plagiarized essay.
Getting recommendations from friends or a school counselor for reputable services is key to avoiding heavy-handed editing that writes essays for you or does too much to change your essay. Including a badly-edited essay like this in your application could cause problems if there are inconsistencies. For example, in interviews it might be clear you didn't write the essay, or the skill of the essay might not be reflected in your schoolwork and test scores.
Should You Buy an Essay Written by Someone Else?
Let me elaborate. There are super sketchy places on the internet where you can simply buy a pre-written essay. Don't do this!
For one thing, you'll be lying on an official, signed document. All college applications make you sign a statement saying something like this:
I certify that all information submitted in the admission process—including the application, the personal essay, any supplements, and any other supporting materials—is my own work, factually true, and honestly presented... I understand that I may be subject to a range of possible disciplinary actions, including admission revocation, expulsion, or revocation of course credit, grades, and degree, should the information I have certified be false. (From the Common Application )
For another thing, if your academic record doesn't match the essay's quality, the admissions officer will start thinking your whole application is riddled with lies.
Admission officers have full access to your writing portion of the SAT or ACT so that they can compare work that was done in proctored conditions with that done at home. They can tell if these were written by different people. Not only that, but there are now a number of search engines that faculty and admission officers can use to see if an essay contains strings of words that have appeared in other essays—you have no guarantee that the essay you bought wasn't also bought by 50 other students.

- You should get college essay help with both editing and proofreading
- A good editor will ask questions about your idea, logic, and structure, and will point out places where clarity is needed
- A good editor will absolutely not answer these questions, give you their own ideas, or write the essay or parts of the essay for you
- A good proofreader will find typos and check your formatting
- All of them agree that getting light editing and proofreading is necessary
- Parents, teachers, guidance or college counselor, and peers or siblings
- If you can't ask any of those, you can pay for college essay help, but watch out for services or coaches who over-edit you work
- Don't buy a pre-written essay! Colleges can tell, and it'll make your whole application sound false.
Ready to start working on your essay? Check out our explanation of the point of the personal essay and the role it plays on your applications and then explore our step-by-step guide to writing a great college essay .
Using the Common Application for your college applications? We have an excellent guide to the Common App essay prompts and useful advice on how to pick the Common App prompt that's right for you . Wondering how other people tackled these prompts? Then work through our roundup of over 130 real college essay examples published by colleges .
Stressed about whether to take the SAT again before submitting your application? Let us help you decide how many times to take this test . If you choose to go for it, we have the ultimate guide to studying for the SAT to give you the ins and outs of the best ways to study.

Anna scored in the 99th percentile on her SATs in high school, and went on to major in English at Princeton and to get her doctorate in English Literature at Columbia. She is passionate about improving student access to higher education.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt
- Asking Analytical Questions
- Introductions
- What Do Introductions Across the Disciplines Have in Common?
- Anatomy of a Body Paragraph
- Transitions
- Tips for Organizing Your Essay
- Counterargument
- Conclusions
- Strategies for Essay Writing: Downloadable PDFs
- Brief Guides to Writing in the Disciplines
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
College admissions
Course: college admissions > unit 4.
- Writing a strong college admissions essay
- Avoiding common admissions essay mistakes
- Brainstorming tips for your college essay
- How formal should the tone of your college essay be?
- Taking your college essay to the next level
- Sample essay 1 with admissions feedback
- Sample essay 2 with admissions feedback
- Student story: Admissions essay about a formative experience
- Student story: Admissions essay about personal identity
- Student story: Admissions essay about community impact
- Student story: Admissions essay about a past mistake
- Student story: Admissions essay about a meaningful poem
Writing tips and techniques for your college essay
Pose a question the reader wants answered, don't focus exclusively on the past, experiment with the unexpected, don't summarize, want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page


Essay Writing: A complete guide for students and teachers
P LANNING, PARAGRAPHING AND POLISHING: FINE-TUNING THE PERFECT ESSAY
Essay writing is an essential skill for every student. Whether writing a particular academic essay (such as persuasive, narrative, descriptive, or expository) or a timed exam essay, the key to getting good at writing is to write. Creating opportunities for our students to engage in extended writing activities will go a long way to helping them improve their skills as scribes.
But, putting the hours in alone will not be enough to attain the highest levels in essay writing. Practice must be meaningful. Once students have a broad overview of how to structure the various types of essays, they are ready to narrow in on the minor details that will enable them to fine-tune their work as a lean vehicle of their thoughts and ideas.

In this article, we will drill down to some aspects that will assist students in taking their essay writing skills up a notch. Many ideas and activities can be integrated into broader lesson plans based on essay writing. Often, though, they will work effectively in isolation – just as athletes isolate physical movements to drill that are relevant to their sport. When these movements become second nature, they can be repeated naturally in the context of the game or in our case, the writing of the essay.
THE ULTIMATE NONFICTION WRITING TEACHING RESOURCE

- 270 pages of the most effective teaching strategies
- 50+ digital tools ready right out of the box
- 75 editable resources for student differentiation
- Loads of tricks and tips to add to your teaching tool bag
- All explanations are reinforced with concrete examples.
- Links to high-quality video tutorials
- Clear objectives easy to match to the demands of your curriculum
Planning an essay

The Boys Scouts’ motto is famously ‘Be Prepared’. It’s a solid motto that can be applied to most aspects of life; essay writing is no different. Given the purpose of an essay is generally to present a logical and reasoned argument, investing time in organising arguments, ideas, and structure would seem to be time well spent.
Given that essays can take a wide range of forms and that we all have our own individual approaches to writing, it stands to reason that there will be no single best approach to the planning stage of essay writing. That said, there are several helpful hints and techniques we can share with our students to help them wrestle their ideas into a writable form. Let’s take a look at a few of the best of these:
BREAK THE QUESTION DOWN: UNDERSTAND YOUR ESSAY TOPIC.
Whether students are tackling an assignment that you have set for them in class or responding to an essay prompt in an exam situation, they should get into the habit of analyzing the nature of the task. To do this, they should unravel the question’s meaning or prompt. Students can practice this in class by responding to various essay titles, questions, and prompts, thereby gaining valuable experience breaking these down.
Have students work in groups to underline and dissect the keywords and phrases and discuss what exactly is being asked of them in the task. Are they being asked to discuss, describe, persuade, or explain? Understanding the exact nature of the task is crucial before going any further in the planning process, never mind the writing process .
BRAINSTORM AND MIND MAP WHAT YOU KNOW:
Once students have understood what the essay task asks them, they should consider what they know about the topic and, often, how they feel about it. When teaching essay writing, we so often emphasize that it is about expressing our opinions on things, but for our younger students what they think about something isn’t always obvious, even to themselves.
Brainstorming and mind-mapping what they know about a topic offers them an opportunity to uncover not just what they already know about a topic, but also gives them a chance to reveal to themselves what they think about the topic. This will help guide them in structuring their research and, later, the essay they will write . When writing an essay in an exam context, this may be the only ‘research’ the student can undertake before the writing, so practicing this will be even more important.
RESEARCH YOUR ESSAY
The previous step above should reveal to students the general direction their research will take. With the ubiquitousness of the internet, gone are the days of students relying on a single well-thumbed encyclopaedia from the school library as their sole authoritative source in their essay. If anything, the real problem for our students today is narrowing down their sources to a manageable number. Students should use the information from the previous step to help here. At this stage, it is important that they:
● Ensure the research material is directly relevant to the essay task
● Record in detail the sources of the information that they will use in their essay
● Engage with the material personally by asking questions and challenging their own biases
● Identify the key points that will be made in their essay
● Group ideas, counterarguments, and opinions together
● Identify the overarching argument they will make in their own essay.
Once these stages have been completed the student is ready to organise their points into a logical order.
WRITING YOUR ESSAY
There are a number of ways for students to organize their points in preparation for writing. They can use graphic organizers , post-it notes, or any number of available writing apps. The important thing for them to consider here is that their points should follow a logical progression. This progression of their argument will be expressed in the form of body paragraphs that will inform the structure of their finished essay.
The number of paragraphs contained in an essay will depend on a number of factors such as word limits, time limits, the complexity of the question etc. Regardless of the essay’s length, students should ensure their essay follows the Rule of Three in that every essay they write contains an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Generally speaking, essay paragraphs will focus on one main idea that is usually expressed in a topic sentence that is followed by a series of supporting sentences that bolster that main idea. The first and final sentences are of the most significance here with the first sentence of a paragraph making the point to the reader and the final sentence of the paragraph making the overall relevance to the essay’s argument crystal clear.
Though students will most likely be familiar with the broad generic structure of essays, it is worth investing time to ensure they have a clear conception of how each part of the essay works, that is, of the exact nature of the task it performs. Let’s review:
Common Essay Structure
Introduction: Provides the reader with context for the essay. It states the broad argument that the essay will make and informs the reader of the writer’s general perspective and approach to the question.
Body Paragraphs: These are the ‘meat’ of the essay and lay out the argument stated in the introduction point by point with supporting evidence.
Conclusion: Usually, the conclusion will restate the central argument while summarising the essay’s main supporting reasons before linking everything back to the original question.
ESSAY WRITING PARAGRAPH WRITING TIPS

● Each paragraph should focus on a single main idea
● Paragraphs should follow a logical sequence; students should group similar ideas together to avoid incoherence
● Paragraphs should be denoted consistently; students should choose either to indent or skip a line
● Transition words and phrases such as alternatively , consequently , in contrast should be used to give flow and provide a bridge between paragraphs.
HOW TO EDIT AN ESSAY

Students shouldn’t expect their essays to emerge from the writing process perfectly formed. Except in exam situations and the like, thorough editing is an essential aspect in the writing process.
Often, students struggle with this aspect of the process the most. After spending hours of effort on planning, research, and writing the first draft, students can be reluctant to go back over the same terrain they have so recently travelled. It is important at this point to give them some helpful guidelines to help them to know what to look out for. The following tips will provide just such help:
One Piece at a Time: There is a lot to look out for in the editing process and often students overlook aspects as they try to juggle too many balls during the process. One effective strategy to combat this is for students to perform a number of rounds of editing with each focusing on a different aspect. For example, the first round could focus on content, the second round on looking out for word repetition (use a thesaurus to help here), with the third attending to spelling and grammar.
Sum It Up: When reviewing the paragraphs they have written, a good starting point is for students to read each paragraph and attempt to sum up its main point in a single line. If this is not possible, their readers will most likely have difficulty following their train of thought too and the paragraph needs to be overhauled.
Let It Breathe: When possible, encourage students to allow some time for their essay to ‘breathe’ before returning to it for editing purposes. This may require some skilful time management on the part of the student, for example, a student rush-writing the night before the deadline does not lend itself to effective editing. Fresh eyes are one of the sharpest tools in the writer’s toolbox.
Read It Aloud: This time-tested editing method is a great way for students to identify mistakes and typos in their work. We tend to read things more slowly when reading aloud giving us the time to spot errors. Also, when we read silently our minds can often fill in the gaps or gloss over the mistakes that will become apparent when we read out loud.
Phone a Friend: Peer editing is another great way to identify errors that our brains may miss when reading our own work. Encourage students to partner up for a little ‘you scratch my back, I scratch yours’.
Use Tech Tools: We need to ensure our students have the mental tools to edit their own work and for this they will need a good grasp of English grammar and punctuation. However, there are also a wealth of tech tools such as spellcheck and grammar checks that can offer a great once-over option to catch anything students may have missed in earlier editing rounds.

Putting the Jewels on Display: While some struggle to edit, others struggle to let go. There comes a point when it is time for students to release their work to the reader. They must learn to relinquish control after the creation is complete. This will be much easier to achieve if the student feels that they have done everything in their control to ensure their essay is representative of the best of their abilities and if they have followed the advice here, they should be confident they have done so.
WRITING CHECKLISTS FOR ALL TEXT TYPES

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
ESSAY WRITING video tutorials

Celebrating 150 years of Harvard Summer School. Learn about our history.
12 Strategies to Writing the Perfect College Essay
College admission committees sift through thousands of college essays each year. Here’s how to make yours stand out.
Pamela Reynolds
When it comes to deciding who they will admit into their programs, colleges consider many criteria, including high school grades, extracurricular activities, and ACT and SAT scores. But in recent years, more colleges are no longer considering test scores.
Instead, many (including Harvard through 2026) are opting for “test-blind” admission policies that give more weight to other elements in a college application. This policy change is seen as fairer to students who don’t have the means or access to testing, or who suffer from test anxiety.
So, what does this mean for you?
Simply that your college essay, traditionally a requirement of any college application, is more important than ever.
A college essay is your unique opportunity to introduce yourself to admissions committees who must comb through thousands of applications each year. It is your chance to stand out as someone worthy of a seat in that classroom.
A well-written and thoughtful essay—reflecting who you are and what you believe—can go a long way to separating your application from the slew of forgettable ones that admissions officers read. Indeed, officers may rely on them even more now that many colleges are not considering test scores.
Below we’ll discuss a few strategies you can use to help your essay stand out from the pack. We’ll touch on how to start your essay, what you should write for your college essay, and elements that make for a great college essay.
Be Authentic
More than any other consideration, you should choose a topic or point of view that is consistent with who you truly are.
Readers can sense when writers are inauthentic.
Inauthenticity could mean the use of overly flowery language that no one would ever use in conversation, or it could mean choosing an inconsequential topic that reveals very little about who you are.
Use your own voice, sense of humor, and a natural way of speaking.
Whatever subject you choose, make sure it’s something that’s genuinely important to you and not a subject you’ve chosen just to impress. You can write about a specific experience, hobby, or personality quirk that illustrates your strengths, but also feel free to write about your weaknesses.
Honesty about traits, situations, or a childhood background that you are working to improve may resonate with the reader more strongly than a glib victory speech.
Grab the Reader From the Start
You’ll be competing with so many other applicants for an admission officer’s attention.
Therefore, start your essay with an opening sentence or paragraph that immediately seizes the imagination. This might be a bold statement, a thoughtful quote, a question you pose, or a descriptive scene.
Starting your essay in a powerful way with a clear thesis statement can often help you along in the writing process. If your task is to tell a good story, a bold beginning can be a natural prelude to getting there, serving as a roadmap, engaging the reader from the start, and presenting the purpose of your writing.
Focus on Deeper Themes
Some essay writers think they will impress committees by loading an essay with facts, figures, and descriptions of activities, like wins in sports or descriptions of volunteer work. But that’s not the point.
College admissions officers are interested in learning more about who you are as a person and what makes you tick.
They want to know what has brought you to this stage in life. They want to read about realizations you may have come to through adversity as well as your successes, not just about how many games you won while on the soccer team or how many people you served at a soup kitchen.
Let the reader know how winning the soccer game helped you develop as a person, friend, family member, or leader. Make a connection with your soup kitchen volunteerism and how it may have inspired your educational journey and future aspirations. What did you discover about yourself?
Show Don’t Tell
As you expand on whatever theme you’ve decided to explore in your essay, remember to show, don’t tell.
The most engaging writing “shows” by setting scenes and providing anecdotes, rather than just providing a list of accomplishments and activities.
Reciting a list of activities is also boring. An admissions officer will want to know about the arc of your emotional journey too.
Try Doing Something Different
If you want your essay to stand out, think about approaching your subject from an entirely new perspective. While many students might choose to write about their wins, for instance, what if you wrote an essay about what you learned from all your losses?
If you are an especially talented writer, you might play with the element of surprise by crafting an essay that leaves the response to a question to the very last sentence.
You may want to stay away from well-worn themes entirely, like a sports-related obstacle or success, volunteer stories, immigration stories, moving, a summary of personal achievements or overcoming obstacles.
However, such themes are popular for a reason. They represent the totality of most people’s lives coming out of high school. Therefore, it may be less important to stay away from these topics than to take a fresh approach.
Explore Harvard Summer School’s College Programs for High School Students
Write With the Reader in Mind
Writing for the reader means building a clear and logical argument in which one thought flows naturally from another.
Use transitions between paragraphs.
Think about any information you may have left out that the reader may need to know. Are there ideas you have included that do not help illustrate your theme?
Be sure you can answer questions such as: Does what you have written make sense? Is the essay organized? Does the opening grab the reader? Is there a strong ending? Have you given enough background information? Is it wordy?
Write Several Drafts
Set your essay aside for a few days and come back to it after you’ve had some time to forget what you’ve written. Often, you’ll discover you have a whole new perspective that enhances your ability to make revisions.
Start writing months before your essay is due to give yourself enough time to write multiple drafts. A good time to start could be as early as the summer before your senior year when homework and extracurricular activities take up less time.
Read It Aloud
Writer’s tip : Reading your essay aloud can instantly uncover passages that sound clumsy, long-winded, or false.
Don’t Repeat
If you’ve mentioned an activity, story, or anecdote in some other part of your application, don’t repeat it again in your essay.
Your essay should tell college admissions officers something new. Whatever you write in your essay should be in philosophical alignment with the rest of your application.
Also, be sure you’ve answered whatever question or prompt may have been posed to you at the outset.
Ask Others to Read Your Essay
Be sure the people you ask to read your essay represent different demographic groups—a teacher, a parent, even a younger sister or brother.
Ask each reader what they took from the essay and listen closely to what they have to say. If anyone expresses confusion, revise until the confusion is cleared up.
Pay Attention to Form
Although there are often no strict word limits for college essays, most essays are shorter rather than longer. Common App, which students can use to submit to multiple colleges, suggests that essays stay at about 650 words.
“While we won’t as a rule stop reading after 650 words, we cannot promise that an overly wordy essay will hold our attention for as long as you’d hoped it would,” the Common App website states.
In reviewing other technical aspects of your essay, be sure that the font is readable, that the margins are properly spaced, that any dialogue is set off properly, and that there is enough spacing at the top. Your essay should look clean and inviting to readers.
End Your Essay With a “Kicker”
In journalism, a kicker is the last punchy line, paragraph, or section that brings everything together.
It provides a lasting impression that leaves the reader satisfied and impressed by the points you have artfully woven throughout your piece.
So, here’s our kicker: Be concise and coherent, engage in honest self-reflection, and include vivid details and anecdotes that deftly illustrate your point.
While writing a fantastic essay may not guarantee you get selected, it can tip the balance in your favor if admissions officers are considering a candidate with a similar GPA and background.
Write, revise, revise again, and good luck!
Experience life on a college campus. Spend your summer at Harvard.
Explore Harvard Summer School’s College Programs for High School Students.
About the Author
Pamela Reynolds is a Boston-area feature writer and editor whose work appears in numerous publications. She is the author of “Revamp: A Memoir of Travel and Obsessive Renovation.”
How Involved Should Parents and Guardians Be in High School Student College Applications and Admissions?
There are several ways parents can lend support to their children during the college application process. Here's how to get the ball rolling.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Joanne Baird Giordano
- A Quick Introduction to College Learning Strategies
- General Academic Literacy and Disciplinary Literacy
- Reading for Understanding
- Reading to Learn and Remember
- Adapting to Disciplinary Literacy Conventions
- Strategies for College Learning
- What Is Strategic Learning?
- What Are Learning Strategies?
- Effective and Efficient Learning Strategies
- Metacognition and College Learning
- Adapting Learning Strategies to Different Learning Situations
STRATEGIES FOR COLLEGE LEARNING
A strategy is a plan of action that an individual or group uses to achieve a goal . Strategies provide a framework (or structure) for making decisions, taking action, self-assessing, and adapting or changing behavior. As you work toward reaching your individual educational goals, you will develop a variety of different academic literacy strategies for different areas of college learning, including reading, writing, studying for tests, taking tests, finding information, conducting original research, completing quantitative (math) tasks, and using technology as a tool for learning. This article provides an overview of concepts that can help students think about and begin to strengthen the strategies that they use for learning.
WHAT IS STRATEGIC LEARNING?
Strategic learning means making decisions and purposefully taking action to increase academic success or achieve an educational goal. Strategic learning in college includes
- taking an active role in the learning process
- learning how to learn and study at an advanced level
- using individual approaches to learning and adapting them to different types of courses and assignments
- applying knowledge about learning for an academic purpose
- self-assessing, monitoring, and self-regulating (controlling) learning
WHAT ARE LEARNING STRATEGIES?
College learning strategies are methods that help students improve their learning and academic success. They are conscious, intentional techniques that students use to adapt how they learn based on the purpose and requirements of an academic task in a specific learning situation.
Here are some examples of general college-level learning strategies:
- spacing out study sessions over time
- previewing a chapter before reading it
- using words in bold in a textbook to help identify important concepts
- creating flashcards to take notes from reading to use while practicing for an exam
- writing notes in the margins of a reading assignment to record ideas for an essay
- organizing ideas for a writing assignment through outlining or prewriting
EFFECTIVE AND EFFICIENT LEARNING STRATEGIES
For most situations, learning strategies should be both effective and efficient. An effective learning strategy works for its intended purpose, and students are successful when they use it in a course. An efficient learning strategy doesn’t take too much time or resources. Some strategies are effective but not efficient. They might work, but students typically don’t have enough time to use them. For example, memory tricks like inventing songs to memorize facts or vocabulary might help some students remember information, but they are time consuming to create. Other strategies are quick and efficient but ineffective, including skimming through a textbook chapter without reading it, cramming for an exam, and highlighting or underlining without note taking. In contrast, annotating a textbook by taking notes directly in the margins of a book or handout is an example of a learning strategy that is both effective and efficient. Students can easily take notes while reading and then use those notes to find information later while studying for an exam.
METACOGNITION AND COLLEGE LEARNING
Metacognition is a concept that describes thinking about thinking. In “ Framework for Success in Postsecondary Writing ,” three national organizations for writing teachers define metacognition as “the ability to reflect on one’s own thinking as well as on the individual and cultural processes used to structure knowledge” (CWPA, NCTE, and NWP 5). Metacognition is an important part of using effective learning strategies. As a college student, you need to build on your previous experiences to develop an awareness of your own learning processes. You also need to monitor (or pay attention to) and reflect on the learning strategies that you use for each course.
ADAPTING LEARNING STRATEGIES TO DIFFERENT LEARNING SITUATIONS
Perhaps the most important part of using effective learning strategies is figuring out what works (and does not work) for a particular field of study, course, assignment, and learning task. Educational researchers Melinda Burchard and Peter Swerdzewski explain that “learning strategies are not tricks or shortcuts; instead, strategic learning focuses on matching specific approaches, processes or strategies to the individual’s learning needs.” By noticing and evaluating (self-assessing) how you learn in specific situations, you will strengthen your ability to adapt your learning strategies based on the requirements and purposes of different academic tasks.
Learning Strategies: Questions for Reflection and Writing
- Based on your own experience, what strategies have been most effective in helping you learn? Why did those strategies work for you?
- What strategies have been the most efficient in helping you reduce the time that it takes to study? Why did those strategies work for you?
- Which learning strategies have worked for you in more than one type of course and with different types of academic tasks? Which learning strategies are unique to a specific type of course or assignment?
- How might you apply your previous experiences with learning strategies to the courses that you are currently taking?
Activity: Exploring Metacognition
Do informal research to look up definitions and examples of metacognition in the learning processes. You might also look up information about cognition and cognitive processes. What did you learn about strategies for monitoring (paying attention to) your own learning? What did you learn about metacognition that you might apply to your work as a college reader and writer?
[Continue to the next section: “General Academic Literacy and Disciplinary Literacy.” ]
Resources for Further Study
- Bain, Ken. What The Best College Students Do . Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 2012.
- Chick, Nancy. “Metacognition.” Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching and Learning.
- Dartmouth Academic Skills Center, “Learning Strategies.”
Works Cited
Burchard, Melinda S. and Peter Swerdzewski. “Learning Effectiveness of a Strategic Learning Course.” Journal of College Reading and Learning , vol. 40, no.1, 2009, pp.14-34.
Council of Writing Program Administrators, National Council of Teachers of English, and National Writing Project. Framework for Success in Postsecondary Writing. CWPA, NCTE, and NWP, 2011.
Open English @ SLCC Copyright © 2016 by Joanne Baird Giordano is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Calendar/Events
- Navigate: Students
- One-Stop Resources
- Navigate: Staff
- My Wisconsin Portal
- More Resources

- LEARN Center
- Research-Based Teaching Tips
Efficient Ways to Improve Student Writing
Strategies, Ideas, and Recommendations from the faculty Development Literature
General Strategies
- View the improvement of students’ writing as your responsibility. Teaching writing is not only the job of the English department alone. Writing is an essential tool for learning a discipline and helping students improve their writing skills is a responsibility for all faculty.
- Let students know that you value good writing. Stress the importance of clear, thoughtful writing. Faculty who tell students that good writing will be rewarded and poor writing will be penalized receive better essays than instructors who don't make such demands. In the syllabus, on the first day, and throughout the term, remind students that they must make their best effort in expressing themselves on paper. Back up your statements with comments on early assignments that show you really mean it, and your students will respond.
- Regularly assign brief writing exercises in your classes. To vary the pace of a lecture course, ask students to write a few minutes during class. Some mixture of in-class writing, outside writing assignments, and exams with open-ended questions will give students the practice they need to improve their skills.
- Provide guidance throughout the writing process. After you have made the assignment, discuss the value of outlines and notes, explain how to select and narrow a topic, and critique the first draft, define plagiarism as well.
- Don't feel as though you have to read and grade every piece of your students' writing. Ask students to analyze each other's work during class, or ask them to critique their work in small groups. Students will learn that they are writing in order to think more clearly, not obtain a grade. Keep in mind, you can collect students' papers and skim their work.
- Find other faculty members who are trying to use writing more effectively in their courses. Pool ideas about ways in which writing can help students learn more about the subject matter. See if there is sufficient interest in your discipline to warrant drawing up guidelines. Students welcome handouts that give them specific instructions on how to write papers for a particular course or in a particular subject area.
Teaching Writing When You Are Not an English Teacher
- Remind students that writing is a process that helps us clarify ideas. Tell students that writing is a way of learning, not an end in itself. Also let them know that writing is a complicated, messy, nonlinear process filled with false starts. Help them to identify the writer's key activities:
- Developing ideas
- Finding a focus and a thesis
- Composing a draft
- Getting feedback and comments from others
- Revising the draft by expanding ideas, clarifying meaning, reorganizing
- Presenting the finished work to readers
- Explain that writing is hard work. Share with your class your own struggles in grappling with difficult topics. If they know that writing takes effort, they won't be discouraged by their own pace or progress. One faculty member shared with students their notebook that contained the chronology of one of his published articles: first ideas, successive drafts, submitted manuscript, reviewers' suggested changes, revised version, galley proofs, and published article.
- Give students opportunities to talk about their writing. Students need to talk about papers in progress so that they can formulate their thoughts, generate ideas, and focus their topics. Take five or ten minutes of class time for students to read their writing to each other in small groups or pairs. It's important for students to hear what their peers have written.
- Encourage students to revise their work. Provide formal steps for revision by asking students to submit first drafts of papers for your review or for peer critique. You can also give your students the option of revising and rewriting one assignment during the semester for a higher grade. Faculty report that 10 to 40 percent of the students take advantage of this option.
- Explain thesis statements. A thesis statement makes an assertion about some issue. A common student problem is to write papers that present overviews of facts with no thesis statement or that have a diffuse thesis statement.
- Stress clarity and specificity. The more the abstract and difficult the topic, the more concrete the student's language should be. Inflated language and academic jargon camouflage rather than clarify their point.
- Explain the importance of grammar and sentence structure, as well as content. Students shouldn't think that English teachers are the only judges of grammar and style. Tell your students that you will be looking at both quality of their writing and the content.
- Distribute bibliographies and tip sheets on good writing practices. Check with your English department or writing center to identify materials that can be easily distributed to students. Consider giving your students a bibliography of writing guides, for example:
Crews, F.C. Random House Handbook. (6th ed.) New York: McGraw-Hill, 1992.
A classic comprehensive textbook for college students. Well written and well worth reading.
Lanham, R.A. Revising Prose . (3rd ed.) New York: Scribner's, 1991. Techniques for eliminating
bureaucratese and restoring energy to tired prose.
Tollefson, S. K. Grammar Grams and Grammar Grams II . New York: HarperCollins, 1989,
1992. Two short, witty guides that answer common questions about grammar, style, and usage. Both are fun to read.
- Science and Engineering Barrass, R. Scientists Must Write. New York: Chapman and Hall, 1978. Biddle, A. W., and Bean, D. J. Writer's Guide: Life Sciences. Lexington, Mass.: Heath, 1987.
- Arts and Humanities Barnet, S. A Short Guide to Writing About Art . Boston: Little, Brown, 1989. Goldman, B. Reading and Writing in the Arts. Detroit: Wayne State University Press, 1978.
- Social Sciences Biddle, A. W., Fulwiler, T., and Holland, K.M. Writer's Guide: Psychology . Lexington, Mass,:
Heath, 1987. McCloskey, D. N. The Writing of Economics . New York: Macmillan, 1987.
- Ask a composition instructor to give a presentation to your students. Invite a guest speaker from the composition department or student learning center to talk to your students about effective writing and common writing problems. Faculty who have invited these experts report that such presentations reinforce the values of the importance of writing.
- Let students know about available tutoring services. Individual or group tutoring in writing is available on most campuses. Ask someone from the tutoring center to give a demonstration in your class.
- Use computers to help students write better. Locally developed and commercially available software are now being used by faculty to help students plan, write, and revise their written work. Some software available allows instructors to monitor students' work in progress and lets students collaborate with their classmates.
Assigning In-Class Writing Activities
- Ask students to write what they know about a topic before you discuss it. Ask your students to write a brief summary of what they already know or what opinions they hold regarding the subject you are about to discuss. The purpose of this is to focus the students' attention, there is no need to collect the summaries.
- Ask students to respond in writing to questions you pose during class. Prior to class starting, list two or three short-answer questions on the board and ask your students to write down their responses. Your questions might call for a review of material you have already discussed or recalling information from assigned readings.
- Ask students to write from a pro or con position. When presenting an argument, stop and ask your students to write down all the reasons and evidence they can think of that supports one side or the other. These statements can be used as the basis for discussion.
- During class, pause for a three-minute write. Periodically ask students to write freely for three minutes on a specific question or topic. They should write whatever pops into their mind without worrying about grammar, spelling, phrasing, or organization. This kind of free writing, according to writing experts, helps students synthesize diverse ideas and identify points they may not understand. There is no need to collect these exercises.
- Have students write a brief summary at the end of class. At the end of the class period, give your students index cards to jot down the key themes, major points, or general principles of the day's discussion. You can easily collect the index cards and review them to see whether the class understood the discussion.
- Have one student keep minutes to be read at the next class meeting. By taking minutes, students get a chance to develop their listening, synthesizing, and writing skills. Boris (1983) suggests the following:
- Prepare your students by having everyone take careful notes for the class period, go home and rework them into minutes, and hand them in for comments. It can be the students' discretion whether the minutes are in outline or narrative form.
- Decide on one to two good models to read or distribute to the class.
- At the beginning of each of the following classes, assign one student to take minutes for the period.
- Give a piece of carbon paper to the student who is taking minutes so that you can have a rough copy. The student then takes the original home and revises it in time to read it aloud at the next class meeting.
- After the student has read their minutes, ask other students to comment on their accuracy and quality. If necessary, the student will revise the minutes and turn in two copies, one for grading and one for your files.
- Structure small group discussion around a writing task. For example, have your students pick three words that are of major importance to the day's session. Ask your class to write freely for two to three minutes on just one of the words. Next, give the students five to ten minutes to meet in groups to share what they have written and generate questions to ask in class.
- Use peer response groups. Divide your class into groups of three or four, no larger. Ask your students to bring to class enough copies of a rough draft of a paper for each person in their group. Give your students guidelines for critiquing the drafts. In any response task, the most important step is for the reader to note the part of the paper that is the strongest and describe to the writer why it worked so well. The following instructions can also be given to the reader:
- State the main point of the paper in a single sentence
- List the major subtopics
- Identify confusing sections of the paper
- Decide whether each section of the paper has enough detail, evidence, and information
- Indicate whether the paper's points follow one another in sequence
- Judge the appropriateness of the opening and concluding paragraphs
- Identify the strengths of the paper
Written critiques done as homework are likely to be more thoughtful, but critiques may also be done during the class period.
- Use read-around groups. Read-around groups are a technique used with short assignments (two to four pages) which allows everyone to read everyone else's paper. Divide the class into groups no larger than four students and divide the papers (coded for anonymity) into as many sets as there are groups. Give each group a set and ask the students to read each paper silently and decide on the best paper in the set. Each group should discuss their choices and come to a consensus on the best paper. The paper's code number is recorded by the group, and the same process is repeated with a new set of papers. After all the groups have read all the sets of papers, someone from each group writes on the board the code number from the best paper in each set. The recurring numbers are circled. Generally, one to three papers stand out.
- Ask students to identify the characteristics of effective writing. After completing the read-around activity, ask your students to reconsider those papers which were voted as excellent by the entire class and to write down features that made each paper outstanding. Write their comments on the board, asking for elaboration and probing vague generalities. In pairs, the students discuss the comments on the board and try to put them into categories such as organization, awareness of audience, thoroughness of detail, etc. You might need to help your students arrange the characteristics into meaningful categories.
The Strategies, Ideas and Recommendations Here Come Primarily From:
Gross Davis, B. Tools for Teaching . San Francisco, Jossey-Bass, 1993.
And These Additional Sources…
Boris, E. Z. "Classroom Minutes: A Valuable Teaching Device." Improving College and
University Teaching, 1983,31(2), 70-73.
Elbow, P. "Using Writing to Teach Something Else." Unpublished paper, 1987.
Hawisher, G. E., and Selfe, C. L. (eds.). Critical Perspectives on Computers and
Composition Instruction. New York: Teachers College Press, 1989.
Holdstein, D. H., and Selfe, C. L. (eds.). Computers and Writing: Theory, Research,
Practice. New York: Modern Language Association, 1990.
Lowman, J. Mastering the Techniques of Teaching . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 1984.
Petersen, B. T. "Additional Resources in the Practice of Writing Across the Disciplines."
In C. W. Griffin (ed.), Teaching Writing in All Disciplines . New Directions in Teaching and Learning, no. 12. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 1982.
Professional and Organizational Development Network in Higher Education.
Bright Idea Network , 1989. (For information contact David Graf, Iowa State University, Ames.)
Pytlik, B. P. "Teaching Teachers of Writing: Workshops on Writing as a Collaborative
Process." College Teaching , 1989, 37(1), 12-14.
Tollefson, S. K. Encouraging Student Writing . Berkeley: Office of Educational
Development, University of California, 1988.
Walvoord, B. F. Helping Students Write Well: A Guide for Teachers in All Disciplines.
(2nd ed.) New York: Modern Language Association, 1986.
Watkins, B. T. "More and More Professors in Many Academic Disciplines Routinely
Require Students to Do Extensive Writing." Chronicle of Higher Education, 1990, 36(44), pp. A13-14, A16.
We use cookies on this site. By continuing to browse without changing your browser settings to block or delete cookies you agree to the UW-Whitewater Privacy Notice .
Chapter 11 Academic Writing
11.2 using strategies for writing college essays, learning objectives.
- Use time-management skills to lay out a work plan for major writing assignments.
- Develop strategies for reading college assignments strategically.
As a college student, you must take complete responsibility for your writing assignments. Your professors are assessing your ability to think for yourself, so they’re less likely to give you ready-made templates on how to write a given essay. This lack of clarity will be unsettling, but it’s part of an important growth process. By using strategies, you can systematically approach each assignment and gather the information you need for your writing requirements.
Plotting a Course for Your Writing Project
Once you know you have an upcoming writing project, you have some basic decisions to make. The following list of questions will lead you to make some preliminary choices for your writing project. (To learn more, see Chapter 5 “Planning,” Section 5.3 “Developing Your Purposes for Writing.”)
- What am I trying to accomplish? Writing can serve a variety of purposes , such as to explain, to persuade, to describe, to entertain, or to compare. Your assignment might specifically dictate the purpose of the writing project. Or the assignment might simply indicate, for example, that you are to show you understand a topic. In such a situation, you would then be free to choose a writing purpose through which you could demonstrate your understanding.
- Who do I want my readers to be? Traditionally the audience for a college student’s paper has been the instructor, but technology is rapidly changing that. Many instructors actively make use of the web’s collaborative opportunities. Your fellow students (or even people outside the class) may now be your audience, and this will change how you approach your assignment. Even if your instructor is the only person who will see your finished product, you have the right (and even the responsibility) to identify an ideal reader or readership for your work. Whoever your audience is, take care to avoid writing too far above or too far beneath their knowledge or interest level.
- What am I writing about? Your topic might be set by your instructor. If so, make sure you know if you have the option of writing about different angles of the topic. If the topic is not preset, choose a topic in which you will be happy to immerse yourself.
- What’s my position on this topic? Analyze your ideas and opinions before you start the writing project, especially if the assignment calls for you to take a position. Leave room for new ideas and changes in your opinion as you research and learn about the topic. Keep in mind that taking a stand is important in your efforts to write a paper that is truly yours rather than a compilation of others’ ideas and opinions, but the stand you take should evolve from encounters with the opinions of others. Monitor your position as you write your first draft, and attend to how it changes over the course of your writing and reading. If your purpose is to compare ideas and opinions on a given topic, clarifying your opinion may not be so critical, but remember that you are still using an interpretive point of view even when you are “merely” summarizing or analyzing data.
- How long does this piece of writing need to be? How much depth should I go into? Many assignments have a predetermined range of page numbers, which somewhat dictates the depth of the topic. If no guidance is provided regarding length, it will be up to you to determine the scope of the writing project. Discussions with other students or your instructor might be helpful in making this determination.
- How should I format this piece of writing? In today’s digital world, you have several equally professional options for completing and presenting your writing assignments. Unless your professor dictates a specific method for awareness and learning purposes, you will probably be free to make these format choices. Even your choice of font can be significant.
- How or where will I publish this piece of writing? You are “publishing” every time you place an essay on a course management system or class-wide wiki or blog , or even when you present an essay orally. More likely than not, if your writing means something to you, you will want to share it with others beyond your instructor in some manner. Knowing how you will publish your work will affect some of the choices you make during the writing process.
- How should my writing look beyond questions of format and font? College essays used to be completely devoid of visuals. Nowadays, given the ease of including them, an essay that does not include visuals might be considered weak. On the other hand, you do not want to include a visual just for the sake of having one. Every visual must be carefully chosen for its value-adding capacity. (To learn more about visuals, see Chapter 9 “Designing,” Section 9.3 “Incorporating Images, Charts, and Graphs.”)
Planning the basics for your essay ahead of time will help assure proper organization for both the process and the product. It is almost a certainty that an unorganized process will lead to an unorganized product.
Reading Assignments Closely and Critically
A close and careful reading of any given writing assignment will help you sort out the ideas you want to develop in your writing assignment and make sense of how any assigned readings fit with the required writing.
Use the following strategies to make the most of every writing assignment you receive:
- Look for key words, especially verbs such as analyze , summarize , evaluate , or argue , in the assignment itself that will give clues to the genre , structure , and medium of writing required.
- Do some prewriting that establishes your base of knowledge and your initial opinions about the subject if the topic is predetermined. Make a list of ideas you will need to learn more about in order to complete the assignment.
- Develop a list of possible ideas you could pursue if the topic is more open. (For more about choosing a topic, see Chapter 5 “Planning,” Section 5.1 “Choosing a Topic.”)
Use the following strategies to help you make the most of readings that support the writing assignment:
- Make a note if you question something in any assigned reading related to the writing assignment.
- Preview each reading assignment by jotting down your existing opinions about the topic before reading. As you read, monitor whether your preconceived opinions prevent you from giving the text a fair reading. After finishing the text, check for changes in your opinions as result of your reading.
- Mark the locations of different opinions in your readings, so you can easily revisit them. (For more on how this works with research, see Chapter 7 “Researching,” Section 7.8 “Creating an Annotated Bibliography.”)
- Note the points in your readings that you consider most interesting and most useful. Consider sharing your thoughts on the text in class discussions.
- Note any inconsistencies or details in your readings with which you disagree. Plan to discuss these details with other students or your professor.
Above all, when questions or concerns arise as you apply these strategies, take them up with your professor directly, either in class or during office hours. Making contact with your professor by asking substantive questions about your reading and writing helps you stand out from the crowd and demonstrates that you are an engaged student.
Connecting Your Reading with Your Writing
College writing often requires the use of others’ opinions and ideas to support, compare, and ground your opinions. You read to understand others’ opinions; you write to express your opinions in the context of what you’ve read. Remember that your writing must be just that—yours. Take care to use others’ opinions and ideas only as support. Make sure your ideas create the core of your writing assignments. (For more on documentation, see Chapter 22 “Appendix B: A Guide to Research and Documentation,” Section 22.5 “Developing a List of Sources.”)

Sharing and Testing Your Thinking with Others
Discussion and debate are mainstays of a college education. Sharing and debating ideas with instructors and other students allows all involved to learn from each other and grow. You often enter into a discussion with your opinions and exit with a widened viewpoint. Although you can read an assignment and generate your understandings and opinions without speaking to another person, you would be limiting yourself by those actions. Instead it is in your best interest to share your opinions and listen to or read others’ opinions on a steady, ongoing basis.
In order to share your ideas and opinions in a scholarly way, you must properly prepare your knowledge bank. Reading widely and using the strategies laid out in the Section 11.2.3 “Connecting Your Reading with Your Writing” are excellent methods for developing that habit.
Make sure to maintain fluidity in your thoughts and opinions. Be prepared to make adjustments as you learn new ideas through discussions with others or through additional readings. You can discuss and debate in person or online, in real time or asynchronously. One advantage to written online discussions and debates is that you have an archived copy for later reference, so you don’t have to rely on memory. For this reason, some instructors choose to develop class sites for student collaboration, discussion, and debate.
Key Takeaways
- The assignments you receive from your instructors in college are as worthy of a close and careful reading as any other texts you are assigned to read. You can learn to employ certain strategies to get the most out of the assignments you are being asked to perform.
- Success in college and life depends on time- and project-management skills: being able to break large projects into smaller, manageable tasks and learning how to work independently and collaboratively.
For every assignment you receive with an open topic, get into the habit of writing a journal or blog entry that answers the following four questions:
- What are some topics that interest you?
- What topics will fit within the time frame you have for the project?
- Of the possible topics, which have enough depth for the required paper?
- For which topics can you think of an angle about which you are passionate?
Figure 11.1 Sample Assignment with Student Annotations

- Writers Handbook. Authored by : Anonymous. Provided by : Anonymous. Located at : http://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/writers-handbook/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy
Learning Strategies That Work
Dr. Mark A. McDaniel shares effective, evidence-based strategies about learning to replace less effective but widely accepted practices.

How do we learn and absorb new information? Which learning strategies actually work and which are mere myths?
Such questions are at the center of the work of Mark McDaniel , professor of psychology and the director of the Center for Integrative Research on Cognition, Learning, and Education at Washington University in St. Louis. McDaniel coauthored the book Make it Stick: The Science of Successful Learning .
In this Q&A adapted from a Career & Academic Resource Center podcast episode , McDaniel discusses his research on human learning and memory, including the most effective strategies for learning throughout a lifetime.
Harvard Extension: In your book, you talk about strategies to help students be better learners in and outside of the classroom. You write, “We harbor deep convictions that we learn better through single-minded focus and dogged repetition. And these beliefs are validated time and again by the visible improvement that comes during practice, practice, practice.”
McDaniel: This judgment that repetition is effective is hard to shake. There are cues present that your brain picks up when you’re rereading, when you’re repeating something that give you the metacognitive, that is your judgment about your own cognition, give you the misimpression that you really have learned this stuff well.
Older learners shouldn’t feel that they’re at a definitive disadvantage, because they’re not. Older learners really want to try to leverage their prior knowledge and use that as a basis to structure and frame and understand new information coming in.
And two of the primary cues are familiarity. So as you keep rereading, the material becomes more familiar to you. And we mistakenly judge familiarity as meaning robust learning.
And the second cue is fluency. It’s very clear from much work in reading and cognitive processes during reading that when you reread something at every level, the processes are more fluent. Word identification is more fluent. Parsing the structure of the sentence is more fluent. Extracting the ideas is more fluent. Everything is more fluent. And we misinterpret these fluency cues that the brain is getting. And these are accurate cues. It is more fluent. But we misinterpret that as meaning, I’ve really got this. I’ve really learned this. I’m not going to forget this. And that’s really misleading.
So let me give you another example. It’s not just rereading. It’s situations in, say, the STEM fields or any place where you’ve got to learn how to solve certain kinds of problems. One of the standard ways that instructors present homework is to present the same kind of problem in block fashion. You may have encountered this in your own math courses, your own physics courses.
So for example, in a physics course, you might get a particular type of work problem. And the parameters on it, the numbers might change, but in your homework, you’re trying to solve two or three or four of these work problems in a row. Well, it gets more and more fluid because exactly what formula you have to use. You know exactly what the problem is about. And as you get more fluid, and as we say in the book, it looks like you’re getting better. You are getting better at these problems.
But the issue is that can you remember how to identify which kinds of problems go with which kinds of solutions a week later when you’re asked to do a test where you have all different kinds of problems? And the answer is no, you cannot when you’ve done this block practice. So even though instructors who feel like their students are doing great with block practice and students will feel like they’re doing great, they are doing great on that kind of block practice, but they’re not at all good now at retaining information about what distinguishing features or problems are signaling certain kinds of approaches.
What you want to do is interleave practice in these problems. You want to randomly have a problem of one type and then solve a problem of another type and then a problem of another type. And in doing that, it feels difficult and it doesn’t feel fluent. And the signals to your brain are, I’m not getting this. I’m not doing very well. But in fact, that effort to try to figure out what kinds of approaches do I need for each problem as I encounter a different kind of problem, that’s producing learning. That’s producing robust skills that stick with you.
So this is a seductive thing that we have to, instructors and students alike, have to understand and have to move beyond those initial judgments, I haven’t learned very much, and trust that the more difficult practice schedule really is the better learning.
And I’ve written more on this since Make It Stick . And one of my strong theoretical tenets now is that in order for students to really embrace these techniques, they have to believe that they work for them. Each student has to believe it works for them. So I prepare demonstrations to show students these techniques work for them.
The net result of adopting these strategies is that students aren’t spending more time. Instead they’re spending more effective time. They’re working better. They’re working smarter.
When students take an exam after doing lots of retrieval practice, they see how well they’ve done. The classroom becomes very exciting. There’s lots of buy-in from the students. There’s lots of energy. There’s lots of stimulation to want to do more of this retrieval practice, more of this difficulty. Because trying to retrieve information is a lot more difficult than rereading it. But it produces robust learning for a number of reasons.
I think students have to trust that these techniques, and I think they also have to observe that these techniques work for them. It’s creating better learning. And then as a learner, you are more motivated to replace these ineffective techniques with more effective techniques.
Harvard Extension: You talk about tips for learners , how to make it stick. And there are several methods or tips that you share: elaboration, generation, reflection, calibration, among others. Which of these techniques is best?
McDaniel: It depends on the learning challenges that are faced. So retrieval practice, which is practicing trying to recall information from memory is really super effective if the requirements of your course require you to reproduce factual information.
For other things, it may be that you want to try something like generating understanding, creating mental models. So if your exams require you to draw inferences and work with new kinds of problems that are illustrative of the principles, but they’re new problems you haven’t seen before, a good technique is to try to connect the information into what I would call mental models. This is your representation of how the parts and the aspects fit together, relate together.
It’s not that one technique is better than the other. It’s that different techniques produce certain kinds of outcomes. And depending on the outcome you want, you might select one technique or the other.
I really firmly believe that to the extent that you can make learning fun and to the extent that one technique really seems more fun to you, that may be your go to technique. I teach a learning strategy course and I make it very clear to students. You don’t need to use all of these techniques. Find a couple that really work for you and then put those in your toolbox and replace rereading with these techniques.
Harvard Extension: You reference lifelong learning and lifelong learners. You talk about the brain being plastic, mutability of the brain in some ways, and give examples of how some lifelong learners approach their learning.
McDaniel: In some sense, more mature learners, older learners, have an advantage because they have more knowledge. And part of learning involves relating new information that’s coming into your prior knowledge, relating it to your knowledge structures, relating it to your schemas for how you think about certain kinds of content.
And so older adults have the advantage of having this richer knowledge base with which they can try to integrate new material. So older learners shouldn’t feel that they’re at a definitive disadvantage, because they’re not. Older learners really want to try to leverage their prior knowledge and use that as a basis to structure and frame and understand new information coming in.
Our challenges as older learners is that we do have these habits of learning that are not very effective. We turn to these habits. And if these aren’t such effective habits, we maybe attribute our failures to learn to age or a lack of native ability or so on and so forth. And in fact, that’s not it at all. In fact, if you adopt more effective strategies at any age, you’re going to find that your learning is more robust, it’s more successful, it falls into place.
You can learn these strategies at any age. Successful lifelong learning is getting these effective strategies in place, trusting them, and having them become a habit for how you’re going to approach your learning challenges.
6 Benefits of Connecting with an Enrollment Coach
Thinking about pursuing a degree or certificate at Harvard Extension School? Learn more about how working with an enrollment coach will get you off to a great start.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

- Utility Menu
- ARC Scheduler
- Student Employment
- Effective Learning Practices
Learning at college requires processing and retaining a high volume of information across various disciplines and subjects at the same time, which can be a daunting task, especially if the information is brand new. In response, college students try out varied approaches to their learning – often drawing from their high school experiences and modeling what they see their peers doing. While it’s great to try different styles and approaches to learning and studying for your courses, it's smart to incorporate into your daily habits some learning practices that are backed up by current research.
Below are some effective learning practices suggested by research in the cognitive and learning sciences:
Take ownership of your educational experience.
As an engaged learner, it is important to take an active, self-directed role in your academic experience. Taking agency might feel new to you. In high school, you might have felt like you had little control over your learning experience, so transitioning to an environment where you are implicitly expected to be in the driver’s seat can be disorienting.
A shift in your mindset regarding your agency, however, can make a big difference in your ability to learn effectively and get the results you want out of your courses.
Here are four concrete actions you can take to assert ownership over your education :
- Attend office hours . Come prepared with questions for your instructor about lectures, readings, or other aspects of the course.
- Schedule meetings with administrators and faculty to discuss your academic trajectory and educational goals. You might meet with your academic adviser, course heads, or the Director of Undergraduate Studies (DUS) in your concentration.
- Identify areas for growth and development based on your academic goals. Then, explore opportunities to shape and further refine your skills in those areas.
- Advocate for support, tools, equipment, or considerations that address your learning needs.
Seek out opportunities for active learning.
Many courses include opportunities for active and engaged learning within their structure. Take advantage of those opportunities in order to enhance your understanding of the material. If such opportunities are not built into the course structure, you can develop your own active learning strategies, including joining study groups and using other active studying techniques. Anytime you grapple actively with your course material, rather than taking it in passively, you’re engaging in active learning. By doing so, you are increasing your retention of key course concepts.
One particularly effective way to help yourself stay focused and engaged in the learning process is to cultivate learning communities, such as accountability groups and study groups. Working in the company of other engaged learners can help remind you why you love learning or why you chose a particular course, concentration, research project, or field of study. Those reminders can re-energize and refocus your efforts.
Practice study strategies that promote deep learning.
In an attempt to keep up with the demands of college, many students learn concepts just in time for assessment benchmarks (tests, exams, and quizzes). The problem with this methodology is that, for many disciplines (and especially in STEM), the concepts build on one another. Students survive the course only to be met at the final with concepts from the first quiz that they have forgotten long ago. This is why deep learning is important. Deep learning occurs when students use study strategies that ensure course ideas and concepts are embedded into long-term, rather than just short-term, memory. Building your study plans and review sessions in a way that helps create a conceptual framing of the material will serve you now and in the long run.
Here are some study strategies that promote deep learning:
Concept Mapping : A concept map is a visualization of knowledge that is organized by the relationships between the topics. At its core, it is made of concepts that are connected together by lines (or arrows) that are labeled with the relationship between the concepts.
Collaboration : You don’t have to go it alone. In fact, research on learning suggests that it’s best not to. Using study groups, ARC accountability hours, office hours, question centers, and other opportunities to engage with your peers helps you not only test your understanding but also learn different approaches to tackling the material.
Self-test : Quiz yourself about the material you need to know with your notes put away. Refamiliarize yourself with the answers to questions you get wrong, wait a few hours, and then try asking yourself again. Use practice tests provided by your courses or use free apps to create quizzes for yourself.
Create a connection : As you try to understand how all the concepts and ideas from your course fit together, try to associate new information with something you already know. Making connections can help you create a more holistic picture of the material you’re learning.
Teach someone (even yourself!) : Try teaching someone the concept you’re trying to remember. You can even try to talk to yourself about it! Vocalizing helps activate different sensory processes, which can enhance memory and help you embed concepts more deeply.
Interleave : We often think we’ll do best if we study one subject for long periods of time, but research contradicts this. Try to work with smaller units of time (a half-hour to an hour) and switch up your subjects. Return to concepts you studied earlier at intervals to ensure you learned them sufficiently.
Be intentional about getting started and avoiding procrastination.
When students struggle to complete tasks and projects, their procrastination is not because of laziness, but rather because of the anxiety and negative emotions that accompany starting the task. Understanding what conditions promote or derail your intention to begin a task can help you avoid procrastinating.
Consider the following tips for getting started:
Eat the Frog : The frog is that one thing you have on your to-do list that you have absolutely no motivation to do and that you’re most likely to procrastinate on. Eating the frog means to just do it, as the first thing you do, and get it over with. If you don’t, odds are that you’ll procrastinate all day. With that one task done, you will experience a sense of accomplishment at the beginning of your day and gain some momentum that will help you move through the rest of your tasks.
Pomodoro Technique : Sometimes, we can procrastinate because we’re overwhelmed by the sheer amount of time we expect it will take to complete a task. But, while it might feel hard to sit down for several hours to work on something, most of us feel we can easily work for a half hour on almost any task. Enter the Pomodoro Technique! When faced with any large task or series of tasks, break the work down into short, timed intervals (25 minutes or so) that are spaced out by short breaks (5 minutes). Working in short intervals trains your brain to focus for manageable periods of time and helps you stay on top of deadlines. With time, the Pomodoro Technique can even help improve your attention span and concentration. Pomodoro is a cyclical system. You work in short sprints, which makes sure you’re consistently productive. You also get to take regular breaks that bolster your motivation and get you ready for your next pomodoro.
Distraction Pads : Sometimes we stop a task that took us a lot of time to get started on because we get distracted by something else. To avoid this, have a notepad beside you while working, and every time you get distracted with a thought, write it down, then push it aside for later. Distracting thoughts can be anything from remembering that you still have another assignment to complete to daydreaming about your next meal. Later on in the day, when you have some free time, you can review your distraction pad to see if any of those thoughts are important and need to be addressed.
Online Apps : It can be hard to rely on our own force of will to get ourselves to start a task, so consider using an external support. There are many self-control apps available for free online (search for "self-control apps"). Check out a few and decide on one that seems most likely to help you eliminate the distractions that can get in the way of starting and completing your work.
Engage in metacognition.
An effective skill for learning is metacognition. Metacognition is the process of “thinking about thinking” or reflecting on personal habits, knowledge, and approaches to learning. Engaging in metacognition enables students to become aware of what they need to do to initiate and persist in tasks, to evaluate their own learning strategies, and to invest the adequate mental effort to succeed. When students work at being aware of their own thinking and learning, they are more likely to recognize patterns and to intentionally transfer knowledge and skills to solve increasingly complex problems. They also develop a greater sense of self-efficacy.
Mentally checking in with yourself while you study is a great metacognitive technique for assessing your level of understanding. Asking lots of “why,” “how,” and “what” questions about the material you’re reviewing helps you to be reflective about your learning and to strategize about how to tackle tricky material. If you know something, you should be able to explain to yourself how you know it. If you don’t know something, you should start by identifying exactly what you don’t know and determining how you can find the answer.
Metacognition is important in helping us overcome illusions of competence (our brain’s natural inclination to think that we know more than we actually know). All too often students don’t discover what they really know until they take a test. Metacognition helps you be a better judge of how well you understand your course material, which then enables you to refine your approach to studying and better prepare for tests.
Accordion style
- Assessing Your Understanding
- Building Your Academic Support System
- Common Class Norms
- First-Year Students
- How to Prepare for Class
- Interacting with Instructors
- Know and Honor Your Priorities
- Memory and Attention
- Minimizing Zoom Fatigue
- Note-taking
- Office Hours
- Perfectionism
- Scheduling Time
- Senior Theses
- Study Groups
- Tackling STEM Courses
- Test Anxiety
Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Austin Community College
- Effective Learning Strategies
- Student Success
- https-www-oercommons-org-courseware-module-25870-s
- https://www.oercommons.org/courseware/module/25870/student/206121
- pre-assesment
Chapter 13: Test Taking Strategies

Learning Framework: Effective Strategies for College Success
Chapter 13: Test Taking Strategies
Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Understand the role of tests in the Learning Cycle.
- Define test anxiety, identify sources of test anxiety and techniques for preventing and controlling it.
- Identify long-term study strategies.
- Become familiar with different types of tests and test formats.
- Implement specific test strategies for before, during and after a test.
- Identify strategies for answering typical kinds of test questions (multiple choice, true/false, matching, short answer and essay).
- Understand the importance of academic integrity and the consequences of dishonesty.
- Effectively evaluate your test results and correct your mistakes.
- Use your test results as a study guide.
Test Taking Strategies
Testing As Part Of The Learning Cycle
Testing is a part of life. Have you ever participated in an athletic event? Completed a crossword puzzle? Acted in a play? Cooked dinner? Answered a child’s question? Prepared a cost estimate? All of these common life situations are forms of tests because they measure how much we know about a specific subject at a single point in time. They alone are not good measurements about how smart or gifted you are—they show only how much you know or can do at that moment. We can learn from how we have performed, and we can think about how to apply what we have learned to do even better next time. We can have fun measuring our progress.
Many of our daily activities are measurements of progress toward mastery of skills or knowledge. We welcome these opportunities for both work and fun. But when these opportunities are part of our academic life, we often dread them and rarely feel any sense of fun. In reality, however, academic tests are similar to real-life tests in the following ways:
- They help us measure our progress toward mastery of a particular skill.
- They are not a representation of how smart, talented, or skilled we are but rather are a measurement only of what we know about a specific subject at a specific point in time.
- They are extraordinary learning opportunities.
Academic tests in college are different from those you took in high school. College instructors expect to see much more of you in an exam: your thoughts, your interpretations, your thinking process, your conclusions. High school teachers usually look for your ability to repeat precisely what you read in your text or heard in your class. Success on high school tests relies much more on memorization than on understanding the material. This is why you need to modify your study habits and your strategies for taking exams in college.
Take a look at the learning cycle “The Learning Cycle: Review and Apply”. In this chapter, we cover reviewing and applying the material you learn; preparing for and taking exams is the practical application of this phase.
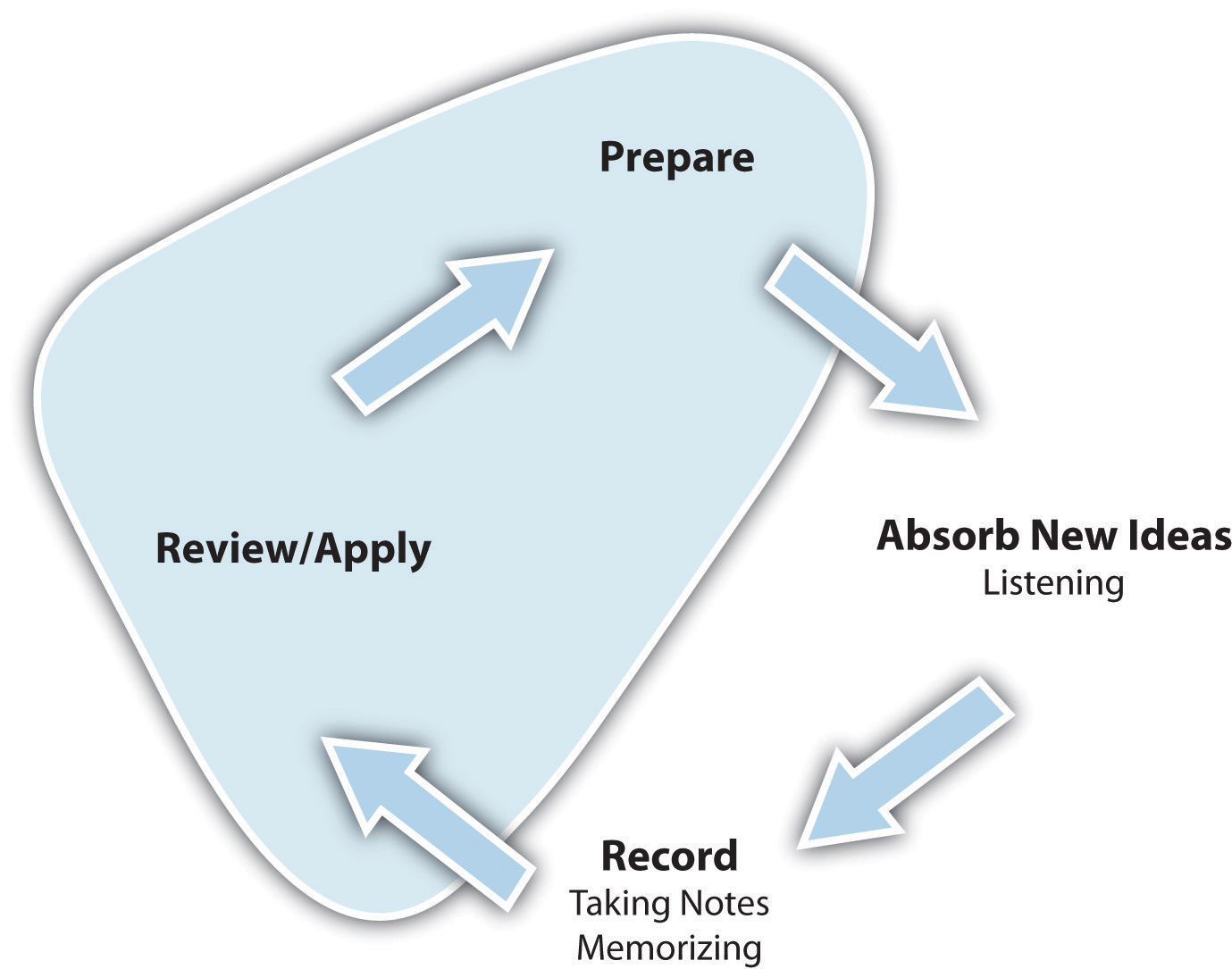
Let’s start at the top of the cycle. You have invested your time in preparing for class, you have been an active listener in class, and you have asked questions and taken notes. You have summarized what you learned and have looked for opportunities to apply the material. You have completed your reading assignments and compared your reading notes with your class notes. And now you hear your instructor say, “Remember the exam next week.”
A sense of dread takes over. You worry about the exam and what might be on it. You stay up for a couple of nights trying to work through the volumes of material the course has covered. Learning or remembering it all seems hopeless. You find yourself staring at the same paragraph in your text over and over again, but you just don’t seem to get it. As the exam looms closer, you feel your understanding of the material is slipping away. You show up for the exam and the first questions look familiar, but then you draw a blank—you’re suffering from test anxiety.
Test Anxiety And How To Control It
For many test-takers, preparing for a test and taking a test can easily cause worry and anxiety. In fact, most students report that they are more stressed by tests and schoolwork than by anything else in their lives, according to the American Test Anxiety Association. Most of us have experienced this. It is normal to feel stress before an exam, and in fact, that may be a good thing. Stress motivates you to study and review, generates adrenaline to help sharpen your reflexes and focus while taking the exam, and may even help you remember some of the material you need. But suffering too many stress symptoms or suffering any of them severely will impede your ability to show what you have learned. Test anxiety is a psychological condition in which a person feels distressed before, during, or after a test or exam to the point where stress causes poor performance. Anxiety during a test interferes with your ability to recall knowledge from memory as well as your ability to use higher-level thinking skills effectively.
- Roughly 16–20 percent of students have high test anxiety.
- Another 18 percent have moderately high test anxiety.
- Test anxiety is the most common academic impairment in grade school, high school, and college.
Below are some effects of moderate anxiety:
- Being distracted during a test
- Having difficulty comprehending relatively simple instructions
- Having trouble organizing or recalling relevant information
- Eating disturbance
- High blood pressure
- Toileting accidents
- Sleep disturbance
- Negative attitudes towards self, school, subjects
Below are some effects of extreme test anxiety:
- Overanxious disorder
- Social phobia
Poor test performance is also a significant outcome of test anxiety. Test-anxious students tend to have lower study skills and lower test-taking skills, but research also suggests that high levels of emotional distress correlate with reduced academic performance overall. Highly test-anxious students score about 12 percentile points below their low-anxiety peers. Students with test anxiety also have higher overall dropout rates. And test anxiety can negatively affect a student’s social, emotional, and behavioral development, as well as feelings about themselves and school.
Why does test anxiety occur? Inferior performance arises not because of intellectual problems or poor academic preparation. It occurs because testing situations create a sense of threat for those who experience test anxiety. The sense of threat then disrupts the learner’s attention and memory.
Other factors can influence test anxiety, too. Students with disabilities and students in gifted education classes tend to experience high rates of test anxiety.
If you experience test anxiety, have hope! Experiencing test anxiety doesn’t mean that there’s something wrong with you or that you aren’t capable of performing well in college. The trick is to keep stress and anxiety at a level where it can help you do your best rather than get in your way.
ACTIVITY: TESTING YOUR TEST ANXIETY
Strategies for preventing and controlling test anxiety.
There are steps you should take if you find that stress is getting in your way:
- Be prepared. A primary cause of test anxiety is not knowing the material. If you take good class and reading notes and review them regularly, this stressor should be greatly reduced if not eliminated. You should be confident going into your exam (but not overconfident).
- Practice! One of the best ways to prepare for an exam is to take practice tests. To overcome test-taking anxiety, practice test-taking in a test-like environment, like a study room in the library. Practice staying calm, relaxed, and confident. If you find yourself feeling overly anxious, stop and start again.
- Avoid negative thoughts. Your own negative thoughts—“I’ll never pass this exam” or “I can’t figure this out, I must be really stupid!”—may move you into a spiraling stress cycle that in itself causes enough anxiety to block your best efforts. When you feel you are brewing a storm of negative thoughts, stop what you are doing and clear your mind. Don’t practice having anxiety! Allow yourself to daydream a little; visualize yourself in pleasant surroundings with good friends. Don’t go back to work until you feel the tension release. Sometimes it helps to take a deep breath and shout “STOP!” and then proceed with clearing your mind. Once your mind is clear, repeat a reasonable affirmation to yourself—“I know this stuff”—before continuing your work.
- Visualize success. Picture what it will feel like to get that A. Translate that vision into specific, reasonable goals and work toward each individual goal. Take one step at a time and reward yourself for each goal you complete.
- It’s all about you! Don’t waste your time comparing yourself to other students in the class, especially during the exam. Keep focused on your own work and your own plan. Exams are not a race, so it doesn’t matter who turns in their paper first. Certainly, you have no idea how they did on their exam, so a thought like “Kristen is already done, she must have aced it, I wish I had her skills” is counterproductive and will only cause additional anxiety.
- Have a plan and follow it. As soon as you know that an exam is coming, you can develop a plan for studying. As soon as you get your exam paper, you should develop a plan for the exam itself. We’ll discuss this later in this chapter. Don’t wait to cram for an exam at the last minute; the pressure you put on yourself and the late-night will cause more anxiety, and you won’t learn or retain much.
- Make sure you eat well and get a good night’s sleep before the exam. Hunger, poor eating habits, energy drinks, and lack of sleep all contribute to test anxiety.
- Chill! You perform best when you are relaxed, so learn some relaxation exercises you can use during an exam. Before you begin your work, take a moment to listen to your body. Which muscles are tense? Move them slowly to relax them. Tense them and relax them. Exhale, then continue to exhale for a few more seconds until you feel that your lungs are empty. Inhale slowly through your nose and feel your ribcage expand as you do. This will help oxygenate your blood and reenergize your mind.
- Come early and prepared. Come to the exam with everything you need like your pencils, erasers, calculator, etc. Arrive to class early so you aren’t worried about time. Try to avoid the pre-exam chatter of your classmates, as this may contribute to your anxiety. Instead, pick your favorite chair and focus on relaxing.
- Put it in perspective. Take a minute to think about the three most important things in your life. They may be your family, your health, your friendships. Will you lose any of these important things as a result of the exam? An exam is not life or death and it needs to be put in perspective.
Health and wellness cannot be overstated as factors in test anxiety. Studying and preparing for exams can be easier when you take care of your mental and physical health. The following are a few tips for better health, better focus, and better grades:
- Try mini-meditation to reduce stress and improve focus. Breathe in deeply, count to five, and exhale slowly. Watch your lower abdomen expand and deflate. Repeat five times.
- Get sleep! Although some students may stay up until 4 a.m. studying, it’s not a healthy habit and is usually counter-productive. Your mind is more efficient when you get enough quality sleep, so make sure to schedule enough time for rest. If you practice a good study schedule, there is no need for all-night cramming. Stick to your study plan, review for about an hour, and get a good night’s sleep.
- Eat well. Have a healthy meal before your exam. Avoid energy drinks that will give you a temporary energy spurt, followed by a crash. Stay hydrated.
- Don’t try to be perfect. You’ll alleviate a lot of anxiety by learning that just “doing your best” is something to be proud of—it doesn’t have to be perfect.
- Reach out for help. If you feel you need assistance with your mental or physical health, talk to a counselor or visit a doctor.
Complete Section #2 Below: ACTIVITY: CONTROLLING NEGATIVE TALK
Watch this video from College Info Geek on Test Anxiety: How to Take On Your Exams Without Stress
Studying To Learn (Not Cram!)
You have truly learned material when you can readily recall it and actually use it, on tests or in real-life situations. Effective studying is your most important tool to combat test anxiety, but more importantly, effective studying helps you truly master the material and be able to apply it as you need to, in school and beyond.
In previous chapters, we set the foundation for effective learning. You learned how to listen and how to take notes. You learned how to read actively and how to capture information from written sources. Now we’ll follow up on some of those key ideas and take the learning cycle to its conclusion and a new beginning.
The reviewing and applying stage of the learning cycle involves studying and using the material you have been exposed to in your course. Recall that we emphasized the importance of reviewing your notes soon after the class or assignment. This review is largely what studying is all about.
Effective studying is an ongoing process of reviewing course material. The first and most important thing you should know is that studying is not something you do a few days before an exam. To be effective, studying is something you do as part of an ongoing learning process, throughout the duration of the term.
Studying Every Day
Studying begins after each class or assignment when you review your notes. Each study session should involve three steps:
- Gather your learning materials. Take time to merge your class notes with your reading notes. How do they complement each other? Stop and think. What do the notes tell you about your material? What aspects of the material are you unsure about? Do you need to reread a part of your text? Write down any questions you have for your instructor and pay a visit during office hours. It is better to clear up any misconceptions and get your questions answered soon after you are exposed to the material, rather than to wait, for two reasons: (1) the question or doubt is fresh in your mind and you won’t forget about it and (2) instructors usually build their lessons on material already presented. If you don’t take these steps now, you are setting yourself up for problems later in the course.
- Apply or visualize. What does this material mean to you ? How will you use this new knowledge? Try to find a way to apply it in your own life or thoughts. If you can’t use the knowledge right away, visualize yourself using the knowledge to solve a problem or visualize yourself teaching the material to other students.
- Cement your knowledge. If you use the two-column note-taking method, cover up the right side of your notes with a piece of paper, leaving the questions in the left column exposed. Test yourself by trying to answer your questions without referring to your notes. How did you do? If you are unsure about anything, look up the answer and write it down right away. Don’t let a wrong answer be the last thing you wrote on a subject because you will most likely continue to remember the wrong answer.
Studying in Course Units
At the end of each unit, or at least every two weeks or so, use your notes and textbook to write an outline or summary of the material in your own words. (Remember the paragraphs you wrote to summarize each class or reading? They’ll be very helpful to you here.) After you have written the summary or outline, go back and reread your outline from the prior unit followed by the one you just wrote. Does the new one build on the earlier one? Do you feel confident you understand the material?
Studying before the Exam
At least a week before a major exam, ask yourself these questions: What has the instructor said about what is included in the exam? Has the instructor said anything about what types of questions will be included? If you were the instructor, what questions would you ask on an exam? Challenge yourself to come up with some really tough open-ended questions. Think about how you might answer them. Be sure to go to any review sessions the instructor or your section leader holds.
Now go back and review your outlines. Do they cover what the instructor has suggested might be on the exam? After reviewing your outlines, reread the sections of your notes that are most closely associated with expected exam questions. Pay special attention to those items the instructor emphasized during class. Read key points aloud and write them down on index cards. Make flashcards to review in downtimes, such as when you’re waiting for a bus or for a class to start.
More Tips for Success
- Schedule a consistent study and review time for each course at least once a week , in addition to your class and assignment time. Keep to that schedule as rigorously as you do your class schedule. Use your study time to go through the steps outlined earlier; this is not meant to be a substitute for your assignment time.
- Get yourself in the right space. Choose to study in a quiet, well-lit space. Your chair should be comfortable but provide good support. Remember that libraries were designed for reading and should be your first option.
- Minimize distractions. Turn off your cell phone and get away from Facebook, television, other nearby activities, and chatty friends or roommates. All of these can cut into the effectiveness of your study efforts. Multitasking and studying don’t mix.
- If you will be studying for a long time, take short breaks at least once an hour. Get up, stretch, breathe deeply, and then get back to work. (If you keep up with your daily assignments and schedule weekly review sessions for yourself—and keep them—there should be almost no need for long study sessions.)
Studying in Groups
Study groups are a great idea, as long as they are thoughtfully managed. A study group can give you new perspectives on course material and help you fill in gaps in your notes. Discussing course content will sharpen your critical thinking related to the subject, and being part of a group to which you are accountable will help you study consistently. In a study group, you will end up “teaching” each other the material, which is the strongest way to retain new material. But remember, being in a group working together doesn’t mean there will be less work for you as an individual; your work will just be much more effective.
Here are some tips for creating and managing effective study groups:
- Think small. Limit your study group to no more than three or four people. A larger group would limit each student’s participation and make scheduling of regular study sessions a real problem.
- Go for quality. Look for students who are doing well in the course, who ask questions, and who participate in class discussions. Don’t make friendship the primary consideration for who should be in your group. Meet up with your friends instead during “social time”—study time is all about learning.
- Look for complementary skills and learning styles. Complementary skills make for a good study group because your weaknesses will be countered by another student’s strengths. When a subject requires a combination of various skills, strengths in each of those skills are helpful (e.g., a group with one student who is really good at physics and another at math would be perfect for an engineering course). Finally, a variety of learning styles is helpful because each of you picks up differing signals and emphases from the instructor that you can share with each other, so you will not likely miss important points.
- Meet regularly. When you first set up a study group, agree to a regular meeting schedule and stick to it. Moving study session times around can result in nonparticipation, lack of preparation, and eventually the collapse of the study group. Equally important is keeping your sessions to the allotted times. If you waste time and regularly meet much longer than you agreed to, participants will not feel they are getting study value for their time invested.
- Define an agenda and objectives. Give your study sessions focus so that you don’t get sidetracked. Based on requests and comments from the group, the moderator should develop the agenda and start each session by summarizing what the group expects to cover and then keep the group to task.
- Review and discuss class and assignment notes since your last meeting.
- Discuss assigned readings.
- Quiz each other on class material.
- “Reteach” aspects of the material team participants are unsure of.
- Brainstorm possible test questions and responses.
- Review quiz and test results and correct misunderstandings.
- Critique each other’s ideas for paper themes and approaches.
- Define questions to ask the instructor.
- Assign follow-up work. If there is any work that needs to be done between meetings, make sure that all team members know specifically what is expected of them and agree to do the work.
- Rotate the role of moderator or discussion leader. This helps ensure “ownership” of the group is spread equally across all members and ensures active participation and careful preparation.
Types of Tests
All tests are designed to determine how much you know about a particular subject at a particular point in time. There are many ways to understand how tests and exams fit into academia and college culture. One way is to ask what purpose the tests (also called assessments) serve. For example, what is your professor trying to achieve if they give you a survey-type test on the first day of class? How might the purpose of that test differ from that of, say, a practice quiz given before a midterm? And what is the purpose of a midterm?
Obviously, each survey, quiz, practice test, midterm, and final exam can serve different purposes. Depending upon the purpose, the assessment will fall into one of the following three categories:
- Pre-assessment
- Formative assessment
- Summative assessment
Pre-assessments : Tests in this category are used to measure the beliefs, assumptions, knowledge, and skills that you have when you begin a class or before you begin working on a new topic. With pre-assessments, your professor gathers baseline data to use at a later time to evaluate change—that is, by comparing former knowledge or skills against what you learn in class.
One approach to pre-assessment is for a professor to ask students at the start of the term to describe a term or concept that’s foundational to the course. Then, later in the course, the professor revisits that data to determine how the instruction changed your understanding of the same concept. Comparing what you know or believe before and after a course or lesson is a productive way to gauge how successful your learning was and how successful the teaching was.
Formative assessments : Tests in this category are typically quizzes, unit tests, pop quizzes, and review quizzes from a textbook or its Web site. Their main objective is to make sure you know the fundamental material before moving on to more challenging topics. Because these quizzes usually don’t count much toward your final grade, many students think they are not very important. In fact, these quizzes are very important, particularly to you; they can help you to identify what you know and what you still need to learn to be successful in the course and in applying the material. A poor result on a quiz may not negatively affect your final grade much, but learning from its results and correcting your mistakes will affect your final grade, on the positive side, when you take midterms and finals!
Summative assessments : Tests in this category are the assessments that students are most familiar with: midterms and finals. They are used by the instructor to determine if you are mastering a large portion of the material, and as such, they usually carry a heavyweight toward your final grade for the course. Because of this, summative assessments can be stressful, but they can also be an effective measurement tool.
Test Formats
Tests vary in style, rigor, and requirements. For example, in a closed book test, a test taker is typically required to rely upon memory to respond to specific items. In an open-book test, though, a test taker may use one or more supplementary resources such as a reference book or notes. Open-book testing may be used for subjects in which many technical terms or formulas are required to effectively answer questions, like in chemistry or physics.
In addition, tests may be administered formally or informally. In an informal test, you might simply respond in a class to questions posed by the instructor. In a formal test, you are usually expected to work alone, and the stakes are higher.
Below is a sampling of common test formats you may encounter. If you know what kind of test you’ll be taking, you can tailor your study approach to the format.
Common Test Types
There are three common test types: written tests, oral tests, and electronic tests. Let’s look at the kinds of things you’ll be expected to complete in each test type.
Written tests can be open book, closed book, or anywhere in between. Students are required to give written answers (as the name of this test type implies).
- Paper tests are still the most common type of test, requiring students to write answers on the test pages or in a separate test booklet or answer sheet. They are typically used for in-class tests. Neatness and good grammar count, even if it’s not an English exam. Remember that the instructor will be reading dozens of test papers and will not likely spend much time trying to figure out your hieroglyphics, arrows, and cross-outs.
- Open-book tests allow the student to consult their notes, textbook, or both while taking the exam. Instructors often give this type of test when they are more interested in seeing your thoughts and critical thinking than your memory power. Be prepared to expose and defend your own viewpoints. When preparing, know where key material is present in your book and notes; create an index for your notes and use sticky notes to flag key pages of your textbook before the exam. Be careful when copying information or formulas to your test answers, because nothing looks worse in an open-book exam than misusing the material at your disposal.
- Take-home tests are like open-book tests except you have the luxury of time on your side. Make sure you submit the exam on time. Know what the instructor’s expectations are about the content of your answers. The instructor will likely expect more detail and complete work because you are not under a strict time limit and because you have access to reference materials. Be clear about when the test is due. (Some instructors will ask you to e-mail your exam to them by a specific time.) Also, find out if the instructor allows or expects you to collaborate with classmates. Be sure to type your exam and don’t forget to spell-check!
Below you’ll find a table of the most common question types in written tests:
Oral Tests or Presentations are a discussion type of test. They are also subjective: there isn’t just one correct answer to the test questions. The oral test is practiced in many schools and disciplines in which an examiner verbally poses questions to the student. The student must answer the question in such a way as to demonstrate sufficient knowledge of the subject. Usually, study guides or a syllabus are made available so that the students may prepare for the exam by reviewing practice questions and topics likely to be on the exam. The instructor can (and likely will) probe you on certain points, question your assumptions, or ask you to defend your point of view. Make sure you practice your presentation many times with and without an audience (your study group is good for this). Have a clear and concise point of view and keep to the allotted time. (You don’t want to miss delivering a killer close if your instructor cuts you off because you weren’t aware of the time!)
Electronic Tests or Online Tests are most commonly used for formative assessments, although they are starting to find their way into high-stakes exams, particularly in large lecture classes that fulfill a graduation requirement (like introductory psychology or history survey courses). The main advantage of online tests is that they can be computer-graded, providing fast feedback to the student (with formative tests) and allowing the instructor to grade hundreds of exams easily (with summative assessments). Since these tests are computer-graded, be aware that the instructor’s judgment is not involved in the grading. Your answers will be either right or wrong; there is no room for partially correct responses. With online tests, be sure you understand the testing software. Are there practice questions? If so, make sure you use them. Find out if you will be allowed to move freely between test sections to go back and check your work or to complete questions you might have skipped. Some testing software does not allow you to return to sections once they are “submitted.” Unless your exam needs to be taken at a specific time, don’t wait until the last minute to take the test. Should you have technical problems, you want to have time to resolve the issues. To avoid any conflicts with the testing software, close all other software applications before beginning the testing software. Electronic tests in the classroom are becoming more common as colleges install “smart classrooms” with technology such as wireless “clicker” technology that instructors may use to get a quick read of students’ understanding of a lecture. This testing method allows for only true-or-false and multiple-choice questions, so it is rarely used for summative assessments. When taking this kind of quick quiz, take notes on questions you miss so that you can focus on them when you do your own review.
Complete Section #3 Below: ACTIVITY: Test your Test Knowledge Crossword
Test-taking strategies.
You have used all the study skills you learned in this course. You listen in class, take clear notes, read your textbook, compare your textbook and classroom notes, and review regularly. You have brought your test anxiety into control. Your upcoming test is now an opportunity for you to show what you have learned What else can you do to ensure success on a test?
Before the Test
- Use your study skills as you go.
- What is the test format?
- What chapters does it cover?
- How many questions are on it?
- What is the time limit?
- What materials are allowed?
- Is a study guide provided?
- Are practice tests available?
- What percentage of your final grade is the test?
- Classroom notes
- Textbook notes
- Master set of notes
- Study guides
- Practice tests
- Slides or presentations
- Make a study plan for several days before the exam
- Have a clear goal for each study session
- Study in 45-60 minutes chunks and then take a break
- Create flashcards
- Make a study guide
- Predict test questions
- Practice answering essay questions
- Get a good night’s sleep.
- Have a healthy breakfast
- Answer sheets/test booklets
- Calculators
- Arrive early and relax

During the Test
Scan the test first to see what it covers
- This often reduces anxiety and boosts confidence
- Identify the point value of each test section
- If you are trying to remember things like formulas, definitions, lists, etc., flip your test over and write down everything you are trying to remember. This will clear your brain, allowing you to focus 100% on the exam, rather than using part of your attention to remember specific information.
- Now that you have scanned your test, how much time should you spend on each section?
- This can often reduce anxiety and keeps you from unnecessarily rushing
- Check on the time often to make sure you are on track. Slow down or speed up as necessary.
- Work on high point-value questions first
- Don’t assume you know what the instructions are. Be sure!
- Go through the test and answer all of the ones you know first.
- Skip the ones you are unsure of. There are often clues later in the exam or another question that will spark your memory.
- Stay positive by not getting down about a question you don’t know. Skip it and return to it later.
- Read each question carefully!
- Answer everything. Don’t leave anything blank, even if you have to guess.
- Don’t rush! Use all the time available. There are no points for finishing first.
- Check to make sure you have answered all parts of a question.
- Check your answer sheet every 10 questions to make sure you aren’t mismarking.
- Only change an answer if you are SURE you made a mistake. Your first instinct is most likely correct.
After the Test
- Reward yourself for a job well done!
- We have a tendency to take a break from our studies after an exam, often resulting in being behind the next week.
- What did you well?
- What can you do differently for the next test?
- What did you learn about this instructor’s testing style and how will that impact your study plan?
- Did you lose points for not answering all parts of the essay?
- Did you not read questions or instructions carefully?
- Do you need to focus more on dates, vocabulary, formulas, etc.?
- Review your test carefully and fix all errors so you don’t make the same mistakes again.
- Apply the feedback to the next test
Strategies For Specific Question Types
You can gain even more confidence in your test-taking abilities by understanding the different kinds of questions an instructor may ask and apply the following proven strategies for answering them. Most instructors will likely use various conventional types of questions. Here are some tips for handling the most common types.
Multiple-Choice Questions
- If there are multiple right answers, does the instructor expect you to choose just one, or do you need to mark all correct options?
- Then consider all the options.
- Eliminate first the options that are clearly incorrect.
- Compare the remaining answers with your own answer before choosing one and marking your paper.
- If you are stuck, treat the remaining answers as True/Fale statements. This often helps pick the correct answer.
- Absolute words like “never,” “always,” “every,” or “none” are rarely found in a correct option.
- Less absolute words like “usually,” “often,” or “rarely” are regularly found in correct options.
- Be on the lookout for the word “not” in the stem phrase and in the answer choice options; it is an easy word to miss if you are reading too quickly, but it completely changes the meaning of the possible statements.
- There are often clues in later questions. Or, you may recall information that you had forgotten
- Do not leave any questions blank, unless there is a penalty for wrong answers (this is often on standardized tests like the SAT and LSAT but rarely on college tests.)
True-or-False Questions
- Most of the tips for multiple-choice questions apply here as well.
- Be particularly aware of the words “never,” “always,” “every,” “none,” and “not” because they can determine the correct answer.
- Answer the questions that are obvious to you first. Then go back to statements that require more thought.
- If the question is stated in the positive, restate it to yourself in the negative by adding the word “not” or “never.” Does the new statement sound truer or more false?
- If you still are unsure whether a statement is true or false and must guess, choose “true” because most tests include more true statements than false (but don’t guess if a wrong answer penalizes you more than one left blank).
Matching Columns
- Start by looking at the two columns to be matched. Is there an equal number of items in both columns? If they are not equal, do you have to match some items in the shorter column to two or more items in the longer column, or can you leave some items unmatched? Read the directions to be sure.
- If one column has a series of single words to be matched to phrases in the other column, read all the phrases first, then all the single words before trying to make any matches. Now go back and read each phrase and find the word that best suits the phrase.
- If both columns have single words to be matched, look to cut down the number of potential matches by grouping them by parts of speech (nouns with nouns, verbs with verbs, etc.).
- As always, start by making the matches that are obvious to you, and then work on the ones that require more thought. Mark off all items you have already used so you can easily see which words or phrases still remain to be matched.
Short Answer Questions
- Short answer questions are designed for you to recall and provide some very specific information (unlike essay questions, which also ask you to apply critical thinking to that information). When you read the question, ask yourself what exactly the instructor wants to know. Keep your answers short and specific .
Essay Questions
- Essay questions are used by instructors to evaluate your thinking and reasoning applied to the material covered in a course. Good essay answers are based on your thoughts, supported by examples from classes and reading assignments.
- Careful planning is critical to answering essay questions effectively. Note how many essay questions you have to answer and how difficult each question seems. Then allocate your time accordingly.
- Watch for words that describe the instructor’s expectations for your response (see the table below.)
- Use other parts of the exam, like multiple choice, to help you recall vocabulary or specific information.
- Jot down the specific information you might want to use, such as names, dates, and places.
- For example, rather than writing, “In our study of the Civil War, it is helpful to consider the many facets that lead to conflict, especially the economic factors that help explain this important turning point in our nation’s history,” write a more direct and concise statement like this: “Economic factors help explain the start of the Civil War.”
- Allow time to proofread your essay. You want your instructor to want to read your essay, not dread it.
- Remember that grading essays is are largely subjective, and a favorable impression can lead to more favorable grading.
- Be sure to answer all parts of the question. Essay questions often have more than one part. Remember, too, that essay questions often have multiple acceptable answers.
Words to Watch for in Essay Questions
Below is another video from College Info Geek called 10 Ways to Avoid Making Stupid Mistakes on Exams.
Practicing Academic Integrity On Exams
Throughout this book, we have focused on the active process of learning , not just on how to get good grades. The attitude of some students that grades are the end-all in academics has led many students to resort to academic dishonesty to try to get the best possible grades or handle the pressure of an academic program. Although you may be further tempted if you’ve heard people say, “Everybody does it,” or “It’s no big deal at my school,” you should be mindful of the consequences of cheating:
- You don’t learn as much. Cheating may get you the right answer on a particular exam question, but it won’t teach you how to apply knowledge in the world after school, nor will it give you a foundation of knowledge for learning the more advanced material. When you cheat, you cheat yourself out of opportunities.
- You risk failing the course or even expulsion from school. Each institution has its own definitions of and penalties for academic dishonesty, but most include cheating, plagiarism, and fabrication or falsification. The exact details of what is allowed or not allowed vary somewhat among different colleges and even instructors, so you should be sure to check your school’s Web site and your instructor’s guidelines to see what rules apply. Ignorance of the rules is seldom considered a valid defense.
- Cheating causes stress. Fear of getting caught will cause you stress and anxiety; this will get in the way of performing well with the information you do know.
- You’re throwing away your money and time. Getting a college education is a big investment of money and effort. You’re simply not getting your full value when you cheat because you don’t learn as much.
- You are trashing your integrity. Cheating once and getting away with it makes it easier to cheat again, and the more you cheat, the more comfortable you will feel with giving up your integrity in other areas of life—with perhaps even more serious consequences.
- Cheating lowers your self-esteem. If you cheat, you are telling yourself that you are simply not smart enough to handle learning. It also robs you of the feeling of satisfaction from genuine success.
Technology has made it easier to cheat. Your credit card and an Internet connection can procure a paper for you on just about any subject and length. You can copy and paste for free from various Web sites. Students have made creative use of texting and video on their cell phones to gain unauthorized access to material for exams. But be aware that technology has also created ways for instructors to easily detect these forms of academic dishonesty. Most colleges make these tools available to their instructors. Instructors are also modifying their testing approaches to reduce potential academic misconduct by using methods that are harder to cheat at (such as in-class essays that evaluate your thinking and oral presentations).
If you feel uneasy about doing something in your college work, trust your instincts. Confirm with the instructor that your intended form of research or use of the material is acceptable. Cheating just doesn’t pay.
Examples of Academic Dishonesty
Academic dishonesty can take many forms, and you should be careful to avoid them. The following list from Northwestern University is a clear and complete compilation of what most institutions will consider unacceptable academic behavior.
- Cheating: using unauthorized notes, study aids, or information on an examination; altering a graded work after it has been returned, then submitting the work for regrading; allowing another person to do one’s work and submitting that work under one’s own name; submitting identical or similar papers for credit in more than one course without prior permission from the course instructors.
- Plagiarism: submitting material that in part or whole is not entirely one’s own work without attributing those same portions to their correct source. You can read more about plagiarism in Chapters 2 and 14.
- Fabrication: falsifying or inventing any information, data, or citation; presenting data that were not gathered in accordance with standard guidelines defining the appropriate methods for collecting or generating data and failing to include an accurate account of the method by which the data were gathered or collected.
- Obtaining an Unfair Advantage: (a) stealing, reproducing, circulating, or otherwise gaining access to examination materials prior to the time authorized by the instructor; (b) stealing, destroying, defacing, or concealing library materials with the purpose of depriving others of their use; (c) unauthorized collaboration on an academic assignment; (d) retaining, possessing, using or circulating previously given examination materials, where those materials clearly indicate that they are to be returned to the instructor at the conclusion of the examination; (e) intentionally obstructing or interfering with another student’s academic work; or (f) otherwise undertaking an activity with the purpose of creating or obtaining an unfair academic advantage over other students’ academic work.
- Aiding and Abetting Academic Dishonesty: (a) providing material, information, or other assistance to another person with knowledge that such aid could be used in any of the violations stated above, or (b) providing false information in connection with any inquiry regarding academic integrity.
- Falsification of Records and Official Documents: altering documents affecting academic records; forging signatures of authorization or falsifying information on an official academic document, grade report, letter of permission, petition, drop/add form, ID card, or any other official University document.
- Unauthorized Access to computerized academic or administrative records or systems: viewing or altering computer records, modifying computer programs or systems, releasing or dispensing information gained via unauthorized access, or interfering with the use or availability of computer systems or information.
Using Test Results
So far, we have focused on how to study for and take tests effectively. This section discusses how to use test results to their greatest benefit. Some of your most important learning begins when your graded test paper is returned to you. Your first reaction, of course, is to see what grade you received and how you did compared with your classmates. This is a natural reaction.
Make sure you listen to the instructor as the papers are returned. What is the instructor saying about the test? Is there a particular point everyone had trouble with? Does the instructor generally think everyone did well? The instructor’s comments at this point may give you important information about what you should study more, about the value of review sessions, and even about possible questions for the next exam.
Although you may be tempted to throw away the exam, don’t. It is a very helpful tool for the next phase of preparing for learning. This is a three-step process, beginning with evaluating your results.
Evaluating Your Test Results
When you receive your test back, sit quietly and take a close look at it. What questions did you get wrong? What kind of mistakes were they? (See Table: “Exam Errors and How to Correct Them”.) Do you see a pattern? What questions did you get right? What were your strengths? What can you learn from the instructor’s comments?
Now think of the way in which you prepared for the exam and the extent to which you applied the exam strategies described earlier in this chapter. Were you prepared for the exam? Did you study the right material? What surprised you? Did you read the entire test before starting? Did your time allocation work well, or were you short of time on certain parts of the exam?
Table: Exam Errors and How to Correct Them
Based on your analysis of your test, identify the kind of corrective steps you should take to improve your learning and test performance. Implement those steps as you begin your preparation for your next class. If you don’t learn from your mistakes, you are doomed to repeat them; if you don’t learn from your successes, it will be harder to repeat them.
Correcting Your Mistakes
The second step in making your test work for you is to correct your wrong answers. The last time you wrote the information (when you took the test), you created a link to the wrong information in your memory, so that must be corrected.
- For multiple-choice questions, write out the question stem with the correct answer to form a single correct sentence or phrase.
- For true-or-false questions, write the full statement if it is true; if it is false, reword it in such a way that it is true (such as by inserting the word “not”). Then write the new statement.
- For math and science questions involving calculations, redo the entire solution with the calculations written out fully.
- You need not rewrite an entire essay question if you did not do well, but you should create a new outline for what would be a correct answer. Make sure you incorporate any ideas triggered by your instructor’s comments.
- When you have rewritten all your answers, read them all out loud before incorporating your new answers in your notes.
I ntegrating Your Test into Your Study Guide
Your corrected quizzes and midterm exams are important study tools for final exams. Make sure you file them with your notes for the study unit. Take the time to annotate your notes based on the exam. Pay particular attention to any gaps in your notes on topics that appeared in the quiz or exam. Research those points in your text or online and complete your notes. Review your exams throughout the term (not just before the final) to be sure you cement the course material into your memory.
When you prepare for the final exam, start by reviewing your quizzes and other tests to predict the kinds of questions the instructor may ask on the final. This will help focus your final studying when you have a large amount of coursework to cover.
If You Don’t Get Your Test Back
If your instructor chooses not to return tests to students, make an appointment to see the instructor soon after the test to review it and your performance. Take notes on what you had trouble with and the expected answers. Add these notes to your study guide. Make sure you don’t lose out on the opportunity to learn from your results.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Some stress before a test or exam is common and beneficial but test anxiety is stress that gets in the way of performing effectively.
- The most common causes of test anxiety are a lack of preparation and negative attitudes.
- The key to combating test anxiety is to try to reduce stressors to a manageable level rather than try to eliminate them totally.
- Effective studying happens over time, not just a few days before an exam. Consistent and regular review time helps you learn the material better and saves you time and anguish as exam time approaches.
- Study groups are a great idea, provided they are thoughtfully managed.
- In addition to studying, prepare for exams and quizzes by getting plenty of rest, eating well, and getting some exercise the day before the exam.
- Before the exam, learn as much as you can about the kinds of questions your instructor will be asking and the specific material that will be covered.
- The first step to the successful completion of an exam is to browse the entire exam and develop a plan (including a “time budget”) for completing the exam.
- Read questions carefully. Underline keywords in questions, particularly in essay questions and science questions.
- Being dishonest can have major consequences that can affect not only your college career but also your life beyond college.
- When you cheat, you are primarily cheating yourself.
- Working with exams does not end when your instructor hands back your graded test.
- Quizzes and midterms are reliable predictors of the kind of material that will be on the final exam.
- When evaluating your test performance, don’t look only at the content you missed. Identify the types of mistakes you commonly make and formulate plans to prevent these mistakes in future assessments.
ACTIVITY: CONTROLLING NEGATIVE TALK
You’ve learned how negative thoughts contribute to test anxiety and keep you from doing as well as you can. Take some time to disarm your most frequent offenders. From the following list, select three negative thoughts that you have experienced (or write your own). Then fill in the second and third columns for each statement, as shown in the example.
- I don’t know anything.…What’s the matter with me?
- If I fail this test, I’ll flunk the course.
- I should have studied more.…I’ll never make it through.
- I just can’t think.…Why did I ever take this course?
- I know everyone’s doing better than I am.
- If I fail this test, my dad (or husband/wife, boyfriend/girlfriend, teacher) will be mad. I don’t know how I can face them again.
- I’m going to be the last one done again.…I must really be stupid.
- I’m getting really tense again; my hands are shaking.…I can’t even hold the pen.
- I can’t remember a thing.…This always happens to me.…I never do well on anything.
ACTIVITY: Test Your Test Knowledge: Crossword

LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
CC LICENSED CONTENT, ORIGINAL
- Test Taking Strategies. Authored by : Heather Syrett. Provided by : Austin Community College. License : CC BY-NC-SA-4.0
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
- Chapter 6: Preparing for and Taking Tests . in College Success. Authored by: Anonymous. Provided by: University of Minnesota. Located at : http://www.oercommons.org/courses/college-success/view . License : CC BY-NC-SA-4.0
- Testing Strategies in EDUC 1300. Authored by: Linda Bruce. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/sanjacinto-learningframework/chapter/testing-strategies/ . License : CC BY 4.0
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED CONTENT
- Test Anxiety: How to Take On Your Exams Without Stress - College Info Geek. Authored by : Thomas Frank. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fHfHSq7PVDU . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube
- 10 Ways to Avoid Making Stupid Mistakes on Exams - College Info Geez. Authored by : Thomas Frank. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OY6Z8gNKp-w . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
Version History

Studying 101: Study Smarter Not Harder
Do you ever feel like your study habits simply aren’t cutting it? Do you wonder what you could be doing to perform better in class and on exams? Many students realize that their high school study habits aren’t very effective in college. This is understandable, as college is quite different from high school. The professors are less personally involved, classes are bigger, exams are worth more, reading is more intense, and classes are much more rigorous. That doesn’t mean there’s anything wrong with you; it just means you need to learn some more effective study skills. Fortunately, there are many active, effective study strategies that are shown to be effective in college classes.
This handout offers several tips on effective studying. Implementing these tips into your regular study routine will help you to efficiently and effectively learn course material. Experiment with them and find some that work for you.
Reading is not studying
Simply reading and re-reading texts or notes is not actively engaging in the material. It is simply re-reading your notes. Only ‘doing’ the readings for class is not studying. It is simply doing the reading for class. Re-reading leads to quick forgetting.
Think of reading as an important part of pre-studying, but learning information requires actively engaging in the material (Edwards, 2014). Active engagement is the process of constructing meaning from text that involves making connections to lectures, forming examples, and regulating your own learning (Davis, 2007). Active studying does not mean highlighting or underlining text, re-reading, or rote memorization. Though these activities may help to keep you engaged in the task, they are not considered active studying techniques and are weakly related to improved learning (Mackenzie, 1994).
Ideas for active studying include:
- Create a study guide by topic. Formulate questions and problems and write complete answers. Create your own quiz.
- Become a teacher. Say the information aloud in your own words as if you are the instructor and teaching the concepts to a class.
- Derive examples that relate to your own experiences.
- Create concept maps or diagrams that explain the material.
- Develop symbols that represent concepts.
- For non-technical classes (e.g., English, History, Psychology), figure out the big ideas so you can explain, contrast, and re-evaluate them.
- For technical classes, work the problems and explain the steps and why they work.
- Study in terms of question, evidence, and conclusion: What is the question posed by the instructor/author? What is the evidence that they present? What is the conclusion?
Organization and planning will help you to actively study for your courses. When studying for a test, organize your materials first and then begin your active reviewing by topic (Newport, 2007). Often professors provide subtopics on the syllabi. Use them as a guide to help organize your materials. For example, gather all of the materials for one topic (e.g., PowerPoint notes, text book notes, articles, homework, etc.) and put them together in a pile. Label each pile with the topic and study by topics.
For more information on the principle behind active studying, check out our tipsheet on metacognition .
Understand the Study Cycle
The Study Cycle , developed by Frank Christ, breaks down the different parts of studying: previewing, attending class, reviewing, studying, and checking your understanding. Although each step may seem obvious at a glance, all too often students try to take shortcuts and miss opportunities for good learning. For example, you may skip a reading before class because the professor covers the same material in class; doing so misses a key opportunity to learn in different modes (reading and listening) and to benefit from the repetition and distributed practice (see #3 below) that you’ll get from both reading ahead and attending class. Understanding the importance of all stages of this cycle will help make sure you don’t miss opportunities to learn effectively.
Spacing out is good
One of the most impactful learning strategies is “distributed practice”—spacing out your studying over several short periods of time over several days and weeks (Newport, 2007). The most effective practice is to work a short time on each class every day. The total amount of time spent studying will be the same (or less) than one or two marathon library sessions, but you will learn the information more deeply and retain much more for the long term—which will help get you an A on the final. The important thing is how you use your study time, not how long you study. Long study sessions lead to a lack of concentration and thus a lack of learning and retention.
In order to spread out studying over short periods of time across several days and weeks, you need control over your schedule . Keeping a list of tasks to complete on a daily basis will help you to include regular active studying sessions for each class. Try to do something for each class each day. Be specific and realistic regarding how long you plan to spend on each task—you should not have more tasks on your list than you can reasonably complete during the day.
For example, you may do a few problems per day in math rather than all of them the hour before class. In history, you can spend 15-20 minutes each day actively studying your class notes. Thus, your studying time may still be the same length, but rather than only preparing for one class, you will be preparing for all of your classes in short stretches. This will help focus, stay on top of your work, and retain information.
In addition to learning the material more deeply, spacing out your work helps stave off procrastination. Rather than having to face the dreaded project for four hours on Monday, you can face the dreaded project for 30 minutes each day. The shorter, more consistent time to work on a dreaded project is likely to be more acceptable and less likely to be delayed to the last minute. Finally, if you have to memorize material for class (names, dates, formulas), it is best to make flashcards for this material and review periodically throughout the day rather than one long, memorization session (Wissman and Rawson, 2012). See our handout on memorization strategies to learn more.
It’s good to be intense
Not all studying is equal. You will accomplish more if you study intensively. Intensive study sessions are short and will allow you to get work done with minimal wasted effort. Shorter, intensive study times are more effective than drawn out studying.
In fact, one of the most impactful study strategies is distributing studying over multiple sessions (Newport, 2007). Intensive study sessions can last 30 or 45-minute sessions and include active studying strategies. For example, self-testing is an active study strategy that improves the intensity of studying and efficiency of learning. However, planning to spend hours on end self-testing is likely to cause you to become distracted and lose your attention.
On the other hand, if you plan to quiz yourself on the course material for 45 minutes and then take a break, you are much more likely to maintain your attention and retain the information. Furthermore, the shorter, more intense sessions will likely put the pressure on that is needed to prevent procrastination.
Silence isn’t golden
Know where you study best. The silence of a library may not be the best place for you. It’s important to consider what noise environment works best for you. You might find that you concentrate better with some background noise. Some people find that listening to classical music while studying helps them concentrate, while others find this highly distracting. The point is that the silence of the library may be just as distracting (or more) than the noise of a gymnasium. Thus, if silence is distracting, but you prefer to study in the library, try the first or second floors where there is more background ‘buzz.’
Keep in mind that active studying is rarely silent as it often requires saying the material aloud.
Problems are your friend
Working and re-working problems is important for technical courses (e.g., math, economics). Be able to explain the steps of the problems and why they work.
In technical courses, it is usually more important to work problems than read the text (Newport, 2007). In class, write down in detail the practice problems demonstrated by the professor. Annotate each step and ask questions if you are confused. At the very least, record the question and the answer (even if you miss the steps).
When preparing for tests, put together a large list of problems from the course materials and lectures. Work the problems and explain the steps and why they work (Carrier, 2003).
Reconsider multitasking
A significant amount of research indicates that multi-tasking does not improve efficiency and actually negatively affects results (Junco, 2012).
In order to study smarter, not harder, you will need to eliminate distractions during your study sessions. Social media, web browsing, game playing, texting, etc. will severely affect the intensity of your study sessions if you allow them! Research is clear that multi-tasking (e.g., responding to texts, while studying), increases the amount of time needed to learn material and decreases the quality of the learning (Junco, 2012).
Eliminating the distractions will allow you to fully engage during your study sessions. If you don’t need your computer for homework, then don’t use it. Use apps to help you set limits on the amount of time you can spend at certain sites during the day. Turn your phone off. Reward intensive studying with a social-media break (but make sure you time your break!) See our handout on managing technology for more tips and strategies.
Switch up your setting
Find several places to study in and around campus and change up your space if you find that it is no longer a working space for you.
Know when and where you study best. It may be that your focus at 10:00 PM. is not as sharp as at 10:00 AM. Perhaps you are more productive at a coffee shop with background noise, or in the study lounge in your residence hall. Perhaps when you study on your bed, you fall asleep.
Have a variety of places in and around campus that are good study environments for you. That way wherever you are, you can find your perfect study spot. After a while, you might find that your spot is too comfortable and no longer is a good place to study, so it’s time to hop to a new spot!
Become a teacher
Try to explain the material in your own words, as if you are the teacher. You can do this in a study group, with a study partner, or on your own. Saying the material aloud will point out where you are confused and need more information and will help you retain the information. As you are explaining the material, use examples and make connections between concepts (just as a teacher does). It is okay (even encouraged) to do this with your notes in your hands. At first you may need to rely on your notes to explain the material, but eventually you’ll be able to teach it without your notes.
Creating a quiz for yourself will help you to think like your professor. What does your professor want you to know? Quizzing yourself is a highly effective study technique. Make a study guide and carry it with you so you can review the questions and answers periodically throughout the day and across several days. Identify the questions that you don’t know and quiz yourself on only those questions. Say your answers aloud. This will help you to retain the information and make corrections where they are needed. For technical courses, do the sample problems and explain how you got from the question to the answer. Re-do the problems that give you trouble. Learning the material in this way actively engages your brain and will significantly improve your memory (Craik, 1975).
Take control of your calendar
Controlling your schedule and your distractions will help you to accomplish your goals.
If you are in control of your calendar, you will be able to complete your assignments and stay on top of your coursework. The following are steps to getting control of your calendar:
- On the same day each week, (perhaps Sunday nights or Saturday mornings) plan out your schedule for the week.
- Go through each class and write down what you’d like to get completed for each class that week.
- Look at your calendar and determine how many hours you have to complete your work.
- Determine whether your list can be completed in the amount of time that you have available. (You may want to put the amount of time expected to complete each assignment.) Make adjustments as needed. For example, if you find that it will take more hours to complete your work than you have available, you will likely need to triage your readings. Completing all of the readings is a luxury. You will need to make decisions about your readings based on what is covered in class. You should read and take notes on all of the assignments from the favored class source (the one that is used a lot in the class). This may be the textbook or a reading that directly addresses the topic for the day. You can likely skim supplemental readings.
- Pencil into your calendar when you plan to get assignments completed.
- Before going to bed each night, make your plan for the next day. Waking up with a plan will make you more productive.
See our handout on calendars and college for more tips on using calendars as time management.
Use downtime to your advantage
Beware of ‘easy’ weeks. This is the calm before the storm. Lighter work weeks are a great time to get ahead on work or to start long projects. Use the extra hours to get ahead on assignments or start big projects or papers. You should plan to work on every class every week even if you don’t have anything due. In fact, it is preferable to do some work for each of your classes every day. Spending 30 minutes per class each day will add up to three hours per week, but spreading this time out over six days is more effective than cramming it all in during one long three-hour session. If you have completed all of the work for a particular class, then use the 30 minutes to get ahead or start a longer project.
Use all your resources
Remember that you can make an appointment with an academic coach to work on implementing any of the strategies suggested in this handout.
Works consulted
Carrier, L. M. (2003). College students’ choices of study strategies. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 96 (1), 54-56.
Craik, F. I., & Tulving, E. (1975). Depth of processing and the retention of words in episodic memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 104 (3), 268.
Davis, S. G., & Gray, E. S. (2007). Going beyond test-taking strategies: Building self-regulated students and teachers. Journal of Curriculum and Instruction, 1 (1), 31-47.
Edwards, A. J., Weinstein, C. E., Goetz, E. T., & Alexander, P. A. (2014). Learning and study strategies: Issues in assessment, instruction, and evaluation. Elsevier.
Junco, R., & Cotten, S. R. (2012). No A 4 U: The relationship between multitasking and academic performance. Computers & Education, 59 (2), 505-514.
Mackenzie, A. M. (1994). Examination preparation, anxiety and examination performance in a group of adult students. International Journal of Lifelong Education, 13 (5), 373-388.
McGuire, S.Y. & McGuire, S. (2016). Teach Students How to Learn: Strategies You Can Incorporate in Any Course to Improve Student Metacognition, Study Skills, and Motivation. Stylus Publishing, LLC.
Newport, C. (2006). How to become a straight-a student: the unconventional strategies real college students use to score high while studying less. Three Rivers Press.
Paul, K. (1996). Study smarter, not harder. Self Counsel Press.
Robinson, A. (1993). What smart students know: maximum grades, optimum learning, minimum time. Crown trade paperbacks.
Wissman, K. T., Rawson, K. A., & Pyc, M. A. (2012). How and when do students use flashcards? Memory, 20, 568-579.

If you enjoy using our handouts, we appreciate contributions of acknowledgement.
Make a Gift
Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
Four Strategies for Effective Writing Instruction

- Share article
(This is the first post in a two-part series.)
The new question-of-the-week is:
What is the single most effective instructional strategy you have used to teach writing?
Teaching and learning good writing can be a challenge to educators and students alike.
The topic is no stranger to this column—you can see many previous related posts at Writing Instruction .
But I don’t think any of us can get too much good instructional advice in this area.
Today, Jenny Vo, Michele Morgan, and Joy Hamm share wisdom gained from their teaching experience.
Before I turn over the column to them, though, I’d like to share my favorite tool(s).
Graphic organizers, including writing frames (which are basically more expansive sentence starters) and writing structures (which function more as guides and less as “fill-in-the-blanks”) are critical elements of my writing instruction.
You can see an example of how I incorporate them in my seven-week story-writing unit and in the adaptations I made in it for concurrent teaching.
You might also be interested in The Best Scaffolded Writing Frames For Students .
Now, to today’s guests:
‘Shared Writing’
Jenny Vo earned her B.A. in English from Rice University and her M.Ed. in educational leadership from Lamar University. She has worked with English-learners during all of her 24 years in education and is currently an ESL ISST in Katy ISD in Katy, Texas. Jenny is the president-elect of TexTESOL IV and works to advocate for all ELs:
The single most effective instructional strategy that I have used to teach writing is shared writing. Shared writing is when the teacher and students write collaboratively. In shared writing, the teacher is the primary holder of the pen, even though the process is a collaborative one. The teacher serves as the scribe, while also questioning and prompting the students.
The students engage in discussions with the teacher and their peers on what should be included in the text. Shared writing can be done with the whole class or as a small-group activity.
There are two reasons why I love using shared writing. One, it is a great opportunity for the teacher to model the structures and functions of different types of writing while also weaving in lessons on spelling, punctuation, and grammar.
It is a perfect activity to do at the beginning of the unit for a new genre. Use shared writing to introduce the students to the purpose of the genre. Model the writing process from beginning to end, taking the students from idea generation to planning to drafting to revising to publishing. As you are writing, make sure you refrain from making errors, as you want your finished product to serve as a high-quality model for the students to refer back to as they write independently.
Another reason why I love using shared writing is that it connects the writing process with oral language. As the students co-construct the writing piece with the teacher, they are orally expressing their ideas and listening to the ideas of their classmates. It gives them the opportunity to practice rehearsing what they are going to say before it is written down on paper. Shared writing gives the teacher many opportunities to encourage their quieter or more reluctant students to engage in the discussion with the types of questions the teacher asks.
Writing well is a skill that is developed over time with much practice. Shared writing allows students to engage in the writing process while observing the construction of a high-quality sample. It is a very effective instructional strategy used to teach writing.

‘Four Square’
Michele Morgan has been writing IEPs and behavior plans to help students be more successful for 17 years. She is a national-board-certified teacher, Utah Teacher Fellow with Hope Street Group, and a special education elementary new-teacher specialist with the Granite school district. Follow her @MicheleTMorgan1:
For many students, writing is the most dreaded part of the school day. Writing involves many complex processes that students have to engage in before they produce a product—they must determine what they will write about, they must organize their thoughts into a logical sequence, and they must do the actual writing, whether on a computer or by hand. Still they are not done—they must edit their writing and revise mistakes. With all of that, it’s no wonder that students struggle with writing assignments.
In my years working with elementary special education students, I have found that writing is the most difficult subject to teach. Not only do my students struggle with the writing process, but they often have the added difficulties of not knowing how to spell words and not understanding how to use punctuation correctly. That is why the single most effective strategy I use when teaching writing is the Four Square graphic organizer.
The Four Square instructional strategy was developed in 1999 by Judith S. Gould and Evan Jay Gould. When I first started teaching, a colleague allowed me to borrow the Goulds’ book about using the Four Square method, and I have used it ever since. The Four Square is a graphic organizer that students can make themselves when given a blank sheet of paper. They fold it into four squares and draw a box in the middle of the page. The genius of this instructional strategy is that it can be used by any student, in any grade level, for any writing assignment. These are some of the ways I have used this strategy successfully with my students:
* Writing sentences: Students can write the topic for the sentence in the middle box, and in each square, they can draw pictures of details they want to add to their writing.
* Writing paragraphs: Students write the topic sentence in the middle box. They write a sentence containing a supporting detail in three of the squares and they write a concluding sentence in the last square.
* Writing short essays: Students write what information goes in the topic paragraph in the middle box, then list details to include in supporting paragraphs in the squares.
When I gave students writing assignments, the first thing I had them do was create a Four Square. We did this so often that it became automatic. After filling in the Four Square, they wrote rough drafts by copying their work off of the graphic organizer and into the correct format, either on lined paper or in a Word document. This worked for all of my special education students!
I was able to modify tasks using the Four Square so that all of my students could participate, regardless of their disabilities. Even if they did not know what to write about, they knew how to start the assignment (which is often the hardest part of getting it done!) and they grew to be more confident in their writing abilities.
In addition, when it was time to take the high-stakes state writing tests at the end of the year, this was a strategy my students could use to help them do well on the tests. I was able to give them a sheet of blank paper, and they knew what to do with it. I have used many different curriculum materials and programs to teach writing in the last 16 years, but the Four Square is the one strategy that I have used with every writing assignment, no matter the grade level, because it is so effective.

‘Swift Structures’
Joy Hamm has taught 11 years in a variety of English-language settings, ranging from kindergarten to adult learners. The last few years working with middle and high school Newcomers and completing her M.Ed in TESOL have fostered stronger advocacy in her district and beyond:
A majority of secondary content assessments include open-ended essay questions. Many students falter (not just ELs) because they are unaware of how to quickly organize their thoughts into a cohesive argument. In fact, the WIDA CAN DO Descriptors list level 5 writing proficiency as “organizing details logically and cohesively.” Thus, the most effective cross-curricular secondary writing strategy I use with my intermediate LTELs (long-term English-learners) is what I call “Swift Structures.” This term simply means reading a prompt across any content area and quickly jotting down an outline to organize a strong response.
To implement Swift Structures, begin by displaying a prompt and modeling how to swiftly create a bubble map or outline beginning with a thesis/opinion, then connecting the three main topics, which are each supported by at least three details. Emphasize this is NOT the time for complete sentences, just bulleted words or phrases.
Once the outline is completed, show your ELs how easy it is to plug in transitions, expand the bullets into detailed sentences, and add a brief introduction and conclusion. After modeling and guided practice, set a 5-10 minute timer and have students practice independently. Swift Structures is one of my weekly bell ringers, so students build confidence and skill over time. It is best to start with easy prompts where students have preformed opinions and knowledge in order to focus their attention on the thesis-topics-supporting-details outline, not struggling with the rigor of a content prompt.
Here is one easy prompt example: “Should students be allowed to use their cellphones in class?”
Swift Structure outline:
Thesis - Students should be allowed to use cellphones because (1) higher engagement (2) learning tools/apps (3) gain 21st-century skills
Topic 1. Cellphones create higher engagement in students...
Details A. interactive (Flipgrid, Kahoot)
B. less tempted by distractions
C. teaches responsibility
Topic 2. Furthermore,...access to learning tools...
A. Google Translate description
B. language practice (Duolingo)
C. content tutorials (Kahn Academy)
Topic 3. In addition,...practice 21st-century skills…
Details A. prep for workforce
B. access to information
C. time-management support
This bare-bones outline is like the frame of a house. Get the structure right, and it’s easier to fill in the interior decorating (style, grammar), roof (introduction) and driveway (conclusion). Without the frame, the roof and walls will fall apart, and the reader is left confused by circuitous rubble.
Once LTELs have mastered creating simple Swift Structures in less than 10 minutes, it is time to introduce complex questions similar to prompts found on content assessments or essays. Students need to gain assurance that they can quickly and logically explain and justify their opinions on multiple content essays without freezing under pressure.

Thanks to Jenny, Michele, and Joy for their contributions!
Please feel free to leave a comment with your reactions to the topic or directly to anything that has been said in this post.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email (The RSS feed for this blog, and for all Ed Week articles, has been changed by the new redesign—new ones are not yet available). And if you missed any of the highlights from the first nine years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below.
- This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
- Race & Racism in Schools
- School Closures & the Coronavirus Crisis
- Classroom-Management Advice
- Best Ways to Begin the School Year
- Best Ways to End the School Year
- Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
- Implementing the Common Core
- Facing Gender Challenges in Education
- Teaching Social Studies
- Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
- Using Tech in the Classroom
- Student Voices
- Parent Engagement in Schools
- Teaching English-Language Learners
- Reading Instruction
- Writing Instruction
- Education Policy Issues
- Differentiating Instruction
- Math Instruction
- Science Instruction
- Advice for New Teachers
- Author Interviews
- Entering the Teaching Profession
- The Inclusive Classroom
- Learning & the Brain
- Administrator Leadership
- Teacher Leadership
- Relationships in Schools
- Professional Development
- Instructional Strategies
- Best of Classroom Q&A
- Professional Collaboration
- Classroom Organization
- Mistakes in Education
- Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

35 Effective Writing Strategies for College Level
Graduating from high school and entering college, you may feel intimidated by the upcoming courses. As you wait for the first essay or another writing task, you might feel completely overwhelmed. Fortunately, there are plenty of effective writing strategies to help you get through your homework in one piece. And no, walking around and asking your peers “Will you do an assignment for me ?” isn’t one of them.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
What strategies are helpful for college-level writing assignments? The ones that explain you the following:
- how your brain works;
- how to minimize distractions;
- how to keep yourself motivated;
This article covers them and explores the essential elements of college essay writing, such as research, structuring, and revising.
Look through these writing strategies for college students from our custom writing service . Select the ones you feel will work the best for you and use them in your tasks.
🔎 Conducting Research
Every writing starts with prewriting. Whether you choose your topic or a topic is assigned, your first task is to know how to perform research properly. You have to gather relevant sources to craft a thorough and informative essay. The process might begin with you examining your assigned topic or selecting one.

Either way:
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Your goal here is to collect as much appropriate information as possible. Here is a list of writing strategies to help you do that.
- Whenever possible, choose a topic of interest. In the case you are assigned a specific topic, you can still choose an interesting angle or an unusual perspective.
- Always feel free to ask for help. While this might not seem like one of the most obvious writing strategies, don’t be afraid of asking. If you don’t think you know how to follow the requirements, you should question your instructor.
- Make good use of the Internet. If your professor has provided any links as sources, then you should use them for sure and expand from there. Remember to use only credible sources. Not all guidelines, articles, and research on the Internet are provided by writing professionals or experts in your subject matter. And remember that the Internet can be an incredible source of inspiration. The Muse can jump out from where you least expect it. Sometimes the social media sites, such as Pinterest or Reddit, can be quite inspiring and useful.
- Visit a library . They are still very relevant when researching for an assignment. A library is an incredibly valuable place if you have to get a comprehensive understanding of the subject. Start in the reference section and make use of available resources. Search the library’s catalog. Finally, take a trip to “the stacks” and browse the shelves in your subject area to see what titles are available.
Owl Purdue also provides some great tips on how to conduct research. And now that you’ve got it, you have to move on to the next stage. Do something with all those sources and information you have uncovered.
🏁 Getting Started
Sometimes, getting started is the most challenging part of a writing assignment, especially when you have to pick your topic. Knowing what is expected of you and having a good idea of what interests you are crucial.
But that’s not all:
Effective writing strategies include learning brainstorming techniques that will help you narrow down your essay topic and sift through the information you found. Then, you should be able to identify only relevant and up to date information.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!

Check out the following writing strategies for college students that offer brainstorming techniques and teach you how to start organizing that information.
- Use the free-writing technique. It is the first of the helpful strategies to master your writing skills. Take a pen and a piece of paper, relax, and just write down your stream of consciousness for a selected topic. It can be clumsy or grammatically incorrect, but who cares if it works for you and helps you to focus. Try to generate as many ideas relevant to your topic as possible. Never mind how good they are. At this stage, the more concepts, the better. Write down even the silliest ideas coming to your head. Set a timer if you wish. When your time is over, carefully check what you have written and evaluate it. Choose only the best ideas to include in your homework.
- Try mind-mapping. In the middle of the paper sheet, draw your question and use lines to connect that question to relevant ideas, words, and images. These elements might branch out to other concepts. Write them all down and connect one to another. In such a way, you will find out the trend in the ideas that will help direct you in researching and writing your paper.
- Begin constructing paragraphs. Sometimes the most challenging part of writing is to start. Use the information and data from your research and brainstorming sessions. You can distribute the information you have chosen to use between paragraphs. Note how many parts you will need and which points you will use in each.
- Come up with a topic sentence . You need one for each paragraph. Topic sentences are handy when you want to save time because it provides you with a summary of what you wish to include in the section
What’s now?
Well, it is time for the main event. Stayed tuned for strategies that will help you better understand the act of writing.
✍️ The Writing
Yes, it is inevitable. You do have to begin writing now. As long as you have done the previous steps well, you will be well organized and prepared.
But here’s the thing:
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Writing can still be a complicated process , even when you know the above techniques. For this reason, you need to have a good grasp of the following writing strategies to ensure you can compose something that is intelligent and expresses your views appropriately.

- Use an active voice whenever possible. Towson University gives an excellent description of active and passive voice in writing. Writing in the active voice demonstrates that there is a subject (someone or something) and that this subject is conduction the action expressed by the verb. The opposite is when the subject is being acted upon, which is the passive voice. Keep in mind that the active voice is much more potent and is the preferred option.
- Minimize the use of “there is/there are.” Do not hide the doer of the action using these phrases. (For example, you have to write “Three ways exist to tackle the problem” instead of writing “There are three ways to tackle the problem.”)
- Start quoting with the author’s name. Do not confuse your readers by starting sentences with phrases like “It has been…,” like “It has been hypothesized that…” A reader cannot understand who has done the hypothesizing. Since a hypothesis must have an author, start your sentence with the author’s name and give the proper reference at the end of the sentence: “John Doe hypothesized that…(Doe, 2005)”
- Avoid redundant words. You should delete any redundant words, such as “completely,” “extremely,” and “absolutely” in the majority of situations.
- Make sure your writing is clear. The reader needs to understand all the points you have made.
- Ensure your writing is concise. Avoid using general statements to make your readers think that there is more valuable information than there actually is; stick to the point.
- Make your writing precise. Your written work has to communicate the meaning you intend to get across to the reader.
- Remember that accuracy is vital. Be sure to double-check facts before using them.
- Approach your writing with honesty. Good writing has to be free of prejudice and has to reference all sources of information.
- Don’t edit while you are writing. Otherwise, you will interrupt the flow. You can save the editing until after you are finished writing your rough draft.
- Don’t be afraid to skip an introduction . If you have difficulty writing it, leave it for now. It is OK to start writing with the essay’s body and go back to the introduction when you are ready.
- Be sure to look up synonyms for words you find repetitive. The significant thing is the use of different vocabulary when writing. It’s amazing how effective and inspiring a synonyms search can be. Look for them in online dictionaries or choose the suggestion option in MS Word.
The writing will take care of itself, as long as you can focus.
🤔 Staying Focused
It is easy to lose focus when you are working. Either you are becoming tired and lacking concentration or procrastinating. Finding other things to do than settling down to write can seem desirable. You should focus and be highly productive during your work time.
How do you accomplish this?

These tips for struggling writers are some of the writing skills that are useful in college. They can help you stay focused:
- Work with the rhythms of your brain. The human brain goes through a process called the ultradian cycle. It takes you through periods of active concentration and focuses and then into periods during which it needs rest. Fast Company explains that the natural cycle is to work for 90 minutes and rest your mind for 20 minutes. You will then be energized enough to work for another 90 minutes. If you take advantage of this natural cycle, you will always be working at peak efficiency, and you won’t lose focus and waste your time.
- Incorporate physical activity into your breaks. When you do take some rest during your writing time, doing some form of exercise is essential. Stand up and do a couple of stretches or go for a walk. Sing, dance, wave your hands, or even scream. It will help you wake up and complete your essay as soon as possible.
- Try listening to music . If you are working in a place with various distractions, it is a good idea. Music can help you reduce tension and concentrate. Make sure you don’t start singing because it can be very distracting. Choose tracks without lyrics or songs in another language.
- Block out all potential distractions. If you don’t need to use the Internet, then work offline. If you need access to the Internet to do research, close any tabs related to your email and social media. Oh, and turn off your phone! All the Twitter updates and text messages can wait. Avoid drinking too much liquid because bathroom breaks can be very disruptive. Avoid anything that could distract you during a work session.
- Plan something fun to do for after you are done with your work. Sometimes, an immediate reward means a lot. Think of what you will do after you finish that essay because this will motivate you to write faster. Promise yourself that you will take a walk, eat a treat, or call a friend. Then your writing will move at lightning speed. Knowing that you have to complete your project by a particular time can be very motivating, but knowing you have something exciting to do when it’s done can be even more motivating. With this in mind, just get your work done and enjoy life!
- Use the carrot and stick method to keep yourself motivated. This approach is practical. Praise yourself if you start early and punish yourself if you fail to start on time. Be ruthless. Stick options include not using Facebook for a day or two or working out longer than one hour. Carrot options could be eating a nice treat or watching your favorite series or funny cat videos.
- Think of the worst consequences of failing that assignment. Let these motivate you. What might happen if things go wrong? Will you fail the entire course? Will you have to drop out of college?
- Compete with someone. Suggest to one or more classmates that you compete in writing your assignments to see who can get theirs done first. Of course, it’s not the most exciting game ever, but since you have to write the essay anyway, a little competitive spirit might just improve your time management.
Now you are done writing, but there is still more to do…
📑 After the Writing
You have finished writing, and it’s brilliant! Or is it? Just because you have finished writing doesn’t mean your essay is done. You still have work to do because strategies for good writing include the following tips.
- Proofread, proofread, proofread! Now is the best time to start re-reading the paper and editing it, making any necessary changes. When revising, the University of Pennsylvania recommends you begin with fixing the big things, like organization and content. Then adjust the details, such as spelling and grammar.
- Nail the format. Chances are one of the conditions for submitting your assignment includes a precise style of formatting. Make sure that font and margins are correct. For help with formatting, check out this guide to formatting .
- Check your reference list and quotes. These are the must-have for academic writing. Be sure you have inserted all the citations and references you have used while writing your paper. For help on including them in your work, check out these articles on APA style and MLA style .
📰 Practice Essays
If you are still unsure about the above writing strategies, you can always choose to write one or two practice essays. While this sounds like it’s a lot of extra work, doing so will help you sharpen your college-level writing skills so that when you write your assignment, you will do a better job. Here are some activities for struggling writers that will help you write a practice composition.
- Prepare several pieces of paper . Writing your practice essays may be more manageable on the sheets than in MS Word. Paper lacks distractions.
- Surf the web to find practice essay topics. You may use any search engine and type in something like “topics for essays.” Pick a subject according to your grade level.
- Use the five-paragraph essay structure. Even in your practice writing, you cannot escape the academic organization.
- Pay attention to details. Keep in mind other critical criteria of composition evaluation like content, grammar, and style. You have to show your literacy.
Writing assignments don’t have to be scary, but you have to grasp the right writing strategies. Just click on this video to see how stress-free it can be.
If you are still struggling with writing when assigned an essay or another type of paper, you can find more help with Harvard College . You can also hire a custom writing company that knows how to help struggling writers.
Regardless of how you produce your assignment, you will have a top-notch paper to hand in to your professor. And thanks for reading! Share our writing strategies with those who may need them.
Further reading:
- Useful Revising and Editing Checklists
- Essay Checklist: How to Write an A+ Essay
- Common Mistakes in Essay Writing
- How to Control Words per Page
- Basic Writing Rules – Common Mistakes & Fixes
- 200 Powerful Words to Use Instead of “Good”
- List of Credible Sources
- An Ultimate Punctuation Guide
🔗 References
- Writing Strategies: Ministry of Education (Ontario, Canada)
- The Basics of Essay Writing: UNSW
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay: Thought Co.
- Example Five-Paragraph Essay: UW Libraries
- 50 Conducting Research: WU Libraries
- Brainstorming: UNC Writing Center
- Academic Writing Style: USC Libraries
- Formatting a Research Paper: UMN Libraries
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

As a student, you might be wondering how to increase your IQ and boost your academic success. After all, students with a high IQ level are really lucky, right? They can study easily, sail through exams, build a successful career, and end up with a very high salary. All in...

Student life can be stressful even in the best of times. And it has become almost axiomatic that student life comes with substantial weight gain in the first few semesters of college. Causes of the infamous freshman 15 are manifold, and keeping those pounds off may prove tricky.

To the uninitiated, journalistic writing may appear intimidating at first. Even if you’ve done other kinds of writing before, chances are you’re feeling the pressure to “deliver.” Because unlike essays and research papers that have a guaranteed invested audience (your teacher), articles have the additional task of gaining and keeping...

Are you struggling with the attention-getter for your motivational speech about school? Or maybe you need to add some humor to your creative essay on learning? Don’t hesitate to use funny quotes about education! We are sure you will impress everybody with your creative ideas and our funny sayings.

Every student knows that a boring lecture can be the best sleeping pill ever – especially when you are tired. You might start blinking slowly, and then the lecturer’s words will seem so far away and without any meaning, sounding like a sweet lullaby. Students beware: avoid classroom naps! They...

Descriptive writing is the equivalent of drawing with words instead of lines and colors. You need to create vivid pictures, using only your words and memory or imagination. Your goal is to make your readers see, hear, taste, smell, and feel what you want to say. How can you start...

If you never gave a persuasive speech before a large audience, you probably want to know how this task can be approached. First and foremost, you need to construct a good persuasive speech outline that will be the cornerstone of your success. There are several ways in which you can...

Online classes are becoming increasingly popular each year; after all, it’s convenient and allows you to study from the comfort of your home! What’s not to like? Unfortunately, online students have tons of classes and assignments each semester, and it isn’t easy to complete them all. In your search for...

Finding a perfect study helper website can give you an incredible advantage in academic life. Sadly, most of them are scams and a waste of time. But then there are services like Wow Essays.com that have a near-spotless reputation. That’s why in today’s review, we will be looking at WowEssays...

The Internet is full of websites ready to provide an upper hand for students in their stress-filled academic life. One such website—Transtutors.com—has recently caught our attention. Our initial interest was piqued by their affiliate programs and advanced plagiarism checker. It all looks promising, but is it really that good? Filled...

Are you looking for an excellent academic help website? If so, you’ve probably seen one of the most promising ones—UKEssays.com. The web is full of glowing 5-star UKEssays reviews. But can you really trust them? And most importantly, is it legit? We’ll answer all these questions and more in this...

Many websites can provide help in academic writing, but not all of them deserve your attention. With so many options available, it can be hard to distinguish between a legitimate service and a fraudulent one. We’re here to change it and provide honest reviews of such services! Recently we’ve stumbled...
Beautiful content! Thx for sharing!
Very helpful, thanks so much for sharing.
The news is very interesting. Thank you very much for the information.

The Learning Strategies Center
- Meet the Staff
- –Supplemental Course Schedule
- AY Course Offerings
- Anytime Online Modules
- Winter Session Workshop Courses
- –About Tutoring
- –Office Hours and Tutoring Schedule
- –LSC Tutoring Opportunities
- –How to Use Office Hours
- –Campus Resources and Support
- –Student Guide for Studying Together
- –Find Study Partners
- –Productivity Power Hour
- –Effective Study Strategies
- –Concept Mapping
- –Guidelines for Creating a Study Schedule
- –Five-Day Study Plan
- –What To Do With Practice Exams
- –Consider Exam Logistics
- –Online Exam Checklist
- –Open-Book Exams
- –How to Tackle Exam Questions
- –What To Do When You Get Your Graded Test (or Essay) Back
- –The Cornell Note Taking System
- –Learning from Digital Materials
- –3 P’s for Effective Reading
- –Textbook Reading Systems
- –Online Learning Checklist
- –Things to Keep in Mind as you Participate in Online Classes
- –Learning from Online Lectures and Discussions
- –Online Group Work
- –Learning Online Resource Videos
- –Start Strong!
- –Effectively Engage with Classes
- –Plans if you Need to Miss Class
- –Managing Time
- –Managing Stress
- –The Perils of Multitasking
- –Break the Cycle of Procrastination!
- –Finish Strong
- –Neurodiversity at Cornell
- –LSC Scholarship
- –Pre-Collegiate Summer Scholars Program
- –Study Skills Workshops
- –Private Consultations
- –Resources for Advisors and Faculty
- –Presentation Support (aka Practice Your Talk on a Dog)
- –About LSC
- –Meet The Team
- –Contact Us
Effective Study Strategies
So, what are effective study strategies for long-term learning, retrieval practice 1.
Retrieval practice is when you actively recall information (concepts, ideas, etc) from memory and “put it on paper” in different formats (writing, flow charts, diagrams, graphs). At the LSC we often call retrieval practice “Blank Page Testing,” because you just start with a blank piece of paper and write things down. It’s especially helpful because it shows you what you do (and do not) understand, so you can identify what topics you need to review/practice more. Retrieval practice can be challenging and requires a lot of mental effort — but this struggle to remember, recall, and make connections is how we learn.
To learn more about Blank Page Testing , see Mike Chen’s video:
Interleaving 2
Interleaving is when you work on or practice several related skills or concepts together. You practice one skill or concept for a short period of time, then switch to another one, and perhaps another, then back to the first. It not only helps you learn better, it keeps you from falling behind in your other classes! So please go ahead and do some work for the classes you don’t have an exam in this week! It will not only help you learn your exam material better, it will help you stay caught up.
Spaced (or distributed) practice 3
In spaced practice, you spread out practice or study of material in spaced intervals, which leads to better learning and retention. Spaced practice is the opposite of cramming!
Get sleep and make sure you eat and stay hydrated!

Your brain works better when you are rested, hydrated, and nourished. Though it might seem effective to push through without taking a break and stay up studying all night (see the page on strategies that don’t work), it won’t help you in the long run. Instead, develop a study plan, eat a good meal, and have a bottle of water nearby when you take your exam. You will learn and understand the material better if you have a plan – and you will probably need to this information for the next prelim anyway!
Tip: Piper knows that sleeping with your books under your pillow can help with learning! How does this magic work, you might wonder? Though the information in your book won’t travel via osmosis to your brain through the pillow, you will get sleep which improves your long-term learning! Sleep and a good study plan are a great study strategy combo!
Up Next: Guidelines for creating a study schedule
1 Agarwal, P. K. (2020). Retrieval Practice: A Powerful Strategy for Learning – Retrieval Practice. Unleash the Science of Learning. Retrieved from https://www.retrievalpractice.org/retrievalpractice .
2 Pan, S.C. (2015). The Interleaving Effect: Mixing It Up Boosts Learning. Retrieved from https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/the-interleaving-effect-mixing-it-up-boosts-learning/
3 Weinstein, Y. & Smith, M. (2016). Learn How to Study Using… Spaced Practice. Retrieved from https://www.learningscientists.org/blog/2016/7/21-1
- The Student Experience
- Financial Aid
- Degree Finder
- Undergraduate Arts & Sciences
- Departments and Programs
- Research, Scholarship & Creativity
- Centers & Institutes
- Geisel School of Medicine
- Guarini School of Graduate & Advanced Studies
- Thayer School of Engineering
- Tuck School of Business
Campus Life
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Athletics & Recreation
- Student Groups & Activities
- Residential Life
Academic Skills Center
- [email protected] Contact & Department Info Mail
- Mission & History
- Business Hours
- Reasons to Visit
- Academic Skills Center Internships
- Peer Tutoring Program Positions
- Academic Coaching
- Peer Tutoring
- About Peer Tutoring
- Current Courses Supported
- Register for Peer Tutoring
- Become a Peer Tutor
- Request an ART Tutor
- Become an ART Tutor
- First-Year Students
- MoTEAvational Mondays
- Get It Done
- Finals Programs
- Learning Resources
- Organization + Time Management
- Reading + Notetaking
- Test Prep + Study Skills
- Habit Building & Goal Setting
- Campus Resources
- BLOG & E-GUIDE
Learning Assessment
- Strategic Learning Videos & Books
Search form
Learning strategies.
Enhance your ability to comprehend more in less time.
Listening & Participation
Tips on how to improve your listening and retention, as well as participation
Resources on how to take effective class notes for yourself and your classmates.
Strategic Learning Videos & Books
Three books and twelve videos that present the effective ways to learn and study.
Memory & Retention
Resources on staying motivated and improving your memory.
Tests & Exams
Information about preparing for tests and exams as well as test-taking strategies.
Information on how to determine your learning style.
Engaging with Faculty
Information about how to get to know your professors.
- Academic Resources
- Digital Resources
18 Learning Strategies Examples

Learning strategies refer to a range of strategies that can be implemented to improve learning. Examples include using memory cards, spaced repetition, practice tests, strategic highlighting, and reciprocal questioning.
Although there are numerous learning strategies available for students to try, none of them should be considered “the best.” Each one can be applied to a given learning situation and some methods may work better for some students than others.
In practice, students should use multiple learning strategies when studying a subject. Over time, students will discover which ones work best for them.
Learning Strategy Examples
- Spaced Studying – many students try to learn all of the material the night before the exam. It is far better to study sections of the material over several weeks.
- Dual Coding – instead of just reading text, it is better to input information through more than one modality. So, in addition to reading, also use visuals such as graphs to help understand information. Videos and listening to audio explanations of material are also extremely helpful.
- Acronyms –Memorizing lists in the form of an acronym is a very effective way of taking a large amount of information and condensing into just one “chunk” of data. An example is ROYBGIV to remember the colors of the rainbow – red, orange, yellow, blue, green, indigo, violet.
- Tactile Learning – being able to touch and feel an object that is connected to a concept works very well for some students, especially younger ones.
- Reciprocal Questioning – this involves students working in pairs; one acts as the teacher and asks the other student questions about the topic, reading assignment, or class lesson.
- Strategic Pauses – teachers can help students consolidate information during lectures by pausing every 10-15 minutes and letting students reflect upon the material or go back through their notes.
- Reading Buddies – this is a cooperative learning strategy good for younger learners where pairs of students read the same passage together. They can help each with pronunciation and understanding the definition of specific words.
- Outlining – after taking notes during a lecture, it is a good idea to help organize your understanding by creating an outline of the material. This can help you see how concepts are related and may also point-out concepts that you missed.
- Highlighting – using a highlighter to emphasize key points in a text is one of the oldest learning strategies ever created. The problem is that most students highlight way too much text. Two or three-word phrases and a few key terms in a paragraph are more than enough.
- Practice Testing – taking a practice test or responding to the reading comprehension questions at the end of a chapter improves memory and helps students identify areas they need to study again.
- Cognitive tools – Students use technology to help stimulate learning, such as by using computer games or computational software. See a full explanation on our cognitive tools article .
- Think-pair-share – Students individually brainstorm a topic , then share their idea with a peer and discuss, then the pair share their ideas with the whole class.
- Role playing – Students can role play a scenario in order to mock being ‘in the moment’ – for example, they could role play being the teacher, being a scientist, or being an engineer.
- Gamification – Gamification refers to implementing game-based incentives into a learning scenario. For example, students can ‘level up’, use a token economy , or receive awards for reaching checkpoints.
- Active learning – Active learning refers to the process of learning by doing – such as conducting tests, doing a project, or inquiry-based learning . This helps contextualize and consolidate knowledge (see also: advantages of active learning ).
- Brainstorming – Brainstorming can help a learner push through a blockage by generating ideas (in a process called divergent thinking ) that could subsequently lead to lightbulb moments
- Concept mapping – Concept mapping helps learners to identify connections between ideas, which adds context and deepens the learning experience.
- Thinking aloud – Thinking aloud can help push through brain blocks because the act of speaking and writing is a cognitive sorting process.
Learning Strategy Case Studies
1. rotating chair discussion.
This is a learning strategy that encourages students to actively listen to each other and participate in a class discussion. It improves student engagement, communication skills, and enhances understanding of complex material.
One student starts by acting as the class “chair.” They define the key issue for discussion and express their opinion. Then other students that want to express their views raise their hand and wait (patiently and quietly) to be called upon by the chair.
When the chair has selected the next speaker, that person stands and summarizes the previous chair’s remarks. Then they express their own.
It’s important that everyone in the class listens completely to each speaker without interrupting. Only the acting chair can select the next speaker. No one can be selected twice until all those that want to participate have had a turn.
In addition to the benefits mentioned above, this learning strategy also teaches students about civility and respecting the views of others even though they disagree with us.
2. The Pre-reading Skim
Most students open their book to the first page of the chapter and immediately start reading. This might seem like a good idea because it gets right to the task at hand, but there are better ways to approach a new chapter.
For example, before jumping right in, take a few moments and browse the chapter first. Read the subheadings, take a look at the photos and graphs, and read the captions. If there is an index of key words or concepts at the end of the chapter, take a few moments to skim those as well.
The pre-reading skim gets your mind ready for the upcoming information. It activates your memory and creates a context for all that data that will be bombarding your mind later.
Although it might seem like this takes too long, it will actually save time later because you will be able to remember information more easily and efficiently. You won’t have to spend as much time trying to rehearse information because it was already stored more strongly in the beginning.
3. Mind Mapping
This technique involves creating a diagram that visually represents the information being studied. It is a relatively simple learning strategy, but has numerous benefits.
The procedure is simple. First, draw a circle in the center of a sheet of paper that represents the central concept you want to study. Then, start brainstorming all of the other concepts you can think of that are related. Put each one in their own circle around the central circle. Don’t worry about organization or relevance yet.
Next, go around the map and list any facts associated with each concept. Keep these statements short and simple.
Draw lines connecting the concepts that are related. If you want, make the lines thicker to represent concepts that are more strongly connected.
The benefits of mind mapping are numerous. Not only does it improve memory of concepts and related facts, but also helps organize the information and understand how concepts are related.
4. Think-Pair-Share (TPS)
TPS is a cooperative learning strategy that stimulates cognitive processing and interest. It was first described by Frank Lyman (1982) as a way to increase student motivation.
The steps are relatively simple. First, the teacher explains the activity and then presents an open-ended question. Then, students think about the question on their own, quietly, and jot down their thoughts.
Next, the students form pairs and share their notes with each other. After each student has taken a turn, they summarize the key points and then share with the class. They can identify points of agreement or disagreement, or areas of shared confusion.
The class discussion can then help students hone in on key concepts and clarify any misunderstandings.
5. The After-Class One-Minute Paper
Reviewing class notes is one way to help strengthen memory of a lot of material that has just be presented in a short period of time. However, it is still a relatively passive exercise. To make this strategy more active and engaging, the one-minute paper makes for an effective alternative.
At the end of class, write a summary of that day’s material. Allow yourself one minute to complete the summary. Try not to go over this time limit because it will force you to be succinct and focused on the highlights.
Writing is a much more active learning process than reading notes. It forces you to recall information and then reproduce it in the form of a written sentence.
This will call attention to concepts that you don’t understand thoroughly. It’s also a great way to improve writing skills and train yourself to be concise.
There are a lot of very effective learning strategies for students to choose from. Some of them have been around since the beginning of the printable text.
Other strategies are a little more recent and have been created by experts in cognitive science and education.
The fundamental premise behind most of these strategies is that learning that involves deep cognitive processing is more effective than learning that is passive. Therefore, the more the strategy requires active engagement in the material, the better.
Mind maps, one-minute papers, and taking practice tests are just a few examples of ways to consolidate information and identify areas that require more study time.
Amer A. A. (1994). The effect of knowledge-map and underlining training on the reading comprehension of scientific texts. English for Specific Purposes , 13 , 35–45.
Anderson R. C., Hidde J. L. (1971). Imagery and sentence learning. Journal of Educational Psychology , 62 , 526–530.
Bretzing B. H., Kulhavy R. W. (1979). Notetaking and depth of processing. Contemporary Educational Psychology , 4 , 145–153.
Dunlosky, J., Rawson, K. A., Marsh, E. J., Nathan, M. J., & Willingham, D. T. (2013). Improving students’ learning with effective learning techniques: Promising directions from cognitive and educational psychology. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 14 (1), 4-58. https://doi.org/10.1177/1529100612453266
Lyman, F. (1981). The responsive classroom discussion. In A. S. Anderson (Ed.), Mainstreaming digest (pp. 109-113). College Park, MD: University of Maryland College of Education.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
More From Forbes
6 college success strategies for gen-z.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Large group of happy college students celebrating their graduation day outdoors while throwing their ... [+] caps up in the air.
Success in college demands more than just academic knowledge—it requires a robust set of executive function skills . These skills, which include managing time, planning long-term projects, and regulating emotions, are essential for navigating the complex demands of college life. With more than 60% of Gen-Z reporting an anxiety disorder , per a report from data management firm Harmony Healthcare IT, it is necessary that students be intentional about developing executive function skills that allow them to decrease their anxiety and improve performance. Let's explore the crucial executive function skills every college student should develop, complete with practical strategies to enhance these skills.
Time Management
Princeton’s McGraw Center for Teaching and Learning highlights that effective time management is perhaps the most critical skill for college success. It involves not only keeping track of daily classes and assignments but also managing long-term projects and social engagements. The ability to balance these tasks efficiently can reduce stress and enhance academic performance.
A structured daily schedule helps you manage your time effectively, ensuring that you allocate enough time for both academic responsibilities and personal care. Complement this with a longer-term task list that outlines major projects, upcoming exams, and application deadlines. This method keeps you motivated and engaged, with a clear view of upcoming responsibilities and milestones.
Planning And Prioritization
College students face myriad tasks each day, from homework assignments to extracurricular activities. Learning to prioritize these tasks based on urgency and importance is crucial , according to best practices from WeWork. This skill ensures that students meet deadlines and allocate their time to projects that require more focus and effort. For example, use a digital planner to mark critical deadlines and exams at the start of the semester. This will allow you to prioritize study time around these key dates, ensuring you are well prepared without last-minute stress.
Likewise, it is essential to schedule downtime, or white space, on your calendar. This time is not for social media scrolling or video gaming; rather, it’s for being bored and letting your mind wander. This practice is crucial for creativity and problem-solving. It allows the brain to form connections and come up with new ideas without the pressure of constant input.
Microsoft Warns Windows Users Of Ongoing Russian Hack Attack
New apple id password reset issue hitting iphone ipad and macbook users, the good, bad and ugly from the green bay packers’ draft, goal setting.
Setting clear, achievable goals provides a road map for success in college. These goals can range from academic achievements, like maintaining a certain GPA, to personal development objectives, such as learning a new skill or participating in community service. A study by Taylor W. Acee and colleagues investigated how various properties of college students' self-set academic goals relate to their academic achievement. Key findings from the study suggest that students who set more specific academic goals tended to achieve higher GPAs. Specific goals provided clear performance standards and deadlines, aiding in better planning and effort allocation.
In addition, goals driven by external pressures, like rewards or punishments, negatively affected students' GPA. This suggests that extrinsic motivators, such as rewarding yourself with leisure time or food, may undermine your intrinsic interest and autonomy, leading to poorer performance.
Self-Control And Emotional Regulation
College life comes with its ups and downs. The ability to control impulses and manage emotional responses to both successes and setbacks can significantly affect a student’s well-being and academic performance. For example, when a student receives a lower grade than expected, they can take the time to process their emotions rather than reacting impulsively. Scheduling a meeting with the professor to discuss how to improve can turn disappointment into a learning opportunity.
The Journal of Educational Psychology article " A Stitch in Time: Strategic Self-Control in High School and College Students " by Angela L. Duckworth and colleagues, explores the role of self-control in achieving academic success and its broader implications.Overall, the research highlighted that strategic self-control, especially strategies implemented early in the impulse generation process, significantly influences academic success. Students often recognize the utility of these strategies but may not always use them effectively. The findings suggest the importance of teaching and encouraging the use of effective self-control strategies to improve educational outcomes.
This research highlights the importance of early intervention in combatting habits that have the potential to diminish our self-control and emotional regulation. One obvious habit many people struggle with is smartphone use, which can be a significant distraction . Setting aside phone-free times during study sessions can help improve focus and efficiency. This practice not only aids concentration but also encourages deeper engagement with the material, fostering better understanding and retention.
Flexible Thinking
The ability to adapt to new situations and solve problems as they arise is invaluable in the dynamic college environment. Flexible thinkers can handle unexpected changes, such as shifts in course schedules or group project dynamics, without excessive stress. A Journal of Postsecondary Education and Disability study by Kercood et al. investigates the role of cognitive flexibility in the academic and career trajectories of college students, focusing on those with and without attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The study demonstrated that cognitive flexibility positively predicts academic achievement, particularly in reading, where higher subjective cognitive flexibility leads to better reading skills. It also influences mathematical and writing skills but through objective measures of cognitive flexibility. In addition, there is a significant relationship between cognitive flexibility, especially subjective cognitive flexibility, and career confidence. Students with ADHD who have high cognitive flexibility tend to feel less confident about their career choices compared to those with lower cognitive flexibility. In contrast, non-ADHD students with higher cognitive flexibility feel more confident about their career paths.
Enhance your cognitive flexibility by taking time each week to reflect on what’s working and what isn’t. Self-reflection can help you adjust your strategies, whether it’s reshuffling how you prioritize tasks or finding better ways to manage stress. This habit encourages continuous improvement and personal growth.
Use Tools And Resources
Leverage tools such as digital planners, apps that block distracting websites, or methods like the Pomodoro Technique to enhance focus during study times. The Pomodoro Technique, a popular time management tool, is designed to enhance focus and productivity. The technique uses a timer to break work into intervals, traditionally 25 minutes in length, separated by short breaks, typically 5 minutes.
In addition to self-management tools, don’t hesitate to seek resources available in high school and colleges such as tutors, counseling centers, and executive function coaches, which can provide additional support to meet academic and personal challenges.
Developing strong executive function skills is a dynamic process that extends beyond mastering a set of tasks—it involves cultivating a mindset geared toward continuous improvement and adaptation. For college students, these skills are not just about achieving academic success; they are about setting the foundation for lifelong resilience and achievement. By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you’ll be well on your way to a fulfilling and successful college experience.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Open access
- Published: 17 April 2024
Deciphering the influence: academic stress and its role in shaping learning approaches among nursing students: a cross-sectional study
- Rawhia Salah Dogham 1 ,
- Heba Fakieh Mansy Ali 1 ,
- Asmaa Saber Ghaly 3 ,
- Nermine M. Elcokany 2 ,
- Mohamed Mahmoud Seweid 4 &
- Ayman Mohamed El-Ashry ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7718-4942 5
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 249 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
380 Accesses
Metrics details
Nursing education presents unique challenges, including high levels of academic stress and varied learning approaches among students. Understanding the relationship between academic stress and learning approaches is crucial for enhancing nursing education effectiveness and student well-being.
This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of academic stress and its correlation with learning approaches among nursing students.
Design and Method
A cross-sectional descriptive correlation research design was employed. A convenient sample of 1010 nursing students participated, completing socio-demographic data, the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS), and the Revised Study Process Questionnaire (R-SPQ-2 F).
Most nursing students experienced moderate academic stress (56.3%) and exhibited moderate levels of deep learning approaches (55.0%). Stress from a lack of professional knowledge and skills negatively correlates with deep learning approaches (r = -0.392) and positively correlates with surface learning approaches (r = 0.365). Female students showed higher deep learning approach scores, while male students exhibited higher surface learning approach scores. Age, gender, educational level, and academic stress significantly influenced learning approaches.
Academic stress significantly impacts learning approaches among nursing students. Strategies addressing stressors and promoting healthy learning approaches are essential for enhancing nursing education and student well-being.
Nursing implication
Understanding academic stress’s impact on nursing students’ learning approaches enables tailored interventions. Recognizing stressors informs strategies for promoting adaptive coping, fostering deep learning, and creating supportive environments. Integrating stress management, mentorship, and counseling enhances student well-being and nursing education quality.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Nursing education is a demanding field that requires students to acquire extensive knowledge and skills to provide competent and compassionate care. Nursing education curriculum involves high-stress environments that can significantly impact students’ learning approaches and academic performance [ 1 , 2 ]. Numerous studies have investigated learning approaches in nursing education, highlighting the importance of identifying individual students’ preferred approaches. The most studied learning approaches include deep, surface, and strategic approaches. Deep learning approaches involve students actively seeking meaning, making connections, and critically analyzing information. Surface learning approaches focus on memorization and reproducing information without a more profound understanding. Strategic learning approaches aim to achieve high grades by adopting specific strategies, such as memorization techniques or time management skills [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
Nursing education stands out due to its focus on practical training, where the blend of academic and clinical coursework becomes a significant stressor for students, despite academic stress being shared among all university students [ 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Consequently, nursing students are recognized as prone to high-stress levels. Stress is the physiological and psychological response that occurs when a biological control system identifies a deviation between the desired (target) state and the actual state of a fitness-critical variable, whether that discrepancy arises internally or externally to the human [ 9 ]. Stress levels can vary from objective threats to subjective appraisals, making it a highly personalized response to circumstances. Failure to manage these demands leads to stress imbalance [ 10 ].
Nursing students face three primary stressors during their education: academic, clinical, and personal/social stress. Academic stress is caused by the fear of failure in exams, assessments, and training, as well as workload concerns [ 11 ]. Clinical stress, on the other hand, arises from work-related difficulties such as coping with death, fear of failure, and interpersonal dynamics within the organization. Personal and social stressors are caused by an imbalance between home and school, financial hardships, and other factors. Throughout their education, nursing students have to deal with heavy workloads, time constraints, clinical placements, and high academic expectations. Multiple studies have shown that nursing students experience higher stress levels compared to students in other fields [ 12 , 13 , 14 ].
Research has examined the relationship between academic stress and coping strategies among nursing students, but no studies focus specifically on the learning approach and academic stress. However, existing literature suggests that students interested in nursing tend to experience lower levels of academic stress [ 7 ]. Therefore, interest in nursing can lead to deep learning approaches, which promote a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter, allowing students to feel more confident and less overwhelmed by coursework and exams. Conversely, students employing surface learning approaches may experience higher stress levels due to the reliance on memorization [ 3 ].
Understanding the interplay between academic stress and learning approaches among nursing students is essential for designing effective educational interventions. Nursing educators can foster deep learning approaches by incorporating active learning strategies, critical thinking exercises, and reflection activities into the curriculum [ 15 ]. Creating supportive learning environments encouraging collaboration, self-care, and stress management techniques can help alleviate academic stress. Additionally, providing mentorship and counselling services tailored to nursing students’ unique challenges can contribute to their overall well-being and academic success [ 16 , 17 , 18 ].
Despite the scarcity of research focusing on the link between academic stress and learning methods in nursing students, it’s crucial to identify the unique stressors they encounter. The intensity of these stressors can be connected to the learning strategies employed by these students. Academic stress and learning approach are intertwined aspects of the student experience. While academic stress can influence learning approaches, the choice of learning approach can also impact the level of academic stress experienced. By understanding this relationship and implementing strategies to promote healthy learning approaches and manage academic stress, educators and institutions can foster an environment conducive to deep learning and student well-being.
Hence, this study aims to investigate the correlation between academic stress and learning approaches experienced by nursing students.
Study objectives
Assess the levels of academic stress among nursing students.
Assess the learning approaches among nursing students.
Identify the relationship between academic stress and learning approach among nursing students.
Identify the effect of academic stress and related factors on learning approach and among nursing students.
Materials and methods
Research design.
A cross-sectional descriptive correlation research design adhering to the STROBE guidelines was used for this study.
A research project was conducted at Alexandria Nursing College, situated in Egypt. The college adheres to the national standards for nursing education and functions under the jurisdiction of the Egyptian Ministry of Higher Education. Alexandria Nursing College comprises nine specialized nursing departments that offer various nursing specializations. These departments include Nursing Administration, Community Health Nursing, Gerontological Nursing, Medical-Surgical Nursing, Critical Care Nursing, Pediatric Nursing, Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing, Nursing Education, and Psychiatric Nursing and Mental Health. The credit hour system is the fundamental basis of both undergraduate and graduate programs. This framework guarantees a thorough evaluation of academic outcomes by providing an organized structure for tracking academic progress and conducting analyses.
Participants and sample size calculation
The researchers used the Epi Info 7 program to calculate the sample size. The calculations were based on specific parameters such as a population size of 9886 students for the academic year 2022–2023, an expected frequency of 50%, a maximum margin of error of 5%, and a confidence coefficient of 99.9%. Based on these parameters, the program indicated that a minimum sample size of 976 students was required. As a result, the researchers recruited a convenient sample of 1010 nursing students from different academic levels during the 2022–2023 academic year [ 19 ]. This sample size was larger than the minimum required, which could help to increase the accuracy and reliability of the study results. Participation in the study required enrollment in a nursing program and voluntary agreement to take part. The exclusion criteria included individuals with mental illnesses based on their response and those who failed to complete the questionnaires.
socio-demographic data that include students’ age, sex, educational level, hours of sleep at night, hours spent studying, and GPA from the previous semester.
Tool two: the perceived stress scale (PSS)
It was initially created by Sheu et al. (1997) to gauge the level and nature of stress perceived by nursing students attending Taiwanese universities [ 20 ]. It comprises 29 items rated on a 5-point Likert scale, where (0 = never, 1 = rarely, 2 = sometimes, 3 = reasonably often, and 4 = very often), with a total score ranging from 0 to 116. The cut-off points of levels of perceived stress scale according to score percentage were low < 33.33%, moderate 33.33–66.66%, and high more than 66.66%. Higher scores indicate higher stress levels. The items are categorized into six subscales reflecting different sources of stress. The first subscale assesses “stress stemming from lack of professional knowledge and skills” and includes 3 items. The second subscale evaluates “stress from caring for patients” with 8 items. The third subscale measures “stress from assignments and workload” with 5 items. The fourth subscale focuses on “stress from interactions with teachers and nursing staff” with 6 items. The fifth subscale gauges “stress from the clinical environment” with 3 items. The sixth subscale addresses “stress from peers and daily life” with 4 items. El-Ashry et al. (2022) reported an excellent internal consistency reliability of 0.83 [ 21 ]. Two bilingual translators translated the English version of the scale into Arabic and then back-translated it into English by two other independent translators to verify its accuracy. The suitability of the translated version was confirmed through a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), which yielded goodness-of-fit indices such as a comparative fit index (CFI) of 0.712, a Tucker-Lewis index (TLI) of 0.812, and a root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) of 0.100.
Tool three: revised study process questionnaire (R-SPQ-2 F)
It was developed by Biggs et al. (2001). It examines deep and surface learning approaches using only 20 questions; each subscale contains 10 questions [ 22 ]. On a 5-point Likert scale ranging from 0 (never or only rarely true of me) to 4 (always or almost always accurate of me). The total score ranged from 0 to 80, with a higher score reflecting more deep or surface learning approaches. The cut-off points of levels of revised study process questionnaire according to score percentage were low < 33%, moderate 33–66%, and high more than 66%. Biggs et al. (2001) found that Cronbach alpha value was 0.73 for deep learning approach and 0.64 for the surface learning approach, which was considered acceptable. Two translators fluent in English and Arabic initially translated a scale from English to Arabic. To ensure the accuracy of the translation, they translated it back into English. The translated version’s appropriateness was evaluated using a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). The CFA produced several goodness-of-fit indices, including a Comparative Fit Index (CFI) of 0.790, a Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) of 0.912, and a Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) of 0.100. Comparative Fit Index (CFI) of 0.790, a Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) of 0.912, and a Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) of 0.100.
Ethical considerations
The Alexandria University College of Nursing’s Research Ethics Committee provided ethical permission before the study’s implementation. Furthermore, pertinent authorities acquired ethical approval at participating nursing institutions. The vice deans of the participating institutions provided written informed consent attesting to institutional support and authority. By giving written informed consent, participants confirmed they were taking part voluntarily. Strict protocols were followed to protect participants’ privacy during the whole investigation. The obtained personal data was kept private and available only to the study team. Ensuring participants’ privacy and anonymity was of utmost importance.
Tools validity
The researchers created tool one after reviewing pertinent literature. Two bilingual translators independently translated the English version into Arabic to evaluate the applicability of the academic stress and learning approach tools for Arabic-speaking populations. To assure accuracy, two additional impartial translators back-translated the translation into English. They were also assessed by a five-person jury of professionals from the education and psychiatric nursing departments. The scales were found to have sufficiently evaluated the intended structures by the jury.
Pilot study
A preliminary investigation involved 100 nursing student applicants, distinct from the final sample, to gauge the efficacy, clarity, and potential obstacles in utilizing the research instruments. The pilot findings indicated that the instruments were accurate, comprehensible, and suitable for the target demographic. Additionally, Cronbach’s Alpha was utilized to further assess the instruments’ reliability, demonstrating internal solid consistency for both the learning approaches and academic stress tools, with values of 0.91 and 0.85, respectively.
Data collection
The researchers convened with each qualified student in a relaxed, unoccupied classroom in their respective college settings. Following a briefing on the study’s objectives, the students filled out the datasheet. The interviews typically lasted 15 to 20 min.
Data analysis
The data collected were analyzed using IBM SPSS software version 26.0. Following data entry, a thorough examination and verification were undertaken to ensure accuracy. The normality of quantitative data distributions was assessed using Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests. Cronbach’s Alpha was employed to evaluate the reliability and internal consistency of the study instruments. Descriptive statistics, including means (M), standard deviations (SD), and frequencies/percentages, were computed to summarize academic stress and learning approaches for categorical data. Student’s t-tests compared scores between two groups for normally distributed variables, while One-way ANOVA compared scores across more than two categories of a categorical variable. Pearson’s correlation coefficient determined the strength and direction of associations between customarily distributed quantitative variables. Hierarchical regression analysis identified the primary independent factors influencing learning approaches. Statistical significance was determined at the 5% (p < 0.05).
Table 1 presents socio-demographic data for a group of 1010 nursing students. The age distribution shows that 38.8% of the students were between 18 and 21 years old, 32.9% were between 21 and 24 years old, and 28.3% were between 24 and 28 years old, with an average age of approximately 22.79. Regarding gender, most of the students were female (77%), while 23% were male. The students were distributed across different educational years, a majority of 34.4% in the second year, followed by 29.4% in the fourth year. The students’ hours spent studying were found to be approximately two-thirds (67%) of the students who studied between 3 and 6 h. Similarly, sleep patterns differ among the students; more than three-quarters (77.3%) of students sleep between 5- to more than 7 h, and only 2.4% sleep less than 2 h per night. Finally, the student’s Grade Point Average (GPA) from the previous semester was also provided. 21% of the students had a GPA between 2 and 2.5, 40.9% had a GPA between 2.5 and 3, and 38.1% had a GPA between 3 and 3.5.
Figure 1 provides the learning approach level among nursing students. In terms of learning approach, most students (55.0%) exhibited a moderate level of deep learning approach, followed by 25.9% with a high level and 19.1% with a low level. The surface learning approach was more prevalent, with 47.8% of students showing a moderate level, 41.7% showing a low level, and only 10.5% exhibiting a high level.
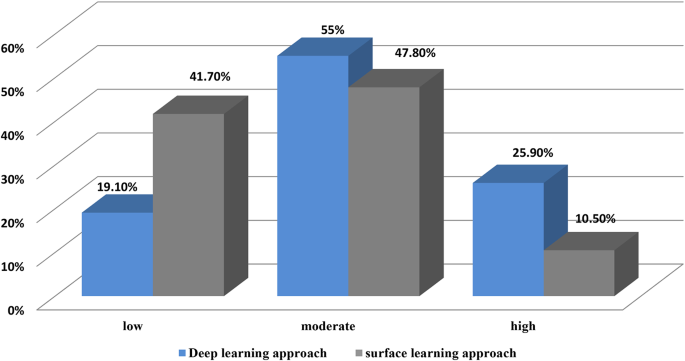
Nursing students? levels of learning approach (N=1010)
Figure 2 provides the types of academic stress levels among nursing students. Among nursing students, various stressors significantly impact their academic experiences. Foremost among these stressors are the pressure and demands associated with academic assignments and workload, with 30.8% of students attributing their high stress levels to these factors. Challenges within the clinical environment are closely behind, contributing significantly to high stress levels among 25.7% of nursing students. Interactions with peers and daily life stressors also weigh heavily on students, ranking third among sources of high stress, with 21.5% of students citing this as a significant factor. Similarly, interaction with teachers and nursing staff closely follow, contributing to high-stress levels for 20.3% of nursing students. While still significant, stress from taking care of patients ranks slightly lower, with 16.7% of students reporting it as a significant factor contributing to their academic stress. At the lowest end of the ranking, but still notable, is stress from a perceived lack of professional knowledge and skills, with 15.9% of students experiencing high stress in this area.
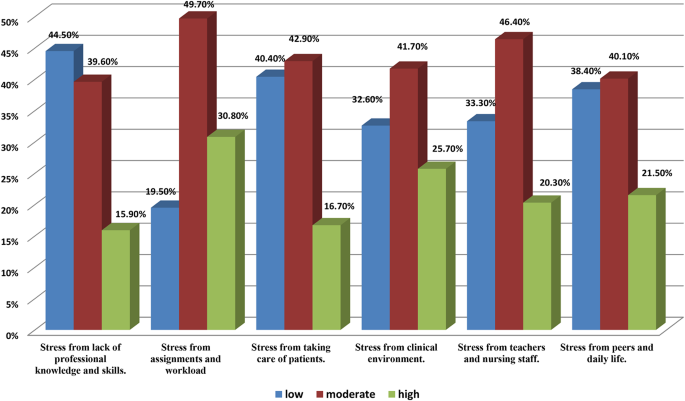
Nursing students? levels of academic stress subtypes (N=1010)
Figure 3 provides the total levels of academic stress among nursing students. The majority of students experienced moderate academic stress (56.3%), followed by those experiencing low academic stress (29.9%), and a minority experienced high academic stress (13.8%).
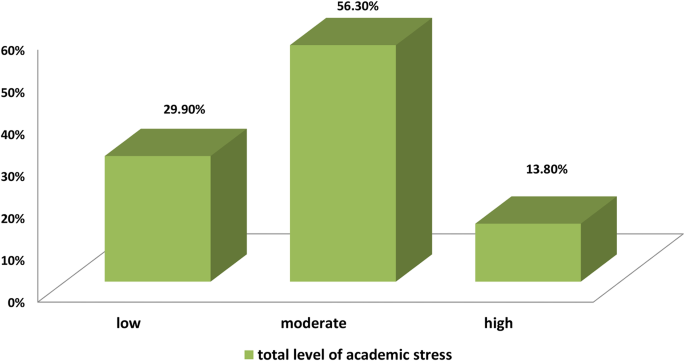
Nursing students? levels of total academic stress (N=1010)
Table 2 displays the correlation between academic stress subscales and deep and surface learning approaches among 1010 nursing students. All stress subscales exhibited a negative correlation regarding the deep learning approach, indicating that the inclination toward deep learning decreases with increasing stress levels. The most significant negative correlation was observed with stress stemming from the lack of professional knowledge and skills (r=-0.392, p < 0.001), followed by stress from the clinical environment (r=-0.109, p = 0.001), stress from assignments and workload (r=-0.103, p = 0.001), stress from peers and daily life (r=-0.095, p = 0.002), and stress from patient care responsibilities (r=-0.093, p = 0.003). The weakest negative correlation was found with stress from interactions with teachers and nursing staff (r=-0.083, p = 0.009). Conversely, concerning the surface learning approach, all stress subscales displayed a positive correlation, indicating that heightened stress levels corresponded with an increased tendency toward superficial learning. The most substantial positive correlation was observed with stress related to the lack of professional knowledge and skills (r = 0.365, p < 0.001), followed by stress from patient care responsibilities (r = 0.334, p < 0.001), overall stress (r = 0.355, p < 0.001), stress from interactions with teachers and nursing staff (r = 0.262, p < 0.001), stress from assignments and workload (r = 0.262, p < 0.001), and stress from the clinical environment (r = 0.254, p < 0.001). The weakest positive correlation was noted with stress stemming from peers and daily life (r = 0.186, p < 0.001).
Table 3 outlines the association between the socio-demographic characteristics of nursing students and their deep and surface learning approaches. Concerning age, statistically significant differences were observed in deep and surface learning approaches (F = 3.661, p = 0.003 and F = 7.983, p < 0.001, respectively). Gender also demonstrated significant differences in deep and surface learning approaches (t = 3.290, p = 0.001 and t = 8.638, p < 0.001, respectively). Female students exhibited higher scores in the deep learning approach (31.59 ± 8.28) compared to male students (29.59 ± 7.73), while male students had higher scores in the surface learning approach (29.97 ± 7.36) compared to female students (24.90 ± 7.97). Educational level exhibited statistically significant differences in deep and surface learning approaches (F = 5.599, p = 0.001 and F = 17.284, p < 0.001, respectively). Both deep and surface learning approach scores increased with higher educational levels. The duration of study hours demonstrated significant differences only in the surface learning approach (F = 3.550, p = 0.014), with scores increasing as study hours increased. However, no significant difference was observed in the deep learning approach (F = 0.861, p = 0.461). Hours of sleep per night and GPA from the previous semester did not exhibit statistically significant differences in deep or surface learning approaches.
Table 4 presents a multivariate linear regression analysis examining the factors influencing the learning approach among 1110 nursing students. The deep learning approach was positively influenced by age, gender (being female), educational year level, and stress from teachers and nursing staff, as indicated by their positive coefficients and significant p-values (p < 0.05). However, it was negatively influenced by stress from a lack of professional knowledge and skills. The other factors do not significantly influence the deep learning approach. On the other hand, the surface learning approach was positively influenced by gender (being female), educational year level, stress from lack of professional knowledge and skills, stress from assignments and workload, and stress from taking care of patients, as indicated by their positive coefficients and significant p-values (p < 0.05). However, it was negatively influenced by gender (being male). The other factors do not significantly influence the surface learning approach. The adjusted R-squared values indicated that the variables in the model explain 17.8% of the variance in the deep learning approach and 25.5% in the surface learning approach. Both models were statistically significant (p < 0.001).
Nursing students’ academic stress and learning approaches are essential to planning for effective and efficient learning. Nursing education also aims to develop knowledgeable and competent students with problem-solving and critical-thinking skills.
The study’s findings highlight the significant presence of stress among nursing students, with a majority experiencing moderate to severe levels of academic stress. This aligns with previous research indicating that academic stress is prevalent among nursing students. For instance, Zheng et al. (2022) observed moderated stress levels in nursing students during clinical placements [ 23 ], while El-Ashry et al. (2022) found that nearly all first-year nursing students in Egypt experienced severe academic stress [ 21 ]. Conversely, Ali and El-Sherbini (2018) reported that over three-quarters of nursing students faced high academic stress. The complexity of the nursing program likely contributes to these stress levels [ 24 ].
The current study revealed that nursing students identified the highest sources of academic stress as workload from assignments and the stress of caring for patients. This aligns with Banu et al.‘s (2015) findings, where academic demands, assignments, examinations, high workload, and combining clinical work with patient interaction were cited as everyday stressors [ 25 ]. Additionally, Anaman-Torgbor et al. (2021) identified lectures, assignments, and examinations as predictors of academic stress through logistic regression analysis. These stressors may stem from nursing programs emphasizing the development of highly qualified graduates who acquire knowledge, values, and skills through classroom and clinical experiences [ 26 ].
The results regarding learning approaches indicate that most nursing students predominantly employed the deep learning approach. Despite acknowledging a surface learning approach among the participants in the present study, the prevalence of deep learning was higher. This inclination toward the deep learning approach is anticipated in nursing students due to their engagement with advanced courses, requiring retention, integration, and transfer of information at elevated levels. The deep learning approach correlates with a gratifying learning experience and contributes to higher academic achievements [ 3 ]. Moreover, the nursing program’s emphasis on active learning strategies fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. These findings align with Mahmoud et al.‘s (2019) study, reporting a significant presence (83.31%) of the deep learning approach among undergraduate nursing students at King Khalid University’s Faculty of Nursing [ 27 ]. Additionally, Mohamed &Morsi (2019) found that most nursing students at Benha University’s Faculty of Nursing embraced the deep learning approach (65.4%) compared to the surface learning approach [ 28 ].
The study observed a negative correlation between the deep learning approach and the overall mean stress score, contrasting with a positive correlation between surface learning approaches and overall stress levels. Elevated academic stress levels may diminish motivation and engagement in the learning process, potentially leading students to feel overwhelmed, disinterested, or burned out, prompting a shift toward a surface learning approach. This finding resonates with previous research indicating that nursing students who actively seek positive academic support strategies during academic stress have better prospects for success than those who do not [ 29 ]. Nebhinani et al. (2020) identified interface concerns and academic workload as significant stress-related factors. Notably, only an interest in nursing demonstrated a significant association with stress levels, with participants interested in nursing primarily employing adaptive coping strategies compared to non-interested students.
The current research reveals a statistically significant inverse relationship between different dimensions of academic stress and adopting the deep learning approach. The most substantial negative correlation was observed with stress arising from a lack of professional knowledge and skills, succeeded by stress associated with the clinical environment, assignments, and workload. Nursing students encounter diverse stressors, including delivering patient care, handling assignments and workloads, navigating challenging interactions with staff and faculty, perceived inadequacies in clinical proficiency, and facing examinations [ 30 ].
In the current study, the multivariate linear regression analysis reveals that various factors positively influence the deep learning approach, including age, female gender, educational year level, and stress from teachers and nursing staff. In contrast, stress from a lack of professional knowledge and skills exert a negative influence. Conversely, the surface learning approach is positively influenced by female gender, educational year level, stress from lack of professional knowledge and skills, stress from assignments and workload, and stress from taking care of patients, but negatively affected by male gender. The models explain 17.8% and 25.5% of the variance in the deep and surface learning approaches, respectively, and both are statistically significant. These findings underscore the intricate interplay of demographic and stress-related factors in shaping nursing students’ learning approaches. High workloads and patient care responsibilities may compel students to prioritize completing tasks over deep comprehension. This pressure could lead to a surface learning approach as students focus on meeting immediate demands rather than engaging deeply with course material. This observation aligns with the findings of Alsayed et al. (2021), who identified age, gender, and study year as significant factors influencing students’ learning approaches.
Deep learners often demonstrate better self-regulation skills, such as effective time management, goal setting, and seeking support when needed. These skills can help manage academic stress and maintain a balanced learning approach. These are supported by studies that studied the effect of coping strategies on stress levels [ 6 , 31 , 32 ]. On the contrary, Pacheco-Castillo et al. study (2021) found a strong significant relationship between academic stressors and students’ level of performance. That study also proved that the more academic stress a student faces, the lower their academic achievement.
Strengths and limitations of the study
This study has lots of advantages. It provides insightful information about the educational experiences of Egyptian nursing students, a demographic that has yet to receive much research. The study’s limited generalizability to other people or nations stems from its concentration on this particular group. This might be addressed in future studies by using a more varied sample. Another drawback is the dependence on self-reported metrics, which may contain biases and mistakes. Although the cross-sectional design offers a moment-in-time view of the problem, it cannot determine causation or evaluate changes over time. To address this, longitudinal research may be carried out.
Notwithstanding these drawbacks, the study substantially contributes to the expanding knowledge of academic stress and nursing students’ learning styles. Additional research is needed to determine teaching strategies that improve deep-learning approaches among nursing students. A qualitative study is required to analyze learning approaches and factors that may influence nursing students’ selection of learning approaches.
According to the present study’s findings, nursing students encounter considerable academic stress, primarily stemming from heavy assignments and workload, as well as interactions with teachers and nursing staff. Additionally, it was observed that students who experience lower levels of academic stress typically adopt a deep learning approach, whereas those facing higher stress levels tend to resort to a surface learning approach. Demographic factors such as age, gender, and educational level influence nursing students’ choice of learning approach. Specifically, female students are more inclined towards deep learning, whereas male students prefer surface learning. Moreover, deep and surface learning approach scores show an upward trend with increasing educational levels and study hours. Academic stress emerges as a significant determinant shaping the adoption of learning approaches among nursing students.
Implications in nursing practice
Nursing programs should consider integrating stress management techniques into their curriculum. Providing students with resources and skills to cope with academic stress can improve their well-being and academic performance. Educators can incorporate teaching strategies that promote deep learning approaches, such as problem-based learning, critical thinking exercises, and active learning methods. These approaches help students engage more deeply with course material and reduce reliance on surface learning techniques. Recognizing the gender differences in learning approaches, nursing programs can offer gender-specific support services and resources. For example, providing targeted workshops or counseling services that address male and female nursing students’ unique stressors and learning needs. Implementing mentorship programs and peer support groups can create a supportive environment where students can share experiences, seek advice, and receive encouragement from their peers and faculty members. Encouraging students to reflect on their learning processes and identify effective study strategies can help them develop metacognitive skills and become more self-directed learners. Faculty members can facilitate this process by incorporating reflective exercises into the curriculum. Nursing faculty and staff should receive training on recognizing signs of academic stress among students and providing appropriate support and resources. Additionally, professional development opportunities can help educators stay updated on evidence-based teaching strategies and practical interventions for addressing student stress.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to restrictions imposed by the institutional review board to protect participant confidentiality, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Liu J, Yang Y, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zeng Y, Li J. Stress and coping styles among nursing students during the initial period of the clinical practicum: A cross-section study. Int J Nurs Sci. 2022a;9(2). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2022.02.004 .
Saifan A, Devadas B, Daradkeh F, Abdel-Fattah H, Aljabery M, Michael LM. Solutions to bridge the theory-practice gap in nursing education in the UAE: a qualitative study. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02919-x .
Alsayed S, Alshammari F, Pasay-an E, Dator WL. Investigating the learning approaches of students in nursing education. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2021;16(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2020.10.008 .
Salah Dogham R, Elcokany NM, Saber Ghaly A, Dawood TMA, Aldakheel FM, Llaguno MBB, Mohsen DM. Self-directed learning readiness and online learning self-efficacy among undergraduate nursing students. Int J Afr Nurs Sci. 2022;17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijans.2022.100490 .
Zhao Y, Kuan HK, Chung JOK, Chan CKY, Li WHC. Students’ approaches to learning in a clinical practicum: a psychometric evaluation based on item response theory. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2018.04.015 .
Huang HM, Fang YW. Stress and coping strategies of online nursing practicum courses for Taiwanese nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative study. Healthcare. 2023;11(14). https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11142053 .
Nebhinani M, Kumar A, Parihar A, Rani R. Stress and coping strategies among undergraduate nursing students: a descriptive assessment from Western Rajasthan. Indian J Community Med. 2020;45(2). https://doi.org/10.4103/ijcm.IJCM_231_19 .
Olvera Alvarez HA, Provencio-Vasquez E, Slavich GM, Laurent JGC, Browning M, McKee-Lopez G, Robbins L, Spengler JD. Stress and health in nursing students: the Nurse Engagement and Wellness Study. Nurs Res. 2019;68(6). https://doi.org/10.1097/NNR.0000000000000383 .
Del Giudice M, Buck CL, Chaby LE, Gormally BM, Taff CC, Thawley CJ, Vitousek MN, Wada H. What is stress? A systems perspective. Integr Comp Biol. 2018;58(6):1019–32. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/icy114 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bhui K, Dinos S, Galant-Miecznikowska M, de Jongh B, Stansfeld S. Perceptions of work stress causes and effective interventions in employees working in public, private and non-governmental organisations: a qualitative study. BJPsych Bull. 2016;40(6). https://doi.org/10.1192/pb.bp.115.050823 .
Lavoie-Tremblay M, Sanzone L, Aubé T, Paquet M. Sources of stress and coping strategies among undergraduate nursing students across all years. Can J Nurs Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1177/08445621211028076 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ahmed WAM, Abdulla YHA, Alkhadher MA, Alshameri FA. Perceived stress and coping strategies among nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review. Saudi J Health Syst Res. 2022;2(3). https://doi.org/10.1159/000526061 .
Pacheco-Castillo J, Casuso-Holgado MJ, Labajos-Manzanares MT, Moreno-Morales N. Academic stress among nursing students in a Private University at Puerto Rico, and its Association with their academic performance. Open J Nurs. 2021;11(09). https://doi.org/10.4236/ojn.2021.119063 .
Tran TTT, Nguyen NB, Luong MA, Bui THA, Phan TD, Tran VO, Ngo TH, Minas H, Nguyen TQ. Stress, anxiety and depression in clinical nurses in Vietnam: a cross-sectional survey and cluster analysis. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2019;13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13033-018-0257-4 .
Magnavita N, Chiorri C. Academic stress and active learning of nursing students: a cross-sectional study. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2018.06.003 .
Folkvord SE, Risa CF. Factors that enhance midwifery students’ learning and development of self-efficacy in clinical placement: a systematic qualitative review. Nurse Educ Pract. 2023;66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2022.103510 .
Myers SB, Sweeney AC, Popick V, Wesley K, Bordfeld A, Fingerhut R. Self-care practices and perceived stress levels among psychology graduate students. Train Educ Prof Psychol. 2012;6(1). https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026534 .
Zeb H, Arif I, Younas A. Nurse educators’ experiences of fostering undergraduate students’ ability to manage stress and demanding situations: a phenomenological inquiry. Nurse Educ Pract. 2022;65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2022.103501 .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. User Guide| Support| Epi Info™ [Internet]. Atlanta: CDC; [cited 2024 Jan 31]. Available from: CDC website.
Sheu S, Lin HS, Hwang SL, Yu PJ, Hu WY, Lou MF. The development and testing of a perceived stress scale for nursing students in clinical practice. J Nurs Res. 1997;5:41–52. Available from: http://ntur.lib.ntu.edu.tw/handle/246246/165917 .
El-Ashry AM, Harby SS, Ali AAG. Clinical stressors as perceived by first-year nursing students of their experience at Alexandria main university hospital during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2022;41:214–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apnu.2022.08.007 .
Biggs J, Kember D, Leung DYP. The revised two-factor study process questionnaire: R-SPQ-2F. Br J Educ Psychol. 2001;71(1):133–49. https://doi.org/10.1348/000709901158433 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Zheng YX, Jiao JR, Hao WN. Stress levels of nursing students: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Med (United States). 2022;101(36). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000030547 .
Ali AM, El-Sherbini HH. Academic stress and its contributing factors among faculty nursing students in Alexandria. Alexandria Scientific Nursing Journal. 2018; 20(1):163–181. Available from: https://asalexu.journals.ekb.eg/article_207756_b62caf4d7e1e7a3b292bbb3c6632a0ab.pdf .
Banu P, Deb S, Vardhan V, Rao T. Perceived academic stress of university students across gender, academic streams, semesters, and academic performance. Indian J Health Wellbeing. 2015;6(3):231–235. Available from: http://www.iahrw.com/index.php/home/journal_detail/19#list .
Anaman-Torgbor JA, Tarkang E, Adedia D, Attah OM, Evans A, Sabina N. Academic-related stress among Ghanaian nursing students. Florence Nightingale J Nurs. 2021;29(3):263. https://doi.org/10.5152/FNJN.2021.21030 .
Mahmoud HG, Ahmed KE, Ibrahim EA. Learning Styles and Learning Approaches of Bachelor Nursing Students and its Relation to Their Achievement. Int J Nurs Didact. 2019;9(03):11–20. Available from: http://www.nursingdidactics.com/index.php/ijnd/article/view/2465 .
Mohamed NAAA, Morsi MES, Learning Styles L, Approaches. Academic achievement factors, and self efficacy among nursing students. Int J Novel Res Healthc Nurs. 2019;6(1):818–30. Available from: www.noveltyjournals.com.
Google Scholar
Onieva-Zafra MD, Fernández-Muñoz JJ, Fernández-Martínez E, García-Sánchez FJ, Abreu-Sánchez A, Parra-Fernández ML. Anxiety, perceived stress and coping strategies in nursing students: a cross-sectional, correlational, descriptive study. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-020-02294-z .
Article Google Scholar
Aljohani W, Banakhar M, Sharif L, Alsaggaf F, Felemban O, Wright R. Sources of stress among Saudi Arabian nursing students: a cross-sectional study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(22). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182211958 .
Liu Y, Wang L, Shao H, Han P, Jiang J, Duan X. Nursing students’ experience during their practicum in an intensive care unit: a qualitative meta-synthesis. Front Public Health. 2022;10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.974244 .
Majrashi A, Khalil A, Nagshabandi E, Al MA. Stressors and coping strategies among nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic: scoping review. Nurs Rep. 2021;11(2):444–59. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep11020042 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Our sincere thanks go to all the nursing students in the study. We also want to thank Dr/ Rasha Badry for their statistical analysis help and contribution to this study.
The research was not funded by public, commercial, or non-profit organizations.
Open access funding provided by The Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) in cooperation with The Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Nursing Education, Faculty of Nursing, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
Rawhia Salah Dogham & Heba Fakieh Mansy Ali
Critical Care & Emergency Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
Nermine M. Elcokany
Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
Asmaa Saber Ghaly
Faculty of Nursing, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, Egypt
Mohamed Mahmoud Seweid
Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
Ayman Mohamed El-Ashry
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Ayman M. El-Ashry & Rawhia S. Dogham: conceptualization, preparation, and data collection; methodology; investigation; formal analysis; data analysis; writing-original draft; writing-manuscript; and editing. Heba F. Mansy Ali & Asmaa S. Ghaly: conceptualization, preparation, methodology, investigation, writing-original draft, writing-review, and editing. Nermine M. Elcokany & Mohamed M. Seweid: Methodology, investigation, formal analysis, data collection, writing-manuscript & editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript and accept for publication.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ayman Mohamed El-Ashry .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The research adhered to the guidelines and regulations outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki (DoH-Oct2008). The Faculty of Nursing’s Research Ethical Committee (REC) at Alexandria University approved data collection in this study (IRB00013620/95/9/2022). Participants were required to sign an informed written consent form, which included an explanation of the research and an assessment of their understanding.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Dogham, R.S., Ali, H.F.M., Ghaly, A.S. et al. Deciphering the influence: academic stress and its role in shaping learning approaches among nursing students: a cross-sectional study. BMC Nurs 23 , 249 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01885-1
Download citation
Received : 31 January 2024
Accepted : 21 March 2024
Published : 17 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01885-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Academic stress
- Learning approaches
- Nursing students
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Harvard College Writing Center 5 Asking Analytical Questions When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a
Harvard College Writing Center. menu close Menu. Search. Search search. Questions about Expos? Writing Support for Instructors; Faculty of Arts and Sciences. ... Strategies for Essay Writing: PDFs Strategies for Essay Writing--Complete. description. Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt. description. Asking Analytical Questions. description.
Have a fresh pair of eyes give you some feedback. Don't allow someone else to rewrite your essay, but do take advantage of others' edits and opinions when they seem helpful. ( Bates College) Read your essay aloud to someone. Reading the essay out loud offers a chance to hear how your essay sounds outside your head.
Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt. Asking Analytical Questions. Thesis. Introductions. What Do Introductions Across the Disciplines Have in Common? Anatomy of a Body Paragraph. Transitions. Tips for Organizing Your Essay. Counterargument.
Don't summarize. Avoid explicitly stating the point of your essay. It's far less effective when you spell it out for someone. Delete every single "That's when I realized," "I learned," and "The most important lesson was...". It's unnecessary, unconvincing, and takes the reader out of the moment.
270 pages of the most effective teaching strategies; 50+ digital tools ready right out of the box 75 editable resources for student differentiation ; Loads of tricks and tips to add to your teaching tool bag; All explanations are reinforced with concrete examples.; Links to high-quality video tutorials; Clear objectives easy to match to the demands of your curriculum
Don't Repeat. If you've mentioned an activity, story, or anecdote in some other part of your application, don't repeat it again in your essay. Your essay should tell college admissions officers something new. Whatever you write in your essay should be in philosophical alignment with the rest of your application.
Joanne Baird Giordano. This chapter is one section of a five-part series on academic literacy strategies: A Quick Introduction to College Learning Strategies. General Academic Literacy and Disciplinary Literacy. Reading for Understanding. Reading to Learn and Remember. Adapting to Disciplinary Literacy Conventions. Strategies for College Learning.
General Strategies. View the improvement of students' writing as your responsibility. Teaching writing is not only the job of the English department alone. Writing is an essential tool for learning a discipline and helping students improve their writing skills is a responsibility for all faculty. Let students know that you value good writing.
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
Develop strategies for reading college assignments strategically. As a college student, you must take complete responsibility for your writing assignments. Your professors are assessing your ability to think for yourself, so they're less likely to give you ready-made templates on how to write a given essay. ... College essays used to be ...
Harvard Extension: In your book, you talk about strategies to help students be better learners in and outside of the classroom. You write, "We harbor deep convictions that we learn better through single-minded focus and dogged repetition. And these beliefs are validated time and again by the visible improvement that comes during practice ...
Effective Learning Practices. Learning at college requires processing and retaining a high volume of information across various disciplines and subjects at the same time, which can be a daunting task, especially if the information is brand new. In response, college students try out varied approaches to their learning - often drawing from ...
Austin Community College; EDUC; Effective Learning Strategies; Student Success; https-www-oercommons-org-courseware-module-25870-s; ... Effective Strategies for College Success. Chapter 13: Test Taking Strategies . ... Essay questions allow students to demonstrate critical thinking, creative thinking, and writing skills.
Teach Students How to Learn: Strategies You Can Incorporate in Any Course to Improve Student Metacognition, Study Skills, and Motivation. Stylus Publishing, LLC. Newport, C. (2006). How to become a straight-a student: the unconventional strategies real college students use to score high while studying less. Three Rivers Press. Paul, K. (1996).
Thesis - Students should be allowed to use cellphones because (1) higher engagement (2) learning tools/apps (3) gain 21st-century skills Topic 1. Cellphones create higher engagement in students...
Take a pen and a piece of paper, relax, and just write down your stream of consciousness for a selected topic. It can be clumsy or grammatically incorrect, but who cares if it works for you and helps you to focus. Try to generate as many ideas relevant to your topic as possible. Never mind how good they are.
In fact, students are often incorrect in their assumptions about effective ways to learn and simultaneously have difficulty assessing their own learning accurately (Bjork et al., 2013; Brown et al., 2014).Performance on early assessments is a strong predictor of performance later in a course (Bowen & Wingo, 2012), suggesting that students who begin a course using effective learning strategies ...
Your brain works better when you are rested, hydrated, and nourished. Though it might seem effective to push through without taking a break and stay up studying all night (see the page on strategies that don't work), it won't help you in the long run. Instead, develop a study plan, eat a good meal, and have a bottle of water nearby when you ...
Learning Strategies. Reading. Enhance your ability to comprehend more in less time. ... Notetaking. Resources on how to take effective class notes for yourself and your classmates. Read More. Strategic Learning Videos & Books. Three books and twelve videos that present the effective ways to learn and study. ... Dartmouth College Hanover, NH ...
18 Learning Strategies Examples. Learning strategies refer to a range of strategies that can be implemented to improve learning. Examples include using memory cards, spaced repetition, practice tests, strategic highlighting, and reciprocal questioning. Although there are numerous learning strategies available for students to try, none of them ...
The top barriers in teaching academic essay writing were as follows: teaching essay writing to second language learners, lack of time for explicit instruction, no strategies in place for the part ...
Staying Motivated: Be Active to be Engaged. Another key to overcoming procrastination is to stay actively engaged in your classes. If you are passive in class you're probably not "getting into" the course and its topics, and that weakens your motivation. What's more, if you are passive you are probably not making as much sense out of the course ...
896 Words. 4 Pages. 1 Works Cited. Open Document. Learning Strategies. The new year begins and Learning Strategies is on your schedule. Truly, you are probably not knowing what to expect and you think that this class is not for you. Boy, are you wrong. This class will save you plenty of time, so you better listen closely.
College students face myriad tasks each day, from homework assignments to extracurricular activities. Learning to prioritize these tasks based on urgency and importance is crucial , according to ...
National Small Business Week is an annual celebration of the small businesses and entrepreneurs across America who've made essential contributions to our economy and culture. Few figures are more fundamentally American in spirit than the small business owner. From a child opening a lemonade stand to gold prospectors striking it out West to seek riches, the independent mover-and-shaker is as ...
Background Nursing education presents unique challenges, including high levels of academic stress and varied learning approaches among students. Understanding the relationship between academic stress and learning approaches is crucial for enhancing nursing education effectiveness and student well-being. Aim This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of academic stress and its correlation ...