- Preferences


Chapter 6 Introduction to Network Operating Systems - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

Chapter 6 Introduction to Network Operating Systems
Chapter 6 introduction to network operating systems 6.1 characteristics of a network operating system 6.2 windows 6.3 linux 6.4 determining software requirements a ... – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- 6.1 Characteristics of a Network Operating System
- 6.2 Windows
- 6.4 Determining Software Requirements a Linux NOS
- Network operating systems (NOSs) distribute their functions over a number of networked computers.
- It then adds functions that allow access to shared resources by a number of users concurrently.
- NOS computers take on specialized roles to accomplish concurrent access to shared resources.
- Client systems contain specialized software that allows them to request shared resources that are controlled by server systems responding to a client request.
- The NOS enhances the reach of the client PC by making remote services available as extensions of the local native operating system.
- Although a number of users may have accounts on a PC, only a single account is active on the system at any given time.
- NOS supports multiple user accounts at the same time and enables concurrent access to shared resources by multiple clients.
- A NOS server is a multitasking system. Internally, the OS must be capable of executing multiple tasks or processes at the same time.
- Some systems are equipped with more than one processor, called multiprocessing systems.
- They are capable of executing multiple tasks in parallel by assigning each task to a different processor.
- The aggregate amount of work that the server can perform in a given time is greatly enhanced in multiprocessor systems.
- NOS servers are large systems with additional memory to support multiple tasks that are all active, or resident, in memory at the same time.
- Additional disk space is also required on servers to hold shared files and to function as an extension to the internal memory on the system.
- Because a NOS depends on the continuous operation of its servers, the extra hardware components justify the additional expense.
- The main features to consider when selecting a NOS include
- Performance
- Management and monitoring tools
- Scalability
- Robustness/fault tolerance
- It is important to know the basics about popular NOS families.
- Many networks now include more than one server type, and knowing how to get these diverse systems to interoperate is an important skill for a network administrator.
- Operating systems on the network have their own language.
- Different NOS vendors use the same terms in different ways.
- Windows server-based networks that run Windows NT Server or Windows 2000 Server are based on the concept of the domain.
- A domain is a group of computers and users that serves as a boundary of administrative authority.
- Windows NT domains and Windows 2000 domains, although similar in function, interact with one another differently.
- The Domain Structure of Windows NT was entirely different from the Domain Structure in Windows 2000.
- Instead of Active Directory, Windows NT provides an administrative tool called the User Manager for Domains.
- It is accessed from the domain controller and is used to create, manage, and remove domain user accounts.
- Each NT domain requires one Primary Domain Controller (PDC).
- This is a "master" server that contains the Security Accounts Management Database (SAM).
- A domain can also have one or more Backup Domain Controllers (BDCs), each of which contains a read-only copy of the SAM.
- The SAM is what controls the authentication process when a user logs onto the domain.
- The offline folders feature enables users to copy and synchronize documents from the network to the local system so that they can be accessed when the computer is not connected to the network.
- The Internet Printing Protocol (IPP) enables users to print to a URL and manage printers through a web browser interface.
- Built-in disk defragmenters and other tools and utilities help users maintain and manage the operating system.
- It supports Kerberos security (developing standard for authenticating network users), and the features of a Windows 2000 domain as an Active Directory client.
- XP also offers
- More extensive hardware and driver support.
- More user-friendly file-sharing and network configuration for setting up home networks.
- Enhanced wireless network features
- Increased security
- Remote Desktop control
- Overall improvements to the GUI, including the welcome screen additions, start menu improvements.
- Enhanced multimedia support for digital video, audio, and pictures.
- The Windows 2000 family of operating systems includes
- Windows 2000 Professional
- Windows 2000 Server
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server
- The specific needs of the network will determine the best version of Windows 2000 for the installation.
- The Windows 2003 family of operating systems includes
- Standard Edition
- Enterprise Edition
- Datacenter Edition
- Web Edition
- Small Business Server Edition
- 2003 Server release is the available support for 64-bit systems in order to compete in the enterprise level server arena.
- Linux is an operating system similar to UNIX. It runs on many different computers and was first released in 1991.
- Linux is portable, which means versions can be found running on name brand or clone PCs.
- Linux offers many features adopted from other versions of UNIX.
- The UNIX NOS was developed in 1969, and it has evolved into many varieties.
- The source code is opened, that is, available at no cost to anyone who wants to modify it.
- It is written in C programming language so businesses, academic institutions, and even individuals can develop their own versions.
- There are hundreds of different versions of UNIX.
- Linux is sometimes referred to as "UNIX Lite", and it is designed to run on Intel-compatible PCs.
- However, Linux will run on other machines as well.
- Linux brings the advantages of UNIX to home and small business computers.
- The following are a few of the most popular types
- Red Hat Linux
- Linux Mandrake
- Caldera eDesktop and eServer
- Debian GNU/Linux
- Corel Linux
- Turbo Linux
- Windows clients can access Linux servers without client software if the UNIX servers run Samba, which is a program that uses the Server Message Block (SMB) application layer protocol.
- Windows computers use SMB for file access across the network.
- Samba permits them to see the Linux file system.
- The X Window System is what comprises the Linux GUI environment.
- Corels WordPerfect and Sun StarOffice are the top two office suites capable of running on Linux.
- There also single packages rather than full office suits that come shipped with Linux and some are installed by default during the installation process.
- Some examples of these are LyX and AbiWord.
- Some of the popular audio and visual programs available for Linux include tools for viewing and editing graphics like XV and GIMP.
- A popular use of a Linux system is a web server.
- Web server software uses Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to deliver files to users that request them, using a web browser from their workstation.
- A Mail Server is a system that is configured with the proper programs and services that enable handling the exchange of e-mail sent from one client to another.
- The Linux operating system provides file server either in a Linux environment or in a cross-platform environment consisting of Windows, Macintosh, UNIX, or OS/2 workstation.
- There are some programs and software that are essential to add to a Linux system regardless of whether it is configured as a workstation or a server.
- Text editors are essential for performing any type of maintenance tasks that a user or an administrator may need to do.
- Some examples of text editors available in Linux are vi, jed, pico, or Emacs.
- Programming tools are helpful Linux servers as well to specific users at workstations if they are programmers.
- These programming tools are also referred to as compilers or interpreters.
- A complier converts the program source code, which is written by the programmer into binary form the computer can read.
- Common scripting languages include Javascript, Python, and Perl.
- Every Linux system relies on a library called the C library (libc). Linux systems rely on the C library for the routines that are necessary for C programs to run in Linux.
- When installing a package, the first step should be to always check and make sure that the operating system supports the package.
- Generally, any Linux software and package can be installed on any UNIX-like operating system.
- Check CPU requirements, library requirements, and development tools.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.

- Engineering Mathematics
- Discrete Mathematics
- Operating System
- Computer Networks
- Digital Logic and Design
- C Programming
- Data Structures
- Theory of Computation
- Compiler Design
- Computer Org and Architecture
- Operating System Tutorial
- What is an Operating System?
- Functions of Operating System
- Types of Operating Systems
- Need and Functions of Operating Systems
- Commonly Used Operating System
Structure of Operating System
- Operating System Services
- Introduction of System Call
- System Programs in Operating System
- Operating Systems Structures
- History of Operating System
- Booting and Dual Booting of Operating System
Types of OS
- Batch Processing Operating System
- Multiprogramming in Operating System
- Time Sharing Operating System
What is a Network Operating System?
- Real Time Operating System (RTOS)
Process Management
- Introduction of Process Management
- Process Table and Process Control Block (PCB)
- Operations on Processes
- Process Schedulers in Operating System
- Inter Process Communication (IPC)
- Context Switching in Operating System
- Preemptive and Non-Preemptive Scheduling
CPU Scheduling in OS
- CPU Scheduling in Operating Systems
- CPU Scheduling Criteria
- Multiple-Processor Scheduling in Operating System
- Thread Scheduling
Threads in OS
- Thread in Operating System
- Threads and its types in Operating System
- Multithreading in Operating System
Process Synchronization
- Introduction of Process Synchronization
- Race Condition Vulnerability
- Critical Section in Synchronization
- Mutual Exclusion in Synchronization
Critical Section Problem Solution
- Peterson's Algorithm in Process Synchronization
- Semaphores in Process Synchronization
- Semaphores and its types
- Producer Consumer Problem using Semaphores | Set 1
- Readers-Writers Problem | Set 1 (Introduction and Readers Preference Solution)
- Dining Philosopher Problem Using Semaphores
- Hardware Synchronization Algorithms : Unlock and Lock, Test and Set, Swap
Deadlocks & Deadlock Handling Methods
- Introduction of Deadlock in Operating System
- Conditions for Deadlock in Operating System
- Banker's Algorithm in Operating System
- Wait For Graph Deadlock Detection in Distributed System
- Handling Deadlocks
- Deadlock Prevention And Avoidance
- Deadlock Detection And Recovery
- Deadlock Ignorance in Operating System
- Recovery from Deadlock in Operating System
Memory Management
- Memory Management in Operating System
- Implementation of Contiguous Memory Management Techniques
- Non-Contiguous Allocation in Operating System
- Compaction in Operating System
- Best-Fit Allocation in Operating System
- Worst-Fit Allocation in Operating Systems
- First-Fit Allocation in Operating Systems
- Fixed (or static) Partitioning in Operating System
- Variable (or Dynamic) Partitioning in Operating System
- Paging in Operating System
- Segmentation in Operating System
- Virtual Memory in Operating System
Page Replacement Algorithms
- Page Replacement Algorithms in Operating Systems
- Program for Page Replacement Algorithms | Set 2 (FIFO)
- Belady's Anomaly in Page Replacement Algorithms
- Optimal Page Replacement Algorithm
- Program for Least Recently Used (LRU) Page Replacement algorithm
- Techniques to handle Thrashing
- Storage Management
- File Systems in Operating System
- File Allocation Methods
- Free space management in Operating System
- Disk Scheduling Algorithms
- RAID (Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks)
OS Interview Questions
- Last Minute Notes – Operating Systems
- Operating System Interview Questions
OS Quiz and GATE PYQ's
- OS Process Management
- OS Memory Management
- OS Input Output Systems
- OS CPU Scheduling
- 50 Operating System MCQs with Answers
The basic definition of an operating system is that the operating system is the interface between the computer hardware and the user. In daily life, we use the operating system on our devices which provides a good GUI, and many more features. Similarly, a network operating system(NOS) is software that connects multiple devices and computers on the network and allows them to share resources on the network. Let’s see what are the functions of the network operating system.
Functions of the NOS (Network Operating System)
The following are the main functions of NOS:
- Creating and managing user accounts on the network.
- Controlling access to resources on the network.
- Provide communication services between the devices on the network.
- Monitor and troubleshoot the network.
- Configuring and Managing the resources on the network.
Now let’s see the type of Network Operating systems.
Types of Network Operating Systems
There are mainly two types of networks, one is peer-to-peer and another is client/server. Now let’s see each type one by one.
- Peer to Peer: Peer-to-peer network operating systems allow the sharing of resources and files with small-sized networks and having fewer resources. In general, peer-to-peer network operating systems are used on LAN.
- Client/server: Client-server network operating systems provide users access to resources through the central server. This NOS is too expensive to implement and maintain. This operating system is good for the big networks which provide many services.
Features of Network Operating Systems
Let’s see what are the functions of the network operating system.
- Printers and application sharing on the network.
- File systems and database sharing.
- Provide good security by using functionality like user authentication and access control.
- Create backups of data.
- Inter-networking.
Now let’s see what are the advantages of NOS.
Advantages of Network Operating Systems
- Highly stable due to central server.
- Provide good security.
- Upgradation of new technology and hardware can be easily implemented in the network.
- Provide remote access to servers from different locations.
Disadvantages of Network Operating Systems
- Depend on the central location to perform the operations.
- High cost to buying server.
- Regular updating and maintenance are required.
Now let’s see what are the examples of network operating systems.
Examples of Network Operating Systems
Following are the examples of network operating systems.
- Microsoft Windows Server
- Artisoft’s LANtastic
- Banyan’s VINES
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.

- Operating Systems

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Lesson 13. Network Operating Systems (NOS). Objectives At the end of this Presentation, you will be able to:
Published by Jack Ross Modified over 8 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Lesson 13. Network Operating Systems (NOS). Objectives At the end of this Presentation, you will be able to:"— Presentation transcript:

Chapter 7 LAN Operating Systems LAN Software Software Compatibility Network Operating System (NOP) Architecture NOP Functions NOP Trends.

Chapter One The Essence of UNIX.

Network+ Guide to Networks, Fourth Edition Chapter 10 Netware-Based Networking.

Chapter Nine NetWare-Based Networking. Objectives Identify the advantages of using the NetWare network operating system Describe NetWare’s server hardware.

Local Area Networks Part III. 2 Introduction Proper support of a local area network requires hardware, software, and miscellaneous support devices. A.

Computer Forensics Principles and Practices by Volonino, Anzaldua, and Godwin Chapter 6: Operating Systems and Data Transmission Basics for Digital Investigations.

F2032 Fundamental of OS Chapter 1 Introduction to Operating System Part 4.

Understanding Networks I. Objectives Compare client and network operating systems Learn about local area network technologies, including Ethernet, Token.

70-290: MCSE Guide to Managing a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Environment Chapter 8: Implementing and Managing Printers.

Hands-On Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Networking Chapter 1 Windows Server 2003 Networking Overview.

Guide To UNIX Using Linux Third Edition

Chapter 1 Introducing Windows Server 2012/R2

Chapter 12 Reading assignment n From “Running Linux”, on reserve at PSU Main library (2-hour checkout) Chapter 1 (pages 1 through 41)Chapter 1 (pages 1.

Hussain Ali Department of Computer Engineering KFUPM, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia Microsoft Networking.

Chapter 8: Network Operating Systems and Windows Server 2003-Based Networking Network+ Guide to Networks Third Edition.

1 DOS with Windows 3.1 and 3.11 Operating Environments n Designed to allow applications to have a graphical interface DOS runs in the background as the.

Chapter 6 Introduction to Network Operating Systems 6.1 Characteristics of a Network Operating System 6.2 Windows 6.3 Linux 6.4 Determining Software Requirements.
Installing Windows XP Professional Using Attended Installation Slide 1 of 41Session 2 Ver. 1.0 CompTIA A+ Certification: A Comprehensive Approach for all.

Windows 2008 Overview Lecture 1. Windows Networking Evolution Windows for Workgroups – peer-to-peer networking built into the OS Windows NT – separate.

1 Module 2 Installing Windows NT. 2 Overview Preparing for Installation Installing Windows NT Performing a Server-based Installation Troubleshooting.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
The OSI Model – The 7 Layers of Networking Explained in Plain English

This article explains the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model and the 7 layers of networking, in plain English.
The OSI model is a conceptual framework that is used to describe how a network functions. In plain English, the OSI model helped standardize the way computer systems send information to each other.
Learning networking is a bit like learning a language - there are lots of standards and then some exceptions. Therefore, it’s important to really understand that the OSI model is not a set of rules. It is a tool for understanding how networks function.
Once you learn the OSI model, you will be able to further understand and appreciate this glorious entity we call the Internet, as well as be able to troubleshoot networking issues with greater fluency and ease.
All hail the Internet!
Prerequisites
You don’t need any prior programming or networking experience to understand this article. However, you will need:
- Basic familiarity with common networking terms (explained below)
- A curiosity about how things work :)
Learning Objectives
Over the course of this article, you will learn:
- What the OSI model is
- The purpose of each of the 7 layers
- The problems that can happen at each of the 7 layers
- The difference between TCP/IP model and the OSI model
Common Networking Terms
Here are some common networking terms that you should be familiar with to get the most out of this article. I’ll use these terms when I talk about OSI layers next.
A node is a physical electronic device hooked up to a network, for example a computer, printer, router, and so on. If set up properly, a node is capable of sending and/or receiving information over a network.
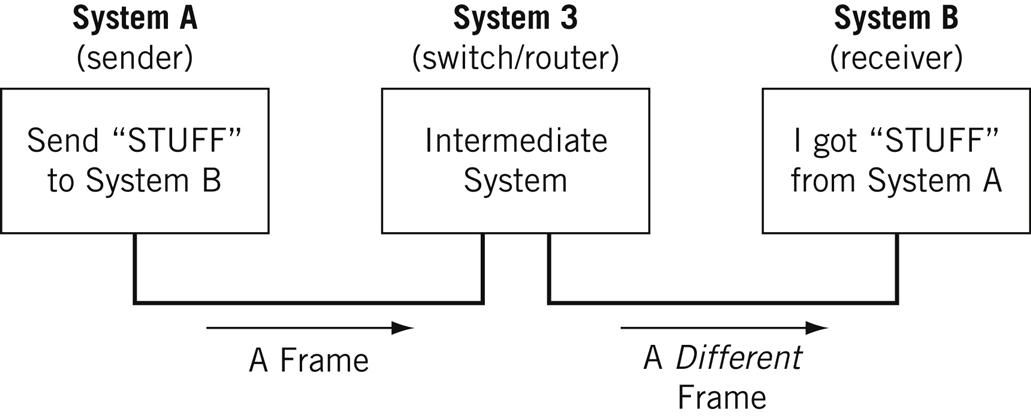
Nodes may be set up adjacent to one other, wherein Node A can connect directly to Node B, or there may be an intermediate node, like a switch or a router, set up between Node A and Node B.
Typically, routers connect networks to the Internet and switches operate within a network to facilitate intra-network communication. Learn more about hub vs. switch vs. router.
Here's an example:
For the nitpicky among us (yep, I see you), host is another term that you will encounter in networking. I will define a host as a type of node that requires an IP address. All hosts are nodes, but not all nodes are hosts. Please Tweet angrily at me if you disagree.
Links connect nodes on a network. Links can be wired, like Ethernet, or cable-free, like WiFi.
Links to can either be point-to-point, where Node A is connected to Node B, or multipoint, where Node A is connected to Node B and Node C.
When we’re talking about information being transmitted, this may also be described as a one-to-one vs. a one-to-many relationship.
A protocol is a mutually agreed upon set of rules that allows two nodes on a network to exchange data.
“A protocol defines the rules governing the syntax (what can be communicated), semantics (how it can be communicated), and synchronization (when and at what speed it can be communicated) of the communications procedure. Protocols can be implemented on hardware, software, or a combination of both. Protocols can be created by anyone, but the most widely adopted protocols are based on standards.” - The Illustrated Network.
Both wired and cable-free links can have protocols.
While anyone can create a protocol, the most widely adopted protocols are often based on standards published by Internet organizations such as the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
A network is a general term for a group of computers, printers, or any other device that wants to share data.
Network types include LAN, HAN, CAN, MAN, WAN, BAN, or VPN. Think I’m just randomly rhyming things with the word can ? I can ’t say I am - these are all real network types. Learn more here .
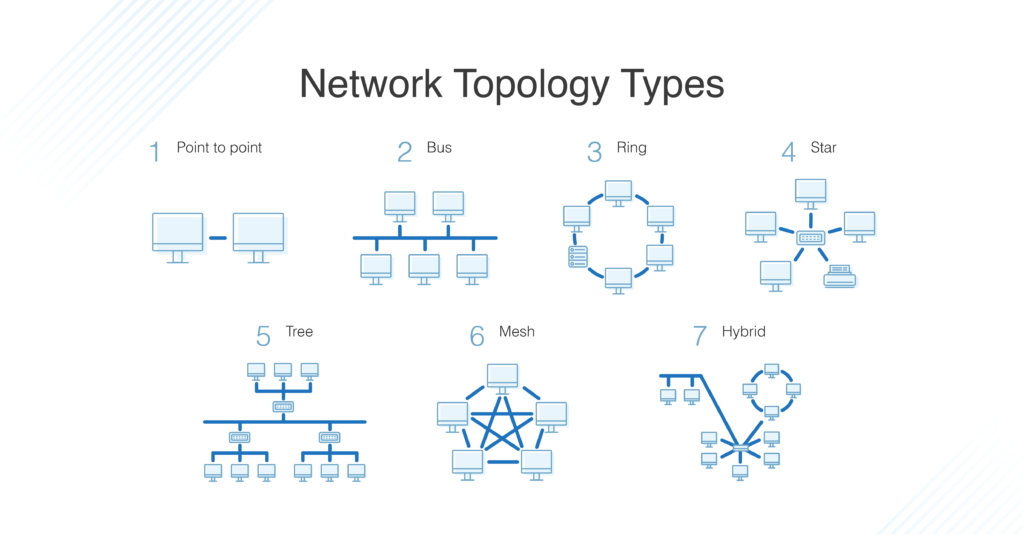
Topology describes how nodes and links fit together in a network configuration, often depicted in a diagram. Here are some common network topology types:
A network consists of nodes, links between nodes, and protocols that govern data transmission between nodes.
At whatever scale and complexity networks get to, you will understand what’s happening in all computer networks by learning the OSI model and 7 layers of networking.

What is the OSI Model?
The OSI model consists of 7 layers of networking.
First, what’s a layer?

No, a layer - not a lair . Here there are no dragons.
A layer is a way of categorizing and grouping functionality and behavior on and of a network.
In the OSI model, layers are organized from the most tangible and most physical, to less tangible and less physical but closer to the end user.
Each layer abstracts lower level functionality away until by the time you get to the highest layer. All the details and inner workings of all the other layers are hidden from the end user.
How to remember all the names of the layers? Easy.
- Please | Physical Layer
- Do | Data Link Layer
- Not | Network Layer
- Tell (the) | Transport Layer
- Secret | Session Layer
- Password (to) | Presentation Layer
- Anyone | Application Layer
Keep in mind that while certain technologies, like protocols, may logically “belong to” one layer more than another, not all technologies fit neatly into a single layer in the OSI model. For example, Ethernet, 802.11 (Wifi) and the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) procedure operate on >1 layer.
The OSI is a model and a tool, not a set of rules.
OSI Layer 1
Layer 1 is the physical layer . There’s a lot of technology in Layer 1 - everything from physical network devices, cabling, to how the cables hook up to the devices. Plus if we don’t need cables, what the signal type and transmission methods are (for example, wireless broadband).
Instead of listing every type of technology in Layer 1, I’ve created broader categories for these technologies. I encourage readers to learn more about each of these categories:
- Nodes (devices) and networking hardware components. Devices include hubs, repeaters, routers, computers, printers, and so on. Hardware components that live inside of these devices include antennas, amplifiers, Network Interface Cards (NICs), and more.
- Device interface mechanics. How and where does a cable connect to a device (cable connector and device socket)? What is the size and shape of the connector, and how many pins does it have? What dictates when a pin is active or inactive?
- Functional and procedural logic. What is the function of each pin in the connector - send or receive? What procedural logic dictates the sequence of events so a node can start to communicate with another node on Layer 2?
- Cabling protocols and specifications. Ethernet (CAT), USB, Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) , and more. Specifications include maximum cable length, modulation techniques, radio specifications, line coding, and bits synchronization (more on that below).
- Cable types. Options include shielded or unshielded twisted pair, untwisted pair, coaxial and so on. Learn more about cable types here .
- Signal type. Baseband is a single bit stream at a time, like a railway track - one-way only. Broadband consists of multiple bit streams at the same time, like a bi-directional highway.
- Signal transmission method (may be wired or cable-free). Options include electrical (Ethernet), light (optical networks, fiber optics), radio waves (802.11 WiFi, a/b/g/n/ac/ax variants or Bluetooth). If cable-free, then also consider frequency: 2.5 GHz vs. 5 GHz. If it’s cabled, consider voltage. If cabled and Ethernet, also consider networking standards like 100BASE-T and related standards.
The data unit on Layer 1 is the bit.
A bit the smallest unit of transmittable digital information. Bits are binary, so either a 0 or a 1. Bytes, consisting of 8 bits, are used to represent single characters, like a letter, numeral, or symbol.
Bits are sent to and from hardware devices in accordance with the supported data rate (transmission rate, in number of bits per second or millisecond) and are synchronized so the number of bits sent and received per unit of time remains consistent (this is called bit synchronization). The way bits are transmitted depends on the signal transmission method.
Nodes can send, receive, or send and receive bits. If they can only do one, then the node uses a simplex mode. If they can do both, then the node uses a duplex mode. If a node can send and receive at the same time, it’s full-duplex – if not, it’s just half-duplex.
The original Ethernet was half-duplex. Full-duplex Ethernet is an option now, given the right equipment.
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 1 Problems
Here are some Layer 1 problems to watch out for:
- Defunct cables, for example damaged wires or broken connectors
- Broken hardware network devices, for example damaged circuits
- Stuff being unplugged (...we’ve all been there)
If there are issues in Layer 1, anything beyond Layer 1 will not function properly.
Layer 1 contains the infrastructure that makes communication on networks possible.
It defines the electrical, mechanical, procedural, and functional specifications for activating, maintaining, and deactivating physical links between network devices. - Source
Fun fact: deep-sea communications cables transmit data around the world. This map will blow your mind: https://www.submarinecablemap.com/
And because you made it this far, here’s a koala:

OSI Layer 2
Layer 2 is the data link layer . Layer 2 defines how data is formatted for transmission, how much data can flow between nodes, for how long, and what to do when errors are detected in this flow.
In more official tech terms:
- Line discipline. Who should talk for how long? How long should nodes be able to transit information for?
- Flow control. How much data should be transmitted?
- Error control - detection and correction . All data transmission methods have potential for errors, from electrical spikes to dirty connectors. Once Layer 2 technologies tell network administrators about an issue on Layer 2 or Layer 1, the system administrator can correct for those errors on subsequent layers. Layer 2 is mostly concerned with error detection, not error correction. ( Source )
There are two distinct sublayers within Layer 2:
- Media Access Control (MAC): the MAC sublayer handles the assignment of a hardware identification number, called a MAC address, that uniquely identifies each device on a network. No two devices should have the same MAC address. The MAC address is assigned at the point of manufacturing. It is automatically recognized by most networks. MAC addresses live on Network Interface Cards (NICs). Switches keep track of all MAC addresses on a network. Learn more about MAC addresses on PC Mag and in this article . Learn more about network switches here .
- Logical Link Control (LLC): the LLC sublayer handles framing addressing and flow control. The speed depends on the link between nodes, for example Ethernet or Wifi.
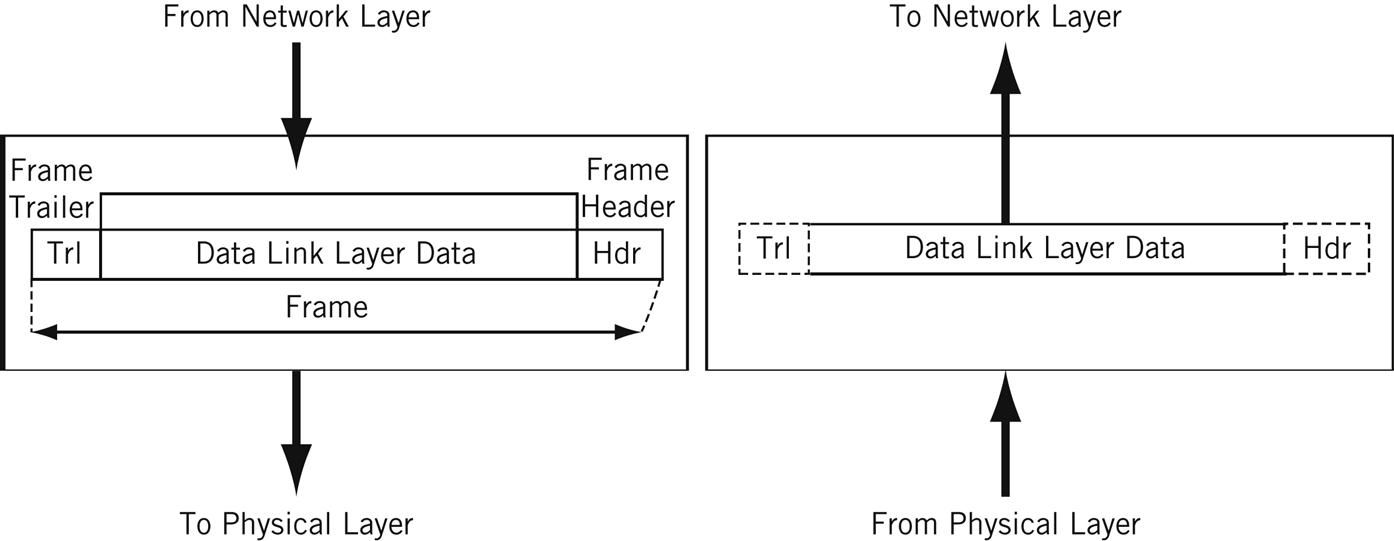
The data unit on Layer 2 is a frame .
Each frame contains a frame header, body, and a frame trailer:
- Header: typically includes MAC addresses for the source and destination nodes.
- Body: consists of the bits being transmitted.
- Trailer: includes error detection information. When errors are detected, and depending on the implementation or configuration of a network or protocol, frames may be discarded or the error may be reported up to higher layers for further error correction. Examples of error detection mechanisms: Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) and Frame Check Sequence (FCS). Learn more about error detection techniques here .
Typically there is a maximum frame size limit, called an Maximum Transmission Unit, MTU. Jumbo frames exceed the standard MTU, learn more about jumbo frames here .
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 2 Problems
Here are some Layer 2 problems to watch out for:
- All the problems that can occur on Layer 1
- Unsuccessful connections (sessions) between two nodes
- Sessions that are successfully established but intermittently fail
- Frame collisions
The Data Link Layer allows nodes to communicate with each other within a local area network. The foundations of line discipline, flow control, and error control are established in this layer.
OSI Layer 3
Layer 3 is the network layer . This is where we send information between and across networks through the use of routers. Instead of just node-to-node communication, we can now do network-to-network communication.
Routers are the workhorse of Layer 3 - we couldn’t have Layer 3 without them. They move data packets across multiple networks.
Not only do they connect to Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to provide access to the Internet, they also keep track of what’s on its network (remember that switches keep track of all MAC addresses on a network), what other networks it’s connected to, and the different paths for routing data packets across these networks.
Routers store all of this addressing and routing information in routing tables.
Here’s a simple example of a routing table:

The data unit on Layer 3 is the data packet . Typically, each data packet contains a frame plus an IP address information wrapper. In other words, frames are encapsulated by Layer 3 addressing information.
The data being transmitted in a packet is also sometimes called the payload . While each packet has everything it needs to get to its destination, whether or not it makes it there is another story.
Layer 3 transmissions are connectionless, or best effort - they don't do anything but send the traffic where it’s supposed to go. More on data transport protocols on Layer 4.
Once a node is connected to the Internet, it is assigned an Internet Protocol (IP) address, which looks either like 172.16. 254.1 (IPv4 address convention) or like 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 (IPv6 address convention). Routers use IP addresses in their routing tables.
IP addresses are associated with the physical node’s MAC address via the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which resolves MAC addresses with the node’s corresponding IP address.
ARP is conventionally considered part of Layer 2, but since IP addresses don’t exist until Layer 3, it’s also part of Layer 3.
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 3 Problems
Here are some Layer 3 problems to watch out for:
- All the problems that can crop up on previous layers :)
- Faulty or non-functional router or other node
- IP address is incorrectly configured
Many answers to Layer 3 questions will require the use of command-line tools like ping , trace , show ip route , or show ip protocols . Learn more about troubleshooting on layer 1-3 here .
The Network Layer allows nodes to connect to the Internet and send information across different networks.
OSI Layer 4
Layer 4 is the transport layer . This where we dive into the nitty gritty specifics of the connection between two nodes and how information is transmitted between them. It builds on the functions of Layer 2 - line discipline, flow control, and error control.
This layer is also responsible for data packet segmentation, or how data packets are broken up and sent over the network.
Unlike the previous layer, Layer 4 also has an understanding of the whole message, not just the contents of each individual data packet. With this understanding, Layer 4 is able to manage network congestion by not sending all the packets at once.
The data units of Layer 4 go by a few names. For TCP, the data unit is a packet. For UDP, a packet is referred to as a datagram. I’ll just use the term data packet here for the sake of simplicity.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) are two of the most well-known protocols in Layer 4.
TCP, a connection-oriented protocol, prioritizes data quality over speed.
TCP explicitly establishes a connection with the destination node and requires a handshake between the source and destination nodes when data is transmitted. The handshake confirms that data was received. If the destination node does not receive all of the data, TCP will ask for a retry.
TCP also ensures that packets are delivered or reassembled in the correct order. Learn more about TCP here .
UDP, a connectionless protocol, prioritizes speed over data quality. UDP does not require a handshake, which is why it’s called connectionless.
Because UDP doesn’t have to wait for this acknowledgement, it can send data at a faster rate, but not all of the data may be successfully transmitted and we’d never know.
If information is split up into multiple datagrams, unless those datagrams contain a sequence number, UDP does not ensure that packets are reassembled in the correct order. Learn more about UDP here .
TCP and UDP both send data to specific ports on a network device, which has an IP address. The combination of the IP address and the port number is called a socket.
Learn more about sockets here .
Learn more about the differences and similarities between these two protocols here .
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 4 Problems
Here are some Layer 4 problems to watch out for:
- Blocked ports - check your Access Control Lists (ACL) & firewalls
- Quality of Service (QoS) settings. QoS is a feature of routers/switches that can prioritize traffic, and they can really muck things up. Learn more about QoS here .
The Transport Layer provides end-to-end transmission of a message by segmenting a message into multiple data packets; the layer supports connection-oriented and connectionless communication.
OSI Layer 5
Layer 5 is the session layer . This layer establishes, maintains, and terminates sessions.
A session is a mutually agreed upon connection that is established between two network applications. Not two nodes! Nope, we’ve moved on from nodes. They were so Layer 4.
Just kidding, we still have nodes, but Layer 5 doesn’t need to retain the concept of a node because that’s been abstracted out (taken care of) by previous layers.
So a session is a connection that is established between two specific end-user applications. There are two important concepts to consider here:
- Client and server model: the application requesting the information is called the client, and the application that has the requested information is called the server.
- Request and response model: while a session is being established and during a session, there is a constant back-and-forth of requests for information and responses containing that information or “hey, I don’t have what you’re requesting.”
Sessions may be open for a very short amount of time or a long amount of time. They may fail sometimes, too.
Depending on the protocol in question, various failure resolution processes may kick in. Depending on the applications/protocols/hardware in use, sessions may support simplex, half-duplex, or full-duplex modes.
Examples of protocols on Layer 5 include Network Basic Input Output System (NetBIOS) and Remote Procedure Call Protocol (RPC), and many others.
From here on out (layer 5 and up), networks are focused on ways of making connections to end-user applications and displaying data to the user.
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 5 Problems
Here are some Layer 5 problems to watch out for:
- Servers are unavailable
- Servers are incorrectly configured, for example Apache or PHP configs
- Session failure - disconnect, timeout, and so on.
The Session Layer initiates, maintains, and terminates connections between two end-user applications. It responds to requests from the presentation layer and issues requests to the transport layer.
OSI Layer 6
Layer 6 is the presentation layer . This layer is responsible for data formatting, such as character encoding and conversions, and data encryption.
The operating system that hosts the end-user application is typically involved in Layer 6 processes. This functionality is not always implemented in a network protocol.
Layer 6 makes sure that end-user applications operating on Layer 7 can successfully consume data and, of course, eventually display it.
There are three data formatting methods to be aware of:
- American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII): this 7-bit encoding technique is the most widely used standard for character encoding. One superset is ISO-8859-1, which provides most of the characters necessary for languages spoken in Western Europe.
- Extended Binary-Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBDCIC): designed by IBM for mainframe usage. This encoding is incompatible with other character encoding methods.
- Unicode: character encodings can be done with 32-, 16-, or 8-bit characters and attempts to accommodate every known, written alphabet.
Learn more about character encoding methods in this article , and also here .
Encryption: SSL or TLS encryption protocols live on Layer 6. These encryption protocols help ensure that transmitted data is less vulnerable to malicious actors by providing authentication and data encryption for nodes operating on a network. TLS is the successor to SSL.
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 6 Problems
Here are some Layer 6 problems to watch out for:
- Non-existent or corrupted drivers
- Incorrect OS user access level
The Presentation Layer formats and encrypts data.
OSI Layer 7
Layer 7 is the application layer .
True to its name, this is the layer that is ultimately responsible for supporting services used by end-user applications. Applications include software programs that are installed on the operating system, like Internet browsers (for example, Firefox) or word processing programs (for example, Microsoft Word).
Applications can perform specialized network functions under the hood and require specialized services that fall under the umbrella of Layer 7.
Electronic mail programs, for example, are specifically created to run over a network and utilize networking functionality, such as email protocols, which fall under Layer 7.
Applications will also control end-user interaction, such as security checks (for example, MFA), identification of two participants, initiation of an exchange of information, and so on.
Protocols that operate on this level include File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Secure Shell (SSH), Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP), Domain Name Service (DNS), and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
While each of these protocols serve different functions and operate differently, on a high level they all facilitate the communication of information. ( Source )
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 7 Problems
Here are some Layer 7 problems to watch out for:
- All issues on previous layers
- Incorrectly configured software applications
- User error (... we’ve all been there)
The Application Layer owns the services and functions that end-user applications need to work. It does not include the applications themselves.
Our Layer 1 koala is all grown up.

Learning check - can you apply makeup to a koala?
Don’t have a koala?
Well - answer these questions instead. It’s the next best thing, I promise.
- What is the OSI model?
- What are each of the layers?
- How could I use this information to troubleshoot networking issues?
Congratulations - you’ve taken one step farther to understanding the glorious entity we call the Internet.
Learning Resources
Many, very smart people have written entire books about the OSI model or entire books about specific layers. I encourage readers to check out any O’Reilly-published books about the subject or about network engineering in general.
Here are some resources I used when writing this article:
- The Illustrated Network, 2nd Edition
- Protocol Data Unit (PDU): https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-segments-packets-and-frames/
- Troubleshooting Along the OSI Model: https://www.pearsonitcertification.com/articles/article.aspx?p=1730891
- The OSI Model Demystified: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HEEnLZV2wGI
- OSI Model for Dummies: https://www.dummies.com/programming/networking/layers-in-the-osi-model-of-a-computer-network/
Chloe Tucker is an artist and computer science enthusiast based in Portland, Oregon. As a former educator, she's continuously searching for the intersection of learning and teaching, or technology and art. Reach out to her on Twitter @_chloetucker and check out her website at chloe.dev .
Read more posts .
If you read this far, thank the author to show them you care. Say Thanks
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started

Network Operating Systems
Jul 10, 2013
160 likes | 349 Views
Network Operating Systems. Organizational Communications and Technologies Prithvi N. Rao H. John Heinz III School of Public Policy and Management Carnegie Mellon University. Readings. High Speed and Wireless LANs(Stallings and van Slyke) Class Notes. Objectives.
Share Presentation
- public policy
- network operating systems
- multiple link interface driver
- nos service

Presentation Transcript
Network Operating Systems Organizational Communications and Technologies Prithvi N. Rao H. John Heinz III School of Public Policy and Management Carnegie Mellon University
Readings High Speed and Wireless LANs(Stallings and van Slyke) Class Notes
Objectives • List several popular network operating systems • Cite features of a network operating system • Recognize services provided by NOS • List several client/server NOS • List several peer-to-peer operating systems
Network Operating Systems • Fundamental function of network (review) • File transfer • Remote program execution • Virtual terminal service • NOS service layers more flexible • Common elements of NOS • Support for multiple station access • Data integrity features (transaction, security) • Provide shared access to network resources
Network Operating Systems • Client/Server • Novell Netware • Microsoft LanManager • Microsoft WindowsNT • Banyan Vines • Peer-to-peer • Novel Netware Light • Artisoft Lantastic • Appletalk • Windows for Workgroups
Comparison of OSI and LAN Manager OSI LAN Manager Application Redirector Named Pipes Server Message Block (SMB) Presentation NetBios Session Transport NetBios Extended User Interface (NetBEUI) Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Network DataLink Network Driver Interface Specification (NDIS) Network Drivers, 802.x Specifications Physical 802.x Specifications
Comparison of OSI and Novel l Netware OSI Netware Service Advertising Protocol (sap) Application Network Loadable Module (NLM) Presentation Netware Core Protocol (NCP) Operating System Connection Mgmt. Session NETBios SPX Sequence Package Exchange Novell Virtual Terminal (NVT) Transport Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Network Multiple Protocol Interface (MPI) Link Support Level (LSL) Multiple Link Interface Driver (MLID) 802 Specification – Token Ring, Ethernet, ARCnet, Appletalk Data Link Physical Media
Comparison of OSI and Vines OSI VINES VINES Services (Printing and apps) VINES File System Application Presentation NetRPC Service Msg Blk (SMB) Session Socket Interface VINES Interprocess Communication Prot (VCIP) Transmission Control Prot (TCP) Sequence Packet Protocol (SPP) User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Transport VINES Internet Protocol (VIP) VINES Internet Control Protocol (ICP) VINES Address Resolution Protoclol (ARP) VINES Routing Update Protocol (RTP) Internet Protocol (IP) Network X.25 VINES Fragmentation Protocol (FRP) DataLink X.25 HDLC Network Drivers NDIS Physical 802.x Specifications, X.25 network connection
Comparison of OSI and Windows-NT OSI Windows-NT t Redirector, Requestor Named Pipes TLI Socket Interface Application Service Message Block (SMB) Windows Presentation Manager Presentation Session NetBIOS Transport Transmission Control Protocol TCP/IP NetBIOS Extended User Interface (NetBEUI) Network DataLink Network Driver Interface Specification (NDIS) Network Drivers, 802.x Specifications Physical 802.x Specifications
Comparison of OSI and Netware Lite OSI Netware Lite Service Advertising Protocol (SAP) Application Network Lite Applications Presentation Netware Core Protocol (NCP) Operating System Connection Management Session NetBIOS Sequence Packet Exchange (SPX) Transport Internet Packet Exchange (IPX) Network Link Support Layer (LSL) Multiple Link Interface Drivers (MLID) 802.x specifications Token Ring, Ethernet ARCnet, Appletalk DataLink Physical Media
Comparison of OSI and Appletalk OSI Appletalk Appleshare Print Services Postscript Application Appleshare File Svcs Presentation Appletake Filing Prot Appletalk Session Protocol (ASP) Zone Information Protocol (ZIP) Printer AccessProtocol (PAP) Appletalk Data Stream Session Routing Table Maintenance Protocol (RTMP) Appletalk Echo Protocol (AEP) Appletalk Transaction Protocol Name Binding Protocol Transport Network Datagram Delivery Protocol (DDP) Token Talk Link Access Protocol (TLAP) EtherTalk Link Access Protocol (ELAP) LocalTalk Link Access (LLAP) LocalTalk Hardware DataLink 802.x Physical
Comparison of OSI and TCP/IP Systems OSI TCP/IP TFTP. BOOTP, NFS-XDR-RPC SNMP SMTP, FTP,TELNET Application Presentation Universal Datagram (UDP) Session Transmission Control (TCP) Transport Internet Protocol (IP) Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Internet Gateway Message Protocol (IGMP) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) and Reverse ARP (RARP) Network Ethernet - II DataLink Token Ring Media Physical
Comparison of OSI and Windows for Workgroups OSI Windows for Workgroups Windows Applications Application MS-Windows Presentation MS Windows Presentation Manager Session NetBIOS Transport NetBIOS Extended User Interface (NetBEUI) Network DataLink Network Driver Interface Specification (NDIS) Network Drivers, 802.x Specifications Physical 802.x Specifications
Summary • NOS provide logical communication support for LANs • Provide application interface between user and network protocols, hardware and media • NOS available from variety of vendors • Client/server from Novell Netware • Peer-to-peer as in TCP/IP
- More by User

Network Operating Systems. ISQA424 Instructor: Rob Knauerhase Portland State University. Chapter 1: Networking with Microsoft Windows NT Server. Learning Objectives. Explain workgroup networking Explain domain networking and the advantages of file server operating systems
1.35k views • 46 slides

. Can be peer-to-peer or client server or server basedEach machine is identified by unique computer namesResources are specified with their UNC names - \\computername\sharename\directory\fileThese resources are referred to as shares.The access a user is granted to a share is referred to as a permission..
902 views • 49 slides

2. Objectives. A general Revision of Network Operating SystemsBy the end of the session you should understandThe different forms of TransparencyAn overview of Directory ServicesMain Security IssuesNOS FunctionalityHow to choose a NOS. 3. Network Operating Systems (NOS). The objective is to design to create a
487 views • 31 slides

Development of network-aware operating systems
Development of network-aware operating systems. Tom Dunigan [email protected]. Net100: developing network-aware operating systems. New (9/01) DOE-funded (Office of Science) project ($1M/yr, 3 yrs) Principal investigators Matt Mathis, PSC ( [email protected] )
226 views • 10 slides

Basic Network Concepts:. 1.06 Network Operating Systems. Network Operating Systems
674 views • 56 slides

Network Operating Systems versus Operating Systems
Network Operating Systems versus Operating Systems. Computer Networks. NOS have dedicated servers C lient server networks Servers provide a variety of services for other computers on the network. Network Operating System (NOS). Networks that don’t use NOS are peer-to-peer networks
441 views • 14 slides

Net100: developing network-aware operating systems
Net100: developing network-aware operating systems. New (9/01) DOE-funded (Office of Science) project ($1M/yr, 3 yrs) Principal investigators Matt Mathis, PSC ( [email protected] ) Brian Tierney, LBNL ( [email protected] ) Tom Dunigan, ORNL ( [email protected] ) Objective:
163 views • 7 slides

Network Operating Systems. Users are aware of multiplicity of machines. Access to resources of various machines is done explicitly by: Logging into the appropriate remote machine, via telnet or something like that.
398 views • 20 slides

Network Operating Systems. Windows NT. Windows NT Networking. Windows NT operating system was designed with fully integrated networking capabilities . In MS-DOS, OS/2 and UNIX network capabilities are installed separately from the core of operating system
1.58k views • 14 slides

Networks, Network operating systems and Databases
Networks, Network operating systems and Databases. Networking - Basics. Network defined The difference between Standalone and networked Systems Advantages of networking Disadvantages of networking Why use network To share information To Share hardware and software
605 views • 50 slides

COMP2122 Network Operating Systems
COMP2122 Network Operating Systems. University of Worcester Richard Henson November 2009. Week 7: Booting up into Windows. Objectives: Describe each of the six boot-up stages Explain the terms firmware, ACPI, and plug-n-play
677 views • 36 slides

Networks, Network operating systems
Networks, Network operating systems. Networking - Basics. Network defined The difference between Standalone and networked Systems Advantages of networking Disadvantages of networking Why use network To share information To Share hardware and software Centralizing administration.
419 views • 26 slides

Lesson 13. Network Operating Systems (NOS)
Lesson 13. Network Operating Systems (NOS). Objectives. At the end of this Presentation, you will be able to:. Explain the difference between a Network Operating System (NOS) and a desktop Operating System.
831 views • 61 slides

Interconnecting Network Operating Systems
Interconnecting Network Operating Systems. Chapter 18. Contents. Describe the issues involved with interconnecting Windows 9 x , NT, 2000, XP, and 2003 with other network operating systems Define the issues involved with interconnecting NetWare with other network operating systems
551 views • 39 slides

CT 1503 Network Operating Systems
CT 1503 Network Operating Systems. Instructor: Dr. Najla Al- Nabhan 2014. Course Overview. Course Instructor. Course Website: http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/nalnabhan/course/. Course Syllabus. Course Syllabus Aimed to impart Network operating systems (NOS): Definition, tasks,
459 views • 21 slides

Computer Network Operating Systems
Computer Network Operating Systems. Richard Evans BSEE, MS. Networks. Definition: Computers and other devices connected together for the purpose of data exchange. Purpose is to share Data Devices Resources (Software & Email). Why Networks. Sharing Information
505 views • 37 slides

Survey of Network Operating Systems (NOS)
Survey of Network Operating Systems (NOS). Introduction Novell Operating Systems Microsoft Network Operating Systems Other Network Operating Systems NOS in Multivendor Environments. 1. Introduction to Network Operating Systems (NOS). Coordinating Hardware and Software Multitasking
375 views • 18 slides

107 views • 10 slides

CT 1503 Network Operating Systems. Instructor: Dr. Najla Al- Nabhan 2014. Course Overview. Course Instructor. Course Website: http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/nalnabhan/course/. Course Syllabus. Course Syllabus Aimed to impart Network operating systems (NOS): Definition, tasks, examples,
191 views • 16 slides
Copyright Note

- Network Operating Systems
- Popular Categories
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Powerpoint Templates and Google slides for Network Operating Systems
Save your time and attract your audience with our fully editable ppt templates and slides..
Item 1 to 60 of 106 total items
- You're currently reading page 1

This slide showcases the statistical graph highlighting automated networking operations which helps an organization to improve scalability, security and reduce operational costs. It include details such as configuration generation, data collection, software updates, etc. Introducing our Statistical Graph Illustrating Automated Networking Operations set of slides. The topics discussed in these slides are Configuration Generation, Highest Automated Network Operations, Potential Benefits. This is an immediately available PowerPoint presentation that can be conveniently customized. Download it and convince your audience.

Presenting Network Security Audit Remote Operations Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Outline Information Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase four stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Network Security Audit Remote Operations. This well-structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting Fixed Network Operator In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase three stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Fixed Network Operator. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.
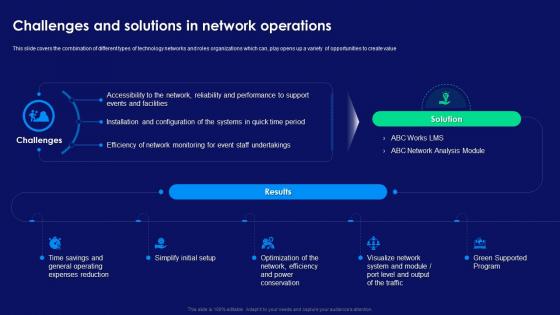
This slide covers the combination of different types of technology networks and roles organizations which can, play opens up a variety of opportunities to create value. Increase audience engagement and knowledge by dispensing information using Step By Step Technology Implementation Challenges And Solutions In Network Operations. This template helps you present information on five stages. You can also present information on Power Conservation, Simplify Initial Setup, Operating Expenses Reduction, Visualize Network System using this PPT design. This layout is completely editable so personaize it now to meet your audiences expectations.
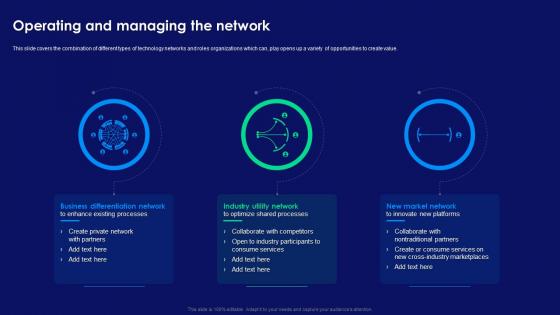
This slide covers the combination of different types of technology networks and roles organizations which can, play opens up a variety of opportunities to create value. Introducing Step By Step Technology Implementation Operating And Managing The Network to increase your presentation threshold. Encompassed with three stages, this template is a great option to educate and entice your audience. Dispence information on Business Differentiation Network, Industry Utility Network, New Market Network, Innovate New Platforms, using this template. Grab it now to reap its full benefits.
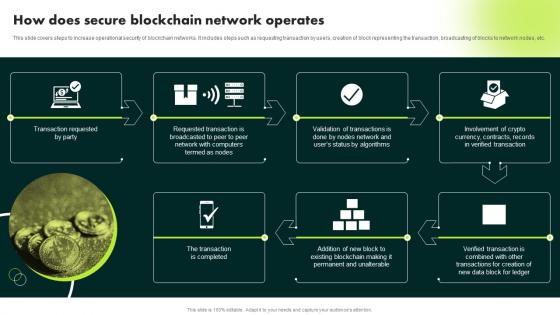
This slide covers steps to increase operational security of blockchain networks. It includes steps such as requesting transaction by users, creation of block representing the transaction, broadcasting of blocks to network nodes, etc. Introducing How Does Secure Blockchain Network Operates Ultimate Guide To Blockchain BCT SS to increase your presentation threshold. Encompassed with seven stages, this template is a great option to educate and entice your audience. Dispence information on Transaction Requested, Verified Transaction, Network Operates, using this template. Grab it now to reap its full benefits.

Presenting Roles Network Operating System In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase three stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Roles Network Operating System. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

This slide covers the combination of different types of technology networks and roles organizations which can, play opens up a variety of opportunities to create value. Introducing Implementation Of Technology Action Challenges And Solutions In Network Operations to increase your presentation threshold. Encompassed with three stages, this template is a great option to educate and entice your audience. Dispence information on Technology Networks, Roles Organizations, Variety Of Opportunities, Green Supported Program, using this template. Grab it now to reap its full benefits.
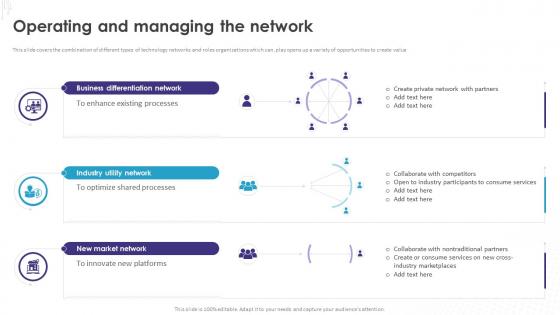
This slide covers the combination of different types of technology networks and roles organizations which can, play opens up a variety of opportunities to create value. Introducing Implementation Of Technology Action Operating And Managing The Network to increase your presentation threshold. Encompassed with three stages, this template is a great option to educate and entice your audience. Dispence information on Business Differentiation Network, Industry Utility Network, New Market Network, Cross Industry Marketplaces, using this template. Grab it now to reap its full benefits.
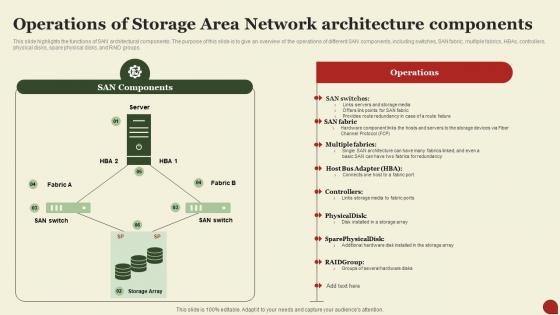
This Slide Highlights The Functions Of SAN Architectural Components. The Purpose Of This Slide Is To Give An Overview Of The Operations Of Different SAN Components, Including Switches, SAN Fabric, Multiple Fabrics, Hbas, Controllers, Physical Disks, Spare Physical Disks, And RAID Groups. Deliver An Outstanding Presentation On The Topic Using This Storage Area Network San Operations Of Storage Area Network Architecture Components. Dispense Information And Present A Thorough Explanation Of Architecture, Components, Operations Using The Slides Given. This Template Can Be Altered And Personalized To Fit Your Needs. It Is Also Available For Immediate Download. So Grab It Now.

The purpose of this slide is to represent advantages of using network slicing for operators from busin ess perspective. It covers various benefits such as on-demand time-bound capacity, choosing preconfigured slices, providing adaptable security etc. Presenting our set of slides with Benefits Of Using Network Slicing For Operators From Business Perspective This exhibits information on six stages of the process. This is an easy to edit and innovatively designed PowerPoint template. So download immediately and highlight information on Network Slicing, Optimal Experience, Customized Slices
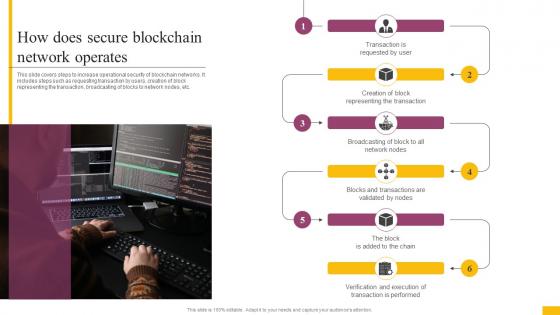
This slide covers steps to increase operational security of blockchain networks. It includes steps such as requesting transaction by users, creation of block representing the transaction, broadcasting of blocks to network nodes, etc. Introducing How Does Secure Blockchain Network Operates Complete Guide To Understand BCT SS to increase your presentation threshold. Encompassed with six stages, this template is a great option to educate and entice your audience. Dispence information on Representing The Transaction, Network Nodes, Transaction Is Performed using this template. Grab it now to reap its full benefits.

This slide represents network of self evolving autonomous operations to improve production. It further includes various levels such as workflow automation, interactive and conditional autonomous operation, etc. Presenting our well structured Self Evolving Autonomous Network Operation. The topics discussed in this slide are Work Flow Automation, Conditional Autonomous Operations
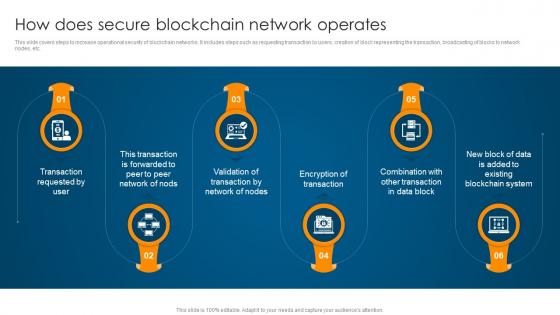
This slide covers steps to increase operational security of blockchain networks. It includes steps such as requesting transaction by users, creation of block representing the transaction, broadcasting of blocks to network nodes, etc. Introducing How Does Secure Blockchain Network Operates Ultimate Guide To Understand Role BCT SS to increase your presentation threshold. Encompassed with six stages, this template is a great option to educate and entice your audience. Dispence information on Transaction Requested, Network Of Nodes, Encryption Of Transaction, using this template. Grab it now to reap its full benefits.
Presenting our set of slides with Networking Automation Icon For Operating Business Activities. This exhibits information on three stages of the process. This is an easy to edit and innovatively designed PowerPoint template. So download immediately and highlight information on Networking Automation, Icon, Operating Business Activities.
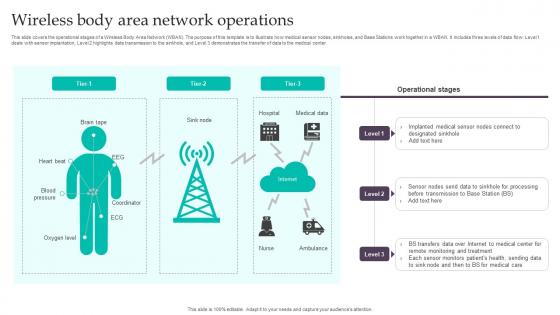
This slide covers the operational stages of a Wireless Body Area Network WBAN. The purpose of this template is to illustrate how medical sensor nodes, sinkholes, and Base Stations work together in a WBAN. It includes three levels of data flow Level 1 deals with sensor implantation, Level 2 highlights data transmission to the sinkhole, and Level 3 demonstrates the transfer of data to the medical center. Introducing Wireless Body Area Network Operations to increase your presentation threshold. Encompassed with Three stages, this template is a great option to educate and entice your audience. Dispence information on Designated Sinkhole, Operational Stages, Medical Care using this template. Grab it now to reap its full benefits.
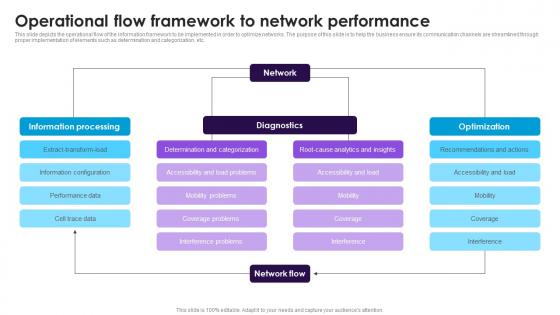
This slide depicts the operational flow of the information framework to be implemented in order to optimize networks. The purpose of this slide is to help the business ensure its communication channels are streamlined through proper implementation of elements such as determination and categorization, etc. Introducing our Operational Flow Framework To Network Performance set of slides. The topics discussed in these slides are Diagnostics, Optimization, Information Processing This is an immediately available PowerPoint presentation that can be conveniently customized. Download it and convince your audience.

This slide talks about the ways in which ZTNA improves the business operations and security. The purpose of this slide is to showcase the various domains that zero trust network access improves, including increased user experience, remote workforce protection, improve data protection, and network visibility. Present the topic in a bit more detail with this Role Of ZTNA To Improve Business Operations And Security Identity Defined Networking. Use it as a tool for discussion and navigation on Traditional Method, Workforce Protection, Data Protection. This template is free to edit as deemed fit for your organization. Therefore download it now.

This slide represents 30-60-90 plan to implement Generative Adversarial Networks GANs. The purpose of this slide is to illustrate the plans of the first 90 days from the start, including steps to be followed at interval of one month. Increase audience engagement and knowledge by dispensing information using Generative Adversarial Networks 30 60 90 Days Plan To Operate Generative Adversarial Networks. This template helps you present information on three stages. You can also present information on Generate Sample Images, Generative Adversarial Networks, Train Discriminator And Generator using this PPT design. This layout is completely editable so personaize it now to meet your audiences expectations.

This slide represents various network automation tools that assist companies to reduce manual networking tasks and focus on complex business strategies. It includes various tools such as Apstra, AppviewX and Infoblox Introducing our premium set of slides with Network Automation Tools To Enhance Operational Efficiency Ellicudate the three stages and present information using this PPT slide. This is a completely adaptable PowerPoint template design that can be used to interpret topics like Platform, Juniper Apstra System, Network Automation So download instantly and tailor it with your information.
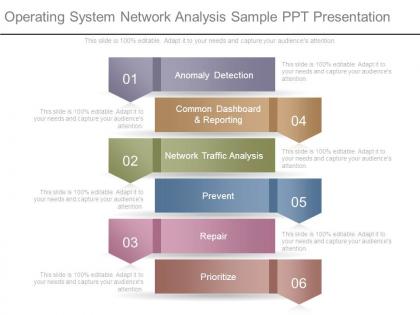
Presenting operating system network analysis sample ppt presentation. This is a operating system network analysis sample ppt presentation. This is a six stage process. The stages in this process are anomaly detection, common dashboard and reporting, network traffic analysis, prevent, repair, prioritize.
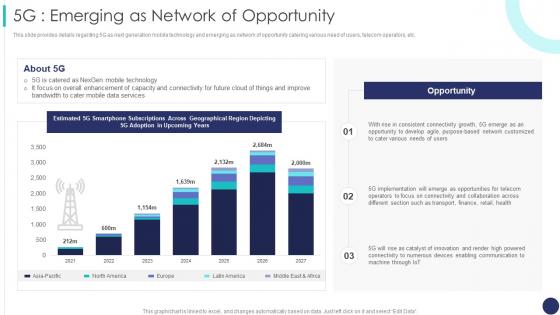
This slide provides details regarding 5G as next generation mobile technology and emerging as network of opportunity catering various need of users, telecom operators, etc. Present the topic in a bit more detail with this 5g Emerging As Network Of Opportunity 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators. Use it as a tool for discussion and navigation on Customized, Connectivity, Growth. This template is free to edit as deemed fit for your organization. Therefore download it now.
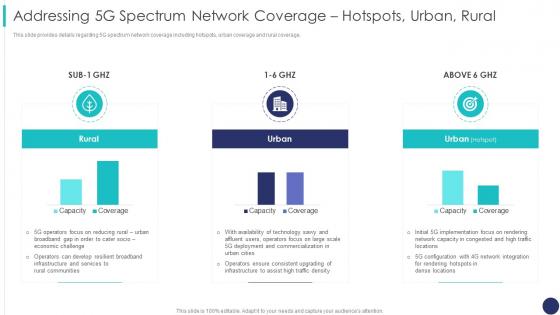
This slide provides details regarding 5G spectrum network coverage including hotspots, urban coverage and rural coverage. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators Addressing 5g Spectrum Network Coverage Hotspots. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Configuration, Integration, Resilient Broadband using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.
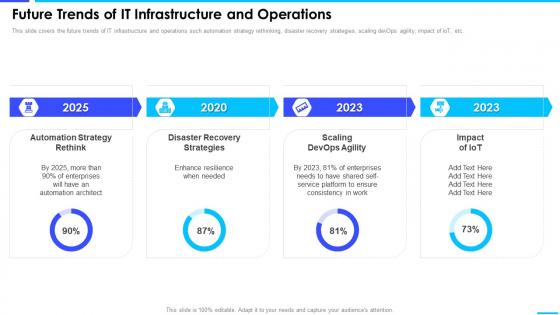
This slide covers the future trends of IT infrastructure and operations such automation strategy rethinking, disaster recovery strategies, scaling devOps agility, impact of IoT, etc.Present the topic in a bit more detail with this Future Trends Of It Infrastructure And Operations Enterprise Server And Network Monitoring. Use it as a tool for discussion and navigation on Automation Architect, Self Service Platform, Devops Agility. This template is free to edit as deemed fit for your organization. Therefore download it now.
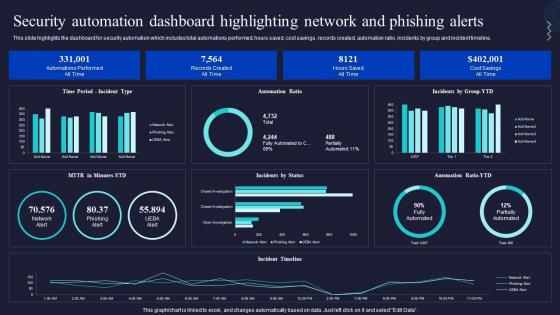
This slide highlights the dashboard for security automation which includes total automations performed, hours saved, cost savings, records created, automation ratio, incidents by group and incident timeline. Present the topic in a bit more detail with this Security Automation Dashboard Highlighting Network Enabling Automation In Cyber Security Operations. Use it as a tool for discussion and navigation on Automation, Dashboard, Highlighting. This template is free to edit as deemed fit for your organization. Therefore download it now.

Presenting network operation and maintenance powerpoint slide background. This is a network operation and maintenance powerpoint slide background. This is a four stage process. The stages in this process are technical support for network evolution, network operation and maintenance, network trend, planning and design.
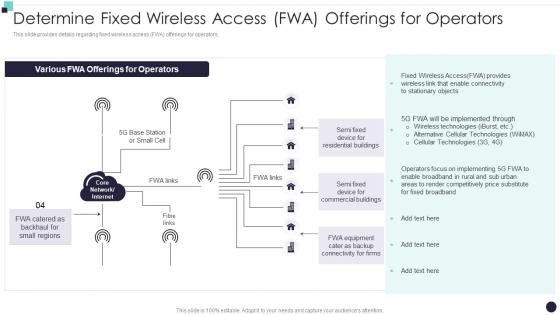
This slide provides details regarding fixed wireless access FWA offerings for operators. Present the topic in a bit more detail with this Determine Fixed Wireless Access FWA Offerings For Operators Building 5G Wireless Mobile Network. Use it as a tool for discussion and navigation on Offerings For Operators, Stationary Objects, Cellular Technologies. This template is free to edit as deemed fit for your organization. Therefore download it now.
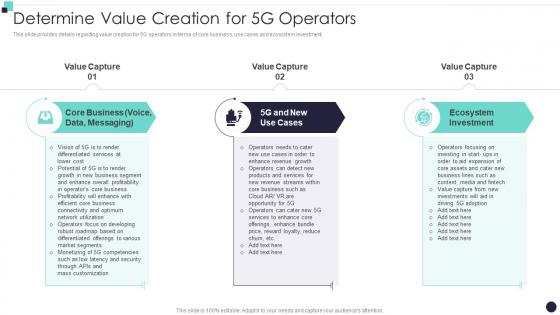
This slide provides details regarding value creation for 5G operators in terms of core business, use cases and ecosystem investment. Increase audience engagement and knowledge by dispensing information using Determine Value Creation For 5G Operators Building 5G Wireless Mobile Network. This template helps you present information on three stages. You can also present information on Business, Ecosystem Investment, Data Messaging using this PPT design. This layout is completely editable so personaize it now to meet your audiences expectations.
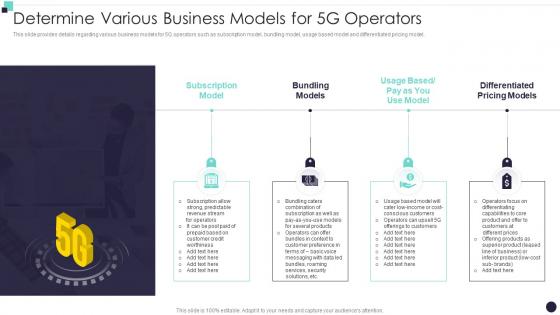
This slide provides details regarding various business models for 5G operators such as subscription model, bundling model, usage based model and differentiated pricing model. Introducing Determine Various Business Models For 5G Operators Building 5G Wireless Mobile Network to increase your presentation threshold. Encompassed with four stages, this template is a great option to educate and entice your audience. Dispence information on Subscription Model, Bundling Models, Differentiated Pricing Models, using this template. Grab it now to reap its full benefits.

This slide provides details regarding value enabler for operator as operator cloud including its importance and key drivers such as operational effectiveness, enhanced customer experience, etc. Increase audience engagement and knowledge by dispensing information using Value Enabler 3 Operator Cloud Building 5G Wireless Mobile Network. This template helps you present information on three stages. You can also present information on Operational Effectiveness, Enhanced Customer Experience, Monetizing New Competencies using this PPT design. This layout is completely editable so personaize it now to meet your audiences expectations.
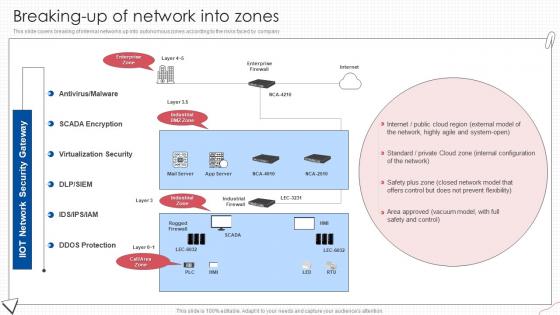
This slide covers breaking of internal networks up into autonomous zones according to the risks faced by company.Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this Breaking Up Of Network Into Zones Digital Transformation Of Operational Industries. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Security Gateway, Internal Configuration, Prevent Flexibility using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.
Presenting our Network Management Operating System Ppt Powerpoint Demonstration Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases four stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Network Management Operating System. This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

This slide provides details regarding policy framework for 5G in terms of facilitating access to site locations, enabling backhaul deployments, harmonizing power density limitations, etc. Increase audience engagement and knowledge by dispensing information using Discovering Policy Framework For 5g Network 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators. This template helps you present information on four stages. You can also present information on Framework, Partnerships, Deployments using this PPT design. This layout is completely editable so personaize it now to meet your audiences expectations.
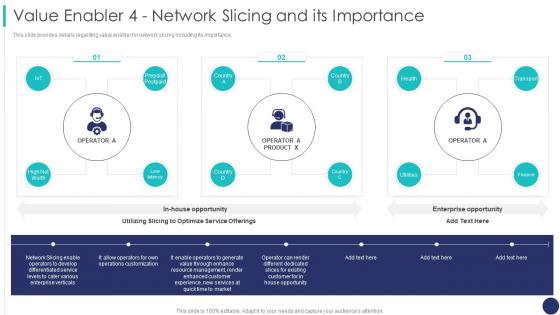
This slide provides details regarding value enabler for network slicing including its importance. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this Value Enabler 4 Network Slicing And Its Importance 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Opportunity, Service Offerings, Enterprise Opportunity using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.
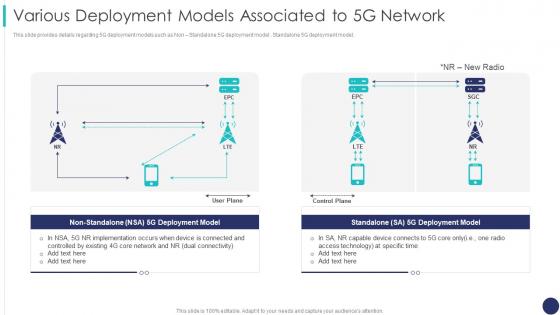
This slide provides details regarding 5G deployment models such as Non Standalone 5G deployment model , Standalone 5G deployment model. Present the topic in a bit more detail with this Various Deployment Models Associated To 5g Network 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators. Use it as a tool for discussion and navigation on Deployment Model, Implementation, Associated. This template is free to edit as deemed fit for your organization. Therefore download it now.

This slide provides details regarding various ways to optimize 5G network energy efficiency by utilizing alternate energy sources and network load optimization. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this Ways To Optimize 5g Network Energy Efficiency 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Optimization, Consumption, Automation using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.

This slide provides details regarding 5G era network flexibility in terms of NFV or SDN and cloud RAN in order to cater customized services for major clients. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators Determine 5g Era Network Flexibility Nfv Sdn And Cloud Ran. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Technology, Centralized, Management using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.
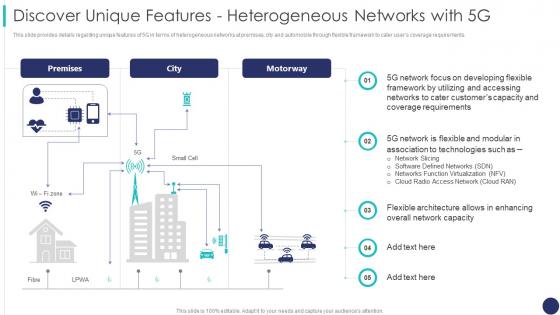
This slide provides details regarding unique features of 5G in terms of heterogeneous networks at premises, city and automobile through flexible framework to cater users coverage requirements. Present the topic in a bit more detail with this 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators Discover Unique Features Heterogeneous Networks With 5g. Use it as a tool for discussion and navigation on Framework, Requirements, Technologies. This template is free to edit as deemed fit for your organization. Therefore download it now.

This slide provides details regarding value enabler for operator as 5G resilient networks system including importance and key components associated to it. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators Value Enabler 1 5g Resilient Networks System. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Environment, Performance, Security Assurance using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.
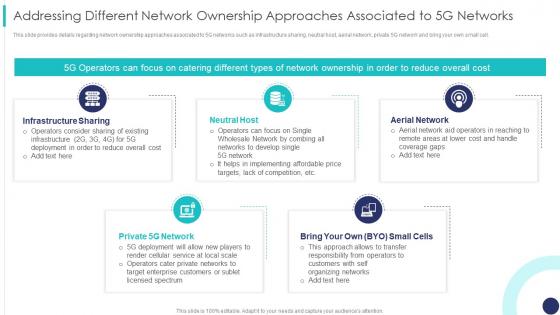
This slide provides details regarding network ownership approaches associated to 5G networks such as infrastructure sharing, neutral host, aerial network, private 5G network and bring your own small cell. Increase audience engagement and knowledge by dispensing information using Addressing Different Network Ownership Approaches Associated 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators. This template helps you present information on five stages. You can also present information on Infrastructure Sharing, Neutral Host, Aerial Network using this PPT design. This layout is completely editable so personaize it now to meet your audiences expectations.

This slide provides details regarding network deployment regulations of 5G addressing key consideration for policymakers. Present the topic in a bit more detail with this Addressing Network Deployment Regulations Of 5g 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators. Use it as a tool for discussion and navigation on Requirement, Planning, Processes. This template is free to edit as deemed fit for your organization. Therefore download it now.

This slide provides details regarding 5G network equipment sourcing by operators such as open source or mobile operators and system integrators. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this Determine 5g Network Equipment Sourcing Open Source 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Equipment, Source, Integrators using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.

This slide provides details regarding network capacity drivers such as spectral efficiency and spectral capacity. Present the topic in a bit more detail with this Determine Network Capacity Drivers Spectral Efficiency And 5g Mobile Technology Guidelines Operators. Use it as a tool for discussion and navigation on Spectral Efficiency, Spectral Capacity, Communication. This template is free to edit as deemed fit for your organization. Therefore download it now.
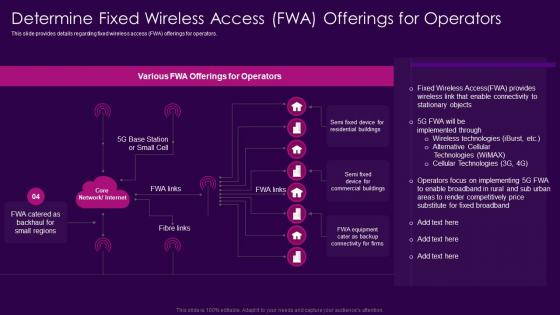
This slide provides details regarding fixed wireless access FWA offerings for operators. Present the topic in a bit more detail with this Determine Fixed Wireless Access Fwa Offerings For Operators 5g Network Architecture Guidelines. Use it as a tool for discussion and navigation on Technologies, Competitively, Implemented. This template is free to edit as deemed fit for your organization. Therefore download it now.

This slide provides details regarding value creation for 5G operators in terms of core business, use cases and ecosystem investment. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this Determine Value Creation For 5g Operators 5g Network Architecture Guidelines. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Developing, Customization, Growth using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.

This slide provides details regarding various business models for 5G operators such as subscription model, bundling model, usage based model and differentiated pricing model. Introducing Determine Various Business Models For 5g Operators 5g Network Architecture Guidelines to increase your presentation threshold. Encompassed with four stages, this template is a great option to educate and entice your audience. Dispence information on Operators, Business, Subscription Model , using this template. Grab it now to reap its full benefits.

This slide provides details regarding value enabler for operator as operator cloud including its importance and key drivers such as operational effectiveness, enhanced customer experience, etc. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this Value Enabler 3 Operator Cloud Importance And Key Drivers 5g Network Architecture Guidelines. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Operational Effectiveness, Enhanced Customer Experience, Monetizing New Competencies using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.

Presenting Distribution Network Operator Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Picture Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase four stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Distribution Network Operator. This well-structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

This slide defines the operational security element of cyber security. It also shows the best practices for operational security such as change management processes, deploys automation, etc. Introducing Elements Of Network Security Operational Security Ppt Styles Example File to increase your presentation threshold. Encompassed with five stages, this template is a great option to educate and entice your audience. Dispence information on Management, Sensitive, Administration, Operations, using this template. Grab it now to reap its full benefits.
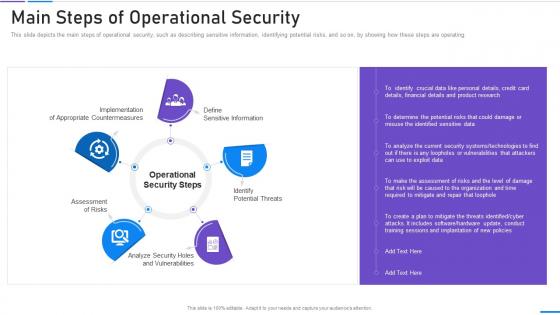
This slide depicts the main steps of operational security, such as describing sensitive information, identifying potential risks, and so on, by showing how these steps are operating. Increase audience engagement and knowledge by dispensing information using Network Security Main Steps Of Operational Security. This template helps you present information on five stages. You can also present information on Sensitive Information, Potential Threats, Vulnerabilities, Implementation using this PPT design. This layout is completely editable so personaize it now to meet your audiences expectations.
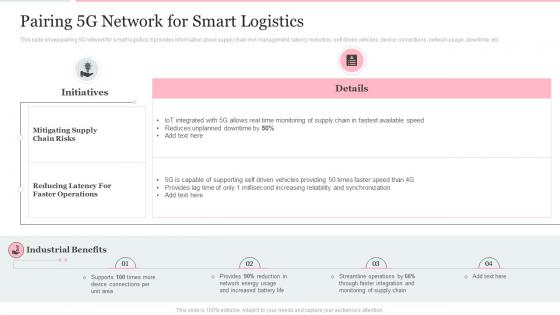
This slide shows pairing 5G network for smart logistics. It provides information about supply chain risk management, latency reduction, self driven vehicles, device connections, network usage, downtime, etc. Present the topic in a bit more detail with this Pairing 5g Network For Smart Logistics Deploying Internet Logistics Efficient Operations. Use it as a tool for discussion and navigation on Logistics, Information, Connections. This template is free to edit as deemed fit for your organization. Therefore download it now.
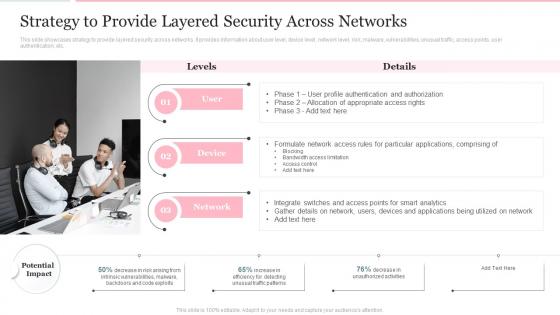
This slide showcases strategy to provide layered security across networks. It provides information about user level, device level, network level, risk, malware, vulnerabilities, unusual traffic, access points, user authentication, etc. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this Strategy To Provide Layered Security Across Networks Deploying Internet Logistics Efficient Operations. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Strategy, Information, Authentication using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.
Introducing our premium set of slides with Business Networking Operating Model Icon. Elucidate the three stages and present information using this PPT slide. This is a completely adaptable PowerPoint template design that can be used to interpret topics like Business Networking, Operating Model Icon. So download instantly and tailor it with your information.
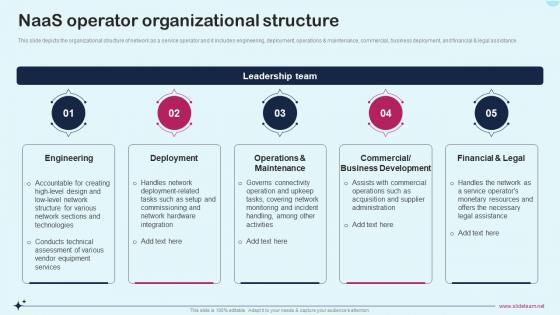
This slide depicts the organizational structure of network as a service operator and it includes engineering, deployment, operations and maintenance, commercial, business deployment, and financial and legal assistance. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this Naas Operator Organizational Structure Network As A Service Naas It. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Organizational, Structure, Deployment using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.
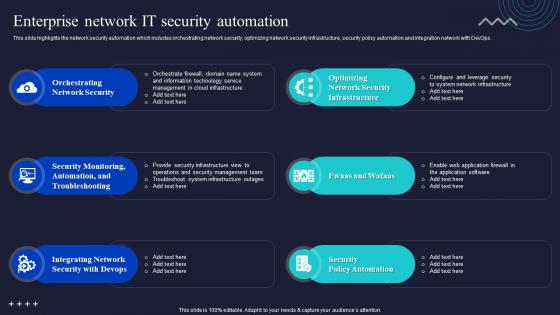
This slide highlights the network security automation which includes orchestrating network security, optimizing network security infrastructure, security policy automation and integration network with DevOps. Deliver an outstanding presentation on the topic using this Enterprise Network It Security Automation Enabling Automation In Cyber Security Operations. Dispense information and present a thorough explanation of Orchestrating Network Security, Troubleshooting, Integrating Network using the slides given. This template can be altered and personalized to fit your needs. It is also available for immediate download. So grab it now.
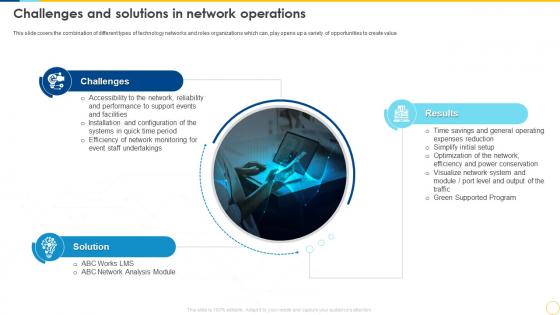
This slide covers the combination of different types of technology networks and roles organizations which can, play opens up a variety of opportunities to create value. Increase audience engagement and knowledge by dispensing information using Technology Planning And Implementation Challenges And Solutions In Network Operations. This template helps you present information on three stages. You can also present information on Challenges, Network Operations, Optimization Of The Network, Staff Undertakings using this PPT design. This layout is completely editable so personaize it now to meet your audiences expectations.
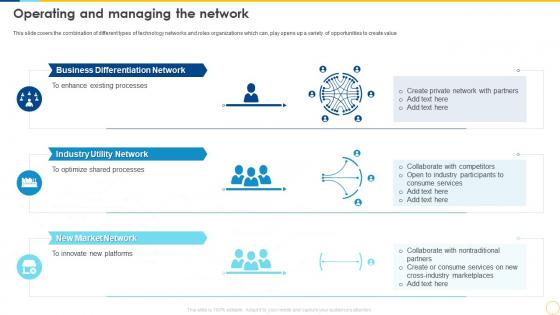
This slide covers the combination of different types of technology networks and roles organizations which can, play opens up a variety of opportunities to create value. Introducing Technology Planning And Implementation Operating And Managing The Network to increase your presentation threshold. Encompassed with three stages, this template is a great option to educate and entice your audience. Dispence information on Business Differentiation Network, Industry Utility Network, New Market Network, using this template. Grab it now to reap its full benefits.

The following slide exhibits types of online transferring of funds from one person to another. It enables instant transactions which are seamlessly executed across borders. It involves information related to closed and open virtual currency. Presenting our set of slides with name Approaches Of Virtual Currency Operating Network This exhibits information on two stages of the process. This is an easy to edit and innovatively designed PowerPoint template. So download immediately and highlight information on Closed Virtual Currency, Open Virtual Currency, Features, Impact.
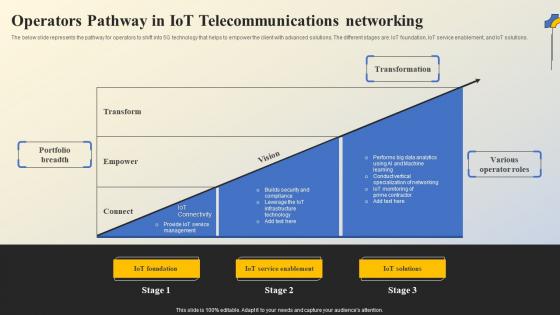
The below slide represents the pathway for operators to shift into 5G technology that helps to empower the client with advanced solutions. The different stages are IoT foundation, IoT service enablement, and IoT solutions.Introducing our Operators Pathway In IoT Telecommunications Networking set of slides. The topics discussed in these slides are Specialization Networking, Infrastructure Technology, Compliance Leverage. This is an immediately available PowerPoint presentation that can be conveniently customized. Download it and convince your audience.

This slide covers the combination of different types of technology networks and roles organizations which can, play opens up a variety of opportunities to create value. Increase audience engagement and knowledge by dispensing information using Planning Technology Initiatives Challenges And Solutions In Network Operations. This template helps you present information on three stages. You can also present information on Technology Networks, Roles Organizations, Variety Of Opportunities, Challenges And Solutions, Network Operations using this PPT design. This layout is completely editable so personaize it now to meet your audiences expectations.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Types of Network Operating System • Client/Server Network Operating Systems can be based on a client/server architecture in which a server enables multiple clients to share resources.Client/server network operating systems allow the network to centralize functions and applications in one or more dedicated file servers. The server is the ...
29. Difference between Operating System and Network Operating System OS runs the computer itself Example: Windows Network OS run on a server and can be accessed through client machines connected on the network Example: Novell Netware and Linux run on a server and can be used as NOS, even there are Windows server OS's which can be used by ...
Find PPT & PDF at:https://learneveryone.viden.io/OPERATING SYSTEMShttps://viden.io/knowledge/operating-systemsOPERATING SYSTEM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERShttps://v...
Download ppt "Lecture 1: Network Operating Systems (NOS)" Overview of basic networking concepts Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI): is a conceptual model that characterizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system. network model: PAN LAN MAN WAN Created By Dr.Najla AlNabhan edited by Maysoon ...
With our ready-made Network Operating System template for Microsoft PowerPoint and Google Slides, you can present the essential features, functions, pros, an...
10 Networks Operating Systems Network operating system refers to software that implements an operating system of some kind that is oriented to computer networking. For example, one that runs on a server and enables the server to manage data, users, groups, security, applications, and other networking functions. The network operating system is designed to allow shared file and printer access ...
Chapter 6 Introduction to Network Operating Systems 6.1 Characteristics of a Network Operating System 6.2 Windows 6.3 Linux 6.4 Determining Software Requirements a ... - A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as an HTML5 slide show) on PowerShow.com - id: 3b70d9-MzJjZ
Download our Network Operating System (NOS) presentation template for MS PowerPoint and Google Slides to describe the operating system designed to manage and control the operations of a computer network. You can also explain how this system provides the essential functionalities required for network communication, such as file sharing, network ...
Network Operating Systems - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Network Operating System (NOS) provides an environment in which users, who are aware of multiplicity of machines, can access remote resources either: -> logging in to the remote machine or -> transferring data from the remote machine to their own ...
2. NETWORK OPERATING SYSTEM Unlike operating systems, such as DOS and Windows, that are designed for single users to control one computer, network operating systems (NOS) coordinate the activities of multiple computers across a network. The network operating system acts as a director to keep the network running smoothly. The two major types of network operating systems are: • Peer-to-Peer ...
network operating system (NOS): A network operating system (NOS) is a computer operating system system that is designed primarily to support workstation , personal computer , and, in some instances, older terminal that are connected on a local area network (LAN). Artisoft's LANtastic, Banyan VINES, Novell's NetWare , and Microsoft's LAN ...
A network operating system (NOS) is a specialized operating system for a network device such as a router, switch or firewall.. Historically operating systems with networking capabilities were described as network operating systems, because they allowed personal computers (PCs) to participate in computer networks and shared file and printer access within a local area network (LAN).
The basic definition of an operating system is that the operating system is the interface between the computer hardware and the user. In daily life, we use the operating system on our devices which provides a good GUI, and many more features. Similarly, a network operating system(NOS) is software that connects multiple devices and computers on the network and allows them to share resources on ...
Presentation on theme: "Module 1 Introduction to Network Operating Systems"— Presentation transcript: ... Network operating systems (NOSs) distribute their functions over a number of networked computers. It then adds functions that allow access to shared resources by a number of users concurrently.
The slides below are copyright Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne, 2018. The slides are authorized for personal use, and for use in conjunction with a course for which Operating System Concepts is the prescribed text. Instructors are free to modify the slides to their taste, as long as the modified slides acknowledge the source and the fact that ...
Explain the difference between a Network Operating System (NOS) and a desktop Operating System. Identify and compare the major Network Operating Systems including Windows NT, Novell Netware, UNIX and Macintosh OS. Specify the network clients that best serve specific network operating systems and their resources. Identify the directory services of the major network operating systems.
• A network refers to two or more connected computers that can share resources such as data, a printer, an Internet connection, applications, or a combination of these
Presentation Transcript. Lecture 1: Network Operating Systems (NOS) An Introduction. Overview of basic networking concepts • Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI): • is a conceptual model that characterizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system. • network model: • PAN • LAN • MAN ...
Layer 6 is the presentation layer. This layer is responsible for data formatting, such as character encoding and conversions, and data encryption. The operating system that hosts the end-user application is typically involved in Layer 6 processes. This functionality is not always implemented in a network protocol.
Network Operating Systems. Organizational Communications and Technologies Prithvi N. Rao H. John Heinz III School of Public Policy and Management Carnegie Mellon University. Readings. High Speed and Wireless LANs (Stallings and van Slyke) Class Notes. Objectives. Slideshow 1299559 by helena.
Operating System Concepts - slides. Avi Silberschatz. Peter Baer Galvin. Greg Gagne. We provide a set of slides to accompany each chapter. Click on the links below to download the slides in Powerpoint format. We also provide zip files of the all Powerpoint files , PDF files, and all figures used in the text. Chapter.
Network operating system - Download as a PDF or view online for free. Submit Search. Upload. Network operating system ... Operating System Presentation. Operating System Presentation Sajid Khan ...
This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Roles Network Operating System. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG.