Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKS

Related Papers
Santi Ngoran
Siyazini Vhutuzah
Qsn no. 15 is your written assignment due September and 16 is your presentation qsn due next block. Question 1 a) Explain the ethical and societal challenges one can face when using Information Technology? [10] • Intellectual property-Millions of dollars of software is illegally copied each year all over the world. This phenomenon has a great impact on the software industry in the region. Local and foreign software industries need consumers support all over the world to maintain the progress of technology. Most importantly, for the sake of growth in indigenous ICT innovation and invention, local software industries in Asia-Pacific need local support in protecting their intellectual property rights and investment • Crime-Stolen and counterfeit ATM cards are used to steal millions of dollars each year throughout the region. The anonymity of the machines makes some crimes easier and creates many new types of crimes. • Loss of privacy-Transactions are transmitted and recorded in databases at banks, hospitals, shopping complexes, and various organizations, in the public or private sector. The contents of electronic communications and databases can provide important and private information to unauthorised individuals and organizations if they are not securely guarded. • Errors-Information input into the databases is prone to human and device error. Computer programmes that process the information may contain thousands of errors. These errors can create wrong and misleading information about individuals and organizations. Information and programme errors might result in financial loss, or even the loss of lives. • Freedom of speech and press-How do the constitutional rights of individuals in terms of the freedoms of speech and press apply to electronic media? How seriously do the problems of pornography, harassment, libel, and censorship on the net affect individuals and society? What government initiatives have been used in handling this crisis? • Digital Divide-How does ICT affect local community life? The increasing use of computers has increased the 0 0 9 3 0 0 9 4 0 0 9 3 0 0 9 4 separation of rich and poor, creating a digital divide between the information haves and have-nots. What subsidies and programmes have been provided by governments of the region to address the issue? • Unemployment-The automation of work has caused creative destruction by eliminating some vocations and creating new ones. How does this affect the employment or unemployment of the work force of a nation? • Professional Ethics-How well trained and ethical are our ICT professionals in dispensing their duties? Faulty and useless systems that cause disasters and hardships to users might be built by incompetent ICT professionals. In dispensing their duties ICT professionals must demonstrate their best practices and standards as set by professional bodies for quality assurance. b) List and explain factors you would consider before buying computer hardware [10] • Warranty
Ata Ul Munim Aseel Shaikh
Neeraj Kumar
Odhiambo Thomas
Inncoent Unwujo
Computer networks are a system of interconnected computers for the purpose of sharing digital information. Two kinds of peers’ relationship are usually considered for reputation management in P2P network. One of them is direct trust relationship that the reputation is got with two peers interacting directly; the other is recommendation trust that the reputation is got by recommendation of the third party. In this paper, we presented an improved trust model based on recommended in P2P environment. In order to weight the transaction reputation and recommendation reputation, we introduced a risk value which resists the influence of false recommendation and collaborative cheating from malicious peers. The global reputation value of target peer can be calculated by using the different portions of transaction reputation, recommendation reputation and risk value Keywords: Network, LAN, Computer, operating system, wifi, connectivity,
Adewale Ademola
endris geta
International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology -IJRASET
IJRASET Publication
Computer networks have become increasingly everywhere. In today's world, a computer network is much more than a collected works of interconnected devices. Computer networks are a system of interconnected computers for the purpose of transferring digital information. Networking not only helps in communication the data but also to share the available resources, to share the information, to send and receive emails, to update and analyses the data to reduce the cost and so on. The computer network enables to analyze, organize and disseminate the information that is essential to profitability. This paper provides information about different types of network. In this review paper we are presenting the basic concepts of network, network architecture and network type's i.e. LAN, MAN and WAN with its advantages and disadvantages.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Mancharagopan Ponnampalam
virendra thoke
catherine salazar
Edwin Ndiema , Dorothy Apondi Rambim
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- An Introduction to Computer Networks »
An Introduction to Computer Networks ¶
Welcome to the website for An Introduction to Computer Networks , a free and open general-purpose computer-networking textbook, complete with diagrams and exercises. It covers the LAN, internetworking and transport layers, focusing primarily on TCP/IP. Particular attention is paid to congestion; other special topics include queuing, real-time traffic, network management, security, mininet and the ns simulator.
The book is suitable as the primary text for an undergraduate or introductory graduate course in computer networking, as a supplemental text for a wide variety of network-related courses, and as a reference work.
It is released under the Creative Commons license Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs , though note that some commercial use is allowed (see the preface for licensing details).
Further information about classroom use is available in the preface .
As of the end of July 2020 I am pleased to introduce the second edition . The first version of the second edition, 2.0.1, is essentially identical to the final release of the first edition, 1.9.21, except that the chapters have been divided into more manageable size; see the discussion in the preface for more. Here are the versions for the second edition:
- Second Edition online html , starting at the Table of Contents
- Second Edition pdf
- unicode-safer online html (if these characters do not display properly: ⟨𝛼,𝛽,𝛾,⟩)
- mobile version (experimental; works reasonably well on Android and iPhones)
- Zipped html
- unicode-safer zipped html
- epub (warning: not compatible with some epub readers)
The last version of the first edition , 1.9.21, is available in the following forms:
- Online html
- unicode-safer online html
- mobile version
A comment form is now available. Let me know what you think!
In the html versions the per-chapter table-of-contents sidebar is now collapsible, for better use of screen space on smaller devices. Unfortunately, this has broken the search feature. Repairs are underway, but progress has been slow.
See the preface for more information on the unicode issues that have led to the unicode-safer versions above.
Edition 1.0 of the book is permanently available as Online html , Zipped html , pdf and epub although most users are more likely to want the current version above.
Peter Dordal

An Introduction to Computer Networks - Second Edition
(6 reviews)
Peter Lars Dordal, Loyola University of Chicago
Copyright Year: 2014
Last Update: 2020
Publisher: Peter L Dordal
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Stuart Anderson, Adjunct Instructor, Norfolk State University on 11/13/23
The textbook is complete and thorough. The index correctly points to the material in the chapters. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The textbook is complete and thorough. The index correctly points to the material in the chapters.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The information in the book is accurate as it applies to networking concepts.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The book's content is current.
Clarity rating: 4
The material is clear however, it does make assumptions about the reader's level of current knowledge about the material.
Consistency rating: 5
The material is consistent and flows in a good order.
Modularity rating: 4
The is very good in how the information is broken down into specific modules. Some modules need more information to make them more complete.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The information is organized in a fashion that allows future topics to build on the previous topics.
Interface rating: 5
There were no interface issues.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
There are no grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
The test is inclusive of all cultures.
This is a good textbook for networking information. Some of the material could be explained in more detail to make it more of an introductory topic. A reader with networking experience would find this book a good reference, however, a reader new to the networks might find some of the material a bit light. As a network engineer, I found the information thorough and would work well with other networking material.
Reviewed by Terri Devlin, Instructor, Aims Community College on 7/23/19
Even though the title of the text is "An Introduction to Networking", the author seems to assume that the student or reader knows a lot about the subject matter and terminology. Topics and some definitions are presented, however the author does a... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
Even though the title of the text is "An Introduction to Networking", the author seems to assume that the student or reader knows a lot about the subject matter and terminology. Topics and some definitions are presented, however the author does a deep dive into the topic area quickly. This text would not be beneficial to students seeking CompTia Network + Certification because many of the terms and concepts tested in the certification exam are not covered in this text.
The author presents the material in an unbiased manner. Errors were not identified
Relevance/Longevity rating: 2
Out-of-date information was identified. The text is written in a manner that updates could be made in a straightforward manner.
Clarity rating: 2
The text was difficult to read because precise definitions and content were not provided. Other textbooks and internet sources were used to look up definitions and refresh understanding of technical terms and concepts
Consistency rating: 4
The terminology, framework, and chapter exercises followed a consistent approach.
The layout of the book is easy to understand and follow.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 3
The topics were organized in a logical fashion. It was a challenge to determine the network “big picture” and how the components fit into the picture. The topics make sense to people familiar with Networks. This text would be challenging to people new to Computer Network concepts.
Interface rating: 3
The text is free of navigation problems. The figures and tables were easily identified. An improvement could be made with providing better images or pictures.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
The text was free of grammatical errors.
The text is appropriate for globally-based students.
Many computer concept textbooks have associated software that helps student learn topics and practice. Computer Networks is an area where practice helps students learn. This text did not have associated software available.
Reviewed by Audrey Styer, Instructor, CIS/CPS, Morton College on 12/21/18
This textbook provides a very comprehensive and in-depth introduction to computer networking. read more
This textbook provides a very comprehensive and in-depth introduction to computer networking.
All information presented is accurate.
This textbook is continually being updated to accommodate the ever-changing nature of computer networking.
Clarity rating: 5
Material is presented in a clear manner, but does require a prior basic understanding of computer networking.
Consistency of presentation and methodology is maintained throughout the text.
Modularity rating: 5
The chapters are well defined by topic
The material is presented in a logical manner that helps learners develop their understanding.
The PDF version is easy to read and navigate. The linked Table of Contents and Index make finding and moving to specific topics simple.
I found no grammatical errors.
This is not applicable to this topic.
The callout boxes provide a visual break for readers and increase learning with interesting facts and supporting information. Unfortunately, this textbook is too advanced for my undergraduate learners and does not map to CompTIA’s Network+ certification.
Reviewed by Sunho Lim, Assistant Professor, Texas Tech University on 3/27/18
The text covers all five layers (phy, link, net, trans, and app) and their associated algorithms and communication protocols in the network, and provides an effective index and/or golssary. read more
The text covers all five layers (phy, link, net, trans, and app) and their associated algorithms and communication protocols in the network, and provides an effective index and/or golssary.
The content is accurate and unbiased.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
The most content is up-to-date and the text is written in a way to easily be updated. Since network technology is time-sensitive, some sections in the text should be updated.
The text is easy to read but some advanced sections (e.g., network simulator ns-2 and ns-3) would be challenging to read and understand technical terminology used.
The text is consistent in using terminology and framework.
The text is well divided into a set of sections. It is easy to selectively choose a section depending on the level of class or students.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The topics in the text are presented in a bottom-up way, but grouping sections in terms of layer would be great.
The text has an interface issue, such as some contents are displayed out of page or cut off.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 1
The text is not related to any culture.
The text is appropriate to both undergraduate to graduate students. A set of selective chapters can be used depending on the instructor. The text is good to use for a reference book.
Reviewed by Lisa Bain, Professor, Rhode Island College on 2/1/18
The book covers all the major topics required for a computer networking course. read more
The book covers all the major topics required for a computer networking course.
Yes, this book is accurate in the major areas that the reviewer read. The entire text was not reviewed.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
Yes, the book is up-to-date with the major concepts that do not change (e.g. TCP, IP, UDP) and also includes the latest standards for Wi-Fi. However, some networking technologies will need to be updated as advancements are made (e.g. newer Wi-Fi standards).
Yes, the text is clearly written. However, the content is very technical and would be challenging for a non-technical person to understand all aspects. It is very straight-forward and appropriate for a technical audience.
Yes, the book is consistent and uses the same technical terminology throughout.
Yes the book is very modular and provides many small sections within each chapter for specific topics.
The flow of the book is similar to other networking books in that is starts with an introduction then provides additional details in following chapters.
The interface in PDF is easy to navigate using the table of contents and embedded links.
Of the information read, no grammar errors were found.
This is not relative to this book.
This book would be appropriate for an instructor with a strong background in teaching networking and using a more technical approach.
Reviewed by Luke Osterritter, Adjunct Instructor, Penn State New Kensington on 2/1/18
This text does a great job of covering the basics of computer networks while also presenting in-depth information, as well as diving into some somewhat tangential, but important, areas (e.g. security). read more
This text does a great job of covering the basics of computer networks while also presenting in-depth information, as well as diving into some somewhat tangential, but important, areas (e.g. security).
There are some terms here that I have seen presented differently than I have learned them or encountered in industry, but nothing inaccurate.
It would seem that this book is kept rather up-to-date, though much of the content is so fundamental as to not have too much of an expiration date, even in this field.
I believe the text is clear in most cases. However, I do feel many of the topics become very in-depth, very fast. It would be nice to have some concepts factored out to their basics early in the chapters, then expounded upon later.
The text does not appear to have any major inconsistencies.
When viewing online, the table of contents makes the content very browsable. However, when viewing in PDF, the large amount of subheadings for any one chapter can be a bit tough to navigate.
As the author notes, there isn't much agreement in how to present this topic, and it can be very difficult to explain one portion without referencing another topic that may not have been presented. I think factoring out some basics and explaining them up front, as this book has done, is a clever way of handling this.
I did not encounter any issues with the text interface.
I did not see any obvious grammatical errors.
This book is very matter-of-fact, with little in the way of irreverence. Likewise, there isn't much to work with here to be proactively inclusive. I think it works to be somewhat inert in this manner.
Overall, I think that this book is a great resource to have given its open availability. It's not the simplest book, so using this in a first level class or in a more general IT, CS, or survey course will take some shepherding on the part of the instructor. The comprehensiveness does suggest to me that this might be able to fill two courses worth of content, as well. It would be nice to have some of the information factored out, with some of the highlights available as lecture materials. On its own though, I feel this would be a strong resource to use in a computer networking course.
Table of Contents
- 1 An Overview of Networks
- 3 Other LANs
- 6 Abstract Sliding Windows
- 7 IP version 4
- 8 IP version 6
- 9 Routing-Update Algorithms
- 10 Large-Scale IP Routing
- 11 UDP Transport
- 12 TCP Transport
- 13 TCP Reno and Congestion Management
- 14 Dynamics of TCP Reno
- 15 Newer TCP Implementations
- 16 Network Simulations: ns-2
- 17 The ns-3 Network Simulator
- 19 Queuing and Scheduling
- 20 Quality of Service
- 21 Network Management and SNMP
- 22 Security
- 23 Bibliography
- 24 Selected Solutions
Ancillary Material
- Peter L Dordal
About the Book
An Introduction to Computer Networks is a free and open general-purpose computer-networking textbook, complete with diagrams and exercises.It covers the LAN, internetworking and transport layers, focusing primarily on TCP/IP. Particular attention is paid to congestion; other special topics include queuing, real-time traffic, network management, security and the ns simulator.
The book is suitable as the primary text for an undergraduate or introductory graduate course in computer networking, as a supplemental text for a wide variety of network-related courses, and as a reference work.
About the Contributors
Peter Lars Dordal is an associate professor within the Department of Computer Science at Loyola University of Chicago. His research interests are in programming languages and computer networks.
Contribute to this Page
- Engineering Mathematics
- Discrete Mathematics
- Operating System
- Computer Networks
- Digital Logic and Design
- C Programming
- Data Structures
- Theory of Computation
- Compiler Design
- Computer Org and Architecture
Basics of Computer Networking
- Types of Network Topology
- Transmission Modes in Computer Networks (Simplex, Half-Duplex and Full-Duplex)
- Manchester Encoding in Computer Network
- Difference between Broadband and Baseband Transmission
- What is OSI Model? - Layers of OSI Model
- TCP/IP Model
- Multiple Access Protocols in Computer Network
- Framing in Data Link Layer
- What is Ethernet?
- Ethernet Frame Format
- Token Ring frame format
- Difference between Byte stuffing and Bit stuffing
- Hamming Code in Computer Network
- Back-off Algorithm for CSMA/CD
- Collision Detection in CSMA/CD
- Efficiency of CSMA/CD
- Efficiency Of Token Ring
- Stop and Wait ARQ
- Sliding Window Protocol | Set 1 (Sender Side)
- What is MAC Address?
- Collision Avoidance in wireless networks
- Difference between Unicast, Broadcast and Multicast in Computer Network
- Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain in Computer Network
- Introduction of Classful IP Addressing
Computer Networking is the practice of connecting computers together to enable communication and data exchange between them. In general, Computer Network is a collection of two or more computers. It helps users to communicate more easily. In this article, we are going to discuss the basics which everyone must know before going deep into Computer Networking.
.jpg)
Computer Networking
How Does a Computer Network Work?
Basics building blocks of a Computer network are Nodes and Links. A Network Node can be illustrated as Equipment for Data Communication like a Modem, Router, etc., or Equipment of a Data Terminal like connecting two computers or more. Link in Computer Networks can be defined as wires or cables or free space of wireless networks.
The working of Computer Networks can be simply defined as rules or protocols which help in sending and receiving data via the links which allow Computer networks to communicate. Each device has an IP Address, that helps in identifying a device.
Basic Terminologies of Computer Networks
- Network: A network is a collection of computers and devices that are connected together to enable communication and data exchange.
- Nodes: Nodes are devices that are connected to a network. These can include computers, Servers, Printers, Routers, Switches , and other devices.
- Protocol: A protocol is a set of rules and standards that govern how data is transmitted over a network. Examples of protocols include TCP/IP , HTTP , and FTP .
- Topology: Network topology refers to the physical and logical arrangement of nodes on a network. The common network topologies include bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree.
- Service Provider Networks: These types of Networks give permission to take Network Capacity and Functionality on lease from the Provider. Service Provider Networks include Wireless Communications, Data Carriers, etc.
- IP Address : An IP address is a unique numerical identifier that is assigned to every device on a network. IP addresses are used to identify devices and enable communication between them.
- DNS: The Domain Name System (DNS) is a protocol that is used to translate human-readable domain names (such as www.google.com) into IP addresses that computers can understand.
- Firewall: A firewall is a security device that is used to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewalls are used to protect networks from unauthorized access and other security threats.
Types of Enterprise Computer Networks
- LAN: A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that covers a small area, such as an office or a home. LANs are typically used to connect computers and other devices within a building or a campus.
- WAN: A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that covers a large geographic area, such as a city, country, or even the entire world. WANs are used to connect LANs together and are typically used for long-distance communication.
- Cloud Networks: Cloud Networks can be visualized with a Wide Area Network (WAN) as they can be hosted on public or private cloud service providers and cloud networks are available if there is a demand. Cloud Networks consist of Virtual Routers, Firewalls, etc.
These are just a few basic concepts of computer networking. Networking is a vast and complex field, and there are many more concepts and technologies involved in building and maintaining networks. Now we are going to discuss some more concepts on Computer Networking.
- Open system: A system that is connected to the network and is ready for communication.
- Closed system: A system that is not connected to the network and can’t be communicated with.
Types of Computer Network Architecture
Computer Network falls under these broad Categories:
- Client-Server Architecture: Client-Server Architecture is a type of Computer Network Architecture in which Nodes can be Servers or Clients. Here, the server node can manage the Client Node Behaviour.
- Peer-to-Peer Architecture: In P2P (Peer-to-Peer) Architecture , there is not any concept of a Central Server. Each device is free for working as either client or server.
Network Devices
An interconnection of multiple devices, also known as hosts, that are connected using multiple paths for the purpose of sending/receiving data or media. Computer networks can also include multiple devices/mediums which help in the communication between two different devices; these are known as Network devices and include things such as routers, switches, hubs, and bridges.
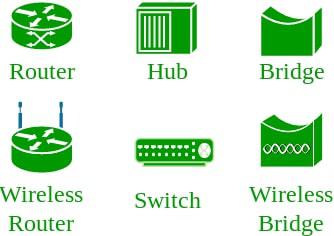
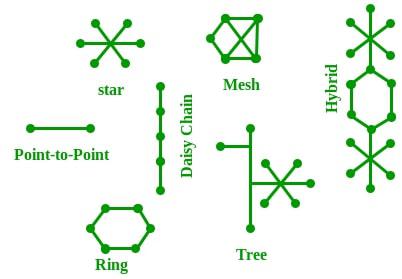
Network Topology
The Network Topology is the layout arrangement of the different devices in a network. Common examples include Bus, Star, Mesh, Ring, and Daisy chain.
OSI Model
OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection . It is a reference model that specifies standards for communications protocols and also the functionalities of each layer. The OSI has been developed by the International Organization For Standardization and it is 7 layer architecture. Each layer of OSI has different functions and each layer has to follow different protocols. The 7 layers are as follows:
- Physical Layer
- Data link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer
A protocol is a set of rules or algorithms which define the way how two entities can communicate across the network and there exists a different protocol defined at each layer of the OSI model. A few such protocols are TCP, IP, UDP, ARP, DHCP, FTP, and so on.
Unique Identifiers of Network
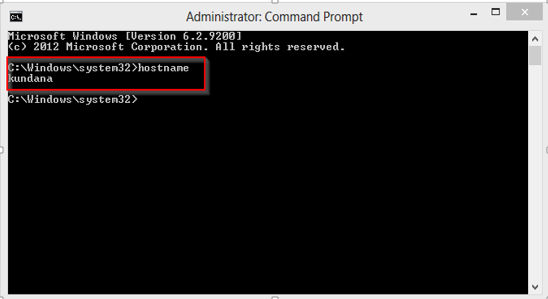
Hostname: Each device in the network is associated with a unique device name known as Hostname. Type “hostname” in the command prompt(Administrator Mode) and press ‘Enter’, this displays the hostname of your machine.
IP Address (Internet Protocol address): Also known as the Logical Address, the IP Address is the network address of the system across the network. To identify each device in the world-wide-web, the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) assigns an IPV4 (Version 4) address as a unique identifier to each device on the Internet. The length of an IPv4 address is 32 bits, hence, we have 2 32 IP addresses available. The length of an IPv6 address is 128 bits. Type “ipconfig” in the command prompt and press ‘Enter’, this gives us the IP address of the device.
MAC Address (Media Access Control address): Also known as physical address, the MAC Address is the unique identifier of each host and is associated with its NIC (Network Interface Card) . A MAC address is assigned to the NIC at the time of manufacturing. The length of the MAC address is: 12-nibble/ 6 bytes/ 48 bits Type “ipconfig/all” in the command prompt and press ‘Enter’, this gives us the MAC address.
Port: A port can be referred to as a logical channel through which data can be sent/received to an application. Any host may have multiple applications running, and each of these applications is identified using the port number on which they are running.
A port number is a 16-bit integer, hence, we have 2 16 ports available which are categorized as shown below:
Number of ports: 65,536 Range: 0 – 65535 Type “ netstat -a ” in the command prompt and press ‘Enter’, this lists all the ports being used.
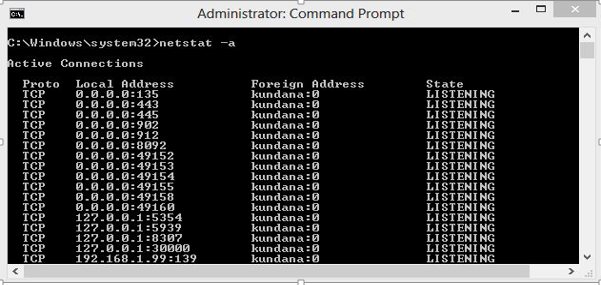
List of Ports
Socket: The unique combination of IP address and Port number together is termed a Socket.
Other Related Concepts
DNS Server: DNS stands for Domain Name System . DNS is basically a server that translates web addresses or URLs (ex: www.google.com) into their corresponding IP addresses. We don’t have to remember all the IP addresses of each and every website. The command ‘ nslookup ’ gives you the IP address of the domain you are looking for. This also provides information on our DNS Server. \
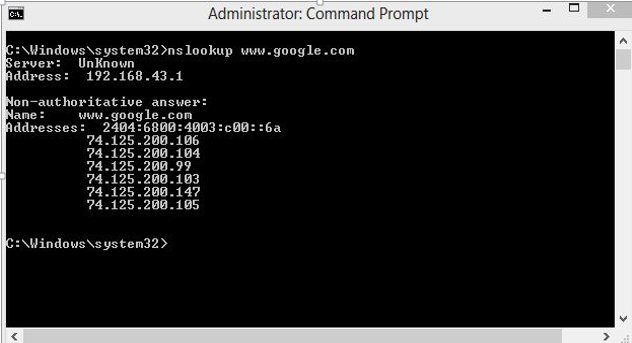
Domain IP Address
ARP: ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol . It is used to convert an IP address to its corresponding physical address(i.e., MAC Address). ARP is used by the Data Link Layer to identify the MAC address of the Receiver’s machine.
RARP: RARP stands for Reverse Address Resolution Protocol . As the name suggests, it provides the IP address of the device given a physical address as input. But RARP has become obsolete since the time DHCP has come into the picture.
Please Login to comment...
- 10 Best Free Social Media Management and Marketing Apps for Android - 2024
- 10 Best Customer Database Software of 2024
- How to Delete Whatsapp Business Account?
- Discord vs Zoom: Select The Efficienct One for Virtual Meetings?
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

solar eclipse
25 templates

autism awareness
28 templates

26 templates

16 templates

6 templates

32 templates
Computer Presentation templates
Use these google slides themes or download our ppt files for powerpoint or keynote to give a presentation about a computer-related topic, including information technology..

Computer Science Degree for College
Computer science degrees prepare students for the jobs of the future (and the present!). If you are interested in getting an education about coding, math, computers, and robots, this is the degree for you! Speak about it with this futuristic template that will take the viewers to another digital dimension....
Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
Silicon Valley Programmer Minitheme
No matter your actual profession, you can’t say you’ve never ever imagined being one of those fabled Silicon Valley programmers that make alternate realities come to life and can make us question the structures that govern our world. The good news: With this minitheme, you can join them for a...
Linear Grid Newsletter
Give an original touch to your employee newsletters with this grid design. It perfectly combines colors like green, yellow or orange with geometric icons to give dynamism to your news. You can use a different tone for each section, so they can be easily differentiated. Report on the latest company...

Computer Science Proposal
A slide deck whose overall look and feel is very techie is what you need to put forward a proposal for a computer science project. And that’s what you’ll get with this template. The details on the backgrounds are so enticing and the neon tone used for the text contrasts...

Healthy Relationships and Communication Skills - 6th Grade
Download the Healthy Relationships and Communication Skills - 6th Grade presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and easily edit it to fit your own lesson plan! Designed specifically for elementary school education, this eye-catching design features engaging graphics and age-appropriate fonts; elements that capture the students' attention and make the...

Virtual Slides for Education Day
Digital learning is making its way into the world of education. For this reason, we've designed this new template so that the slides look like the screen of a laptop (complete with reflections!). Apart from graphs and infographics, the font is quite computer-esque and a perfect fit for this theme....

Computer Science College Major
If you are a guru of computers, most likely you've studied computer science in college. Would you like to show others what a major in this field has to offer and what it could contribute to their professional development? Customize this template and let them feel the future, at least...

Soft Colors UI Design for Agencies
Agencies have the most creative employees, so having boring meetings with traditional Google Slides & PowerPoint presentations would be a waste. Make the most out of this potential with this creative design full of editable resources and beautiful decorations in calming, pastel tones. Let the creativity of your agency be...

Work Program Project Proposal
Download the Work Program Project Proposal presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. A well-crafted proposal can be the key factor in determining the success of your project. It's an opportunity to showcase your ideas, objectives, and plans in a clear and concise manner, and to convince others to invest their...

Multimedia Software Pitch Deck
Download the Multimedia Software Pitch Deck presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Whether you're an entrepreneur looking for funding or a sales professional trying to close a deal, a great pitch deck can be the difference-maker that sets you apart from the competition. Let your talent shine out thanks to...

How to Code Workshop
Are you an expert of Java? Yes, it's a beautiful island in Indonesia and more than half of the population of this country lives there... No! Well, yes, those facts are true, but we were talking about the programming language! We think workshops on how to code are a necessity,...
Robotic Workshop Infographics
Download the Robotic Workshop Infographics template for PowerPoint or Google Slides and discover the power of infographics. An infographic resource gives you the ability to showcase your content in a more visual way, which will make it easier for your audience to understand your topic. Slidesgo infographics like this set...
Silicon Valley Programmer Portfolio
Download the Silicon Valley Programmer Portfolio presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. When a potential client or employer flips through the pages of your portfolio, they're not just looking at your work; they're trying to get a sense of who you are as a person. That's why it's crucial to...

Global Technology Investments Project Proposal Infographics
Download the Global Technology Investments Project Proposal Infographics template for PowerPoint or Google Slides to get the most out of infographics. Whether you want to organize your business budget in a table or schematically analyze your sales over the past year, this set of infographic resources will be of great...


Statistics and Data Analysis - 6th Grade
Download the Statistics and Data Analysis - 6th Grade presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. If you’re looking for a way to motivate and engage students who are undergoing significant physical, social, and emotional development, then you can’t go wrong with an educational template designed for Middle School by Slidesgo!...

Candycore Aesthetics Social Media Strategy
Download the Candycore Aesthetics Social Media Strategy presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. How do you use social media platforms to achieve your business goals? If you need a thorough and professional tool to plan and keep track of your social media strategy, this fully customizable template is your ultimate...

Web Project Proposal
We live in the internet era, which means that web design is currently one of the most demanded skills. This free template is perfect for those designers who want to present their web project proposal to their clients and see a preview of the final work.

Software Testing Company
Software testing might not be the sexiest part of coding, but that doesn't mean it lacks intrigue or importance. After all, who wants to use a buggy app? It's software testing that ensures smooth operation and prevents annoying glitches from making it into the final product. Without it, our lives...
- Page 1 of 28
New! Make quick presentations with AI
Slidesgo AI presentation maker puts the power of design and creativity in your hands, so you can effortlessly craft stunning slideshows in minutes.

Register for free and start editing online

Computer Network Topologies
Jul 13, 2014
850 likes | 2.23k Views
Computer Network Topologies. Maninder Kaur [email protected]. What is a Topology?. Network topologies describe the ways in which the elements of a network are mapped. They describe the physical and logical arrangement of the network nodes.
Share Presentation
- network topologies
- single cable
- computer network topologies
- small data packet
- long distances
- central device

Presentation Transcript
Computer Network Topologies Maninder Kaur [email protected]
What is a Topology? • Network topologies describe the ways in which the elements of a network are mapped. They describe the physical and logical arrangement of the network nodes. • The physical topology of a network refers to the configuration of cables, computers, and other peripherals
Different Types of Topologies • Bus Topology • Star Topology • Ring Topology • Mesh Topology • Tree Topology • Hybrid Topology
Bus Topology • All the nodes (file server, workstations, and peripherals) on a bus topology are connected by one single cable. • A bus topology consists of a main run of cable with a terminator at each end. All nodes (file server, workstations, and peripherals) are connected to the linear cable. • Popular on LANs because they are inexpensive and easy to install.
Bus Topology
Bus Topology Advantages of Bus Topology • It is Cheap, easy to handle and implement. • Require less cable • It is best suited for small networks. Disadvantages of Bus Topology • The cable length is limited. This limits the number of stations that can be connected. • This network topology can perform well only for a limited number of nodes.
Ring Topology • In a ring network, every device has exactly two neighbours for communication purposes. • All messages travel through a ring in the same direction. • A failure in any cable or device breaks the loop and can take down the entire network. • To implement a ring network we use the Token Ring technology • A token, or small data packet, is continuously passed around the network. When a device needs to transmit, it reserves the token for the next trip around, then attaches its data packet to it.
Ring Topology
Ring Topology Advantage of Ring Topology • Very orderly network where every device has access to the token and the opportunity to transmit. • Easier to Mange than a Bus Network • Good Communication over long distances • Handles high volume of traffic Disadvantages of Ring Topology • The failure of a single node of the network can cause the entire network to fail. • The movement or changes made to network nodes affects the performance of the entire network.
Star Topology • In a star network, each node (file server, workstations, and peripherals) is connected to a central device called a hub. • The hub takes a signal that comes from any node and passes it along to all the other nodes in the network. • Data on a star network passes through the hub, switch, or concentrator before continuing to its destination. • The hub, switch, or concentrator manages and controls all functions of the network. • The star topology reduces the chance of network failure by connecting all of the systems to a central node.
Star Topology
Star Topology Advantages of Star Topology • Easy to manage • Easy to locate problems (cable/workstations) • Easier to expand than a bus or ring topology. • Easy to install and wire. • Easy to detect faults and to remove parts. Disadvantages of Star Topology • Requires more cable length than a linear topology. • If the hub or concentrator fails, nodes attached are disabled. • More expensive because of the cost of the concentrators.
Tree Topology • A tree topology (hierarchical topology) can be viewed as a collection of star networks arranged in a hierarchy. • This tree has individual peripheral nodes which are required to transmit to and receive from one other only and are not required to act as repeaters or regenerators. • The tree topology arranges links and nodes into distinct hierarchies in order to allow greater control and easier troubleshooting. • This is particularly helpful for colleges, universities and schools so that each of the connect to the big network in some way.
Tree Topology
Tree Topology Advantages of a Tree Topology • Point-to-point wiring for individual segments. • Supported by several hardware and software vendors. • All the computers have access to the larger and their immediate networks. Disadvantages of a Tree Topology • Overall length of each segment is limited by the type of cabling used. • If the backbone line breaks, the entire segment goes down. • More difficult to configure and wire than other topologies.
Mesh Topology • In this topology, each node is connected to every other node in the network. • Implementing the mesh topology is expensive and difficult. • In this type of network, each node may send message to destination through multiple paths. • While the data is travelling on the Mesh Network it is automatically configured to reach the destination by taking the shortest route which means the least number of hops.
Mesh Topology
Mesh Topology Advantage of Mesh Topology • No traffic problem as there are dedicated links. • It has multiple links, so if one route is blocked then other routes can be used for data communication. • Points to point links make fault identification easy. Disadvantage of Mesh Topology • There is mesh of wiring which can be difficult to manage. • Installation is complex as each node is connected to every node. • Cabling cost is high.
Hybrid Topology • A combination of any two or more network topologies. • A hybrid topology always accrues when two different basic network topologies are connected. • It is a mixture of above mentioned topologies. Usually, a central computer is attached with sub-controllers which in turn participate in a variety of topologies
Hybrid Topology
Hybrid Topology Advantages of a Hybrid Topology • It is extremely flexible. • It is very reliable. Disadvantages of a Hybrid Topology • Expensive
Thanks a LotHave a nice Day
- More by User

Network Topologies
Network Topologies. Objectives. Describe the basic and hybrid LAN physical topologies, and their uses, advantages and disadvantages Describe the backbone structures that form the foundation for most LANs. Simple Physical Topologies. Physical topology: physical layout of nodes on a network
844 views • 27 slides

Network Topologies. Objectives. Describe the basic and hybrid LAN physical topologies, their uses, advantages, and disadvantages Describe a variety of enterprise-wide and WAN physical topologies, their uses, advantages, and disadvantages
1.12k views • 44 slides
Fundamentals. A LAN (Local Area Network) is a
669 views • 41 slides

Network Security Topologies
Network Security Topologies. Chapter 11. Learning Objectives. Identify place and role of the demilitarized zone NAT and PAT Tunneling in network security Describe security features of VLANS Network perimeter’s importance to an organization’s security policies. Perimeter Security Topologies.
706 views • 35 slides

Network topologies
Network topologies. What is a network topology?. Physical arrangement of the devices in a communications network. Most commonly used are bus and star. Usually a combination of these two, referred to as hybrid or tree networks. Bus topology.
665 views • 11 slides

NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
NETWORK TOPOLOGIES. WHAT IS A NETWORK TOPOLOGY?. The number in which nodes are linked in a computer network A pure form of these basic topologies is seldom found in practice. TYPES OF CLIENT. - Dumb terminals - Thin client - Fat client. BUS TOPOLOGY.
248 views • 6 slides
Network Topologies. Topology – how nodes are connected – where there is a wire between 2 nodes. Routing – the path a message takes to get from one node to another. Network connections can be static or dynamic (ex. Bus). Network Properties. Diameter – Maximum distance between nodes
378 views • 23 slides

Network Topologies. Objectives. Describe the basic and hybrid LAN physical topologies, and their uses, advantages and disadvantages. Describe the backbone structures that form the foundation for most LANs. Simple Physical Topologies. Physical topology: physical layout of nodes on a network
430 views • 20 slides

Network Topologies. A network topology describes ways of configuring or laying out a network. The main topologies: Star Bus Hybrid or tree network. Bus Topology.
606 views • 7 slides

Network Topologies. Network Topology. The topology of a network specifies the geometric arrangement of the network. The complete physical structure of the cable (or data-transmission media) , workstations, nodes, routers and gateways are called the physical topology.
790 views • 13 slides

NETWORK TOPOLOGIES. There are three basic configurations used to connect computers they are the Bus Ring Star. Bus topology. This type of network was widely used in the 1980’s In this configuration every computer (node) shares the networks total bus capacities.
523 views • 27 slides

3-19. Network Topologies. T. T. Free Topology . 3-20. Ring, star or combination layout of network media All except ring are polarity insensitive One terminator installed anywhere on the segment Typical for device channels May be difficult to troubleshoot bad devices
797 views • 44 slides

Network Topologies. William M. Jones Assistant Professor Computer Science Department Coastal Carolina University. Network Classifications. Networks have two broad classifications Static Dynamic Static Networks
786 views • 41 slides
Network Security Topologies. Chapter 11. Learning Objectives. Explain network perimeter’s importance to an organization’s security policies Identify place and role of the demilitarized zone in the network Explain how network address translation is used to help secure networks
490 views • 35 slides

Network Security Topologies. Jason Kennedy March 23, 2004. Network Security Topics . Perimeter Security Topologies Demilitarized zone (DMZ) Network Address Translation Tunneling Virtual Local Area Networks. Perimeter Security Topologies.
504 views • 29 slides

317 views • 29 slides

256 views • 20 slides

Network Topologies. LAN topologies WAN topologies. LAN Topologies(Physical). Bus Star Ring. Bus topology. All networked nodes are interconnected, peer to peer, using a single, open-ended cable Both ends of the bus must be terminated with a terminating resistor to prevent signal bounce.
172 views • 12 slides

339 views • 27 slides
- Generative AI
- Office Suites
- Collaboration Software
- Productivity Software
- Augmented Reality
- Emerging Technology
- Remote Work
- Artificial Intelligence
- Operating Systems
- IT Leadership
- IT Management
- IT Operations
- Cloud Computing
- Computers and Peripherals
- Data Center
- Enterprise Applications
- Vendors and Providers
- United States
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
- Newsletters
- Foundry Careers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- Member Preferences
- About AdChoices
- E-commerce Affiliate Relationships
- Your California Privacy Rights
Our Network
- Network World
Google Slides cheat sheet: How to get started
How to use Google Slides to create, collaborate on, and lead business presentations.

Need to build a slide presentation for a meeting, training, or other event? Google Slides is an easy-to-use web app that comes with the essential tools and more. It stores your presentations in the cloud with Google Drive. Anyone with a Google account can use Slides and Drive for free, and they’re also included with a Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) subscription for business and enterprise customers. There are Google Sheets mobile apps for Android and iOS, too.
This guide will help you become familiar with the Google Slides web interface and show you how to start a new presentation, upload a Microsoft PowerPoint file to edit in Google Slides, collaborate with others on your presentation, and finally, present it to others.
Create or open a presentation
Log in to your Google or Workspace account. Then:
From Google Slides : At the top of the home page, you’ll see a “Start a new presentation” header, with a row of thumbnails underneath. To start a new, blank presentation, click the Blank thumbnail. To start a new presentation in a template, select one of the thumbnails to the right or click Template gallery toward the upper-right corner, then click any thumbnail on the page that appears.
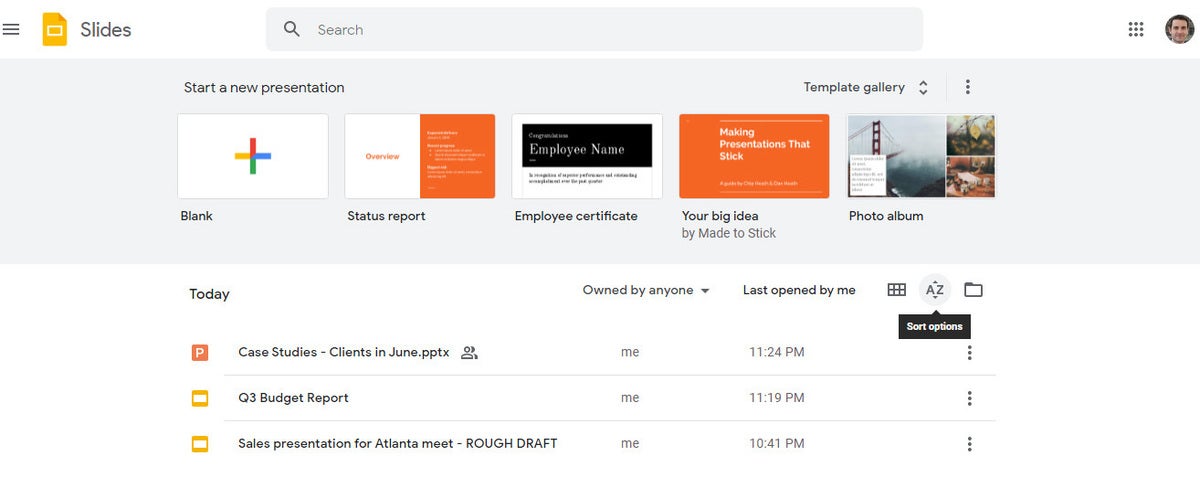
The Google Slides home page. (Click image to enlarge it.)
Below the “Start a new presentation” area you’ll see a list of presentations that are stored in your Google Drive or shared with you. To open a presentation, click it in this list.
The list of your presentations appears in reverse chronological order starting with the presentation you most recently opened. Clicking the “AZ” icon at the upper right of this list changes the sort order to Last modified by me , Last modified , or in alphabetical order by presentation title. You can also browse to a specific folder by clicking the folder icon next to the “AZ” icon.
From Google Drive : Presentations stored in your Google Drive are listed in the main window of the Drive home page. To see a listing of presentations that others are sharing with you, click Shared with me in the left column. From either list, double-click a presentation to open it in Google Slides.
To start a new, blank presentation, click the New button at the upper-left of the screen and then click Google Slides .
If you want to use a template to start a new presentation, click the New button, then move the cursor over the right arrow next to Google Slides and select From a template . The template gallery for Google Slides will open; click a thumbnail to start a new presentation in that template.
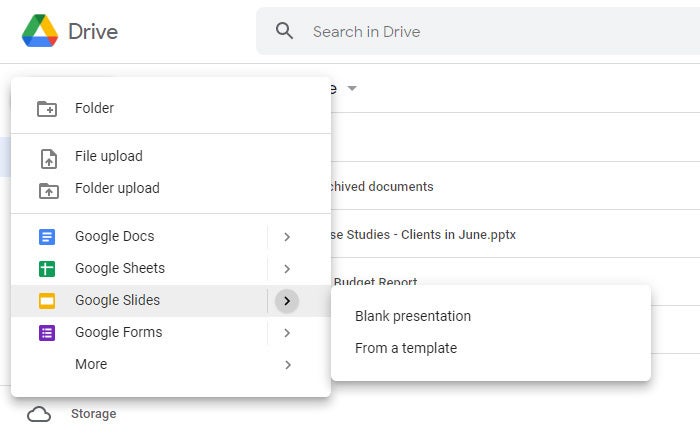
Creating a new presentation from Google Drive.
From Google Slides or Drive: You also can use the search box at the top to find presentations in your Google Drive or shared with you. Enter words or numbers that may be in the presentation you’re looking for.
Upload a PowerPoint presentation to Slides
You can edit a Microsoft PowerPoint presentation in Google Slides, but first you must upload it to Google Drive.
From Google Slides: Click the folder icon ( Open file picker ) that’s above and toward the right corner of your presentations list. On the panel that opens, click the Upload tab. Drag-and-drop your PowerPoint file (.ppt or .pptx) onto this panel, or browse your PC’s drive to select it.
From Google Drive: Click the New button, then File upload , and select the PowerPoint file from your PC’s drive and click Open .
Traditionally, when you uploaded PowerPoint files to Google Drive, they were automatically converted to Slides format. That’s still the case when you upload PowerPoint files via the Google Slides home page .
However, Google now supports the ability to edit Microsoft Office files in their native format. By default, any .pptx files that you upload via Google Drive will remain formatted as PowerPoint documents. You can edit and collaborate on a PowerPoint file right in Slides, with all changes made by you or your collaborators saved directly to the PowerPoint file.
On the Google Slides and Drive home pages, native PowerPoint files will be denoted with an orange “P” icon, and when you open a native PowerPoint file in Sheets, you’ll see a “.PPTX” flag to the right of the document title.
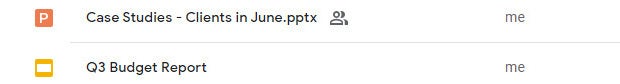
Native PowerPoint files show the PowerPoint icon (top) instead of the Google Slides icon (bottom).
If you’d rather have Google convert PowerPoint files to Slides format automatically when you upload them via Google Drive, click the gear icon in the upper-right corner of the Drive home screen and select Settings from the drop-down menu. In the Settings box next to “Convert uploads,” check the checkbox marked Convert uploaded files to Google Docs editor format .
Work in a presentation
When you open a new or existing presentation, its first slide appears in the main window of Google Slides. Here’s a breakdown of the toolbars, menus, panes, and sidebars that appear around your presentation.
The left pane shows thumbnails of all the slides in your presentation. Click a thumbnail, and the slide it represents will appear in the main window, where you can edit it.
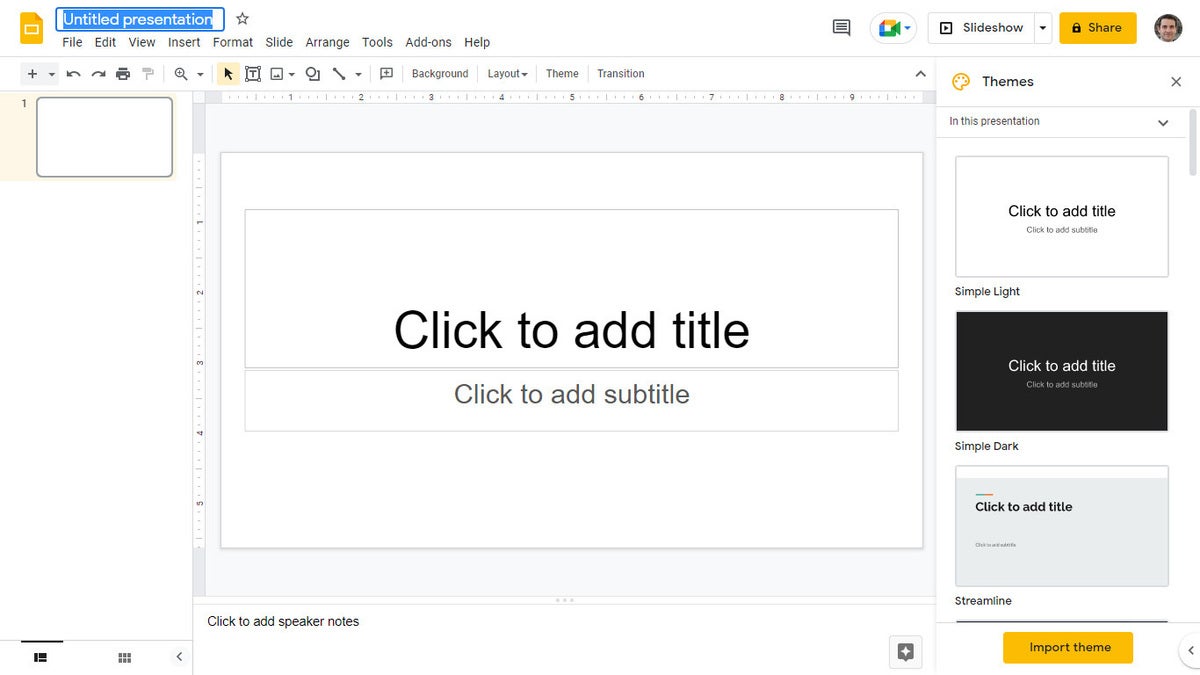
The Google Slides editing interface. (Click image to enlarge it.)
Your presentation’s title appears along the top of the screen. To change it, click anywhere inside the title and start typing.
The menu bar below your presentation’s title has a complete set of tools for working with presentations. These are the main submenus to know:
- File has commands for taking action on the whole presentation, including Print, Rename, and Share.
- Edit lists the standard editing commands such as copy, cut, paste, delete, duplicate, and find and replace.
- View lists several ways that you can view your slides as you design and edit them. This includes arranging them into a grid, previewing them as a slideshow, or zooming in on them. You can also watch the transition effect that takes place between slides when they’re played in a slideshow.
- Insert lets you add several objects to your slides, including charts, diagrams, pictures, tables, and text. You can also add links to YouTube videos or sound or video files that are stored in your Google Drive.
- Format lets you change the look of your slides. Certain functions on this submenu become clickable depending on whether you’ve selected an image or text on a slide, or selected the slide itself.
- Slide is where you can add, delete, or duplicate a slide that you’ve selected. You can also add a preset layout to a slide, change its background or theme color, or add and edit a transition effect that takes place between slides when your presentation is played as a slideshow.
- Arrange lists tools that let you group or reorder objects on a slide in relation to another. For example, you can place an image behind another image or group an image and a block of text together to make them easier to move at once.
- Tools leads to several miscellaneous functions. These include letting you record a voice clip to go with a slide, running a spell checker, and showing you a list of objects in your presentation that are linked to other files.
The toolbar directly above your presentation puts commonly used commands in easy reach. From this toolbar, you can click buttons to add to a slide or change its background, comments, layout, objects (images, lines, shapes, text), text style, theme colors for the whole presentation, transition effects during a slideshow, and more. The buttons on the toolbar change depending on whether you’ve selected image or text on a slide or the slide itself.
Notice that there’s no Save button in the toolbar — or anywhere in Google Slides. That’s because Slides automatically saves any changes you make to your presentation.
Speaker notes: Along the bottom of each slide you’ll see an area marked Click to add speaker notes . Here you can type in brief notes to remind yourself what to do or say when the slide is being shown. Only you will see these notes when you show your presentation to an audience.
Themes sidebar: When you start a new blank presentation, the Themes sidebar opens on the right side of the screen. (You can also open this sidebar at any time by clicking Theme on the toolbar above your presentation.) Themes apply the same fonts, colors, and other design elements to all the slides in a presentation, giving it a consistent look and feel. Click a thumbnail in this sidebar to change your presentation to that theme.
Create and manage slides
Here are the basic things to know about working with slides in a presentation.
Add a new, blank slide to your presentation: Click the + button at the left end of the toolbar above your presentation. Alternatively, if you click the down arrow next to the +, you can choose a layout to use as the basis for a new slide.
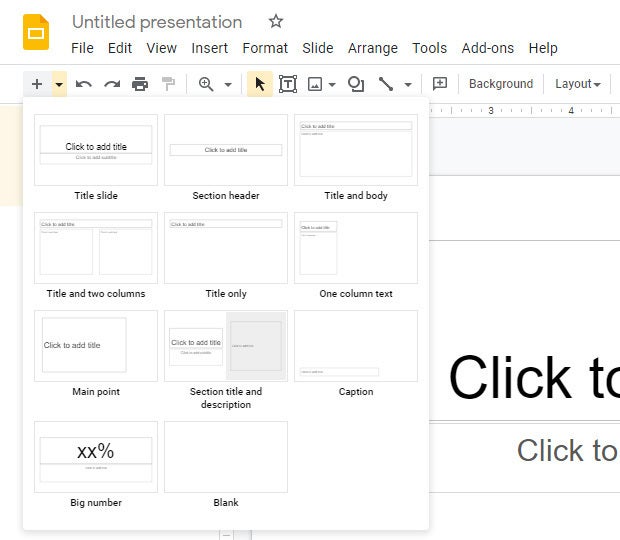
Click the down arrow next to the + button in the toolbar to choose a layout for a new slide.
Apply or change a slide’s background: Select the slide’s thumbnail in the left sidebar and click Background on the toolbar above your presentation. On the panel that opens, you can change the slide’s background color or use an image file from your Google Drive, Google Photos account, or PC as the background.
Apply or change a slide’s layout: Select the slide’s thumbnail in the left pane, then click Layout on the toolbar above your presentation. On the panel that opens, select the layout you want to apply to this slide.
Apply or change a slide’s transition: Select the slide’s thumbnail in the left sidebar and click Transition on the toolbar above your presentation. In the Motion sidebar that opens along the right side of the screen, you can apply or change the animated transition effect that is played before this slide.
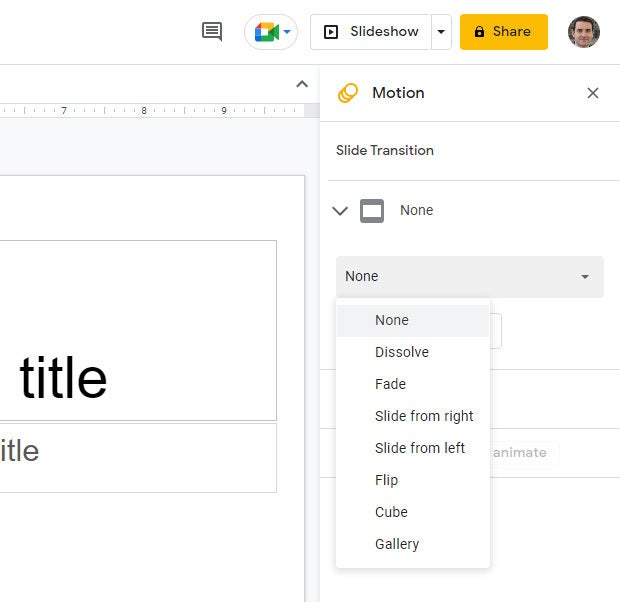
Choosing a transition style in the Motion pane.
Move a slide to a different spot in the slideshow sequence: Click and hold its thumbnail in the left sidebar, drag it up or down to another place in the sequence, and release it.
Delete a slide: Right-click its thumbnail in the left sidebar and select Delete from the pop-up menu. Alternatively, select its thumbnail and select Edit > Delete from the menu bar or just press the Delete key.
Share and collaborate on a presentation
Presentations are often a group effort, with several team members contributing to and polishing a presentation. In Slides, it’s easy for multiple collaborators to work on a presentation together.
First, you need to share the presentation. When you’re viewing your presentation in Google Slides, click the Share button at the upper-right. Or, from your Google Drive homepage, click to highlight the presentation that you want to share. Then, in the toolbar toward the upper right, click the Share icon (a head-and-shoulders silhouette with a +).
Either way, the “Share” panel will open.
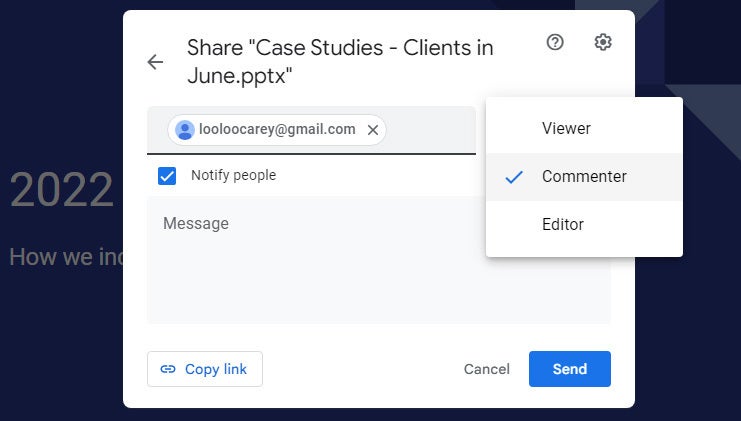
Setting permissions for a file being shared privately.
Share a presentation privately
In the entry box, enter the email addresses (or names of your Google Contacts) of the people with whom you want to share. By default, the people you invite to your presentation can edit it and reshare it with others.
To change access permissions for invitees: Click Editor to the right of the entry box and choose another option from the drop-down menu. Commenter means they can view your spreadsheet and add comments but can’t change it. Viewer means they can view your presentation but can’t edit it or add comments.
To prevent your presentation from being reshared, downloaded, or printed: Click the gear icon at the upper-right of this panel. On the smaller panel that opens, uncheck the boxes by Editors can change permissions and share and Viewers and commenters can see the option to download, print, and copy .
When you’re done setting permissions (and, optionally, typing in a message to your invitees), click Send , and everyone you’ve added will receive an email with a link they can click to access the document.
The shared presentation icon.
A presentation you’ve shared (or that others have shared with you) will have an icon of two silhouetted heads next to it in the presentations list on your Google Sheets and Google Drive home pages.
To limit or change a person’s access to your presentation: With the presentation open in Google Slides, click the Share button at the upper-right. Or, from Google Drive, highlight the presentation and click the Share icon.
The Share panel reopens showing a list of all the people you’ve invited, along with their permission status. Click the down arrow to the right of a person’s name, change their permission level or remove their access entirely, and click Save .
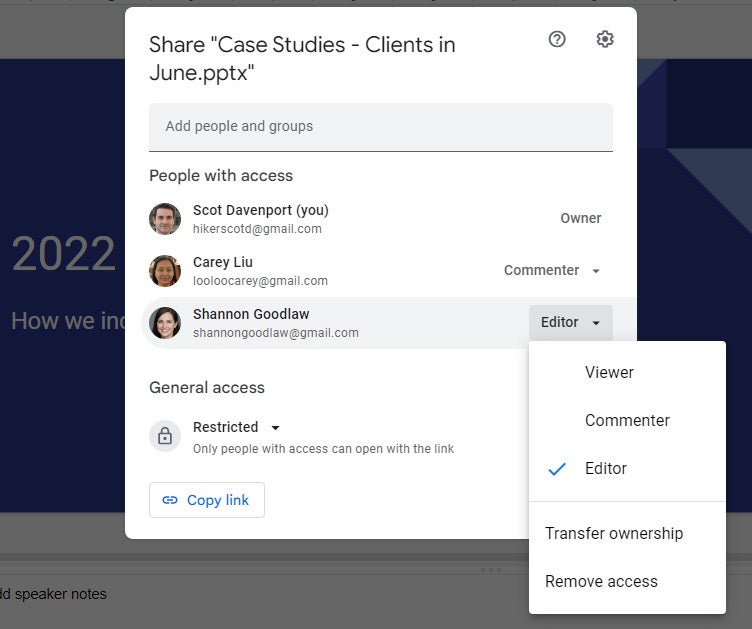
You can change permissions for people you’ve shared a presentation with on an individual basis.
If you have a Google Workspace subscription, another option is to select Give temporary access and, next to Access expires , select a date within one year of the current date. If you set an expiration date for a person that you’ve assigned as Editor, their access will be downgraded to Commenter on the expiration date.
Share a presentation publicly
Most business users will want to share presentations privately with select colleagues or clients, but you do have the option to share a presentation publicly. At the bottom of the Share panel is a “General access” area where you can copy a link to the document. By default, this link is restricted to those you invite to the document. To change it to a public link, click Restricted and select Anyone with the link from the menu that appears.
Click Copy link and the link to your presentation will be copied to your PC’s clipboard. You can share this link by pasting it into a chat message, document, email, forum post, or most other means of online written communication. Anyone who clicks this link will be able to view your presentation online. (Be aware that anyone can copy and reshare this link.)
To allow anyone in the public to comment on or edit your presentation: At the bottom right of the Share panel, click Viewer and select Commenter or Editor from the drop-down menu. Then click the Done button. Now the web link to your presentation will let anyone who clicks it add a comment or edit it.
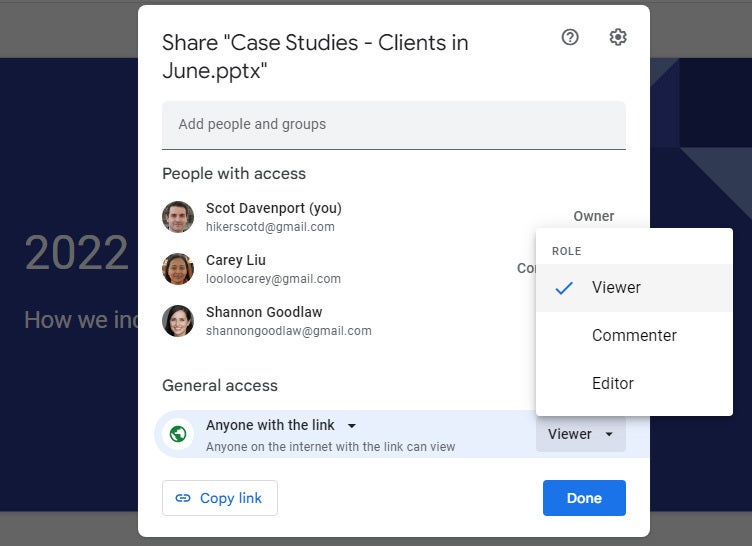
Sharing a spreadsheet publicly.
To turn off public sharing for your presentation: Bring up the Share panel again. Near the bottom, click Anyone with the link and select Restricted from the menu, then click the Done button.
Note: You can apply both public and private sharing methods to your presentation. For example, you could allow the public to only view your presentation, but allow specific people that you’ve invited to comment on or edit it.
Collaborate on a presentation
The people you’ve shared a spreadsheet with can view or work on it at the same time as you or at other times. Remember that people who have Editor privileges to your presentation can change all aspects of it. Having multiple people making changes to a presentation can get confusing. In most cases, setting everyone to Commenter is the best way to collaborate in Slides: People can attach comments to a slide or to objects in a slide, but their comments won’t alter your presentation’s information or design.
To add a comment to a slide: Right-click its thumbnail in the left sidebar and select Comment from the menu that opens. Alternatively, you can select its thumbnail and select Insert > Comment from the menu bar or click the Add comment button (a speech balloon with a + sign).
A blank comment card with your name on it opens to the right of the slide in the main window. On this card’s entry line, type a brief comment, and when you’re finished, click the Comment button.
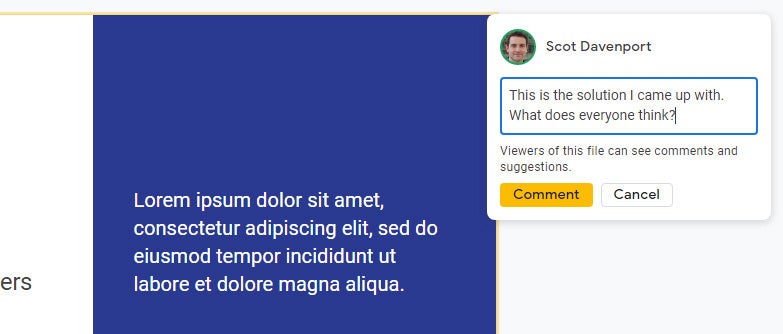
Typing in a new comment.
To add a comment to an object on a slide: Right-click the object (a block of text, chart, image, picture, etc.) and select Comment from the menu that opens. Alternatively, you can select the object and select Insert > Comment from the menu bar.
To draw someone’s attention to a comment: As you’re composing the comment, type the @ symbol and begin typing their name, then select the person from the list of suggested Google contacts that appears. They’ll receive an email notifying them of the comment and linking to it.
To read, reply to, or remove a comment: A slide that contains a comment is denoted in the left sidebar with a speech balloon by its thumbnail. Click the slide’s thumbnail to make the slide appear in the main window, and you’ll see all its comment cards on the right.
To reply to a comment, click its card. The card will expand to reveal an entry line where you can add a comment in response.
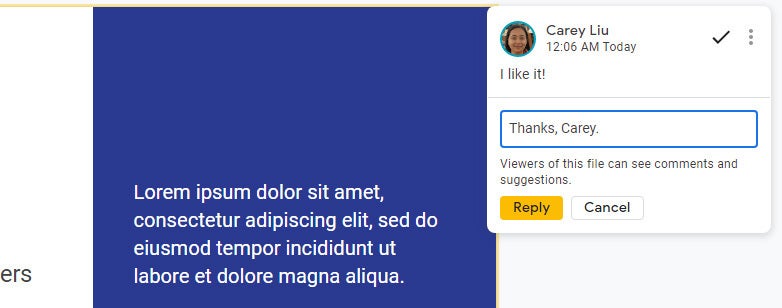
Replying to a comment.
Clicking the checkmark at the upper right marks the comment card as “resolved” and removes the card from the presentation. Clicking the card’s three-dot icon opens a menu that lets you edit or delete your comment.
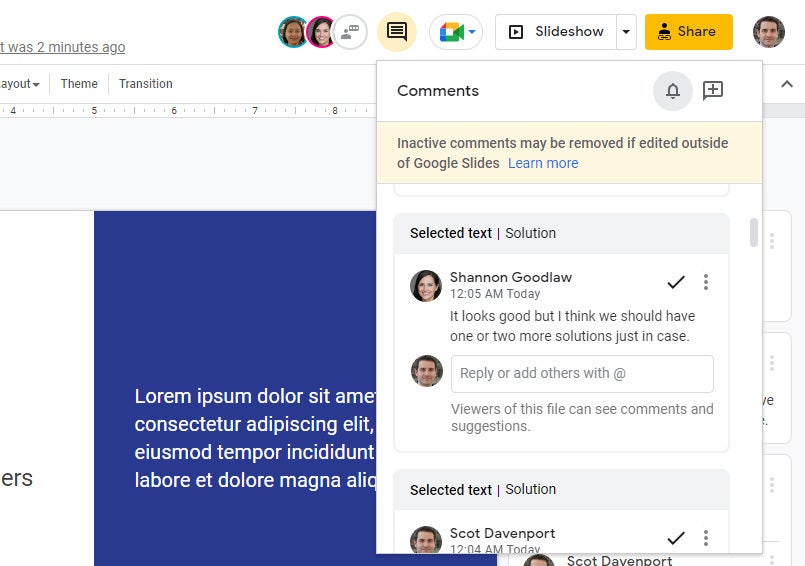
To see a list of all comments: Click the Open comment history icon (the speech balloon) to the left of the Slideshow button. A sidebar will open along the right side of the screen; it lists all the comment cards in your presentation. When you click a comment on this list, the view of your presentation in the main window will jump to the cell where the comment is located and open its comment card.
The Comments pane lets you quickly review all comments and jump to specific ones.
For more details about collaborating on your presentation, including what it’s like to collaborate in real time, see “ How to collaborate on a document ” in our Google Drive guide. You can also collaborate on a presentation in Google Chat; that’s covered later in this story.
Recover older versions of a presentation
It’s easy to go too far when making tweaks to a presentation. Fortunately, it’s also easy to roll back to an earlier version of the presentation. Click File > Version history > See version history . This opens a panel on the right that shows a list of older versions of your presentation.
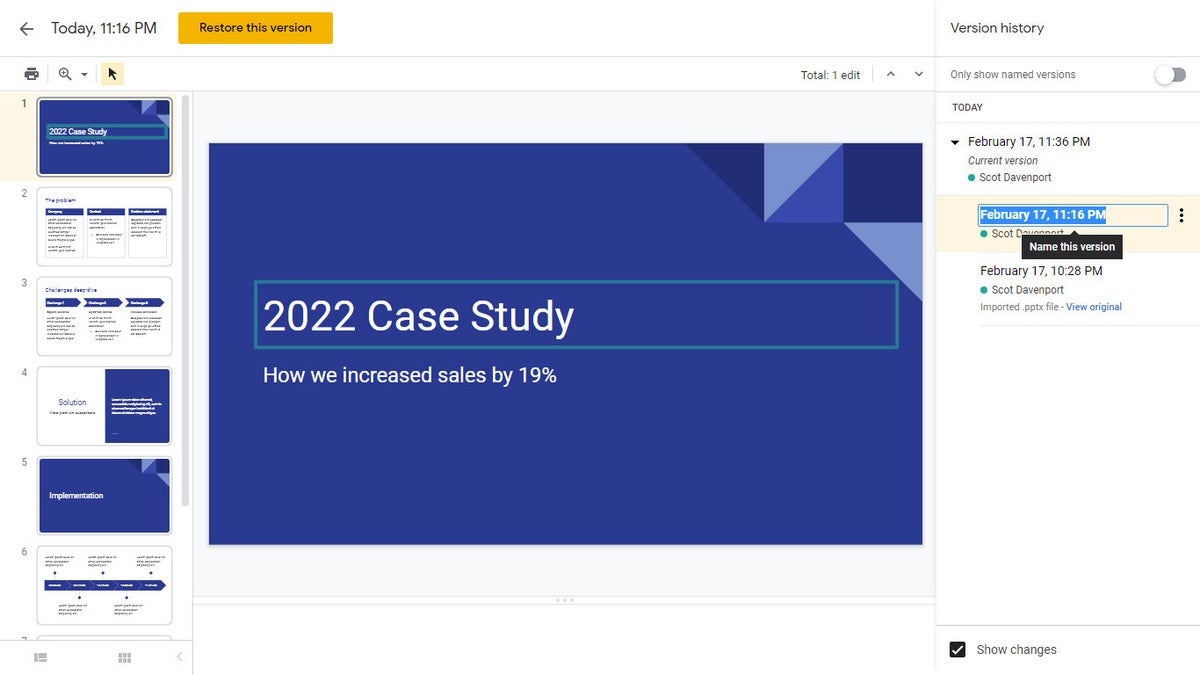
Using Version history to view an earlier version of a presentation. (Click image to enlarge it.)
To view an earlier version of your presentation: Click the date for it in the list. That version of the presentation will then appear in the main window.
To restore an earlier version so it replaces your current presentation: With the version you want to restore showing in the main window, click the yellow Restore this version button at the top of the screen. The restored version will then appear at the top of the version history list.
To give an older version a unique name: Click on its date. You’ll be prompted to type in words to replace the date. (The date and time will then appear in smaller size underneath the new name.)
Give a presentation
When it’s time to play your presentation to an audience, Google Slides has two modes: Slideshow and Presenter view. Slideshow mode essentially shows what your audience will see. Presenter view mode provides additional tools for your eyes only that run alongside Slideshow mode.
Slideshow mode: Click the Slideshow button at the upper-right corner of the screen. Google Slides will expand to full-screen view and show the slide that’s currently in the main window. (If you want to start the slideshow from the first slide in your presentation, click the down arrow to the right of the Slideshow button and select Start from beginning .)

The control bar in Slideshow mode lets you click through the slides, turn on auto-play, use a laser pointer effect, and more. (Click image to enlarge it.)
When you move the on-screen pointer to the lower-left corner of your presentation, a control bar appears. You use this to click forward and back through the slides. Clicking the three-dot icon on the control bar opens a menu with other controls, such as starting auto-play and adjusting how quickly it moves from slide to slide.
On this menu, Turn on the laser pointer turns the mouse pointer into a simulated red laser dot. Captions preferences — available only if you’re using a Chrome browser or Chromebook — lets you turn on real-time, automatic transcribing of your words as you say them (English only) and shows them to your audience as on-screen captions. Open speaker notes takes your presentation out of full screen and opens a separate “Presenter view” window, as described below.
Presenter view mode: Click the down arrow to the right of the Slideshow button and select Presenter view . This shows the presentation in your browser window and launches a separate window that assists you while you’re giving your presentation.
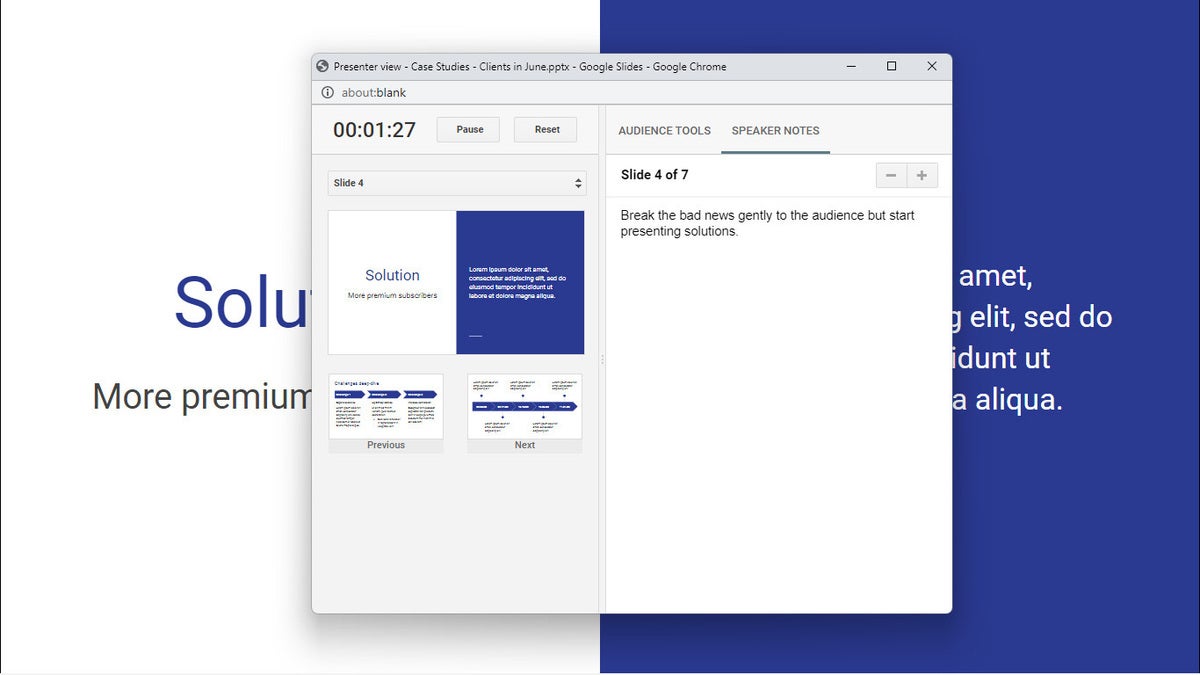
Presenter view lets you (but not your audience) see your speaker notes while presenting. (Click image to enlarge it.)
From the Presenter view window, you can jump to any slide in your presentation, read the speaker notes you wrote for a slide, and control the Q&A feature. There’s also a timer that you can set to remind yourself how much time you’re spending showing a slide — or the entire presentation — to your audience.
Click the AUDIENCE TOOLS tab to use the Q&A feature, which lets you take questions from your audience. To open questions for a slideshow, click the Start new button. A web link appears at the top of your presentation. An audience member watching your presentation on their computer, phone, or tablet can click/tap that link, which will take them to a page where they can type a question for you. You’ll see the question in your Presenter view window, and you can choose whether to show their question to the rest of your audience during the presentation. To close questions for a presentation, turn the switch from ON to OFF .
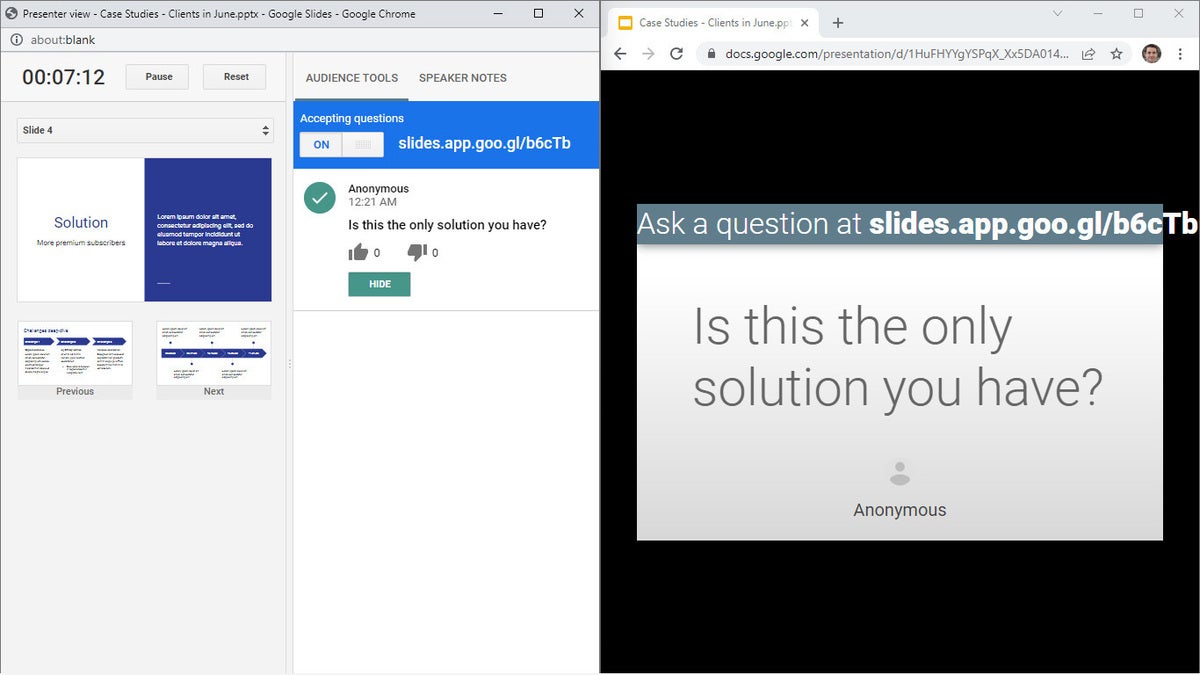
Audience members can submit questions from their devices, and the presenter can decide whether to display them as part of the slideshow. (Click image to enlarge it.)
Present in Google Meet
Need to give a presentation during a Google Meet video meeting? As long as you’re using a Chromium-based browser (Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Opera, etc.), it’s easy: Toward the upper right of the Google Slides page, click the Google Meet icon. From the panel that opens, select a meeting that’s scheduled on your Google calendar today, start a new meeting, or type/paste in the web link or code that you have for another meeting.
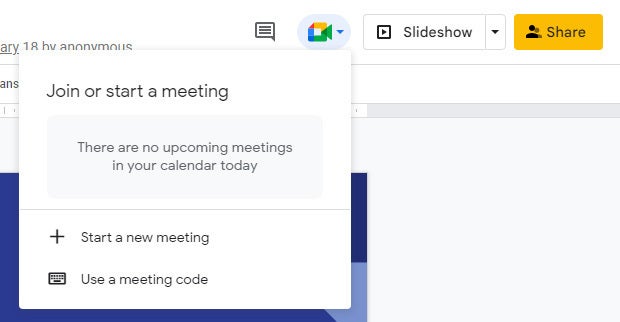
Click the Meet icon to get started presenting to a video meeting.
If you start a new meeting, a sidebar for the meeting will open on the right. At the bottom of the sidebar, click the Present now icon (a box with an up arrow). On the panel that appears, select your presentation and click the Share button, and you’ll be presenting to the meeting.
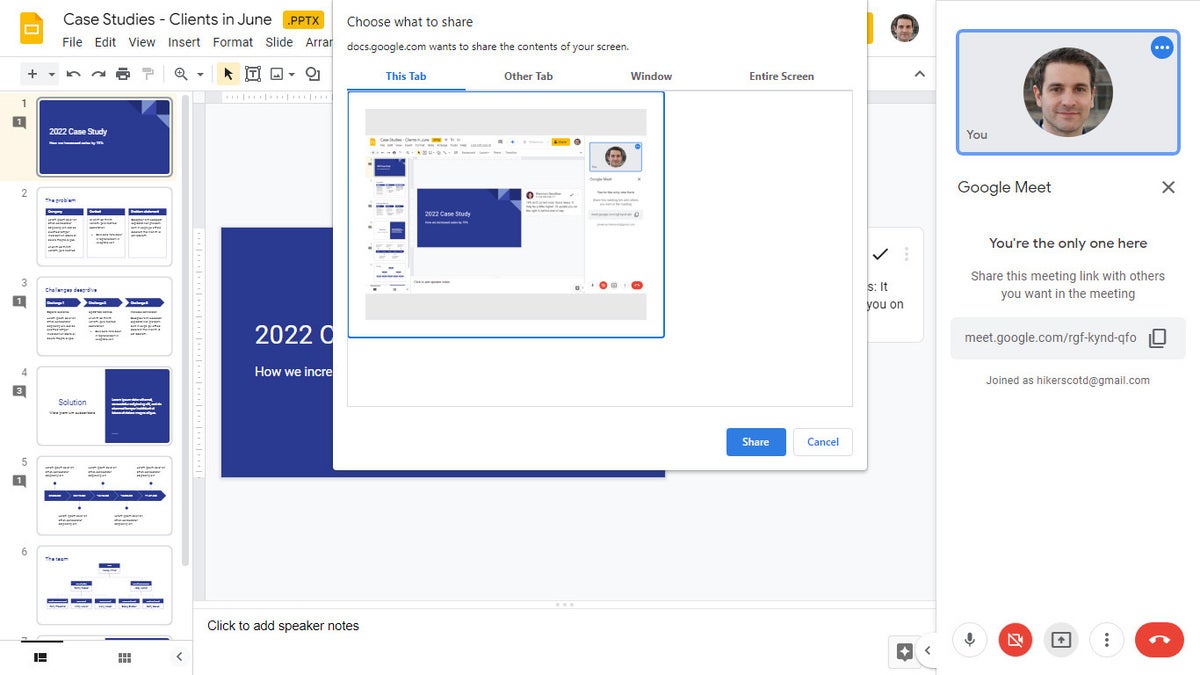
Choose which tab or window you want to share and click the Share button. (Click image to enlarge it.)
If you join a scheduled meeting, you have two choices: “Join the call” and “Just present this tab.” If you click Join the call , a sidebar for the meeting will open on the right. Follow the same steps as above to present to the meeting. If you click Just present this tab , you’ll go directly to the panel where you select your presentation and click Share , but you won’t have a sidebar where you can follow the main meeting.
To stop sharing your presentation to the meeting, click the Stop sharing button at the top left of your browser window.
For more details about using Google Meet, see our Google Meet cheat sheet .
Download and export a presentation
Google Slides lets you download presentations for use offline. On the top menu, select File > Download and choose a file format. You can save your presentation to your PC as a PowerPoint (.pptx) file or in other formats such as PDF, or as JPG or PNG for an individual slide.
5 tips for working with Google Slides
Now that you’re comfortable working in Google Slides, try these intermediate tips.
Use the Google Slides mobile app
With the exception of the “Version history” tool, the Google Slides app for Android , iPhone , and iPad has many of the same features described in this guide.
When you have a slideshow open, the toolbar at the top of the screen lets you take a variety of actions:
- To present your slides on your phone or tablet, on a Chromecast device, or in a Google Meet meeting, tap the triangle icon.
- To share your presentation with other people, the headshot silhouette. (See “How to share from the Google Drive, Docs, Sheets, and Slides mobile apps” in our Google Drive cheat sheet .)
- To view all the comments in the presentation, tap the Comments icon (a chat balloon) if you see it in the toolbar, or tap the three-dot icon and select View comments from the menu that appears.
- The three-dot menu also lets you see the presentation’s Q&A history, export it, make it available offline, and more.
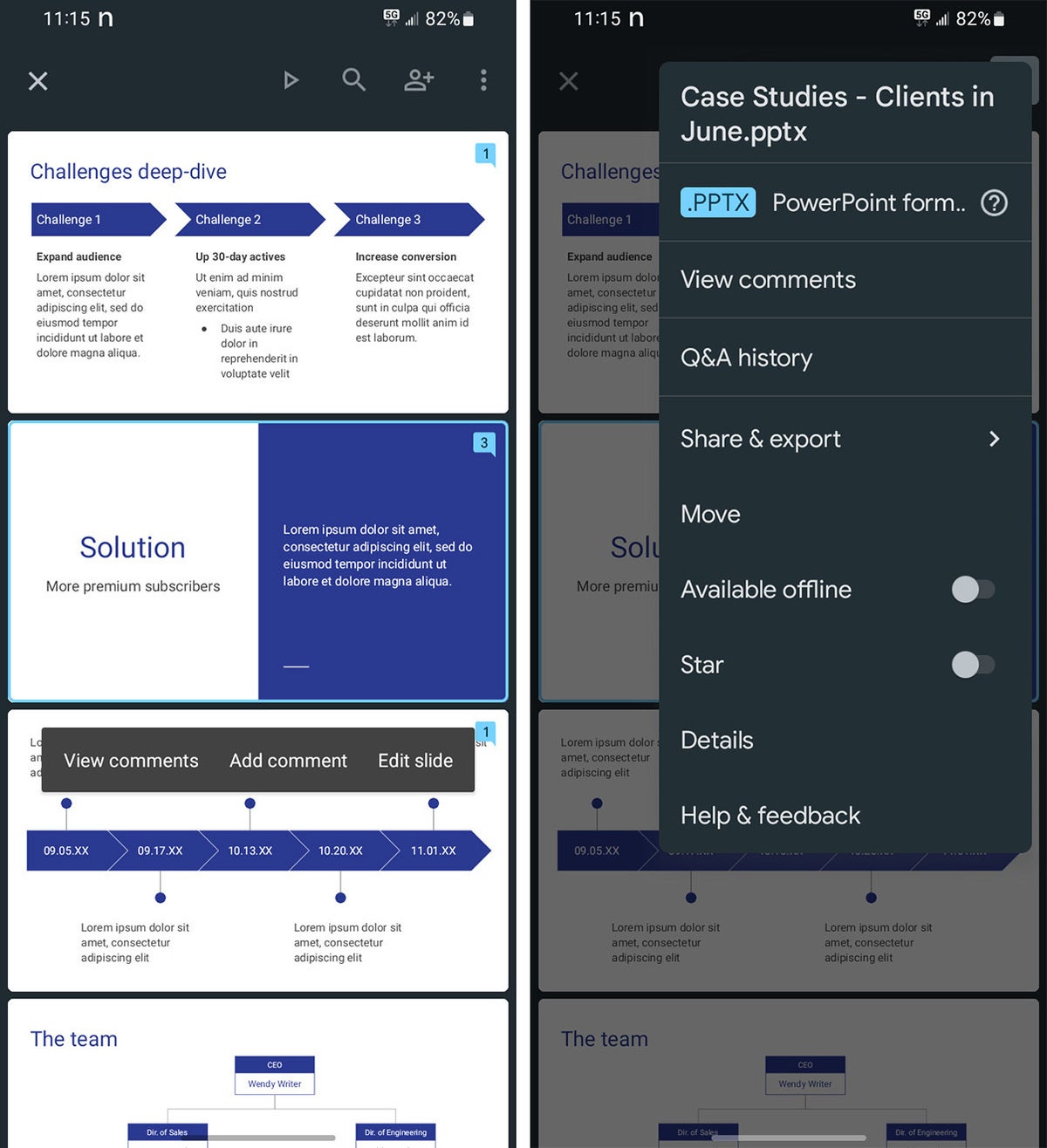
The Google Slides Android app.
To edit or comment on a slide: Tap the slide, and a menu will appear that lets you add or view comments for that slide or edit it. Tap an element on a slide, such as text or an image, and tools to edit that element will appear.
Any changes you make to your presentation in the mobile app are automatically saved and will appear the next time you open it in the Google Slides web app.
Get suggested slide layouts and content
Click the Explore icon at the lower-right corner of the screen. The Explore sidebar will open along the right side. In most cases, you’ll be presented with thumbnails of suggested layouts that Google Slides has automatically customized for the slide that’s open in the main window. Click the one you want, and it will be applied to the slide.
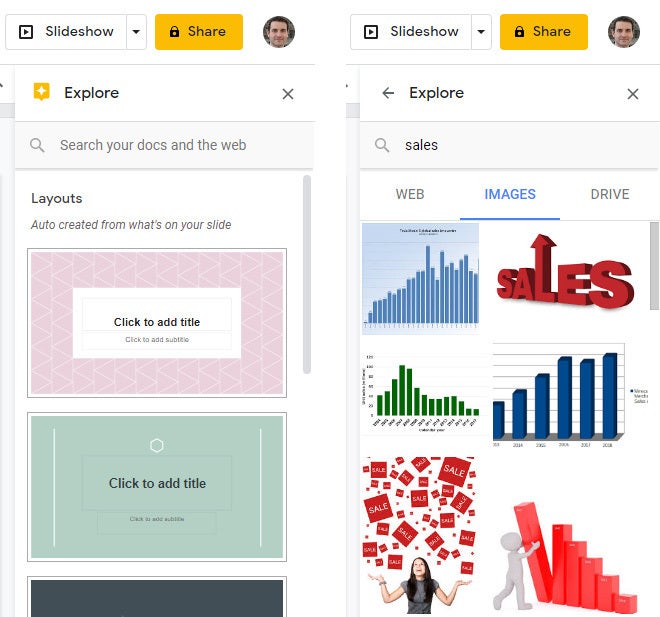
Use the Explore tool to get suggested layouts (left) and search for images (right).
At the top of the Explore sidebar is a search box. You can type in a word or phrase to find related content on the web or in your Google Drive. Search results appear on separate Web, Images, and Drive tabs in the sidebar. Click a web or Drive result to open it in a new browser tab. On the Images tab, click the + icon on the upper-right corner of an image to insert it onto your slide.
Create custom slide layouts to use as templates
You can design your own slide layouts to use as templates in any future presentation. First, open a new, blank presentation as described above. Then:
- On the menu bar over the blank presentation, select View > Theme builder .
- The main window switches to a layout editor. Toward the left you’ll see a column with the heading THEME on top and LAYOUTS just below that. Click the thumbnail of any layout in the LAYOUTS list. It will appear in the main window.
- You can remove objects that are already in any layout. For example, click on a block of text. A frame appears around the text. Without selecting the text itself, move the pointer to ward an edge of the frame, right-click, and select Delete from the menu that opens.
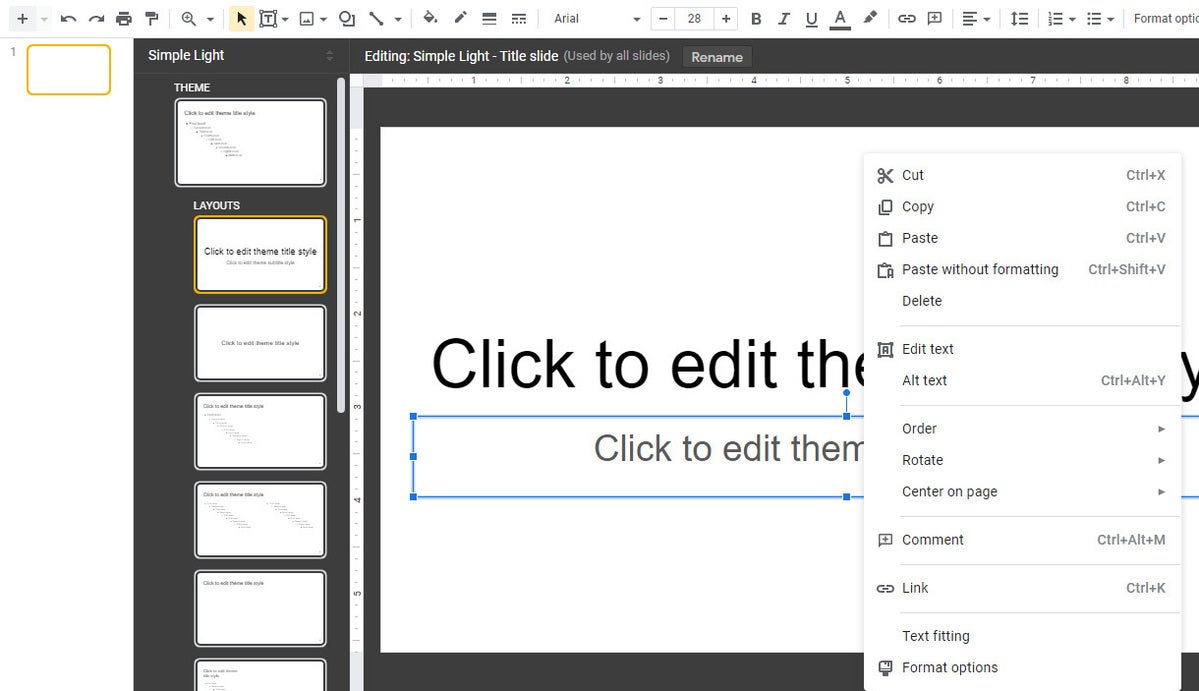
Creating a custom slide layout. (Click image to enlarge it.)
- Using the formatting toolbar above the slide, you can add new objects to the slide, including images, image placeholders, shapes, lines, and blocks for text. (Tip: enter placeholder words inside the text blocks.) When you click on any object, a frame appears around it. Drag and drop the frame to relocate it on the slide, or drag its edges to change its shape or size. You can also add or change the border and background colors for any object on the slide and/or change the background color for the whole slide.
- When you’re finished designing your layout, click the Rename button above the slide and give the layout a unique name.
- If you want to create another custom layout, click on the thumbnail of another layout under the column LAYOUTS and repeat the above steps starting from #3.
- When you are finished custom-designing all your layouts, click the X toward the upper-right of the slide layout in the main window.
- Along the top of the screen, click anywhere inside Untitled presentation and start typing. Tip: Use a name that indicates this is a template (e.g., “Annual Budget Presentation – Template”).
In the future, you can make new presentations starting from this template, and your custom slide layouts will be available.
- Open the template presentation you created in the steps above. On the menu bar, click File > Make a copy > Entire presentation . On the panel that opens, type in a name for the new presentation you want to create and click the Make a copy button. Google Slides will open this new presentation in a new browser tab.
- On the toolbar above the first slide of your new presentation, click Layout . From the panel of thumbnails that opens, select one of the layouts that you created. It will then be applied to the slide in the main window.
Collaborate on a presentation in Google Chat
An alternative way to collaborate on a presentation is to share it in Google Chat. Other people in your chat can add comments and help make changes to your presentation.
Start in Google Chat . To the left of the box where you type in your chat messages, click the + icon and select Drive file from the menu that opens. A panel will open over the screen listing the files in your Google Drive. Find and click your presentation to highlight it, then click INSERT on the lower-right corner.
You’ll be taken back to the chat message box. Click the blue right-pointing arrow to the right of the box, and a panel will open over the screen designating permissions for the shared presentation. By default, permissions are set to Comment. To change this, click Comment and select View or Edit . You can also allow the people in the chat to share a web link to your presentation with others outside of the chat by selecting Turn link sharing on .
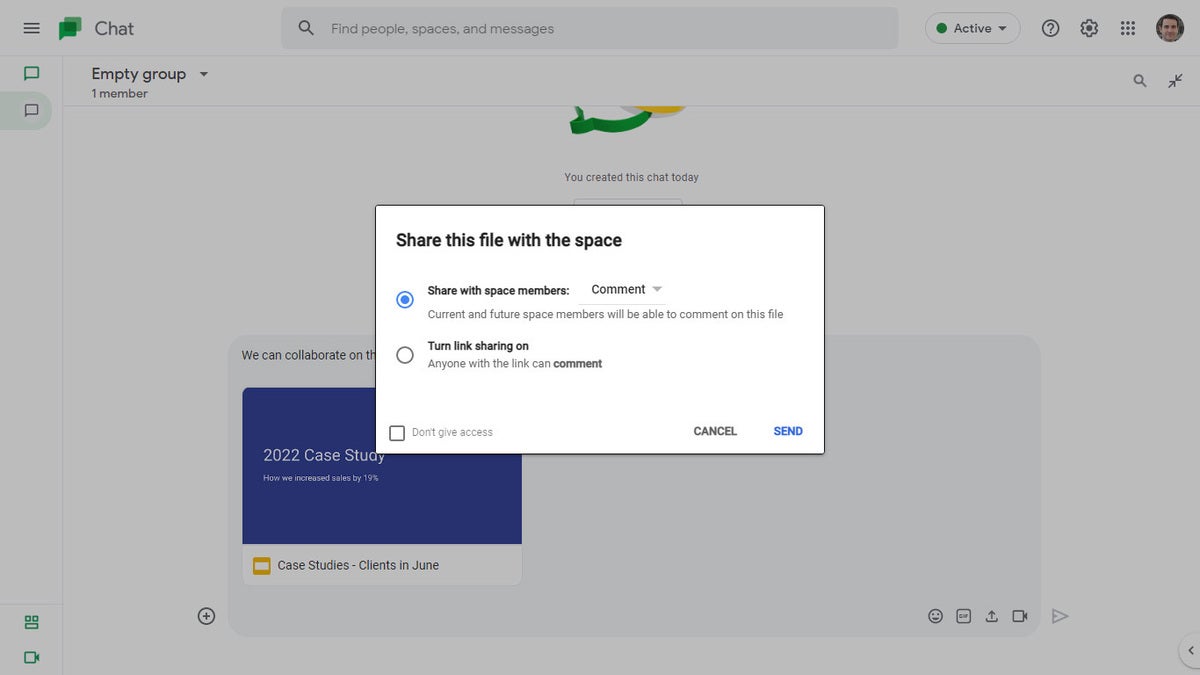
You can share a presentation to individual or group chats in Google Chats. (Click image to enlarge it.)
After you’ve set the permissions, click SEND , and your message will appear in the chat stream with a large thumbnail of your presentation. To open a presentation in the chat, click the thumbnail. The presentation will open inside a large window that’s laid out alongside the right of the chat stream.
This is actually Google Slides running inside the chat window with your presentation loaded in it. Thus, most of the Slides commenting and editing tools are available for you and others in the chat to use on your presentation (if you granted them permission to comment or edit). The user interface is the same, except there’s no menu bar.
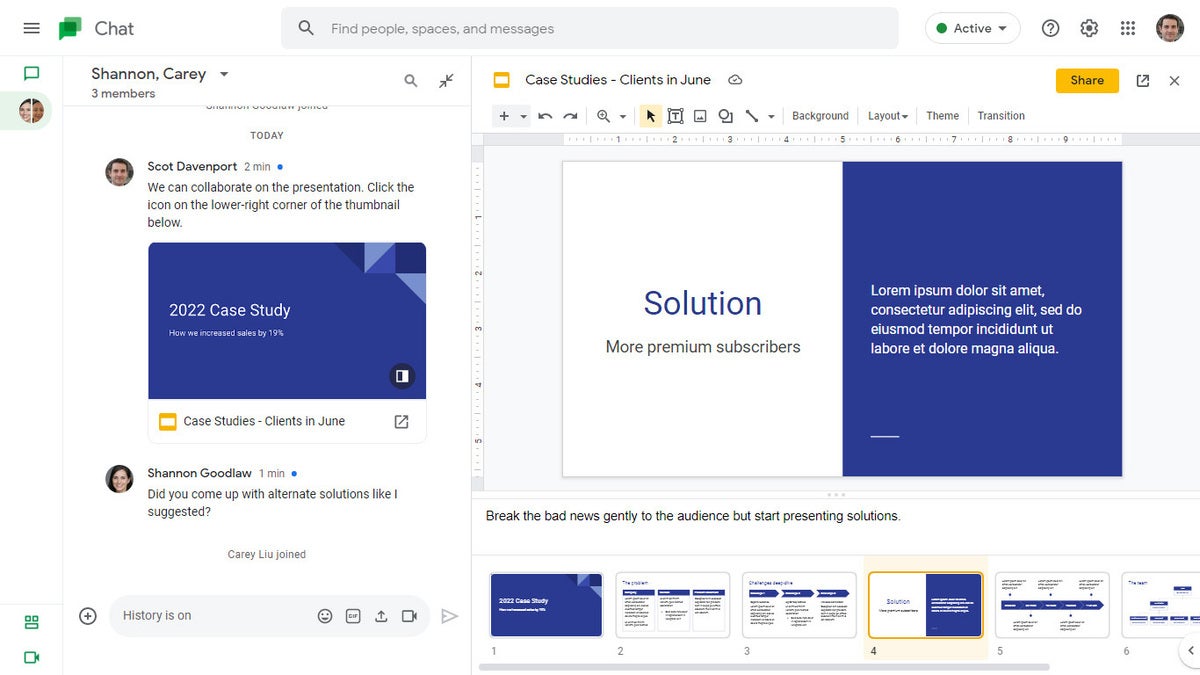
Collaborating on a presentation from within a Google Chat. (Click image to enlarge it.)
Use keyboard shortcuts
Save time in Slides by using keyboard shortcuts for common tasks. Below are some of the most useful to know. For more, select Help > Keyboard shortcuts from the top menu when you have a spreadsheet open or press Ctrl + / (Windows, Chrome OS) or ⌘ + / (macOS).
Handy Google Slides keyboard shortcuts
This story was originally published in September 2019 and updated in August 2022.
Related content
Is ai driving tech layoffs, 100 billion reasons apple is putting up a fight, the best ways to share files between windows pcs, just how good is ai-assisted code generation, from our editors straight to your inbox.
Howard Wen ( www.howardwen.com ) is a longtime contributor to Computerworld . He specializes in explainer guides, how-tos, and reviews of office applications and productivity tools.
More from this author
Google docs cheat sheet: how to get started, 8 highly useful slack bots for teams, microsoft onedrive cheat sheet, 9 chrome extensions that supercharge google drive, most popular authors.

- Howard Wen Contributing Writer
Show me more
Windows 11 insider previews: what’s in the latest build.

Tech layoffs in 2024: A timeline

Microsoft unbundles Teams and Office globally to avoid antitrust fight

Sam Bankman-Fried gets 25 years in prison

How to combat social media addiction

How social media companies are addicting adolescents


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Lecture 13: Introduction to Networking Networking is simply communicating between two computers connected on a network. You can actually set up a network connection on a single computer, as well. A network requires one computer to act as the server , waiting patiently for an incoming connection from another computer, the client .
To learn the fundamentals of computer networks 2. Learn how the Internet works • What really happens when you "browse the web"? • TCP/IP, DNS, HTTP, NAT, VPNs, 802.11 etc. 3. Understand why the internet is designed how it is designed • SDN, Load Balancers, Architectures.
87 Horde groupware is an open source web application. Information Technology Center. Download ppt "INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKS". Computer Networks Two or more computers or communications devices connected by transmission media and channels and guided by a set of rules for communication purposes that allow users to communicate with each ...
A network can be defined as two or more computers connected together in such a way that they can share resources. The purpose of a network is to share resources. resource may be: A file. A folder. A printer. A disk drive Or just about anything else that exists on a computer.
Inncoent Unwujo. Computer networks are a system of interconnected computers for the purpose of sharing digital information. Two kinds of peers' relationship are usually considered for reputation management in P2P network. One of them is direct trust relationship that the reputation is got with two peers interacting directly; the other is ...
Welcome to the website for An Introduction to Computer Networks, a free and open general-purpose computer-networking textbook, complete with diagrams and exercises.It covers the LAN, internetworking and transport layers, focusing primarily on TCP/IP. Particular attention is paid to congestion; other special topics include queuing, real-time traffic, network management, security, mininet and ...
An Introduction to Computer Networksis a free and open general-purpose computer-networking textbook, complete with diagrams and exercises.It covers the LAN, internetworking and transport layers, focusing primarily on TCP/IP. Particular attention is paid to congestion; other special topics include queuing, real-time traffic, network management, security and the ns simulator.
380 likes | 488 Views. Introduction to Computer Network. Dr. Rania R Ziedan. Agenda. Introduction Network types Network topology Network connection models OSI model. Computer network. A collection of computing devices that are connected in various ways in order to communicate and share resources or files. Download Presentation.
Computer Network falls under these broad Categories: ... Presentation Layer; Application Layer; Protocol. A protocol is a set of rules or algorithms which define the way how two entities can communicate across the network and there exists a different protocol defined at each layer of the OSI model. A few such protocols are TCP, IP, UDP, ARP ...
Introduction To Computer Networking. A computer network is a set of computers connected together for the purpose of sharing resources. The most common resource shared today is connection to the Internet. Other shared resources can include a printer or a file server.
Introduction to Computer Networking. Definition. Network Any interconnected group or system. Multiple computers and other devices connected together to share information. (nodes). History. 1957 USSR launches Sputnik, first artificial earth satellite 1958. Download Presentation. network.
These presentation templates are suitable for presentations related to computer networks. They can be used by IT professionals, network administrators, or anyone looking to explain or discuss topics such as network architecture, cybersecurity, or data communication. SlidesCarnival templates have all the elements you need to effectively ...
Introduction to Computer Networks Computer Networks • Computer network connects two or more autonomous computers. • The computers can be geographically located anywhere. Introduction to Computer Networks Network Topology • The network topology defines the way in which computers, printers, and other devices are connected.
Download your presentation as a PowerPoint template or use it online as a Google Slides theme. 100% free, no registration or download limits. Get these network templates to create dynamic presentations that showcase the interconnectedness of your ideas. No Download Limits Free for Any Use No Signups.
Download our Computer-related Google Slides themes and PowerPoint templates and create outstanding presentations Free Easy to edit Professional ... Use these Google Slides themes or download our PPT files for PowerPoint or Keynote to give a presentation about a Computer-related topic, including Information Technology. Filter by. Filters ...
They describe the physical and logical arrangement of the network nodes. • The physical topology of a network refers to the configuration of cables, computers, and other peripherals. Bus Topology • All the nodes (file server, workstations, and peripherals) on a bus topology are connected by one single cable. • A bus topology consists of a ...
Open the template presentation you created in the steps above. On the menu bar, click File > Make a copy > Entire presentation. On the panel that opens, type in a name for the new presentation you ...