- YouTube Thumbnail Downloader
- Image Compressor
- QR Code Generator
- Environment
- Submit An Article
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions

What is Insulation Material and its Uses
- by Refresh Science
- January 15, 2022 January 15, 2022
Many people make the mistake of not taking insulation seriously. They think that they only need the insulation layer to work just fine. They severely underestimate the materials and maintenance cost.
Several insulation materials are essential for a building . They are thermal and sound. And if you plan to have a studio, you should look for acoustic insulation.
What is insulation materials?
In short, it is the material that works as a buffer inside the walls. It acts as extra protection for your house from the temperature outside. These materials can help you stay warm in the winter and cool during summer.

Benefits of insulation
Having insulation can provide several benefits. Here are to name a few.
- Controlling the temperature inside the house
You may still need to install a heater and air conditioner for your house. But in general, your place will stay warm enough to keep you comfortable.
- Fire-proofing your house
Some insulators also have fire-retardant qualities. But keep in mind that it doesn’t mean it’s total fireproof. It only means that your walls and roof will last a little longer during the fire.
- Keeping the maintenance cost low
Having a good insulator means you don’t have to spend a lot of money on the heater and air conditioners. You can save up to 75% on maintenance costs for one year.
- Adding the house value
You can have a higher ROI value by installing the right insulation material. On average, the initial cost from the installation will return within six months to two years.
Which is the example of insulating material?
Many materials can work as insulation. However, you still need to know which materials can give you the best result for the price. Here are several insulation materials that you may have encountered.
- Polyurethane Foam
- Mineral Wool
- Foam boards
- Polystyrene (EPS)
What is the most common insulating material?
There are some materials that you can find in any building supply store. As some of them are affordable and you can install them yourself.
- polystyrene
- Mineral wool
Download Insulation Materials PowerPoint Presentation:
What are the 4 main types of insulation used in homes.
Depending on how big a house is, there are various types of insulation that you can choose. However, four main types are popular, especially in a residential area.
- Rigid foam or fiber
- Sprayed foam
- Structural Insulation Panels
Several insulation materials are applicable through multiple types. For example, fiberglass and mineral wool. You can install them using the blanket type or a rigid fiber type.
Please remember that some types require a professional HVAC to do the installation. As it’s common to wear protective gear when installing an insulation layer.
What are thermal insulation materials?
Thermal insulation works to control the temperature inside the room. As you know, 25% of the heat goes inside your house through the roof, and 15% is from the walls.
These materials can block most of the heat from getting inside the house. In general, most insulation materials can do this. But the most affordable ones are fiberglass and Polystyrene foam (EPS).
What are sound insulation materials?
Unlike heat, sound requires a different type of insulation. With heat, it is only a matter of transferring the energy to a comfortable level. But sound requires a complete block of sound.
Most common sound insulations are great for soundproofing. Depending on how much noise cancellation you need, you can choose from the options below.
- Mass loaded vinyl
- Soundproof sheetrock
- Green glue vibration dampening compound

What are acoustic insulation materials?
One thing to keep in mind is the difference between soundproofing and acoustic insulation. People often use both terms interchangeably when they refer to different usage. Here are some examples.
- Foam panels
- acoustical panels
As you can see, they are different from the sound insulation ones. That is because these materials only absorb instead of blocking the sound. Thus it has a different effect in the room.
What insulation material is most efficient?
So far, the most efficient insulation material is the Pyrogel XT. This industrial insulation works with less than 80% thickness of other materials. To illustrate, people usually have to install 1-inch thick fiberglass as insulation. With Pyrogel XT, they only need to do 0.5-0.2 inches.
Is Copper an insulating material?
Copper is a conductor and not an insulator. It transfers heat and electricity throughout the material. That is why you see copper as the main material for cables and other wiring products.
What is the best insulator?
The best insulator is the one that can work the best within your budget. But it doesn’t mean that you can trim some edges by cutting down the insulation budget.
This is the best insulator that money can buy. It can hold up to 2000 degrees Fahrenheit. And even essential to NASA spaceships.
This gel can be difficult to attain, but it’s very effective and efficient. It’s great for large buildings since it can cover a lot of space for a small amount.
This insulation is lightweight and fire-retardant. It uses non-CFC gas as a blowing agent to fill the space. This material works as a sound insulator as well. However, it can be expensive to have and install.
Eco-friendly and fireproof. This natural material is one of the favorite insulators to many. However, it can be difficult to apply on an uneven surface.
This is the most popular option since it’s affordable, eco-friendly, fire-retardant, and easy to work with. Many people often choose to install fiberglass insulation by themselves.
Thermal insulation materials for buildings
A larger building requires a different type of insulation from a house. It requires a different technique, and perhaps a different set of materials as well.
However, it also needs to comply with the regulation on the climate zone. You need to check if the location requires extra or specific insulation.
Insulation covers a wide array of options. Keep in mind that a residential building has different needs than a larger commercial one. Therefore, it needs different insulation to install.
And if you’re looking to build a studio in the house, you can start looking for which acoustic insulation you want to add to the room.

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
INSULATING MATERIALS Presentation by : Barjinder Singh
Published by Louis Naish Modified over 10 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "INSULATING MATERIALS Presentation by : Barjinder Singh"— Presentation transcript:

Electricity Chapter 13.

Unit 10 - Electricity.

IES Mariano José de Larra - Technologies UNIT 4

Understanding Thermoset Plastic Materials

Chapter 9 Capacitors.

UNDERGROUND CABLES.

REFRIGERATION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of removing heat from a substance under controlled conditions and reducing and maintaining the.

Inspection & Preventive maintenance of breakers
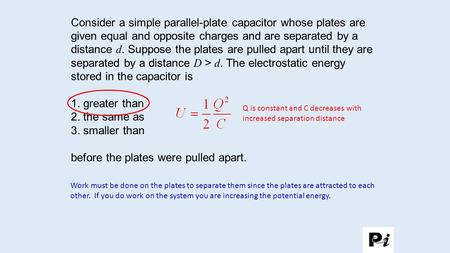
before the plates were pulled apart.

Chapter 15 Capacitance and RC Circuits © Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc.Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Objectives Define capacitance.
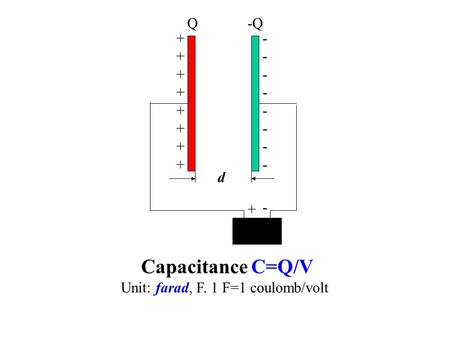
d + - Q-Q Capacitance C=Q/V Unit: farad, F. 1 F=1 coulomb/volt.

Why use plastics Plastic are easily formed materials. The advantage to the manufacturer is that plastic products can be mass- produced and require less.

Physical Science Ch.5 State of Matter
Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. Boylestad

LIQUIDS AS INSULATORS Liquid dielectrics are used mainly as impregnants in high voltage cables and capacitors, and for filling up of transformers, circuit.

Integrated Science I. Electrical conductors – a material that allows electrons to flow easily through it Ex) gold, silver, copper, etc. Electrical insulators.

CHAPTER 9 Electrical Design of Overhead Lines

CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS.

BASIC CONSIDERATIONS IN DESIGN The aim of the design is to completely obtain the dimensions of all the parts of the machine to furnish the data to the.

Underground Cables Chapter 11 V K MEHTA.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Join TheConstructor to ask questions, answer questions, write articles, and connect with other people. When you join you get additional benefits.
Confirm Password *
First Name *
Last Name *
Country Select a country… Åland Islands Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Anguilla Antarctica Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belau Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bolivia Bonaire, Saint Eustatius and Saba Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Bouvet Island Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory British Virgin Islands Brunei Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands Colombia Comoros Congo (Brazzaville) Congo (Kinshasa) Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba CuraÇao Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Falkland Islands Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia French Southern Territories Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guatemala Guernsey Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Heard Island and McDonald Islands Honduras Hong Kong Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Isle of Man Israel Italy Ivory Coast Jamaica Japan Jersey Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macao S.A.R., China Macedonia Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island North Korea Norway Oman Pakistan Palestinian Territory Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Pitcairn Poland Portugal Qatar Republic of Ireland Reunion Romania Russia Rwanda São Tomé and Príncipe Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin (Dutch part) Saint Martin (French part) Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Georgia/Sandwich Islands South Korea South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Svalbard and Jan Mayen Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Syria Taiwan Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom (UK) United States (US) Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Vatican Venezuela Vietnam Wallis and Futuna Western Sahara Western Samoa Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe
By registering, you agree to the Terms of Service and Privacy Policy . *
Log in to TheConstructor to ask questions, answer people’s questions, write articles & connect with other people. When you join you get additional benefits.
Join for free or log in to continue reading...
Username or email *
Forgot Password
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive a link and will create a new password via email.
Sorry, you do not have permission to ask a question, You must log in to ask a question. Join now!

The Constructor
Materials and methods of thermal insulation of buildings.
Do you need to remove the ads? Join now!
🕑 Reading time: 1 minute
What is Thermal Insulation of Buildings?

- Slab or block insulation
- Blanket insulation
- Loose fill insulation
- Bat insulating materials
- Insulating boards
- Reflective sheet materials
- Lightweight materials
1. Slab or Block Insulation

2. Blanket Insulation

3. Loose Fill Insulation
4. bat insulating materials.

5. Insulating Boards

6. Reflective Sheet Materials

7. Lightweight Materials
Other general methods of building thermal insulation.
- By providing roof shading
- By proper height of ceiling
- Orientation of building
8. By Providing Roof Shading
9. by proper height of ceiling, 10. orientation of building.
Sadanandam Anupoju
Related posts.

What is Substructure and Superstructure in Building Construction?

Penetration Value of Bitumen -Determination for Road Construction
CHAPTER 5. APPLICATIONS OF INSULATING MATERIAL
Jan 05, 2020
450 likes | 1.25k Views
CHAPTER 5. APPLICATIONS OF INSULATING MATERIAL. Temperature Classification for Insulating Materials Application of Insulating Materials in electrical apparatus: In Power Transformer In Rotating Machines In Circuit Breaker In Power Capacitors
Share Presentation
- high voltage
- organic materials
- high dielectric
- organic materials class
- gas insulated power transformers

Presentation Transcript
CHAPTER 5. APPLICATIONS OF INSULATING MATERIAL • Temperature Classification for Insulating Materials • Application of Insulating Materials in electrical apparatus: • In Power Transformer • In Rotating Machines • In Circuit Breaker • In Power Capacitors • In High Voltage bushing • In Small Machines
There are four principal areas where insulation must be applied • Between coils and earth (phase to earth) • Between coils of different phases (phase to phase) • Between turn (inter-turn), and • Between the coils of the same phase (inter coil)
Insulating material must be able to withstand electrical stresses, in addition to it should be able to withstand certain other stress namely during manufacture, storage and operation. • The performance of the insulation depends on its operating temperature. The higher temperature, the higher will be the rate of its chemical deterioration. • The insulating materials are grouped into different classes with temperature limit : • - Organic materials: Class O : 90 0C and Class A : 105 0C • - Inorganic materials :Class B : 130 0C ; • Class C : No Specific Limit
The insulating materials are grouped into different classes with temperature limit : - Organic materials: Class O : 90 0C and Class A : 105 0C - Inorganic materials : Class B : 130 0C ; Class C : No Specific Limit
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) Class Y (Paper, cotton, Silk,natural rubber,etc) : 90 0C Class A ( Same class Y but impregnated) : 105 0c Class E (Polyethlene terephthalate) : 120 0C Class B (Mica and Fiberglass) : 130 0C Class F ( same class B but with alkyd and epoxy based resin) : 155 0C Class H (like class B with silicone rubber, polymide film) : 180 0C Class C (As class B but with non organic binder, teflon, and high temperature polymers) : above 180 0C
APPLICATIONS IN POWER TRANSFORMERS • The Transformer insulation is divided into: • a). Conductor or turn to turn insulation; • using directly organic enamel on conductor for smaller rating. • Using paper or glass type wrapped on the rectangular conductors. • b). Coil to coil insulation, • Kraft paper is used in smaller transformer • Pressboard, glass fabric, or porcelain are used in the case of higher rating transformer.
c).Low voltage coil to earth insulation, Normally consist of solid tubes combined with liquid or gas filled spaces. d). Low voltage coil to low voltage coil insulation, Generally of the insulation system used in oil-filled transformers consist of oil impregnated pressboard. e). High voltage coil to ground insulation, Same at c.
The winding Insulation is normally made of paper. Cellulose board is also used as internal insulation in liquid-filled transformers. Cellulose insulation is impregnable with the insulating fluid of transformers.
Conductor insulations is usually paper, in the form pressboard. Insulating board is made of wood or mixture of wood and cotton. Cast resin also used as insulating system at lower voltage rating. Higher temperature systems, employ synthetic fluid Gas Insulated Power Transformers use sheet aluminum conductors for windings, a polymer film for turn-turn insulation.
Insulation of Dry type transformers is now using prepress (manufactured using the following baking materials: glass fibres, Nomex, Aramid paper etc.
APPLICATIONS IN ROTATING MACHINES Usually insulation has been used for machines are mica. Mica available in the form of very thin splitting. The selection of the right material depends on the power rating and the conditions under which it operates. Polyester film with or without impregnation being used for slot insulation. A Particularly important of the machines are the insulation of rotors and stators. The main insulation of the stators have always been mica based. For the support between the winding bars, slots and the core lamination used glass fiber reinforced epoxy.
APPLICATIONS IN CIRCUIT BREAKERS Low voltage breakers use synthetic resin mouldings to carry the metallic part. For higher temperature ceramic parts are used. Medium and High voltage, nowadays using SF6 Gas Medium voltage use vacuum as insulating medium. Gas Mixtures CB SF6 gas causes environmental effect and expensive Several gas mixture such SF6 / N2 has dielectric strength, is 80% of pure SF6 but the short circuit rating is normally lower (reduce to 40 kA from 50 kA)
Table The Various Insulating MaterialFor High Voltage Switchgear • Epoxy Resins Low pressure castings for bushings, Switchgear, bus-bars, instruments transformer. • Epoxy Resins bonded For components such as arc control devices, CB • glassfibre • Poly ester resins Insulating lever for CB and phase barrier plate in switch board. • Porcelain Insulators and bushings of power transformer • Sysnthetic resin bonded Bushings, arc chambers, etc • paper • Nylon Injection mouldings for arc control devoces in CB • Silicone rubber Filling for moulded joint boxes in SF6 insulated CB
APPLICATIONS IN CABLES The physical properties required for wire and cable insulation depend on the type of application. have good elongation, tensile strength and toughness, so that will withstand handling during installation and service Have a low dielectric constant and power factor but high dielectric strength and insulation resistance. Have excellent resistance to ageing at high temperature Have very low water absorption. Not become stiff and brittle when operate at low temperature
The main type of insulations used in the cable industries are paper, rubber, plastic and compressed gas. Paper insulated lead sheathed cables are still used because of the reliability, high dielectric strength, low dielectric loss, and long life. Low and medium voltage (up to 3.3 kv), polyvinylchloride (PVC), Polyethylene and cross-linked Polyethylene (XLPE) is most used. PVC is not suitable for high voltage because High dielectric constant and high loss Polyethylene has low dielectric constant and low loss but high dielectric strength. The best material for high voltage and high temperature is teflon (PTFE) which can be employed up to 250 0C
PVC INSULATED CABLES
APPLICATION IN POWER CAPACITOR • Normally made using impregnated paper dielectric. • Made of several layers of insulation paper of adequate thickness and • aluminum foil of 6 microns thickness as electrodes interleaved and • wound. • Properties required for the insulation paper for capacitor applications • are high dielectric, low dielectric strength, low dielectric loss, high • dielectric constant, uniform thickness, and minimum conducting • particles. • The impregnates for power capacitors should have high dielectric • Strength, high dielectric constant, good chemical and thermal • stability and adequate viscosity for efficient conduction heat.
The Concept of The Dielectric in paper and all paper film In Capacitor
APPLICATIONS IN FRACTIONAL HORSE POWER MOTORS Small Generator : The insulation system must guarantee reliability, combined with good processing capability, mechanical strength an tolerance to severe short thermal stress while in operation. Kind of application the following materials have been found to have excellent insulation properties, viz. presspaper reels, NMN multilayers (made of nomex and polyester film) as well as saturated DMD (made from non-woven polyester and polyester film). Small size motors : Kinds of Polymers have been developed and are beeing widely used as insulating materials.
- More by User

SMART MATERIAL APPLICATIONS
212 views • 12 slides

Your Electro-Mechanical Insulating Material Specialist
Your Electro-Mechanical Insulating Material Specialist. Welcome to Consulation Supplies, specialists in the import, manufacture and distribution of electro-mechanical insulating materials. We stock, supply and distribute a wide range of insulating materials for the following
228 views • 6 slides

Chapter 5: Network Applications
Chapter 5: Network Applications. Categories of Net Applications Discovery, Communication, Collaboration Web 2.0 E-Learning and Telecommuting. Net Applications 1: Discovery. Search engines General- or special-purpose Metasearch (aggregator). Discovery (cont.): Portals.
741 views • 15 slides

Chapter 5 Review: Star Material
Chapter 5 Review: Star Material. Take simple review notes in book not copying the entire PPT Will be on Mr. K’s sharepoint site for review and study tonight!. Hydrogen POWer. Engage. Paragraph 2: Chemical reactions involve inputs and outputs (also called products and reactants).
409 views • 29 slides

Chapter 5 Applications of Newton’s Law
Chapter 5 Applications of Newton’s Law. Static friction vs Kinetic friction. Static Friction. Kinetic friction is the friction when the object is moving. Static friction is when it is at rest. Example: Incline.
338 views • 17 slides

Chapter 5 Applications of Newton’s Law. Sec. 5-1 Force Laws. Sec. 5-2 Tension and normal forces. ★. Sec. 5-3 Friction forces. ★. Sec. 5-4 The dynamics of uniform circular motion. Sec. 5-5 Time-dependent force. ★. Sec. 5-6 Noninertial frames and pseudoforces .
634 views • 33 slides

Chapter 5 Authentication Applications Kerberos
Chapter 5 Authentication Applications Kerberos . Kerberos. X.509. How To Secure Network. How do you secure your network and each workstation or server with one tool?. How To Secure Network.
725 views • 56 slides

Ch 5: Star Material – Chapter Overview
Ch 5: Star Material – Chapter Overview. Chapter Goals: Do the amounts of energy produced by chemical and nuclear reactions differ dramatically? What are the similarities and differences between chemical and nuclear reactions?
206 views • 13 slides

Chapter 5 Simple Applications of Macroscopic Thermodynamics
Chapter 5 Simple Applications of Macroscopic Thermodynamics. Preliminary Discussion. Classical, Macroscopic, Thermodynamics Drop the statistical mechanics notation for average quantities. We know that All Variables are Averages Only !
899 views • 33 slides

Chapter 5 Simple Applications of Macroscopic Thermodynamics. Preliminary Discussion. Classical, Macroscopic, Thermodynamics : Drop the statistical mechanics notation for average quantities. We know that all variables are averages only.
301 views • 10 slides

Chapter 5: Hybridisation & applications
Chapter 5: Hybridisation & applications. Hybridisation Southern In situ RFLP micro-array & SNP analysis. Hybridisation. The double-stranded DNA molecule is a very stable structure Strands can be separated by high temperature, high pH (in vitro) or enzymes (in vivo)
549 views • 32 slides

Chapter 5 Internet Security Applications
Chapter 5 Internet Security Applications. 5.0 Internet Access. In a secure remote access system, it must ensure the privacy and integrity of data as it traverses the Internet To achieve this, the system should provide user authentication, data encryption and key management.
600 views • 43 slides

DSCI 3870 Chapter 5 ADVANCED LP APPLICATIONS Additional Reading Material
DSCI 3870 Chapter 5 ADVANCED LP APPLICATIONS Additional Reading Material. Chapter 5 – Advanced LP Applications Additional Reading Material. Revenue Management Portfolio Models and Asset Allocation Game Theory – Part II. Revenue Management. Another LP application is revenue management.
593 views • 49 slides

Material Based on Chapter 5
Material Based on Chapter 5. The Planetary Boundary Layer. The Planetary Boundary Layer. Class Slide. Class Slide. Class Slide. Class Slide. Class Slide. Class Slide. Class Slide. Class Slide. Red = w ’ (t) Blue = q ’ (t). Class Slide. Class Slide. Class Slide. Class Slide.
1.12k views • 98 slides

A Few Applications of Review Material
A Few Applications of Review Material. Budget Constraints Isocosts Utility Functions Production Functions. Deriving the Budget Constraint. A consumer consumes goods X and Y, which have prices P x and P y with income I Expenditures are: P x X + P y Y
207 views • 11 slides

Some applications related to Chapter 11 material:
Some applications related to Chapter 11 material: We will see how the kind of basic science we discussed in Chapter 11 will probably lead to good advances in applied areas such as: 1- Design of efficient solar cell dyes based on charge transfer absorption.
411 views • 30 slides
Chapter 5: Linear Algebra Applications
Chapter 5: Linear Algebra Applications. Homogeneous Linear Equations Non-homogeneous equation Eigen v alue problem. 5.1 Homogeneous linear Equations. N=3; The problem is to solve : There is an obvious solution: But is it the only one?
511 views • 15 slides

Electrical Insulating Material
Polyglass Tape,Heat Resistant Materials,Fire Protection Sleeve, Fiberglass Woven Roving Tape,Resin Impregnated Fiber Glass Banding Tape,Pyrojacket,Banding Tape Provider. For more Details please visit us at : www.vardhmanresiglass.com
269 views • 12 slides

Insulating Paint
Owatrol Dilunett Oil is an effective paint remover to remove paint from wall ceiling. Find here the best insulating paint & patch wall for fast drywall repair.
171 views • 2 slides

INSULATING Materials
INSULATING Materials. Insulator. The Insulator is a material that retards the flow of electricity. There are different insulators used in the electrical and electronic component and assemblies. Some of the insulators are Porcelain, plastic, ceramic, polymer etc.
159 views • 13 slides

Various Applications of Aluminum Cap Material
Because of excellent sealing performance, great corrosion resistance, attractive performance and cheap price, aluminum cap material is widely used for the cap closure of red wine, medicine, cosmetics and beer.
63 views • 5 slides

Acoustic And Heat Insulating Material Manufacturer - Park Non Woven
Buy the best quality Acoustic And Heat Insulating Material from Park Non Woven at the lowest price. Call now. High quality. visit us : https://www.parknonwoven.com/pp-melt-blown-filter-media/
47 views • 4 slides
What is Insulation Material – Types of Insulation – Definition
Insulation materials.
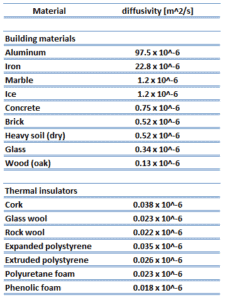
It must be added, thermal insulation is primarily based on the very low thermal conductivity of gases. Gases possess poor thermal conduction properties compared to liquids and solids, and thus makes a good insulation material if they can be trapped (e.g. in a foam-like structure ). Air and other gases are generally good insulators. But the main benefit is in the absence of convection . Therefore, many insulation materials (e.g.polystyrene) function simply by having a large number of gas-filled pockets which prevent large-scale convection . In all types of thermal insulation, evacuation of the air in the void space will further reduce the overall thermal conductivity of the insulator.
Alternation of gas pocket and solid material causes that the heat must be transferred through many interfaces causing rapid decrease in heat transfer coefficient.
It must be noted, heat losses from hotter objects occurs by three mechanisms (either individually or in combination):
- Heat Conduction
- Heat Convection
- Thermal Radiation
So far we have not discussed thermal radiation as a mode of heat losses . Radiation heat transfer is mediated by electromagnetic radiation and therefore it does not require any medium for heat transfer. In fact, energy transfer by radiation is fastest (at the speed of light) and it suffers no attenuation in a vacuum. Any material that has a temperature above absolute zero gives off some radiant energy . Most energy of this type is in the infra-red region of the electromagnetic spectrum although some of it is in the visible region. In order to decrease this type of heat transfer, materials with low emissivity (high reflectivity) should be used. Reflective insulations are usually composed of multilayered, parallel foils of high reflectivity, which are spaced to reflect thermal radiation back to its source. The emissivity , ε , of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in emitting energy as thermal radiation and varies between 0.0 and 1.0. In general, polished metals have very low emissivity and therefore are widely used to reflect radiant energy back to its source as in case of first aid blankets .
Types of Insulation – Categorization of Insulation Materials
For insulation materials, three general categories can be defined. These categories are based on the chemical composition of the base material from which the insulating material is produced.
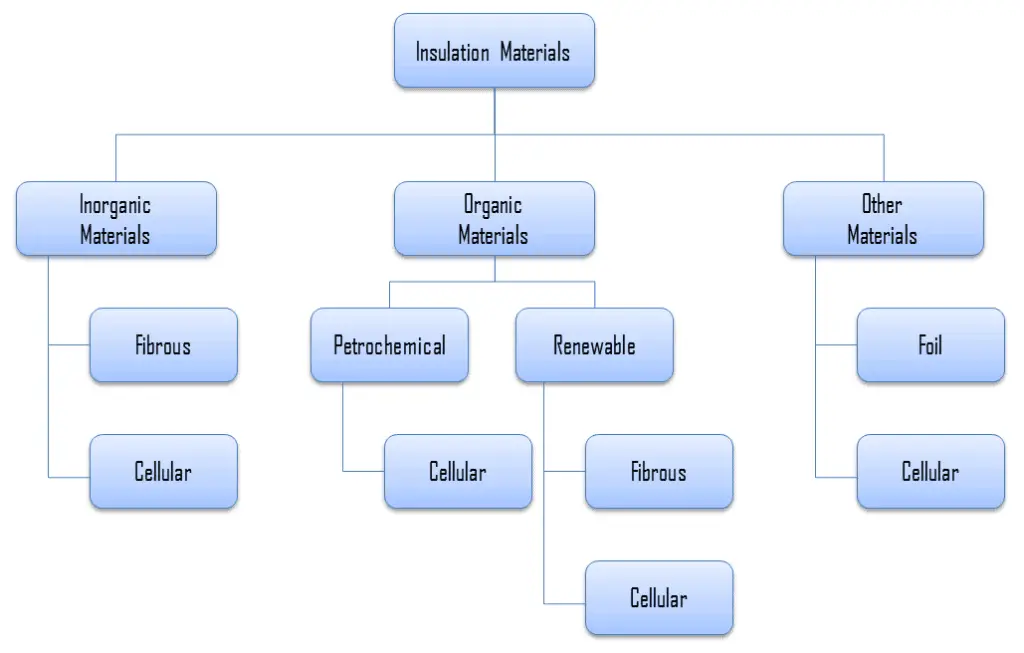
In further reading, there is a brief description of these types of insulation materials.
Inorganic Insulation Materials
As can be seen from the figure, inorganic materials can be classified accordingly:
- Calcium silicate
- Cellular glass
Organic Insulation Materials
The organic insulation materials treated in this section are all derived from a petrochemical or renewable feedstock (bio-based). Almost all of the petrochemical insulation materials are in the form of polymers. As can be see from the figure, all petrochemical insulation materials are cellular. A material is cellular when the structure of the material consists of pores or cells. On the other hand, many plants contain fibres for their strength, therefore almost all the bio-based insulation materials are fibrous (except expanded cork, which is cellular).
Organic insulation materials can be classified accordingly:
- Expanded polystyrene (EPS)
- Extruded polystyrene (XPS)
- Polyurethane (PUR)
- Phenolic foam
- Polyisocyanurate foam (PIR)
- Sheeps wool
- Cotton insulation
Other Insulation Materials
- Cellular Glass
- Vacuum Panels
Example of Insulation – Polystyrene
Generally, polystyrene is a synthetic aromatic polymer made from the monomer styrene, which is derived from benzene and ethylene, both petroleum products. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. Polystyrene is a colorless, transparent thermoplastic, which is commonly used to make foam board or beadboard insulation and a type of loose-fill insulation consisting of small beads of polystyrene. Polystyrene foams are 95-98% air. Polystyrene foams are good thermal insulators and are therefore often used as building insulation materials, such as in insulating concrete forms and structural insulated panel building systems. Expanded (EPS) and extruded polystyrene (XPS) are both made from polystyrene, but EPS is composed of small plastic beads that are fused together and XPS begins as a molten material that is pressed out of a form into sheets. XPS is most commonly used as foam board insulation.

Although both expanded and extruded polystyrene have a closed-cell structure, they are permeable by water molecules and can not be considered a vapor barrier. In expanded polystyrene there are interstitial gaps between the expanded closed-cell pellets that form an open network of channels between the bonded pellets. If the water freezes into ice, it expands and can cause polystyrene pellets to break off from the foam.
Example of Insulation – Vacuum Insulation Panels
Example – Heat Loss through a Wall
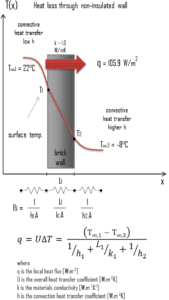
- Calculate the heat flux ( heat loss ) through this non-insulated wall.
- Now assume thermal insulation on the outer side of this wall. Use expanded polystyrene insulation 10 cm thick (L 2 ) with the thermal conductivity of k 2 = 0.03 W/m.K and calculate the heat flux ( heat loss ) through this composite wall.
As was written, many of the heat transfer processes involve composite systems and even involve a combination of both conduction and convection . With these composite systems, it is often convenient to work with an overall heat transfer coefficient , known as a U-factor . The U-factor is defined by an expression analogous to Newton’s law of cooling :

The overall heat transfer coefficient is related to the total thermal resistance and depends on the geometry of the problem.
Assuming one-dimensional heat transfer through the plane wall and disregarding radiation, the overall heat transfer coefficient can be calculated as:
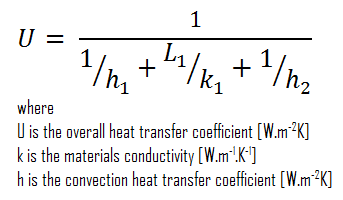
The overall heat transfer coefficient is then:
U = 1 / (1/10 + 0.15/1 + 1/30) = 3.53 W/m 2 K
The heat flux can be then calculated simply as:
q = 3.53 [W/m 2 K] x 30 [K] = 105.9 W/m 2
The total heat loss through this wall will be:
q loss = q . A = 105.9 [W/m 2 ] x 30 [m 2 ] = 3177W
- composite wall with thermal insulation
Assuming one-dimensional heat transfer through the plane composite wall, no thermal contact resistance and disregarding radiation, the overall heat transfer coefficient can be calculated as:
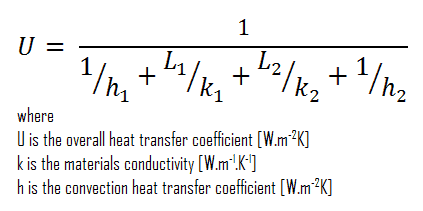
U = 1 / (1/10 + 0.15/1 + 0.1/0.03 + 1/30) = 0.276 W/m 2 K
q = 0.276 [W/m 2 K] x 30 [K] = 8.28 W/m 2
q loss = q . A = 8.28 [W/m 2 ] x 30 [m 2 ] = 248 W
As can be seen, an addition of thermal insulator causes significant decrease in heat losses. It must be added, an addition of next layer of thermal insulator does not cause such high savings. This can be better seen from the thermal resistance method, which can be used to calculate the heat transfer through composite walls . The rate of steady heat transfer between two surfaces is equal to the temperature difference divided by the total thermal resistance between those two surfaces.
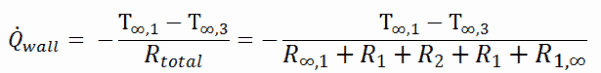
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 7th Edition. Theodore L. Bergman, Adrienne S. Lavine, Frank P. Incropera. John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated, 2011. ISBN: 9781118137253.
- Heat and Mass Transfer. Yunus A. Cengel. McGraw-Hill Education, 2011. ISBN: 9780071077866.
- U.S. Department of Energy, Thermodynamics, Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow. DOE Fundamentals Handbook, Volume 2 of 3. May 2016.
Nuclear and Reactor Physics:
- J. R. Lamarsh, Introduction to Nuclear Reactor Theory, 2nd ed., Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA (1983).
- J. R. Lamarsh, A. J. Baratta, Introduction to Nuclear Engineering, 3d ed., Prentice-Hall, 2001, ISBN: 0-201-82498-1.
- W. M. Stacey, Nuclear Reactor Physics, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, ISBN: 0- 471-39127-1.
- Glasstone, Sesonske. Nuclear Reactor Engineering: Reactor Systems Engineering, Springer; 4th edition, 1994, ISBN: 978-0412985317
- W.S.C. Williams. Nuclear and Particle Physics. Clarendon Press; 1 edition, 1991, ISBN: 978-0198520467
- G.R.Keepin. Physics of Nuclear Kinetics. Addison-Wesley Pub. Co; 1st edition, 1965
- Robert Reed Burn, Introduction to Nuclear Reactor Operation, 1988.
- U.S. Department of Energy, Nuclear Physics and Reactor Theory. DOE Fundamentals Handbook, Volume 1 and 2. January 1993.
- Paul Reuss, Neutron Physics. EDP Sciences, 2008. ISBN: 978-2759800414.
Advanced Reactor Physics:
- K. O. Ott, W. A. Bezella, Introductory Nuclear Reactor Statics, American Nuclear Society, Revised edition (1989), 1989, ISBN: 0-894-48033-2.
- K. O. Ott, R. J. Neuhold, Introductory Nuclear Reactor Dynamics, American Nuclear Society, 1985, ISBN: 0-894-48029-4.
- D. L. Hetrick, Dynamics of Nuclear Reactors, American Nuclear Society, 1993, ISBN: 0-894-48453-2.
- E. E. Lewis, W. F. Miller, Computational Methods of Neutron Transport, American Nuclear Society, 1993, ISBN: 0-894-48452-4.
Heat Losses
We hope, this article, Insulation Material – Types of Insulation , helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about thermal engineering.
Related Posts
- What is Inorganic Insulation Material - Definition
- What is Organic Insulation Material - Definition
- What is Cork Insulation - Definition

Thermal Insulation PPT Download Free
In this post, we share ppt of thermal insulation material topic which covered almost all topics related to insulation materials. We explained the different types of insulating material used in building. And also this ppt is absolutely Free.
Table of Contents
Thermal Insulation PPT Download

What is Thermal Insulation?
Thermal insulation is defined as a retard or transmission of the flow of heat in a room. And the material which is used to retard the flow of heat is known as thermal insulating material.

What is Conduction?
Conduction is defined as a transfer of heat energy from one atom to another atom in the object by direct contact.
What is Convection?
Convection is defined as transfer of heat energy in within fluid that may be either a gas of liquid.
What is Radiation?
Radiation is defined as the transfer of heat energy into space with the help of electromagnetic waves. Radiation energy comes from a source and travels into the space at speed of light.
Also Read: What is Geosynthetic | Types of Geosynthetics
Requirement of Thermal Insulation in Building
- Thermal insulation is needed to maintain a comfortable living environment in the building.
- Thermal Insulation in buildings is required to protect the health of human beings against atmospheric effects.
- Thermal insulation is required to protect the structural elements of a building against Thermal Impact.
Advantages of Thermal Insulation in Building
- It provides comfortable living.
- It keeps the room cool in summer and warms the room in winter.
- Due to reduction of uses of Refrigerator and air-conditioner, its saves the electricity and fuel cost.
- It saves the maintenance cost.
- It prevents condensation on the internal wall and ceiling.
Thermal Insulating Material
Fiber glass, mineral wool, polyurethane foam, polystyrene.
Fiber Glass is a most common thermal insulating material which is used in modern time. It is used to minimize the heat transfer and made by finely woven Silicon, glass powder and tiny shards of glass.
Cellulose is Eco Friendly thermal insulation material that is used to reduce and gain the heat loss of the building. It is also used for noise transmission purposes.
Cellulose is a fire-resistance insulating material. It is made from recycled cardboard, paper, and other similar materials.
Mineral wool is a fiber glass material that is made from recycled glass. it is also called as glass wool.
Polystyrene is a waterproof thermoplastic foam material that is a good thermal and sound insulation material. It is also called styrofoam. Polystyrene is created or cut into blocks for wall insulation purposes.
Polyurethane Foam is excellent thermal insulation material. It is available in the liquid sprayed form or rigid foam board.
2 thoughts on “Thermal Insulation PPT Download Free”
For the Poultry farm, the body temperature of the chicken must be 106-degree Fahrenheit (41-degree Celsius). To maintain the temperature of the inner environment, our experts provide roof and wall insulation to your poultry farm. The Poultry Farm Insulation materials installed by our experts are tested and have certification of being the best insulation service provider.
Hii freind amit, Thank you for comment and discuss about poultry farm insulation. But still my not have any poultry farm. If I interest in than say you
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Insulating Materials
- First Online: 17 May 2017
Cite this chapter

- Andreas Küchler 2
Part of the book series: VDI-Buch ((VDI-BUCH))
5230 Accesses
4 Citations
Electrical insulation materials cannot be applied only on the basis of their dielectric strength. For practical application, the whole characteristic profile including electrical, mechanical, thermal, physical and chemical properties is relevant because materials in electrical systems and equipment also always fulfil the non-electric functions as “construction materials”. For this, basic information is given for selected important insulating materials, such as the significance in high voltage engineering applications, the basic material structure, special dielectric properties, other special properties, the manufacturing and processing technology as well as the performance in operation. The classification of material groups follows specific high voltage engineering features: Gases (air, SF6, alternative gases), inorganic solid insulating materials(ceramics, porcelain, glass, mica), thermoplastic insulating materials (polyethylene, PVC), thermosetting plastics and elastomers (epoxy resin, polyurethane, silicone elastomers), nano-composites, insulating liquids (mineral oil, synthetic liquids, vegetable-based liquids) as well as impregnated fibrous materials(paper, pressboard, synthetic materials).
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Hochschule Würzburg-Schweinfurt, Schweinfurt, Bayern, Germany
Andreas Küchler
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Andreas Küchler .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany
About this chapter
Küchler, A. (2018). Insulating Materials. In: High Voltage Engineering. VDI-Buch. Springer Vieweg, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-11993-4_5
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-11993-4_5
Published : 17 May 2017
Publisher Name : Springer Vieweg, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN : 978-3-642-11992-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-642-11993-4
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

What is an Insulating Material : Classification & Its Applications
An Electrical Insulating Material/Insulating Material is used to obstruct the flow of current. It forms ionic bonds and the materials that have low conductivity and high resistivity are available in the form of solid, liquid, gaseous like the plastic used for plugs, insulating oil used in transformer , etc. These materials have very high resistance so the flow of electric current requires an extremely high voltage like kilo or megavolts to send a few milliamperes of current to them. The insulators are used primarily for storage and also in all domestic and commercial electrical equipment to isolate the conductor from the earth.
What is Insulating Material/Electrical Insulating Material?
The Electrical Insulating Material/insulating materials are the materials that inhibit heat transmission, electric current, or noise. All the insulating materials have a negative temperature coefficient of resistance and as such resistivity is reduced with an increase in temperature. The function of the insulator is very important without which no electrical machine can work, the majority of the breakdown in the field of electrical engineering is due to the failure of insulation. The importance of the insulating materials is ever-increasing in day by day as there is an innumerable number of types of insulators available in the market. The selection of the right type of insulating matter is very important because the life of the equipment depends on the type of material used.
Basics of Insulating Material
The insulators are the materials that have the valence electrons eight or nearer to eight. When the valence electrons are eight obviously the atom is in a stable condition and they offer very high resistance as there are no free electrons, also the forbidden gap between conduction and valence band is more. The atomic structure of insulating material neon is shown in the below figure.

As shown in the above figure, that atom has eight electrons in the outermost orbit, hence they are stable and it can be considered as an insulator. The atomic structure of fluorine has seven electrons in their outermost orbit in a valence electron. The atomic structure of insulating material fluorine is shown in the below figure.

The atoms like oxygen which have only six electrons in a valence electron they can be classified also as an insulator but the insulating properties of oxygen are less than that of fluorine and neon.

The atoms having eight electrons and seven electrons in an outermost orbit behave as good insulator compared to the atoms having six valence electrons.
What is Glass Insulator?
At high temperature, the glass insulators are designed or manufactured by mixing the different types of materials, including quartz and lime powder, and then cools in the mold. The main disadvantage of the glass insulator is, compared to the other type of insulators the contaminations are observed easily by the glass insulator and on the surface of the glass insulator, the moisture can be distilled easily.
The properties of the glass insulator are
- Dielectric Strength: The approximate value of dielectric strength is 140 kV/cm.
- Compressive Strength: The approximate value of compressive strength is 10,000 Kg/cm².
- Tensile Strength: The approximate value of tensile strength is 35,000 Kg/cm².
The advantages of the glass insulator are
- Compare to porcelain the dielectric strength is very high in a glass insulator
- High resistivity
- The tensile strength is higher than porcelain
- It is cheaper than porcelain insulator
What is Polymer Insulator?
The polymer or polymeric insulator is also known as a composite insulator. It is a light-weight insulating material and has high mechanical strength. The disadvantage of the polymer insulator is if there is any unwanted gap between weather shed and core their moisture may enter.
The polymeric or polymer insulator has excellent properties they are hydrophobicity, lightweight, and anti-weather ability.
The advantages of the polymer insulator are
- Compare to porcelain and glass insulator the polymer insulator is very lightweight
- Installation cost is low
- Tensile strength is higher than porcelain
- Better performance
What is a Porcelain Insulator?
The porcelain insulator is an aluminum silicate insulating material. In the present day, this material is used for the overhead insulator. The week in tension and poor shock resistance is the disadvantages of a porcelain insulator. The porcelain can also be called as ceramic. The applications of this insulator are distribution and transmission lines, isolators, transformer bushings, fuse units, plugs, and sockets
The properties of the porcelain insulator are
- Dielectric Strength: The approximate value of dielectric strength is 60 kV/cm.
- Compressive Strength: The approximate value of compressive strength is 70,000 Kg/cm² .
- Tensile Strength: The approximate value of tensile strength is 500 Kg/cm².
The advantages of the porcelain insulator are
- Compared to glass insulator the mechanical strength of porcelain insulator is very high
- Leakage current is low
- It is less affected by temperature
- Easy to maintain
- Highly Flexible
- Highly reliable
Properties of Insulating Material
All the insulators when used should not only behave as an insulator over a wide range of electric voltage but must strong mechanically. They shouldn’t be affected by heat, atmosphere, chemical effects and should be free from deformation due to aging. Therefore before selecting an insulating material, it is quite essential to know the various properties and their effects on insulation. The various properties of insulating materials are electrical properties, visual properties, mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties.
Electrical Properties
The electrical properties of insulating materials are divided into two types they are insulating resistance and dielectric strength. The insulating resistance is again classified into two types they are volume resistance and surface resistance. The factors affecting insulating resistance are temperature, aging, applied voltage and moisture and the factors affecting dielectric strength are temperature and humidity.
Visual Properties
The visual properties of insulating material are appearance, color, and its crystallinity.
Mechanical Properties
Some of the mechanical properties which are to be taken care of while selecting the insulating material are tension & compression, resistance to abrasion, tear, shear & impact, viscosity, porosity, solubility, moisture absorption, and machinability and mouldability.
Thermal Properties
The thermal properties of insulating material are melting point, flash, volatility, thermal conductivity, thermal expansion, and heat resistance.
Chemical Properties
The various chemical properties of insulating material are resistance to external chemical effects, effects on other materials, chemical changes in the material, hygroscopicity, and aging.
Classification of Insulating Material
The classification of insulating material is based on the thermal classification, physical classification, structural, chemical classification, and the process of manufacture.
Thermal Classification
Thermally the insulators are classified into seven types or seven classes they are class-Y, class-A, class-E, class-B, class-F, class-H, and class-C.
The class-Y limitation temperature is 90°C and the materials come under class-Y are cotton, paper, silk, and similar organic materials.
The class-A limitation temperature is 105°C and the materials come under class-A are impregnated paper, silk, polyamide, cotton, and resins.
The class-E limitation temperature is 120°C and the materials come under class-E are enameled wire insulation on the base of powdered plastics, polyvinyl epoxy resins, etc.
The class-B limitation temperature is 130°C and the materials come under class-B are inorganic materials impregnated with varnish.
The class-F limitation temperature is 155°C and the materials come under class-F are mica, polyester epoxide varnished in the high heat resistance.
The class-H limitation temperature is 180°C and the materials come under class-H are composite materials on mica, glass, fiber, etc.
The class-C limitation temperature is >180°C and the materials come under class-C are glass, mica, quartz, ceramics, Teflon, etc
Physical Classification of Insulating Material
The physical classification of insulating material is classified into three types they are solid, liquid, and gaseous. The physical classification of insulators is shown in the below figure.

The solid insulating materials are fibrous, ceramic, mica, glass, rubber, and resinous. The liquid insulating materials are mineral oils, synthetic oils, transformer oils, and miscellaneous oils. The gaseous insulating materials are air, hydrogen, nitrogen, and Sulphur hexafluoride.
Structural Classification
The structural classification of insulating material is classified into two types they are cellulose and fibrous.
Chemical Classification
The chemical classification of insulating material is classified into two types they are organic and inorganic.
Process of Manufacture
The process of manufacture is classified into two types they are natural and synthetic.
Some of the insulating materials are fiberglass, mineral wool, cellulose, natural fibers, polystyrene, polyisocyanurate, polyurethane, insulation facings, phenolic foam, urea-formaldehyde foam, etc.
Applications of Insulating Material
The applications of insulating material are
- Cable and transmission lines
- Electronic systems
- Power systems
- Domestic portable appliances
- Electrical cable insulating tape
- Personal protective equipment
- Electrical rubber mats
1). What are the common insulating materials?
Some of the common insulating materials like ceramic, glass, Teflon, silicone, etc.
2). Which materials are used to insulate wires?
Some of the best good electrical insulating materials are glass, paper, Teflon, PVC, varnish, and rubber.
3). What are the common thermal insulator materials?
The common thermal insulating materials are mineral wool, fiberglass, polystyrene, cellulose, polyurethane foam, etc.
4). What are the applications of insulating materials?
The applications of insulating material are electrical rubber mats, power and electronic systems, cable and transmission lines, etc.
5). What is the importance of insulating materials?
The selection of the right type of insulating material is very important because the life of the equipment depends on the type of material used.
In this article what are insulating materials/electrical insulating materials , classification of insulating materials, applications, advantages and properties of glass insulation, porcelain insulator and polymer or polymeric insulator, properties of insulating materials are discussed. Here is a question for you what type of insulating materials are used in the home?
Share This Post:

- Electronics
- Communication
- Free Circuits
- Interview Questions
- ECE Projects
- EEE Projects
- Project Ideas
- Resistor Color Code Calculator
- Ohms Law Calculator
- Circuit Design
- Infographics
Maintenance work is planned for Wednesday 1st May 2024 from 9:00am to 11:00am (BST).
During this time, the performance of our website may be affected - searches may run slowly and some pages may be temporarily unavailable. If this happens, please try refreshing your web browser or try waiting two to three minutes before trying again.
We apologise for any inconvenience this might cause and thank you for your patience.

Journal of Materials Chemistry A
Morphology- and defect-coordinated prominent microwave absorption, thermal exhaustion, and electrical insulation in sno 2 @snp 2 o 7 @sn 2 p 2 o 7 hierarchical architectures.
To solve the severe problems of electromagnetic pollution and thermal exhaustion in electronics, this work pioneers the utilization of SnO 2 @SnP 2 O 7 @Sn 2 P 2 O 7 hierarchical architectures (HAs) as an electrically insulated filler with strong microwave absorption and high heat conduction. The HAs are produced through a simple hydrothermal-annealing approach, in which their morphology and defects are precisely tuned by controlling the concentration of Sn 2+ ([Sn 2+ ]) and solvent types. Due to the self-assembly of SnO 2 nonbuilding blocks determined by the minimal surface free energy, a morphological evolution occurs from hexagonal stars to leaves and then to leaf-shaped flowers with an increase in the [Sn 2+ ] and further to rod-based flowers when water is used as the solvent. Results show that the SnO 2 @SnP 2 O 7 @Sn 2 P 2 O 7 HAs obtained under [Sn 2+ ] = 0.4 mol/L, resembling a dense leaf-shaped flower, exhibits a synergistic enhancement in electrical insulation (0.00983 S/m), MWACs (6.48 GHz; 2.0 mm), and heat conduction (4.745 W/(m·K), a 20% load). This enhancement is due to the cooperative action of defects and a unique hierarchical configuration. The defects can not only provide free electrons for various polarizations and conductive loss but also act as polarization centers for dipole polarization. Moreover, the flower-shaped hierarchical architecture easily forms 3D continuously conductive micro-networks for electron/phonon transfer, conductive loss, and multiple EMW scattering. Overall, this work establishes a theoretical basis for the design and utilization of SnO 2 @SnP 2 O 7 @Sn 2 P 2 O 7 HAs as advanced electronic packaging materials with outstanding microwave absorption, thermal exhaustion, and electrical insulation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers
Supplementary files
- Supplementary information PDF (492K)
Article information
Download citation, permissions.
X. Liu, S. Xie, S. Cai, K. Fu, X. Liu, L. Lin, Z. Yu, G. Tong and W. Wu, J. Mater. Chem. A , 2024, Accepted Manuscript , DOI: 10.1039/D4TA01541J
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements
- Share full article

The 10 Best Things We Saw at Salone del Mobile
From an exhibition in a 1940s-era Modernist house to a blood-red sofa, the highlights of Milan’s annual design fair.
A Mario Bellini for Tacchini Le Mura sofa remade in Gucci’s new signature shade of red, Ancora Rosso, on view in the fashion brand’s Milan flagship store. Credit... Courtesy of Gucci
Supported by
By Monica Khemsurov
- April 19, 2024
The annual Salone del Mobile furniture fair has always been big — it’s the event of the year for the international design world, drawing hundreds of thousands of makers, curators, editors and buyers to Milan each April for a week’s worth of inspiration, shop talk and aperitivi. Even more so than fashion week, the fair consumes the city. But this year’s edition seemed to buzz with a new level of excitement, with more people from outside the design industry joining the throngs and hourlong lines forming outside events like the launch of the French luxury brand Hermès’s interiors collection, the annual installation by the Milanese architecture firm Dimorestudio and the satellite fair Alcova’s takeover of the Modernist architect Osvaldo Borsani’s former home — this despite the house being a 45-minute drive north of the city center. Luckily, there were so many interesting presentations on view that braving the crowds felt well worth it. Here, 10 standouts.

Formafantasma’s Floral Chairs and Futuristic Lights
One of the most talked-about openings of the week was the Milan-based design duo Formafantasma’s solo show at the Fondazione ICA Milano, for which the pair — Andrea Trimarchi and Simone Farresin — drew on memories of their childhood homes in Italy to create surprising hybrid chairs and lamps that pair steel armatures with colorful wood, frilly fabrics and hand-painted or embroidered floral motifs. The aesthetic was institutional furniture meets Italian grandma’s house. Formafantasma also debuted a new series of utilitarian but delicate lights for Flos made from LED strips enclosed in thick glass panels.
A New Furniture Line From Dimorestudio
Once people began posting photos on social media of the launch of Interni Venosta, a new furniture brand from Britt Moran and Emiliano Salci, the founders of Dimorestudio, the line’s exhibition quickly became a must-see — partly for its pairing of bold minimalist forms with luxe materials like walnut and steel, and partly because it was presented in an extremely photogenic local plaster workshop. The brand’s name pays homage to the cult Italian designer Carla Venosta, who created modernist furniture and interiors in the 1970s and ’80s.
Gucci’s Blood-Red Design Icons
Having recently redone part of Gucci’s Milan flagship store entirely in a deep oxblood red, the brand’s creative director, Sabato De Sarno, partnered with five Italian design companies to reimagine some of their classic pieces in the house’s new signature color, Ancora Rosso. The lineup, installed for the week on the store’s second floor — inside a lime-green carpet maze created by the Spanish designer Guillermo Santomà — included Gae Aulenti and Piero Castiglioni’s Parola lamp, Nanda Vigo’s Storet cabinet, Mario Bellini’s Le Mura sofa, Tobia Scarpa’s Opatchi vase and a new rug created by Nicolò Castellini Baldissera based on motifs by his great-grandfather Piero Portaluppi. Each item will be produced in a limited edition of 100.
A Takeover of a Modernist Architect’s Fomer Home
Since its inception in 2018, the Alcova satellite fair has become the place to discover new talent during Salone. This year, it occupied two historic mansions outside the city: the 19th-century Villa Balgatti Valsecchi and the 1945 Villa Borsani. The latter venue, the former residence of the architect Osvaldo Borsani, was the hotter ticket and featured pieces like a two-tone wood room divider by Anthony Guerrée for Atelier de Troupe, a family of marble tables with columnar legs by Agglomerati and Tino Seubert and a suite of galvanized-steel office furniture by the Russian designer Supaform, which was exhibited in Borsani’s onetime home office.
A Dispatch From the Americas
Hidden down a long, dark hallway directly next door to Hermès’s big Salone presentation was “Origen,” a comparatively understated show of works by four up-and-coming Latin American(-ish) designers for the New York- and Mexico City-based Unno Gallery. Among the pieces on display were brown lacquer desks and shelves with reverse-waterfall legs by Mark Grattan, an American designer who was based in Mexico City for many years, and a series of glittering stools and mirrors, covered in crushed iridescent seashells, by the Colombian designer Andrea Vargas Dieppa (a co-founder of the 2010s-era shoe brand Dieppa Restrepo).
Unusual Lamps Commissioned by Loewe
For its eighth and biggest Salone exhibition, the Spanish luxury house Loewe commissioned 24 artists and designers from around the world to create lamps in materials and styles of their own choosing. The results range from the futuristic (a tangle of neon tubes by the London-based artist Cerith Wyn Evans) to the eccentric (a miniature storefront with metal shutters and a pull cord by the London-based painter Alvaro Barrington) to the rustic (an ancient-looking ceramic vessel punched with holes, and lit from within, by the Japanese artist Kazunori Hamana).
Interesting Beds From a Georgian Design Duo
Eye-catching beds are a true rarity in the design world, which is why there was so much interest this week in an exhibition of six of them, all produced by the Tbilisi, Georgia-based firm Rooms Studio — founded by Nata Janberidze and Keti Toloraia — in materials ranging from chunky wood to thin steel tubes with steer-head finials. The design duo were inspired to focus on the oft-overlooked category by their struggles to source great bed frames for their own interiors projects.
Dolce & Gabbana’s Next Generation of Design Talents
The Italian fashion brand Dolce & Gabbana’s second annual Gen D project reflects the company’s commitment to supporting young talent both within and beyond the fashion world. For the ambitious group exhibition, the house enlisted the Italian curator Federica Sala to pair 10 international designers with sixteen Italian craft workshops. Among the resulting pieces are interesting stylistic and cultural mash-ups like the Chinese designer Jie Wu’s wild, squiggly vessels, which feature Chinese and Sicilian good-luck motifs and are coated in classical Venetian enamel.
Close-up Photographs of Modernist Interiors
In a simple but memorable exhibition mounted in one of the tunnels that flanks Milan’s central train station, the Czech writer, curator and photographer Adam Štěch — along with his colleagues Matěj Činčera and Jan Kloss — displayed over 3,000 photos of details from famed Modernist homes and buildings. In shooting the photos, which he’s shared on his Instagram account, @okolo_architecture , over the years, Štěch focused on interiors and furnishings that were custom-made for each project by their architects. It was easy to get lost in the show, poring over doorknobs, stair rails and lamps from around the world.
A Circular Ping-Pong Table
The exhibition “Design Duo Double Feature,” also curated by Federica Sala, was a thoughtful example of a materials brand commissioning designers to show off the potential of its products: The six pieces in the show were all made from the acrylic-resin surface material Fenix and designed by up-and-coming Italian studios like Cara \ Davide, Mist-O and Zanellato/Bortotto. A standout was the Match table by Martinelli Venezia, a circular two-tone Ping-Pong table whose “net” is formed from a tenting of its top.
Explore T Magazine
A Party In Milan: To toast the Salone del Mobile and the 20th anniversary of T Magazine , the designer Ramdane Touhami transformed the Villa Necchi Campiglio into an ode to the letter T.
A Beloved Copenhagen Cafe: The chef Frederik Bille Brahe has transformed the Apollo Bar & Kantine into his version of a fine dining restaurant , and celebrated with a meal for his family and collaborators.
The Beginners Issue: From debuts to do-overs, what it means to start an artistic life — at any age
We Saw at Salone del Mobile: From an exhibition in a 1940s-era Modernist house to a blood-red sofa , these were the highlights of Milan’s annual design fair.
Hawaii’s Favorite Shave Ice Shops: Cups of flaky ice topped with flavored syrups are easy to find in the state. But the best shops set themselves apart with fresh ingredients and old-school charm.
Ellen Gallagher’s Futuristic Archives: In an interview, the artist discussed marine life and African American myth from her studio in the Netherlands.
Advertisement
- Future Students
- Parents/Families
- Alumni/Friends
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff
- MyOHIO Student Center
- Visit Athens Campus
- Regional Campuses
- OHIO Online
- Faculty/Staff Directory
Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine
- Faculty and Staff Directory
- Mission and Vision
- Our Campuses
- Osteopathic Medicine
- Accreditation
- Code of Ethics
- College Policies and Procedures
- College Leadership
- Shared Governance
- Annual Report
- Our Partners
- Student and Alumni Facts
- Overview (all offices)
- Office of Medical Education
- Alumni Affairs
- Administrative Services
- Advancement and Development
- Communications
- Consortium for Health Education in Appalachia Ohio
- CORE / Clinical Education
- Executive Dean's Office
- External Relations
- Office of Faculty Learning and Advancement
- Financial Services
- Government Relations
- Graduate Medical Education
- Human Resources
- Institutional Assessment and Accreditation
- Office of Medical Education Technology
- Ohio Musculoskeletal and Neurological Institute
- Research and Grants
- Rural and Underserved Programs
- Strategic Initiatives
- Student Affairs
- Overview (all departments)
- Biomedical Sciences
- Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine (OMM)
- Primary Care
- Social Medicine
- Specialty Medicine
- Strategic Plan
- Osteopathic Heritage Foundation Award
- Pathways to Health and Wellness Curriculum
- New Heritage Hall Medical Facilities in Athens
- Dublin Campus Master Plan
- Research Strategic Plan
- Academic Requirements
- Transfer and International Applicants
- Summer Programs
- Premedical Education
- Dual-Degree Programs
- Early Assurance Program
- Biological Sciences
- Molecular and Cellular Biology
- Translational Biomedical Sciences
- Financial Aid Checklist
- Cost of Attendance
- Scholarships
- Student Loans
- Exit Information
- Computer Requirements
- Orientation Checklist
- Student Resource Manual
- College Catalog
- Health and Technical Standards
- Criminal Background Check
- Premedical Overview
- Early Assurance Programs
- Post-Baccalaureate
- Prematriculation
- AmeriCorps/COMcorps
- High School Programs
- Curriculum Overview
- Preclinical Education
- Clinical Education
- Learning Resource Center
- Student Manuals, Policies and Resources
- Clinical Training Assessment Centers
- Osteopathic Integration
- GME Overview
- ACGME Single Accreditation System
- Ohio University Graduate Programs (M.S., Ph.D)
- Continuing Medical Education
- Health Policy Fellowship
- Our Research
- Office of Research and Grants
- Annual Reports and Forms
- Faculty and Staff Resources
- Resident Resources
- Student Resources
- Vice President of Research, Ohio University
- Funding Resources
- LEO Electronic Awards Administration
- Research Compliance
- Edison Biotechnology Institute
- Centers and Institutes
- Clinical and Translational Research Unit (CTRU)
- Life Sciences Research Facility
- Diabetes Institute
- Infectious and Tropical Disease Institute
- Academic and Research Center (ARC)
- Musculoskeletal and Neurological Diseases
- About Our Programs
- Patient Portal
- Adult Health Screenings
- AmeriCorps/COMCorps
- Body Donor Program
- Breast and Cervical Cancer Screenings
- Family Navigator Services
- Heritage Community Clinic
- Immunizations
- Privacy Notice
- Continuing Education
- American Heart Association Training Centers
- Health Resources Library
- Premedical Observation
- Schweitzer Fellowship
- T.O.U.C.H. Program
- Society of Alumni and Friends
- How to Give
- Osteopathic Heritage Foundation Gift
- Social Media
- Publications
- For the Media
- Shop the Bobcat Store
- Engage with the Global Health Initiative
- Arrange Visit
- Student Affairs Resource Manual
- Manuals, Policies, and Resources
- Academic Schedule
- Blackboard Login
- Medical Education
- Web E-mail (OHIO Catmail)
- Faculty Resources (Years 1 and 2)
- College Research
- Request Technology Assistance
- Room and Videoconference Scheduling
- Faculty Learning
Helpful Links
Navigate OHIO
Connect With Us
Inclusion scholars bring attention to health equity issues
While progress has been made to improve health equity, more needs to be done on many fronts, from medical education to patient care. That was a key message delivered by the Ohio University Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine Inclusion Scholars in a research presentation.
As part of the Inclusion Scholars program for first- and second-year students, participants design a small research project and annually, share their findings. This year’s scholars looked at challenges faced by LGBTQ+ patients in health care settings, the ability of medical students to identify skin diseases and conditions on different skin tones, challenges facing inclusion in medical education, the development of a high school mentorship program and implementation of an affinity group for Black men in medical school.
“The inclusion scholar’s program is so valuable to participating students. The experience provides first and second years with an opportunity to delve deep into research and a literature review on a topic of their choosing relevant to equity in medicine or medical education,” said Tanisha King, chief inclusion officer. “Scholars enhance the knowledge of our faculty, staff and students often inspiring and influencing positive change.”
Increasing inclusivity in medical training materials

That was the goal of second-year student Alyson Johnson.
For her project, Johnson surveyed medical students to see if they could identify skin conditions on various skin tones. Most medical education materials only show skin conditions on lighter skin, but diseases often look different on darker skin.
This, Johnson noted, can lead to misdiagnosis. She used skin cancer as an example. Most dermatologists have little to no experience diagnosing skin cancer on people with darker skin tones, so it’s often discovered at a late stage when it’s harder to treat, making it more likely the patient will die from skin cancer. She told a story about her own mother’s misdiagnosis of a spot on her face that turned out to be basal cell carcinoma.
“The bottom line is there is a lack of diversity in medical education texts and lectures,” she said.
In her IRB approved study, medical students were asked to look at images of dark and light skin with 10 common skin conditions and make a diagnosis. Next, they indicated how confident they were in that diagnosis. Johnson said while students performed well overall, preliminary results showed they also did not have much confidence in their diagnosis of conditions on darker skin.
Johnson said she hopes data from her study can be used to “lead us forward in the right direction.

Improving health outcomes
In her presentation, Inclusion Scholar Caitlin Pastor, a first-year student on the Cleveland campus, said she has witnessed first-hand how a lack of inclusivity and respect can lead to poor treatment of patients. Pastor looked at LGBTQ+ patient care, and shared details about a patient and her mother who left a practice because the provider would not use the patient’s pronouns or new name.
Pastor held a training for clinical staff to raise more awareness about the significance of pronouns and its effect on the patient/provider relationship. She pointed out that a strong relationship between a doctor and their patient will lead to better health outcomes.
“A considerable number of people won’t go to a provider because of concerns about how they’re treated,” said Pastor. She pointed out that on her first day of classes, instructors emphasized the patient/physician relationship and told students to leave their biases at the door.
“All patients deserve your best holistic care,” she said.

Broadening representation to enhance a sense of belonging
Many incoming medical students say they were inspired to pursue a career in medicine by someone they’ve met who works in health care. That was the case with Inclusion Scholar Jacee Moore, OMS I, who was introduced to medicine by her pediatrician, Jacqueline Moore (no relation).
“She served as a constant reminder that I could do anything that I wanted to do at a young age,” said Moore. “And seeing her being a black woman in medicine, seeing her name on a plaque that said Dr. J. Moore…I wouldn’t be future Dr. Moore if there wasn’t a Dr. Moore already.”
For her project, Moore conducted a survey of medical students to better understand their motivations for pursuing a career in medicine and the barriers they have faced along the way.
During her presentation, Moore made the point that some people may not ever meet a physician who looks like them or shares their background or culture.
“Luckily for me I was able to have that exposure, earlier, before my career even started, but I know for some people that’s not the case,” she said.
When students who are underrepresented in medicine (URM) attend medical school, they often have a low sense of belonging or don’t feel they belong at all. This was one of Moore’s findings. Many students also reported facing barriers, such as a lack of mentorship (12%), instances of bias or discrimination (12%), overall lack of diversity (26%) and financial hardship (28%) in medical school. However, a large number of the survey’s overall respondents felt a strong interest in academic medicine and a desire to lead the next generation of providers and train them to be culturally competent physicians.
In her presentation, Moore said it was important to get in front of young people from URM groups and let them know that a career in medicine is possible. To improve inclusion efforts, she recommended several other steps including hiring and retaining more diverse faculty.
“This call to action is one that is near my heart being a student of an underrepresented minority group in medical school,” said Moore. “By increasing diversity and inclusion within medical education, I believe we are one step closer to providing a community of doctors who look like the patient populations we intend to serve, and we take a great step closer towards equitable, culturally competent patient centered care that our patients deserve.”

Building pipelines that help medical school recruitment
Inclusion Scholar Alcario Williams’ idea of creating a pipeline program for URM students from high schools and community colleges blossomed as he thought about where he was raised and his journey to medical school.
“I believe increasing diversity in medicine helps address these health care disparities by tailoring care to different populations,” said Williams. “So more representation leads to more physicians who understand and are aware of these varied patient experiences that these patients come in with, and these doctors can serve in these diverse communities which I believe leads to better health outcomes.”
Through the pipeline program, prospective students would partner with mentors who can guide them on their journey to medical school, from preparing for the MCAT to offering shadowing opportunities.
“We want to help these students who qualify for medical school but may be disadvantaged economically and/or socially find their path into medicine,” said Williams.
He explained how he faced what’s called academic redlining, where academic metrics can keep qualified applicants from underrepresented backgrounds from entering medical school. Redlining is a historical practice that isolates neighborhoods often based on race or ethnicity and then denies economic opportunities and other services to that community. Academic redlining is an extension of this concept as students in these communities often attend schools with significantly less funding and resources than schools in wealthier districts. Students in these neighborhoods usually face other barriers, such as inadequate housing, difficulty accessing health care and food deserts, which can affect their education.

The Heritage College currently offers several programs that help reduce barriers to medical school, including Medical Student for a Day, a program where university students get exposure to a day in the life of a medical student. Williams said he participated in that program three times.
“Each time I learned something new from it, but I also saw the representation, and I gained that confidence over time that I can really do this,” he said.
Other programs the college offers include Summer Scholars and Pre-Matriculation, which Williams calls, “so impactful, so powerful, so influential,” and says he owes his success in medical school to them. Summer Scholars is a rigorous five-week immersive program that gives participants a realistic introduction to the first year of medical school. The Pre-matriculation program is an accelerated introduction to medical school.
Williams sees his pipeline program integrating with these. He said he wants to bridge the gap between underrepresented students and patients.
“If I can help more students who look like me get into medical school… that’s what I’m doing it for,” said Williams who hopes he can be the same kind of doctor as the pediatrician who cared for him when he was a child.
Finding space to gather and connect
After seeing data showing that less than half of Black male applicants accepted to the Heritage College chose to attend, Inclusion Scholar Kendale Watson developed an affinity group for Black men at the college.
He spoke with applicants to better understand what was happening. They told him they didn’t see Black men on campus, that they only saw him.
Watson said, he felt his affinity group, the Medicine Equity and Diversity or M.E.D. program, would be a good way to bring Black men to the forefront so that incoming students could see them, not just hear about them.
Watson started M.E.D. to create a healthy social environment and safe space for Black men across all three campuses at the college to gather and connect with each other, and to help increase the number of Black male applicants and graduates at the college.
The program ran four weeks and included a weekly seminar with guest speakers, many of them alumni. It also provided fellowship for the group’s 17 participants.
“We were able to see each other in person for the first time as one group,” said Watson, adding that one alumnus who spoke to the group told members that it was the most Black men he had ever seen together at one time at the college.
By bringing in alumni, Watson hoped they would provide mentorship and knowledge and could share their medical school experiences.
“I believe that by fostering a sense of community and mentorship, we can enhance the experience on campus and contribute to long-term success for Black men at OUHCOM.”
To evaluate the group’s effectiveness, Watson conducted a pre- and post-survey. He found that the group was diverse with a handful having a physician in their family and less than half being first generation college students. He also discovered that two-thirds of students had a mentor, although for many of them, their mentor was not in their chosen specialty.
While most participants said they feel supported by the college, they said there are challenges. More diversity among the faculty, a larger number of Black male students and having networks of support were some of the recommendations participants gave for improving their medical school experience.
The students also reported feeling pressure to succeed as a Black male in medicine.

“It was an overwhelmingly yes from everyone,” said Watson. One participant said he felt he had to prove people wrong because they had been surprised he was going to be a doctor. Another said being the first in college and the first in medicine was both a drive and burden.
“I can relate to this personally… It’s a lot of pressure to go through this experience without having anyone who came before you,” said Watson. “You’re the first. So, navigating this experience can be very difficult.”
Watson also asked participants what they hoped to accomplish as a Black physician. One said he hoped to improve health outcomes in his community, remove stigma in health care, have a positive impact and become a trusted role model and leader in his community.
“I feel like that was the overwhelming response as well during the program, that everyone wants to be that pivotal role model for their community because there’s not a lot of people who look like us in this field, and it gives us a little bit of grit to keep continuing even if we do have setbacks,” said Watson.
Inclusion scholars are paired with either a faculty mentor or an assistant director of inclusion. They receive a stipend and are considered ambassadors for the Office of Inclusion, helping to facilitate dialogue on inclusion topics among their peers.
“What we’ve seen with the Inclusion Scholars program is that it increases student empathy as well as understanding of diversity, equity and inclusion and how broad it is,” said King. “This year’s scholars developed a strong bond and collaborated more with each other than we’ve seen in prior years.”
Information about how to apply can be found online .
Related Articles
Featured news, class of 2024 graduate profile: kamara hyatt.
Class of 2024 graduate Kamara Hyatt is headed to a family medicine residency at The Christ Hospital in Cincinnati. In this profile, Hyatt, who was raised in South Florida, explains how her mom has inspired her journey through medical school.
Heritage College Class of 2024 Graduate Profile: Ashleigh Chiedo
Born to immigrants and with a background in health care, graduate Ashleigh Chiedo took on a leadership role in medical school that led her to create Public Day of Service, an event which has been adopted by many colleges of osteopathic medicine across the country. In this profile, she shares what led her to medical school and where she's headed next.
Class of 2024 Graduate Profile: Charlie Spieser
Charlie Spieser became interested in medicine after shadowing a D.O. in the eighth grade. Learn more about his medical school experience in this profile as we celebrate the Class of 2024 by talking with some of our graduates about their time at the college and where they are headed after graduation.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Thermal insulation works to control the temperature inside the room. As you know, 25% of the heat goes inside your house through the roof, and 15% is from the walls. These materials can block most of the heat from getting inside the house. In general, most insulation materials can do this. But the most affordable ones are fiberglass and ...
Feb 10, 2018 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 15 likes • 14,698 views. S. Shreyas Sasapara. shreyas saspara. Education. 1 of 27. Download now. Thermal insulation materilials and its application - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Download Insulation Material and its Uses - PowerPoint Presentation.Download PPT - https://refreshscience.com/insulation-material-ppt/Many people make the mi...
PowerPoint Presentation. Spray foam insulation has outstanding insulation properties when compared to traditional insulation materials. It can be an important tool in designing and installing a well-sealed, energy-efficient building envelope. This section will briefly look at the most common types of insulation used in commercial construction ...
Insulation. Insulation Materials. Insulation materials run the gamut from bulky fiber materials such as fiberglass, rock and slag wool, cellulose, and natural fibers to rigid foam boards to sleek foils. Bulky materials resist conductive and -- to a lesser degree -- convective heat flow in a building cavity. Rigid foam boards trap air or another ...
Electrical insulation materials include mica, asbestos, rubber and porcelain. Their requisite qualities and uses are also noted. Sound insulation aims to reduce sound transmission and lists reasons for its use including noisy neighbors and audio recording studios. Common sound insulating materials and their applications are also provided.
INSULATING Materials. Insulator. The Insulator is a material that retards the flow of electricity. There are different insulators used in the electrical and electronic component and assemblies. Some of the insulators are Porcelain, plastic, ceramic, polymer etc. Download Presentation. electrical. electrical appliances. electrical current.
Effects different insulating materials have on heat transfer through exterior house walls. Effects different insulating materials have on heat transfer through exterior house walls. Tim Doot and Sabin Gautam. Wall Detail. Thermal Resistance of wall components. Gypsum Sheathing - (13 mm) - 0.079 K·m 2 /W Gypsum Wallboard - (50 mm) - 0.085 K·m 2 /W
24 likes • 13,002 views. B. Bekark. HVAC Lecture, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. Education. 1 of 37. Download now. Download to read offline. Lecture 7 thermal insulation - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
4 INTRODUCTION The materials which have very high resistivity i.e. offers a very high resistance to the flow of electric current. Insulating materials plays an important part in various electrical and electronic circuits. In domestic wiring insulating material protect us from shock and also prevent leakage current.
Worked example 1: A solid insulating material of relative permittivity 2.5 is used in a capacitor between two metal electrodes. The thickness of the insulating sheet is 0.3 cm. Voids are known to occur in the sheet and their sizes are small relative to the insulation. The depth of each void lies in between 0.01 cm and.
Blanket insulation. Loose fill insulation. Bat insulating materials. Insulating boards. Reflective sheet materials. Lightweight materials. 1. Slab or Block Insulation. The blocks are made of mineral wool, cork board, cellular glass, and cellular rubber or saw dust etc.
The winding Insulation is normally made of paper. Cellulose board is also used as internal insulation in liquid-filled transformers. Cellulose insulation is impregnable with the insulating fluid of transformers. Conductor insulations is usually paper, in the form pressboard. Insulating board is made of wood or mixture of wood and cotton.
These materials are known as insulation materials. Common insulation materials are wool, fiberglass, rock wool, polystyrene, polyurethane, and goose feather etc. These materials are very poor conductors of heat and are therefore good thermal insulators. It must be added, thermal insulation is primarily based on the very low thermal conductivity ...
Thermal Insulation PPT Download Free. October 8, 2019 by Sanjay Singh. In this post, we share ppt of thermal insulation material topic which covered almost all topics related to insulation materials. We explained the different types of insulating material used in building. And also this ppt is absolutely Free.
5.4 Insulating liquids (mineral oil, synthet-ic fluids, vegetable oils) 5.5 Fibrous materials (paper, pressboard, synthetic materials) The extensiveness of the topic and the variety of materials do not nearly allow an exhaustive approach. The presentation therefore must be restricted to certain important fundamentals and points. The user ...
An Electrical Insulating Material/Insulating Material is used to obstruct the flow of current. It forms ionic bonds and the materials that have low conductivity and high resistivity are available in the form of solid, liquid, gaseous like the plastic used for plugs, insulating oil used in transformer, etc.These materials have very high resistance so the flow of electric current requires an ...
SECTION 2 INSULATION MATERIALS AND PROPERTIES MP-4 l. Fire retardancy: Flame spread and smoke developed ratings are of vital importance; referred to as "surface burning characteristics". m. Resistance to ultraviolet light: Significant if application is outdoors and high intensity indoors. n. Resistance to fungal or bacterial growth: Is important in all insulation applications.
4. INTRODUCTION The materials which have very high resistivity i.e. offers a very high resistance to the flow of electric current. Insulating materials plays an important part in various electrical and electronic circuits. In domestic wiring insulating material protect us from shock and also prevent leakage current.
insulating material ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. insulating material
To solve the severe problems of electromagnetic pollution and thermal exhaustion in electronics, this work pioneers the utilization of SnO 2 @SnP 2 O 7 @Sn 2 P 2 O 7 hierarchical architectures (HAs) as an electrically insulated filler with strong microwave absorption and high heat conduction. The HAs are produced through a simple hydrothermal-annealing approach, in which their morphology and ...
The primary mission of the SBI is to provide retirement security for over 840,000 Minnesota public employees and their families. We are entrusted with this mission on behalf of plan members who contribute a meaningful portion of their salaries in return for their retirement security. The Minnesota public employees we serve include bus drivers ...
Thermal insulation of building. Apr 12, 2020 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 7 likes • 1,325 views. Manoj Mota. In this presentation we will learn how the thermal insulation of building can be done. Different materials used for thermal insulation and methods to do it are explained.
Last month at the annual Game Developers Conference, Epic Games Engineering Fellow Graham Wihlidal presented "Nanite GPU-Driven Materials," an advanced technical talk that takes a deep dive into Nanite's novel GPU-driven material pipeline and you can download the slides here. This presentation details the GPU-driven material pipeline's core components and explains how they fit into ...
Courtesy of Gucci. 21. By Monica Khemsurov. April 19, 2024. The annual Salone del Mobile furniture fair has always been big — it's the event of the year for the international design world ...
Nov 9, 2017 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 52 likes • 24,102 views. GAURAV. H .TANDON. Insulating material. Engineering. 1 of 43. Download now. Insulating material - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Inclusion scholars bring attention to health equity issues. While progress has been made to improve health equity, more needs to be done on many fronts, from medical education to patient care. That was a key message delivered by the Ohio University Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine Inclusion Scholars in a research presentation. As part ...
Thermal insulation is used in air conditioning systems to reduce heat transfer. It prevents heat gain or loss through piping and helps inhibit condensation. Insulation materials include fiberglass, mineral wool, cellulose, polyurethane foam, and polystyrene. Each material has advantages - fiberglass is cheap but requires safe handling ...