
Research Design 101
Everything You Need To Get Started (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewers: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) & Kerryn Warren (PhD) | April 2023

Navigating the world of research can be daunting, especially if you’re a first-time researcher. One concept you’re bound to run into fairly early in your research journey is that of “ research design ”. Here, we’ll guide you through the basics using practical examples , so that you can approach your research with confidence.
Overview: Research Design 101
What is research design.
- Research design types for quantitative studies
- Video explainer : quantitative research design
- Research design types for qualitative studies
- Video explainer : qualitative research design
- How to choose a research design
- Key takeaways
Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project , from its conception to the final data analysis. A good research design serves as the blueprint for how you, as the researcher, will collect and analyse data while ensuring consistency, reliability and validity throughout your study.
Understanding different types of research designs is essential as helps ensure that your approach is suitable given your research aims, objectives and questions , as well as the resources you have available to you. Without a clear big-picture view of how you’ll design your research, you run the risk of potentially making misaligned choices in terms of your methodology – especially your sampling , data collection and data analysis decisions.
The problem with defining research design…
One of the reasons students struggle with a clear definition of research design is because the term is used very loosely across the internet, and even within academia.
Some sources claim that the three research design types are qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods , which isn’t quite accurate (these just refer to the type of data that you’ll collect and analyse). Other sources state that research design refers to the sum of all your design choices, suggesting it’s more like a research methodology . Others run off on other less common tangents. No wonder there’s confusion!
In this article, we’ll clear up the confusion. We’ll explain the most common research design types for both qualitative and quantitative research projects, whether that is for a full dissertation or thesis, or a smaller research paper or article.

Research Design: Quantitative Studies
Quantitative research involves collecting and analysing data in a numerical form. Broadly speaking, there are four types of quantitative research designs: descriptive , correlational , experimental , and quasi-experimental .
Descriptive Research Design
As the name suggests, descriptive research design focuses on describing existing conditions, behaviours, or characteristics by systematically gathering information without manipulating any variables. In other words, there is no intervention on the researcher’s part – only data collection.
For example, if you’re studying smartphone addiction among adolescents in your community, you could deploy a survey to a sample of teens asking them to rate their agreement with certain statements that relate to smartphone addiction. The collected data would then provide insight regarding how widespread the issue may be – in other words, it would describe the situation.
The key defining attribute of this type of research design is that it purely describes the situation . In other words, descriptive research design does not explore potential relationships between different variables or the causes that may underlie those relationships. Therefore, descriptive research is useful for generating insight into a research problem by describing its characteristics . By doing so, it can provide valuable insights and is often used as a precursor to other research design types.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational design is a popular choice for researchers aiming to identify and measure the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them . In other words, this type of research design is useful when you want to know whether a change in one thing tends to be accompanied by a change in another thing.
For example, if you wanted to explore the relationship between exercise frequency and overall health, you could use a correlational design to help you achieve this. In this case, you might gather data on participants’ exercise habits, as well as records of their health indicators like blood pressure, heart rate, or body mass index. Thereafter, you’d use a statistical test to assess whether there’s a relationship between the two variables (exercise frequency and health).
As you can see, correlational research design is useful when you want to explore potential relationships between variables that cannot be manipulated or controlled for ethical, practical, or logistical reasons. It is particularly helpful in terms of developing predictions , and given that it doesn’t involve the manipulation of variables, it can be implemented at a large scale more easily than experimental designs (which will look at next).
That said, it’s important to keep in mind that correlational research design has limitations – most notably that it cannot be used to establish causality . In other words, correlation does not equal causation . To establish causality, you’ll need to move into the realm of experimental design, coming up next…
Need a helping hand?
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to determine if there is a causal relationship between two or more variables . With this type of research design, you, as the researcher, manipulate one variable (the independent variable) while controlling others (dependent variables). Doing so allows you to observe the effect of the former on the latter and draw conclusions about potential causality.
For example, if you wanted to measure if/how different types of fertiliser affect plant growth, you could set up several groups of plants, with each group receiving a different type of fertiliser, as well as one with no fertiliser at all. You could then measure how much each plant group grew (on average) over time and compare the results from the different groups to see which fertiliser was most effective.
Overall, experimental research design provides researchers with a powerful way to identify and measure causal relationships (and the direction of causality) between variables. However, developing a rigorous experimental design can be challenging as it’s not always easy to control all the variables in a study. This often results in smaller sample sizes , which can reduce the statistical power and generalisability of the results.
Moreover, experimental research design requires random assignment . This means that the researcher needs to assign participants to different groups or conditions in a way that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group (note that this is not the same as random sampling ). Doing so helps reduce the potential for bias and confounding variables . This need for random assignment can lead to ethics-related issues . For example, withholding a potentially beneficial medical treatment from a control group may be considered unethical in certain situations.
Quasi-Experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used when the research aims involve identifying causal relations , but one cannot (or doesn’t want to) randomly assign participants to different groups (for practical or ethical reasons). Instead, with a quasi-experimental research design, the researcher relies on existing groups or pre-existing conditions to form groups for comparison.
For example, if you were studying the effects of a new teaching method on student achievement in a particular school district, you may be unable to randomly assign students to either group and instead have to choose classes or schools that already use different teaching methods. This way, you still achieve separate groups, without having to assign participants to specific groups yourself.
Naturally, quasi-experimental research designs have limitations when compared to experimental designs. Given that participant assignment is not random, it’s more difficult to confidently establish causality between variables, and, as a researcher, you have less control over other variables that may impact findings.
All that said, quasi-experimental designs can still be valuable in research contexts where random assignment is not possible and can often be undertaken on a much larger scale than experimental research, thus increasing the statistical power of the results. What’s important is that you, as the researcher, understand the limitations of the design and conduct your quasi-experiment as rigorously as possible, paying careful attention to any potential confounding variables .

Research Design: Qualitative Studies
There are many different research design types when it comes to qualitative studies, but here we’ll narrow our focus to explore the “Big 4”. Specifically, we’ll look at phenomenological design, grounded theory design, ethnographic design, and case study design.
Phenomenological Research Design
Phenomenological design involves exploring the meaning of lived experiences and how they are perceived by individuals. This type of research design seeks to understand people’s perspectives , emotions, and behaviours in specific situations. Here, the aim for researchers is to uncover the essence of human experience without making any assumptions or imposing preconceived ideas on their subjects.
For example, you could adopt a phenomenological design to study why cancer survivors have such varied perceptions of their lives after overcoming their disease. This could be achieved by interviewing survivors and then analysing the data using a qualitative analysis method such as thematic analysis to identify commonalities and differences.
Phenomenological research design typically involves in-depth interviews or open-ended questionnaires to collect rich, detailed data about participants’ subjective experiences. This richness is one of the key strengths of phenomenological research design but, naturally, it also has limitations. These include potential biases in data collection and interpretation and the lack of generalisability of findings to broader populations.
Grounded Theory Research Design
Grounded theory (also referred to as “GT”) aims to develop theories by continuously and iteratively analysing and comparing data collected from a relatively large number of participants in a study. It takes an inductive (bottom-up) approach, with a focus on letting the data “speak for itself”, without being influenced by preexisting theories or the researcher’s preconceptions.
As an example, let’s assume your research aims involved understanding how people cope with chronic pain from a specific medical condition, with a view to developing a theory around this. In this case, grounded theory design would allow you to explore this concept thoroughly without preconceptions about what coping mechanisms might exist. You may find that some patients prefer cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) while others prefer to rely on herbal remedies. Based on multiple, iterative rounds of analysis, you could then develop a theory in this regard, derived directly from the data (as opposed to other preexisting theories and models).
Grounded theory typically involves collecting data through interviews or observations and then analysing it to identify patterns and themes that emerge from the data. These emerging ideas are then validated by collecting more data until a saturation point is reached (i.e., no new information can be squeezed from the data). From that base, a theory can then be developed .
As you can see, grounded theory is ideally suited to studies where the research aims involve theory generation , especially in under-researched areas. Keep in mind though that this type of research design can be quite time-intensive , given the need for multiple rounds of data collection and analysis.
Ethnographic Research Design
Ethnographic design involves observing and studying a culture-sharing group of people in their natural setting to gain insight into their behaviours, beliefs, and values. The focus here is on observing participants in their natural environment (as opposed to a controlled environment). This typically involves the researcher spending an extended period of time with the participants in their environment, carefully observing and taking field notes .
All of this is not to say that ethnographic research design relies purely on observation. On the contrary, this design typically also involves in-depth interviews to explore participants’ views, beliefs, etc. However, unobtrusive observation is a core component of the ethnographic approach.
As an example, an ethnographer may study how different communities celebrate traditional festivals or how individuals from different generations interact with technology differently. This may involve a lengthy period of observation, combined with in-depth interviews to further explore specific areas of interest that emerge as a result of the observations that the researcher has made.
As you can probably imagine, ethnographic research design has the ability to provide rich, contextually embedded insights into the socio-cultural dynamics of human behaviour within a natural, uncontrived setting. Naturally, however, it does come with its own set of challenges, including researcher bias (since the researcher can become quite immersed in the group), participant confidentiality and, predictably, ethical complexities . All of these need to be carefully managed if you choose to adopt this type of research design.
Case Study Design
With case study research design, you, as the researcher, investigate a single individual (or a single group of individuals) to gain an in-depth understanding of their experiences, behaviours or outcomes. Unlike other research designs that are aimed at larger sample sizes, case studies offer a deep dive into the specific circumstances surrounding a person, group of people, event or phenomenon, generally within a bounded setting or context .
As an example, a case study design could be used to explore the factors influencing the success of a specific small business. This would involve diving deeply into the organisation to explore and understand what makes it tick – from marketing to HR to finance. In terms of data collection, this could include interviews with staff and management, review of policy documents and financial statements, surveying customers, etc.
While the above example is focused squarely on one organisation, it’s worth noting that case study research designs can have different variation s, including single-case, multiple-case and longitudinal designs. As you can see in the example, a single-case design involves intensely examining a single entity to understand its unique characteristics and complexities. Conversely, in a multiple-case design , multiple cases are compared and contrasted to identify patterns and commonalities. Lastly, in a longitudinal case design , a single case or multiple cases are studied over an extended period of time to understand how factors develop over time.
As you can see, a case study research design is particularly useful where a deep and contextualised understanding of a specific phenomenon or issue is desired. However, this strength is also its weakness. In other words, you can’t generalise the findings from a case study to the broader population. So, keep this in mind if you’re considering going the case study route.
How To Choose A Research Design
Having worked through all of these potential research designs, you’d be forgiven for feeling a little overwhelmed and wondering, “ But how do I decide which research design to use? ”. While we could write an entire post covering that alone, here are a few factors to consider that will help you choose a suitable research design for your study.
Data type: The first determining factor is naturally the type of data you plan to be collecting – i.e., qualitative or quantitative. This may sound obvious, but we have to be clear about this – don’t try to use a quantitative research design on qualitative data (or vice versa)!
Research aim(s) and question(s): As with all methodological decisions, your research aim and research questions will heavily influence your research design. For example, if your research aims involve developing a theory from qualitative data, grounded theory would be a strong option. Similarly, if your research aims involve identifying and measuring relationships between variables, one of the experimental designs would likely be a better option.
Time: It’s essential that you consider any time constraints you have, as this will impact the type of research design you can choose. For example, if you’ve only got a month to complete your project, a lengthy design such as ethnography wouldn’t be a good fit.
Resources: Take into account the resources realistically available to you, as these need to factor into your research design choice. For example, if you require highly specialised lab equipment to execute an experimental design, you need to be sure that you’ll have access to that before you make a decision.
Keep in mind that when it comes to research, it’s important to manage your risks and play as conservatively as possible. If your entire project relies on you achieving a huge sample, having access to niche equipment or holding interviews with very difficult-to-reach participants, you’re creating risks that could kill your project. So, be sure to think through your choices carefully and make sure that you have backup plans for any existential risks. Remember that a relatively simple methodology executed well generally will typically earn better marks than a highly-complex methodology executed poorly.

Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. Let’s recap by looking at the key takeaways:
- Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project, from its conception to the final analysis of data.
- Research designs for quantitative studies include descriptive , correlational , experimental and quasi-experimenta l designs.
- Research designs for qualitative studies include phenomenological , grounded theory , ethnographic and case study designs.
- When choosing a research design, you need to consider a variety of factors, including the type of data you’ll be working with, your research aims and questions, your time and the resources available to you.
If you need a helping hand with your research design (or any other aspect of your research), check out our private coaching services .

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

Is there any blog article explaining more on Case study research design? Is there a Case study write-up template? Thank you.
Thanks this was quite valuable to clarify such an important concept.
Thanks for this simplified explanations. it is quite very helpful.
This was really helpful. thanks
Thank you for your explanation. I think case study research design and the use of secondary data in researches needs to be talked about more in your videos and articles because there a lot of case studies research design tailored projects out there.
Please is there any template for a case study research design whose data type is a secondary data on your repository?
This post is very clear, comprehensive and has been very helpful to me. It has cleared the confusion I had in regard to research design and methodology.
This post is helpful, easy to understand, and deconstructs what a research design is. Thanks
how to cite this page
Thank you very much for the post. It is wonderful and has cleared many worries in my mind regarding research designs. I really appreciate .
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Learn / Blog / Article
Back to blog
How to do market research in 4 steps: a lean approach to marketing research
From pinpointing your target audience and assessing your competitive advantage, to ongoing product development and customer satisfaction efforts, market research is a practice your business can only benefit from.
Learn how to conduct quick and effective market research using a lean approach in this article full of strategies and practical examples.

Last updated
Reading time.
A comprehensive (and successful) business strategy is not complete without some form of market research—you can’t make informed and profitable business decisions without truly understanding your customer base and the current market trends that drive your business.
In this article, you’ll learn how to conduct quick, effective market research using an approach called 'lean market research'. It’s easier than you might think, and it can be done at any stage in a product’s lifecycle.
How to conduct lean market research in 4 steps
What is market research, why is market research so valuable, advantages of lean market research, 4 common market research methods, 5 common market research questions, market research faqs.
We’ll jump right into our 4-step approach to lean market research. To show you how it’s done in the real world, each step includes a practical example from Smallpdf , a Swiss company that used lean market research to reduce their tool’s error rate by 75% and boost their Net Promoter Score® (NPS) by 1%.
Research your market the lean way...
From on-page surveys to user interviews, Hotjar has the tools to help you scope out your market and get to know your customers—without breaking the bank.
The following four steps and practical examples will give you a solid market research plan for understanding who your users are and what they want from a company like yours.
1. Create simple user personas
A user persona is a semi-fictional character based on psychographic and demographic data from people who use websites and products similar to your own. Start by defining broad user categories, then elaborate on them later to further segment your customer base and determine your ideal customer profile .
How to get the data: use on-page or emailed surveys and interviews to understand your users and what drives them to your business.
How to do it right: whatever survey or interview questions you ask, they should answer the following questions about the customer:
Who are they?
What is their main goal?
What is their main barrier to achieving this goal?
Pitfalls to avoid:
Don’t ask too many questions! Keep it to five or less, otherwise you’ll inundate them and they’ll stop answering thoughtfully.
Don’t worry too much about typical demographic questions like age or background. Instead, focus on the role these people play (as it relates to your product) and their goals.
How Smallpdf did it: Smallpdf ran an on-page survey for a couple of weeks and received 1,000 replies. They learned that many of their users were administrative assistants, students, and teachers.
Next, they used the survey results to create simple user personas like this one for admins:
Who are they? Administrative Assistants.
What is their main goal? Creating Word documents from a scanned, hard-copy document or a PDF where the source file was lost.
What is their main barrier to achieving it? Converting a scanned PDF doc to a Word file.
💡Pro tip: Smallpdf used Hotjar Surveys to run their user persona survey. Our survey tool helped them avoid the pitfalls of guesswork and find out who their users really are, in their own words.
You can design a survey and start running it in minutes with our easy-to-use drag and drop builder. Customize your survey to fit your needs, from a sleek one-question pop-up survey to a fully branded questionnaire sent via email.
We've also created 40+ free survey templates that you can start collecting data with, including a user persona survey like the one Smallpdf used.
2. Conduct observational research
Observational research involves taking notes while watching someone use your product (or a similar product).
Overt vs. covert observation
Overt observation involves asking customers if they’ll let you watch them use your product. This method is often used for user testing and it provides a great opportunity for collecting live product or customer feedback .
Covert observation means studying users ‘in the wild’ without them knowing. This method works well if you sell a type of product that people use regularly, and it offers the purest observational data because people often behave differently when they know they’re being watched.
Tips to do it right:
Record an entry in your field notes, along with a timestamp, each time an action or event occurs.
Make note of the users' workflow, capturing the ‘what,’ ‘why,’ and ‘for whom’ of each action.

Don’t record identifiable video or audio data without consent. If recording people using your product is helpful for achieving your research goal, make sure all participants are informed and agree to the terms.
Don’t forget to explain why you’d like to observe them (for overt observation). People are more likely to cooperate if you tell them you want to improve the product.
💡Pro tip: while conducting field research out in the wild can wield rewarding results, you can also conduct observational research remotely. Hotjar Recordings is a tool that lets you capture anonymized user sessions of real people interacting with your website.
Observe how customers navigate your pages and products to gain an inside look into their user behavior . This method is great for conducting exploratory research with the purpose of identifying more specific issues to investigate further, like pain points along the customer journey and opportunities for optimizing conversion .
With Hotjar Recordings you can observe real people using your site without capturing their sensitive information
How Smallpdf did it: here’s how Smallpdf observed two different user personas both covertly and overtly.
Observing students (covert): Kristina Wagner, Principle Product Manager at Smallpdf, went to cafes and libraries at two local universities and waited until she saw students doing PDF-related activities. Then she watched and took notes from a distance. One thing that struck her was the difference between how students self-reported their activities vs. how they behaved (i.e, the self-reporting bias). Students, she found, spent hours talking, listening to music, or simply staring at a blank screen rather than working. When she did find students who were working, she recorded the task they were performing and the software they were using (if she recognized it).
Observing administrative assistants (overt): Kristina sent emails to admins explaining that she’d like to observe them at work, and she asked those who agreed to try to batch their PDF work for her observation day. While watching admins work, she learned that they frequently needed to scan documents into PDF-format and then convert those PDFs into Word docs. By observing the challenges admins faced, Smallpdf knew which products to target for improvement.
“Data is really good for discovery and validation, but there is a bit in the middle where you have to go and find the human.”
3. Conduct individual interviews
Interviews are one-on-one conversations with members of your target market. They allow you to dig deep and explore their concerns, which can lead to all sorts of revelations.
Listen more, talk less. Be curious.
Act like a journalist, not a salesperson. Rather than trying to talk your company up, ask people about their lives, their needs, their frustrations, and how a product like yours could help.
Ask "why?" so you can dig deeper. Get into the specifics and learn about their past behavior.
Record the conversation. Focus on the conversation and avoid relying solely on notes by recording the interview. There are plenty of services that will transcribe recorded conversations for a good price (including Hotjar!).
Avoid asking leading questions , which reveal bias on your part and pushes respondents to answer in a certain direction (e.g. “Have you taken advantage of the amazing new features we just released?).
Don't ask loaded questions , which sneak in an assumption which, if untrue, would make it impossible to answer honestly. For example, we can’t ask you, “What did you find most useful about this article?” without asking whether you found the article useful in the first place.
Be cautious when asking opinions about the future (or predictions of future behavior). Studies suggest that people aren’t very good at predicting their future behavior. This is due to several cognitive biases, from the misguided exceptionalism bias (we’re good at guessing what others will do, but we somehow think we’re different), to the optimism bias (which makes us see things with rose-colored glasses), to the ‘illusion of control’ (which makes us forget the role of randomness in future events).
How Smallpdf did it: Kristina explored her teacher user persona by speaking with university professors at a local graduate school. She learned that the school was mostly paperless and rarely used PDFs, so for the sake of time, she moved on to the admins.
A bit of a letdown? Sure. But this story highlights an important lesson: sometimes you follow a lead and come up short, so you have to make adjustments on the fly. Lean market research is about getting solid, actionable insights quickly so you can tweak things and see what works.
💡Pro tip: to save even more time, conduct remote interviews using an online user research service like Hotjar Engage , which automates the entire interview process, from recruitment and scheduling to hosting and recording.
You can interview your own customers or connect with people from our diverse pool of 200,000+ participants from 130+ countries and 25 industries. And no need to fret about taking meticulous notes—Engage will automatically transcribe the interview for you.
4. Analyze the data (without drowning in it)
The following techniques will help you wrap your head around the market data you collect without losing yourself in it. Remember, the point of lean market research is to find quick, actionable insights.
A flow model is a diagram that tracks the flow of information within a system. By creating a simple visual representation of how users interact with your product and each other, you can better assess their needs.
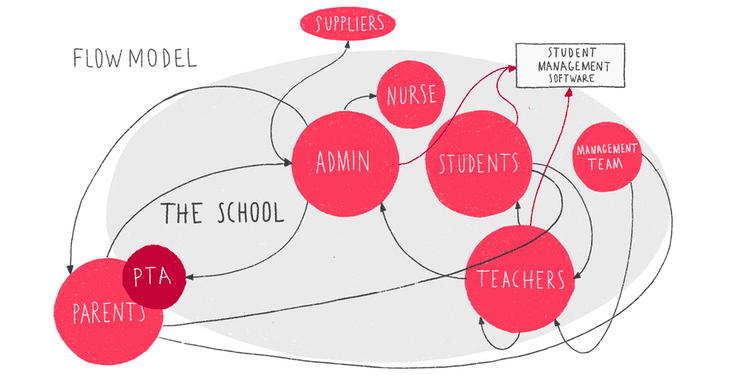
You’ll notice that admins are at the center of Smallpdf’s flow model, which represents the flow of PDF-related documents throughout a school. This flow model shows the challenges that admins face as they work to satisfy their own internal and external customers.
Affinity diagram
An affinity diagram is a way of sorting large amounts of data into groups to better understand the big picture. For example, if you ask your users about their profession, you’ll notice some general themes start to form, even though the individual responses differ. Depending on your needs, you could group them by profession, or more generally by industry.
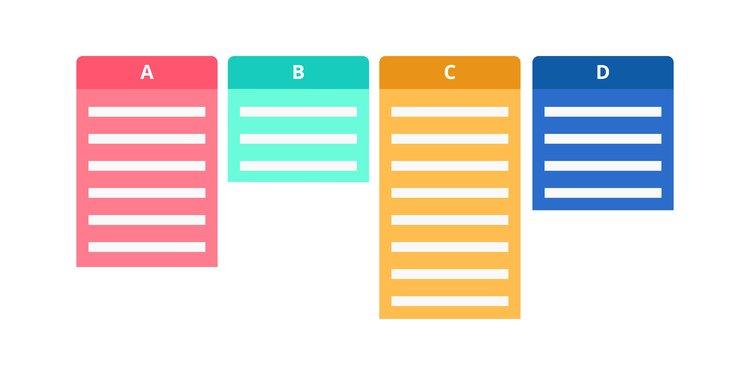
We wrote a guide about how to analyze open-ended questions to help you sort through and categorize large volumes of response data. You can also do this by hand by clipping up survey responses or interview notes and grouping them (which is what Kristina does).
“For an interview, you will have somewhere between 30 and 60 notes, and those notes are usually direct phrases. And when you literally cut them up into separate pieces of paper and group them, they should make sense by themselves.”
Pro tip: if you’re conducting an online survey with Hotjar, keep your team in the loop by sharing survey responses automatically via our Slack and Microsoft Team integrations. Reading answers as they come in lets you digest the data in pieces and can help prepare you for identifying common themes when it comes time for analysis.
Hotjar lets you easily share survey responses with your team
Customer journey map
A customer journey map is a diagram that shows the way a typical prospect becomes a paying customer. It outlines their first interaction with your brand and every step in the sales cycle, from awareness to repurchase (and hopefully advocacy).
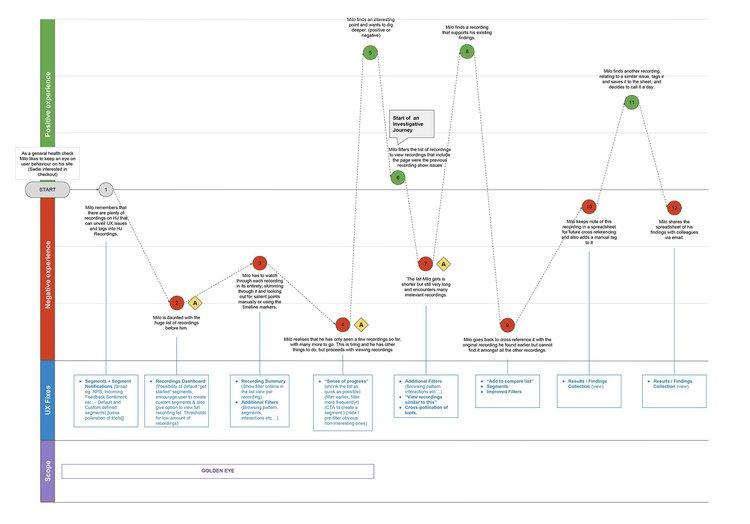
The above customer journey map , created by our team at Hotjar, shows many ways a customer might engage with our tool. Your map will be based on your own data and business model.
📚 Read more: if you’re new to customer journey maps, we wrote this step-by-step guide to creating your first customer journey map in 2 and 1/2 days with free templates you can download and start using immediately.
Next steps: from research to results
So, how do you turn market research insights into tangible business results? Let’s look at the actions Smallpdf took after conducting their lean market research: first they implemented changes, then measured the impact.

Implement changes
Based on what Smallpdf learned about the challenges that one key user segment (admins) face when trying to convert PDFs into Word files, they improved their ‘PDF to Word’ conversion tool.
We won’t go into the details here because it involves a lot of technical jargon, but they made the entire process simpler and more straightforward for users. Plus, they made it so that their system recognized when you drop a PDF file into their ‘Word to PDF’ converter instead of the ‘PDF to Word’ converter, so users wouldn’t have to redo the task when they made that mistake.
In other words: simple market segmentation for admins showed a business need that had to be accounted for, and customers are happier overall after Smallpdf implemented an informed change to their product.
Measure results
According to the Lean UX model, product and UX changes aren’t retained unless they achieve results.
Smallpdf’s changes produced:
A 75% reduction in error rate for the ‘PDF to Word’ converter
A 1% increase in NPS
Greater confidence in the team’s marketing efforts
"With all the changes said and done, we've cut our original error rate in four, which is huge. We increased our NPS by +1%, which isn't huge, but it means that of the users who received a file, they were still slightly happier than before, even if they didn't notice that anything special happened at all.”
Subscribe to fresh and free monthly insights.
Over 50,000 people interested in UX, product, digital empathy, and beyond, receive our newsletter every month. No spam, just thoughtful perspectives from a range of experts, new approaches to remote work, and loads more valuable insights. If that floats your boat, why not become a subscriber?
I have read and accepted the message outlined here: Hotjar uses the information you provide to us to send you relevant content, updates and offers from time to time. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the link at the bottom of any email.
Market research (or marketing research) is any set of techniques used to gather information and better understand a company’s target market. This might include primary research on brand awareness and customer satisfaction or secondary market research on market size and competitive analysis. Businesses use this information to design better products, improve user experience, and craft a marketing strategy that attracts quality leads and improves conversion rates.
David Darmanin, one of Hotjar’s founders, launched two startups before Hotjar took off—but both companies crashed and burned. Each time, he and his team spent months trying to design an amazing new product and user experience, but they failed because they didn’t have a clear understanding of what the market demanded.
With Hotjar, they did things differently . Long story short, they conducted market research in the early stages to figure out what consumers really wanted, and the team made (and continues to make) constant improvements based on market and user research.
Without market research, it’s impossible to understand your users. Sure, you might have a general idea of who they are and what they need, but you have to dig deep if you want to win their loyalty.
Here’s why research matters:
Obsessing over your users is the only way to win. If you don’t care deeply about them, you’ll lose potential customers to someone who does.
Analytics gives you the ‘what’, while research gives you the ‘why’. Big data, user analytics , and dashboards can tell you what people do at scale, but only research can tell you what they’re thinking and why they do what they do. For example, analytics can tell you that customers leave when they reach your pricing page, but only research can explain why.
Research beats assumptions, trends, and so-called best practices. Have you ever watched your colleagues rally behind a terrible decision? Bad ideas are often the result of guesswork, emotional reasoning, death by best practices , and defaulting to the Highest Paid Person’s Opinion (HiPPO). By listening to your users and focusing on their customer experience , you’re less likely to get pulled in the wrong direction.
Research keeps you from planning in a vacuum. Your team might be amazing, but you and your colleagues simply can’t experience your product the way your customers do. Customers might use your product in a way that surprises you, and product features that seem obvious to you might confuse them. Over-planning and refusing to test your assumptions is a waste of time, money, and effort because you’ll likely need to make changes once your untested business plan gets put into practice.
Lean User Experience (UX) design is a model for continuous improvement that relies on quick, efficient research to understand customer needs and test new product features.
Lean market research can help you become more...
Efficient: it gets you closer to your customers, faster.
Cost-effective: no need to hire an expensive marketing firm to get things started.
Competitive: quick, powerful insights can place your products on the cutting edge.
As a small business or sole proprietor, conducting lean market research is an attractive option when investing in a full-blown research project might seem out of scope or budget.
There are lots of different ways you could conduct market research and collect customer data, but you don’t have to limit yourself to just one research method. Four common types of market research techniques include surveys, interviews, focus groups, and customer observation.
Which method you use may vary based on your business type: ecommerce business owners have different goals from SaaS businesses, so it’s typically prudent to mix and match these methods based on your particular goals and what you need to know.
1. Surveys: the most commonly used
Surveys are a form of qualitative research that ask respondents a short series of open- or closed-ended questions, which can be delivered as an on-screen questionnaire or via email. When we asked 2,000 Customer Experience (CX) professionals about their company’s approach to research , surveys proved to be the most commonly used market research technique.
What makes online surveys so popular?
They’re easy and inexpensive to conduct, and you can do a lot of data collection quickly. Plus, the data is pretty straightforward to analyze, even when you have to analyze open-ended questions whose answers might initially appear difficult to categorize.
We've built a number of survey templates ready and waiting for you. Grab a template and share with your customers in just a few clicks.
💡 Pro tip: you can also get started with Hotjar AI for Surveys to create a survey in mere seconds . Just enter your market research goal and watch as the AI generates a survey and populates it with relevant questions.
Once you’re ready for data analysis, the AI will prepare an automated research report that succinctly summarizes key findings, quotes, and suggested next steps.
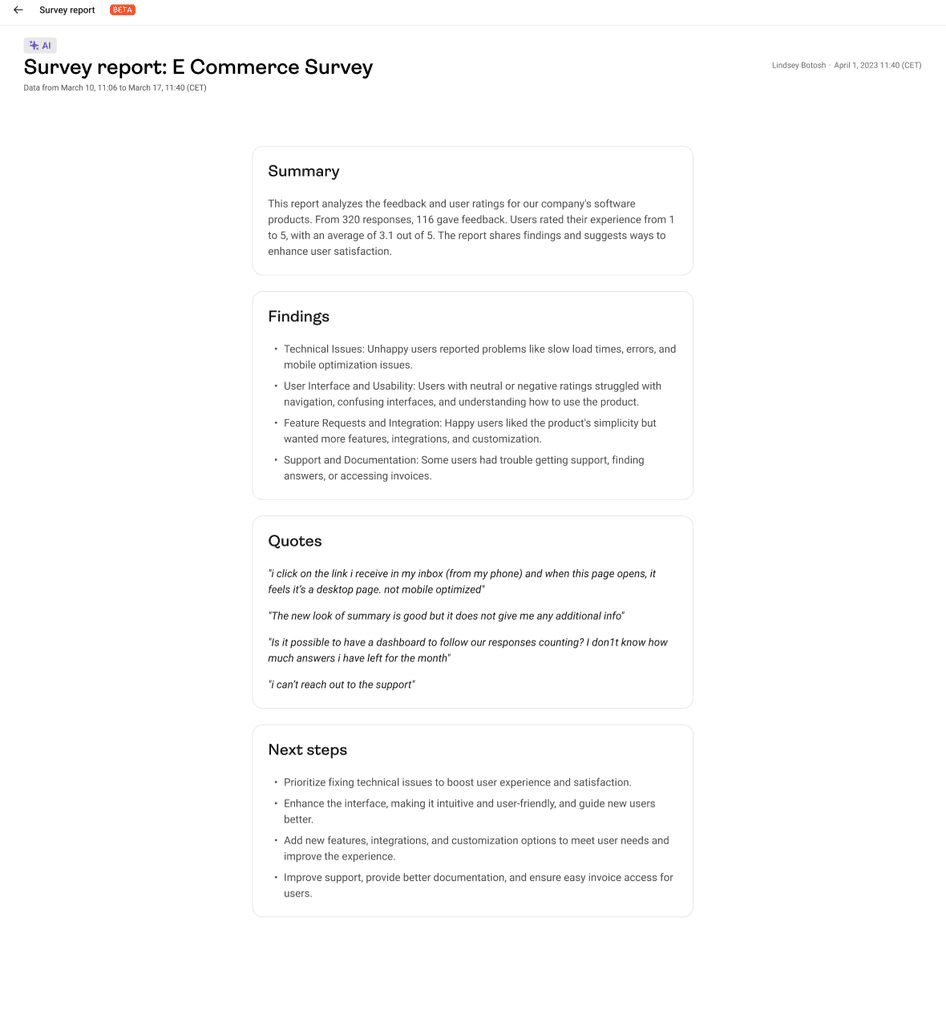
An example research report generated by Hotjar AI for Surveys
2. Interviews: the most insightful
Interviews are one-on-one conversations with members of your target market. Nothing beats a face-to-face interview for diving deep (and reading non-verbal cues), but if an in-person meeting isn’t possible, video conferencing is a solid second choice.
Regardless of how you conduct it, any type of in-depth interview will produce big benefits in understanding your target customers.
What makes interviews so insightful?
By speaking directly with an ideal customer, you’ll gain greater empathy for their experience , and you can follow insightful threads that can produce plenty of 'Aha!' moments.
3. Focus groups: the most unreliable
Focus groups bring together a carefully selected group of people who fit a company’s target market. A trained moderator leads a conversation surrounding the product, user experience, or marketing message to gain deeper insights.
What makes focus groups so unreliable?
If you’re new to market research, we wouldn’t recommend starting with focus groups. Doing it right is expensive , and if you cut corners, your research could fall victim to all kinds of errors. Dominance bias (when a forceful participant influences the group) and moderator style bias (when different moderator personalities bring about different results in the same study) are two of the many ways your focus group data could get skewed.
4. Observation: the most powerful
During a customer observation session, someone from the company takes notes while they watch an ideal user engage with their product (or a similar product from a competitor).
What makes observation so clever and powerful?
‘Fly-on-the-wall’ observation is a great alternative to focus groups. It’s not only less expensive, but you’ll see people interact with your product in a natural setting without influencing each other. The only downside is that you can’t get inside their heads, so observation still isn't a recommended replacement for customer surveys and interviews.
The following questions will help you get to know your users on a deeper level when you interview them. They’re general questions, of course, so don’t be afraid to make them your own.
1. Who are you and what do you do?
How you ask this question, and what you want to know, will vary depending on your business model (e.g. business-to-business marketing is usually more focused on someone’s profession than business-to-consumer marketing).
It’s a great question to start with, and it’ll help you understand what’s relevant about your user demographics (age, race, gender, profession, education, etc.), but it’s not the be-all-end-all of market research. The more specific questions come later.
2. What does your day look like?
This question helps you understand your users’ day-to-day life and the challenges they face. It will help you gain empathy for them, and you may stumble across something relevant to their buying habits.
3. Do you ever purchase [product/service type]?
This is a ‘yes or no’ question. A ‘yes’ will lead you to the next question.
4. What problem were you trying to solve or what goal were you trying to achieve?
This question strikes to the core of what someone’s trying to accomplish and why they might be willing to pay for your solution.
5. Take me back to the day when you first decided you needed to solve this kind of problem or achieve this goal.
This is the golden question, and it comes from Adele Revella, Founder and CEO of Buyer Persona Institute . It helps you get in the heads of your users and figure out what they were thinking the day they decided to spend money to solve a problem.
If you take your time with this question, digging deeper where it makes sense, you should be able to answer all the relevant information you need to understand their perspective.
“The only scripted question I want you to ask them is this one: take me back to the day when you first decided that you needed to solve this kind of problem or achieve this kind of a goal. Not to buy my product, that’s not the day. We want to go back to the day that when you thought it was urgent and compelling to go spend money to solve a particular problem or achieve a goal. Just tell me what happened.”
— Adele Revella , Founder/CEO at Buyer Persona Institute
Bonus question: is there anything else you’d like to tell me?
This question isn’t just a nice way to wrap it up—it might just give participants the opportunity they need to tell you something you really need to know.
That’s why Sarah Doody, author of UX Notebook , adds it to the end of her written surveys.
“I always have a last question, which is just open-ended: “Is there anything else you would like to tell me?” And sometimes, that’s where you get four paragraphs of amazing content that you would never have gotten if it was just a Net Promoter Score [survey] or something like that.”
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research?
Qualitative research asks questions that can’t be reduced to a number, such as, “What is your job title?” or “What did you like most about your customer service experience?”
Quantitative research asks questions that can be answered with a numeric value, such as, “What is your annual salary?” or “How was your customer service experience on a scale of 1-5?”
→ Read more about the differences between qualitative and quantitative user research .
How do I do my own market research?
You can do your own quick and effective market research by
Surveying your customers
Building user personas
Studying your users through interviews and observation
Wrapping your head around your data with tools like flow models, affinity diagrams, and customer journey maps
What is the difference between market research and user research?
Market research takes a broad look at potential customers—what problems they’re trying to solve, their buying experience, and overall demand. User research, on the other hand, is more narrowly focused on the use (and usability ) of specific products.
What are the main criticisms of market research?
Many marketing professionals are critical of market research because it can be expensive and time-consuming. It’s often easier to convince your CEO or CMO to let you do lean market research rather than something more extensive because you can do it yourself. It also gives you quick answers so you can stay ahead of the competition.
Do I need a market research firm to get reliable data?
Absolutely not! In fact, we recommend that you start small and do it yourself in the beginning. By following a lean market research strategy, you can uncover some solid insights about your clients. Then you can make changes, test them out, and see whether the results are positive. This is an excellent strategy for making quick changes and remaining competitive.
Net Promoter, Net Promoter System, Net Promoter Score, NPS, and the NPS-related emoticons are registered trademarks of Bain & Company, Inc., Fred Reichheld, and Satmetrix Systems, Inc.
Related articles

6 traits of top marketing leaders (and how to cultivate them in yourself)
Stepping into a marketing leadership role can stir up a mix of emotions: excitement, optimism, and, often, a gnawing doubt. "Do I have the right skills to truly lead and inspire?" If you've ever wrestled with these uncertainties, you're not alone.
Hotjar team

The 7 best BI tools for marketers in 2024 (and how to use them)
Whether you're sifting through campaign attribution data or reviewing performance reports from different sources, extracting meaningful business insights from vast amounts of data is an often daunting—yet critical—task many marketers face. So how do you efficiently evaluate your results and communicate key learnings?
This is where business intelligence (BI) tools come in, transforming raw data into actionable insights that drive informed, customer-centric decisions.

6 marketing trends that will shape the future of ecommerce in 2023
Today, marketing trends evolve at the speed of technology. Ecommerce businesses that fail to update their marketing strategies to meet consumers where they are in 2023 will be left out of the conversations that drive brand success.

Geoff Whiting
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimise digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered straight to teams on the ground
Know exactly how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Meet the operating system for experience management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Research Design
Try Qualtrics for free
The ultimate guide to research design for business.
17 min read To get the information you need to drive key business decisions and answer burning questions, you need a research methodology that works — and it all starts with research design. But what is it? In our ultimate guide to research design for businesses, we breakdown the process, including research methods, examples, and best practice tips to help you get started.
If you have a business problem that you’re trying to solve — from product usage to customer engagement — doing research is a great way to understand what is going wrong.
Yet despite this, less than 40% of marketers use consumer research to drive decisions [1] .
So why are businesses missing out on vital business insights that could help their bottom line?
One reason is that many simply don’t know which research method to use to correctly investigate their problem and uncover insights.
This is where our ultimate guide to research design can help. But first…
What is research design?
Research design is the overall strategy (or research methodology) used to carry out a study. It defines the framework and plan to tackle established problems and/or questions through the collection, interpretation, analysis, and discussion of data.
While there are several types of research design (more on that later), the research problem defines which should be used — not the other way around. In working this way, researchers can be certain that their methods match their aims — and that they’re capturing useful and actionable data.
For example, you might want to know why sales are falling for a specific product. You already have your context and other research questions to help uncover further insights. So, you start with your research problem (or problem statement) and choose an approach to get the information you need.
Download our free eBook: How to get inclusive research design right
Key considerations before a research project
After you have your research problem and research questions to find out more information, you should always consider the following elements:
- Do you want to use a qualitative or quantitative approach ?
- What type of research would you like to do (e.g. — create a survey or conduct telephone interviews)?
- How will you choose your population and sample size fairly?
- How will you choose a method to collect the data for ease of operation? The research tool you use will determine the validity of your study
- How will you analyse data after collection to help the business concern?
- How will you ensure your research is free from bias and neutral?
- What’s your timeline?
- In what setting will you conduct your research study?
- Are there any challenges or objections to conducting your research — and if so, how can you address them?
Ultimately, the data received should be unambiguous, so that the analysts can find accurate and trustworthy insights to act upon. Neutrality is key!
Types of approaches in research design
There are two main approaches to research design that we’ll explore in more detail — quantitative and qualitative.
Qualitative research design
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive (broad generalisations rather than specific observations), allowing you to adjust your approach based on the information you find throughout the research process. It looks at customer or prospect data (X data).
For example, if you want to generate new ideas for content campaigns, a qualitative approach would make the most sense. You can use this approach to find out more about what your audience would like to see, the particular challenges they are facing (from a business perspective), their overall experiences, and if any topics are under-researched.
To put it simply, qualitative research design looks at the whys and hows — as well as participants’ thoughts, feelings, and beliefs. It seeks to find reasons to explain decisions using the data captured.
However, as the data collected from qualitative research is typically written rather than numerical, it can be difficult to quantify information using statistical techniques.
When should you use qualitative research design?
It is best used when you want to conduct a detailed investigation of a topic to understand a holistic view. For example, to understand cultural differences in society, qualitative research design would create a research plan that allowed as many people from different cultures to participate and provided space for elaboration and anecdotal evidence.
If you want to incorporate a qualitative research design, you may choose to use methods like semi-structured focus groups, surveys with open-ended questions, or in-depth interviews in person or on the phone.
Quantitative research design
Quantitative research design looks at data that helps answer the key questions beginning with ‘Who’, ‘How’, ‘How many’ and ‘What’. This can include business data that explores operation statistics and sales records and quantifiable data on preferences.
Unlike qualitative research design, quantitative research design can be more controlled and fixed. It establishes variables, hypotheses, and correlations and tests participants against this knowledge. The aim is to explore the numerical data and understand its value against other sets of data, providing us with a data-driven way to measure the level of something.
When should you use quantitative research design?
If you want to quantify attitudes, opinions, behaviours, or any other defined variable (and general results from a large sample population), a quantitative approach is a way to go.
You could use quantitative research to validate findings from qualitative research. One provides depth and insight into the whys and hows, while the other delivers data to support them.
If you want to incorporate a quantitative research design, you may choose to use methods like secondary research collection or surveys with closed-ended questions.
Now that you know the differences between the two research approaches ( though you can find out more ), we can go further and address their sub-categories.
Research methods: the subsets of qualitative and quantitative research
Depending on the aim/objective of your research, there are several research methods (for both qualitative and quantitative research) for you to choose from:
Types of quantitative research design:
- Descriptive – provides information on the current state of affairs, by observing participants in a natural situation
- Experimental – provides causal relationship information between variables within a controlled situation
- Quasi-experimental – attempts to build a cause and effect relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable
- Correlational – as the name suggests, correlational design allows the researcher to establish some kind of relation between two closely related topics or variables
Types of qualitative research design:
- Case studies – a detailed study of a specific subject (place, event, organization)
- Ethnographic research – in-depth observational studies of people in their natural environment (this research aims to understand the cultures, challenges, motivations and settings of those involved)
- Grounded theory – collecting rich data on a topic of interest and developing theories inductively
- Phenomenology – investigating a phenomenon or event by describing and interpreting the shared experiences of participants
- Narrative research – examining how stories are told to understand how participants perceive and make sense of their experiences
Other subsets of qualitative and quantitative research design
- Exploratory – explores a new subject area by taking a holistic viewpoint and gathering foundational insights
- Cross-sectional – provides a snapshot of a moment in time to reflect the state
- Longitudinal – provides several snapshots of the same sample over a period to understand causal relationships
- Mixed methods – provide a bespoke application of design subsets to create more precise and nuanced results
- Observational – involves observing participants’ ongoing behavior in a natural situation
Let’s talk about these research methods in more detail.
Experimental
As a subset of quantitative research design types, experimental research design aims to control variables in an experiment to test a hypothesis. Researchers will alter one of the variables to see how it affects the others.
Experimental research design provides an understanding of the causal relationships between two variables – which variable impacts the other, to what extent they are affected, and how consistent is the effect if the experiment is repeated.
To incorporate experimental research design, researchers create an artificial environment to more easily control the variables affecting participants. This can include creating two groups of participants – one acting as a control group to provide normal data readings, and another that has a variable altered. Therefore, having representative and random groups of participants can give better results to compare.
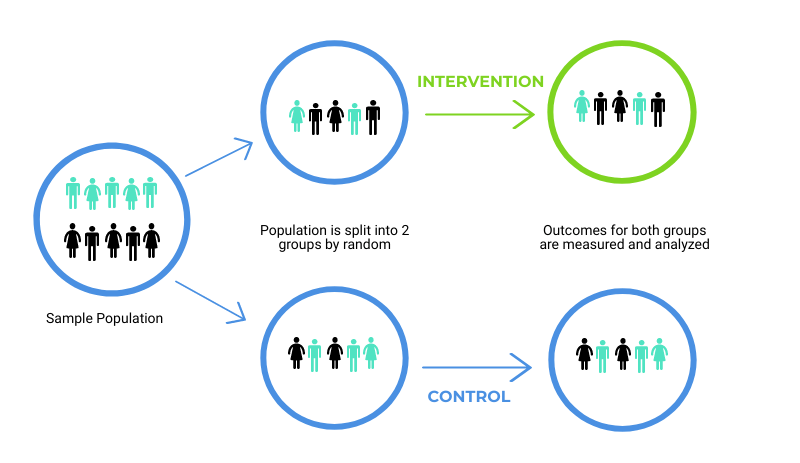
Image source: World Bank Blogs
Descriptive
Descriptive research design is a subset of qualitative design research and, unlike experimental design research, it provides descriptive insights on participants by observing participants in an uncontrolled, geographically-bound natural environment.
This type gives information on the current state of participants when faced with variables or changing circumstances. It helps answer who, what, when, where, and how questions on behaviour, but it can’t provide a clear understanding of the why.
To incorporate a descriptive research design, researchers create situations where observation of participants can happen without notice. In capturing the information, researchers can analyse data to understand the different variables at play or find additional research areas to investigate.
Exploratory
Exploratory research design aims to investigate an area where little is known about the subject and there are no prior examples to draw insight from. Researchers want to gain insights into the foundational data (who, what, when, where, and how) and the deeper level data (the why).
Therefore, an exploratory research design is flexible and a subset of both quantitative and qualitative research design.
Like descriptive research design, this type of research method is used at the beginning stages of research to get a broader view, before proceeding with further research.
To incorporate exploratory research design, researchers will use several methods to gain the right data. These can include focus groups, surveys, interviews in person or on the phone, secondary desk research, controlled experiments, and observation in a natural setting.
Cross-sectional
Just like slicing through a tomato gives us a slice of the whole fruit, cross-sectional research design gives us a slice representing a specific point in time. Researchers can observe different groups at the same time to discover what makes the participant behaviour different from one another and how behaviour correlates. This is then used to form assumptions that can be further tested.
There are two types to consider. In descriptive cross-sectional research design, researchers do not get involved or influence the participants through any controls, so this research design type is a subset of quantitative research design. Researchers will use methods that provide a descriptive (who, what, when, where, and how) understanding of the cross-section. This can be done by survey or observation, though researcher bias can be an undesirable outcome if the method is not conscious of this.
Analytical cross-sectional research design looks at the why behind the outcome found in the cross-section, aligning this as a subset of qualitative research design. This understanding can be gained through emailed surveys. To gain stronger insights, group sample selection can be altered from a random selection of participants to researchers selecting participants into groups based on their differences.
Since only one cross-section is taken, this can be a cheaper and quicker way to carry out research when resources are limited. Yet, no causal relationships can be gained by comparing data across time, unlike longitudinal research design.
Longitudinal
Longitudinal research design takes multiple measures from the same participants or groups over an extended period. These repeated observations enable researchers to track variables, identify correlations and see if there are causal relationships that can confirm hypothesis predictions.
As the research design is focused on understanding the why behind the data, this is a subset of qualitative research design. However, the real-time data collection at each point in time will also require analysis based on the quantitative markers found through quantitative research design.
Researchers can incorporate longitudinal research design by using methods like panel studies for collecting primary data first-hand. The study can be retrospective (based on event data that has already occurred) or prospective (based on event data that is yet to happen).
While being the most useful method to get the data you need to address your business concern, this can be time-consuming and there can be issues with maintaining the integrity of the sample over time. Alternatively, you can use existing data sets to provide historical trends (which could be verified through a cross-sectional research design).
Mixed methods
Mixed methods aim to provide an advanced and bespoke response to solving your business problem. It combines the methods and subsets above to create a tailored method that gives researchers flexibility and options for carrying out research.
The mixed-method research design gives a thorough holistic view of the layers of data through quantitative and qualitative subset design methods. The resulting data is strengthened by the application of context and scale (quantitative) in alignment with the meaning behind behaviour (qualitative), giving a richer picture of participants.
Mixed method research design is useful for getting greater ‘texture’ to your data, resulting in precise and meaningful information for analysis. The disadvantages and boundaries of a single subset can be offset by the benefits of using another to complement the investigation.
This subset does place more responsibility on the researcher to apply the subset designs appropriately to gain the right information. The data is interpreted and assessed by the researcher for its validity to the end results, so there is potential for researcher bias if they miss out on vital information that skews results.
Image Source: Full Stack Researcher
Find the research design method(s) that work for you
No matter what information you want to find out — there’s a research design method that’s right for you.
However, it’s up to you to determine which of the methods above are the most viable and can deliver the insight you need. Remember, each research method has its advantages and disadvantages.
It’s also important to bear in mind (at all times), the key considerations before your research project:
- Do you want to use a qualitative or quantitative approach?
- Are there any challenges or objections to conducting your research — and if so, how can you address them?.
But if you’re unsure about where to begin, start by answering these questions with our decision tree:
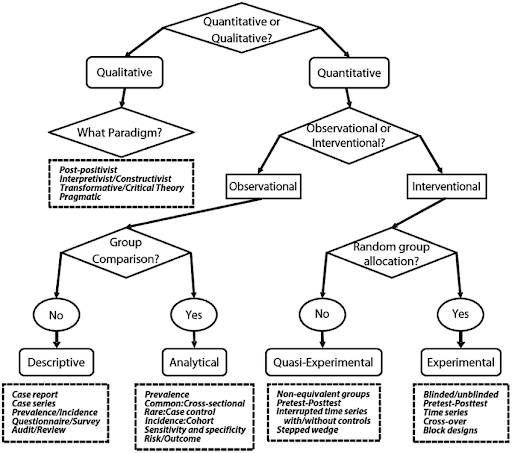
Image Source: Research Gate
If you need more help, why not try speaking to one of our Qualtrics team members?
Our team of experts can help you with all your market research needs — from designing your study and finding respondents, to fielding it and reporting on the results.
[1] https://www.thinkwithgoogle.com/consumer-insights/consumer-trends/marketing-consumer-research-statistics/
eBook: How to get inclusive research design right
Related resources
Market intelligence 9 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, business research methods 12 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, business research 10 min read, qualitative research interviews 11 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6 Types of Research Design
Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, students must be able to:
- Explain the three types of research design used by marketers
- Understand the application of these designs
Research Design
This chapter looks at the types of research designs that are utilized by marketers. A research design is an overall plan or structure for a research project. A research design will use different combinations of primary, secondary, qualitative, and quantitative data. Depending on the overall research questions, research designs in marketing may fall into one of the following three categories:
- Exploratory research design
- Descriptive research design
- Causal research design (experiments)
An exploratory research design is more informal and unstructured than the other two types of designs. Exploratory design is used to explore a situation, especially when the researcher is in unfamiliar territory. Most academic projects begin with exploratory research when researchers undertake desk research. Similarly, when marketers plan to venture into new markets, such as India, it is advisable to employ an exploratory research design. This could mean going through case studies, accessing published reports (i.e., secondary data) on the market, undertaking experience interviews with experts, and conducting focus groups – if needed. Exploratory design is useful in gaining background information and deciding about future research approaches. It may generate more questions, which need to be tackled with other research designs.
As the name suggests, descriptive research design is employed to describe the market or respondents’ characteristics. This type of research design generates quantitative information. Therefore, such a design would often involve surveys. Surveys are useful to measure the descriptive numbers relating to respondents’ age groups, income levels, expenditure patterns, and even attitudes. This can be done by employing relevant scales, such as, “On a scale of 1–5, how satisfied were you with this organisation’s service?”.
Physiological measurements, such as people’s involuntary responses (such as heart rate, skin changes, and eye movement) to marketing stimuli, such as an advertisement may also be categorised in descriptive research. While recording such information requires special instruments, it is nevertheless a type of descriptive information that can be useful for marketers.
Source: Meanthat and authentic data science [1]
Causal research design (also known as experimental research design) examines cause-and-effect relationships. A well-designed experiment is the best way of understanding how one variable (e.g., advertisement) may influence another variable (e.g., sale of a product). An experiment involves one or more independent variables (for example, price level, and product features) which are manipulated to determine how they may impact one or more dependent variables (such as customer preference or customer satisfaction). Independent variables can be ‘manipulated’ by the researcher while the dependent variables are variables that get influenced due to changes in the independent variables.
Experiments can be categorised as field experiments or lab experiments . When an experiment is conducted in a natural setting – such as in a retail store – it is referred to as a field experiment . On the other hand, experiments conducted in a researcher’s office or a university classroom are lab experiments. A lab experiment may be undertaken to measure the impact of an ad on the subject’s attitude.
A field experiment is often seen as providing researchers with reliable results as it is undertaken in the actual environment. However, it is not easy to implement a field experiment. It is difficult to control other factors – in the real environment – which may also impact the final results. Moreover, running an experiment requires expertise in the design of the experiment. It may also require financial and time resources. As an example, Mcdonald’s may wish to see if a drop in the price of its cheeseburger results in greater sales. The fast-food restaurant may drop the price in one locality, such as Fairfield. It may also tediously measure the sales around the time of a price reduction. While interpreting the results, it would need to be assured that any changes in sales figures can be attributed to the price change – and not to other environmental factors such as an increase in prices at Hungry Jacks or an overall increase in customers due to a local football match. Thus, controlling such extraneous variables – that is, all those variables besides the identified independent variables which may also affect the dependent variable.
One of the popular experimental research designs is the ‘Before-After’ Testing design . As the name suggests, it measures the dependent variable, before and after a change in the independent variable. An example will help clarify the concept:
Experimental Group (R) O 1 X O 2
Control Group O 3 O 4
Experimental Effect (E) = (O 2 – O 1 ) – (O 4 – O 3 )
R = random allocation of subjects to experimental or control group
O = observation
X = treatment or manipulation of the independent variable, such as a change in price
Explanation of the above example:
- Subjects or research participants are randomly allocated to one of the groups
- The experimental group is the one in which the independent variable (e.g., price) is manipulated (e.g., reduced)
- The control group is not exposed to any changes in the independent variable
- Measurements (i.e., O) for the dependent variable (e.g., sales) – for both groups – are taken before the change in price (X) – PRE-TEST
- Measurements (i..e., O) for the dependent variable are taken after the change in price – POST-TEST
- The difference between O 2 and O 1 demonstrates the change in the dependent variable due to the change in X (independent variable)
- The difference between O 4 and O 3 demonstrate any change in the dependent variable due to factors other than X
- Therefore, the difference between the two groups (O 2 – O 1 ) – (O 4 – O 3 ) demonstrates the true effect of the independent variable as it removes any influence of extraneous variables.
- Meanthat and authentic data science 2016, 1.3 Exploratory, descriptive and explanatory nature of research , 17 March, online video, viewed 3 March 2022, <https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FlBFdEgrTBM>. ↵
Customer Insights Copyright © 2022 by Aila Khan is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

9 Highly Successful Market Research Examples

In the battle of instinct vs insight, there’s clear evidence that data-driven decision-making pays off.
A McKinsey study into the impact of market research found that organizations using data to make decisions are more likely to be profitable, and can more effectively retain and acquire customers vs those who fail to use this approach.
I’ve curated nine of the best market research examples to help you find innovative ways to fuel growth , adapt, and impact change when and where it’s most needed. This post guides you through the problems faced along with the processes and tools used so you can replicate actions and outcomes in your business.

Market Research Example #1 – Understand the competitive landscape
In any business of any size, having in-depth insights into competitors’ audiences, campaigns, keywords, ( and more ) allows you to shape or refine your own plans for success. You can cut through the noise, see what’s working, and uncover opportunities for growth.

Since 2013, Wonderbly’s business has grown exponentially and now sells personalized books to over six million customers worldwide. In order to validate its go-to-market strategy, it needed granular insights into competitors and market trends.
Here’s how it played out.
1. Competitive insights
Challenge: Low visibility into a key competitor’s activity
Action: By analyzing competitor audience demographics that showed both gender and age distribution of its rival’s audience, Wonderbly saw its competition was better at attracting a younger audience.
Impact: Through the development of a new audience profile and key changes to future campaign strategies, it was able to grow the business and attract new customers.
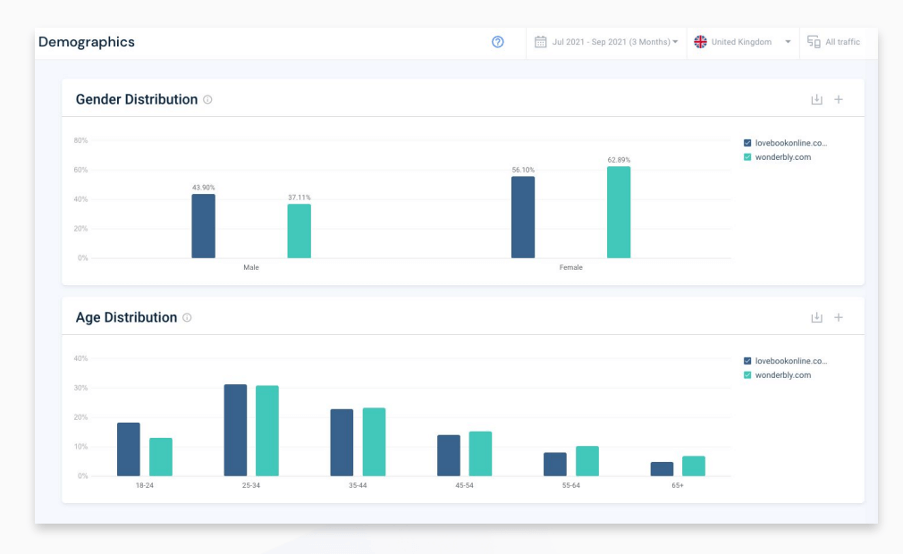
This snapshot shows competitors’ website demographics side-by-side. While it was attracting a larger female audience of 62% vs. 56%, they saw their rivals were better at appealing to a male audience, with a respective split of 43% vs. 37%. In age distribution, its share in the 18-24 bracket was just 12% vs. 19%. Showing a clear opportunity to do more to reach that younger audience.
2. Keyword seasonality
Challenge: Lack of data to enter new markets
Action: Using seasonal trends keywords that showed where competitors were winning traffic from paid ad channels, Wonderbly discovered an emerging category (weddings and anniversaries) that was not addressed with its own offering.
Impact: By demonstrating competitors’ success and subsequent consumer interest, a new product line was developed. It went on to achieve a 69% revenue increase in books purchased by a more mature audience.

Keyword seasonality screenshot shows traffic leaders for specific keyword sets, their seasonality, traffic share , volume, and CPC data. This shows where competitors are using paid ads to win traffic share.
3. Audience data
Challenge: Limited view of audience browsing behavior
Action: By looking into audience data that showed which sites its visitors were cross-browsing, Wonderbly was able to determine audience loyalty vs. that of its rivals.
Impact: The information was used to forge new content-focused partnerships in the UK, US, and Canada with several organizations and drove more traffic to its own site as a result.

Audience overlap screenshot shows which sites its customers are browsing, how loyal they are, and presented new information about a referral partnership.
See the full story behind Wonderly’s success here.

Market Research Example #2 – Market intelligence
Most business leaders and marketers have a solid understanding of their market. But if you want to stay ahead of the game, you need to reach deep inside a market, and often. Dynamic market intel enables you to do this and achieve sustainable growth by spotting emerging opportunities as they happen.

Red Arbor is the third-largest job board website in the world . Market intelligence is an integral part of its business; with granular data across multiple markets, it knows the how and why behind individual brands’ performance.
Challenge: Difficult to see what’s happening across websites, apps, and digital entities in relevant markets.
Action: By using competitive and market intelligence tools, Red Arbor could see market movements and shifts in rival traffic share in all relevant markets as they occurred.
Impact: Key data can be constantly monitored to provide intel around emerging competitors and enables Red Arbor brands to quickly close the gap on respective market leaders. Based on these insights, it helps brands become the ultimate competitor and retain their positions as market leaders.
Read the full article about Red Arbur’s successful market research example here.

Market Research Example #3 – Entering new markets
Diversification is key to survival. For both product and service-based businesses, entering a new market can, without question, yield huge rewards. But before investing time and effort, the crucial work of fleshing out the opportunity in its entirety is key.

Airbnb is a household name, and a huge part of its success has been breaking into new markets. Each market has unique factors, risks, and opportunities. When this global powerhouse wanted to enter the Israeli market, it needed to get a clear handle on both local and international leaders, along with emerging players; all of whom had deployed aggressive marketing efforts.
Let’s look at how it went on to achieve success in a bustling new market.
Challenge: Analyze a new, highly competitive market and get clear insights into its rivals’ traffic sources to enable them to build an effective marketing strategy.
Action: Airbnb already knew who the leaders and most active local competitors were, but to enter with confidence, it wanted to see its respective rivals’ growth strategies. Using detailed website analytics, it was able to see its top competitors were all focussed on four core marketing activities.
- Building partnerships with niche sites
- AdWords, display, and search campaigns
- Local social network ads via organic and paid campaigns
- Running local digital news publisher’s ads
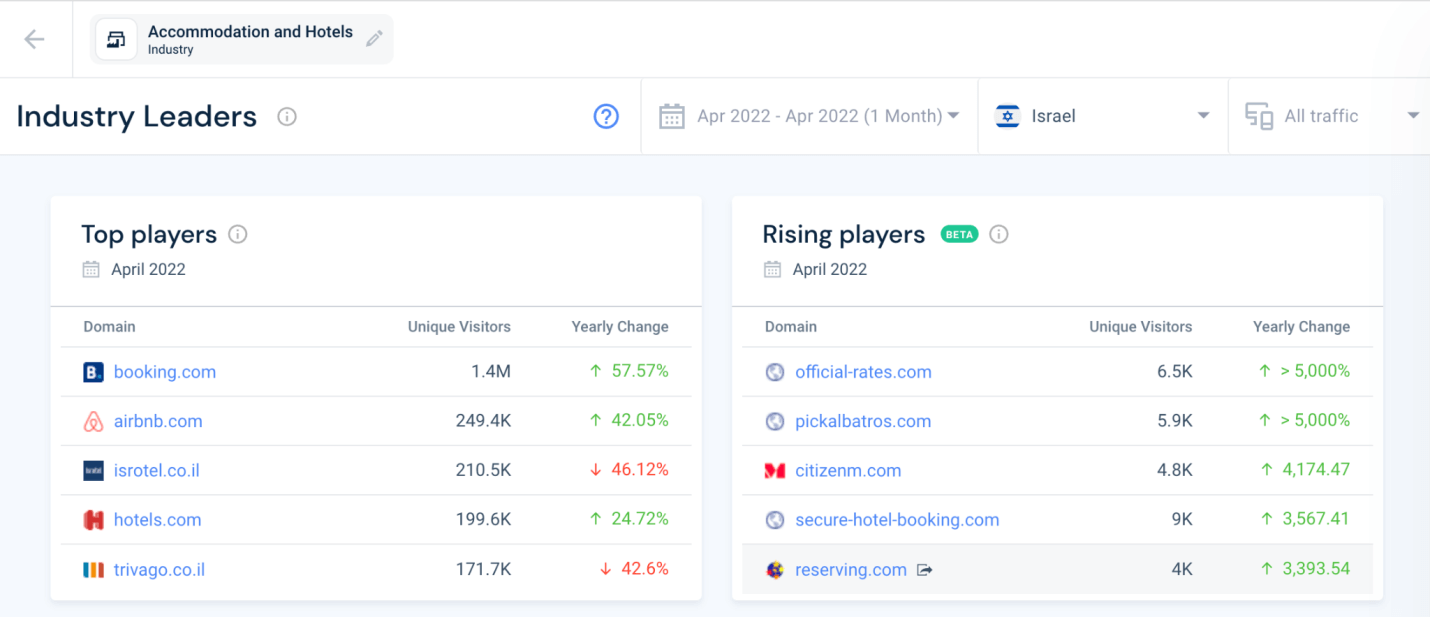
The snapshot shows at a glance who the top industry players are, with booking.com attracting 1.4 million unique visitors in the period with a yearly change of 57% vs. Airbnb’s unique visitors of 249k and a traffic increase of 42%. Two key players are losing traffic, with a 42%+ reduction in traffic share. It also identifies five emerging players in the market with significant growth of over 3000%.
Airbnb chose to focus its resources on social marketing, display and search ads, and partnerships. Its findings revealed specific keywords, social sites, and referrals that enabled it to enter a new market in a position of strength.
Impact: It entered a new market with a 360-degree view of what marketing channels and tactics to use.
Stop Guessing, Start Analyzing
Get actionable insights for market research here
Market Research Example #4 – Business benchmarking & competitive landscaping
Benchmarking in business is a great way to see how well you’re doing. But it’s so much more than just this – it lets you discover, understand, improve, grow, and set goals. If there’s one crucial thing I want you to know about successful market research examples, it’s the importance of doing benchmarking – often and well.

Croud is a global digital marketing partner to some of the world’s greatest brands. It develops and iterates marketing strategies on a daily basis..
Want to find out how it consistently shapes successful growth strategies? Read on.
Challenge: Brand and category-level traffic analysis across different markets are limited.
Action: Using detailed site-level traffic data and competitor app engagement metrics , Cloud could quickly understand what sites people visit, traffic share, growth of a sector over time, and how a client’s own growth compares with its rivals.
Impact: The impact of market research intelligence on Croud’s business is multifaceted. It can serve clients’ fresh data insights that shape marketing channels and revenue opportunities. This, in turn, builds trust, loyalty, and revenue:
- A global lingerie client was able to fine-tune localized marketing strategies and adjust media mixes to reflect category benchmarks. Ad copy was ‘tweaked,’ and new audiences were uncovered.
- A video-on-demand client was alerted to emerging players entering the market, as well as what tactics were being used to obtain traffic.
- A homecare retail client has been able to see the successful ad channels of its clients and adjust the marketing mix accordingly.
Read the full market research success story from Croud here.

Market Research Example #5 – New product development
When organizations develop plans for a new product or service, it requires insight, investment, and often a little intuition. Dynamic market intel can help you reveal shifts in consumer trends or behaviors before your rivals.

As a business in the travel sector, the pandemic hit Staysure harder than most – in fact the travel sector experienced losses of around 70% year on year. Market demands became an anomaly, and many rivals were forced to close their doors. To survive one of the toughest periods a business could ever face, Staysure needed to pivot, adapt, and go in a new direction.
Here’s how it turned things around.
Challenge: Survive the global pandemic and pivot its digital marketing strategy to meet the demand for new products in a shifting industry.
Action: Using Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence , Staysure analyzed competitors’ marketing tactics in real-time. This continuous monitoring enabled it to know when post-lockdown recoveries were occurring in real-time and allowed it to spot emerging trends , one of which was identified as an opportunity to bring a new product to market to address a shift in consumer demand.
Impact: Armed with this intel, it was able to develop a new insurance product that protected consumers against cancellations, medical expenses, and repatriation.
See more about how Staysure identified a new product opportunity for its business during one of the most challenging of times.

Market Research Example #6 – Shape stronger strategies
Making key business decisions about the future is tough at the best of times. Add in a global pandemic, the possible end of globalization as we know it, and who knows what other variables – business leaders have never (likely) known a time like it. Creating future-proof strategies is a must for any organization, and with the current climate, it’s harder than ever. A data-informed approach is the only logical route to take at any time, but none more so than now.

eToro is a market-leading social investing platform with a presence in over 100 countries and more than 27 million registered users. Each region operates within a different set of regulations and caters to unique market demands. To support eToro’s international expansion, the most up-to-date and accurate intel is needed to spearhead successful customer acquisition efforts across the globe.
Challenge: Finding reliable, competitive intelligence across international markets in a timely fashion
Action: The dedicated media buying at eToro used Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence to monitor competitor campaigns and evaluate potential media outlets, partnerships, and ad networks. Using deeper insights into website traffic , trends, and competitors’ campaigns, it could evaluate trends periodically, at both a regional and national level, to discover new traffic sources, evaluate and optimize existing media partnerships, and conduct keyword research each month.
Impact: The improved access to granular data insights has helped eToro negotiate with its publishers. As a result of being able to clearly see ad placement and creative campaign performance, it has improved ROI and increased its ability to out-trade rivals and gain market share .
Read more about how the team at eToro used digital insights to save time and make smarter decisions.

Market Research Example #7 – Identify the target audience
Every successful market research example I’ve ever seen starts and ends with the customer. Buyer personas shape product, price, and placement – and the development of these personas are relevant to all organizations. Being able to clearly identify a target audience in any market is crucial. Market dynamics mean a target audience is susceptible to change, so even established businesses need to keep watch.

Simplr is a customer support solution for growing brands, delivering staffing solutions via remote specialists and AI. As with any service-based business, being able to find and attract the right audience is crucial for growth and sustainability. It used market research to find and qualify high-caliber prospects and secure a more effective sales process.
Challenge: Targeting the right customers at the right time
Action: Simplr was able to get a detailed view of which new brands were growing the fastest by using digital performance data. This gave its sales team the ability to identify, qualify and prioritize potential companies based on solution fit and increasing need. Using a range of reports that show monthly traffic changes and traffic spikes in a custom sector, it saw high-growth sites with an expanding customer base and with this, an increased need for support services like Simplr.
Impact: Market sizing is now more dynamic and well-informed than ever before. Sales efficiency has increased, lead quality has improved, and sales performance is more effective as outreach is done in a more timely manner. Now, Simplr can identify and reach out to prospects during peak growth periods, and it’s seeing better conversions as a result.
Read more about how Simplr used successful market research to close more deals and improve pipeline efficiency here.

Market Research Example #8 – Find out what marketing channels deliver ROI
In good times and bad, it’s important to optmize marketing spend to ensure you invest time, efforts, and money in channels that deliver. A great example of market research in action is to apply research efforts and take the time to know which channels work, and where rival’s are winning and losing in your space.
Anything is Possible (AIP) is a data-driven, communications strategy, media planning & buying company that covers all digital and offline media. Needless to say, it’s a business that depends on reliable, insightful, timely data to impact its clients and their goals.
Challenge: During COVID, a key client (the Institute of Cancer Research) faced declining donations. To survive, it needed to find new ways to find and convert audiences to donate.
Action: AIP utilized Similarweb’s Digital Research Intelligence to do a basic competitive analysis on key rivals of its client. This identified which channels were optimal, and where the most referrals on rival sites were originating from. It shows that premium publisher sites, such as The Guardian were sending significant traffic to competitor sites. With this information, it was able to develop a paid-ads campaign that displayed advertising on targetted guardian.com pages.

Impact: The campaign was a huge success, exceeding previous campaign conversion rates by 817%. Read more about how AIP used Similarweb to understand the right marketing channels to use.
Market Research Example #9 – Trendspotting to find growth opportunities
During the pandemic, many companies in the hospitality sector were forced to close their doors. It was a case of fight or flight, and there were clear winners and losers. Having the ability to spot industry trends and adapt fast was key to the survival of many firms. In this market research example, we explore how one consulting firm was able to help its customers pivot and thrive during turbulent times.
Wiideman Consulting Group provides multi-location brands with SEO research, audits, and strategy services.
Challenge: During the pandemic, food chains had to pivot from offering dining-in services to takeout and delivery services. With IHOP and Applebee’s as key clients of its firm, it needed to develop robust strategies quickly to help its clients survive. With consumers performing non-banded searches to find food delivery and take-out services, these traditional dine-in venues have no visibility online and were at risk of not being found by people looking to order alternative dining solutions while dine-in restaurants were closed.
Action: Using Similarweb, it identified the right keyword opportunities, industry trends, and delivery service provider insights. This enabled it to develop a strategy that focused on increasing visibility in the locations where the business could provide takeaway and delivery services. With this data, it was able to help reposition brands within the search engine results pages, and optimize content to generate leads and sales.
Doing this market research enabled it to make three key changes.
- Optimize the Google My business profile to emphasize new service options for lunch, evening, and family meals.
- Design and deploy optimized content with new delivery and takeout subpages for each location.
- Addition of the ‘start order’ button as a floating call-to-action across all localized pages.
Impact: Driven by Similarweb insights, these tactics delivered favourable results for both of its clients in the hospitality sector.
- Organic traffic for both brands improved by 63% & 37%
- Revenues increased by 167% & 70% yoy

Ultimately, this market research enabled its clients to adapt to a changing market, and thrive when many others were forced to cease trading.
You can view the full write-up here to hear more about this success story.
Market research isn’t a one-and-done activity – rather, it’s a highly-habitual process and a powerful tool in your marketing arsenal. Due to fast-changing market dynamics, business leaders and strategists need market insights on the fly to respond and react to shifts in consumer behavior while staying focused on growth.
I’ve shared with you nine market research examples demonstrating how companies around the globe have successfully used market analysis to strategize, adapt, and grow. Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence impacted each of these examples, helping take the guesswork out of market research; so you can confidently make informed strategic decisions to grow your business.
Related Posts

From AI to Buy: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Retail
How to Conduct a Social Media Competitor Analysis: 5 Quick Steps

Industry Research: The Data-Backed Approach
Wondering what similarweb can do for you.
Here are two ways you can get started with Similarweb today!


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.2 Steps in the Marketing Research Process
Learning objective.
- Describe the basic steps in the marketing research process and the purpose of each step.
The basic steps used to conduct marketing research are shown in Figure 10.6 “Steps in the Marketing Research Process” . Next, we discuss each step.
Figure 10.6 Steps in the Marketing Research Process
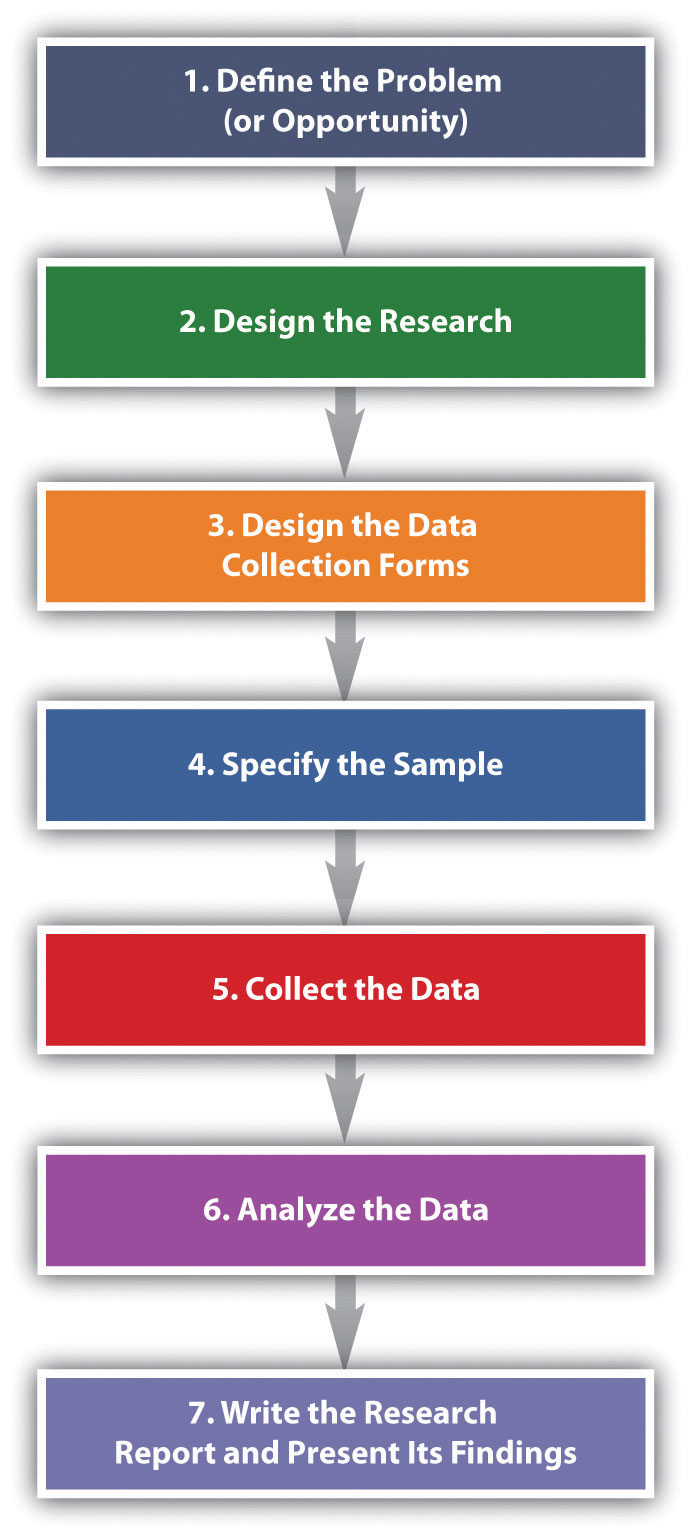
Step 1: Define the Problem (or Opportunity)
There’s a saying in marketing research that a problem half defined is a problem half solved. Defining the “problem” of the research sounds simple, doesn’t it? Suppose your product is tutoring other students in a subject you’re a whiz at. You have been tutoring for a while, and people have begun to realize you’re darned good at it. Then, suddenly, your business drops off. Or it explodes, and you can’t cope with the number of students you’re being asked help. If the business has exploded, should you try to expand your services? Perhaps you should subcontract with some other “whiz” students. You would send them students to be tutored, and they would give you a cut of their pay for each student you referred to them.
Both of these scenarios would be a problem for you, wouldn’t they? They are problems insofar as they cause you headaches. But are they really the problem? Or are they the symptoms of something bigger? For example, maybe your business has dropped off because your school is experiencing financial trouble and has lowered the number of scholarships given to incoming freshmen. Consequently, there are fewer total students on campus who need your services. Conversely, if you’re swamped with people who want you to tutor them, perhaps your school awarded more scholarships than usual, so there are a greater number of students who need your services. Alternately, perhaps you ran an ad in your school’s college newspaper, and that led to the influx of students wanting you to tutor them.
Businesses are in the same boat you are as a tutor. They take a look at symptoms and try to drill down to the potential causes. If you approach a marketing research company with either scenario—either too much or too little business—the firm will seek more information from you such as the following:
- In what semester(s) did your tutoring revenues fall (or rise)?
- In what subject areas did your tutoring revenues fall (or rise)?
- In what sales channels did revenues fall (or rise): Were there fewer (or more) referrals from professors or other students? Did the ad you ran result in fewer (or more) referrals this month than in the past months?
- Among what demographic groups did your revenues fall (or rise)—women or men, people with certain majors, or first-year, second-, third-, or fourth-year students?
The key is to look at all potential causes so as to narrow the parameters of the study to the information you actually need to make a good decision about how to fix your business if revenues have dropped or whether or not to expand it if your revenues have exploded.
The next task for the researcher is to put into writing the research objective. The research objective is the goal(s) the research is supposed to accomplish. The marketing research objective for your tutoring business might read as follows:
To survey college professors who teach 100- and 200-level math courses to determine why the number of students referred for tutoring dropped in the second semester.
This is admittedly a simple example designed to help you understand the basic concept. If you take a marketing research course, you will learn that research objectives get a lot more complicated than this. The following is an example:
“To gather information from a sample representative of the U.S. population among those who are ‘very likely’ to purchase an automobile within the next 6 months, which assesses preferences (measured on a 1–5 scale ranging from ‘very likely to buy’ to ‘not likely at all to buy’) for the model diesel at three different price levels. Such data would serve as input into a forecasting model that would forecast unit sales, by geographic regions of the country, for each combination of the model’s different prices and fuel configurations (Burns & Bush, 2010).”
Now do you understand why defining the problem is complicated and half the battle? Many a marketing research effort is doomed from the start because the problem was improperly defined. Coke’s ill-fated decision to change the formula of Coca-Cola in 1985 is a case in point: Pepsi had been creeping up on Coke in terms of market share over the years as well as running a successful promotional campaign called the “Pepsi Challenge,” in which consumers were encouraged to do a blind taste test to see if they agreed that Pepsi was better. Coke spent four years researching “the problem.” Indeed, people seemed to like the taste of Pepsi better in blind taste tests. Thus, the formula for Coke was changed. But the outcry among the public was so great that the new formula didn’t last long—a matter of months—before the old formula was reinstated. Some marketing experts believe Coke incorrectly defined the problem as “How can we beat Pepsi in taste tests?” instead of “How can we gain market share against Pepsi?” (Burns & Bush, 2010)
New Coke Is It! 1985
(click to see video)
This video documents the Coca-Cola Company’s ill-fated launch of New Coke in 1985.
1985 Pepsi Commercial—“They Changed My Coke”
This video shows how Pepsi tried to capitalize on the blunder.
Step 2: Design the Research
The next step in the marketing research process is to do a research design. The research design is your “plan of attack.” It outlines what data you are going to gather and from whom, how and when you will collect the data, and how you will analyze it once it’s been obtained. Let’s look at the data you’re going to gather first.
There are two basic types of data you can gather. The first is primary data. Primary data is information you collect yourself, using hands-on tools such as interviews or surveys, specifically for the research project you’re conducting. Secondary data is data that has already been collected by someone else, or data you have already collected for another purpose. Collecting primary data is more time consuming, work intensive, and expensive than collecting secondary data. Consequently, you should always try to collect secondary data first to solve your research problem, if you can. A great deal of research on a wide variety of topics already exists. If this research contains the answer to your question, there is no need for you to replicate it. Why reinvent the wheel?
Sources of Secondary Data
Your company’s internal records are a source of secondary data. So are any data you collect as part of your marketing intelligence gathering efforts. You can also purchase syndicated research. Syndicated research is primary data that marketing research firms collect on a regular basis and sell to other companies. J.D. Power & Associates is a provider of syndicated research. The company conducts independent, unbiased surveys of customer satisfaction, product quality, and buyer behavior for various industries. The company is best known for its research in the automobile sector. One of the best-known sellers of syndicated research is the Nielsen Company, which produces the Nielsen ratings. The Nielsen ratings measure the size of television, radio, and newspaper audiences in various markets. You have probably read or heard about TV shows that get the highest (Nielsen) ratings. (Arbitron does the same thing for radio ratings.) Nielsen, along with its main competitor, Information Resources, Inc. (IRI), also sells businesses scanner-based research . Scanner-based research is information collected by scanners at checkout stands in stores. Each week Nielsen and IRI collect information on the millions of purchases made at stores. The companies then compile the information and sell it to firms in various industries that subscribe to their services. The Nielsen Company has also recently teamed up with Facebook to collect marketing research information. Via Facebook, users will see surveys in some of the spaces in which they used to see online ads (Rappeport, Gelles, 2009).
By contrast, MarketResearch.com is an example of a marketing research aggregator. A marketing research aggregator is a marketing research company that doesn’t conduct its own research and sell it. Instead, it buys research reports from other marketing research companies and then sells the reports in their entirety or in pieces to other firms. Check out MarketResearch.com’s Web site. As you will see there are a huge number of studies in every category imaginable that you can buy for relatively small amounts of money.
Figure 10.7
Market research aggregators buy research reports from other marketing research companies and then resell them in part or in whole to other companies so they don’t have to gather primary data.
Source: http://www.marketresearch.com .
Your local library is a good place to gather free secondary data. It has searchable databases as well as handbooks, dictionaries, and books, some of which you can access online. Government agencies also collect and report information on demographics, economic and employment data, health information, and balance-of-trade statistics, among a lot of other information. The U.S. Census Bureau collects census data every ten years to gather information about who lives where. Basic demographic information about sex, age, race, and types of housing in which people live in each U.S. state, metropolitan area, and rural area is gathered so that population shifts can be tracked for various purposes, including determining the number of legislators each state should have in the U.S. House of Representatives. For the U.S. government, this is primary data. For marketing managers it is an important source of secondary data.
The Survey Research Center at the University of Michigan also conducts periodic surveys and publishes information about trends in the United States. One research study the center continually conducts is called the “Changing Lives of American Families” ( http://www.isr.umich.edu/home/news/research-update/2007-01.pdf ). This is important research data for marketing managers monitoring consumer trends in the marketplace. The World Bank and the United Nations are two international organizations that collect a great deal of information. Their Web sites contain many free research studies and data related to global markets. Table 10.1 “Examples of Primary Data Sources versus Secondary Data Sources” shows some examples of primary versus secondary data sources.
Table 10.1 Examples of Primary Data Sources versus Secondary Data Sources
Gauging the Quality of Secondary Data
When you are gathering secondary information, it’s always good to be a little skeptical of it. Sometimes studies are commissioned to produce the result a client wants to hear—or wants the public to hear. For example, throughout the twentieth century, numerous studies found that smoking was good for people’s health. The problem was the studies were commissioned by the tobacco industry. Web research can also pose certain hazards. There are many biased sites that try to fool people that they are providing good data. Often the data is favorable to the products they are trying to sell. Beware of product reviews as well. Unscrupulous sellers sometimes get online and create bogus ratings for products. See below for questions you can ask to help gauge the credibility of secondary information.
Gauging the Credibility of Secondary Data: Questions to Ask
- Who gathered this information?
- For what purpose?
- What does the person or organization that gathered the information have to gain by doing so?
- Was the information gathered and reported in a systematic manner?
- Is the source of the information accepted as an authority by other experts in the field?
- Does the article provide objective evidence to support the position presented?
Types of Research Design
Now let’s look specifically at the types of research designs that are utilized. By understanding different types of research designs, a researcher can solve a client’s problems more quickly and efficiently without jumping through more hoops than necessary. Research designs fall into one of the following three categories:
- Exploratory research design
- Descriptive research design
- Causal research design (experiments)
An exploratory research design is useful when you are initially investigating a problem but you haven’t defined it well enough to do an in-depth study of it. Perhaps via your regular market intelligence, you have spotted what appears to be a new opportunity in the marketplace. You would then do exploratory research to investigate it further and “get your feet wet,” as the saying goes. Exploratory research is less structured than other types of research, and secondary data is often utilized.
One form of exploratory research is qualitative research. Qualitative research is any form of research that includes gathering data that is not quantitative, and often involves exploring questions such as why as much as what or how much . Different forms, such as depth interviews and focus group interviews, are common in marketing research.
The depth interview —engaging in detailed, one-on-one, question-and-answer sessions with potential buyers—is an exploratory research technique. However, unlike surveys, the people being interviewed aren’t asked a series of standard questions. Instead the interviewer is armed with some general topics and asks questions that are open ended, meaning that they allow the interviewee to elaborate. “How did you feel about the product after you purchased it?” is an example of a question that might be asked. A depth interview also allows a researcher to ask logical follow-up questions such as “Can you tell me what you mean when you say you felt uncomfortable using the service?” or “Can you give me some examples?” to help dig further and shed additional light on the research problem. Depth interviews can be conducted in person or over the phone. The interviewer either takes notes or records the interview.
Focus groups and case studies are often utilized for exploratory research as well. A focus group is a group of potential buyers who are brought together to discuss a marketing research topic with one another. A moderator is used to focus the discussion, the sessions are recorded, and the main points of consensus are later summarized by the market researcher. Textbook publishers often gather groups of professors at educational conferences to participate in focus groups. However, focus groups can also be conducted on the telephone, in online chat rooms, or both, using meeting software like WebEx. The basic steps of conducting a focus group are outlined below.
The Basic Steps of Conducting a Focus Group
- Establish the objectives of the focus group. What is its purpose?
- Identify the people who will participate in the focus group. What makes them qualified to participate? How many of them will you need and what they will be paid?
- Obtain contact information for the participants and send out invitations (usually e-mails are most efficient).
- Develop a list of questions.
- Choose a facilitator.
- Choose a location in which to hold the focus group and the method by which it will be recorded.
- Conduct the focus group. If the focus group is not conducted electronically, include name tags for the participants, pens and notepads, any materials the participants need to see, and refreshments. Record participants’ responses.
- Summarize the notes from the focus group and write a report for management.
A case study looks at how another company solved the problem that’s being researched. Sometimes multiple cases, or companies, are used in a study. Case studies nonetheless have a mixed reputation. Some researchers believe it’s hard to generalize, or apply, the results of a case study to other companies. Nonetheless, collecting information about companies that encountered the same problems your firm is facing can give you a certain amount of insight about what direction you should take. In fact, one way to begin a research project is to carefully study a successful product or service.
Two other types of qualitative data used for exploratory research are ethnographies and projective techniques. In an ethnography , researchers interview, observe, and often videotape people while they work, live, shop, and play. The Walt Disney Company has recently begun using ethnographers to uncover the likes and dislikes of boys aged six to fourteen, a financially attractive market segment for Disney, but one in which the company has been losing market share. The ethnographers visit the homes of boys, observe the things they have in their rooms to get a sense of their hobbies, and accompany them and their mothers when they shop to see where they go, what the boys are interested in, and what they ultimately buy. (The children get seventy-five dollars out of the deal, incidentally.) (Barnes, 2009)
Projective techniques are used to reveal information research respondents might not reveal by being asked directly. Asking a person to complete sentences such as the following is one technique:
People who buy Coach handbags __________.
(Will he or she reply with “are cool,” “are affluent,” or “are pretentious,” for example?)
KFC’s grilled chicken is ______.
Or the person might be asked to finish a story that presents a certain scenario. Word associations are also used to discern people’s underlying attitudes toward goods and services. Using a word-association technique, a market researcher asks a person to say or write the first word that comes to his or her mind in response to another word. If the initial word is “fast food,” what word does the person associate it with or respond with? Is it “McDonald’s”? If many people reply that way, and you’re conducting research for Burger King, that could indicate Burger King has a problem. However, if the research is being conducted for Wendy’s, which recently began running an advertising campaign to the effect that Wendy’s offerings are “better than fast food,” it could indicate that the campaign is working.
Completing cartoons is yet another type of projective technique. It’s similar to finishing a sentence or story, only with the pictures. People are asked to look at a cartoon such as the one shown in Figure 10.8 “Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique” . One of the characters in the picture will have made a statement, and the person is asked to fill in the empty cartoon “bubble” with how they think the second character will respond.
Figure 10.8 Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique

In some cases, your research might end with exploratory research. Perhaps you have discovered your organization lacks the resources needed to produce the product. In other cases, you might decide you need more in-depth, quantitative research such as descriptive research or causal research, which are discussed next. Most marketing research professionals advise using both types of research, if it’s feasible. On the one hand, the qualitative-type research used in exploratory research is often considered too “lightweight.” Remember earlier in the chapter when we discussed telephone answering machines and the hit TV sitcom Seinfeld ? Both product ideas were initially rejected by focus groups. On the other hand, relying solely on quantitative information often results in market research that lacks ideas.
The Stone Wheel—What One Focus Group Said
Watch the video to see a funny spoof on the usefulness—or lack of usefulness—of focus groups.

Descriptive Research
Anything that can be observed and counted falls into the category of descriptive research design. A study using a descriptive research design involves gathering hard numbers, often via surveys, to describe or measure a phenomenon so as to answer the questions of who , what , where , when , and how . “On a scale of 1–5, how satisfied were you with your service?” is a question that illustrates the information a descriptive research design is supposed to capture.
Physiological measurements also fall into the category of descriptive design. Physiological measurements measure people’s involuntary physical responses to marketing stimuli, such as an advertisement. Elsewhere, we explained that researchers have gone so far as to scan the brains of consumers to see what they really think about products versus what they say about them. Eye tracking is another cutting-edge type of physiological measurement. It involves recording the movements of a person’s eyes when they look at some sort of stimulus, such as a banner ad or a Web page. The Walt Disney Company has a research facility in Austin, Texas, that it uses to take physical measurements of viewers when they see Disney programs and advertisements. The facility measures three types of responses: people’s heart rates, skin changes, and eye movements (eye tracking) (Spangler, 2009).
Figure 10.9

A woman shows off her headgear for an eye-tracking study. The gear’s not exactly a fashion statement but . . .
lawrencegs – Google Glass – CC BY 2.0.
A strictly descriptive research design instrument—a survey, for example—can tell you how satisfied your customers are. It can’t, however, tell you why. Nor can an eye-tracking study tell you why people’s eyes tend to dwell on certain types of banner ads—only that they do. To answer “why” questions an exploratory research design or causal research design is needed (Wagner, 2007).
Causal Research
Causal research design examines cause-and-effect relationships. Using a causal research design allows researchers to answer “what if” types of questions. In other words, if a firm changes X (say, a product’s price, design, placement, or advertising), what will happen to Y (say, sales or customer loyalty)? To conduct causal research, the researcher designs an experiment that “controls,” or holds constant, all of a product’s marketing elements except one (or using advanced techniques of research, a few elements can be studied at the same time). The one variable is changed, and the effect is then measured. Sometimes the experiments are conducted in a laboratory using a simulated setting designed to replicate the conditions buyers would experience. Or the experiments may be conducted in a virtual computer setting.
You might think setting up an experiment in a virtual world such as the online game Second Life would be a viable way to conduct controlled marketing research. Some companies have tried to use Second Life for this purpose, but the results have been somewhat mixed as to whether or not it is a good medium for marketing research. The German marketing research firm Komjuniti was one of the first “real-world” companies to set up an “island” in Second Life upon which it could conduct marketing research. However, with so many other attractive fantasy islands in which to play, the company found it difficult to get Second Life residents, or players, to voluntarily visit the island and stay long enough so meaningful research could be conducted. (Plus, the “residents,” or players, in Second Life have been known to protest corporations invading their world. When the German firm Komjuniti created an island in Second Life to conduct marketing research, the residents showed up waving signs and threatening to boycott the island.) (Wagner, 2007)
Why is being able to control the setting so important? Let’s say you are an American flag manufacturer and you are working with Walmart to conduct an experiment to see where in its stores American flags should be placed so as to increase their sales. Then the terrorist attacks of 9/11 occur. In the days afterward, sales skyrocketed—people bought flags no matter where they were displayed. Obviously, the terrorist attacks in the United States would have skewed the experiment’s data.
An experiment conducted in a natural setting such as a store is referred to as a field experiment . Companies sometimes do field experiments either because it is more convenient or because they want to see if buyers will behave the same way in the “real world” as in a laboratory or on a computer. The place the experiment is conducted or the demographic group of people the experiment is administered to is considered the test market . Before a large company rolls out a product to the entire marketplace, it will often place the offering in a test market to see how well it will be received. For example, to compete with MillerCoors’ sixty-four-calorie beer MGD 64, Anheuser-Busch recently began testing its Select 55 beer in certain cities around the country (McWilliams, 2009).
Figure 10.10
Select 55 beer: Coming soon to a test market near you? (If you’re on a diet, you have to hope so!)
Martine – Le champagne – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Many companies use experiments to test all of their marketing communications. For example, the online discount retailer O.co (formerly called Overstock.com) carefully tests all of its marketing offers and tracks the results of each one. One study the company conducted combined twenty-six different variables related to offers e-mailed to several thousand customers. The study resulted in a decision to send a group of e-mails to different segments. The company then tracked the results of the sales generated to see if they were in line with the earlier experiment it had conducted that led it to make the offer.
Step 3: Design the Data-Collection Forms
If the behavior of buyers is being formally observed, and a number of different researchers are conducting observations, the data obviously need to be recorded on a standardized data-collection form that’s either paper or electronic. Otherwise, the data collected will not be comparable. The items on the form could include a shopper’s sex; his or her approximate age; whether the person seemed hurried, moderately hurried, or unhurried; and whether or not he or she read the label on products, used coupons, and so forth.
The same is true when it comes to surveying people with questionnaires. Surveying people is one of the most commonly used techniques to collect quantitative data. Surveys are popular because they can be easily administered to large numbers of people fairly quickly. However, to produce the best results, the questionnaire for the survey needs to be carefully designed.
Questionnaire Design
Most questionnaires follow a similar format: They begin with an introduction describing what the study is for, followed by instructions for completing the questionnaire and, if necessary, returning it to the market researcher. The first few questions that appear on the questionnaire are usually basic, warm-up type of questions the respondent can readily answer, such as the respondent’s age, level of education, place of residence, and so forth. The warm-up questions are then followed by a logical progression of more detailed, in-depth questions that get to the heart of the question being researched. Lastly, the questionnaire wraps up with a statement that thanks the respondent for participating in the survey and information and explains when and how they will be paid for participating. To see some examples of questionnaires and how they are laid out, click on the following link: http://cas.uah.edu/wrenb/mkt343/Project/Sample%20Questionnaires.htm .
How the questions themselves are worded is extremely important. It’s human nature for respondents to want to provide the “correct” answers to the person administering the survey, so as to seem agreeable. Therefore, there is always a hazard that people will try to tell you what you want to hear on a survey. Consequently, care needs to be taken that the survey questions are written in an unbiased, neutral way. In other words, they shouldn’t lead a person taking the questionnaire to answer a question one way or another by virtue of the way you have worded it. The following is an example of a leading question.
Don’t you agree that teachers should be paid more ?
The questions also need to be clear and unambiguous. Consider the following question:
Which brand of toothpaste do you use ?
The question sounds clear enough, but is it really? What if the respondent recently switched brands? What if she uses Crest at home, but while away from home or traveling, she uses Colgate’s Wisp portable toothpaste-and-brush product? How will the respondent answer the question? Rewording the question as follows so it’s more specific will help make the question clearer:
Which brand of toothpaste have you used at home in the past six months? If you have used more than one brand, please list each of them 1 .
Sensitive questions have to be asked carefully. For example, asking a respondent, “Do you consider yourself a light, moderate, or heavy drinker?” can be tricky. Few people want to admit to being heavy drinkers. You can “soften” the question by including a range of answers, as the following example shows:
How many alcoholic beverages do you consume in a week ?
- __0–5 alcoholic beverages
- __5–10 alcoholic beverages
- __10–15 alcoholic beverages
Many people don’t like to answer questions about their income levels. Asking them to specify income ranges rather than divulge their actual incomes can help.
Other research question “don’ts” include using jargon and acronyms that could confuse people. “How often do you IM?” is an example. Also, don’t muddy the waters by asking two questions in the same question, something researchers refer to as a double-barreled question . “Do you think parents should spend more time with their children and/or their teachers?” is an example of a double-barreled question.
Open-ended questions , or questions that ask respondents to elaborate, can be included. However, they are harder to tabulate than closed-ended questions , or questions that limit a respondent’s answers. Multiple-choice and yes-and-no questions are examples of closed-ended questions.
Testing the Questionnaire
You have probably heard the phrase “garbage in, garbage out.” If the questions are bad, the information gathered will be bad, too. One way to make sure you don’t end up with garbage is to test the questionnaire before sending it out to find out if there are any problems with it. Is there enough space for people to elaborate on open-ended questions? Is the font readable? To test the questionnaire, marketing research professionals first administer it to a number of respondents face to face. This gives the respondents the chance to ask the researcher about questions or instructions that are unclear or don’t make sense to them. The researcher then administers the questionnaire to a small subset of respondents in the actual way the survey is going to be disseminated, whether it’s delivered via phone, in person, by mail, or online.
Getting people to participate and complete questionnaires can be difficult. If the questionnaire is too long or hard to read, many people won’t complete it. So, by all means, eliminate any questions that aren’t necessary. Of course, including some sort of monetary incentive for completing the survey can increase the number of completed questionnaires a market researcher will receive.
Step 4: Specify the Sample
Once you have created your questionnaire or other marketing study, how do you figure out who should participate in it? Obviously, you can’t survey or observe all potential buyers in the marketplace. Instead, you must choose a sample. A sample is a subset of potential buyers that are representative of your entire target market, or population being studied. Sometimes market researchers refer to the population as the universe to reflect the fact that it includes the entire target market, whether it consists of a million people, a hundred thousand, a few hundred, or a dozen. “All unmarried people over the age of eighteen who purchased Dirt Devil steam cleaners in the United States during 2011” is an example of a population that has been defined.
Obviously, the population has to be defined correctly. Otherwise, you will be studying the wrong group of people. Not defining the population correctly can result in flawed research, or sampling error. A sampling error is any type of marketing research mistake that results because a sample was utilized. One criticism of Internet surveys is that the people who take these surveys don’t really represent the overall population. On average, Internet survey takers tend to be more educated and tech savvy. Consequently, if they solely constitute your population, even if you screen them for certain criteria, the data you collect could end up being skewed.
The next step is to put together the sampling frame , which is the list from which the sample is drawn. The sampling frame can be put together using a directory, customer list, or membership roster (Wrenn et. al., 2007). Keep in mind that the sampling frame won’t perfectly match the population. Some people will be included on the list who shouldn’t be. Other people who should be included will be inadvertently omitted. It’s no different than if you were to conduct a survey of, say, 25 percent of your friends, using friends’ names you have in your cell phone. Most of your friends’ names are likely to be programmed into your phone, but not all of them. As a result, a certain degree of sampling error always occurs.
There are two main categories of samples in terms of how they are drawn: probability samples and nonprobability samples. A probability sample is one in which each would-be participant has a known and equal chance of being selected. The chance is known because the total number of people in the sampling frame is known. For example, if every other person from the sampling frame were chosen, each person would have a 50 percent chance of being selected.
A nonprobability sample is any type of sample that’s not drawn in a systematic way. So the chances of each would-be participant being selected can’t be known. A convenience sample is one type of nonprobability sample. It is a sample a researcher draws because it’s readily available and convenient to do so. Surveying people on the street as they pass by is an example of a convenience sample. The question is, are these people representative of the target market?
For example, suppose a grocery store needed to quickly conduct some research on shoppers to get ready for an upcoming promotion. Now suppose that the researcher assigned to the project showed up between the hours of 10 a.m. and 12 p.m. on a weekday and surveyed as many shoppers as possible. The problem is that the shoppers wouldn’t be representative of the store’s entire target market. What about commuters who stop at the store before and after work? Their views wouldn’t be represented. Neither would people who work the night shift or shop at odd hours. As a result, there would be a lot of room for sampling error in this study. For this reason, studies that use nonprobability samples aren’t considered as accurate as studies that use probability samples. Nonprobability samples are more often used in exploratory research.
Lastly, the size of the sample has an effect on the amount of sampling error. Larger samples generally produce more accurate results. The larger your sample is, the more data you will have, which will give you a more complete picture of what you’re studying. However, the more people surveyed or studied, the more costly the research becomes.
Statistics can be used to determine a sample’s optimal size. If you take a marketing research or statistics class, you will learn more about how to determine the optimal size.
Of course, if you hire a marketing research company, much of this work will be taken care of for you. Many marketing research companies, like ResearchNow, maintain panels of prescreened people they draw upon for samples. In addition, the marketing research firm will be responsible for collecting the data or contracting with a company that specializes in data collection. Data collection is discussed next.
Step 5: Collect the Data
As we have explained, primary marketing research data can be gathered in a number of ways. Surveys, taking physical measurements, and observing people are just three of the ways we discussed. If you’re observing customers as part of gathering the data, keep in mind that if shoppers are aware of the fact, it can have an effect on their behavior. For example, if a customer shopping for feminine hygiene products in a supermarket aisle realizes she is being watched, she could become embarrassed and leave the aisle, which would adversely affect your data. To get around problems such as these, some companies set up cameras or two-way mirrors to observe customers. Organizations also hire mystery shoppers to work around the problem. A mystery shopper is someone who is paid to shop at a firm’s establishment or one of its competitors to observe the level of service, cleanliness of the facility, and so forth, and report his or her findings to the firm.
Make Extra Money as a Mystery Shopper
Watch the YouTube video to get an idea of how mystery shopping works.
Survey data can be collected in many different ways and combinations of ways. The following are the basic methods used:
- Face-to-face (can be computer aided)
- Telephone (can be computer aided or completely automated)
- Mail and hand delivery
- E-mail and the Web
A face-to-face survey is, of course, administered by a person. The surveys are conducted in public places such as in shopping malls, on the street, or in people’s homes if they have agreed to it. In years past, it was common for researchers in the United States to knock on people’s doors to gather survey data. However, randomly collected door-to-door interviews are less common today, partly because people are afraid of crime and are reluctant to give information to strangers (McDaniel & Gates, 1998).
Nonetheless, “beating the streets” is still a legitimate way questionnaire data is collected. When the U.S. Census Bureau collects data on the nation’s population, it hand delivers questionnaires to rural households that do not have street-name and house-number addresses. And Census Bureau workers personally survey the homeless to collect information about their numbers. Face-to-face surveys are also commonly used in third world countries to collect information from people who cannot read or lack phones and computers.
A plus of face-to-face surveys is that they allow researchers to ask lengthier, more complex questions because the people being surveyed can see and read the questionnaires. The same is true when a computer is utilized. For example, the researcher might ask the respondent to look at a list of ten retail stores and rank the stores from best to worst. The same question wouldn’t work so well over the telephone because the person couldn’t see the list. The question would have to be rewritten. Another drawback with telephone surveys is that even though federal and state “do not call” laws generally don’t prohibit companies from gathering survey information over the phone, people often screen such calls using answering machines and caller ID.
Probably the biggest drawback of both surveys conducted face-to-face and administered over the phone by a person is that they are labor intensive and therefore costly. Mailing out questionnaires is costly, too, and the response rates can be rather low. Think about why that might be so: if you receive a questionnaire in the mail, it is easy to throw it in the trash; it’s harder to tell a market researcher who approaches you on the street that you don’t want to be interviewed.
By contrast, gathering survey data collected by a computer, either over the telephone or on the Internet, can be very cost-effective and in some cases free. SurveyMonkey and Zoomerang are two Web sites that will allow you to create online questionnaires, e-mail them to up to one hundred people for free, and view the responses in real time as they come in. For larger surveys, you have to pay a subscription price of a few hundred dollars. But that still can be extremely cost-effective. The two Web sites also have a host of other features such as online-survey templates you can use to create your questionnaire, a way to set up automatic reminders sent to people who haven’t yet completed their surveys, and tools you can use to create graphics to put in your final research report. To see how easy it is to put together a survey in SurveyMonkey, click on the following link: http://help.surveymonkey.com/app/tutorials/detail/a_id/423 .
Like a face-to-face survey, an Internet survey can enable you to show buyers different visuals such as ads, pictures, and videos of products and their packaging. Web surveys are also fast, which is a major plus. Whereas face-to-face and mailed surveys often take weeks to collect, you can conduct a Web survey in a matter of days or even hours. And, of course, because the information is electronically gathered it can be automatically tabulated. You can also potentially reach a broader geographic group than you could if you had to personally interview people. The Zoomerang Web site allows you to create surveys in forty different languages.
Another plus for Web and computer surveys (and electronic phone surveys) is that there is less room for human error because the surveys are administered electronically. For instance, there’s no risk that the interviewer will ask a question wrong or use a tone of voice that could mislead the respondents. Respondents are also likely to feel more comfortable inputting the information into a computer if a question is sensitive than they would divulging the information to another person face-to-face or over the phone. Given all of these advantages, it’s not surprising that the Internet is quickly becoming the top way to collect primary data. However, like mail surveys, surveys sent to people over the Internet are easy to ignore.
Lastly, before the data collection process begins, the surveyors and observers need to be trained to look for the same things, ask questions the same way, and so forth. If they are using rankings or rating scales, they need to be “on the same page,” so to speak, as to what constitutes a high ranking or a low ranking. As an analogy, you have probably had some teachers grade your college papers harder than others. The goal of training is to avoid a wide disparity between how different observers and interviewers record the data.
Figure 10.11

Training people so they know what constitutes different ratings when they are collecting data will improve the quality of the information gathered in a marketing research study.
Ricardo Rodriquez – Satisfaction survey – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
For example, if an observation form asks the observers to describe whether a shopper’s behavior is hurried, moderately hurried, or unhurried, they should be given an idea of what defines each rating. Does it depend on how much time the person spends in the store or in the individual aisles? How fast they walk? In other words, the criteria and ratings need to be spelled out.
Collecting International Marketing Research Data
Gathering marketing research data in foreign countries poses special challenges. However, that doesn’t stop firms from doing so. Marketing research companies are located all across the globe, in fact. Eight of the ten largest marketing research companies in the world are headquartered in the United States. However, five of these eight firms earn more of their revenues abroad than they do in the United States. There’s a reason for this: many U.S. markets were saturated, or tapped out, long ago in terms of the amount that they can grow. Coke is an example. As you learned earlier in the book, most of the Coca-Cola Company’s revenues are earned in markets abroad. To be sure, the United States is still a huge market when it comes to the revenues marketing research firms generate by conducting research in the country: in terms of their spending, American consumers fuel the world’s economic engine. Still, emerging countries with growing middle classes, such as China, India, and Brazil, are hot new markets companies want to tap.
What kind of challenges do firms face when trying to conduct marketing research abroad? As we explained, face-to-face surveys are commonly used in third world countries to collect information from people who cannot read or lack phones and computers. However, face-to-face surveys are also common in Europe, despite the fact that phones and computers are readily available. In-home surveys are also common in parts of Europe. By contrast, in some countries, including many Asian countries, it’s considered taboo or rude to try to gather information from strangers either face-to-face or over the phone. In many Muslim countries, women are forbidden to talk to strangers.
And how do you figure out whom to research in foreign countries? That in itself is a problem. In the United States, researchers often ask if they can talk to the heads of households to conduct marketing research. But in countries in which domestic servants or employees are common, the heads of households aren’t necessarily the principal shoppers; their domestic employees are (Malhotra).
Translating surveys is also an issue. Have you ever watched the TV comedians Jay Leno and David Letterman make fun of the English translations found on ethnic menus and products? Research tools such as surveys can suffer from the same problem. Hiring someone who is bilingual to translate a survey into another language can be a disaster if the person isn’t a native speaker of the language to which the survey is being translated.
One way companies try to deal with translation problems is by using back translation. When back translation is used, a native speaker translates the survey into the foreign language and then translates it back again to the original language to determine if there were gaps in meaning—that is, if anything was lost in translation. And it’s not just the language that’s an issue. If the research involves any visual images, they, too, could be a point of confusion. Certain colors, shapes, and symbols can have negative connotations in other countries. For example, the color white represents purity in many Western cultures, but in China, it is the color of death and mourning (Zouhali-Worrall, 2008). Also, look back at the cartoon-completion exercise in Figure 10.8 “Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique” . What would women in Muslim countries who aren’t allowed to converse with male sellers think of it? Chances are, the cartoon wouldn’t provide you with the information you’re seeking if Muslim women in some countries were asked to complete it.
One way marketing research companies are dealing with the complexities of global research is by merging with or acquiring marketing research companies abroad. The Nielsen Company is the largest marketing research company in the world. The firm operates in more than a hundred countries and employs more than forty thousand people. Many of its expansions have been the result of acquisitions and mergers.
Step 6: Analyze the Data
Step 6 involves analyzing the data to ensure it’s as accurate as possible. If the research is collected by hand using a pen and pencil, it’s entered into a computer. Or respondents might have already entered the information directly into a computer. For example, when Toyota goes to an event such as a car show, the automaker’s marketing personnel ask would-be buyers to complete questionnaires directly on computers. Companies are also beginning to experiment with software that can be used to collect data using mobile phones.
Once all the data is collected, the researchers begin the data cleaning , which is the process of removing data that have accidentally been duplicated (entered twice into the computer) or correcting data that have obviously been recorded wrong. A program such as Microsoft Excel or a statistical program such as Predictive Analytics Software (PASW, which was formerly known as SPSS) is then used to tabulate, or calculate, the basic results of the research, such as the total number of participants and how collectively they answered various questions. The programs can also be used to calculate averages, such as the average age of respondents, their average satisfaction, and so forth. The same can done for percentages, and other values you learned about, or will learn about, in a statistics course, such as the standard deviation, mean, and median for each question.
The information generated by the programs can be used to draw conclusions, such as what all customers might like or not like about an offering based on what the sample group liked or did not like. The information can also be used to spot differences among groups of people. For example, the research might show that people in one area of the country like the product better than people in another area. Trends to predict what might happen in the future can also be spotted.
If there are any open-ended questions respondents have elaborated upon—for example, “Explain why you like the current brand you use better than any other brand”—the answers to each are pasted together, one on top of another, so researchers can compare and summarize the information. As we have explained, qualitative information such as this can give you a fuller picture of the results of the research.
Part of analyzing the data is to see if it seems sound. Does the way in which the research was conducted seem sound? Was the sample size large enough? Are the conclusions that become apparent from it reasonable?
The two most commonly used criteria used to test the soundness of a study are (1) validity and (2) reliability. A study is valid if it actually tested what it was designed to test. For example, did the experiment you ran in Second Life test what it was designed to test? Did it reflect what could really happen in the real world? If not, the research isn’t valid. If you were to repeat the study, and get the same results (or nearly the same results), the research is said to be reliable . If you get a drastically different result if you repeat the study, it’s not reliable. The data collected, or at least some it, can also be compared to, or reconciled with, similar data from other sources either gathered by your firm or by another organization to see if the information seems on target.
Stage 7: Write the Research Report and Present Its Findings
If you end up becoming a marketing professional and conducting a research study after you graduate, hopefully you will do a great job putting the study together. You will have defined the problem correctly, chosen the right sample, collected the data accurately, analyzed it, and your findings will be sound. At that point, you will be required to write the research report and perhaps present it to an audience of decision makers. You will do so via a written report and, in some cases, a slide or PowerPoint presentation based on your written report.
The six basic elements of a research report are as follows.
- Title Page . The title page explains what the report is about, when it was conducted and by whom, and who requested it.
- Table of Contents . The table of contents outlines the major parts of the report, as well as any graphs and charts, and the page numbers on which they can be found.
- Executive Summary . The executive summary summarizes all the details in the report in a very quick way. Many people who receive the report—both executives and nonexecutives—won’t have time to read the entire report. Instead, they will rely on the executive summary to quickly get an idea of the study’s results and what to do about those results.
Methodology and Limitations . The methodology section of the report explains the technical details of how the research was designed and conducted. The section explains, for example, how the data was collected and by whom, the size of the sample, how it was chosen, and whom or what it consisted of (e.g., the number of women versus men or children versus adults). It also includes information about the statistical techniques used to analyze the data.
Every study has errors—sampling errors, interviewer errors, and so forth. The methodology section should explain these details, so decision makers can consider their overall impact. The margin of error is the overall tendency of the study to be off kilter—that is, how far it could have gone wrong in either direction. Remember how newscasters present the presidential polls before an election? They always say, “This candidate is ahead 48 to 44 percent, plus or minus 2 percent.” That “plus or minus” is the margin of error. The larger the margin of error is, the less likely the results of the study are accurate. The margin of error needs to be included in the methodology section.
- Findings . The findings section is a longer, fleshed-out version of the executive summary that goes into more detail about the statistics uncovered by the research that bolster the study’s findings. If you have related research or secondary data on hand that back up the findings, it can be included to help show the study did what it was designed to do.
- Recommendations . The recommendations section should outline the course of action you think should be taken based on the findings of the research and the purpose of the project. For example, if you conducted a global market research study to identify new locations for stores, make a recommendation for the locations (Mersdorf, 2009).
As we have said, these are the basic sections of a marketing research report. However, additional sections can be added as needed. For example, you might need to add a section on the competition and each firm’s market share. If you’re trying to decide on different supply chain options, you will need to include a section on that topic.
As you write the research report, keep your audience in mind. Don’t use technical jargon decision makers and other people reading the report won’t understand. If technical terms must be used, explain them. Also, proofread the document to ferret out any grammatical errors and typos, and ask a couple of other people to proofread behind you to catch any mistakes you might have missed. If your research report is riddled with errors, its credibility will be undermined, even if the findings and recommendations you make are extremely accurate.
Many research reports are presented via PowerPoint. If you’re asked to create a slideshow presentation from the report, don’t try to include every detail in the report on the slides. The information will be too long and tedious for people attending the presentation to read through. And if they do go to the trouble of reading all the information, they probably won’t be listening to the speaker who is making the presentation.
Instead of including all the information from the study in the slides, boil each section of the report down to key points and add some “talking points” only the presenter will see. After or during the presentation, you can give the attendees the longer, paper version of the report so they can read the details at a convenient time, if they choose to.
Key Takeaway
Step 1 in the marketing research process is to define the problem. Businesses take a look at what they believe are symptoms and try to drill down to the potential causes so as to precisely define the problem. The next task for the researcher is to put into writing the research objective, or goal, the research is supposed to accomplish. Step 2 in the process is to design the research. The research design is the “plan of attack.” It outlines what data you are going to gather, from whom, how, and when, and how you’re going to analyze it once it has been obtained. Step 3 is to design the data-collection forms, which need to be standardized so the information gathered on each is comparable. Surveys are a popular way to gather data because they can be easily administered to large numbers of people fairly quickly. However, to produce the best results, survey questionnaires need to be carefully designed and pretested before they are used. Step 4 is drawing the sample, or a subset of potential buyers who are representative of your entire target market. If the sample is not correctly selected, the research will be flawed. Step 5 is to actually collect the data, whether it’s collected by a person face-to-face, over the phone, or with the help of computers or the Internet. The data-collection process is often different in foreign countries. Step 6 is to analyze the data collected for any obvious errors, tabulate the data, and then draw conclusions from it based on the results. The last step in the process, Step 7, is writing the research report and presenting the findings to decision makers.
Review Questions
- Explain why it’s important to carefully define the problem or opportunity a marketing research study is designed to investigate.
- Describe the different types of problems that can occur when marketing research professionals develop questions for surveys.
- How does a probability sample differ from a nonprobability sample?
- What makes a marketing research study valid? What makes a marketing research study reliable?
- What sections should be included in a marketing research report? What is each section designed to do?
1 “Questionnaire Design,” QuickMBA , http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/research/qdesign (accessed December 14, 2009).
Barnes, B., “Disney Expert Uses Science to Draw Boy Viewers,” New York Times , April 15, 2009, http://www.nytimes.com/2009/04/14/arts/television/14boys.html?pagewanted=1&_r=1 (accessed December 14, 2009).
Burns A. and Ronald Bush, Marketing Research , 6th ed. (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2010), 85.
Malhotra, N., Marketing Research: An Applied Approach , 6th ed. (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall), 764.
McDaniel, C. D. and Roger H. Gates, Marketing Research Essentials , 2nd ed. (Cincinnati: South-Western College Publishing, 1998), 61.
McWilliams, J., “A-B Puts Super-Low-Calorie Beer in Ring with Miller,” St. Louis Post-Dispatch , August 16, 2009, http://www.stltoday.com/business/next-matchup-light-weights-a-b-puts-super-low-calorie/article_47511bfe-18ca-5979-bdb9-0526c97d4edf.html (accessed April 13, 2012).
Mersdorf, S., “How to Organize Your Next Survey Report,” Cvent , August 24, 2009, http://survey.cvent.com/blog/cvent-survey/0/0/how-to-organize-your-next-survey-report (accessed December 14, 2009).
Rappeport A. and David Gelles, “Facebook to Form Alliance with Nielsen,” Financial Times , September 23, 2009, 16.
Spangler, T., “Disney Lab Tracks Feelings,” Multichannel News 30, no. 30 (August 3, 2009): 26.
Wagner, J., “Marketing in Second Life Doesn’t Work…Here Is Why!” GigaOM , April 4, 2007, http://gigaom.com/2007/04/04/3-reasons-why-marketing-in-second-life-doesnt-work (accessed December 14, 2009).
Wrenn, B., Robert E. Stevens, and David L. Loudon, Marketing Research: Text and Cases , 2nd ed. (Binghamton, NY: Haworth Press, 2007), 180.
Zouhali-Worrall, M., “Found in Translation: Avoiding Multilingual Gaffes,” CNNMoney.com , July 14, 2008, http://money.cnn.com/2008/07/07/smallbusiness/language_translation.fsb/index.htm (accessed December 14, 2009).
Principles of Marketing Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Why Use Market Research in Marketing Design?
Discover the benefits of conducting market research before creating your marketing design strategy.
Table of Contents
Design is one of the most important aspects of a good marketing strategy, so here’s how to use marketing research to help you create designs that convert prospects into customers.
Market research and good design go hand in hand, since conducting market research can help you make decisions about the look and feel of everything you design for your business.
Of course, while you can rely on research for ad hoc business decisions, it’s much better to incorporate these findings into your strategic planning. Since design is one of the key assets of an effective marketing strategy,
So let’s take a closer look at the reasons why you need to do market research before creating a marketing design strategy.
Reason 1: Knowing your target audience
Let’s start with the big one. If you know who you’re marketing to, chances are your efforts will be much more successful. Your marketing strategy should include concrete marketing personas or personalizations of your ideal customers .
Market research methods such as interviews or focus groups can decrease your trial and error period when it comes to design. Of course, while it’s important to understand what your target market likes, it’s much more important to understand what they need .
In that respect, different research methods can be helpful, such as:
- Interviews : they allow you to understand the users’ feelings and needs, beyond just asking them to choose a preference.
- Survey : usually much simpler and easier to conduct than an interview, they usually provide quantifiable data; they’re good to use at a later stage, once you have a choice between different options;
- Focus groups : similar to interviews, but they involve a group of people with similar demographics and interests, so they can be more reliable than interviews for a specific market segment.
- Experiments and field trials : these test out actual products in demo or trial versions, or samples for physical products.
- Observation tests : this method is highly effective for understanding customers beyond what they say about your product, to how they actually interact with it; it can have different forms, such as eye-tracking observation, usability testing or in-home/store observation.
Reason 2: Identifying new opportunities for marketing
One of the biggest benefits of market research is that it allows you to make informed decisions and plan strategically.
For example, a SaaS business might not see a lot of sense in advertising offline. After all, most of your business presumably comes from Internet users looking for services online.
And yet, doing something different can be a great way to boost brand awareness and stand out.
A famous example is Spotify’s Wrapped campaign (later called A Year in Music), which included very funny billboards that presented their users’ unique listening habits. As a music streaming service, many people use Spotify outside their home (e.g. on their daily commute) so it made a lot of sense to place these billboards in places like the subway or bus stations.
Next, it further promoted one of Spotify’s key value propositions: personalization . The platform offers users personalized playlists and suggestions based on their listening habits, so this was just another way to show how much the company cares about users’ individual experiences. And the prospect of being featured on a billboard like this is pretty exciting, right?

Business Insider
Tortoise Media
But this approach has been a part of Apple’s marketing strategy for decades. Their key value propositions (based on market research of course), which are minimalism and superior design, have always made their ads memorable and unique .
Or this one that boasts a superior app store
Cult of Mac
Another way the campaign sparked users’ interest was the connection it created between the musicians and their fans . Alongside every users’ personalized listening data, they created the same for musicians, who shared these flattering stats on their social media, helping the platform get even more buzz.

Reason 3: Making a unique offer
Researching your competitors is a necessary step in the market research process . If you understand their strengths and weaknesses, then you will also be able to create a unique value proposition and communicate it through marketing design .
One of the largest and most well-known companies that uses market research is Apple. Since superb design and advanced features are key value propositions of their products, it’s also necessary for their marketing campaigns to reflect this.
This series of ads that compare iPhones to their competitors (implicity, Android phones) are a perfect example of how to achieve this through effective design. This one effortlessly shows the superior portrait mode which was introduced with the new camera of iPhone 8.

Reason 4: Tracking campaign results
The key to a successful marketing campaign is monitoring and iteration . Doing research early on can save you time and effort down the road with making sure your marketing efforts are optimized at all times.
For example, if you’ve noticed your social media campaign isn’t performing as well as you’ve hoped, you can use marketing research to refine your targeting: perhaps you’ve only included demographic data, but excluded relevant interests and experiences that make people drawn to your product or service.
You can also use marketing research to create a sophisticated lead qualification system, so that you’re making sales pitches to the people most likely to purchase from you.

Having lived and studied in London and Berlin, I'm back in native Serbia, working remotely and writing short stories and plays in my free time. With previous experience in the nonprofit sector, I'm currently writing about the universal language of good graphic design. I make mix CDs and my playlists are almost exclusively 1960s.
Hack your marketing design
Enjoyed the read? Get inspired with some of ManyPixels best work by downloading our social media design portfolio.
Wait... there’s more!
Enjoyed the read? Subscribe to our mailing list for all the latest tips, how-tos and news on graphic design and marketing.

- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Design
Definition:
Research design refers to the overall strategy or plan for conducting a research study. It outlines the methods and procedures that will be used to collect and analyze data, as well as the goals and objectives of the study. Research design is important because it guides the entire research process and ensures that the study is conducted in a systematic and rigorous manner.
Types of Research Design
Types of Research Design are as follows:
Descriptive Research Design
This type of research design is used to describe a phenomenon or situation. It involves collecting data through surveys, questionnaires, interviews, and observations. The aim of descriptive research is to provide an accurate and detailed portrayal of a particular group, event, or situation. It can be useful in identifying patterns, trends, and relationships in the data.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to determine if there is a relationship between two or more variables. This type of research design involves collecting data from participants and analyzing the relationship between the variables using statistical methods. The aim of correlational research is to identify the strength and direction of the relationship between the variables.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This type of research design involves manipulating one variable and measuring the effect on another variable. It usually involves randomly assigning participants to groups and manipulating an independent variable to determine its effect on a dependent variable. The aim of experimental research is to establish causality.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks one or more of the features of a true experiment. For example, there may not be random assignment to groups or a control group. This type of research design is used when it is not feasible or ethical to conduct a true experiment.
Case Study Research Design
Case study research design is used to investigate a single case or a small number of cases in depth. It involves collecting data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis. The aim of case study research is to provide an in-depth understanding of a particular case or situation.
Longitudinal Research Design
Longitudinal research design is used to study changes in a particular phenomenon over time. It involves collecting data at multiple time points and analyzing the changes that occur. The aim of longitudinal research is to provide insights into the development, growth, or decline of a particular phenomenon over time.
Structure of Research Design
The format of a research design typically includes the following sections:
- Introduction : This section provides an overview of the research problem, the research questions, and the importance of the study. It also includes a brief literature review that summarizes previous research on the topic and identifies gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Research Questions or Hypotheses: This section identifies the specific research questions or hypotheses that the study will address. These questions should be clear, specific, and testable.
- Research Methods : This section describes the methods that will be used to collect and analyze data. It includes details about the study design, the sampling strategy, the data collection instruments, and the data analysis techniques.
- Data Collection: This section describes how the data will be collected, including the sample size, data collection procedures, and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis: This section describes how the data will be analyzed, including the statistical techniques that will be used to test the research questions or hypotheses.
- Results : This section presents the findings of the study, including descriptive statistics and statistical tests.
- Discussion and Conclusion : This section summarizes the key findings of the study, interprets the results, and discusses the implications of the findings. It also includes recommendations for future research.
- References : This section lists the sources cited in the research design.
Example of Research Design
An Example of Research Design could be:
Research question: Does the use of social media affect the academic performance of high school students?
Research design:
- Research approach : The research approach will be quantitative as it involves collecting numerical data to test the hypothesis.
- Research design : The research design will be a quasi-experimental design, with a pretest-posttest control group design.
- Sample : The sample will be 200 high school students from two schools, with 100 students in the experimental group and 100 students in the control group.
- Data collection : The data will be collected through surveys administered to the students at the beginning and end of the academic year. The surveys will include questions about their social media usage and academic performance.
- Data analysis : The data collected will be analyzed using statistical software. The mean scores of the experimental and control groups will be compared to determine whether there is a significant difference in academic performance between the two groups.
- Limitations : The limitations of the study will be acknowledged, including the fact that social media usage can vary greatly among individuals, and the study only focuses on two schools, which may not be representative of the entire population.
- Ethical considerations: Ethical considerations will be taken into account, such as obtaining informed consent from the participants and ensuring their anonymity and confidentiality.
How to Write Research Design
Writing a research design involves planning and outlining the methodology and approach that will be used to answer a research question or hypothesis. Here are some steps to help you write a research design:
- Define the research question or hypothesis : Before beginning your research design, you should clearly define your research question or hypothesis. This will guide your research design and help you select appropriate methods.
- Select a research design: There are many different research designs to choose from, including experimental, survey, case study, and qualitative designs. Choose a design that best fits your research question and objectives.
- Develop a sampling plan : If your research involves collecting data from a sample, you will need to develop a sampling plan. This should outline how you will select participants and how many participants you will include.
- Define variables: Clearly define the variables you will be measuring or manipulating in your study. This will help ensure that your results are meaningful and relevant to your research question.
- Choose data collection methods : Decide on the data collection methods you will use to gather information. This may include surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, or secondary data sources.
- Create a data analysis plan: Develop a plan for analyzing your data, including the statistical or qualitative techniques you will use.
- Consider ethical concerns : Finally, be sure to consider any ethical concerns related to your research, such as participant confidentiality or potential harm.
When to Write Research Design
Research design should be written before conducting any research study. It is an important planning phase that outlines the research methodology, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques that will be used to investigate a research question or problem. The research design helps to ensure that the research is conducted in a systematic and logical manner, and that the data collected is relevant and reliable.
Ideally, the research design should be developed as early as possible in the research process, before any data is collected. This allows the researcher to carefully consider the research question, identify the most appropriate research methodology, and plan the data collection and analysis procedures in advance. By doing so, the research can be conducted in a more efficient and effective manner, and the results are more likely to be valid and reliable.
Purpose of Research Design
The purpose of research design is to plan and structure a research study in a way that enables the researcher to achieve the desired research goals with accuracy, validity, and reliability. Research design is the blueprint or the framework for conducting a study that outlines the methods, procedures, techniques, and tools for data collection and analysis.
Some of the key purposes of research design include:
- Providing a clear and concise plan of action for the research study.
- Ensuring that the research is conducted ethically and with rigor.
- Maximizing the accuracy and reliability of the research findings.
- Minimizing the possibility of errors, biases, or confounding variables.
- Ensuring that the research is feasible, practical, and cost-effective.
- Determining the appropriate research methodology to answer the research question(s).
- Identifying the sample size, sampling method, and data collection techniques.
- Determining the data analysis method and statistical tests to be used.
- Facilitating the replication of the study by other researchers.
- Enhancing the validity and generalizability of the research findings.
Applications of Research Design
There are numerous applications of research design in various fields, some of which are:
- Social sciences: In fields such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology, research design is used to investigate human behavior and social phenomena. Researchers use various research designs, such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and correlational designs, to study different aspects of social behavior.
- Education : Research design is essential in the field of education to investigate the effectiveness of different teaching methods and learning strategies. Researchers use various designs such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and case study designs to understand how students learn and how to improve teaching practices.
- Health sciences : In the health sciences, research design is used to investigate the causes, prevention, and treatment of diseases. Researchers use various designs, such as randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, and case-control studies, to study different aspects of health and healthcare.
- Business : Research design is used in the field of business to investigate consumer behavior, marketing strategies, and the impact of different business practices. Researchers use various designs, such as survey research, experimental research, and case studies, to study different aspects of the business world.
- Engineering : In the field of engineering, research design is used to investigate the development and implementation of new technologies. Researchers use various designs, such as experimental research and case studies, to study the effectiveness of new technologies and to identify areas for improvement.
Advantages of Research Design
Here are some advantages of research design:
- Systematic and organized approach : A well-designed research plan ensures that the research is conducted in a systematic and organized manner, which makes it easier to manage and analyze the data.
- Clear objectives: The research design helps to clarify the objectives of the study, which makes it easier to identify the variables that need to be measured, and the methods that need to be used to collect and analyze data.
- Minimizes bias: A well-designed research plan minimizes the chances of bias, by ensuring that the data is collected and analyzed objectively, and that the results are not influenced by the researcher’s personal biases or preferences.
- Efficient use of resources: A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the resources (time, money, and personnel) are used efficiently and effectively, by focusing on the most important variables and methods.
- Replicability: A well-designed research plan makes it easier for other researchers to replicate the study, which enhances the credibility and reliability of the findings.
- Validity: A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the findings are valid, by ensuring that the methods used to collect and analyze data are appropriate for the research question.
- Generalizability : A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the findings can be generalized to other populations, settings, or situations, which increases the external validity of the study.
Research Design Vs Research Methodology
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...
Leave a comment x.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Free Resources

14 Market Research Examples

This article was originally published in the MarketingSherpa email newsletter .
Example #1: National bank’s A/B testing
You can learn what customers want by conducting experiments on real-life customer decisions using A/B testing. When you ensure your tests do not have any validity threats, the information you garner can offer very reliable insights into customer behavior.
Here’s an example from Flint McGlaughlin, CEO of MarketingSherpa and MECLABS Institute, and the creator of its online marketing course .
A national bank was working with MECLABS to discover how to increase the number of sign-ups for new checking accounts.
Customers who were interested in checking accounts could click on an “Open in Minutes” link on the bank’s homepage.
Creative Sample #1: Anonymized bank homepage

After clicking on the homepage link, visitors were taken to a four-question checking account selector tool.
Creative Sample #2: Original checking account landing page — account recommendation selector tool

After filling out the selector tool, visitors were taken to a results page that included a suggested package (“Best Choice”) along with a secondary option (“Second Choice”). The results page had several calls to action (CTAs). Website visitors were able to select an account and begin pre-registration (“Open Now”) or find out more information about the account (“Learn More”), go back and change their answers (“Go back and change answers”), or manually browse other checking options (“Other Checking Options”).
Creative Sample #3: Original checking account landing page — account recommendation selector tool results page

After going through the experience, the MECLABS team hypothesized that the selector tool wasn’t really delivering on the expectation the customer had after clicking on the “Open in Minutes” CTA. They created two treatments (new versions) and tested them against the control experience.
In the first treatment, the checking selector tool was removed, and instead, customers were directly presented with three account options in tabs from which customers could select.
Creative Sample #4: Checking account landing page Treatment #1

The second treatment’s landing page focused on a single product and had only one CTA. The call-to-action was similar to the CTA customers clicked on the homepage to get to this page — “Open Now.”
Creative Sample #5: Checking account landing page Treatment #2

Both treatments increased account applications compared to the control landing page experience, with Treatment #2 generating 65% more applicants at a 98% level of confidence.
Creative Sample #6: Results of bank experiment that used A/B testing

You’ll note the Level of Confidence in the results. With any research tactic or tool you use to learn about customers, you have to consider whether the information you’re getting really represents most customers, or if you’re just seeing outliers or random chance.
With a high Level of Confidence like this, it is more likely the results actually represent a true difference between the control and treatment landing pages and that the results aren’t just a random event.
The other factor to consider is — testing in and of itself will not produce results. You have to use testing as research to actually learn about the customer and then make changes to better serve the customer.
In the video How to Discover Exactly What the Customer Wants to See on the Next Click: 3 critical skills every marketer must master , McGlaughlin discussed this national bank experiment and explained how to use prioritization, identification and deduction to discover what your customers want.
This example was originally published in Marketing Research: 5 examples of discovering what customers want .
Example #2: Consumer Reports’ market intelligence research from third-party sources
The first example covers A/B testing. But keep in mind, ill-informed A/B testing isn’t market research, it’s just hoping for insights from random guesses.
In other words, A/B testing in a vacuum does not provide valuable information about customers. What you are testing is crucial, and then A/B testing is a means to help better understand whether insights you have about the customer are either validated or refuted by actual customer behavior. So it’s important to start with some research into potential customers and competitors to inform your A/B tests.
For example, when MECLABS and MarketingExperiments (sister publisher to MarketingSherpa) worked with Consumer Reports on a public, crowdsourced A/B test, we provided a market intelligence report to our audience to help inform their test suggestions.
Every successful marketing test should confirm or deny an assumption about the customer. You need enough knowledge about the customer to create marketing messages you think will be effective.
For this public experiment to help marketers improve their split testing abilities, we had a real customer to work with — donors to Consumer Reports.
To help our audience better understand the customer, the MECLABS Marketing Intelligence team created the 26-page ConsumerReports Market Intelligence Research document (which you can see for yourself at that link).
This example was originally published in Calling All Writers and Marketers: Write the most effective copy for this Consumer Reports email and win a MarketingSherpa Summit package and Consumer Reports Value Proposition Test: What you can learn from a 29% drop in clickthrough .
Example #3: Virtual event company’s conversation
What if you don’t have the budget for A/B testing? Or any of the other tactics in this article?
Well, if you’re like most people you likely have some relationships with other human beings. A significant other, friends, family, neighbors, co-workers, customers, a nemesis (“Newman!”). While conducting market research by talking to these people has several validity threats, it at least helps you get out of your own head and identify some of your blind spots.
WebBabyShower.com’s lead magnet is a PDF download of a baby shower thank you card ‘swipe file’ plus some extras. “Women want to print it out and have it where they are writing cards, not have a laptop open constantly,” said Kurt Perschke, owner, WebBabyShower.com.
That is not a throwaway quote from Perschke. That is a brilliant insight, so I want to make sure we don’t overlook it. By better understanding customer behavior, you can better serve customers and increase results.
However, you are not your customer. So you must bridge the gap between you and them.
Often you hear marketers or business leaders review an ad or discuss a marketing campaign and say, “Well, I would never read that entire ad” or “I would not be interested in that promotion.” To which I say … who cares? Who cares what you would do? If you are not in the ideal customer set, sorry to dent your ego, but you really don’t matter. Only the customer does.
Perschke is one step ahead of many marketers and business leaders because he readily understands this. “Owning a business whose customers are 95% women has been a great education for me,” he said.
So I had to ask him, how did he get this insight into his customers’ behavior? Frankly, it didn’t take complex market research. He was just aware of this disconnect he had with the customer, and he was alert for ways to bridge the gap. “To be honest, I first saw that with my wife. Then we asked a few customers, and they confirmed it’s what they did also. Writing notes by hand is viewed as a ‘non-digital’ activity and reading from a laptop kinda spoils the mood apparently,” he said.
Back to WebBabyShower. “We've seen a [more than] 100% increase in email signups using this method, which was both inexpensive and evergreen,” Perschke said.
This example was originally published in Digital Marketing: Six specific examples of incentives that worked .
Example #4: Spiceworks Ziff Davis’ research-informed content marketing
Marketing research isn’t just to inform products and advertising messages. Market research can also give your brand a leg up in another highly competitive space – content marketing.
Don’t just jump in and create content expecting it to be successful just because it’s “free.” Conducting research beforehand can help you understand what your potential audience already receives and where they might need help but are currently being served.
When Spiceworks Ziff Davis (SWZD) published its annual State of IT report, it invested months in conducting primary market research, analyzing year-over-year trends, and finally producing the actual report.
“Before getting into the nuts and bolts of writing an asset, look at market shifts and gaps that complement your business and marketing objectives. Then, you can begin to plan, research, write, review and finalize an asset,” said Priscilla Meisel, Content Marketing Director, SWZD.
This example was originally published in Marketing Writing: 3 simple tips that can help any marketer improve results (even if you’re not a copywriter) .
Example #5: Business travel company’s guerilla research
There are many established, expensive tactics you can use to better understand customers.
But if you don’t have the budget for those tactics, and don’t know any potential customers, you might want to brainstorm creative ways you can get valuable information from the right customer target set.
Here’s an example from a former client of Mitch McCasland, Founding Partner and Director, Brand Inquiry Partners. The company sold a product related to frequent business flyers and was interested in finding out information on people who travel for a living. They needed consumer feedback right away.
“I suggested that they go out to the airport with a bunch of 20-dollar bills and wait outside a gate for passengers to come off their flight,” McCasland said. When people came off the flight, they were politely asked if they would answer a few questions in exchange for the incentive (the $20). By targeting the first people off the flight they had a high likelihood of reaching the first-class passengers.
This example was originally published in Guerrilla Market Research Expert Mitch McCasland Tells How You Can Conduct Quick (and Cheap) Research .
Example #6: Intel’s market research database
When conducting market research, it is crucial to organize your data in a way that allows you to easily and quickly report on it. This is especially important for qualitative studies where you are trying to do more than just quantify the data, but need to manage it so it is easier to analyze.
Anne McClard, Senior Researcher, Doxus worked with Shauna Pettit-Brown of Intel on a research project to understand the needs of mobile application developers throughout the world.
Intel needed to be able to analyze the data from several different angles, including segment and geography, a daunting task complicated by the number of interviews, interviewers, and world languages.
“The interviews were about an hour long, and pretty substantial,” McClard says. So, she needed to build a database to organize the transcripts in a way that made sense.
Different types of data are useful for different departments within a company; once your database is organized you can sort it by various threads.
The Intel study had three different internal sponsors. "When it came to doing the analysis, we ended up creating multiple versions of the presentation targeted to individual audiences," Pettit-Brown says.
The organized database enabled her to go back into the data set to answer questions specific to the interests of the three different groups.
This example was originally published in 4 Steps to Building a Qualitative Market Research Database That Works Better .
Example #7: National security survey’s priming
When conducting market research surveys, the way you word your questions can affect customers’ response. Even the way you word previous questions can put customers in a certain mindset that will skew their answers.
For example, when people were asked if they thought the U.S. government should spend money on an anti-missile shield, the results appeared fairly conclusive. Sixty-four percent of those surveyed thought the country should and only six percent were unsure, according to Opinion Makers: An Insider Exposes the Truth Behind the Polls .
But when pollsters added the option, "...or are you unsure?" the level of uncertainty leaped from six percent to 33 percent. When they asked whether respondents would be upset if the government took the opposite course of action from their selection, 59 percent either didn’t have an opinion or didn’t mind if the government did something differently.
This is an example of how the way you word questions can change a survey’s results. You want survey answers to reflect customer’s actual sentiments that are as free of your company’s previously held biases as possible.
This example was originally published in Are Surveys Misleading? 7 Questions for Better Market Research .
Example #8: Visa USA’s approach to getting an accurate answer
As mentioned in the previous example, the way you ask customers questions can skew their responses with your own biases.
However, the way you ask questions to potential customers can also illuminate your understanding of them. Which is why companies field surveys to begin with.
“One thing you learn over time is how to structure questions so you have a greater likelihood of getting an accurate answer. For example, when we want to find out if people are paying off their bills, we'll ask them to think about the card they use most often. We then ask what the balance was on their last bill after they paid it,” said Michael Marx, VP Research Services, Visa USA.
This example was originally published in Tips from Visa USA's Market Research Expert Michael Marx .
Example #9: Hallmark’s private members-only community
Online communities are a way to interact with and learn from customers. Hallmark created a private members-only community called Idea Exchange (an idea you could replicate with a Facebook or LinkedIn Group).
The community helped the greeting cards company learn the customer’s language.
“Communities…let consumers describe issues in their own terms,” explained Tom Brailsford, Manager of Advancing Capabilities, Hallmark Cards. “Lots of times companies use jargon internally.”
At Hallmark they used to talk internally about “channels” of distribution. But consumers talk about stores, not channels. It is much clearer to ask consumers about the stores they shop in than what channels they shop.
For example, Brailsford clarified, “We say we want to nurture, inspire, and lift one’s spirits. We use those terms, and the communities have defined those terms for us. So we have learned how those things play out in their lives. It gives us a much richer vocabulary to talk about these things.”
This example was originally published in Third Year Results from Hallmark's Online Market Research Experiment .
Example #10: L'Oréal’s social media listening
If you don’t want the long-term responsibility that comes with creating an online community, you can use social media listening to understand how customers talking about your products and industry in their own language.
In 2019, L'Oréal felt the need to upgrade one of its top makeup products – L'Oréal Paris Alliance Perfect foundation. Both the formula and the product communication were outdated – multiple ingredients had emerged on the market along with competitive products made from those ingredients.
These new ingredients and products were overwhelming consumers. After implementing new formulas, the competitor brands would advertise their ingredients as the best on the market, providing almost magical results.
So the team at L'Oréal decided to research their consumers’ expectations instead of simply crafting a new formula on their own. The idea was to understand not only which active ingredients are credible among the audience, but also which particular words they use while speaking about foundations in general.
The marketing team decided to combine two research methods: social media listening and traditional questionnaires.
“For the most part, we conduct social media listening research when we need to find out what our customers say about our brand/product/topic and which words they use to do it. We do conduct traditional research as well and ask questions directly. These surveys are different because we provide a variety of readymade answers that respondents choose from. Thus, we limit them in terms of statements and their wording,” says Marina Tarandiuk, marketing research specialist, L'Oréal Ukraine.
“The key value of social media listening (SML) for us is the opportunity to collect people’s opinions that are as ‘natural’ as possible. When someone leaves a review online, they are in a comfortable environment, they use their ‘own’ language to express themselves, there is no interviewer standing next to them and potentially causing shame for their answer. The analytics of ‘natural’ and honest opinions of our customers enables us to implement the results in our communication and use the same language as them,” Tarandiuk said.
The team worked with a social media listening tool vendor to identify the most popular, in-demand ingredients discussed online and detect the most commonly used words and phrases to create a “consumer glossary.”
Questionnaires had to confirm all the hypotheses and insights found while monitoring social media. This part was performed in-house with the dedicated team. They created custom questionnaires aiming to narrow down all the data to a maximum of three variants that could become the base for the whole product line.
“One of our recent studies had a goal to find out which words our clients used to describe positive and negative qualities of [the] foundation. Due to a change in [the] product’s formula, we also decided to change its communication. Based on the opinions of our customers, we can consolidate the existing positive ideas that our clients have about the product,” Tarandiuk said.
To find the related mentions, the team monitored not only the products made by L'Oréal but also the overall category. “The search query contained both brand names and general words like foundation, texture, smell, skin, pores, etc. The problem was that this approach ended up collecting thousands of mentions, not all of which were relevant to the topic,” said Elena Teselko, content marketing manager, YouScan (L'Oréal’s social media listening tool).
So the team used artificial intelligence-based tagging that divided mentions according to the category, features, or product type.
This approach helped the team discover that customers valued such foundation features as not clogging pores, a light texture, and not spreading. Meanwhile, the most discussed and appreciated cosmetics component was hyaluronic acid.
These exact phrases, found with the help of social media monitoring, were later used for marketing communication.
Creative Sample #7: Marketing communicating for personal care company with messaging based on discoveries from market research

“Doing research and detecting audience’s interests BEFORE starting a campaign is an approach that dramatically lowers any risks and increases chances that the campaign would be appreciated by customers,” Teselko said.
This example was originally published in B2C Branding: 3 quick case studies of enhancing the brand with a better customer experience .
Example #11: Levi’s ethnographic research
In a focus group or survey, you are asking customers to explain something they may not even truly understand. Could be why they bought a product. Or what they think of your competitor.
Ethnographic research is a type of anthropology in which you go into customers’ homes or places of business and observe their actual behavior, behavior they may not understand well enough to explain to you.
While cost prohibitive to many brands, and simply unfeasible for others, it can elicit new insights into your customers.
Michael Perman, Senior Director Cultural Insights, Levi Strauss & Co. uses both quantitative and qualitative research on a broad spectrum, but when it comes to gathering consumer insight, he focuses on in-depth ethnographic research provided by partners who specialize in getting deep into the “nooks and crannies of consumer life in America and around the world.” For example, his team spends time in consumers’ homes and in their closets. They shop with consumers, looking for the reality of a consumer’s life and identifying themes that will enable designers and merchandisers to better understand and anticipate consumer needs.
Perman then puts together multi-sensory presentations that illustrate the findings of research. For example, “we might recreate a teenager’s bedroom and show what a teenage girl might have on her dresser.”
This example was originally published in How to Get Your Company to Pay Attention to Market Research Results: Tips from Levi Strauss .
Example #12: eBags’ ethnographic research
Ethnographic research isn’t confined to a physical goods brand like Levi’s. Digital brands can engage in this form of anthropology as well.
While usability testing in a lab is useful, it does miss some of the real-world environmental factors that play a part in the success of a website. Usability testing alone didn’t create a clear enough picture for Gregory Casey, User Experience Designer and Architect, eBags.
“After we had designed our mobile and tablet experience, I wanted to run some contextual user research, which basically meant seeing how people used it in the wild, seeing how people are using it in their homes. So that’s exactly what I did,” Gregory said.
He found consumers willing to open their home to him and be tested in their normal environment. This meant factors like the television, phone calls and other family members played a part in how they experienced the eBags mobile site.
“During these interview sessions, a lot of times we were interrupted by, say, a child coming over and the mother having to do something for the kid … The experience isn’t sovereign. It’s not something where they just sit down, work through a particular user flow and complete their interaction,” Gregory said.
By watching users work through the site as they would in their everyday life, Gregory got to see what parts of the site they actually use.
This example was originally published in Mobile Marketing: 4 takeaways on how to improve your mobile shopping experience beyond just responsive design .
Example #13: John Deere’s shift from product-centric market research to consumer-centric research
One of the major benefits of market research is to overcome company blind spots. However, if you start with your blind spots – i.e., a product focus – you will blunt the effectiveness of your market research.
In the past, “they’d say, Here’s the product, find out how people feel about it,” explained David van Nostrand, Manager, John Deere's Global Market Research. “A lot of companies do that.” Instead, they should be saying, “Let's start with the customers: what do they want, what do they need?”
The solution? A new in-house program called “Category Experts” brings the product-group employees over as full team members working on specific research projects with van Nostrand’s team.
These staffers handle items that don’t require a research background: scheduling, meetings, logistics, communication and vendor management. The actual task they handle is less important than the fact that they serve as human cross-pollinators, bringing consumer-centric sensibility back to their product- focused groups.
For example, if van Nostrand’s team is doing research about a vehicle, they bring in staffers from the Vehicles product groups. “The information about vehicle consumers needs to be out there in the vehicle marketing groups, not locked in here in the heads of the researchers.”
This example was originally published in How John Deere Increased Mass Consumer Market Share by Revamping its Market Research Tactics .
Example #14: LeapFrog’s market research involvement throughout product development (not just at the beginning and the end)
Market research is sometimes thought of as a practice that can either inform the development of a product, or research consumer attitudes about developed products. But what about the middle?
Once the creative people begin working on product designs, the LeapFrog research department stays involved.
They have a lab onsite where they bring moms and kids from the San Francisco Bay area to test preliminary versions of the products. “We do a lot of hands-on, informal qualitative work with kids,” said Craig Spitzer, VP Marketing Research, LeapFrog. “Can they do what they need to do to work the product? Do they go from step A to B to C, or do they go from A to C to B?”
When designing the LeapPad Learning System, for example, the prototype went through the lab “a dozen times or so,” he says.
A key challenge for the research department is keeping and building the list of thousands of families who have agreed to be on call for testing. “We've done everything from recruiting on the Internet to putting out fliers in local schools, working through employees whose kids are in schools, and milking every connection we have,” Spitzer says.
Kids who test products at the lab are compensated with a free, existing product rather than a promise of the getting the product they're testing when it is released in the future.
This example was originally published in How LeapFrog Uses Marketing Research to Launch New Products .
Related resources
The Marketer’s Blind Spot: 3 ways to overcome the marketer’s greatest obstacle to effective messaging
Get Your Free Test Discovery Tool to Help Log all the Results and Discoveries from Your Company’s Marketing Tests
Marketing Research: 5 examples of discovering what customers want
Online Marketing Tests: How do you know you’re really learning anything?
Improve Your Marketing
Join our thousands of weekly case study readers.
Enter your email below to receive MarketingSherpa news, updates, and promotions:
Note: Already a subscriber? Want to add a subscription? Click Here to Manage Subscriptions
Get Better Business Results With a Skillfully Applied Customer-first Marketing Strategy

The customer-first approach of MarketingSherpa’s agency services can help you build the most effective strategy to serve customers and improve results, and then implement it across every customer touchpoint.
Get headlines, value prop, competitive analysis, and more.
Marketer Vs Machine

Marketer Vs Machine: We need to train the marketer to train the machine.
Free Marketing Course

Become a Marketer-Philosopher: Create and optimize high-converting webpages (with this free online marketing course)
Project and Ideas Pitch Template

A free template to help you win approval for your proposed projects and campaigns
Six Quick CTA checklists

These CTA checklists are specifically designed for your team — something practical to hold up against your CTAs to help the time-pressed marketer quickly consider the customer psychology of your “asks” and how you can improve them.
Infographic: How to Create a Model of Your Customer’s Mind
You need a repeatable methodology focused on building your organization’s customer wisdom throughout your campaigns and websites. This infographic can get you started.
Infographic: 21 Psychological Elements that Power Effective Web Design

To build an effective page from scratch, you need to begin with the psychology of your customer. This infographic can get you started.
Receive the latest case studies and data on email, lead gen, and social media along with MarketingSherpa updates and promotions.
- Your Email Account
- Customer Service Q&A
- Search Library
- Content Directory:
Questions? Contact Customer Service at [email protected]
© 2000-2024 MarketingSherpa LLC, ISSN 1559-5137 Editorial HQ: MarketingSherpa LLC, PO Box 50032, Jacksonville Beach, FL 32240
The views and opinions expressed in the articles of this website are strictly those of the author and do not necessarily reflect in any way the views of MarketingSherpa, its affiliates, or its employees.
6.3 Steps in a Successful Marketing Research Plan
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- 1 Identify and describe the steps in a marketing research plan.
- 2 Discuss the different types of data research.
- 3 Explain how data is analyzed.
- 4 Discuss the importance of effective research reports.
Define the Problem
There are seven steps to a successful marketing research project (see Figure 6.3 ). Each step will be explained as we investigate how a marketing research project is conducted.
The first step, defining the problem, is often a realization that more information is needed in order to make a data-driven decision. Problem definition is the realization that there is an issue that needs to be addressed. An entrepreneur may be interested in opening a small business but must first define the problem that is to be investigated. A marketing research problem in this example is to discover the needs of the community and also to identify a potentially successful business venture.
Many times, researchers define a research question or objectives in this first step. Objectives of this research study could include: identify a new business that would be successful in the community in question, determine the size and composition of a target market for the business venture, and collect any relevant primary and secondary data that would support such a venture. At this point, the definition of the problem may be “Why are cat owners not buying our new cat toy subscription service?”
Additionally, during this first step we would want to investigate our target population for research. This is similar to a target market, as it is the group that comprises the population of interest for the study. In order to have a successful research outcome, the researcher should start with an understanding of the problem in the current situational environment.
Develop the Research Plan
Step two is to develop the research plan. What type of research is necessary to meet the established objectives of the first step? How will this data be collected? Additionally, what is the time frame of the research and budget to consider? If you must have information in the next week, a different plan would be implemented than in a situation where several months were allowed. These are issues that a researcher should address in order to meet the needs identified.
Research is often classified as coming from one of two types of data: primary and secondary. Primary data is unique information that is collected by the specific researcher with the current project in mind. This type of research doesn’t currently exist until it is pulled together for the project. Examples of primary data collection include survey, observation, experiment, or focus group data that is gathered for the current project.
Secondary data is any research that was completed for another purpose but can be used to help inform the research process. Secondary data comes in many forms and includes census data, journal articles, previously collected survey or focus group data of related topics, and compiled company data. Secondary data may be internal, such as the company’s sales records for a previous quarter, or external, such as an industry report of all related product sales. Syndicated data , a type of external secondary data, is available through subscription services and is utilized by many marketers. As you can see in Table 6.1 , primary and secondary data features are often opposite—the positive aspects of primary data are the negative side of secondary data.
There are four research types that can be used: exploratory, descriptive, experimental, and ethnographic research designs (see Figure 6.4 ). Each type has specific formats of data that can be collected. Qualitative research can be shared through words, descriptions, and open-ended comments. Qualitative data gives context but cannot be reduced to a statistic. Qualitative data examples are categorical and include case studies, diary accounts, interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys. By comparison, quantitative data is data that can be reduced to number of responses. The number of responses to each answer on a multiple-choice question is quantitative data. Quantitative data is numerical and includes things like age, income, group size, and height.
Exploratory research is usually used when additional general information in desired about a topic. When in the initial steps of a new project, understanding the landscape is essential, so exploratory research helps the researcher to learn more about the general nature of the industry. Exploratory research can be collected through focus groups, interviews, and review of secondary data. When examining an exploratory research design, the best use is when your company hopes to collect data that is generally qualitative in nature. 7
For instance, if a company is considering a new service for registered users but is not quite sure how well the new service will be received or wants to gain clarity of exactly how customers may use a future service, the company can host a focus group. Focus groups and interviews will be examined later in the chapter. The insights collected during the focus group can assist the company when designing the service, help to inform promotional campaign options, and verify that the service is going to be a viable option for the company.
Descriptive research design takes a bigger step into collection of data through primary research complemented by secondary data. Descriptive research helps explain the market situation and define an “opinion, attitude, or behavior” of a group of consumers, employees, or other interested groups. 8 The most common method of deploying a descriptive research design is through the use of a survey. Several types of surveys will be defined later in this chapter. Descriptive data is quantitative in nature, meaning the data can be distilled into a statistic, such as in a table or chart.
Again, descriptive data is helpful in explaining the current situation. In the opening example of LEGO , the company wanted to describe the situation regarding children’s use of its product. In order to gather a large group of opinions, a survey was created. The data that was collected through this survey allowed the company to measure the existing perceptions of parents so that alterations could be made to future plans for the company.
Experimental research , also known as causal research , helps to define a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more factors. This type of research goes beyond a correlation to determine which feature caused the reaction. Researchers generally use some type of experimental design to determine a causal relationship. An example is A/B testing, a situation where one group of research participants, group A, is exposed to one treatment and then compared to the group B participants, who experience a different situation. An example might be showing two different television commercials to a panel of consumers and then measuring the difference in perception of the product. Another example would be to have two separate packaging options available in different markets. This research would answer the question “Does one design sell better than the other?” Comparing that to the sales in each market would be part of a causal research study. 9
The final method of collecting data is through an ethnographic design. Ethnographic research is conducted in the field by watching people interact in their natural environment. For marketing research, ethnographic designs help to identify how a product is used, what actions are included in a selection, or how the consumer interacts with the product. 10
Examples of ethnographic research would be to observe how a consumer uses a particular product, such as baking soda. Although many people buy baking soda, its uses are vast. So are they using it as a refrigerator deodorizer, a toothpaste, to polish a belt buckle, or to use in baking a cake?
Select the Data Collection Method
Data collection is the systematic gathering of information that addresses the identified problem. What is the best method to do that? Picking the right method of collecting data requires that the researcher understand the target population and the design picked in the previous step. There is no perfect method; each method has both advantages and disadvantages, so it’s essential that the researcher understand the target population of the research and the research objectives in order to pick the best option.
Sometimes the data desired is best collected by watching the actions of consumers. For instance, how many cars pass a specific billboard in a day? What website led a potential customer to the company’s website? When are consumers most likely to use the snack vending machines at work? What time of day has the highest traffic on a social media post? What is the most streamed television program this week? Observational research is the collecting of data based on actions taken by those observed. Many data observations do not require the researched individuals to participate in the data collection effort to be highly valuable. Some observation requires an individual to watch and record the activities of the target population through personal observations .
Unobtrusive observation happens when those being observed aren’t aware that they are being watched. An example of an unobtrusive observation would be to watch how shoppers interact with a new stuffed animal display by using a one-way mirror. Marketers can identify which products were handled more often while also determining which were ignored.
Other methods can use technology to collect the data instead. Instances of mechanical observation include the use of vehicle recorders, which count the number of vehicles that pass a specific location. Computers can also assess the number of shoppers who enter a store, the most popular entry point for train station commuters, or the peak time for cars to park in a parking garage.
When you want to get a more in-depth response from research participants, one method is to complete a one-on-one interview . One-on-one interviews allow the researcher to ask specific questions that match the respondent’s unique perspective as well as follow-up questions that piggyback on responses already completed. An interview allows the researcher to have a deeper understanding of the needs of the respondent, which is another strength of this type of data collection. The downside of personal interviews it that a discussion can be very time-consuming and results in only one respondent’s answers. Therefore, in order to get a large sample of respondents, the interview method may not be the most efficient method.
Taking the benefits of an interview and applying them to a small group of people is the design of a focus group . A focus group is a small number of people, usually 8 to 12, who meet the sample requirements. These individuals together are asked a series of questions where they are encouraged to build upon each other’s responses, either by agreeing or disagreeing with the other group members. Focus groups are similar to interviews in that they allow the researcher, through a moderator, to get more detailed information from a small group of potential customers (see Figure 6.5 ).
Link to Learning
Focus groups.
Focus groups are a common method for gathering insights into consumer thinking and habits. Companies will use this information to develop or shift their initiatives. The best way to understand a focus group is to watch a few examples or explanations. TED-Ed has this video that explains how focus groups work.
You might be asking when it is best to use a focus group or a survey. Learn the differences, the pros and cons of each, and the specific types of questions you ask in both situations in this article .
Preparing for a focus group is critical to success. It requires knowing the material and questions while also managing the group of people. Watch this video to learn more about how to prepare for a focus group and the types of things to be aware of.
One of the benefits of a focus group over individual interviews is that synergy can be generated when a participant builds on another’s ideas. Additionally, for the same amount of time, a researcher can hear from multiple respondents instead of just one. 11 Of course, as with every method of data collection, there are downsides to a focus group as well. Focus groups have the potential to be overwhelmed by one or two aggressive personalities, and the format can discourage more reserved individuals from speaking up. Finally, like interviews, the responses in a focus group are qualitative in nature and are difficult to distill into an easy statistic or two.
Combining a variety of questions on one instrument is called a survey or questionnaire . Collecting primary data is commonly done through surveys due to their versatility. A survey allows the researcher to ask the same set of questions of a large group of respondents. Response rates of surveys are calculated by dividing the number of surveys completed by the total number attempted. Surveys are flexible and can collect a variety of quantitative and qualitative data. Questions can include simplified yes or no questions, select all that apply, questions that are on a scale, or a variety of open-ended types of questions. There are four types of surveys (see Table 6.2 ) we will cover, each with strengths and weaknesses defined.
Let’s start off with mailed surveys —surveys that are sent to potential respondents through a mail service. Mailed surveys used to be more commonly used due to the ability to reach every household. In some instances, a mailed survey is still the best way to collect data. For example, every 10 years the United States conducts a census of its population (see Figure 6.6 ). The first step in that data collection is to send every household a survey through the US Postal Service (USPS). The benefit is that respondents can complete and return the survey at their convenience. The downside of mailed surveys are expense and timeliness of responses. A mailed survey requires postage, both when it is sent to the recipient and when it is returned. That, along with the cost of printing, paper, and both sending and return envelopes, adds up quickly. Additionally, physically mailing surveys takes time. One method of reducing cost is to send with bulk-rate postage, but that slows down the delivery of the survey. Also, because of the convenience to the respondent, completed surveys may be returned several weeks after being sent. Finally, some mailed survey data must be manually entered into the analysis software, which can cause delays or issues due to entry errors.
Phone surveys are completed during a phone conversation with the respondent. Although the traditional phone survey requires a data collector to talk with the participant, current technology allows for computer-assisted voice surveys or surveys to be completed by asking the respondent to push a specific button for each potential answer. Phone surveys are time intensive but allow the respondent to ask questions and the surveyor to request additional information or clarification on a question if warranted. Phone surveys require the respondent to complete the survey simultaneously with the collector, which is a limitation as there are restrictions for when phone calls are allowed. According to Telephone Consumer Protection Act , approved by Congress in 1991, no calls can be made prior to 8:00 a.m. or after 9:00 p.m. in the recipient’s time zone. 12 Many restrictions are outlined in this original legislation and have been added to since due to ever-changing technology.
In-person surveys are when the respondent and data collector are physically in the same location. In-person surveys allow the respondent to share specific information, ask questions of the surveyor, and follow up on previous answers. Surveys collected through this method can take place in a variety of ways: through door-to-door collection, in a public location, or at a person’s workplace. Although in-person surveys are time intensive and require more labor to collect data than some other methods, in some cases it’s the best way to collect the required data. In-person surveys conducted through a door-to-door method is the follow-up used for the census if respondents do not complete the mailed survey. One of the downsides of in-person surveys is the reluctance of potential respondents to stop their current activity and answer questions. Furthermore, people may not feel comfortable sharing private or personal information during a face-to-face conversation.
Electronic surveys are sent or collected through digital means and is an opportunity that can be added to any of the above methods as well as some new delivery options. Surveys can be sent through email, and respondents can either reply to the email or open a hyperlink to an online survey (see Figure 6.7 ). Additionally, a letter can be mailed that asks members of the survey sample to log in to a website rather than to return a mailed response. Many marketers now use links, QR codes, or electronic devices to easily connect to a survey. Digitally collected data has the benefit of being less time intensive and is often a more economical way to gather and input responses than more manual methods. A survey that could take months to collect through the mail can be completed within a week through digital means.
Design the Sample
Although you might want to include every possible person who matches your target market in your research, it’s often not a feasible option, nor is it of value. If you did decide to include everyone, you would be completing a census of the population. Getting everyone to participate would be time-consuming and highly expensive, so instead marketers use a sample , whereby a portion of the whole is included in the research. It’s similar to the samples you might receive at the grocery store or ice cream shop; it isn’t a full serving, but it does give you a good taste of what the whole would be like.
So how do you know who should be included in the sample? Researchers identify parameters for their studies, called sample frames . A sample frame for one study may be college students who live on campus; for another study, it may be retired people in Dallas, Texas, or small-business owners who have fewer than 10 employees. The individual entities within the sampling frame would be considered a sampling unit . A sampling unit is each individual respondent that would be considered as matching the sample frame established by the research. If a researcher wants businesses to participate in a study, then businesses would be the sampling unit in that case.
The number of sampling units included in the research is the sample size . Many calculations can be conducted to indicate what the correct size of the sample should be. Issues to consider are the size of the population, the confidence level that the data represents the entire population, the ease of accessing the units in the frame, and the budget allocated for the research.
There are two main categories of samples: probability and nonprobability (see Figure 6.8 ). Probability samples are those in which every member of the sample has an identified likelihood of being selected. Several probability sample methods can be utilized. One probability sampling technique is called a simple random sample , where not only does every person have an identified likelihood of being selected to be in the sample, but every person also has an equal chance of exclusion. An example of a simple random sample would be to put the names of all members of a group into a hat and simply draw out a specific number to be included. You could say a raffle would be a good example of a simple random sample.
Another probability sample type is a stratified random sample , where the population is divided into groups by category and then a random sample of each category is selected to participate. For instance, if you were conducting a study of college students from your school and wanted to make sure you had all grade levels included, you might take the names of all students and split them into different groups by grade level—freshman, sophomore, junior, and senior. Then, from those categories, you would draw names out of each of the pools, or strata.
A nonprobability sample is a situation in which each potential member of the sample has an unknown likelihood of being selected in the sample. Research findings that are from a nonprobability sample cannot be applied beyond the sample. Several examples of nonprobability sampling are available to researchers and include two that we will look at more closely: convenience sampling and judgment sampling.
The first nonprobability sampling technique is a convenience sample . Just like it sounds, a convenience sample is when the researcher finds a group through a nonscientific method by picking potential research participants in a convenient manner. An example might be to ask other students in a class you are taking to complete a survey that you are doing for a class assignment or passing out surveys at a basketball game or theater performance.
A judgment sample is a type of nonprobability sample that allows the researcher to determine if they believe the individual meets the criteria set for the sample frame to complete the research. For instance, you may be interested in researching mothers, so you sit outside a toy store and ask an individual who is carrying a baby to participate.
Collect the Data
Now that all the plans have been established, the instrument has been created, and the group of participants has been identified, it is time to start collecting data. As explained earlier in this chapter, data collection is the process of gathering information from a variety of sources that will satisfy the research objectives defined in step one. Data collection can be as simple as sending out an email with a survey link enclosed or as complex as an experiment with hundreds of consumers. The method of collection directly influences the length of this process. Conducting personal interviews or completing an experiment, as previously mentioned, can add weeks or months to the research process, whereas sending out an electronic survey may allow a researcher to collect the necessary data in a few days. 13
Analyze and Interpret the Data
Once the data has been collected, the process of analyzing it may begin. Data analysis is the distillation of the information into a more understandable and actionable format. The analysis itself can take many forms, from the use of basic statistics to a more comprehensive data visualization process. First, let’s discuss some basic statistics that can be used to represent data.
The first is the mean of quantitative data. A mean is often defined as the arithmetic average of values. The formula is:
A common use of the mean calculation is with exam scores. Say, for example, you have earned the following scores on your marketing exams: 72, 85, 68, and 77. To find the mean, you would add up the four scores for a total of 302. Then, in order to generate a mean, that number needs to be divided by the number of exam scores included, which is 4. The mean would be 302 divided by 4, for a mean test score of 75.5. Understanding the mean can help to determine, with one number, the weight of a particular value.
Another commonly used statistic is median. The median is often referred to as the middle number. To generate a median, all the numeric answers are placed in order, and the middle number is the median. Median is a common statistic when identifying the income level of a specific geographic region. 14 For instance, the median household income for Albuquerque, New Mexico, between 2015 and 2019 was $52,911. 15 In this case, there are just as many people with an income above the amount as there are below.
Mode is another statistic that is used to represent data of all types, as it can be used with quantitative or qualitative data and represents the most frequent answer. Eye color, hair color, and vehicle color can all be presented with a mode statistic. Additionally, some researchers expand on the concept of mode and present the frequency of all responses, not just identifying the most common response. Data such as this can easily be presented in a frequency graph, 16 such as the one in Figure 6.9 .
Additionally, researchers use other analyses to represent the data rather than to present the entirety of each response. For example, maybe the relationship between two values is important to understand. In this case, the researcher may share the data as a cross tabulation (see Figure 6.10 ). Below is the same data as above regarding social media use cross tabulated with gender—as you can see, the data is more descriptive when you can distinguish between the gender identifiers and how much time is spent per day on social media.
Not all data can be presented in a graphical format due to the nature of the information. Sometimes with qualitative methods of data collection, the responses cannot be distilled into a simple statistic or graph. In that case, the use of quotations, otherwise known as verbatims , can be used. These are direct statements presented by the respondents. Often you will see a verbatim statement when reading a movie or book review. The critic’s statements are used in part or in whole to represent their feelings about the newly released item.
Infographics
As they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. For this reason, research results are often shown in a graphical format in which data can be taken in quickly, called an infographic .
Check out this infographic on what components make for a good infographic. As you can see, a good infographic needs four components: data, design, a story, and the ability to share it with others. Without all four pieces, it is not as valuable a resource as it could be. The ultimate infographic is represented as the intersection of all four.
Infographics are particularly advantageous online. Refer to this infographic on why they are beneficial to use online .
Prepare the Research Report
The marketing research process concludes by sharing the generated data and makes recommendations for future actions. What starts as simple data must be interpreted into an analysis. All information gathered should be conveyed in order to make decisions for future marketing actions. One item that is often part of the final step is to discuss areas that may have been missed with the current project or any area of further study identified while completing it. Without the final step of the marketing research project, the first six steps are without value. It is only after the information is shared, through a formal presentation or report, that those recommendations can be implemented and improvements made. The first six steps are used to generate information, while the last is to initiate action. During this last step is also when an evaluation of the process is conducted. If this research were to be completed again, how would we do it differently? Did the right questions get answered with the survey questions posed to the respondents? Follow-up on some of these key questions can lead to additional research, a different study, or further analysis of data collected.
Methods of Quantifying Marketing Research
One of the ways of sharing information gained through marketing research is to quantify the research . Quantifying the research means to take a variety of data and compile into a quantity that is more easily understood. This is a simple process if you want to know how many people attended a basketball game, but if you want to quantify the number of students who made a positive comment on a questionnaire, it can be a little more complicated. Researchers have a variety of methods to collect and then share these different scores. Below are some of the most common types used in business.
Is a customer aware of a product, brand, or company? What is meant by awareness? Awareness in the context of marketing research is when a consumer is familiar with the product, brand, or company. It does not assume that the consumer has tried the product or has purchased it. Consumers are just aware. That is a measure that many businesses find valuable. There are several ways to measure awareness. For instance, the first type of awareness is unaided awareness . This type of awareness is when no prompts for a product, brand, or company are given. If you were collecting information on fast-food restaurants, you might ask a respondent to list all the fast-food restaurants that serve a chicken sandwich. Aided awareness would be providing a list of products, brands, or companies and the respondent selects from the list. For instance, if you give a respondent a list of fast-food restaurants and ask them to mark all the locations with a chicken sandwich, you are collecting data through an aided method. Collecting these answers helps a company determine how the business location compares to those of its competitors. 17
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT)
Have you ever been asked to complete a survey at the end of a purchase? Many businesses complete research on buying, returning, or other customer service processes. A customer satisfaction score , also known as CSAT, is a measure of how satisfied customers are with the product, brand, or service. A CSAT score is usually on a scale of 0 to 100 percent. 18 But what constitutes a “good” CSAT score? Although what is identified as good can vary by industry, normally anything in the range from 75 to 85 would be considered good. Of course, a number higher than 85 would be considered exceptional. 19
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Customer Effort Score (CES)
Other metrics often used are a customer acquisition cost (CAC) and customer effort score (CES). How much does it cost a company to gain customers? That’s the purpose of calculating the customer acquisition cost. To calculate the customer acquisition cost , a company would need to total all expenses that were accrued to gain new customers. This would include any advertising, public relations, social media postings, etc. When a total cost is determined, it is divided by the number of new customers gained through this campaign.
The final score to discuss is the customer effort score , also known as a CES. The CES is a “survey used to measure the ease of service experience with an organization.” 20 Companies that are easy to work with have a better CES than a company that is notorious for being difficult. An example would be to ask a consumer about the ease of making a purchase online by incorporating a one-question survey after a purchase is confirmed. If a number of responses come back negative or slightly negative, the company will realize that it needs to investigate and develop a more user-friendly process.
Knowledge Check
It’s time to check your knowledge on the concepts presented in this section. Refer to the Answer Key at the end of the book for feedback.
- Defining the problem
- Developing the research plan
- Selecting a data collection method
- Designing the sample
- you are able to send it to all households in an area
- it is inexpensive
- responses are automatically loaded into the software
- the data comes in quickly
- Primary data
- Secondary data
- Secondary and primary data
- Professional data
- It shows how respondents answered two variables in relation to each other and can help determine patterns by different groups of respondents.
- By presenting the data in the form of a picture, the information is easier for the reader to understand.
- It is an easy way to see how often one answer is selected by the respondents.
- This analysis can used to present interview or focus group data.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Dr. Maria Gomez Albrecht, Dr. Mark Green, Linda Hoffman
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Marketing
- Publication date: Jan 25, 2023
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/6-3-steps-in-a-successful-marketing-research-plan
© Jan 9, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
What is a Marketing Research Report and How to Write It?

Table of contents
There is nothing more embarrassing for a marketer than to hear a client say “…this doesn’t quite address the business questions that we need to answer.” And unfortunately, this is a rather common occurrence in market research reporting that most marketers would care to admit.
So, why do most market research reports fail to meet client expectations? Well, in most cases, because there is more emphasis on methodology and analytic techniques used to craft the report rather than relying on data visualization, creative story-telling, and outlining actionable direction/steps.
Now, our next big question is, how do you avoid your client’s dreaded deer-in-the-headlights reaction when presenting such a report? This blog post will answer this and much more, as we go through the following:
What Is a Market Research Report?
Why is market research important, differences between primary and secondary market research, types of market research, market research reports advantages and disadvantages, how to do market research, how to prepare a market research report: 5 steps, marketing research report templates, marketing research reports best practices, bring your market research reports a step further with databox.
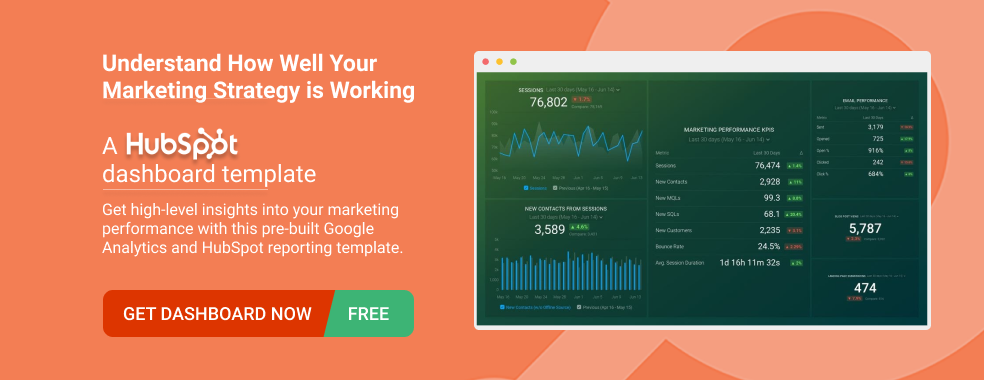
The purpose of creating a market research report is to make calculated decisions about business ideas. Market research is done to evaluate the feasibility of a new product or service, through research conducted with potential consumers. The information obtained from conducting market research is then documented in a formal report that should contain the following details:
- The characteristics of your ideal customers
- You customers buying habits
- The value your product or service can bring to those customers
- A list of your top competitors
Every business aims to provide the best possible product or service at the lowest cost possible. Simply said, market research is important because it helps you understand your customers and determine whether the product or service that you are about to launch is worth the effort.
Here is an example of a customer complaint that may result in more detailed market research:
Suppose you sell widgets, and you want your widget business to succeed over the long term. Over the years, you have developed many different ways of making widgets. But a couple of years ago, a customer complained that your widgets were made of a cheap kind of foam that fell apart after six months. You didn’t think at the time that this was a major problem, but now you know it.
The customer is someone you really want to keep. So, you decide to research this complaint. You set up a focus group of people who use widgets and ask them what they think about the specific problem. After the conducted survey you’ll get a better picture of customer opinions, so you can either decide to make the changes regarding widget design or just let it go.
PRO TIP: How Well Are Your Marketing KPIs Performing?
Like most marketers and marketing managers, you want to know how well your efforts are translating into results each month. How much traffic and new contact conversions do you get? How many new contacts do you get from organic sessions? How are your email campaigns performing? How well are your landing pages converting? You might have to scramble to put all of this together in a single report, but now you can have it all at your fingertips in a single Databox dashboard.
Our Marketing Overview Dashboard includes data from Google Analytics 4 and HubSpot Marketing with key performance metrics like:
- Sessions . The number of sessions can tell you how many times people are returning to your website. Obviously, the higher the better.
- New Contacts from Sessions . How well is your campaign driving new contacts and customers?
- Marketing Performance KPIs . Tracking the number of MQLs, SQLs, New Contacts and similar will help you identify how your marketing efforts contribute to sales.
- Email Performance . Measure the success of your email campaigns from HubSpot. Keep an eye on your most important email marketing metrics such as number of sent emails, number of opened emails, open rate, email click-through rate, and more.
- Blog Posts and Landing Pages . How many people have viewed your blog recently? How well are your landing pages performing?
Now you can benefit from the experience of our Google Analytics and HubSpot Marketing experts, who have put together a plug-and-play Databox template that contains all the essential metrics for monitoring your leads. It’s simple to implement and start using as a standalone dashboard or in marketing reports, and best of all, it’s free!
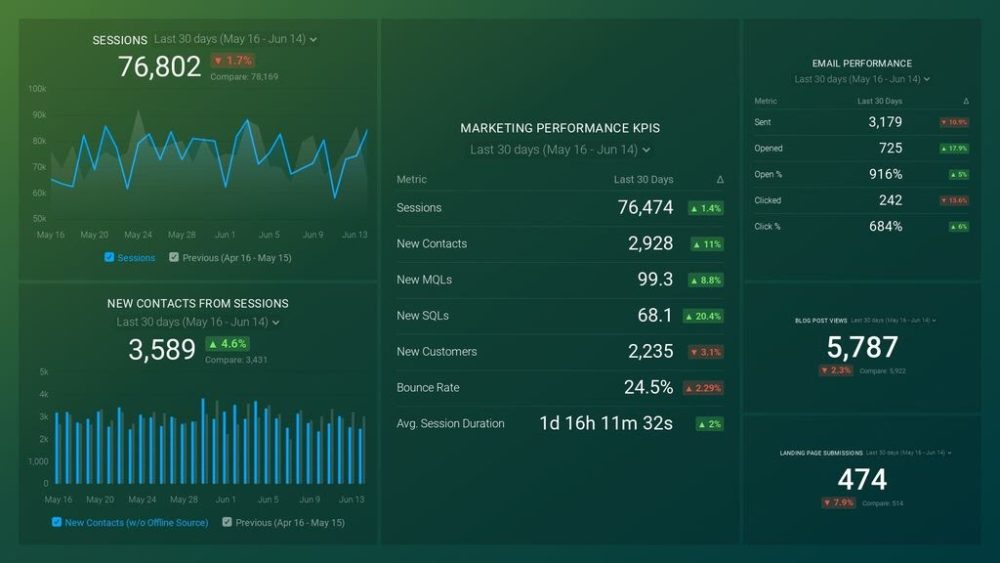
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your HubSpot and Google Analytics 4 accounts with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
Marketing research requires both primary and secondary market research. But what does that mean and what are the main differences?
Primary market research takes in information directly from customers, usually as participants in surveys. Usually, it is consisted of:
- Exploratory Primary Research – This type of research helps to identify possible problem areas, and it’s not focused on discovering specific information about customers. As with any research, exploratory primary research should be conducted carefully. Researchers need to craft an interviewing or surveying plan, and gather enough respondents to ensure reasonable levels of statistical reliability.
- Specific Primary Research – This type of research is one of the best ways to approach a problem because it relies on existing customer data. Specific research provides a deeper, more thorough understanding of the problem and its potential solutions. The greatest advantage of specific research is that it lets you explore a very specific question, and focus on a specific problem or an opportunity.
Secondary market research collects information from other sources such as databases, trend reports, market or government statistics, industry content, etc. We can divide secondary market research into 3 categories:
- Public market data – Public sources range from academic journals and government reports to tax returns and court documents. These sources aren’t always easy to find. Many are available only in print in libraries and archives. You have to look beyond search engines like Google to find public source documents.
- Commercial data – Those are typically created by specialized agencies like Pew, Gartner or Forrester. the research agencies are quite expensive, but they provide a lot of useful information.
- Internal data – Your organization’s databases are gold mines for market research. In the best cases, your salespeople can tell you what they think about customers. Your salespeople are your direct sources of information about the market. Don’t underestimate your internal data.
In general, primary research is more reliable than secondary research, because researchers have to interview people directly. But primary research is expensive and time-consuming. Secondary research can be quicker and less expensive.
There are plenty of ways to conduct marketing research reports. Mostly, the type of research done will depend on your goals. Here are some types of market research often conducted by marketers.
Focus Groups
Product/service use research, observation-based research, buyer persona research, market segmentation research, pricing research, competitive analysis research, customer satisfaction and loyalty research, brand awareness research, campaign research.
An interview is an interactive process of asking and answering questions and observing your respondent’s responses. Interviews are one of the most commonly used tools in market research . An interview allows an organization to observe, in detail, how its consumers interact with its products and services. It also allows an organization to address specific questions.
A focus group is a group of people who get together to discuss a particular topic. A moderator leads the discussion and takes notes. The main benefit of focus groups is that they are quick and easy to conduct. You can gather a group of carefully-selected people, give them a product to try out, and get their feedback within a few hours/days.
Product or service use research helps you obtain useful information about your product or service such as:
- What your current customers do with the product/service
- Which features of the product/service are particularly important to your customers
- What they dislike about the product/service
- What they would change about the product/service
Observation-based research helps you to observe your target audience interacting with your product or service. You will see the interactions and which aspects work well and which could be improved. The main point is to directly experience the feedback from your target audience’s point of view.
Personas are an essential sales tool. By knowing your buyers’ pain points and the challenges they face, you can create better content, target messaging, and campaigns for them. Buyer persona research is based on market research, and it’s built around data that describes your customers’ demographics, behaviors, motivations, and concerns. Sales reporting software can significantly help you develop buyer personas when you gain insights after you collected all information.
Market segmentation research is carried out to better understand existing and potential market segments. The objective is to determine how to target different market segments and how they differ from each other. The three most important steps in writing a market segmentation research report are:
- Defining the problem
- Determining the solution [and]
- Defining the market
Related : 9 Customer Segmentation Tips to Personalize Ecommerce Marketing and Drive More Sales
A price that is too high, or too low, can kill a business. And without good market research, you don’t really know what is a good price for your product. Pricing research helps you define your pricing strategy.
In a competitive analysis, you define your “competition” as any other entity that competes with you in your market, whether you’re selling a widget or a piece of real estate. With competitive analysis research, you can find out things like:
- Who your competitors are
- What they’ve done in the past
- What’s working well for them
- Their weaknesses
- How they’re positioned in the market
- How they market themselves
- What they’re doing that you’re not
Related : How to Do an SEO Competitive Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide
In today’s marketplace, companies are increasingly focused on customer loyalty. What your customers want is your product, but, more importantly, they want it delivered with a service that exceeds their expectations. Successful companies listen to their customers and respond accordingly. That’s why customer satisfaction and loyalty research is a critical component of that basic equation.
Related : 11 Tactics for Effectively Measuring Your Customer Service ROI
Who you are, what you stand for, what you offer, what you believe in, and what your audience thinks of you is all wrapped up in brand. Brand awareness research tells what your target audience knows about your brand and what’s their experience like.
A campaign research report is a detailed account of how your marketing campaign performed. It includes all the elements that went into creating the campaign: planning, implementation, and measurement.
Here are some of the top advantages and disadvantages of doing market research and crafting market research reports.
- Identify business opportunities – A market research report can be used to analyze potential markets and new products. It can give information about customer needs, preferences, and attitudes. Also, it compare products and services.
- A clear understanding of your customers – A market report gives company’s marketing department an in-depth picture about customers’ needs and wants. This knowledge can be used to improve products, prices, and advertising.
- Mitigates risks – 30% of small businesses fail within the first two years. Why is this so? The answer is that entrepreneurs are risk takers. However, there are risks that could be avoided. A good marketing research will help you identify those risks and allow you to mitigate them.
- Clear data-driven insights – Market research encompasses a wide range of activities, from determining market size and segment to forecasting demand, and from identifying competitors to monitoring pricing. All of these are quantified and measurable which means that gives you a clear path for building unique decisions based on numbers.
Disadvantages
- It’s not cheap – Although market research can be done for as little as $500, large markets like the United States can run into millions of dollars. If a research is done for a specific product, the budget may be even much higher. The budget also depends on the quality of the research. The more expensive it is, the more time the research will take.
- Some insights could be false – For example, if you are conducting a survey, data may be inadequate or inaccurate because respondents can, well, simply be dishonest and lie.
Here are the essential steps you need to take when doing market research:
Define your buyer persona
Identify a persona group to engage, prepare research questions for your market research participants, list your primary competitors, summarize your findings.
The job of a marketing persona is to describe your ideal customer and to tell you what they want, what motivates them, what frustrates them, and what limits them. Finding out these things means you have a better chance of designing your products, services, marketing messages, and brand around real customers. There is no one right way to create a buyer persona, though.
For example, if you’re in an industry focused on education, you could include things like:
- Educational level
- Education background
It’s recommended that you create 3-5 buyer personas for your products, based on your ideal customer.
This should be a representative sample of your target customers so you can better understand their behavior. You want to find people who fit both your target personas and who represent the broader demographic of your market. People who recently made a purchase or purposefully decided not to make one are a good sample to start with.
The questions you use determine the quality of your results. Of course, the quality of your results also depends on the quality of your participants.
Don’t ask questions that imply a yes or no answer. Instead, use open questions. For example, if you are researching customers about yogurt products, you could ask them: „ What have you heard about yogurt ?” or “ What do you think of yogurt ?“.
Avoid questions that use numbers, such as “ How many times a week do you eat yogurt ?”
Avoid questions that suggest a set of mutually exclusive answers, such as “ Do you like yogurt for breakfast, lunch, or dinner ?”
Avoid questions that imply a scale, such as “ Do you like chocolate-flavored yogurt ?”
Market researchers sometimes call one company the top competitor, another middle competitor, and the third one small competitor. However you classify them, you want to identify at least three companies in each category. Now, for each business on your list, list its key characteristics. For example, if your business sells running shoes, a key characteristic might be the product’s quality.
Next, make a list of your small business’s competitive advantages. These include the unique qualities or features of your business that make it the best choice of customers for the products or services it offers. Make a list of these competitive advantages and list them next to the key characteristics you listed for your business.
You have just finished writing your marketing research report. Everything is out there quantified or qualified. You just have to sum it up and focus on the most important details that are going to make a big impact on your decisions. Clear summary leads to a winning strategy!
Related : How to Prepare a Complete Marketing Report: The KPIs, Analysis, & Action Plan You Need
Here’s how to prepare a market research report in 5 simple steps:
Step 1: Cluster the data
Step 2: prepare an outline, step 3: mention the research methods, step 4: include visuals with narrative explanations, step 5: conclude the report with recommendations.
Your first step is to cluster all the available information into a manageable set. Clustering is the process of grouping information together in a way that emphasizes commonalities and minimizes differences. So, in market research, this will help to organize all the information you have about a product, service, or target market and identify your focus areas.
A marketing research report should be written so that other people can understand it:
- Include background information at the beginning to explain who your audience is and what problem you are trying to solve for them.
- In the body of the report, include a description of the methodology – Explain to the reader how your research was done, what was involved, and why you selected the methodology you used.
- Also in the body of the report, include the results of your market research. These may be quantitative or qualitative, but either way they should answer the questions you posed at the beginning.
- Include the executive summary – A summary of the entire report.
The market research methodology section includes details on the type of research, sample size, any limitations of the studies, research design, sample selection, data collection procedures, and statistical analyses used.
Visuals are an essential part of the presentation. Even the best-written text can be difficult to understand. Charts and graphs are easier to understand than text alone, and they help the reader see how the numbers fit the bigger picture.
But visuals are not the whole story. They are only one part of the presentation. Visuals are a cue for the reader. The narrative gives the story, not just the numbers.
Recommendations tend to follow logically from conclusions and are a response to a certain problem. The recommendation should always be relevant to the research rationale, that is, the recommendation should be based on the results of the research reported in the body of the report.
Now, let’s take a look at some dashboard reporting templates you could use to enhance your market research:
- Semrush (Position Tracking) Report
Brand Awareness Report
Sales pipeline performance report, customer success overview report, stripe (mrr & churn) report, semrush (position tracking) report template.
This free SEMRush dashboard template will help you monitor how your website’s search visibility on search engines evolves on a monthly basis. This dashboard contains all of the information you need to make changes and improve the ranking results of your business in Google Search.
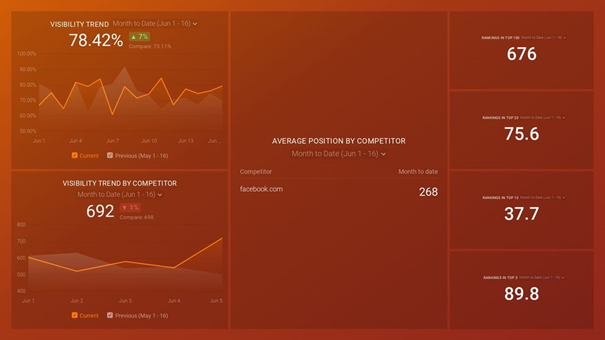
This Brand Awareness Report will help you to get a sense of your brand awareness performance in Google Analytics, Google Organic Search, and Facebook. Use this dashboard to track brand awareness the same way you track other marketing campaigns.
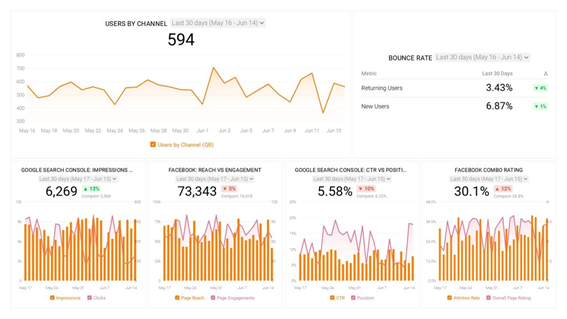
Are your sales and marketing funnel healthy and growing? How is your sales and marketing funnel performing? What are the key conversion rates between your lifecycle stages? With a pipeline performance dashboard , you’ll get all of the answers quickly.
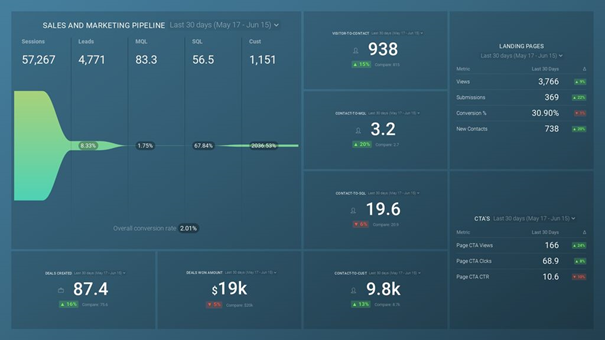
This Customer Success Overview Dashboard allows you to analyze how your customer service team’s responsiveness impacts your business. Use this dashboard to assess the correlation between your customer service performance and churn rate.
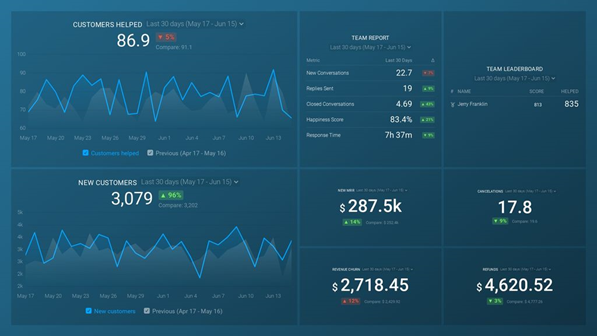
This Stripe dashboard tracks your churn rate and MRR growth in real-time and shows you which customers (and how many of them) you have at any given point in time. All you have to do to get started is to connect your Stripe account.
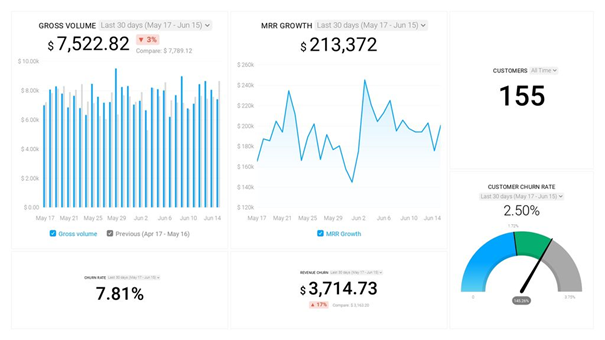
As we said earlier, there are no strict rules when it comes to writing marketing research reports. On the other hand, you must find your focus if you want to write a report that will make a difference. Here are some best practices you should keep in mind when writing a research report.
- Objectives – The objective of a market research report is to define the problems, identify key issues, and suggest recommendations for further research. If you answer them successfully, you’re on the right way.
- Don’t worry about the format – Be creative. The report could be in a form of a PowerPoint presentation, Excel sheet, interactive dashboard or even a video. Use the format that best fits your audience, but make sure to make it easy to read.
- Include an executive summary, scorecard , or a dashboard – This is really important because time is money, and most people don’t have time to waste. So, how to put everything important in a short role? Address all of the objectives and put them in a graphic dashboard or scorecard. Also, you can write an executive summary template (heart of the report) that can be easily updated and read by managers or CEOs.
- Use storytelling – A good story always makes a great point because it’s so memorable. Your research report results can double the effect with a catchy story.
- Keep it short – It’s not a secret that we are reading so little in the digital era. Use a lot of white space and bullet points. Too much text on a page means less focus for the reader.
- Be organized – Maintain the order of information. It’s important for the reader to navigate through the report easily. If they want to find some details or specific information it would be great to divide all sections with appropriate references.
- Methodological information – Methodological details could be boring. Include only the most important details that the reader needs to know to understand the big picture.
- Use images (or other visualizations) whenever you can – A good picture speaks for 1.000 words! If you can communicate the point visually, don’t hesitate to do it. It would be a lot easier for those who don’t like a lot of text to understand your results. But don’t push them where you can’t.
- Create readable graphs – The crown of marketing research reports is a comprehensive graph. Make sure to design precise and attractive graphs that will power up and round your story.
- Use the Appendix – You can include all secondary information such as methodological details and other miscellaneous data in the Appendix at the end of the report.
Market research reports are all about presenting your data in an easy-to-understand way and making calculated decisions about business ideas. But this is something easier said than done.
When busy stakeholders and executives grab a report, they need something that will give them an idea of the results – the big picture that addresses company wide-business goals.
Can a PowerPoint presentation or a PDF report meet those expectations? Most likely not. But a dashboard can.
Keep in mind that even with the best market analysis in the world, your market research report won’t be actionable if you don’t present the data efficiently and in a way that everyone understands what the next steps are. Databox is your key ally in the matter.
Databox dashboards are designed to help you present your market research data with clarity – from identifying what is influencing your business, and understanding where your brand is situated in the market, to gauging the temperature of your niche or industry before a new product/service launch.
Present your research results with efficient, interactive dashboards now by signing up for a free trial .
Get practical strategies that drive consistent growth
12 Tips for Developing a Successful Data Analytics Strategy

What Is Data Reporting and How to Create Data Reports for Your Business

What Is KPI Reporting? KPI Report Examples, Tips, and Best Practices
Build your first dashboard in 5 minutes or less
Latest from our blog
- Playmaker Spotlight: Tory Ferrall, Director of Revenue Operations March 27, 2024
- New in Databox: Safeguard Your Data With Advanced Security Settings March 18, 2024
- Metrics & KPIs
- vs. Tableau
- vs. Looker Studio
- vs. Klipfolio
- vs. Power BI
- vs. Whatagraph
- vs. AgencyAnalytics
- Product & Engineering
- Inside Databox
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Talent Resources
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- API Documentation
- Request info
- Majors & Degrees
- Prospective Students
- Current Undergraduate Students
- Current Graduate Students
- Online Students
- Alumni and Friends
- Faculty and Staff
USM Honors College Students Present Thesis Research at Marketing Conference
Tue, 03/26/2024 - 09:14am | By: Van Arnold

University of Southern Mississippi (USM) Honors College students Haeden Overby and Patrick Tyson presented their thesis research during the 2024 Association of Marketing Theory and Practice Conference (AMTP) held earlier this month in Hilton Head, S.C.
Overby, a hospitality and tourism management major, and Tyson, an anthropology, sociology, and Spanish major, presented individual research papers, as well as a collaborative project, at the international and interdisciplinary academic marketing conference which brings together academic theory and real-world marketing practices.
This year’s conference saw more than 100 submissions. Of the 33 student paper submissions across undergraduate, Master's, and Ph.D. levels, Overby’s thesis paper – “Service robots’ effect on branding and consumers' intentions through online reviews” - won the James E. Randall Best Student Paper Award.
“Haeden and Patrick are exceptional students in my class. Their passion for research and dedication to their thesis projects have impressed me,” said Dr. Wei Wang, Associate Professor, Hospitality and Tourism Management Program Coordinator who served as both students’ thesis advisor. “Moreover, their active involvement and leadership roles on campus exemplify their commitment to excellence beyond academics,”
Tyson presented a research paper titled, “Uncertainty avoidance moderation over film-motivated tourists' views on destination image, place attachment, and intentions.”
Collaboratively, they presented a paper titled, “Cookies and calamari: Squid Game’s “Dalgona” and cutting shapes from its impact on Korean product purchase and travel intentions.”
“My advisors, Dr. Wei Wang and Dr. Banu Bas, have been incredibly patient teaching me about the research process, and I would not have been able to succeed without their support,” said Overby. “Dr. Randall is retiring from the AMTP conference this year, and the award was named after him for the first time. I am pleased to be the first recipient of the award under his name and am incredibly thankful I had the chance to meet him when I was presented the award.”
Added Overby, “This accomplishment has become great motivation to continue my research in marketing and to cross the finish line of submitting my thesis. I am glad to bring home a new award for Southern Miss Business!"
More information about the conference can be found here .
To learn more about USM’s College of Business and Economic Development, call 601.266.4659.
Categories: Business and Economic Development Honors College
Recent News Articles
Six individuals to receive young professional scholarship at the 2024 national sports safety and security conference & exhibition, usm to host annual public health symposium april 3, usm names kennedy as associate vice president for research.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In marketing, an example of experimental research would be comparing the effects of a television commercial versus an online advertisement conducted in a controlled environment (e.g. a lab). ... Research Design Examples. Let's explore how leading brands employ different types of research design. In most cases, companies combine several ...
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project, from its conception to the final analysis of data. Research designs for quantitative studies include descriptive, correlational, experimental and quasi-experimenta l designs. Research designs for qualitative studies include phenomenological ...
Quantitative research design relies on substantial sample sizes, focusing on the response volume which is then broken down numerically and filtered through statistical analysis. Thus, it examines how respondents react to the same stimuli, not why. In other words, it doesn't get into the emotional and cognitive drivers behind the responses.
Step 4: Developing a research program: research design. Research design is a plan or framework for conducting marketing research and collecting data. It is defined as the specific methods and procedures you use to get the information you need. There are three core types of marketing research designs: exploratory, descriptive, and causal. A ...
How to conduct lean market research in 4 steps. The following four steps and practical examples will give you a solid market research plan for understanding who your users are and what they want from a company like yours. 1. Create simple user personas. A user persona is a semi-fictional character based on psychographic and demographic data ...
In our ultimate guide to research design for businesses, we breakdown the process, including research methods, examples, and best practice tips to help you get started. If you have a business problem that you're trying to solve — from product usage to customer engagement — doing research is a great way to understand what is going wrong.
Research Design. A research design is a blueprint describing how to conduct a research project. It is a plan describing which estimates are to be computed, how they are to be computed and how models are to be tested and refined. A good research design is one that identifies all the things that need to be estimated and works out the best way to ...
Research is what marketing pros do to plan their moves, and outperform their competition. ... you're doing secondary market research. Examples: Second-party and third-party sources like articles, whitepapers, reports, industry statistics, ... It's really hard to design products by focus groups. A lot of times, people don't know what they ...
A research design will use different combinations of primary, secondary, qualitative, and quantitative data. Depending on the overall research questions, research designs in marketing may fall into one of the following three categories: An exploratory research design is more informal and unstructured than the other two types of designs.
Read more about how AIP used Similarweb to understand the right marketing channels to use. Market Research Example #9 - Trendspotting to find growth opportunities. During the pandemic, many companies in the hospitality sector were forced to close their doors. It was a case of fight or flight, and there were clear winners and losers.
Step 2. Design Research Plan. Once the objectives are defined, the next step is to design a research plan that outlines the methodology, data collection techniques, sample size, and timeline. The research plan should be tailored to address the research objectives and provide reliable and valid data. Step 3 Data Collection
Step 2: Design the Research. The next step in the marketing research process is to do a research design. The research design is your "plan of attack.". It outlines what data you are going to gather and from whom, how and when you will collect the data, and how you will analyze it once it's been obtained.
Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples. Published on June 20, 2019 by Shona McCombes.Revised on June 22, 2023. When you start planning a research project, developing research questions and creating a research design, you will have to make various decisions about the type of research you want to do.. There are many ways to categorize different types of research.
Reason 4: Tracking campaign results. The key to a successful marketing campaign is monitoring and iteration.Doing research early on can save you time and effort down the road with making sure your marketing efforts are optimized at all times.. For example, if you've noticed your social media campaign isn't performing as well as you've hoped, you can use marketing research to refine your ...
Here the sample size is restricted to 6-10 members. Specific research, on the other hand, is more pinpointed and is used to solve the problems that are identified by exploratory research. LEARN ABOUT: Marketing Insight. As mentioned earlier, primary market research is a combination of qualitative market research and quantitative market research.
An Example of Research Design could be: Research question: Does the use of social media affect the academic performance of high school ... Research design is used in the field of business to investigate consumer behavior, marketing strategies, and the impact of different business practices. Researchers use various designs, such as survey ...
Curiosity. At the heart of every successful marketing campaign is a curious marketer who learned how to better serve a customer. In this industry, we scratch that curiosity itch with market research. To help give you ideas to learn about your customer, in this article we bring you examples from Consumer Reports, Intel, Visa USA, Hallmark, Levi Strauss, John Deere, LeapFrog, Spiceworks Ziff ...
A marketing research problem in this example is to discover the needs of the community and also to identify a potentially successful business venture. ... employees, or other interested groups. 8 The most common method of deploying a descriptive research design is through the use of a survey. Several types of surveys will be defined later in ...
The market research methodology section includes details on the type of research, sample size, any limitations of the studies, research design, sample selection, data collection procedures, and statistical analyses used. Step 4: Include visuals with narrative explanations. Visuals are an essential part of the presentation.
Integrate with 100+ apps and plug-ins to get more done. SurveyMonkey Forms. Build and customize online forms to collect info and payments. SurveyMonkey Genius. Create better surveys and spot insights quickly with built-in AI. Market Research Solutions. Purpose-built solutions for all of your market research needs. INDUSTRIES.
Conclusion. Research design is a critical component of marketing research. It helps to ensure that the data collected is reliable, valid, and relevant to the research problem. A well-designed research plan provides a clear structure for conducting research and helps to avoid bias and errors. By understanding the different types of research ...
Overby, a hospitality and tourism management major, and Tyson, an anthropology, sociology, and Spanish major, presented individual research papers, as well as a collaborative project, at the international and interdisciplinary academic marketing conference which brings together academic theory and real-world marketing practices.