- Engineering Mathematics
- Discrete Mathematics
- Operating System
- Computer Networks
- Digital Logic and Design
- C Programming
- Data Structures
- Theory of Computation
- Compiler Design
- Computer Org and Architecture
- Computer Network Tutorial

Basics of Computer Network
- Basics of Computer Networking
- Introduction to basic Networking Terminology
- Goals of Networks
- Basic characteristics of Computer Networks
- Challenges of Computer Network
- Physical Components of Computer Network
Network Hardware and Software
- Types of Computer Networks
- LAN Full Form
- How to Set Up a LAN Network?
- MAN Full Form in Computer Networking
- MAN Full Form
- WAN Full Form
- Introduction of Internetworking
- Difference between Internet, Intranet and Extranet
- Protocol Hierarchies in Computer Network
- Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)
- Introduction of a Router
- Introduction of Gateways
- What is a network switch, and how does it work?
Network Topology
- Types of Network Topology
- Difference between Physical and Logical Topology
- What is OSI Model? - Layers of OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer
- Session Layer in OSI model
- Presentation Layer in OSI model
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Protocol and Standard in Computer Networks
- Examples of Data Link Layer Protocols
- TCP/IP Model
- TCP/IP Ports and Its Applications
- What is Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)?
- TCP 3-Way Handshake Process
- Services and Segment structure in TCP
- TCP Connection Establishment
- TCP Connection Termination
- Fast Recovery Technique For Loss Recovery in TCP
- Difference Between OSI Model and TCP/IP Model
Medium Access Control
- MAC Full Form
- Channel Allocation Problem in Computer Network
- Multiple Access Protocols in Computer Network
- Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA)
- Collision Detection in CSMA/CD
- Controlled Access Protocols in Computer Network
SLIDING WINDOW PROTOCOLS
- Stop and Wait ARQ
- Sliding Window Protocol | Set 3 (Selective Repeat)
- Piggybacking in Computer Networks
IP Addressing
- What is IPv4?
- What is IPv6?
- Introduction of Classful IP Addressing
- Classless Addressing in IP Addressing
- Classful Vs Classless Addressing
- Classless Inter Domain Routing (CIDR)
- Supernetting in Network Layer
- Introduction To Subnetting
- Difference between Subnetting and Supernetting
- Types of Routing
- Difference between Static and Dynamic Routing
- Unicast Routing - Link State Routing
- Distance Vector Routing (DVR) Protocol
- Fixed and Flooding Routing algorithms
- Introduction of Firewall in Computer Network
Congestion Control Algorithms
- Congestion Control in Computer Networks
- Congestion Control techniques in Computer Networks
- Computer Network | Leaky bucket algorithm
- TCP Congestion Control
Network Switching
- Circuit Switching in Computer Network
- Message switching techniques
- Packet Switching and Delays in Computer Network
- Differences Between Virtual Circuits and Datagram Networks
Application Layer:DNS
- Domain Name System (DNS) in Application Layer
- Details on DNS
- Introduction to Electronic Mail
- E-Mail Format
World Wide Web (WWW)
- HTTP Full Form
- Streaming Stored Video
- What is a Content Distribution Network and how does it work?
CN Interview Quetions
- Top 50 Networking Interview Questions (2024)
- Top 50 TCP/IP interview questions and answers
- Top 50 IP addressing interview questions and answers
- Last Minute Notes - Computer Networks
- Computer Network - Cheat Sheet
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Application Layer
All public websites or web pages that people may access on their local computers and other devices through the internet are collectively known as the World Wide Web or W3. Users can get further information by navigating to links interconnecting these pages and documents. This data may be presented in text, picture, audio, or video formats on the internet.
What is WWW?
WWW stands for World Wide Web and is commonly known as the Web. The WWW was started by CERN in 1989. WWW is defined as the collection of different websites around the world, containing different information shared via local servers(or computers).
Web pages are linked together using hyperlinks which are HTML-formatted and, also referred to as hypertext, these are the fundamental units of the Internet and are accessed through Hyper Text Transfer Protocol(HTTP) . Such digital connections, or links, allow users to easily access desired information by connecting relevant pieces of information. The benefit of hypertext is it allows you to pick a word or phrase from the text and click on other sites that have more information about it.
History of the WWW
It is a project created, by Tim Berner Lee in 1989, for researchers to work together effectively at CERN. It is an organization, named the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) , which was developed for further development of the web. This organization is directed by Tim Berner’s Lee, aka the father of the web. CERN, where Tim Berners worked, is a community of more than 1700 researchers from more than 100 country. These researchers spend a few time on CERN, and rest of the time they work at their colleges and national research facilities in their home country, so there was a requirement for solid communication so that they can exchange data.
System Architecture
From the user’s point of view, the web consists of a vast, worldwide connection of documents or web pages. Each page may contain links to other pages anywhere in the world. The pages can be retrieved and viewed by using browsers of which internet explorer, Netscape Navigator, Google Chrome, etc are the popular ones. The browser fetches the page requested interprets the text and formatting commands on it, and displays the page, properly formatted, on the screen.
The basic model of how the web works are shown in the figure below. Here the browser is displaying a web page on the client machine. When the user clicks on a line of text that is linked to a page on the abd.com server, the browser follows the hyperlink by sending a message to the abd.com server asking it for the page.
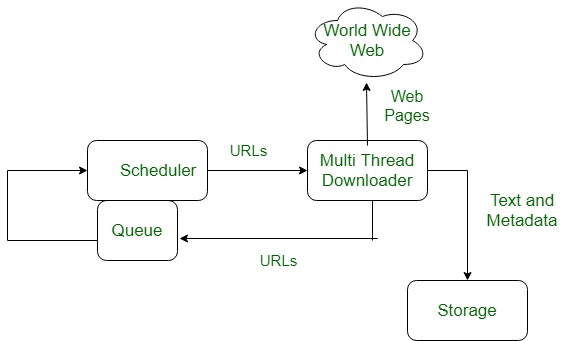
Working of WWW
A Web browser is used to access web pages. Web browsers can be defined as programs which display text, data, pictures, animation and video on the Internet. Hyperlinked resources on the World Wide Web can be accessed using software interfaces provided by Web browsers. Initially, Web browsers were used only for surfing the Web but now they have become more universal.
The below diagram indicates how the Web operates just like client-server architecture of the internet. When users request web pages or other information, then the web browser of your system request to the server for the information and then the web server provide requested services to web browser back and finally the requested service is utilized by the user who made the request.

World Wide Web
Web browsers can be used for several tasks including conducting searches, mailing, transferring files, and much more. Some of the commonly used browsers are Internet Explorer, Opera Mini, and Google Chrome.
Features of WWW
- WWW is open source.
- It is a distributed system spread across various websites.
- It is a Hypertext Information System.
- It is Cross-Platform.
- Uses Web Browsers to provide a single interface for many services.
- Dynamic, Interactive and Evolving.
Components of the Web
There are 3 components of the web:
- Uniform Resource Locator (URL): serves as a system for resources on the web.
- Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP): specifies communication of browser and server.
- Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML): defines the structure, organisation and content of a web page.
Difference Between WWW and Internet
Frequently asked question on world wide web – faqs, can we use the web without an internet .
If a website is on your computer or a computer connected to the same local area network , you can browse it without an internet .
What problems does World Wide Web face?
Our private data is no longer under our control. Misinformation on the internet spreads very easily.
What is the world’s first website?
The first website is info.cern.ch.
What is a URL?
URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator , it is an online address that is given to the web page.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Web technologies
- 10 Ways to Use Slack for Effective Communication
- 10 Ways to Use Google Docs for Collaborative Writing
- NEET MDS 2024 Result: Toppers List, Category-wise Cutoff, and Important Dates
- NDA Admit Card 2024 Live Updates: Download Your Hall Ticket Soon on upsc.gov.in!
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Session 01 - The Internet, World Wide Web, Web Browsers, Web Sites, and HTML
Harvard Extension School Fall 2023
Course Web Site: https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/
How does the web work?
The internet and the world wide web, how do we make the web work, csci e-12 course, a web address - urls, components of the web, client-side web parts: markup, style, function, html introduction, essential html5 document structure, common html5 elements - a element - anchor, relative urls, "hello world" first assigment, file management, course web hosting server: urls and file locations.
Session 01 - The Internet, World Wide Web, Web Browsers, Web Sites, and HTML, slide1 Welcome!, slide2 How does the web work?, slide3 How does the web work?, slide4 The Internet and the World Wide Web, slide5 The Internet: Schematic, slide6 Tim Berners-Lee on The World Wide Web, slide7 The World Wide Web — key aspects, slide8 How has the web changed? A brief look at Southwest Airlines website evolution, slide9 How do we make the web work?, slide10 How do we make the web work — some tools for our toolbox, slide11 Approaching a Web Project, slide12 CSCI E-12 Course, slide13 CSCI E-12 — Goals for the Course, slide14 CSCI E-12 — Key factors for success in the course, slide15 A Web Address - URLs, slide16 Aside: URLs, URIs, and URNs, slide17 Components of the Web, slide18 Client-side Web Parts: Markup, Style, Function, slide19 Our Solar System: Markup, slide20 Our Solar System: Markup + Style, slide21 Our Solar System: Markup + Style + Function, slide22 HTML Introduction, slide23 Markup - HTML, slide24 Essential HTML5 Document Structure, slide25 HTML Elements - the basic building blocks structure, slide26 HTML Elements - Content can be other HTML elements, slide27 HTML Elements - Sometimes you will have more than one attribute, slide28 HTML Elements that are "empty", slide29 HTML Elements - Sometimes HTML allows you to leave off end tags, slide30 HTML5, slide31 Most commonly used or seen elements, slide32 Learning about HTML elements, slide33 HTML Purpose, slide34 Web Page Structure - header, main, footer, slide35 HTML5 Document Template, slide36 Benefits of Web Standards, slide37 HTML Best Practices to start out with, slide38 Common HTML5 Elements - a element - anchor, slide39 Creating Links, slide40 Relative URLs, slide41 Absolute and Relative Locations, slide42 Relative Paths to Parent Locations, slide43 "Hello World" First Assigment, slide44 File Management, slide45 File Management, slide46 Course Web Hosting Server: URLs and File locations, slide47 Workflow, slide48
Presentation contains 48 slides
CSCI E-12, Fundamentals of Website Development Fall Term 2023 Harvard Extension School
Essential Questions to Consider
Four phases for tonight.
- A bit about the course
- Getting started with the web and HTML
- Orientation to the first assignment
What happens when you enter https://extension.harvard.edu/ into your browser?

- Web Browser
- Web Address (URL) and Communication
- Web Content (HTML, CSS, JS, images)

1. Web Browser (HTTP Client)

2. Web Server (HTTP Server)

3. Communication
Communication between the web browser and web server, including how they communicate (HTTP) and the network.

Image credit: Barrett Lyon / The Opte Project "Visualization of the routing paths of the Internet."" Used under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The Internet: Schematic

The Internet came before the Web, and Web "traffic" is not the only type of traffic on the Internet
Tim Berners-Lee on The World Wide Web
Suppose all the information stored on computers everywhere were linked. Suppose I could program my computer to create a space in which everything could be linked to everything. Tim Berners-Lee
The Web evolved into a powerful, ubiquitous tool because it was built on egalitarian principles and because thousands of individuals, universities and companies have worked, both independently and together as part of the World Wide Web Consortium, to expand its capabilities based on those principles. Tim Berners-Lee in Long Live the Web (Scientific American, Nov/Dec 2010)
Today, and throughout this year, we should celebrate the Web’s first 25 years. But though the mood is upbeat, we also know we are not done . We have much to do for the Web to reach its full potential. We must continue to defend its core principles and tackle some key challenges . Tim Berners-Lee in Welcome to the Web's 25 Anniversary (2014)
The web is for everyone, and collectively we hold the power to change it. It won’t be easy. But if we dream a little and work a lot, we can get the web we want. Tim Berners-Lee interview on 30 years of the world wide web in The Guardian (2019)
What is Tim Berners-Lee up to today? He's concerned about personal data sovereignty — and has software and a company to help address it.
The World Wide Web — key aspects
- HyperText Information System
- Cross-Platform and Cross-Device ...then and now
- 255 million unique domains, 201 million active sites, and 12 million "web-facing" computers ( Netcraft Web Server Survey , August 2023)
- HTML, CSS, JavaScript, HTTP, networking
- Browsers and engines (Chromium, Webkit, Mozilla), languages (PHP, Python), server software (Apache, nginx, WordPress)
- Information, Shopping, Banking and Finance, Communication, Business workflows, etc.
- Dynamic, Interactive, Evolving
How has the web changed? A brief look at Southwest Airlines website evolution

- Physical Desk

- Main categories and functions

- Quick Links

- Travel Tools as icons

- Travel tools as panels
- Main imagery chages

- Travel Products

- Travel Products expanded, multiple locations
- Travel tool panels
- Mega footer beginning

- Less is more
- "Action" or "Do" panel clearer
- Social media links

Screenshots from my collection and from Internet Archive Wayback Machine
Understand the parts, and how they work individually and how they work together.
- HTML, CSS, JavaScript
- Hosting, Web server software, programming languages (JavaScript, Python, etc.)
- User Experience and Design
This works at multiple layers too —
- we need to understand HTML, CSS, and JavaScript individually as well as how they interact or relate to one another
- we also need to understand how we use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript together to accomplish a specific design or interface that will be useful to our users
How do we make the web work — some tools for our toolbox
- A code editor . Recommendation: Visual Studio Code with a few extensions: Live Server , HTMLHint , Prettier - Code Formatter
I'm not going to ask you to change the browser that you know and use all the time, but I will ask you to have a couple more in the rotation for testing, and to remember that not everyone who views your site will be using your favorite browser.
- An SFTP client (SFTP = secure file transfer protocol), such as Cyberduck . An SFTP client lets you move files you have edited locally to your web server account.
- VPN client (VPN = virtual private network). A VPN client lets you connect securely to a network in order to access restricted resources. You will need to be using Harvard VPN in order to SFTP content to your course web hosting account.
There are some more to add to the list eventually, but for now, let's keep it with these!
Approaching a Web Project

5 Planes from The Elements of User Experience: User-Centered Design for the Web

- Class & Sections
- Announcements
CSCI E-12 — Goals for the Course
- Think like a web developer (programmer, content, project management)
- Learn syntax of HTML, CSS, JavaScript.
- Break problems down in parts and build parts up to whole in iterations
- Learn tools and workflows to improve results and efficiency
- Understand how things relate to one another.
- Troubleshoot effectively when things are not working as expected.
CSCI E-12 — Key factors for success in the course
- Complete and submit the assignments (and to do this you'll likely need to watch the class recordings, attend or view sections, engage in the readings or other resources)
- Connect with students and course staff
- Engage with resources available to you: class meetings, sections, Slack, textbook, office hours
- Start early (even if it is just reading through it)
- Work to understand a concept outside the context of an assignment — use a 'playground' or 'sandbox' folder on your computer or even something like Codepen or JSFiddle, then apply your understanding to the assignment.
- leave yourself time to review and revise an assignment
- Seek out help! Running into roadblocks? Read through thad MDN doc! Check out the text! Attend or watch sections! Communicate early with David or your TA through Slack or Canvas Inbox!
URL = Uniform Resource Locator
"The crucial thing is the URL. The crucial thing is that you can link to anything." — Tim Berners Lee

URL/URI https://www.archives.gov/historical-docs/voting-rights-act
- Scheme (also Protocol ) https ://www.archives.gov/historical-docs/voting-rights-act
- Host (also Authority ) https:// www.archives.gov /historical-docs/voting-rights-act
- Path https://www.archives.gov /historical-docs/voting-rights-act
Aside: URLs, URIs, and URNs
In the context of the web, all URIs are URLs!
- URL : Uniform Resource Locator
- URN : Uniform Resource Name

Huh? A name may be unique, but may not tell you anything about how to locate it.
"Designing Your New Work Life" by Bill Burnett and Dave Evans is a book. It can be uniquely identified by the URN isbn:9780593467459 , and various URLs can be used to locate it (well, if not locate it, at least locate how to purchase or locate it in a library) https://www.amazon.com/Designing-Your-Work-Life-Happiness/dp/0593467450/ https://www.barnesandnoble.com/w/designing-your-new-work-life-bill-burnett/1140537816 https://designingyour.life/designing-your-new-work-life/ https://www.abebooks.com/9780593467459/Designing-New-Work-Life-Thrive-0593467450/plp https://www.worldcat.org/title/1256628247?oclcNum=1256628247

- Presentation
- Manipulations
Our Solar System: Markup

Our Solar System: Markup + Style

Our Solar System: Markup + Style + Function

- solarsystem.css
Markup - HTML
How a browser displays it.

How Your Browser Thinks About It

HTML Elements - the basic building blocks structure
- Element Name
- Attribute and Value Pairs
A Hypertext Link
Markup for a Hypertext link:

Start Tag <a href="https://www.harvard.edu/"> Harvard</a>
Element Name < a href="https://www.harvard.edu/">Harvard</a>
Attribute <a href ="https://www.harvard.edu/">Harvard</a>
Attribute Value <a href=" https://www.harvard.edu/ ">Harvard</a>
Content <a href="htts://www.harvard.edu/"> Harvard </a>
End Tag <a href="https://www.harvard.edu/">Harvard </a>
HTML Elements - Content can be other HTML elements

ul is an unordered list li is a list item
HTML Elements - Sometimes you will have more than one attribute

img is to embed an image
HTML Elements that are "empty"
Note the "end tag" is part of the "start tag" — <link />

link is used to reference a CSS stylesheet, a separate document that contains style rules to apply to the HTML document
HTML Elements - Sometimes HTML allows you to leave off end tags
In these cases the "end tags" are "implied" because of what follows.
Learning tip: Always use end tags!

More information: HTML5 Living Standard from the WHATWG . Section 4 contains the List of elements in HTML .
I've highlighted the 23 elements that you will use and/or see most commonly.
- h1 , h2 , h3 , h4 , h5 , h6
Most commonly used or seen elements
Learning about html elements.
How to find out more about HTML elements?
Two places that I would start are:
HTML Purpose
- Gives structure and meaning to our content
Think about three aspects of structure :
- HTML document structure html , head , body
- Web page structure header , main , nav , footer
- Content structure Headings ( h1 , h2 , h3 ), lists ( ul and li ), paragraphs ( p ), images ( img ), text, etc.
Example: solarsystem.html
Web Page Structure - header, main, footer
First, recall the basic document structure:
header, main, footer
MDN HTML elements reference: header , main , footer .
HTML5 Document Template
Benefits of web standards.
- Markup (HTML) Nu Html Checker https://validator.w3.org/nu/
- Style (CSS) CSS Validation Service https://jigsaw.w3.org/css-validator/
- Function (JavaScript)
- Search Engines
- Forward-compatibility and backward-compatibility.
- simpler, cleaner pages
- easier maintenance
- easier redesign
- Validation provides baseline when you go to edit.
" Postel's Law " or the " Robustness Principle "
HTML Best Practices to start out with
- Use start and end tags, even if optional
- Lower case element and attribute names
- Use quotes around attribute values
These best practices essentially follow the "XML" syntax rules for HTML5
The anchor — a — element is at the center of the key "hypertext" feature of the web. The a element is how to create hyperlinks from resource to another!
To go along with the a element is the href attribute. The value of the href attribute is the URL that the browser will load when the link is activated (e.g. a mouse click).
The following paragraph was taken from "'Sunshine vitamin' looks a little brighter", Harvard Gazette, February 5, 2013 :
Adequate levels of vitamin D during young adulthood may reduce the risk of adult-onset type 1 diabetes by as much as 50 percent, according to researchers at the Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH). If confirmed in future studies, the findings could lead to a role for vitamin D supplementation in preventing this serious autoimmune disease in adults.
Creating Links
Build confidence by making your links predictable and differentiable .
- Am I getting 'closer' to my goal?
- What is the difference between clicking here or clicking there?
- Link several words or a phrase, not just one or two words
- Use "title" attribute to elaborate
- Lie or Mislead
- " Click Here "
- Find out more in this knowledge base article
URL https://www.archives.gov/historical-docs/voting-rights-act
- Scheme https ://www.archives.gov/historical-docs/voting-rights-act
- Host https:// www.archives.gov /historical-docs/voting-rights-act
Absolute and Relative Locations
- Where does https://summer.harvard.edu/ go to?
- How about /images/mug.png ?
- What about ../styles/site.css ?
Relative locations (URLs) are resolved according to the location (URL) of the containing (starting) document!
Absolute or Fully Qualified URLs
Absolute, or fully-qualified, URLs specify the complete information (scheme, host, port, path).
https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2020/07/public-health-experts-unite-to-bring-clarity-to-coronavirus-response/
Relative or Partial URLs
Relative, or partial, URIs specify partial information. The information not provided is resolved from the current location.
<a href="slide2.html">Slide 2</a>
Relative to Server Root
Is this relative or absolute? Scheme, host, and port would be resolved from current location, but path is absolute
<a href="/copyright.html">copyright information</a>
Relative Paths to Parent Locations
- ../ refers to the parent directory
- ./ refers to current directory
Relative links are "transportable":
Hello World - Publishing a web page
- Get the tools (editor, browser, vpn client, sftp client) in place, and begin to use them.
- working with ".zip" files with Expand/Compress (Windows) or Unzip/Zip (Mac)
- keeping everything together in a folder and working with that folder (e.g. "File → Open Folder")
- Edit an existing HTML document
- Practice validating your HTML
- Go through the publishing process on your course web hosting server account
- Understand how to determine the URL to your published content
For Your Class Work
- Create a directory or folder for your class work.
- Create a "playground" or "sandbox" folder where you can play in and experiment in without worrying.
- Assignments - unzip/extract the materials, then move into your class work folder
For Web Sites
- Use folders or directories to help organize files. Recommendation is to adopt folder names of styles (for CSS files), scripts (for JavaScript files), and images (for images). . ├── images/ ├── index.html ├── scripts/ └── styles/ └── site.css
- Use index.html filename as appropriate
- Prefer filenames that only have lowercase, numeric, underscore or dashes (e.g. avoid spaces, and other things like !@#$%^&*(){}\|?/>
See: Course Web Hosting Server (Dreamhost) on the course web site.
Directory Requests and "index.html"
URL paths that map to a directory. For example the request: https://cwe871.students.cs12.net/big_ideas/ would return the index.html document in the big_ideas directory (e.g. /users/cwe871/public_html/big_ideas/index.html ).
Setup Once for Course
- Editor . Install Visual Studio Code , with Live Server, W3C Validation, and HTMLHint extensions
- SFTP client . Install Cyberduck or use Dreamhost File Manager ( https://files.dreamhost.com
- VPN client . Install Harvard Cisco AnyConnect VPN client software
- On your computer, create a "course work folder" to keep your work for the course. I recommend something like cscie12-work on your Desktop.
For Assignments
- Accept the assignment via the GitHub link that creates a repo for you. Then get that repo code locally to edit.
- Download the assignment ZIP file.
- Unzip or Extract the ZIP file.
- Move the folder into your "course work folder" you created above. Move the entire folder.
- Start Visual Studio Code, and "File → Open Folder" and navigate to the assignment folder to open. In VS Code, I recommend always opening the assignment folder as opposed to opening individual files (treat the assginment folder contents as a unit!)
- Use VS Code "Live Server" to provide a place to check your work.
- Edit the HTML, CSS, and/or JavaScript. Save.
- Periodically check in the browser (a reload may be needed) as well as other checks that may be needed such as validation or accessibility.
- Repeat the "Edit, Check" cycle until you've satisfied the rubric, yourself, or when the assignment is due.
- Check in your browser that you can access your work. Copy the URL in your browser, and submit that URL via Canvas
- Submit the code by giving us the URL to your GitHub repo, or give us the ZIP file of your completed assignment.
The World Wide Web

Tim Berners-Lee, Faculty
Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web in 1989. His key concepts are familiar to anyone using the Web: HTML (HyperText Markup Language), HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol), and URLs (Uniform Resource Locators). When he came to MIT in 1994, he formed the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) at MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory to create and maintain open standards for this essential global system. In 2017 he won the Turing Award, the most prestigious honor in computer science.
With your support, we will build a better world.
Explore Topics
More Stories
Want a daily email of lesson plans that span all subjects and age groups?
What is the world wide web.
1,256,976 Views
43,743 Questions Answered
Let’s Begin…
The World Wide Web is used every day by millions of people for everything from checking the weather to sharing cat videos. But what is it exactly? Twila Camp describes this interconnected information system as a virtual city that everyone owns and explains how it’s organized in a way that mimics our brain’s natural way of thinking.
About TED-Ed Animations
TED-Ed Animations feature the words and ideas of educators brought to life by professional animators. Are you an educator or animator interested in creating a TED-Ed Animation? Nominate yourself here »
Meet The Creators
- Educator Twila Camp
- Producer Darcy Vorhees
- Director Tom Beuerlein
- Script Editor Alex Gendler
- Narrator Addison Anderson
More from Inventions that Shape History


One of the world’s oldest condiments
Lesson duration 05:20
417,612 Views

How humanity got hooked on coffee
Lesson duration 05:35
725,774 Views

What did people do before anesthesia?
Lesson duration 05:27
1,248,898 Views

How will AI change the world?
Lesson duration 05:56
1,743,467 Views
World Wide Web
Assignment #1, assignment #2, search engines, assignments, internet search, foreign language search engines.
The World Wide Web Consortium July 2019
Introduction.

In 2016, the United Nations declared that “ the spread of information and communications technology and global interconnectedness has great potential to accelerate human progress, to bridge the digital divide and to develop knowledge societies. ” Although billions of people use the World Wide Web each day, a variety of obstacles stand in the way of its full potential to accelerate human progress:
- Hacking, snooping, and the theft of personal information have eroded trust in the Web. Misinformation, impersonation, and radicalization undermine democratic institutions.
- The World Wide Web Consortium has done pioneering work in the fields of accessibility and internationalization. However, without the proper features built in, modern Web experiences such as streaming media and virtual reality may be denied to hundreds of millions of users, increasing the digital divide.
- Web innovation must accelerate in order to keep pace with rapidly changing proprietary technology "silos." If not, we risk losing the world's premiere information commons.
Addressing these types of complex challenges requires global, multi-stakeholder initiatives with trusted mediation. For 25 years the World Wide Web Consortium ( W3C ) has played this role for the Web community. The Web Consortium community is now well-positioned to forge new partnerships in order to address today's most significant digital threats and opportunities. Please join us.
About the Web Consortium
Tim Berners-Lee founded the World Wide Web Consortium in 1994 to ensure the long-term growth of the Web. The organization primarily pursues this mission by convening industry, researchers, and the global community of Web developers to create open standards. Software developers implement these standards in browsers, servers, blogs, graphics editors, search engines, and all the other software that powers the Web experience. Web standards are blueprints for the digitally connected world.
As such, standards play an essential role in any strategy to address the complex challenges we face. Global standards constitute the toolkit for solutions that scale. Innovators build on open standards to solve hard problems. Furthermore, without the proper foundation, it can be nearly impossible to meet requirements for accessibility, internationalization, privacy, and security on the Web.
Standards that meet the varied needs of society do not happen by chance. They are created not by one company or country but through the work of the extended Web Consortium community. This community consists of:
- Members : More than 450 Members from around the world lead the development and implementation of standards.
- Staff : The Web Consortium is a not-for-profit organization. Its revenues come primarily from Membership dues. These dues and some grants support a staff of 50 to 60 people, led by Tim Berners-Lee and CEO Jeff Jaffe.
- Developers : More than 10,000 developers worldwide share their experiences with the standards and bring new ideas to the table.
This community has developed hundreds of open standards that have enabled the creation of more than a billion Web sites, including transformative phenomena such as social media, e-commerce, and search engines. W3C standards may be used by anyone at no cost: if they were not free, developers would ignore them. W3C technologies and guidelines make it possible for people with disabilities to access the Web. The Web supports communication in many of the world's languages. New W3C standards improve Web security through the development of authentication technologies that can replace weak passwords and reduce phishing and other sophisticated cyberattacks. In orchestrating these activities, the Web Consortium has earned a reputation for fairness, quality, and efficiency.
Though not well-known by the general public, the Web Consortium has earned recognition for its global impact: the Boston Globe ranked W3C the most important achievement associated with MIT in its first 150 years. The organization has won two Emmy Awards : in 2016 for its work to make online videos more accessible with captions and subtitles, and again in 2019 for standardization of a Full TV Experience on the Web. The Web Consortium's impact even extends beyond this planet: NASA has used W3C standards in both the Spirit and Opportunity Mars rovers.
Partnership Opportunities
To meet the greater online challenges society now faces, the Web Consortium seeks new partnerships in support of its mission, and new funding beyond its traditional sources of revenue.
Organizations committed to improving digital inclusion and online security and privacy would make ideal partners. Below we describe some of the Web Consortium's current activities in these areas.
Enhancing Privacy and Security
Privacy and security —both integral to human rights and civil liberties— have long held an important place on the Web Consortium agenda. We have begun discussions about how to help users find trustworthy content on the Web without increasing censorship. However, we at the Web Consortium recognize that there is much more to do in this important area.
Digital Inclusion
2019 marked a milestone - in 2009 only 20% of the world was online; now 50% of the world are connected. As the next 50% of the world join the Web, we must ensure that the Web they join is safe, inclusive, international and accessible.
Accessibility
In 2006, the United Nations adopted the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) which reaffirmed that all persons with all types of disabilities should be able to enjoy all human rights and fundamental freedoms. The Convention defined access to information, including web and digital content, as a human right. Digital accessibility, including web accessibility, is key for equal access, opportunity and participation for all.
When websites and Web tools are properly designed and coded, people with disabilities can use them, and individuals, businesses, and society all benefit. The Web Consortium’s Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) , launched in 1997, develops technical specifications, guidelines, and techniques, as well as supporting resources such as outreach and training materials to promote awareness and implementation. WAI’s Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) is regarded as the authoritative international standard for Web accessibility, and has been adopted or referenced by many governments around the world. However, as the complexity of the Web increases, and as technologies as diverse as digital publishing and virtual reality converge onto the Web, the need for up-to-date accessibility support in advanced technologies is increasing exponentially. Without the Web Consortium's efforts, people with disabilities would be left further behind.
Internationalization
Only a fraction of the world's population of almost 8 billion speaks English, and yet over 50% of online content is written in that one language. Those whose voice and language are not included on the Web will be increasingly marginalized and excluded. They will not receive the economic, educational or democratic benefits of the Web and by not having their presence, we lose the potential of the Web to reflect the richness of the world.
The Web Consortium launched the Internationalization of the World Wide Web Activity in 1998 to make the Web truly 'world wide'. For the Web to truly work for stakeholders all around the world engaging with content in various languages, there must be a collaboration of language experts, Web site designers, developers, and vendors who are active in moving the Web forward. We will only connect all communities that share a language when the Web supports all the world's languages.
Assignment on World Wide Web
Web Site:
A web site is a collection of web pages, images, videos or other digital assets that is hosted on one or several web server(s), usually accessible via the Internet, cell phone or a LAN. A web page is a document, typically written in HTML, that is almost always accessible via HTTP, a protocol that transfers information from the web server to display in the user’s web browser. All publicity accessible websites are seen collectively as constituting the “World Wide Web”.
The pages of websites can usually be accessed from a common root URL called the homepage, and usually reside on the same physical server. The URLs of the pages organize them into a hierarchy, although the hyperlinks between them control how the reader perceives the overall structure and how the traffic flows between the different parts of the sites. Some websites require a subscription to access some or all of their content. Examples of subscription sites include many business sites, parts of many news sites, academic journal sites, gaming sites, message boards, Web-based e-mail, services, social networking website and sites providing real-time stock market data.
Organized by the function, a website may be-
» A personal website
» A commercial website
» A government website
» A non-profit organization website
It could be the work of an individual, a business or other organization and is typically dedicated to some particular topic or purpose.
Web The New Arena:
Life was just going on fine, when along came the Internet and just about everything changed. You just have to look back over the past five year or six and think of different things were before that. Today, everyone’s young, smart and online. Oh yes, we are well into the Net Age. Whether you are working in a high-tech corporation or setting up your home office, trying to learn or two at college or having a whale of a time at school, life’s on the Internet .
Content Is The King:
No matter how great a site looks, no amount of design ever makes up for poor content. This is a fact that many web author lose sight of. That’s why we have so many sites around us that offer the visitor the same old thing – a bit of this a bit of that. A really good site must have solid unique content. That’s why as experts recommend we started with strategy and purpose first – no with design. First off you must quite clear of the purpose of your site. This holds true for any type of web sites, whether it’s a personal web sites, a small business set up, a hobbyist’s page or e- commerce or anything else. A web site without purpose just takes space and please no one but its own author. So unless you are just using your site for storage, start with putting down your purpose, your objectives, and message.
Types Of Web Site:
There are many variety of web sites, each specializing in a particular type of content or use and they may be arbitrarily classified in any number of ways. A few such classifications might include:-
Affiliated Sites: Enabled portal that renders not only its custom CMS but also syndicated content from other content providers for an agreed fee. There are usually three relationship tiers. Affiliate Agencies ( e.g. Commission Junction), Advertisers ( e.g. Ebay) and consumer ( e.g. Yahoo).
Archive Site: Used to preserve valuable electronic content threatened with extinction. Two examples are – Internet Archive which since 1996 has preserved billions of old ( and new ) web pages and Google Groups which in early 2005 was archiving over 845,000,000 messages posted to Usenet news / discussion groups.
Blog Site: Sites generally used to post online diaries which may include discussion forums ( e.g. blogger, xanga).
Content Site: Sites whose business is the creation and distribution of original content ( e.g. Slant, About.com).
Corporate Site: Used to provide background information about a business, organization or service.
E-Commerce Site: For purchasing goods such as Amazon.com.
Community Site: A site where persons with similar interests communicate with each other usually by chat or message boards such as MySpace.
Database Site: A site whose main use is the search and display of a specific database’s content such as the Internet Movie Database or the Political Graveyard.
Development Site: A site whose purpose is to provide information and resources related to software development, web design and the like.
Directory Site: A site that contains varied contents which are divided into categories and subcategories such as Yahoo! directory, Google directory and open directory project.
Download Site: Strictly used for downloading electronic content such as software, game demos or computer wall paper.
Employment Site: Allows employers to post job requirements for a position or positions and prospective employees to fill an application.
Erotica Websites: Shows sexual videos and images.
Fan Site: A web site created and maintained by fans of and for a particular celebrity as opposed to a web site created, maintained and controlled by a celebrity through their own paid webmaster. May also be known as a Shine in the case of certain subjects such as anime and manga characters.
Game Site: A site that is itself a game or “playground” where many people come to play such as MSN Games, POGO.com and Newgrounds.com.
Gripe Site: A site devoted to the critique of a person, place, corporation, government or institution.
Humor Site: Satirizes, parodies or otherwise exists solely to amuse.
Information Site: Contains content that is intended to inform visitors but not necessarily for commercial purposes such as: RateMyProfessors.com, free internet lexicon and encyclopedia. Most government, educational and non-profit institutions have an informational site.
Java Applet Site: Contains software to run over the web as a web application.
Mirror ( Computing ) Site: A complete reproduction of a website.
News Site: Similar to an information site but dedicated to dispensing news and commentary.
Personal Homepage: Run by an individual or a small group ( such as a family ) that contains information or any content that the individual wishes to include.
Political Site: A site on which people may voice political views.
Pornography ( porn ) Site: Site that shows pornographic images & videos.
Rating Site: Site on which people can praise or disparage what is featured.
Review Site: Site on which people can post reviews for product or service.
Search Engine Site: A site that provides general information and is intended as a gateway or lookup for other sites. A pure example is Google and the most widely known extended type is Yahoo! .
Shock Site: Includes images or other material that is intended to be offensive to most viewers ( e.g. Rotten.com ).
Phish Site: Website created to fraudulently acquire sensitive information such as passwords and credit card details by masquerading as a trustworthy person or business ( such as social security administration, paypal ) in an electronic communication.
Warez: A site filled with illegal downloads.
Web Portal: A site that provides a starting point or a gateway to other resources on the internet or an intranet.
Wiki Site: A site which users collaboratively edit ( such as Wikipedia ).
World Wide Web:
The letters “www” are commonly found at the beginning of Web addresses because of the long-standing practice if naming Internet hosts ( servers ) according to the services they provide. So for example, the host name for a Web server is often “www” for an FTP server, “ftp”; and for a USENET news server, “news” or “ nntp ” ( after the news protocol NNTP). These host names appear as DNS subdomain names as in www.example.com. This use of such prefix is not require by any technical standard; indeed, the web server was at “ nxoc01.cern.ch”, [ 15 ] and even today many web sites exist without a “ www ” prefix has no meaning in the way the main web site is shown. The “ www ” prefix is simply one choice for a web site’s subdomain name. Some web browsers will automatically try adding “ www ” to the beginning and possibly “ .com ” to the end of typed URLs if no host is found without them. Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Safari and opera will also prefix “ http://www” and append “ .com ” to the address bar contents if the Control and Enter keys are pressed simulteniously. For example, entering “ example ” in the address bar and then press either just Enter or Control+Enter will usually resolve to “ http://www.example.com ” depending on the exact browser version and its settings.
The World Wide Web ( commonly shortened to the web ) is a system of interlinked, hypertext documents accessed via the Internet. With a web browser, a user views web pages that contain text, images, videos and other multimedia and navigates between them using hyperlinks. The World Wide Web was created in 1989 by Sir Tim Berners Lee, working at CERN in Geneva, Switzerland. Since then, Berners Lee has played an active role in guiding the development of web standards ( such as the markup languages in which web pages are composed), and in recent years has advocated his vision of a Semantic Web. Robert Cailliau, also at CERN, was an early evangelist for the project.
How The Web Works:
Viewing a web page on the World Wide Web normally begins either by typing the URL of the page into a web browser or by following a hyperlink to that page or resource. The web browser then initiates a series of communication messages behind the scenes in order to fetch and display it.
First the server-name portion of the URL is resolved into an IP address using the global, distributed Internet database known as the domain name system or DNS. This IP address is necessary to contact and send data packets to the web server.
The browser then requests the resource by sending an HTTP request to the web server at that particular address. In the case of a typical web page the HTML text of the page is requested first and parsed immediately by the web browser which will then make additional requests for images and any other files that form a part of the page. Statistics measuring a website’s popularity are usually based on the number of ‘ page views’ or associated server ‘ hits’ or requests which take place.
Having received the require files from the web server the browser renders the page onto the screen as specified by its HTML, CSS and other web languages. Any images and other resources are incorporated to produce the on-screen web page that the user sees.
Contents Of Web Site:
No matter how great a site looks, no amount of design ever makes up for poor content. This is a fact that many web author lose sight of. That’s why we have so many sites around us that offer the visitor the same old thing – a bit of this, a bit of that. A really good site must have solid unique content. That’s why as exports recommend we started with strategy and purpose first – no with design. First off you must quite clear of the purpose of your site. This hold true for any type of websites, whether it’s a personal websites, a small business setup, a hobbyist’s page or e-commerce or anything else. A website without purpose just takes space and please no one but its own author. So unless you are just using your site for storage, start with putting down your purpose, your objectives, and the message.
Writing Web Site:
Writing for the web is in many ways different form writing for print. For one, the reader’s purpose in reading may be different. His attention span is different. The reading experience online and the way the reader’s eye moves across a page are different. With a printed page, there is only one sort of navigation-turn the page. But on a web page, there can be dozens and dozens of options all visible at once. And there’s your reader, finger poised over the mouse button, ready to be interactive. But with a web page, interactivity is important because readers want to do something. All this means that information has to be tailored and arranged specially for online reading. Writing for the web skillfully involves learning how to keep in mind new online reading habits and patterns. It means being able to put forward information in a way that draws the reader in quickly and keeps him at the website or at least that it gives him what he wants so that he comes back again and again.
Web Site Styles:
A static web site is one that has web pages stored on the server in the same form as the user will view them. They are edited using three broad categories of software:
Text editor such as notepad or text editor, where the HTML is manipulated directly within the editor program.
Editor such as Microsoft Frontpage and Macromedia Dreamweaver where the site is edited using a GUI interface and the underlying HTML is generated automatically by the editor software. Template-based editors such as Rapidweaver and iWeb which allow users to quickly create and upload websites to a web server without having to know anything about HTML as they just pick a suitable template from a palette and add pictures and text to it in a DTP-like fashion without ever having to see any HTML code. A dynamic website is one that has frequently changing information or collates information on the hop each time a page is requested. For example- it would call various bits of information from a database and put them together in a pre-defined format to present the reader with a coherent page. It interacts with users in a variety of ways including by reading cookies recognizing user’s previous history, session variables, server side variables etc, or by using direct interaction ( form elements, mouseovers, etc ). A site can display the current state of a dialog between users, monitor a changing situation or provide information in some way personalized to the requirements of the individual users.
What makes the World Wide Web so exciting is the limitless ways in which information and content can be put up. Using color, picture, sounds, movie clips, animation and interactivity, you can make sure your site is compelling enough to draw visitors again and again which is what every website wants. Naturally, this makes the site’s design, its layout, navigation and general look and feel an important aspect to work on. What usually tends to happen is that people over-design a website, filling it with bright starting colors, a feast of different fonts and too many pictures for its own good. Many resource sites have design is term that is used rather loosely sometimes it can include usability issues, navigation, browser compatibility and so on. If your page is about a regional specific topic, then make sure you include that.
Preferably right in the title of the page. Put the region in the keywords and page description as well. Remember too that even if your topic is regional, it has value to global viewers. What if someone from Germany is visiting your home town and needs any information there? You also might want to expand your site to give more generic information that would appeal to a more global audience.
Language On the Web:
Right now, most of the pages on the web are in English but just because you’re writing your page in English in Australia does not mean that a Canadian would understand it or find it useful. Make sure that you avoid slang on your site as that is the most non-translatable element of a page. When you list a price, indicate what currency you’re using. And when you list sizes or measurements, it helps if you list conversions or link to a conversion web site.
Static Versus Dynamic: Static HTML sites have not changed much since their development and the advent of the web. Essentially websites are presented using a wide array of tags that offer means for usually laying out a site. Search engines have become very good at recognizing static websites. In general search engines can navigate through a static website very easily and thus locate information. However, there is one significant disadvantage of static sites, you may need a separate page ( file ) for every page on your site. For example, if you want to make a design change that affects the entire site you may need to adjust all pages. For small sites this is not a problem but for large content or e-commerce sites creating new pages or updating existing pages can be time consuming and expensive. Certainly there is web development software that makes this a little easier but in the end static sites take time to manage. Interaction with visitors is a key feature of the best sites on the web. After all the most popular computer operating systems in the world may be the ones used for game playing machines. It seems that people hate the pickiness and precision of computer that allow them to do the things they do. On the other hand they love the illusion of the computer as another person with dynamism comes interaction. Dynamic websites means that different actions by the visitor cause different behaviors i.e. outputs by the site. That means pages are created as the user views the site. In most cases this requires the use of a database which contains the site’s information and some kind of scripting setup that is programmed to retrieve the information from the database.
What A Dynamic web Site can do?:
building a database driven web site is one of the best ways to insure that your site will grow into the future. Here are some of the reasons why – – –
Manage Your Own Content: A database-backed website brings unprecedented flexibility to how information is stored and displayed on the web. That means you can add and manage stories, information, schedules and photographs without having to calla web master. It’s a great way to take control of your site while saving money on maintenance.
Keep Your Visitors Coming Back: With fresh content that you can update at your site will always be relevant. So instead of finding the same stories and information on your site, returning visitors will find information that’s new and current. Its easy, inexpensive and will keep your visitors coming back time and time again.
Grow into The Future: Building a dynamic, database-driven site is strategically superior because changes to the site are incredibly easy to make. Want a new look on the site? No problem, since design ( presentation ) is separated from the site’s content. Need to change content, that’s only a few keystrokes away with easy-to-use administrative interfaces. Want to add new pages or section’s? not a problem when you have built your site on a foundation that’s both solid and flexible.
Manage Visitors Securely: With a data driven site you can let visitors see only information that you want them to see. Build member’s-only sections, handle passwords, lockout unwanted requests, handle subscription services, allow your staff access to areas where others are not allowed. A database-backed site can perform these secure functions with ease.
Be Searchable: letting visitors find the information they need quickly and easily is a snap with a dynamic site. Whether you are a publisher hosting thousands of articles or a merchant selling hundreds of widgets, a dynamic site allows your visitors to find what they need in a heartbeat.
Harness Your Site’s potential: Unlike traditional “ static ” sites, a dynamic site is far more than useful than simple “ brochure ware”. With dynamic architecture, your site can be put to an infinite variety of valuable uses. For example: you can easily connect a visitor with a near by distributor, connect a specific salesperson to a customer or deliver an instant response customer service request. In short, a dynamic site delivers more than a “ static ” site ever could.
Spend Less Time Managing Your Site: A dynamic site can reduce or eliminate many of the most time-consuming functions facing your staffs. That’s because many administrative functions can now be automated. For example: if a deadline has passed or an inventory sold-out, the site can automatically remove those items from display. It could notify automatically and update product pages on its own. Now your staff can spend less time on the web managing our site and more time doing the things they do best.
Handle Complex Tasks: while dynamic sites are superb for publishing and e-commerce, they can also be used far complex tasks such as quoting, estimating and presenting customized sales information anywhere, any time. Handling complex tasks is par for the course with a dynamic site.
Connect To Your customers: When visitors come to your site, do you gather information that can help you serve them better? With a built-in database, a dynamic site is a natural for gathering customer preferences. Ask them if they want to subscribe to news letters or if they are interested in new products. Test market new products. Survey them for valuable feedback. A dynamic web site can help you connect to customers in ways you were never able to before.
Customize your message: is it possible to respond on an individual basis to an infinite number of site visitors? If you build a dynamic site, it is. From greeting customers individually after log-in to sending carefully-crafted customized emails, a dynamic site will help you send the message that your customers are more than just numbers.
Developing A Dynamic Site:
In most cases this requires the use of a database which contains the site’s information and some kind of scripting setup that is programmed to retrieve the information from the database. Some popular scripting languages are ASP, ASP.Net, PHP, Pearl, ColdFusion, JavaScript. Some popular databases are MySql, MS SQL Server, Oracle etc.
ASP: Active Server Pages, Microsoft’s technology to enables HTML pages to be dynamic and interactive by embedding scripts i.e. either VBScript or Jscript, Microsoft’s alternative of JavaScript. Since the scripts in ASP pages ( suffix asp ) are processed by the server, any browser can work with ASP pages regardless of its Support for the scripting language used there in.
ASP.Net: Microsoft ASP.Net is a set of technologies in the Microsoft .NET Framework for building web applications and XML web services. ASP.Net pages execute on the server and generate markup such as HTML, WML or XML that is sent to a desktop or mobile browser. ASP.Net pages use a compiled, event-driven programming model that improves performance and enables the separation of application logic and user interface. ASP.Net pages and ASP.Net XML web services files contain server-side logic ( as opposed to client-side logic ) written in Microsoft Visual Basic.NET, Microsoft Visual C#.NET or any Microsoft.NET framework-compatible language.
PHP: A recursive acronym for “ hypertext Preprocessor ” is an open source server side scripting language designed for creating robust and reliable dynamic web pages for e-commerce and other mission critical web applications.
Perl: Practical Extraction and Reporting Language A robust programming language frequently used for creating CGI programs on web servers because it is faster than UNIX shell script programs, it can read and write binary files and it can process very large files.
Cold Fusion: It is an advanced website program that runs on our servers here at Thelix. Cold Fusion works in conjunction with a database of information that it draws from. You can use Cold Fusion to create dynamic web pages that display a variety of data, depending on what the viewer clicks on.
JavaScript: a scripting language from Netscape that is only marginally related to java. Java and JavaScript are not the same thing. JavaScript was designed to resemble Java which in turn looks a lot like C and C++. The difference is that java was built as a general-purpose object language while JavaScript is intended to provide a quicker and simpler language in a web page that is interpreted and executed by the web client. The script writer controls from within a web document, often executed by mouse function, buttons or other actions from the user. JavaScript can be used to fully control Netscape and Microsoft web browsers including all the familiar browser attributes.
MySQL: The MySQL database server is the world’s most popular open source database. Over six million installations use MySQL to power high-volume websites and other critical business systems – including industry- leaders like the associated press, Yahoo, NASA, Sabre Holdings and Suzuki. MySQL is an attractive alternative to higher-cost, more complex database technology. Its award-winning speed, scalability and reliability make it the right choice for corporate IT departments, web developers and packaged software vendors.
Microsoft SQL : Microsoft SQL server is a relation database management system produced by Microsoft. It supports a dialect of SQL, the most common database language. It is commonly used by governments and businesses for small to medium sized databases and completes with other SQL databases for this market segment.
Oracle database: An Oracle database, strictly speaking, is a collection of data, is sometimes imprecisely used to refer to the DBMS software itself. This error is made in the title of this article and below. The oracle managed by an Oracle database management system or DBMS. The term ” Oracle database management system” can be referred to without ambiguity as Oracle DBMS or the databases which it manages being relational in character, as oracle RDBMS. The very useful distinction between data managed by Oracle, an Oracle database and the Oracle RDBMS is blurred by Oracle Corporation itself when they refer now a days to the Oracle RDBMS, the software they sell to manage databases as the Oracle Database. The distinction between the managed data ( the database ) and the software which manages the ( DBMS / RDBMS ) relies, in Oracle’s marketing literature. On the capitalization of the world database. The Oracle DBMS is produced and marketed by Oracle Corporation. The Oracle DBMS is extensively used by many database applications on most popular computing platforms.
Scripts & Database:
We used PHP as scripting language and MySQL as backend Database. In the upcoming chapter we will discuss briefly about PHP and MySQL and their beneficiary side over others similar tools.
Publishing Web Page:
Web page production is available to individuals outside the mass media. In order to publish a web page, one does not have to go through a publisher or other media institution and potential readers could be found in all corners of the globe. Many different kinds of information are available on the web and for those who wish to know other societies, cultures and peoples, it has become easier. The increased opportunity to publish materials is observable in the countless personal and social networking pages, as well as sites by families, small shops etc. facilitated by the emergence of free web hosting services.
Web Analytics:
Web analytics is the study of the behavior of website visitors. In a commercial context, web analytics especially refers to the use of data collected from a web site to determine which aspects of the website work towards the business objectives for example which landing pages encourage people to make a purchase.
Data collected almost always includes web traffic reports. It may also include e-mail response rates, direct mail campaign data, sales and lead information, user performance data such as click heat mapping or other custom metrics as needed. This data is typically compared against key performance indicators for performance and used to improve a web site or marketing campaign’s audience response. Many different vendors provide web analyt
Soil Science Resource
Assignment on computer businessmarketing system of index it limited, a report on garment industries bangladesh (part-1), explain on scientific instruments, report on non banking financial activities of idlc finance limited, sample sympathy letter with a gift, annual report 2012-2013 of gmr infrastructure limited, radiometry – a branch of science, major facts for deep vein thrombosis, reverse engineering microscribe, latest post, mid-ocean ridge (mor), harnessing hydrogen at the genesis of life, ngc 5728’s faint characteristics are exposed, astronomers discover the oldest black hole ever observed, atomic hydrogen welding, variable-frequency transformer (vft).

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.4: Reading- The World Wide Web
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 18629
Introduction

British computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee is the inventor of the Web. As a CERN employee, Berners-Lee distributed a proposal on 12 March 1989 for what would eventually become the World Wide Web. The initial proposal intended a more effective CERN communication system, but Berners-Lee also realized the concept could be implemented throughout the world. Berners-Lee and Belgian computer scientist Robert Cailliau proposed in 1990 to use hypertext “to link and access information of various kinds as a web of nodes in which the user can browse at will”, and Berners-Lee finished the first website in December of that year. The first test was completed around 20 December 1990 and Berners-Lee reported about the project on the newsgroup alt.hypertext on 7 August 1991.
On March 12, 1989, Tim Berners-Lee issued a proposal to the management at CERN that referenced ENQUIRE , a database and software project he had built in 1980, and described a more elaborate information management system based on links embedded in readable text: “Imagine, then, the references in this document all being associated with the network address of the thing to which they referred, so that while reading this document you could skip to them with a click of the mouse.” Such a system, he explained, could be referred to using one of the existing meanings of the word hypertext , a term that he says was coined in the 1950s. There is no reason, the proposal continues, why such hypertext links could not encompass multimedia documents including graphics, speech and video, so that Berners-Lee goes on to propose the term hypermedia .
With help from Robert Cailliau, he published a more formal proposal (on 12 November 1990) to build a “Hypertext project” called “WorldWideWeb” (one word, also “W3”) as a “web” of “hypertext documents” to be viewed by “browsers” using a client–server architecture. This proposal estimated that a read-only web would be developed within three months and that it would take six months to achieve “the creation of new links and new material by readers, [so that] authorship becomes universal” as well as “the automatic notification of a reader when new material of interest to him/her has become available.” While the read-only goal was met, accessible authorship of web content took longer to mature, with the wiki concept, WebDAV, blogs, Web 2.0 and RSS/Atom.
The proposal was modeled after the SGML reader Dynatext by Electronic Book Technology, a spin-off from the Institute for Research in Information and Scholarship at Brown University. The Dynatext system, licensed by CERN, was a key player in the extension of SGML ISO 8879:1986 to Hypermedia within HyTime, but it was considered too expensive and had an inappropriate licensing policy for use in the general high energy physics community, namely a fee for each document and each document alteration.

A NeXT Computer was used by Berners-Lee as the world’s first web server and also to write the first web browser,WorldWideWeb, in 1990. By Christmas 1990, Berners-Lee had built all the tools necessary for a working Web: the first web browser (which was a web editor as well); the first web server; and the first web pages, which described the project itself.
The first web page may be lost, but Paul Jones of UNC-Chapel Hill in North Carolina announced in May 2013 that Berners-Lee gave him what he says is the oldest known web page during a 1991 visit to UNC. Jones stored it on amagneto-optical drive and on his NeXT computer.
On 6 August 1991, Berners-Lee published a short summary of the World Wide Web project on the newsgroup alt.hypertext . This date also marked the debut of the Web as a publicly available service on the Internet, although new users only accessed it after 23 August. For this reason this is considered the internaut’s day. Several news media have reported that the first photo on the Web was published by Berners-Lee in 1992, an image of the CERN house band Les Horribles Cernettes taken by Silvano de Gennaro; Gennaro has disclaimed this story, writing that media were “totally distorting our words for the sake of cheap sensationalism.”
The first server outside Europe was installed at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC) in Palo Alto, California, to host the SPIRES-HEP database. Accounts differ substantially as to the date of this event. The World Wide Web Consortium says December 1992, whereas SLAC itself claims 1991. This is supported by a W3C document titled A Little History of the World Wide Web .
The underlying concept of hypertext originated in previous projects from the 1960s, such as the Hypertext Editing System (HES) at Brown University, Ted Nelson’s Project Xanadu, and Douglas Engelbart’s oN-Line System (NLS). Both Nelson and Engelbart were in turn inspired by Vannevar Bush’s microfilm-based memex , which was described in the 1945 essay “As We May Think”.
Berners-Lee’s breakthrough was to marry hypertext to the Internet. In his book Weaving The Web , he explains that he had repeatedly suggested that a marriage between the two technologies was possible to members of both technical communities, but when no one took up his invitation, he finally assumed the project himself. In the process, he developed three essential technologies:
- a system of globally unique identifiers for resources on the Web and elsewhere, the universal document identifier (UDI), later known as uniform resource locator (URL) and uniform resource identifier (URI);
- the publishing language HyperText Markup Language (HTML);
- the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
The World Wide Web had a number of differences from other hypertext systems available at the time. The Web required only unidirectional links rather than bidirectional ones, making it possible for someone to link to another resource without action by the owner of that resource. It also significantly reduced the difficulty of implementing web servers and browsers (in comparison to earlier systems), but in turn presented the chronic problem of link rot . Unlike predecessors such as HyperCard, the World Wide Web was non-proprietary, making it possible to develop servers and clients independently and to add extensions without licensing restrictions. On 30 April 1993, CERN announced that the World Wide Web would be free to anyone, with no fees due. Coming two months after the announcement that the server implementation of the Gopher protocol was no longer free to use, this produced a rapid shift away from Gopher and towards the Web. An early popular web browser was ViolaWWW for Unix and the X Windowing System.

Scholars generally agree that a turning point for the World Wide Web began with the introduction of the Mosaic web browser in 1993, a graphical browser developed by a team at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (NCSA-UIUC), led by Marc Andreessen. Funding for Mosaic came from the U.S. High-Performance Computing and Communications Initiative and the High Performance Computing and Communication Act of 1991 , one of several computing developments initiated by U.S. Senator Al Gore. Prior to the release of Mosaic, graphics were not commonly mixed with text in web pages and the web’s popularity was less than older protocols in use over the Internet, such as Gopher and Wide Area Information Servers (WAIS). Mosaic’s graphical user interface allowed the Web to become, by far, the most popular Internet protocol.
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) was founded by Tim Berners-Lee after he left the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) in October 1994. It was founded at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Laboratory for Computer Science (MIT/LCS) with support from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which had pioneered the Internet; a year later, a second site was founded at INRIA (a French national computer research lab) with support from the European Commission DG InfSo; and in 1996, a third continental site was created in Japan at Keio University. By the end of 1994, the total number of websites was still relatively small, but many notable websites were already active that foreshadowed or inspired today’s most popular services.
Connected by the existing Internet, other websites were created around the world, adding international standards for domain names and HTML. Since then, Berners-Lee has played an active role in guiding the development of web standards (such as the markup languages to compose web pages in), and has advocated his vision of a Semantic Web. The World Wide Web enabled the spread of information over the Internet through an easy-to-use and flexible format. It thus played an important role in popularizing use of the Internet. Although the two terms are sometimes conflated in popular use, World Wide Web is not synonymous with Internet . The Web is an information space containing hyperlinked documents and other resources, identified by their URIs. It is implemented as both client and server software using Internet protocols such as TCP/IP and HTTP.
Tim Berners-Lee was knighted in 2004 by Queen Elizabeth II for “services to the global development of the Internet”.
The terms Internet and World Wide Web are often used without much distinction. However, the two things are not the same. The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks. In contrast, the World Wide Web is one of the services transferred over these networks. It is a collection of text documents and other resources, linked by hyperlinks and URLs, usually accessed by web browsers, from web servers.
Viewing a web page on the World Wide Web normally begins either by typing the URL of the page into a web browser, or by following a hyperlink to that page or resource. The web browser then initiates a series of background communication messages to fetch and display the requested page. In the 1990s, using a browser to view web pages—and to move from one web page to another through hyperlinks—came to be known as ‘browsing,’ ‘web surfing,’ (after channel surfing), or ‘navigating the Web’. Early studies of this new behavior investigated user patterns in using web browsers. One study, for example, found five user patterns: exploratory surfing, window surfing, evolved surfing, bounded navigation and targeted navigation.
The following example demonstrates the functioning of a web browser when accessing a page at the URL http://example.org/wiki/World_Wide_Web . The browser resolves the server name of the URL ( example.org ) into an Internet Protocol address using the globally distributed Domain Name System (DNS). This lookup returns an IP address such as 203.0.113.4 . The browser then requests the resource by sending an HTTP request across the Internet to the computer at that address. It requests service from a specific TCP port number that is well known for the HTTP service, so that the receiving host can distinguish an HTTP request from other network protocols it may be servicing. The HTTP protocol normally uses port number 80. The content of the HTTP request can be as simple as two lines of text:
The computer receiving the HTTP request delivers it to web server software listening for requests on port 80. If the web server can fulfill the request it sends an HTTP response back to the browser indicating success:
followed by the content of the requested page. The Hypertext Markup Language for a basic web page looks like <html> <head> <title>Example.org – The World Wide Web</title> </head> <body> <p>The World Wide Web, abbreviated as WWW and commonly known …</p> </body> </html>
The web browser parses the HTML and interprets the markup (<title>, <p> for paragraph, and such) that surrounds the words to format the text on the screen. Many web pages use HTML to reference the URLs of other resources such as images, other embedded media, scripts that affect page behavior, and Cascading Style Sheets that affect page layout. The browser makes additional HTTP requests to the web server for these other Internet media types. As it receives their content from the web server, the browser progressively renders the page onto the screen as specified by its HTML and these additional resources.
Most web pages contain hyperlinks to other related pages and perhaps to downloadable files, source documents, definitions and other web resources. In the underlying HTML, a hyperlink looks like <a href=” http://example.org/wiki/Main_Page “> Example.org, a free encyclopedia </a>
Such a collection of useful, related resources, interconnected via hypertext links is dubbed a web of information. Publication on the Internet created what Tim Berners-Lee first called the WorldWideWeb (in its original CamelCase, which was subsequently discarded) in November 1990.
The hyperlink structure of the WWW is described by the webgraph: the nodes of the webgraph correspond to the web pages (or URLs) the directed edges between them to the hyperlinks.
Over time, many web resources pointed to by hyperlinks disappear, relocate, or are replaced with different content. This makes hyperlinks obsolete, a phenomenon referred to in some circles as link rot, and the hyperlinks affected by it are often called dead links. The ephemeral nature of the Web has prompted many efforts to archive web sites. The Internet Archive, active since 1996, is the best known of such efforts.
Dynamic updates of web pages
JavaScript is a scripting language that was initially developed in 1995 by Brendan Eich, then of Netscape, for use within web pages. The standardised version is ECMAScript. To make web pages more interactive, some web applications also use JavaScript techniques such as Ajax (asynchronous JavaScript and XML). Client-side script is delivered with the page that can make additional HTTP requests to the server, either in response to user actions such as mouse movements or clicks, or based on elapsed time. The server’s responses are used to modify the current page rather than creating a new page with each response, so the server needs only to provide limited, incremental information. Multiple Ajax requests can be handled at the same time, and users can interact with the page while data is retrieved. Web pages may also regularly poll the server to check whether new information is available.
Many hostnames used for the World Wide Web begin with www because of the long-standing practice of naming Internet hosts according to the services they provide. The hostname of a web server is often www , in the same way that it may be ftp for an FTP server, and news or nntp for a USENET news server. These host names appear as Domain Name System (DNS) or subdomain names, as in www.example.com . The use of www is not required by any technical or policy standard and many web sites do not use it; indeed, the first ever web server was called nxoc01.cern.ch . According to Paolo Palazzi, who worked at CERN along with Tim Berners-Lee, the popular use of www as subdomain was accidental; the World Wide Web project page was intended to be published at www.cern.ch while info.cern.ch was intended to be the CERN home page, however the DNS records were never switched, and the practice of prepending www to an institution’s website domain name was subsequently copied. Many established websites still use the prefix, or they employ other subdomain names such as www2 , secure or en for special purposes. Many such web servers are set up so that both the main domain name (e.g., example.com) and the www subdomain (e.g., www.example.com) refer to the same site; others require one form or the other, or they may map to different web sites.
The use of a subdomain name is useful for load balancing incoming web traffic by creating a CNAME record that points to a cluster of web servers. Since, currently, only a subdomain can be used in a CNAME, the same result cannot be achieved by using the bare domain root.
When a user submits an incomplete domain name to a web browser in its address bar input field, some web browsers automatically try adding the prefix “www” to the beginning of it and possibly “.com”, “.org” and “.net” at the end, depending on what might be missing. For example, entering ‘microsoft’ may be transformed to http://www.microsoft.com/ and ‘openoffice’ to http://www.openoffice.org . This feature started appearing in early versions of Mozilla Firefox, when it still had the working title ‘Firebird’ in early 2003, from an earlier practice in browsers such as Lynx. It is reported that Microsoft was granted a US patent for the same idea in 2008, but only for mobile devices.
In English, www is usually read as double-u double-u double-u . Some users pronounce it dub-dub-dub , particularly in New Zealand. Stephen Fry, in his “Podgrammes” series of podcasts, pronounces it wuh wuh wuh. The English writer Douglas Adams once quipped in The Independent on Sunday(1999): “The World Wide Web is the only thing I know of whose shortened form takes three times longer to say than what it’s short for”. In Mandarin Chinese, World Wide Web is commonly translated via a phono-semantic matching to wàn wéi wǎng ( 万维网 ), which satisfies www and literally means “myriad dimensional net”, a translation that reflects the design concept and proliferation of the World Wide Web. Tim Berners-Lee’s web-space states that World Wide Web is officially spelled as three separate words, each capitalised, with no intervening hyphens.
Use of the www prefix is declining as Web 2.0 web applications seek to brand their domain names and make them easily pronounceable. As the mobile web grows in popularity, services like Gmail.com, MySpace.com, Facebook.com and Twitter.com are most often mentioned without adding “www.” (or, indeed, “.com”) to the domain.
Scheme specifiers
The scheme specifiers http:// and https:// at the start of a web URI refer to Hypertext Transfer Protocol or HTTP Secure, respectively. They specify the communication protocol to use for the request and response. The HTTP protocol is fundamental to the operation of the World Wide Web, and the added encryption layer in HTTPS is essential when browsers send or retrieve confidential data, such as passwords or banking information. Web browsers usually automatically prepend http:// to user-entered URIs, if omitted.
Web security
For criminals, the web has become the preferred way to spread malware. Cybercrime on the web can include identity theft, fraud, espionage and intelligence gathering. Web-based vulnerabilities now outnumber traditional computer security concerns, and as measured by Google, about one in ten web pages may contain malicious code. Most web-based attacks take place on legitimate websites, and most, as measured by Sophos, are hosted in the United States, China and Russia. The most common of all malware threats is SQL injection attacks against websites. Through HTML and URIs, the Web was vulnerable to attacks like cross-site scripting (XSS) that came with the introduction of JavaScript and were exacerbated to some degree by Web 2.0 and Ajax web design that favors the use of scripts.Today by one estimate, 70% of all websites are open to XSS attacks on their users. P hishing is another common threat to the Web. “SA, the Security Division of EMC, today announced the findings of its January 2013 Fraud Report, estimating the global losses from phishing at $1.5 Billion in 2012.” Two of the well-known phishing methods are Covert Redirect and Open Redirect.
Proposed solutions vary to extremes. Large security vendors like McAfee already design governance and compliance suites to meet post-9/11 regulations, and some, like Finjan have recommended active real-time inspection of code and all content regardless of its source. Some have argued that for enterprise to see security as a business opportunity rather than a cost center, “ubiquitous, always-on digital rights management” enforced in the infrastructure by a handful of organizations must replace the hundreds of companies that today secure data and networks. Jonathan Zittrain has said users sharing responsibility for computing safety is far preferable to locking down the Internet.
Every time a client requests a web page, the server can identify the request’s IP address and usually logs it. Also, unless set not to do so, most web browsers record requested web pages in a viewable history feature, and usually cache much of the content locally. Unless the server-browser communication uses HTTPS encryption, web requests and responses travel in plain text across the internet and can be viewed, recorded, and cached by intermediate systems.
When a web page asks for, and the user supplies, personally identifiable information—such as their real name, address, e-mail address, etc.—web-based entities can associate current web traffic with that individual. If the website uses HTTP cookies, username and password authentication, or other tracking techniques, it can relate other web visits, before and after, to the identifiable information provided. In this way it is possible for a web-based organisation to develop and build a profile of the individual people who use its site or sites. It may be able to build a record for an individual that includes information about their leisure activities, their shopping interests, their profession, and other aspects of their demographic profile. These profiles are obviously of potential interest to marketeers, advertisers and others. Depending on the website’s terms and conditions and the local laws that apply information from these profiles may be sold, shared, or passed to other organisations without the user being informed. For many ordinary people, this means little more than some unexpected e-mails in their in-box, or some uncannily relevant advertising on a future web page. For others, it can mean that time spent indulging an unusual interest can result in a deluge of further targeted marketing that may be unwelcome. Law enforcement, counter terrorism and espionage agencies can also identify, target and track individuals based on their interests or proclivities on the Web.
Social networking sites try to get users to use their real names, interests, and locations. They believe this makes the social networking experience more realistic, and therefore more engaging for all their users. On the other hand, uploaded photographs or unguarded statements can be identified to an individual, who may regret this exposure. Employers, schools, parents, and other relatives may be influenced by aspects of social networking profiles that the posting individual did not intend for these audiences. On-line bullies may make use of personal information to harass or stalk users. Modern social networking websites allow fine grained control of the privacy settings for each individual posting, but these can be complex and not easy to find or use, especially for beginners.

Photographs and videos posted onto websites have caused particular problems, as they can add a person’s face to an on-line profile. With modern and potential facial recognition technology, it may then be possible to relate that face with other, previously anonymous, images, events and scenarios that have been imaged elsewhere. Because of image caching, mirroring and copying, it is difficult to remove an image from the World Wide Web.
Many formal standards and other technical specifications and software define the operation of different aspects of the World Wide Web, the Internet, and computer information exchange. Many of the documents are the work of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), headed by Berners-Lee, but some are produced by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and other organizations.
Usually, when web standards are discussed, the following publications are seen as foundational:
- Recommendations for markup languages, especially HTML and XHTML, from the W3C. These define the structure and interpretation of hypertext documents.
- Recommendations for stylesheets, especially CSS, from the W3C.
- Standards for ECMAScript (usually in the form of JavaScript), from Ecma International.
- Recommendations for the Document Object Model, from W3C.
Additional publications provide definitions of other essential technologies for the World Wide Web, including, but not limited to, the following:
- Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), which is a universal system for referencing resources on the Internet, such as hypertext documents and images. URIs, often called URLs, are defined by the IETF’s RFC 3986 / STD 66: Uniform Resource Identifier (URI): Generic Syntax , as well as its predecessors and numerous URI scheme-defining RFCs;
- HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) , especially as defined by RFC 2616: HTTP/1.1 and RFC 2617: HTTP Authentication , which specify how the browser and server authenticate each other.
Accessibility
There are methods for accessing the Web in alternative mediums and formats to facilitate use by individuals with disabilities. These disabilities may be visual, auditory, physical, speech related, cognitive, neurological, or some combination. Accessibility features also help people with temporary disabilities, like a broken arm, or aging users as their abilities change. The Web receives information as well as providing information and interacting with society. The World Wide Web Consortium claims it essential that the Web be accessible, so it can provide equal access and equal opportunity to people with disabilities. Tim Berners-Lee once noted, “The power of the Web is in its universality. Access by everyone regardless of disability is an essential aspect.” Many countries regulate web accessibility as a requirement for websites. International cooperation in the W3C Web Accessibility Initiative led to simple guidelines that web content authors as well as software developers can use to make the Web accessible to persons who may or may not be using assistive technology.
Internationalization
The W3C Internationalization Activity assures that web technology works in all languages, scripts, and cultures. Beginning in 2004 or 2005, Unicode gained ground and eventually in December 2007 surpassed both ASCII and Western European as the Web’s most frequently used character encoding. OriginallyRFC 3986 allowed resources to be identified by URI in a subset of US-ASCII. RFC 3987 allows more characters—any character in the Universal Character Set—and now a resource can be identified by IRI in any language.
Between 2005 and 2010, the number of web users doubled, and was expected to surpass two billion in 2010. Early studies in 1998 and 1999 estimating the size of the Web using capture/recapture methods showed that much of the web was not indexed by search engines and the Web was much larger than expected. According to a 2001 study, there was a massive number, over 550 billion, of documents on the Web, mostly in the invisible Web, or Deep Web. A 2002 survey of 2,024 million web pages determined that by far the most web content was in the English language: 56.4%; next were pages in German (7.7%), French (5.6%), and Japanese (4.9%). A more recent study, which used web searches in 75 different languages to sample the Web, determined that there were over 11.5 billion web pages in the publicly indexable web as of the end of January 2005. As of March 2009, the indexable web contains at least 25.21 billion pages. On 25 July 2008, Google software engineers Jesse Alpert and Nissan Hajaj announced that Google Search had discovered one trillion unique URLs. As of May 2009, over 109.5 million domains operated. Of these, 74% were commercial or other domains operating in the generic top-level domain com .
Statistics measuring a website’s popularity are usually based either on the number of page views or on associated server ‘hits’ (file requests) that it receives.
Speed issues
Frustration over congestion issues in the Internet infrastructure and the high latency that results in slow browsing has led to a pejorative name for the World Wide Web: the World Wide Wait . Speeding up the Internet is an ongoing discussion over the use of peering and QoS technologies. Other solutions to reduce the congestion can be found at W3C. Guidelines for web response times are:
- 0.1 second (one tenth of a second). Ideal response time. The user does not sense any interruption.
- 1 second. Highest acceptable response time. Download times above 1 second interrupt the user experience.
- 10 seconds. Unacceptable response time. The user experience is interrupted and the user is likely to leave the site or system.
Web caching
A web cache is a server computer located either on the public Internet, or within an enterprise that stores recently accessed web pages to improve response time for users when the same content is requested within a certain time after the original request.
Most web browsers also implement a browser cache for recently obtained data, usually on the local disk drive. HTTP requests by a browser may ask only for data that has changed since the last access. Web pages and resources may contain expiration information to control caching to secure sensitive data, such as in online banking, or to facilitate frequently updated sites, such as news media. Even sites with highly dynamic content may permit basic resources to be refreshed only occasionally. Web site designers find it worthwhile to collate resources such as CSS data and JavaScript into a few site-wide files so that they can be cached efficiently.
Enterprise firewalls often cache Web resources requested by one user for the benefit of many. Some search engines store cached content of frequently accessed websites.
- World Wide Web. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Wide_Web#See_also . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Taking a selfie. Authored by : Susanne Nilsson. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/infomastern/14162668916/ . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- World Wide Web. Authored by : sandra_schoen. Located at : https://pixabay.com/en/world-wide-web-www-lettering-world-341418/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
Academic integrity and documentation, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Types of Documentation
Citing World Wide Web Sources

Web sources, like any other source material, must be documented if you use them in your assignment. In fact, all material on the web—text and graphics alike—is protected by copyright , regardless of whether the individual source or page has a copyright notice.
Review the style guide your assignment requires to determine what information you need to cite the web source accurately and appropriately.
Important Tips for Citing Web Sources
Sometimes an author name is not evident. If a person is not listed as an author, your style guide may permit using a corporate author or no author.
Some information, such as publication date, maybe be listed in the bottom banner of the website.
For more information, please consult UMGC Library’s page on Writing and Citing.
Key Takeaway
Web sources, like any other source material, must be documented if you use them in your assignment.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
World Wide Web Assignment
Your website must contain:
Standard homepage (no deviations in format or colors on first page please until after the assignment is graded) ; 3 image references, including a recent personal photograph; 2 hypertext links to other pages you created and stored on your UMSL web server account, these pages may contain your resume or any other type of document; ONE of these two pages must be another . htm or. html page one bulleted list; one table;
Link to your personal blog: BE SURE YOUR NAME IS ON YOUR BLOG PAGE SO I KNOW THAT IT IS YOU;
Link to your LINKED in Account
MAILTO command to your UMSL email address ; change in font colors on one of your other two pages (not the home page);
Of course, you are encouraged to be creative. You can put more images, pictures, hypertext links to other pages, embed forms, animation, video, etc.
To complete this assignment you will use 3 software applications:
1. a browser to copy files from the internet (explorer, firefox—instructions below are for firefox, etc.), 2. an editor to change the files you copied (i recommend notepad because it does not add extra html codes), 3. access to your public_html folder on the jinx server (student k drive), how to create your homepage; directions are for firefox, i. copy the four files from my standard homepage.
Using A Browser (FIREFOX), click on Standard homepage
On Browser menu, click on "file"
Select " Save Page As":
Save file to the DESKTOP (If DESKTOP is not appearing as an option, select Libraries-Documents and it will save to your desktop) using the filename index.html save as type WEBPAGE, HTML ONLY
Please note index.html must be in lower case.
Stay where you are to copy three images
Point the curser on the yellow line, hit the right mouse button, and select SAVE IMAGE AS , line_gol.gif to desktop
Point the curser on the umsl logo, hit the right mouse button, and select SAVE IMAGE AS , umsllogo.gif to desktop
Point the curser on the yellow ball, hit the right mouse button, and select SAVE IMAGE AS regball.gif to desktop
MINIMIZE your browser and verify that you have four files on your desktop:
line_gol.gif
umsllogo.gif
regball.gif
To edit the index.html file, right click on the file and select OPEN WITH and select notepad
Edit the file to personalize your webpage; As a first step, just insert your name.
Let’s make pretend your name is Sally Smith:
Be sure to SAVE your index.html file each time you edit it.
Please be sure to change all references to /~ lacitym to your /~SSOID
II. Upload your files to the PUBLIC _HTML FOLDER ON UNIX SERVER FROM CAMPUS
In this step, you will copy your files that are stored locally (desktop, c drive, flash drive) onto your public_html folder on the k: server. , if you are on campus , logon to mygateway ., minimize the mygateway window, on the desktop, click on the icon my computer. you should see your k: drive., click on the k: drive, you should see a public_html subdirectory, click on the public_html subdirectory.
Drag and drop your files from the DESKTOP (or C: drive or flash drive—wherever your files are locally stored) to the the public_html subdirectory
These files include:
§ index.html ( must be in lower case!)
§ line_gol.gif
§ umsllogo.gif
§ regball.gif
Note: It is vital that your active subdirectory is public_html everytime you want to upload files to your website.
Note: You may have an existing index_html file on your public_html , so you will have to answer YES to the question “Do you want to replace the file?”
Note: If you want to save a copy of your old index.html, save it under another names like indexold.html.
Be sure to test your homepage using a browser.
Sometimes you have to hit the refresh button to see the changes.
To continue editing, you make open index.html with NOTEPAD from your K drive (Please note—faculty use a different drive so follow the text instructions and ignore the part of the picture that points to a Z drive)
III. Upload your files to the PUBLIC _HTML FOLDER ON K: SERVER FROM OFF CAMPUS
Follow the instructions for FTP SSH Secure Shell or VPN on:
http://www.umsl.edu/technology/tsc/StudentResources/filestorage.html
http://www.umsl.edu/technology/networking/TritonVPN/index.html
https://tritonvpn.umsl.edu/+CSCOE+/logon.html
I can’t help you diagnose problems if you are having connection problems from home. But you can always work on the assignment in the on campus computing labs:
http://www.umsl.edu/technology/iss/StudentLabs/index.html
IV. ADDING FILES TO YOUR WEB PAGES
The previous steps successfully loaded your homepage on the WWW.
The assignment calls for two additional pages that are linked from your homepage. There are many options:
Option A: You may copy page2.html and page3.html using the same procedure for copying my standard home page. Process is copy-edit-upload.
Option B. Link to a document you created.
Suppose you want to load a resume stored in a file called myresume.doc . The process is:
1. Open your index_html file with NOTEPAD and find this code:
< img src ="regball.gif" ><a href ="http://www.umsl.edu/~lacitym/page2.html">Add meaningful lable to page2</a>< br >
2. Edit this line of code to read:
< img src ="regball.gif" ><a href ="http://www.umsl.edu/~ SSOid/myresume.doc "> Click here for my resume </a>< br >
Of course, you type in your actual SSOid not the word SSOid
3. Save index_html file
4. Make sure myresume.doc is stored in your public_html subdirectory
IF YOU DON’T SEE YOUR K: DRIVE WHEN YOU OPEN MY COMPUTER:
Right click on My Computer
Select Map Network Drive
In the FOLDER window type \\soulard.umsl.edu\SSOid
(Of course, you type in your actual SSOid not the word SSOid )
Click on reconnect at logon option
Click on finish
- Faculty/Staff
- Faculty Affairs
- Administration
- Financial Aid
- University Catalog
- Human Resources
- Career Center
- Careers at CSUDH
- IT Help Desk
World Wide Web Assignment
Latest News
This assignment is a basic exercise is using the WWW. Unlike the other assignments, all you need to do is print this page or copy the assignment down. As you work through the assignment, the most effective way to provide evidence of the completion of a step is to print the web page. If your search has returned a very large web document, just print the first page.
- Identify three different internet search engines, excluding Yahoo!, go to their home pages and print the page. If everyone in the class turns in the same three search engines, I won't be a happy camper.
- Select any element.
- Using the search engines chosen above, find the total number of sites which "respond" to the search on your element.Tabulate the results (or print the first page of the search response).
- Select one of the three search engines which permits Boolean keys. Perform an advanced search which contains both "or" and "and" with your element as the first search term. Print the first page of the search response.
- From the Boolean search select a single web site. For the site provide the complete URL as well as a one or two sentence summary of the content of the web site.
Find a chemistry related news story (must be in the print media within the last month). Select a topic from the news story. Using only Yahoo! find at least five sites with information related to your topic. For this section report:
- The complete reference to the original news story.
- The topic you selected from the news story and how it relates to the original story.
- The complete URLs for the fives sites with an brief statement of the content found at each.
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests...
Provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications
MoizFarooquii/World-Wide-Web-Coursera-Assignment
Folders and files, repository files navigation, the world wide web project.
The son of computer scientists, Berners-Lee was born in London in 1955 (the same year as Steve Jobs and Bill Gates) and studied physics at Oxford. While employed at CERN in the 1980s, Berners-Lee observed how tough it was to keep track of the projects and computer systems of the organization’s thousands of researchers, who were spread around the globe. As he later stated: "In those days, there was different information on different computers, but you had to log on to different computers to get at it. Also, sometimes you had to learn a different program on each computer."
In March 1989, Berners-Lee gave managers at CERN a proposal for an information management system that used hypertext to link documents on different computers that were connected to the Internet. (Hypertext, a term coined in 1963, allows a person to get a document or piece of content by clicking on a coded word or phrase.) Labelled “vague but exciting” by his boss, the proposal at first wasn’t accepted. Berners-Lee teamed up with Robert Cailliau, a Belgian engineer at CERN, to refine the proposal, and in 1990 the Englishman’s boss gave him time to work on the project. After originally calling the project Information Management, Berners-Lee tried out names such as Mine of Information and Information Mesh before settling on WorldWideWeb.
By the end of 1990, Berners-Lee, using a Steve Jobs-designed NeXT computer, had developed the key technologies that are the bedrock of the Web, including Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), for creating Web pages; Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), a set of rules for transferring data across the Web; and Uniform Resource Locators (URLs), or Web addresses for finding a document or page. He also had devised a basic browser and Web server software.
The beginning of the Web as a publicly available service on the Internet arrived on August 6, 1991, when Berners-Lee published the first-ever website. Fittingly, the site was about the World Wide Web project, describing the Web and how to use it. Hosted at CERN on Berners-Lee’s NeXT computer.
Problem Statement
Replicate the World's First Web Site as shared in the PDF .
Instructions
- Download and unzip the boilerplate code.
- Run the command npm install to install the dependencies required for automated testing.
- Open the boilerplate code in VSCode to develop the assignment solution.
- Add required code in the index.html file
- First, test the solution locally by running the command npm run test .
- Refactor the solution to ensure all test cases are passing.
- DO NOT MODIFY THE PROVIDED CODE, ELSE THIS MAY IMPACT THE TEST CODE EXECUTION.
- Zip the solution code by selecting all the files and folders excluding the node_modules folder and give the name same as assignment name to the zipped file.
- Upload the zipped solution for submission.
- HTML 100.0%
- Assignment Help Australia
- Assignment Writing Help
- Do My Assignment
- Writing assignment for University
- Project Management Assignment Help
- In-Class Assignment Help
- Top Homework Helpers
- Coursework Writing Service
- Dissertation Writing Services in UK
- Thesis Writing Service
- Programming Language Assignment Help
- Adobe InDesign Assignment Help
- Advanced Network Design Assignment Help
- Artificial Intelligence Assignment Help
- Assembly Language Assignment Help
- Computer Programming Assignment Help
- C Assignment Help
- Coding Assignment Help
- Data Structure Assignment Help
- IT Assignment Help
- Machine Learning Assignment Help
- ODOO Assignment Help
- R Programming Assignment Help
- UML Assignment Help
- Web Designing Assignment Help
- Big Data Assignment Help
- Data Mining Assignment Help
- Matlab Assignment Help
- Xero Accounting Pod Assignment Help
Accounting Assignment Help
- MYOB Assignment Help
- Statistics Assignment Help
- Research Proposal Assignment Help
- Industry Research Project Assignment Help
- Civil Engineering Assignment Help
- AUTOCAD Assignment help
- ANSYS Assignment Help
- SOLIDWORKS Assignment Help
- Predictive Analytics Assignment Help
Article Writing
- Strategic Business Plan
- Capstone Project Writing Services in Australia
Tap to Chat Get instant assignment help
Get Assisted by Experience Writers for Custom Assignment Help Service
Cherish personalized and custom assignment writing services at a fair price from assignment world.
How Assignment Help Happens?
To get assignment help, comply to the following 4 steps and avail professional help you can be proud of
Request a Quote
Fill out the form or contact us by using live chat or WhatsApp to place an order for Assignment.
Chat with Us
Share all the instructions for the expert to help you effectively per your demand.
Complete the Transaction
Pay using secure gateway mode using a Credit/Debit Card or bank transfer.
Get Desired Delivery
Our professional writers ensure that you receive on-time every time.

Assignment Help Features by Assignment World
Assignment Help is a vast service and to lead the industry following are some service attributes that help us stand ahead of others & ensure the best assignment assistance.
Select among the most skilled writers who hold PHDs and master's degrees from our team and let them handle your Assignment.
Get assistance upfront with our active customer support. We are available 24*7 all 365 days.
Our services are AI and plagiarism-free, written from scratch without grammatical errors.
We provide reasonable prices with great discounts so every student can benefit from our services.
On-time delivery is our primary responsibility. We are dedicated to delivering the Assignment before the given deadlines.
Our professional experts are available 24*7 to meet even the tightest deadlines and provide urgent assignment help.
Assignment World: Services
Assignment help.
Assignment. world is a one-stop solution for all your academic needs. With a team of PhD and master's level experts, we assure you to provide the best quality service in online assignment assistance. Our experts ensure all the assignments are made according to your guidelines and are 100% plagiarism free, unique, and made from scratch. Assignment help is an online platform for academic students to complete assignments and get better assessment results. Assignment help covers almost all the subjects at every level of an educational career. Our Assignment Helper Australia experts provide authentic solutions to all students across the globe. Writers thoroughly know subjects and ensure you score apex grades in your batch. On our website, you can get custom-made solutions for various subjects.
Homework Help
As a homework help provider, our website provides good-quality assignments. It helps students score exceptionally high grades in their academic careers. Our team has the best homework experts who always ensure your homework is written according to your requirements. Each online homework help is done from scratch using genuine sources and references. We desire to serve every student with quality work and promise to deliver timely assignments. Irrespective of your academic level, we ensure that our top homework helpers deliver every homework assignment per the guidelines and instructions shared.
Coursework Help
Completing students' coursework with superior content quality is our main target. We provide high-standard work at affordable prices and offer discounts on all types of coursework help . Our team is always here to help you with your coursework, allowing you to handle your other college responsibilities. We have over 500+ professional experts on staff. They are all highly trained and qualified to assist in any difficult subject coursework. As a result, our customers can expect to receive high-quality projects within predetermined timeframes.
Essay Writing
Many students find it hard to write essays, especially when they lack the skills and resources to do it themselves. They can use our essay writing services to get custom essays written for them. We provide top-notch support with our simple-to-order essay writing service. Our experts are well-trained to provide a structured essay with 100% original and plagiarism-free content per your needs and guidelines. With the help of our efficient essay writing services , you may succeed academically and reach new heights.
Article writing is a skill that requires creativity, knowledge, and expertise. The article-writing process starts with brainstorming ideas and then narrowing them down to a few. Ultimately it requires a huge effort and is time-consuming. Assignment. world takes great pride in providing professional article writing services with the best mixture of experience, expertise, and opinions. Our skilled writers know the ideal tone, style, and length for each piece to have the greatest impact.
Thesis Help
Your search for an ideal thesis writing service ends with us. Our team of writers conducts high-level research to help you with your thesis. Most of our writers hold PhD degrees and will help you meet your professor’s expectations. With Assignment.World. Your aspiration of earning a master’s degree with a high score is within your reach. We promise to dedicate our full time to relieve you from the stress of writing a thesis.
Dissertation Help
A prolonged form of academic writing is the dissertation. A dissertation must be submitted in time to qualify for degree conferral for all PhD candidates. Assignment.world provides research-based quality work on Dissertation writing services and Dissertation Help . Our website is the perfect companion for helping you with the arduous task of writing a dissertation. Years of experience have aided us in building a systematic strategy for writing the best dissertations for our students.
Programming Assignment Help
Our team of writers is efficient and qualified enough to cater to you with coding and programming assignment help. We assure supreme standards of quality to meet your requirements. All the services are available to you effortlessly, around the clock. We have solutions to every problem you face with programming assignments. Our team aims to meet your academic needs and provide substantial computer programming assignment help . You name it; we have it, whether it’s Java, C++, C, Matlab, HTML, etc. We have multiple services like Big Data, Data Mining, along with AI and ML Services like Machine Learning Assignment Help . Our team of Programming Assignment Helpers is efficient and qualified enough to cater to you with programming and coding assignment help. We assure supreme standards for quality to meet your requirements. All the services are available to you effortlessly any time round the clock.
Web Development
Get your project built, code reviewed, and problems solved by web development help services online from a simple to a complicated website. We create gorgeous, fully responsive, and mobile-friendly websites. Our experts are skilled enough to tackle programming problems at any level. Assignment. world is a one-stop solution for all web development assignment help . Count on us for great results. We are committed to excellence and go the extra mile to satisfy clients.
Research Paper Writing
Writing a research paper requires a high standard of understanding and effort, which can sometimes be tough for students. Here at Assignment.world, we aim to make your academic life stress free by providing you with all the research paper writing services . We offer excellent work within a speculated time frame, ensuring speedy delivery. Professionals undertake qualitative, quantitative, analytical, and scientific research to draw reliable solutions and summarise the content appropriately. We will do you all the Research Paper assignment help at the most affordable prices.
Research Proposal
The research proposal assignment is a dreadful task for many students. Writing the proposal requires a lot of time and effort, but it also requires an in-depth understanding of the topic. At Assignment. world, we have a pool of writers who use the most authentic sources for gathering materials. Our bunch of writers are proficient enough in their several fields. Experts provide authentic solutions to all students across the globe and help to release their stress. So, no need to wait anymore; avail our best research proposal assignment help and boost your grades.
Data Assignment Help
Data Assignment Help covers all data-related projects. It provides the tools needed to manage and analyze data effectively. Some of the services include Big Data Assignment Help Data Mining Assignment Help Data Structure Assignment Help At Assignment.world, we have experts in data assignment help who provide impeccable quality assignments within the required timeframe. With the help of experienced professionals, you can get your data assignments done quickly and accurately. You can save time and effort while still achieving your desired results.
CAD Assignment Help
CAD Assignment help services cover software tools and technical concepts well utilized in Assignment.world. Related our CAD Assignment help services include: Civil Engineering Assignment Help AutoCAD Assignment help Solidworks assignment help and many more We have top-notch experts available 24*7 at your services. With the help of their experience and skills, Assignment.world provides the top quality CAD assignment help services at the most reasonable price.
Accounting assignment help is a great way for students to get the support they need to complete their accounting assignments. With the help of experts, students can get assistance with topics such as Xero Assignment Help, financial statements, and many more. With the help of our accounting assignment help service, students can be sure that their assignments are completed accurately and on time.
Marketing Plan
Creating a detailed marketing plan is an essential part of any business. It will help you develop a strategy for reaching your target audience and achieving your goals. Having a well-crafted marketing plan that helps identify potential customers, defines the most effective tactics and channels, and creates measurable objectives. Assignment.world can provide valuable assistance in creating an effective marketing plan. Our experts have extensive experience creating successful plans tailored to meet the needs of different businesses and industries. Our services give students a comprehensive marketing plan to reach their desired outcomes.
Subjects Covered by Assignment World
Our professional writers have in-depth knowledge in every subject to fetch you top quality assignment help.
Programming and Mobile App Development
We serve in all Languages like Python, Java, C/C++, iOS / Android Apps, and Software Engineering.
Science & Mathematics
We offer help in Physics, Chemistry, Geology, Mathematics, Oceanology, Topology, Number Theory & etc.
Business Management & Law
We offer a wide range of expertise in Marketing, HRM, Strategic Mgmt, Contract / Company Law & etc.
Nursing, Biology & Medicine
We assist in Biology, Medical, Pharma, Nursing, healthcare, child care, pedagogy, mental health, Ecology, Life Science, & etc.
Computer Science and Business Intelligence
Comp. Architecture, Network & Security, Project Mgmt, Database, Digital Forensics, Capstone.
Engineering & Architecture
We cater services to Mechanical, Electrical, Civil, Chemical Automobile Engineerings, & etc.
Economics & Statistics
Providing help in Micro. Macro, Managerial, Linear Programming, Quantitative Economics & etc.
Accounting & Finance
We cater Accounting, Taxation, MYOB / PERDISCO, Ratio Analysis, Management Accounting, Capital Market, Financial Modelling & etc.
Assignment World: Hallmark & Benefits
Assignment World is a domain where one should take quality seriously and here we go an extra mile to ensure all orders meet the highest academic standards.
Our University Pages
Have a look at our magnificent University Page and select any course. We have got your back for the daunting assignments !

Over-the-top universities are where education meets experience

Make your dreams come true by enrolling yourself in Kaplan

Melbourne institute of technology is all set to fulfil all your dreams.

Enroll now at the #1 University in student support.

Encash this golden ticket to study at one of the finest Universitie.

Get admission to the #1 University for two years Higher Education Ranking.

Assignment.world has been the leading organization in assignment writing services for the last 10 years. We have a team of 2150+ experts working with us who are always ready to assist you with any assignment help queries. We have the best PhD experts who can provide quality plagiarism-free work, student-friendly pricing, and certain discounts. Our top-notch services are available within a stipulated delivery time for custom and urgent assignments. Our services are spread across the USA, UK, Australia, Canada, and almost worldwide. Our primary focus areas are dissertations, thesis help, research papers, programming assignments, homework help, coursework help, and many more. Many university students have benefited from our service and achieved top grades in their assignments. As a result of our quality assignment writing, students keep returning to us when it comes to assignments. With tremendous customer satisfaction and support, we could put our name forward as a standard for others.
Excellent work, the assignment was clear and concise, and all the calculations were done properly. Thank you.

Amazing paper. They provided it to me ahead of schedule, it was properly written, and I earned an excellent grade.

I appreciate the experts that worked on it. Very precise work. Also received before the timeframe. Great work. Thank you so much.

United Kingdom (UK)
Twice revision was more satisfying. I received the assignment before the deadline. Overall, it was a good experience.

Thank you so much for your hard work; Keep it up, Assignment.world. The specialists have solid knowledge and understanding of their subject.
Awesome assignment work. The project was well-organized as per my requirement. I appreciated the assignment's writing style.

The Assignment work was of excellent quality, and the information was relevant. The specialist worked superbly. Great work.

United Arab Emirates (UAE)
Both a strong vocabulary and the absence of plagiarism were awesome parts. Prompt delivery of an assignment. Very satisfied with work.

I received the assignment service customized as per my university's guidelines. On-time delivery. Very pleased with the work.
Thank you for the timely delivery, proper feedback, and high-quality content. Excellent referencing. I will advise my friends as well.
Secure And Confidential Assignment Help
Put all your doubts aside. Assignment.world works for its customer loyalty. We never share and reveal our customers’ information and details to outside parties. No third-party services have access to our customer list or any data. We guarantee that your personal information is secure and confidential with us. We are here to provide you with quality assignment help. Assignment help from certified and qualified writers only wishes to serve you with high standards and plagiarism-free content, maintaining your privacy. We do not collect or disclose personal information with unscrupulous ad agencies or academic institutions.
As a result, your professor will have no idea you used our custom assignment writing help services. Everything is done online, which is how we deliver your assignments, completed papers, dissertations, thesis, research papers, and discounts to you. We never see your credit card information because payments are made through secure channels. So put your worries aside and leave your academic assignments to us!
Assignment Help By Top Experts
Our website has a team of the brightest and most skilled academic writers on the internet. We’re delighted to present them to you! Our assignment writers are the cream of society, with most holding PhD degrees in their respective fields. Suppose you require assistance in completing your university assignments. We will gladly provide you with a list of qualified and seasoned writers to choose from. A rigorous hiring technique is used to pick only the best academic writers. Our subject experts are ready to work for you and provide you with the highest-quality content. Experts are well-versed in different academic formats and can help you with your assignments quickly and accurately. A wide range of services, including proofreading, editing, formatting, and plagiarism checking, ensures your assignments are perfect before submission. Assignment help by top experts covers all subjects at academic levels. Whether you are in school, college, university, or have professional degrees. Our writers can handle all assignment writing services, like complex dissertations, thesis, research papers, homework, coursework, essays, etc.

Assignment Help At Affordable Prices
Assignment help, which balances price and quality, might be challenging for students. But not anymore, Assignment.world provides custom and legit assignment help at pocket-friendly prices. Students worldwide recognize that we provide an excellent balance of affordability and professionalism for all academic writing services. We guarantee high-quality solutions and believe that excellent service does not have to be expensive.
We are committed to aiding students in all subject areas at all stages of their academic careers at the most affordable prices, along with 30% discount offers. Although this may appear to be a tall aim, we are committed to attaining it. Hire an expert for all your academic assignments and experience excellent quality at a reasonable price.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The development of the World Wide Web was begun in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee and his colleagues at CERN, an international scientific organization based in Geneva, Switzerland. They created a protocol, HyperText Transfer Protocol ( HTTP ), which standardized communication between servers and clients. Their text-based Web browser was made available ...
Web browsers can be defined as programs which display text, data, pictures, animation and video on the Internet. Hyperlinked resources on the World Wide Web can be accessed using software interfaces provided by Web browsers. Initially, Web browsers were used only for surfing the Web but now they have become more universal.
Then get that repo code locally to edit. Download the assignment ZIP file. Unzip or Extract the ZIP file. Move the folder into your "course work folder" you created above. Move the entire folder. Start Visual Studio Code, and "File → Open Folder" and navigate to the assignment folder to open.
A web page from Wikipedia displayed in Google Chrome. The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond IT specialists and hobbyists. It allows documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to specific rules of the Hypertext Transfer ...
The world-wide web T.J. Berners-Lee, R. Cailliau and J.-F. Groff CERN, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Abstract Berners-Lee, T.J., R. Cailliau and J.-F. Groff, The world-wide web, Computer Networks and ISDN Systems 25 (1992) 454-459. This paper describes the World-Wide Web (W3) global information system initiative, its protocols and data formats ...
The World Wide Web enabled the spread of information over the Internet through an easy-to-use and flexible format. It thus played an important role in popularizing use of the Internet. Although the two terms are sometimes conflated in popular use, World Wide Web is not synonymous with Internet. The Web is an information space containing ...
When he came to MIT in 1994, he formed the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) at MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory to create and maintain open standards for this essential global system. In 2017 he won the Turing Award, the most prestigious honor in computer science. With your support, we will build a better world.
The World Wide Web has a dedicated series of conferences run by an independent committee. For papers on advances and proposals on Web related topics, the reader is directed to past and future conferences. The proceedings of the last two conferences to date are as below. Proceedings of the Fourth International World Wide Web Conference(Boston ...
The World Wide Web is used every day by millions of people for everything from checking the weather to sharing cat videos. But what is it exactly? Twila Camp describes this interconnected information system as a virtual city that everyone owns and explains how it's organized in a way that mimics our brain's natural way of thinking.
World Wide Web Worm. Yahoo. Assignments Your assignment, should you decide to accept it (remember that? **;-) is to become familiar with search engines so that you can use them to your benefit in finding materials and resources for your FL classroom. Assignment #1 Internet Search
World Wide Web. Provides access to Internet information through documents including text, graphics, audio, and video files that use a special formatting language called Hypertext Markup Language. Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) Publishes hypertext on the World Wide Web, which allows users to move from one document to another simply by clicking ...
The Internet—and its graphically attractive application, the World Wide Web (WWW)—is potentially a powerful educational tool. Barrie and Presti discuss three ways in which the WWW can be profitably used in education: as a giant encyclopedia, as a virtual classroom, and as a supplement to conventional courses. T he Internet was born in ...
About the Web Consortium. Tim Berners-Lee founded the World Wide Web Consortium in 1994 to ensure the long-term growth of the Web. The organization primarily pursues this mission by convening industry, researchers, and the global community of Web developers to create open standards. Software developers implement these standards in browsers ...
Assignment on World Wide Web. Assignment. Web Site: A web site is a collection of web pages, images, videos or other digital assets that is hosted on one or several web server (s), usually accessible via the Internet, cell phone or a LAN. A web page is a document, typically written in HTML, that is almost always accessible via HTTP, a protocol ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The World Wide Web (WWW) was invented in the 1980s. This was a time when the demand to communicate and share information among users connected to the Internet reached a peak. Tim Berners-Lee of the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) built the ENQUIRE database system. This database had a rule that, whenever someone ...
Online learning can increase collaboration between educators and students as well as students and peers. Your class can use wikis and cloud-based apps to share information they've discovered, post comments and questions, upload assignments, and reflect on their learning. As well, group work can take place outside the classroom, virtually.
Introduction. The World Wide Web (www, W3) is an information space where documents and other web resources are identified by URIs, interlinked by hypertext links, and can be accessed via the Internet. It has become known simply as the Web.Hypertext documents are commonly called web pages, which are primarily text documents formatted and annotated with the Hypertext Markup Language (HTML).
Citing World Wide Web Sources. Web sources, like any other source material, must be documented if you use them in your assignment. In fact, all material on the web—text and graphics alike—is protected by copyright, regardless of whether the individual source or page has a copyright notice. Review the style guide your assignment requires to ...
World Wide Web Assignment. Your website must contain: Standard homepage (no deviations in format or colors on first page please until after the assignment is graded); 3 image references, including a recent personal photograph; 2 hypertext links to other pages you created and stored on your UMSL web server account, these pages may contain your resume or any other type of document; ONE of these ...
The use of new technologies of communication, like the World Wide Web, can allow teachers to assign collaborative writing assignments incorporating hypertextual principles of composition that require students to prepare texts to publish on the Web. Two such assignments are considered as examples of a class-wide collaborative composition project allowing students to be the producers of a text ...
Unlike the other assignments, all you need to do is print this page or copy the assignment down. As you work through the assignment, the most effective way to provide evidence of the completion of a step is to print the web page. If your search has returned a very large web document, just print the first page. Part One
Instructions. Download and unzip the boilerplate code. Run the command npm install to install the dependencies required for automated testing. Open the boilerplate code in VSCode to develop the assignment solution. Add required code in the index.html file. First, test the solution locally by running the command npm run test.
Assignment.world provides research-based quality work on Dissertation writing services ... Assignment. world is a one-stop solution for all web development assignment help. Count on us for great results. ... Experts are well-versed in different academic formats and can help you with your assignments quickly and accurately. A wide range of ...