Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper

Writing a Research Paper Conclusion | Step-by-Step Guide
Published on October 30, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on April 13, 2023.
- Restate the problem statement addressed in the paper
- Summarize your overall arguments or findings
- Suggest the key takeaways from your paper
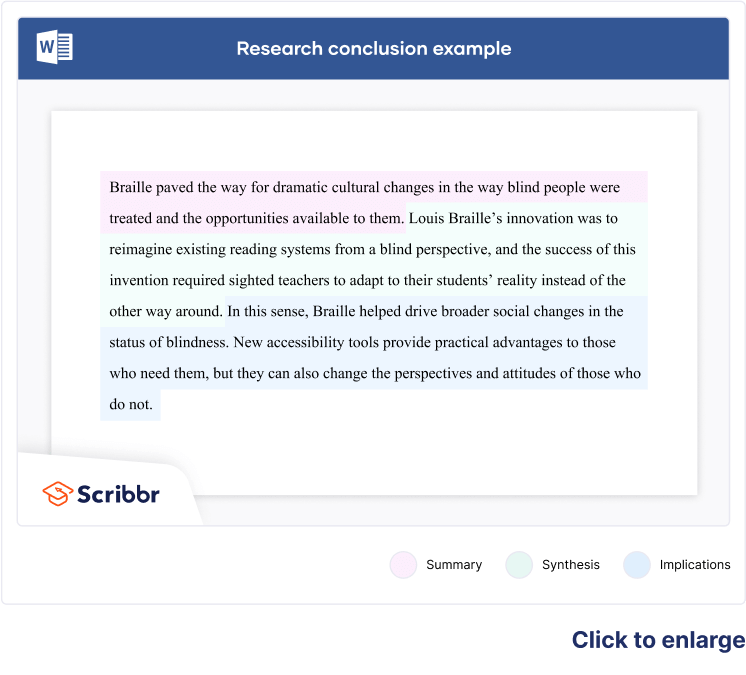
The content of the conclusion varies depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or constructs an argument through engagement with sources .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: restate the problem, step 2: sum up the paper, step 3: discuss the implications, research paper conclusion examples, frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
The first task of your conclusion is to remind the reader of your research problem . You will have discussed this problem in depth throughout the body, but now the point is to zoom back out from the details to the bigger picture.
While you are restating a problem you’ve already introduced, you should avoid phrasing it identically to how it appeared in the introduction . Ideally, you’ll find a novel way to circle back to the problem from the more detailed ideas discussed in the body.
For example, an argumentative paper advocating new measures to reduce the environmental impact of agriculture might restate its problem as follows:
Meanwhile, an empirical paper studying the relationship of Instagram use with body image issues might present its problem like this:
“In conclusion …”
Avoid starting your conclusion with phrases like “In conclusion” or “To conclude,” as this can come across as too obvious and make your writing seem unsophisticated. The content and placement of your conclusion should make its function clear without the need for additional signposting.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

Having zoomed back in on the problem, it’s time to summarize how the body of the paper went about addressing it, and what conclusions this approach led to.
Depending on the nature of your research paper, this might mean restating your thesis and arguments, or summarizing your overall findings.
Argumentative paper: Restate your thesis and arguments
In an argumentative paper, you will have presented a thesis statement in your introduction, expressing the overall claim your paper argues for. In the conclusion, you should restate the thesis and show how it has been developed through the body of the paper.
Briefly summarize the key arguments made in the body, showing how each of them contributes to proving your thesis. You may also mention any counterarguments you addressed, emphasizing why your thesis holds up against them, particularly if your argument is a controversial one.
Don’t go into the details of your evidence or present new ideas; focus on outlining in broad strokes the argument you have made.
Empirical paper: Summarize your findings
In an empirical paper, this is the time to summarize your key findings. Don’t go into great detail here (you will have presented your in-depth results and discussion already), but do clearly express the answers to the research questions you investigated.
Describe your main findings, even if they weren’t necessarily the ones you expected or hoped for, and explain the overall conclusion they led you to.
Having summed up your key arguments or findings, the conclusion ends by considering the broader implications of your research. This means expressing the key takeaways, practical or theoretical, from your paper—often in the form of a call for action or suggestions for future research.
Argumentative paper: Strong closing statement
An argumentative paper generally ends with a strong closing statement. In the case of a practical argument, make a call for action: What actions do you think should be taken by the people or organizations concerned in response to your argument?
If your topic is more theoretical and unsuitable for a call for action, your closing statement should express the significance of your argument—for example, in proposing a new understanding of a topic or laying the groundwork for future research.
Empirical paper: Future research directions
In a more empirical paper, you can close by either making recommendations for practice (for example, in clinical or policy papers), or suggesting directions for future research.
Whatever the scope of your own research, there will always be room for further investigation of related topics, and you’ll often discover new questions and problems during the research process .
Finish your paper on a forward-looking note by suggesting how you or other researchers might build on this topic in the future and address any limitations of the current paper.
Full examples of research paper conclusions are shown in the tabs below: one for an argumentative paper, the other for an empirical paper.
- Argumentative paper
- Empirical paper
While the role of cattle in climate change is by now common knowledge, countries like the Netherlands continually fail to confront this issue with the urgency it deserves. The evidence is clear: To create a truly futureproof agricultural sector, Dutch farmers must be incentivized to transition from livestock farming to sustainable vegetable farming. As well as dramatically lowering emissions, plant-based agriculture, if approached in the right way, can produce more food with less land, providing opportunities for nature regeneration areas that will themselves contribute to climate targets. Although this approach would have economic ramifications, from a long-term perspective, it would represent a significant step towards a more sustainable and resilient national economy. Transitioning to sustainable vegetable farming will make the Netherlands greener and healthier, setting an example for other European governments. Farmers, policymakers, and consumers must focus on the future, not just on their own short-term interests, and work to implement this transition now.
As social media becomes increasingly central to young people’s everyday lives, it is important to understand how different platforms affect their developing self-conception. By testing the effect of daily Instagram use among teenage girls, this study established that highly visual social media does indeed have a significant effect on body image concerns, with a strong correlation between the amount of time spent on the platform and participants’ self-reported dissatisfaction with their appearance. However, the strength of this effect was moderated by pre-test self-esteem ratings: Participants with higher self-esteem were less likely to experience an increase in body image concerns after using Instagram. This suggests that, while Instagram does impact body image, it is also important to consider the wider social and psychological context in which this usage occurs: Teenagers who are already predisposed to self-esteem issues may be at greater risk of experiencing negative effects. Future research into Instagram and other highly visual social media should focus on establishing a clearer picture of how self-esteem and related constructs influence young people’s experiences of these platforms. Furthermore, while this experiment measured Instagram usage in terms of time spent on the platform, observational studies are required to gain more insight into different patterns of usage—to investigate, for instance, whether active posting is associated with different effects than passive consumption of social media content.
If you’re unsure about the conclusion, it can be helpful to ask a friend or fellow student to read your conclusion and summarize the main takeaways.
- Do they understand from your conclusion what your research was about?
- Are they able to summarize the implications of your findings?
- Can they answer your research question based on your conclusion?
You can also get an expert to proofread and feedback your paper with a paper editing service .
The conclusion of a research paper has several key elements you should make sure to include:
- A restatement of the research problem
- A summary of your key arguments and/or findings
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
No, it’s not appropriate to present new arguments or evidence in the conclusion . While you might be tempted to save a striking argument for last, research papers follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the results and discussion sections if you are following a scientific structure). The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, April 13). Writing a Research Paper Conclusion | Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-conclusion/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, writing a research paper introduction | step-by-step guide, how to create a structured research paper outline | example, checklist: writing a great research paper, what is your plagiarism score.
How to Write a Conclusion for Research Papers (with Examples)

The conclusion of a research paper is a crucial section that plays a significant role in the overall impact and effectiveness of your research paper. However, this is also the section that typically receives less attention compared to the introduction and the body of the paper. The conclusion serves to provide a concise summary of the key findings, their significance, their implications, and a sense of closure to the study. Discussing how can the findings be applied in real-world scenarios or inform policy, practice, or decision-making is especially valuable to practitioners and policymakers. The research paper conclusion also provides researchers with clear insights and valuable information for their own work, which they can then build on and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
The research paper conclusion should explain the significance of your findings within the broader context of your field. It restates how your results contribute to the existing body of knowledge and whether they confirm or challenge existing theories or hypotheses. Also, by identifying unanswered questions or areas requiring further investigation, your awareness of the broader research landscape can be demonstrated.
Remember to tailor the research paper conclusion to the specific needs and interests of your intended audience, which may include researchers, practitioners, policymakers, or a combination of these.
Table of Contents
What is a conclusion in a research paper, summarizing conclusion, editorial conclusion, externalizing conclusion, importance of a good research paper conclusion, how to write a conclusion for your research paper, research paper conclusion examples.
- How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
A conclusion in a research paper is the final section where you summarize and wrap up your research, presenting the key findings and insights derived from your study. The research paper conclusion is not the place to introduce new information or data that was not discussed in the main body of the paper. When working on how to conclude a research paper, remember to stick to summarizing and interpreting existing content. The research paper conclusion serves the following purposes: 1
- Warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend specific course(s) of action.
- Restate key ideas to drive home the ultimate point of your research paper.
- Provide a “take-home” message that you want the readers to remember about your study.

Types of conclusions for research papers
In research papers, the conclusion provides closure to the reader. The type of research paper conclusion you choose depends on the nature of your study, your goals, and your target audience. I provide you with three common types of conclusions:
A summarizing conclusion is the most common type of conclusion in research papers. It involves summarizing the main points, reiterating the research question, and restating the significance of the findings. This common type of research paper conclusion is used across different disciplines.
An editorial conclusion is less common but can be used in research papers that are focused on proposing or advocating for a particular viewpoint or policy. It involves presenting a strong editorial or opinion based on the research findings and offering recommendations or calls to action.
An externalizing conclusion is a type of conclusion that extends the research beyond the scope of the paper by suggesting potential future research directions or discussing the broader implications of the findings. This type of conclusion is often used in more theoretical or exploratory research papers.
Align your conclusion’s tone with the rest of your research paper. Start Writing with Paperpal Now!
The conclusion in a research paper serves several important purposes:
- Offers Implications and Recommendations : Your research paper conclusion is an excellent place to discuss the broader implications of your research and suggest potential areas for further study. It’s also an opportunity to offer practical recommendations based on your findings.
- Provides Closure : A good research paper conclusion provides a sense of closure to your paper. It should leave the reader with a feeling that they have reached the end of a well-structured and thought-provoking research project.
- Leaves a Lasting Impression : Writing a well-crafted research paper conclusion leaves a lasting impression on your readers. It’s your final opportunity to leave them with a new idea, a call to action, or a memorable quote.

Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper is essential to leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here’s a step-by-step process to help you create and know what to put in the conclusion of a research paper: 2
- Research Statement : Begin your research paper conclusion by restating your research statement. This reminds the reader of the main point you’ve been trying to prove throughout your paper. Keep it concise and clear.
- Key Points : Summarize the main arguments and key points you’ve made in your paper. Avoid introducing new information in the research paper conclusion. Instead, provide a concise overview of what you’ve discussed in the body of your paper.
- Address the Research Questions : If your research paper is based on specific research questions or hypotheses, briefly address whether you’ve answered them or achieved your research goals. Discuss the significance of your findings in this context.
- Significance : Highlight the importance of your research and its relevance in the broader context. Explain why your findings matter and how they contribute to the existing knowledge in your field.
- Implications : Explore the practical or theoretical implications of your research. How might your findings impact future research, policy, or real-world applications? Consider the “so what?” question.
- Future Research : Offer suggestions for future research in your area. What questions or aspects remain unanswered or warrant further investigation? This shows that your work opens the door for future exploration.
- Closing Thought : Conclude your research paper conclusion with a thought-provoking or memorable statement. This can leave a lasting impression on your readers and wrap up your paper effectively. Avoid introducing new information or arguments here.
- Proofread and Revise : Carefully proofread your conclusion for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Ensure that your ideas flow smoothly and that your conclusion is coherent and well-structured.
Write your research paper conclusion 2x faster with Paperpal. Try it now!
Remember that a well-crafted research paper conclusion is a reflection of the strength of your research and your ability to communicate its significance effectively. It should leave a lasting impression on your readers and tie together all the threads of your paper. Now you know how to start the conclusion of a research paper and what elements to include to make it impactful, let’s look at a research paper conclusion sample.

How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
A research paper conclusion is not just a summary of your study, but a synthesis of the key findings that ties the research together and places it in a broader context. A research paper conclusion should be concise, typically around one paragraph in length. However, some complex topics may require a longer conclusion to ensure the reader is left with a clear understanding of the study’s significance. Paperpal, an AI writing assistant trusted by over 800,000 academics globally, can help you write a well-structured conclusion for your research paper.
- Sign Up or Log In: Create a new Paperpal account or login with your details.
- Navigate to Features : Once logged in, head over to the features’ side navigation pane. Click on Templates and you’ll find a suite of generative AI features to help you write better, faster.
- Generate an outline: Under Templates, select ‘Outlines’. Choose ‘Research article’ as your document type.
- Select your section: Since you’re focusing on the conclusion, select this section when prompted.
- Choose your field of study: Identifying your field of study allows Paperpal to provide more targeted suggestions, ensuring the relevance of your conclusion to your specific area of research.
- Provide a brief description of your study: Enter details about your research topic and findings. This information helps Paperpal generate a tailored outline that aligns with your paper’s content.
- Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on ‘generate’. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline.
- Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion. The outline serves as a guide, ensuring you cover all critical aspects of a strong conclusion, from summarizing key findings to highlighting the research’s implications.
- Refine and enhance: Paperpal’s ‘Make Academic’ feature can be particularly useful in the final stages. Select any paragraph of your conclusion and use this feature to elevate the academic tone, ensuring your writing is aligned to the academic journal standards.
By following these steps, Paperpal not only simplifies the process of writing a research paper conclusion but also ensures it is impactful, concise, and aligned with academic standards. Sign up with Paperpal today and write your research paper conclusion 2x faster .
The research paper conclusion is a crucial part of your paper as it provides the final opportunity to leave a strong impression on your readers. In the research paper conclusion, summarize the main points of your research paper by restating your research statement, highlighting the most important findings, addressing the research questions or objectives, explaining the broader context of the study, discussing the significance of your findings, providing recommendations if applicable, and emphasizing the takeaway message. The main purpose of the conclusion is to remind the reader of the main point or argument of your paper and to provide a clear and concise summary of the key findings and their implications. All these elements should feature on your list of what to put in the conclusion of a research paper to create a strong final statement for your work.
A strong conclusion is a critical component of a research paper, as it provides an opportunity to wrap up your arguments, reiterate your main points, and leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here are the key elements of a strong research paper conclusion: 1. Conciseness : A research paper conclusion should be concise and to the point. It should not introduce new information or ideas that were not discussed in the body of the paper. 2. Summarization : The research paper conclusion should be comprehensive enough to give the reader a clear understanding of the research’s main contributions. 3 . Relevance : Ensure that the information included in the research paper conclusion is directly relevant to the research paper’s main topic and objectives; avoid unnecessary details. 4 . Connection to the Introduction : A well-structured research paper conclusion often revisits the key points made in the introduction and shows how the research has addressed the initial questions or objectives. 5. Emphasis : Highlight the significance and implications of your research. Why is your study important? What are the broader implications or applications of your findings? 6 . Call to Action : Include a call to action or a recommendation for future research or action based on your findings.
The length of a research paper conclusion can vary depending on several factors, including the overall length of the paper, the complexity of the research, and the specific journal requirements. While there is no strict rule for the length of a conclusion, but it’s generally advisable to keep it relatively short. A typical research paper conclusion might be around 5-10% of the paper’s total length. For example, if your paper is 10 pages long, the conclusion might be roughly half a page to one page in length.
In general, you do not need to include citations in the research paper conclusion. Citations are typically reserved for the body of the paper to support your arguments and provide evidence for your claims. However, there may be some exceptions to this rule: 1. If you are drawing a direct quote or paraphrasing a specific source in your research paper conclusion, you should include a citation to give proper credit to the original author. 2. If your conclusion refers to or discusses specific research, data, or sources that are crucial to the overall argument, citations can be included to reinforce your conclusion’s validity.
The conclusion of a research paper serves several important purposes: 1. Summarize the Key Points 2. Reinforce the Main Argument 3. Provide Closure 4. Offer Insights or Implications 5. Engage the Reader. 6. Reflect on Limitations
Remember that the primary purpose of the research paper conclusion is to leave a lasting impression on the reader, reinforcing the key points and providing closure to your research. It’s often the last part of the paper that the reader will see, so it should be strong and well-crafted.
- Makar, G., Foltz, C., Lendner, M., & Vaccaro, A. R. (2018). How to write effective discussion and conclusion sections. Clinical spine surgery, 31(8), 345-346.
- Bunton, D. (2005). The structure of PhD conclusion chapters. Journal of English for academic purposes , 4 (3), 207-224.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- Paraphrasing in Academic Writing: Answering Top Author Queries
Preflight For Editorial Desk: The Perfect Hybrid (AI + Human) Assistance Against Compromised Manuscripts
You may also like, what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how..., 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Conclusion
Definition:
A research paper conclusion is the final section of a research paper that summarizes the key findings, significance, and implications of the research. It is the writer’s opportunity to synthesize the information presented in the paper, draw conclusions, and make recommendations for future research or actions.
The conclusion should provide a clear and concise summary of the research paper, reiterating the research question or problem, the main results, and the significance of the findings. It should also discuss the limitations of the study and suggest areas for further research.
Parts of Research Paper Conclusion
The parts of a research paper conclusion typically include:
Restatement of the Thesis
The conclusion should begin by restating the thesis statement from the introduction in a different way. This helps to remind the reader of the main argument or purpose of the research.
Summary of Key Findings
The conclusion should summarize the main findings of the research, highlighting the most important results and conclusions. This section should be brief and to the point.
Implications and Significance
In this section, the researcher should explain the implications and significance of the research findings. This may include discussing the potential impact on the field or industry, highlighting new insights or knowledge gained, or pointing out areas for future research.
Limitations and Recommendations
It is important to acknowledge any limitations or weaknesses of the research and to make recommendations for how these could be addressed in future studies. This shows that the researcher is aware of the potential limitations of their work and is committed to improving the quality of research in their field.
Concluding Statement
The conclusion should end with a strong concluding statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. This could be a call to action, a recommendation for further research, or a final thought on the topic.
How to Write Research Paper Conclusion
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion:
- Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study.
- Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results of your research. This can be done by highlighting the most important aspects of your research and the evidence that supports them.
- Discuss the implications: Discuss the implications of your findings for the research area and any potential applications of your research. You should also mention any limitations of your research that may affect the interpretation of your findings.
- Provide a conclusion : Provide a concise conclusion that summarizes the main points of your paper and emphasizes the significance of your research. This should be a strong and clear statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
- Offer suggestions for future research: Lastly, offer suggestions for future research that could build on your findings and contribute to further advancements in the field.
Remember that the conclusion should be brief and to the point, while still effectively summarizing the key findings and implications of your research.
Example of Research Paper Conclusion
Here’s an example of a research paper conclusion:
Conclusion :
In conclusion, our study aimed to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students. Our findings suggest that there is a significant association between social media use and increased levels of anxiety and depression among college students. This highlights the need for increased awareness and education about the potential negative effects of social media use on mental health, particularly among college students.
Despite the limitations of our study, such as the small sample size and self-reported data, our findings have important implications for future research and practice. Future studies should aim to replicate our findings in larger, more diverse samples, and investigate the potential mechanisms underlying the association between social media use and mental health. In addition, interventions should be developed to promote healthy social media use among college students, such as mindfulness-based approaches and social media detox programs.
Overall, our study contributes to the growing body of research on the impact of social media on mental health, and highlights the importance of addressing this issue in the context of higher education. By raising awareness and promoting healthy social media use among college students, we can help to reduce the negative impact of social media on mental health and improve the well-being of young adults.
Purpose of Research Paper Conclusion
The purpose of a research paper conclusion is to provide a summary and synthesis of the key findings, significance, and implications of the research presented in the paper. The conclusion serves as the final opportunity for the writer to convey their message and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
The conclusion should restate the research problem or question, summarize the main results of the research, and explain their significance. It should also acknowledge the limitations of the study and suggest areas for future research or action.
Overall, the purpose of the conclusion is to provide a sense of closure to the research paper and to emphasize the importance of the research and its potential impact. It should leave the reader with a clear understanding of the main findings and why they matter. The conclusion serves as the writer’s opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
When to Write Research Paper Conclusion
The conclusion of a research paper should be written after the body of the paper has been completed. It should not be written until the writer has thoroughly analyzed and interpreted their findings and has written a complete and cohesive discussion of the research.
Before writing the conclusion, the writer should review their research paper and consider the key points that they want to convey to the reader. They should also review the research question, hypotheses, and methodology to ensure that they have addressed all of the necessary components of the research.
Once the writer has a clear understanding of the main findings and their significance, they can begin writing the conclusion. The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, and should reiterate the main points of the research while also providing insights and recommendations for future research or action.
Characteristics of Research Paper Conclusion
The characteristics of a research paper conclusion include:
- Clear and concise: The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, summarizing the key findings and their significance.
- Comprehensive: The conclusion should address all of the main points of the research paper, including the research question or problem, the methodology, the main results, and their implications.
- Future-oriented : The conclusion should provide insights and recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the research.
- Impressive : The conclusion should leave a lasting impression on the reader, emphasizing the importance of the research and its potential impact.
- Objective : The conclusion should be based on the evidence presented in the research paper, and should avoid personal biases or opinions.
- Unique : The conclusion should be unique to the research paper and should not simply repeat information from the introduction or body of the paper.
Advantages of Research Paper Conclusion
The advantages of a research paper conclusion include:
- Summarizing the key findings : The conclusion provides a summary of the main findings of the research, making it easier for the reader to understand the key points of the study.
- Emphasizing the significance of the research: The conclusion emphasizes the importance of the research and its potential impact, making it more likely that readers will take the research seriously and consider its implications.
- Providing recommendations for future research or action : The conclusion suggests practical recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the study.
- Providing closure to the research paper : The conclusion provides a sense of closure to the research paper, tying together the different sections of the paper and leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
- Demonstrating the writer’s contribution to the field : The conclusion provides the writer with an opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
Limitations of Research Paper Conclusion
While the conclusion of a research paper has many advantages, it also has some limitations that should be considered, including:
- I nability to address all aspects of the research: Due to the limited space available in the conclusion, it may not be possible to address all aspects of the research in detail.
- Subjectivity : While the conclusion should be objective, it may be influenced by the writer’s personal biases or opinions.
- Lack of new information: The conclusion should not introduce new information that has not been discussed in the body of the research paper.
- Lack of generalizability: The conclusions drawn from the research may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, limiting the generalizability of the study.
- Misinterpretation by the reader: The reader may misinterpret the conclusions drawn from the research, leading to a misunderstanding of the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
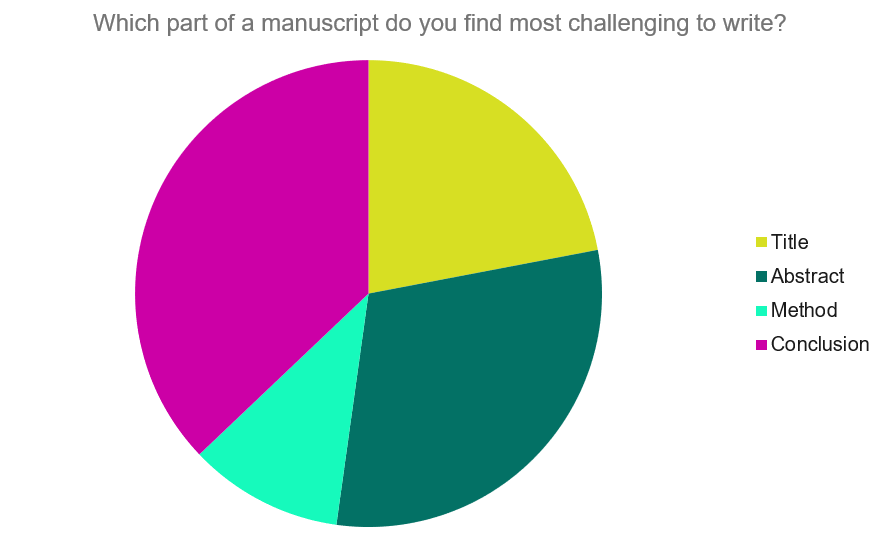
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
How to structure a discussion
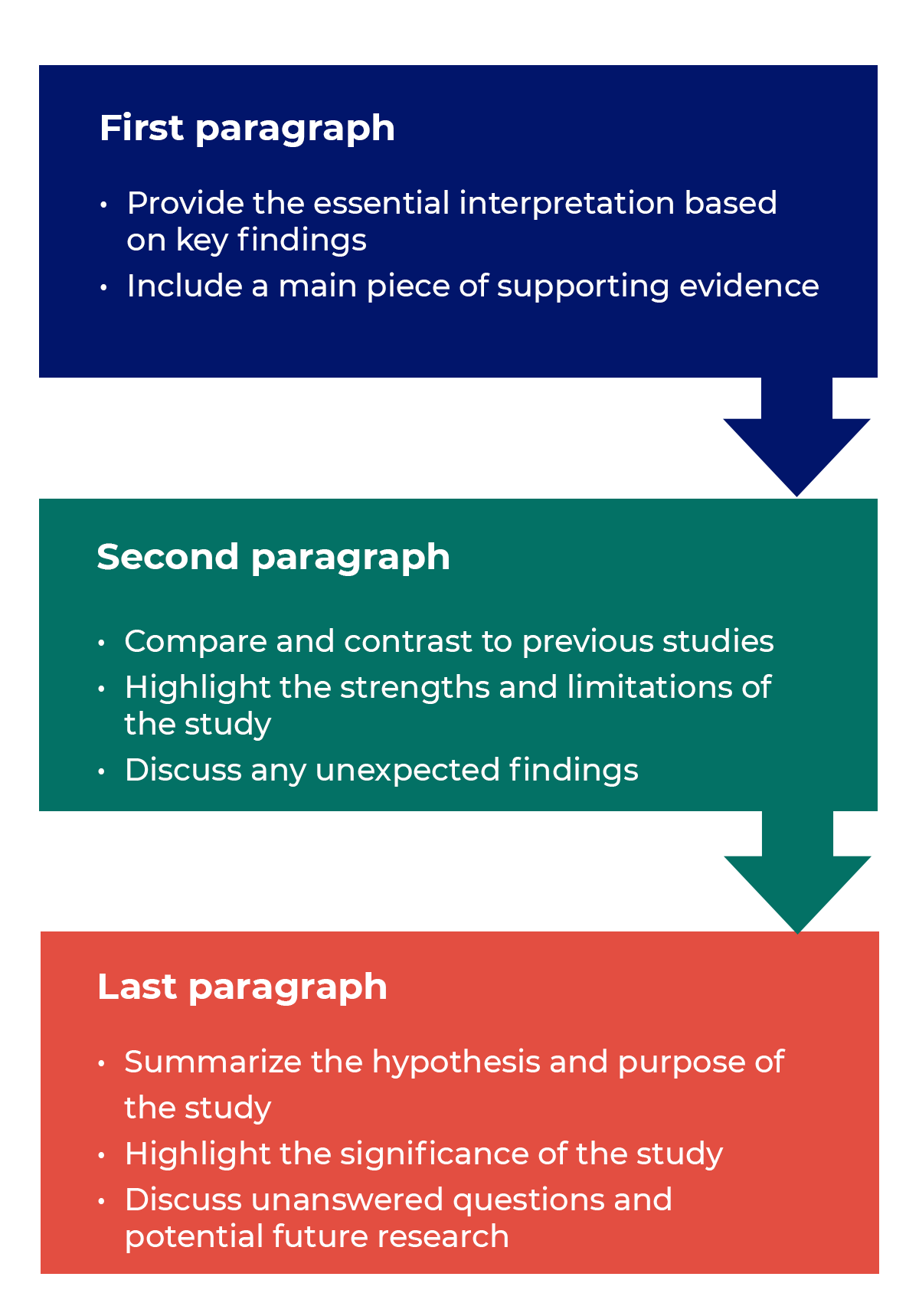
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research. For most college-level research papers, one or two well-developed paragraphs is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, more paragraphs may be required in summarizing key findings and their significance.
Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides you with important opportunities to demonstrate to the reader your understanding of the research problem. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key findings in your analysis that advance new understanding about the research problem, that are unusual or unexpected, or that have important implications applied to practice.
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger significance of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly re-emphasize the "So What?" question by placing the study within the context of how your research advances past research about the topic.
- Identifying how a gap in the literature has been addressed . The conclusion can be where you describe how a previously identified gap in the literature [described in your literature review section] has been filled by your research.
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers you the opportunity to elaborate on the impact and significance of your findings. This is particularly important if your study approached examining the research problem from an unusual or innovative perspective.
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information [which should be avoided], but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing or contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study.
Bunton, David. “The Structure of PhD Conclusion Chapters.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 4 (July 2005): 207–224; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
The function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of the strengths of your main argument(s) and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Do this by stating clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem you investigated in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found in the literature. Make sure, however, that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings. This reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your essay.
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- Present your conclusions in clear, simple language. Re-state the purpose of your study, then describe how your findings differ or support those of other studies and why [i.e., what were the unique or new contributions your study made to the overall research about your topic?].
- Do not simply reiterate your findings or the discussion of your results. Provide a synthesis of arguments presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem and the overall objectives of your study.
- Indicate opportunities for future research if you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper. Highlighting the need for further research provides the reader with evidence that you have an in-depth awareness of the research problem and that further investigations should take place.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is presented well:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data.
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate the research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have conducted will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way.
NOTE : If asked to think introspectively about the topics, do not delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply, not to guess at possible outcomes or make up scenarios not supported by the evidence.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Although an effective conclusion needs to be clear and succinct, it does not need to be written passively or lack a compelling narrative. Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following strategies:
- If your essay deals with a critical, contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem proactively.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action that, if adopted, could address a specific problem in practice or in the development of new knowledge.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion already noted in your paper in order to lend authority and support to the conclusion(s) you have reached [a good place to look is research from your literature review].
- Explain the consequences of your research in a way that elicits action or demonstrates urgency in seeking change.
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to emphasize the most important finding of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point by drawing from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you presented in your introduction, but add further insight derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results to recast it in new or important ways.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a succinct, declarative statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid
Failure to be concise Your conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too lengthy often have unnecessary information in them. The conclusion is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, and other forms of analysis that you make. Strategies for writing concisely can be found here .
Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from the general [the field of study] to the specific [the research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move from a specific discussion [your research problem] back to a general discussion [i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In short, the conclusion is where you should place your research within a larger context [visualize your paper as an hourglass--start with a broad introduction and review of the literature, move to the specific analysis and discussion, conclude with a broad summary of the study's implications and significance].
Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. These are problems, deficiencies, or challenges encountered during your study should be summarized as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative or unintended results [i.e., findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section and discuss their implications in the discussion section of your paper. In the conclusion, use your summary of the negative results as an opportunity to explain their possible significance and/or how they may form the basis for future research.
Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to be able to discuss how your research fits within your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize briefly and succinctly how it contributes to new knowledge or a new understanding about the research problem. This element of your conclusion may be only a few sentences long.
Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives in the social sciences change while the research is being carried out. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine the original objectives in your introduction. As these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you presumably should know a good deal about it [perhaps even more than your professor!]. Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches that...." The overall tone of your conclusion should convey confidence to the reader.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin Madison; Miquel, Fuster-Marquez and Carmen Gregori-Signes. “Chapter Six: ‘Last but Not Least:’ Writing the Conclusion of Your Paper.” In Writing an Applied Linguistics Thesis or Dissertation: A Guide to Presenting Empirical Research . John Bitchener, editor. (Basingstoke,UK: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), pp. 93-105; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining to read, when an essay is about to end. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper and, as such, the conclusion rarely has citations to sources. If you have new information to present, add it to the discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no actual new information is introduced, the conclusion, along with the discussion section, is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; the conclusion is where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate that you understand the material that you’ve presented, and locate your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic, including describing how your research contributes new insights or valuable insight to that scholarship.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 10:40 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
In a short paper—even a research paper—you don’t need to provide an exhaustive summary as part of your conclusion. But you do need to make some kind of transition between your final body paragraph and your concluding paragraph. This may come in the form of a few sentences of summary. Or it may come in the form of a sentence that brings your readers back to your thesis or main idea and reminds your readers where you began and how far you have traveled.
So, for example, in a paper about the relationship between ADHD and rejection sensitivity, Vanessa Roser begins by introducing readers to the fact that researchers have studied the relationship between the two conditions and then provides her explanation of that relationship. Here’s her thesis: “While socialization may indeed be an important factor in RS, I argue that individuals with ADHD may also possess a neurological predisposition to RS that is exacerbated by the differing executive and emotional regulation characteristic of ADHD.”
In her final paragraph, Roser reminds us of where she started by echoing her thesis: “This literature demonstrates that, as with many other conditions, ADHD and RS share a delicately intertwined pattern of neurological similarities that is rooted in the innate biology of an individual’s mind, a connection that cannot be explained in full by the behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
Highlight the “so what”
At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what’s at stake—why they should care about the argument you’re making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put those stakes into a new or broader context.
In the conclusion to her paper about ADHD and RS, Roser echoes the stakes she established in her introduction—that research into connections between ADHD and RS has led to contradictory results, raising questions about the “behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
She writes, “as with many other conditions, ADHD and RS share a delicately intertwined pattern of neurological similarities that is rooted in the innate biology of an individual’s mind, a connection that cannot be explained in full by the behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
Leave your readers with the “now what”
After the “what” and the “so what,” you should leave your reader with some final thoughts. If you have written a strong introduction, your readers will know why you have been arguing what you have been arguing—and why they should care. And if you’ve made a good case for your thesis, then your readers should be in a position to see things in a new way, understand new questions, or be ready for something that they weren’t ready for before they read your paper.
In her conclusion, Roser offers two “now what” statements. First, she explains that it is important to recognize that the flawed behavioral mediation hypothesis “seems to place a degree of fault on the individual. It implies that individuals with ADHD must have elicited such frequent or intense rejection by virtue of their inadequate social skills, erasing the possibility that they may simply possess a natural sensitivity to emotion.” She then highlights the broader implications for treatment of people with ADHD, noting that recognizing the actual connection between rejection sensitivity and ADHD “has profound implications for understanding how individuals with ADHD might best be treated in educational settings, by counselors, family, peers, or even society as a whole.”
To find your own “now what” for your essay’s conclusion, try asking yourself these questions:
- What can my readers now understand, see in a new light, or grapple with that they would not have understood in the same way before reading my paper? Are we a step closer to understanding a larger phenomenon or to understanding why what was at stake is so important?
- What questions can I now raise that would not have made sense at the beginning of my paper? Questions for further research? Other ways that this topic could be approached?
- Are there other applications for my research? Could my questions be asked about different data in a different context? Could I use my methods to answer a different question?
- What action should be taken in light of this argument? What action do I predict will be taken or could lead to a solution?
- What larger context might my argument be a part of?
What to avoid in your conclusion
- a complete restatement of all that you have said in your paper.
- a substantial counterargument that you do not have space to refute; you should introduce counterarguments before your conclusion.
- an apology for what you have not said. If you need to explain the scope of your paper, you should do this sooner—but don’t apologize for what you have not discussed in your paper.
- fake transitions like “in conclusion” that are followed by sentences that aren’t actually conclusions. (“In conclusion, I have now demonstrated that my thesis is correct.”)
- picture_as_pdf Conclusions
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

3-minute read
- 29th August 2023
If you’re writing a research paper, the conclusion is your opportunity to summarize your findings and leave a lasting impression on your readers. In this post, we’ll take you through how to write an effective conclusion for a research paper and how you can:
· Reword your thesis statement
· Highlight the significance of your research
· Discuss limitations
· Connect to the introduction
· End with a thought-provoking statement
Rewording Your Thesis Statement
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a way that is slightly different from the wording used in the introduction. Avoid presenting new information or evidence in your conclusion. Just summarize the main points and arguments of your essay and keep this part as concise as possible. Remember that you’ve already covered the in-depth analyses and investigations in the main body paragraphs of your essay, so it’s not necessary to restate these details in the conclusion.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Highlighting the Significance of Your Research
The conclusion is a good place to emphasize the implications of your research . Avoid ambiguous or vague language such as “I think” or “maybe,” which could weaken your position. Clearly explain why your research is significant and how it contributes to the broader field of study.
Here’s an example from a (fictional) study on the impact of social media on mental health:
Discussing Limitations
Although it’s important to emphasize the significance of your study, you can also use the conclusion to briefly address any limitations you discovered while conducting your research, such as time constraints or a shortage of resources. Doing this demonstrates a balanced and honest approach to your research.
Connecting to the Introduction
In your conclusion, you can circle back to your introduction , perhaps by referring to a quote or anecdote you discussed earlier. If you end your paper on a similar note to how you began it, you will create a sense of cohesion for the reader and remind them of the meaning and significance of your research.
Ending With a Thought-Provoking Statement
Consider ending your paper with a thought-provoking and memorable statement that relates to the impact of your research questions or hypothesis. This statement can be a call to action, a philosophical question, or a prediction for the future (positive or negative). Here’s an example that uses the same topic as above (social media and mental health):
Expert Proofreading Services
Ensure that your essay ends on a high note by having our experts proofread your research paper. Our team has experience with a wide variety of academic fields and subjects and can help make your paper stand out from the crowd – get started today and see the difference it can make in your work.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

OASIS: Writing Center
Writing a paper: conclusions, writing a conclusion.
A conclusion is an important part of the paper; it provides closure for the reader while reminding the reader of the contents and importance of the paper. It accomplishes this by stepping back from the specifics in order to view the bigger picture of the document. In other words, it is reminding the reader of the main argument. For most course papers, it is usually one paragraph that simply and succinctly restates the main ideas and arguments, pulling everything together to help clarify the thesis of the paper. A conclusion does not introduce new ideas; instead, it should clarify the intent and importance of the paper. It can also suggest possible future research on the topic.
An Easy Checklist for Writing a Conclusion
It is important to remind the reader of the thesis of the paper so he is reminded of the argument and solutions you proposed.
Think of the main points as puzzle pieces, and the conclusion is where they all fit together to create a bigger picture. The reader should walk away with the bigger picture in mind.
Make sure that the paper places its findings in the context of real social change.
Make sure the reader has a distinct sense that the paper has come to an end. It is important to not leave the reader hanging. (You don’t want her to have flip-the-page syndrome, where the reader turns the page, expecting the paper to continue. The paper should naturally come to an end.)
No new ideas should be introduced in the conclusion. It is simply a review of the material that is already present in the paper. The only new idea would be the suggesting of a direction for future research.
Conclusion Example
As addressed in my analysis of recent research, the advantages of a later starting time for high school students significantly outweigh the disadvantages. A later starting time would allow teens more time to sleep--something that is important for their physical and mental health--and ultimately improve their academic performance and behavior. The added transportation costs that result from this change can be absorbed through energy savings. The beneficial effects on the students’ academic performance and behavior validate this decision, but its effect on student motivation is still unknown. I would encourage an in-depth look at the reactions of students to such a change. This sort of study would help determine the actual effects of a later start time on the time management and sleep habits of students.
Related Webinar
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Previous Page: Thesis Statements
- Next Page: Writer's Block
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
- Posted on May 12, 2023
The key to an impactful research paper is crafting an effective conclusion. The conclusion provides a final opportunity to make a lasting impression on the reader by providing a powerful summary of the main argument and key findings.
A well-written conclusion not only summarizes your research but also ties everything back to your thesis statement. Plus, it provides important takeaways for your reader, highlighting what they should remember from your research and how it contributes to the larger academic discourse.
Crafting an impactful conclusion can be tricky, especially in argumentative papers. However, with our expert tips and tricks, you can rest assured that your conclusion will effectively restate the main argument and thesis statement in a way that resonates with your audience and elevates your research to new heights.
Why is a Conclusion Necessary for a Research Paper?
The conclusion of a research paper is essential in tying together the different parts of the paper and offering a final perspective on the topic. It reinforces the main idea or argument presented and summarizes the key points and findings of the research, highlighting its significance.
Additionally, the conclusion creates a full circle of the research by connecting back to the thesis statement presented at the paper’s beginning. It provides an opportunity to showcase the writer’s critical thinking skills by demonstrating how the research supports the main argument.
The conclusion is essential for a research paper because it provides closure for the reader. It serves as a final destination that helps the reader understand how all the different pieces of information fit together to support the main argument presented. It also offers insights into how the research can inform future studies and contribute to the larger academic discourse.
It also ensures that the reader does not get lost in the vast amount of information presented in the paper by providing a concise and coherent summary of the entire research. Additionally, it helps the reader identify the paper’s main takeaway and understand how the research contributes to the larger body of knowledge in the field.
Leave a Lasting Impression
A well-crafted conclusion is an essential element of any research paper. Its purpose is to leave a lasting impression on the reader and tie together the different parts of the paper.
To achieve this goal, a conclusion should summarize the main points and highlight the key findings of the research. By doing so, the reader can easily understand the focus and significance of the study.
A strong conclusion should also discuss any important findings that can be applied in the real world. This practical perspective gives readers a better sense of the impact and relevance of the research.
Summarize Your Thoughts
The conclusion of a research paper should be concise and provide a summary of the writer’s thoughts and ideas about the research.
It should go beyond simply restating the main points and findings and address the “so what” of the research by explaining how it contributes to the existing body of knowledge on the same topic. This way, the conclusion can give readers a better understanding of the research’s significance and relevance to the broader academic community.
Demonstrate How Important Your Idea Is
Moving beyond a superficial overview and delving into the research in-depth is crucial to create a compelling conclusion. This entails summarizing the key findings of the study, highlighting its main contributions to the field, and placing the results in a broader context. Additionally, it would help if you comprehensively analyzed your work and its implications, underscoring its value to the broader academic community.
New Insights
The conclusion section of a research paper offers an opportunity for the writer to present new insights and approaches to addressing the research problem.
Whether the research outcome is positive or negative, the conclusion provides a platform to discuss practical implications beyond the scope of the research paper. This discussion can help readers understand the potential impact of the research on the broader field and its significance for future research endeavors.
How to Write a Killer Conclusion with Key Points
When writing a conclusion for a research paper, it is important to cover several key points to create a solid and effective conclusion.
Restate the Thesis
When crafting a conclusion, restating the thesis statement is an important step that reminds readers of the research paper’s central focus. However, it should not be a verbatim repetition of the introduction.
By restating the thesis concisely and clearly, you can effectively tie together the main ideas discussed in the body of the paper and emphasize the significance of the research question. However, keep in mind that the restated thesis should capture the essence of the paper and leave the reader with a clear understanding of the main topic and its importance.
Summarize the Main Points
To write an impactful conclusion, summarizing the main points discussed in the body of the paper is essential. This final section provides the writer with a last opportunity to highlight the significance of their research findings.
However, it is equally important to avoid reiterating information already discussed in the body of the paper. Instead, you should synthesize and summarize the most significant points to emphasize the key findings. By doing so, the conclusion can effectively tie together the research findings and provide a clear understanding of the importance of the research topic.
Discuss the Results or Findings
The next step is to discuss the results or findings of the research. The discussion of the results or findings should not simply be a repetition of the information presented in the body of the paper.
Instead, it should provide a more in-depth analysis of the significance of the findings. This can involve explaining why the findings are important, what they mean in the context of the research question, and how they contribute to the field or area of study.
Additionally, it’s crucial to address any limitations or weaknesses of the study in this section. This can provide a more balanced and nuanced understanding of the research and its implications. By doing so, the reader will have a better understanding of the scope and context of the study, which can ultimately enhance the credibility and validity of the research.
Ruminate on Your Thoughts
The final step to crafting an effective conclusion is to ruminate on your thoughts. This provides an opportunity to reflect on the meaning of the research and leaves the reader with something to ponder. Remember, the concluding paragraph should not introduce new information but rather summarize and reflect on the critical points made in the paper.
Furthermore, the conclusion should be integrated into the paper rather than presented as a separate section. It should provide a concise overview of the main findings and suggest avenues for further research.
Different Types of Conclusions
There are various types of conclusions that can be employed to conclude a research paper effectively, depending on the research questions and topic being investigated.
Summarizing
Summarizing conclusions are frequently used to wrap up a research paper effectively. They restate the thesis statement and provide a brief overview of the main findings and outcomes of the research. This type of conclusion serves as a reminder to the reader of the key points discussed throughout the paper and emphasizes the significance of the research topic.
To be effective, summarizing conclusions should be concise and to the point, avoiding any new information not previously discussed in the body of the paper. Moreover, they are particularly useful when there is a clear and direct answer to the research question. This allows you to summarize your findings succinctly and leave the reader with a clear understanding of the implications of the research.
Externalizing
On the opposite end of the spectrum are externalizing conclusions. Unlike summarizing conclusions, externalizing conclusions introduce new ideas that may not be directly related to the research findings. This type of conclusion can be beneficial because it broadens the scope of the research topic and can lead to new insights and directions for future research.
By presenting new ideas, externalizing conclusions can challenge conventional thinking in the field and open up new avenues for exploration. This approach is instrumental in fields where research is ongoing, and new ideas and approaches are constantly being developed.
Editorial conclusions are a type of conclusion that allows the writer to express their commentary on the research findings. They can be particularly effective in connecting the writer’s insights with the research conducted and can offer a unique perspective on the research topic. Adding a personal touch to the conclusion can help engage the reader and leave a lasting impression.
Remember that regardless of the type of conclusion you choose, it should always start with a clear and concise restatement of the thesis statement, followed by a summary of the main findings in the body paragraphs. The first sentence of the conclusion should be impactful and attention-grabbing to make a strong impression on the reader.
What to Avoid in Your Conclusion
When crafting your conclusion, it’s essential to keep in mind several key points to ensure that it is effective and well-received by your audience:
- Avoid introducing new ideas or topics that have not been covered in the body of your paper.
- Refrain from simply restating what has already been said in your paper without adding new insights or analysis.
- Do not apologize for any shortcomings or limitations of your research, as this can undermine the importance of your findings.
- Avoid using overly emotional or flowery language, as it can detract from the professionalism and objectivity of the research.
- Lastly, avoid any examples of plagiarism. Be sure to properly cite any sources you have used in your research and writing.
Example of a Bad Conclusion
- Recapitulation without Insight: In conclusion, this paper has discussed the importance of exercise for physical and mental health. We hope this paper has been helpful to you and encourages you to start exercising today.
- Introduction of New Ideas: In conclusion, we have discussed the benefits of exercise and how it can improve physical and mental health. Additionally, we have highlighted the benefits of a plant-based diet and the importance of getting enough sleep for overall well-being.
- Emotional Language: In conclusion, exercise is good for your body and mind, and you should definitely start working out today!
Example of a Good Conclusion
- Insights and Implications: In light of our investigation, it is evident that regular exercise is undeniably beneficial for both physical and mental well-being, especially if performed at an appropriate duration and frequency. These findings hold significant implications for public health policies and personal wellness decisions.
- Limitations and Future Directions: While our investigation has shed light on the benefits of exercise, our study is not without limitations. Future research can delve deeper into the long-term effects of exercise on mental health and explore the impact of exercise on specific populations, such as older adults or individuals with chronic health conditions.
- Call to Action: In conclusion, we urge individuals to prioritize exercise as a critical component of their daily routine. By making exercise a habit, we can reap the many benefits of a healthy and active lifestyle.
Final Thoughts
When writing a research paper, the conclusion is one of the most crucial elements to leave a lasting impression on the reader. It should effectively summarize the research and provide valuable insights, leaving the reader with something to ponder.
To accomplish this, it is essential to include vital elements, such as restating the thesis , summarizing the main points, and discussing the findings. However, it is equally important to avoid common mistakes that can undermine the effectiveness of the conclusion, such as introducing new information or repeating the introduction.
So to ensure that your research is of the highest quality, it’s crucial to use proper citations and conduct a thorough literature review. Additionally, it is crucial to proofread the work to eliminate any errors.
Fortunately, there are many available resources to help you with both writing and plagiarism prevention. Quetext , for example, offers a plagiarism checker, citation assistance, and proofreading tools to ensure the writing is top-notch. By incorporating these tips and using available resources, you can create a compelling and memorable conclusion for readers.
Sign Up for Quetext Today!
Click below to find a pricing plan that fits your needs.
You May Also Like

Can You Go to Jail for Plagiarism?
- Posted on March 22, 2024 March 22, 2024

Empowering Educators: How AI Detection Enhances Teachers’ Workload
- Posted on March 14, 2024

The Ethical Dimension | Navigating the Challenges of AI Detection in Education
- Posted on March 8, 2024

How to Write a Thesis Statement & Essay Outline
- Posted on February 29, 2024 February 29, 2024

The Crucial Role of Grammar and Spell Check in Student Assignments
- Posted on February 23, 2024 February 23, 2024

Revolutionizing Education: The Role of AI Detection in Academic Integrity
- Posted on February 15, 2024

How Reliable are AI Content Detectors? Which is Most Reliable?
- Posted on February 8, 2024 February 8, 2024

What Is an Article Spinner?
- Posted on February 2, 2024 February 2, 2024
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

Table of Contents
Writing a conclusion for a research paper is a critical step that often determines the overall impact and impression the paper leaves on the reader. While some may view the conclusion as a mere formality, it is actually an opportunity to wrap up the main points, provide closure, and leave a lasting impression. In this article, we will explore the importance of a well-crafted conclusion and discuss various tips and strategies to help you write an engaging and impactful conclusion for your research paper.
Introduction
Before delving into the specifics of writing a conclusion, it is important to understand why it is such a crucial component of a research paper. The conclusion serves to summarize the main points of the paper and reemphasize their significance. A well-written conclusion can leave the reader satisfied and inspired, while a poorly executed one may undermine the credibility of the entire paper. Therefore, it is essential to give careful thought and attention to crafting an effective conclusion.
When writing a research paper, the conclusion acts as the final destination for the reader. It is the point where all the information, arguments, and evidence presented throughout the paper converge. Just as a traveler reaches the end of a journey, the reader reaches the conclusion to find closure and a sense of fulfillment. This is why the conclusion should not be taken lightly; it is a critical opportunity to leave a lasting impact on the reader.
Moreover, the conclusion is not merely a repetition of the introduction or a summary of the main points. It goes beyond that by providing a deeper understanding of the research findings and their implications. It allows the writer to reflect on the significance of their work and its potential contributions to the field. By doing so, the conclusion elevates the research paper from a mere collection of facts to a thought-provoking piece of scholarship.
In the following sections, we will explore various strategies and techniques for crafting a compelling conclusion. By understanding the importance of the conclusion and learning how to write one effectively, you will be equipped to create impactful research papers.
Structuring the Conclusion
In order to create an effective conclusion, it is important to consider its structure. A well-structured conclusion should begin by restating the thesis statement and summarizing the main points of the paper. It should then move on to provide a concise synthesis of the key findings and arguments, highlighting their implications and relevance. Finally, the conclusion should end with a thought-provoking statement that leaves the reader with a lasting impression.
Additionally, using phrases like "this research demonstrates," "the findings show," or "it is clear that" can help to highlight the significance of your research and emphasize your main conclusions.
Tips for Writing an Engaging Conclusion
Writing an engaging conclusion requires careful consideration and attention to detail. Here are some tips to help you create an impactful conclusion for your research paper:
- Revisit the Introduction: Start your conclusion by referencing your introduction. Remind the reader of the research question or problem you initially posed and show how your research has addressed it.
- Summarize Your Main Points: Provide a concise summary of the main points and arguments presented in your paper. Be sure to restate your thesis statement and highlight the key findings.
- Offer a Fresh Perspective: Use the conclusion as an opportunity to provide a fresh perspective or offer insights that go beyond the main body of the paper. This will leave the reader with something new to consider.
- Leave a Lasting Impression: End your conclusion with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action. This will leave a lasting impression on the reader and encourage further exploration of the research topic.
Addressing Counter Arguments In Conclusion
While crafting your conclusion, you can address any potential counterarguments or limitations of your research. This will demonstrate that you have considered alternative perspectives and have taken them into account in your conclusions. By acknowledging potential counterarguments, you can strengthen the credibility and validity of your research. And by openly discussing limitations, you demonstrate transparency and honesty in your research process.
Language and Tone To Be Used In Conclusion
The language and tone of your conclusion play a crucial role in shaping the overall impression of your research paper. It is important to use clear and concise language that is appropriate for the academic context. Avoid using overly informal or colloquial language that may undermine the credibility of your research. Additionally, consider the tone of your conclusion – it should be professional, confident, and persuasive, while still maintaining a respectful and objective tone.
When it comes to the language used in your conclusion, precision is key. You want to ensure that your ideas are communicated effectively and that there is no room for misinterpretation. Using clear and concise language will not only make your conclusion easier to understand but will also demonstrate your command of the subject matter.
Furthermore, it is important to strike the right balance between formality and accessibility. While academic writing typically requires a more formal tone, you should still aim to make your conclusion accessible to a wider audience. This means avoiding jargon or technical terms that may confuse readers who are not familiar with the subject matter. Instead, opt for language that is clear and straightforward, allowing anyone to grasp the main points of your research.
Another aspect to consider is the tone of your conclusion. The tone should reflect the confidence you have in your research findings and the strength of your argument. By adopting a professional and confident tone, you are more likely to convince your readers of the validity and importance of your research. However, it is crucial to strike a balance and avoid sounding arrogant or dismissive of opposing viewpoints. Maintaining a respectful and objective tone will help you engage with your audience in a more persuasive manner.
Moreover, the tone of your conclusion should align with the overall tone of your research paper. Consistency in tone throughout your paper will create a cohesive and unified piece of writing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Writing a Conclusion
When writing a conclusion, there are several common mistakes that researchers often make. By being aware of these pitfalls, you can avoid them and create a more effective conclusion for your research paper. Some common mistakes include:
- Repeating the Introduction: A conclusion should not simply be a reworded version of the introduction. While it is important to revisit the main points, try to present them in a fresh and broader perspective, by foregrounding the implications/impacts of your research.
- Introducing New Information: The conclusion should not introduce any new information or arguments. Instead, it should focus on summarizing and synthesizing the main points presented in the paper.
- Being Vague or General: Avoid using vague or general statements in your conclusion. Instead, be specific and provide concrete examples or evidence to support your main points.
- Ending Abruptly: A conclusion should provide a sense of closure and completeness. Avoid ending your conclusion abruptly or leaving the reader with unanswered questions.
Editing and Revising the Conclusion
Just like the rest of your research paper, the conclusion should go through a thorough editing and revising process. This will help to ensure clarity, coherence, and impact in the conclusion. As you revise your conclusion, consider the following:
- Check for Consistency: Ensure that your conclusion aligns with the main body of the paper and does not introduce any new or contradictory information.
- Eliminate Redundancy: Remove any repetitive or redundant information in your conclusion. Instead, focus on presenting the key points in a concise and engaging manner.
- Proofread for Clarity: Read your conclusion aloud or ask someone else to read it to ensure that it is clear and understandable. Check for any grammatical or spelling errors that may distract the reader.
- Seek Feedback: Consider sharing your conclusion with peers or mentors to get their feedback and insights. This can help you strengthen your conclusion and make it more impactful.
How to Write Conclusion as a Call to Action
Finally, consider using your conclusion as a call to action. Encourage the reader to take further action, such as conducting additional research or considering the implications of your findings. By providing a clear call to action, you can inspire the reader to actively engage with your research and continue the conversation on the topic.
Adapting to Different Research Paper Types
It is important to adapt your conclusion approach based on the type of research paper you are writing. Different research paper types may require different strategies and approaches to writing the conclusion. For example, a scientific research paper may focus more on summarizing the key findings and implications, while a persuasive research paper may emphasize the call to action and the potential impact of the research. Tailor your conclusion to suit the specific goals and requirements of your research paper.
Final Thoughts
A well-crafted conclusion can leave a lasting impression on the reader and enhance the impact of your research. By following the tips and strategies outlined in this article, you can create an engaging and impactful conclusion that effectively summarizes your main points, addresses potential counterarguments, and leaves the reader with a sense of closure and inspiration. Embrace the importance of the conclusion and view it as an opportunity to showcase the significance and relevance of your research.
Important Reads
How To Humanize AI Text In Scientific Articles
Elevate Your Writing Game With AI Grammar Checker Tools
A Guide to Using AI Tools to Summarize Literature Reviews
AI for Essay Writing — Exploring Top 10 Essay Writers
Role of AI in Systematic Literature Review
You might also like

How To Write An Argumentative Essay

Beyond Google Scholar: Why SciSpace is the best alternative

Types of Literature Review — A Guide for Researchers

Join thousands of product people at Insight Out Conf on April 11. Register free.
Insights hub solutions
Analyze data
Uncover deep customer insights with fast, powerful features, store insights, curate and manage insights in one searchable platform, scale research, unlock the potential of customer insights at enterprise scale.
Featured reads
Tips and tricks

Make magic with your customer data in Dovetail

Four ways Dovetail helps Product Managers master continuous product discovery
Product updates
Dovetail retro: our biggest releases from the past year
Events and videos
© Dovetail Research Pty. Ltd.
How to write a strong conclusion for your research paper
Last updated
17 February 2024
Reviewed by
Writing a research paper is a chance to share your knowledge and hypothesis. It's an opportunity to demonstrate your many hours of research and prove your ability to write convincingly.
Ideally, by the end of your research paper, you'll have brought your readers on a journey to reach the conclusions you've pre-determined. However, if you don't stick the landing with a good conclusion, you'll risk losing your reader’s trust.
Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper involves a few important steps, including restating the thesis and summing up everything properly.
Find out what to include and what to avoid, so you can effectively demonstrate your understanding of the topic and prove your expertise.
- Why is a good conclusion important?
A good conclusion can cement your paper in the reader’s mind. Making a strong impression in your introduction can draw your readers in, but it's the conclusion that will inspire them.
- What to include in a research paper conclusion
There are a few specifics you should include in your research paper conclusion. Offer your readers some sense of urgency or consequence by pointing out why they should care about the topic you have covered. Discuss any common problems associated with your topic and provide suggestions as to how these problems can be solved or addressed.
The conclusion should include a restatement of your initial thesis. Thesis statements are strengthened after you’ve presented supporting evidence (as you will have done in the paper), so make a point to reintroduce it at the end.
Finally, recap the main points of your research paper, highlighting the key takeaways you want readers to remember. If you've made multiple points throughout the paper, refer to the ones with the strongest supporting evidence.
- Steps for writing a research paper conclusion
Many writers find the conclusion the most challenging part of any research project . By following these three steps, you'll be prepared to write a conclusion that is effective and concise.
- Step 1: Restate the problem
Always begin by restating the research problem in the conclusion of a research paper. This serves to remind the reader of your hypothesis and refresh them on the main point of the paper.
When restating the problem, take care to avoid using exactly the same words you employed earlier in the paper.
- Step 2: Sum up the paper
After you've restated the problem, sum up the paper by revealing your overall findings. The method for this differs slightly, depending on whether you're crafting an argumentative paper or an empirical paper.
Argumentative paper: Restate your thesis and arguments
Argumentative papers involve introducing a thesis statement early on. In crafting the conclusion for an argumentative paper, always restate the thesis, outlining the way you've developed it throughout the entire paper.
It might be appropriate to mention any counterarguments in the conclusion, so you can demonstrate how your thesis is correct or how the data best supports your main points.
Empirical paper: Summarize research findings
Empirical papers break down a series of research questions. In your conclusion, discuss the findings your research revealed, including any information that surprised you.
Be clear about the conclusions you reached, and explain whether or not you expected to arrive at these particular ones.
- Step 3: Discuss the implications of your research
Argumentative papers and empirical papers also differ in this part of a research paper conclusion. Here are some tips on crafting conclusions for argumentative and empirical papers.
Argumentative paper: Powerful closing statement
In an argumentative paper, you'll have spent a great deal of time expressing the opinions you formed after doing a significant amount of research. Make a strong closing statement in your argumentative paper's conclusion to share the significance of your work.
You can outline the next steps through a bold call to action, or restate how powerful your ideas turned out to be.
Empirical paper: Directions for future research
Empirical papers are broader in scope. They usually cover a variety of aspects and can include several points of view.
To write a good conclusion for an empirical paper, suggest the type of research that could be done in the future, including methods for further investigation or outlining ways other researchers might proceed.
If you feel your research had any limitations, even if they were outside your control, you could mention these in your conclusion.
After you finish outlining your conclusion, ask someone to read it and offer feedback. In any research project you're especially close to, it can be hard to identify problem areas. Having a close friend or someone whose opinion you value read the research paper and provide honest feedback can be invaluable. Take note of any suggested edits and consider incorporating them into your paper if they make sense.
- Things to avoid in a research paper conclusion
Keep these aspects to avoid in mind as you're writing your conclusion and refer to them after you've created an outline.
Dry summary
Writing a memorable, succinct conclusion is arguably more important than a strong introduction. Take care to avoid just rephrasing your main points, and don't fall into the trap of repeating dry facts or citations.
You can provide a new perspective for your readers to think about or contextualize your research. Either way, make the conclusion vibrant and interesting, rather than a rote recitation of your research paper’s highlights.
Clichéd or generic phrasing
Your research paper conclusion should feel fresh and inspiring. Avoid generic phrases like "to sum up" or "in conclusion." These phrases tend to be overused, especially in an academic context and might turn your readers off.
The conclusion also isn't the time to introduce colloquial phrases or informal language. Retain a professional, confident tone consistent throughout your paper’s conclusion so it feels exciting and bold.
New data or evidence
While you should present strong data throughout your paper, the conclusion isn't the place to introduce new evidence. This is because readers are engaged in actively learning as they read through the body of your paper.
By the time they reach the conclusion, they will have formed an opinion one way or the other (hopefully in your favor!). Introducing new evidence in the conclusion will only serve to surprise or frustrate your reader.
Ignoring contradictory evidence
If your research reveals contradictory evidence, don't ignore it in the conclusion. This will damage your credibility as an expert and might even serve to highlight the contradictions.
Be as transparent as possible and admit to any shortcomings in your research, but don't dwell on them for too long.
Ambiguous or unclear resolutions
The point of a research paper conclusion is to provide closure and bring all your ideas together. You should wrap up any arguments you introduced in the paper and tie up any loose ends, while demonstrating why your research and data are strong.
Use direct language in your conclusion and avoid ambiguity. Even if some of the data and sources you cite are inconclusive or contradictory, note this in your conclusion to come across as confident and trustworthy.
- Examples of research paper conclusions
Your research paper should provide a compelling close to the paper as a whole, highlighting your research and hard work. While the conclusion should represent your unique style, these examples offer a starting point:
Ultimately, the data we examined all point to the same conclusion: Encouraging a good work-life balance improves employee productivity and benefits the company overall. The research suggests that when employees feel their personal lives are valued and respected by their employers, they are more likely to be productive when at work. In addition, company turnover tends to be reduced when employees have a balance between their personal and professional lives. While additional research is required to establish ways companies can support employees in creating a stronger work-life balance, it's clear the need is there.
Social media is a primary method of communication among young people. As we've seen in the data presented, most young people in high school use a variety of social media applications at least every hour, including Instagram and Facebook. While social media is an avenue for connection with peers, research increasingly suggests that social media use correlates with body image issues. Young girls with lower self-esteem tend to use social media more often than those who don't log onto social media apps every day. As new applications continue to gain popularity, and as more high school students are given smartphones, more research will be required to measure the effects of prolonged social media use.
What are the different kinds of research paper conclusions?
There are no formal types of research paper conclusions. Ultimately, the conclusion depends on the outline of your paper and the type of research you’re presenting. While some experts note that research papers can end with a new perspective or commentary, most papers should conclude with a combination of both. The most important aspect of a good research paper conclusion is that it accurately represents the body of the paper.
Can I present new arguments in my research paper conclusion?
Research paper conclusions are not the place to introduce new data or arguments. The body of your paper is where you should share research and insights, where the reader is actively absorbing the content. By the time a reader reaches the conclusion of the research paper, they should have formed their opinion. Introducing new arguments in the conclusion can take a reader by surprise, and not in a positive way. It might also serve to frustrate readers.
How long should a research paper conclusion be?
There's no set length for a research paper conclusion. However, it's a good idea not to run on too long, since conclusions are supposed to be succinct. A good rule of thumb is to keep your conclusion around 5 to 10 percent of the paper's total length. If your paper is 10 pages, try to keep your conclusion under one page.
What should I include in a research paper conclusion?
A good research paper conclusion should always include a sense of urgency, so the reader can see how and why the topic should matter to them. You can also note some recommended actions to help fix the problem and some obstacles they might encounter. A conclusion should also remind the reader of the thesis statement, along with the main points you covered in the paper. At the end of the conclusion, add a powerful closing statement that helps cement the paper in the mind of the reader.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 17 February 2024
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- RANDOM QUIZ
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
Last Updated: June 29, 2023 Approved
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 42 testimonials and 82% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 2,255,862 times.
The conclusion of a research paper needs to summarize the content and purpose of the paper without seeming too wooden or dry. Every basic conclusion must share several key elements, but there are also several tactics you can play around with to craft a more effective conclusion and several you should avoid to prevent yourself from weakening your paper's conclusion. Here are some writing tips to keep in mind when creating a conclusion for your next research paper.
Sample Conclusions
Writing a basic conclusion.

- Do not spend a great amount of time or space restating your topic.
- A good research paper will make the importance of your topic apparent, so you do not need to write an elaborate defense of your topic in the conclusion.
- Usually a single sentence is all you need to restate your topic.
- An example would be if you were writing a paper on the epidemiology of infectious disease, you might say something like "Tuberculosis is a widespread infectious disease that affects millions of people worldwide every year."
- Yet another example from the humanities would be a paper about the Italian Renaissance: "The Italian Renaissance was an explosion of art and ideas centered around artists, writers, and thinkers in Florence."

- A thesis is a narrowed, focused view on the topic at hand.
- This statement should be rephrased from the thesis you included in your introduction. It should not be identical or too similar to the sentence you originally used.
- Try re-wording your thesis statement in a way that complements your summary of the topic of your paper in your first sentence of your conclusion.
- An example of a good thesis statement, going back to the paper on tuberculosis, would be "Tuberculosis is a widespread disease that affects millions of people worldwide every year. Due to the alarming rate of the spread of tuberculosis, particularly in poor countries, medical professionals are implementing new strategies for the diagnosis, treatment, and containment of this disease ."

- A good way to go about this is to re-read the topic sentence of each major paragraph or section in the body of your paper.
- Find a way to briefly restate each point mentioned in each topic sentence in your conclusion. Do not repeat any of the supporting details used within your body paragraphs.
- Under most circumstances, you should avoid writing new information in your conclusion. This is especially true if the information is vital to the argument or research presented in your paper.
- For example, in the TB paper you could summarize the information. "Tuberculosis is a widespread disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Due to the alarming rate of the spread of tuberculosis, particularly in poor countries, medical professionals are implementing new strategies for the diagnosis, treatment, and containment of this disease. In developing countries, such as those in Africa and Southeast Asia, the rate of TB infections is soaring. Crowded conditions, poor sanitation, and lack of access to medical care are all compounding factors in the spread of the disease. Medical experts, such as those from the World Health Organization are now starting campaigns to go into communities in developing countries and provide diagnostic testing and treatments. However, the treatments for TB are very harsh and have many side effects. This leads to patient non-compliance and spread of multi-drug resistant strains of the disease."

- Note that this is not needed for all research papers.
- If you already fully explained what the points in your paper mean or why they are significant, you do not need to go into them in much detail in your conclusion. Simply restating your thesis or the significance of your topic should suffice.
- It is always best practice to address important issues and fully explain your points in the body of your paper. The point of a conclusion to a research paper is to summarize your argument for the reader and, perhaps, to call the reader to action if needed.

- Note that a call for action is not essential to all conclusions. A research paper on literary criticism, for instance, is less likely to need a call for action than a paper on the effect that television has on toddlers and young children.
- A paper that is more likely to call readers to action is one that addresses a public or scientific need. Let's go back to our example of tuberculosis. This is a very serious disease that is spreading quickly and with antibiotic-resistant forms.
- A call to action in this research paper would be a follow-up statement that might be along the lines of "Despite new efforts to diagnose and contain the disease, more research is needed to develop new antibiotics that will treat the most resistant strains of tuberculosis and ease the side effects of current treatments."

- For example, if you are writing a history paper, then you might discuss how the historical topic you discussed matters today. If you are writing about a foreign country, then you might use the conclusion to discuss how the information you shared may help readers understand their own country.
Making Your Conclusion as Effective as Possible

- Since this sort of conclusion is so basic, you must aim to synthesize the information rather than merely summarizing it.
- Instead of merely repeating things you already said, rephrase your thesis and supporting points in a way that ties them all together.
- By doing so, you make your research paper seem like a "complete thought" rather than a collection of random and vaguely related ideas.

- Ask a question in your introduction. In your conclusion, restate the question and provide a direct answer.
- Write an anecdote or story in your introduction but do not share the ending. Instead, write the conclusion to the anecdote in the conclusion of your paper.
- For example, if you wanted to get more creative and put a more humanistic spin on a paper on tuberculosis, you might start your introduction with a story about a person with the disease, and refer to that story in your conclusion. For example, you could say something like this before you re-state your thesis in your conclusion: "Patient X was unable to complete the treatment for tuberculosis due to severe side effects and unfortunately succumbed to the disease."
- Use the same concepts and images introduced in your introduction in your conclusion. The images may or may not appear at other points throughout the research paper.

- Include enough information about your topic to back the statement up but do not get too carried away with excess detail.
- If your research did not provide you with a clear-cut answer to a question posed in your thesis, do not be afraid to indicate as much.
- Restate your initial hypothesis and indicate whether you still believe it or if the research you performed has begun swaying your opinion.
- Indicate that an answer may still exist and that further research could shed more light on the topic at hand.

- This may not be appropriate for all types of research papers. Most research papers, such as one on effective treatment for diseases, will have the information to make the case for a particular argument already in the paper.
- A good example of a paper that might ask a question of the reader in the ending is one about a social issue, such as poverty or government policy.
- Ask a question that will directly get at the heart or purpose of the paper. This question is often the same question, or some version of it, that you may have started with when you began your research.
- Make sure that the question can be answered by the evidence presented in your paper.
- If desired you can briefly summarize the answer after stating the question. You could also leave the question hanging for the reader to answer, though.

- Even without a call to action, you can still make a recommendation to your reader.
- For instance, if you are writing about a topic like third-world poverty, you can various ways for the reader to assist in the problem without necessarily calling for more research.
- Another example would be, in a paper about treatment for drug-resistant tuberculosis, you could suggest donating to the World Health Organization or research foundations that are developing new treatments for the disease.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls

- These sayings usually sound stiff, unnatural, or trite when used in writing.
- Moreover, using a phrase like "in conclusion" to begin your conclusion is a little too straightforward and tends to lead to a weak conclusion. A strong conclusion can stand on its own without being labeled as such.

- Always state the main argument or thesis in the introduction. A research paper is an analytical discussion of an academic topic, not a mystery novel.
- A good, effective research paper will allow your reader to follow your main argument from start to finish.
- This is why it is best practice to start your paper with an introduction that states your main argument and to end the paper with a conclusion that re-states your thesis for re-iteration.

- All significant information should be introduced in the body of the paper.
- Supporting evidence expands the topic of your paper by making it appear more detailed. A conclusion should narrow the topic to a more general point.
- A conclusion should only summarize what you have already stated in the body of your paper.
- You may suggest further research or a call to action, but you should not bring in any new evidence or facts in the conclusion.

- Most often, a shift in tone occurs when a research paper with an academic tone gives an emotional or sentimental conclusion.
- Even if the topic of the paper is of personal significance for you, you should not indicate as much in your paper.
- If you want to give your paper a more humanistic slant, you could start and end your paper with a story or anecdote that would give your topic more personal meaning to the reader.
- This tone should be consistent throughout the paper, however.

- Apologetic statements include phrases like "I may not be an expert" or "This is only my opinion."
- Statements like this can usually be avoided by refraining from writing in the first-person.
- Avoid any statements in the first-person. First-person is generally considered to be informal and does not fit with the formal tone of a research paper.
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/724/04/
- ↑ http://www.crlsresearchguide.org/18_Writing_Conclusion.asp
- ↑ http://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/PlanResearchPaper.html#conclusion
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/conclusions/
- ↑ http://writing2.richmond.edu/writing/wweb/conclude.html
About This Article

To write a conclusion for a research paper, start by restating your thesis statement to remind your readers what your main topic is and bring everything full circle. Then, briefly summarize all of the main points you made throughout your paper, which will help remind your readers of everything they learned. You might also want to include a call to action if you think more research or work needs to be done on your topic by writing something like, "Despite efforts to contain the disease, more research is needed to develop antibiotics." Finally, end your conclusion by explaining the broader context of your topic and why your readers should care about it, which will help them understand why your topic is relevant and important. For tips from our Academic co-author, like how to avoid common pitfalls when writing your conclusion, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Ummay Aimen
Sep 30, 2016
Did this article help you?

Oct 22, 2017
Sally Larrin
Mar 17, 2018
Maya Loeven
Jun 4, 2017
Sep 26, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Research Paper Conclusion Section
What is a conclusion in a research paper?
The conclusion in a research paper is the final paragraph or two in a research paper. In scientific papers, the conclusion usually follows the Discussion section , summarizing the importance of the findings and reminding the reader why the work presented in the paper is relevant.
However, it can be a bit confusing to distinguish the conclusion section/paragraph from a summary or a repetition of your findings, your own opinion, or the statement of the implications of your work. In fact, the conclusion should contain a bit of all of these other parts but go beyond it—but not too far beyond!
The structure and content of the conclusion section can also vary depending on whether you are writing a research manuscript or an essay. This article will explain how to write a good conclusion section, what exactly it should (and should not) contain, how it should be structured, and what you should avoid when writing it.
Table of Contents:
What does a good conclusion section do, what to include in a research paper conclusion.
- Conclusion in an Essay
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Conclusion Paragraph Outline and Example
- What Not to Do When Writing a Conclusion
The conclusion of a research paper has several key objectives. It should:
- Restate your research problem addressed in the introduction section
- Summarize your main arguments, important findings, and broader implications
- Synthesize key takeaways from your study
The specific content in the conclusion depends on whether your paper presents the results of original scientific research or constructs an argument through engagement with previously published sources.
You presented your general field of study to the reader in the introduction section, by moving from general information (the background of your work, often combined with a literature review ) to the rationale of your study and then to the specific problem or topic you addressed, formulated in the form of the statement of the problem in research or the thesis statement in an essay.
In the conclusion section, in contrast, your task is to move from your specific findings or arguments back to a more general depiction of how your research contributes to the readers’ understanding of a certain concept or helps solve a practical problem, or fills an important gap in the literature. The content of your conclusion section depends on the type of research you are doing and what type of paper you are writing. But whatever the outcome of your work is, the conclusion is where you briefly summarize it and place it within a larger context. It could be called the “take-home message” of the entire paper.
What to summarize in the conclusion
Your conclusion section needs to contain a very brief summary of your work , a very brief summary of the main findings of your work, and a mention of anything else that seems relevant when you now look at your work from a bigger perspective, even if it was not initially listed as one of your main research questions. This could be a limitation, for example, a problem with the design of your experiment that either needs to be considered when drawing any conclusions or that led you to ask a different question and therefore draw different conclusions at the end of your study (compared to when you started out).
Once you have reminded the reader of what you did and what you found, you need to go beyond that and also provide either your own opinion on why your work is relevant (and for whom, and how) or theoretical or practical implications of the study , or make a specific call for action if there is one to be made.
How to Write an Essay Conclusion
Academic essays follow quite different structures than their counterparts in STEM and the natural sciences. Humanities papers often have conclusion sections that are much longer and contain more detail than scientific papers. There are three main types of academic essay conclusions.
Summarizing conclusion
The most typical conclusion at the end of an analytical/explanatory/argumentative essay is a summarizing conclusion . This is, as the name suggests, a clear summary of the main points of your topic and thesis. Since you might have gone through a number of different arguments or subtopics in the main part of your essay, you need to remind the reader again what those were, how they fit into each other, and how they helped you develop or corroborate your hypothesis.
For an essay that analyzes how recruiters can hire the best candidates in the shortest time or on “how starving yourself will increase your lifespan, according to science”, a summary of all the points you discussed might be all you need. Note that you should not exactly repeat what you said earlier, but rather highlight the essential details and present those to your reader in a different way.
Externalizing conclusion
If you think that just reminding the reader of your main points is not enough, you can opt for an externalizing conclusion instead, that presents new points that were not presented in the paper so far. These new points can be additional facts and information or they can be ideas that are relevant to the topic and have not been mentioned before.
Such a conclusion can stimulate your readers to think about your topic or the implications of your analysis in a whole new way. For example, at the end of a historical analysis of a specific event or development, you could direct your reader’s attention to some current events that were not the topic of your essay but that provide a different context for your findings.
Editorial conclusion
In an editorial conclusion , another common type of conclusion that you will find at the end of papers and essays, you do not add new information but instead present your own experiences or opinions on the topic to round everything up. What makes this type of conclusion interesting is that you can choose to agree or disagree with the information you presented in your paper so far. For example, if you have collected and analyzed information on how a specific diet helps people lose weight, you can nevertheless have your doubts on the sustainability of that diet or its practicability in real life—if such arguments were not included in your original thesis and have therefore not been covered in the main part of your paper, the conclusion section is the place where you can get your opinion across.
How to Conclude an Empirical Research Paper
An empirical research paper is usually more concise and succinct than an essay, because, if it is written well, it focuses on one specific question, describes the method that was used to answer that one question, describes and explains the results, and guides the reader in a logical way from the introduction to the discussion without going on tangents or digging into not absolutely relevant topics.
Summarize the findings
In a scientific paper, you should include a summary of the findings. Don’t go into great detail here (you will have presented your in-depth results and discussion already), but do clearly express the answers to the research questions you investigated.
Describe your main findings, even if they weren’t necessarily the ones anticipated, and explain the conclusion they led you to. Explain these findings in as few words as possible.
Instead of beginning with “ In conclusion, in this study, we investigated the effect of stress on the brain using fMRI …”, you should try to find a way to incorporate the repetition of the essential (and only the essential) details into the summary of the key points. “ The findings of this fMRI study on the effect of stress on the brain suggest that …” or “ While it has been known for a long time that stress has an effect on the brain, the findings of this fMRI study show that, surprisingly… ” would be better ways to start a conclusion.
You should also not bring up new ideas or present new facts in the conclusion of a research paper, but stick to the background information you have presented earlier, to the findings you have already discussed, and the limitations and implications you have already described. The one thing you can add here is a practical recommendation that you haven’t clearly stated before—but even that one needs to follow logically from everything you have already discussed in the discussion section.
Discuss the implications
After summing up your key arguments or findings, conclude the paper by stating the broader implications of the research , whether in methods , approach, or findings. Express practical or theoretical takeaways from your paper. This often looks like a “call to action” or a final “sales pitch” that puts an exclamation point on your paper.
If your research topic is more theoretical in nature, your closing statement should express the significance of your argument—for example, in proposing a new understanding of a topic or laying the groundwork for future research.
Future research example
Future research into education standards should focus on establishing a more detailed picture of how novel pedagogical approaches impact young people’s ability to absorb new and difficult concepts. Moreover, observational studies are needed to gain more insight into how specific teaching models affect the retention of relationships and facts—for instance, how inquiry-based learning and its emphasis on lateral thinking can be used as a jumping-off point for more holistic classroom approaches.
Research Conclusion Example and Outline
Let’s revisit the study on the effect of stress on the brain we mentioned before and see what the common structure for a conclusion paragraph looks like, in three steps. Following these simple steps will make it easy for you to wrap everything up in one short paragraph that contains all the essential information:
One: Short summary of what you did, but integrated into the summary of your findings:
While it has been known for a long time that stress has an effect on the brain, the findings of this fMRI study in 25 university students going through mid-term exams show that, surprisingly, one’s attitude to the experienced stress significantly modulates the brain’s response to it.
Note that you don’t need to repeat any methodological or technical details here—the reader has been presented with all of these before, they have read your results section and the discussion of your results, and even (hopefully!) a discussion of the limitations and strengths of your paper. The only thing you need to remind them of here is the essential outcome of your work.
Two: Add implications, and don’t forget to specify who this might be relevant for:
Students could be considered a specific subsample of the general population, but earlier research shows that the effect that exam stress has on their physical and mental health is comparable to the effects of other types of stress on individuals of other ages and occupations. Further research into practical ways of modulating not only one’s mental stress response but potentially also one’s brain activity (e.g., via neurofeedback training) are warranted.
This is a “research implication”, and it is nicely combined with a mention of a potential limitation of the study (the student sample) that turns out not to be a limitation after all (because earlier research suggests we can generalize to other populations). If there already is a lot of research on neurofeedback for stress control, by the way, then this should have been discussed in your discussion section earlier and you wouldn’t say such studies are “warranted” here but rather specify how your findings could inspire specific future experiments or how they should be implemented in existing applications.
Three: The most important thing is that your conclusion paragraph accurately reflects the content of your paper. Compare it to your research paper title , your research paper abstract , and to your journal submission cover letter , in case you already have one—if these do not all tell the same story, then you need to go back to your paper, start again from the introduction section, and find out where you lost the logical thread. As always, consistency is key.
Problems to Avoid When Writing a Conclusion
- Do not suddenly introduce new information that has never been mentioned before (unless you are writing an essay and opting for an externalizing conclusion, see above). The conclusion section is not where you want to surprise your readers, but the take-home message of what you have already presented.
- Do not simply copy your abstract, the conclusion section of your abstract, or the first sentence of your introduction, and put it at the end of the discussion section. Even if these parts of your paper cover the same points, they should not be identical.
- Do not start the conclusion with “In conclusion”. If it has its own section heading, that is redundant, and if it is the last paragraph of the discussion section, it is inelegant and also not really necessary. The reader expects you to wrap your work up in the last paragraph, so you don’t have to announce that. Just look at the above example to see how to start a conclusion in a natural way.
- Do not forget what your research objectives were and how you initially formulated the statement of the problem in your introduction section. If your story/approach/conclusions changed because of methodological issues or information you were not aware of when you started, then make sure you go back to the beginning and adapt your entire story (not just the ending).
Consider Receiving Academic Editing Services
When you have arrived at the conclusion of your paper, you might want to head over to Wordvice AI’s AI Writing Assistant to receive a free grammar check for any academic content.
After drafting, you can also receive English editing and proofreading services , including paper editing services for your journal manuscript. If you need advice on how to write the other parts of your research paper , or on how to make a research paper outline if you are struggling with putting everything you did together, then head over to the Wordvice academic resources pages , where we have a lot more articles and videos for you.

Organizing Academic Research Papers: 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of your points or a re-statement of your research problem but a synthesis of key points. For most essays, one well-developed paragraph is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, a two-or-three paragraph conclusion may be required.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides you with several important opportunities to demonstrate your overall understanding of the research problem to the reader. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key points in your analysis or findings.
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger implications of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly answer the "so what?" question by placing the study within the context of past research about the topic you've investigated.
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers you a chance to elaborate on the significance of your findings.
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information [which should be avoided], but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing/contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study.
Conclusions . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion . San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008.
Structure and Writing Style
https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2018/07/conclusions_uwmadison_writingcenter_aug2012.pdf I. General Rules
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- State your conclusions in clear, simple language.
- Do not simply reiterate your results or the discussion.
- Indicate opportunities for future research, as long as you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of the strengths of your main argument(s) and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Make sure, however, that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings because this reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your essay.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or point of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data.
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented, or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have done will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way.
NOTE : Don't delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply not to guess at possible outcomes.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following.
- If your essay deals with a contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion to lend authority to the conclusion you have reached [a good place to look is research from your literature review].
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to drive home the ultimate point of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point with a relevant narrative drawn from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you introduced in your introduction, but add further insight that is derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results to reframe it in new ways.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a strong, succient statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid Failure to be concise The conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too long often have unnecessary detail. The conclusion section is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, etc. that you make. Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from general [the field of study] to specific [your research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move from specific [your research problem] back to general [your field, i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In other words, the conclusion is where you place your research within a larger context. Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. Problems, drawbacks, and challenges encountered during your study should be included as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative results [findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section of your paper. In the conclusion, use the negative results as an opportunity to explain how they provide information on which future research can be based. Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to be able to discuss how your research fits back into your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize it briefly and directly. Often this element of your conclusion is only a few sentences long. Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives change while the research is being carried out. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine your original objectives in your introduction, as these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you now know a good deal about it, perhaps even more than your professor! Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches...."
Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions . The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion . San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions . Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization . Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining to read, when an essay is about to end. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your Conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper. If you have new information to present, add it to the Discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no actual new information is introduced, the conclusion is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; it's where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate your understanding of the material that you’ve presented, and locate your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Conclusion
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide

People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
Finishing a research paper feels great, but getting to the end—especially the conclusion—can be a bit tricky.
People often wonder, "How do I wrap up my findings nicely?" or "What tone should I use in the conclusion?"
If you're dealing with these questions, you're not alone! Many researchers find writing a good conclusion a bit challenging since it's a crucial part that is meant to leave a strong impression on your readers.
No need to worry!
In this guide, we'll show you how to write a conclusion that not only ties up your research paper neatly but also leaves a strong impression. We'll cover everything from summarizing effectively to creating the right feeling.
So, let’s get started.
- 1. What is a Research Paper Conclusion?
- 2. How to Write a Research Paper Conclusion: 7 Steps
- 3. Research Paper Conclusion Examples
- 4. Things to Avoid While Writing the Research Paper Conclusion
What is a Research Paper Conclusion?
A research paper conclusion is like the final chapter of your paper. It's where you bring everything together and leave a lasting impression on your readers.
In simple terms, it's the last part where you sum up what you found during your research and explain why it matters.
The conclusion isn't just a summary; it's a chance to make your research memorable and show its importance.
Types of Research Paper Conclusions
When it comes to writing the conclusion of your research paper, there isn't a one-size-fits-all approach. Different types of research papers call for different types of conclusions. Here are some common types:
- Summarizing Conclusion
This type recaps the key points and findings of your research. It's like giving your readers a quick overview of what you discovered without introducing new information. Summarizing conclusions works well for straightforward research papers.
- Reflective Conclusion
A reflective conclusion allows you to share your personal thoughts on the research process, challenges faced, and lessons learned. It adds a human touch to your paper, giving readers insight into your journey as a researcher.
- Open-ended Conclusion
Some research papers benefit from an open-ended conclusion that leaves room for further exploration. This type invites readers to think critically, ask questions, or even conduct additional research on the same topic.
How to Write a Research Paper Conclusion: 7 Steps
Writing an effective conclusion for your research paper involves more than just summarizing your findings. Follow these six essential steps to ensure your conclusion leaves a lasting impact:
Step 1: Restate the Research Problem
Start wrapping up your paper by going back to the main research question or issue you were investigating.
Remind your readers about what you were trying to find out or understand. This gives your conclusion a clear connection to the original goal of your research, helping readers see the bigger picture.
Step 2: Revisit Your Thesis Statement
Go back to the main idea or argument you had in your paper—this is called your thesis statement. Double-check that your conclusion matches and supports what you wanted to prove or talk about in the beginning.
This step is important because it keeps your conclusion connected to the main point of your research, making everything fit together nicely.
Step 3: Summarize Key Points
Give a short and clear recap of the most important things you found in your research. Keep it simple and stick to what you've already talked about—don't bring in new details now.
The goal is to remind your readers of the important stuff you covered earlier. This helps to underline why your research is important and what you want them to take away from it.
Step 4: Discuss the Implications
Address the broader implications of your research. Explain why your findings matter and how they contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your field.
Discuss the practical applications of your research and highlight any potential areas for further exploration.
Step 5: Connect with the Introduction
Create a seamless connection between your conclusion and the introduction. Referencing key elements from the introduction helps to create a cohesive narrative for your paper.
This connection gives your research a sense of completeness and unity.
Step 6: Consider the "So What?" Factor
Ask yourself the question, "So what?" Why should readers care about your research? Clearly articulate the significance of your findings and their relevance to the broader academic or real-world context.
Demonstrating the impact of your research adds depth to your conclusion.
Step 7: End with a Strong Closing Statement:
Conclude your research paper with a memorable closing statement. This could be a thought-provoking reflection, a call to action, or a suggestion for future research.
A strong closing leaves a lasting impression on your readers and emphasizes the importance of your work.
Research Paper Conclusion Examples
When it comes to writing a conclusion for your research paper, examining examples can offer valuable insights. Let’s take a look at this comprehensive example given below:
Still wondering how to write the conclusion for your research paper? Check out these examples for better understanding:
Conclusion For A Research Paper APA
Conclusion For A Research Paper Example Pdf
Conclusion For A Research Paper Pdf
Conclusion For A Research Paper Middle School
Conclusion For A Scientific Paper
Conclusion For A Research Paper Sample
Things to Avoid While Writing the Research Paper Conclusion
While crafting a conclusion for your research paper, it's crucial to steer clear of common pitfalls that can diminish the impact of your final remarks.
Here are some things to avoid:
- Repetition: Avoid rehashing the exact language used in the introduction or body of your paper. A conclusion should summarize key points without duplicating content.
- Introducing New Information: Resist the temptation to introduce new ideas or data in the conclusion. This section is for summarizing existing content and reinforcing key findings.
- Overly Complex Language: Keep your conclusion clear and accessible. Avoid introducing overly complex or technical language that might confuse your readers.
- Lack of Connection to Introduction: Ensure that your conclusion ties back to the introduction. Failing to connect these sections can make your paper feel disjointed.
- Vague Statements: Steer clear of vague statements that lack substance. Clearly articulate the significance of your findings and their broader implications.
- Apologies or Excuses: Avoid including apologies or excuses for limitations in your research. While acknowledging limitations is important, the conclusion is not the place to dwell on them.
- New Arguments or Debates: The conclusion is not the space to introduce new debates or arguments. Keep the focus on summarizing your research and its implications.
- Abrupt Endings: A conclusion should not end abruptly. Instead, provide a thoughtful and well-rounded closing statement about the results of your study.
To sum it up, we've gone through important steps to make your research paper conclusion strong. We covered things like going back to your main question, talking about the most important points, and thinking about why your research matters in the real world.
Remember, a good ending is more than just a summary; it captures the heart of your research and answers the big "So what?" question.
Remember, don't say the same things too much, don't add new details at the end, and keep your language simple!
If you ever need help with your academic writing, MyPerfectWords.com is here for you. Our expert writers are committed to helping you excel in your research papers and beyond.
Take the next step towards academic success with MyPerfectWords.com, and hire our essay writing service today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Conclusions

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource outlines the generally accepted structure for introductions, body paragraphs, and conclusions in an academic argument paper. Keep in mind that this resource contains guidelines and not strict rules about organization. Your structure needs to be flexible enough to meet the requirements of your purpose and audience.
Conclusions wrap up what you have been discussing in your paper. After moving from general to specific information in the introduction and body paragraphs, your conclusion should begin pulling back into more general information that restates the main points of your argument. Conclusions may also call for action or overview future possible research. The following outline may help you conclude your paper:
In a general way,
- Restate your topic and why it is important,
- Restate your thesis/claim,
- Address opposing viewpoints and explain why readers should align with your position,
- Call for action or overview future research possibilities.
Remember that once you accomplish these tasks, unless otherwise directed by your instructor, you are finished. Done. Complete. Don't try to bring in new points or end with a whiz bang(!) conclusion or try to solve world hunger in the final sentence of your conclusion. Simplicity is best for a clear, convincing message.
The preacher's maxim is one of the most effective formulas to follow for argument papers:
Tell what you're going to tell them (introduction).
Tell them (body).
Tell them what you told them (conclusion).
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: mm1: methods, analysis & insights from multimodal llm pre-training.
Abstract: In this work, we discuss building performant Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). In particular, we study the importance of various architecture components and data choices. Through careful and comprehensive ablations of the image encoder, the vision language connector, and various pre-training data choices, we identified several crucial design lessons. For example, we demonstrate that for large-scale multimodal pre-training using a careful mix of image-caption, interleaved image-text, and text-only data is crucial for achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) few-shot results across multiple benchmarks, compared to other published pre-training results. Further, we show that the image encoder together with image resolution and the image token count has substantial impact, while the vision-language connector design is of comparatively negligible importance. By scaling up the presented recipe, we build MM1, a family of multimodal models up to 30B parameters, including both dense models and mixture-of-experts (MoE) variants, that are SOTA in pre-training metrics and achieve competitive performance after supervised fine-tuning on a range of established multimodal benchmarks. Thanks to large-scale pre-training, MM1 enjoys appealing properties such as enhanced in-context learning, and multi-image reasoning, enabling few-shot chain-of-thought prompting.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Download PDF
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Perspective
- Open access
- Published: 26 March 2024
Ecological countermeasures to prevent pathogen spillover and subsequent pandemics
- Raina K. Plowright ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3338-6590 1 ,
- Aliyu N. Ahmed ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6039-1101 2 ,
- Tim Coulson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9371-9003 3 ,
- Thomas W. Crowther ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5674-8913 4 ,
- Imran Ejotre 5 ,
- Christina L. Faust ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8824-7424 6 ,
- Winifred F. Frick ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9469-1839 7 , 8 ,
- Peter J. Hudson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0468-3403 9 ,
- Tigga Kingston ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3552-5352 10 ,
- P. O. Nameer ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7110-6740 11 ,
- M. Teague O’Mara ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6951-1648 7 ,
- Alison J. Peel ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3538-3550 12 ,
- Hugh Possingham ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7755-996X 13 ,
- Orly Razgour ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3186-0313 14 ,
- DeeAnn M. Reeder ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8651-2012 15 ,
- Manuel Ruiz-Aravena ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8463-7858 1 , 12 nAff26 ,
- Nancy B. Simmons ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8807-7499 16 ,
- Prashanth N. Srinivas ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0968-0826 17 ,
- Gary M. Tabor ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4711-1018 18 ,
- Iroro Tanshi 19 , 20 , 21 ,
- Ian G. Thompson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3445-8696 22 ,
- Abi T. Vanak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2435-4260 23 , 24 ,
- Neil M. Vora ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4989-3108 25 ,
- Charley E. Willison ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7272-1080 1 &
- Annika T. H. Keeley ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7237-6259 18
Nature Communications volume 15 , Article number: 2577 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
519 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Epidemiology
- Policy and public health in microbiology
- Viral infection
Substantial global attention is focused on how to reduce the risk of future pandemics. Reducing this risk requires investment in prevention, preparedness, and response. Although preparedness and response have received significant focus, prevention, especially the prevention of zoonotic spillover, remains largely absent from global conversations. This oversight is due in part to the lack of a clear definition of prevention and lack of guidance on how to achieve it. To address this gap, we elucidate the mechanisms linking environmental change and zoonotic spillover using spillover of viruses from bats as a case study. We identify ecological interventions that can disrupt these spillover mechanisms and propose policy frameworks for their implementation. Recognizing that pandemics originate in ecological systems, we advocate for integrating ecological approaches alongside biomedical approaches in a comprehensive and balanced pandemic prevention strategy.
Similar content being viewed by others
The role of environmental factors on transmission rates of the COVID-19 outbreak: an initial assessment in two spatial scales
Canelle Poirier, Wei Luo, … Mauricio Santillana
Pathogen spillover driven by rapid changes in bat ecology
Peggy Eby, Alison J. Peel, … Raina K. Plowright
A generalizable one health framework for the control of zoonotic diseases
Ria R. Ghai, Ryan M. Wallace, … Casey Barton Behravesh
Introduction
Reducing the risk of future pandemics requires investment in prevention, preparedness, and response. At present, most attention and funding is allocated to mitigation after a pathogen is already circulating in humans, prioritizing outbreak detection and medical countermeasures such as vaccines and therapeutics 1 . By contrast, primary pandemic prevention—defined as reducing the likelihood a pathogen transmits from its animal host into humans (zoonotic spillover; Fig. 1 ) 2 —has received less attention in global conversations, policy guidance, and practice 1 , 2 . Given the time delays in identifying and responding to outbreaks, and the inequity in treatment distributions, investing in pandemic prevention is essential to achieve efficient, equitable, and cost-effective protection from disease.
Primary pandemic prevention is the set of actions taken to reduce the risk of pathogen spillover from animals to humans, focusing on processes upstream of the spillover event (left panel). By contrast, secondary pandemic prevention (middle panel) focuses on limiting the spread of an outbreak to prevent its escalation into an epidemic or a pandemic. Pandemic response (right panel) involves actions taken to address a pandemic once one is underway. Although not illustrated here, pandemic preparedness involves developing capabilities to respond to a pandemic if one were to occur, and can be implemented concurrently with primary and secondary pandemic prevention. The nature of interventions varies across these phases: Primary pandemic prevention emphasizes ecological and behavioral interventions, but also encompasses biosafety practices in virological research 83 , whereas secondary pandemic prevention and response prioritize epidemiological and biomedical interventions. Definitions: an outbreak is “an increase, often sudden, in the number of cases of a disease in a particular area 84 ”; an epidemic is an outbreak extending over a wider geographic area 84 ; and a pandemic is “an epidemic occurring worldwide, or over a very wide area, crossing international boundaries and usually affecting a large number of people 84 ”.
To effectively prevent pandemics, we must recognize two key points: first that pandemics almost always start with a microbe infecting a wild animal in a natural environment and second that human-caused land-use change often triggers the events–whether through wildlife trade or other distal activities–that facilitate spillover of microbes from wild animals to humans 3 . As land-use change becomes more intense and extensive, the risk of zoonotic spillovers, and subsequent epidemics and pandemics, will increase. Designing land management and conservation strategies to explicitly limit spillover is central to meeting the challenge of pandemic prevention at a global scale.
Herein, we present a roadmap for reducing pathogen transmission from wildlife to humans and other animals. We show how strategic conservation and restoration of nature for reservoir hosts, and mitigation of risks for humans most at risk—what we define as ecological countermeasures—can prevent spillover and protect human and animal health, while also addressing key drivers of climate change and biodiversity loss.
Mechanisms of spillover
Despite hundreds of thousands of potentially zoonotic microbes circulating in nature 4 , pandemics are rare. Microbes, termed pathogens if they cause disease, must overcome a series of barriers, simplified and described below, to transmit from a wild animal to a human. Crossing those barriers requires the alignment of specific conditions—including ecological, epidemiological, immunological, and behavioral conditions—that are often complex and dynamic 5 .
First, the distribution of the species that maintains the zoonotic pathogen in nature (the reservoir host) and the species that is infected (the recipient host) must be connected, usually through overlapping distributions. Once wildlife reservoir hosts and humans overlap, the second barrier is the immune functions within wildlife hosts that keep potential zoonotic pathogens at low levels. Particular stressors (e.g., habitat loss, lack of food) can increase host viral infection and shedding 6 . A pathogen that passes through this second barrier and is shed by the animal host encounters a third barrier: humans must be exposed to a pathogen for spillover to occur. That exposure depends on specific interactions or behaviors of humans and the virus-shedding host. Exposure to the pathogen may be through direct contact, such as a bite, or indirect contact with the reservoir host’s excreta or a non-vertebrate vector (e.g., blood-feeding parasite). Often a bridging host species, such as commercially traded wildlife or a domestic animal, is infected by the reservoir host and subsequently amplifies and transmits the pathogen to humans. The fourth barrier is human susceptibility. The pathogen must be able to establish an infection within humans by overcoming structural and immunological barriers (e.g., binding to a human cell). Those barriers are substantial–one reason pandemics are rare–protecting humans from a continuous rain of microbes from soils, plants, and animals 5 . Fifth, after establishing an infection within a single human, the pathogen must be able to amplify within this new host, be excreted (e.g., through respiration), and then transmitted onward and exponentially 7 . If any of these barriers is not overcome, a pandemic cannot occur 5 .
Land use-induced spillover
Intact ecosystems provide the first line of defense against new pandemics because they strengthen the first three barriers to spillover (minimizing distribution overlap, host stress, and human exposure) and hence decrease the likelihood that the conditions for spillover occur or align 3 . Conversely, land-use changes and other environmental disturbances erode those first three barriers to spillover by changing the reservoir hosts’ spatial behavior and allostatic load (energy and stress budget), as well as altering human behavior. In this context, we identify targeted ecological countermeasures designed to decrease these risks (Fig. 2 ).
Historic (left panel): Historically, reservoir hosts and large human populations (and their domestic animals) were more separated, viruses circulated at low levels with seasonal fluctuations in prevalence, and the holes in the barriers to spillover were small and did not align 5 . Land use-induced spillover (middle panel): Land-use change increases the risk of spillover by driving two phenotypic changes in reservoir hosts: changes in behavior that alter how they use space, and changes in reservoir host energy and stress levels (allostatic load) that influence viral infection and shedding. Land-use change can also lead to emergent human behaviors that increase exposure to pathogens. Land-use change generally increases the overlap of reservoir, human, and bridging hosts; increases the probability that reservoir hosts are shedding pathogens; and increases the probability that humans are exposed to those pathogens. In sum, these changes increase the size and alignment of the holes in the barrier to spillover. Ecological countermeasures (right panel): Ecological countermeasures can address all three issues. Retaining natural resources reduces the overlap of humans and domestic recipient hosts in space and time, reduces the probability of allostatic overload and reduces the likelihood of emergent human behaviors that facilitate exposure.
We focus on ecological countermeasures in bats since several major epidemics and pandemics (e.g., those caused by SARS-CoV-2, Ebola virus, SARS-CoV-1, MERS-CoV, and Nipah virus) have an evolutionary origin in bats (but notably do not cause disease in their bat reservoir hosts) 8 . Certain bat species are also the hosts of four of the nine diseases prioritized by the World Health Organization as having the potential to generate epidemics that pose a great risk to public health, and for which there are insufficient countermeasures 9 . However, the ecological countermeasures we present also apply to other host taxa, particularly species that are susceptible to local resource depletion and can sustain the circulation of potential pathogens (e.g., species that aggregate in large numbers like colonial nesting birds, or in spatially structured but extensive aggregations, such as prairie dogs and other rodents). For species tied to permanent refuges (roosts, breeding grounds, burrow systems and warrens), loss of habitat may quickly push populations into allostatic overload or in more mobile species, prompt resource tracking and migration with attendant energetic costs and risks.
Reservoir host energy and stress (allostatic load)
Healthy animals maintain a positive energy balance, where energy inputs either from foraging or stored reserves of fat, balance or exceed energy expenditure required for survival and reproduction (Fig. 3 ). This balance of energy in physiological systems occurs through allostasis—a dynamic process that integrates the neuroendocrine, metabolic, cardiovascular, and immune systems to adapt to varying conditions. Animals regularly adapt to increased energy demands needed to migrate, hibernate, or reproduce. The total resources an animal requires at any given time is an animal’s “allostatic load” 10 , 11 . Allostatic load is frequently estimated with biomarkers such as cortisol, a glucocorticoid hormone indicative of stress 12 , or related energetic and immune metrics, such as total white-blood-cell count, the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and immune regulatory markers. When in balance, glucocorticoid hormones help manage energy usage and have generally beneficial effects on immunity. For example, they mediate anti-inflammatory processes, support T cell maintenance, and enhance the functions of Th2, Th17 and B cells, which collectively bolster the body’s defense against infection and keep immune responses in check 13 , 14 . Across millennia, animals evolved the capacity to maintain allostasis under predictable variations in their environments, precisely aligning energetically expensive activities with periods of maximum food availability 15 (Fig. 3 ).
Bats have evolved mechanisms to meet their exceptionally high energy needs under prevailing environmental conditions. A Baseline levels of energy (green) are required for basic daily activities – to fuel cells, to move around, to find food and water, and to maintain the immune system. At any given time, a certain amount of food - or energy - is available (blue+purple+green), which varies seasonally. Bats optimize their energy intake and energy expenditure, timing expensive activities like migration and reproduction (purple) to periods in which more food is available. Under normal conditions, an energetic buffer (blue) exists providing energetic wiggle room for years with poor food availability. B Perturbations in the environment, whether natural (e.g., fire in some instances) or man-made (e.g., downstream effects of global climate change, habitat destruction, etc.) increase the amount of energy needed for survival and reproduction. For example, animals may be required to travel greater distances to locate food and resting sites. Such increased exertion diminishes the energetic buffer that enables them to withstand periods of resource scarcity. C At its worst, these perturbations result in a reversal of fortune; less energy is available than the bat needs. In these conditions, or with disturbance or harassment, animals experience allostatic overload (red). This leads to suppression of immune function, and increased susceptibility to viral infection and shedding. Figure adapted, in part, from concepts in 10 .
Animals are less able to manage the physiological and behavioral challenges that arise from unpredictable environmental changes, particularly those caused by human activities. Perhaps the most common consequence of environmental change is decreased food availability, leading to weight loss 16 . When food is limited, energy expenditure may exceed energy input and the animal shifts into a state of allostatic overload (Fig. 3 ).
Habitat destruction, degradation, and fragmentation profoundly increase the likelihood of allostatic overload. This risk is compounded when animals face repeated stressors, such as cave disturbance or harassment 17 . To survive, animals must divert energy from other systems, including their immune defenses 14 , 16 . The effects of allostatic overload are largely mediated by the chronically elevated glucocorticoid hormones, which can lead to immune system dysregulation, impaired resistance to infection, and a shift in the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory processes. This state, the effects of which accumulate over an animal’s lifetime, facilitates viral infection and shedding 13 , 18 , 19 , 20 . Consequently, animals experiencing allostatic overload may shed more pathogens for longer periods, increasing the risk of spillover. Empirical evidence underscores the link between stress, acute food deprivation, and low body weight with higher probability, magnitude, and duration of viral shedding, as observed in bats 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 and birds 26 , 27 .
Reservoir host spatial behavior
Changes in land use not only affect the energy needs of reservoir hosts but also alter how reservoir hosts use space, including how they encounter humans, livestock, or other bridging hosts. Typically, animals have home ranges sufficient for them to acquire the resources they need such as food, water, shelter, and mates. Some species, especially those dependent on unpredictable or briefly available food, may need to migrate or move regularly to find these resources. Land-use changes can limit the amount and accessibility of food resources. In response, and to avoid or mitigate allostatic overload, animals often need to expand their search area or modify their home ranges to find sufficient food 28 , 29 . For example, fruit-eating bats Dermanura watsoni were observed to have larger daily feeding ranges in degraded habitats 30 . Such adaptations may increase the likelihood of encounters and, consequently, pathogen transmission between reservoir hosts, humans, and livestock. This may be especially true if they must traverse resource-sparse areas to find food, increasing stress and mortality risk. A study in Uganda, for example, showed increased contact between humans and non-human primates with increasing forest fragmentation 31 .
Moreover, wildlife populations may adapt to areas where they historically did not occur, and some species that host zoonotic pathogens have proven more likely to thrive in disturbed landscapes than in undisturbed sites 32 . For example, in response to the loss of winter habitat, Australian Pteropus alecto bats, carriers of Hendra virus, are shifting to agricultural and urban areas. Here, they feed on suboptimal but reliable foods in proximity to livestock 33 .
Increased zoonotic risk, then, often coincides with stressful life stages or times and places of resource scarcity 21 , 33 , 34 . Understanding which animals are most likely to modify their distributions, or are at the highest risk of allostatic overload, helps target countermeasures to spillover. For example, the P. alecto bats that shifted to novel agricultural and urban habitats shed higher levels of Hendra virus than bats in traditional habitats, especially during winter and after periods of food scarcity 22 , 35 . This combination of factors breaches the barriers earlier noted and has led to a higher probability of spillover 22 .
Human behavior
Although human interaction with a pathogen is a fundamental component of pathogen spillover, mere spatial overlap between humans and virus-shedding reservoir hosts is not sufficient for spillover. Specific human behaviors (not always within one’s control) that provide a transmission route and sufficient dose for infection are usually required—for example, harvesting guano or date palm sap 36 , 37 , 38 , visiting a tourist cave 34 , or butchering wildlife with inadequate protection 39 . Such behaviors, which increase the frequency and intensity of contact with wildlife and wildlife excreta, can become more prevalent because of land-use change, frequently precipitated by the construction of new roads. While road construction, if designed well, can bring benefits such as employment, reduced transportation costs, and development 40 , roads also facilitate increased access to wildlife habitats. This access can enable activities such as the extraction of wild animals for food and trade, timber harvest, and livestock grazing, following deforestation 41 , 42 . New settlements that follow roads may also promote synanthropic responses of wildlife; for example, bats are commonly found roosting on roofs of rural homes 43 .
Road construction not only alters exposure opportunities but also introduces people into communities that lack immunity to local pathogens. By contrast, Indigenous Peoples and local communities (IPLCs) who have coexisted with these environments may have some protective immunity to local pathogens through repeated exposures. This is evident from the presence of antibodies to various outbreak-prone viruses in populations with frequent wildlife exposure. For example, antibodies to filoviruses were detected in bat harvesters in remote northeast India 44 and antibodies to SARS-related coronavirus have been identified in people residing near caves in Yunnan Province, China 45 . Such evidence suggests that while pandemics may be rare, local spillovers could be relatively common. Furthermore, the construction of roads not only increases the risk of exposure for those lacking immunity but also facilitates the rapid spread of novel pathogens once they have entered the human population, thereby increasing the likelihood of a pandemic.
Apart from the direct impact of road construction, there is a multitude of factors relating to deforestation and forest degradation that could affect human exposure to pathogens, including agricultural practices such as the cultivation of palm oil and extractive industries, notably mining 46 . Typically, such activities are either preceded by or necessitate the building of roads, further intertwining human exposure with infrastructural development. IPLCs living in and around forests, aren’t always the main beneficiaries of these activities and can be actively harmed by them 47 , 48 . For example, land-use change can result in decreased income and food security, incentivizing some individuals to increase hunting and bush travel. This underscores the need for development projects, including road construction, to take holistic approaches that optimize outcomes for people rather than focusing on single outcomes that can have unintended consequences. Such an approach could deliver much of the economic benefits to people while reducing environmental and social damage. Individual human behaviors that increase spillover risk must be considered in the context of such socio-ecological factors–including vulnerabilities and inequalities—as well as in a historical and cultural context 49 .
Ecological countermeasures defined
We define ecological countermeasures as actions that protect and restore wildlife habitat or mitigate wildlife-human interactions to reduce the risk of pathogen spillover. These measures are strategically designed to increase the resilience of reservoir host populations, reduce stress and likelihood of viral shedding, prevent distributional shifts, and protect vulnerable human communities. By addressing these factors, ecological countermeasures target the root causes of spillover. They effectively strengthen barriers to spillover and decrease the likelihood that the conditions for spillover align.
We propose a tiered approach that considers the land-use context surrounding the habitats of reservoir hosts (Fig. 4 ), focusing on enhancing habitat integrity, heterogeneity, and connectivity. In our view, the most effective strategy to reduce the probability of another pandemic is to preserve intact ecosystems and bolster their resilience through restoration and the creation of buffer zones. This priority is driven by the likelihood that the next pandemic will be triggered by an as-yet-unknown pathogen, referred to as “Disease X” by the World Health Organization 50 , that has had scarce opportunities for spillover or for evolutionary adaptation in bridging hosts. Our primary emphasis should be on maintaining and enhancing the integrity and resilience of still-intact landscapes to prevent new interfaces that could enable the emergence of Disease X.
We propose a tiered approach that considers the land-use context surrounding the habitats of reservoir hosts. Because the next pandemic is most likely to be triggered by a pathogen that is currently limited in its exposure to human populations, the highest priority should be to preserve intact ecosystems and enhance their resilience through restoration and increasing connectivity. In regions where humans and reservoir hosts share landscapes, we prioritize the safeguarding of critical areas needed for reservoir hosts’ feeding, resting, and social aggregation. Simultaneously, we aim to protect human communities and livestock most at risk of exposure to zoonotic pathogens.
In regions where humans and reservoir hosts share landscapes, we prioritize the safeguarding of critical areas needed for reservoir hosts’ feeding, resting, and social aggregation. Simultaneously, we aim to protect human communities most at risk of exposure to zoonotic pathogens. In the following sections, we explain how these strategies target the fundamental drivers of pathogen spillover and promote the health of both wildlife and human populations. While we focus on bats as reservoir hosts, ecological countermeasures are relevant across diverse reservoir host species, as long as specific ecological contexts and local practices are considered 51 . We present these strategies with a simple policy-focused message as they would apply to bats: protect where bats forage (where bats eat), protect where bats roost (where bats sleep), and protect people at risk (Fig. 4 ).
Protect where bats forage
The quality of foraging areas determines the energetic buffer protecting individuals from allostatic overload in times of increased energetic costs or reduced resource availability (Fig. 2b ). If animals have enough nutritious food, they are less likely to become energetically or physiologically stressed, reducing the risk of allostatic overload and infection and shedding (Fig. 2c ). Moreover, the location of bat foraging areas relative to human activity determines the spatial overlap with potential recipient hosts. If enough food is available in relatively unmodified landscapes, or immediately around roosts, bats are also less likely to use areas with higher human population densities. Thus, protecting where bats eat not only ensures that they are healthy, but that they are spatially separated from people.
In natural landscapes (Fig. 4 , left panel), the overarching priority is to preserve or improve the integrity of ecosystems that animals inhabit, as previously outlined. This may entail securing extensive areas of unmodified habitats, and proactively managing these landscapes to prevent fragmentation and degradation.
In landscapes that have already been degraded (Fig. 4 , middle panel), the focus should shift to protecting, restoring, and connecting key food sources that sustain reservoir hosts during periods of resource scarcity (e.g., winter or the dry season) and through energy-demanding life stages (e.g., pregnancy and lactation). Additionally, in environments facing degradation from land-use and climate change, ecological countermeasures are crucial for mitigating food shortages caused by habitat deterioration across multiple scales.
The natural-rural interface often presents a heterogeneous landscape to bats, characterized by a mix of high-quality foraging habitats embedded in or interdigitating with degraded habitats or areas of human land use. These areas, while fragmented, can still offer valuable nutritional resources. It is crucial to protect key foraging sites, especially those outside of protected areas, and to preserve habitats surrounding roosts. A priority is to maintain or create connectivity among quality habitat patches to ensure a consistent flow of resources. Thereafter, efforts should be directed towards the restoration of critical habitats and water sources, particularly in the vicinity of roosts, coupled with strategic livestock management to reduce interactions with bats. Active management strategies should aim to maximize the benefits of human land-uses such as croplands and plantations, for both humans and bats 52 , 53 .
In suburban and urban settings (Fig. 4 , right panel), priority activities focus on the separation of bats and people through strategic planning and restricting human access. At the broadest scale, urban expansion plans should avoid encroaching on large wildlife habitats. Within urban areas, it is crucial to preserve bat foraging resources without inadvertently increasing contact with human populations. This necessitates a collaborative effort between local communities, urban planners and bat experts who understand the requirements of local species. For example, ornamental or landscaping trees used in city planning may attract fruit-eating bats (such as members of the Pteropodidae and Phyllostomidae families) in subtropical and tropical regions. This is also true for fruit trees in residential backyards 54 . A practical approach might include selecting alternative landscaping species and planting bat-attractive trees in areas that are less accessible to humans. Wildlife-safe protective netting around backyard fruit trees can also limit bats’ access to ripe fruits and minimize fruit loss 43 , 52 , 53 . Box 1 provides real-life examples of preserving or enhancing bat foraging habitat and Supplementary Table 1 provides more examples of ecological countermeasures.
Box 1 Real-life examples illustrate the importance of protecting or enhancing where bats forage
In subtropical Australia, no Hendra virus spillovers occurred when Pteropus species bats left agricultural areas to feed on pulses of nectar in winter-flowering forests 33 . In some areas of the subtropics, over 90% of these crucial habitats have been cleared and the remaining forest flowers on multi-year cycles. Consequently, the occurrence of abundant winter flowering has become increasingly rare 33 . Restoring these habitats would target animals’ needs during predictable periods of scarcity, decrease their allostatic load, and reduce their reliance on human-dominated areas for food. Replanting winter habitats would be a sustainable, scalable, and effective strategy to reduce the risk of spillover of not just Hendra virus, but other viruses carried by Pteropus species bats.
Great fruit-eating bats ( Artibeus lituratus ) captured in areas of Colombia that used agroforestry had higher body weights and body condition scores than those within conventional farming areas 85 . Thus, emphasizing agroforestry in agricultural landscapes can provide critical food and shelter for bats 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 . In turn, bat predation of agricultural insect pests provides economic and ecological benefits to agriculture by increasing crop yields and reducing pesticide applications 90 .
To improve the foraging efficiency of wild little brown bats ( Myotis lucifugus ), insect density was increased using UV light lures 91 . This approach aimed to reduce the bats’ allostatic load and their susceptibility to white-nose syndrome, a disease caused by a fungal pathogen that does not pose a risk of spillover to people. Increased fat reserves can improve a bat’s ability to survive this disease. Bats had reduced commuting costs and increasing foraging efficiency, demonstrating that bats behaviorally respond to increased prey availability during critical energetic periods. This work highlights the potential benefits of restoring and enhancing habitats near bat hibernacula to improve the resilience of reservoir host species.
Agave plants are being restored along bat migration corridors in the southwest United States and northeast Mexico to provide nectar for Mexican Long-nosed bats ( Leptonycteris nivali ) and Lesser Long-nosed bats ( Leptonycteris yerbabuenae ) during energetically expensive migration 92 . In the first five years, over 80,000 agaves were planted within 50 km of six key bat roosts, encompassing both migratory and maternity roosts. This restoration effort not only aids bats but also benefits farmers and rural communities in Mexico, as wild agaves are also harvested for food and beverages, livestock fodder, fencing materials, and other uses. Agaves hold significant cultural value and contribute to the livelihoods of rural Mexican communities 92 . Consequently, restoring bat foraging habitat is an example of how conservation efforts can simultaneously enhance human well-being when co-benefits are identified and integrated.
Protect where bats roost
Roosts are locations where bats sleep, shelter, mate, socialize, and raise their young. With few exceptions, bats cannot construct shelters and must roost in pre-existing natural (e.g., caves, rock crevices, tree cavities, and tree foliage) or human-made (e.g., buildings, bridges, mines) structures. Moreover, species are typically highly selective of their roost sites, seeking out particular microclimates, light conditions, ingress, and egress conditions. The number of bats using a roost can vary greatly, containing anywhere from a few bats to hundreds of thousands, depending on the species and nature of the roost.
Protecting the roost includes minimizing disturbance and persecution—conversely, often a first response to an outbreak of a bat-borne pathogen. Disturbance not only causes stress, impairing their immune responses but can also force bats into new areas. This increases their energy expenditure and likelihood of contact with humans 22 , 55 . Moreover, culling bats has been linked to increased active infection within bat populations (e.g., rabies in vampire bats [ Desmodus rotundus 56 ] and Marburg virus in Egyptian fruit bats [ Rousettus aegyptiacus 21 ], and a greater risk of spillover.
Roosts are typically small natural features, and protecting roost sites is a specific management action that can reduce the risk of pathogen spillover. This may require establishing protection buffers around roosts or installing physical barriers (Fig. 4 , and Supplementary Table 1 ). Such buffers are also vital for preserving the quality and quantity of foraging habitats surrounding the roost. Engaging local communities is another key strategy, especially if the roost holds cultural or use value, as is common with caves 57 . Local communities are less likely to harm bats if they are aware of bat natural history, and have previously engaged in environmental education 58 , and are aware of the benefits of bat presence 59 .
Protect people at risk
The third countermeasure, focused on the safety of humans and livestock in proximity to reservoir hosts, is less ecologically oriented but is crucial in mitigating pathogen exposure risk (Fig. 4 , Supplementary Table 1 ). Pathogen exposure can occur through contact with reservoir hosts, their body fluids, excreta, or through aerosols and droplets derived from these sources. Thus, identifying and modifying human behaviors that elevate the risk of such exposures is essential.
For communities reliant on bat-associated economic activities, such as guano harvesting, tourism, and wildlife consumption 45 , 56 , 60 , 61 , adopting safe practices is critical (Supplementary Table 1 ). Additional measures may include restricting and regulating the trade of bats 62 and preventing contact between bats and farmed wildlife 63 . When the specific mechanisms of pathogen spillover are understood, the implementation of preventative measures can be relatively straightforward. In Bangladesh, an effective measure to prevent Nipah virus transmission is covering the areas of date palm trees where sap is collected, which prevents bats from contaminating the sap and transmitting the Nipah virus to humans 64 . In Malaysia, a regulation requiring fruit trees to be planted at a distance from pig sties may explain the lack of subsequent Nipah virus spillovers 65 . Similarly, keeping horses away from trees frequented by bats at night may reduce the risk of Hendra virus transmission between bats and horses 66 .
Box 2 lists interventions in the context of the degree of human landscape modification. Future work must assess the relative effectiveness, feasibility, and prioritization of these countermeasures across different countries and regions since the underlying conditions and legal landscapes will vary. Additionally, given the dynamic nature of climate and land use-induced changes impacting natural and human environments, a flexible, iterative, and adaptive approach is essential for prioritization of these countermeasures 67 .
Box 2 Countermeasures in the context of degree of human landscape modification
Ecological countermeasures that protect where bats eat and roost, and protect people at risk, must consider the activities of bats and humans in the landscape. Countermeasures can be implemented at a range of geographic extents and within different contexts of degrees of human modification (Fig. 4 and Supplementary Table 1 )
In large wild areas, protect where bats forage and roost:
Maintain or increase the integrity of ecosystems by preventing the destruction and fragmentation of natural areas.
In shared landscapes dominated by natural areas interspersed with human land uses:
Protect where bats eat:
Connect protected areas.
Preserve and restore vegetation diversity and structural complexity in bat foraging habitats.
Protect and restore habitats that provide food during periods of resource scarcity and high energetic demand.
Maintain or restore landscape heterogeneity through, for example, wide buffers of natural vegetation along sensitive habitat like streams and wetlands.
Promote sustainable agriculture and forestry practices that support bat foraging and roosting.
Minimize disruption to water sources used by bats.
Protect natural areas when planning new developments.
Protect where bats roost:
Limit human access to roost sites to minimize disturbances.
Create buffers of foraging habitat around known roosts.
Protect a diversity of roosting options for bats, including large cavity-bearing trees, tree snags, and caves.
Provide alternative roosting options such as boxes and hollow trees.
Protect people at risk:
Manage livestock to reduce interactions with bats and bat excreta.
Provide information on risks and risk mitigation associated with certain activities.
Use personal protective equipment for individuals in contact with bats or their excreta.
Vaccinate at-risk populations for endemic bat-borne pathogens such as Ebola or rabies and potentially against pandemic potential pathogens in the future.
Empower communities as stewards of the local land and wildlife, including bats.
In heavily modified landscapes such as intensively farmed and urban areas:
Preserve where bats eat and roost:
Conserve remaining natural habitats that provide shelter or food.
Maintain and restore connectivity.
Restore foraging habitat near roosts.
Restore habitat buffers around roosts.
Increase the proportion of native plant species that provide food and shelter for bats in remnant natural areas away from people.
Exclude bats from human food (e.g. fruit trees) and water supplies.
Exclude humans from roosts in public buildings and structures (e.g. churches, bridges, culverts).
Humanely exclude bats from houses and construct bat-proof housing.
Actively involve communities in risk mitigation measures.
Policy outlook
Currently, multilateral policy discussions focus predominantly on enhancing pandemic preparedness (e.g., developing new vaccines, readying healthcare systems) 1 , 68 . While these capacities are undeniably important, integrating a more balanced approach that also prioritizes spillover prevention could reduce human suffering and negative economic impacts in the long term. Despite this, prioritizing prevention proves challenging and is overshadowed by reactive strategies that are activated only after a pathogen is already circulating among humans. This is evident in the current draft of the World Health Organization (WHO) Pandemic Agreement, which does not mention “primary pandemic prevention” and uses the word “prevention” only in the context of secondary prevention measures such as early detection and outbreak response 69 .
Although the importance of pandemic prevention is well-acknowledged, the concept of using ecological countermeasures—actions that protect and restore wildlife habitat or mitigate wildlife-human interactions—as a preventative strategy is only emerging. Ecological countermeasures offer multiple advantages: not only can they prevent spillover, but they engage multiple sectors in action beyond public health, and they contribute multiple co-benefits including climate change mitigation, biodiversity protection, and added ecosystem services (e.g., pest control and pollination by bats). Feedback among these sectors calls for integrated approaches. For example, both climate change and biodiversity loss can intensify processes that drive spillover. Excess heat, extreme climate events, and changing plant phenology are likely to increase allostatic load and alter wildlife (and human) spatial behavior 70 . The loss of biodiversity, including predator species, often leaves ecosystems dominated by species that are more competent hosts for zoonotic pathogens 32 . Together these processes escalate the need for ecological countermeasures.
Ecological countermeasures support, strengthen, and work in accord with existing and future policy frameworks, including those under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change’s Paris Agreement, the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)’s Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, the UN Sustainable Development Goals, the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration, the new Pandemic Fund through the World Bank, and the WHO Pandemic Agreement. Such existing policy efforts offer opportunities for nations to invest in and incorporate primary pandemic prevention alongside preparedness efforts 1 .
Centrally, ecological countermeasures are fundamentally equitable because health benefits almost always accrue regardless of access to health systems. We’ve seen with COVID-19 and mpox that the most vulnerable populations, at greatest risk of infection and adverse outcomes, often had limited access to vaccines 71 . By contrast, spillover prevention benefits everyone globally, irrespective of individuals’ access to health systems 1 , 72 , 73 .
An Intergovernmental Panel for Pandemics
Many international entities have mandates that include enhancing pandemic prevention, preparedness, and response, including the One Health High-Level Expert Panel, the Global Preparedness Monitoring Board, and the Quadripartite. Such bodies all address unique and important issues, but none acts as an official scientific body that regularly assesses and synthesizes the full breadth of the latest data on pandemic prevention, preparedness, and response.
To address this, we strongly support the establishment of an Intergovernmental Panel for Pandemics, which could eventually come to fruition with the passage of the WHO Pandemic Agreement. This panel, if created, would provide regular scientific assessments to guide governments as they implement policies and programs related to pandemics. The scope of such a panel must include primary pandemic prevention alongside preparedness and response. The panel could be modeled after the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change or the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services 74 , 75 .
We recognize a risk of fragmentation with multiple different panels focused on climate, biodiversity, and pandemics. It is critical, therefore, to assure their coordination. By doing so, repeated efforts can be avoided, and, where applicable, intersectoral solutions can be implemented to harness co-benefits and synergies across sectors.
Moreover, there is a need to critically evaluate the evidence for the effectiveness of various pandemic prevention, preparedness, and response strategies. Although the global health community widely endorses strategies such as disease surveillance, perhaps largely due to their familiarity and experience with such methods, investments in primary prevention remain unprioritized. This raises a critical question: is there evidence that surveillance offers a greater reduction in pandemic risk compared to primary pandemic prevention (for example, is surveillance likely to activate response strategies in time to prevent spread of a pathogen with high transmissibility and pre-symptomatic spread)? To address these issues, an independent, broadly representative body could provide unbiased and politically neutral evaluation of the various strategies, encompassing prevention, preparedness, mitigation, and response 75 .
Metrics for pandemic prevention
Any program to mitigate pandemic risk through the conservation and restoration of nature must be evaluated to ensure it has the intended impact. Thus, we propose that the Intergovernmental Panel for Pandemics develop clear and robust metrics. These metrics should not only evaluate primary pandemic prevention efforts but also integrate them into existing biodiversity and climate change frameworks. Such metrics could monitor program performance, ensure accountability and transparency, and guide equitable wealth distribution to local communities based on program outcomes.
Numerous existing biodiversity assessment metrics could be shared with pandemic prevention metrics. Examples include the Ecological Integrity Index, STAR biodiversity index, and SEED biocomplexity metric, all in line with the CBD protocols. Additionally, there needs to be metrics specifically addressing spillover risk, including the guidance presented here (e.g., protect habitats where reservoir hosts forage and rest, especially during periods of resource scarcity; and reduce land-use changes that increase human-wildlife encounters).
The development of these metrics presents an opportunity to maximize the co-benefits of biodiversity preservation, climate change mitigation, and pandemic prevention. Such an integrated and synergistic approach should increase the success of program implementation globally 75 , 76 . For instance, restoration of koala ( Phascolarctos cinereus ) habitats in Australia, if strategically focused on trees that both support koalas and provide nectar for bats, could concurrently restore water catchments, sequester carbon, and reduce the risk of bat virus spillovers 33 .
Empowering local communities through One Health efforts
The One Health approach–popularized in recent years to optimize the health of people, animals, and ecosystems 77 –offers opportunities to implement ecological countermeasures for primary pandemic prevention. Currently, however, One Health efforts are overwhelmingly focused on disease surveillance in livestock and humans, rarely considering environmental drivers of emerging health threats 78 . One of the bottlenecks to advancing a more holistic One Health practice is the lack of practitioners across the animal-human-environment fields. To bridge this gap, we propose the creation of networks of ecosystem health workers to operationalize One Health and support local communities in implementing primary pandemic prevention. Those ecosystem health workers—who may include local forestry, wildlife, veterinary, medical, or public health officers–could be trained in, and help develop and implement, locally relevant ecological countermeasures, while embedded in larger governmental One Health teams. Their duties could include environmental education and ecological consultation (Supplementary Table 1 ), and information collection relevant to management actions (Box 3 ). They could also engage local universities and create pipelines for research on ecological countermeasure implementation and monitoring. They could ensure that local information is reported to national and international entities to inform effective, equitable decision-making 79 .
In parallel, it is essential to recognize the vital role of IPLCs in this framework. Integrating the perspectives and knowledge of IPLCs is not just a matter of cultural respect and justice; it is also a pragmatic strategy for designing and implementing appropriate, feasible and practical ecological countermeasures. Collaborating with IPLCs will help ensure that countermeasures align with local context and meaningfully incorporate local and Indigenous knowledge. IPLCs have managed natural ecosystems for thousands of years, and their involvement is increasingly seen as critical for reaching global climate and conservation goals 80 . Engaging IPLCs as equal partners in designing and implementing solutions to threats such as pandemics and climate change will increase the chances of successful outcomes 80 , 81 .
Box 3 Key questions for risk assessment and mitigation through ecological countermeasures, using bats as an example
Natural systems focus:
Which species of bats are present?
To what extent are local roost sites and foraging areas mapped?
Are local roost sites, and buffers around these sites, protected from disturbance?
What and where are the highest-quality habitats for these species in each season?
What resources are limited, either seasonally or consistently?
What habitat is required to ensure food is available during critical life stages?
How well are the local bat biology and movement patterns understood?
Human interactions focus:
Is land-use change likely to change the distribution and decrease the availability of bat foraging grounds, increase encounter rates with humans, or increase disturbance to roosts?
What is the nature of current bat-human interactions?
Are bat-human interactions increasing and, if so, why?
What are the attitudes of local communities toward bats, and why?
Who has regulatory authority to implement countermeasures?
Who are the key stakeholders needed to develop implementation mechanisms?
Is the available information sufficient to make informed decisions or actions?
Can areas critical to bats’ viability and health be protected or restored?
What steps can be taken to reduce contact between people and bats?
Expand the evidence base for ecological countermeasures
Our current understanding of pathogen spillover is characterized by vast knowledge inequalities. Biomedical aspects of spillover are extensively explored, while ecological components of spillover are under-represented. For example, thousands of publications detail the entry of bat-origin coronaviruses into human cells, but only a few studies explore their circulation in nature 82 . Moreover, studies on spillover are relatively rare but studies that examine the entire spillover process—from environmental drivers to reservoir hosts to human infections—are exceptionally rare. Therefore, our understanding of spillover is built on partial knowledge, such as studies demonstrating increased frequency of animal-human contact following habitat loss, or higher shedding in animals under stress (Supplementary Table 2 ). Although there is strong evidence for these component drivers of spillover, there is a critical need for studies that encompass the entire spectrum of spillover stages, including wildlife ecology, wildlife viral dynamics, human exposure, and human infection. Such studies need to be transdisciplinary, landscape-scale, with replication in space and time, shared data, and integration of local knowledge. Critically, these investigations must be grounded in the ecological systems where pandemics are likely to originate.
Pandemics have predominantly been addressed through a biomedical lens. While biomedical approaches are an essential part of the pandemic response toolbox, the genesis of a pandemic is rooted in ecological systems, necessitating ecological approaches for prevention. By aligning our research priorities with this understanding, we can build a comprehensive set of preemptive countermeasures that mitigate pandemic risk.
Conclusions
Spillover is an ecological process and, in the realm of human health, an ecological problem. While the human health issues arising from spillover events, such as outbreaks and pandemics, are addressed by epidemiological and biomedical countermeasures (e.g., testing, isolation, vaccines), the ecological aspects of spillover necessitate ecological solutions. In an ideal world, successful ecological countermeasures, which prevent spillover, would greatly reduce the need for biomedical countermeasures. We do not live in an ideal world; thus, we must move forward on both fronts.
To date, biomedical countermeasures to treat pandemics have received far more attention than ecological countermeasures. Our goal here has been to highlight the use of targeted ecological interventions as sensible, equitable, and efficient methods to prevent pandemics. While currently underutilized, ecological countermeasures have demonstrated potential in preventing spillover 33 , 76 . As challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and a growing global population intensify, the relevance and necessity of ecological approaches for pandemic prevention are expected to increase.
Although we illustrate the science of ecological countermeasures using bats as a case study, the concepts are applicable across various wildlife reservoir host taxa, including ungulates, primates, and rodents. To reduce the likelihood of pandemics, we must protect where animals forage and rest so that we can keep wildlife healthy, minimize allostatic load, reduce the need for animals to alter their spatial behavior, and minimize risky human-wildlife encounters.
The current confluence of political will, resources, and scientific evidence for primary pandemic prevention provides an opportunity to incorporate ecological countermeasures into multiple policy frameworks. Such countermeasures can help prevent pandemics by, in part, protecting and restoring nature across the globe. Explicit consideration of such countermeasures within global land management and conservation strategies is key to simultaneously addressing the intertwined threats of biodiversity loss, climate change and global pandemics.
Vora, N. M. et al. Want to prevent pandemics? Stop spillovers. Nature 605 , 419–422 (2022).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Markotter, W. et al. Prevention of zoonotic spillover: From relying on response to reducing the risk at source. PLoS Pathog. 19 , e1011504 (2023).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Plowright, R. K. et al. Land use-induced spillover: a call to action to safeguard environmental, animal, and human health. Lancet Planet Health 5 , e237–e245 (2021).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Carroll, D. et al. The Global Virome Project. Science 359 , 872–874 (2018).
Plowright, R. K. et al. Pathways to zoonotic spillover. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 15 , 502–510 (2017).
Plowright, R. K. et al. Transmission or within-host dynamics driving pulses of zoonotic viruses in reservoir–host populations. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 10 , e0004796 (2016).
Wasik, B. R. et al. Onward transmission of viruses: how do viruses emerge to cause epidemics after spillover? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 374 , 20190017 (2019).
Banerjee, A. et al. Novel insights into immune systems of bats. Front. Immunol. 11 , 26 (2020).
World Health Organization. Prioritizing Diseases for Research and Development in Emergency Contexts https://www.who.int/activities/prioritizing-diseases-for-research-and-development-in-emergency-contexts (2022).
Wingfield, J. C. et al. How birds cope physiologically and behaviourally with extreme climatic events. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 372 , 20160140 (2017).
McEwen, B. S. & Wingfield, J. C. Allostasis and allostatic load*. In Encyclopedia of Stress 2nd edn (ed. Fink, G.) 135–141 (Academic Press, 2007).
Wingfield, J. C. The concept of allostasis: coping with a capricious environment. J. Mammal. 86 , 248–254 (2005).
Article Google Scholar
Shimba, A., Ejima, A. & Ikuta, K. Pleiotropic effects of glucocorticoids on the immune system in circadian rhythm and stress. Front. Immunol. 12 , 706951 (2021).
Shimba, A. & Ikuta, K. Immune-enhancing effects of glucocorticoids in response to day-night cycles and stress. Int. Immunol. 32 , 703–708 (2020).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Reeder, D. M. & Kramer, K. M. Stress in free-ranging mammals: integrating physiology, ecology, and natural history. J. Mammal. 86 , 225–235 (2005).
Acevedo-Whitehouse, K. & Duffus, A. L. J. Effects of environmental change on wildlife health. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 364 , 3429–3438 (2009).
Phelps, K. L. & Kingston, T. Environmental and biological context modulates the physiological stress response of bats to human disturbance. Oecologia 188 , 41–52 (2018).
Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
Godbout, J. P. & Glaser, R. Stress-induced immune dysregulation: implications for wound healing, infectious disease and cancer. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 1 , 421–427 (2006).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Shimba, A. & Ikuta, K. Control of immunity by glucocorticoids in health and disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 42 , 669–680 (2020).
Guito, J.C. et al. Coordinated inflammatory responses dictate Marburg virus control by reservoir bats. Nat. Commun. 15 , 1826 (2024).
Amman, B. R. et al. Marburgvirus resurgence in Kitaka Mine bat population after extermination attempts, Uganda. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 20 , 1761–1764 (2014).
Becker, D. J., Eby, P., Madden, W., Peel, A. J. & Plowright, R. K. Ecological conditions predict the intensity of Hendra virus excretion over space and time from bat reservoir hosts. Ecol. Lett. 26 , 23–36 (2023).
Seltmann, A. et al. Seasonal fluctuations of astrovirus, but not coronavirus shedding in bats inhabiting human-modified tropical forests. Ecohealth 14 , 272–284 (2017).
Ruhs, E. C. et al. Applications of VirScan to broad serological profiling of bat reservoirs for emerging zoonoses. Front. Public Health 11 , 1212018 (2023).
Subudhi, S., Rapin, N. & Misra, V. Immune system modulation and viral persistence in bats: understanding viral spillover. Viruses 11 , 192 (2019).
Owen, J. C. et al. Reservoir hosts experiencing food stress alter transmission dynamics for a zoonotic pathogen. Proc. Biol. Sci. 288 , 20210881 (2021).
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gervasi, S. S., Burgan, S. C., Hofmeister, E., Unnasch, T. R. & Martin, L. B. Stress hormones predict a host superspreader phenotype in the West Nile virus system. Proc. Biol. Sci. 284 , 20171090 (2017).
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mueller, T. et al. How landscape dynamics link individual- to population-level movement patterns: a multispecies comparison of ungulate relocation data. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 20 , 683–694 (2011).
Tucker, M. A. et al. Moving in the Anthropocene: global reductions in terrestrial mammalian movements. Science 359 , 466–469 (2018).
Ripperger, S. P., Kalko, E. K. V., Rodríguez-Herrera, B., Mayer, F. & Tschapka, M. Frugivorous bats maintain functional habitat connectivity in agricultural landscapes but rely strongly on natural forest fragments. PLoS ONE 10 , e0120535 (2015).
Bloomfield, L. S. P., McIntosh, T. L. & Lambin, E. F. Habitat fragmentation, livelihood behaviors, and contact between people and nonhuman primates in Africa. Landsc. Ecol. 35 , 985–1000 (2020).
Gibb, R. et al. Zoonotic host diversity increases in human-dominated ecosystems. Nature 584 , 398–402 (2020).
Eby, P. et al. Pathogen spillover driven by rapid changes in bat ecology. Nature 613 , 340–344 (2023).
Schmidt, J. P. et al. Spatiotemporal fluctuations and triggers of ebola virus spillover. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 23 , 415–422 (2017).
Lunn, T. J. et al. Periodic shifts in viral load increase risk of spillover from bats. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.09.06.556454 (2023).
Luby, S. P. et al. Recurrent zoonotic transmission of Nipah virus into humans, Bangladesh, 2001–2007. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 15 , 1229–1235 (2009).
Arankalle, V. A. et al. Genomic characterization of Nipah virus, West Bengal, India. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 17 , 907–909 (2011).
Hegde, S. T. et al. Investigating rare risk factors for Nipah virus in Bangladesh: 2001–2012. Ecohealth 13 , 720–728 (2016).
Leroy, E. M. et al. Human Ebola outbreak resulting from direct exposure to fruit bats in Luebo, Democratic Republic of Congo, 2007. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 9 , 723–728 (2009).
Vilela, T. et al. A better Amazon road network for people and the environment. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117 , 7095–7102 (2020).
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Laurance, W. F., Goosem, M. & Laurance, S. G. W. Impacts of roads and linear clearings on tropical forests. Trends Ecol. Evol. 24 , 659–669 (2009).
Poulsen, J. R., Clark, C. J., Mavah, G. & Elkan, P. W. Bushmeat supply and consumption in a tropical logging concession in northern Congo. Conserv. Biol. 23 , 1597–1608 (2009).
Voigt, C. C. et al. Bats and buildings: the conservation of synanthropic bats. In Bats in the Anthropocene: Conservation of Bats in a Changing World (eds Voigt, C. C. & Kingston, T.) 427–462 (Springer International Publishing, 2016).
Dovih, P. et al. Filovirus-reactive antibodies in humans and bats in Northeast India imply zoonotic spillover. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 13 , e0007733 (2019).
Wang, N. et al. Serological evidence of bat SARS-related coronavirus infection in humans, China. Virol. Sin. 33 , 104–107 (2018).
Pacheco, P. et al. Deforestation: A Threat to People and Nature https://www.worldwildlife.org/stories/deforestation-fronts (2021).
Nicas, J. & Moriyama, V. The Amazon’s largest isolated tribe is dying. N. Y. Times Illegal Gold Rush Poisons Indigenous People in Amazon Haven. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2023/03/25/world/americas/brazil-amazon-indigenous-tribe.html (2023).
Cornwall, W. Illegal gold mines flood Amazon forests with toxic mercury. Science https://doi.org/10.1126/science.ada0701 (2022).
Nakkeeran, N. et al. Beyond behaviour as individual choice: a call to expand understandings around social science in health research. Wellcome Open Res 6 , 212 (2021).
Honigsbaum, M. Disease X and other unknowns. Lancet 393 , 1496–1497 (2019).
Prist, P. R. et al. Promoting landscapes with a low zoonotic disease risk through forest restoration: the need for comprehensive guidelines. J. Appl. Ecol. 60 , 1510–1521 (2023).
Law, B., Park, K. J. & Lacki, M. J. Insectivorous bats and silviculture: balancing timber production and bat conservation. In Bats in the Anthropocene: Conservation of Bats in a Changing World (eds. Voigt, C. & Kingston, T.) 105–150 (Springer, Cham, 2016).
Williams-Guillén, K., Olimpi, E., Maas, B., Taylor, P. J. & Arlettaz, R. Bats in the anthropogenic matrix: challenges and opportunities for the conservation of Chiroptera and their ecosystem services in agricultural landscapes. In Bats in the Anthropocene: Conservation of bats in a Changing World (eds. Voigt, C. & Kingston, T.) 151–186 (Springer, Cham, 2016).
Amman, B. R., Schuh, A. J., Albariño, C. G. & Towner, J. S. Marburg virus persistence on fruit as a plausible route of bat to primate filovirus transmission. Viruses 13 , 2394 (2021).
Seltmann, A. et al. Habitat disturbance results in chronic stress and impaired health status in forest-dwelling paleotropical bats. Conserv Physiol. 5 , cox020 (2017).
Streicker, D. G. et al. Ecological and anthropogenic drivers of rabies exposure in vampire bats: implications for transmission and control. Proc. Biol. Sci. 279 , 3384–3392 (2012).
Furey, N. M. & Racey, P. A. Conservation ecology of cave bats. In Bats in the Anthropocene: Conservation of Bats in a Changing World 463–500 (2016).
Reid, J. L. Knowledge and experience predict indiscriminate bat‐killing intentions among Costa Rican men. Biotropica 48 , 394–404 (2016).
Deshpande, K., Vanak, A. T., Devy, M. S. & Krishnaswamy, J. Forbidden fruits? Ecosystem services from seed dispersal by fruit bats in the context of latent zoonotic risk. Oikos 2022 , (2022).
Huong, N. Q. et al. Coronavirus testing indicates transmission risk increases along wildlife supply chains for human consumption in Vietnam, 2013–2014. PLoS ONE 15 , e0237129 (2020).
Vora, N. M. et al. Bat and lyssavirus exposure among humans in area that celebrates bat festival, Nigeria, 2010 and 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 26 , 1399–1408 (2020).
Osofsky, S. A., Lieberman, S., Walzer, C., Lee, H. L. & Neme, L. A. An immediate way to lower pandemic risk: (not) seizing the low-hanging fruit (bat). Lancet Planet Health 7 , e518–e526 (2023).
Biggs, D. et al. Governance principles for the wildlife trade to reduce spillover and pandemic risk. CABI One Health https://doi.org/10.1079/cabionehealth.2023.0013 (2023).
Khan, S. U. et al. A randomized controlled trial of interventions to impede date palm sap contamination by bats to prevent nipah virus transmission in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 7 , e42689 (2012).
Pulliam, J. R. C. et al. Agricultural intensification, priming for persistence and the emergence of Nipah virus: a lethal bat-borne zoonosis. J. R. Soc. Interface 9 , 89–101 (2012).
Martin, G., Webb, R. J., Chen, C., Plowright, R. K. & Skerratt, L. F. Microclimates might limit indirect spillover of the bat borne zoonotic Hendra virus. Microb. Ecol. 74 , 106–115 (2017).
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Plowright, R. K., Sokolow, S. H., Gorman, M. E., Daszak, P. & Foley, J. E. Causal inference in disease ecology: investigating ecological drivers of disease emergence. Front. Ecol. Environ. 6 , 420–429 (2008).
Kache, P. A., Cook, S., Sizer, N., Hannah, L. & Vora, N. M. Urgent need for integrated pandemic policies on pathogen spillover. Lancet Planet Health 5 , e668–e669 (2021).
Mettenleiter, T. C. et al. Draft of WHO Pandemic Agreement plays down primary prevention. Lancet 403 , 525–526 (2024).
Carlson, C. J. et al. Climate change increases cross-species viral transmission risk. Nature 607 , 555–562 (2022).
Asiedu, K. G. A year after outbreak, Africa waits for its share of mpox vaccines. Los Angel. Times (2023).
Adetifa, I., Muyembe, J.-J., Bausch, D. G. & Heymann, D. L. Mpox neglect and the smallpox niche: a problem for Africa, a problem for the world. Lancet 401 , 1822–1824 (2023).
Kozlov, M. WHO may soon end mpox emergency—but outbreaks rage in Africa. Nature 614 , 600–601 (2023).
ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Phelan, A. L. How climate law can help to prevent the next pandemic. Nature 605 , 397 (2022).
Oppenheim, B., Brown, K. & Waldman, R. The world needs an intergovernmental panel on pandemic risk. Nat. Med. 27 , 934 (2021).
Hopkins, S. R. et al. How to identify win–win interventions that benefit human health and conservation. Nat. Sustain. 4 , 298–304 (2020).
World Health Organization News. Tripartite and UNEP support OHHLEP’s definition of ‘One Health’ (World Health Organization, 2021). https://www.who.int/news/item/01-12-2021-tripartite-and-unep-support-ohhlep-s-definition-of-one-health .
Ahmed, T., Tahir, M. F., Boden, L. & Kingston, T. Future directions for One Health research: regional and sectoral gaps. One Health 17 , 100584 (2023).
Greer, S. L., Bekker, M. P. M., Azzopardi-Muscat, N. & McKee, M. Political analysis in public health: middle-range concepts to make sense of the politics of health. Eur. J. Public Health 28 , 3–6 (2018).
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Walker, W. S. et al. The role of forest conversion, degradation, and disturbance in the carbon dynamics of Amazon indigenous territories and protected areas. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117 , 3015–3025 (2020).
Jones, I. J. et al. Improving rural health care reduces illegal logging and conserves carbon in a tropical forest. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117 , 28515–28524 (2020).
Ruiz-Aravena, M. et al. Ecology, evolution and spillover of coronaviruses from bats. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 20 , 299–314 (2022).
Rasmussen, A. L. et al. Virology—the path forward. J. Virol. 98 , e0179123 (2024).
The World Bank. Establishment of a Financial Intermediary Fund for Pandemic Prevention, Preparedness and Response . http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/733191656685369495/Establishment-of-a-Financial-Intermediary-Fund-for-Pandemic-Prevention-Preparedness-and-Response (2022).
Chacón-Pacheco, J. J. & Ballesteros-Correa, J. MEJOR CONDICIÓN CORPORAL DE Artibeus lituratus EN FRAGMENTOS DE BOSQUE SECO ASOCIADOS A SISTEMAS SILVOPASTORILES QUE EN SISTEMAS CONVENCIONALES DE GANADERÍA EN CÓRDOBA, COLOMBIA. Oecol. Aust. 23 , 589–605 (2019).
Harvey, C. A. & González Villalobos, J. A. Agroforestry systems conserve species-rich but modified assemblages of tropical birds and bats. Biodivers. Conserv. 16 , 2257–2292 (2007).
Helbig-Bonitz, M. et al. Bats are not birds—different responses to human land‐use on a tropical mountain. Biotropica 47 , 497–508 (2015).
Williams-Guillén, K. & Perfecto, I. Effects of agricultural intensification on the assemblage of leaf-nosed bats (phyllostomidae) in a coffee landscape in Chiapas, Mexico. Biotropica 42 , 605–613 (2010).
Olimpi, E. M. & Philpott, S. M. Agroecological farming practices promote bats. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 265 , 282–291 (2018).
Tuneu-Corral, C. et al. Pest suppression by bats and management strategies to favour it: a global review. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 98 , 1564–1582 (2023).
Frick, W. F. et al. Bats increased foraging activity at experimental prey patches near hibernacula. Ecol. Solut. Evid. 4 , e12217 (2023).
Frick, W. F., de Wit, L. A., Ibarra, A., Lear, K. & O’Mara, M. T. Conserving bats and their foraging habitats. In A Natural History of Bat Foraging (eds. Russo, D. & Fenton, B.) Ch. 16, 305–325 (Academic Press, 2024).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Sonia Altizer, Andrew Breed, Daphne Carlson-Bremer, Peggy Eby, Lee Hannah, Eric Moise Bakwo Fils, and Paul Webala for the discussions that helped shape this manuscript. Thank you to Mary Noel at Blu Skye Consulting for helping organize a workshop that generated ideas for this manuscript, Robyn Egloff for help with figures, and Scott Bischke, Erica Fleishman, and Brooklin Hunt for comments on a draft of the manuscript. Funding: Cornell Center for Pandemic Prevention, Preparedness, and Response (R.K.P., C.E.W.); National Science Foundation DEB-1716698, EF-2133763, EF-2231624 (R.K.P., P.J.H., A.J.P., M.R.A.); Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency PREEMPT program Cooperative Agreement D18AC00031 (R.K.P., P.J.H., A.J.P., M.R.A., A.T.H.K.); National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health R01AI151144 (D.M.R. and I.E.); Montpellier Advanced Knowledge Institute On Transitions (R.K.P.); Natural Environment Research Council NE/V014730/1 (C.L.F.). The views, opinions, or findings expressed are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing the official views or policies of the Department of Defense or the U.S. Government.
Author information
Manuel Ruiz-Aravena
Present address: Department of Wildlife, Fisheries and Aquaculture, Mississippi State University, Starkville, USA
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Public and Ecosystem Health, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, 14853, USA
Raina K. Plowright, Manuel Ruiz-Aravena & Charley E. Willison
Medical Research Council Unit The Gambia, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London, WC1E 7HT, UK
Aliyu N. Ahmed
Department of Biology, University of Oxford, Oxford, OX1 3SZ, UK
Tim Coulson
Department of Environmental Systems Science, ETH Zürich, Zürich, 8092, Switzerland
Thomas W. Crowther
Department of Biology, Muni University, P.O. Box 725, Arua, Uganda
Imran Ejotre
School of Biodiversity, One Health and Veterinary Medicine, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, G12 8QQ, UK
Christina L. Faust
Bat Conservation International, Austin, TX, 78746, USA
Winifred F. Frick & M. Teague O’Mara
Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA, 95064, USA
Winifred F. Frick
Centre for Infectious Disease Dynamics, Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA, 16801, USA
Peter J. Hudson
Department of Biological Sciences, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, TX, 79409-3131, USA
Tigga Kingston
College of Climate Change and Environmental Science, Kerala Agricultural University, Kerala, 680 656, India
P. O. Nameer
Centre for Planetary Health and Food Security, Griffith University, Nathan, QLD, 4111, Australia
Alison J. Peel & Manuel Ruiz-Aravena
School of Biological Sciences, University of Queensland, Brisbane, QLD, 4072, Australia
Hugh Possingham
Biosciences, University of Exeter, Exeter, EX4 4PS, UK
Orly Razgour
Department of Biology, Bucknell University, Lewisburg, PA, 17937, USA
DeeAnn M. Reeder
Department of Mammalogy, Division of Vertebrate Zoology, American Museum of Natural History, New York City, NY, 10024, USA
Nancy B. Simmons
Institute of Public Health, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560070, India
Prashanth N. Srinivas
Center for Large Landscape Conservation, Bozeman, MT, 59771, USA
Gary M. Tabor & Annika T. H. Keeley
Department of Biology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, 98195, USA
Iroro Tanshi
Small Mammal Conservation Organization, Benin City, 300251, Nigeria
Department of Animal and Environmental Biology, University of Benin, Benin City, 300000, Nigeria
Australian Capital Territory, Canberra, 2605, Australia
Ian G. Thompson
Centre for Policy Design, Ashoka Trust for Research in Ecology and the Environment, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560064, India
Abi T. Vanak
School of Life Sciences, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban, 4041, South Africa
Conservation International, Arlington, VA, 22202, USA
Neil M. Vora
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to idea generation, writing, and editing. R.K.P., A.T.H.K., I.G.T., T.C., O.R., C.L.F., and A.T.V. led working groups that facilitated the first draft of each section; R.K.P., D.M.R., and O.R. developed the figures.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Raina K. Plowright .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Plowright, R.K., Ahmed, A.N., Coulson, T. et al. Ecological countermeasures to prevent pathogen spillover and subsequent pandemics. Nat Commun 15 , 2577 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46151-9
Download citation
Received : 31 January 2024
Accepted : 16 February 2024
Published : 26 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46151-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

There is unequivocal evidence that Earth is warming at an unprecedented rate. Human activity is the principal cause.

- While Earth’s climate has changed throughout its history , the current warming is happening at a rate not seen in the past 10,000 years.
- According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change ( IPCC ), "Since systematic scientific assessments began in the 1970s, the influence of human activity on the warming of the climate system has evolved from theory to established fact." 1
- Scientific information taken from natural sources (such as ice cores, rocks, and tree rings) and from modern equipment (like satellites and instruments) all show the signs of a changing climate.
- From global temperature rise to melting ice sheets, the evidence of a warming planet abounds.
The rate of change since the mid-20th century is unprecedented over millennia.
Earth's climate has changed throughout history. Just in the last 800,000 years, there have been eight cycles of ice ages and warmer periods, with the end of the last ice age about 11,700 years ago marking the beginning of the modern climate era — and of human civilization. Most of these climate changes are attributed to very small variations in Earth’s orbit that change the amount of solar energy our planet receives.
The current warming trend is different because it is clearly the result of human activities since the mid-1800s, and is proceeding at a rate not seen over many recent millennia. 1 It is undeniable that human activities have produced the atmospheric gases that have trapped more of the Sun’s energy in the Earth system. This extra energy has warmed the atmosphere, ocean, and land, and widespread and rapid changes in the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere, and biosphere have occurred.
Earth-orbiting satellites and new technologies have helped scientists see the big picture, collecting many different types of information about our planet and its climate all over the world. These data, collected over many years, reveal the signs and patterns of a changing climate.
Scientists demonstrated the heat-trapping nature of carbon dioxide and other gases in the mid-19th century. 2 Many of the science instruments NASA uses to study our climate focus on how these gases affect the movement of infrared radiation through the atmosphere. From the measured impacts of increases in these gases, there is no question that increased greenhouse gas levels warm Earth in response.
Scientific evidence for warming of the climate system is unequivocal.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Ice cores drawn from Greenland, Antarctica, and tropical mountain glaciers show that Earth’s climate responds to changes in greenhouse gas levels. Ancient evidence can also be found in tree rings, ocean sediments, coral reefs, and layers of sedimentary rocks. This ancient, or paleoclimate, evidence reveals that current warming is occurring roughly 10 times faster than the average rate of warming after an ice age. Carbon dioxide from human activities is increasing about 250 times faster than it did from natural sources after the last Ice Age. 3
The Evidence for Rapid Climate Change Is Compelling:

Global Temperature Is Rising
The planet's average surface temperature has risen about 2 degrees Fahrenheit (1 degrees Celsius) since the late 19th century, a change driven largely by increased carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere and other human activities. 4 Most of the warming occurred in the past 40 years, with the seven most recent years being the warmest. The years 2016 and 2020 are tied for the warmest year on record. 5 Image credit: Ashwin Kumar, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic.

The Ocean Is Getting Warmer
The ocean has absorbed much of this increased heat, with the top 100 meters (about 328 feet) of ocean showing warming of 0.67 degrees Fahrenheit (0.33 degrees Celsius) since 1969. 6 Earth stores 90% of the extra energy in the ocean. Image credit: Kelsey Roberts/USGS

The Ice Sheets Are Shrinking
The Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets have decreased in mass. Data from NASA's Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment show Greenland lost an average of 279 billion tons of ice per year between 1993 and 2019, while Antarctica lost about 148 billion tons of ice per year. 7 Image: The Antarctic Peninsula, Credit: NASA

Glaciers Are Retreating
Glaciers are retreating almost everywhere around the world — including in the Alps, Himalayas, Andes, Rockies, Alaska, and Africa. 8 Image: Miles Glacier, Alaska Image credit: NASA

Snow Cover Is Decreasing
Satellite observations reveal that the amount of spring snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere has decreased over the past five decades and the snow is melting earlier. 9 Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech

Sea Level Is Rising
Global sea level rose about 8 inches (20 centimeters) in the last century. The rate in the last two decades, however, is nearly double that of the last century and accelerating slightly every year. 10 Image credit: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Norfolk District

Arctic Sea Ice Is Declining
Both the extent and thickness of Arctic sea ice has declined rapidly over the last several decades. 11 Credit: NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio

Extreme Events Are Increasing in Frequency
The number of record high temperature events in the United States has been increasing, while the number of record low temperature events has been decreasing, since 1950. The U.S. has also witnessed increasing numbers of intense rainfall events. 12 Image credit: Régine Fabri, CC BY-SA 4.0 , via Wikimedia Commons

Ocean Acidification Is Increasing
Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, the acidity of surface ocean waters has increased by about 30%. 13 , 14 This increase is due to humans emitting more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and hence more being absorbed into the ocean. The ocean has absorbed between 20% and 30% of total anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions in recent decades (7.2 to 10.8 billion metric tons per year). 1 5 , 16 Image credit: NOAA
1. IPCC Sixth Assessment Report, WGI, Technical Summary . B.D. Santer et.al., “A search for human influences on the thermal structure of the atmosphere.” Nature 382 (04 July 1996): 39-46. https://doi.org/10.1038/382039a0. Gabriele C. Hegerl et al., “Detecting Greenhouse-Gas-Induced Climate Change with an Optimal Fingerprint Method.” Journal of Climate 9 (October 1996): 2281-2306. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<2281:DGGICC>2.0.CO;2. V. Ramaswamy, et al., “Anthropogenic and Natural Influences in the Evolution of Lower Stratospheric Cooling.” Science 311 (24 February 2006): 1138-1141. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1122587. B.D. Santer et al., “Contributions of Anthropogenic and Natural Forcing to Recent Tropopause Height Changes.” Science 301 (25 July 2003): 479-483. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1084123. T. Westerhold et al., "An astronomically dated record of Earth’s climate and its predictability over the last 66 million years." Science 369 (11 Sept. 2020): 1383-1387. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094123
2. In 1824, Joseph Fourier calculated that an Earth-sized planet, at our distance from the Sun, ought to be much colder. He suggested something in the atmosphere must be acting like an insulating blanket. In 1856, Eunice Foote discovered that blanket, showing that carbon dioxide and water vapor in Earth's atmosphere trap escaping infrared (heat) radiation. In the 1860s, physicist John Tyndall recognized Earth's natural greenhouse effect and suggested that slight changes in the atmospheric composition could bring about climatic variations. In 1896, a seminal paper by Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius first predicted that changes in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels could substantially alter the surface temperature through the greenhouse effect. In 1938, Guy Callendar connected carbon dioxide increases in Earth’s atmosphere to global warming. In 1941, Milutin Milankovic linked ice ages to Earth’s orbital characteristics. Gilbert Plass formulated the Carbon Dioxide Theory of Climate Change in 1956.
3. IPCC Sixth Assessment Report, WG1, Chapter 2 Vostok ice core data; NOAA Mauna Loa CO2 record O. Gaffney, W. Steffen, "The Anthropocene Equation." The Anthropocene Review 4, issue 1 (April 2017): 53-61. https://doi.org/abs/10.1177/2053019616688022.
4. https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/monitoring https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/temperature/ http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp
5. https://www.giss.nasa.gov/research/news/20170118/
6. S. Levitus, J. Antonov, T. Boyer, O Baranova, H. Garcia, R. Locarnini, A. Mishonov, J. Reagan, D. Seidov, E. Yarosh, M. Zweng, " NCEI ocean heat content, temperature anomalies, salinity anomalies, thermosteric sea level anomalies, halosteric sea level anomalies, and total steric sea level anomalies from 1955 to present calculated from in situ oceanographic subsurface profile data (NCEI Accession 0164586), Version 4.4. (2017) NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. https://www.nodc.noaa.gov/OC5/3M_HEAT_CONTENT/index3.html K. von Schuckmann, L. Cheng, L,. D. Palmer, J. Hansen, C. Tassone, V. Aich, S. Adusumilli, H. Beltrami, H., T. Boyer, F. Cuesta-Valero, D. Desbruyeres, C. Domingues, A. Garcia-Garcia, P. Gentine, J. Gilson, M. Gorfer, L. Haimberger, M. Ishii, M., G. Johnson, R. Killick, B. King, G. Kirchengast, N. Kolodziejczyk, J. Lyman, B. Marzeion, M. Mayer, M. Monier, D. Monselesan, S. Purkey, D. Roemmich, A. Schweiger, S. Seneviratne, A. Shepherd, D. Slater, A. Steiner, F. Straneo, M.L. Timmermans, S. Wijffels. "Heat stored in the Earth system: where does the energy go?" Earth System Science Data 12, Issue 3 (07 September 2020): 2013-2041. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-12-2013-2020.
7. I. Velicogna, Yara Mohajerani, A. Geruo, F. Landerer, J. Mouginot, B. Noel, E. Rignot, T. Sutterly, M. van den Broeke, M. Wessem, D. Wiese, "Continuity of Ice Sheet Mass Loss in Greenland and Antarctica From the GRACE and GRACE Follow-On Missions." Geophysical Research Letters 47, Issue 8 (28 April 2020): e2020GL087291. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL087291.
8. National Snow and Ice Data Center World Glacier Monitoring Service
9. National Snow and Ice Data Center D.A. Robinson, D. K. Hall, and T. L. Mote, "MEaSUREs Northern Hemisphere Terrestrial Snow Cover Extent Daily 25km EASE-Grid 2.0, Version 1 (2017). Boulder, Colorado USA. NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center. doi: https://doi.org/10.5067/MEASURES/CRYOSPHERE/nsidc-0530.001 . http://nsidc.org/cryosphere/sotc/snow_extent.html Rutgers University Global Snow Lab. Data History
10. R.S. Nerem, B.D. Beckley, J. T. Fasullo, B.D. Hamlington, D. Masters, and G.T. Mitchum, "Climate-change–driven accelerated sea-level rise detected in the altimeter era." PNAS 15, no. 9 (12 Feb. 2018): 2022-2025. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1717312115.
11. https://nsidc.org/cryosphere/sotc/sea_ice.html Pan-Arctic Ice Ocean Modeling and Assimilation System (PIOMAS, Zhang and Rothrock, 2003) http://psc.apl.washington.edu/research/projects/arctic-sea-ice-volume-anomaly/ http://psc.apl.uw.edu/research/projects/projections-of-an-ice-diminished-arctic-ocean/
12. USGCRP, 2017: Climate Science Special Report: Fourth National Climate Assessment, Volume I [Wuebbles, D.J., D.W. Fahey, K.A. Hibbard, D.J. Dokken, B.C. Stewart, and T.K. Maycock (eds.)]. U.S. Global Change Research Program, Washington, DC, USA, 470 pp, https://doi.org/10.7930/j0j964j6 .
13. http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/co2/story/What+is+Ocean+Acidification%3F
14. http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/co2/story/Ocean+Acidification
15. C.L. Sabine, et al., “The Oceanic Sink for Anthropogenic CO2.” Science 305 (16 July 2004): 367-371. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1097403.
16. Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate , Technical Summary, Chapter TS.5, Changing Ocean, Marine Ecosystems, and Dependent Communities, Section 5.2.2.3. https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc/chapter/technical-summary/
Header image shows clouds imitating mountains as the sun sets after midnight as seen from Denali's backcountry Unit 13 on June 14, 2019. Credit: NPS/Emily Mesner Image credit in list of evidence: Ashwin Kumar, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic.
Discover More Topics From NASA
Explore Earth Science

Earth Science in Action

Earth Science Data
Facts About Earth


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: Restate the problem. Step 2: Sum up the paper. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Research paper conclusion examples. Frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper is essential to leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here's a step-by-step process to help you create and know what to put in the conclusion of a research paper: 2. Research Statement: Begin your research paper conclusion by restating your research statement.
A research paper conclusion is the final section of a research paper that summarizes the key findings, significance, and implications of the research. It is the writer's opportunity to synthesize the information presented in the paper, draw conclusions, and make recommendations for future research or actions. ...
Learn how to write an effective discussion section for your research paper. Find out what makes an effective discussion, how to structure it, and what questions to ask yourself. See examples of how to summarize your results, highlight your implications, and compare your results with your hypothesis.
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research.
For example, while the conclusion to a STEM paper could focus on questions for further study, the conclusion of a literature paper could include a quotation from your central text that can now be understood differently in light of what has been discussed in the paper. ... In a short paper—even a research paper—you don't need to provide an ...
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a way that is slightly different from the wording used in the introduction. Avoid presenting new information or evidence in your conclusion. Just summarize the main points and arguments of your essay and keep this part as concise as possible. Remember that you've already covered the ...
Writing a Conclusion. A conclusion is an important part of the paper; it provides closure for the reader while reminding the reader of the contents and importance of the paper. It accomplishes this by stepping back from the specifics in order to view the bigger picture of the document. In other words, it is reminding the reader of the main ...
The conclusion of a research paper is essential in tying together the different parts of the paper and offering a final perspective on the topic. It reinforces the main idea or argument presented and summarizes the key points and findings of the research, highlighting its significance. Additionally, the conclusion creates a full circle of the ...
A well-written conclusion can leave the reader satisfied and inspired, while a poorly executed one may undermine the credibility of the entire paper. Therefore, it is essential to give careful thought and attention to crafting an effective conclusion. When writing a research paper, the conclusion acts as the final destination for the reader.
The conclusion is where you describe the consequences of your arguments by justifying to your readers why your arguments matter (Hamilton College, 2014). Derntl (2014) also describes conclusion as the counterpart of the introduction. Using the Hourglass Model (Swales, 1993) as a visual reference, Derntl describes conclusion as the part of the ...
Step 1: Restate the problem. Always begin by restating the research problem in the conclusion of a research paper. This serves to remind the reader of your hypothesis and refresh them on the main point of the paper. When restating the problem, take care to avoid using exactly the same words you employed earlier in the paper.
Research paper conclusion examples. Below, we've created basic templates showing the key parts of a research paper conclusion. Keep in mind that the length of your conclusion will depend on the length of your paper. The order of the parts may vary, too; these templates only demonstrate how to tie them together. 1. Empirical research paper ...
The point of a conclusion to a research paper is to summarize your argument for the reader and, perhaps, to call the reader to action if needed. 5. Make a call to action when appropriate. If and when needed, you can state to your readers that there is a need for further research on your paper's topic.
Conclusion Section for Research Papers. Conclusions are often the last section your audience reads, so they are just as important as introductions in research papers. They are your final opportunity to leave a good impression on the reader. Some academic readers will even jump to read the conclusion to help them decide if they should read the ...
The conclusion of a research paper has several key objectives. It should: Restate your research problem addressed in the introduction section. Summarize your main arguments, important findings, and broader implications. Synthesize key takeaways from your study. The specific content in the conclusion depends on whether your paper presents the ...
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of your points or a re-statement of your research problem but a synthesis of key points. For most essays, one well-developed paragraph is sufficient for a conclusion ...
Step 7: End with a Strong Closing Statement: Conclude your research paper with a memorable closing statement. This could be a thought-provoking reflection, a call to action, or a suggestion for future research. A strong closing leaves a lasting impression on your readers and emphasizes the importance of your work.
A conclusion is the final paragraph of a research paper and serves to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them. The conclusion of a conclusion should: Restate your topic and why it is important. Restate your thesis/claim. Address opposing viewpoints and explain why readers should align with your position.
Conclusions wrap up what you have been discussing in your paper. After moving from general to specific information in the introduction and body paragraphs, your conclusion should begin pulling back into more general information that restates the main points of your argument. Conclusions may also call for action or overview future possible research.
Download a PDF of the paper titled MM1: Methods, Analysis & Insights from Multimodal LLM Pre-training, by Brandon McKinzie and 31 other authors. Download PDF Abstract: In this work, we discuss building performant Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). In particular, we study the importance of various architecture components and data choices.
By aligning our research priorities with this understanding, we can build a comprehensive set of preemptive countermeasures that mitigate pandemic risk. Conclusions
Takeaways The rate of change since the mid-20th century is unprecedented over millennia. Earth's climate has changed throughout history. Just in the last 800,000 years, there have been eight cycles of ice ages and warmer periods, with the end of the last ice age about 11,700 years ago marking the beginning of the modern climate […]