Spanish translation of 'dissertation'
- dissertation


Browse Collins English collocations dissertation

Examples of 'dissertation' in a sentence dissertation
Trends of dissertation
View usage for: All Years Last 10 years Last 50 years Last 100 years Last 300 years
In other languages dissertation
- American English : dissertation / dɪsərˈteɪʃən /
- Brazilian Portuguese : dissertação
- Chinese : 论文 学位
- European Spanish : tesina
- French : mémoire
- German : Dissertation
- Italian : tesi
- Japanese : 学位論文
- Korean : 논문 학위
- European Portuguese : dissertação
- Latin American Spanish : tesina
Browse alphabetically dissertation
- dissentient
- dissenting view
- dissertation research
- All ENGLISH words that begin with 'D'
Related terms of dissertation
- doctoral dissertation
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5
Wordle Helper

Scrabble Tools
To support our work, we invite you to accept cookies or to subscribe.
You have chosen not to accept cookies when visiting our site.
The content available on our site is the result of the daily efforts of our editors. They all work towards a single goal: to provide you with rich, high-quality content. All this is possible thanks to the income generated by advertising and subscriptions.
By giving your consent or subscribing, you are supporting the work of our editorial team and ensuring the long-term future of our site.
If you already have purchased a subscription, please log in
What is the translation of "dissertation" in Spanish?
"dissertation" in spanish, dissertation {noun}.
- volume_up disertación
- tesis doctoral
Spanish translations powered by Oxford Languages
Dissertation noun, translations.
- "for PhD", education, American English
- "for lower degree", education, American English
- open_in_new Link to source
- warning Request revision
Context sentences
English spanish contextual examples of "dissertation" in spanish.
These sentences come from external sources and may not be accurate. bab.la is not responsible for their content.
Monolingual examples
English how to use "dissertation" in a sentence, collocations, "dissertation focus" in spanish.
- volume_up enfoque de disertación
- volume_up foco de tesis
"dissertation research" in Spanish
- volume_up investigación de disertación
- volume_up investigación de tesis
"dissertation writing" in Spanish
- volume_up escritura de disertación
- volume_up tesis de tesis
Synonyms (English) for "dissertation":
Pronunciation.
- dissenting justice
- dissenting member
- dissenting opinion
- dissenting opinions
- dissenting view
- dissenting views
- dissenting voice
- dissenting voices
- dissenting vote
- dissepiment
- dissertation
- dissertation focus
- dissertation research
- dissertation writing
- dissident activity
- dissident factions
- dissident group
- dissident movement
Do you want to translate into other languages? Have a look at our Malay-English dictionary .
Social Login
The Sheridan Libraries
- Spanish Language and Literature
- Sheridan Libraries
- Dissertations
- Information on an AUTHOR
- Information on a WORK
- Information on a THEME
- Research in Archives
- Essential Tools
- Language Tools
- Using the Library
Access to Dissertations
- ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global Includes more than 2 million entries.The single, central, authoritative resource for information about doctoral dissertations and master's theses.
- EBSCO Open Dissertations
- Interlibrary Loan the Library does not routinely purchase dissertations from other institutions. However, many are available through InterLibrary Services. Search in WorldCat for easiest ordering.
- Request a purchase for the library If you would like the Library to purchase a dissertation, contact the Librarian for the Department.
Databases in Europe and Latin America
TESEO : theses from Spanish universities since 1976.
Portal de tesis digitales de REBIUN : links to databases of theses of Spanish universities.
Biblioteca Virtual Miguel de Cervantes Tesis doctorales : theses in literature from Spanish universities. Some full-text available.
DART-Europe : E-theses Portal
EthOs : British Library dissertations
ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global : comprehensive listing of theses with abstracts in universities in the US, UK, and Ireland. Full-text coverage spans from 1743 to the present, with citation coverage dating back to 1637.
Buy Your Own
As a last resort, you can purchase dissertations directly.
Dissertation Express : US, from ProQuest
- Verify using the tools listed above that the document is not otherwise available to you free before ordering.
- If Interlibrary Loan can't locate a copy to borrow.
- Use a credit card or fax payment.
- Orders are shipped directly to you.
Submitting your dissertation
- Guidelines at JHU
- Graduate Board formatting details
Related Guide
- Electronic Theses & Dissertations
- << Previous: How to Find....
- Next: Essential Tools >>
- Last Updated: Aug 3, 2023 10:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/spanish
- Locations and Hours
- UCLA Library
- Research Guides
Spanish and Portuguese Studies
- Dissertations
- Primary Sources
UCLA Dissertations
Dissertations at ucla and beyond, spanish and portuguese dissertations, latin american dissertations, borrowing dissertations.
- EndNote and EndNote Basic
- Video and FIlm
- Citing and Writing
Search the Library Catalog for UCLA dissertations by author, title, or subject. Dissertations also have the form subject heading: Dissertations, academic — UCLA — department .
- UC Library Search This link opens in a new window UC Library Search is the unified discovery and borrowing system for all 10 UC Campuses. Select the UCLA Library Catalog scope to search holdings of materials owned by the UCLA Library and other UCLA collections, whether online or in print. Does not contain full-text articles or article citations. Select the Articles, books and more scope to search for materials in all 10 UC campuses. More information in this guide . OPAC, SRLF, UCLA Library Catalog
- Center for Research Libraries (CRL) Foreign Dissertations Search the CRL Catalog for dissertations already held at the Center. If a foreign dissertation is not at CRL, UCLA's Interlibrary Loan Service will request that CRL acquire it for your use. This special issue of Focus on Global Resources describes CRL's extensive collection of foreign dissertations.
- Networked Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations This international organization promotes the adoption, creation, use, dissemination, and preservation of electronic analogues to traditional paper-based theses and dissertations in order to more effectively share knowledge.
- TESEO Database of dissertations from Spanish universities.
- Biblioteca Virtual Miguel de Cervantes Tesis doctorales Provides an electronic catalog of theses from Spanish universities. Arranged alphabetically by university. Some full-text available.
- Repositórios Científicos de Acesso Aberto de Portugal (RCAAP) RCAAP constitutes a single entry point for searching, discovery and recall of thousands of scientific and scholarly publications, namely journal articles, conference papers, thesis and dissertations, distributed by several Portuguese repositories. It includes theses and dissertations.
Many electronic theses and dissertations (EDT) databases contain full text content.
- Biblioteca Digital Brasileira de Teses e Dissertações (BDTD) A portal to Brazilian theses and dissertations coordinated by IBICT. Contains more than 130,000 records to theses and dissertations of 92 Brazilian institutions. Links to full text may be restricted.
- TESIUNAM Database of masters and doctoral theses of the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México since 1986. Full-text PDFs available for most.
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL) Instructions for making an interlibrary loan request for materials not located at UCLA.
- << Previous: Primary Sources
- Next: EndNote and EndNote Basic >>
- Last Updated: Mar 18, 2024 10:12 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucla.edu/spanish
- University of Michigan Library
- Research Guides
Spanish Language and Literature
- Dissertations
- Getting Started
- Dictionaries
- Reference Works
- Digital Collections and Libraries
- Web Resources
- Dialnet: Tesis Repository of full text PhD dissertations from some 40 Spanish universities.
- Tesis Doctorales en Red / Tesis Doctorals en Xarxa Repository of full text PhD dissertations from the universities in Catalonia and other autonomous regions in Spain.
- Tesis Doctorales (TESEO) Catalog of PhD dissertations registered by the Spanish Ministry of Education. No full text.
- Biblioteca Virtual Miguel de Cervantes: Tesis Doctorales Catalog of PhD dissertations written in Spanish at any university in the world. Not comprehensive.
Latin America
- Portal de Tesis Latinoamericanas Full text theses and dissertations from Latin American universities.
- Tesis de UNAM Catalog of dissertations since 1900, some in full text format.
International
- Global Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Search ETDs from more than 200 universities on all continents.
- ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global This link opens in a new window Descriptions, sometimes with full text, of doctoral dissertations & master theses from US, UK, Canada, Ireland, etc.
- WorldCat Dissertations and Theses This link opens in a new window A subset of WorldCat containing records of dissertations, theses, and published material based on theses; many international titles not included elsewhere.
- Dissertation Reviews Overviews of recently defended, unpublished doctoral dissertations in a wide variety of disciplines across the Humanities and Social Sciences.
- Center for Research Libraries: Dissertations Dissertations from universities outside the U.S. and Canada.
Spanish Language and Literature Ph.D.
The Ph.D. is primarily a research and specialization degree, culminating in the writing of a dissertation.
Quick Links
- Spanish Program Home
- Spanish Graduate Programs
- Spanish Ph.D. Dissertation Abstracts
- Spanish Language and Literature M.A.
- Hispanic Applied Linguistics M.A.
- Spanish Program Graduate Funding
Our graduate programs include a Ph. D degree with specializations in both Spanish and Latin American Literature and Culture. Our Ph.D. students are mentored by our faculty, engage in substantive research projects, and benefit from rigorous teaching training. We offer courses that cover most geographical areas and time periods and guide students through relevant theoretical and methodological developments. Courses are complemented with lecture series and events that enrich our students’ intellectual and life experiences.
To be considered for admission applicants must:
- Have earned an M.A. degree or have equivalent training;
- Submit a paper in Spanish produced at the M.A. level;
- Submit a statement of purpose;
- Submit three letters of recommendation from academic references;
In addition, non-native speakers of English are required to take the TOEFL examination prior to admittance. Candidates must meet the minimum TOEFL standards established by the University of Maryland Graduate School (score of 100). For information students should contact the SLLC graduate coordinator.
Students on the "short list" may be interviewed by the graduate director in person or by phone.
Prior to admission to candidacy the student must demonstrate/fulfill the following:
- A thorough knowledge of the literary and cultural production in the main area of study;
- An in-depth knowledge of research tendencies in the field of specialization;
- At least two courses in the secondary area;
- A graduate course in the History of the Spanish Language;
- A minimum of one course in literary theory and/or criticism;
- A total of 30 credits of coursework (in very exceptional cases, fewer);
- Reading proficiency in a third language other than Spanish or English, appropriate to the student's field of study.
What do I need to apply?
To be considered for admission applicants must submit:
- Online application
- Application fee $75 -> Information about fee waiver
- Official transcripts of an M.A. degree or equivalent training.
- A paper in Spanish produced at the M.A. level.
- A statement of purpose.
- Three letters of recommendation from academic references.
- Non-native speakers of English are required to take the TOEFL examination prior to admittance. Candidates must meet the minimum TOEFL standards established by the University of Maryland Graduate School (score of 100). For information students should contact the SLLC graduate coordinator. Apply here Step-by-Step Guide to Applying English Language Proficiency Requirements for International Students **Due to deferrals, graduation delays during pandemic and reductions in available funding, admissions to our graduate programs will be more competitive for Fall 2021. Applicants should note that we are an affirmative action department and that we remain especially interested in recruiting strong African American, Hispanic American, and Native American students to our Ph.D. and M.A. programs.
Qualifying Examination: Procedures and Evaluation
Students who obtained their M.A. at another institution must take a qualifying examination after their first semester in the Ph.D. program. The goal of the exam is to ensure that students have both the specific field knowledge and the theoretical and/or critical background to continue in the program.
A student must declare her/his intention to take the qualifying examination in writing to the director of graduate Studies at least 60 days prior to the examination date, and at this time s/he should select the areas or fields and faculty advisor with whom s/he wants to work in preparation for the qualifying. The exam will be given every January, before the beginning of the spring semester. A committee consisting of two department faculty members (including the advisor) will meet to evaluate the examination and discuss the student's overall progress in the Ph.D. program. Written notification of the results will be sent to the student within one month of completing the exam. In the event that the student does not pass the exam, her/his advisor and the director of graduate studies may recommend that the student retake the examination in May. If a student does not pass the retake exam, s/he will not be allowed to continue in the Ph.D. program.
The examination is based on a list of 10 primary texts in the fields of Latin American and/or Spanish literature chosen by the student in consultation with her/his faculty advisor. The list of 10 books should focus on the student’s specific area of interest, as the purpose of the exam is to evaluate a student’s reading and writing skills as s/he continues to pursue a doctoral degree. The director of graduate studies must receive and approve the list of 10 texts as soon as the decision is made. Once the list is approved by the DGS, the student will have a maximum of 10 business days to select five (5) books from the list of 10 primary texts to prepare for the exam and inform the DGS and her/his faculty advisor of her/his decision. The DGS will then, in consultation with the student, establish the exact date of the examination in January (or May in the event of a retake).
The examination will be formulated by the faculty advisor and will include the following: (a) a close reading of a passage of no more than 500 words from one (1) book from the student’s list of five, which would lead to (b) an extrapolation to a wider set of ideas pertaining to the whole book and/or to the five (5) books selected. The student will receive the examination question by hand at the time of the exam and will have 4 hours to answer it in a room on a computer provided by the department with no internet access. The exam will be written in Spanish, with the exception of English for students who are specialized in U.S. Latina/o Studies. No notes or bibliography may be consulted, although a bilingual dictionary may be used.
The exam will be proctored by the Director of Graduate Studies or the SLLC Graduate Coordinator.
Route to Ph.D. Candidacy
After Ph.D. coursework has been completed, students proceed through a pre-candidacy stage consisting of three components: the comprehensive examination, the language reading (or “translation”) exam and the dissertation proposal and defense. Following successful completion of these three elements, students are advanced to candidacy and are considered “ABD” (all but dissertation).
Comprehensive Examination The comprehensive examination consists of three essays written over a span of three weeks. The essays are based on the courses a student has taken and on reading lists tailored to his or her sub-fields of focus (two in the main area and one in the secondary area). The three reading lists are created in consultation with faculty specialists in the areas of examination.
The comprehensive examination is offered three times per year, in January, May and August. On three consecutive Mondays, the student will receive a question to be answered in essay form, each related to a particular sub-field. These essays will be due by 3:00 p.m. on the Thursday of each respective week.
Sixty days prior to the desired examination start date, the candidate must inform the director of graduate studies as well as the professor assigned to administer the exam of his/her intention to sit for the examination. This notification should be submitted in writing, outlining the areas and sub-fields in which the student will be examined.
Exams will be evaluated by a committee consisting of two faculty members per subfield. Where appropriate, and in only one instance per student, the same faculty member may be called upon to evaluate two of the essays.
In the case of an unsuccessful examination, the student’s Ph.D. advisor and the director of graduate studies may recommend that the student sit a second time for the comprehensive examination. Continuation in the Ph.D. program depends on the successful outcome of any second attempt.
Language Reading (“Translation”) Examination This examination consists of a “for sense” translation from a third language into English or Spanish. The topic of the text will be related to the student's field of specialization. The choice of the language will be determined by its usefulness as a tool for the student's dissertation research. This exam may be repeated once. The student will choose a book or a long article together with a professor qualified to evaluate the third language (the examiner) and then notify the DGS of when the exam is to take place. The examiner will select a passage from the book or long article, which must be between 1,000 and 1,500 words. The examiner must submit the passage to the DGS for review at least two weeks prior to the exam. The student will have three hours to complete the exam, which will take place on campus and be proctored. Please note that only a printed dictionary (not an electronic source) is allowed to assist with the translation exam. For your information, please note that professors Igel and Lima are authorized to conduct examinations in Portuguese; and professors Naharro and Benito-Vessels are authorized to conduct examinations in French. Any questions about who is qualified to conduct the exam should be directed to the DGS. Please note also that dissertation advisors are not allowed to administer exams to their advisees. The examiner evaluates the exam and communicates the result directly to the DGS, who will then advise the student. The reading exam can be taken at any point prior to advancement to candidacy.
Dissertation Proposal and Defense The final stage of the pre-candidacy period is focused on preparation for the writing of the dissertation. In consultation with an advisory committee consisting of the dissertation director and three members of the faculty, the student will write a dissertation proposal that aims to give a clear sense of the intended corpus of study, intellectual aims and methodology. The proposal should include a review of the literature, an outline of projected chapters and a selected bibliography. Proposals should be about 25-30 pages in length and are expected to be completed within four months to one year after the comprehensive examination.
The advisory committee and the candidate will then convene for the defense of the proposal. All faculty in the department are welcome to attend the defense.
The Dissertation
As stated previously, the Ph.D. is essentially a research degree. This means that coursework taken for the Ph.D. is intended as a preparation for the dissertation. It is therefore of the utmost importance that the student identify his/her field of interest as soon as possible. Early in the first semester, students should consult with one or more professors and explore the research possibilities in the field, period, genre, author(s) of his/her particular interest and select an academic advisor accordingly.
Dissertation Defense
When the candidate has completed the dissertation, the director of graduate studies notifies the Graduate School of its completion. The dean of the Graduate School, upon the recommendation of the director of graduate studies, appoints an examining committee for the candidate. This examining committee will include four members of the department and one member from another academic unit who acts as the graduate dean's representative. The committee will be chaired by the dissertation director.
All members of the examining committee will read the dissertation in its final form and take part in an oral examination in which the candidate defends his/her findings. Copies of the dissertation must be given to members of the examining committee at least 10 days before the date set for the oral examination. The Graduate School has established procedures for the dissertation examination. For details on these and all other aspects regarding the dissertation, please see the Thesis and Dissertation Forms and Guidelines. In addition, the student must provide the department with one copy of the final version of his/her dissertation.
Students are expected to defend the dissertation within 4 years of advancing to candidacy. The director of graduate studies may approve an extension of up to one year in cases of extenuating circumstances.

Application for Graduation
Students must apply for a graduate diploma early in the semester in which they intend to receive their degree. Deadlines are published in the Schedule of Classes.
Note: Once students are done they MUST file an EXIT form with the Graduate School and, if applicable, an address change form.
Graduate Student Handbook
The purpose of the Graduate Student Handbook is to aid you in understanding the context of graduate education at UMD. The goal is to provide you with resources, information, practices, and policies that will help you in navigating the graduate experience.
Teaching Handbook
The Teaching Handbook is intended to familiarize graduate students with the procedures, policies, and expectations in teaching, research and administrative environments as an integral part of their education.
Steven J. Green School of International & Public Affairs
Search this website
Doctor of philosophy in spanish, general information:.
The Department of Modern Languages offers a variety of opportunities for advanced study. The Ph.D. program in Hispanic Literature is designed to prepare students to become first-rate scholars and teachers, primarily in institutions of higher learning. In addition to two major fields of specialization (Peninsular Spanish Literature and Spanish American Literature), minors are available in Peninsular Spanish Literature, Spanish American Literature, and Hispanic Linguistics. Candidates to the Ph.D. must pass a qualifying examination .
Description of the Program
The doctoral program consists of 75 semester hours of graduate level work beyond the Bachelor's degree, distributed as follows: 57 graduate credits of courses and 18 credits of dissertation. Students holding Master of Arts degrees in Spanish or Hispanic Studies will be considered for admission and some or all of their graduate credits may be counted toward the doctoral degree after being evaluated and approved by the Graduate Studies Committee. Student will be able to transfer a maximum of 36 graduate credits from an earned graduate degree.
Course Distribution
Core Courses: (9 credits)
All core courses must be taken as graduate courses offered by the University and may not be taken as independent studies:
- FOL 5943 Foreign Language Teaching Methodology
- SPW 5806 Methods of literary research
- SPW 6825 Literary Theory and Criticism
Distribution Requirement: (15 credits)
All students must take:
- One course in Medieval or Golden Age Peninsular Spanish Literature
- One course in Peninsular Spanish Literature of the 18th-21st century
- One course in Colonial/19th century Spanish American Literature
- One course in 20th century Spanish American Literature
- One additional course in Spanish American Literature
Electives: (33 credits)
Students may choose from graduate courses in literature, linguistics, culture, and translation/interpretation.
Dissertation: (18 credits)
Independent Studies
Students who want to conduct research in a very specialized field with a particular faculty member will be allowed to register for a 3-credit independent study course. No more than two such independent study will be allowed without permission from the Graduate Program Director and only in exceptional cases. Under no circumstances will a student be authorized to take a regularly-taught course as an independent study. Independent studies are envisioned as an opportunity for students to carry out specialized research, not as a substitute for regular courses.
__________________________________________________________________________________________
Dissertation Proposal
The dissertation proposal consists of two documents: 1) A concise (max. 5 pages double-spaced) dissertation proposal following University Graduate School guidelines; 2) a more developed statement of research purpose and plans (15-20 pages long). Students should circulate these two documents among all the members of the committee at least two weeks prior to the oral defense. The dissertation proposal has to be approved by the four members of the dissertation committee. Please see the Graduate Student Handbook for more details Here
The dissertation proposal is a five-page document with an appended bibliography that explains in detail the proposed thesis topic, the critical instrument chosen to approach it, existing scholarship on the subject, and an overarching plan for its development. The proposal is prepared in consultation with the thesis adviser but it is revised and evaluated by all the members of the student's graduate committee. The proposal should follow the general guidelines in the Regulations for Thesis and Dissertation Preparation. A copy of the approved proposal must be filed with the Dean of Graduate Studies at least one full semester prior to defense of the dissertation or thesis.
Students who have completed all coursework must register in SPW 7910 Pre-dissertation Research during the semester in which he or she expects to be admitted to candidacy. Students fully admitted to candidacy subsequently register in SPN 7980 Dissertation Research. Candidates must be registered in at least three credit-hours of dissertation research every semester --including at least one summer term-- once he or she begins such preparation. The candidate must be enrolled for at least three dissertation credits during the semester in which the doctoral degree is awarded.
The statement of research purpose and plans is internal to the department.
Dissertation
A dissertation or thesis is a formal and systematic discourse or treatise advancing an original point of view as a result of research. A dissertation is required of all candidates for the doctoral degree.
Upon completion of a dissertation or thesis, the degree candidate will submit to the Dean of Graduate Studies an application for thesis or dissertation defense signed by the dissertation director. The application must be filed in sufficient time to allow the Dean of Graduate Studies to publish the notice in a monthly calendar of dissertation and theses defenses for the University community.
Copies of the final version of the dissertation, prepared in accordance with the most recent edition of the MLA Style Manual or MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Paper and the FIU Guidelines for Thesis and Dissertation Writers (available from the Office of Graduate Studies), together with an abstract in English of a maximum of 350 words, must be submitted to the Dissertation Committee at least four weeks before the Oral Defense of the Dissertation, which must be scheduled following UGS calendar.
Dissertation Defense
The date, time, and place of the Defense will be announced by memo from the Dissertation Director at least two weeks in advanced to the rest of the committee, the candidate, the Director of Graduate Studies, the department Chairperson, the Dean of the College of Arts and Sciences, the Dean of Graduate Studies and Media Relations.
The oral defense, which is open to public, will take the following form: 10-15 minute presentation by candidate, 10 minute question period from each member of the dissertation committee.
Following the successful defense, as determined by a majority vote of the student's committee, the dissertation or thesis is forwarded to the Academic Dean and to the dean of graduate studies for their approval.
The Ph.D. dissertation must be completed within five years of the doctoral comprehensive examination, or the examination will have to be retaken.
Seminars on Professional Concerns
The Department of Modern Languages recognizes the need to inform graduate students regarding a wide range of professional issues directly related to the successful development of their academic careers. To that end, each year it sponsors a series of meetings during which these concerns can be more fully addressed and explored. The professional concerns seminars meet as needed and are led by one or several faculty members. Topics to be covered include "Publishing your work," "Participating in conferences and symposia," "Applying for grants and fellowships," "Writing the curriculum vitae," "Applying for jobs," and "Preparing for an interview." Other possible topics for discussion might include book reviewing, publishing the dissertation and networking. Students may also propose a seminar on a topic not listed here that is of special professional concern to them. Such proposals are channeled through the Director of Graduate Studies.
Graduate and Teaching Assistantships
A limited number of assistantships are available each year for doctoral students. Candidates seeking an assistantship must apply in writing to the Graduate Program Director by December 15th. Assistantships normally consist of a stipend of $20,000 per academic year (including the summer terms) and a matriculation fee-waiver.
In exchange, students who receive assistantships must work twenty hours per week for the Department and must take a minimum of nine credits per semester and six credits in the summer. Students with more than eighteen graduate credits generally fulfill their work requirements by teaching one language class per term.
Assistantships are incompatible with outside employment. Please see the Graduate Program Director for further information. Renewal is not automatic but contingent upon the student's successful performance in the following areas: (1) academics (2) work as graduate or teaching assistant, (3) participation in all the meetings and activities organized by the department. Renewals must be approved by the graduate committee in consultation with the student’s advisor and the Language Coordinator. In order to have the Teaching Assistantship renewed, ABDs will have to show adequate progress towards the completion of their dissertation.
For information on additional special scholarships, please contact the Graduate Program Director.
Selected Course Offerings
- Methods of Literary Research
- Literary Theory and Criticism
- Historiography of Literature
- The Structure of Spanish
- History of the Spanish Language
- Spanish in the United States
- Dialectology of the Spanish Caribbean
- Learning Technology in Spanish Pedagogy and Research
- Spanish Culture
- Spanish American Culture
- Hispanic Culture in the US
- Afro-Cuban Culture
- The Latin American Experience in Literature and Film
- Colonial Latin American Literature
- 19th Century Latin American Literature
- Spanish American Modernism
- The Traditional Spanish American Novel
- Primitivism in Spanish American Literature
- Magical Realism
- Contemporary Spanish American Novel
- Spanish American Historical Novel
- Spanish American Essay
- Prose and Poetry of Jorge Luis Borges
- Poetry of Pablo Neruda
- Eros in the Poetry of Spanish American Women Writers
- Spanish American Women Writers
- Hispanic Literature of the US
- Mexico in Poetry
- Literature of the Spanish Caribbean
- 19th Century Spanish Caribbean Literature
- Cuban Theater
- Cuban Narrative
- Prose and Poetry of José Martí
- Literature of Hispanics in the United States
- Medieval Spanish Literature
- The Renaissance in Spain
- Golden Age Prose
- Golden Age Poetry
- Spanish Romanticism and Neoclassicism
- Spanish Realism and Naturalism
- Seminar on Benito Pérez Galdós
- Generation of 98
- 20th Century Spanish Novel
- Poetry of Jorge Guillén
- Seminar on Federico García Lorca
- Seminar on Antonio Buero Vallejo
- Modern Spanish Women Writers
- Representation of Women in Spanish Literature and Film
- 20th Century Spanish Poetry
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Translation of disertación – Spanish–English dictionary
Disertación.
(Translation of disertación from the GLOBAL Spanish–English Dictionary © 2021 K Dictionaries Ltd)
Translation of disertación | PASSWORD Spanish–English Dictionary
(Translation of disertación from the PASSWORD Spanish–English Dictionary © 2014 K Dictionaries Ltd)

Word of the Day
not a living soul

Dead ringers and peas in pods (Talking about similarities, Part 2)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- GLOBAL Spanish–English Noun
- PASSWORD Spanish–English Noun
- All translations
To add disertación to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add disertación to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- Pronunciation
THE BEST SPANISH-ENGLISH DICTIONARY
Get more than a translation, written by experts, translate with confidence, spanish and english example sentences, examples for everything, regional translations, say it like a local.
Making educational experiences better for everyone.
Immersive learning for 25 languages
Marketplace for millions of educator-created resources
Fast, easy, reliable language certification
Fun educational games for kids
Comprehensive K-12 personalized learning
Trusted tutors for 300+ subjects
35,000+ worksheets, games, and lesson plans
Adaptive learning for English vocabulary
- UConn Library
- Spanish Studies Subject Guide
- Thinking about Topics
Spanish Studies Subject Guide — Thinking about Topics
- Exploring Broad Topics in Spanish Studies
- Narrowing Topics in Spanish Studies
- Forming a Research Question
- Finding Primary Sources
- Finding Secondary Sources
- Finding Open Access Sources
- Finding Audiovisual Materials
- Finding Current News
- Finding Materials on Microform
- Citing Sources
- Finding Additional Resources

Exploring broad topics in Spanish Studies scholarship is a good way to start thinking about potential topics for your essay, research paper, or project. As you explore some of the broad topics in recent scholarship, consider:
- What are the expectations around the essay, paper, or project? Are there specific geographic or temporal requirements for the assignment?
- What interests you most about some of the broad topics? What are some of the ways that they connect with your interests inside and outside of the classroom?

If you have identified a broad topic, the next step is to adapt or narrow the topic to match the course expectations and requirements for your essay, paper, or project. As you narrow your topic, consider:
- What are expectations around the length of the paper or project?
- What are the requirements around the use of primary and secondary sources?

Identifying a topic and sources to support your analysis is an important first step in the research process. For many essays and projects, forming a research question and thesis statement is an important next step. As you form a research question, plan to use additional resources:
- Visit your professors during drop-in office hours or make an appointment with them to discuss your research question and thesis statement early in the process.
- Use the UConn Writing Center to formulate or revise a research question or preliminary thesis statement. The writing center offers free in-person and online tutoring. You can make an appointment, drop-in with a quick question, or request written feedback.
- Email or make an appointment with the Research Services Librarian for Spanish Studies for help finding additional primary or secondary sources.
- << Previous: Overview
- Next: Exploring Broad Topics in Spanish Studies >>
- Last Updated: Mar 27, 2024 3:43 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/Spanish

File(s) under embargo
until file(s) become available
Prosody and politeness: The effect of power, distance, and imposition on the production and perception of polar questions in requests
The present dissertation addresses the gap of how the three contextual variables (power, distance, and imposition) affect the use and perception of pitch range and final pitch contours in Central Peninsular Spanish polar questions. The methodological approach in this dissertation combines a production experiment in the form of a contextualized sentence-reading task (e.g., Brown et al., 2014; Henriksen, 2013) and a perception experiment using a pragmatic judgment task (e.g., Nadeu & Prieto, 2011). Both tasks systematically incorporated a set of situations that included the contextual variables of power, distance, and imposition. Thus, this dissertation provides a systematic analysis of power, distance, and imposition to investigate their influence on the use and perception of pitch range and pitch contours. To analyze pitch in the production experiment, a categorical analysis of final pitch contours (e.g., low-rising contour) and a quantitative analysis of prosodic features (i.e., pitch range and its conversion into semitones) were conducted. For the perception experiment, analyses included the comparison of linear mixed models to examine the perceived degree of politeness.
The findings presented in this dissertation support the Frequency Code Hypothesis in that they showed the relevance of pitch for signaling and perceiving politeness in requests in Spanish. The results from the production experiment suggested there are no effects of power, distance, and imposition on the selection of final intonational contours. Regarding the analysis of pitch range, the results from the production experiment indicated that the use of greater pitch range was associated with an increase in the social distance between the speakers. In the perception experiment, the results indicated that an increase in pitch range was directly associated with an increase in the perceived degree of politeness. Furthermore, the findings from this dissertation provided evidence for including a systematic analysis of the contextual variables of power, distance, and imposition to conduct analyses within the politeness framework instead of analyzing the formal/informal dimension in isolation The overall results of this dissertation contribute to the understanding of how suprasegmental features are employed in showing and perceivicing politeness.
Degree Type
- Doctor of Philosophy
- Languages and Cultures
Campus location
- West Lafayette
Advisor/Supervisor/Committee Chair
Advisor/supervisor/committee co-chair, additional committee member 2, additional committee member 3, additional committee member 4, usage metrics.
- Linguistic structures (incl. phonology, morphology and syntax)
- Phonetics and speech science
- Discourse and pragmatics
- Sociolinguistics
- Speech production
- Speech recognition
- Psycholinguistics (incl. speech production and comprehension)

Let your curiosity lead the way:
Apply Today
- Arts & Sciences
- Graduate Studies in A&S
Shelei Pan wins 2024 Spector Prize
Shelei-pan.jpg.
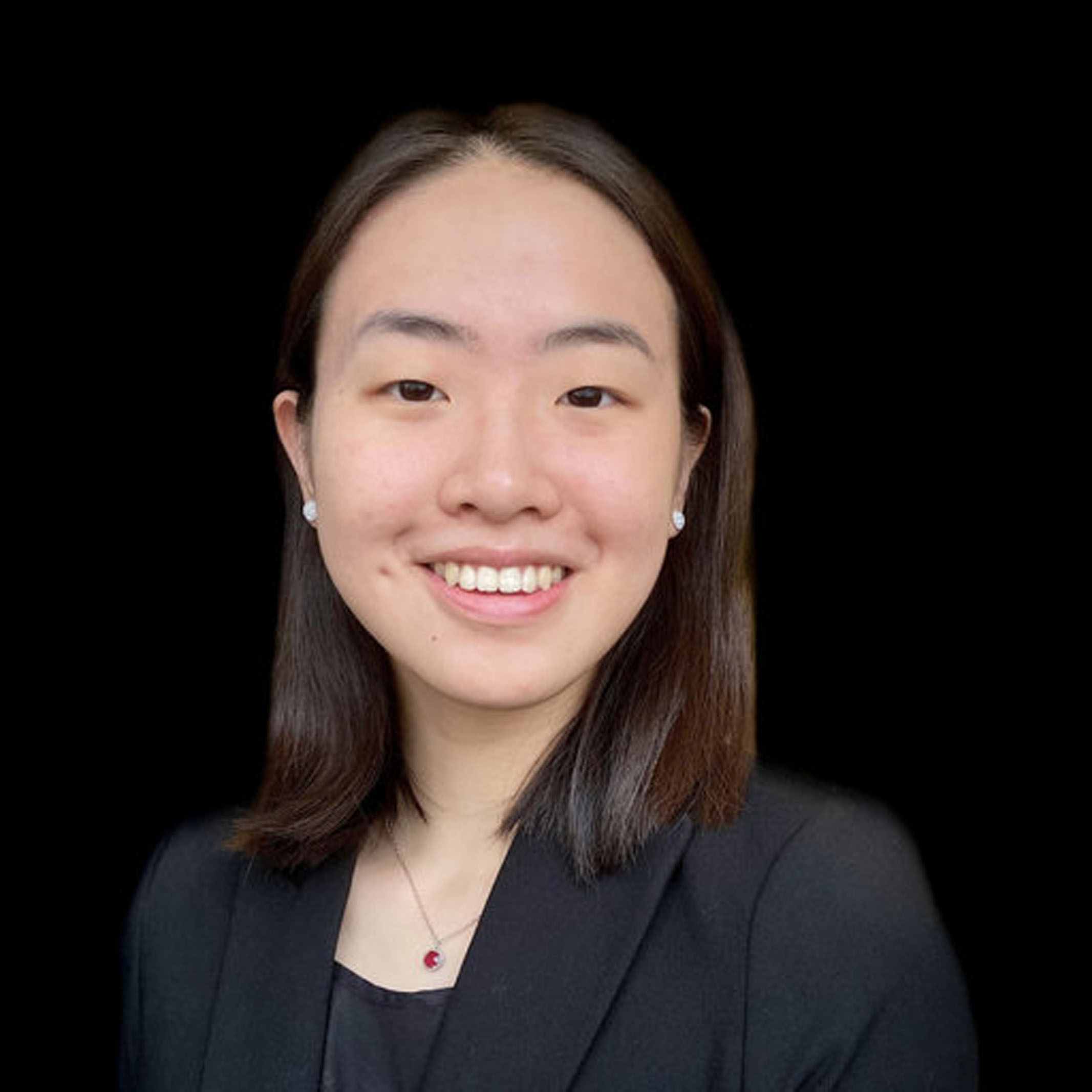

Each year, the Department of Biology in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis awards a prize to a graduating senior in memory of Marion Smith Spector, a 1938 graduate who studied zoology under the late Viktor Hamburger. The Spector Prize, first awarded in 1974, recognizes academic excellence and outstanding undergraduate achievement in research. Students are nominated by their research mentors for outstanding research that has made substantial contributions to a field.
This year’s winner, Shelei Pan, is a December graduate who majored in the Neuroscience track of the Biology Major, and minored in Spanish. Her thesis research The dynamic roles of cerebrospinal fluid in brain development and pediatric central nervous system pathology was completed in the Strahle Lab.
In her nomination letter, Jennifer Strahle , Professor of Neurosurgery, Orthopedic Surgery and Pediatrics, wrote, “Shelei’s work clearly demonstrates extraordinary achievement. From a scientific standpoint, her work has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of cerebrospinal fluid flow. This would be a substantial achievement for a PhD student. For it to occur during her time as an undergraduate is nothing short of phenomenal. In the last year, her contributions have accelerated despite carrying a full academic course load. Her ability to do so bodes well for her future career as a physician-scientist. Her work on the novel identification of specific CSF circulation routes within the brain was published in Nature Communications with Shelei as the sole first author. I have not seen this level of commitment and unending intellectual curiosity from anyone with whom I have worked. Shelei’s work has resulted in significant advances in our understanding of CSF interaction with the central nervous system.”
Pan says “I am honored to join the rich legacy of undergraduates to receive the Spector Prize. Partaking in research over the past 4-5 years has presented innumerable opportunities for my personal and professional growth, above all the privilege of receiving unparalleled mentorship from faculty who I consider to be my greatest role models. I would like to express my deepest gratitude to my PI, Dr. Jennifer Strahle, for her wholehearted dedication and enthusiasm towards facilitating my development as a scientist, and for providing an invaluable grounding influence in connecting the importance of bench work to the humans it may one day impact. I would also like to give special thanks to Dr. Erik Herzog and Dr. Joan Downey for their unwavering support and wisdom through the years. Winning the Spector Prize is a reflection of the amazing environment all of my mentors and the Biology Department at WashU have created to truly make a difference in my life.”
Honorable mentions for the Spector Prize include Erica Hurley for her work in Joseph Corbo’s lab, Braxton Sizemore for his work in Ashley Edes’ lab, Jessica Greven for her work in Thomas Brett’s lab, and Yuhua (Amelia) Li for her work in Albert (Gus) Davis’ lab. All Spector Prize winners will present their research in a special seminar, and will receive a prize and formal acknowledgement at a celebration of biology honors and research emphasis students in May.
in the news:

Davis wins 2024 Quatrano Prize

Walensky calls for collaborative approach to public health policy, education

Scientists track red-tailed hawks nesting near WashU campus
Unlocking the ‘chain of worms’
Books | How a French Ph.D. dissertation became a…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Food & Drink
- Amusement Parks
- Theater & Arts
Things To Do
Books | how a french ph.d. dissertation became a southern california beach read, after coming to study at ucla, paris-born elsa devienne spent years working on her book, 'sand rush: the revival of the beach in twentieth-century los angeles.'.

Originally from Paris, Elsa Devienne spent a year studying at UCLA in the late ‘00s. With a gig as a dog sitter in Santa Monica, she had affordable rent and the chance to visit the local beaches .
“I remember, first of all, being wowed by this incredible landscape, the beauty of the Pacific Ocean ,” Devienne, now based in Manchester, U.K., recalls on a recent video call. But she says the heavily built-up areas around the beaches “shocked” her. “You could find parking lots, freeways, houses, buildings.”
SEE ALSO : Sign up for our free Book Pages newsletter about bestsellers, authors and more
Devienne, who had never visited Los Angeles before her year at UCLA, was most perplexed by the parking lots that are ubiquitous along the otherwise gorgeous landscape: Who, she wondered, had envisioned the landscape this way – and why?

The winners of the Mr. Muscle Beach Contest in 1951. (Credit Los Angeles Herald Examiner Collection, University of Southern California Digital Library /Courtesy of Oxford University Press)

A parking lot built in 1950 on the newly expanded Venice Beach. (Credit California Coast Aug. 1950, Water Resources Collections & Archives, University of California, Riverside / Courtesy of Oxford University Press)

Employees of a real estate company do group calisthenics at Playa Del Rey in the 1920s. (Credit Fritz Burns Papers William H. Hannon Library, Loyola Marymount University / Courtesy of Oxford University Press)

Santa Monica Harbor as seen from above in 1949. (Credit Los Angeles City Archives / Courtesy of Oxford University Press)

The lack of facilities and popularity with teenagers caused some consternation of the beach lobby. (Credit California Coast Aug. 1950, Water Resources Collections & Archives, University of California, Riverside / Courtesy of Oxford University Press)

A scene from Muscle Beach, circa 1947. (Photo credit Los Angeles Daily News Negatives, Library Special Collections, Charles E. Young Research Library, University of California, Los Angeles / Courtesy of Oxford University Press)

Abbye “Pudgy” Stockton with her admirers at Muscle Beach, circa 1947. (Photo credit Los Angeles Daily News Negatives, Library Special Collections, Charles E. Young Research Library, University of California, Los Angeles / Courtesy of Oxford University Press)

A 1936 diagram from California Beaches Association for a project to develop the beach and highway along Santa Monica. (Credit Water Resources Collections & Archives, University of California, Riverside / Courtesy of Oxford University Press)

Historian Elsa Devienne is the author of “Sand Rush: The Revival of the Beach in Twentieth-Century Los Angeles,” out from Oxford University Press. (Courtesy of Oxford University Press)
Experiencing the sand first-hand
These questions launched her upon a years-long investigation into the history of the beaches that line the western edge of Los Angeles County. Originally researched for her Ph.D. dissertation at Ecole des Hautes Etudes en Sciences Sociales, Devienne continued to work on the material, which was then translated by Troy J. Tice, for her nonfiction book, “Sand Rush: The Revival of the Beach in Twentieth-Century Los Angeles,” which is out May 1 on Oxford University Press.
The book tracks the development of the coastline from the 1920s – when the beaches were more polluted and difficult to access – through the midcentury and beyond as a so-called “beach lobby” worked to develop, clean and expand the coastline, often with the goal of making it a bastion of the White middle-class. As well, Devienne examines the landscape from its real estate significance to its ascendance as a place to celebrate physical beauty.
However, as well as research, Devienne says it’s important to experience the landscape you’re writing about.
“You have to observe how people behave at the beach and who goes to what beach for what reason,” she says. For her year in L.A., Devienne immersed herself in the city. She took a class led by the historian Eric Avila at UCLA and worked with people who had been writing about the city for years. She spent time at Santa Monica Public Library , Santa Monica History Museum , Long Beach Historical Society and Los Angeles Public Library .
“I was a library rat,” she says, but talked to plenty of locals. “The lifeguards, surfers, people who hung out at the beach in the ‘60s, anybody who was ready to talk to me about beaches.”
She later returned to L.A., this time as a Fulbright Scholar for a six-month stint at USC, and interviewed Venice High School and Santa Monica High School alumni. She also took a deep dive into beach reading.
“I read some really, really interesting, funky, wonky, crazy, pornographic ‘50s books about the L.A. beach culture, which, in some cases, I was able to use in the book,” she says.
Devienne would return to Los Angeles again during her time teaching at Princeton. For that trip, she brought students and toured Malibu with them, using the Our Malibu Beaches app to locate entrances to the sand. It was a way of applying her research with people who were largely from the East Coast, where beaches can be harder to access than they are in California.
“That’s basically because the law about what part of the beach is public or private has been interpreted differently in different states,” Devienne explains. “In some states, this has been interpreted strictly and other states much more expansively. The main idea is that the beach that is always wet – that is covered by tide – should always be public, should always be accessible, but the part that is dry can be privatized.”
She adds that some states had more ambitious programs to buy back beaches than others. “In some places, like on the East Coast, there’s such a large history of implementation and establishment of settlements that it was very difficult to buy back the beaches,” says Devienne. “Because California has a history of the presence of Anglo Americans that is a bit less old, there were possibilities to buy back bigger lands that hadn’t yet been broken up into smaller properties.”
Throughout her research, Devienne traces a history of L.A.’s beach life filled with ironies. It’s a history steeped in making the coast accessible, yet marred by racist restrictions. While it’s a human-engineered landscape, the beach has also spawned environmentalist movements.
Climate change and the coastline
Devienne writes that local activism has led to beaches that are “cleaner, more accessible, and more inclusive than they have been in over a century,” but that, as a result of our changing climate, the beaches still face a precarious future.
“It’s so important to keep on pushing for these places to be accessible to all people, to be easily accessible. But also for them to continue existing,” says Devienne. “For this to happen, we need to continue pushing for climate change legislation, for reducing our carbon emissions.”
She adds, “Literally, this is a question of survival. My children could see the end of California beaches as we know them within their lifetime.”
SEE ALSO : Read Laylan Connelly’s coverage of Southern California’s beaches and coastline.
Ultimately, “Sand Rush” took a turn that Devienne didn’t anticipate when she began looking at L.A. beach history. “I didn’t realize when I started writing that this is how I would conclude it,” says Devienne of the discussion of climate change. “As I was writing, the scientific evidence became more and more clear that we could lose something so incredibly wonderful as a beach.”
Next up for Devienne is the history of beach cleanups. She came across the stories of women in Oregon and Texas who began organizing cleanups in the 1980s where volunteers categorized the trash that they found.
“That, for me, is an important chapter and milestone in the history of the anti-plastic movement, which I intend on writing about in my second book,” she says.
- Newsroom Guidelines
- Report an Error
More in Books

Books | This week’s bestsellers at Southern California’s independent bookstores

Books | 10 Independent Bookstore Day tips to find books, authors and giveaways

Books | Why Rachel Khong says novel ‘Real Americans’ explores issues society still faces

COMMENTS
dissertation n. US (doctoral thesis) tesis doctoral nf inv + adj. The student was pleased to have finally finished the dissertation for her doctorate. La estudiante estaba contenta de haber por fin acabado la tesis doctoral para su doctorado. dissertation n. UK (master's extended essay) (de maestría) tesis nf inv.
A dissertation is a long formal piece of writing on a particular subject, especially for a university degree. He is currently writing a dissertation on the civil war. American English: dissertation / dɪsərˈteɪʃən /. Brazilian Portuguese: dissertação. Chinese: 论文 学位. European Spanish: tesina.
noun. 1. (extended doctoral paper) (United States) a. la tesis. (F) Robert's dissertation for his PhD discussed the optimal choice of vocabulary in pedagogical settings.La tesis de doctorado de Robert versó sobre la elección óptima de vocabulario en contextos pedagógicos. 2. (extended master's essay) (United Kingdom)
DISSERTATION translations: tesina, tesis [feminine]. Learn more in the Cambridge English-Spanish Dictionary.
traducir DISSERTATION: tesina, tesis [feminine]. Más información en el diccionario inglés-español.
Spanish Translation of "DISSERTATION" | The official Collins English-Spanish Dictionary online. Over 100,000 Spanish translations of English words and phrases.
Translation for 'dissertation' in the free English-Spanish dictionary and many other Spanish translations.
Say It like a Local. Browse Spanish translations from Spain, Mexico, or any other Spanish-speaking country. Translate Disertación. See 3 authoritative translations of Disertación in English with example sentences and audio pronunciations.
Biblioteca Virtual Miguel de Cervantes Tesis doctorales: theses in literature from Spanish universities. Some full-text available. DART-Europe: E-theses Portal. EthOs: British Library dissertations. ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global: comprehensive listing of theses with abstracts in universities in the US, UK, and Ireland. Full-text ...
Dissertations at UCLA and Beyond. Index to doctoral dissertations from 1637 to the present, with abstracts since 1980. A number of master's theses are also indexed, with abstracts since 1988. Many are available for download in pdf format. UCLA has access to all full text dissertations in the database.
A subset of WorldCat containing records of dissertations, theses, and published material based on theses; many international titles not included elsewhere. Overviews of recently defended, unpublished doctoral dissertations in a wide variety of disciplines across the Humanities and Social Sciences. Dissertations from universities outside the U.S ...
What is the difference between thesis and dissertation? Compare and contrast the definitions and Spanish translations of thesis and dissertation on SpanishDictionary.com, the world's most accurate Spanish-English reference website.
Submit a paper in Spanish produced at the M.A. level; Submit a statement of purpose; Submit three letters of recommendation from academic references; ... Dissertation Proposal and Defense The final stage of the pre-candidacy period is focused on preparation for the writing of the dissertation. In consultation with an advisory committee ...
disertación translations: lecture, dissertation. Learn more in the Cambridge Spanish-English Dictionary.
Doctor of Philosophy in Spanish. Department of Modern Languages PhD in Spanish Deuxieme Maison, Room 480 11200 SW 8th Street Miami, FL 33199 Phone: 305-348-2851 Fax: 305-348-1085 ... The dissertation proposal is a five-page document with an appended bibliography that explains in detail the proposed thesis topic, the critical instrument chosen ...
The Department of Modern Languages offers a variety of opportunities for advanced study. The Ph.D. program in Hispanic Literature is designed to prepare students to become first-rate scholars and teachers, primarily in institutions of higher learning. In addition to two major fields of specialization (Peninsular Spanish Literature and Spanish ...
A thesis statement in Spanish is called a planteamiento del problema or formulación del problema. An effective statement should have language that is accurate, argumentative, and academic.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
disertación translate: lecture, dissertation. Learn more in the Cambridge Spanish-English Dictionary.
Use the UConn Writing Center to formulate or revise a research question or preliminary thesis statement. The writing center offers free in-person and online tutoring. You can make an appointment, drop-in with a quick question, or request written feedback. At UConn Storrs, the writing center is located on Level 2 of the Homer Babbidge Library ...
1. (argument) a. la tesis. (F) I love your writing style, but you need to strengthen your thesis.Me encanta tu estilo de escritura, pero tienes que reforzar tu tesis. 2. (education) a. la tesis. (F) This afternoon, she is going to defend her thesis on the civil wars of the 20th century.Esta tarde va a defender su tesis sobre las guerras civiles ...
Identifying a topic and sources to support your analysis is an important first step in the research process. For many essays and projects, forming a research question and thesis statement is an important next step. As you form a research question, plan to use additional resources: Visit your professors during drop-in office hours or make an ...
Thesis Title; May 8: 9-10am: Sydney Johnson: A (Brief) Black, Panamanian History of Reggaeton: Connecting The Streets of Panamá to New York, Puerto Rico, and the World: May 8: ... Department of Spanish and Portuguese 359 East Pyne Princeton, New Jersey 08544-5264. Contact Information. Tel: (609) 258-7180 Fax: (609) 258-7155 [email protected ...
The present dissertation addresses the gap of how the three contextual variables (power, distance, and imposition) affect the use and perception of pitch range and final pitch contours in Central Peninsular Spanish polar questions. The methodological approach in this dissertation combines a production experiment in the form of a contextualized sentence-reading task (e.g., Brown et al., 2014 ...
This year's winner, Shelei Pan, is a December graduate who majored in the Neuroscience track of the Biology Major, and minored in Spanish. Her thesis research The dynamic roles of cerebrospinal fluid in brain development and pediatric central nervous system pathology was completed in the Strahle Lab.
How a French Ph.D. dissertation became a Southern California beach read After coming to study at UCLA, Paris-born Elsa Devienne spent years working on her book, 'Sand Rush: The Revival of the ...