

How to write an essay: Body
- What's in this guide
- Introduction
- Essay structure
- Additional resources
Body paragraphs
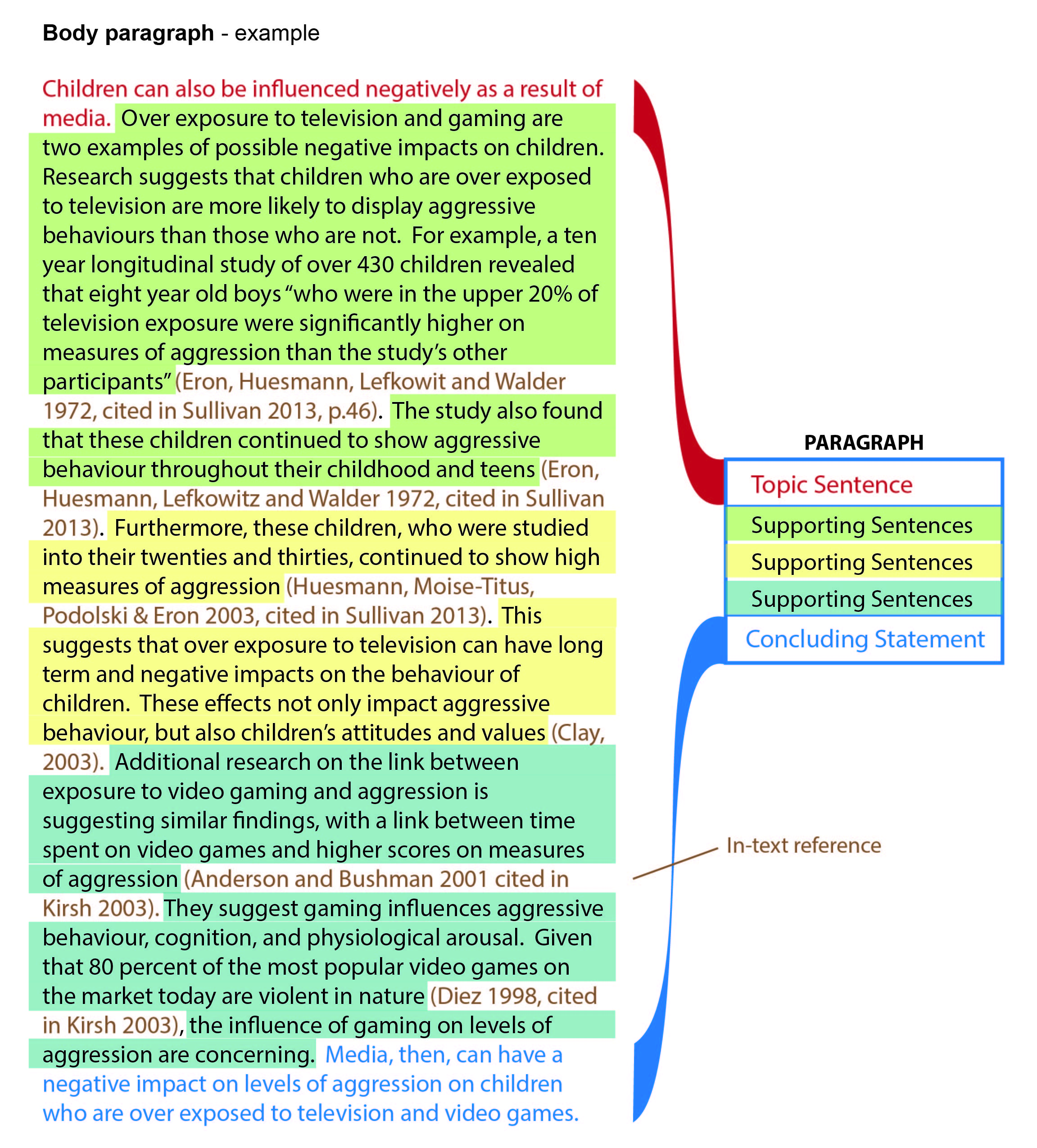
The essay body itself is organised into paragraphs, according to your plan. Remember that each paragraph focuses on one idea, or aspect of your topic, and should contain at least 4-5 sentences so you can deal with that idea properly.
Each body paragraph has three sections. First is the topic sentence . This lets the reader know what the paragraph is going to be about and the main point it will make. It gives the paragraph’s point straight away. Next – and largest – is the supporting sentences . These expand on the central idea, explaining it in more detail, exploring what it means, and of course giving the evidence and argument that back it up. This is where you use your research to support your argument. Then there is a concluding sentence . This restates the idea in the topic sentence, to remind the reader of your main point. It also shows how that point helps answer the question.
Pathways and Academic Learning Support

- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Nov 29, 2023 1:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay
- Departments and Units
- Majors and Minors
- LSA Course Guide
- LSA Gateway
Search: {{$root.lsaSearchQuery.q}}, Page {{$root.page}}
- Accessibility
- Undergraduates
- Instructors
- Alums & Friends

- ★ Writing Support
- Minor in Writing
- First-Year Writing Requirement
- Transfer Students
- Writing Guides
- Peer Writing Consultant Program
- Upper-Level Writing Requirement
- Writing Prizes
- International Students
- ★ The Writing Workshop
- Dissertation ECoach
- Fellows Seminar
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Rackham / Sweetland Workshops
- Dissertation Writing Institute
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- Teaching Support and Services
- Support for FYWR Courses
- Support for ULWR Courses
- Writing Prize Nominating
- Alums Gallery
- Commencement Archive
- Giving Opportunities
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph?
- How Do I Make Sure I Understand an Assignment?
- How Do I Decide What I Should Argue?
- How Can I Create Stronger Analysis?
- How Do I Effectively Integrate Textual Evidence?
- How Do I Write a Great Title?
- What Exactly is an Abstract?
- How Do I Present Findings From My Experiment in a Report?
- What is a Run-on Sentence & How Do I Fix It?
- How Do I Check the Structure of My Argument?
- How Do I Incorporate Quotes?
- How Can I Create a More Successful Powerpoint?
- How Can I Create a Strong Thesis?
- How Can I Write More Descriptively?
- How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument?
- How Do I Check My Citations?
See the bottom of the main Writing Guides page for licensing information.
Traditional Academic Essays In Three Parts
Part i: the introduction.
An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you’re writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things:
- Gets the reader’s attention. You can get a reader’s attention by telling a story, providing a statistic, pointing out something strange or interesting, providing and discussing an interesting quote, etc. Be interesting and find some original angle via which to engage others in your topic.
- Provides a specific and debatable thesis statement. The thesis statement is usually just one sentence long, but it might be longer—even a whole paragraph—if the essay you’re writing is long. A good thesis statement makes a debatable point, meaning a point someone might disagree with and argue against. It also serves as a roadmap for what you argue in your paper.
Part II: The Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs help you prove your thesis and move you along a compelling trajectory from your introduction to your conclusion. If your thesis is a simple one, you might not need a lot of body paragraphs to prove it. If it’s more complicated, you’ll need more body paragraphs. An easy way to remember the parts of a body paragraph is to think of them as the MEAT of your essay:
Main Idea. The part of a topic sentence that states the main idea of the body paragraph. All of the sentences in the paragraph connect to it. Keep in mind that main ideas are…
- like labels. They appear in the first sentence of the paragraph and tell your reader what’s inside the paragraph.
- arguable. They’re not statements of fact; they’re debatable points that you prove with evidence.
- focused. Make a specific point in each paragraph and then prove that point.
Evidence. The parts of a paragraph that prove the main idea. You might include different types of evidence in different sentences. Keep in mind that different disciplines have different ideas about what counts as evidence and they adhere to different citation styles. Examples of evidence include…
- quotations and/or paraphrases from sources.
- facts , e.g. statistics or findings from studies you’ve conducted.
- narratives and/or descriptions , e.g. of your own experiences.
Analysis. The parts of a paragraph that explain the evidence. Make sure you tie the evidence you provide back to the paragraph’s main idea. In other words, discuss the evidence.
Transition. The part of a paragraph that helps you move fluidly from the last paragraph. Transitions appear in topic sentences along with main ideas, and they look both backward and forward in order to help you connect your ideas for your reader. Don’t end paragraphs with transitions; start with them.
Keep in mind that MEAT does not occur in that order. The “ T ransition” and the “ M ain Idea” often combine to form the first sentence—the topic sentence—and then paragraphs contain multiple sentences of evidence and analysis. For example, a paragraph might look like this: TM. E. E. A. E. E. A. A.
Part III: The Conclusion
A conclusion is the last paragraph of your essay, or, if you’re writing a really long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to conclude. A conclusion typically does one of two things—or, of course, it can do both:
- Summarizes the argument. Some instructors expect you not to say anything new in your conclusion. They just want you to restate your main points. Especially if you’ve made a long and complicated argument, it’s useful to restate your main points for your reader by the time you’ve gotten to your conclusion. If you opt to do so, keep in mind that you should use different language than you used in your introduction and your body paragraphs. The introduction and conclusion shouldn’t be the same.
- For example, your argument might be significant to studies of a certain time period .
- Alternately, it might be significant to a certain geographical region .
- Alternately still, it might influence how your readers think about the future . You might even opt to speculate about the future and/or call your readers to action in your conclusion.
Handout by Dr. Liliana Naydan. Do not reproduce without permission.

- Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- Alumni and Friends
- More about LSA
- How Do I Apply?
- LSA Magazine
- Student Resources
- Academic Advising
- Global Studies
- LSA Opportunity Hub
- Social Media
- Update Contact Info
- Privacy Statement
- Report Feedback
How to Write a Body Paragraph for a College Essay
January 29, 2024

No matter the discipline, college success requires mastering several academic basics, including the body paragraph. This article will provide tips on drafting and editing a strong body paragraph before examining several body paragraph examples. Before we look at how to start a body paragraph and how to write a body paragraph for a college essay (or other writing assignment), let’s define what exactly a body paragraph is.
What is a Body Paragraph?
Simply put, a body paragraph consists of everything in an academic essay that does not constitute the introduction and conclusion. It makes up everything in between. In a five-paragraph, thesis-style essay (which most high schoolers encounter before heading off to college), there are three body paragraphs. Longer essays with more complex arguments will include many more body paragraphs.
We might correlate body paragraphs with bodily appendages—say, a leg. Both operate in a somewhat isolated way to perform specific operations, yet are integral to creating a cohesive, functioning whole. A leg helps the body sit, walk, and run. Like legs, body paragraphs work to move an essay along, by leading the reader through several convincing ideas. Together, these ideas, sometimes called topics, or points, work to prove an overall argument, called the essay’s thesis.
If you compared an essay on Kant’s theory of beauty to an essay on migratory birds, you’d notice that the body paragraphs differ drastically. However, on closer inspection, you’d probably find that they included many of the same key components. Most body paragraphs will include specific, detailed evidence, an analysis of the evidence, a conclusion drawn by the author, and several tie-ins to the larger ideas at play. They’ll also include transitions and citations leading the reader to source material. We’ll go into more detail on these components soon. First, let’s see if you’ve organized your essay so that you’ll know how to start a body paragraph.
How to Start a Body Paragraph
It can be tempting to start writing your college essay as soon as you sit down at your desk. The sooner begun, the sooner done, right? I’d recommend resisting that itch. Instead, pull up a blank document on your screen and make an outline. There are numerous reasons to make an outline, and most involve helping you stay on track. This is especially true of longer college papers, like the 60+ page dissertation some seniors are required to write. Even with regular writing assignments with a page count between 4-10, an outline will help you visualize your argumentation strategy. Moreover, it will help you order your key points and their relevant evidence from most to least convincing. This in turn will determine the order of your body paragraphs.
The most convincing sequence of body paragraphs will depend entirely on your paper’s subject. Let’s say you’re writing about Penelope’s success in outwitting male counterparts in The Odyssey . You may want to begin with Penelope’s weaving, the most obvious way in which Penelope dupes her suitors. You can end with Penelope’s ingenious way of outsmarting her own husband. Because this evidence is more ambiguous it will require a more nuanced analysis. Thus, it’ll work best as your final body paragraph, after readers have already been convinced of more digestible evidence. If in doubt, keep your body paragraph order chronological.
It can be worthwhile to consider your topic from multiple perspectives. You may decide to include a body paragraph that sets out to consider and refute an opposing point to your thesis. This type of body paragraph will often appear near the end of the essay. It works to erase any lingering doubts readers may have had, and requires strong rhetorical techniques.
How to Start a Body Paragraph, Continued
Once you’ve determined which key points will best support your argument and in what order, draft an introduction. This is a crucial step towards writing a body paragraph. First, it will set the tone for the rest of your paper. Second, it will require you to articulate your thesis statement in specific, concise wording. Highlight or bold your thesis statement, so you can refer back to it quickly. You should be looking at your thesis throughout the drafting of your body paragraphs.
Finally, make sure that your introduction indicates which key points you’ll be covering in your body paragraphs, and in what order. While this level of organization might seem like overkill, it will indicate to the reader that your entire paper is minutely thought-out. It will boost your reader’s confidence going in. They’ll feel reassured and open to your thought process if they can see that it follows a clear path.
Now that you have an essay outline and introduction, you’re ready to draft your body paragraphs.
How to Draft a Body Paragraph
At this point, you know your body paragraph topic, the key point you’re trying to make, and you’ve gathered your evidence. The next thing to do is write! The words highlighted in bold below comprise the main components that will make up your body paragraph. (You’ll notice in the body paragraph examples below that the order of these components is flexible.)
Start with a topic sentence . This will indicate the main point you plan to make that will work to support your overall thesis. Your topic sentence also alerts the reader to the change in topic from the last paragraph to the current one. In making this new topic known, you’ll want to create a transition from the last topic to this one.
Transitions appear in nearly every paragraph of a college essay, apart from the introduction. They create a link between disparate ideas. (For example, if your transition comes at the end of paragraph 4, you won’t need a second transition at the beginning of paragraph 5.) The University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Writing Center has a page devoted to Developing Strategic Transitions . Likewise, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s Writing Center offers help on paragraph transitions .
How to Draft a Body Paragraph for a College Essay ( Continued)
With the topic sentence written, you’ll need to prove your point through tangible evidence. This requires several sentences with various components. You’ll want to provide more context , going into greater detail to situate the reader within the topic. Next, you’ll provide evidence , often in the form of a quote, facts, or data, and supply a source citation . Citing your source is paramount. Sources indicate that your evidence is empirical and objective. It implies that your evidence is knowledge shared by others in the academic community. Sometimes you’ll want to provide multiple pieces of evidence, if the evidence is similar and can be grouped together.
After providing evidence, you must provide an interpretation and analysis of this evidence. In other words, use rhetorical techniques to paraphrase what your evidence seems to suggest. Break down the evidence further and explain and summarize it in new words. Don’t simply skip to your conclusion. Your evidence should never stand for itself. Why? Because your interpretation and analysis allow you to exhibit original, analytical, and critical thinking skills.
Depending on what evidence you’re using, you may repeat some of these components in the same body paragraph. This might look like: more context + further evidence + increased interpretation and analysis . All this will add up to proving and reaffirming your body paragraph’s main point . To do so, conclude your body paragraph by reformulating your thesis statement in light of the information you’ve given. I recommend comparing your original thesis statement to your paragraph’s concluding statement. Do they align? Does your body paragraph create a sound connection to the overall academic argument? If not, you’ll need to fix this issue when you edit your body paragraph.
How to Edit a Body Paragraph
As you go over each body paragraph of your college essay, keep this short checklist in mind.
- Consistency in your argument: If your key points don’t add up to a cogent argument, you’ll need to identify where the inconsistency lies. Often it lies in interpretation and analysis. You may need to improve the way you articulate this component. Try to think like a lawyer: how can you use this evidence to your advantage? If that doesn’t work, you may need to find new evidence. As a last resort, amend your thesis statement.
- Language-level persuasion. Use a broad vocabulary. Vary your sentence structure. Don’t repeat the same words too often, which can induce mental fatigue in the reader. I suggest keeping an online dictionary open on your browser. I find Merriam-Webster user-friendly, since it allows you to toggle between definitions and synonyms. It also includes up-to-date example sentences. Also, don’t forget the power of rhetorical devices .
- Does your writing flow naturally from one idea to the next, or are there jarring breaks? The editing stage is a great place to polish transitions and reinforce the structure as a whole.
Our first body paragraph example comes from the College Transitions article “ How to Write the AP Lang Argument Essay .” Here’s the prompt: Write an essay that argues your position on the value of striving for perfection.
Here’s the example thesis statement, taken from the introduction paragraph: “Striving for perfection can only lead us to shortchange ourselves. Instead, we should value learning, growth, and creativity and not worry whether we are first or fifth best.” Now let’s see how this writer builds an argument against perfection through one main point across two body paragraphs. (While this writer has split this idea into two paragraphs, one to address a problem and one to provide an alternative resolution, it could easily be combined into one paragraph.)
“Students often feel the need to be perfect in their classes, and this can cause students to struggle or stop making an effort in class. In elementary and middle school, for example, I was very nervous about public speaking. When I had to give a speech, my voice would shake, and I would turn very red. My teachers always told me “relax!” and I got Bs on Cs on my speeches. As a result, I put more pressure on myself to do well, spending extra time making my speeches perfect and rehearsing late at night at home. But this pressure only made me more nervous, and I started getting stomach aches before speaking in public.
“Once I got to high school, however, I started doing YouTube make-up tutorials with a friend. We made videos just for fun, and laughed when we made mistakes or said something silly. Only then, when I wasn’t striving to be perfect, did I get more comfortable with public speaking.”
Body Paragraph Example 1 Dissected
In this body paragraph example, the writer uses their personal experience as evidence against the value of striving for perfection. The writer sets up this example with a topic sentence that acts as a transition from the introduction. They also situate the reader in the classroom. The evidence takes the form of emotion and physical reactions to the pressure of public speaking (nervousness, shaking voice, blushing). Evidence also takes the form of poor results (mediocre grades). Rather than interpret the evidence from an analytical perspective, the writer produces more evidence to underline their point. (This method works fine for a narrative-style essay.) It’s clear that working harder to be perfect further increased the student’s nausea.
The writer proves their point in the second paragraph, through a counter-example. The main point is that improvement comes more naturally when the pressure is lifted; when amusement is possible and mistakes aren’t something to fear. This point ties back in with the thesis, that “we should value learning, growth, and creativity” over perfection.
This second body paragraph example comes from the College Transitions article “ How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay .” Here’s an abridged version of the prompt: Rosa Parks was an African American civil rights activist who was arrested in 1955 for refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Read the passage carefully. Write an essay that analyzes the rhetorical choices Obama makes to convey his message.
Here’s the example thesis statement, taken from the introduction paragraph: “Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did.” Now read the body paragraph example, below.
“To further illustrate Parks’ impact, Obama incorporates Biblical references that emphasize the importance of “that single moment on the bus” (lines 57-58). In lines 33-35, Obama explains that Parks and the other protestors are “driven by a solemn determination to affirm their God-given dignity” and he also compares their victory to the fall the “ancient walls of Jericho” (line 43). By including these Biblical references, Obama suggests that Parks’ action on the bus did more than correct personal or political wrongs; it also corrected moral and spiritual wrongs. Although Parks had no political power or fortune, she was able to restore a moral balance in our world.”
Body Paragraph Example 2 Dissected
The first sentence in this body paragraph example indicates that the topic is transitioning into biblical references as a means of motivating ordinary citizens. The evidence comes as quotes taken from Obama’s speech. One is a reference to God, and the other an allusion to a story from the bible. The subsequent interpretation and analysis demonstrate that Obama’s biblical references imply a deeper, moral and spiritual significance. The concluding sentence draws together the morality inherent in equal rights with Rosa Parks’ power to spark change. Through the words “no political power or fortune,” and “moral balance,” the writer ties the point proven in this body paragraph back to the thesis statement. Obama promises that “All of us” (no matter how small our influence) “are capable of achieving greater good”—a greater moral good.
What’s Next?
Before you body paragraphs come the start and, after your body paragraphs, the conclusion, of course! If you’ve found this article helpful, be sure to read up on how to start a college essay and how to end a college essay .
You may also find the following blogs to be of interest:
- 6 Best Common App Essay Examples
- How to Write the Overcoming Challenges Essay
- UC Essay Examples
- How to Write the Community Essay
- How to Write the Why this Major? Essay
- College Essay

Kaylen Baker
With a BA in Literary Studies from Middlebury College, an MFA in Fiction from Columbia University, and a Master’s in Translation from Université Paris 8 Vincennes-Saint-Denis, Kaylen has been working with students on their writing for over five years. Previously, Kaylen taught a fiction course for high school students as part of Columbia Artists/Teachers, and served as an English Language Assistant for the French National Department of Education. Kaylen is an experienced writer/translator whose work has been featured in Los Angeles Review, Hybrid, San Francisco Bay Guardian, France Today, and Honolulu Weekly, among others.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
I am a... Student Student Parent Counselor Educator Other First Name Last Name Email Address Zip Code Area of Interest Business Computer Science Engineering Fine/Performing Arts Humanities Mathematics STEM Pre-Med Psychology Social Studies/Sciences Submit

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.2 Writing Body Paragraphs
Learning objectives.
- Select primary support related to your thesis.
- Support your topic sentences.
If your thesis gives the reader a roadmap to your essay, then body paragraphs should closely follow that map. The reader should be able to predict what follows your introductory paragraph by simply reading the thesis statement.
The body paragraphs present the evidence you have gathered to confirm your thesis. Before you begin to support your thesis in the body, you must find information from a variety of sources that support and give credit to what you are trying to prove.
Select Primary Support for Your Thesis
Without primary support, your argument is not likely to be convincing. Primary support can be described as the major points you choose to expand on your thesis. It is the most important information you select to argue for your point of view. Each point you choose will be incorporated into the topic sentence for each body paragraph you write. Your primary supporting points are further supported by supporting details within the paragraphs.
Remember that a worthy argument is backed by examples. In order to construct a valid argument, good writers conduct lots of background research and take careful notes. They also talk to people knowledgeable about a topic in order to understand its implications before writing about it.
Identify the Characteristics of Good Primary Support
In order to fulfill the requirements of good primary support, the information you choose must meet the following standards:
- Be specific. The main points you make about your thesis and the examples you use to expand on those points need to be specific. Use specific examples to provide the evidence and to build upon your general ideas. These types of examples give your reader something narrow to focus on, and if used properly, they leave little doubt about your claim. General examples, while they convey the necessary information, are not nearly as compelling or useful in writing because they are too obvious and typical.
- Be relevant to the thesis. Primary support is considered strong when it relates directly to the thesis. Primary support should show, explain, or prove your main argument without delving into irrelevant details. When faced with lots of information that could be used to prove your thesis, you may think you need to include it all in your body paragraphs. But effective writers resist the temptation to lose focus. Choose your examples wisely by making sure they directly connect to your thesis.
- Be detailed. Remember that your thesis, while specific, should not be very detailed. The body paragraphs are where you develop the discussion that a thorough essay requires. Using detailed support shows readers that you have considered all the facts and chosen only the most precise details to enhance your point of view.
Prewrite to Identify Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
Recall that when you prewrite you essentially make a list of examples or reasons why you support your stance. Stemming from each point, you further provide details to support those reasons. After prewriting, you are then able to look back at the information and choose the most compelling pieces you will use in your body paragraphs.
Choose one of the following working thesis statements. On a separate sheet of paper, write for at least five minutes using one of the prewriting techniques you learned in Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
- Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
- Students cheat for many different reasons.
- Drug use among teens and young adults is a problem.
- The most important change that should occur at my college or university is ____________________________________________.
Select the Most Effective Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
After you have prewritten about your working thesis statement, you may have generated a lot of information, which may be edited out later. Remember that your primary support must be relevant to your thesis. Remind yourself of your main argument, and delete any ideas that do not directly relate to it. Omitting unrelated ideas ensures that you will use only the most convincing information in your body paragraphs. Choose at least three of only the most compelling points. These will serve as the topic sentences for your body paragraphs.
Refer to the previous exercise and select three of your most compelling reasons to support the thesis statement. Remember that the points you choose must be specific and relevant to the thesis. The statements you choose will be your primary support points, and you will later incorporate them into the topic sentences for the body paragraphs.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
When you support your thesis, you are revealing evidence. Evidence includes anything that can help support your stance. The following are the kinds of evidence you will encounter as you conduct your research:
- Facts. Facts are the best kind of evidence to use because they often cannot be disputed. They can support your stance by providing background information on or a solid foundation for your point of view. However, some facts may still need explanation. For example, the sentence “The most populated state in the United States is California” is a pure fact, but it may require some explanation to make it relevant to your specific argument.
- Judgments. Judgments are conclusions drawn from the given facts. Judgments are more credible than opinions because they are founded upon careful reasoning and examination of a topic.
- Testimony. Testimony consists of direct quotations from either an eyewitness or an expert witness. An eyewitness is someone who has direct experience with a subject; he adds authenticity to an argument based on facts. An expert witness is a person who has extensive experience with a topic. This person studies the facts and provides commentary based on either facts or judgments, or both. An expert witness adds authority and credibility to an argument.
- Personal observation. Personal observation is similar to testimony, but personal observation consists of your testimony. It reflects what you know to be true because you have experiences and have formed either opinions or judgments about them. For instance, if you are one of five children and your thesis states that being part of a large family is beneficial to a child’s social development, you could use your own experience to support your thesis.
Writing at Work
In any job where you devise a plan, you will need to support the steps that you lay out. This is an area in which you would incorporate primary support into your writing. Choosing only the most specific and relevant information to expand upon the steps will ensure that your plan appears well-thought-out and precise.
You can consult a vast pool of resources to gather support for your stance. Citing relevant information from reliable sources ensures that your reader will take you seriously and consider your assertions. Use any of the following sources for your essay: newspapers or news organization websites, magazines, encyclopedias, and scholarly journals, which are periodicals that address topics in a specialized field.
Choose Supporting Topic Sentences
Each body paragraph contains a topic sentence that states one aspect of your thesis and then expands upon it. Like the thesis statement, each topic sentence should be specific and supported by concrete details, facts, or explanations.
Each body paragraph should comprise the following elements.
topic sentence + supporting details (examples, reasons, or arguments)
As you read in Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” , topic sentences indicate the location and main points of the basic arguments of your essay. These sentences are vital to writing your body paragraphs because they always refer back to and support your thesis statement. Topic sentences are linked to the ideas you have introduced in your thesis, thus reminding readers what your essay is about. A paragraph without a clearly identified topic sentence may be unclear and scattered, just like an essay without a thesis statement.
Unless your teacher instructs otherwise, you should include at least three body paragraphs in your essay. A five-paragraph essay, including the introduction and conclusion, is commonly the standard for exams and essay assignments.
Consider the following the thesis statement:
Author J.D. Salinger relied primarily on his personal life and belief system as the foundation for the themes in the majority of his works.
The following topic sentence is a primary support point for the thesis. The topic sentence states exactly what the controlling idea of the paragraph is. Later, you will see the writer immediately provide support for the sentence.
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced themes in many of his works.
In Note 9.19 “Exercise 2” , you chose three of your most convincing points to support the thesis statement you selected from the list. Take each point and incorporate it into a topic sentence for each body paragraph.
Supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Topic sentence: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
Draft Supporting Detail Sentences for Each Primary Support Sentence
After deciding which primary support points you will use as your topic sentences, you must add details to clarify and demonstrate each of those points. These supporting details provide examples, facts, or evidence that support the topic sentence.
The writer drafts possible supporting detail sentences for each primary support sentence based on the thesis statement:
Thesis statement: Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
Supporting point 1: Dogs can scare cyclists and pedestrians.
Supporting details:
- Cyclists are forced to zigzag on the road.
- School children panic and turn wildly on their bikes.
- People who are walking at night freeze in fear.
Supporting point 2:
Loose dogs are traffic hazards.
- Dogs in the street make people swerve their cars.
- To avoid dogs, drivers run into other cars or pedestrians.
- Children coaxing dogs across busy streets create danger.
Supporting point 3: Unleashed dogs damage gardens.
- They step on flowers and vegetables.
- They destroy hedges by urinating on them.
- They mess up lawns by digging holes.
The following paragraph contains supporting detail sentences for the primary support sentence (the topic sentence), which is underlined.
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced the themes in many of his works. He did not hide his mental anguish over the horrors of war and once told his daughter, “You never really get the smell of burning flesh out of your nose, no matter how long you live.” His short story “A Perfect Day for a Bananafish” details a day in the life of a WWII veteran who was recently released from an army hospital for psychiatric problems. The man acts questionably with a little girl he meets on the beach before he returns to his hotel room and commits suicide. Another short story, “For Esmé – with Love and Squalor,” is narrated by a traumatized soldier who sparks an unusual relationship with a young girl he meets before he departs to partake in D-Day. Finally, in Salinger’s only novel, The Catcher in the Rye , he continues with the theme of posttraumatic stress, though not directly related to war. From a rest home for the mentally ill, sixteen-year-old Holden Caulfield narrates the story of his nervous breakdown following the death of his younger brother.
Using the three topic sentences you composed for the thesis statement in Note 9.18 “Exercise 1” , draft at least three supporting details for each point.
Thesis statement: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Supporting details: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
You have the option of writing your topic sentences in one of three ways. You can state it at the beginning of the body paragraph, or at the end of the paragraph, or you do not have to write it at all. This is called an implied topic sentence. An implied topic sentence lets readers form the main idea for themselves. For beginning writers, it is best to not use implied topic sentences because it makes it harder to focus your writing. Your instructor may also want to clearly identify the sentences that support your thesis. For more information on the placement of thesis statements and implied topic statements, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
Print out the first draft of your essay and use a highlighter to mark your topic sentences in the body paragraphs. Make sure they are clearly stated and accurately present your paragraphs, as well as accurately reflect your thesis. If your topic sentence contains information that does not exist in the rest of the paragraph, rewrite it to more accurately match the rest of the paragraph.
Key Takeaways
- Your body paragraphs should closely follow the path set forth by your thesis statement.
- Strong body paragraphs contain evidence that supports your thesis.
- Primary support comprises the most important points you use to support your thesis.
- Strong primary support is specific, detailed, and relevant to the thesis.
- Prewriting helps you determine your most compelling primary support.
- Evidence includes facts, judgments, testimony, and personal observation.
- Reliable sources may include newspapers, magazines, academic journals, books, encyclopedias, and firsthand testimony.
- A topic sentence presents one point of your thesis statement while the information in the rest of the paragraph supports that point.
- A body paragraph comprises a topic sentence plus supporting details.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

TOPIC SENTENCE/ In his numerous writings, Marx critiques capitalism by identifying its flaws. ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ By critiquing the political economy and capitalism, Marx implores his reader to think critically about their position in society and restores awareness in the proletariat class. EVIDENCE/ To Marx, capitalism is a system characterized by the “exploitation of the many by the few,” in which workers accept the exploitation of their labor and receive only harm of “alienation,” rather than true benefits ( MER 487). He writes that “labour produces for the rich wonderful things – but for the worker it produces privation. It produces palaces—but for the worker, hovels. It produces beauty—but for the worker, deformity” (MER 73). Marx argues capitalism is a system in which the laborer is repeatedly harmed and estranged from himself, his labor, and other people, while the owner of his labor – the capitalist – receives the benefits ( MER 74). And while industry progresses, the worker “sinks deeper and deeper below the conditions of existence of his own class” ( MER 483). ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ But while Marx critiques the political economy, he does not explicitly say “capitalism is wrong.” Rather, his close examination of the system makes its flaws obvious. Only once the working class realizes the flaws of the system, Marx believes, will they - must they - rise up against their bourgeois masters and achieve the necessary and inevitable communist revolution.
Not every paragraph will be structured exactly like this one, of course. But as you draft your own paragraphs, look for all three of these elements: topic sentence, evidence, and analysis.
- picture_as_pdf Anatomy Of a Body Paragraph
Body Paragraph: Craft the Heart of Your Essay
Table of contents
- 1 Purpose of a Body Paragraph
- 2 Key Elements in the Structure of a Body Paragraph
- 3 Body Paragraph Structure
- 4 Transition Sentences of a Body Paragraph
- 5 How Do You Write a Body Paragraph of an Essay?
- 6.1 Using Different Types of Evidence.
- 6.2 Varying Sentence Length and Structure.
- 6.3 Avoiding Irrelevant Information.
- 6.4 Maintaining Consistency.
- 6.5 Supporting the Overall Thesis.
- 6.6 Using Clear and Concise Sentences.
- 6.7 Avoiding Transitions at the End.
- 7 Essay Body Paragraph Example
- 8 Conclusion
Completing an essay is more than just combining words – creating effective body paragraphs. They are like the building blocks of your text, giving it substance and strengthening your main point.
In this article, we’ll explore how to write a body paragraph for an essay and what methods to use to make it impactful.
- We’ll walk you through the body paragraph format, purpose, and principal elements,
- Cover using evidence wisely and make sure your sentences connect well,
- Deliver step-by-step guidelines and tips to create paragraphs that grab attention,
- Provide a body essay example.
Let’s start this journey into the writing world and learn how to make your essay interesting and well-structured.
Purpose of a Body Paragraph
This section is the backbone of any essay. A well-organized structure of the body paragraph helps your writing be readable. That’s why organizing the information to achieve this goal is essential. When writing body paragraphs in an essay, you focus on presenting and developing one point that supports the main argument.
Whether you write the text for yourself or go for essay papers for sale , each paragraph focuses on a specific aspect of the topic. It provides evidence, examples, analysis, or elaboration to strengthen and clarify the main point. The body of a paper helps guide the reader by making the ideas flow smoothly. This section aims to make a strong case for the essay’s thesis. It should keep the reader interested with well-developed and organized content.
Key Elements in the Structure of a Body Paragraph
Knowledge is the basis for any writing. Thus, any text you deliver should reflect your level of knowledge. For this, posing strategic and insightful questions to refine your thoughts and reinforce your argument is essential. A well-written body section is a compulsory component of any impactful document.
There are several key parts of a body paragraph in an essay.
- The first element is a transition, linking the preceding and current paragraphs. It should be clear, helping the reader in tracking the conversation. Using starting words for body paragraphs signals a change in focus or introduces a fresh idea.
- The second body paragraph element is the main idea, which is crucial for any text. You must state your argument in the topic sentence, which should be precise and brief. The main statements should relate to the thesis and support the idea.
- The third component is analysis, where the writer elaborates on the perspective. Providing proof and explaining how it supports the thesis statement is necessary. The examination should also be relevant and focused on the introduced topic. This way, you will make the essay structure coherent and easy to follow.
- The final element is the warrant, which explains how the evidence supports the main view. The warrant must be clear and connect the data to the principal argument. It should also focus on the topic and strengthen the argument.
Body Paragraph Structure
Well-thought-out body paragraphs are critical in an essay outline and the writer’s arguments. To effectively structure the body paragraph, you must understand its overall organization. A well-formatted academic essay helps writers communicate their reasoning and convince their audience. However, it’s better not to consider this a fixed and immovable object. Depending on the treated argument, its goal, length, and structure can be adapted to your needs.
You can imagine the skeleton of this part of the text in the following way:
- Topic sentence
- Supporting sentences
- Concluding sentence
The topic sentence is one of the ways to start a body paragraph. It should be a precise and focused statement that encapsulates the main argument of the passage. It connects the introduction paragraph in the essay with a thesis and provides a roadmap for the rest of the section. It will help the reader understand the point and how it relates to the writing. In some cases, it can even be formulated as a question.
Following the topic sentence for the body paragraph, you must provide supporting sentences. They present evidence and analysis to underpin the central idea. They should connect to the topic sentence and be clear and concise. Use language that is easy for the reader to understand.
To create a persuasive assertion, provide information that supports the main argument. The evidence can take many forms, including facts, statistics, or examples. Data should be reliable and relevant to the topic discussed. Research-based proof helps the writer convince the reader that their position is credible.
The concluding sentence is the ultimate statement and a kind of short conclusion you should use when you base your essay on body paragraphs. Its purpose is to summarize the idea and provide a transition to the later passage. This sentence helps the reader comprehend the main claim and its implications. Think of it as the answer to a question or the core information.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
Transition Sentences of a Body Paragraph
To make your writing flow smoothly and be more engaging, use transition words that help connect ideas. You can utilize three types of linking words and phrases:
- Bridging the introductory paragraph to subsequent sections (e.g., a transition from introduction to body): To begin with; In the first place; Initially; As an introduction; Turning to; As we delve into; Now that we have established.
- Connecting body paragraphs: Furthermore; Moreover; In addition; Additionally; Similarly; Likewise; Not only…but also; Besides that; In the same vein; Another key point.
- Linking the final body sentence to the conclusion: In conclusion; To sum up; Finally; In summary; Ultimately; Concluding; To conclude; To wrap things up; As a final point; All in all.
These words and phrases contribute to a coherent and logical essay, guiding the reader through the content. Use transitions to introduce a body paragraph and make your ideas clear and captivating to the audience.
How Do You Write a Body Paragraph of an Essay?
Completing this section requires consideration and attention to detail. It can be challenging to organize your thoughts and reasoning. However, it might be daunting, and professional assistance may be necessary. And this is where PapersOwl can be of great help. Our seasoned paper writing website offers expert homework help to achieve your academic goals.
How long should a body paragraph be? A general recommendation is to aim for 5-7 sentences. It allows you to explore one idea without giving too much information. The most important thing is to keep in mind the following guidelines:
- Introducing a concise topic sentence will be a good way to start a first body paragraph. Topic sentences should be specific and concise. Using them, you provide the reader with a clear understanding of the point you will discuss further. It should also relate to the thesis and connect to the perspective.
- After the topic sentence, use supporting sentences to provide additional information and analysis. This way, you will bolster the main argument. These parts of a body paragraph can include examples, facts, statistics, or expert opinions. Ensure that the information used is reliable and relevant to your idea.
- Employ transition sentences to link your ideas to the preceding and subsequent paragraphs. They make it easier for the reader to follow the main argument.
- Use brief and clear language to present your ideas and rationale. Avoid using complicated vocabulary or technical jargon that may confuse the reader. Instead, be straightforward when writing a body paragraph.
- Finally, end this section with a conclusion sentence. It acts as a summary of the main statement and offers a transition to the next section. The concluding sentence should bring closure to the point in one paragraph. It should also prepare the reader for the next parts of the writing.
When you write a body paragraph in an essay, follow these steps to ensure clarity, conciseness, and persuasiveness in your essay. Adhere to these guidelines to make your ideas concise and transparent and your arguments strong and persuasive. If you follow these steps, your essay will be concise and compelling. Implementing these measures ensures that your text is clear, persuasive, and effective.
Essential Tips to Write Flawless Body Paragraphs
Discover the following comprehensive strategies for crafting effective body paragraphs for your research.
Using Different Types of Evidence.
Incorporate a variety of quotes, statistics, and anecdotes to provide evidence and enhance the appeal and credibility of your writing. This multifaceted approach captivates the reader and reinforces your argument with diverse supporting elements.
Varying Sentence Length and Structure.
Mitigate monotony in the body of an essay by diversifying sentence length and structure. Integrate a mix of simple, compound, and complex sentences to enhance the overall readability of your composition. This nuanced use of syntax contributes to a more engaging and dynamic writing style.
Avoiding Irrelevant Information.
Don’t introduce irrelevant information that might distract or dilute the focus of your paragraph. Each sentence should serve a purpose, aligning seamlessly with the central theme and your essay’s purpose.
Maintaining Consistency.
Stay consistent with the tone and style throughout your text. The body paragraphs should harmonize with the established voice of your writing, creating a cohesive and unified reading experience for your audience.
Supporting the Overall Thesis.
When you start a body paragraph, ensure that each sentence significantly reinforces your overall thesis. Every argument, example, or piece of evidence should advance the central claim of your essay, reinforcing its coherence and persuasiveness.
Using Clear and Concise Sentences.
Break down complex topic sentences into clear and concise points. It facilitates a better understanding of your ideas and prevents the reader from feeling overwhelmed by overly intricate or convoluted language.
Avoiding Transitions at the End.
Refrain from using transition words and phrases at the end of paragraphs, as this can disrupt the natural flow of your writing. Instead, strive for seamless transitions within the paragraph’s content, allowing ideas to connect organically without explicitly signaling the conclusion.
Follow these tips to create a strong body paragraph layout for your document. If you need support or lack time and energy to craft your academic papers, do not hesitate to contact our writing experts. When you pay for a paper at PapersOwl, be sure your essay will adhere to all these instructions and requirements with zero flaws. Our team of writers has expertise in various fields and crafts quality papers for you. We deliver plagiarism-free essays and guarantee timely delivery. Whether you need an essay for school, college, or university, PapersOwl is the right choice.
Essay Body Paragraph Example
What is a body paragraph, and how to complete it correctly? Here is a good example to clarify these questions:
[Start with a topic sentence] J K Rowling, in her first book – Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone, claims that the appearance of a person can sometimes be misleading, [followed by supporting details] showing one of the kindest and most favorite characters – Hagrid as a scary person. His eyes are ‘glinting like black beetles,’ and his face is ‘almost completely hidden by a long, shaggy mane of hair and a wild, tangled beard,’ says the author (Rowling 46). [Then goes an explanation] The author declares that the main character of the book – Harry Potter, is frightened by this intimidating figure, which misleads the reader, making Hagrid appear as a villain. [Explains the significance] However, this image is wrong. Later the reader gets to know Hagrid’s true character, which is the opposite. [Ends with a conclusion and transition to the following part] This example proves how misleading an appearance of someone can be, which is easily proved by many other examples from literature and real life.”
Crafting effective body paragraphs in an essay is an indispensable skill for anyone seeking to elevate their writing. This article gives suggestions to help you write a good body paragraph. Our recommendations allow you to transform your essays into compelling and persuasive texts. These strategies can help both experienced writers and beginners with essay construction. They serve as a valuable toolkit for enhancing the impact and coherence of your text. When you write, remember that a well-organized essay body helps express thoughts clearly, engage readers, and convince them.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
What is the body section of an academic essay?

This is the first of four chapters About Body Paragraphs . To complete this reader, read each chapter carefully and then unlock and complete our materials to check your understanding.
– Introduce the concept of introduction, body and conclusion sections and how they are used in essays
– Discuss the purpose of a body section in an academic essay
– Highlight some of the key elements and features of a successful body paragraph
Chapter 1: What is the body section of an academic essay?
Chapter 2: Which elements build successful body paragraphs?
Chapter 3: Which academic phrases belong in an essay body?
Chapter 4: Which tips make for effective essay body sections?
Before you begin reading...
- video and audio texts
- knowledge checks and quizzes
- skills practices, tasks and assignments
Writing a successful essay takes considerable skill and practice, and the body section of any essay is of critical importance. To complete a bachelor’s or master’s degree , students around the world will be required to carefully plan, construct, write, edit and proofread essays of various lengths about various topics, and to do that successfully usually requires a confident understanding of the formula that makes for a clear, concise and effective essay. This short introductory reader therefore aims to introduce students to the overall concept and purpose of body paragraphs (Chapter 1), discuss the elements that build them ( Chapter 2), highlight the phrases that help their navigation ( Chapter 3), and provide the best tips for making an essay’s body convincing for the reader ( Chapter 4).
Do essays have different sections?
While there might be a wide variety of different essay types for students to learn ( cause-and-effect , compare-and-contrast , theses , dissertations , etc.) almost any of these essays can be divided into three key sections: the introduction , the body , and the conclusion :
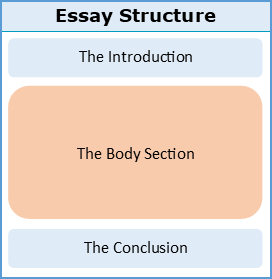
As can be seen in this diagram, the body section, which may be comprised of many different paragraphs, forms the main bulk of any essay (usually about 70%). As a general rule, any paragraph that comes between the introduction and the conclusion is a body paragraph that forms part of the body section . While an essay’s introduction and conclusion can be more generic and easier to write, the body section is the most varied and complex aspect, taking the most practice and time.
Does the body section have purpose?
If the introduction provides the topic and focus of the essay and its variables, and the conclusion summarises its findings and key arguments, the body section is where the topic is discussed and explored – where philosophical battles are fought and won. The body section is purposeful but variable, as it is the precise purpose of the essay that determines the purpose of the body paragraph. If, for example, you are asked to write an evaluative essay , then the purpose of your essay’s body section would be to provide sufficient evaluation (both sides of the argument) for a given topic; likewise, the problems and solutions of a problem-solution essay would be explored in that essay’s body section, as would the causes and effects of a specific situation in a cause-and-effect essay .
What makes a body section successful?
Because of the variation inherent in the body of an essay, students will not be able to find or memorise a sure-fire formula that achieves academic success. Subjectively speaking, the best essays can in fact be the ones that do not follow any prescribed pattern, instead being those which are compelling, well-research and well argued. Nevertheless, and as the following three c hapter s will demonstrate, there are a number of essay elements and features that when successfully included should greatly increase the success of any academic essay. These elements and features are summarised in the table below, with more detail provided in Chapter 2:

To reference this reader:
Academic Marker (2022) About Body Paragraphs . Available at: https://academicmarker.com/essay-writing/body-paragraphs/about-body-paragraphs/ (Accessed: Date Month Year).
- Purdue University Online Writing Lab
- University of Arizona Writing Center
Downloadables
Once you’ve completed all four chapters in this short reader About Body Paragraphs , you might then wish to download our Chapter Worksheets to check your progress or print for your students. These professional PDF worksheets can be easily accessed for only a few Academic Marks
Chapter 1 explores the topic: What is the body section of an academic essay? Our Chapter 1 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Chapter 2 explores the topic: Which elements build successful body paragraphs? Our Chapter 2 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Chapter 3 explores the topic: Which academic phrases belong in an essay body? Our Chapter 3 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Chapter 4 explores the topic: Which tips make for effective essay body sections? Our Chapter 4 Worksheet (containing guidance, activities and answer keys) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
To save yourself 3 Marks , click on the button below to gain unlimited access to all of our About Body Paragraphs Chapter Worksheets. This All-in-1 Pack includes every chapter, activity and answer key related this topic in one handy and professional PDF.
Collect Academic Marks
- 100 Marks for joining
- 25 Marks for daily e-learning
- 100-200 for feedback/testimonials
- 100-500 for referring your colleages/friends
Find Study Materials for
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- English Literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Social Studies
- Browse all subjects
- Read our Magazine
Create Study Materials
Good writing has a beginning, middle, and end. Beginnings and endings are brief. The majority of an essay is the middle part. That middle part is called the body . The paragraphs that make up that body are called body paragraphs . The purpose of body paragraphs is to explain your ideas. But even body paragraphs have a structure: a beginning, middle, and end. Good writing uses this structure to explain and transition between ideas.

Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free.
- Body Paragraph
- Explanations
- StudySmarter AI
- Textbook Solutions
- A Hook for an Essay
- Essay Outline
- Language Used in Academic Writing
- MHRA Referencing
- Opinion vs Fact
- Works Cited
- Argumentative Essay
- Cues and Conventions
- English Grammar
- English Language Study
- Essay Prompts
- Essay Writing Skills
- Global English
- History of English Language
- International English
- Key Concepts in Language and Linguistics
- Language Acquisition
- Language Analysis
- Language and Social Groups
- Lexis and Semantics
- Linguistic Terms
- Listening and Speaking
- Multiple Choice Questions
- Research and Composition
- Rhetorical Analysis Essay
- Single Paragraph Essay
- Sociolinguistics
- Summary Text
- Synthesis Essay
- Textual Analysis
Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Nie wieder prokastinieren mit unseren Lernerinnerungen.
Body Paragraph: Meaning
A body paragraph is one of several paragraphs that make up the body of an essay. Let's take a closer look at what body paragraphs are.
Body paragraphs are the paragraphs that make up the bulk of an essay. They appear between the introduction and conclusion. Each body paragraph covers a different aspect of your main idea .
In a 5-paragraph essay, there are three body paragraphs. Each body paragraph supports your main idea by explaining a different aspect of it.
The Purpose of Body Paragraph
The purpose of body paragraphs is to explain your ideas. In the body paragraphs, you make your arguments, provide evidence , and explain your reasoning. Think of your essay as a literal body. It has feet, a head, and everything in between.

A good essay starts with a solid foundation. The introduction is the essay's feet, providing that solid foundation. This foundation sets up the essay so you can build on it.
As you build the essay, you work your way upward, ending at the conclusion. The conclusion is the head of the essay. It completes the picture and allows you to summarize your ideas and look forward to the future.
So, what is between the head and the feet? Everything else! The body paragraphs are like the actual body of your essay. They take up most of the essay. Body paragraphs explain the bulk of your arguments and ideas.
Without the body paragraphs, you would have no essay!
What is the Purpose of Each Body Paragraph?
In a 5-paragraph essay, each body paragraph serves a different purpose. Look at the table below to learn about the purpose of each body paragraph.
Body Paragraph Structure With Examples
The structure of a body paragraph includes a topic sentence, supporting sentences with evidence , and a concluding sentence. Let's take a closer look at each of these features and how to write them.
Topic Sentence
Every body paragraph should begin with a topic sentence .
A topic sentence is a sentence that states the main idea of a paragraph. It states the one thing you want the reader to understand from that paragraph.
A good topic sentence focuses the paragraph. It should be the very first sentence of the paragraph. When writing a topic sentence, ask yourself: what is the one thing I want the reader to get from this paragraph?
A good topic sentence clearly connects to the essay's thesis statement .
A thesis statement is a sentence that summarizes the main point of an essay. It appears at the end of the introduction.
Think of the topic sentence as one part of the thesis statement. It states one important piece of your main idea.
Thesis statement : If we are going to provide equal education for all, teachers will need more support in terms of funding, resources, and professional development.
Topic Sentence Body Paragraph 1: T eachers need more funding to obtain more resources and give them the time and energy needed to focus on student learning.
Topic Sentence Body Paragraph 2 : Teachers must be provided with the necessary resources to ensure every student has equal access to classroom materials and content.
Topic Sentence Body Paragraph 3 : Teachers need more professional development to learn how to utilize equality-building resources in the classroom and beyond.
Supporting Sentences
If the topic sentence supports the thesis statement, then what supports the topic sentence? Supporting sentences!
Supporting sentences explain the reasons for the main idea of the paragraph. Each paragraph should have multiple supporting sentences that explain the topic sentence.

Topic Sentence : T eachers need more funding to obtain more resources and give them the time and energy needed to focus on student learning.
Supporting Sentence 1 : Teachers often pay for resources out of their own pockets, which limits what they can provide students.
Supporting Sentence 2 : Teachers do not make enough money to live on, let alone provide their own educational resources.
Supporting Sentence 3 : Working multiple jobs distracts teachers from their classes, drains them of energy, and keeps them from seeking out professional development opportunities.
Note how each supporting sentence offers a different reason for the argument. Think of supporting sentences as reasons for your argument. What are your reasons?

Back up every supporting sentence with evidence .
Evidence is what you use to support a claim. It includes any facts, examples, or sources that back up your ideas.

Here are some different types of evidence you might use to back up your ideas:
- Facts or statistics
- Quotes from interviews
- Opinions from authors
- Descriptions of events, locations, or images
- Examples from sources
- Definitions of terms
Supporting Sentence : Teachers often pay for resources out of their own pockets, which limits what they can provide students.
Evidence : According to a 2018 survey, 94% percent of teachers spend their own money on supplies and resources for their classrooms every year. 1
How can you communicate evidence? There are 3 different ways to do so:
You can summarize a source by overviewing the main ideas of that source. For example, you might summarize the findings of a study. Summaries are helpful when the general gist of a source is all you need to support your idea.
2. Paraphrase
You can also summarize one or two points from a source. This is called paraphrasing . For instance, the evidence in the above example paraphrased one point from an article. Paraphrasing is perfect for pulling important ideas from a source.
3. Direct Quote
Sometimes you need to use the exact words from a source to convey its message. We call the use of a source's exact words a direct quote. Direct quotes are helpful when a source words something perfectly.
Concluding Sentence
Every body paragraph must come to a close. Let the reader know you are wrapping up the paragraph with a concluding sentence. The concluding sentence is the last sentence of the paragraph. It wraps up the paragraph and lets the reader know you are ready to move on to the next point.
A good concluding sentence:
- Briefly summarizes the ideas of the paragraph.
- Provides a sense of closure.
- Signals what is coming next.
Teachers are expected to pay for their own resources with limited funds, limited time, and limited attention to their students' needs.
Body Paragraph Transitions
Once you have the basic structure of a body paragraph, add transitions . Tr ansitions are important for showing how your ideas fit together.
Transitions are words and phrases that show the relationships between ideas.
Transitions help your paper flow from one paragraph to the next. They also show how your paragraphs connect to the thesis statement.

Transitioning from the Introduction
Add a transition to the topic sentence of Body Paragraph 1. Use transition words (e.g., therefore) that emphasize the relationship between the topic sentence and the thesis statement.
Ask yourself, what part of the thesis statement is this paragraph? Is it the most important idea? The first event? The strongest argument?
Transitioning Between Body Paragraphs
Consider the logical relationship between your paragraphs. Map how one idea goes into the next idea following a line of reasoning. Also, study transitions between paragraphs!
Ask yourself, how do these ideas build on each other? How do reveal another aspect of the main idea of my essay?
Transitioning to Your Conclusion
Urge your reader toward the conclusion using a concluding word (e.g., finally).
Ask yourself, how can I let the reader know this is my final point? How can I show the relationship between this final point and my other ideas?
Body Paragraph Example
Let's look at an example of a body paragraph. Note how each feature is in a different color. Pay attention to how these different features work together to explain the main idea.
Use this table for reference to identify each element:
Most importantly , t eachers need more funding to obtain resources, as well as to give them the time and energy needed to focus on student learning. Teachers often pay for resources out of their own pockets, which limits what they can provide students. According to a 2018 survey, 94% percent of teachers spend their own money on supplies and resources for their classrooms every year. 1 Teachers do not make enough money to live on, let alone provide their own educational resources. The same survey found that teachers pay anywhere from $400 to over $1000 per year on average for classroom supplies. Couple this fact with teachers' notoriously low wages, and it's no wonder over one-third of teachers take second jobs. T eachers are expected to pay for their own resources with limited funds, limited time, and limited attention to their students' needs, so how can they be expected to ensure these resources are available to students that need them most?
Body Paragraph - Key Takeaways
- Body paragraphs are the paragraphs that make up the bulk of an essay.
The purpose of body paragraphs is to explain your ideas.
- In a 5-paragraph essay, each of the three body paragraphs serves a different purpose.
- The structure of a body paragraph includes a topic sentence, supporting sentences with evidence, and a concluding sentence.
- Once you have the basic features of a body paragraph, add transitions to those features to show the relationships between your ideas.
1 Grace Sparks, "94% of teachers spend their own money on school supplies," CNN. 2018.
Frequently Asked Questions about Body Paragraph
--> what is the meaning of body paragraph .
Body paragraphs are the paragraphs that make up the bulk of an essay. They appear between the introduction and conclusion. Each body paragraph covers a different aspect of the essay's main idea.
--> What are the features of a body paragraph?
The features of a body paragraph are a topic sentence, supporting sentences with evidence, and a concluding sentence.
--> What is a good example of a body paragraph?
A good example of a body paragraph is as follows:
Most importantly, t eachers need more funding to obtain resources, as well as to give them the time and energy needed to focus on student learning. Teachers often pay for resources out of their own pockets, which limits what they can provide students. According to a 2018 survey, 94% percent of teachers spend their own money on supplies and resources for their classrooms every year. Teachers do not make enough money to live on, let alone to provide their own educational resources. The same survey found that teachers pay anywhere from $400 to over $1000 per year on average for classroom supplies. Couple this fact with teachers' notoriously low wages, and it's no wonder over one-third of teachers take second jobs. Working multiple jobs distracts teachers from their classes, drains them of energy, and keeps them from seeking out professional development opportunities. According to the National Education Association, "Moonlighting can increase stress and drive disengagement, as teachers are forced to juggle multiple schedules and have their family and leisure time reduced." Teachers are expected to pay for their own resources with limited funds, limited time, and limited attention to their students' needs, so how can they be expected to ensure these resources are available to students that need them most?
--> How do you start a body paragraph example?
Start a body paragraph example with a topic sentence stating the main idea of the paragraph. Then add support sentences, evidence, and a concluding sentence.
--> What is the purpose of body paragraphs?
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards.
If something has failed to acquire verification, what is it?
Fact is what has continually withstood the test of _____.
Opinion is not concerned with _____, while facts are.
Your score:

Join the StudySmarter App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Learn with 236 body paragraph flashcards in the free studysmarter app.
Already have an account? Log in
What is an opinion?
Opinion is a personal conjecture.
Should you use an opinion to support your thesis?
"An opinion does not require verification."
True or false?
"Humans will evolve into beings of pure energy." Is this an opinion or a potential fact?
An opinion. It cannot be verified, whereas potential facts are in the process of verification.
Fact is not ____. Fact is what is found out during the search for the truth.

- English Grammar Summary
of the users don't pass the Body Paragraph quiz! Will you pass the quiz?
How would you like to learn this content?
Free english cheat sheet!
Everything you need to know on . A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our StudySmarter App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Study Planner
- Smart Note-Taking

Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
This is still free to read, it's not a paywall.
You need to register to keep reading, create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Entdecke Lernmaterial in der StudySmarter-App

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Body Paragraphs

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Body paragraphs: Moving from general to specific information
Your paper should be organized in a manner that moves from general to specific information. Every time you begin a new subject, think of an inverted pyramid - The broadest range of information sits at the top, and as the paragraph or paper progresses, the author becomes more and more focused on the argument ending with specific, detailed evidence supporting a claim. Lastly, the author explains how and why the information she has just provided connects to and supports her thesis (a brief wrap-up or warrant).

Moving from General to Specific Information
The four elements of a good paragraph (TTEB)
A good paragraph should contain at least the following four elements: T ransition, T opic sentence, specific E vidence and analysis, and a B rief wrap-up sentence (also known as a warrant ) –TTEB!
- A T ransition sentence leading in from a previous paragraph to assure smooth reading. This acts as a hand-off from one idea to the next.
- A T opic sentence that tells the reader what you will be discussing in the paragraph.
- Specific E vidence and analysis that supports one of your claims and that provides a deeper level of detail than your topic sentence.
- A B rief wrap-up sentence that tells the reader how and why this information supports the paper’s thesis. The brief wrap-up is also known as the warrant. The warrant is important to your argument because it connects your reasoning and support to your thesis, and it shows that the information in the paragraph is related to your thesis and helps defend it.
Supporting evidence (induction and deduction)
Induction is the type of reasoning that moves from specific facts to a general conclusion. When you use induction in your paper, you will state your thesis (which is actually the conclusion you have come to after looking at all the facts) and then support your thesis with the facts. The following is an example of induction taken from Dorothy U. Seyler’s Understanding Argument :
There is the dead body of Smith. Smith was shot in his bedroom between the hours of 11:00 p.m. and 2:00 a.m., according to the coroner. Smith was shot with a .32 caliber pistol. The pistol left in the bedroom contains Jones’s fingerprints. Jones was seen, by a neighbor, entering the Smith home at around 11:00 p.m. the night of Smith’s death. A coworker heard Smith and Jones arguing in Smith’s office the morning of the day Smith died.
Conclusion: Jones killed Smith.
Here, then, is the example in bullet form:
- Conclusion: Jones killed Smith
- Support: Smith was shot by Jones’ gun, Jones was seen entering the scene of the crime, Jones and Smith argued earlier in the day Smith died.
- Assumption: The facts are representative, not isolated incidents, and thus reveal a trend, justifying the conclusion drawn.
When you use deduction in an argument, you begin with general premises and move to a specific conclusion. There is a precise pattern you must use when you reason deductively. This pattern is called syllogistic reasoning (the syllogism). Syllogistic reasoning (deduction) is organized in three steps:
- Major premise
- Minor premise
In order for the syllogism (deduction) to work, you must accept that the relationship of the two premises lead, logically, to the conclusion. Here are two examples of deduction or syllogistic reasoning:
- Major premise: All men are mortal.
- Minor premise: Socrates is a man.
- Conclusion: Socrates is mortal.
- Major premise: People who perform with courage and clear purpose in a crisis are great leaders.
- Minor premise: Lincoln was a person who performed with courage and a clear purpose in a crisis.
- Conclusion: Lincoln was a great leader.
So in order for deduction to work in the example involving Socrates, you must agree that (1) all men are mortal (they all die); and (2) Socrates is a man. If you disagree with either of these premises, the conclusion is invalid. The example using Socrates isn’t so difficult to validate. But when you move into more murky water (when you use terms such as courage , clear purpose , and great ), the connections get tenuous.
For example, some historians might argue that Lincoln didn’t really shine until a few years into the Civil War, after many Union losses to Southern leaders such as Robert E. Lee.
The following is a clear example of deduction gone awry:
- Major premise: All dogs make good pets.
- Minor premise: Doogle is a dog.
- Conclusion: Doogle will make a good pet.
If you don’t agree that all dogs make good pets, then the conclusion that Doogle will make a good pet is invalid.
When a premise in a syllogism is missing, the syllogism becomes an enthymeme. Enthymemes can be very effective in argument, but they can also be unethical and lead to invalid conclusions. Authors often use enthymemes to persuade audiences. The following is an example of an enthymeme:
If you have a plasma TV, you are not poor.
The first part of the enthymeme (If you have a plasma TV) is the stated premise. The second part of the statement (you are not poor) is the conclusion. Therefore, the unstated premise is “Only rich people have plasma TVs.” The enthymeme above leads us to an invalid conclusion (people who own plasma TVs are not poor) because there are plenty of people who own plasma TVs who are poor. Let’s look at this enthymeme in a syllogistic structure:
- Major premise: People who own plasma TVs are rich (unstated above).
- Minor premise: You own a plasma TV.
- Conclusion: You are not poor.
To help you understand how induction and deduction can work together to form a solid argument, you may want to look at the United States Declaration of Independence. The first section of the Declaration contains a series of syllogisms, while the middle section is an inductive list of examples. The final section brings the first and second sections together in a compelling conclusion.
Body Paragraph
Definition of body paragraph.
A body paragraph in an essay is a paragraph that comes between the introduction and the conclusion . In a five-paragraph essay, there are three body paragraphs, while in longer essays there could be five or even ten. In major research papers, there are hundreds of body paragraphs.
Components of a Body Paragraph
A body paragraph has three major components: (1) topic sentence , (2) explanation, (3) supporting details. Without any of them, the body paragraph seems to be missing something, and will not add anything to the theme and central idea of the essay.
- Topic Sentence The topic sentence is the first sentence of a paragraph, and states the main idea to be discussed in the paragraph. In a body paragraph, the topic sentence is always about the evidence given in the thesis statement of the essay. It could be a claim , an assertion , or a fact needing explanation. It is generally a statement or a declarative sentence.
- Explanation / Example The topic sentence is followed by an explanation and/or an example. Whatever it is, it generally starts with “in other words” or “it means;” or “for example,” “for instance,” etc. This is called “metacommentary,” or telling of the same thing in different words to explain it further, so that readers can understand.
- Supporting Details Supporting details include concrete examples, rather than explanation or metacommentary. In common essays, or five-paragraph essays, this is just a one-sentence example from everyday life. However, in the case of research essays, these are usually quotes and statistics from research studies.
Different Between an Introduction and a Body Paragraph
Although both are called paragraphs, both are very different from each other not only in terms of functions but also in terms of components. An introduction occurs in the beginning and has three major components; a hook , background information , and a thesis statement . However, a body paragraph is comprised of a topic sentence making a claim, an explanation or example of the claim, and supporting details.
Examples of Body Paragraph in Literature
Example #1: autobiography of bertrand russell (by bertrand russell).
“Three passions, simple but overwhelmingly strong, have governed my life: the longing for love, the search for knowledge, and unbearable pity for the suffering of mankind. These passions, like great winds, have blown me hither and thither, in a wayward course, over a great ocean of anguish, reaching to the very verge of despair. I have sought love, first, because it brings ecstasy – ecstasy so great that I would often have sacrificed all the rest of life for a few hours of this joy. I have sought it, next, because it relieves loneliness – that terrible loneliness in which one shivering consciousness looks over the rim of the world into the cold unfathomable lifeless abyss. I have sought it finally, because in the union of love I have seen, in a mystic miniature, the prefiguring vision of the heaven that saints and poets have imagined. This is what I sought, and though it might seem too good for human life, this is what – at last – I have found.”
This is a paragraph from the prologue of the autobiography of Bertrand Russell. Check its first topic sentence, which explains something that is further elaborated in the following sentences.
Example #2: Politics and the English Language (by George Orwell)
“The inflated style itself is a kind of euphemism . A mass of Latin words falls upon the facts like soft snow , blurring the outline and covering up all the details. The great enemy of clear language is insincerity. When there is a gap between one’s real and one’s declared aims, one turns as it were instinctively to long words and exhausted idioms , like a cuttlefish spurting out ink. In our age there is no such thing as ‘keeping out of politics.’ All issues are political issues, and politics itself is a mass of lies, evasions, folly, hatred, and schizophrenia. When the general atmosphere is bad, language must suffer. I should expect to find — this is a guess which I have not sufficient knowledge to verify — that the German, Russian and Italian languages have all deteriorated in the last ten or fifteen years, as a result of dictatorship.”
This paragraph has a very short topic sentence. However, its explanation and further supporting details are very long.

Function of Body Paragraph
The elements of a body paragraph help to elaborate a concept, organize ideas into a single whole, and help bridge a gap in thoughts. The major task of a body paragraph is the organization of thoughts in a unified way. It also helps an author to give examples to support his claim, given in the topic sentence of that body paragraph. A good paragraph helps readers understand the main idea with examples.
Related posts:
- Simple Paragraph
Post navigation

- Place order
Parts of a Body Paragraph in an Essay, Assignment, or any Paper

Whether you are writing an essay, thesis, research dissertation, report, proposal, college essay, or personal statement, you must write the body paragraphs at some point. The body paragraphs come immediately after the introduction paragraph.

Majorly, professors, markers, and instructors can tell good writing just by reading a few components of the body paragraphs.
Body paragraphs are the building blocks of essays and other papers written in prose form. They provide all the information and reasoning to prove the thesis statement.
Without wasting too much time, let�s delve into what elements make a body paragraph, how to craft the best paragraphs, and some tips you can use when stuck.
Purpose of Writing a Body Paragraph
Body paragraphs play a critical role in proving the thesis of an essay or paper. As a matter of sequence, the body paragraphs come after the introduction and just before the concluding paragraph of an essay or paper.
The body paragraphs fulfill the predictions made in the introduction and give room for the summary in the conclusion. Therefore, the body paragraphs must relate to what comes before them and what comes after.
Eliminating a body paragraph from the sequence of body paragraphs without altering the flow means that you derailed when writing. Furthermore, it is a solid signal for editing, proofreading, and, if possible, rewriting the paragraph. Technically, body paragraphs link to one another to support the thesis.
Each body paragraph must relate logically to the one immediately before ( introduction paragraph ) or after ( concluding paragraph ). It should only bear or focus on a single idea or topic reflected in the topic sentence. If your topic is complex or has multiple parts, you can split a paragraph into two to maintain this rule.
A paragraph is about 150 words in length and cannot be one sentence, especially in academia. As a result, one-sentence paragraphs are usually underdeveloped.
Essential Parts or Elements of a Good Body Paragraph
The body of your essay or paper is referred to as developmental paragraphs in the sense that it is the arena where all the action takes place. It is where you develop your central idea or thesis. Depending on the length of your paper, the number of body paragraphs will differ. For instance, if you are writing a one-page paper of 300-400 words, you can ideally have two well-balanced short body paragraphs. Similarly, when writing an essay from 500 to 1000 words, you can write at least three body paragraphs to support the thesis statement of your essay or paper.
The main components of a body paragraph of your essay or whatever written assignment you are undertaking are topic sentences, supporting sentences, transitions, and concluding sentences. Each of these elements works side by side with another to bring out the message of the entire body paragraph as a whole.
When you successfully marry every part to another, you end up with a solid body paragraph that supports the thesis statement of your essay or paper.
Components of a Good Body Paragraph
In a nutshell, we can break a good body paragraph into four main parts. Here is a breakdown of the four parts and the functions that each plays in the body paragraph:
- Transition - linking the body paragraphs to one another.
- Topic Sentence - introducing the paragraph.
- Supporting Sentences - Explain the topic sentence and support the thesis.
- Concluding Sentence/Summary - briefly summarize the paragraph and link/transition to the next paragraph.
Given that you now have a rough idea of each part, let's comprehensively explore all the components in detail to figure out how to use each when writing. In the following section, we explain each element of a good body paragraph in detail and give cogent reasons you should incorporate it when writing the developing paragraphs of your essays or papers.
1. Transitions
For you to achieve coherence, flow, and organization in an essay or paper, using transition words and phrases is inevitable. For example, when writing a body paragraph, it must have a transition sentence. Sometimes it comes just before the topic sentence, while you can incorporate it as part of the closing sentence.
Instead of opening a paragraph with an abrupt change of topic, you can use transitions to offer a soft landing to your readers. You slowly guide them into a new conversation that maintains a good flow of ideas. Transitions do a fantastic job of removing confusion and distractions when moving from one paragraph to the next.
The transition sentence is the one that leads from a previous paragraph to ensure that there is smooth reading or flow of ideas. It transitions you from the previous idea to another idea that is related to the former.
And the good thing is that transition phrases and signal words don't have to be complicated. Check out the list of transition or linking words to incorporate into your paragraphs.
2. Topic Sentence
It is also known as the opening sentence or key sentence .
The topic sentence is usually the first sentence of the paragraph. It is sometimes known as the opening sentence. It states one of the topics related to your thesis and bears assertions about how the topic supports the central idea.
A topic sentence serves two purposes:
- It ties the details of the paragraph together
- It relates the details of the paragraph to the thesis statement
It is usually a generalization you can support using evidence and facts when writing the essay. As a characteristic, the topic sentences are short and stand independently when the supporting details are stripped.
3. Supporting Sentences
After writing your topic sentence, you need to follow it immediately with a series of supporting sentences. Supporting sentences offer details, facts, examples, and explanations to support the ideas in your paragraph.
The supporting sentences aim to back up your arguments and claims by highlighting the examples, research findings, quotes, citations, and facts.
Since a good essay or research paper must explain your ideas, evidence, and examples, you must also incorporate supporting evidence. You should involve some analysis. Here is where you pull your analytical, organization, and presentation skills.
Supporting evidence can include paraphrased ideas, summaries of ideas, direct quotes, and specific details (such as statistics) from your scholarly reference or source. It is best to ensure a good flow of these ideas.
4. Concluding or Closing Sentence
Although it is not the end of your writing, a closing or concluding sentence is critical in wrapping up your paragraph.
It should be a brief sentence that wraps up the paragraph. It is sometimes called the warrant as it connects your reasoning and support to the thesis. It also shows the relevance of the information provided in supporting the thesis. In most cases, the transition sentence then fits here.
Learn other aspects of paragraph writing in our guide on how to write essays . We have also put together an article on paragraph writing rules , which can be helpful. The process is standard when writing papers such as theses, capstones, case studies, term papers, or white papers. As long as you grasp it, you are good to go.
Your body paragraphs should be organized, coherent, and linked to ensure a good flow.
Related Article: Using first person in academic writing .
The Typical Structure of a Body Paragraph
We can look at the body paragraph like many things. The two main approaches used include the PIE and Hamburger analogy. Let�s look at each in detail to understand how to frame ideas into a body paragraph, score excellent grades, or deliver a masterpiece when writing papers.
Note that regardless of your structure or format for the body paragraph, you will end up with the four components or ingredients we discussed.
The PIE Analogy
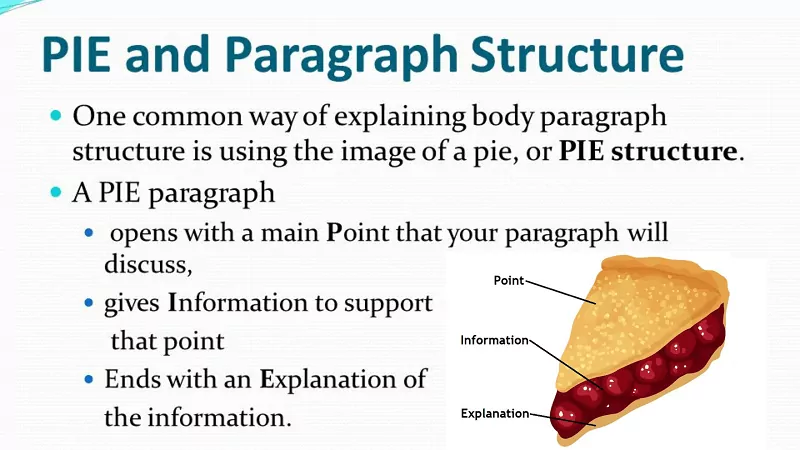
The PIE analogy stands for Point Information Explanation. Typically, considering that a body paragraph can be between 2-5 sentences (both short and long), you can arrange the ideas to fit this analogy. Mainly, the length of a body paragraph depends on the length of your paper or essay (measured in word count or page count), your audience, the purpose of writing, and the chosen topic.
The Point (introduction sentence) - This is the first sentence of your body paragraph. It should entail the idea that supports the central idea or thesis of your essay or paper.
The information (supporting sentences) - This refers to a series of sentences, usually 2-3 sentences, that provide information, explanation, and facts to back up the topic sentence. There is no specific order for the supporting sentences. However, ensure that there is a good flow. For example, the first one introduces the supporting idea while the subsequent sentences each provide examples, illustrations, and explanations.
The Explanation (closing sentence) - The concluding sentence closes the body paragraph. It is one sentence, just like the topic sentence. Therefore, it should wrap up the paragraph in brief. Besides, it also predicts and suggests what to expect in the next paragraph.
The Hamburger Analogy
The hamburger paragraph technique or analogy is widely used. It is sometimes referred to as sandwich paragraph, hamburger paragraph, or Oreo method. It helps write the body paragraphs that appear between the introduction and conclusion paragraphs.
Here is the Hamburger Paragraph Template ( Download link) that you can use to develop a strong body paragraph for your essay or paper.
How to Write the Body Paragraph for an Essay or any Paper
Now that we have explored the components or elements of a good body paragraph let's delve into the steps you should take to ensure that you successfully write a body paragraph.
Even though you may know the main parts of a body paragraph, you can only achieve mastery by understanding the process of putting each up and all together. So if that's your main worry, you came to the right place.
In this section, we explain and discuss at length how to write a body paragraph for an essay. Your body paragraph should support the thesis statement. If you succeed in writing good body paragraphs for the essay, even the conclusion paragraph gets easier.
You should take six steps to write an effective body paragraph: writing the topic sentence, unpacking the topic sentence, presenting evidence, analyzing the evidence, proving your objective, and providing a conclusion and transition.
The strategies we share have been used by our top essay writers and are highly recommended by our essay tutors for students who want to score top grades for their essays and assignments that involve writing in prose. Here is the process of writing a body paragraph:
Step 1: Write the Topic Sentence
To write a great body paragraph, start with the first sentence, a mini-thesis statement for your paragraph.
Next, the topic sentence establishes the main point or argument of the paragraph and defines its relationship to the overarching thesis.
Reading the topic sentence, a reader should know what the paragraph is about and how it sits in the essay's context.
Do not use too complex topic sentences as that only leads to confusion and creates room for confusing paragraphs, often lengthy, ambiguous, confusing, and making no sense.
Step 2: Unload the topic sentence
After listing the topic sentence, develop the claims in it by expounding, explaining, and expanding all the individual components.
This step entails parsing out the discussion points addressed in your paragraph to support the topic sentence.
Use as many sentences as possible, but be brief to avoid confusion. In simple terms, elaborate on the significance of the topic sentence.
Step 3: Present Evidence
To prove the claim or argument in your topic sentence, use facts, arguments, illustrations, data, statistics, quotes, paraphrased ideas, and evidence from reputable scholarly sources.
In addition, ensure that you provide the correct in-text citations.
This step aims to back up or support the topic sentence using original ideas from primary and secondary sources to contextualize the idea and support the overarching thesis statement.
Step 4: Analyze the presented evidence
Using your own words, interpret, evaluate, explain, expand, and comment on the evidence you have provided.
Help your readers link the ideas to the topic sentence and the main thesis.
Where applicable, debunk the evidence you have presented, especially when introducing a counterargument to show your prowess and maturity in writing.
Step 5: Prove your point
Writing takes an objective approach, at least most academic writing, unless it is personalized, such as college essays, first-person essays, personal statements, or scholarship essays. To be objective in your writing, tie the body paragraph to the topic sentence and then explain how the body of evidence helps the paragraph connect to the thesis.
For example, how does the body paragraph address the topic? Has the paragraph addressed its purpose of proving the thesis? You should then elaborate on why each paragraph matters to ensure a coherent link between the main aim of your essay and the discussion.
Step 6: Conclude and Transition
Finally, wind up your paragraph by wrapping the entire paragraph in one sentence and transitioning to the next one. The transition sentence should redirect the reader from one topic or paragraph to the other. The transition process should be smooth and should be stronger and clear to the readers.
Related Read: H ow to write a great case study analysis paper.
Tips to help you write Strong Body Paragraphs
Writing persuasive and organized paragraphs is a tough call for many people, yet it is the only way to achieve excellent grades. With 80% of your word count reserved for the body paragraphs, learning how to write the best is inevitable.
If you constantly make mistakes, try these hacks or tips when writing the body paragraphs next.
1. Follow the outline
You must stick to your essay outline to write a perfect body paragraph. We always recommend developing an outline for your paper before writing. Outlining helps you plan your writing, organize ideas and thoughts, and strategically visualize your paper even though you have not started or completed it.
If you have an outline that you have refined, write your body paragraphs as per the outline. In most cases, writing body paragraphs becomes easier with an outline because you will only be filling in the blanks.
2. Focus when writing
As you develop the ideas in your body paragraphs, pay close attention to your central thesis.
Your focus should be on the chronological sequence of the ideas. If you notice that you have to rearrange the paragraphs for flow, do so.
Besides, ensure that each body paragraph only discusses one main point related to your thesis. Finally, balance the word count of your paragraphs. It should total 80% of your word count.
Mix long and short sentences to achieve coherence and flow as you write. As well, ensure that you include linking words or transition words. Finally, do not use phrases that are taboo in academic writing.
3. Include counterarguments
When writing the body paragraphs of analytical and argumentative essays, ensure that you reserve one of the body paragraphs for counterarguments where you explain why your thesis is stronger.
Present the facts, evidence, examples, and illustrations to strengthen the understanding of your audience.
4. Don�t be afraid to start over
If you notice that you have veered off-topic, which is likely when you write without an outline, start over again.
As you write the second time, ensure that the paragraphs are interlinked, relevant, and support the thesis. The aim is to ensure that the ideas in each paragraph are interlinked with the main idea of your essay. Do away with vague paragraphs that have weak supporting sentences.
You can also refine and polish your sentences to create a seamless flow of ideas.
Do not cram too much information into a single body paragraph. Instead, split a long paragraph into two and create some flow whenever necessary. You can also shift the paragraphs around.
5. Break Complex Topic Sentences
Since a topic sentence only focuses on one idea, don�t hesitate to break down ambiguous ones for better, shorter, and more direct ones. Ambiguous topic sentences only lead to confused paragraphs or paragraphs that are too long and out of place.
6. Maximize on Transitions
Even though a body paragraph conventionally begins with a topic sentence, you can include a transition right before the topic sentence to allow a smooth flow to the next section.
7. Be Clear and Concise
When writing body paragraphs, brevity should reign. Ensure that your body paragraphs are no longer than three-quarters of a double-spaced page. An ideal paragraph is about 150 words. Above that, you have a long paragraph that is probably a disservice to your essay. A little longer is acceptable, but too long is worthless.
8. Revise and edit well
Review, revise, and proofread each body paragraph to eliminate writing errors. Do away with grammatical, spelling, punctuation, and syntax errors. Equally, remove all the unnecessary words and redundancies in your paragraphs. Only ensure you have a clear, concise, and authoritative body paragraph. Finally, remove all the repeated information between paragraphs. Each paragraph should be unique.
The successful students have mastered how to write good body paragraphs. Ideally, the process itself might be challenging. However, it is imperative to understand it to attain coherence in your essay. When the body paragraphs are on point, they together fortify the main thesis statement.
We have covered some unique techniques or paragraphing analogies to help you structure your paragraphs. Then, if you outline your paragraph according to each, you will end up with a high score essay or paper.
You are guaranteed to meet the writing objectives when the paragraphs flow with ideas and points. The only best reward you can get is high scores since you have displayed maturity in your writing. If that feels hard, we have expert essay writers you can count on, talk to us.
Need a Discount to Order?
15% off first order, what you get from us.

Plagiarism-free papers
Our papers are 100% original and unique to pass online plagiarism checkers.

Well-researched academic papers
Even when we say essays for sale, they meet academic writing conventions.

24/7 online support
Hit us up on live chat or Messenger for continuous help with your essays.

Easy communication with writers
Order essays and begin communicating with your writer directly and anonymously.
What is a Body Paragraph? (Definition, Examples, How to Start)

What is a body paragraph? How do I start a body paragraph? A body paragraph is the most important part of the sentence subject . It delivers the most impactful information and helps to transition in and out of paragraphs more effectively.

What is a body paragraph?
Any essay, article, or academic writing starts with an introduction and ends with a conclusion. The text between the introduction and conclusion is the body paragraph.
A body paragraph supports the idea that was mentioned in the introduction by shedding light on new details using facts, statistics, arguments, or other information.
What role does a body paragraph play in an article or an essay?
A body paragraph acts as a connection between the introduction and the conclusion. The body paragraph’s role is to justify the thesis stated in the introduction of an essay or article. As mentioned previously it comes between the introduction and the conclusion which is where most of the writing is done. This signifies its importance.
There can be multiple body paragraphs in an article or an essay. That said, each of the body paragraphs should logically connect with one another. In addition to this, all the body paragraphs should focus on the main idea stated in the introduction. Also, the sentences should not be long, so that readers can easily consume the information.
Here is a brief breakdown of the structure of a body paragraph:
How to structure a body paragraph
Every body paragraph has four main parts. They are:
- Topic Sentence
- Evidence Or Supporting Sentences
- Ending Or Conclusion
Here is a detailed breakdown of each one of them.
Topic sentence
The topic sentence is the first sentence in a body paragraph. This sentence discusses the main idea of the topic and indicates what information to expect in the rest of the paragraph. It sets the stage for the rest of the paragraph.
Evidence or supporting sentences
After the topic sentence comes the supporting sentences. These sentences are used to justify the claim that was stated in the topic sentence. Text citations, evidence, statistics, and examples are used to justify the claim. For example, if the topic sentence discusses “Switzerland is a must visit place”, then the supporting sentences should discuss the beautiful parts of Switzerland with examples to justify the claim.
One sentence to another sentence should flow seamlessly and this is possible by using transition words . Transition words like “however”, “although”, “in addition to”, “next”, and “in contrast” helps in doing exactly the same.
Ending or concluding sentence
Every body paragraph should end with a conclusion which comes after the supporting sentences. It summarizes the main idea of the body paragraph and emphasizes the supporting details. The conclusion gives way to the next line of the next paragraph.
Transitions are a few words that help in the smooth flow of the previous paragraph to the next paragraph. These words can be at the beginning of topic sentences or at the end of the body paragraph. They connect one idea of a paragraph to the next idea of another paragraph.
How to write an effective body paragraph
Keep the body paragraph’s focus on the topic.
All the body paragraphs should support the claim made in the introduction of an essay or an article. It should be consistent with the main idea of the topic. It is recommended to avoid adding unnecessary information in the body paragraph that doesn’t relate to the main idea of the topic.
Break complicated topic sentences into smaller parts
If the topic sentence has many parts to it, the topic sentence should be divided into smaller ideas and each idea should be expressed in a different body paragraph. Having too many parts in a topic sentence will lead to many support sentences in the body paragraph which will be too lengthy for readers to grasp.
Add counterarguments
If it is an academic essay or an opinion article, counterarguments should be included in the piece. Adding counterarguments in such pieces will give a broader perspective of the piece. Such inclusions will strengthen the essay or article.
Use signals when more than one paragraph deals with the same evidence
If multiple body paragraphs deal with the same evidence, there are a few signal phrases that will help the reader connect with evidence used earlier in other paragraphs. The signal phrases like “As mentioned previously” and “As already mentioned” can be used.
Include paragraph breaks
It is a single-line space that divides one paragraph from another. This is necessary because too long paragraphs make it difficult for readers to grasp the information. A space between paragraphs will help the readers to easily wade through the text. A paragraph break also signals the transition of one idea of one body paragraph to an idea of another body paragraph.
The body paragraph should be short
The body paragraph should be short and concise . The paragraphs should not exceed one page. Paragraphs exceeding a page will make the article or essay complicated to comprehend the information.
Body paragraphs should be proofread
After writing the body paragraph, proofreading is done. This will help in finding and fixing mistakes. It will also help in removing unnecessary sentences in the body paragraph. The ideal way to proofread is by reading the body paragraph loudly. Doing so will help in identifying awkward word placements in the sentence.
In addition to this, asking questions like “is the body paragraph sticking to the main idea of the topic?” should be exercised. It will give a sense that if the paragraph is heading in the right direction or not.
How to start a body paragraph
The first sentence in a body paragraph is the topic sentence and it is the hardest sentence to write. The topic sentence sets the stage for the rest of the sentences in the paragraph.
Once the reader reads the topic sentence, the reader should get a sense that what the rest of the paragraph will be.
So, it should be concise and to the point, revealing enough information that will help the reader to know what the paragraph will be all about.
How to conclude a body paragraph
At the end of the body paragraph, the sentence should summarize the claim stated in the topic sentence and should also include a brief explanation of the supporting sentences. It should be written in such a way that the sentence is concise and at the same time reveals the main points.
This sentence will help the reader to get a gist of what the paragraph is all about.
Difference between body paragraph and introduction
Though both of them are paragraphs, they are very different. Firstly, the structure of an introduction is constructed differently than the body paragraph. An introduction consists of a thesis statement and a brief explanation. On the other hand, the body paragraph consists of a topic sentence, supporting sentences, and a conclusion.
Secondly, the introduction comes first in an essay or an article. In comparison, the body paragraph comes after the introduction. It comes after the introduction and before the conclusion of an essay or article.
A typical body paragraph should contain at least six sentences.
To develop a well-structured paragraph:
- Construct a topic sentence.
- Include evidence to support the claim expressed in the topic sentence.
- Add analysis to the paragraph.
- End it with a conclusion summarizing the key points of the paragraph.
- Finally, proofread the paragraph to identify and fix mistakes.
An introduction is the first paragraph of an essay or article. It gets the reader’s attention regarding the topic and provides the thesis statement of the topic. To write a good introduction:
- Keep the introduction paragraph short.
- In one to two sentences explain the thesis statement of the article or essay.
There is no fixed number of words that a body paragraph should have. That said, typically a paragraph contains about a hundred to two hundred words which are six to seven sentences.
Yes, an essay or article can have more than one body paragraph. Some essays have three to four body paragraphs. That said, having two of these is enough to cover important points of the essay.
A conclusion comes after the body paragraph at the end of the essay. A long essay can have two or three paragraphs to conclude. It summarizes the main idea of the topic.
- Body Paragraphs: How to Write Perfect Ones | Grammarly blog
- Body Paragraph Example & Structure
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph
- How to Write a Body Paragraph | BestColleges
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy
Essay writing: Main body
- Introductions
- Conclusions
- Analysing questions
- Planning & drafting
- Revising & editing
- Proofreading
- Essay writing videos
Jump to content on this page:
“An appropriate use of paragraphs is an essential part of writing coherent and well-structured essays.” Don Shiach, How to write essays
The main body of your essay is where you deliver your argument . Its building blocks are well structured, academic paragraphs. Each paragraph is in itself an individual argument and when put together they should form a clear narrative that leads the reader to the inevitability of your conclusion.
The importance of the paragraph
A good academic paragraph is a special thing. It makes a clear point, backed up by good quality academic evidence, with a clear explanation of how the evidence supports the point and why the point is relevant to your overall argument which supports your position . When these paragraphs are put together with appropriate links, there is a logical flow that takes the reader naturally to your essay's conclusion.
As a general rule there should be one clear key point per paragraph , otherwise your reader could become overwhelmed with evidence that supports different points and makes your argument harder to follow. If you follow the basic structure below, you will be able to build effective paragraphs and so make the main body of your essay deliver on what you say it will do in your introduction.
Paragraph structure

- A topic sentence – what is the overall point that the paragraph is making?
- Evidence that supports your point – this is usually your cited material.
- Explanation of why the point is important and how it helps with your overall argument.
- A link (if necessary) to the next paragraph (or to the previous one if coming at the beginning of the paragraph) or back to the essay question.
This is a good order to use when you are new to writing academic essays - but as you get more accomplished you can adapt it as necessary. The important thing is to make sure all of these elements are present within the paragraph.
The sections below explain more about each of these elements.

The topic sentence (Point)
This should appear early in the paragraph and is often, but not always, the first sentence. It should clearly state the main point that you are making in the paragraph. When you are planning essays, writing down a list of your topic sentences is an excellent way to check that your argument flows well from one point to the next.

This is the evidence that backs up your topic sentence. Why do you believe what you have written in your topic sentence? The evidence is usually paraphrased or quoted material from your reading . Depending on the nature of the assignment, it could also include:
- Your own data (in a research project for example).
- Personal experiences from practice (especially for Social Care, Health Sciences and Education).
- Personal experiences from learning (in a reflective essay for example).
Any evidence from external sources should, of course, be referenced.

Explanation (analysis)
This is the part of your paragraph where you explain to your reader why the evidence supports the point and why that point is relevant to your overall argument. It is where you answer the question 'So what?'. Tell the reader how the information in the paragraph helps you answer the question and how it leads to your conclusion. Your analysis should attempt to persuade the reader that your conclusion is the correct one.
These are the parts of your paragraphs that will get you the higher marks in any marking scheme.

Links are optional but it will help your argument flow if you include them. They are sentences that help the reader understand how the parts of your argument are connected . Most commonly they come at the end of the paragraph but they can be equally effective at the beginning of the next one. Sometimes a link is split between the end of one paragraph and the beginning of the next (see the example paragraph below).
Paragraph structure video
Length of a paragraph
Academic paragraphs are usually between 200 and 300 words long (they vary more than this but it is a useful guide). The important thing is that they should be long enough to contain all the above material. Only move onto a new paragraph if you are making a new point.
Many students make their paragraphs too short (because they are not including enough or any analysis) or too long (they are made up of several different points).
Example of an academic paragraph
Using storytelling in educational settings can enable educators to connect with their students because of inborn tendencies for humans to listen to stories. Written languages have only existed for between 6,000 and 7,000 years (Daniels & Bright, 1995) before then, and continually ever since in many cultures, important lessons for life were passed on using the oral tradition of storytelling. These varied from simple informative tales, to help us learn how to find food or avoid danger, to more magical and miraculous stories designed to help us see how we can resolve conflict and find our place in society (Zipes, 2012). Oral storytelling traditions are still fundamental to native American culture and Rebecca Bishop, a native American public relations officer (quoted in Sorensen, 2012) believes that the physical act of storytelling is a special thing; children will automatically stop what they are doing and listen when a story is told. Professional communicators report that this continues to adulthood (Simmons, 2006; Stevenson, 2008). This means that storytelling can be a powerful tool for connecting with students of all ages in a way that a list of bullet points in a PowerPoint presentation cannot. The emotional connection and innate, almost hardwired, need to listen when someone tells a story means that educators can teach memorable lessons in a uniquely engaging manner that is common to all cultures.
This cross-cultural element of storytelling can be seen when reading or listening to wisdom tales from around the world...
Key: Topic sentence Evidence (includes some analysis) Analysis Link (crosses into next paragraph)
- << Previous: Introductions
- Next: Conclusions >>
- Last Updated: Nov 3, 2023 3:17 PM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/essays
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem
The Function and Structures of the Human Heart Essay
Introduction, the function of the heart, types of blood circulation, the external structure of the heart, the internal structure of the heart.
The human heart is a critical organ in the nervous system, and it is responsible for sustaining life throughout its lifespan. The muscular organ is characterized by four major functionally distinct chambers and several valves responsible for regulating the normal flow of blood within the body (Litviňuková et al., 2020). It is found at the center of the chest between the lungs, underneath the thoracic cavity.
The primary function of the human heart is to ensure that blood constantly flows by pumping it throughout the body (Willie et al., 2015). It is also responsible for delivering and replenishing oxygen, hormones, glucose, nutrients, and other components to the cells and tissues in various parts of the body (Miranda, 2019; Willie et al., 2015). Maintaining a constant blood flow also helps in ensuring adequate blood pressure in the body. It also removes carbon dioxide and waste from the body system.
There are three major types of blood circulation. Pulmonary circulation involves the transfer of deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs and then the movement of oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart (Visible Body, 2020).
Systematic circulation is distinct from pulmonary circulation in the sense that oxygenated blood is carried from the heart to all other organs and tissues in the body, and deoxygenated blood is transferred back to the heart (Visible Body, 2020).
Coronary circulation is responsible for replenishing the heart with oxygen and involves the supply of oxygenated blood to the heart. Other organs, such as the brain, depend hugely on the steady supply of fresh, oxygenated blood to survive (Miranda, 2019).
The pericardium and walls of the heart make up the external structure. The pericardium is the membrane covering the heart, which comprises two layers: serous and fibrous (Saikat, 2016). It has three distinct layers (myocardium, endocardium, and epicardium) and a cavity, as illustrated above. It is responsible for preventing excessive stretching, insufflation, or inflation of the heart and protecting it by secreting a lubricant that reduces the risk of friction with adjacent organs (Saikat, 2016; Miranda, 2019). Moreover, the pericardium is responsible for holding this organ in its position (Saikat, 2016).
The internal structure of the heart is more complex and consists of four chambers (which differ in terms of their morphology and function) and several blood vessels and valves which are responsible for controlling the flow of blood in the body (Litviňuková et al., 2020).
The four chambers (the left atrium, right atrium, left ventricle, and right ventricle) receive blood and pump it away from the heart.
The heart has three major blood vessels (veins, capillaries, and arteries) which distribute blood throughout the body.
Finally, the heart has two types of valves (atrioventricular valves and semilunar valves) which ensure that the blood flows in a single direction (Miranda, 2019).
Litviňuková, Talavera-López, C., Maatz, H., Reichart, D., Worth, C., Lindberg, E., Kanda, M., Polanski,K., Heinig, M., Lee, M., Nadelmann, E., Roberts, K., Tuck, L., Fasouli, E., DeLaughter, D., McDonough, B., Wakimoto, H., Gorham, J., Samari, S., … Teichmann, S. A. (2020). Cells of the adult human heart. Nature . Web.
Miranda, M., G. (2019 ). Structure and function of the heart. New Medical. Web.
Saikat, R. (2016). What is the structure of the pericardium? What is its function ? Socratic. Web.
Visible Body (2020). Pulmonary Circulation and systemic circulation: the routes and function of blood flow . Web.
Willie, C. K., Tzeng, Y. C., Fisher, J. A., & Ainslie, P. N. (2014). Integrative regulation of human brain blood flow. The Journal of Physiology , 592 (5), 841–859.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, January 23). The Function and Structures of the Human Heart. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-function-and-structures-of-the-human-heart/
"The Function and Structures of the Human Heart." IvyPanda , 23 Jan. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/the-function-and-structures-of-the-human-heart/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'The Function and Structures of the Human Heart'. 23 January.
IvyPanda . 2023. "The Function and Structures of the Human Heart." January 23, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-function-and-structures-of-the-human-heart/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Function and Structures of the Human Heart." January 23, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-function-and-structures-of-the-human-heart/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Function and Structures of the Human Heart." January 23, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-function-and-structures-of-the-human-heart/.
- Cardiovascular Physiology: The Heart Electrical Activity
- Blood Vessels - Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries
- Lubricants Oil Production in Refineries
- “How the Heart Works”: Brief Description of the Functions of the Heart
- Asbestos and Rising of Cancer
- Human Circulatory System and Evolution
- The MEK lubricant and de-waxing method
- Sliding Friction: Static and Kinetic Friction
- Respiratory Care of Thoracic Injuries
- Fibrous Aerosol Filters and Their Evolution
- Experiment on the Bacteriophages
- Discussion of Body Image Concerns Problem
- Epithelial Tissue: Structure and Functions
- Nitrobacter's Features and Position in the Ecosystem
- Neural Stem Cells in Therapeutic Purposes
Human Body Essay
Introduction.
It is surprising to see how a human body functions with maximum capability. Whether we are talking, walking or seeing, there are distinct parts in our body that are destined to perform a particular function. The importance of each part is discussed in this human body essay. When we feel tired, we often take a rest and lie down for a moment. But our body continues to work, even when we take a break. Even if you are tired, your heart will not stop beating. It pumps blood and transports nutrients to your body.
The human body is made up of many parts and organs that work together to sustain life in our body. No organ or body part is more important than the other, and if you ignore one of them, then the whole body will be in pain. So, let us teach the significance of different parts of the body to our children through this essay on human body parts in English. To explore other exciting content for kids learning , head to our website.

Different Systems in the Human Body
The human body looks very simple from the outside with hands, legs, face, eyes, ears and so on. But, there is a more complex and significant structure inside the body that helps us to live. The human body is made up of many small structures like cells, tissues, organs and systems. It is covered by the skin, beneath which you could find muscles, veins, and blood. This structure is formed on the base of a skeleton, which consists of many bones. All these are arranged in a specific way to help the body function effectively. In this human body essay, we will see the different systems in the human body and their functions.
The circulatory system, respiratory system, digestive system and nervous system are the main systems of the human body. Each system has different organs, and they function together to accomplish several tasks. The circulatory system consists of organs like the heart, blood and blood vessels, and its main function is to pump blood from the heart to the lungs and carry oxygen to different parts of the body.
Next, we will understand the importance of the respiratory system through this human body essay in English. The respiratory system enables us to breathe easily, and it includes organs like the lungs, airways, windpipe, nose and mouth. While the digestive system helps in breaking down the food we eat and gives the energy to work with the help of organs like the mouth, food pipe, stomach, intestines, pancreas, liver, and anus, the nervous system controls our actions, thoughts and movements. It mainly consists of organs like the brain, spinal cord and nerves.
All these systems are necessary for the proper functioning of the human body, which is discussed in this essay on human body parts in English. By inculcating good eating habits, maintaining proper hygiene and doing regular exercises, we can look after our bodies. You can refer to more essays for kids on our website.
Frequently Asked Questions on Human Body Essay
Why should we take care of our bodies.
Most of the tasks we do like walking, running, eating etc., are only possible if we have a healthy body. To ensure we have a healthy body, all the systems must function properly, which is determined by our lifestyle and eating habits. Only a healthy body will have a healthy mind, and hence, we must take good care of our bodies.
What are some of the body parts and their functions?
We see with our eyes, listen with our ears, walk with our legs, touch with our hands, breathe through our nose and taste with our tongue.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Body — The Functions Of Water In A Human Body
The Functions of Water in a Human Body
- Categories: Body
About this sample

Words: 1572 |
Published: Jan 28, 2021
Words: 1572 | Pages: 3 | 8 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, water function(s), water toxicity, implications for health promotion and disease prevention, conclusions, water and weight loss, water and quitting smoking, water deficiency.
- Armstrong LE (2005). Hydration assessment techniques. Nut Rev 63, S40–S54.
- Draft dietary reference values for water. Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies.
- Lang F, Waldegger S (1997). Regulating cell volume. Am Scientist 85, 456–463.
- Maughan RJ, Shirreffs SM, Watson P (2007). Exercise, heat, hydration, and the brain. J Am Coll Nutr 26
- Phillips PA, Rolls BJ, Ledingham JG, Forsling ML, Morton JJ, Crowe MJ et al. (1984). Reduced thirst after water deprivation in healthy elderly men.
- Ritz P, Berrut G (2005). The importance of good hydration for day-to-day health. Nutr Rev 63, S6–S13.
- Sawka MN (1992). Physiological consequences of hypohydration: exercise performance and thermoregulation. Med Sci Sports Exerc
- Sawka MN, Cheuvront SN, Carter III R (2005). Human water needs. Nutr Rev
- Shirreffs SM (2003). Markers of hydration status.
- Eur J Clin Nutr xoDietary Reference Intakes (2006). The Essential Guide to Nutrients Requirements. Institute of Medicine of the National Academies: Washington DC, 543 Fields Chasity Hardnett Jailah

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Nursing & Health

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 573 words
4 pages / 1936 words
2 pages / 1105 words
2 pages / 858 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Body
Body positivity is more than a mere movement; it is a transformative ideology that challenges society's narrow beauty standards and encourages individuals to embrace and celebrate their bodies as they are. In a world dominated [...]
Minerals and water are foundational components of the human body, each playing a unique and essential role in maintaining physiological functions and overall health. In this essay, we will explore the importance of minerals, [...]
The functions and sources of minerals are important aspects of maintaining overall health and well-being. Minerals can be found in various sources, including coconut water. According to Fife (2011), coconut water has been used [...]
Oxygen is inhaled into alveoli and is passed into the capillaries and carbon dioxide is passed from the capillaries into the alveoli to be exhaled. The second step is called the internal respiration where the exchange of gases [...]
Weight loss is the major concern for anyone in this generation, which should be. The kind of lives we live, demand us to be fit and up on our feet 24/7. We have to be up for the challenges always. The ways we resort to, to [...]
Predominantly controlling breath is nothing but Pranayama. The word Pranayama is comprised of two Sanskrit words Prana which means life force and ayama which means to suppress the Prana. Implementation done deliberately on the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

UC researchers develop new CPAP device
The vortexpap could result in more patient compliance.

An estimated 40 million adults in the United States have obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a chronic sleep-related breathing disorder that involves a decrease or complete halt in airflow. Continuous positive airway pressure (or CPAP) is broadly considered first-line therapy for OSA.
CPAP technology is effective, but only if used regularly. Largely due to discomfort related to the mask and associated headgear required to maintain prescribed airway pressures by current devices, today’s CPAP is not well tolerated by patients. Noncompliance is estimated to impact at least a third of patients .
Researchers at the University of Cincinnati are developing a VortexPAP machine that takes advantage of vortex airflow technology. A preliminary clinical study with current CPAP users demonstrated that the VortexPAP can deliver the pressure levels that are used in the subjects’ CPAP therapy, but the mask is more comfortable to wear. It has a minimalistic design that is less intrusive and barely touches the patient’s face.
“Despite the clinical efficacy for CPAP in controlling OSA, patient compliance with the therapy remains a major cause of treatment failure,” says Liran Oren, PhD, research associate professor in the Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery at the UC College of Medicine.
Dr. Liran Oren is shown with Dr. Ephraim Gutmark and Dr. Ann Romaker and the VortexPAP device. Photo by Andrew Higley/UC Marketing + Communications.
“The vast majority of complaints from patients in CPAP therapy revolve around improving the comfort of the mask,” explains Oren. “However, regardless of the design, they all require a tight seal over the face, so that the airway can be pressurized. This design requirement for a tight seal is the main limitation for making CPAP therapy more comfortable.”
Oren says the VortexPAP eliminates the requirement for a tight seal since it’s based on reapplication of vortical airflow, a flow control mechanism commonly used in aerospace engineering application.
“The unique aerodynamic properties of vortical airflow enables the device to pressurize the upper airways without needing a tight-fitting mask,” says Oren. “As a result, this game-changing innovation will make CPAP therapy more comfortable, better tolerated and may increase patient compliance, a win for patients, doctors and third-party payers. Over 40 million people in the U.S. are diagnosed with OSA but the actual number is likely even higher because many remain undiagnosed.”
The project is a collaboration between Oren; Roy Kulick, MD, UC Entrepreneur-in-Residence; Ephraim Gutmark, PhD, Distinguished Professor, Ohio Eminent Scholar in the UC Department of Aerospace Engineering; and Ann Romaker, MD, director of the UC Sleep Medicine Center and professor in the UC Department of Internal Medicine.
Dr. Roy Kulick/photo provided.
Gutmark is director of the UC Laryngeal Biomechanics Lab. “The main strength of our lab is marrying advanced knowledge in aerospace with medicine,” Oren says. “For example, we know that vortices emanating from a jet engine would generate sound that people perceive as a type of ‘noise.’ As such, there is much active research on eliminating these vortices to reduce the sound (noise) produced by the jet.
“Our lab takes this knowledge and tries to reverse it. We found that vortices form in the airway when our vocal cords vibrate when we speak.”
Oren says it is well-established in aerospace engineering that vortex airflow has unique aerodynamic properties that are different from conventional, continuous airflow. This type of airflow is used in various applications, such as enhancing fuel mixing in combustion processes, improving convective cooling of electronic components or as a flow control mechanism that reduces drag over a body (such as an airplane wing or a car). The co-inventors and Oren realized the unique properties of vortex airflow could also be leveraged for CPAP therapy.
“The development work of the VortexPAP draws on the strengths that UC offers,” Oren says. “This idea was born from distinguished departments (aerospace engineering and otolaryngology) and developed into a functional, suitable medical device using expertise in biomedical engineering.
“We collaborate with Dr. Ann Romaker, a sleep medicine doctor from UC, who helped us identify the main reasons for patient noncompliance with CPAP therapy and ensure our technology offers an alternative, effective solution.”
Dr. Oren shown with Dr. Gutmark and the VortexPAP device. Photo by Andrew Higley/UC Marketing + Communications.
Dr. Oren and the Dr. Romaker discuss the function of the VortexPAP device. Photo by Andrew Higley/UC Marketing + Communicatiions.
Romaker says the biggest design change is the lack of a need for a seal. The interface will not be tight nor will it have to be enclosed, so people with a degree of claustrophobia will be much more comfortable, as well as everyone else.
“The lower pressures produced by this method will also decrease air swallowing, which can be uncomfortable for some CPAP users and, again, will be more comfortable,” Romaker says.
According to Oren, the development work is also done with the goal of eventually commercializing the VortexPAP in the U.S. As such, they received strong support from the UC Venture Lab. They paired with Entrepreneur-in-Residence Kulick, who has been instrumental in helping build out a business plan for the VortexPAP.
“I think this project is the epitome of UC,” Oren adds.
Featured image at top of the VortexPAP displayed in the laboratory of Dr. Liran Oren in the UC College of Medicine. Photo by Andrew Higley/UC Marketing + Communications.
Impact Lives Here
The University of Cincinnati is leading public urban universities into a new era of innovation and impact. Our faculty, staff and students are saving lives, changing outcomes and bending the future in our city's direction. Next Lives Here .
- Academic Health Center
- Office of Research
- College of Engineering and Applied Science
- College of Medicine
Related Stories
Classes begin for increasingly diverse student body at uc.
August 23, 2021
The first day of classes for the fall semester at the University of Cincinnati starts Monday, Aug. 23, and more than 46,700 students are expected to begin instruction with a more traditional fall term, focusing on in-person instruction and activities.
April 17, 2024
President Pinto's 2021 year-in-review message
December 17, 2021
University of Cincinnati President Neville G. Pinto looks back on a historic year that brought students, faculty, staff and the community back together like never before.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The body is always divided into paragraphs. You can work through the body in three main stages: Create an outline of what you want to say and in what order. Write a first draft to get your main ideas down on paper. Write a second draft to clarify your arguments and make sure everything fits together.
A body paragraph is any paragraph in the middle of an essay, paper, or article that comes after the introduction but before the conclusion.Generally, body paragraphs support the work's thesis and shed new light on the main topic, whether through empirical data, logical deduction, deliberate persuasion, or anecdotal evidence.
Basic essay structure: the 3 main parts of an essay. Almost every single essay that's ever been written follows the same basic structure: Introduction. Body paragraphs. Conclusion. This structure has stood the test of time for one simple reason: It works. It clearly presents the writer's position, supports that position with relevant ...
The essay body itself is organised into paragraphs, according to your plan. Remember that each paragraph focuses on one idea, or aspect of your topic, and should contain at least 4-5 sentences so you can deal with that idea properly. Each body paragraph has three sections. First is the topic sentence. This lets the reader know what the ...
Part I: The Introduction. An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you're writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things: Gets the reader's attention. You can get a reader's attention by telling a story, providing a statistic ...
Writing Body Paragraphs. Follow these steps below to write good body paragraphs. Step 1: Develop a Topic Sentence. Step 2: Provide Evidence to Support your Topic Sentence and Overall Argument. Step 3: Add your Own Analysis and Interpretation. Step 4: Conclude. Step 5: Revise and Proofread. A P.I.E. Paragraph. For Example.
Kaylen is an experienced writer/translator whose work has been featured in Los Angeles Review, Hybrid, San Francisco Bay Guardian, France Today, and Honolulu Weekly, among others. How to Write a Body Paragraph - we explain the best way to start a body paragraph in a college essay or other school writing assignment.
Key Takeaways. Your body paragraphs should closely follow the path set forth by your thesis statement. Strong body paragraphs contain evidence that supports your thesis. Primary support comprises the most important points you use to support your thesis. Strong primary support is specific, detailed, and relevant to the thesis.
A strong paragraph in an academic essay will usually include these three elements: A topic sentence. The topic sentence does double duty for a paragraph. First, a strong topic sentence makes a claim or states a main idea that is then developed in the rest of the paragraph. Second, the topic sentence signals to readers how the paragraph is ...
These parts of a body paragraph can include examples, facts, statistics, or expert opinions. Ensure that the information used is reliable and relevant to your idea. Employ transition sentences to link your ideas to the preceding and subsequent paragraphs. They make it easier for the reader to follow the main argument.
As can be seen in this diagram, the body section, which may be comprised of many different paragraphs, forms the main bulk of any essay (usually about 70%). As a general rule, any paragraph that comes between the introduction and the conclusion is a body paragraph that forms part of the body section. While an essay's introduction and ...
The second body paragraph explains the second most important idea or second strongest argument of the essay. Body Paragraph 3. The third body paragraph explains the essay's least important or weakest argument. It builds on the ideas from body paragraphs 1 & 2. It can also be used to address possible counterclaims to your argument IF you were ...
Body paragraphs: Moving from general to specific information. Your paper should be organized in a manner that moves from general to specific information. Every time you begin a new subject, think of an inverted pyramid - The broadest range of information sits at the top, and as the paragraph or paper progresses, the author becomes more and more ...
Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 2 min read. From magazines to academic essays, you can find body paragraphs across many forms of writing. Learn more about how to write engaging body paragraphs that support the central idea of your writing project.
A body paragraph has three major components: (1) topic sentence, (2) explanation, (3) supporting details.Without any of them, the body paragraph seems to be missing something, and will not add anything to the theme and central idea of the essay.. Topic Sentence The topic sentence is the first sentence of a paragraph, and states the main idea to be discussed in the paragraph.
Here is a breakdown of the four parts and the functions that each plays in the body paragraph: Transition - linking the body paragraphs to one another. Topic Sentence - introducing the paragraph. Supporting Sentences - Explain the topic sentence and support the thesis.
A body paragraph acts as a connection between the introduction and the conclusion. The body paragraph's role is to justify the thesis stated in the introduction of an essay or article. As mentioned previously it comes between the introduction and the conclusion which is where most of the writing is done. This signifies its importance.
Don Shiach, How to write essays. The main body of your essay is where you deliver your argument. Its building blocks are well structured, academic paragraphs. Each paragraph is in itself an individual argument and when put together they should form a clear narrative that leads the reader to the inevitability of your conclusion.
89. It is important to give your body the essentials it needs. They can be classified into four different categories. To operate properly, your body needs proper hydration; nutrients and vitamins; exercise and physical activity; and sleep (newhealthbasics.com). Although all support basic function throughout the day, sleep is one of the more ...
Definition. The muscular system of a human body is the system of organs (muscles) that is responsible for any type of body movement (Muscolino 35). Muscles, of which the titular system is composed, are the tissue that is made of fiber and tissue and can contract and relax (Muscolino 38). The muscular system incorporates not only the skeletal ...
The Function of the Heart. The primary function of the human heart is to ensure that blood constantly flows by pumping it throughout the body (Willie et al., 2015). It is also responsible for delivering and replenishing oxygen, hormones, glucose, nutrients, and other components to the cells and tissues in various parts of the body (Miranda ...
The human body is made up of many small structures like cells, tissues, organs and systems. It is covered by the skin, beneath which you could find muscles, veins, and blood. This structure is formed on the base of a skeleton, which consists of many bones. All these are arranged in a specific way to help the body function effectively.
Water is also required for digestion, absorption, transportation, dissolving nutrients, elimination of waste products and thermoregulation.Water accounts for 60-80% of body weight, depending on lean body mass. On average, men have a higher lean body mass than women and higher percentage of body mass as water than in women.
Previous publication: Hwang S, Pahys J, Toll B, Quinonez A, Grewal H, Samdani A: Paper 18 [abstract]: The impact of vertebral body tethering on pulmonary function. 15th International Congress on Early Onset Scoliosis and the Growing Spine. Spine Deform 10 (1):222, January 2022. Investigation Performed at Shriners Children's—Philadelphia.
Researchers at the University of Cincinnati are developing a VortexPAP machine that takes advantage of vortex airflow technology. A preliminary clinical study with current CPAP users demonstrated that the VortexPAP can deliver the pressure levels that are used in the subjects' CPAP therapy, but the mask is more comfortable to wear. It has a minimalistic design that is less intrusive and ...