How to write an undergraduate university dissertation
Writing a dissertation is a daunting task, but these tips will help you prepare for all the common challenges students face before deadline day.


Grace McCabe
Writing a dissertation is one of the most challenging aspects of university. However, it is the chance for students to demonstrate what they have learned during their degree and to explore a topic in depth.
In this article, we look at 10 top tips for writing a successful dissertation and break down how to write each section of a dissertation in detail.
10 tips for writing an undergraduate dissertation
1. Select an engaging topic Choose a subject that aligns with your interests and allows you to showcase the skills and knowledge you have acquired through your degree.
2. Research your supervisor Undergraduate students will often be assigned a supervisor based on their research specialisms. Do some research on your supervisor and make sure that they align with your dissertation goals.
3. Understand the dissertation structure Familiarise yourself with the structure (introduction, review of existing research, methodology, findings, results and conclusion). This will vary based on your subject.
4. Write a schedule As soon as you have finalised your topic and looked over the deadline, create a rough plan of how much work you have to do and create mini-deadlines along the way to make sure don’t find yourself having to write your entire dissertation in the final few weeks.
5. Determine requirements Ensure that you know which format your dissertation should be presented in. Check the word count and the referencing style.
6. Organise references from the beginning Maintain an alphabetically arranged reference list or bibliography in the designated style as you do your reading. This will make it a lot easier to finalise your references at the end.
7. Create a detailed plan Once you have done your initial research and have an idea of the shape your dissertation will take, write a detailed essay plan outlining your research questions, SMART objectives and dissertation structure.
8. Keep a dissertation journal Track your progress, record your research and your reading, and document challenges. This will be helpful as you discuss your work with your supervisor and organise your notes.
9. Schedule regular check-ins with your supervisor Make sure you stay in touch with your supervisor throughout the process, scheduling regular meetings and keeping good notes so you can update them on your progress.
10. Employ effective proofreading techniques Ask friends and family to help you proofread your work or use different fonts to help make the text look different. This will help you check for missing sections, grammatical mistakes and typos.
What is a dissertation?
A dissertation is a long piece of academic writing or a research project that you have to write as part of your undergraduate university degree.
It’s usually a long essay in which you explore your chosen topic, present your ideas and show that you understand and can apply what you’ve learned during your studies. Informally, the terms “dissertation” and “thesis” are often used interchangeably.
How do I select a dissertation topic?
First, choose a topic that you find interesting. You will be working on your dissertation for several months, so finding a research topic that you are passionate about and that demonstrates your strength in your subject is best. You want your topic to show all the skills you have developed during your degree. It would be a bonus if you can link your work to your chosen career path, but it’s not necessary.
Second, begin by exploring relevant literature in your field, including academic journals, books and articles. This will help you identify gaps in existing knowledge and areas that may need further exploration. You may not be able to think of a truly original piece of research, but it’s always good to know what has already been written about your chosen topic.
Consider the practical aspects of your chosen topic, ensuring that it is possible within the time frame and available resources. Assess the availability of data, research materials and the overall practicality of conducting the research.
When picking a dissertation topic, you also want to try to choose something that adds new ideas or perspectives to what’s already known in your field. As you narrow your focus, remember that a more targeted approach usually leads to a dissertation that’s easier to manage and has a bigger impact. Be ready to change your plans based on feedback and new information you discover during your research.
How to work with your dissertation supervisor?
Your supervisor is there to provide guidance on your chosen topic, direct your research efforts, and offer assistance and suggestions when you have queries. It’s crucial to establish a comfortable and open line of communication with them throughout the process. Their knowledge can greatly benefit your work. Keep them informed about your progress, seek their advice, and don’t hesitate to ask questions.
1. Keep them updated Regularly tell your supervisor how your work is going and if you’re having any problems. You can do this through emails, meetings or progress reports.
2. Plan meetings Schedule regular meetings with your supervisor. These can be in person or online. These are your time to discuss your progress and ask for help.
3. Share your writing Give your supervisor parts of your writing or an outline. This helps them see what you’re thinking so they can advise you on how to develop it.
5. Ask specific questions When you need help, ask specific questions instead of general ones. This makes it easier for your supervisor to help you.
6. Listen to feedback Be open to what your supervisor says. If they suggest changes, try to make them. It makes your dissertation better and shows you can work together.
7. Talk about problems If something is hard or you’re worried, talk to your supervisor about it. They can give you advice or tell you where to find help.
8. Take charge Be responsible for your work. Let your supervisor know if your plans change, and don’t wait if you need help urgently.
Remember, talking openly with your supervisor helps you both understand each other better, improves your dissertation and ensures that you get the support you need.
How to write a successful research piece at university How to choose a topic for your dissertation Tips for writing a convincing thesis
How do I plan my dissertation?
It’s important to start with a detailed plan that will serve as your road map throughout the entire process of writing your dissertation. As Jumana Labib, a master’s student at the University of Manchester studying digital media, culture and society, suggests: “Pace yourself – definitely don’t leave the entire thing for the last few days or weeks.”
Decide what your research question or questions will be for your chosen topic.
Break that down into smaller SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound) objectives.
Speak to your supervisor about any overlooked areas.
Create a breakdown of chapters using the structure listed below (for example, a methodology chapter).
Define objectives, key points and evidence for each chapter.
Define your research approach (qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods).
Outline your research methods and analysis techniques.
Develop a timeline with regular moments for review and feedback.
Allocate time for revision, editing and breaks.
Consider any ethical considerations related to your research.
Stay organised and add to your references and bibliography throughout the process.
Remain flexible to possible reviews or changes as you go along.
A well thought-out plan not only makes the writing process more manageable but also increases the likelihood of producing a high-quality piece of research.
How to structure a dissertation?
The structure can depend on your field of study, but this is a rough outline for science and social science dissertations:
Introduce your topic.
Complete a source or literature review.
Describe your research methodology (including the methods for gathering and filtering information, analysis techniques, materials, tools or resources used, limitations of your method, and any considerations of reliability).
Summarise your findings.
Discuss the results and what they mean.
Conclude your point and explain how your work contributes to your field.
On the other hand, humanities and arts dissertations often take the form of an extended essay. This involves constructing an argument or exploring a particular theory or analysis through the analysis of primary and secondary sources. Your essay will be structured through chapters arranged around themes or case studies.
All dissertations include a title page, an abstract and a reference list. Some may also need a table of contents at the beginning. Always check with your university department for its dissertation guidelines, and check with your supervisor as you begin to plan your structure to ensure that you have the right layout.
How long is an undergraduate dissertation?
The length of an undergraduate dissertation can vary depending on the specific guidelines provided by your university and your subject department. However, in many cases, undergraduate dissertations are typically about 8,000 to 12,000 words in length.
“Eat away at it; try to write for at least 30 minutes every day, even if it feels relatively unproductive to you in the moment,” Jumana advises.
How do I add references to my dissertation?
References are the section of your dissertation where you acknowledge the sources you have quoted or referred to in your writing. It’s a way of supporting your ideas, evidencing what research you have used and avoiding plagiarism (claiming someone else’s work as your own), and giving credit to the original authors.
Referencing typically includes in-text citations and a reference list or bibliography with full source details. Different referencing styles exist, such as Harvard, APA and MLA, each favoured in specific fields. Your university will tell you the preferred style.
Using tools and guides provided by universities can make the referencing process more manageable, but be sure they are approved by your university before using any.
How do I write a bibliography or list my references for my dissertation?
The requirement of a bibliography depends on the style of referencing you need to use. Styles such as OSCOLA or Chicago may not require a separate bibliography. In these styles, full source information is often incorporated into footnotes throughout the piece, doing away with the need for a separate bibliography section.
Typically, reference lists or bibliographies are organised alphabetically based on the author’s last name. They usually include essential details about each source, providing a quick overview for readers who want more information. Some styles ask that you include references that you didn’t use in your final piece as they were still a part of the overall research.
It is important to maintain this list as soon as you start your research. As you complete your research, you can add more sources to your bibliography to ensure that you have a comprehensive list throughout the dissertation process.
How to proofread an undergraduate dissertation?
Throughout your dissertation writing, attention to detail will be your greatest asset. The best way to avoid making mistakes is to continuously proofread and edit your work.
Proofreading is a great way to catch any missing sections, grammatical errors or typos. There are many tips to help you proofread:
Ask someone to read your piece and highlight any mistakes they find.
Change the font so you notice any mistakes.
Format your piece as you go, headings and sections will make it easier to spot any problems.
Separate editing and proofreading. Editing is your chance to rewrite sections, add more detail or change any points. Proofreading should be where you get into the final touches, really polish what you have and make sure it’s ready to be submitted.
Stick to your citation style and make sure every resource listed in your dissertation is cited in the reference list or bibliography.
How to write a conclusion for my dissertation?
Writing a dissertation conclusion is your chance to leave the reader impressed by your work.
Start by summarising your findings, highlighting your key points and the outcome of your research. Refer back to the original research question or hypotheses to provide context to your conclusion.
You can then delve into whether you achieved the goals you set at the beginning and reflect on whether your research addressed the topic as expected. Make sure you link your findings to existing literature or sources you have included throughout your work and how your own research could contribute to your field.
Be honest about any limitations or issues you faced during your research and consider any questions that went unanswered that you would consider in the future. Make sure that your conclusion is clear and concise, and sum up the overall impact and importance of your work.
Remember, keep the tone confident and authoritative, avoiding the introduction of new information. This should simply be a summary of everything you have already said throughout the dissertation.
You may also like

.css-185owts{overflow:hidden;max-height:54px;text-indent:0px;} How to use digital advisers to improve academic writing

How to deal with exam stress
Seeta Bhardwa

5 revision techniques to help you ace exam season (plus 7 more unusual approaches)
Register free and enjoy extra benefits

How Long is a Dissertation

How Long is a Dissertation? Concrete Answers
An undergraduate dissertation usually falls within the range of 8,000 to 15,000 words, while a master's dissertation typically spans from 12,000 to 50,000 words. In contrast, a PhD thesis is typically of book length, ranging from 70,000 to 100,000 words.
Let’s unravel the mystery of how long should a dissertation be. If you’ve ever wondered about this, look no further. Our comprehensive guide delves into the nitty-gritty of dissertation lengths across diverse academic realms. Whether you're a budding grad student, an academic advisor, or just curious, we've got you covered.
From Master's to PhD programs, we decode the variations in length requirements and shed light on disciplinary disparities. In general, dissertations are 150 to 300 words. But factors influence the length of these daunting scholarly requirements! But fear not as we break it down for you.
We’ll unveil the secrets behind dissertation writing, from how they reflect the depth and breadth of research to offering invaluable tips for planning and writing. So, if you're ready to demystify the daunting dissertation journey, hop on board! Let's navigate the labyrinth of academia together and empower you to conquer your scholarly aspirations.
Institutional guidelines on dissertation length
You can think of institutional guidelines as purveyors of academic excellence. Ever wondered why schools impose specific requirements like "Chapter 1: The Introduction must be at least 35 pages long and no more than 50 pages"?
It's not just about arbitrary rules! However, it's about striking the perfect balance between guidance and practicality. These guidelines serve as guardrails, steering students like you towards scholarly success without overwhelming faculty with endless pages to peruse.
Moreover, credibility is key here! A mere 8-page literature review won't cut it in the realm of academia. But fear not, for most institutions provide dissertation templates, complete with essential headings to streamline the process.
And for those seeking a helping hand, a dissertation writing service like ours stands ready to assist, ensuring your masterpiece meets the lofty standards of academic rigor. So, embrace the guidelines, weave your narrative, and let your dissertation shine with scholarly prowess.
Variations in dissertation length across academic disciplines
Dissertation length varies significantly across academic disciplines due to differences in research methods, data presentation, and writing conventions. Here's a general overview of how dissertation length can differ by discipline:
- Humanities and Social Sciences: Dissertations in these fields tend to be longer because they often involve comprehensive literature reviews, detailed theoretical analyses, and extensive qualitative data. It's not uncommon for dissertations in history, literature, or sociology to exceed 200 pages.
- Sciences and Engineering: Dissertations in the sciences and engineering might be shorter in terms of page count but are dense with technical details, data, charts, and appendices. They often range between 100 to 200 pages. However, the length can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the work and the requirements of the specific program.
- Arts and Design: In creative disciplines, the dissertation might include a practical component (like a portfolio, exhibition, or performance) alongside a written thesis. The written component might be shorter, focusing on the conceptual and contextual analysis of the creative work, usually ranging from 40 to 80 pages.
- Professional Fields (Business, Education, etc.): Dissertations in professional fields such as business or education often focus on case studies, practical applications, and policy analysis. These dissertations can vary widely in length but often fall in the range of 100 to 200 pages.
Dissertations vary in length due to many factors, which shows the diverse nature of academic research. Disciplinary differences are significant, as each field may have distinct expectations regarding the depth and scope of the study.
The type of analysis conducted, whether qualitative, quantitative, or a combination of both, also impacts the length.
For instance, qualitative studies may involve extensive textual analysis, resulting in longer manuscripts, while quantitative studies may require detailed statistical analyses. Additionally, the specific area of research within a discipline can also affect the length, as certain topics may necessitate more:
- extensive literature reviews
- data collection (e.g., fieldwork, surveys, interviews, lab work)
- discussion sections
While the average length typically falls within the range of 150-300 pages, it's essential to recognize the nuanced factors contributing to variations in dissertation length. You must remain informed about the variables shaping your document's overall size and structure to deliver exemplary results.
Factors influencing the length of doctoral dissertations
Various factors determine the length of a dissertation, such as the specific guidelines set by universities, the type of research conducted, the extent of analysis required, and the presence of supplementary materials.
Several factors come into play when determining the ideal length of a dissertation. University guidelines set the tone, with institutions offering word count ranges typically between 8,000 to 15,000 words for undergraduates and masters and 75,000 to 100,000 words for PhD.
Yet, beyond these guidelines, the nature of your research holds sway.
Disciplines vary, with humanities favoring extensive literature reviews and scientific fields emphasizing methodological intricacies. Depth of analysis matters, too; a thorough exploration demands more space.
Balancing these elements ensures a well-rounded dissertation. So, as you embark on your scholarly journey, consider these factors carefully. By understanding them, you'll craft a dissertation that not only meets academic standards but also showcases your analytical prowess and depth of intelligence.
Length, components, and scholarly dedication
Many aspiring scholars think, "How long is a doctoral dissertation?" However, the answer isn't straightforward. Yes, length varies, but let's not forget to factor in a crucial element: time. And we know because many students have instructed us to “ write my dissertation !”
Remember, a dissertation isn't penned in one sitting. Rather, it often evolves from smaller academic chapters. This gradual process allows students to explore diverse topics before committing to a book-length project they're passionate about.
Beyond the central argument lie various components that contribute to the overall length. Take the literature review, for example—an essential segment that contextualizes the research by analyzing existing scholarship. Then there's the myriad of ancillary elements like the title page, acknowledgments, abstract, and appendix, each adding to the dissertation's page count.
It’s the accumulation of these parts that determines the length. So, while the answer may not be a precise number, it's crucial to acknowledge many elements that make up a doctoral dissertation. And for those embarking on this scholarly journey, we can help you conquer this challenge.
How Long is a Dissertation Chapter? Uncover the Mystery
When it comes to dissertation length, most grad students fret over how long each chapter should be. While there's no one-size-fits-all answer, there is a golden rule–chapters should be long enough to address the research question comprehensively.
Think quality over quantity! Ask any dissertation adviser, and they’ll say aiming to fill a predetermined number of pages shouldn’t be the goal. Rather, you must thoroughly explore your topic, conduct extensive research, and present your findings effectively.
Your writing style and the unique nature of your research also play pivotal roles. So, whether your chapter spans 50 pages or 150, ensure it's packed with substantive content that advances your study. Ultimately, it's not about hitting a page count but about delivering a high-quality scholarly contribution.
Writing an Excellent PhD Dissertation: Strategies and Tips
After you’re done pondering on how many pages should a dissertation be, you can move on with production. Wondering how to write a dissertation , here are some tips:
- Start with a significant research topic that inspires you and formulate a clear research question.
- Thoroughly review existing literature to contextualize your study.
- Develop a robust methodology and collect comprehensive data.
- Analyze findings meticulously and synthesize them effectively.
- Ensure logical flow throughout your writing, striving for clarity and coherence.
- Engage with other scholars, both peers and mentors, to refine your work.
- Maintain consistency in formatting and adhere to academic standards.
Remember, with meticulous planning and dedication, you'll produce a dissertation that makes you and your mentors proud.
How long is a PhD dissertation?: The Conundrum
Do you belong to the list of students who feel bewildered about PhD dissertation length? Many wonder because of the length’s variability across disciplines and institutions. The general ballpark figure for a completed doctoral dissertation is typically between 150 to 300 pages. Yet, this can vary widely depending on factors such as:
- field of study
- research methodology used
- individual institutional requirements
- guidelines of mentors
Although there's no one-size-fits-all answer, understanding these variables can help you navigate the ambiguity surrounding dissertation length. And with proper planning, you can create an impressive output.
Frequently asked questions
How to properly plan and prepare for a long dissertation .
Thinking about how long is a dissertation for PhD stops students on their track. It can indeed be overwhelming when you think of the amount of work involved. But with proper planning, you can crush your goals. Here are some helpful tips:
- Break down your work into manageable steps.
- Define your research question clearly and set realistic milestones.
- Create an outline to help you write. `
- Have a schedule for research, writing, and revisions.
- Stay organized with notes, citations, and references.
- Seek feedback from advisors and peers throughout the process.
Remember, embrace the challenges you face as opportunities for growth!
Are supporting materials counted in the dissertation word count?
Worried about how long is a dissertation paper and if yours will make the cut? Remember, appendices, tables, and figures, while essential, aren't factored into the word count. So, you can incorporate these supplementary elements without concerns about exceeding word limits.
If you’re pressed for time, you can buy dissertation online . Just ensure to give appropriate instructions so the final output adheres to your institution's formatting guidelines. With these supporting materials appropriately included, your dissertation will be comprehensive.
Are there different types of dissertations?
When asking how long are dissertations, one of the first things to consider is the field of study. Various types of dissertations exist, often shaped by research methodology. It can be quantitative to qualitative studies or triangulation (a blend of both).
Instead of worrying about the length, determine your research approach—whether it's primary or secondary, qualitative or quantitative. This decision significantly impacts the depth and breadth of your investigation, ultimately influencing the expected length of your dissertation. By aligning your research methods with your academic goals, you'll gain clarity on the scope of your writing project.
Another aspect of the length of the entire document is the type of thesis - be it an undergraduate thesis, masters thesis, or thesis for an advanced degree, most dissertations for academic programs are lengthy. The more advanced the degree, the longer the thesis usually is.
Are dissertations just for PhDs?
How many pages in a dissertation is something most students worry about. But is a dissertation just for doctoral candidates? In some countries, dissertations are exclusive to PhDs. However, for other countries, the term “dissertation” is interchangeable with "thesis." Why so?
Because both are research projects completed for undergraduate or postgraduate degrees. Keep in mind that whether you’re pursuing a bachelor's, an MA, or a doctorate, dissertation writing demonstrates your research skills and academic proficiency.
Your doctoral degree, just like your graduate degree from a graduate school, shows you can successfully navigate the research process, theoretical framework, and dissertation defense. Sure, the scope of research was less focused while you were a graduate student with a master's thesis. Nonetheless, it shows consistent work and dedication.
How many chapters in a dissertation?
Still mulling over how long does a dissertation have to be and how many chapters you must write? Dissertations usually consist of five to seven chapters. These typically cover the following:
- introduction
- literature review
- methodology
However, the structure can vary depending on your field of study and specific institutional guidelines. Each chapter plays a vital role, leading readers through your research journey, from laying the groundwork to presenting findings and drawing conclusions.
How do I find a reputable dissertation writer to help me?
Worried about how long are PhD dissertations? No need to worry. You can opt for professional help, and there’s no shame in that! Research for online platforms that specialize in academic writing services like our Studyfy team.
You can take a peek at our positive reviews and testimonials, showing our track record of delivering high-quality work. Choose a writer who possesses expertise in your field of study and can meet your specific requirements. Prioritize the following:
- clear communication
- appropriate instructions (from word count to deadlines)
- transparency regarding pricing
- upfront about revision policies.
By vetting potential writers and choosing a reputable service, you can secure the assistance of a reliable professional to guide you through the dissertation writing process.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started
Published on 26 March 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 5 May 2022.
A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree.
The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the level and field of study. However, there are some key questions that can help you understand the requirements and get started on your dissertation project.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
When and why do you have to write a dissertation, who will supervise your dissertation, what type of research will you do, how should your dissertation be structured, what formatting and referencing rules do you have to follow, frequently asked questions about dissertations.
A dissertation, sometimes called a thesis, comes at the end of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree. It is a larger project than the other essays you’ve written, requiring a higher word count and a greater depth of research.
You’ll generally work on your dissertation during the final year of your degree, over a longer period than you would take for a standard essay . For example, the dissertation might be your main focus for the last six months of your degree.
Why is the dissertation important?
The dissertation is a test of your capacity for independent research. You are given a lot of autonomy in writing your dissertation: you come up with your own ideas, conduct your own research, and write and structure the text by yourself.
This means that it is an important preparation for your future, whether you continue in academia or not: it teaches you to manage your own time, generate original ideas, and work independently.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
During the planning and writing of your dissertation, you’ll work with a supervisor from your department. The supervisor’s job is to give you feedback and advice throughout the process.
The dissertation supervisor is often assigned by the department, but you might be allowed to indicate preferences or approach potential supervisors. If so, try to pick someone who is familiar with your chosen topic, whom you get along with on a personal level, and whose feedback you’ve found useful in the past.
How will your supervisor help you?
Your supervisor is there to guide you through the dissertation project, but you’re still working independently. They can give feedback on your ideas, but not come up with ideas for you.
You may need to take the initiative to request an initial meeting with your supervisor. Then you can plan out your future meetings and set reasonable deadlines for things like completion of data collection, a structure outline, a first chapter, a first draft, and so on.
Make sure to prepare in advance for your meetings. Formulate your ideas as fully as you can, and determine where exactly you’re having difficulties so you can ask your supervisor for specific advice.
Your approach to your dissertation will vary depending on your field of study. The first thing to consider is whether you will do empirical research , which involves collecting original data, or non-empirical research , which involves analysing sources.
Empirical dissertations (sciences)
An empirical dissertation focuses on collecting and analysing original data. You’ll usually write this type of dissertation if you are studying a subject in the sciences or social sciences.
- What are airline workers’ attitudes towards the challenges posed for their industry by climate change?
- How effective is cognitive behavioural therapy in treating depression in young adults?
- What are the short-term health effects of switching from smoking cigarettes to e-cigarettes?
There are many different empirical research methods you can use to answer these questions – for example, experiments , observations, surveys , and interviews.
When doing empirical research, you need to consider things like the variables you will investigate, the reliability and validity of your measurements, and your sampling method . The aim is to produce robust, reproducible scientific knowledge.
Non-empirical dissertations (arts and humanities)
A non-empirical dissertation works with existing research or other texts, presenting original analysis, critique and argumentation, but no original data. This approach is typical of arts and humanities subjects.
- What attitudes did commentators in the British press take towards the French Revolution in 1789–1792?
- How do the themes of gender and inheritance intersect in Shakespeare’s Macbeth ?
- How did Plato’s Republic and Thomas More’s Utopia influence nineteenth century utopian socialist thought?
The first steps in this type of dissertation are to decide on your topic and begin collecting your primary and secondary sources .
Primary sources are the direct objects of your research. They give you first-hand evidence about your subject. Examples of primary sources include novels, artworks and historical documents.
Secondary sources provide information that informs your analysis. They describe, interpret, or evaluate information from primary sources. For example, you might consider previous analyses of the novel or author you are working on, or theoretical texts that you plan to apply to your primary sources.
Dissertations are divided into chapters and sections. Empirical dissertations usually follow a standard structure, while non-empirical dissertations are more flexible.
Structure of an empirical dissertation
Empirical dissertations generally include these chapters:
- Introduction : An explanation of your topic and the research question(s) you want to answer.
- Literature review : A survey and evaluation of previous research on your topic.
- Methodology : An explanation of how you collected and analysed your data.
- Results : A brief description of what you found.
- Discussion : Interpretation of what these results reveal.
- Conclusion : Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your findings contribute to knowledge in your field.
Sometimes the order or naming of chapters might be slightly different, but all of the above information must be included in order to produce thorough, valid scientific research.
Other dissertation structures
If your dissertation doesn’t involve data collection, your structure is more flexible. You can think of it like an extended essay – the text should be logically organised in a way that serves your argument:
- Introduction: An explanation of your topic and the question(s) you want to answer.
- Main body: The development of your analysis, usually divided into 2–4 chapters.
- Conclusion: Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your analysis contributes to knowledge in your field.
The chapters of the main body can be organised around different themes, time periods, or texts. Below you can see some example structures for dissertations in different subjects.
- Political philosophy
This example, on the topic of the British press’s coverage of the French Revolution, shows how you might structure each chapter around a specific theme.

This example, on the topic of Plato’s and More’s influences on utopian socialist thought, shows a different approach to dividing the chapters by theme.

This example, a master’s dissertation on the topic of how writers respond to persecution, shows how you can also use section headings within each chapter. Each of the three chapters deals with a specific text, while the sections are organised thematically.

Like other academic texts, it’s important that your dissertation follows the formatting guidelines set out by your university. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
Formatting guidelines concern things like:
- line spacing
- page numbers
- punctuation
- title pages
- presentation of tables and figures
If you’re unsure about the formatting requirements, check with your supervisor or department. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
How will you reference your sources?
Referencing means properly listing the sources you cite and refer to in your dissertation, so that the reader can find them. This avoids plagiarism by acknowledging where you’ve used the work of others.
Keep track of everything you read as you prepare your dissertation. The key information to note down for a reference is:
- The publication date
- Page numbers for the parts you refer to (especially when using direct quotes)
Different referencing styles each have their own specific rules for how to reference. The most commonly used styles in UK universities are listed below.
You can use the free APA Reference Generator to automatically create and store your references.
APA Reference Generator
The words ‘ dissertation ’ and ‘thesis’ both refer to a large written research project undertaken to complete a degree, but they are used differently depending on the country:
- In the UK, you write a dissertation at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a thesis to complete a PhD.
- In the US, it’s the other way around: you may write a thesis at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a dissertation to complete a PhD.
The main difference is in terms of scale – a dissertation is usually much longer than the other essays you complete during your degree.
Another key difference is that you are given much more independence when working on a dissertation. You choose your own dissertation topic , and you have to conduct the research and write the dissertation yourself (with some assistance from your supervisor).
Dissertation word counts vary widely across different fields, institutions, and levels of education:
- An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000–15,000 words
- A master’s dissertation is typically 12,000–50,000 words
- A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000–100,000 words
However, none of these are strict guidelines – your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided by your university to determine how long your own dissertation should be.
At the bachelor’s and master’s levels, the dissertation is usually the main focus of your final year. You might work on it (alongside other classes) for the entirety of the final year, or for the last six months. This includes formulating an idea, doing the research, and writing up.
A PhD thesis takes a longer time, as the thesis is the main focus of the degree. A PhD thesis might be being formulated and worked on for the whole four years of the degree program. The writing process alone can take around 18 months.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, May 05). What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started. Scribbr. Retrieved 25 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/what-is-a-dissertation/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples.

How long is a Thesis or dissertation? [the data]
Writing a thesis for your undergraduate, master’s, or PhD can be a very daunting task. Especially when you consider how long a thesis can get. However, not all theses are the same length and the expected submission length is dependent on the level of study that you are currently enrolled in and the field in which you are studying.
An undergraduate thesis is likely to be about 20 to 50 pages long. A Master’s thesis is likely to be between 30 and 100 pages in length and a PhD dissertation is likely to be between 50 and 450 pages long.
In the table below I highlight the typical length of an undergraduate, master’s, and PhD.
It is important to note that this is highly dependent on the field of study and the expectations of your university, field, and research group.
If you want to know more about how long a Masters’s thesis and PhD dissertation is you can check out my other articles:
- How Long is a Masters Thesis? [Your writing guide]
- How long is a PhD dissertation? [Data by field]
- How to write a masters thesis in 2 months [Easy steps to start writing]
These articles go into a lot more detail and specifics of each level of study.
Let’s take a more detailed look at the length of a thesis or dissertation. We’ll start from the very basics including what a thesis or dissertation really is.
What exactly is a thesis or a dissertation?
A thesis or a dissertation is a research project that is typically required of students in order to gain an advanced degree.
A dissertation is usually much longer and more detailed than a thesis, but they both involve extensive research and provide an in-depth analysis of their given subject.
Many people use the term interchangeably but quite often a Masters level research project results in a thesis. While a PhD research project results in a much longer dissertation.
Thesis work is usually completed over the course of several months and can require multiple drafts and revisions before being accepted. These will be looked over by your supervisor to ensure that you are meeting the expectations and standards of your research field.
PhD Dissertations are typically even more involved, taking years to complete. My PhD took me three years to complete but it is usual for them to take more than five years.
Both a thesis and a dissertation involve researching a particular topic, formulating an argument based on evidence gathered from the research, and presenting the findings in written form for review by peers or faculty members.
My Master’s thesis was reviewed by the chemistry Department whilst my PhD thesis was sent to experts in the field around the world.
Ultimately, these experts provide a commentary on whether or not you have reached the standards required of the University for admittance into the degree and the final decision will be made upon reviewing these comments by your universities graduation committee.
There are several outcomes including:
- accepted without changes – this is where you must make no changes to your thesis and is accepted as is.
- accepted with minor changes this is where your thesis will require some minor changes before being admitted to the degree. Usually, it is not sent back to the reviewers.
- Major changes – this is where the committee has decided that you need to rework a number of major themes in your thesis and will likely want to see it at a later stage.
- Rejected – this is where the thesis is rejected and the recommendation to downgrade your degree is made.
What is the typical length of a thesis or dissertation?
The length of a thesis or dissertation varies significantly according to the field of study and institution.
Generally, an undergraduate thesis is between 20-50 pages long while a PhD dissertation can range from 90-500 pages in length.
However, longer is not necessarily better as a highly mathematical PhD thesis with proofs may only be 50 pages long.
It also depends on the complexity of the topic being studied and the amount of research required to complete it.
A PhD dissertation should contain as many pages and words as it takes to outline the current state of your field and provide adequate background information, present your results, and provide confidence in your conclusions. A PhD dissertation will also contain figures, graphs, schematics, and other large pictorial items that can easily inflate the page count.
Here is a boxplot summary of many different fields of study and the number of pages of a typical PhD dissertation in the field. It has been created by Marcus Beck from all of the dissertations at the University of Minnesota.

Typically, the mathematical sciences, economics, and biostatistics theses and dissertations tend to be shorter because they rely on mathematical formulas to provide proof of their results rather than diagrams and long explanations.
On the other end of the scale, English, communication studies, political science, history and anthropology are often the largest theses in terms of pages and word count because of the number of words it takes to provide proof and depth of their results.
At the end of the day, it is important that your thesis gets signed off by your review committee and other experts in the field. Your supervisor will be the main judge of whether or not your dissertation is capable of satisfying the requirements of a master’s or doctoral degree in your field.
How Many Pages Should a Master or PhD Thesis Have? Length of a thesis?
The length of a master’s thesis can vary greatly depending on the subject and format.
Generally, a masters thesis is expected to be around 100 pages long and should include:
- a title page,
- table of contents,
- introduction,
- literature review,
- main test and body of work,
- discussions and citations,
- conclusion,
- bibliography
- and (sometimes) appendix.
Your supervisor should provide you with a specific format that you are expected to follow.
Depending on your field of study and the word count specified by your supervisor, these guidelines may change. The student must ask their advisor for examples of past student thesis and doctoral dissertations.
For example, if there is a limited number of words allowed in the thesis then it may not be possible to have 100 pages or more for the thesis.
Additionally, if you are including a lot of technical information such as diagrams or tables in the appendix then this could increase the page count as well. For example, my PhD thesis contained a page like the one below. This page only contains images from atomic force microscopy. Because my PhD was very visual many pages like this exist.

Ultimately it is important to consult with your supervisor and determine how many pages your master’s thesis or PhD dissertation will be expected to have.
How long does it take to write a graduate thesis? Write your thesis quickly
Writing a graduate thesis can be a daunting task.
It is typically expected to take anywhere from one to three years, depending on the subject and scope of the project.
However, this is not just writing. A typical thesis or dissertation will require you to:
- formulate a research question
- do a literature review
- create research methodology
- perform original research
- collect and analyse results
- write peer-reviewed research papers
- write a PhD/masters thesis
- submit thesis and respond to examiners comments.
The actual writing component of a thesis or dissertation can take anywhere from one month to 6 months depending on how focused the graduate student is.
The amount of time it takes to write a thesis or dissertation can vary based on many factors, such as the type of research required, the length of the project, and other commitments that may interfere with progress.
Some students may have difficulty focusing or understanding their topic which can also add to the amount of time it takes to complete the project.
Regardless, writing a thesis is an important part of obtaining a graduate degree and should not be taken lightly.
It requires dedication and determination in order for one to successfully complete a thesis or dissertation within an appropriate timeframe.
In my YouTube video, below, I talk about how to finish your thesis or dissertation quickly:
it is full of a load of secrets including owning your day, managing your supervisor relationship, setting many goals, progress over perfection, and working with your own body clock to maximise productivity.
Wrapping up
This article has been through everything you need to know about the typical length of a thesis.
The answer to this question is highly dependent on your field of study and the expectations of your supervisor and university.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
How long does it take to write a dissertation, published by steve tippins on july 11, 2019 july 11, 2019.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 05:00 am
How long does it take to write a dissertation? The most accurate (and least helpful) answer is, it depends. Since that’s probably not the answer you’re looking for, I’ll use the rest of the article to address the realities of how long it takes to write a dissertation.
How Long Does It Take to Write a Dissertation?
Based on my experience, writing your dissertation should take somewhere between 13-20 months. These are average numbers based upon the scores of doctoral students that I have worked with over the years, and they generally hold true.
I have seen people take less time and more time, but I believe that with concerted effort, the 13-20 month timeframe is reasonable.
“Based on my experience, writing your dissertation should take somewhere between 13-20 months.”
University Requirements
Once you hit the dissertation stage, some schools require a minimum number of hours in the dissertation area before you can graduate. Many schools require the equivalent of one year of dissertation credits to graduate.
So, even if you can finish your dissertation in three months, you will still have to pay for nine more months of dissertation credits before you can graduate. However, unless research and writing is your superpower, I wouldn’t worry about having to pay extra tuition.
But this requirement does offer some insight into how long it takes to write a dissertation. Based on this requirement, it’s reasonable to expect that writing your dissertation will take a year of more. This is consistent with my experience.

However, this timeframe is based on several assumptions. First, I am assuming that you are continually working towards finishing your dissertation. This means that no family emergencies, funding conundrums, or work issues get in the way of completing. Second, there are no major changes in your dissertation committee. Third, you will have access to the data that you need.
Assuming these assumptions hold true, this article should give you a general idea of how long it might take to write your dissertation.
How Long Does it Take to Write A Dissertation? Stage-By-Stage
Let’s break down each stage of the dissertation writing process and how long it takes.
Prospectus
This is the hardest one to judge, as this is where you lay the groundwork for the rest of your dissertation and get buy-in from committee members. Normally this takes from 3-6 months. Not all of this is writing time, though–much of it is spent refining your topic and your approach.
Why does this stage take so long? For many people, starting to express themselves using an academic voice can take time. This can hold up the review process as your committee members ask for writing-related revisions before they even get to evaluating the content. Don’t worry, once you learn the academic language things will start to flow more easily.
One common mistake students make is lack of specificity, both in their writing in general and in their topic focus.
Proposal (Chapters 1-3)

Chapter 1 is often an expansion of your Prospectus. However, you’ll be expected to develop your ideas more and have even more specificity on things like your research question and methodology, so don’t underestimate how long this chapter will take.
Chapter 2 can take some time as you will be digging deep into the literature but I think this can be done in 3-4 months. One caution, some people, and committees, like to start with Chapter 2 so that you are immersed in the literature before completing Chapters 1 and 3. Regardless of where you start, 3-4 months is a good estimate.
Chapter 3 requires an in-depth explanation of your methodology. I suggest working closely with your Chair on this one to avoid multiple submissions and revisions. Get clear on your methodology and make sure you and your chair are on the same page before you write, and continue to check in with your chair, if possible, throughout the process.
IRB Approval
While this step can be full of details and require several iterations it seems that allowing 2 months is sufficient. Most schools have an IRB form that must be submitted. To save time you can usually start filling out the form while your committee is reviewing your Proposal.
Collecting Data
This step varies a great deal. If you are using readily available secondary data this can take a week but if you are interviewing hard to get individuals or have trouble finding a sufficient number of people for your sample this can take 4 months or more. I think 1-4 months should be appropriate
Chapters 4 and 5
These two chapters are the easiest to write as in Chapter 4 you are reporting your results and in Chapter 5 you explain what the results mean. I believe that these two chapters can be written in 2 months.

Defense and Completion
You will need to defend your dissertation and then go through all of the university requirements to finalize the completion of your dissertation. I would allow 2 months for this process.
Variables That Affect How Long It Takes to Write A Dissertation
When students say something like, “I’m going to finish my dissertation in three months,” they likely aren’t considering all of the variables besides the actual writing. Even if you’re a fast writer, you’ll have to wait on your committee’s comments,
Timing Issues
Many schools have response times for committee members. This is important when looking at how long it takes to finish a dissertation. For example, it you have two committee members and they each get up to 2 weeks for a review, it can take up to a month to get a document reviewed, each time you submit. So, plan for these periods of time when thinking about how long that it will take you.
Addressing Comments
How long it takes to write your dissertation also depends on your ability to address your committee’s comments thoroughly. It’s not uncommon for a committee member to send a draft back several times, even if their comments were addressed adequately, because they notice new issues each time they read it. Save yourself considerable time by making sure you address their comments fully, thus avoiding unnecessary time waiting to hear the same feedback.

This is the biggest variable in the dissertation model. How dedicated are you to the process? How much actual time do you have? How many outside interests/requirements do you have? Are you easily distracted? How clean does your workspace need to be? (This may seem like a strange thing to discuss, but many people need to work in a clean space and can get very interested in cleaning if they have to write). Are you in a full-time program or in a part time program? Are you holding down a job? Do you have children?
All of these things will affect how much time you have to put into writing–or rather, how disciplined you need to be about making time to write.
One of the things that can influence how long it takes to write your dissertation is your committee. Choose your committee wisely. If you work under the assumption that the only good dissertation is a done dissertation, then you want a committee that will be helpful and not trying to prove themselves on your back. When you find a Chair that you can work with ask her/him which of their colleagues they work well with (it’s also worth finding out who they don’t work well with).
Find out how they like to receive material to review. Some members like to see pieces of chapters and some like to see completed documents. Once you know their preferences, you can efficiently submit what they want when they want it.
How Long Does it Take to Write a Dissertation? Summary
Barring unforeseen events, the normal time range for finishing a dissertation seems to be 13-19 months, which can be rounded to one to one and a half years. If you are proactive and efficient, you can usually be at the shorter end of the time range.

That means using downtime to do things like changing the tense of your approved Proposal from future tense to past tense and completing things like you Abstract and Acknowledgement sections before final approval.
I hope that you can be efficient in this process and finish as quickly as possible. Remember, “the only good dissertation is a done dissertation.”
On that note, I offer coaching services to help students through the dissertation writing process, as well as editing services for those who need help with their writing.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
What makes a good research question.
Creating a good research question is vital to successfully completing your dissertation. Here are some tips that will help you formulate a good research question. What Makes a Good Research Question? These are the three Read more…

Dissertation Structure
When it comes to writing a dissertation, one of the most fraught questions asked by graduate students is about dissertation structure. A dissertation is the lengthiest writing project that many graduate students ever undertake, and Read more…

Choosing a Dissertation Chair
Choosing your dissertation chair is one of the most important decisions that you’ll make in graduate school. Your dissertation chair will in many ways shape your experience as you undergo the most rigorous intellectual challenge Read more…
Make This Your Last Round of Dissertation Revision.
Learn How to Get Your Dissertation Accepted .
Discover the 5-Step Process in this Free Webinar .
Almost there!
Please verify your email address by clicking the link in the email message we just sent to your address.
If you don't see the message within the next five minutes, be sure to check your spam folder :).
Hack Your Dissertation
5-Day Mini Course: How to Finish Faster With Less Stress
Interested in more helpful tips about improving your dissertation experience? Join our 5-day mini course by email!
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | Guide, Examples, & Template
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program.
Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you’ve ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating to know where to begin.
Your department likely has guidelines related to how your dissertation should be structured. When in doubt, consult with your supervisor.
You can also download our full dissertation template in the format of your choice below. The template includes a ready-made table of contents with notes on what to include in each chapter, easily adaptable to your department’s requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
- In the US, a dissertation generally refers to the collection of research you conducted to obtain a PhD.
- In other countries (such as the UK), a dissertation often refers to the research you conduct to obtain your bachelor’s or master’s degree.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
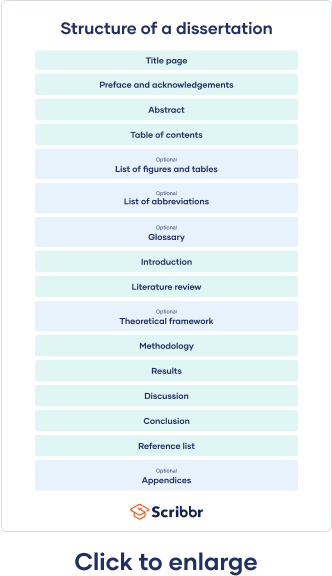
Dissertation committee and prospectus process, how to write and structure a dissertation, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your dissertation, free checklist and lecture slides.
When you’ve finished your coursework, as well as any comprehensive exams or other requirements, you advance to “ABD” (All But Dissertation) status. This means you’ve completed everything except your dissertation.
Prior to starting to write, you must form your committee and write your prospectus or proposal . Your committee comprises your adviser and a few other faculty members. They can be from your own department, or, if your work is more interdisciplinary, from other departments. Your committee will guide you through the dissertation process, and ultimately decide whether you pass your dissertation defense and receive your PhD.
Your prospectus is a formal document presented to your committee, usually orally in a defense, outlining your research aims and objectives and showing why your topic is relevant . After passing your prospectus defense, you’re ready to start your research and writing.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The structure of your dissertation depends on a variety of factors, such as your discipline, topic, and approach. Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an overall argument to support a central thesis , with chapters organized around different themes or case studies.
However, hard science and social science dissertations typically include a review of existing works, a methodology section, an analysis of your original research, and a presentation of your results , presented in different chapters.
Dissertation examples
We’ve compiled a list of dissertation examples to help you get started.
- Example dissertation #1: Heat, Wildfire and Energy Demand: An Examination of Residential Buildings and Community Equity (a dissertation by C. A. Antonopoulos about the impact of extreme heat and wildfire on residential buildings and occupant exposure risks).
- Example dissertation #2: Exploring Income Volatility and Financial Health Among Middle-Income Households (a dissertation by M. Addo about income volatility and declining economic security among middle-income households).
- Example dissertation #3: The Use of Mindfulness Meditation to Increase the Efficacy of Mirror Visual Feedback for Reducing Phantom Limb Pain in Amputees (a dissertation by N. S. Mills about the effect of mindfulness-based interventions on the relationship between mirror visual feedback and the pain level in amputees with phantom limb pain).
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you. In some cases, your acknowledgements are part of a preface.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150 to 300 words long. Though this may seem very short, it’s one of the most important parts of your dissertation, because it introduces your work to your audience.
Your abstract should:
- State your main topic and the aims of your research
- Describe your methods
- Summarize your main results
- State your conclusions
Read more about abstracts
The table of contents lists all of your chapters, along with corresponding subheadings and page numbers. This gives your reader an overview of your structure and helps them easily navigate your document.
Remember to include all main parts of your dissertation in your table of contents, even the appendices. It’s easy to generate a table automatically in Word if you used heading styles. Generally speaking, you only include level 2 and level 3 headings, not every subheading you included in your finished work.
Read more about tables of contents
While not usually mandatory, it’s nice to include a list of figures and tables to help guide your reader if you have used a lot of these in your dissertation. It’s easy to generate one of these in Word using the Insert Caption feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
Similarly, if you have used a lot of abbreviations (especially industry-specific ones) in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
In addition to the list of abbreviations, if you find yourself using a lot of highly specialized terms that you worry will not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary. Here, alphabetize the terms and include a brief description or definition.
Read more about glossaries
The introduction serves to set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance. It tells the reader what to expect in the rest of your dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving the background information needed to contextualize your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of your research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your research questions and objectives
- Outline the flow of the rest of your work
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant. By the end, the reader should understand the what, why, and how of your research.
Read more about introductions
A formative part of your research is your literature review . This helps you gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic.
Literature reviews encompass:
- Finding relevant sources (e.g., books and journal articles)
- Assessing the credibility of your sources
- Critically analyzing and evaluating each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g., themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps) to strengthen your overall point
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing sources. Your literature review should have a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear justification for your own research. It may aim to:
- Address a gap in the literature or build on existing knowledge
- Take a new theoretical or methodological approach to your topic
- Propose a solution to an unresolved problem or advance one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework. Here, you define and analyze the key theories, concepts, and models that frame your research.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to critically assess its credibility. Your methodology section should accurately report what you did, as well as convince your reader that this was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- The overall research approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative ) and research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment )
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Any tools and materials you used (e.g., computer programs, lab equipment)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses , or themes, but avoid including any subjective or speculative interpretation here.
Your results section should:
- Concisely state each relevant result together with relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Briefly state how the result relates to the question or whether the hypothesis was supported
- Report all results that are relevant to your research questions , including any that did not meet your expectations.
Additional data (including raw numbers, full questionnaires, or interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix. You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results. Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is your opportunity to explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research question. Here, interpret your results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. Refer back to relevant source material to show how your results fit within existing research in your field.
Some guiding questions include:
- What do your results mean?
- Why do your results matter?
- What limitations do the results have?
If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your dissertation’s conclusion should concisely answer your main research question, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your central argument and emphasizing what your research has contributed to the field.
In some disciplines, the conclusion is just a short section preceding the discussion section, but in other contexts, it is the final chapter of your work. Here, you wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you found, with recommendations for future research and concluding remarks.
It’s important to leave the reader with a clear impression of why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known? Why is your research necessary for the future of your field?
Read more about conclusions
It is crucial to include a reference list or list of works cited with the full details of all the sources that you used, in order to avoid plagiarism. Be sure to choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your dissertation. Each style has strict and specific formatting requirements.
Common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA , but which style you use is often set by your department or your field.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
Your dissertation should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents such as interview transcripts or survey questions can be added as appendices, rather than adding them to the main body.
Read more about appendices
Making sure that all of your sections are in the right place is only the first step to a well-written dissertation. Don’t forget to leave plenty of time for editing and proofreading, as grammar mistakes and sloppy spelling errors can really negatively impact your work.
Dissertations can take up to five years to write, so you will definitely want to make sure that everything is perfect before submitting. You may want to consider using a professional dissertation editing service , AI proofreader or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect prior to submitting.
After your written dissertation is approved, your committee will schedule a defense. Similarly to defending your prospectus, dissertation defenses are oral presentations of your work. You’ll present your dissertation, and your committee will ask you questions. Many departments allow family members, friends, and other people who are interested to join as well.
After your defense, your committee will meet, and then inform you whether you have passed. Keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality; most committees will have resolved any serious issues with your work with you far prior to your defense, giving you ample time to fix any problems.
As you write your dissertation, you can use this simple checklist to make sure you’ve included all the essentials.
Checklist: Dissertation
My title page includes all information required by my university.
I have included acknowledgements thanking those who helped me.
My abstract provides a concise summary of the dissertation, giving the reader a clear idea of my key results or arguments.
I have created a table of contents to help the reader navigate my dissertation. It includes all chapter titles, but excludes the title page, acknowledgements, and abstract.
My introduction leads into my topic in an engaging way and shows the relevance of my research.
My introduction clearly defines the focus of my research, stating my research questions and research objectives .
My introduction includes an overview of the dissertation’s structure (reading guide).
I have conducted a literature review in which I (1) critically engage with sources, evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, (2) discuss patterns, themes, and debates in the literature, and (3) address a gap or show how my research contributes to existing research.
I have clearly outlined the theoretical framework of my research, explaining the theories and models that support my approach.
I have thoroughly described my methodology , explaining how I collected data and analyzed data.
I have concisely and objectively reported all relevant results .
I have (1) evaluated and interpreted the meaning of the results and (2) acknowledged any important limitations of the results in my discussion .
I have clearly stated the answer to my main research question in the conclusion .
I have clearly explained the implications of my conclusion, emphasizing what new insight my research has contributed.
I have provided relevant recommendations for further research or practice.
If relevant, I have included appendices with supplemental information.
I have included an in-text citation every time I use words, ideas, or information from a source.
I have listed every source in a reference list at the end of my dissertation.
I have consistently followed the rules of my chosen citation style .
I have followed all formatting guidelines provided by my university.
Congratulations!
The end is in sight—your dissertation is nearly ready to submit! Make sure it's perfectly polished with the help of a Scribbr editor.
If you’re an educator, feel free to download and adapt these slides to teach your students about structuring a dissertation.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation Binding and Printing | Options, Tips, & Comparison
- Example of a dissertation abstract
- Figure and Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Purpose and structure of an advisory report
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Shorten your abstract or summary
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples

What is your plagiarism score?
What is an Undergraduate Dissertation?
While most discussions of ‘dissertations’ focus on postgraduate study, undergraduate students also frequently complete undergraduate dissertations as one part of their overall degree. This article will provide an overview of the undergraduate dissertation and its standard requirements at UK universities.
What is a Bachelor’s or Undergraduate Dissertation?
An undergraduate dissertation (or Bachelors dissertation) is essentially an extended piece of research and writing on a single subject. It is typically completed in the final year of a degree programme and the topic is chosen based on a student’s own area of interest. It allows the student to explore a narrow topic in greater depth than a traditional module. The student works with a single supervisor chosen from their departmental faculty, and this individual provides guidance and support throughout the course of the research.
How does Undergraduate Dissertation differ from Postgraduate Dissertation?
The bachelor’s dissertation varies significantly from postgraduate dissertations. First, it is considerably shorter in length, averaging only 10,000 – 15,000 words. While this is much shorter than a Masters or PhD dissertation, it is much longer than any other piece of writing required in undergraduate programmes.
Secondly, the undergraduate dissertation is not required to contain the same level of originality as postgraduate work. Students are still expected to complete the work independently and cite all sources, but they do not need to present any new ideas. It is sufficient to conduct thorough, sustained research and present a critical discussion of a relatively narrow research topic. It is not necessary to discuss the philosophical context of the research or to design a distinct methodology. However, it is important to note that the best bachelor’s dissertations demonstrate genuine critical thinking skills and an ability to combine information derived from many different sources.
Finally, the undergraduate dissertation also varies in the type of research conducted, which will be more focused on texts and documents rather than active field research. For the most part students will examine secondary sources or easily accessible primary sources, and they will not be required to pursue obscure or costly data sources. In some disciplines a practical element may be incorporated into the dissertation, but this is usually performed with less independence than would be expected at the postgraduate level.
Undergraduate Dissertation Requirements
- Topic selection : At the end of the penultimate year of study students will be asked to select an area of research for the dissertation. You should be sure to choose a topic that is likely to hold your interest over a long period of time, as it is difficult and dangerous to change your topic once your research period has begun.
- Finding a supervisor : Depending on the university, there may be a formal process in place for allocating supervisors or students may simply approach a member of faculty that they are interested in working with. It can be helpful to meet with potential supervisors before registering an intended research area, as they can help you to refine your proposed topic and give you suggestions for specific research questions. Once the formal dissertation period begins you will meet with your supervisor regularly to discuss your progress and refine your study.
- Early research : Most students begin general reading around their chosen subject area in the summer before the final year. This period is truly key in developing a broad awareness of the subject, and it prepares you for more targeted research once your final year commences.
- Research outline : Once the undergraduate dissertation module begins (usually at the start of year 3) you will be asked to draft a brief dissertation outline of about 2-3 pages in length. This should include a summary of chapters and a full bibliography. By now you should have decided upon a narrower aspect of your topic, and this should be formulated into a research title with the help of your supervisor.
- Refined research and writing : At this stage, your research will be much more targeted, in order to pursue your proposed dissertation agenda. You should also begin writing as soon as possible. Most departments require students to submit a substantial piece of writing (3,000-5,000 words) by the end of the first term. Remember that you should submit at least one draft to your supervisor before this deadline, in order to give you time to make necessary revisions.
- Final dissertation : When you’ve completed the writing process you should have roughly three or four chapters, as well as an Introduction and Conclusion. It must all be formatted according to university guidelines, and you must be certain to properly cite all if your sources.
- Binding and submission : Unlike undergraduate essays, the undergraduate dissertation must be professionally bound before being submitted. This is usually done on campus but you need to allow enough time for the process before your submission deadline. The final due date is usually at the end of the second term of the student’s final year.
The marking system for undergraduate dissertations is the same that is used for all other aspects of the undergraduate degree. Students must generally achieve a minimum mark of 40 to pass, but most will aspire to higher marks than this. Marks of 60-69 earn a classification of 2:1 or B; Marks over 70 earn a First classification or A.
The dissertation is marked as a stand-alone module and it is combined with other module marks to determine the overall degree classification. There is no standard rule for UK universities regarding the weight of the dissertation mark when calculating the degree average, so it’s best to check with your university to understand their individual regulations.
For many students, the undergraduate dissertation provides their first taste of prolonged independent research. This can be a daunting experience but it is helpful to remember that your departmental supervisor can be called upon frequently for advice and support. If you work at a consistent and dedicated pace you will have no problem completing the dissertation on time. You will also develop important research skills that can prepare you for postgraduate study.
Bryan Greetham, 2009. How to Write your Undergraduate Dissertation (Palgrave Study Skills). Edition. Palgrave Macmillan.
Manchester Metropolitan University, 2008. Guidance on the Writing of Undergraduate Dissertations. Available: http://www.ioe.mmu.ac.uk/cpd/downloads/UNDERGRAD%20DISSERTATION%20HANDBOOK.pdf. Last accessed 08 Apr 2013.
University of Warwick, 2010. Dissertation Guidelines for Undergraduate Study. Available: http://www2.warwick.ac.uk/study/cll/currentstudents/undergraduatemodules/ce302dissertation/dissertation_guidelines_2010.pdf. Last accessed 08 Apr 2013. Nicholas Walliman, 2004. Your Undergraduate Dissertation: The Essential Guide for Success (SAGE Study Skills Series). 1 Edition. SAGE Publications Ltd.
You may also like

- Log in
- Site search
7 steps to writing a dissertation
While you may be experienced in revising and writing essays, your dissertation requires careful planning, extensive research, and time management to succeed
Your dissertation is a key part of your degree course and a testament to your ability to conduct research, analyse data, and write a clear argument. Dissertations can be challenging, but they are also rewarding experiences that allow you to explore a topic in-depth and make a significant contribution to your field of study.
To achieve your academic goals, it is important to act on feedback, use your supervision time to your advantage, and demonstrate a strong knowledge of your subject. Whether you're writing an undergraduate, Masters , or PhD dissertation, these seven steps can help you stay on track.
1. Choose your topic wisely
Selecting the right topic is the foundation of a successful dissertation. It is important to choose a topic that is:
- Relevant to your academic discipline and interests. This will ensure that you are passionate about your topic and have the necessary background knowledge to conduct meaningful research.
- Intriguing and thought-provoking . A well-chosen topic will inspire you to ask interesting questions and develop original insights.
- Specific enough to allow for in-depth analysis, yet broad enough to provide enough research material. A topic that is too narrow may be difficult to research or produce meaningful findings, while a topic that is too broad may be difficult to cover in the allowed time and word count.
Consider your career goals and what topics are relevant to the field you hope to work in after graduation. It's also important to be open to change, as it's common for students to modify their dissertation topic as they explore the subject more.
Once you have identified a potential topic, seek guidance from your supervisor. They can help you to refine your choice, identify relevant sources, and develop a research plan.
2. Check what's required of you
Read your marking criteria carefully. It is also important to consult the module guidelines and follow the instructions on any additional parts to your main assignment, such as a project plan, literature review or a critical reflection.
Neal Bamford, associate lecturer at London Metropolitan University, reports that his marking process always begins by 'distilling criteria to what students need to provide and how many marks this is worth.'
'Several dissertations I mark don't include a project plan in their submission. This is worth 20% of the overall mark, so students lose out on a significant portion of their grade'.
Before you begin to plan, make sure you understand what's expected of you. Find out:
- what academic writing looks like in your discipline
- the word count
- when and where you must submit your dissertation.
3. Conduct in-depth research
Research at this stage in the process is often referred to as a literature review. This is where you are expected to gather relevant sources, articles, and studies from libraries, and online academic resources to identify the existing research on your topic and to develop your own research questions.
'Form your own opinion and argue for it using research. A history of the topic is always helpful, as it shows that you understand how things got to this point in time,' says Neal.
Be sure to take careful notes on each source and organise them for easy reference. You need to critically evaluate and analyse the sources to ensure their credibility and relevance to your research. This will be helpful when citing your sources in the writing stage.
Don't forget to seek guidance from your advisor throughout the research process. They can provide you with valuable feedback, relevant sources, and support.
4. Develop a strong thesis statement
A well-defined thesis statement is a roadmap for your dissertation. It should concisely state your main argument or research question and provide a clear direction for your paper. Your thesis statement will guide your entire writing process, so take the time to fully understand it before you begin to write.
When writing a thesis statement:
- Be specific and focused - avoid broad or vague statements.
- Remember that your thesis needs to be arguable - it should be a statement that can be supported or proved false with evidence.
- Make sure your thesis is realistic - you need to be able to research and write about it in the allotted time and space.
Once you have a draft of your thesis statement, share it with your supervisor and other trusted peers. They can provide you with feedback and help you to refine your statement.
If your research disproves your original statement, it can be a disappointing experience. However, it is important to remember that this is a normal part of the research process.
'Many of my students believe that if they don't find the answer they're expecting, then their work is worthless,' says Neal.
'This is not the case. You don't have to find the answer to produce valuable research. Documenting your process and conclusions, even if they are inconclusive, can help others to avoid repeating your work and may lead to new approaches.'
5. Proofread and edit
After working on your dissertation for such a long time, it can be tempting to end the process once you have finished writing, but proofreading is an essential step in ensuring that it is polished and error-free.
To help with the proofreading process:
- Read your dissertation aloud . This can help you to catch errors that you might miss when reading silently.
- Change your environment to see your work with fresh eyes.
- Focus on one thing at a time such as grammar, spelling, or punctuation to avoid getting overwhelmed.
To edit your dissertation, begin by reviewing its overall structure and flow. Make sure that your arguments are well-organised and that your ideas are presented in a logical order.
Next, check your grammar, spelling, and punctuation carefully. You can use a grammar checker, but it is important to proofread your work yourself to identify stylistic or subject-specific errors.
'Make sure you understand the reference style your university prefers. Formatting and labelling of images, tables etc. is vitally important and will be marked,' says Neal.
You should also ensure that your dissertation is formatted using the correct font, font size, margins, and line spacing.
6. Seek feedback and finalise
Once you have made your final revisions, seek feedback from your advisor or board members.
To get the most out of your feedback, be specific about what you are looking for. For example, you might ask for feedback on the overall structure and flow of your dissertation, the strength of your arguments, or the clarity of your writing.
Be open to feedback, even if it's negative. Remember that your advisor is there to help you improve your work, so it's important to take the time to understand and implement the feedback you receive.
Once you have addressed all the feedback, you can prepare your final submission. It's important to follow the guidelines carefully before submitting. Be sure to hand in your dissertation on time, as late submissions may be penalised or even rejected.
Online hand in is the most common method of dissertation submission, and you will typically need to upload a PDF file to an online portal. Follow the instructions carefully - you may need to provide additional information, such as your student ID number or the title of your dissertation.
Some institutions still require dissertations to be submitted in hard copy. If this is the case, you will need to submit a bound copy of your dissertation to your department office. You may also need to pay the binding fee.
Be sure to check with your advisor or department office for specific instructions on how to submit your dissertation in hard copy. You may have to submit multiple copies of your dissertation, and you be required to to include a title page, abstract, and table of contents.
Find out more
- Read our 5 ways to manage student stress .
- Discover how to write an essay .
- Consider our 7 time management tips for students .
How would you rate this page?
On a scale where 1 is dislike and 5 is like
- Dislike 1 unhappy-very
- Like 5 happy-very
Thank you for rating the page
How to write a dissertation
- September 12, 2023

When you start university, one of the final pieces of work – your dissertation – seems like a long way off. Three years passes more quickly than you think, and before you know it, you’re being told it is time to start work on your dissertation. It can feel incredibly daunting, especially if you aren’t accustomed to writing extended pieces of work. Although it probably won’t feel like an easy task (it is supposed to challenge you!) with the right preparation, you can minimise the amount of stress you encounter, and manage your project with enough time.
We’re not going to focus on how to carry out your research in this post, because there are too many variables between subjects, but rather, looking at how to tackle the writing-up process.
Table of Contents
What is a dissertation.
A dissertation is an independent piece of academic work that reports on research that you have carried out, and is much longer and more in-depth than a regular essay or research project. Word counts for UK dissertations are typically between 8,000 words to 20,000 words, but the length, along with the criteria for the sections that are required depend on the subject of your degree and the university you’re studying with.
In the UK, dissertations are different from theses. Although they are similar in that they are independent works, theses are significantly longer, and tend to refer to research projects for doctoral degrees. Theses are normally made accessible in the university library when the candidate has been awarded their doctorate. Undergraduate dissertations and theses for master’s degrees aren’t routinely available in libraries, but are sometimes made available by faculties.

How long does a dissertation take to write?
How long your dissertation takes to write will be influenced by the word count, and how long your research takes. However, many professional writers who know their subject (and perhaps don’t require such accuracy) don’t write more than 5,000 words in a day – so don’t assume you can write your dissertation during the week before the deadline! You’ll have a good idea how many words you can write comfortably in a day, so take that figure, divide it and work backwards. If you can do 1000 words (many people work with a much lower number!) and your dissertation is 10,000 words – then you need an absolute minimum of 12 days, since you’ll need time for reading, editing, spotting mistakes, and getting your dissertation bound and handed in.
Although many people thrive under a certain amount of time pressure, don’t leave getting started to the last minute. Give yourself more time than you think you’ll need for writing each section, and when you have completed a section, move straight on – don’t waste time waiting for the next writing window you have scheduled. You might find that other sections need extra time to complete.
Don’t forget to leave plenty of time for editing your work – most students need to do a lot of editing – and leave contingency time in case of IT failure, illness, or any other interruptions.
Why are dissertations so hard?
During dissertation time, university campuses worldwide are full of stressed students. Dissertation projects are massive pieces of work that have to be tackled by yourself, and your degree classification can be dramatically impacted by the mark you receive for your dissertation – which is why many students feel the pressure!
Dissertations present all kinds of problems, here are a few of the best tips we can to prevent you getting too stressed.
- Planning ahead is essential – by planning, you’ll be able to manage your time much better, including breaks for eating, relaxing and exercise, which means you can think much more clearly and won’t be as stressed.
- Create a plan for your work – knowing what you’re working on and when will keep you on track and ensure you don’t go off on a tangent or get too far behind.
- Allow contingency time for emergencies – you don’t know if something will interrupt your writing time. Be sure to leave plenty of time ahead of the deadline to make sure you’re not over-stressed.
- Don’t procrastinate – running out of time is one of the biggest problems that students encounter. Pulling a string of all-nighters to meet the deadline won’t result in your best work.
- Set up autosave, and back up your work – IT staff aren’t miracle workers – so don’t work for three hours without saving, and be sure to save research in the cloud (in your Google Drive, OneDrive or Dropbox) as well as on your PC.
- Do enough research – a dissertation requires much more than finding a few papers and quoting from them. You need to analyse resources in depth, and use the information correctly to support the points you are making.
How do I get started?
Start by attending all the sessions provided by the course team, and read all the information and guidance that are provided by the faculty, since this is where you’ll find out any specific requirements. Before you start writing, make sure you know:
- The word count (and whether you will be penalised for being too many words over or under)
- Any compulsory sections and the structure required
- The style of writing required
- What types of sources are permitted
- The types of methodology you are allowed to use
- The deadline for submission
- The requirements for submitting your paper copy for marking, such as formatting and binding
- Where, when, and how you submit your dissertation
Once you know these important points, you can start to get into the details and decide on your research topic.
You can read much more about the different types of roles in these areas here .
By choosing an area that you find interesting and meaningful, you’re more likely to put more effort in, and your enthusiasm will be evident, which is likely to result in a higher mark.
How should i choose my research topic.
Choosing your research topic is possibly the most important part of your dissertation. By choosing an area that you find interesting and meaningful, you’re more likely to put more effort in, and your enthusiasm will be evident, which is likely to result in a higher mark. If you choose an area that is related to your career aims, you’ll be able to mention your work at future job interviews.
If you don’t feel inspired, check course materials for modules that particularly interested you and head for the library. Academic journals and other publications in the field will contain ideas, and help you to know what is currently of interest in the field.
You can also work with your dissertation supervisor or personal tutor to narrow the focus of your research topic, discuss the best methods and to ensure your proposal is a realistic study in the time you have to work with.
Do I need to write a dissertation proposal?
Dissertation proposals aren’t mandatory at every university, but where they are, they tend to have a 500 or 1000 word limit. Even if it isn’t a requirement for you, taking the time to put together a dissertation proposal can help you understand how to plan the project. It will help you to define:
- The research area that your dissertation will focus on
- The questions you will examine
- Some existing theories that you’ll refer to
- The research methods you will be using
- What you expect the outcome will be

What structure should my dissertation take?
In this next section, we’ll cover the sections that are usually required in a dissertation. Different universities and subjects have different requirements, so check the guidance from your faculty to ensure you have all the sections you need.
There are usually strict guidelines for formatting your dissertation’s title page, but normally you’ll need to include:
- The title of your dissertation
- The faculty or school you’re studying in
- The name of the institution
- The degree programme you’re studying
- Your student number
- The name of your supervisor
- The university’s logo
If your university requires your dissertation to be printed and bound, your title page is usually your front cover.
Acknowledgements
This section may not be mandatory, but gives you space to thank people who have supported you through your dissertation. You might mention specific members of the course team, research participants, or simply friends and family.
This is a short summary section that gives readers a brief overview of what is contained in your dissertation. Abstracts are usually less than 300 words, and should include:
- The topic and the aim of your research
- Details of your methods
- A short summary of the results
- Your conclusions
Since it needs to detail what is contained in your dissertation, abstracts should always be written when you have finished the rest of your dissertation.
Table of contents
Most institutions require dissertations to have page numbers and a list of chapters and subheadings, including any appendices. You can generate this automatically in Word when you have finished writing your dissertation.
List of assets
If you have included lots of tables, graphs, or images in your dissertation, you may need to include an itemised list. You can generate this automatically using the Insert Caption function in Word.
List of abbreviations/glossary
This optional section may be appropriate if you have included a lot of specialist terms or abbreviations. If you have used both, you may need to include both sections separately.
Introduction
This is where you detail the topic, and explain what the reader can expect. The introduction provides more detail than your abstract, and will help readers to understand:
- Your research topic and background information
- The focus and extent of the research
- Current research and discourse around the topic
- How the research will contribute to a wider issue or discussion
- The objectives and research questions
- Details of how you intend to answer the questions
- The structure of your dissertation
Keep your introduction succinct, and only include information that is relevant, so the reader can understand what your study is about, why you have chosen the topic, and how you plan to carry out the research.
Literature review
Your literature review should show a deep understanding of existing academic work. It should be a substantial section, and you’ll need to gather sources, critically evaluate, and analyse the works, and make connections between them. Your literature review may help you to identify:
- A gap in the literature
- An opportunity to use a new theoretical or methodological approach
- A solution for a problem that was previously unsolved
- That you can contribute to existing theoretical debate
- That existing research needs strengthening with your data
You’ll be able to use your literature review to justify why you have chosen to carry out the research in your dissertation, so be sure to complete it in detail.
Methodology
This section will detail what research you carried out, and the methods you used, which is essential to show the validity of your work. This section is an account of what you did, and why you did it. You will need to include:
- The approach and type of research (was it qualitative, quantitative, experimental, ethnographic?)
- The methods used to collect data (did you carry out interviews, surveys, or use information from archives?)
- Where and when your research took place, and information about any participants (you’ll need to anonymise personal information)
- How you analysed the data (did you use statistical analysis or discourse analysis, for example)
- Which tools or materials you used (computer programs or specialist lab equipment)
- Information about any restrictions or hindrances you encountered and how you moved past them
- An assessment or evaluation of your methods
The results section should clearly illustrate what you found. This could mean you include tables, graphs, and charts to present the findings. Think carefully about the best method to show your results, and only use graphs, tables and charts where they provide extra information – don’t use them to repeat what is in the text.
Don’t include raw data here – you can add that in your appendices. Depending on the type of research you have carried out (and faculty guidance) results may be combined with the discussion.
This section reflects on the meaning of the work you have done. You’ll demonstrate understanding of what the results show, and whether they match what you expected. You’ll also examine other ways of interpreting the data, and if your findings are at odds with what you expected, you’ll suggest reasons for why this could have happened.
Whether your results support your hypotheses or not, you’ll contextualise your study with existing research to explain how it contributes to wider discussions about the topic.
Here you’ll go back to your research question, and demonstrate understanding of your research, and the validity of the study. You may make recommendations for future research in this section.
As you already know, there are different referencing formatting conventions that are used by different subject fields. But since you’ll lose marks if you don’t do them correctly, it is essential to have your references stored accurately, and to format them correctly before you submit your dissertation.
You’ve probably already found the method of keeping references that suits you, such as using reference management software, or using Word referencing, but keep notes as you go, so you can compile your references section easily.
Referencing Help: FREE Harvard Referencing Generator >>
If there is information that you want to be included but isn’t essential to understanding your research, you may add this as part of an appendices. This could include transcripts, copies of surveys or complete tables of raw data.
Where can I get help with my dissertation?
Although your dissertation must be an independent piece of work, there are still sources of help if you get stuck. There are thousands of online resources, but here are a few more points of help:
Study skills support is available at most universities, and the team may be able to offer you assistance with your dissertation. Bear in mind there is likely to be a huge demand on this service during dissertation time, so ask early if you need their support.
Your personal tutor or dissertation supervisor can provide general advice, and you’ll probably have several review meetings during the writing period. However, your supervisor is likely to have a large number of students and their availability may be restricted.
Subject librarians will be able to advise you where to find relevant resources.
If your mental health is the issue, support can be found from counselling services that are available both from university and from external agencies, while the multifaith chaplaincy team may be able to support you with spiritual matters during your dissertation.
Final thoughts
Your dissertation project is a major part of your final year, and with exams and the pressure to decide your next steps, life can get a bit stressful. You might be planning to apply for a postgraduate degree such as a master’s degree , another type of qualification or moving into employment, but the results of your dissertation will have a huge impact on your prospects, so performing to the best of your abilities is essential.
One top tip we have is to make sure you’re not getting overworked with stress. Try studying outside of your dorm room, in a coffee shop or library. You can discover the best places to study in London on our blog.
While your dissertation is a large piece of work, with great planning and careful management, you can start to enjoy the process.
- Student Life
- dissertation , student life
You might also like

Do You Get Paid for a PhD?
Do You Get Paid for a PhD? For many students who don’t have the luxury of never worrying about money, one of the main considerations

Where Can a PhD in Finance Take Me?
Where Can a PhD in Finance Take Me? In the dynamic world of finance, a PhD is not just an academic accolade; it’s a launchpad

Should I Do a PhD in London?
Should I Do a PhD in London? Embarking on a PhD journey is a significant decision, one that shapes your academic and professional future. Once
Enquire with us
We are here to help and to make your journey to UWS London as smooth as possible. Please use the relevant button below to enquiry about a course you would like to apply, or to clarify any questions you may have about us and our admission’s process. After you submit your enquiry, one of our advisers will get back to you as soon as possible.
Cookie preferences
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We'll assume you're ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish.
Privacy Overview
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
Functional cookies help to perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collect feedbacks, and other third-party features.
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. These cookies track visitors across websites and collect information to provide customized ads.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Ten things I wish I'd known before starting my dissertation
The sun is shining but many students won't see the daylight. Because it's that time of year again – dissertation time.
Luckily for me, my D-Day (dissertation hand-in day) has already been and gone. But I remember it well.
The 10,000-word spiral-bound paper squatted on my desk in various forms of completion was my Allied forces; the history department in-tray was my Normandy. And when Eisenhower talked about a "great crusade toward which we have striven these many months", he was bang on.
I remember first encountering the Undergraduate Dissertation Handbook, feeling my heart sink at how long the massive file took to download, and began to think about possible (but in hindsight, wildly over-ambitious) topics. Here's what I've learned since, and wish I'd known back then…
1 ) If your dissertation supervisor isn't right, change. Mine was brilliant. If you don't feel like they're giving you the right advice, request to swap to someone else – providing it's early on and your reason is valid, your department shouldn't have a problem with it. In my experience, it doesn't matter too much whether they're an expert on your topic. What counts is whether they're approachable, reliable, reassuring, give detailed feedback and don't mind the odd panicked email. They are your lifeline and your best chance of success.
2 ) If you mention working on your dissertation to family, friends or near-strangers, they will ask you what it's about, and they will be expecting a more impressive answer than you can give. So prepare for looks of confusion and disappointment. People anticipate grandeur in history dissertation topics – war, genocide, the formation of modern society. They don't think much of researching an obscure piece of 1970s disability legislation. But they're not the ones marking it.
3 ) If they ask follow-up questions, they're probably just being polite.
4 ) Do not ask friends how much work they've done. You'll end up paranoid – or they will. Either way, you don't have time for it.
5 ) There will be one day during the process when you will freak out, doubt your entire thesis and decide to start again from scratch. You might even come up with a new question and start working on it, depending on how long the breakdown lasts. You will at some point run out of steam and collapse in an exhausted, tear-stained heap. But unless there are serious flaws in your work (unlikely) and your supervisor recommends starting again (highly unlikely), don't do it. It's just panic, it'll pass.
6 ) A lot of the work you do will not make it into your dissertation. The first few days in archives, I felt like everything I was unearthing was a gem, and when I sat down to write, it seemed as if it was all gold. But a brutal editing down to the word count has left much of that early material at the wayside.
7 ) You will print like you have never printed before. If you're using a university or library printer, it will start to affect your weekly budget in a big way. If you're printing from your room, "paper jam" will come to be the most dreaded two words in the English language.
8 ) Your dissertation will interfere with whatever else you have going on – a social life, sporting commitments, societies, other essay demands. Don't even try and give up biscuits for Lent, they'll basically become their own food group when you're too busy to cook and desperate for sugar.
9 ) Your time is not your own. Even if you're super-organised, plan your time down to the last hour and don't have a single moment of deadline panic, you'll still find that thoughts of your dissertation will creep up on you when you least expect it. You'll fall asleep thinking about it, dream about it and wake up thinking about. You'll feel guilty when you're not working on it, and mired in self-doubt when you are.
10 ) Finishing it will be one of the best things you've ever done. It's worth the hard work to know you've completed what's likely to be your biggest, most important, single piece of work. Be proud of it.

- Blogging students
- Higher education
- Advice for students
Most viewed
How Long is a Dissertation?
In General , University by Think Student Editor December 7, 2022 2 Comments
Dissertations can definitely seem terrifying! They require immense amounts of focus and research. You will probably need to spend a lot of time working on your dissertation if you want to achieve an impressive degree at university. Therefore, they can be extremely overwhelming when you first begin. Many people wonder how long it actually takes to complete a dissertation.
There is no set length required for a university dissertation. The amount of words you need to write can extremely vary. How long it needs to be depends on a number of factors. For example, an undergraduate dissertation is much shorter than a postgraduate dissertation. Therefore, the amount of words you need to write could range from 8,000 to 25,000 words. However, a PhD level dissertation could vary from 50,000 to 100,000 words.
If you are worrying about how long your dissertation has to be and want to find out more, carry on reading!
Table of Contents
How long are university dissertations?
Dissertations can vary in length depending on what level of education you are currently in at university. Undergraduate dissertations are the shortest.
However, the length of this can vary from 8,000 to 15,000 words. This depends on what subject you are studying and how in depth your research needs to be.
You can find more detail about how many words are needed in a dissertation if you click here , to read an article about this from Think Student.
Postgraduate dissertations are generally longer, they can sometimes be up to 25,000 words. However, you may be shocked to learn how long PhD dissertations are.
As you probably know, receiving a PhD is an amazing accomplishment. Therefore, the length of the dissertation reflects this.
You could be asked to write 50,000 to 100,000 words. Click here to find out more information about this on the Assignment Desk website.
How long does a dissertation take to write?
The length of time it takes to write a dissertation depends on each individual person. This depends on a number of factors.
One of these factors is how much time you have access to each week in order to write your dissertation. If you don’t have much time each week, then writing your dissertation will clearly take you much longer.
Further to this, your actual research could take a very long time . Without collecting your research, you are unable to actually write your dissertation.
You will also need to receive feedback from your professors. If you take a while to respond to the feedback, or if they take a while to provide you with any, then writing could take longer.
Therefore, some students are able to write their dissertation in six months. However, some students might take twelve to eighteen months!
To find out more about this, click here , to visit the Supreme Dissertations website.
How long is a master’s dissertation?
Master’s dissertations are usually 15,000 to 50,000 words in length. However, this length can depend on the subject and how detailed you are required to be.
Master’s dissertations are shorter than PhD dissertations but longer than undergraduate dissertations. It requires all the same components as other dissertations.
For example, you need an abstract, literature review, methodology, analysis, conclusion and a bibliography. To find out more information specific to a master’s dissertation, click here to visit the Ivory Research website.
Alternatively, if you want to discover what a PhD is and how this differs, check out this article from Think Student.
Why do you have to write a dissertation?
A dissertation is a piece of research you have to write at the end of your undergraduate or postgraduate degree . It will be the largest and most important essay you will ever have to write during your degree.
You will be working on this in the final year of your degree and this will be your main focus during this time.
Writing a dissertation is important because it allows you to test your capacity for independent research. You will be coming up with your own ideas, conducting your own research and writing the whole essay by yourself.
The experience of writing a dissertation will provide you with important preparation for your future. For example, you will need to be able to time manage, work independently and be able to think of your own, original ideas.
As you can see, dissertations require an immense amount of work. However, completing one is a fantastic accomplishment. They can seem impossible to achieve, due to their length.
However, if you break up what you have to do down into smaller chunks, you will definitely be able to do it.
University is hard work, but it will definitely be worth it. Check out this article from Think Student for help deciding whether you should go to university or not.
The length of a dissertation can vary widely depending on factors such as the academic discipline, the specific requirements of the institution or program, and the nature of the research. However, as a general guideline: Undergraduate Dissertation: An undergraduate dissertation is typically shorter than those at higher academic levels. It might range from around 6,000 to 15,000 words. Master’s Dissertation: A master’s dissertation is generally longer than an undergraduate one, often ranging from 15,000 to 25,000 words. However, this can vary significantly based on the field of study and program requirements. Ph.D. Dissertation: A Ph.D. dissertation is the longest and … Read more »
To get the most out of using our website please make sure you have read our Cookie Policy page and then click Accept.
- My discounts
- My Feedbacks
- Affilate Program
- Dissertation writing services
- Buy Dissertations
- Thesis Writing Service
- Editing and Proofreading Services
- More services
- Write my Dissertation
- Custom Dissertation Writing Help
- Best Dissertation Writers
- Testimonials
- Our Writers
- How Long Does It Take to Write a Dissertation

The obvious short answer is, it varies. But, in general, it depends upon these factors:
- How much time you have to devote to the project on a weekly basis, given your other responsibilities and obligations. You may have a part-time job, famly responsibilities, and you may be a TA during this process. You must devise a schedule for your dissertation work that provides definite times for your work.
- How long your research will take. It is not unusual for implementations of research to take as long as a year (or even more). While you are conducting your research, however, you can certainly be working on your literature review and at least part of your methodology chapter.
- Your advisor and committee will provide feedback and suggestions along the way. How responsive they are and how quickly they provide this will impact your timeline.
In general, and based upon actual data, the answer to how long it takes to write a dissertation is 12-18 months, but perhaps more, depending on the timeline to collect your research data.
So, let’s take a look at this entire process in terms of the average dissertation project from start to finish.
The Research Question and the Proposal
You have probably had many discussions with your advisor regarding your research question. You have picked a topic area of interest and have completed some initial research, in order to narrow that topic area to a specific research question you want to pursue. It has been approved by your advisor and you are now ready to write that proposal for your committee.
The question now becomes, how long does it take to write a dissertation proposal? And again, the answer varies. For some students, this is a longer project, because committees, and individual members, can be very picky. They may send the student back to re-write certain parts before final approval. You will discover that every committee member has individual agendas and pet peeves. These will come out in their assessment of your proposal. Do not be discouraged if you have to re-write – it is common and expected.
The proposal must include a clear statement of the research question and a justification of its importance to the field. The other parts include a short synopsis of the research you have conducted thus far that leads to your research question, a preliminary explanation of your research design, and a timeline for completion.
The Literature Review
The five chapters of your dissertation will of course begin with an introduction. However, this should not be written until the entire piece is finished. It will be much better if you wait.
Here is the thing about the literature review. Many students need to complete it in full before they can really refine their research methodology; others, because of the nature of the research, may refine their methodology and begin the implementation of the project at the same time that they are working on their literature review.
This will be the most tedious and often least interesting of the dissertation project. It will be like a large research paper, and it must contain a synopsis of all research that directly relates to your question. At times, you will read abstracts that appear to be a fit, pull out the actual piece and discover, about halfway through that it will not work for your lit review. This is common, but frustrating. For this reason, students will often contact a writing service that has a Ph.D.’s in their fields and ask if they can, “ Write my dissertation lit review.” This is often a decent solution to an otherwise time-consuming task.
Just how long should a literature review be in a dissertation? Again, it varies. You have to include all relevant research studies. Focus on that rather than on length. These can run from 20-30 pages and include from 20-30 resources.
The Design and Methodology Chapter
Here is where you explain to your reader exactly how you have designed your research, why you designed it as you did, and speak to the instruments, if any, that you will be using. The purpose of this chapter is to provide all of the details, so that a future researcher could replicate your research exactly. Having never done so before, many student writers are not sure how to write a dissertation methodology. The best thing to do is to read the methodology sections of other dissertations and follow the format that those researchers have used.
You will need to explain exactly how you chose samplings or the control and experimental groups (if you have them), and exactly the treatment(s) you used or the information your instruments are gathering from your sample population.
Depending upon your institution or department, the data you gathered is either reported in this chapter or the next. Data should always be reported in both prose and graphic forms
The Analysis/Discussion Chapter
This is the “meat” of your dissertation. You will be analyzing that data you collected and determining if your research question was answered and what significance has been the result.
Consider yourself fortunate that you are not doing this 30 years ago, when the statistical workup was all completed by hand – yes, paper and pencil. No software programs to crunch your numbers as there are now.
The biggest issues students have with this chapter are determining which formulae to use and plugging the numbers in correctly, especially if they are not STEM majors. Of all chapters in a dissertation, this is the one for which students most commonly seek help. And hiring a statistician to crunch these numbers is the best way to ensure that it is done correctly.
Again, the analysis must be reported in both graphic and prose forms.
Just how long to write the analysis chapter in a dissertation? It will depend upon individual students’ abilities to craft it on their own or how quickly they can secure the help they need.
Writing the Conclusion Chapter
Most students have had experience writing conclusion for essays and papers. But understanding how to write a conclusion for a dissertation will require a different approach. Most dissertation conclusions are highly organized into specific sections.
First, you must declare that your research question has been answered, how you have shown this, and the contribution you have made to your field of knowledge.
Second, you must identify any constraints or nuisance factors within your research, so that future researchers can account for them as well.
Third, you should point future researchers in directions that will replicate or add to what you have accomplished.
Not Quite Finished – the Introduction and the Abstract
Now you are ready to write that introduction. If you are wondering how long a dissertation introduction should be, understand that it will be your shortest chapter. The goal of the introduction is the same as any that is written for other academic pieces. You can use some of the information from your proposal to write this chapter – introduce your research question, provide a bit of background for choosing it, justify its significance, and give a very brief summary of your research design and methodology. Obviously, you will not give away the analysis and conclusion.
The abstract is composed after all else. This is the piece that others will read to discover exactly what your dissertation is about. You have already read many of them, so you should not have any questions about how long a dissertation abstract should be. It is no longer than one page. Again, you will state your research question and provide a very brief summary of what you did. The goal is for other researchers to determine if your study relates to their research and if your work should be used as a resource. Use other abstracts as model as you write your own.
Just Starting Out? Plan on the Next 12-18 Months for your Time Frame
If you have read other dissertations, you understand how long is a dissertation. Most will be 200 pages, more or less. You have a lot of work ahead of you, but if you commit to a regular schedule of work and get the help you need when you need it, you’ll make it. And the prize, that PH.D., will all be worth it.
Neighthan White is a writer and an undergraduate specialist in education sciences. In his late twenties he is a regular member of Montessori techniques for children under 10 seminars, a volunteer at Education without Borders and LDS, a startup inventor, a language learner, a writer and a happy husband.
over 187 subscribers
- Dissertation Writing
- What are the Highest Paying Masters Degrees?
- What is a dissertation?
- How to write an abstract for a dissertation
- Top 10 Universities to Apply for MBA Scholarships in the US
Price per page :
Total price:
Limitless Amendments
Bibliography
Plagiarism Report
Get all these features for $70.94 FREE

Check the discount here
Do not forget your 15% discount
Your first order with 15%OFF discount - 15OFF!
How long does it take to write a dissertation with a dissertation time plan?
6 minutes reading time

- 01. Pick a topic
- 02. Doing the research
- 03. Sit down and write!
- 04. Don't forget citations
The vast majority of students in the world will end up doing at least one dissertation in their life. However, not everyone has a clear idea of what exactly a dissertation is.
In some countries and schools, the dissertation is called a thesis, which ultimately is a research paper completed as part of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree.
The thesis or dissertation is a project that students have to complete to obtain their university degree. This project is an opportunity for each student to show their work and what they've learned during their years in school.
It doesn't matter if you are a science major or a literature major, you will have to write a dissertation to graduate and obtain your degree. Writing is a big part of our academic education, regardless of our department or field of interest.
The majority of undergraduate degrees will require a dissertation, but sometimes students are given the option of doing an internship instead. On the other hand, graduate, P.h.D, and doctoral students will always be required to do one.
Typically, a dissertation gives students the chance to discuss their research in response to a question or thesis that they've selected themselves.
Students have the freedom to pick a topic to research and they work hand in hand with a dissertation advisor who will give them tips, help them with a methodology, guide them with any question they student has, provide a review of a first draft, and overall an advisor will provide the student with advice on their project.
Continue reading and learn how long it will take you to write a dissertation, find tips on how to pick a topic, do your research, do the writing portion of the dissertation, and more.
Find an experienced dissertation coach here on Superprof.

Pick a topic

People often struggle when it comes to starting a big project . They don't know where to get started, what step to take first, or what methodology to follow.
Students in university (undergraduate or graduate) tend to get frustrated because they don't know how to start and they only think about how long it'll take them.
To get past this, first, know that if you organize yourself and come up with a clever plan to execute every step of writing a dissertation, you'll be done in no time!
Writing a thesis or dissertation from start to finish usually takes an entire school year. Some people who are getting their undergraduate degree do their thesis in under six months. But anyone getting a graduate or doctoral degree will take at least a year.
The first step has to do with asking questions. What would you like to research? What could be a good topic to dedicate time to? What am I interested in? What kind of research do I have the capacity of doing?
By answering all of these questions you'll have a better idea of what topic to choose. Make sure you explore different ideas before settling on one topic.
After picking a topic, you can write a proposal and show it to your advisor. You can review it with your advisor to get an idea of how long every stage of your dissertation will take, the advisor can help you find an example or several examples of similar work, and come up with ideas on methodology, process, analysis, and more.
Keep in mind that you can also find help while writing your dissertation right here on Superprof. There are over a hundred tutors on Superprof offering their wisdom to people who need help writing their thesis or in any other part of the process.
Doing the research
Once you've picked a topic, you need to get your hands dirty and start doing the research. The research portion of any proposal won't take only a day. You'll be working on your research for a minimum of a month, depending on your university department (science or social science).
If you are doing an academic dissertation you'll have to sit down and read a book, recollect data, find examples, find doctoral literature, and you'll probably spend all day in the library with other study partners.

However, if you are doing a scientific dissertation, there are plenty of different questions you'll have to answer using the scientific method. You'll do experiments and trials, and you'll possibly be working in a lab recollecting data all day.
This is why there are different types of dissertations, time frames for their completion, and processes of what to do. Keep in mind that it is very common for your original proposal to change once you've gathered data and you see that you aren't going anywhere.
People tend to get frustrated when this happens, but keep in mind that you can always find support during this process right here on Superprof.
Tutors who guide students with their dissertations have experience in finding a way around obstacles. A tutor can guide you in the process, give you advice, help you through your analysis of data , find important academic literature for you to read, and so on.
Don't forget that the research part of your dissertation has nothing to do with the analysis of your research. The analysis will last through the entirety of your project. You'll have to analyze data, information, results, examples, and so on.
Sit down and write!
Once you're done with the research and you have all the results you require you can start writing your dissertation. Many people believe that writing a dissertation takes more time than the actual work. However, this is not true.

If you learn to work efficiently, you can finish writing in no time. People who are stuck in the writing portion because they aren't organized or are procrastinating.
But, if you are organized and plan out every chapter of the dissertation from the introduction to the conclusions, and plan how long you'll take per chapter, there's no need to make this process longer by procrastinating or being disorganized.
To stay on top of things you can work with the help of a tutor from Superprof and ask them to help you set deadlines and help you stay on track. Tutors might have more tips or advice on how to become organized, for example.
A tutor can also give you tips on what not to do while writing each chapter of your dissertation. For example, you should avoid going back to do research. If you've concluded doing the research then you should focus on writing the introduction of your paper. Remember to take the process step by step.
We also recommend you search for tips that'll help you become a better and faster writer if you feel like writing is not your strong suit. However, since you'll be writing about something you know (since you'll be responsible for developing every chapter of the project), it won't be hard to do it.
All you have to do is explain your project and your research and put it down on paper. It can be long and it can take weeks and months, but it is not like you have to write a novel about something you know nothing about.
Don't forget citations

Since dissertations are research projects, you need to keep track of all of your sources. It is very common for students to be rushed and stressed by the end of their writing process because they don't have their citations.
Many are obligated to go back to the library and go through every book to find the one book they used for their research. You can save yourself this pain by keeping track of every reference and resource you use. This way you can already have your citations ready to go even before you start writing.
Keeping track of your citations will help you save time because by the end you'll have everything ready to go instead of having to go back and spend time going over things you've already gone over.
Remember that each university has its parameters and formats for citations; there's MLA, APA, and so on. Make sure you are using the format required by your school or else you might end up losing points or get in even bigger trouble.
Citations are important because it helps you show what work is yours and what is the intellectual property of someone else.
Enjoyed this article? Leave a rating.

Online contact creator for Superprof. I am passionate about coffee, blogging, and exchanging ideas through online mediums.
Frequently asked questions
What is the average cost a tutoring lesson.
The cost of tutoring lessons can vary depending on different factors like location, years of experience of the tutor, learning techniques used, the demand of the subject being taught, and so on. The price of a tutoring lesson can go from $12 to $40.
How to find a private tutor?
Finding a private tutor can be a tricky endeavor. As a student, you need to define your budget and your needs. Do you live really far away? Then finding an online tutor might be the best option for you. Are you easily distracted? Then finding a tutor who has experience teaching to different kinds of learners is important. Can you only afford a $20 hourly rate per lesson? Then don’t waste your time interviewing tutors who charge over $30 per hour.
Cancel reply
Your comment
Current ye@r *
Leave this field empty
Exploring: How Long is an Undergraduate Thesis?
Have you ever wondered how long an undergraduate thesis is? In this article, we will unravel the mystery and shed light on the typical length of an undergraduate thesis. Let’s dive in!
An undergraduate thesis is typically between 10 and 20 double-spaced pages, excluding tables, figures, and references.
- It follows the format of a scientific article , including sections such as abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, references, and tables/figures.
- The thesis should fully develop ideas , present data , and discuss the implications of the work.
- Master’s theses are longer, ranging from 60 to 100 pages, while doctoral dissertations can be at least 90 pages and upwards of 200 pages.
- The length of the thesis or dissertation can depend on various factors, including the faculty’s instructions , the topic’s technicalities, and the extent of research conducted .
- Adhering to the guidelines provided by the university and the professor supervising the project is crucial.
Understanding the Average Length of an Undergraduate Thesis
The average length of an undergraduate thesis can vary, but typically falls between 10 and 20 double-spaced pages, excluding tables, figures, and references. It is important to note that this range serves as a general guideline and may vary depending on the specific requirements of the university or department. However, adhering to this recommended length ensures that the thesis is comprehensive enough to fulfill its objectives while still maintaining a concise and focused approach.
An undergraduate thesis is a research paper that follows the format of a scientific article . It consists of various sections, including an abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, references, and tables/figures. Each section plays a vital role in presenting the research study in a structured and coherent manner.
To fully develop ideas and present data effectively, it is crucial to devote sufficient space within the thesis. The length should allow for a detailed exploration of the topic, a comprehensive analysis of the research methodology employed, and a thorough discussion of the findings. Additionally, the implications of the work should be discussed to demonstrate its significance and potential impact on the field of study.
While undergraduate theses are typically shorter in length than master’s theses and doctoral dissertations, it is important to note the distinctions between them. Master’s theses can range from 60 to 100 pages, providing more room for in-depth research and analysis. On the other hand, doctoral dissertations can span at least 90 pages, and in some cases, exceed 200 pages, as they require a more extensive exploration of the topic.
Factors Influencing Thesis Length
The length of an undergraduate thesis can be influenced by various factors. Firstly, the faculty’s instructions play a significant role in determining the expected page count. Therefore, it is essential to carefully review the guidelines provided and understand the specific requirements set by the university or department.
Secondly, the technicalities of the topic being researched can impact the length of the thesis. Some subjects may necessitate a more extensive discussion and analysis, resulting in a longer document. Conversely, less complex topics may require a more concise presentation.
Lastly, the extent of research conducted can also influence the length of the undergraduate thesis. In-depth studies that involve extensive data collection, experimentation, or fieldwork may require a more substantial presentation of findings, leading to a longer thesis.
In summary, the average length of an undergraduate thesis typically falls between 10 and 20 double-spaced pages, excluding tables, figures, and references. The thesis should follow the format of a scientific article and fully develop ideas , present data , and discuss the implications of the work. The length of the thesis can vary depending on the faculty’s instructions , the technicalities of the topic, and the extent of research conducted . Adhering to the guidelines provided by the university and the professor supervising the project is crucial to ensure the successful completion of the undergraduate thesis.
Following the Format of a Scientific Article
Much like a scientific article, an undergraduate thesis consists of various sections, such as an abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, references, and tables/figures. Each section serves a specific purpose in presenting the research and its findings. The following table provides an overview of the sections typically included in an undergraduate thesis:
These sections work together to provide a comprehensive and organized framework for the research. It is essential to adhere to the guidelines and formatting requirements provided by the university and the professor supervising the project . Following the format of a scientific article ensures that the thesis is well-structured and effectively communicates the research process and outcomes.
Fully Developing Ideas and Presenting Data
A crucial aspect of an undergraduate thesis is the ability to fully develop ideas and present data in a clear and concise manner. This requires thoughtful analysis, effective organization, and meticulous attention to detail. By fully developing ideas, students can showcase their understanding of the research topic and demonstrate critical thinking skills. This involves presenting a comprehensive and logical argument, supported by relevant evidence and examples.
One effective way to present data in an undergraduate thesis is through the use of tables and figures. Tables can help organize and summarize complex information, making it easier for readers to grasp the key findings or trends. Similarly, figures such as charts or graphs can visually represent data, enhancing its comprehension and impact. When using tables and figures, it is important to label and caption them appropriately, providing clear explanations of the presented data.
Furthermore, incorporating quotes from reputable sources can strengthen the credibility of an undergraduate thesis. Quoting experts in the field or citing relevant studies can add depth and support to the arguments being made. When including quotes, it is essential to attribute them correctly and provide proper citations following the specified referencing style.
Example Table:
By fully developing ideas and presenting data effectively, students can create a compelling undergraduate thesis that showcases their research skills and contributes to the academic discourse in their field.
An undergraduate thesis should not only present data but also discuss the implications of the research and its potential impact. This section is crucial as it allows the writer to delve deeper into the significance of their findings and provide relevant context to their work. By discussing the implications, the writer demonstrates a thorough understanding of the subject matter and how it relates to the broader academic community.
“The implications of this study suggest that further research is needed to explore the long-term effects of X on Y,” says Dr. Jane Smith, a renowned expert in the field. “These findings have the potential to revolutionize current practices and pave the way for innovative solutions.”
Furthermore, discussing the implications allows the writer to showcase their critical thinking skills, analytical abilities, and their ability to draw connections between their research and real-world applications. It also provides an opportunity to address any limitations or constraints that may have influenced the results, offering suggestions for future research.
Table: Implications of the Research
In conclusion, the implications and discussion section of an undergraduate thesis not only highlights the importance of the research findings but also provides an opportunity for the writer to showcase their intellectual rigor and contribute to their respective field of study.
The time required to complete an undergraduate thesis can vary depending on various factors such as the project’s complexity, the level of research involved, and individual circumstances. Unlike shorter assignments, an undergraduate thesis demands a more substantial commitment of time and effort. It is essential to allocate sufficient time to conduct thorough research, analyze data, and fully develop ideas. Rushing through the process may compromise the quality of the work.
On average, it can take anywhere from several months to a year to complete an undergraduate thesis. The duration is influenced by factors such as the scope of the research, the availability of resources, and the student’s familiarity with the topic. It is advisable to start the thesis early, allowing ample time for literature review, experimentation, and drafting the final document.
It is crucial to establish a realistic timeline and set achievable milestones to ensure timely progress. Regular communication and collaboration with the thesis advisor or professor can help in better managing the workload and staying on track. These mentors can provide guidance, offer feedback, and help navigate any challenges that may arise during the research process.
Ultimately, the amount of time required to complete an undergraduate thesis will depend on the individual’s dedication, organization, and ability to manage competing commitments. By carefully planning and executing each stage of the thesis, students can successfully navigate the research journey and produce a high-quality piece of work.
Factors Affecting the Time Required
- The complexity of the research question or topic
- The extent of data collection and analysis required
- The availability of resources and access to relevant literature
- The student’s prior knowledge and familiarity with the subject
- External commitments, such as part-time jobs or extracurricular activities
By considering these factors and planning accordingly, students can better estimate the time needed to complete their undergraduate thesis and ensure a successful research experience.
Table: Comparison of the lengths of undergraduate, master’s, and doctoral theses.
In summary, completing an undergraduate thesis requires careful planning, dedication, and effective time management. The time required can vary based on factors such as the project’s complexity, scope of research, and individual circumstances. By allocating sufficient time, staying organized, and seeking guidance when needed, students can successfully complete their undergraduate thesis and contribute valuable research to their field.
Faculty Guidelines and Supervision
To ensure a successful undergraduate thesis, it is essential to adhere to the guidelines provided by the university and follow the instructions of the professor supervising the project. The faculty’s instructions serve as a roadmap, guiding you through the process and ensuring that you meet the necessary requirements.
Your professor, as the project supervisor, plays a crucial role in providing guidance, support, and feedback throughout the thesis journey. They will offer valuable insights, help shape your research questions, and provide direction on the methodology and analysis. Regular meetings with your professor will allow for discussions, revisions, and clarifications, ultimately refining your work to meet the academic standards.
Moreover, your professor can offer expertise in your specific field of study, helping you navigate through any challenges that may arise. Their knowledge and experience will contribute to the development of your thesis, ensuring that it aligns with current research and scholarly expectations.
Faculty Guidelines and Project Success
The adherence to faculty guidelines and the close supervision of your professor are key factors in the success of your undergraduate thesis. By following these guidelines and seeking regular input from your supervisor, you will be well-positioned to produce a high-quality thesis that meets the academic standards set by your university and faculty.
References:
Comparing undergraduate, master’s, and doctoral theses.
While undergraduate theses typically range between 10 and 20 pages, master’s theses can be longer, usually ranging from 60 to 100 pages, while doctoral dissertations can span at least 90 pages and sometimes even exceed 200 pages. The length of these academic papers varies based on the level of the degree being pursued.
Master’s theses require a more extensive exploration of the chosen topic compared to undergraduate theses. This is why they tend to have a higher page count. With more research conducted and a deeper analysis of the subject matter, the length of a master’s thesis increases to accommodate the additional details and findings.
Doctoral dissertations, on the other hand, are the longest of the three. They involve in-depth research and original contributions to the field of study, necessitating a larger volume of content. Doctoral students are expected to delve into their subjects extensively, conducting extensive research, experiments, and overall comprehensive analyses. Consequently, their dissertations tend to have a substantial page count to encompass all the research conducted and the insights gained.
It is important to keep in mind that these page counts are general guidelines and can vary depending on the specific requirements of individual institutions and programs. However, understanding the typical length of undergraduate, master’s, and doctoral theses provides students with a sense of the level of detail and breadth expected at each stage of their academic journey.
The length of an undergraduate thesis can be influenced by various factors, including the technical complexities of the topic chosen and the extent of research conducted. When exploring a complex subject matter with intricate technicalities, it often requires a more comprehensive analysis and explanation, leading to a longer thesis. On the other hand, a less complex topic may allow for a more concise presentation.
The volume of research conducted is another key factor. Extensive research often leads to a greater amount of data and information that needs to be incorporated into the thesis, resulting in a longer document. In contrast, limited research may yield a shorter thesis.
It is important to note that while there may be some guidelines or expectations regarding thesis length, these factors can vary depending on the specific requirements of the faculty and university. Some institutions may have specific page count requirements, while others may prioritize the quality and depth of research over the length. It is crucial for students to familiarize themselves with the guidelines provided by their respective faculties and to consult with their professors for guidance and clarification.
Table 1: Comparison of Undergraduate, Master’s, and Doctoral Theses Length
The table above provides a general overview of the expected page lengths for undergraduate, master’s, and doctoral theses. While these are typical ranges, it is important to note that the actual length can still vary depending on other factors discussed earlier.
The image above serves as a visual representation of the complex technicalities that can influence the length of an undergraduate thesis, highlighting the need for thorough research and analysis.
In conclusion, the length of an undergraduate thesis typically ranges between 10 and 20 double-spaced pages, excluding tables, figures, and references, and should be sufficient to fully develop ideas, present data, and discuss the implications of the work.
An undergraduate thesis follows the format of a scientific article, including sections such as abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, references, and tables/figures. These sections provide a structured framework for presenting research findings and analyzing their significance.
While the length of an undergraduate thesis may seem shorter compared to master’s theses and doctoral dissertations, which can be at least 60 pages and upwards of 90 pages respectively, it is important to note that the focus of an undergraduate thesis is on presenting a comprehensive exploration of a specific topic within a limited scope.
When working on an undergraduate thesis, it is crucial to adhere to the guidelines provided by the university and the professor supervising the project. These guidelines may include specific instructions regarding page count, formatting, and content requirements. By following these guidelines and conducting thorough research, students can produce a well-structured and impactful undergraduate thesis.
How long is an undergraduate thesis?
What format does an undergraduate thesis follow.
An undergraduate thesis follows the format of a scientific article, including sections such as abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, references, and tables/figures.
What should an undergraduate thesis accomplish?
An undergraduate thesis should fully develop ideas, present data, and discuss the implications of the work.
How long does it take to complete an undergraduate thesis?
The time required to complete an undergraduate thesis can vary, but it typically depends on the topic’s technicalities and the extent of research conducted.
How important is it to adhere to faculty guidelines and supervision?
It is crucial to adhere to the guidelines provided by the university and the professor supervising the project to ensure the successful completion of an undergraduate thesis.
How does the length of an undergraduate thesis compare to master’s and doctoral theses?
Undergraduate theses are typically shorter, ranging from 10-20 pages, while master’s theses can be 60-100 pages and doctoral dissertations can exceed 200 pages.
What factors can influence the length of an undergraduate thesis?
The length of an undergraduate thesis can be influenced by various factors, including the technicalities of the topic and the extent of research conducted.
Source Links
- https://blogs.studentlife.utoronto.ca/lifeatuoft/2020/12/10/my-experience-writing-an-undergraduate-thesis/
- https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/Honors-Thesis-Guide-2019.pdf
- https://gradebees.com/thesis-dissertation-length/
Baron Cooke has been writing and editing for 7 years. He grew up with an aptitude for geometry, statistics, and dimensions. He has a BA in construction management and also has studied civil infrastructure, engineering, and measurements. He is the head writer of measuringknowhow.com
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Academics Hub
020 4525 3366
4.6 Rated 4.6 out of 5

How Long Should an Undergraduate Dissertation Be? Write a Perfect One
What is an undergraduate dissertation’s length? This is the common question asked by an undergraduate. The easiest response to this query is that a dissertation should be long enough to address the posed query adequately. A dissertation is a long, research-based piece of writing that aims to present a fresh perspective on a subject. It resembles a PhD thesis in some aspects, but it is a larger research project that is frequently started at the postgraduate level to get a higher degree. Its goal is to demonstrate your capacity for both planning and carrying out a study, as well as your accuracy and originality of thought. Students must finish a dissertation as part of the majority of undergraduate business courses and graduate MBA programs. This is a lengthy piece of writing that is why students get stuck when they have to write an undergraduate dissertation .
Students get stressed when they have to submit dissertations. They often ask the question: is there anyone from whom I can buy dissertation online ? Can I get dissertation writing services? Well! Many dissertation writing services assist students struggling with their academic career. In this blog, I have discussed how long an undergraduate dissertation should be and how to write a dissertation that gets appreciated by your professor.
What Is Meant by Undergraduate Dissertation?
In essence, an undergraduate dissertation, also known as a bachelor’s dissertation, is a lengthy essay that combines research and writing on a single topic. The topic is often chosen based on a student’s area of interest, typically finished in the final year of a degree program. Compared to a conventional module, it enables the learner to go deeper into a specific subject. Throughout the research project, the student collaborates with a single supervisor who is a departmental faculty member and offers direction and support.
How Long Should an Undergraduate Dissertation Be?

The question has no definitive answer. Several things influence the length of the undergraduate dissertation. Dissertations are a requirement at every university for students. The regulations are the same whether the institution is a well-known educational institution or a smaller, lesser-known one: a dissertation is an essential component of every program. It frequently causes anxiety in undergraduate students since, in many respects, it is the most significant task at this point of life, which inevitably leads to certain questions. What should the length of the undergraduate dissertation be? How much word count? Dissertation length is a topic of discussion because everyone wants to be ready for important academic endeavors in advance. This assignment may initially seem difficult, so it’s critical to understand more about dissertations and their size. No matter what level of writing one is at, knowledge aids in overcoming uncertainty and enabling the beginning of planning.
How long is the Average Undergraduate Dissertation Length?
There is no single answer to this question. But the majority of dissertations are between 100 and 200 pages in length. It can be suggested that it should be 146 pages long, while another person suggests 90. Someone else might argue that it has to be 200 pages. Basically, the length of this significant academic piece should be determined by the subject, writing style, and author’s objectives. Dissertations are required of students pursuing master’s and doctoral degree programs in universities. But most undergraduate students are concerned about the length because it plays a significant role in their academic careers.
There are typically helpful recommendations about how long an undergraduate dissertation should be. Your dissertation project’s length, for instance, should be influenced by the areas on which it concentrates. A history dissertation, for example, will probably be longer than the typical dissertation on chemistry. That implies that the length of your dissertation will depend on your academic discipline.
How Long Does It Take to Write A Dissertation?

Well! This question is asked by many people: how long does it take to write a dissertation? The simple answer to this question is that it depends on the nature of the subject matter, the area in which you are writing and the dissertation length. Actually, the time required to write a dissertation varies depending on these factors:
- How much time each week you can commit to the project, taking into account your other commitments and obligations. During this process, you can also have part-time work, obligations to your family, and other duties. For your dissertation work, you must create a schedule that specifies certain periods for your work.
- It is fairly uncommon for research implementation to take up to a year (or even more). However, you may undoubtedly work on your literature review and at least a portion of your methodology chapter while completing your research.
- Your adviser and committee will offer comments and recommendations during the dissertation process. Your timeline will be impacted by how responsive and promptly they respond.
How to Write an Undergraduate Dissertation?
It’s not easy to write a dissertation. To get to the finish line, you need a lot of time, effort, and energy. Your research journey will be much easier if you comprehend the overall procedure of writing an undergraduate dissertation. In this blog, we will outline the overall procedure of writing a dissertation.
Topic Selection: The topic for the dissertation must be chosen by the students at the end of their academic year. Your dissertation offers you the chance to present your ideas, delve further into a subject, and solidify prior learning. In order to obtain inspiration for your dissertation topic and uncover current topics relevant to your field, you can conduct research in course materials, scholarly journals, newspapers, and other media. As it is difficult and risky to change your topic after your study period has started, you should be sure to select a topic that is likely to maintain your interest for a lengthy amount of time.
Research outline: You will be required to write a dissertation outline of about 2-3 pages in length once the undergraduate dissertation module starts. A complete bibliography and a chapter summary ought to be included. By this point, you ought to have selected a more focused part of your topic, which you should shape into a study title with the assistance of your supervisor.
Research & Writing: At this point, your research will be considerably more focused on achieving the goals of your suggested dissertation agenda. Also, you should start writing as soon as you can. By the end of the first term, most departments require students to turn in a lengthy writing assignment. (Keep in mind that to give yourself enough time to make the necessary adjustments, you should hand in at least one draft to your supervisor before this deadline.
Final Dissertation: You should have around three to four chapters, an introduction, and a conclusion when you are finished writing. Everything must be formatted in accordance with the university’s requirements, and you must be sure to credit all of your sources correctly.
Editing & Proofreading:
To ensure that you generate a piece of work that is well-structured, cohesive, and polished, you must engage in a thorough editing process. Give yourself enough time to connect with your work on various levels, from reevaluating the overall piece’s logic to editing and ensuring that you have paid attention to details like the proper reference structure.
Binding & Submission: The undergraduate dissertation must be professionally bound before submission, in contrast to undergraduate essays. Although this is typically done on campus, you must allow adequate time for the process before the deadline for submission.
Get Professional Writing Help Online!

Writing a dissertation is a complicated task. Especially for undergraduate students. Dissertation writing requires time, energy, and research skills. Many students get stressed when they have to submit dissertations at the end of their final semester. Your overall grades depend on the submission of your dissertation. Well-thought and well-written dissertations are necessary if you want to score high in your academic career. But, students, due to many reasons, find it hard to compose and submit their dissertations. If you are going through a similar situation, getting writing help from professional academic writing services is ideal. Many online dissertations writing websites provide writing help to students in their academia and get them to score well. Online professional writers and researchers with knowledge in the industry will draft your dissertation. With extensive knowledge in the writing industry, online academic writers consider each aspect and guideline mentioned by your university professors. So, now you can buy a dissertation online by hiring experts.
Few Final Thoughts
This blog is aimed to provide information about the undergraduate dissertation. Many students get stressed when they have to complete their dissertations. Students ask how long an undergraduate dissertation should be. How long does it take the write a dissertation? Writing a dissertation is tricky, and students get stressed when they have to submit their dissertation. Earlier in this blog, I discussed the writing tips for an undergraduate dissertation. You can seek writing help online from professionals to get high scores.
Get Discount

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000-15,000 words. A master's dissertation is typically 12,000-50,000 words. A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000-100,000 words. However, none of these are strict guidelines - your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided ...
10 tips for writing an undergraduate dissertation. 1. Select an engaging topic. Choose a subject that aligns with your interests and allows you to showcase the skills and knowledge you have acquired through your degree. 2. Research your supervisor. Undergraduate students will often be assigned a supervisor based on their research specialisms.
An undergraduate dissertation usually falls within the range of 8,000 to 15,000 words, while a master's dissertation typically spans from 12,000 to 50,000 words. In contrast, a PhD thesis is typically of book length, ranging from 70,000 to 100,000 words. Let's unravel the mystery of how long should a dissertation be.
How long does it take to write a dissertation? At the bachelor's and master's levels, the dissertation is usually the main focus of your final year. You might work on it (alongside other classes) for the entirety of the final year, or for the last six months. ... An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000-15,000 words; A master's ...
Revised on 5 May 2022. A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree. The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the ...
An undergraduate thesis is likely to be about 20 to 50 pages long. A Master's thesis is likely to be between 30 and 100 pages in length and a PhD dissertation is likely to be between 50 and 450 pages long. In the table below I highlight the typical length of an undergraduate, master's, and PhD. Level of study. Pages. Words.
Based on my experience, writing your dissertation should take somewhere between 13-20 months. These are average numbers based upon the scores of doctoral students that I have worked with over the years, and they generally hold true.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
Most dissertations run a minimum of 100-200 pages, with some hitting 300 pages or more. When editing your dissertation, break it down chapter by chapter. Go beyond grammar and spelling to make sure you communicate clearly and efficiently. Identify repetitive areas and shore up weaknesses in your argument.
How does Undergraduate Dissertation differ from Postgraduate Dissertation? The bachelor's dissertation varies significantly from postgraduate dissertations. First, it is considerably shorter in length, averaging only 10,000 - 15,000 words. ... You should be sure to choose a topic that is likely to hold your interest over a long period of ...
Whether you're writing an undergraduate, Masters, or PhD dissertation, these seven steps can help you stay on track. 1. Choose your topic wisely. Selecting the right topic is the foundation of a successful dissertation. It is important to choose a topic that is: Relevant to your academic discipline and interests.
A dissertation is an independent piece of academic work that reports on research that you have carried out, and is much longer and more in-depth than a regular essay or research project. Word counts for UK dissertations are typically between 8,000 words to 20,000 words, but the length, along with the criteria for the sections that are required depend on the subject of your degree and the ...
4) Do not ask friends how much work they've done. You'll end up paranoid - or they will. Either way, you don't have time for it. 5) There will be one day during the process when you will freak ...
An undergraduate dissertation may be as little as 8,000 words. In contrast, a PhD thesis will likely be 50,000 words or more. Obviously, the higher your target word count, the longer it will take you to write. ... The main reason dissertations take so long is that there is much more work to do than just writing a long essay.
How long does a dissertation take to write? ... However, as a general guideline: Undergraduate Dissertation: An undergraduate dissertation is typically shorter than those at higher academic levels. It might range from around 6,000 to 15,000 words. Master's Dissertation: A master's dissertation is generally longer than an undergraduate one ...
In general, and based upon actual data, the answer to how long it takes to write a dissertation is 12-18 months, but perhaps more, depending on the timeline to collect your research data. So, let's take a look at this entire process in terms of the average dissertation project from start to finish.
Writing a thesis or dissertation from start to finish usually takes an entire school year. Some people who are getting their undergraduate degree do their thesis in under six months. But anyone getting a graduate or doctoral degree will take at least a year. The first step has to do with asking questions.
In the humanities, this is measured in years, not months. It is standard in my field (Religious Studies) for the dissertation to take from 1.5 to 3 years. Humanities programs are typically in the 5-7 year expectation for the whole program, where the first 3-4 are coursework, exams, and prospectus. Once you're done with all that, you're ABD and ...
Summary. In summary, the average length of an undergraduate thesis typically falls between 10 and 20 double-spaced pages, excluding tables, figures, and references. The thesis should follow the format of a scientific article and fully develop ideas, present data, and discuss the implications of the work.
How long is the Average Undergraduate Dissertation Length? There is no single answer to this question. But the majority of dissertations are between 100 and 200 pages in length. It can be suggested that it should be 146 pages long, while another person suggests 90. Someone else might argue that it has to be 200 pages.
Anonymous #3. Original post by xoxAngel_Kxox. It took me half an hour to collect data, 4 hours to analyse data, half an hour to find stats and sources backing up what I wanted to say (typing key words and phrases into Science Direct and just referencing the papers without really reading them), 4 hours to write 10,000 words, 1 hour to reference ...
A. 2. Hi Peeps, Just about to start my dissertation (LLM). How long did your dissertation take to research/write up? I've planned for a good draft to be done in 10 weeks. That's working 5 days per week full on kinda thing. For my undergraduate degree I chose to take a module in Jurisprudence instead of a research dissertation so I've no idea ...