10 Best Problem-Solving Therapy Worksheets & Activities

Cognitive science tells us that we regularly face not only well-defined problems but, importantly, many that are ill defined (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
Sometimes, we find ourselves unable to overcome our daily problems or the inevitable (though hopefully infrequent) life traumas we face.
Problem-Solving Therapy aims to reduce the incidence and impact of mental health disorders and improve wellbeing by helping clients face life’s difficulties (Dobson, 2011).
This article introduces Problem-Solving Therapy and offers techniques, activities, and worksheets that mental health professionals can use with clients.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free . These science-based exercises explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology, including strengths, values, and self-compassion, and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students, or employees.

This Article Contains:
What is problem-solving therapy, 14 steps for problem-solving therapy, 3 best interventions and techniques, 7 activities and worksheets for your session, fascinating books on the topic, resources from positivepsychology.com, a take-home message.
Problem-Solving Therapy assumes that mental disorders arise in response to ineffective or maladaptive coping. By adopting a more realistic and optimistic view of coping, individuals can understand the role of emotions and develop actions to reduce distress and maintain mental wellbeing (Nezu & Nezu, 2009).
“Problem-solving therapy (PST) is a psychosocial intervention, generally considered to be under a cognitive-behavioral umbrella” (Nezu, Nezu, & D’Zurilla, 2013, p. ix). It aims to encourage the client to cope better with day-to-day problems and traumatic events and reduce their impact on mental and physical wellbeing.
Clinical research, counseling, and health psychology have shown PST to be highly effective in clients of all ages, ranging from children to the elderly, across multiple clinical settings, including schizophrenia, stress, and anxiety disorders (Dobson, 2011).
Can it help with depression?
PST appears particularly helpful in treating clients with depression. A recent analysis of 30 studies found that PST was an effective treatment with a similar degree of success as other successful therapies targeting depression (Cuijpers, Wit, Kleiboer, Karyotaki, & Ebert, 2020).
Other studies confirm the value of PST and its effectiveness at treating depression in multiple age groups and its capacity to combine with other therapies, including drug treatments (Dobson, 2011).
The major concepts
Effective coping varies depending on the situation, and treatment typically focuses on improving the environment and reducing emotional distress (Dobson, 2011).
PST is based on two overlapping models:
Social problem-solving model
This model focuses on solving the problem “as it occurs in the natural social environment,” combined with a general coping strategy and a method of self-control (Dobson, 2011, p. 198).
The model includes three central concepts:
- Social problem-solving
- The problem
- The solution
The model is a “self-directed cognitive-behavioral process by which an individual, couple, or group attempts to identify or discover effective solutions for specific problems encountered in everyday living” (Dobson, 2011, p. 199).
Relational problem-solving model
The theory of PST is underpinned by a relational problem-solving model, whereby stress is viewed in terms of the relationships between three factors:
- Stressful life events
- Emotional distress and wellbeing
- Problem-solving coping
Therefore, when a significant adverse life event occurs, it may require “sweeping readjustments in a person’s life” (Dobson, 2011, p. 202).

- Enhance positive problem orientation
- Decrease negative orientation
- Foster ability to apply rational problem-solving skills
- Reduce the tendency to avoid problem-solving
- Minimize the tendency to be careless and impulsive
D’Zurilla’s and Nezu’s model includes (modified from Dobson, 2011):
- Initial structuring Establish a positive therapeutic relationship that encourages optimism and explains the PST approach.
- Assessment Formally and informally assess areas of stress in the client’s life and their problem-solving strengths and weaknesses.
- Obstacles to effective problem-solving Explore typically human challenges to problem-solving, such as multitasking and the negative impact of stress. Introduce tools that can help, such as making lists, visualization, and breaking complex problems down.
- Problem orientation – fostering self-efficacy Introduce the importance of a positive problem orientation, adopting tools, such as visualization, to promote self-efficacy.
- Problem orientation – recognizing problems Help clients recognize issues as they occur and use problem checklists to ‘normalize’ the experience.
- Problem orientation – seeing problems as challenges Encourage clients to break free of harmful and restricted ways of thinking while learning how to argue from another point of view.
- Problem orientation – use and control emotions Help clients understand the role of emotions in problem-solving, including using feelings to inform the process and managing disruptive emotions (such as cognitive reframing and relaxation exercises).
- Problem orientation – stop and think Teach clients how to reduce impulsive and avoidance tendencies (visualizing a stop sign or traffic light).
- Problem definition and formulation Encourage an understanding of the nature of problems and set realistic goals and objectives.
- Generation of alternatives Work with clients to help them recognize the wide range of potential solutions to each problem (for example, brainstorming).
- Decision-making Encourage better decision-making through an improved understanding of the consequences of decisions and the value and likelihood of different outcomes.
- Solution implementation and verification Foster the client’s ability to carry out a solution plan, monitor its outcome, evaluate its effectiveness, and use self-reinforcement to increase the chance of success.
- Guided practice Encourage the application of problem-solving skills across multiple domains and future stressful problems.
- Rapid problem-solving Teach clients how to apply problem-solving questions and guidelines quickly in any given situation.
Success in PST depends on the effectiveness of its implementation; using the right approach is crucial (Dobson, 2011).
Problem-solving therapy – Baycrest
The following interventions and techniques are helpful when implementing more effective problem-solving approaches in client’s lives.
First, it is essential to consider if PST is the best approach for the client, based on the problems they present.
Is PPT appropriate?
It is vital to consider whether PST is appropriate for the client’s situation. Therapists new to the approach may require additional guidance (Nezu et al., 2013).
Therapists should consider the following questions before beginning PST with a client (modified from Nezu et al., 2013):
- Has PST proven effective in the past for the problem? For example, research has shown success with depression, generalized anxiety, back pain, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, and supporting caregivers (Nezu et al., 2013).
- Is PST acceptable to the client?
- Is the individual experiencing a significant mental or physical health problem?
All affirmative answers suggest that PST would be a helpful technique to apply in this instance.
Five problem-solving steps
The following five steps are valuable when working with clients to help them cope with and manage their environment (modified from Dobson, 2011).
Ask the client to consider the following points (forming the acronym ADAPT) when confronted by a problem:
- Attitude Aim to adopt a positive, optimistic attitude to the problem and problem-solving process.
- Define Obtain all required facts and details of potential obstacles to define the problem.
- Alternatives Identify various alternative solutions and actions to overcome the obstacle and achieve the problem-solving goal.
- Predict Predict each alternative’s positive and negative outcomes and choose the one most likely to achieve the goal and maximize the benefits.
- Try out Once selected, try out the solution and monitor its effectiveness while engaging in self-reinforcement.
If the client is not satisfied with their solution, they can return to step ‘A’ and find a more appropriate solution.

Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Exercises (PDF)
Enhance wellbeing with these free, science-based exercises that draw on the latest insights from positive psychology.
Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
Positive self-statements
When dealing with clients facing negative self-beliefs, it can be helpful for them to use positive self-statements.
Use the following (or add new) self-statements to replace harmful, negative thinking (modified from Dobson, 2011):
- I can solve this problem; I’ve tackled similar ones before.
- I can cope with this.
- I just need to take a breath and relax.
- Once I start, it will be easier.
- It’s okay to look out for myself.
- I can get help if needed.
- Other people feel the same way I do.
- I’ll take one piece of the problem at a time.
- I can keep my fears in check.
- I don’t need to please everyone.

5 Worksheets and workbooks
Problem-solving self-monitoring form.
Answering the questions in the Problem-Solving Self-Monitoring Form provides the therapist with necessary information regarding the client’s overall and specific problem-solving approaches and reactions (Dobson, 2011).
Ask the client to complete the following:
- Describe the problem you are facing.
- What is your goal?
- What have you tried so far to solve the problem?
- What was the outcome?
Reactions to Stress
It can be helpful for the client to recognize their own experiences of stress. Do they react angrily, withdraw, or give up (Dobson, 2011)?
The Reactions to Stress worksheet can be given to the client as homework to capture stressful events and their reactions. By recording how they felt, behaved, and thought, they can recognize repeating patterns.
What Are Your Unique Triggers?
Helping clients capture triggers for their stressful reactions can encourage emotional regulation.
When clients can identify triggers that may lead to a negative response, they can stop the experience or slow down their emotional reaction (Dobson, 2011).
The What Are Your Unique Triggers ? worksheet helps the client identify their triggers (e.g., conflict, relationships, physical environment, etc.).
Problem-Solving worksheet
Imagining an existing or potential problem and working through how to resolve it can be a powerful exercise for the client.
Use the Problem-Solving worksheet to state a problem and goal and consider the obstacles in the way. Then explore options for achieving the goal, along with their pros and cons, to assess the best action plan.
Getting the Facts
Clients can become better equipped to tackle problems and choose the right course of action by recognizing facts versus assumptions and gathering all the necessary information (Dobson, 2011).
Use the Getting the Facts worksheet to answer the following questions clearly and unambiguously:
- Who is involved?
- What did or did not happen, and how did it bother you?
- Where did it happen?
- When did it happen?
- Why did it happen?
- How did you respond?
2 Helpful Group Activities
While therapists can use the worksheets above in group situations, the following two interventions work particularly well with more than one person.
Generating Alternative Solutions and Better Decision-Making
A group setting can provide an ideal opportunity to share a problem and identify potential solutions arising from multiple perspectives.
Use the Generating Alternative Solutions and Better Decision-Making worksheet and ask the client to explain the situation or problem to the group and the obstacles in the way.
Once the approaches are captured and reviewed, the individual can share their decision-making process with the group if they want further feedback.
Visualization
Visualization can be performed with individuals or in a group setting to help clients solve problems in multiple ways, including (Dobson, 2011):
- Clarifying the problem by looking at it from multiple perspectives
- Rehearsing a solution in the mind to improve and get more practice
- Visualizing a ‘safe place’ for relaxation, slowing down, and stress management
Guided imagery is particularly valuable for encouraging the group to take a ‘mental vacation’ and let go of stress.
Ask the group to begin with slow, deep breathing that fills the entire diaphragm. Then ask them to visualize a favorite scene (real or imagined) that makes them feel relaxed, perhaps beside a gently flowing river, a summer meadow, or at the beach.
The more the senses are engaged, the more real the experience. Ask the group to think about what they can hear, see, touch, smell, and even taste.
Encourage them to experience the situation as fully as possible, immersing themselves and enjoying their place of safety.
Such feelings of relaxation may be able to help clients fall asleep, relieve stress, and become more ready to solve problems.
We have included three of our favorite books on the subject of Problem-Solving Therapy below.
1. Problem-Solving Therapy: A Treatment Manual – Arthur Nezu, Christine Maguth Nezu, and Thomas D’Zurilla

This is an incredibly valuable book for anyone wishing to understand the principles and practice behind PST.
Written by the co-developers of PST, the manual provides powerful toolkits to overcome cognitive overload, emotional dysregulation, and the barriers to practical problem-solving.
Find the book on Amazon .
2. Emotion-Centered Problem-Solving Therapy: Treatment Guidelines – Arthur Nezu and Christine Maguth Nezu

Another, more recent, book from the creators of PST, this text includes important advances in neuroscience underpinning the role of emotion in behavioral treatment.
Along with clinical examples, the book also includes crucial toolkits that form part of a stepped model for the application of PST.
3. Handbook of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapies – Keith Dobson and David Dozois

This is the fourth edition of a hugely popular guide to Cognitive-Behavioral Therapies and includes a valuable and insightful section on Problem-Solving Therapy.
This is an important book for students and more experienced therapists wishing to form a high-level and in-depth understanding of the tools and techniques available to Cognitive-Behavioral Therapists.
For even more tools to help strengthen your clients’ problem-solving skills, check out the following free worksheets from our blog.
- Case Formulation Worksheet This worksheet presents a four-step framework to help therapists and their clients come to a shared understanding of the client’s presenting problem.
- Understanding Your Default Problem-Solving Approach This worksheet poses a series of questions helping clients reflect on their typical cognitive, emotional, and behavioral responses to problems.
- Social Problem Solving: Step by Step This worksheet presents a streamlined template to help clients define a problem, generate possible courses of action, and evaluate the effectiveness of an implemented solution.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others enhance their wellbeing, check out this signature collection of 17 validated positive psychology tools for practitioners. Use them to help others flourish and thrive.

17 Top-Rated Positive Psychology Exercises for Practitioners
Expand your arsenal and impact with these 17 Positive Psychology Exercises [PDF] , scientifically designed to promote human flourishing, meaning, and wellbeing.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
While we are born problem-solvers, facing an incredibly diverse set of challenges daily, we sometimes need support.
Problem-Solving Therapy aims to reduce stress and associated mental health disorders and improve wellbeing by improving our ability to cope. PST is valuable in diverse clinical settings, ranging from depression to schizophrenia, with research suggesting it as a highly effective treatment for teaching coping strategies and reducing emotional distress.
Many PST techniques are available to help improve clients’ positive outlook on obstacles while reducing avoidance of problem situations and the tendency to be careless and impulsive.
The PST model typically assesses the client’s strengths, weaknesses, and coping strategies when facing problems before encouraging a healthy experience of and relationship with problem-solving.
Why not use this article to explore the theory behind PST and try out some of our powerful tools and interventions with your clients to help them with their decision-making, coping, and problem-solving?
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free .
- Cuijpers, P., Wit, L., Kleiboer, A., Karyotaki, E., & Ebert, D. (2020). Problem-solving therapy for adult depression: An updated meta-analysis. European P sychiatry , 48 (1), 27–37.
- Dobson, K. S. (2011). Handbook of cognitive-behavioral therapies (3rd ed.). Guilford Press.
- Dobson, K. S., & Dozois, D. J. A. (2021). Handbook of cognitive-behavioral therapies (4th ed.). Guilford Press.
- Eysenck, M. W., & Keane, M. T. (2015). Cognitive psychology: A student’s handbook . Psychology Press.
- Nezu, A. M., & Nezu, C. M. (2009). Problem-solving therapy DVD . Retrieved September 13, 2021, from https://www.apa.org/pubs/videos/4310852
- Nezu, A. M., & Nezu, C. M. (2018). Emotion-centered problem-solving therapy: Treatment guidelines. Springer.
- Nezu, A. M., Nezu, C. M., & D’Zurilla, T. J. (2013). Problem-solving therapy: A treatment manual . Springer.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Thanks for your information given, it was helpful for me something new I learned
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

The Empty Chair Technique: How It Can Help Your Clients
Resolving ‘unfinished business’ is often an essential part of counseling. If left unresolved, it can contribute to depression, anxiety, and mental ill-health while damaging existing [...]

29 Best Group Therapy Activities for Supporting Adults
As humans, we are social creatures with personal histories based on the various groups that make up our lives. Childhood begins with a family of [...]

47 Free Therapy Resources to Help Kick-Start Your New Practice
Setting up a private practice in psychotherapy brings several challenges, including a considerable investment of time and money. You can reduce risks early on by [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (48)
- Coaching & Application (57)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (24)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (45)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (28)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (17)
- Positive Parenting (2)
- Positive Psychology (33)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (47)
- Resilience & Coping (35)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (37)
- Strengths & Virtues (30)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)

Decision Making Worksheets

Rate Yourself
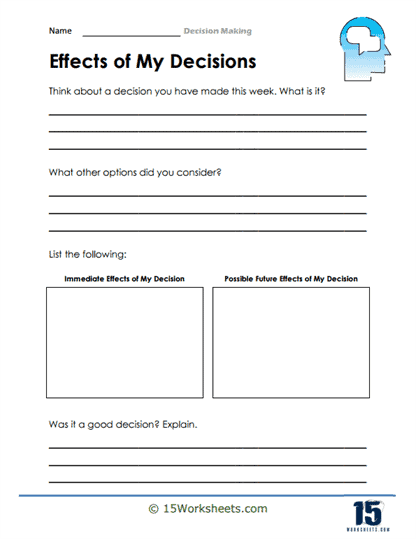
Immediate And Possible Effects

Considering Options
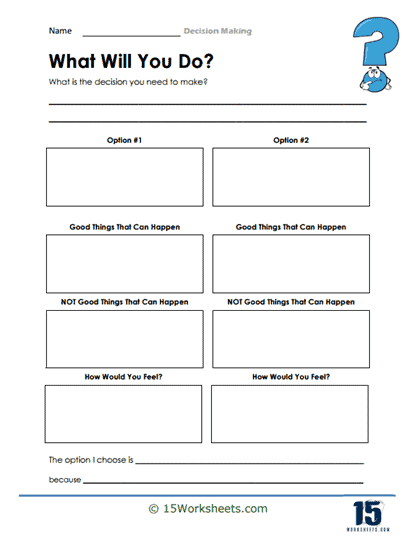
What Will You Do?
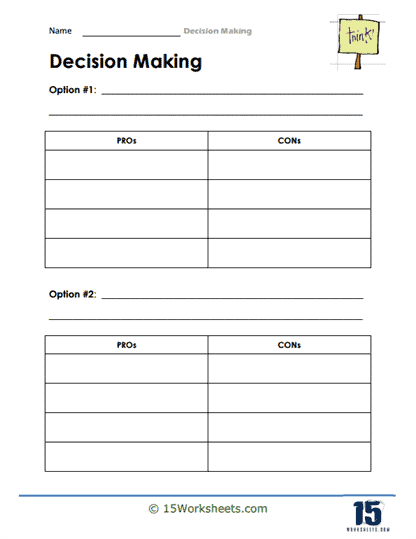
Pros And Cons Table
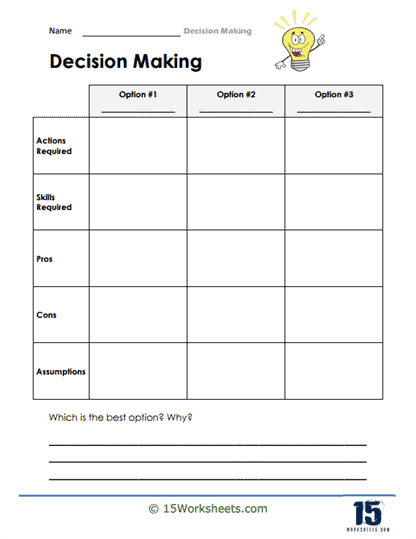
Picking The Best Option
Doing It Or Not
Questions And Listing
Thinking Of Alternatives
Who Decides?
What’s At Stake?
Rational Decision Making

If You Make A Change
Ethical Decisions
The Thinking Process
All about these 15 worksheets.
Effective decision-making is a vital skill for students to develop as they navigate various aspects of their lives. This series of 15 worksheets has been thoughtfully designed to help students understand and practice the process of decision-making. Each worksheet focuses on different aspects of decision-making, providing guidance, prompts, and exercises to enhance students’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
The worksheets in this series cover various elements of decision-making, including identifying options, evaluating pros and cons, considering consequences, weighing priorities, and reflecting on decision outcomes. By engaging with these worksheets, students will develop the skills necessary to make informed choices, consider different perspectives, and evaluate the potential impact of their decisions. Through these worksheets, students will:
- Think creatively and explore different possibilities before evaluating each option;
- Analyze the potential advantages and disadvantages, considering factors such as feasibility, impact, and alignment with their goals;
- Reflect on their personal priorities and use them as a basis for evaluating and ranking their options;
- Assess the effectiveness of their decision-making process, identifying areas for improvement and learning from their experiences;
- And consider ethical dilemmas and apply ethical frameworks to analyze and make decisions that align with their values and principles.
By engaging with these Decision-Making worksheets, students will develop valuable critical thinking skills, enhance their problem-solving abilities, and approach decision-making with confidence. These practical exercises and reflections provide a foundation for them to make well-informed choices, consider different perspectives, and evaluate the potential impact of their decisions. In summary, these worksheets foster a systematic and thoughtful approach to decision-making, empowering students to navigate complex situations effectively and achieve their goals.
How to Improve Your Decision Making
In life, there are many decisions to be made. You will come across countless opportunities and have the freedom and responsibility to make the correct decision. Decision-making is also a considerable part of any workplace. You should be able to make efficient and quick decisions that will help you save time and make the best use of your resources.
When making decisions, you need to sort through some choices in your head and look at information from all angles. This will allow you to make a well-informed decision you will not regret later in life.
Here are some ways you can improve your decision-making skills:
1. Come Up with a Plan
If you know that you will have a decision to make soon, you must come up with a plan beforehand. For example, if you have to decide how to get your team to meet your company’s goals, make notes about the size of your team and come up with individual goals before you address the primary matter.
Before making a decision, you should examine all the resources and materials around you. Most people feel overwhelmed when making a decision, but planning ahead can reduce the stress you might feel at the moment. You must clarify your priorities and how you want to accomplish them. Clear goals are essential to making the correct decision. You should be able to think long-term instead of making decisions that will benefit you at the moment but bring up a stream of problems for you in the future.
2. Be Assertive
Decision-making does not have to be scary. You need to feel in command before you take any big step. Even though you might not feel confident, you mustn’t doubt yourself. Self-doubt only makes it difficult to make decisions.
However, this does not mean rushing into anything. You need to use your three brains. This means listening to the part of your brain that solves problems and is creative, as well as the heart side of the brain that is compassionate and passionate. Lastly, you need to listen to the gut side of your brain that will give you the courage to make decisions.
3. Understand How You Will Benefit
Failure to make good decisions can point to how we manage our interests and how attached we are to people. Before you make a decision, determine how your decision might benefit you. Recognize that you are emotionally attached to the people in the situation.
You should also check in with yourself to see if there is any past memory triggering you or holding you back from making a decision. If need be, ask a trusted partner for help and advice, and then make up your mind.
4. Keep Your Biases in Check
Decision-making is a leadership quality everyone can have, as long as they work towards it. However, sometimes you might find that time pressure is too high, and you do not have enough information available.
Some leaders rely on their gut to make decisions. While being in tune with your intuition is definitely helpful, you must also self-reflect and realize that personal biases may drive your decisions. When making a decision, it is vital to be impartial and factful. Do not favor your friends and overlook those you do not get along with. Instead, making a just decision that would be mutually beneficial to everyone.
Kiddie Matters
Best Guide For Teaching Kids The Decision Making Process Steps
Inside: a guide for teaching children the decision making process steps to help them make responsible decisions..
Have you ever been in a store with a child and asked them to pick out a treat?
It can be like pulling teeth! Granted, they have many racks of chips, cookies, and other assortment of empty calories to choose from.
Then factor in the healthier options you want to direct them towards. I get why the decision can be hard for them. To be completely honest, it’s a tough decision for me too.
Being indecisive about snacks is one thing. However, kids have to make a wide range of decisions on a daily basis.
These decisions include things such as choosing how to behave, what friends to spend time with, or what clothes to wear.
It can get pretty overwhelming if children aren’t armed with the right tools to make good decisions.
Teaching kids how to make decisions is a valuable life skill for children to have. As kids get older, the kinds of decisions they make become increasingly more complicated.
For example, some kids have to decide what college they want to go to, if they want to go to college at all, or what career path they want to take.
When children learn the decision making process steps, they make more responsible decisions. This prepares them to make big decisions that impacts their future.
I’ve included a free printable to help kids practice the decision making process steps.
Related Article: Life Skills Checklists For Children and Teens
Common types of decision-makers.
Making responsible decisions doesn’t come naturally to everyone. It’s a skill that many must be taught. Let’s take a look at three common ways people make decisions. They are:
No Decision
Children fall into the ‘No Decision’ trap when they let their peers or someone other than a trusted adult make decisions for them. They let others tell them what to do instead of making their own decisions.
Many times this happens because children are afraid they will make the wrong decision. They doubt themselves and look to others to decide for them.
Kids who fall into the ‘No Decision’ category need to be reminded that it’s OK to make mistakes. Making mistakes provides an opportunity for learning and growth.
Snap Decisions
Snap decisions happen when children make decisions without properly analyzing the situation. They don’t consider the consequences of their actions and they react to what’s going on.
There are times when snap decisions are OK. Like say choosing between chips and yogurt. That’s not a life altering decision for most people (unless of course you have food allergies or nutritional concerns).
Generally speaking, making a choice between the two foods doesn’t require you to weigh the pros and cons. It’s not a decision that you have to think through in depth.
However, it’s not a good idea to make a snap decision about where you want to go to college. There are many variables and options to consider.
College is an investment and you want to make sure you make the best choice for you.
Kids prone to making snap decision benefit from learning to stop and think before taking action.
Responsible Decisions
Responsible decision makers think about the consequences of their actions and how it will affect them and the people in their lives.
It’s important that children learn to make responsible decisions on their own.
Sometimes kids need guidance from trusted adults to make good choice. However, there will come a time when they need to rely on themselves to make the right choice.
This is when knowing the decision making process steps comes in handy.
Related Article: How To Raise Good Decision Makers
What are the decision making process steps.
The decision-making process steps teaches children how to identify the problem, gather information, and come up with possible solutions to a problem.
When children follow the decision making process steps, they are able to make deliberate and thoughtful decisions.
Since we expect kids to make good choices the majority of the time, we need to teach them the decision making skills that will allow them to do exactly that.
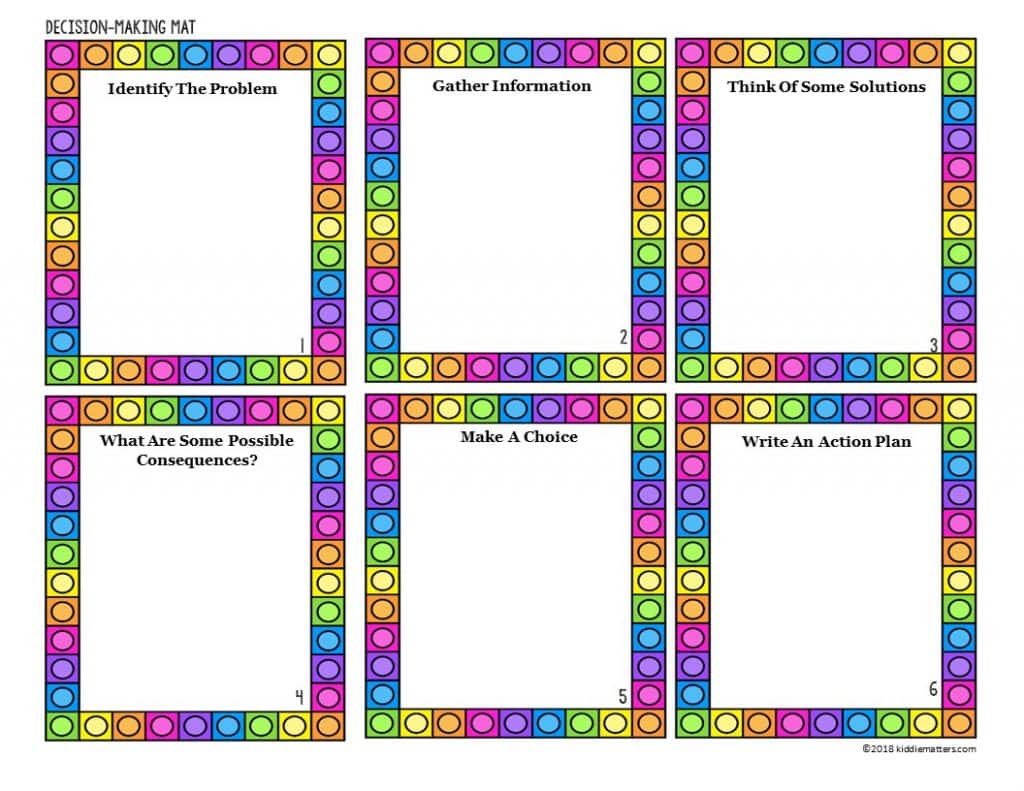
Step 1: Identify The Problem

In this step the problem is analyzed. Questions children can ask themselves include:
- What exactly is the problem?
- Why should this problem be solved? Is it important?
- Who does this problem affect?
- Is there a deadline on how much time I have to solve this problem?
Step 2: Gather Relevant Information

Next, children will figure out what information is needed in order to make their decision. Some information will be gathered through self-assessment. They’ll have to ask themselves:
- What do I want?
- What do I need?
- What are my values?
In addition they might have to get relevant information from books, videos, online, other people, etc.
Step 3: Brainstorm Solutions

During this step, children, children begin listing possible solutions. Initially, they might think that coming up with multiple solutions makes no sense. However, doing this allows them to think about the problem from different angles.
Step 4: Identify Possible Consequences

Now children will examine each option in the Step 3 to determine if any of the alternatives would solve the problem identified in Step 1 .
As they go through this process, certain options will ‘feel’ better than others.
Next, they will prioritize the different options and list them in order based on the solution they believe will best solve the problem.
Step 5: Make A Choice

Once children thoroughly evaluate the alternatives, they are ready to make a choice. The choice may be the solution at the top of their priority list in Step 4 .
It could also be a combination of some of the alternatives they explored.
Step 6: Take Action

Now children are ready to take action and implement the decision they believe best solves the problem.
Having a plan of how they are going to follow through with their decision is helpful.
Also, children can determine if they need help to implement their decision or if they want to do it on their own.
Step 7: Evaluate The Outcome

In this final step, children consider the results of their decision. They make a determination as to whether or not their decision solved the problem.
If it did not solve the problem, they can opt to try one of the other options they brainstormed in Step 3 .
If they believe non of those alternatives will work, they can go back to Step 2 and gather more relevant information.
Decision Making Process Steps Free Printable
The following free printable is a sample taken from the Decision Making Workbook and Activities Resource.
It is a Decision making graphic organizer to help children walk through the steps of making good decisions.
In order to download, please subscribe to our monthly newsletter, Social Emotional Learning Toolbox .
When you subscribe you get VIP access to our growing library of free resources which includes this free printable. Also, you can unsubscribe at any time.
Resources for Teaching Children The Decision Making Process Steps
The Decision Making Workbook w/ Learning Activities

For Ages: 7 to 12
This workbook explains the decision making process steps to children.
Children get to complete a decision making exercise to help them solve a problem they are currently having using the steps outlined in the workbook.
This resource also includes discussion cards that ask children to use the decision making process steps to come up with solutions to problems typically faced by children at home, in school, with peers, and online.
For Ages: 6-12
In this book, Joy Berry lays the ground work for making good decisions and solving problems.
She discusses the process and gives specific advice on how to approach any decision or problem. The topics included in this book are:
- What is a decision
- Three guidelines for making good decisions
- Six steps for making good decisions
- Reasons for making your own decisions
- What is a problem
- Six steps for solving problems
It’s Your Decision For Teens: A Commonsense Guide To Making Better Choices
It’s Your Decision For Teens helps teens understand the decision making process.
It offers common sense approaches to help teens make initial decisions about their education and the field of study they choose, the best career choices for them, their relationships, the quality of their health and wellness, and how they get to spend their free time.
Similar Posts

Helping Kids Learn Stress Management Skills
Stress management isn’t a skill we often teach children. The assumption is that kids live care-free lives and have no experience with stress. However, there…

Autism Awareness: What Kids Need To Know About Autism
April is Autism Awareness Month and this year I wanted to focus on helping kids in elementary school develop an understanding of autism and also…

Social Emotional Learning Activities Using A Mandala
Getting some kids to open up and talk can be like pulling teeth. They don’t always have insight into what they’re thinking and feeling and…

Acts Of Kindness Bingo For Kids With Free Printable
Hi everyone! Welcome to another edition of Freebie Friday where every Friday I share a free product or printable. Don’t forget to stop by every…

Growth Mindset For Kids: How Parents Can Encourage Growth Mindset In Children
Inside: Strategies to encourage a growth mindset in children so that they can take on challenges with confidence. “If parents want to give their children…

How To Make A Snowflake In 3 Easy Steps
Living in New York definitely comes with a lot of perks. However, when it comes to winter…any place warmer looks more appealing. The kiddies and…
Amazing!!!! Thank you for posting. This is a great help
This was terrific I run a social skills program and this is a fun, user friendly way to look at decision making
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
404 Not found
- My Storyboards
Decision Making Worksheets
Customize decision making templates.

If you're assigning this to your students, copy the worksheet to your account and save. When creating an assignment, just select it as a template!
Decision Making Skills Worksheets
Developing strong decision making skills is crucial for students to become responsible citizens. Using targeted handouts in class provides an engaging way for students to practice this vital life skill. This section explores why these printables are valuable for growth and shares ideas to integrate them into diverse lessons.
What is a Decision Making Skills Worksheet?
It is an educational material that scaffolds the decision making process by:
- Clearly defining a problem
- Brainstorming solution options
- Analyzing pros and cons
- Making a well-reasoned final decision
Our free decision making worksheets provide an organized structure to practice and help students understand this critical thinking skill. Using these guided resources helps students determine the best solutions independently over time.
Benefits of Using Decision Making Activities
Integrating activities has many benefits for student growth and engagement:
- Enhances Critical Thinking: Using these handouts guides students to analyze information carefully before acting. The step-by-step process breaks down an otherwise overwhelming task.
- Applies Skill to Real Situations: The scenarios in decision making worksheets for teenagers can reflect realistic dilemmas related to school, family, friends, etc. Analyzing relatable situations makes the process relevant.
- Engages Diverse Learners: These printable decision making worksheets for teens appeal to visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic learners as they incorporate analytical thinking, discussion, writing, and visual components.
- Adaptable Across Subjects and Grades: The complexity differs, but decision making worksheets for kids can be utilized as early as elementary school through high school. You can adjust scenarios to complement current lesson themes in diverse subjects.
Activity Ideas for Integrating A Free Decision Making Worksheet
Decision making skills worksheets for elementary students can be seamlessly incorporated into lessons across various academic subjects through practical activities like:
- English/Language Arts: Analyze the motivations, values, and choices of characters in novels using a printable template. Discuss alternates. After reading persuasive speeches, have students outline pros/cons and make decisions on key issues utilizing a digital handout.
- Science: Evaluate options related to environmental scenarios by completing decision making skill worksheets for youth. When learning the scientific method, map out points for developing hypotheses, testing variables, final determinations, etc.
- Social Studies: Study historical choices world leaders made at critical turning points using an editable decision making activity chart. Debate correct choices famous inventors/innovators made when developing new technologies guided by printable worksheets.
- Health/Life Skills Classes: Practice responding to peer pressure by completing handouts analyzing healthy choices in risky social situations. Discuss the pros and cons of significant milestone options — college, career paths, relationships — via discussion prompts and templates.
Best Practices for Classroom Integration
Effective ways to incorporate these activities into lessons include:
- Introduce vocabulary using a decision making template so kids learn key terms as a foundation.
- Begin with familiar situations before more complex societal issues.
- Have small groups discuss options before individual completion to encourage dialogue.
- Incorporate role-playing scenarios.
- Project interactive digital versions for the whole classroom.
- Send home packets over breaks for added practice.
Help students reinforce skills with these additional printables on thinking critically and social cues:
- Brainstorming Worksheets
- Life Skills Worksheets
- Social Stories Templates
- Social Cues Worksheets
How to Make Decision Making Worksheets
Choose one of the premade templates.
We have lots of templates to choose from. Take a look at our example for inspiration!
Click on “Copy Template”
Once you do this, you will be directed to the storyboard creator.
Give Your Worksheet a Name!
Be sure to call it something related to the topic so that you can easily find it in the future.
Edit Your Worksheet
This is where you will include directions, specific images, and make any aesthetic changes that you would like. The options are endless!
Click "Save and Exit"
When you are finished, click this button in the lower right hand corner to exit your storyboard.
From here you can print, download as a PDF, attach it to an assignment and use it digitally, and more!
Happy Creating!
Frequently Asked Questions about Decision Making Worksheets
What grade levels can effectively utilize these teaching materials.
With adaptable scenarios and analysis, versatile decision making printables are utilized from elementary school through high school learning objectives across core subjects. Educators can also use our user-friendly decision-making worksheet maker to create customized materials that best fit their lesson plans.
Can printable or digital decision-making skills worksheets work for in-classroom and remote teaching?
Yes, with both physical worksheet packets and digital formats that allow access to interactive decision-making graphic organizers, students can practice critical thinking on these relevant skills, whether face-to-face or in remote environments.
Where can I access free decision making teaching resources or customize printables?
Storyboard That provides an array of adaptable templates, samples, and generators to create versatile materials that best suit your instructional activities. Educators can download, print, copy, and share digital resources for classroom integration or remote learning.
Try 1 Month For
30 Day Money Back Guarantee New Customers Only Full Price After Introductory Offer
Learn more about our Department, School, and District packages

- Thousands of images
- Custom layouts, scenes, characters
- And so much more!!
Create a Storyboard
SEL Toolkit
- What's in the Toolkit?
- Strategies and Tools
- Self-Awareness
- Self-Management
- Social Awareness
- Relationship Skills
- Decision Making
SEL Toolkit: Decision Making
Social and Emotional Learning (SEL) fosters the ability to make positive choices about how we behave. On this page of the SEL Toolkit, we link to tools and resources for professionals who seek to strengthen young people's decision-making skills.
Promote Problem-Solving Thinking
There are many simple ways to infuse problem-solving thinking and reflection into program activities:
- Articulate differences and connections
- Identify emotions behind actions
- Brainstorm different approaches or solutions to a task
- Explore possible consequences
- Model and articulate decision-making process
- Reflect on past experiences
- Evaluate actions - did they meet the goal?
- Simulate or role play a task
Teaching Problem Solving
Vanderbilt University's Center for Teaching provides tips and techniques for teaching problem solving.
Teaching Problem Solving: Let students get "stuck" and "unstuck"
This Brookings article describes methods for creating a "culture of problem solvers."
Teach Critical Thinking and Decision-Making Skills
Games for Building Decision-Making Skills
Here, Common Sense Education reviews classroom-friendly games for improving students' decision-making and problem-solving skills.
Decision-making and Problem-solving: Class Activity
This activity from Climate Schools in Australia includes a useful worksheet to help a young person think through a decision.
Edutopia: The Benefits of Teaching Ethical Dilemmas
Introducing ethical dilemmas in the classroom can open up opportunities not only for debate and critical thinking, but also for personal growth, empathy for other viewpoints, and self-reflection.
Reflective Group Conversation
This worksheet can be used to guide critical thinking within a group.
SWOT Analysis
This worksheet can be used in a discussion of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.

Youth Development Professionals

Youth and Media: Activities

Healthy Life Skills

Career Success

Financial Literacy
Join Pilot Waitlist

Home » Blog » General » Free Problem Solving Worksheets: Practical Tools for Success

Free Problem Solving Worksheets: Practical Tools for Success
As a Speech Language Pathologist and Social Emotional Learning expert, I understand the importance of problem-solving skills in personal growth and success. Developing the ability to effectively solve problems not only enhances our cognitive abilities but also plays a crucial role in our social and emotional well-being. In this blog post, I will introduce you to the world of free problem solving worksheets, which are practical tools that can help you develop and strengthen your problem-solving skills.
Understanding Problem Solving
Before we dive into the world of problem solving worksheets, let’s first understand what problem solving entails. Problem solving is the process of identifying, analyzing, and finding solutions to challenges or obstacles that we encounter in our daily lives. It involves critical thinking, decision-making, and creativity.
Effective problem solving consists of several key components. Firstly, it requires the ability to define the problem clearly and understand its underlying causes. Secondly, it involves generating multiple possible solutions and evaluating their potential outcomes. Lastly, it requires implementing and evaluating the chosen solution to determine its effectiveness.
Developing problem-solving skills offers numerous benefits. It enhances our ability to think critically, make informed decisions, and adapt to new situations. It also boosts our self-confidence and resilience, as we become more equipped to handle challenges and overcome obstacles.

The Role of Worksheets in Problem Solving
Worksheets are valuable tools that can facilitate the problem-solving process. They provide structure and guidance, allowing us to break down complex problems into manageable steps. Free problem solving worksheets offer several advantages:
- Structured Approach: Worksheets provide a step-by-step framework for problem solving, ensuring that we cover all necessary aspects of the problem.
- Visual Representation: Worksheets often include visual elements such as diagrams or charts, which can help us visualize the problem and potential solutions.
- Practice and Reinforcement: Worksheets offer opportunities for practice and reinforcement of problem-solving skills, allowing us to apply what we have learned in a structured manner.
By incorporating worksheets into our problem-solving practice, we can enhance our social emotional learning. Social emotional learning (SEL) encompasses the development of self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making. Problem solving is a key component of responsible decision-making, as it involves considering the impact of our choices on ourselves and others.
Exploring Free Problem Solving Worksheets
Now that we understand the value of problem solving worksheets, let’s explore the different types of worksheets available:
- Step-by-step problem solving worksheets: These worksheets guide us through the problem-solving process, providing prompts and questions to help us analyze the problem, generate solutions, and evaluate their effectiveness.
- Decision-making worksheets: Decision-making is a crucial aspect of problem solving. These worksheets focus on helping us make informed decisions by considering the pros and cons of different options.
- Critical thinking worksheets: Critical thinking is an essential skill in problem solving. These worksheets encourage us to think deeply and critically about the problem, analyze information, and evaluate different perspectives.
There are several online resources where you can find free problem solving worksheets:
- Educational websites: Many educational websites offer free resources for problem solving and social emotional learning. Examples include EverydaySpeech, Education.com, and Teach-nology.
- Social emotional learning resources: SEL-focused websites and organizations often provide free problem solving worksheets as part of their curriculum. Look for websites like CASEL (Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning) and SEL for Prevention.
- Printable worksheet collections: Numerous websites offer collections of printable worksheets across various subjects, including problem solving. Websites like Super Teacher Worksheets and WorksheetWorks provide free options.
Tips for Effective Use of Problem Solving Worksheets
While using problem solving worksheets, it’s essential to keep a few tips in mind to maximize their effectiveness:
- Set clear goals and objectives: Before starting a worksheet, clearly define what you want to achieve and what specific problem you want to address.
- Provide guidance and support: If you’re using worksheets with children or students, offer guidance and support as they work through the problems. Encourage them to ask questions and provide explanations when needed.
- Encourage reflection and self-assessment: After completing a worksheet, encourage reflection on the problem-solving process. Ask questions like, “What did you learn from this exercise?” or “How could you apply these problem-solving skills in other situations?”
Incorporating Problem Solving Worksheets in Social Emotional Learning
Problem solving worksheets can be integrated into various aspects of social emotional learning:
- Integrating worksheets into SEL curriculum: Teachers and educators can incorporate problem solving worksheets into their SEL curriculum to enhance students’ problem-solving skills and promote responsible decision-making.
- Using worksheets in individual therapy sessions: Speech Language Pathologists and therapists can utilize problem solving worksheets in individual therapy sessions to help clients develop their problem-solving abilities and improve their social emotional well-being.
- Engaging students in group activities with worksheets: Group activities that involve problem solving worksheets can foster collaboration, communication, and teamwork among students, enhancing their social and emotional skills.
Problem solving skills are essential for personal growth and success. By developing these skills, we become better equipped to navigate challenges, make informed decisions, and achieve our goals. Free problem solving worksheets offer practical tools that can enhance our problem-solving abilities and promote social emotional learning.
So, why not start incorporating free problem solving worksheets into your daily practice? Start your EverydaySpeech Free trial today and explore a wide range of problem solving worksheets and other social emotional learning resources. Take the first step towards unlocking your problem-solving potential and embark on a journey of personal growth and success!

Related Blog Posts:
Pragmatic language: enhancing social skills for meaningful interactions.
Pragmatic Language: Enhancing Social Skills for Meaningful Interactions Pragmatic Language: Enhancing Social Skills for Meaningful Interactions Introduction: Social skills play a crucial role in our daily interactions. They enable us to navigate social situations,...
Preparing for Success: Enhancing Social Communication in Grade 12
Preparing for Success: Enhancing Social Communication in Grade 12 Key Takeaways Strong social communication skills are crucial for academic success and building meaningful relationships in Grade 12. Social communication includes verbal and non-verbal communication,...
Preparing for Success: Enhancing Social Communication in Grade 12 Preparing for Success: Enhancing Social Communication in Grade 12 As students enter Grade 12, they are on the cusp of adulthood and preparing for the next chapter of their lives. While academic success...

FREE MATERIALS
Better doesn’t have to be harder, social skills lessons students actually enjoy.
Be the best educator you can be with no extra prep time needed. Sign up to get access to free samples from the best Social Skills and Social-Emotional educational platform.
Get Started Instantly for Free
Complete guided therapy.
The subscription associated with this email has been cancelled and is no longer active. To reactivate your subscription, please log in.
If you would like to make changes to your account, please log in using the button below and navigate to the settings page. If you’ve forgotten your password, you can reset it using the button below.
Unfortunately it looks like we’re not able to create your subscription at this time. Please contact support to have the issue resolved. We apologize for the inconvenience. Error: Web signup - customer email already exists
Welcome back! The subscription associated with this email was previously cancelled, but don’t fret! We make it easy to reactivate your subscription and pick up right where you left off. Note that subscription reactivations aren't eligible for free trials, but your purchase is protected by a 30 day money back guarantee. Let us know anytime within 30 days if you aren’t satisfied and we'll send you a full refund, no questions asked. Please press ‘Continue’ to enter your payment details and reactivate your subscription
Notice About Our SEL Curriculum
Our SEL Curriculum is currently in a soft product launch stage and is only available by Site License. A Site License is currently defined as a school-building minimum or a minimum cost of $3,000 for the first year of use. Individual SEL Curriculum licenses are not currently available based on the current version of this product.
By clicking continue below, you understand that access to our SEL curriculum is currently limited to the terms above.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 0 min read
Team Building Exercises – Problem Solving and Decision Making
Fun ways to turn problems into opportunities.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Whether there's a complex project looming or your team members just want to get better at dealing with day-to-day issues, your people can achieve much more when they solve problems and make decisions together.
By developing their problem-solving skills, you can improve their ability to get to the bottom of complex situations. And by refining their decision-making skills, you can help them work together maturely, use different thinking styles, and commit collectively to decisions.
In this article, we'll look at three team-building exercises that you can use to improve problem solving and decision making in a new or established team.
Exercises to Build Decision-Making and Problem-Solving Skills
Use the following exercises to help your team members solve problems and make decisions together more effectively.
Exercise 1: Lost at Sea*
In this activity, participants must pretend that they've been shipwrecked and are stranded in a lifeboat. Each team has a box of matches, and a number of items that they've salvaged from the sinking ship. Members must agree which items are most important for their survival.
Download and print our team-building exercises worksheet to help you with this exercise.
This activity builds problem-solving skills as team members analyze information, negotiate and cooperate with one another. It also encourages them to listen and to think about the way they make decisions.
What You'll Need
- Up to five people in each group.
- A large, private room.
- A "lost at sea" ranking chart for each team member. This should comprise six columns. The first simply lists each item (see below). The second is empty so that each team member can rank the items. The third is for group rankings. The fourth is for the "correct" rankings, which are revealed at the end of the exercise. And the fifth and sixth are for the team to enter the difference between their individual and correct score, and the team and correct rankings, respectively.
- The items to be ranked are: a mosquito net, a can of petrol, a water container, a shaving mirror, a sextant, emergency rations, a sea chart, a floating seat or cushion, a rope, some chocolate bars, a waterproof sheet, a fishing rod, shark repellent, a bottle of rum, and a VHF radio. These can be listed in the ranking chart or displayed on a whiteboard, or both.
- The experience can be made more fun by having some lost-at-sea props in the room.
Flexible, but normally between 25 and 40 minutes.
Instructions
- Divide participants into their teams, and provide everyone with a ranking sheet.
- Ask team members to take 10 minutes on their own to rank the items in order of importance. They should do this in the second column of their sheet.
- Give the teams a further 10 minutes to confer and decide on their group rankings. Once agreed, they should list them in the third column of their sheets.
- Ask each group to compare their individual rankings with their collective ones, and consider why any scores differ. Did anyone change their mind about their own rankings during the team discussions? How much were people influenced by the group conversation?
- Now read out the "correct" order, collated by the experts at the US Coast Guard (from most to least important): - Shaving mirror. (One of your most powerful tools, because you can use it to signal your location by reflecting the sun.) - Can of petrol. (Again, potentially vital for signaling as petrol floats on water and can be lit by your matches.) - Water container. (Essential for collecting water to restore your lost fluids.) -Emergency rations. (Valuable for basic food intake.) - Plastic sheet. (Could be used for shelter, or to collect rainwater.) -Chocolate bars. (A handy food supply.) - Fishing rod. (Potentially useful, but there is no guarantee that you're able to catch fish. Could also feasibly double as a tent pole.) - Rope. (Handy for tying equipment together, but not necessarily vital for survival.) - Floating seat or cushion. (Useful as a life preserver.) - Shark repellent. (Potentially important when in the water.) - Bottle of rum. (Could be useful as an antiseptic for treating injuries, but will only dehydrate you if you drink it.) - Radio. (Chances are that you're out of range of any signal, anyway.) - Sea chart. (Worthless without navigational equipment.) - Mosquito net. (Assuming that you've been shipwrecked in the Atlantic, where there are no mosquitoes, this is pretty much useless.) - Sextant. (Impractical without relevant tables or a chronometer.)
Advice for the Facilitator
The ideal scenario is for teams to arrive at a consensus decision where everyone's opinion is heard. However, that doesn't always happen naturally: assertive people tend to get the most attention. Less forthright team members can often feel intimidated and don't always speak up, particularly when their ideas are different from the popular view. Where discussions are one-sided, draw quieter people in so that everyone is involved, but explain why you're doing this, so that people learn from it.
You can use the Stepladder Technique when team discussion is unbalanced. Here, ask each team member to think about the problem individually and, one at a time, introduce new ideas to an appointed group leader – without knowing what ideas have already been discussed. After the first two people present their ideas, they discuss them together. Then the leader adds a third person, who presents his or her ideas before hearing the previous input. This cycle of presentation and discussion continues until the whole team has had a chance to voice their opinions.
After everyone has finished the exercise, invite your teams to evaluate the process to draw out their experiences. For example, ask them what the main differences between individual, team and official rankings were, and why. This will provoke discussion about how teams arrive at decisions, which will make people think about the skills they must use in future team scenarios, such as listening , negotiating and decision-making skills, as well as creativity skills for thinking "outside the box."
A common issue that arises in team decision making is groupthink . This can happen when a group places a desire for mutual harmony above a desire to reach the right decision, which prevents people from fully exploring alternative solutions.
If there are frequent unanimous decisions in any of your exercises, groupthink may be an issue. Suggest that teams investigate new ways to encourage members to discuss their views, or to share them anonymously.
Exercise 2: The Great Egg Drop*
In this classic (though sometimes messy!) game, teams must work together to build a container to protect an egg, which is dropped from a height. Before the egg drop, groups must deliver presentations on their solutions, how they arrived at them, and why they believe they will succeed.
This fun game develops problem-solving and decision-making skills. Team members have to choose the best course of action through negotiation and creative thinking.
- Ideally at least six people in each team.
- Raw eggs – one for each group, plus some reserves in case of accidents!
- Materials for creating the packaging, such as cardboard, tape, elastic bands, plastic bottles, plastic bags, straws, and scissors.
- Aprons to protect clothes, paper towels for cleaning up, and paper table cloths, if necessary.
- Somewhere – ideally outside – that you can drop the eggs from. (If there is nowhere appropriate, you could use a step ladder or equivalent.)
- Around 15 to 30 minutes to create the packages.
- Approximately 15 minutes to prepare a one-minute presentation.
- Enough time for the presentations and feedback (this will depend on the number of teams).
- Time to demonstrate the egg "flight."
- Put people into teams, and ask each to build a package that can protect an egg dropped from a specified height (say, two-and-a-half meters) with the provided materials.
- Each team must agree on a nominated speaker, or speakers, for their presentation.
- Once all teams have presented, they must drop their eggs, assess whether the eggs have survived intact, and discuss what they have learned.
When teams are making their decisions, the more good options they consider, the more effective their final decision is likely to be. Encourage your groups to look at the situation from different angles, so that they make the best decision possible. If people are struggling, get them to brainstorm – this is probably the most popular method of generating ideas within a team.
Ask the teams to explore how they arrived at their decisions, to get them thinking about how to improve this process in the future. You can ask them questions such as:
- Did the groups take a vote, or were members swayed by one dominant individual?
- How did the teams decide to divide up responsibilities? Was it based on people's expertise or experience?
- Did everyone do the job they volunteered for?
- Was there a person who assumed the role of "leader"?
- How did team members create and deliver the presentation, and was this an individual or group effort?
Exercise 3: Create Your Own*
In this exercise, teams must create their own, brand new, problem-solving activity.
This game encourages participants to think about the problem-solving process. It builds skills such as creativity, negotiation and decision making, as well as communication and time management. After the activity, teams should be better equipped to work together, and to think on their feet.
- Ideally four or five people in each team.
- Paper, pens and flip charts.
Around one hour.
- As the participants arrive, you announce that, rather than spending an hour on a problem-solving team-building activity, they must design an original one of their own.
- Divide participants into teams and tell them that they have to create a new problem-solving team-building activity that will work well in their organization. The activity must not be one that they have already participated in or heard of.
- After an hour, each team must present their new activity to everyone else, and outline its key benefits.
There are four basic steps in problem solving : defining the problem, generating solutions, evaluating and selecting solutions, and implementing solutions. Help your team to think creatively at each stage by getting them to consider a wide range of options. If ideas run dry, introduce an alternative brainstorming technique, such as brainwriting . This allows your people to develop one others' ideas, while everyone has an equal chance to contribute.
After the presentations, encourage teams to discuss the different decision-making processes they followed. You might ask them how they communicated and managed their time . Another question could be about how they kept their discussion focused. And to round up, you might ask them whether they would have changed their approach after hearing the other teams' presentations.
Successful decision making and problem solving are at the heart of all effective teams. While teams are ultimately led by their managers, the most effective ones foster these skills at all levels.
The exercises in this article show how you can encourage teams to develop their creative thinking, leadership , and communication skills , while building group cooperation and consensus.
* Original source unknown. Please let us know if you know the original source.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Pdca (plan do check act).
Continually Improving, in a Methodical Way
The Plan-Do-Check-Act Process
How to Minimize Risk
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Team Management
Learn the key aspects of managing a team, from building and developing your team, to working with different types of teams, and troubleshooting common problems.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

SWOT Analysis

SMART Goals
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
How to stop procrastinating.
Overcoming the Habit of Delaying Important Tasks
What Is Time Management?
Working Smarter to Enhance Productivity
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Crucial conversations: tools for talking when stakes are high.
Kerry Patterson, Joseph Grenny, Ron McMillan, and Al Switzler
Book Insights
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
Decision-Making and Problem-Solving Worksheet Pack
Table of Contents
8 steps for Strategic Problem-Solving in Your Homeschool
Teach Critical thinking with the decision-making and problem-solving worksheet pack
Everyone needs help learning decision-making skills and how to problem-solve. It’s not just a math skill, is it?!? It’s a life skill. Using the steps in the Strategic Problem Solving Worksheet pack will help your family master the art of problem-solving for many of life’s challenging situations. So what are we waiting for? Let’s get started!
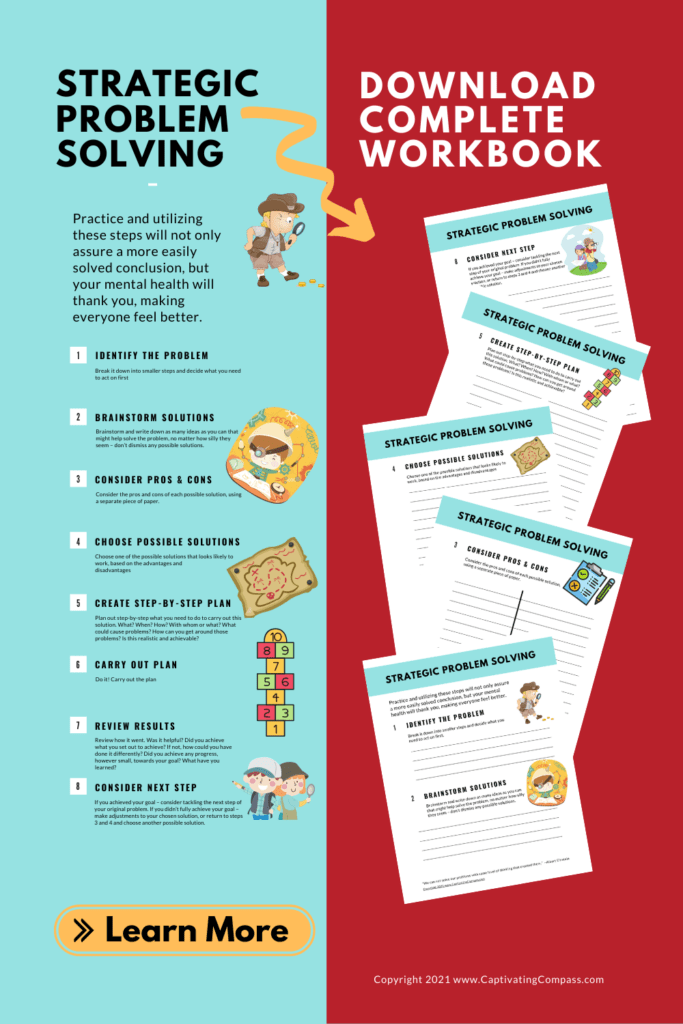
Step 1: Identify The Problem
Younger students may need help with this step, but middle school students and higher should be able to exercise the problem-solving skills needed in this first step.
Break your problem down into smaller steps and decide what you need to act on first. Before you define a problem, it might feel vague or confusing. Writing out your problem will help to:
- organize information,
- see it from a new perspective, and
- identify the most important issues.
You will want to answer these questions:
- When and where does the problem occur?
- What are the causes of the problem? Think about all the possible causes. Consider your own behavior as well as external factors .
- Define your problem. Be as clear and comprehensive as possible. If there are many parts to the problem, describe each of them.
Life Skill Tip: If you are finding it difficult to separate your emotions from the problem, try to complete this step from the perspective of an impartial friend or small group. Emotional learning is a process, hang in there.
Step 2: Brainstorm
Brainstorm and write down as many ideas as you can that might help solve the problem, no matter how silly they seem – don’t dismiss any possible solutions.
Write down at least three solutions as part of your strategic problem-solving strategy. Without thinking about alternative solutions we often get stuck on what worked in the past or the first idea that comes to mind. There are usually many solutions to a problem, and our first idea isn’t always the best.
Step 3: Consider The Pros And Cons
Consider the pros and cons of each possible solution. You might need extra paper for this! For each possible solution list the pros and cons. This will help you see the problem from various angles and choose the best possible solution. The best decisions are realized when you are able to see both sides of the problem and the possible options for each.
Step 4: Choose Possible Solutions
Begin by throwing out any solutions that are obviously ineffective or impractical. Next, look at your remaining solutions and determine which ones are the most likely to be successful by examining them in-depth. This can be done by examining the strengths and weaknesses of each solution.
Oftentimes, you will come up with new solutions during this stage. You might even find that a combination of multiple solutions is better than any, one idea.
Now, choose one of the possible solutions that look likely to work, based on the advantages and disadvantages.
Life Skill Tip: If you are having a hard time thinking of the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, ask yourself these questions:
- Is this a short-term or a long-term
- How likely am I to follow through with this solution?
- How will this solution affect other people?
The goal here is to use critical thinking to learn how to make good decisions. The problem-solving worksheet pack will help you with every step of the process.
Step 5: create step-by-step plan.
There is so much to consider in this step! To ensure you follow through with your solution, it is best to think of how and when it will be implemented. Without doing so, solutions that are difficult might be avoided, or they can slip your mind when the time comes. Also, make sure you are creating steps that are positive choices that ultimately lead to a responsible decision. The step-by-step decision-making process is also an exercise in self-control and patience for kids, as it requires them to slow down and contemplate the potential consequences of their actions before they actually take them.
Plan out step-by-step what you need to do to carry out the chosen solution. Some solutions can happen at a specific time, like 2:00 pm on Wednesday. Others require something unpredictable to happen, like when I get overwhelmed or angry.
If your solution can be scheduled, you will want to create your step-by-step plan considering these questions
- When will you implement your solution? Be specific.
- How will you remember to follow through with your solution?
- List the specific steps you will take to implement your solution.
If your solution is in response to something, you will want to create your step-by-step plan considering these ideas:
- How will you know when to use your solution? List specific warning signs, triggers, or other specific events that will tip you off.
- List the specific steps you will take to implement your solution.
Finally, you want to also consider these questions as you finish up your step-by-step strategic problem-solving plan.
- Do you see any other way you can get around those problems?
- Is this a realistic and achievable plan?
Life Skill Tip: If your solution requires a lot of time or effort, try to break the process into small steps. It’s easier to follow through with several small steps, rather than one giant task.
Step 6: Carry Out Your Plan
Do it! Carry out the plan. If it is helpful and isn’t too awkward, have your list of steps with you so you remember what to do. Take a deep breath and implement your strategic problem-solving plan! You got this!
Step 7: Review Results
Finally, after implementing your solution, you will review what worked and what didn’t. Answer these questions:
- Was it helpful?
- Did you achieve what you set out to achieve? If not, how could you have done it differently?
- Did you achieve any progress, however small, towards your goal?
- What have you learned?
Step 8: Consider Your Next Steps
If you achieved your goal – consider tackling the next step of your original problem. If you didn’t fully achieve your goal – make adjustments to your chosen solution, or return to steps 3 and 4 and choose another possible solution.
Even if your problem was a one-time situation, there are often broader lessons to be learned. Take a moment to reflect on your problem and how you handled it. Specifically, answer these questions:
- In what way was your solution effective?
- In what ways was your solution not effective?
- If you could go back in time, what would you change about how you handled the problem?
- What advice would you give to someone else who was dealing with the same problem?
Tackle problems Like A Pro With The Complete Decision-Making and Problem-Solving Worksheet Pack
The Strategic ProblemSolving Worksheet pack includes the PDF version of this blog post and the 6-page worksheet pack to collect all your thoughts and ideas as you solve life’s big and little problems. The complete worksheet pack is helpful for all ages. Younger homeschoolers will need more help processing and brainstorming ideas and solutions, while older students and adults can work independently. However, a good conversation with a trusted friend or family member is always helpful when solving difficult situations.
Get your Decision-Making and Problem-Solving Worksheet Pack Here
If you have a coupon code, use it at checkout.

check it Out! Decision-Making and Problem-Solving Worksheet – FREE Checklist!

Get the Checklist!
You can unsubscribe anytime. For more details, review our Privacy Policy.
Confirm you would like to receive this download & email updates.
Your download is on its way!
You may also enjoy

The latest on the Blog
- Let’s Study Famous Folks – April Calendar Of Famous People
- Let’s Study Famous Folks – March Calendar of Famous People
- Printable Cornell Note Taking Template | High School
- Summer Mission Trips for Teens: 2024 Planning Guide
- Let’s Study Famous Folks – February Calendar Of Famous People

- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
KidsKonnect
Reading Comprehension Cause and Effect Context Clues Compare and Contrast
Noun Worksheets Writing Prompts Compound Words Figurative Language
The Wizard of Oz Hans Christian Andersen Types of Writing Text Structure
Literary Devices
Alliteration Hyperbole Metaphor Irony
Subject Verb Agreement Poetry Climax Rhyme
View all reading worksheets
Action Verbs Tragedy Transition Words Phonics
View all writing worksheets
Dramatic Irony Cacophony Anaphora Setting
View all literature worksheets
Abbreviations Transition Words Conclusion Situational Irony
View all literary device worksheets
Women’s History
Inspirational Women Women's History Month First Lady of the US Women's Equality Day International Women's Day
View all Women's History worksheets
American Revolution
American Revolution Patriots & Loyalists Patrick Henry Sons of Liberty
View all American Revolution worksheets
US Constitution US Independence Trail of Tears The Pilgrims
View all US History worksheets
Ancient History
Ancient China Ancient Mayan Ancient Rome Ancient Aztec
View all Ancient History worksheets
World History
Roaring Twenties Industrial Revolution Middle Ages The Renaissance
View all World History worksheets
Famous Wars
World War 1 World War 2 Vietnam War American Civil War
View all Famous War worksheets
Anne Frank Sally Ride Neil Armstrong Christopher Columbus
View all famous figure worksheets
Joe Biden Donald Trump Abraham Lincoln George Washington
View all President worksheets
Roald Dahl Dr Seuss JK Rowling Michael Morpurgo
View all author worksheets
Civil Rights
Rosa Parks Sojourner Truth Medger Evers Martin Luther King
Elvis Presley Johann Sebastian Bach Ella Fitzgerald Wolfgang Mozart
View all musician worksheets
Thomas Edison Albert Einstein Henry Ford Wright Brothers
View all inventor worksheets
Muhammad Ali Michael Jordan Jackie Robinson Jesse Owens
View all athlete worksheets
Nat Turner Ruby Bridges Harriet Tubman Booker T Washington Malcolm X
View all civil rights worksheets
Natural Wonders
River Nile Mount Everest Sahara Desert Mount Etna Ancient Pyramids Amazon River
Landmarks/Sights
Mount Rushmore Statue Of Liberty White House Stonehenge Great Wall of China Santa Fe Trail
New York Texas South Carolina Alaska Nevada Ohio
Australia United Kingdom China Canada Argentina Brazil
Mount Fuji Mississippi River Rocky Mountains Volcano Glacier The Great Barrier Reef
View all natural wonders worksheets
Hoover Dam Bermuda Triangle Leaning Tower Of Pisa Arc De Triomphe Golden Gate Bridge Colosseum
View all landmark worksheets
California Colorado Indiana Florida Washington Georgia
View all US state worksheets
Poland Greece Philippines Japan France India
View all country worksheets
April Topics
April Fools’ Day World Autism Awareness Day International Children’s Book Day Passover Eid Al-Fitr Ramadan Patriots’ Day Rama Navami Earth Day World Book Day
View all Seasonal worksheets
Social Emotional Learning
Morals and Values Self Management Ethics Depression Relationship Skills Self-Awareneess Self-Esteem Emotions and Feelings Goal-Setting Interpersonal Skills
View all Social-Emotional Learning worksheets
Celebrations
Easter Saint Patrick’s Day Valentines Day Chinese New Year Rosh Hashanah Thanksgiving Flag Day Cinco de Mayo Beginning Of Lent Yom Kippur View all Celebrations worksheets
Remembrance
Pearl Harbor Day Veterans’ Day Memorial Day Battle Of The Somme D-Day 9/11 Anzac Day Martin Luther King Jr. Day International Women’s Day Victoria Day View all Remembrance worksheets
Camels Fox Bears Penguin Wolf Beavers Mountain Lion Red Panda Snow Leopard White Tigers Silverback Gorilla Okapi
View all mammal worksheets
Marine Life
Crabs Starfish Fish Octopus Great White Shark Dolphin Walrus Narwhal Megalodon Shark Killer Whale Beluga Whale Lionfish
View all marine life worksheets
Insects/Invertebrates/Reptiles
Millipede Praying Mantis Ladybug Ants Spider Iguana Chameleon Komodo Dragon Lizard Bearded Dragon Gila Monster Snakes
View all insect worksheets
Eagle Peregrine Falcon Snowy Owl Emu Woodpecker Albatross Swan Quail Bald Eagle Hummingbird Peacock
View all Bird worksheets
Natural World
Avalanche Flood Tsunami Natural Disasters Fossils Ice Age
View all natural world worksheets
Earth Sciences
Water Cycle Global Warming Deciduous Forests Hurricane Sandy Hurricane Katrina Global Warming
View all earth science worksheets
Food Chain Fossils Photosynthesis Cells Ecosystem Plants
View all biology worksheets
Solar System Black Holes Eclipse Stars and Constellations The Moon Comets
View all space worksheets
Chemistry/Physics
Magnetism Graduated Cylinders Solid, Liquid, Gas Gravity Light Sound
View all science worksheets
Kangaroo Horse Bear Lion Lizard Octopus
View all animal worksheets
Addition Sentences Single Digital Addition Two-Digit Addition Three Digit Addition Repeated Addition
View all Addition Worksheets
Ordinal Numbers Cardinal Numbers Rounding Numbers Odd & Even Numbers Comparing Numbers
View all Numbers Worksheets
Counting Money Subtracting Money Change Money Coin Name & Value Calculate Change (Money)
View all Money Worksheets
Number Line Single Digit Subtraction Place Value Subtraction Sentences Input & Output Tables
View all Math Worksheets
Decision-Making Facts & Worksheets
Decision-making is a cognitive process involving thought, logic, planning, and problem-solving. it is a skill that can be trained., search for worksheets, download the decision-making facts & worksheets.
Click the button below to get instant access to these worksheets for use in the classroom or at a home.
Download This Worksheet
This download is exclusively for KidsKonnect Premium members! To download this worksheet, click the button below to signup (it only takes a minute) and you'll be brought right back to this page to start the download! Sign Me Up
Edit This Worksheet
Editing resources is available exclusively for KidsKonnect Premium members. To edit this worksheet, click the button below to signup (it only takes a minute) and you'll be brought right back to this page to start editing! Sign Up
This worksheet can be edited by Premium members using the free Google Slides online software. Click the Edit button above to get started.
Download This Sample
This sample is exclusively for KidsKonnect members! To download this worksheet, click the button below to signup for free (it only takes a minute) and you'll be brought right back to this page to start the download! Sign Me Up
Table of Contents
Decisions are something we make every day. It may seem automatic, but it’s an important cognitive process that can be trained. Decision-making varies from minor to major and spans the personal, family, relationships, and life in general. Decision-making is a process that requires thought, planning, and logic to anticipate the outcomes.
See the fact file below for more information on Decision-Making, or you can download our 28-page Decision-Making worksheet pack to utilize within the classroom or home environment.
Key Facts & Information
Understanding decision-making.
- Psychology defines decision-making as a cognitive process of selecting particular pathways that will lead to various outcomes.
- Every decision-making process will lead to a final choice. Although, this choice may or may not be acted upon, and this is where consequences lie.
- For example, say you are hungry. You can decide to act on it or not. If you act, you will not be hungry anymore. But if you decide not to act on it, you will continue to be hungry. This is called a consequence – the end result of a decision.
- To add another layer to it, if you decide to eat, you can choose a healthy snack or an unhealthy snack. These too will have future consequences.
- According to CASEL (Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning), responsible decision-making is the ability to make constructive choices about behavior and social interactions based on ethical standards, safety concerns, and social norms.
- Decision-making can also be thought of as problem-solving. At first, you are presented with a problem. You then need to think about and analyze the problem to build ideas and create steps about how to solve it.
- Deciding on choices can be driven by two things – rational thinking, which is being guided by facts and reason, compared to irrational thinking, which is driven without any rational considerations.
- Choices that need to be decided upon range from small and inconsequential, like whether to have vanilla or chocolate ice cream, to much more consequential. For example, if a friend asks you to take part in risky behavior, that decision can have lifelong consequences. Or, when it comes to choosing your career path, what college will you need to go to, what grades will you need to get, and what subjects will you need to take.
- This is why it’s important to develop decision-making skills; firstly so that you feel more in control about your life, secondly so that you’re making the best decisions to get to the best possible outcome, and thirdly so that you can manage feelings of being overwhelmed, stressed, anxious, disappointed, or afraid.
- While it’s easy to see decision-making as black and white, as either positive or negative, it can also be neutral. Responsible decision-making doesn’t mean that choices or decisions made always need to be right or perfect, and that mistakes need to be avoided. It’s about the ability to adapt and adjust the flow of decision-making based on the outcome.
- In learning to be better with decision-making, you’ll become more self-aware and consider your surroundings and the future.
- It also gives you a greater sense of acknowledgement, validation, and the ability to manage your feelings when making choices.
What Type of a Decision-Maker Are You?
Charismatic decision-maker.
- You are open to new ideas and are up for challenges.
- You welcome the latest proposals backed up by data and facts.
- Charismatic decision-makers are results-oriented.
Snap Decision-Maker
- This type of decision-maker makes choices without thinking about the situation.
- They never consider the results and only react to the current situation.
No Decision
- Many young people fall into this category.
- You let other people decide for you because you are afraid of making mistakes or being responsible for the outcome.
- Followers make effective decisions that are already implemented and proven successful.
- You use documented results and facts as the basis for making the right choices.
Responsible Decision-Maker
- You consider the consequences of your choices and how they can affect you and your surroundings.
Steps in Making Decisions
Identify the problem or situation.
- First, recognize the problem and determine how difficult it is to solve.
- What is the problem/situation?
- Why am I solving this problem?
- Why and how important is it that I should solve it?
- Who can be affected by this problem?
- How long will it take to solve the problem?
- What is the problem? I have a sticky ice cream wrapper, but there is no trash can in the park.
- Why am I solving this problem/situation? I don’t want to carry the wrapper, but littering is bad for the environment.
- Why and how important is it that I should solve it? If I throw the wrapper on the ground, I am contributing to polluting the environment.
- Who can be affected by this problem? Myself, my community, and the natural environment will be affected by my decision to litter.
- How long will it take to solve? A temporary solution will take a few minutes until a trash can is found. The longer solution is speaking to your town authority.
Analyze the Situation and Gather Information
- After identifying the problem, you must be able to analyze why the issue existed.
- You can gather the information that you need to make the proper decisions.
Brainstorming
- Discuss the possible solutions to the dilemma.
- You can use different methods to come up with solutions.
- These solutions need evaluation when implemented to identify the consequences that may arise.
Take Note of Ethics and Responsibilities
- You must also be able to foresee your action’s ethical and moral consequences.
- For example, if you are tempted to steal candy from a store, you should consider the ethical and moral effects of what you do.
Take Action and Learn to Evaluate and Reflect
- After making the decision, you must be able to evaluate and reflect on your choices.
- Whether the decision resulted in a positive or negative outcome, you should be able to recognize it and reflect on what went well and what can be improved.
- For example, if you did not do well on an important test because you did not pay attention or revise, you have to accept the results of performing poorly. You can’t be angry or disappointed if you did not even try.
Challenges in Making Responsible Decisions
- Determining the problem is one thing, and making responsible decisions is another.
- Even though the problem is identified and options for solutions are laid out, some challenges can be experienced while trying to implement it.
- Information overload or analysis paralysis can be a challenge.
- You may have all the information you need, but it could be overwhelming and confusing.
- Being under-informed is another challenge because it would make it hard for you to create solutions without the proper information.
- If the problem is misidentified, even if there are solutions, there could be other problems that can come from it.
- The answers to the problem must always be as realistic as possible.
- Making impulse decisions can also lead to improperly managing these challenges.
- Some people forget to follow up on the solutions to their problems.
- Decision-makers should be able to review solutions to assess whether their decisions are right or must be improved.
Knowing Your Students
- For teachers, it will help you guide your students if you know how capable they are of making responsible decisions.
- The student recognizes well when they encounter a problem.
- Being able to analyze where the problem started.
- Explore a variety of options and their consequences.
- The student can face their problems morally and ethically.
- The student takes their time to evaluate how successfully their problem was identified, assessed, and solved.
- It is difficult for them to think about the parts of the problem.
- The solutions are all impulsive, and the student did not consider the consequences of their acts.
- The student has difficulties with social communication, so their problems are not easily recognized.
- Experiences challenges on other options for their solutions.
- Teachers can brainstorm with students in creating a visual representation of the process of constructive decision-making to remind them of how to make effective choices.
- Create activities that will stimulate and practice the decision-making skills of the students.
- Explain the definition of a responsibility and ethical responsibility.
- Give students tools with which they can identify the ethical and moral responsibilities associated with their decisions.
Tips on Making Quality Decisions
- Making responsible decisions is not always an easy task because you have to consider a lot of things.
- First, do not let stress get to you. Tough choices can be overwhelming and can make you feel anxious and stressed. These feelings may lead you to impulsive decisions or an unsolved problem. When you feel anxious or stressed, it is advisable to pause and relax before making decisions.
- Decisions made under pressure are usually not the best options. Give yourself enough time to think about the problem and process options.
- Go over the pros and cons of your options.
- When making decisions, always take into consideration your goals and values.
- Consider all possibilities and consequences of your options.
- It is also healthy to seek guidance from another person.
- Keep track of your feelings and experiences while solving the problem. Keeping a diary can help you.
- If you see that there will be negative feedback to your solution, prepare how you would respond to people kindly and in a way they can understand.
- You can go through your options again whenever you are facing doubts. The first option might be a good one but be open to the possibility of changes.
Decision-Making Worksheets
This fantastic bundle includes everything you need to know about Decision-Making across 28 in-depth pages. These are ready-to-use worksheets that are perfect for teaching kids about Responsible Decision-Making , which is a cognitive process involving thought, planning, and logic to anticipate the outcomes.
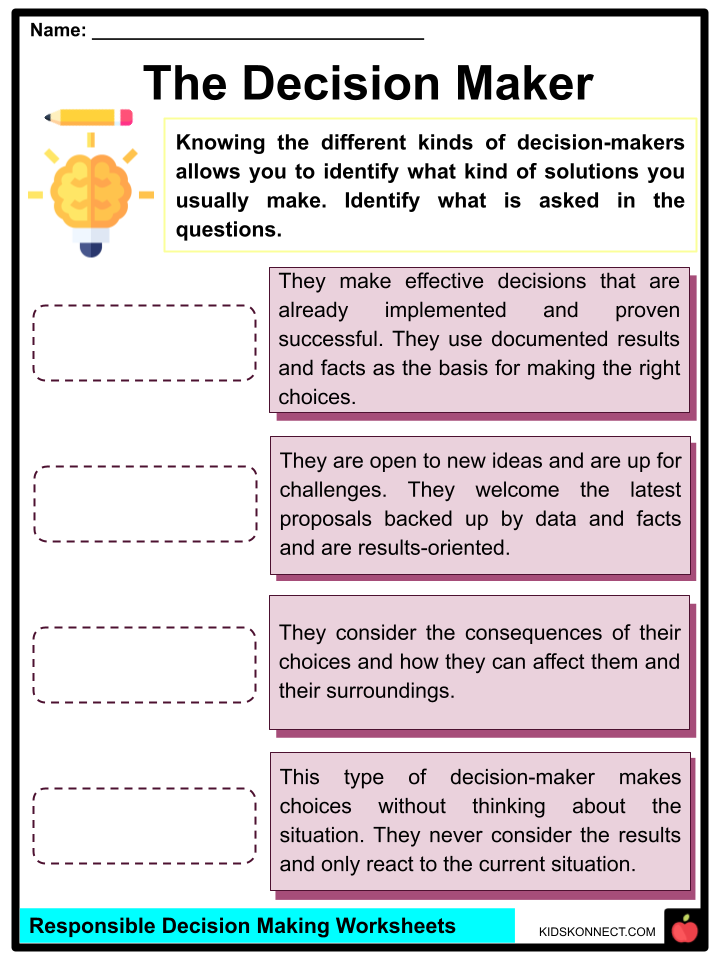
Complete List of Included Worksheets
Below is a list of all the worksheets included in this document.
- Responsible Decision Making
- The Decision Maker
- A Piece of Advice
- Considerate Decisions
- Step By Step
- Take Me Back
- The Party Planner
- Rating Myself
- Tough Decisions
- Tips From Me
Link/cite this page
If you reference any of the content on this page on your own website, please use the code below to cite this page as the original source.
Link will appear as Decision-Making Facts & Worksheets: https://kidskonnect.com - KidsKonnect, November 30, 2022
Use With Any Curriculum
These worksheets have been specifically designed for use with any international curriculum. You can use these worksheets as-is, or edit them using Google Slides to make them more specific to your own student ability levels and curriculum standards.
Related Resources
KidsKonnect is a growing library of high-quality, printable worksheets for teachers and homeschoolers.
Home Facts Privacy About Blog Contact Terms
Safe & Secure
We pride ourselves on being a safe website for both teachers and students. KidsKonnect uses a secure SSL connection to encrypt your data and we only work with trusted payment processors Stripe and PayPal.
Worksheets For Responsible Decision Making and Social Problem Solving

What educators are saying
Also included in.

Description
Use these 20 worksheets to help students develop responsible decision making skills like considering consequences, ethical dilemmas, social problem solving and more. They are a great tool for students who could benefit from learning to think through the choices they make.
They are aligned to the CASEL framework for responsible decision making and are the perfect addition to your individual, small group and classroom lessons!
This resource is part of a SEL worksheet bundle including worksheet sets for other concepts in the CASEL framework.
**********************************************************************************************************************************
What’s Included :
- 6 Worksheets about making positive choices
- 6 Social problem solving worksheets
- 6 Worksheets to help students think through the impact and consequences of their choices
- 2 Worksheets to help kids learn about how their choices can improve their communities
- Answer Keys When Applicable
Ideas For Use:
- To align your lessons and activities with the CASEL (Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning) framework.
- To help students learn positive decision making skills
- In lessons focused on self control, social problem solving, etc.
- This resource was designed for students in grades 4-6, but. can be adapted for students who are slightly older or younger.
If you are satisfied with this resource, please leave feedback. If there is something I can improve upon, please e-mail me at [email protected] and I will do my best to accommodate you.
Check out these other resources you are sure to love:
- Self Awareness Worksheets
- No Prep Friendship Small Group
For more updates on my new products:
Follow me on Teachers Pay Teachers!
Follow me on Pinterest!
Follow me on Facebook!
Follow me on Instagram!
To read the terms of use and copyright information for this resource, please click here.
Questions & Answers
Counselor chelsey.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think

COMMENTS
Worksheet: Decision-Making / Problem-Solving When we think about making changes, most of us don't really consider all "sides" in a complete way. Instead, we often do what we "should" do, avoid doing things we don't feel like doing, or just feel confused or overwhelmed and give up thinking about it at all.
worksheet. Guide your clients and groups through the problem solving process with the help of the Problem Solving Packet. Each page covers one of five problem solving steps with a rationale, tips, and questions. The steps include defining the problem, generating solutions, choosing one solution, implementing the solution, and reviewing the ...
Decision-making Encourage better decision-making through an improved understanding of the consequences of decisions and the value and likelihood of different outcomes. ... Problem-Solving worksheet. Imagining an existing or potential problem and working through how to resolve it can be a powerful exercise for the client.
This series of 15 worksheets has been thoughtfully designed to help students understand and practice the process of decision-making. Each worksheet focuses on different aspects of decision-making, providing guidance, prompts, and exercises to enhance students' critical thinking and problem-solving skills. The worksheets in this series cover ...
Next, they will prioritize the different options and list them in order based on the solution they believe will best solve the problem. Step 5: Make A Choice. Once children thoroughly evaluate the alternatives, they are ready to make a choice. The choice may be the solution at the top of their priority list in Step 4.
This Decision-Making Unit is part of a complete social emotional learning curriculum to support kids and young adults learn critical SEL skills. Specific SEL skills targeted include responsibility, values and morals, owning your choices, problem-solving skills, ethical decisions, peer influence, hea
Worksheet for Problem Solving and Decision Making. Identify and briefly describe a problem you are currently trying to solve in your work. You will follow the CIDER process below to address your problem. C- Clarify the problem. I - Identify ideas and possibilities. D- Decide on actions. E- Execute the plan. R- Review and evaluate outcomes.
These 25 no prep social problem solving worksheets helps students to learn to solve problems instead of just reacting to them. Students will learn and practice using a 4 step proc
4.8. (98) $5.00. PDF. These 25 no prep social problem solving worksheets helps students to learn to solve problems instead of just reacting to them. Students will learn and practice using a 4 step process to solve problems that they face in every day life. These will help students learn to make better choices both at school and at home and can ...
4. Decision-Making & Integrity Activities. In this decision-making activity, students are asked to respond at give separate prompts over decision-making and managing negative emotions. This activity is the perfect way in practice decision-making while also building upon essential skills in reading plus writings.
Decision making skills worksheets for elementary students can be seamlessly incorporated into lessons across various academic subjects through practical activities like: English/Language Arts: Analyze the motivations, values, and choices of characters in novels using a printable template. Discuss alternates.
There are many simple ways to infuse problem-solving thinking and reflection into program activities: Articulate differences and connections. Identify emotions behind actions. Brainstorm different approaches or solutions to a task. Explore possible consequences. Model and articulate decision-making process. Reflect on past experiences.
Decision-making worksheets: Decision-making is a crucial aspect of problem solving. These worksheets focus on helping us make informed decisions by considering the pros and cons of different options. Critical thinking worksheets: Critical thinking is an essential skill in problem solving. These worksheets encourage us to think deeply and ...
Consider your own behavior, as well as external factors. Define your problem. Be as clear and comprehensive as possible. If there are many parts to your problem, describe each of them. TIP: If you find it difficult to separate your emotions from the problem, try to complete this step from the perspective of an impartial friend.
After reviewing the model, what would you say are your problem-solving strengths and weaknesses? What is one thing you can do to start improving your problem-solving skills? •STOP! Picture a stop sign in your head or say (silently) 'stop' to yourself •Don't do something you may regret •Be quiet, get space, calm down, relax STOP •Ask ...
Successful decision making and problem solving are at the heart of all effective teams. While teams are ultimately led by their managers, the most effective ones foster these skills at all levels. The exercises in this article show how you can encourage teams to develop their creative thinking, leadership , and communication skills , while ...
The Strategic ProblemSolving Worksheet pack includes the PDF version of this blog post and the 6-page worksheet pack to collect all your thoughts and ideas as you solve life's big and little problems. The complete worksheet pack is helpful for all ages. Younger homeschoolers will need more help processing and brainstorming ideas and solutions ...
Decision-Making Worksheets. This fantastic bundle includes everything you need to know about Decision-Making across 28 in-depth pages. These are ready-to-use worksheets that are perfect for teaching kids about Responsible Decision-Making, which is a cognitive process involving thought, planning, and logic to anticipate the outcomes.
24 Problem-Solving Therapy DECISION-MAKING WORKSHEET 1. List your alternatives below. 2. For each idea, rate the likelihood that (a) it will help solve the problem; (b) you can carry this idea out optimally; (c) it will have positive imme-diate consequences; and (d) it will have positive long-term consequences. Use a scale of "minus"
Use these 20 worksheets to help students develop responsible decision making skills like considering consequences, ethical dilemmas, social problem solving and more. They are a great tool for students who could benefit from learning to think through the choices they make. They are aligned to the CASEL framework for responsible decision making ...
Decision Making helps us to deal constructively with decisions about our lives. It teaches people how to make decisions about their actions in relation to a healthy assessment of different options and what effects these different decisions are likely to have. Problem Solving helps us to deal constructively with problems in our lives.
About This Quiz & Worksheet. The questions in this quiz and worksheet gauge how much you know about decision making and problem solving for managers. For example, you should understand what it ...