Research Paper Guide
Types Of Qualitative Research

8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
16 min read
People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper
Are you overwhelmed by the multitude of qualitative research methods available? It's no secret that choosing the right approach can leave you stuck at the starting line of your research.
Selecting an unsuitable method can lead to wasted time, resources, and potentially skewed results. But with so many options to consider, it's easy to feel lost in the complexities of qualitative research.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explain the types of qualitative research, their unique characteristics, advantages, and best use cases for each method.
Let's dive in!

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
- 1. What is Qualitative Research?
- 2. Types of Qualitative Research Methods
- 3. Types of Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
What is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is a robust and flexible methodology used to explore and understand complex phenomena in-depth.
Unlike quantitative research , qualitative research dives into the rich and complex aspects of human experiences, behaviors, and perceptions.
At its core, this type of research question seek to answer for:
- Why do people think or behave a certain way?
- What are the underlying motivations and meanings behind actions?
- How do individuals perceive and interpret the world around them?
This approach values context, diversity, and the unique perspectives of participants.
Rather than seeking generalizable findings applicable to a broad population, qualitative research aims for detailed insights, patterns, and themes that come from the people being studied.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research possesses the following characteristics:
- Subjective Perspective: Qualitative research explores subjective experiences, emphasizing the uniqueness of human behavior and opinions.
- In-Depth Exploration: It involves deep investigation, allowing a comprehensive understanding of specific phenomena.
- Open-Ended Questions: Qualitative research uses open-ended questions to encourage detailed, descriptive responses.
- Contextual Understanding: It emphasizes the importance of understanding the research context and setting.
- Rich Descriptions: Qualitative research produces rich, descriptive findings that contribute to a nuanced understanding of the topic.
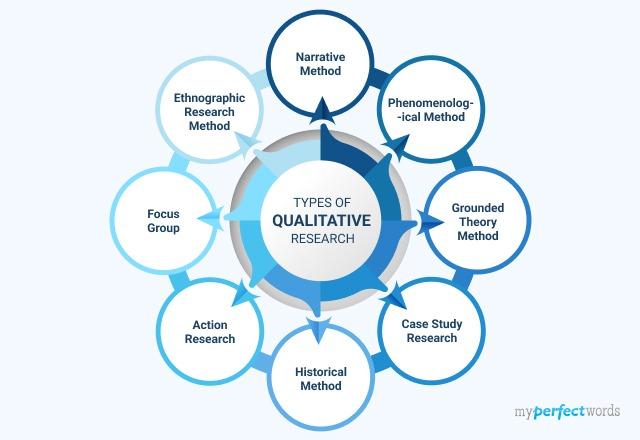
Types of Qualitative Research Methods
Researchers collect data on the targeted population, place, or event by using different types of qualitative research analysis.
Each qualitative research method offers a distinct perspective, enabling researchers to reveal concealed meanings, patterns, and valuable insights.
Below are the most commonly used qualitative research types for writing a paper.
Ethnographic Research Method
Ethnography, a subfield of anthropology, provides a scientific approach to examining human societies and cultures. It ranks among the most widely employed qualitative research techniques.
In ethnographic field notes, researchers actively engage with the environment and live alongside the focus group.
This immersive interaction allows researchers to gain insights into the objectives, motivations, challenges, and distinctive cultural attributes of the individuals under study.
Key cultural characteristics that ethnography helps to illustrate encompass:
- Geographical Location
- Religious Practices
- Tribal Systems
- Shared Experiences
Unlike traditional survey and interview-based research methods, ethnographers don't rely on structured questioning.
Instead, they become observers within the community, emphasizing participant observation over an extended period. However, it may also be appropriate to complement observations with interviews of individuals who possess knowledge of the culture.
Ethnographic research can present challenges if the researcher is unfamiliar with the social norms and language of the group being studied.
Furthermore, interpretations made by outsiders may lead to misinterpretations or confusion. Therefore, thorough validation of data is essential before presenting findings.
Narrative Method
The narrative research design unfolds over an extended period to compile data, much like crafting a cohesive story. Similar to a narrative structure, it begins with a starting point and progresses through various life situations.
In this method, researchers engage in in-depth interviews and review relevant documents. They explore events that have had a significant impact on an individual's personality and life journey. Interviews may occur over weeks, months, or even years, depending on the depth and scope of the narrative being studied.
The outcome of narrative research is the presentation of a concise story that captures essential themes, conflicts, and challenges. It provides a holistic view of the individual's experiences, both positive and negative, which have shaped their unique narrative.
Phenomenological Method
The term "phenomenological" pertains to the study of phenomena, which can encompass events, situations, or experiences.
This method is ideal for examining a subject from multiple perspectives and contributing to existing knowledge, with a particular focus on subjective experiences.
Researchers employing the phenomenological method use various data collection techniques, including interviews, site visits, observations, surveys, and document reviews.
These methods help gather rich and diverse data about the phenomenon under investigation.
A central aspect of this technique is capturing how participants experience events or activities, delving into their subjective viewpoints. Ultimately, the research results in the creation of a thematic database that validates the findings and offers insights from the subject's perspective.
Grounded Theory Method
A grounded theory approach differs from a phenomenological study in that it seeks to explain, provide reasons for, or develop theories behind an event or phenomenon.
It serves as a means to construct new theories by systematically collecting and analyzing data related to a specific phenomenon.
Researchers employing the grounded theory method utilize a variety of data collection techniques, including observation, interviews, literature review , and the analysis of relevant documents.
The focus of content analysis is not individual behaviors but a specific phenomenon or incident.
This method typically involves various coding techniques and large sample sizes to identify themes and develop more comprehensive theories.
Case Study Research
The case study approach entails a comprehensive examination of a subject over an extended period, with a focus on providing detailed insights into the subject, which can be an event, person, business, or place.
Data for case studies is collected from diverse sources, including interviews, direct observation, historical records, and documentation.
Case studies find applications across various disciplines, including law, education, medicine, and the sciences. They can serve both descriptive and explanatory purposes, making them a versatile research methodology .
Researchers often turn to the case study method when they want to explore:
- 'How' and 'why' research questions
- Behaviors under observation
- Understanding a specific phenomenon
- The contextual factors influencing the phenomena
Historical Method
The historical method aims to describe and analyze past events, offering insights into present patterns and the potential to predict future scenarios.
Researchers formulate research questions based on a hypothetical idea and then rigorously test this idea using multiple historical resources.
Key steps in the historical method include:
- Developing a research idea
- Identifying appropriate sources such as archives and libraries
- Ensuring the reliability and validity of these sources
- Creating a well-organized research outline
- Systematically collecting research data
The analysis phase involves critically assessing the collected data, accepting or rejecting it based on credibility, and identifying any conflicting evidence.
Ultimately, the outcomes of the historical method are presented in the form of a biography or a scholarly paper that provides a comprehensive account of the research findings.
Action Research
Action research is a dynamic research approach focused on addressing practical challenges in real-world settings while simultaneously conducting research to improve the situation.
It follows a cyclic process, starting with the identification of a specific issue or problem in a particular context.
The key steps in action research include:
- Planning and implementing actions to address the issue
- Collecting data during the action phase to understand its impact
- Reflecting on the data and analyzing it to gain insights
- Adjusting the action plan based on the analysis
This process may be iterative, with multiple cycles of action and reflection.
The outcomes of action research are practical solutions and improved practices that directly benefit the context in which the research is conducted. Additionally, it leads to a deeper and more nuanced understanding of the issue under investigation.
Focus Groups
Focus groups are a qualitative research method used to gather in-depth insights and perspectives on a specific topic or research question.
This approach involves assembling a small group of participants who possess relevant knowledge or experiences related to the research focus.
Key steps in the focus group method include:
- Selecting participants
- Moderating the discussion
- Structuring the conversation around open-ended questions
- Collecting data through audio or video recordings and note-taking
The discussion is dynamic and interactive, encouraging participants to share their thoughts, experiences, and opinions.
The analysis phase involves reviewing the data collected from the focus group discussion to identify common themes, patterns, and valuable insights. Focus groups provide rich qualitative data that offer a deeper and more nuanced understanding of the research topic or question.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Types of Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research employs different data analysis methods, each suited to specific research goals:
- Thematic Analysis: Identifies recurring themes or concepts within data.
- Content Analysis: Systematically categorizes and quantifies text or media content.
- Narrative Analysis: Focuses on storytelling and narrative elements in data.
- Grounded Theory Analysis: Develops or refines theories based on data.
- Discourse Analysis: Examines language and communication patterns.
- Framework Analysis: Organizes data using predefined categories.
- Visual Analysis: Interprets visual data like photos or videos.
- Cross-case Analysis: Compares patterns across multiple cases.
The choice depends on research questions and data type, enhancing understanding and insights.
Benefits of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers valuable advantages, including:
- Flexibility: Adaptable to various research questions and settings.
- Holistic Approach: Explores multiple dimensions of phenomena.
- Theory Development: Contributes to theory creation or refinement.
- Participant Engagement: Fosters active participant involvement.
- Complements Quantitative Research: Provides a comprehensive understanding.
All in all, different types of qualitative research methodology can assist in understanding the behavior and motivations of people. Similarly, it will also help in generating original ideas and formulating a better research problem.
However, not everyone can write a good research paper. Thus, if you get stuck at any stage, you can get professional help.
MyPerfectWords.com is the best paper writing service, where you can hire a professional writer for all your ' do my essay ' requests.
We assure you that you will receive high-quality paper at the most reasonable rates.
Contact our team with your " pay for my research paper " queries. We are available 24/7!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
- Privacy Policy

Home » Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people’s beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and significance of social phenomena, and it typically involves a more flexible and iterative approach to data collection and analysis compared to quantitative research. Qualitative research is often used in fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education.
Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research Methods are as follows:
One-to-One Interview
This method involves conducting an interview with a single participant to gain a detailed understanding of their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. One-to-one interviews can be conducted in-person, over the phone, or through video conferencing. The interviewer typically uses open-ended questions to encourage the participant to share their thoughts and feelings. One-to-one interviews are useful for gaining detailed insights into individual experiences.
Focus Groups
This method involves bringing together a group of people to discuss a specific topic in a structured setting. The focus group is led by a moderator who guides the discussion and encourages participants to share their thoughts and opinions. Focus groups are useful for generating ideas and insights, exploring social norms and attitudes, and understanding group dynamics.
Ethnographic Studies
This method involves immersing oneself in a culture or community to gain a deep understanding of its norms, beliefs, and practices. Ethnographic studies typically involve long-term fieldwork and observation, as well as interviews and document analysis. Ethnographic studies are useful for understanding the cultural context of social phenomena and for gaining a holistic understanding of complex social processes.
Text Analysis
This method involves analyzing written or spoken language to identify patterns and themes. Text analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative text analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Text analysis is useful for understanding media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
This method involves an in-depth examination of a single person, group, or event to gain an understanding of complex phenomena. Case studies typically involve a combination of data collection methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case. Case studies are useful for exploring unique or rare cases, and for generating hypotheses for further research.
Process of Observation
This method involves systematically observing and recording behaviors and interactions in natural settings. The observer may take notes, use audio or video recordings, or use other methods to document what they see. Process of observation is useful for understanding social interactions, cultural practices, and the context in which behaviors occur.
Record Keeping
This method involves keeping detailed records of observations, interviews, and other data collected during the research process. Record keeping is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data, and for providing a basis for analysis and interpretation.
This method involves collecting data from a large sample of participants through a structured questionnaire. Surveys can be conducted in person, over the phone, through mail, or online. Surveys are useful for collecting data on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, and for identifying patterns and trends in a population.
Qualitative data analysis is a process of turning unstructured data into meaningful insights. It involves extracting and organizing information from sources like interviews, focus groups, and surveys. The goal is to understand people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations
Qualitative Research Analysis Methods
Qualitative Research analysis methods involve a systematic approach to interpreting and making sense of the data collected in qualitative research. Here are some common qualitative data analysis methods:
Thematic Analysis
This method involves identifying patterns or themes in the data that are relevant to the research question. The researcher reviews the data, identifies keywords or phrases, and groups them into categories or themes. Thematic analysis is useful for identifying patterns across multiple data sources and for generating new insights into the research topic.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing the content of written or spoken language to identify key themes or concepts. Content analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative content analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Content analysis is useful for identifying patterns in media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
Discourse Analysis
This method involves analyzing language to understand how it constructs meaning and shapes social interactions. Discourse analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, and narrative analysis. Discourse analysis is useful for understanding how language shapes social interactions, cultural norms, and power relationships.
Grounded Theory Analysis
This method involves developing a theory or explanation based on the data collected. Grounded theory analysis starts with the data and uses an iterative process of coding and analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data. The theory or explanation that emerges is grounded in the data, rather than preconceived hypotheses. Grounded theory analysis is useful for understanding complex social phenomena and for generating new theoretical insights.
Narrative Analysis
This method involves analyzing the stories or narratives that participants share to gain insights into their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. Narrative analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as structural analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. Narrative analysis is useful for understanding how individuals construct their identities, make sense of their experiences, and communicate their values and beliefs.
Phenomenological Analysis
This method involves analyzing how individuals make sense of their experiences and the meanings they attach to them. Phenomenological analysis typically involves in-depth interviews with participants to explore their experiences in detail. Phenomenological analysis is useful for understanding subjective experiences and for developing a rich understanding of human consciousness.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing and contrasting data across different cases or groups to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can be used to identify patterns or themes that are common across multiple cases, as well as to identify unique or distinctive features of individual cases. Comparative analysis is useful for understanding how social phenomena vary across different contexts and groups.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has many applications across different fields and industries. Here are some examples of how qualitative research is used:
- Market Research: Qualitative research is often used in market research to understand consumer attitudes, behaviors, and preferences. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with consumers to gather insights into their experiences and perceptions of products and services.
- Health Care: Qualitative research is used in health care to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education: Qualitative research is used in education to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. Researchers conduct classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work : Qualitative research is used in social work to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : Qualitative research is used in anthropology to understand different cultures and societies. Researchers conduct ethnographic studies and observe and interview members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : Qualitative research is used in psychology to understand human behavior and mental processes. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy : Qualitative research is used in public policy to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
How to Conduct Qualitative Research
Here are some general steps for conducting qualitative research:
- Identify your research question: Qualitative research starts with a research question or set of questions that you want to explore. This question should be focused and specific, but also broad enough to allow for exploration and discovery.
- Select your research design: There are different types of qualitative research designs, including ethnography, case study, grounded theory, and phenomenology. You should select a design that aligns with your research question and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Recruit participants: Once you have your research question and design, you need to recruit participants. The number of participants you need will depend on your research design and the scope of your research. You can recruit participants through advertisements, social media, or through personal networks.
- Collect data: There are different methods for collecting qualitative data, including interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis. You should select the method or methods that align with your research design and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Analyze data: Once you have collected your data, you need to analyze it. This involves reviewing your data, identifying patterns and themes, and developing codes to organize your data. You can use different software programs to help you analyze your data, or you can do it manually.
- Interpret data: Once you have analyzed your data, you need to interpret it. This involves making sense of the patterns and themes you have identified, and developing insights and conclusions that answer your research question. You should be guided by your research question and use your data to support your conclusions.
- Communicate results: Once you have interpreted your data, you need to communicate your results. This can be done through academic papers, presentations, or reports. You should be clear and concise in your communication, and use examples and quotes from your data to support your findings.
Examples of Qualitative Research
Here are some real-time examples of qualitative research:
- Customer Feedback: A company may conduct qualitative research to understand the feedback and experiences of its customers. This may involve conducting focus groups or one-on-one interviews with customers to gather insights into their attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
- Healthcare : A healthcare provider may conduct qualitative research to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education : An educational institution may conduct qualitative research to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. This may involve conducting classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work: A social worker may conduct qualitative research to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : An anthropologist may conduct qualitative research to understand different cultures and societies. This may involve conducting ethnographic studies and observing and interviewing members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : A psychologist may conduct qualitative research to understand human behavior and mental processes. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy: A government agency or non-profit organization may conduct qualitative research to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. This may involve conducting focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
Purpose of Qualitative Research
The purpose of qualitative research is to explore and understand the subjective experiences, behaviors, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to provide in-depth, descriptive information that can help researchers develop insights and theories about complex social phenomena.
Qualitative research can serve multiple purposes, including:
- Exploring new or emerging phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring new or emerging phenomena, such as new technologies or social trends. This type of research can help researchers develop a deeper understanding of these phenomena and identify potential areas for further study.
- Understanding complex social phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring complex social phenomena, such as cultural beliefs, social norms, or political processes. This type of research can help researchers develop a more nuanced understanding of these phenomena and identify factors that may influence them.
- Generating new theories or hypotheses: Qualitative research can be useful for generating new theories or hypotheses about social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data about individuals’ experiences and perspectives, researchers can develop insights that may challenge existing theories or lead to new lines of inquiry.
- Providing context for quantitative data: Qualitative research can be useful for providing context for quantitative data. By gathering qualitative data alongside quantitative data, researchers can develop a more complete understanding of complex social phenomena and identify potential explanations for quantitative findings.
When to use Qualitative Research
Here are some situations where qualitative research may be appropriate:
- Exploring a new area: If little is known about a particular topic, qualitative research can help to identify key issues, generate hypotheses, and develop new theories.
- Understanding complex phenomena: Qualitative research can be used to investigate complex social, cultural, or organizational phenomena that are difficult to measure quantitatively.
- Investigating subjective experiences: Qualitative research is particularly useful for investigating the subjective experiences of individuals or groups, such as their attitudes, beliefs, values, or emotions.
- Conducting formative research: Qualitative research can be used in the early stages of a research project to develop research questions, identify potential research participants, and refine research methods.
- Evaluating interventions or programs: Qualitative research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or programs by collecting data on participants’ experiences, attitudes, and behaviors.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is characterized by several key features, including:
- Focus on subjective experience: Qualitative research is concerned with understanding the subjective experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Researchers aim to explore the meanings that people attach to their experiences and to understand the social and cultural factors that shape these meanings.
- Use of open-ended questions: Qualitative research relies on open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed, in-depth responses. Researchers seek to elicit rich, descriptive data that can provide insights into participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Sampling-based on purpose and diversity: Qualitative research often involves purposive sampling, in which participants are selected based on specific criteria related to the research question. Researchers may also seek to include participants with diverse experiences and perspectives to capture a range of viewpoints.
- Data collection through multiple methods: Qualitative research typically involves the use of multiple data collection methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation. This allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data from multiple sources, which can provide a more complete picture of participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Inductive data analysis: Qualitative research relies on inductive data analysis, in which researchers develop theories and insights based on the data rather than testing pre-existing hypotheses. Researchers use coding and thematic analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data and to develop theories and explanations based on these patterns.
- Emphasis on researcher reflexivity: Qualitative research recognizes the importance of the researcher’s role in shaping the research process and outcomes. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their own biases and assumptions and to be transparent about their role in the research process.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers several advantages over other research methods, including:
- Depth and detail: Qualitative research allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data that provides a deeper understanding of complex social phenomena. Through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation, researchers can gather detailed information about participants’ experiences and perspectives that may be missed by other research methods.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research is a flexible approach that allows researchers to adapt their methods to the research question and context. Researchers can adjust their research methods in real-time to gather more information or explore unexpected findings.
- Contextual understanding: Qualitative research is well-suited to exploring the social and cultural context in which individuals or groups are situated. Researchers can gather information about cultural norms, social structures, and historical events that may influence participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Participant perspective : Qualitative research prioritizes the perspective of participants, allowing researchers to explore subjective experiences and understand the meanings that participants attach to their experiences.
- Theory development: Qualitative research can contribute to the development of new theories and insights about complex social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data and using inductive data analysis, researchers can develop new theories and explanations that may challenge existing understandings.
- Validity : Qualitative research can offer high validity by using multiple data collection methods, purposive and diverse sampling, and researcher reflexivity. This can help ensure that findings are credible and trustworthy.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research also has some limitations, including:
- Subjectivity : Qualitative research relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers, which can introduce bias into the research process. The researcher’s perspective, beliefs, and experiences can influence the way data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
- Limited generalizability: Qualitative research typically involves small, purposive samples that may not be representative of larger populations. This limits the generalizability of findings to other contexts or populations.
- Time-consuming: Qualitative research can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant resources for data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Resource-intensive: Qualitative research may require more resources than other research methods, including specialized training for researchers, specialized software for data analysis, and transcription services.
- Limited reliability: Qualitative research may be less reliable than quantitative research, as it relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers. This can make it difficult to replicate findings or compare results across different studies.
- Ethics and confidentiality: Qualitative research involves collecting sensitive information from participants, which raises ethical concerns about confidentiality and informed consent. Researchers must take care to protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants and obtain informed consent.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.4 Types of qualitative research designs
Learning objectives.
- Define focus groups and outline how they differ from one-on-one interviews
- Describe how to determine the best size for focus groups
- Identify the important considerations in focus group composition
- Discuss how to moderate focus groups
- Identify the strengths and weaknesses of focus group methodology
- Describe case study research, ethnography, and phenomenology.
There are various types of approaches to qualitative research. This chapter presents information about focus groups, which are often used in social work research. It also introduces case studies, ethnography, and phenomenology.
Focus Groups
Focus groups resemble qualitative interviews in that a researcher may prepare a guide in advance and interact with participants by asking them questions. But anyone who has conducted both one-on-one interviews and focus groups knows that each is unique. In an interview, usually one member (the research participant) is most active while the other (the researcher) plays the role of listener, conversation guider, and question-asker. Focus groups , on the other hand, are planned discussions designed to elicit group interaction and “obtain perceptions on a defined area of interest in a permissive, nonthreatening environment” (Krueger & Casey, 2000, p. 5). In focus groups, the researcher play a different role than in a one-on-one interview. The researcher’s aim is to get participants talking to each other, to observe interactions among participants, and moderate the discussion.

There are numerous examples of focus group research. In their 2008 study, for example, Amy Slater and Marika Tiggemann (2010) conducted six focus groups with 49 adolescent girls between the ages of 13 and 15 to learn more about girls’ attitudes towards’ participation in sports. In order to get focus group participants to speak with one another rather than with the group facilitator, the focus group interview guide contained just two questions: “Can you tell me some of the reasons that girls stop playing sports or other physical activities?” and “Why do you think girls don’t play as much sport/physical activity as boys?” In another focus group study, Virpi Ylanne and Angie Williams (2009) held nine focus group sessions with adults of different ages to gauge their perceptions of how older characters are represented in television commercials. Among other considerations, the researchers were interested in discovering how focus group participants position themselves and others in terms of age stereotypes and identities during the group discussion. In both examples, the researchers’ core interest in group interaction could not have been assessed had interviews been conducted on a one-on-one basis, making the focus group method an ideal choice.
Who should be in your focus group?
In some ways, focus groups require more planning than other qualitative methods of data collection, such as one-on-one interviews in which a researcher may be better able to the dialogue. Researchers must take care to form focus groups with members who will want to interact with one another and to control the timing of the event so that participants are not asked nor expected to stay for a longer time than they’ve agreed to participate. The researcher should also be prepared to inform focus group participants of their responsibility to maintain the confidentiality of what is said in the group. But while the researcher can and should encourage all focus group members to maintain confidentiality, she should also clarify to participants that the unique nature of the group setting prevents her from being able to promise that confidentiality will be maintained by other participants. Once focus group members leave the research setting, researchers cannot control what they say to other people.

Group size should be determined in part by the topic of the interview and your sense of the likelihood that participants will have much to say without much prompting. If the topic is one about which you think participants feel passionately and will have much to say, a group of 3–5 could make sense. Groups larger than that, especially for heated topics, can easily become unmanageable. Some researchers say that a group of about 6–10 participants is the ideal size for focus group research (Morgan, 1997); others recommend that groups should include 3–12 participants (Adler & Clark, 2008). The size of the focus group is ultimately the decision of the researcher. When forming groups and deciding how large or small to make them, take into consideration what you know about the topic and participants’ potential interest in, passion for, and feelings about the topic. Also consider your comfort level and experience in conducting focus groups. These factors will help you decide which size is right in your particular case.
It may seem counterintuitive, but in general, it is better to form focus groups consisting of participants who do not know one another than to create groups consisting of friends, relatives, or acquaintances (Agar & MacDonald, 1995). The reason is that group members who know each other may not share some taken-for-granted knowledge or assumptions. In research, it is precisely the taken-for-granted knowledge that is often of interest; thus, the focus group researcher should avoid setting up interactions where participants may be discouraged to question or raise issues that they take for granted. However, group members should not be so different from one another that participants will be unlikely to feel comfortable talking with one another.
Focus group researchers must carefully consider the composition of the groups they put together. In his text on conducting focus groups, Morgan (1997) suggests that “homogeneity in background and not homogeneity in attitudes” (p. 36) should be the goal, since participants must feel comfortable speaking up but must also have enough differences to facilitate a productive discussion. Whatever composition a researcher designs for her focus groups, the important point to keep in mind is that focus group dynamics are shaped by multiple social contexts (Hollander, 2004). Participants’ silences as well as their speech may be shaped by gender, race, class, sexuality, age, or other background characteristics or social dynamics—all of which might be suppressed or exacerbated depending on the composition of the group. Hollander (2004) suggests that researchers must pay careful attention to group composition, must be attentive to group dynamics during the focus group discussion, and should use multiple methods of data collection in order to “untangle participants’ responses and their relationship to the social contexts of the focus group” (p. 632).
The role of the moderator
In addition to the importance of group composition, focus groups also require skillful moderation. A moderator is the researcher tasked with facilitating the conversation in the focus group. Participants may ask each other follow-up questions, agree or disagree with one another, display body language that tells us something about their feelings about the conversation, or even come up with questions not previously conceived of by the researcher. It is just these sorts of interactions and displays that are of interest to the researcher. A researcher conducting focus groups collects data on more than people’s direct responses to her question, as in interviews.
The moderator’s job is not to ask questions to each person individually, but to stimulate conversation between participants. It is important to set ground rules for focus groups at the outset of the discussion. Remind participants you’ve invited them to participate because you want to hear from all of them. Therefore, the group should aim to let just one person speak at a time and avoid letting just a couple of participants dominate the conversation. One way to do this is to begin the discussion by asking participants to briefly introduce themselves or to provide a brief response to an opening question. This will help set the tone of having all group members participate. Also, ask participants to avoid having side conversations; thoughts or reactions to what is said in the group are important and should be shared with everyone.
As the focus group gets rolling, the moderator will play a less active role as participants talk to one another. There may be times when the conversation stagnates or when you, as moderator, wish to guide the conversation in another direction. In these instances, it is important to demonstrate that you’ve been paying attention to what participants have said. Being prepared to interject statements or questions such as “I’d really like to hear more about what Sunil and Joe think about what Dominick and Jae have been saying” or “Several of you have mentioned X. What do others think about this?” will be important for keeping the conversation going. It can also help redirect the conversation, shift the focus to participants who have been less active in the group, and serve as a cue to those who may be dominating the conversation that it is time to allow others to speak. Researchers may choose to use multiple moderators to make managing these various tasks easier.
Moderators are often too busy working with participants to take diligent notes during a focus group. It is helpful to have a note-taker who can record participants’ responses (Liamputtong, 2011). The note-taker creates, in essence, the first draft of interpretation for the data in the study. They note themes in responses, nonverbal cues, and other information to be included in the analysis later on. Focus groups are analyzed in a similar way as interviews; however, the interactive dimension between participants adds another element to the analytical process. Researchers must attend to the group dynamics of each focus group, as “verbal and nonverbal expressions, the tactical use of humour, interruptions in interaction, and disagreement between participants” are all data that are vital to include in analysis (Liamputtong, 2011, p. 175). Note-takers record these elements in field notes, which allows moderators to focus on the conversation.
Strengths and weaknesses of focus groups
Focus groups share many of the strengths and weaknesses of one-on-one qualitative interviews. Both methods can yield very detailed, in-depth information; are excellent for studying social processes; and provide researchers with an opportunity not only to hear what participants say but also to observe what they do in terms of their body language. Focus groups offer the added benefit of giving researchers a chance to collect data on human interaction by observing how group participants respond and react to one another. Like one-on-one qualitative interviews, focus groups can also be quite expensive and time-consuming. However, there may be some savings with focus groups as it takes fewer group events than one-on-one interviews to gather data from the same number of people. Another potential drawback of focus groups, which is not a concern for one-on-one interviews, is that one or two participants might dominate the group, silencing other participants. Careful planning and skillful moderation on the part of the researcher are crucial for avoiding, or at least dealing with, such possibilities. The various strengths and weaknesses of focus group research are summarized in Table 91.
Grounded Theory
Grounded theory has been widely used since its development in the late 1960s (Glaser & Strauss, 1967). Largely derived from schools of sociology, grounded theory involves emersion of the researcher in the field and in the data. Researchers follow a systematic set of procedures and a simultaneous approach to data collection and analysis. Grounded theory is most often used to generate rich explanations of complex actions, processes, and transitions. The primary mode of data collection is one-on-one participant interviews. Sample sizes tend to range from 20 to 30 individuals, sampled purposively (Padgett, 2016). However, sample sizes can be larger or smaller, depending on data saturation. Data saturation is the point in the qualitative research data collection process when no new information is being discovered. Researchers use a constant comparative approach in which previously collected data are analyzed during the same time frame as new data are being collected. This allows the researchers to determine when new information is no longer being gleaned from data collection and analysis — that data saturation has been reached — in order to conclude the data collection phase.
Rather than apply or test existing grand theories, or “Big T” theories, grounded theory focuses on “small t” theories (Padgett, 2016). Grand theories, or “Big T” theories, are systems of principles, ideas, and concepts used to predict phenomena. These theories are backed up by facts and tested hypotheses. “Small t” theories are speculative and contingent upon specific contexts. In grounded theory, these “small t” theories are grounded in events and experiences and emerge from the analysis of the data collected.
One notable application of grounded theory produced a “small t” theory of acceptance following cancer diagnoses (Jakobsson, Horvath, & Ahlberg, 2005). Using grounded theory, the researchers interviewed nine patients in western Sweden. Data collection and analysis stopped when saturation was reached. The researchers found that action and knowledge, given with respect and continuity led to confidence which led to acceptance. This “small t” theory continues to be applied and further explored in other contexts.
Case study research
Case study research is an intensive longitudinal study of a phenomenon at one or more research sites for the purpose of deriving detailed, contextualized inferences and understanding the dynamic process underlying a phenomenon of interest. Case research is a unique research design in that it can be used in an interpretive manner to build theories or in a positivist manner to test theories. The previous chapter on case research discusses both techniques in depth and provides illustrative exemplars. Furthermore, the case researcher is a neutral observer (direct observation) in the social setting rather than an active participant (participant observation). As with any other interpretive approach, drawing meaningful inferences from case research depends heavily on the observational skills and integrative abilities of the researcher.
Ethnography
The ethnographic research method, derived largely from the field of anthropology, emphasizes studying a phenomenon within the context of its culture. The researcher must be deeply immersed in the social culture over an extended period of time (usually 8 months to 2 years) and should engage, observe, and record the daily life of the studied culture and its social participants within their natural setting. The primary mode of data collection is participant observation, and data analysis involves a “sense-making” approach. In addition, the researcher must take extensive field notes, and narrate her experience in descriptive detail so that readers may experience the same culture as the researcher. In this method, the researcher has two roles: rely on her unique knowledge and engagement to generate insights (theory), and convince the scientific community of the trans-situational nature of the studied phenomenon.
The classic example of ethnographic research is Jane Goodall’s study of primate behaviors, where she lived with chimpanzees in their natural habitat at Gombe National Park in Tanzania, observed their behaviors, interacted with them, and shared their lives. During that process, she learnt and chronicled how chimpanzees seek food and shelter, how they socialize with each other, their communication patterns, their mating behaviors, and so forth. A more contemporary example of ethnographic research is Myra Bluebond-Langer’s (1996)14 study of decision making in families with children suffering from life-threatening illnesses, and the physical, psychological, environmental, ethical, legal, and cultural issues that influence such decision-making. The researcher followed the experiences of approximately 80 children with incurable illnesses and their families for a period of over two years. Data collection involved participant observation and formal/informal conversations with children, their parents and relatives, and health care providers to document their lived experience.
Phenomenology
Phenomenology is a research method that emphasizes the study of conscious experiences as a way of understanding the reality around us. Phenomenology is concerned with the systematic reflection and analysis of phenomena associated with conscious experiences, such as human judgment, perceptions, and actions, with the goal of (1) appreciating and describing social reality from the diverse subjective perspectives of the participants involved, and (2) understanding the symbolic meanings (“deep structure”) underlying these subjective experiences. Phenomenological inquiry requires that researchers eliminate any prior assumptions and personal biases, empathize with the participant’s situation, and tune into existential dimensions of that situation, so that they can fully understand the deep structures that drives the conscious thinking, feeling, and behavior of the studied participants.
Some researchers view phenomenology as a philosophy rather than as a research method. In response to this criticism, Giorgi and Giorgi (2003) developed an existential phenomenological research method to guide studies in this area. This method can be grouped into data collection and data analysis phases. In the data collection phase, participants embedded in a social phenomenon are interviewed to capture their subjective experiences and perspectives regarding the phenomenon under investigation. Examples of questions that may be asked include “can you describe a typical day” or “can you describe that particular incident in more detail?” These interviews are recorded and transcribed for further analysis. During data analysis, the researcher reads the transcripts to: (1) get a sense of the whole, and (2) establish “units of significance” that can faithfully represent participants’ subjective experiences. Examples of such units of significance are concepts such as “felt space” and “felt time,” which are then used to document participants’ psychological experiences. For instance, did participants feel safe, free, trapped, or joyous when experiencing a phenomenon (“felt-space”)? Did they feel that their experience was pressured, slow, or discontinuous (“felt-time”)? Phenomenological analysis should take into account the participants’ temporal landscape (i.e., their sense of past, present, and future), and the researcher must transpose herself in an imaginary sense in the participant’s situation (i.e., temporarily live the participant’s life). The participants’ lived experience is described in form of a narrative or using emergent themes. The analysis then delves into these themes to identify multiple layers of meaning while retaining the fragility and ambiguity of subjects’ lived experiences.
Key Takeaways
- In terms of focus group composition, homogeneity of background among participants is recommended while diverse attitudes within the group are ideal.
- The goal of a focus group is to get participants to talk with one another rather than the researcher.
- Like one-on-one qualitative interviews, focus groups can yield very detailed information, are excellent for studying social processes, and provide researchers with an opportunity to observe participants’ body language; they also allow researchers to observe social interaction.
- Focus groups can be expensive and time-consuming, as are one-on-one interviews; there is also the possibility that a few participants will dominate the group and silence others in the group.
- Other types of qualitative research include case studies, ethnography, and phenomenology.
- Data saturation – the point in the qualitative research data collection process when no new information is being discovered
- Focus groups- planned discussions designed to elicit group interaction and “obtain perceptions on a defined area of interest in a permissive, nonthreatening environment” (Krueger & Casey, 2000, p. 5)
- Moderator- the researcher tasked with facilitating the conversation in the focus group
Image attributions
target group by geralt CC-0
workplace team by Free-Photos CC-0
Foundations of Social Work Research Copyright © 2020 by Rebecca L. Mauldin is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Qualitative Research Methods: Types, Analysis + Examples
Qualitative research is based on the disciplines of social sciences like psychology, sociology, and anthropology. Therefore, the qualitative research methods allow for in-depth and further probing and questioning of respondents based on their responses. The interviewer/researcher also tries to understand their motivation and feelings. Understanding how your audience makes decisions can help derive conclusions in market research.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is defined as a market research method that focuses on obtaining data through open-ended and conversational communication .
This method is about “what” people think and “why” they think so. For example, consider a convenience store looking to improve its patronage. A systematic observation concludes that more men are visiting this store. One good method to determine why women were not visiting the store is conducting an in-depth interview method with potential customers.
For example, after successfully interviewing female customers and visiting nearby stores and malls, the researchers selected participants through random sampling . As a result, it was discovered that the store didn’t have enough items for women.
So fewer women were visiting the store, which was understood only by personally interacting with them and understanding why they didn’t visit the store because there were more male products than female ones.
Gather research insights
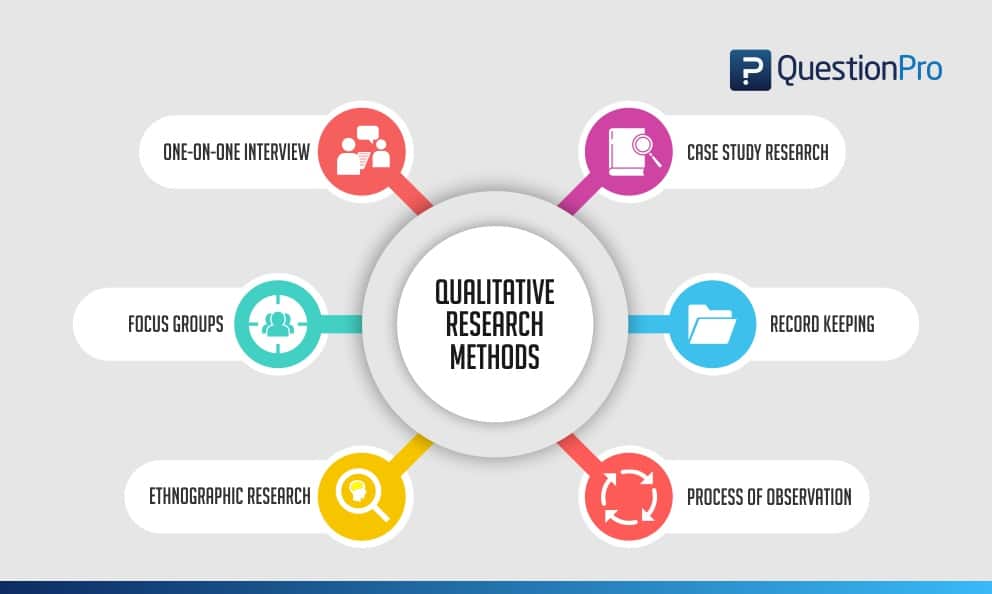
Types of qualitative research methods with examples
Qualitative research methods are designed in a manner that helps reveal the behavior and perception of a target audience with reference to a particular topic. There are different types of qualitative research methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, ethnographic research, content analysis, and case study research that are usually used.
The results of qualitative methods are more descriptive, and the inferences can be drawn quite easily from the obtained data .
Qualitative research methods originated in the social and behavioral research sciences. Today, our world is more complicated, and it is difficult to understand what people think and perceive. Online research methods make it easier to understand that as it is a more communicative and descriptive analysis .
The following are the qualitative research methods that are frequently used. Also, read about qualitative research examples :

1. One-on-one interview
Conducting in-depth interviews is one of the most common qualitative research methods. It is a personal interview that is carried out with one respondent at a time. This is purely a conversational method and invites opportunities to get details in depth from the respondent.
One of the advantages of this method is that it provides a great opportunity to gather precise data about what people believe and their motivations . If the researcher is well experienced, asking the right questions can help him/her collect meaningful data. If they should need more information, the researchers should ask such follow-up questions that will help them collect more information.
These interviews can be performed face-to-face or on the phone and usually can last between half an hour to two hours or even more. When the in-depth interview is conducted face to face, it gives a better opportunity to read the respondents’ body language and match the responses.
2. Focus groups
A focus group is also a commonly used qualitative research method used in data collection. A focus group usually includes a limited number of respondents (6-10) from within your target market.
The main aim of the focus group is to find answers to the “why, ” “what,” and “how” questions. One advantage of focus groups is you don’t necessarily need to interact with the group in person. Nowadays, focus groups can be sent an online survey on various devices, and responses can be collected at the click of a button.
Focus groups are an expensive method as compared to other online qualitative research methods. Typically, they are used to explain complex processes. This method is very useful for market research on new products and testing new concepts.
3. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research is the most in-depth observational research method that studies people in their naturally occurring environment.
This method requires the researchers to adapt to the target audiences’ environments, which could be anywhere from an organization to a city or any remote location. Here, geographical constraints can be an issue while collecting data.
This research design aims to understand the cultures, challenges, motivations, and settings that occur. Instead of relying on interviews and discussions, you experience the natural settings firsthand.
This type of research method can last from a few days to a few years, as it involves in-depth observation and collecting data on those grounds. It’s a challenging and time-consuming method and solely depends on the researcher’s expertise to analyze, observe, and infer the data.
4. Case study research
T he case study method has evolved over the past few years and developed into a valuable quality research method. As the name suggests, it is used for explaining an organization or an entity.
This type of research method is used within a number of areas like education, social sciences, and similar. This method may look difficult to operate; however , it is one of the simplest ways of conducting research as it involves a deep dive and thorough understanding of the data collection methods and inferring the data.
5. Record keeping
This method makes use of the already existing reliable documents and similar sources of information as the data source. This data can be used in new research. This is similar to going to a library. There, one can go over books and other reference material to collect relevant data that can likely be used in the research.
6. Process of observation
Qualitative Observation is a process of research that uses subjective methodologies to gather systematic information or data. Since the focus on qualitative observation is the research process of using subjective methodologies to gather information or data. Qualitative observation is primarily used to equate quality differences.
Qualitative observation deals with the 5 major sensory organs and their functioning – sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing. This doesn’t involve measurements or numbers but instead characteristics.
Explore Insightfully Contextual Inquiry in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research: data collection and analysis
A. qualitative data collection.
Qualitative data collection allows collecting data that is non-numeric and helps us to explore how decisions are made and provide us with detailed insight. For reaching such conclusions the data that is collected should be holistic, rich, and nuanced and findings to emerge through careful analysis.
- Whatever method a researcher chooses for collecting qualitative data, one aspect is very clear the process will generate a large amount of data. In addition to the variety of methods available, there are also different methods of collecting and recording the data.
For example, if the qualitative data is collected through a focus group or one-to-one discussion, there will be handwritten notes or video recorded tapes. If there are recording they should be transcribed and before the process of data analysis can begin.
- As a rough guide, it can take a seasoned researcher 8-10 hours to transcribe the recordings of an interview, which can generate roughly 20-30 pages of dialogues. Many researchers also like to maintain separate folders to maintain the recording collected from the different focus group. This helps them compartmentalize the data collected.
- In case there are running notes taken, which are also known as field notes, they are helpful in maintaining comments, environmental contexts, environmental analysis , nonverbal cues etc. These filed notes are helpful and can be compared while transcribing audio recorded data. Such notes are usually informal but should be secured in a similar manner as the video recordings or the audio tapes.
B. Qualitative data analysis
Qualitative data analysis such as notes, videos, audio recordings images, and text documents. One of the most used methods for qualitative data analysis is text analysis.
Text analysis is a data analysis method that is distinctly different from all other qualitative research methods, where researchers analyze the social life of the participants in the research study and decode the words, actions, etc.
There are images also that are used in this research study and the researchers analyze the context in which the images are used and draw inferences from them. In the last decade, text analysis through what is shared on social media platforms has gained supreme popularity.
Characteristics of qualitative research methods

- Qualitative research methods usually collect data at the sight, where the participants are experiencing issues or research problems . These are real-time data and rarely bring the participants out of the geographic locations to collect information.
- Qualitative researchers typically gather multiple forms of data, such as interviews, observations, and documents, rather than rely on a single data source .
- This type of research method works towards solving complex issues by breaking down into meaningful inferences, that is easily readable and understood by all.
- Since it’s a more communicative method, people can build their trust on the researcher and the information thus obtained is raw and unadulterated.
Qualitative research method case study
Let’s take the example of a bookstore owner who is looking for ways to improve their sales and customer outreach. An online community of members who were loyal patrons of the bookstore were interviewed and related questions were asked and the questions were answered by them.
At the end of the interview, it was realized that most of the books in the stores were suitable for adults and there were not enough options for children or teenagers.
By conducting this qualitative research the bookstore owner realized what the shortcomings were and what were the feelings of the readers. Through this research now the bookstore owner can now keep books for different age categories and can improve his sales and customer outreach.
Such qualitative research method examples can serve as the basis to indulge in further quantitative research , which provides remedies.
When to use qualitative research
Researchers make use of qualitative research techniques when they need to capture accurate, in-depth insights. It is very useful to capture “factual data”. Here are some examples of when to use qualitative research.
- Developing a new product or generating an idea.
- Studying your product/brand or service to strengthen your marketing strategy.
- To understand your strengths and weaknesses.
- Understanding purchase behavior.
- To study the reactions of your audience to marketing campaigns and other communications.
- Exploring market demographics, segments, and customer care groups.
- Gathering perception data of a brand, company, or product.
LEARN ABOUT: Steps in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research methods vs quantitative research methods
The basic differences between qualitative research methods and quantitative research methods are simple and straightforward. They differ in:
- Their analytical objectives
- Types of questions asked
- Types of data collection instruments
- Forms of data they produce
- Degree of flexibility
LEARN MORE ABOUR OUR SOFTWARE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 20 Employee Engagement Software Solutions
May 3, 2024

15 Best Customer Experience Software of 2024
May 2, 2024

Journey Orchestration Platforms: Top 11 Platforms in 2024

Top 12 Employee Pulse Survey Tools Unlocking Insights in 2024
May 1, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- UConn Library
- Scientific Research and Communication
- Qualitative Research: What is it?
Scientific Research and Communication — Qualitative Research: What is it?
- Essential Resources
- The Scientific Method
- Types of Scientific Papers
- Organization of a Scientific Paper
- Peer Review & Academic Journals
- Primary and Secondary Sources
- Scientific Information Literacy
- Critical Reading Methods
- Scientific Writing Guidebooks
- Science Literature Reviews
- Searching Strategies for Science Databases
- Engineering Career Exploration
- Quantitative Research: What Is It?
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- AI Tools for Research
What is qualitative research?
"Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. [1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data."
"Qualitative research at its core, ask open-ended questions whose answers are not easily put into numbers such as ‘how’ and ‘why’. [2] Due to the open-ended nature of the research questions at hand, qualitative research design is often not linear in the same way quantitative design is. [2] One of the strengths of qualitative research is its ability to explain processes and patterns of human behavior that can be difficult to quantify. [3] Phenomena such as experiences, attitudes, and behaviors can be difficult to accurately capture quantitatively, whereas a qualitative approach allows participants themselves to explain how, why, or what they were thinking, feeling, and experiencing at a certain time or during an event of interest."
- Qualitative Study - Steven Tenny; Grace D. Brannan; Janelle M. Brannan; Nancy C. Sharts-Hopko. This article details what qualitative research is, and some of the methodologies used.
Examples of Qualitative Research

- Quantitative vs Qualitative Chart Chart showing examples of quantitative vs. qualitative research.
EBooks on Qualitative Research Methodology
Physical Library Books
- << Previous: Engineering Career Exploration
- Next: Quantitative Research: What Is It? >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 1:46 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/sciencecommunication
News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Research methods--quantitative, qualitative, and more: overview.
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Data Science Methods (Machine Learning, AI, Big Data)
- Text Mining and Computational Text Analysis
- Evidence Synthesis/Systematic Reviews
- Get Data, Get Help!
About Research Methods
This guide provides an overview of research methods, how to choose and use them, and supports and resources at UC Berkeley.
As Patten and Newhart note in the book Understanding Research Methods , "Research methods are the building blocks of the scientific enterprise. They are the "how" for building systematic knowledge. The accumulation of knowledge through research is by its nature a collective endeavor. Each well-designed study provides evidence that may support, amend, refute, or deepen the understanding of existing knowledge...Decisions are important throughout the practice of research and are designed to help researchers collect evidence that includes the full spectrum of the phenomenon under study, to maintain logical rules, and to mitigate or account for possible sources of bias. In many ways, learning research methods is learning how to see and make these decisions."
The choice of methods varies by discipline, by the kind of phenomenon being studied and the data being used to study it, by the technology available, and more. This guide is an introduction, but if you don't see what you need here, always contact your subject librarian, and/or take a look to see if there's a library research guide that will answer your question.
Suggestions for changes and additions to this guide are welcome!
START HERE: SAGE Research Methods
Without question, the most comprehensive resource available from the library is SAGE Research Methods. HERE IS THE ONLINE GUIDE to this one-stop shopping collection, and some helpful links are below:
- SAGE Research Methods
- Little Green Books (Quantitative Methods)
- Little Blue Books (Qualitative Methods)
- Dictionaries and Encyclopedias
- Case studies of real research projects
- Sample datasets for hands-on practice
- Streaming video--see methods come to life
- Methodspace- -a community for researchers
- SAGE Research Methods Course Mapping
Library Data Services at UC Berkeley
Library Data Services Program and Digital Scholarship Services
The LDSP offers a variety of services and tools ! From this link, check out pages for each of the following topics: discovering data, managing data, collecting data, GIS data, text data mining, publishing data, digital scholarship, open science, and the Research Data Management Program.
Be sure also to check out the visual guide to where to seek assistance on campus with any research question you may have!
Library GIS Services
Other Data Services at Berkeley
D-Lab Supports Berkeley faculty, staff, and graduate students with research in data intensive social science, including a wide range of training and workshop offerings Dryad Dryad is a simple self-service tool for researchers to use in publishing their datasets. It provides tools for the effective publication of and access to research data. Geospatial Innovation Facility (GIF) Provides leadership and training across a broad array of integrated mapping technologies on campu Research Data Management A UC Berkeley guide and consulting service for research data management issues

General Research Methods Resources
Here are some general resources for assistance:
- Assistance from ICPSR (must create an account to access): Getting Help with Data , and Resources for Students
- Wiley Stats Ref for background information on statistics topics
- Survey Documentation and Analysis (SDA) . Program for easy web-based analysis of survey data.
Consultants
- D-Lab/Data Science Discovery Consultants Request help with your research project from peer consultants.
- Research data (RDM) consulting Meet with RDM consultants before designing the data security, storage, and sharing aspects of your qualitative project.
- Statistics Department Consulting Services A service in which advanced graduate students, under faculty supervision, are available to consult during specified hours in the Fall and Spring semesters.
Related Resourcex
- IRB / CPHS Qualitative research projects with human subjects often require that you go through an ethics review.
- OURS (Office of Undergraduate Research and Scholarships) OURS supports undergraduates who want to embark on research projects and assistantships. In particular, check out their "Getting Started in Research" workshops
- Sponsored Projects Sponsored projects works with researchers applying for major external grants.
- Next: Quantitative Research >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 11:09 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/researchmethods
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Module 3 Chapter 2: Overview of Qualitative Traditions
In Chapter 1 you read about three different approaches to social work research: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods approaches. In this chapter we examine different traditions and methods commonly utilized in qualitative approaches to research. The qualitative research literature presents a wide array of approaches: ethnography, life histories, symbolic interactionism, grounded theory, phenomenology, hermeneutics/heuristic research, interpretivism, collaborative social research, social or cognitive anthropology, case studies, narrative inquiry, critical inquiry, participatory action research, content analysis, study of artifacts, and participant observation (Creswell & Poth, 2018). Here, we examine four of the five approaches identified by Creswell and Poth (2018), as well as two other approaches. You will read about:
- Narrative research
- Phenomenological research
- Grounded theory research
- Ethnographic research
- Participatory action research
- Content/artifact analysis research
Qualitative Research Approaches
Qualitative research approaches are most appropriately used when the nature of the research questions and study goals meet certain criteria (Padgett, 2008). These include:
- Relatively little is known or understood about the topic of interest
- The topic involves stigma and/or taboos, thereby lending itself to analysis with emotional depth and sensitivity (rather than quantifiable facts)
- The goal is to study and create meaning from the perspectives of individuals who have “lived the experiences” of study interest
- The goal is to understand processes, particularly complex processes, in social work problems and practices/interventions
- The goal is to interpret quantitative research results, particularly unexpected results
- Engaging in action or participatory research, involving social action or advocacy in combination with conducting the research.
Common across qualitative approaches is employing the “researcher-as-instrument” (Padgett, 2008, p. 17). Qualitative research results are heavily influenced by the experiences, perceptions, and personal qualities of the investigator. Thus, a critical component involves the investigator being reflective about the data, participants, analysis process, and results.
Narrative Research. Narrative research “begins with the experiences as expressed in lived and told stories of individuals” (Creswell & Poth, 2018). It is about both the nature of the expressed narratives and exploration of the contexts in which the narratives and narrators are situated. The method of gathering and interpreting these stories is called narrative inquiry . This is typically performed with one or a very few individuals being involved with any one study. The purpose is to learn the individual stories and their meaning to individuals.

Of great interest in narrative inquiry is how a story is presented by the individual: it is seldom presented in a simple, chronological manner. Instead, stories are often conveyed in terms of critical transitions or nodal events where “turning points” occur in a person’s lived experience. Narrative examples are present in biographies, autobiographies (autoethnography), and oral histories. For example, the movie documentary Whitney presents singer Whitney Houston’s stories and lived experiences as a performer, celebrity, and family member, including her relationship with alcohol and other drugs. Parts of the documentary are presented as others’ descriptions, parts are presented in her own words. The point is to better understand this person’s life.
A social work example of narrative inquiry is reported as one woman’s journey of recovery from mental illness (Thomas & Rickwood, 2016). Case interviews were conducted with a woman on three different occasions when she was (re)admitted to a residential mental health program. The woman’s narratives demonstrated changes over time in hope, self-identity, a meaningful life, and assuming responsibility for one’s own recovery. Furthermore, the investigators learned from the woman’s perspective what elements of the services provided were helpful in her road to recovery and that repeated admissions were less indicative of repeated failures and more about progress toward recovery.
Phenomenological Research . Like narrative research, phenomenological research involves recording the stories of individuals who experience a particular phenomenon or event of interest. Unlike narrative inquiry, however, phenomenology is about deriving or constructing a shared meaning about those events among a group of participants: the goal is “meaning making” (Oktay, 2012). The emphasis in this approach is placed on identifying what the participants and their shared stories have in common. The emerging phenomenological description is a composite description of the phenomenon.

Ideally, the investigator engages with a heterogeneous group of individuals, all of whom have experienced the phenomenon of interest. For example, if the phenomenon of interest is about the experiences of siblings to persons with intellectual disabilities, the investigator would want to engage with families of different ages, social or economic standing, religious and cultural background, sibling composition (numbers, genders, and spacing of siblings), and individuals with different types or severity of disability.
One example of this type of research is a qualitative study concerned with how trafficking affects the health and health care access among 15 women engaged in sex work in the red-light district (Kamathipura) of Mumbai, India (Karandikar, Gezinski, & Kaloga, 2016). The investigators worked with transcripts of interviews with the women, preserving the voice and language of the women who participated. They identified themes and relationships between themes in their coding of the data. Three themes were discussed in their manuscript: how participants first entered into sex work (all but two reported deception by family members, friends, or acquaintances as the pathway to prostitution); health problems experienced by the women (physical violence, sexually transmitted infection, alcohol addiction, tuberculosis, HIV infection, miscarriage, abortion, cough/cold, and malaria were most frequently reported as notable events); and, disparities in access to health care resulting from being captively held in isolation or seclusion to prevent escape from trafficking and stigma attached to sex work.
Grounded Theory Research. Grounded theory research develops theoretical explanations about a phenomenon or process being studied—in other words, moving beyond description to generating or discovering a theory (Creswell & Poth, 2018). The theory that emerges can then be tested using other approaches and methods to determine its generalizability. The name of this approach comes from the theory being “grounded” in the data, rather than the data being used to test a theory that has been presented “off the shelf” (Creswell & Poth, 2018, p. 82). This approach, first described as a unified approach by Glaser and Strauss (1967), is particularly relevant to social work:
Because grounded theory creates theories that are derived directly from real-world settings, it has the potential to produce theories that can be used by social workers to guide practice. This theory can also be used to develop theoretically based interventions that can be tested in practice settings. In fact, when grounded theory was developed, the authors envisioned a collaborative venture between researchers and practitioners to test and adapt the theory in practice settings” (Oktay, 2012, p. 5).
Grounded theory as an approach utilizes abductive reasoning, moving back and forth in an iterative manner between data gathering and analysis processes, including inductive and deductive logic in generating and cross-checking, testing the emerging theory (Oktay, 2012). Thus, theories grow from the grounded base of real-world data. The approach is heavily influenced by the discipline of sociology, but is used to inform other professions like social work and nursing. Study participants in grounded theory research are purposively selected because of their ability to provide relevant data.

An example of the grounded theory approach in use was presented in a study of professional decision-making processes undertaken by social workers in child protection roles (Kettle, 2018). Based on 22 interviews with social workers in Scotland, the investigator explored social workers’ own perceptions of negotiating delicate balances between the interests of children and adults; the past, present, and future; functioning as an investigator versus building a relationship; getting too close versus not close enough; and, having power over versus power together. Also studied was the nature of their transactions and exchanges with other professionals. Emerging theory emphasized social workers’ internal mental processes over rational-technical solutions for practice decisions, the role of perceived responsibility in degree of cooperation between professionals, and social workers’ perceptions of different family strategies for managing closeness of and power in their relationships with the social worker.
Ethnographic Research. Like the qualitative approaches that we have explored so far, ethnographic research aims to understand phenomena from the perspectives of those experiencing it. However, there exists a major difference: the unit of analysis in ethnographic research is a collective group where the individuals interact with one another and have shared, common experiences. As a result, the individuals become a “culture-sharing group” by virtue of the “shared patterns of behavior, beliefs and language” that they develop (Creswell & Poth, 2018, p. 90). Ethnographic research focuses on cultural systems, “operating on several levels simultaneously to infer the tacit rules of the culture or subculture from the myriad of actions and interactions being witnessed” (Padgett, 2008, p. 32). The approach is strongly influenced by the discipline of anthropology, but is critically important as an option for social work to understand diverse populations, social work problems, and social phenomena.

Helm (2016) described an ethnographic study of how practice decisions are made within and across a team of social workers when the judgments are made under conditions of subjectivity and uncertainty, and when the available information is incomplete, inconclusive, or possibly contested. The aim of the study conducted in Scotland was to learn about “sense-making” under these circumstances, with attention directed to how this becomes a shared activity, rather than an individual activity. The study participants included a single team manager, four team leaders acting as supervisors, and six social workers from the larger team of professionals working at the study location. Data were collected through the investigator’s direct,non-participatory observation of team member behavior, including what was said in the normal course of practice ( naturalistic observation ). The observation notes were coded for themes, the two strongest being “making sense through ‘framing’ the situation” and “constructing responsibility” (Helm, 2016, p. 29). Social work practitioners were observed to discuss cases with others, usually by opening the discussion with a framing statement, which then guided the discussion; for example, framing it in terms of the worker’s own feelings about a case situation. Marked differences were noted between how social workers framed their discussions with each other, in supervision, and with clients. In addition, the social workers’ sense-making occurred within the context of reference to their perceived professional roles and responsibilities. These perceptions were observed to influence decisions and actions by the social workers. The ethnographic observations help the profession better understand how practice decisions are made in complex, under-defined situations: in sense-making, individual practitioners rely on multiple sources of information, not the least of which is provided by their understanding of the professional context (roles and responsibilities) and input from co-workers and supervisors.
Ethnography might be an important approach for social workers to better understanding diverse populations in the ability/disability arena. Consider, for example, the meaning of a deaf culture. For hearing persons, not being able to hear and communicate through spoken language might seem like an overwhelming disability. For persons who have never been part of the dominant hearing culture, living and thriving in a deaf community is important and meaningful. Deaf culture is experienced as communicating and experiencing the world differently compared to the hearing community. Members of deaf culture do not view themselves as disabled and needing to be “fixed.” Similar discussions have emerged among individuals who experience the world differently than the mainstream by virtue of their neurodiversity experience. These are individuals, many diagnosed with autism spectrum or other neurological disorders, who advocate for recognizing and appreciating variations in functioning as just that, not as mental disorders or disabilities needing to be cured. Ethnographic research helps social workers better understand their lived experiences from a strengths perspective.
Participatory Action Research. Sometimes social workers are members of a group attempting to solve a problem or influence change at the mezzo or macro level; sometimes members of such a group engage social workers to help them promote the problem solving and change-making processes. Either way, the key stakeholders in problem solving or advocating for change may decide to integrate research methodologies into their process. The result might be a participatory action research (PAR) scenario. This is a type of research activity where investigators are engaged in dual roles, both as researchers and change agents in the group or process under study.
PAR is conducted in the context of a non-hierarchical, democratic, engaged partnership of decision-making at every point in the process. Together, stakeholders and social workers develop the aims, questions, methods, analyses, results, and reporting of the change process. The outcomes of PAR are locally relevant solutions, developed by key stakeholders empowered to act as local experts and co-researchers supported by relevant theory and research knowledge shared by social work practitioners in a collaborative, problem-solving process. The results often include enhanced research skills among the key stakeholder partners as a form of further empowerment. What is learned through the PAR collaboration may have generalizable knowledge applicable to other communities, but the generalizability is carefully interpreted since it is, essentially, a single case study at the community level. Lawson (2015) described the relevance of PAR in community development efforts:
“Homogenization is rooted in part in mainstream researchers’ claims about the wholesale generalizability of the knowledge gained from their investigations, and it is facilitated by the worldwide movement toward evidence-based policy and practice. Granting the importance, indeed the strengths, associated with this international development, there are manifest risks and dangers when local voices, choices, and knowledge are neglected, ignored, and discounted. Under these circumstances, rigorous research knowledge has the potential to serve as an instrument for domination, marginalization, and oppression. And when these conditions prevail, research-based knowledge has the potential to cause harm in the name of doing good work. PAR’s expressly local knowledge for locally tailored solutions thus provides an important safeguard and a quality assurance mechanism for policy and practice” (Lawson, 2015, p. ix-x).
Community-based participatory research (CBPR) is a type of participatory research involving a collaborative inquiry process. As above, local experts are “people other than formally trained researchers” engaged to share their good ideas about every aspect of the research being conducted: the questions asked, study design features, how results are interpreted, and how findings should be used (Lawson, 2015, p. xv). University-community collaborations often provide the context through which CBPR occurs.

An example of CBPR was a needs assessment concerning parenting support programs for fathers in Detroit, Michigan (Lee, Hoffman, & Harris, 2016). The key stakeholders engaged in the effort with trained social work investigators from a university’s school of social work included formal service delivery system providers, a community advisory board, other key informants, and fathers. The team proceeded through a five-stage community-engaged research process, and discussed the importance of operating as a “learning community” where team members function as both teachers and learners throughout the collaborative process.
Stage 1. Identification and assessment was centered around locating and interviewing formal service providers in the local community. As part of the interview process, additional providers were identified by the participants.
Stage 2. The team engaged in mapping nontraditional settings, as well. This was directed to identifying places where fathers might seek or receive parenting support outside of formal service delivery systems: barber shops, for example. They developed a map of the community served by formal and informal/nontraditional systems.
Stage 3. This phase was labeled “engagement & relationship building” (Lee, Hoffman, & Harris, 2016, p. 78). It involved creating a project community advisory board made up of key stakeholders, and developing working connections and relationships with researchers involved with this particular community.
Stage 4. At this point, key stakeholder and university partners collaborated to develop strategies and events to build the service providers’ capacity to provide parenting support as needed and desired by fathers in the community.
Stage 5. The final, evaluation stage involved trained investigators coding data, then stakeholders involved in checking/confirming the themes identified in the data (called “member checking” of results). This final phase also included dissemination of the study findings.
In the end, this CBPR project identified multiple themes and at least 15 recommendations. Service providers identified service needs of the community’s fathers and strategies for engaging fathers. The fathers identified themes around engaging with children and interacting with service providers. The recommendations are specific with regards to what can change to provide support for the parenting efforts of fathers in this community, and many are relevant to consider adopting in other communities.
Content or Artifact Analysis Research . Content analysis is not so much a qualitative approach as it is a means of analyzing qualitative data. The important distinction lies in the sources of data compared to studies where interviews are conducted. In content or artifact analysis, the investigator’s source of information is records or artifacts previously produced during or about the phenomenon of interest. Content analysis is typically conducted on artifacts that were created for naturally occurring reasons, rather than for purposes of the study being conducted. Historically, content analysis was frequently conducted with personal diaries and letters written to family members or close associates. Examples include studies of first-hand report artifacts concerning how military personnel experienced military combat or their experiences of being separated from family members.

Given the important role of media on socialization, contents of media to which individuals are exposed might be analyzed for common themes and messages that audiences might be receiving. For example, a social worker might be concerned with learning about the contents of books commonly read to young children in families expecting a new baby. Parents read these books as a form of “bibliotherapy” to inform their children about what to expect and socialize them about how to behave in relation to the expected or new family member. A content analysis of these books divulged a common structure and theme: the new baby’s arrival is initially met with a great deal of negative affect (jealousy, feeling neglected by parents, being annoyed by the baby’s behavior), then in the end the child has an epiphany whereby the baby is fun and becomes loved (Begun, unpublished). Unfortunately, this plot structure and theme approach is adult-centric—young children learn concepts not by the logical sequencing of events but by what is most salient, affect-laden, or recent. Therefore, the message to these children could be “don’t like the baby” as much as it is “like the baby” when exposed to these books.

Recent literature includes studies relying on content presented in social media postings as the studied artifacts (Facebook, twitter, Snapchat, MySpace, and others). For example, investigators reviewed the contents of more than 1,000 MySpace comments posted by adolescents and emerging adults (aged 13-24 years) for the presence of potential suicide statements (Cash et al, 2013). The content analysis resulted in identifying 64 messages where a theme of potential suicidality was present; these statements were associated with subthemes about relationships, mental health concerns, substance misuse, and suicide methods. The lesson learned from this study is that young people are expressing themselves about suicide-related thoughts and behaviors to their social networks using social networking sites. One implication is that individuals using social network sites might need to be educated about how to recognize, interpret, and respond to these types of messages to become part of a suicide prevention network.
Chapter Summary
In this chapter you read about different traditions of qualitative research. You were introduced to narrative, phenomenological, grounded theory, ethnographic, participatory action, and content/artifact analysis research traditions. In future chapters you will learn about the specific methods involved in data collection and engaging participants in qualitative research studies.
Social Work 3401 Coursebook Copyright © by Dr. Audrey Begun is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Original Language Spotlight
- Alternative and Non-formal Education
- Cognition, Emotion, and Learning
- Curriculum and Pedagogy
- Education and Society
- Education, Change, and Development
- Education, Cultures, and Ethnicities
- Education, Gender, and Sexualities
- Education, Health, and Social Services
- Educational Administration and Leadership
- Educational History
- Educational Politics and Policy
- Educational Purposes and Ideals
- Educational Systems
- Educational Theories and Philosophies
- Globalization, Economics, and Education
- Languages and Literacies
- Professional Learning and Development
- Research and Assessment Methods
- Technology and Education
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Qualitative design research methods.
- Michael Domínguez Michael Domínguez San Diego State University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190264093.013.170
- Published online: 19 December 2017
Emerging in the learning sciences field in the early 1990s, qualitative design-based research (DBR) is a relatively new methodological approach to social science and education research. As its name implies, DBR is focused on the design of educational innovations, and the testing of these innovations in the complex and interconnected venue of naturalistic settings. As such, DBR is an explicitly interventionist approach to conducting research, situating the researcher as a part of the complex ecology in which learning and educational innovation takes place.
With this in mind, DBR is distinct from more traditional methodologies, including laboratory experiments, ethnographic research, and large-scale implementation. Rather, the goal of DBR is not to prove the merits of any particular intervention, or to reflect passively on a context in which learning occurs, but to examine the practical application of theories of learning themselves in specific, situated contexts. By designing purposeful, naturalistic, and sustainable educational ecologies, researchers can test, extend, or modify their theories and innovations based on their pragmatic viability. This process offers the prospect of generating theory-developing, contextualized knowledge claims that can complement the claims produced by other forms of research.
Because of this interventionist, naturalistic stance, DBR has also been the subject of ongoing debate concerning the rigor of its methodology. In many ways, these debates obscure the varied ways DBR has been practiced, the varied types of questions being asked, and the theoretical breadth of researchers who practice DBR. With this in mind, DBR research may involve a diverse range of methods as researchers from a variety of intellectual traditions within the learning sciences and education research design pragmatic innovations based on their theories of learning, and document these complex ecologies using the methodologies and tools most applicable to their questions, focuses, and academic communities.
DBR has gained increasing interest in recent years. While it remains a popular methodology for developmental and cognitive learning scientists seeking to explore theory in naturalistic settings, it has also grown in importance to cultural psychology and cultural studies researchers as a methodological approach that aligns in important ways with the participatory commitments of liberatory research. As such, internal tension within the DBR field has also emerged. Yet, though approaches vary, and have distinct genealogies and commitments, DBR might be seen as the broad methodological genre in which Change Laboratory, design-based implementation research (DBIR), social design-based experiments (SDBE), participatory design research (PDR), and research-practice partnerships might be categorized. These critically oriented iterations of DBR have important implications for educational research and educational innovation in historically marginalized settings and the Global South.
- design-based research
- learning sciences
- social-design experiment
- qualitative research
- research methods
Educational research, perhaps more than many other disciplines, is a situated field of study. Learning happens around us every day, at all times, in both formal and informal settings. Our worlds are replete with complex, dynamic, diverse communities, contexts, and institutions, many of which are actively seeking guidance and support in the endless quest for educational innovation. Educational researchers—as a source of potential expertise—are necessarily implicated in this complexity, linked to the communities and institutions through their very presence in spaces of learning, poised to contribute with possible solutions, yet often positioned as separate from the activities they observe, creating dilemmas of responsibility and engagement.
So what are educational scholars and researchers to do? These tensions invite a unique methodological challenge for the contextually invested researcher, begging them to not just produce knowledge about learning, but to participate in the ecology, collaborating on innovations in the complex contexts in which learning is taking place. In short, for many educational researchers, our backgrounds as educators, our connections to community partners, and our sociopolitical commitments to the process of educational innovation push us to ensure that our work is generative, and that our theories and ideas—our expertise—about learning and education are made pragmatic, actionable, and sustainable. We want to test what we know outside of laboratories, designing, supporting, and guiding educational innovation to see if our theories of learning are accurate, and useful to the challenges faced in schools and communities where learning is messy, collaborative, and contested. Through such a process, we learn, and can modify our theories to better serve the real needs of communities. It is from this impulse that qualitative design-based research (DBR) emerged as a new methodological paradigm for education research.
Qualitative design-based research will be examined, documenting its origins, the major tenets of the genre, implementation considerations, and methodological issues, as well as variance within the paradigm. As a relatively new methodology, much tension remains in what constitutes DBR, and what design should mean, and for whom. These tensions and questions, as well as broad perspectives and emergent iterations of the methodology, will be discussed, and considerations for researchers looking toward the future of this paradigm will be considered.
The Origins of Design-Based Research
Qualitative design-based research (DBR) first emerged in the learning sciences field among a group of scholars in the early 1990s, with the first articulation of DBR as a distinct methodological construct appearing in the work of Ann Brown ( 1992 ) and Allan Collins ( 1992 ). For learning scientists in the 1970s and 1980s, the traditional methodologies of laboratory experiments, ethnographies, and large-scale educational interventions were the only methods available. During these decades, a growing community of learning science and educational researchers (e.g., Bereiter & Scardamalia, 1989 ; Brown, Campione, Webber, & McGilley, 1992 ; Cobb & Steffe, 1983 ; Cole, 1995 ; Scardamalia & Bereiter, 1991 ; Schoenfeld, 1982 , 1985 ; Scribner & Cole, 1978 ) interested in educational innovation and classroom interventions in situated contexts began to find the prevailing methodologies insufficient for the types of learning they wished to document, the roles they wished to play in research, and the kinds of knowledge claims they wished to explore. The laboratory, or laboratory-like settings, where research on learning was at the time happening, was divorced from the complexity of real life, and necessarily limiting. Alternatively, most ethnographic research, while more attuned to capturing these complexities and dynamics, regularly assumed a passive stance 1 and avoided interceding in the learning process, or allowing researchers to see what possibility for innovation existed from enacting nascent learning theories. Finally, large-scale interventions could test innovations in practice but lost sight of the nuance of development and implementation in local contexts (Brown, 1992 ; Collins, Joseph, & Bielaczyc, 2004 ).
Dissatisfied with these options, and recognizing that in order to study and understand learning in the messiness of socially, culturally, and historically situated settings, new methods were required, Brown ( 1992 ) proposed an alternative: Why not involve ourselves in the messiness of the process, taking an active, grounded role in disseminating our theories and expertise by becoming designers and implementers of educational innovations? Rather than observing from afar, DBR researchers could trace their own iterative processes of design, implementation, tinkering, redesign, and evaluation, as it unfolded in shared work with teachers, students, learners, and other partners in lived contexts. This premise, initially articulated as “design experiments” (Brown, 1992 ), would be variously discussed over the next decade as “design research,” (Edelson, 2002 ) “developmental research,” (Gravemeijer, 1994 ), and “design-based research,” (Design-Based Research Collective, 2003 ), all of which reflect the original, interventionist, design-oriented concept. The latter term, “design-based research” (DBR), is used here, recognizing this as the prevailing terminology used to refer to this research approach at present. 2
Regardless of the evolving moniker, the prospects of such a methodology were extremely attractive to researchers. Learning scientists acutely aware of various aspects of situated context, and interested in studying the applied outcomes of learning theories—a task of inquiry into situated learning for which canonical methods were rather insufficient—found DBR a welcome development (Bell, 2004 ). As Barab and Squire ( 2004 ) explain: “learning scientists . . . found that they must develop technological tools, curriculum, and especially theories that help them systematically understand and predict how learning occurs” (p. 2), and DBR methodologies allowed them to do this in proactive, hands-on ways. Thus, rather than emerging as a strict alternative to more traditional methodologies, DBR was proposed to fill a niche that other methodologies were ill-equipped to cover.
Effectively, while its development is indeed linked to an inherent critique of previous research paradigms, neither Brown nor Collins saw DBR in opposition to other forms of research. Rather, by providing a bridge from the laboratory to the real world, where learning theories and proposed innovations could interact and be implemented in the complexity of lived socio-ecological contexts (Hoadley, 2004 ), new possibilities emerged. Learning researchers might “trace the evolution of learning in complex, messy classrooms and schools, test and build theories of teaching and learning, and produce instructional tools that survive the challenges of everyday practice” (Shavelson, Phillips, Towne, & Feuer, 2003 , p. 25). Thus, DBR could complement the findings of laboratory, ethnographic, and large-scale studies, answering important questions about the implementation, sustainability, limitations, and usefulness of theories, interventions, and learning when introduced as innovative designs into situated contexts of learning. Moreover, while studies involving these traditional methodologies often concluded by pointing toward implications—insights subsequent studies would need to take up—DBR allowed researchers to address implications iteratively and directly. No subsequent research was necessary, as emerging implications could be reflexively explored in the context of the initial design, offering considerable insight into how research is translated into theory and practice.
Since its emergence in 1992 , DBR as a methodological approach to educational and learning research has quickly grown and evolved, used by researchers from a variety of intellectual traditions in the learning sciences, including developmental and cognitive psychology (e.g., Brown & Campione, 1996 , 1998 ; diSessa & Minstrell, 1998 ), cultural psychology (e.g., Cole, 1996 , 2007 ; Newman, Griffin, & Cole, 1989 ; Gutiérrez, Bien, Selland, & Pierce, 2011 ), cultural anthropology (e.g., Barab, Kinster, Moore, Cunningham, & the ILF Design Team, 2001 ; Polman, 2000 ; Stevens, 2000 ; Suchman, 1995 ), and cultural-historical activity theory (e.g., Engeström, 2011 ; Espinoza, 2009 ; Espinoza & Vossoughi, 2014 ; Gutiérrez, 2008 ; Sannino, 2011 ). Given this plurality of epistemological and theoretical fields that employ DBR, it might best be understood as a broad methodology of educational research, realized in many different, contested, heterogeneous, and distinct iterations, and engaging a variety of qualitative tools and methods (Bell, 2004 ). Despite tensions among these iterations, and substantial and important variances in the ways they employ design-as-research in community settings, there are several common, methodological threads that unite the broad array of research that might be classified as DBR under a shared, though pluralistic, paradigmatic umbrella.
The Tenets of Design-Based Research
Why design-based research.
As we turn to the core tenets of the design-based research (DBR) paradigm, it is worth considering an obvious question: Why use DBR as a methodology for educational research? To answer this, it is helpful to reflect on the original intentions for DBR, particularly, that it is not simply the study of a particular, isolated intervention. Rather, DBR methodologies were conceived of as the complete, iterative process of designing, modifying, and assessing the impact of an educational innovation in a contextual, situated learning environment (Barab & Kirshner, 2001 ; Brown, 1992 ; Cole & Engeström, 2007 ). The design process itself—inclusive of the theory of learning employed, the relationships among participants, contextual factors and constraints, the pedagogical approach, any particular intervention, as well as any changes made to various aspects of this broad design as it proceeds—is what is under study.
Considering this, DBR offers a compelling framework for the researcher interested in having an active and collaborative hand in designing for educational innovation, and interested in creating knowledge about how particular theories of learning, pedagogical or learning practices, or social arrangements function in a context of learning. It is a methodology that can put the researcher in the position of engineer , actively experimenting with aspects of learning and sociopolitical ecologies to arrive at new knowledge and productive outcomes, as Cobb, Confrey, diSessa, Lehrer, and Schauble ( 2003 ) explain:
Prototypically, design experiments entail both “engineering” particular forms of learning and systematically studying those forms of learning within the context defined by the means of supporting them. This designed context is subject to test and revision, and the successive iterations that result play a role similar to that of systematic variation in experiment. (p. 9)
This being said, how directive the engineering role the researcher takes on varies considerably among iterations of DBR. Indeed, recent approaches have argued strongly for researchers to take on more egalitarian positionalities with respect to the community partners with whom they work (e.g., Zavala, 2016 ), acting as collaborative designers, rather than authoritative engineers.
Method and Methodology in Design-Based Research
Now, having established why we might use DBR, a recurring question that has faced the DBR paradigm is whether DBR is a methodology at all. Given the variety of intellectual and ontological traditions that employ it, and thus the pluralism of methods used in DBR to enact the “engineering” role (whatever shape that may take) that the researcher assumes, it has been argued that DBR is not, in actuality a methodology at all (Kelly, 2004 ). The proliferation and diversity of approaches, methods, and types of analysis purporting to be DBR have been described as a lack of coherence that shows there is no “argumentative grammar” or methodology present in DBR (Kelly, 2004 ).
Now, the conclusions one will eventually draw in this debate will depend on one’s orientations and commitments, but it is useful to note that these demands for “coherence” emerge from previous paradigms in which methodology was largely marked by a shared, coherent toolkit for data collection and data analysis. These previous paradigmatic rules make for an odd fit when considering DBR. Yet, even if we proceed—within the qualitative tradition from which DBR emerges—defining methodology as an approach to research that is shaped by the ontological and epistemological commitments of the particular researcher, and methods as the tools for research, data collection, and analysis that are chosen by the researcher with respect to said commitments (Gutiérrez, Engeström, & Sannino, 2016 ), then a compelling case for DBR as a methodology can be made (Bell, 2004 ).
Effectively, despite the considerable variation in how DBR has been and is employed, and tensions within the DBR field, we might point to considerable, shared epistemic common ground among DBR researchers, all of whom are invested in an approach to research that involves engaging actively and iteratively in the design and exploration of learning theory in situated, natural contexts. This common epistemic ground, even in the face of pluralistic ideologies and choices of methods, invites in a new type of methodological coherence, marked by “intersubjectivity without agreement” (Matusov, 1996 ), that links DBR from traditional developmental and cognitive psychology models of DBR (e.g., Brown, 1992 ; Brown & Campione, 1998 ; Collins, 1992 ), to more recent critical and sociocultural manifestations (e.g., Bang & Vossoughi, 2016 ; Engeström, 2011 ; Gutiérrez, 2016 ), and everything in between.
Put in other terms, even as DBR researchers may choose heterogeneous methods for data collection, data analysis, and reporting results complementary to the ideological and sociopolitical commitments of the particular researcher and the types of research questions that are under examination (Bell, 2004 ), a shared epistemic commitment gives the methodology shape. Indeed, the common commitment toward design innovation emerges clearly across examples of DBR methodological studies ranging in method from ethnographic analyses (Salvador, Bell, & Anderson, 1999 ) to studies of critical discourse within a design (Kärkkäinen, 1999 ), to focused examinations of metacognition of individual learners (White & Frederiksen, 1998 ), and beyond. Rather than indicating a lack of methodology, or methodological weakness, the use of varying qualitative methods for framing data collection and retrospective analyses within DBR, and the tensions within the epistemic common ground itself, simply reflects the scope of its utility. Learning in context is complex, contested, and messy, and the plurality of methods present across DBR allow researchers to dynamically respond to context as needed, employing the tools that fit best to consider the questions that are present, or may arise.
All this being the case, it is useful to look toward the coherent elements—the “argumentative grammar” of DBR, if you will—that can be identified across the varied iterations of DBR. Understanding these shared features, in the context and terms of the methodology itself, help us to appreciate what is involved in developing robust and thorough DBR research, and how DBR seeks to make strong, meaningful claims around the types of research questions it takes up.
Coherent Features of Design-Based Research
Several scholars have provided comprehensive overviews and listings of what they see as the cross-cutting features of DBR, both in the context of more traditional models of DBR (e.g., Cobb et al., 2003 ; Design-Based Research Collective, 2003 ), and in regards to newer iterations (e.g., Gutiérrez & Jurow, 2016 ; Bang & Vossoughi, 2016 ). Rather than try to offer an overview of each of these increasingly pluralistic classifications, the intent here is to attend to three broad elements that are shared across articulations of DBR and reflect the essential elements that constitute the methodological approach DBR offers to educational researchers.
Design research is concerned with the development, testing, and evolution of learning theory in situated contexts
This first element is perhaps most central to what DBR of all types is, anchored in what Brown ( 1992 ) was initially most interested in: testing the pragmatic validity of theories of learning by designing interventions that engaged with, or proposed, entire, naturalistic, ecologies of learning. Put another way, while DBR studies may have various units of analysis, focuses, and variables, and may organize learning in many different ways, it is the theoretically informed design for educational innovation that is most centrally under evaluation. DBR actively and centrally exists as a paradigm that is engaged in the development of theory, not just the evaluation of aspects of its usage (Bell, 2004 ; Design-Based Research Collective, 2003 ; Lesh & Kelly, 2000 ; van den Akker, 1999 ).
Effectively, where DBR is taking place, theory as a lived possibility is under examination. Specifically, in most DBR, this means a focus on “intermediate-level” theories of learning, rather than “grand” ones. In essence, DBR does not contend directly with “grand” learning theories (such as developmental or sociocultural theory writ large) (diSessa, 1991 ). Rather, DBR seeks to offer constructive insights by directly engaging with particular learning processes that flow from these theories on a “grounded,” “intermediate” level. This is not, however, to say DBR is limited in what knowledge it can produce; rather, tinkering in this “intermediate” realm can produce knowledge that informs the “grand” theory (Gravemeijer, 1994 ). For example, while cognitive and motivational psychology provide “grand” theoretical frames, interest-driven learning (IDL) is an “intermediate” theory that flows from these and can be explored in DBR to both inform the development of IDL designs in practice and inform cognitive and motivational psychology more broadly (Joseph, 2004 ).
Crucially, however, DBR entails putting the theory in question under intense scrutiny, or, “into harm’s way” (Cobb et al., 2003 ). This is an especially core element to DBR, and one that distinguishes it from the proliferation of educational-reform or educational-entrepreneurship efforts that similarly take up the discourse of “design” and “innovation.” Not only is the reflexive, often participatory element of DBR absent from such efforts—that is, questioning and modifying the design to suit the learning needs of the context and partners—but the theory driving these efforts is never in question, and in many cases, may be actively obscured. Indeed, it is more common to see educational-entrepreneur design innovations seek to modify a context—such as the way charter schools engage in selective pupil recruitment and intensive disciplinary practices (e.g., Carnoy et al., 2005 ; Ravitch, 2010 ; Saltman, 2007 )—rather than modify their design itself, and thus allow for humility in their theory. Such “innovations” and “design” efforts are distinct from DBR, which must, in the spirit of scientific inquiry, be willing to see the learning theory flail and struggle, be modified, and evolve.
This growth and evolution of theory and knowledge is of course central to DBR as a rigorous research paradigm; moving it beyond simply the design of local educational programs, interventions, or innovations. As Barab and Squire ( 2004 ) explain:
Design-based research requires more than simply showing a particular design works but demands that the researcher (move beyond a particular design exemplar to) generate evidence-based claims about learning that address contemporary theoretical issues and further the theoretical knowledge of the field. (pp. 5–6)
DBR as a research paradigm offers a design process through which theories of learning can be tested; they can be modified, and by allowing them to operate with humility in situated conditions, new insights and knowledge, even new theories, may emerge that might inform the field, as well as the efforts and directions of other types of research inquiry. These productive, theory-developing outcomes, or “ontological innovations” (diSessa & Cobb, 2004 ), represent the culmination of an effective program of DBR—the production of new ways to understand, conceptualize, and enact learning as a lived, contextual process.
Design research works to understand learning processes, and the design that supports them in situated contexts
As a research methodology that operates by tinkering with “grounded” learning theories, DBR is itself grounded, and seeks to develop its knowledge claims and designs in naturalistic, situated contexts (Brown, 1992 ). This is, again, a distinguishing element of DBR—setting it apart from laboratory research efforts involving design and interventions in closed, controlled environments. Rather than attempting to focus on singular variables, and isolate these from others, DBR is concerned with the multitude of variables that naturally occur across entire learning ecologies, and present themselves in distinct ways across multiple planes of possible examination (Rogoff, 1995 ; Collins, Joseph, & Bielaczyc, 2004 ). Certainly, specific variables may be identified as dependent, focal units of analysis, but identifying (while not controlling for) the variables beyond these, and analyzing their impact on the design and learning outcomes, is an equally important process in DBR (Collins et al., 2004 ; Barab & Kirshner, 2001 ). In practice, this of course varies across iterations in its depth and breadth. Traditional models of developmental or cognitive DBR may look to account for the complexity and nuance of a setting’s social, developmental, institutional, and intellectual characteristics (e.g., Brown, 1992 ; Cobb et al., 2003 ), while more recent, critical iterations will give increased attention to how historicity, power, intersubjectivity, and culture, among other things, influence and shape a setting, and the learning that occurs within it (e.g., Gutiérrez, 2016 ; Vakil, de Royston, Nasir, & Kirshner, 2016 ).
Beyond these variations, what counts as “design” in DBR varies widely, and so too will what counts as a naturalistic setting. It has been well documented that learning occurs all the time, every day, and in every space imaginable, both formal and informal (Leander, Phillips, & Taylor, 2010 ), and in ways that span strictly defined setting boundaries (Engeström, Engeström, & Kärkkäinen, 1995 ). DBR may take place in any number of contexts, based on the types of questions asked, and the learning theories and processes that a researcher may be interested in exploring. DBR may involve one-to-one tutoring and learning settings, single classrooms, community spaces, entire institutions, or even holistically designed ecologies (Design-Based Research Collective, 2003 ; Engeström, 2008 ; Virkkunen & Newnham, 2013 ). In all these cases, even the most completely designed experimental ecology, the setting remains naturalistic and situated because DBR actively embraces the uncontrollable variables that participants bring with them to the learning process for and from their situated worlds, lives, and experiences—no effort is made to control for these complicated influences of life, simply to understand how they operate in a given ecology as innovation is attempted. Thus, the extent of the design reflects a broader range of qualitative and theoretical study, rather than an attempt to control or isolate some particular learning process from outside influence.
While there is much variety in what design may entail, where DBR takes place, what types of learning ecologies are under examination, and what methods are used, situated ecologies are always the setting of this work. In this way, conscious of naturalistic variables, and the influences that culture, historicity, participation, and context have on learning, researchers can use DBR to build on prior research, and extend knowledge around the learning that occurs in the complexity of situated contexts and lived practices (Collins et al., 2004 ).
Design based research is iterative; it changes, grows, and evolves to meet the needs and emergent questions of the context, and this tinkering process is part of the research
The final shared element undergirding models of DBR is that it is an iterative, active, and interventionist process, interested in and focused on producing educational innovation by actually and actively putting design innovations into practice (Brown, 1992 , Collins, 1992 ; Gutiérrez, 2008 ). Given this interventionist, active stance, tinkering with the design and the theory of learning informing the design is as much a part of the research process as the outcome of the intervention or innovation itself—we learn what impacts learning as much, if not more, than we learn what was learned. In this sense, DBR involves a focus on analyzing the theory-driven design itself, and its implementation as an object of study (Edelson, 2002 ; Penuel, Fishman, Cheng, & Sabelli, 2011 ), and is ultimately interested in the improvement of the design—of how it unfolds, how it shifts, how it is modified, and made to function productively for participants in their contexts and given their needs (Kirshner & Polman, 2013 ).
While DBR is iterative and contextual as a foundational methodological principle, what this means varies across conceptions of DBR. For instance, in more traditional models, Brown and Campione ( 1996 ) pointed out the dangers of “lethal mutation” in which a design, introduced into a context, may become so warped by the influence, pressures, incomplete implementation, or misunderstanding of participants in the local context, that it no longer reflects or tests the theory under study. In short, a theory-driven intervention may be put in place, and then subsumed to such a degree by participants based on their understanding and needs, that it remains the original innovative design in name alone. The assertion here is that in these cases, the research ceases to be DBR in the sense that the design is no longer central, actively shaping learning. We cannot, they argue, analyze a design—and the theory it was meant to reflect—as an object of study when it has been “mutated,” and it is merely a banner under which participants are enacting their idiosyncratic, pragmatic needs.
While the ways in which settings and individuals might disrupt designs intended to produce robust learning is certainly a tension to be cautious of in DBR, it is also worth noting that in many critical approaches to DBR, such mutations—whether “lethal” to the original design or not—are seen as compelling and important moments. Here, where collaboration and community input is more central to the design process, iterative is understood differently. Thus, a “mutation” becomes a point where reflexivity, tension, and contradiction might open the door for change, for new designs, for reconsiderations of researcher and collaborative partner positionalities, or for ethnographic exploration into how a context takes up, shapes, and ultimately engages innovations in a particular sociocultural setting. In short, accounting for and documenting changes in design is a vital part of the DBR process, allowing researchers to respond to context in a variety of ways, always striving for their theories and designs to act with humility, and in the interest of usefulness .
With this in mind, the iterative nature of DBR means that the relationships researchers have with other design partners (educators and learners) in the ecology are incredibly important, and vital to consider (Bang et al., 2016 ; Engeström, 2007 ; Engeström, Sannino, & Virkkunen, 2014 ). Different iterations of DBR might occur in ways in which the researcher is more or less intimately involved in the design and implementation process, both in terms of actual presence and intellectual ownership of the design. Regarding the former, in some cases, a researcher may hand a design off to others to implement, periodically studying and modifying it, while in other contexts or designs, the researcher may be actively involved, tinkering in every detail of the implementation and enactment of the design. With regard to the latter, DBR might similarly range from a somewhat prescribed model, in which the researcher is responsible for the original design, and any modifications that may occur based on their analyses, without significant input from participants (e.g., Collins et al., 2004 ), to incredibly participatory models, in which all parties (researchers, educators, learners) are part of each step of the design-creation, modification, and research process (e.g., Bang, Faber, Gurneau, Marin, & Soto, 2016 ; Kirshner, 2015 ).
Considering the wide range of ideological approaches and models for DBR, we might acknowledge that DBR can be gainfully conducted through many iterations of “openness” to the design process. However, the strength of the research—focused on analyzing the design itself as a unit of study reflective of learning theory—will be bolstered by thoughtfully accounting for how involved the researcher will be, and how open to participation the modification process is. These answers should match the types of questions, and conceptual or ideological framing, with which researchers approach DBR, allowing them to tinker with the process of learning as they build on prior research to extend knowledge and test theory (Barab & Kirshner, 2001 ), while thoughtfully documenting these changes in the design as they go.
Implementation and Research Design
As with the overarching principles of design-based research (DBR), even amid the pluralism of conceptual frameworks of DBR researchers, it is possible, and useful, to trace the shared contours in how DBR research design is implemented. Though texts provide particular road maps for undertaking various iterations of DBR consistent with the specific goals, types of questions, and ideological orientations of these scholarly communities (e.g., Cole & Engeström, 2007 ; Collins, Joseph, & Bielaczyc, 2004 ; Fishman, Penuel, Allen, Cheng, & Sabelli, 2013 ; Gutiérrez & Jurow, 2016 ; Virkkunen & Newnham, 2013 ), certain elements, realized differently, can be found across all of these models, and may be encapsulated in five broad methodological phases.
Considering the Design Focus
DBR begins by considering what the focus of the design, the situated context, and the units of analysis for research will be. Prospective DBR researchers will need to consider broader research in regard to the “grand” theory of learning with which they work to determine what theoretical questions they have, or identify “intermediate” aspects of the theories that might be studied and strengthened by a design process in situated contexts, and what planes of analysis (Rogoff, 1995 ) will be most suitable for examination. This process allows for the identification of the critical theoretical elements of a design, and articulation of initial research questions.
Given the conceptual framework, theoretical and research questions, and sociopolitical interests at play, researchers may undertake this, and subsequent steps in the process, on their own, or in close collaboration with the communities and individuals in the situated contexts in which the design will unfold. As such, across iterations of DBR, and with respect to the ways DBR researchers choose to engage with communities, the origin of the design will vary, and might begin in some cases with theoretical questions, or arise in others as a problem of practice (Coburn & Penuel, 2016 ), though as has been noted, in either case, theory and practice are necessarily linked in the research.
Creating and Implementing a Designed Innovation
From the consideration and identification of the critical elements, planned units of analysis, and research questions that will drive a design, researchers can then actively create (either on their own or in conjunction with potential design partners) a designed intervention reflecting these critical elements, and the overarching theory.
Here, the DBR researcher should consider what partners exist in the process and what ownership exists around these partnerships, determine exactly what the pragmatic features of the intervention/design will be and who will be responsible for them, and consider when checkpoints for modification and evaluation will be undertaken, and by whom. Additionally, researchers should at this stage consider questions of timeline and of recruiting participants, as well as what research materials will be needed to adequately document the design, its implementation, and its outcomes, and how and where collected data will be stored.
Once a design (the planned, theory-informed innovative intervention) has been produced, the DBR researcher and partners can begin the implementation process, putting the design into place and beginning data collection and documentation.
Assessing the Impact of the Design on the Learning Ecology
Chronologically, the next two methodological steps happen recursively in the iterative process of DBR. The researcher must assess the impact of the design, and then, make modifications as necessary, before continuing to assess the impact of these modifications. In short, these next two steps are a cycle that continues across the life and length of the research design.
Once a design has been created and implemented, the researcher begins to observe and document the learning, the ecology, and the design itself. Guided by and in conversation with the theory and critical elements, the researcher should periodically engage in ongoing data analysis, assessing the success of the design, and of learning, paying equal attention to the design itself, and how its implementation is working in the situated ecology.
Within the realm of qualitative research, measuring or assessing variables of learning and assessing the design may look vastly different, require vastly different data-collection and data-analysis tools, and involve vastly different research methods among different researchers.
Modifying the Design
Modification, based on ongoing assessment of the design, is what makes DBR iterative, helping the researcher extend the field’s knowledge about the theory, design, learning, and the context under examination.
Modification of the design can take many forms, from complete changes in approach or curriculum, to introducing an additional tool or mediating artifact into a learning ecology. Moreover, how modification unfolds involves careful reflection from the researcher and any co-designing participants, deciding whether modification will be an ongoing, reflexive, tinkering process, or if it will occur only at predefined checkpoints, after formal evaluation and assessment. Questions of ownership, issues of resource availability, technical support, feasibility, and communication are all central to the work of design modification, and answers will vary given the research questions, design parameters, and researchers’ epistemic commitments.
Each moment of modification indicates a new phase in a DBR project, and a new round of assessing—through data analysis—the impact of the design on the learning ecology, either to guide continued or further modification, report the results of the design, or in some cases, both.
Reporting the Results of the Design
The final step in DBR methodology is to report on the results of the designed intervention, how it contributed to understandings of theory, and how it impacted the local learning ecology or context. The format, genre, and final data analysis methods used in reporting data and research results will vary across iterations of DBR. However, it is largely understood that to avoid methodological confusion, DBR researchers should clearly situate themselves in the DBR paradigm by clearly describing and detailing the design itself; articulating the theory, central elements, and units of analysis under scrutiny, what modifications occurred and what precipitated these changes, and what local effects were observed; and exploring any potential contributions to learning theory, while accounting for the context and their interventionist role and positionality in the design. As such, careful documentation of pragmatic and design decisions for retrospective data analysis, as well as research findings, should be done at each stage of this implementation process.
Methodological Issues in the Design-Based Research Paradigm
Because of its pluralistic nature, its interventionist, nontraditional stance, and the fact that it remains in its conceptual infancy, design-based research (DBR) is replete with ongoing methodological questions and challenges, both from external and internal sources. While there are many more that may exist, addressed will be several of the most pressing the prospective DBR researcher may encounter, or want to consider in understanding the paradigm and beginning a research design.
Challenges to Rigor and Validity
Perhaps the place to begin this reflection on tensions in the DBR paradigm is the recurrent and ongoing challenge to the rigor and validity of DBR, which has asked: Is DBR research at all? Given the interventionist and activist way in which DBR invites the researcher to participate, and the shift in orientation from long-accepted research paradigms, such critiques are hardly surprising, and fall in line with broader challenges to the rigor and objectivity of qualitative social science research in general. Historically, such complaints about DBR are linked to decades of critique of any research that does not adhere to the post-positivist approach set out as the U.S. Department of Education began to prioritize laboratory and large-scale randomized control-trial experimentation as the “gold standard” of research design (e.g., Mosteller & Boruch, 2002 ).
From the outset, DBR, as an interventionist, local, situated, non-laboratory methodology, was bound to run afoul of such conservative trends. While some researchers involved in (particularly traditional developmental and cognitive) DBR have found broader acceptance within these constraints, the rigor of DBR remains contested. It has been suggested that DBR is under-theorized and over-methologized, a haphazard way for researchers to do activist work without engaging in the development of robust knowledge claims about learning (Dede, 2004 ), and an approach lacking in coherence that sheltered interventionist projects of little impact to developing learning theory and allowed researchers to make subjective, pet claims through selective analysis of large bodies of collected data (Kelly, 2003 , 2004 ).
These critiques, however, impose an external set of criteria on DBR, desiring it to fit into the molds of rigor and coherence as defined by canonical methodologies. Bell ( 2004 ) and Bang and Vossoughi ( 2016 ) have made compelling cases for the wide variety of methods and approaches present in DBR not as a fracturing, but as a generative proliferation of different iterations that can offer powerful insights around the different types of questions that exist about learning in the infinitely diverse settings in which it occurs. Essentially, researchers have argued that within the DBR paradigm, and indeed within educational research more generally, the practical impact of research on learning, context, and practices should be a necessary component of rigor (Gutiérrez & Penuel, 2014 ), and the pluralism of methods and approaches available in DBR ensures that the practical impacts and needs of the varied contexts in which the research takes place will always drive the design and research tools.
These moves are emblematic of the way in which DBR is innovating and pushing on paradigms of rigor in educational research altogether, reflecting how DBR fills a complementary niche with respect to other methodologies and attends to elements and challenges of learning in lived, real environments that other types of research have consistently and historically missed. Beyond this, Brown ( 1992 ) was conscious of the concerns around data collection, validity, rigor, and objectivity from the outset, identifying this dilemma—the likelihood of having an incredible amount of data collected in a design only a small fraction of which can be reported and shared, thus leading potentially to selective data analysis and use—as the Bartlett Effect (Brown, 1992 ). Since that time, DBR researchers have been aware of this challenge, actively seeking ways to mitigate this threat to validity by making data sets broadly available, documenting their design, tinkering, and modification processes, clearly situating and describing disconfirming evidence and their own position in the research, and otherwise presenting the broad scope of human and learning activity that occurs within designs in large learning ecologies as comprehensively as possible.
Ultimately, however, these responses are likely to always be insufficient as evidence of rigor to some, for the root dilemma is around what “counts” as education science. While researchers interested and engaged in DBR ought rightly to continue to push themselves to ensure the methodological rigor of their work and chosen methods, it is also worth noting that DBR should seek to hold itself to its own criteria of assessment. This reflects broader trends in qualitative educational research that push back on narrow constructions of what “counts” as science, recognizing the ways in which new methodologies and approaches to research can help us examine aspects of learning, culture, and equity that have continued to be blind spots for traditional education research; invite new voices and perspectives into the process of achieving rigor and validity (Erickson & Gutiérrez, 2002 ); bolster objectivity by bringing it into conversation with the positionality of the researcher (Harding, 1993 ); and perhaps most important, engage in axiological innovation (Bang, Faber, Gurneau, Marin, & Soto, 2016 ), or the exploration of and design for what is, “good right, true, and beautiful . . . in cultural ecologies” (p. 2).
Questions of Generalizability and Usefulness
The generalizability of research results in DBR has been an ongoing and contentious issue in the development of the paradigm. Indeed, by the standards of canonical methods (e.g., laboratory experimentation, ethnography), these local, situated interventions should lack generalizability. While there is reason to discuss and question the merit of generalizability as a goal of qualitative research at all, researchers in the DBR paradigm have long been conscious of this issue. Understanding the question of generalizability around DBR, and how the paradigm has responded to it, can be done in two ways.
First, by distinguishing questions specific to a particular design from the generalizability of the theory. Cole’s (Cole & Underwood, 2013 ) 5th Dimension work, and the nationwide network of linked, theoretically similar sites, operating nationwide with vastly different designs, is a powerful example of this approach to generalizability. Rather than focus on a single, unitary, potentially generalizable design, the project is more interested in variability and sustainability of designs across local contexts (e.g., Cole, 1995 ; Gutiérrez, Bien, Selland, & Pierce, 2011 ; Jurow, Tracy, Hotchkiss, & Kirshner, 2012 ). Through attention to sustainable, locally effective innovations, conscious of the wide variation in culture and context that accompanies any and all learning processes, 5th Dimension sites each derive their idiosyncratic structures from sociocultural theory, sharing some elements, but varying others, while seeking their own “ontological innovations” based on the affordances of their contexts. This pattern reflects a key element of much of the DBR paradigm: that questions of generalizability in DBR may be about the generalizability of the theory of learning, and the variability of learning and design in distinct contexts, rather than the particular design itself.
A second means of addressing generalizability in DBR has been to embrace the pragmatic impacts of designing innovations. This response stems from Messick ( 1992 ) and Schoenfeld’s ( 1992 ) arguments early on in the development of DBR that the consequentialness and validity of DBR efforts as potentially generalizable research depend on the “ usefulness ” of the theories and designs that emerge. Effectively, because DBR is the examination of situated theory, a design must be able to show pragmatic impact—it must succeed at showing the theory to be useful . If there is evidence of usefulness to both the context in which it takes place, and the field of educational research more broadly, then the DBR researcher can stake some broader knowledge claims that might be generalizable. As a result, the DBR paradigm tends to “treat changes in [local] contexts as necessary evidence for the viability of a theory” (Barab & Squire, 2004 , p. 6). This of course does not mean that DBR is only interested in successful efforts. A design that fails or struggles can provide important information and knowledge to the field. Ultimately, though, DBR tends to privilege work that proves the usefulness of designs, whose pragmatic or theoretical findings can then be generalized within the learning science and education research fields.
With this said, the question of usefulness is not always straightforward, and is hardly unitary. While many DBR efforts—particularly those situated in developmental and cognitive learning science traditions—are interested in the generalizability of their useful educational designs (Barab & Squire, 2004 ; Cobb, Confrey, diSessa, Lehrer, & Schauble, 2003 ; Joseph, 2004 ; Steffe & Thompson, 2000 ), not all are. Critical DBR researchers have noted that if usefulness remains situated in the extant sociopolitical and sociocultural power-structures—dominant conceptual and popular definitions of what useful educational outcomes are—the result will be a bar for research merit that inexorably bends toward the positivist spectrum (Booker & Goldman, 2016 ; Dominguez, 2015 ; Zavala, 2016 ). This could potentially, and likely, result in excluding the non-normative interventions and innovations that are vital for historically marginalized communities, but which might have vastly different-looking outcomes, that are nonetheless useful in the sociopolitical context they occur in. Alternative framings to this idea of usefulness push on and extend the intention, and seek to involve the perspectives and agency of situated community partners and their practices in what “counts” as generative and rigorous research outcomes (Gutiérrez & Penuel, 2014 ). An example in this regard is the idea of consequential knowledge (Hall & Jurow, 2015 ; Jurow & Shea, 2015 ), which suggests outcomes that are consequential will be taken up by participants in and across their networks, and over-time—thus a goal of consequential knowledge certainly meets the standard of being useful , but it also implicates the needs and agency of communities in determining the success and merit of a design or research endeavor in important ways that strict usefulness may miss.
Thus, the bar of usefulness that characterizes the DBR paradigm should not be approached without critical reflection. Certainly designs that accomplish little for local contexts should be subject to intense questioning and critique, but considering the sociopolitical and systemic factors that might influence what “counts” as useful in local contexts and education science more generally, should be kept firmly in mind when designing, choosing methods, and evaluating impacts (Zavala, 2016 ). Researchers should think deeply about their goals, whether they are reaching for generalizability at all, and in what ways they are constructing contextual definitions of success, and be clear about these ideologically influenced answers in their work, such that generalizability and the usefulness of designs can be adjudicated based on and in conversation with the intentions and conceptual framework of the research and researcher.
Ethical Concerns of Sustainability, Participation, and Telos
While there are many external challenges to rigor and validity of DBR, another set of tensions comes from within the DBR paradigm itself. Rather than concerns about rigor or validity, these internal critiques are not unrelated to the earlier question of the contested definition of usefulness , and more accurately reflect questions of research ethics and grow from ideological concerns with how an intentional, interventionist stance is taken up in research as it interacts with situated communities.
Given that the nature of DBR is to design and implement some form of educational innovation, the DBR researcher will in some way be engaging with an individual or community, becoming part of a situated learning ecology, complete with a sociopolitical and cultural history. As with any research that involves providing an intervention or support, the question of what happens when the research ends is as much an ethical as a methodological one. Concerns then arise given how traditional models of DBR seem intensely focused on creating and implementing a “complete” cycle of design, but giving little attention to what happens to the community and context afterward (Engeström, 2011 ). In contrast to this privileging of “completeness,” sociocultural and critical approaches to DBR have suggested that if research is actually happening in naturalistic, situated contexts that authentically recognize and allow social and cultural dimensions to function (i.e., avoid laboratory-type controls to mitigate independent variables), there can never be such a thing as “complete,” for the design will, and should, live on as part of the ecology of the space (Cole, 2007 ; Engeström, 2000 ). Essentially, these internal critiques push DBR to consider sustainability, and sustainable scale, as equally important concerns to the completeness of an innovation. Not only are ethical questions involved, but accounting for the unbounded and ongoing nature of learning as a social and cultural activity can help strengthen the viability of knowledge claims made, and what degree of generalizability is reasonably justified.
Related to this question of sustainability are internal concerns regarding the nature and ethics of participation in DBR, whether partners in a design are being adequately invited to engage in the design and modification processes that will unfold in their situated contexts and lived communities (Bang et al., 2016 ; Engeström, 2011 ). DBR has actively sought to examine multiple planes of analysis in learning that might be occurring in a learning ecology but has rarely attended to the subject-subject dynamics (Bang et al., 2016 ), or “relational equity” (DiGiacomo & Gutiérrez, 2015 ) that exists between researchers and participants as a point of focus. Participatory design research (PDR) (Bang & Vossoughi, 2016 ) models have recently emerged as a way to better attend to these important dimensions of collective participation (Engeström, 2007 ), power (Vakil et al., 2016 ), positionality (Kirshner, 2015 ), and relational agency (Edwards, 2007 , 2009 ; Sannino & Engeström, 2016 ) as they unfold in DBR.
Both of these ethical questions—around sustainability and participation—reflect challenges to what we might call the telos —or direction—that DBR takes to innovation and research. These are questions related to whose voices are privileged, in what ways, for what purposes, and toward what ends. While DBR, like many other forms of educational research, has involved work with historically marginalized communities, it has, like many other forms of educational research, not always done so in humanizing ways. Put another way, there are ethical and political questions surrounding whether the designs, goals, and standards of usefulness we apply to DBR efforts should be purposefully activist, and have explicitly liberatory ends. To this point, critical and decolonial perspectives have pushed on the DBR paradigm, suggesting that DBR should situate itself as being a space of liberatory innovation and potential, in which communities and participants can become designers and innovators of their own futures (Gutiérrez, 2005 ). This perspective is reflected in the social design experiment (SDE) approach to DBR (Gutiérrez, 2005 , 2008 ; Gutierréz & Vossoughi, 2010 ; Gutiérrez, 2016 ; Gutiérrez & Jurow, 2016 ), which begins in participatory fashion, engaging a community in identifying its own challenges and desires, and reflecting on the historicity of learning practices, before proleptic design efforts are undertaken that ensure that research is done with , not on , communities of color (Arzubiaga, Artiles, King, & Harris-Murri, 2008 ), and intentionally focused on liberatory goals.
Global Perspectives and Unique Iterations
While design-based research (DBR) has been a methodology principally associated with educational research in the United States, its development is hardly limited to the U.S. context. Rather, while DBR emerged in U.S. settings, similar methods of situated, interventionist research focused on design and innovation were emerging in parallel in European contexts (e.g., Gravemeijer, 1994 ), most significantly in the work of Vygotskian scholars both in Europe and the United States (Cole, 1995 ; Cole & Engeström, 1993 , 2007 ; Engeström, 1987 ).
Particularly, where DBR began in the epistemic and ontological terrain of developmental and cognitive psychology, this vein of design-based research work began deeply grounded in cultural-historical activity theory (CHAT). This ontological and epistemic grounding meant that the approach to design that was taken was more intensively conscious of context, historicity, hybridity, and relational factors, and framed around understanding learning as a complex, collective activity system that, through design, could be modified and transformed (Cole & Engeström, 2007 ). The models of DBR that emerged in this context abroad were the formative intervention (Engeström, 2011 ; Engeström, Sannino, & Virkkunen, 2014 ), which relies heavily on Vygotskian double-stimulation to approach learning in nonlinear, unbounded ways, accounting for the role of learner, educator, and researcher in a collective process, shifting and evolving and tinkering with the design as the context needs and demands; and the Change Laboratory (Engeström, 2008 ; Virkkunen & Newnham, 2013 ), which similarly relies on the principle of double stimulation, while presenting holistic way to approach transforming—or changing—entire learning activity systems in fundamental ways through designs that encourage collective “expansive learning” (Engeström, 2001 ), through which participants can produce wholly new activity systems as the object of learning itself.
Elsewhere in the United States, still parallel to the developmental- or cognitive-oriented DBR work that was occurring, American researchers employing CHAT began to leverage the tools and aims of expansive learning in conversation with the tensions and complexity of the U.S. context (Cole, 1995 ; Gutiérrez, 2005 ; Gutiérrez & Rogoff, 2003 ). Like the CHAT design research of the European context, there was a focus on activity systems, historicity, nonlinear and unbounded learning, and collective learning processes and outcomes. Rather than a simple replication, however, these researchers put further attention on questions of equity, diversity, and justice in this work, as Gutiérrez, Engeström, and Sannino ( 2016 ) note:
The American contribution to a cultural historical activity theoretic perspective has been its attention to diversity, including how we theorize, examine, and represent individuals and their communities. (p. 276)
Effectively, CHAT scholars in parts of the United States brought critical and decolonial perspectives to bear on their design-focused research, focusing explicitly on the complex cultural, racial, and ethnic terrain in which they worked, and ensuring that diversity, equity, justice, and non-dominant perspectives would become central principles to the types of design research conducted. The result was the emergence of the aforementioned social design experiments (e.g., Gutiérrez, 2005 , 2016 ), and participatory design research (Bang & Vossoughi, 2016 ) models, which attend intentionally to historicity and relational equity, tailor their methods to the liberation of historically marginalized communities, aim intentionally for liberatory outcomes as key elements of their design processes, and seek to produce outcomes in which communities of learners become designers of new community futures (Gutiérrez, 2016 ). While these approaches emerged in the United States, their origins reflect ontological and ideological perspectives quite distinct from more traditional learning science models of DBR, and dominant U.S. ontologies in general. Indeed, these iterations of DBR are linked genealogically to the ontologies, ideologies, and concerns of peoples in the Global South, offering some promise for the method in those regions, though DBR has yet to broadly take hold among researchers beyond the United States and Europe.
There is, of course, much more nuance to these models, and each of these models (formative interventions, Change Laboratories, social design experiments, and participatory design research) might itself merit independent exploration and review well beyond the scope here. Indeed, there is some question as to whether all adherents of these CHAT design-based methodologies, with their unique genealogies and histories, would even consider themselves under the umbrella of DBR. Yet, despite significant ontological divergences, these iterations share many of the same foundational tenets of the traditional models (though realized differently), and it is reasonable to argue that they do indeed share the same, broad methodological paradigm (DBR), or at the very least, are so intimately related that any discussion of DBR, particularly one with a global view, should consider the contributions CHAT iterations have made to the DBR methodology in the course of their somewhat distinct, but parallel, development.
Possibilities and Potentials for Design-Based Research
Since its emergence in 1992 , the DBR methodology for educational research has continued to grow in popularity, ubiquity, and significance. Its use has begun to expand beyond the confines of the learning sciences, taken up by researchers in a variety of disciplines, and across a breadth of theoretical and intellectual traditions. While still not as widely recognized as more traditional and well-established research methodologies, DBR as a methodology for rigorous research is unquestionably here to stay.
With this in mind, the field ought to still be cautious of the ways in which the discourse of design is used. Not all design is DBR, and preserving the integrity, rigor, and research ethics of the paradigm (on its own terms) will continue to require thoughtful reflection as its pluralistic parameters come into clearer focus. Yet the proliferation of methods in the DBR paradigm should be seen as a positive. There are far too many theories of learning and ideological perspectives that have meaningful contributions to make to our knowledge of the world, communities, and learning to limit ourselves to a unitary approach to DBR, or set of methods. The paradigm has shown itself to have some core methodological principles, but there is no reason not to expect these to grow, expand, and evolve over time.
In an increasingly globalized, culturally diverse, and dynamic world, there is tremendous potential for innovation couched in this proliferation of DBR. Particularly in historically marginalized communities and across the Global South, we will need to know how learning theories can be lived out in productive ways in communities that have been understudied, and under-engaged. The DBR paradigm generally, and critical and CHAT iterations particularly, can fill an important need for participatory, theory-developing research in these contexts that simultaneously creates lived impacts. Participatory design research (PDR), social design experiments (SDE), and Change Laboratory models of DBR should be of particular interest and attention moving forward, as current trends toward culturally sustaining pedagogies and learning will need to be explored in depth and in close collaboration with communities, as participatory design partners, in the press toward liberatory educational innovations.
Bibliography
The following special issues of journals are encouraged starting points for engaging more deeply with current and past trends in design-based research.
- Bang, M. , & Vossoughi, S. (Eds.). (2016). Participatory design research and educational justice: Studying learning and relations within social change making [Special issue]. Cognition and Instruction , 34 (3).
- Barab, S. (Ed.). (2004). Design-based research [Special issue]. Journal of the Learning Sciences , 13 (1).
- Cole, M. , & The Distributed Literacy Consortium. (2006). The Fifth Dimension: An after-school program built on diversity . New York, NY: Russell Sage Foundation.
- Kelly, A. E. (Ed.). (2003). Special issue on the role of design in educational research [Special issue]. Educational Researcher , 32 (1).
- Arzubiaga, A. , Artiles, A. , King, K. , & Harris-Murri, N. (2008). Beyond research on cultural minorities: Challenges and implications of research as situated cultural practice. Exceptional Children , 74 (3), 309–327.
- Bang, M. , Faber, L. , Gurneau, J. , Marin, A. , & Soto, C. (2016). Community-based design research: Learning across generations and strategic transformations of institutional relations toward axiological innovations. Mind, Culture, and Activity , 23 (1), 28–41.
- Bang, M. , & Vossoughi, S. (2016). Participatory design research and educational justice: Studying learning and relations within social change making. Cognition and Instruction , 34 (3), 173–193.
- Barab, S. , Kinster, J. G. , Moore, J. , Cunningham, D. , & The ILF Design Team. (2001). Designing and building an online community: The struggle to support sociability in the Inquiry Learning Forum. Educational Technology Research and Development , 49 (4), 71–96.
- Barab, S. , & Squire, K. (2004). Design-based research: Putting a stake in the ground. Journal of the Learning Sciences , 13 (1), 1–14.
- Barab, S. A. , & Kirshner, D. (2001). Methodologies for capturing learner practices occurring as part of dynamic learning environments. Journal of the Learning Sciences , 10 (1–2), 5–15.
- Bell, P. (2004). On the theoretical breadth of design-based research in education. Educational Psychologist , 39 (4), 243–253.
- Bereiter, C. , & Scardamalia, M. (1989). Intentional learning as a goal of instruction. In L. B. Resnick (Ed.), Knowing, learning, and instruction: Essays in honor of Robert Glaser (pp. 361–392). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Booker, A. , & Goldman, S. (2016). Participatory design research as a practice for systemic repair: Doing hand-in-hand math research with families. Cognition and Instruction , 34 (3), 222–235.
- Brown, A. L. (1992). Design experiments: Theoretical and methodological challenges in creating complex interventions in classroom settings. Journal of the Learning Sciences , 2 (2), 141–178.
- Brown, A. , & Campione, J. C. (1996). Psychological theory and the design of innovative learning environments: On procedures, principles, and systems. In L. Schauble & R. Glaser (Eds.), Innovations in learning: New environments for education (pp. 289–325). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Brown, A. L. , & Campione, J. C. (1998). Designing a community of young learners: Theoretical and practical lessons. In N. M. Lambert & B. L. McCombs (Eds.), How students learn: Reforming schools through learner-centered education (pp. 153–186). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Brown, A. , Campione, J. , Webber, L. , & McGilley, K. (1992). Interactive learning environments—A new look at learning and assessment. In B. R. Gifford & M. C. O’Connor (Eds.), Future assessment: Changing views of aptitude, achievement, and instruction (pp. 121–211). Boston, MA: Academic Press.
- Carnoy, M. , Jacobsen, R. , Mishel, L. , & Rothstein, R. (2005). The charter school dust-up: Examining the evidence on enrollment and achievement . Washington, DC: Economic Policy Institute.
- Carspecken, P. (1996). Critical ethnography in educational research . New York, NY: Routledge.
- Cobb, P. , Confrey, J. , diSessa, A. , Lehrer, R. , & Schauble, L. (2003). Design experiments in educational research. Educational Researcher , 32 (1), 9–13.
- Cobb, P. , & Steffe, L. P. (1983). The constructivist researcher as teacher and model builder. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education , 14 , 83–94.
- Coburn, C. , & Penuel, W. (2016). Research-practice partnerships in education: Outcomes, dynamics, and open questions. Educational Researcher , 45 (1), 48–54.
- Cole, M. (1995). From Moscow to the Fifth Dimension: An exploration in romantic science. In M. Cole & J. Wertsch (Eds.), Contemporary implications of Vygotsky and Luria (pp. 1–38). Worcester, MA: Clark University Press.
- Cole, M. (1996). Cultural psychology: A once and future discipline . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Cole, M. (2007). Sustaining model systems of educational activity: Designing for the long haul. In J. Campione , K. Metz , & A. S. Palinscar (Eds.), Children’s learning in and out of school: Essays in honor of Ann Brown (pp. 71–89). New York, NY: Routledge.
- Cole, M. , & Engeström, Y. (1993). A cultural historical approach to distributed cognition. In G. Saloman (Ed.), Distributed cognitions: Psychological and educational considerations (pp. 1–46). Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Cole, M. , & Engeström, Y. (2007). Cultural-historical approaches to designing for development. In J. Valsiner & A. Rosa (Eds.), The Cambridge handbook of sociocultural psychology , Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Cole, M. , & Underwood, C. (2013). The evolution of the 5th Dimension. In The Story of the Laboratory of Comparative Human Cognition: A polyphonic autobiography . https://lchcautobio.ucsd.edu/polyphonic-autobiography/section-5/chapter-12-the-later-life-of-the-5th-dimension-and-its-direct-progeny/ .
- Collins, A. (1992). Toward a design science of education. In E. Scanlon & T. O’Shea (Eds.), New directions in educational technology (pp. 15–22). New York, NY: Springer-Verlag.
- Collins, A. , Joseph, D. , & Bielaczyc, K. (2004). Design research: Theoretical and methodological issues. Journal of the Learning Sciences , 13 (1), 15–42.
- Dede, C. (2004). If design-based research is the answer, what is the question? A commentary on Collins, Joseph, and Bielaczyc; DiSessa and Cobb; and Fishman, Marx, Blumenthal, Krajcik, and Soloway in the JLS special issue on design-based research. Journal of the Learning Sciences , 13 (1), 105–114.
- Design-Based Research Collective . (2003). Design-based research: An emerging paradigm for educational inquiry. Educational Researcher , 32 (1), 5–8.
- DiGiacomo, D. , & Gutiérrez, K. D. (2015). Relational equity as a design tool within making and tinkering activities. Mind, Culture, and Activity , 22 (3), 1–15.
- diSessa, A. A. (1991). Local sciences: Viewing the design of human-computer systems as cognitive science. In J. M. Carroll (Ed.), Designing interaction: Psychology at the human-computer interface (pp. 162–202). Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- diSessa, A. A. , & Cobb, P. (2004). Ontological innovation and the role of theory in design experiments. Journal of the Learning Sciences , 13 (1), 77–103.
- diSessa, A. A. , & Minstrell, J. (1998). Cultivating conceptual change with benchmark lessons. In J. G. Greeno & S. Goldman (Eds.), Thinking practices (pp. 155–187). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Dominguez, M. (2015). Decolonizing teacher education: Explorations of expansive learning and culturally sustaining pedagogy in a social design experiment (Doctoral dissertation). University of Colorado, Boulder.
- Edelson, D. (2002). Design research: What we learn when we engage in design. Journal of the Learning Sciences , 11 (1), 105–121.
- Edwards, A. (2007). Relational agency in professional practice: A CHAT analysis. Actio: An International Journal of Human Activity Theory , 1 , 1–17.
- Edwards, A. (2009). Agency and activity theory: From the systemic to the relational. In A. Sannino , H. Daniels , & K. Gutiérrez (Eds.), Learning and expanding with activity theory (pp. 197–211). Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Engeström, Y. (1987). Learning by expanding . Helsinki, Finland: University of Helsinki, Department of Education.
- Engeström, Y. (2000). Can people learn to master their future? Journal of the Learning Sciences , 9 , 525–534.
- Engeström, Y. (2001). Expansive learning at work: Toward an activity theoretical reconceptualization. Journal of Education and Work , 14 (1), 133–156.
- Engeström, Y. (2007). Enriching the theory of expansive learning: Lessons from journeys toward co-configuration. Mind, Culture, and Activity , 14 (1–2), 23–39.
- Engeström, Y. (2008). Putting Vygotksy to work: The Change Laboratory as an application of double stimulation. In H. Daniels , M. Cole , & J. Wertsch (Eds.), Cambridge companion to Vygotsky (pp. 363–382). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
- Engeström, Y. (2011). From design experiments to formative interventions. Theory & Psychology , 21 (5), 598–628.
- Engeström, Y. , Engeström, R. , & Kärkkäinen, M. (1995). Polycontextuality and boundary crossing in expert cognition: Learning and problem solving in complex work activities. Learning and Instruction , 5 (4), 319–336.
- Engeström, Y. , & Sannino, A. (2010). Studies of expansive learning: Foundations, findings and future challenges. Educational Research Review , 5 (1), 1–24.
- Engeström, Y. , & Sannino, A. (2011). Discursive manifestations of contradictions in organizational change efforts: A methodological framework. Journal of Organizational Change Management , 24 (3), 368–387.
- Engeström, Y. , Sannino, A. , & Virkkunen, J. (2014). On the methodological demands of formative interventions. Mind, Culture, and Activity , 2 (2), 118–128.
- Erickson, F. , & Gutiérrez, K. (2002). Culture, rigor, and science in educational research. Educational Researcher , 31 (8), 21–24.
- Espinoza, M. (2009). A case study of the production of educational sanctuary in one migrant classroom. Pedagogies: An International Journal , 4 (1), 44–62.
- Espinoza, M. L. , & Vossoughi, S. (2014). Perceiving learning anew: Social interaction, dignity, and educational rights. Harvard Educational Review , 84 (3), 285–313.
- Fine, M. (1994). Dis-tance and other stances: Negotiations of power inside feminist research. In A. Gitlin (Ed.), Power and method (pp. 13–25). New York, NY: Routledge.
- Fishman, B. , Penuel, W. , Allen, A. , Cheng, B. , & Sabelli, N. (2013). Design-based implementation research: An emerging model for transforming the relationship of research and practice. National Society for the Study of Education , 112 (2), 136–156.
- Gravemeijer, K. (1994). Educational development and developmental research in mathematics education. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education , 25 (5), 443–471.
- Gutiérrez, K. (2005). Intersubjectivity and grammar in the third space . Scribner Award Lecture.
- Gutiérrez, K. (2008). Developing a sociocritical literacy in the third space. Reading Research Quarterly , 43 (2), 148–164.
- Gutiérrez, K. (2016). Designing resilient ecologies: Social design experiments and a new social imagination. Educational Researcher , 45 (3), 187–196.
- Gutiérrez, K. , Bien, A. , Selland, M. , & Pierce, D. M. (2011). Polylingual and polycultural learning ecologies: Mediating emergent academic literacies for dual language learners. Journal of Early Childhood Literacy , 11 (2), 232–261.
- Gutiérrez, K. , Engeström, Y. , & Sannino, A. (2016). Expanding educational research and interventionist methodologies. Cognition and Instruction , 34 (2), 275–284.
- Gutiérrez, K. , & Jurow, A. S. (2016). Social design experiments: Toward equity by design. Journal of Learning Sciences , 25 (4), 565–598.
- Gutiérrez, K. , & Penuel, W. R. (2014). Relevance to practice as a criterion for rigor. Educational Researcher , 43 (1), 19–23.
- Gutiérrez, K. , & Rogoff, B. (2003). Cultural ways of learning: Individual traits or repertoires of practice. Educational Researcher , 32 (5), 19–25.
- Gutierréz, K. , & Vossoughi, S. (2010). Lifting off the ground to return anew: Mediated praxis, transformative learning, and social design experiments. Journal of Teacher Education , 61 (1–2), 100–117.
- Hall, R. , & Jurow, A. S. (2015). Changing concepts in activity: Descriptive and design studies of consequential learning in conceptual practices. Educational Psychologist , 50 (3), 173–189.
- Harding, S. (1993). Rethinking standpoint epistemology: What is “strong objectivity”? In L. Alcoff & E. Potter (Eds.), Feminist epistemologies (pp. 49–82). New York, NY: Routledge.
- Hoadley, C. (2002). Creating context: Design-based research in creating and understanding CSCL. In G. Stahl (Ed.), Computer support for collaborative learning 2002 (pp. 453–462). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Hoadley, C. (2004). Methodological alignment in design-based research. Educational Psychologist , 39 (4), 203–212.
- Joseph, D. (2004). The practice of design-based research: Uncovering the interplay between design, research, and the real-world context. Educational Psychologist , 39 (4), 235–242.
- Jurow, A. S. , & Shea, M. V. (2015). Learning in equity-oriented scale-making projects. Journal of the Learning Sciences , 24 (2), 286–307.
- Jurow, S. , Tracy, R. , Hotchkiss, J. , & Kirshner, B. (2012). Designing for the future: How the learning sciences can inform the trajectories of preservice teachers. Journal of Teacher Education , 63 (2), 147–60.
- Kärkkäinen, M. (1999). Teams as breakers of traditional work practices: A longitudinal study of planning and implementing curriculum units in elementary school teacher teams . Helsinki, Finland: University of Helsinki, Department of Education.
- Kelly, A. (2004). Design research in education: Yes, but is it methodological? Journal of the Learning Sciences , 13 (1), 115–128.
- Kelly, A. E. , & Sloane, F. C. (2003). Educational research and the problems of practice. Irish Educational Studies , 22 , 29–40.
- Kirshner, B. (2015). Youth activism in an era of education inequality . New York: New York University Press.
- Kirshner, B. , & Polman, J. L. (2013). Adaptation by design: A context-sensitive, dialogic approach to interventions. National Society for the Study of Education Yearbook , 112 (2), 215–236.
- Leander, K. M. , Phillips, N. C. , & Taylor, K. H. (2010). The changing social spaces of learning: Mapping new mobilities. Review of Research in Education , 34 , 329–394.
- Lesh, R. A. , & Kelly, A. E. (2000). Multi-tiered teaching experiments. In A. E. Kelly & R. A. Lesh (Eds.), Handbook of research design in mathematics and science education (pp. 197–230). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Matusov, E. (1996). Intersubjectivty without agreement. Mind, Culture, and Activity , 3 (1), 29–45.
- Messick, S. (1992). The interplay of evidence and consequences in the validation of performance assessments. Educational Researcher , 23 (2), 13–23.
- Mosteller, F. , & Boruch, R. F. (Eds.). (2002). Evidence matters: Randomized trials in education research . Washington, DC: Brookings Institution Press.
- Newman, D. , Griffin, P. , & Cole, M. (1989). The construction zone: Working for cognitive change in school . London, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Penuel, W. R. , Fishman, B. J. , Cheng, B. H. , & Sabelli, N. (2011). Organizing research and development at the intersection of learning, implementation, and design. Educational Researcher , 40 (7), 331–337.
- Polman, J. L. (2000). Designing project-based science: Connecting learners through guided inquiry . New York, NY: Teachers College Press.
- Ravitch, D. (2010). The death and life of the great American school system: How testing and choice are undermining education . New York, NY: Basic Books.
- Rogoff, B. (1990). Apprenticeship in thinking: Cognitive development in social context . New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
- Rogoff, B. (1995). Observing sociocultural activity on three planes: Participatory appropriation, guided participation, and apprenticeship. In J. V. Wertsch , P. D. Rio , & A. Alvarez (Eds.), Sociocultural studies of mind (pp. 139–164). Cambridge U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Saltman, K. J. (2007). Capitalizing on disaster: Taking and breaking public schools . Boulder, CO: Paradigm.
- Salvador, T. , Bell, G. , & Anderson, K. (1999). Design ethnography. Design Management Journal , 10 (4), 35–41.
- Sannino, A. (2011). Activity theory as an activist and interventionist theory. Theory & Psychology , 21 (5), 571–597.
- Sannino, A. , & Engeström, Y. (2016). Relational agency, double stimulation and the object of activity: An intervention study in a primary school. In A. Edwards (Ed.), Working relationally in and across practices: Cultural-historical approaches to collaboration (pp. 58–77). Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Scardamalia, M. , & Bereiter, C. (1991). Higher levels of agency for children in knowledge building: A challenge for the design of new knowledge media. Journal of the Learning Sciences , 1 , 37–68.
- Schoenfeld, A. H. (1982). Measures of problem solving performance and of problem solving instruction. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education , 13 , 31–49.
- Schoenfeld, A. H. (1985). Mathematical problem solving . Orlando, FL: Academic Press.
- Schoenfeld, A. H. (1992). On paradigms and methods: What do you do when the ones you know don’t do what you want them to? Issues in the analysis of data in the form of videotapes. Journal of the Learning Sciences , 2 (2), 179–214.
- Scribner, S. , & Cole, M. (1978). Literacy without schooling: Testing for intellectual effects. Harvard Educational Review , 48 (4), 448–461.
- Shavelson, R. J. , Phillips, D. C. , Towne, L. , & Feuer, M. J. (2003). On the science of education design studies. Educational Researcher , 32 (1), 25–28.
- Steffe, L. P. , & Thompson, P. W. (2000). Teaching experiment methodology: Underlying principles and essential elements. In A. Kelly & R. Lesh (Eds.), Handbook of research design in mathematics and science education (pp. 267–307). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
- Stevens, R. (2000). Divisions of labor in school and in the workplace: Comparing computer and paper-supported activities across settings. Journal of the Learning Sciences , 9 (4), 373–401.
- Suchman, L. (1995). Making work visible. Communications of the ACM , 38 (9), 57–64.
- Vakil, S. , de Royston, M. M. , Nasir, N. , & Kirshner, B. (2016). Rethinking race and power in design-based research: Reflections from the field. Cognition and Instruction , 34 (3), 194–209.
- van den Akker, J. (1999). Principles and methods of development research. In J. van den Akker , R. M. Branch , K. Gustafson , N. Nieveen , & T. Plomp (Eds.), Design approaches and tools in education and training (pp. 1–14). Boston, MA: Kluwer Academic.
- Virkkunen, J. , & Newnham, D. (2013). The Change Laboratory: A tool for collaborative development of work and education . Rotterdam, The Netherlands: Sense.
- White, B. Y. , & Frederiksen, J. R. (1998). Inquiry, modeling, and metacognition: Making science accessible to all students. Cognition and Instruction , 16 , 3–118.
- Zavala, M. (2016). Design, participation, and social change: What design in grassroots spaces can teach learning scientists. Cognition and Instruction , 34 (3), 236–249.
1. The reader should note the emergence of critical ethnography (e.g., Carspecken, 1996 ; Fine, 1994 ), and other more participatory models of ethnography that deviated from this traditional paradigm during this same time period. These new forms of ethnography comprised part of the genealogy of the more critical approaches to DBR, described later in this article.
2. The reader will also note that the adjective “qualitative” largely drops away from the acronym “DBR.” This is largely because, as described, DBR, as an exploration of naturalistic ecologies with multitudes of variables, and social and learning dynamics, necessarily demands a move beyond what can be captured by quantitative measurement alone. The qualitative nature of the research is thus implied and embedded as part of what makes DBR a unique and distinct methodology.
Related Articles
- Qualitative Data Analysis
- The Entanglements of Ethnography and Participatory Action Research (PAR) in Educational Research in North America
- Writing Educational Ethnography
- Qualitative Data Analysis and the Use of Theory
- Comparative Case Study Research
- Use of Qualitative Methods in Evaluation Studies
- Writing Qualitative Dissertations
- Ethnography in Early Childhood Education
- A History of Qualitative Research in Education in China
- Qualitative Research in the Field of Popular Education
- Qualitative Methodological Considerations for Studying Undocumented Students in the United States
- Culturally Responsive Evaluation as a Form of Critical Qualitative Inquiry
- Participatory Action Research in Education
- Complexity Theory as a Guide to Qualitative Methodology in Teacher Education
- Observing Schools and Classrooms
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Education. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 04 May 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|185.126.86.119]
- 185.126.86.119
Character limit 500 /500
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

12 Ethnography
Anthony Kwame Harrison, Department of Sociology, Virginia Tech
- Published: 02 September 2020
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This chapter introduces ethnography as a distinct research and writing tradition. It opens with a discussion of ethnography’s current fashionability within transdisciplinary academic spaces and some of the associated challenges. The next section provides a historical overview of ethnography’s emergence as a professionalized research practice within the fields of anthropology and sociology. Focusing on ethnography as a research methodology, the chapter outlines several key attributes that distinguish it from other forms of participant observation–oriented research; provides a general overview of the central paradigms that ethnographers claim and/or move between; and spotlights three principal research methods that most ethnographers utilize—namely, participant observation, field-note writing, and ethnographic interviewing. The final section of the chapter introduces a research disposition called ethnographic comportment , defined as a politics of positionality that reflects both ethnographers’ awarenesses of and their accountabilities to the research tradition they participate in.
Introduction
In a classic 1929 American Mercury article on racial passing and investigating lynchings, the future executive secretary of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People, Walter White, opened with an observation:
In any American village, North or South, East or West, there is no problem which cannot be solved in half an hour by the morons who lounge about the village store. World peace, or the lack of it, the tariff, sex, religion, the settlement of the war debts, short skirts, Prohibition, the carryings-on of the younger generation, the superior moral rectitude of country people over city dwellers (with a wistful eye on urban sins)—all these controversial subjects are disposed of quickly and finally by the bucolic wise men. (White, 1929 , p. 77)
Ethnographers are neither morons nor bucolic wise men. If called on, they may supply truncated answers to difficult questions. But they do this with an understanding that they are merely scratching the surface or offering something along the lines of sweeping tendencies regarding what are typically complicated and often contradictory aspects of human organization and social relations. The closer and deeper one looks, the more one sees. For this reason, ethnography is not particularly well suited for the kinds of business or policy-oriented research that requires statistically verifiable findings or strict evidentiary bases for direct and uncomplicated action plans (Jones, 2010 ). Still, references to ethnography and/or ethnographic thisses-and-thats increasingly appear in these and numerous other settings. To fully appreciate the value of ethnographies, it is important to read them in their entirety. Ethnographies are not built for efficiency in research practice or in communicating research results.
As a reflexive, intersubjective research tradition—that speaks to audiences’ hearts as well as to their minds—ethnography is most at home in spaces where complexity, nuance, and betwixt-and-betweenness are valued. Thus, there is a palpable tension between this research methodology—founded on patience and aspirations for comprehensive understandings—and the increasingly neoliberal academic environments, where the practices of ethnography have historically been nurtured and where a majority of practicing ethnographers continue to reside, settings where, increasingly, time, volume of output, and tangibility of results are key factors determining what is valued. We see this among graduate students of the early 21st century, who are progressively more pressured to have solid publication records upon completing their degrees—a practice that encourages some advisors to discourage students from pursuing ethnographic research. Another consequence of this development is the gradual erosion of ethnographic standards as shorter durations of research and shortened pathways to confirmable findings are accepted, if not heralded, as measures of competency. Under such conditions, the invisible work of ethnography (Forsythe, 1999 ), and the associated belief that anyone can do it, amplifies its current fashionability in problematic ways.
This chapter provides a foundation for understanding ethnography as a research methodology and genre of research reporting. While celebrating ethnography’s flexibility and generative potential—indeed, its refusal to be contained within fixed definitions—I also present it as a distinct research tradition, guided by a series of evolving conventions and commitments. This emphasis on precision is motivated by what I see as a multipronged crisis within the transforming field of ethnographic research. Factors influencing this crisis include but are not limited to: (a) ethnography’s place within neoliberal universities and associated spaces where efforts toward increasing efficiency reign; (b) a “transdisciplinary romance with ethnography” (Kazubowski-Houston & Magnat, 2017 ) that, too often, leads undertrained and underinvested researchers to claim the label—thus, in my view, doing violence to ethnography in both a figurative and a literal sense (Ingold, 2014 ); and (c) increased institutional surveillance and “methodological conservatism,” which creates hostile environments for ethnographers seeking to have their work approved by oversight bodies and agencies (Lincoln, 2005 ). At the same time, ethnography has qualities that make it particularly well suited for grasping and representing complex social phenomena and the contentious bases of knowing during these difficult times. Methodologically, ethnography flourishes in the liminal spaces between research design and improvisation. Through their critical engagements with its sometimes troubled history, trained ethnographers tend to align with marginalized perspectives and the communities they emanate from. Representationally, ethnography refuses to reduce the social world to simplistic binaries or neatly bracketed findings. In the following pages, I elaborate on these and other qualities of the ethnographic enterprise. Specifically, I present ethnography as a distinct methodology—rooted in the professionalization of anthropology and, to a lesser degree, sociology as academic fields—with a particular set of defining attributes, paradigmatic observances, and research conventions.
Defining Ethnography
The term ethnography references both a research and an inscription (i.e., writing process to written product) practice. Ethnography is research in that it describes a methodology (distinguished from a research method in the section Ethnography as Methodology) usually conceptualized as involving participant observations within a community or field of study. 1 Thus, a person can speak of doing ethnographic research among Vermont maple sugarers (Lange, 2017 ) or among people participating in a translocal cultural phenomenon who may not even consciously identify as a group (Amit, 2000 ). At the same time, it is an inscription practice in that the products of ethnographic research—typically books like Edmund Leach’s classic Political Systems of Highland Burma (1954) or Riché J. Daniel Barnes’s Raising the Race (2016)—are referred to as ethnographies. 2
Typically, greater academic attention is given to discussions of ethnography as research. However, to the extent that evaluations of and inferences about research are derived from the resulting written account, this focus on ethnography as research may be overblown. Indeed, since at least its postmodern turn (see Clifford & Marcus, 1986 ; Marcus & Fischer, 1986 ), considerable attention has fallen on ethnography as a literary convention. Scholars have additionally argued that writing practices are integral to ethnographic data collection and analysis and therefore should not be treated separately (Emerson, Fretz, & Shaw, 2011 ; Richardson & St. Pierre, 2005 ; Sanjeck, 1990 ). 3 Elaborating on a concept that I call ethnographic comportment , toward the close of this chapter, I argue that most researchers are guided by a “textual awareness” (Van Maanen, 2011 , p. 158)—an imagined end product that they are working toward—that influences them variously throughout all stages of an ethnographic project, from conception to publication. Nevertheless, if one is looking for a standard definition of ethnography, a research-oriented definition such as the one offered by Martyn Hammersley and Paul Atkinson (1995) is quite typical:
[Ethnography involves] participating, overtly or covertly in people’s daily lives for an extended period of time, watching what happens, listening to what is said, asking questions … [and] collecting whatever [other] data are available to throw light on the issues that are the focus of the research. (p. 1)
Such a simple, straightforward definition highlights ethnography’s resemblance to “the routine ways in which people make sense of the world everyday” (Hammersley & Atkinson, 1995 , p. 2)—thus making it appear to be something anyone can do. But to paraphrase something my colleague Carol A. Bailey once told me, no one would think of doing multiple linear regressions without statistical data analysis training, yet, quite regularly, people with no background in qualitative research claim to be doing ethnography (see also Schwandt, 2000 , p. 206n3). Commenting on the popularity of ethnography in consumer research, Patricia L. Sunderland and Rita M. Denny ( 2007 ) remarked,
A myriad of research techniques … (from the few-minute in-store intercept interview, to the one-hour “depth interview,” to the online focus group) have become redefined as “ethnographic” with barely any change in the underlying assumptions regarding method or analysis. Researchers have transformed themselves into “ethnographers” with few changes in practice beyond the name. (pp. 13–14)
Although these observations are specific to a single nonacademic arena, I argue that, even within the academy, the proliferation of ethnography warrants similar sentiments. In his book The Cosmopolitan Canopy (2011), Elijah Anderson defined folk ethnography as “a form of people watching that allows individuals informally to gather evidence in social interactions that supports their own viewpoints or transforms their commonsense understandings of social life” (p. xv). Although Anderson views this as a positive development, it concerns me that the distinction between folk ethnography and ethnography is blurring. In this chapter, I argue against the notion of ethnography as a qualitative research free-for-all, open for anyone, regardless of background or training, to undertake. As Diana E. Forsythe ( 1999 ) asserted, it is not “just a matter of common sense” (p. 130). Ethnography is a specific approach to research and writing about it, with a rich history and established yet evolving set of guiding principles. For those of us who take ethnography seriously, it involves training (usually through advanced coursework and mentorship), reflection, and accountability.
Historical Foundations of Ethnography
As a research tradition, ethnography’s roots are most firmly planted in the fields of anthropology and qualitative sociology: the former most often credited to the innovations of Polish-born, British-trained Bronislaw Malinowski and the latter usually attributed to a collection of researchers associated with the University of Chicago—commonly referred to as the Chicago School. Though these origin myths have been widely discussed and debated, and some treatments suggest ethnography began as early as the Greeks and Romans (Wax, 1971 ), I nevertheless cast ethnography as a relatively recent methodology, which came of age with the professionalization of both disciplines during the early decades of the 20th century.
In my chapter for the first edition of the Oxford Handbook of Qualitative Research , I discussed this history in great detail (see Harrison, 2014 ) and will therefore offer only a truncated version here. 4 During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, on both sides of the Atlantic, the nascent academic field of social/cultural anthropology crystallized around a reorientation away from the traditional model of armchair theorizing and toward a serious investment in ways of going about collecting and using data. 5 The various learned societies dedicated to anthropological interests that emerged during the 19th century relied primarily on the reports of colonial administrators, military officers, missionaries, traders, and other travelers for their information. The new class of professional anthropological intellectuals who came into being through these organizations prioritized the need for more formal—and less prejudiced, sensationalized, and unequivocally racist—standards of scientific reporting. In this interest, various sets of anthropological questionnaires and field guides were developed, initially for untrained travelers but, over time, increasingly toward the goal of fostering the most “precise and exacting” methods among field anthropologists (Urry, 1972 , p. 51). The most famous of these was Notes and Queries on Anthropology , which appeared in six iterations between 1874 and 1951 (Urry, 1972 ). Another effort to circumvent the limitations of untrained, biased, and otherwise disinterested reporting involved expeditions featuring teams of specialized experts—most notably the Cambridge Torres Straits expedition of 1898 (Stocking, 1983a ) and a series of privately funded and Bureau of American Ethnology–sponsored expeditions to the American Southwest occurring throughout the late 19th century (Judd, 1967 ).
Malinowski, the famed “founding father” of ethnography (Jones, 2010 ), came to anthropology after earning a doctorate in physics and mathematics from Jagiellonian University in Poland. He arrived in England—one of the key centers of anthropological thought—at precisely the right moment to benefit from the decades-long debates regarding appropriate ethnographic data collection methods that had been taking place. A year before his arrival, in a 1909 meeting of the principals from Oxford, Cambridge, and the London School of Economics, it was decided that the term ethnography would be used in specific reference to “descriptive accounts of non-literate peoples”—as distinct from the historical and comparative-based term ethnology (Radcliffe-Brown, 1952 , p. 276). We can thus mark this meeting as arguably the first collective effort to delineate ethnography as the principle data collection method within the rapidly professionalizing field. 6
Arriving in England, Malinowski immediately connected with a small circle of scholars, dedicated to anthropological interests, calling themselves the Cambridge School. This group included Alfred Cort Haddon, William H. R. Rivers, and Charles Seligman, all of whom had participated in the 1898 Torres Straits expedition. The quality of the various anthropological writing projects Malinowski had undertaken prior to landing in England—including what would become his first book, The Family among the Australian Aborigines (1913/1963)—undoubtedly facilitated his acceptance into this distinguished group. Still, Malinowski’s emergence as the most recognized figure in the development of ethnography can largely be attributed to timing. At the time of his arrival, members of the Cambridge School were already grappling with many of the ethnographic revelations that Malinowski would eventually put forward in his seminal work, Argonauts of the Western Pacific (1922/1966). Malinowski can be distinguished as the last member of the Cambridge School to conduct fieldwork prior to the outbreak of World War I (Stocking, 1983b , p. 82) and the first professionally trained anthropologist to carry out research according to the most recent methodological advances of the time (Kuper, 1996 , p. 7). Consequently, when Argonauts was published a few years after the war, it stood alone as an implementation and representation of the culmination of prewar Cambridge School theorizing.
Malinowski embarked on his South Pacific fieldwork in 1914—carrying with him the 1912 edition of Notes and Queries , which had been considerably revised by Rivers (Myers, 1923 ). After a 6-month “apprentice’s trail run” on the island of Mailu in southern New Guinea (Kuper, 1996 , p. 12), the young researcher would more famously carry out two extensive periods—of a year each, 1915–1916 and 1917–1918—in the Trobriand Islands. During his initial Mailu fieldwork, Malinowski realized that his research became more productive when isolated from the prejudicial influences of the European administrators, missionaries, and traders who were also present on the island. Writing about this experience in Argonauts , he recounted, “It was not until I was alone in the district that I began to make some headway” (Malinowski, 1922/1966 , p. 6). This revelation sparked one of Malinowski’s most notable contributions to the practice of ethnography, which George Stocking ( 1983b ) described as “a shift in the primary locus of investigation, from the deck of the mission ship or the verandah of the mission station to the teeming center of the village” (p. 93). Such a positional shift facilitated a corresponding adjustment to his ethnographic posture:
In this type of work, it is good for the Ethnographer sometimes to put aside camera, note book and pencil, and to join in himself in what is going on. 7 … Out of such plunges into the life of the native … I have carried away a distinct feeling that their behavior, their manner of being, in all sorts of tribal transactions, became more transparent and easily understandable than it had before. (Malinowski, 1922/1966 , pp. 21–22)
In his preface to Argonauts of the Western Pacific , esteemed anthropologist James George Frazier hailed it as a “remarkable record of anthropological research” by someone who had “lived as a native among the natives” (J. G. Frazier, 1922 / 1966 , p. vii). For his part, Malinowski was exceedingly deliberate in foregrounding his methodological “innovations.” Thus, the myth of Malinowski—as the first field researcher to voluntarily remove himself from colonial quarters, (essentially) cut off all ties with “civilization,” and immerse himself in the world of “savages” as a methodological imperative for understanding their world—soon took legs. His prescriptive methods for doing this included long-term residence by a trained researcher; learning the local language rather than relying on interpreters; collecting as much data as possible on as wide a range of activities as possible—from the spectacular and ceremonial to the everyday and mundane—and taking copious field notes; and, when possible, partaking in social activities as a participant observer.
One of the most rehearsed explanations of ethnography, contained within the pages of Argonauts , is Malinowski’s oft-cited goal of “grasp[ing] the native’s point of view” (Malinowski, 1922/1966 , p. 25). This decree to recognize and (to some degree) prioritize the subjectivity of non-Western peoples marked a transformative moment in how anthropology was practiced. No longer simply viewed as the objects of study, the perspectives of rational native actors provided the platform for developing anthropology’s relativist doctrines. By advocating for the internal logics underlying each culture, anthropology came to serve a critical role in exposing the prejudice and racism surrounding evaluations of cultural difference (Baker, 2010 ). 8 Together, Malinowski’s prescriptions amounted to a methodological manifesto (Strathern, 1987 ) that championed experiential modes of understanding, contextualization, and the distinction between ideal and actual behavior as signaling the capacity for agency within social structures.
In the most celebrated histories of anthropology, the idea of participant observation–based fieldwork, which is at the core of modern ethnography, came into being through these methodological advancements. Yet, the myth of the “Malinowskian Revolution” (Kuper, 1996 , p. 32) belies the tremendous effort and attention toward refining anthropological research methods that were taking place prior to his arrival in England, as well as across the Atlantic among Franz Boas and his students (see Harrison, 2014 ; Lassiter & Campbell, 2010 ). Although Malinowski was not singly responsible for inventing these ethnographic standards, his archetype status has been significant to their reification. Furthermore, his position during the interwar period as England’s “only master ethnographer” helped him to further cement his progenitor status (Kuper, 1996 , p. 1). 9 For most of the 20th century and now continuing into the 21st, the image of “going off” to a fieldwork site far removed from the university community one is a part of, for a minimum of 1 year, has been a rite of passage within sociocultural anthropology; and for much of this time, the importance of conducting research in non-Western societies—what some have critiqued as anthropology’s intrinsic process of Othering (Deloria, 1969 ; Magubane & Faris, 1985 )—was rationalized as “absolutely essential” to the development of an anthropological perspective (Mead, 1952 , p. 346).
Far and away the most celebrated ethnographic conventions practiced outside anthropology came from a collection of researchers associated with the University of Chicago’s department of sociology. Generally speaking, the Chicago School 10 formed through the combined influences of Malinowskian fieldwork methodologies and German phenomenological theory (Jones, 2010 ). Through their conceptualization of urban life as an assemblage of “natural areas” or “little communities,” researchers affiliated with the Chicago school, under the direction of Robert E. Park, imagined the city as a social laboratory through which to examine secular differences—primarily oriented around ethnicity and various forms of civic otherness. With an extensive background in newspaper work and having served as “a sort of secretary” to Tuskegee Institute founder and notable African American spokesman Booker T. Washington (Faris, 1967 , p. 28), Park arrived in Chicago in 1913 with keen interests in issues surrounding urban life, race relations, ethnic heterogeneity, and processes of assimilation. Soon thereafter, Park dedicated himself to training graduate students and, indeed, several of the most significant works to come out of the program during the interwar period were authored by his students (Blumer, 1998 ). 11
While ethnography has long-standing roots in sociology, its centrality to the discipline has never matched its position as the “hallmark methodology” of anthropology (Sunderland & Denny, 2007 , p. 13). From the outset, sociology’s ethnographic efforts were firmly intertwined with anthropology. 12 Thus, although Chicago sociologists gave a good deal of attention to particular aspects of methodological training, their most inspired forays into fieldwork were often characterized as a closer-to-home version of what anthropologists do. 13 We can see this in Park’s justifications for the kinds of research he was most interested in advancing. In an important essay advocating for the scientific value of researching the city, Park explained:
Anthropology, the science of man, has been mainly concerned up to the present with the study of primitive peoples. But civilized man is quite as interesting an object of investigation.… The same patient methods of observation which anthropologists like Boas and Lowie have expended on the study of the life and manners of the North American Indian might be even more fruitfully employed in the investigation of the customs, beliefs, social practices, and general conceptions of life prevalent in Little Italy on the lower North Side in Chicago, or in recording the more sophisticated folkways of the inhabitants of Greenwich Village and the neighborhood of Washington Square, New York. (Park, 1925/1967 , p. 3)
Years later, in describing his own attraction to this ethnographic tradition, Howard S. Becker ( 1999 ) explained, “You had all the romance of anthropology but could sleep in your own bed and eat decent food” (p. 8).
Still, the model of urban-based fieldwork put forth by Chicago School sociologists was an important predecessor to the way ethnography is thought of and practiced today. For much of the 20th century, anthropological field research focused on small, isolated communities where it was possible to get to know most members, map out kinship relations, and, at least, imagine that one was getting a comprehensive portrayal of society. 14 In the early 21st century, virtually all ethnographers adopt a topic-oriented approach, which focuses on one or more specified aspects of and/or social networks within what are understood to be much more complex and globally interconnected societies. As a result of the metropolitan settings of their research, urban sociologists, unlike their colleagues in anthropology, were compelled to acknowledge that they were dealing with specific dimensions of social life and/or subcultures that were situated within larger societal contexts.
The origins of ethnography as a professionalized methodological (research) and representational (writing) practice are most squarely situated within the discipline of anthropology. Recognizing these foundations in no way implies that ethnography is the exclusive purview of anthropology or, for that matter, that anthropologists should have exclusive right in determining what does and does not qualify as ethnography (Atkinson, 2017 ). Indeed, some of the most significant methodological considerations leading up to ethnography’s now-standard insistence on reflexivity (see the section Ethnographic Comportment) issued from the application of sociology’s symbolic interactionist theories to circumstances surrounding the ethnographic encounter (Berreman, 1962 ; Junker, 1960 ); and today many of the most exciting works surrounding ethnography issue from transdisciplinary spaces. I therefore echo Magdalena Kazubowski-Houston and Virginie Magnat’s ( 2017 ) call for “coalition and collaboration between like-minded ethnographers across the social-sciences, the arts, and the humanities” (p. 11). Yet these historical foundations continue to serve as methodological anchors for ethnographers.
Ethnography as Methodology
In discussing ethnography, commentators sometimes incorrectly treat it as a method rather than a methodology. The difference is significant. A method is simply a tool or technique used to collect and/or analyze data. Ethnographers typically utilize a variety of tools and techniques during the course of their research, including but not limited to establishing rapport; selecting informants; using a range of interview and/or focus group forms; making observations—both participatory and nonparticipatory—and writing field notes based on them; conducting surveys, genealogies, and domain analyses; mapping fields; transcribing texts; and coding data. 15 In contrast, methodologies are established norms of inquiry that are by and large adhered to within distinct research traditions. A methodology, therefore, involves theoretical, ethical, political, and at times moral orientations to research, which guide the decisions researchers make, including their choice of methods. Accordingly, it can be thought of as a philosophy of research practice, analysis, and description. Later in the chapter, I detail three of the most fundamental methods that ethnographers commonly utilize—namely, participant observation, field-note writing, and ethnographic interviews. However, first I outline several key attributes that, in my view, contribute to any instance of research being ethnographic and then highlight three philosophical positions—or what I call paradigms —that ethnographers orient themselves in relation to when conducting research.
Ethnographic Attributes
In this section I outline five essential priorities that distinguish ethnography. I offer these, in part, as a corrective to what I regard as the casual and commonplace misappropriation of it as a stand-in for all types of qualitative research (Kazubowski-Houston & Magnat, 2017 ). Building on my earlier definition, these attributes should be regarded as important orienting principles that scholars trained in ethnography and aware of its historicity hold in common.
Ethnography and Culture
Harry F. Wolcott asserted that the critical attribute distinguishing ethnography from other forms of qualitative research is a focus on describing and interpreting cultural behavior. In other words, at its core an ethnography must include an intentional engagement with and “working resolution” toward understanding culture (Wolcott, 1987 , p. 45). Wolcott called this ethnographic intent . The specifics of this “working resolution” may vary. Culture, according to Stephen A. Tyler ( 1969 ), provides the framework for recognizing and describing how “people make order out of what appears … to be utter chaos” (p. 6). Yet for the inquiring ethnographer, culture might be conceptualized as being revealed through people’s behaviors, the expressed ideals that guide such behaviors, or the discovery of underlying frameworks through which situational choices are made. Each of these, or some combination, can have implications for how ethnographic researchers go about their craft.
Debates over a precise definition of culture notwithstanding, ethnography has traditionally rested on a principle of cultural comparison, perhaps best reflected in the anthropological maxim of “making the strange familiar and the familiar strange.” For earlier generations of ethnographers—primarily anthropologists and sociologists (see the section Historical Foundations of Ethnography)—this was accomplished by traveling to starkly different social settings, which brought about the inevitable comparisons with the home “culture” (as the term was then understood 16 ). As the lens of ethnographic inquiry expanded to include spaces and places that did not initially appear to be particularly distinct from the ethnographer’s home (Messerschmidt, 1981 ), this comparative mode of sense-making became more implicit than explicit. The native ethnographer, for instance, conducting research in her own community, would appear to start from the same cultural foundations as the people she (participant) observes. Yet, as a trained ethnographer—someone who has read cultural theory and been exposed to several cross-cultural ethnographic studies—she makes sense of her observations in relation to the wealth of documented scholarship on cultural diversity. 17 Thus, she is less likely to generalize distinct cultural practices as the “normal way” people do things and more apt to frame her observations and understandings in conversation with foundational and recent thinking about culture.
Ethnography and Contextualization
Ethnographies prioritize contextualization, meaning that particular people and the situations they find themselves in are best understood in relation to broader factors that impact them—including, but not limited to, historical, local, political, economic, and religious factors. Anthropology, in particular, has historically recognized interconnections and mutual influences between various aspects of social life—or what anthropologists call holism . Following from this, ethnographers take an open-minded, inductive approach to what might potentially be considered data. In other fields of research where deductive reasoning —that is, the idea that truth follows from a sequence of conditional premises that can be empirically verified—is prioritized, efforts are made to silence external noises in the interest of focusing on what researchers determine are the most salient factors and variables. The inductive reasoning that guides ethnographic research starts from the assumption that such noises have consequence—they not only impact social conditions but also, at times, reflect deeper structural workings of culture.
Contextualization also impacts situational constructions of meaning. To illustrate what I mean here, I turn to the work of Clifford Geertz ( 1973 ), who famously defined ethnography as “an elaborate venture in … ‘thick description’ ” (p. 6). Referencing a thought experiment conducted by philosopher Gilbert Ryle ( 1971 ), Geertz elaborated on thick description through the example of a rapidly contracting eyelid. Whether such action amounts to an involuntary twitch of the eye or a “conspiratorial signal to a friend” (i.e., a wink) is entirely contextual. Accordingly, a thin description of behavior—“her left eye blinked”—tells us very little. Through understanding such things as the circumstances under which the blink occurred, the intention of the blinker, the prevalent social codes that may or may not mark the blink as meaningful, and whether this meaning was received and understood, we get a better sense of what is going on. Thick description, then, in the words of anthropologist Karin Narayan ( 2012 ), can be summarized as “layering meaning into closely observed details” (p. 8). Noticing and describing something as subtle and instantaneous as a blink requires careful attention to detail; it means observing social life with the same heightened sensitivity that we use when perceiving works of art (Willis, 2000 ). Yet, without proper contextualization, such descriptions have limited ethnographic value.
Ethnography as Iterative
In addition to being governed by inductive principles—meaning that research “starts from the data rather than from a hypothesis to be tested, or even from a fixed research question” (Hammersley, 2008 , p. 69)—ethnography proceeds as an iterative mode of inquiry. By this I mean that ethnographers continually re-engage with their research questions, fundamental assumptions, methods of inquiry, and accumulated data toward the goal of refining their work—which can sometimes include making a radical change in direction. Consequently, ethnographic research designs must be flexible enough to allow for the expected surprises and misadventures that arise when an individual (serving as a research instrument) engages in the daily lives of other people—who are inevitably continuing along the unforeseeable journeys that are their lives—for a prolonged period of time. Even at its most scientific, ethnography is resolutely a human science conducted in a real-world laboratory. As such, the ethnographic enterprise is saturated with circumstances, situations, and personalities that are unanticipated and often uncontrollable. Barbara Tedlock ( 2000 ) elaborated:
No matter how much care the ethnographer devotes to the project, its success depends upon more than individual effort. It is tied to outside forces, including local, national, and sometimes even international relationships that make research possible as well as to a readership that accepts the endeavor as meaningful. (p. 466)
Indeed, one of the most predictable aspects of ethnographic research is its unpredictability, so much so that statements along the lines of “I began my research intending to study X but wound up studying Y ” are now standard ethnographic writing conventions. I would go so far as to suggest that an absence of such sentiments (i.e., everything working out according to plan) is greeted with more suspicion than their presence.
Recognizing how ethnographic data and interpretation evolve simultaneously, James Spradley ( 1980 ) offered a cyclical model of ethnographic inquiry—what he calls the ethnographic research cycle —as distinct from the linear research models (i.e., define the problem, formulate hypotheses, gather and analyze data, draw conclusions) found in the other social sciences. According to Spradley ( 1980 ), each phase of ethnographic inquiry (data collection and analysis) informs new questions:
The cycle cannot wait until you have collected a large amount of data.… You need to analyze your fieldnotes after each period of fieldwork in order to know what to look for during the next period of participant observation. (pp. 33–34)
As such, a strict sequence of prescribed methods will not suffice. Ethnography achieves virtue and vitality through its lack of prescription, by continuously straddling the line between structured research design and improvised inquisitive adventure. Gary Alan Fine and James G. Deegan ( 1996 ) described ethnography as “a puzzle of mysterious design” that is “only known when the researcher has decided that it is close enough to completion” (p. 441). Through iterative processes of tacking back and forth between experiences and reflections, ethnographers piece together their research projects.
Ethnography then should be thought of as involving iterative–inductive–inscription practices . 18 It is iterative in the sense that it involves recurrently engaging with theory, data, and analysis (O’Dell & Willim, 2011 ); it is inductive in that ethnographers approach this engagement with open minds and few preconceptions about where data will lead them; and it is inscriptive in foregrounding writing as its principal mode of recording data, analyzing data, and representing social life (Richardson & St. Pierre, 2005 ).
Ethnography and Empathy
The ethnographic project is variously empathetic. Through intersubjective engagements—most notably via participant observation—ethnographers aspire to “imaginatively experience the feelings, thoughts, and situation” (Davis, 2014 , p. 6) of people they work among. As such, ethnography encourages a degree of intimacy between researcher and researched that, at its best, recognizes and appreciates their mutual implication in the production of knowledge (Lassiter, 2005 ; Sluka & Robben, 2012 ). Ethnographers’ commitments to the people and communities they conduct research among are both moral and political. Academically situated ethnographers—on the basis of their training, disciplinary identities, and institutional affiliations—are mandated to protect the interests of the people and communities they work among by following institutional and disciplinary guidelines surrounding research, most notably those pertaining to informed consent, deception , and confidentiality . 19 In addition, trained and invested ethnographers recognize their charge to reveal, unsettle, and at times undermine the institutions and forces through which social inequalities are maintained and perpetuated. Thus, ethnographers are consistently attentive to the interests of disempowered groups. When working among such groups, these commitments to social justice result in alliances and recognitions of researched communities’ roles in evaluating the quality of ethnographies (Harrison, 2018 ). In contrast, when working among power-wielding groups—what Laura Nader ( 1972 ) called studying up —ethnographers should feel some obligation to use their position and access to uncover and even disrupt the workings of power. This can take many forms. However, its absence—for example, using conventional ethnographic methods for the explicit purpose of perpetuating social inequalities—in these enlightened times 20 is simply not ethnography.
This notion of ethnographic empathy also pertains to the reception of works ethnographers produce. Ethnographic authors write toward the of goal of enabling their readers to envision themselves walking in someone else’s shoes and, what is more, to grasp people’s perspectives and understand their behaviors as resulting from alternative (or previously unrecognized) cultural logics. Ethnographers’ written accounts communicate person-to-person sentiments—inviting readers to imagine the situated interests and actions of someone else. Resembling, to some degree, how a politician might use a handful of personal stories to communicate something about the state of a nation during a national address, 21 the most evocative ethnographic writings utilize sentimentality and emotion in detailing individual’s stories and particular episodes. As such, their representational power lies in their informational richness and ability to communicate affect , as opposed to other research traditions that prioritize statistical validity or theoretical applicability. Indeed, by providing compelling testimonies, which embrace the emotionality and messiness of real life (Law, 2004 ), ethnographies do more to complicate and therefore advance existing theories than to straightforwardly confirm them.
Ethnography and Narrative
Storytelling saturates ethnography. Ethnographers collect stories from people firsthand, on their own terms, or in such close proximity to them that they powerfully reflect something about the way culturally situated actors move through their worlds (Turner, 2007 ). As researchers, we invite such stories through open-ended ethnographic interviews (see the section Ethnographic Interviews) where participants are asked to share their personal histories, their perspectives, and/or what is most meaningful to them about a given topic. Ethnographers are also told personal narratives while building rapport and deeply hanging out (Wogan, 2004 )—for example, when getting a ride home from an open-microphone event (Harrison, 2009 , p. 64) or while sharing cramped living spaces (Holmes, 2013 ). In addition, ethnographers are regularly featured actors in the stories they recount. Contemporary ethnography mandates degrees of reflexivity and transparency, both of which demand that researchers share aspects of their personal stories and provide some accounting of the research experiences that led them to know what they know. These stories—often culled from interview transcripts or field journals or pieced together from various sources (Brand, 2007 )—get recirculated, re-created, or re-placed, sometimes verbatim, in ethnographic texts.
Ethnographers are foremost writers. A primary aspect of their data collection involves writing field notes (see the section Field-Note Writing). In crafting these and other data into finished works, they indulge ethnography’s aspirations and ability to reach broad audiences and to communicate sophisticated meanings through artful storytelling and other experimental modes of academic writing. As a thickly descriptive research genre, ethnographic texts may, at times, appear to threaten too much information; however, when done well, the layered meanings activated through such dense contextualization circle back to show their relevance. Accordingly, ethnographic writing should be undertaken as a writerly endeavor—meaning that authors acknowledge the intelligence of their readers and, therefore, allow space for them to construct their own meanings and make their own sense of certain aspects of an ethnographic account. 22
The Story of the College Visit
A few years after completing my dissertation, I was invited to speak to an anthropology class at a small liberal arts college where I was giving a guest lecture. The students had read a short piece—recounting the story of a gathering in Golden Gate Park following an open-microphone event—that would become the introduction to my first book, Hip Hop Underground (Harrison, 2009 ). 23 I spent a few minutes talking about my research in relation to the passage and then opened the floor for questions. A few questions in, a young man raised his hand and began explaining how he had grown up in San Francisco, had probably “partied” on the same Golden Gate Park picnic tables that I mentioned in my piece, and was someone who considered hip-hop close to his heart. At this point, he looked away, focusing on the paper on his desk and, in thoughtful, measured tones explained that whenever he read an academic piece on hip-hop he found himself getting defensive. Mine was the first piece he had read where he did not have that feeling. “That’s ethnography,” I said.
Paradigmatic Plasticity
Throughout the course of their research and writing, ethnographers orient themselves around certain theoretical, ethical, and political commitments. At their foundation, these commitments involve questions of ontology (concerning the nature of reality), epistemology (how we know what we know), and axiology (relating to morals and values). Following Patricia Leavy ( 2009 ), I use paradigm as an umbrella term that encompasses the range of philosophical stances, assumptions, and goals that surround research endeavors. Although the philosophies guiding ethnographic research are quite often unstated, at moments when they come into conflict the results can be explosive.
The Story of the Conference Incident
Several years ago, I attended an interdisciplinary conference where, in response to a few last-minute cancelations, the organizers decided to combine two panels. This made sense at the time. First, although the panel topics were different, they overlapped under the broader theme of the conference. Second, a single panel would attract a larger audience for all of the presentations—indeed, by the time I arrived it was standing room only. Last, such a move would spare one presenter from the awkwardness of being the lone panelist in a 90-minute session. However, in deciding to combine panels, the organizers overlooked or chose to ignore the paradigmatic differences informing the respective audiences that would be drawn to each panel. This did not become an issue until the final presentation: a masterful explication on the functionality of various strategies for alleviating conflict among competing social groups. During the question-and-answer period, an audience member—who had obviously come to see presentations initially slated for the other panel—questioned the researcher’s right to reduce people’s behaviors to such all-too-neat formulations, the evidentiary basis on which his claims were being made, as well as his investment in the communities through which, in making his academic career, he appeared to be profiting from. Chaos ensued as the two parties went back and forth in a heated exchange—with the accused researcher at one point even blurting out, “You don’t know me!” Thankfully, there were only a few minutes left in the session. As the panel came to a close, various colleagues approached the two combatants to endorse their action and/or console, as appropriate.
As a research tradition, ethnography straddles multiple paradigms. With its roots in anthropology—regarded as the most humanistic of social sciences and the most scientific of humanities (Redfield, 1953 )—such paradigmatic plasticity is to be expected. Yet, as ethnographic practices have migrated to a wide range of academic disciplines and interdisciplinary spaces, the potential for paradigmatic disputes over what is and what is not “good” and/or legitimate research has become more pronounced.
By my reckoning, both parties involved in the conference incident would rightly consider their work ethnographic. Yet where activities of research (i.e., methods) may appear similar, the foundational philosophies of knowledge (i.e., epistemologies) and ideas about how it should be applied through endeavors labeled “research” can look radically different.
In considering different paradigmatic orientations surrounding qualitative inquiry, Thomas Schwandt ( 2000 ) highlighted three areas of concern that are instructive for my discussion of ethnography. I adapt them here:
Cognitive concerns surrounding how to define, justify, and legitimize claims to understanding.
Social concerns regarding (in this case) the goals of ethnography.
Moral concerns as to how to “envision and occupy the ethical space” between ethnographers and those they research in responsible, obligatorily aware, and status conscious ways (see Schwandt, 2000 , p. 200).
Before briefly outlining some of the paradigms that surround ethnography, I offer a few caveats. Whereas defining and labeling paradigmatic frameworks is useful, it would be a mistake to give too much attention to trying to fit a particular researcher or even an instance of ethnographic research neatly into one category. Ethnographic experience is perpetually ephemeral, meaning that at times ethnographers are prone to move, transform, and shape shift between different paradigmatic classifications. Attempts to categorize also tend to highlight differences over time and disciplinary space. While differences clearly exist—the above-mentioned conference incident stands as a testament to this—the need to neatly place individuals or projects in particular boxes closes down the possibility of also seeing commonalities and furthermore belies the nuanced nature and theoretic eclecticism of ethnographic inquiry. Nonetheless, in what follows, I discuss three philosophical traditions that ethnographers might move between and draw from as paradigmatic resources.
Positivism is premised on a belief in what is referred to as naive realism —that is, the notion that there is a reality out there that can be grasped through sensory perception. As such, it holds empirical data—that which is produced though direct observations—as definitive evidence through which to construct claims to truth. In doing so, positivism prioritizes objectivity, assuming that it is possible for a researcher to detach him- or herself from values, interests, or the clouding contamination of bias and prejudice. Following this formula, good research is achieved through conventional rigor—that is, dutifully following a prescribed, systematic series of steps surrounding data accumulation and analysis. In that positivism recognizes a fundamental (capital “T”) Truth, which it is believed researchers can apprehend, researchers anchored in this tradition are more prone to concern themselves with questions of transferability (i.e., can the findings from one setting be applied to another?) and generalizability (i.e., can the findings from a particular context be generalized to the whole?) on the assumption that such Truth has potential relevance for a broad range of social circumstances and cultural contexts. Although few, if any, contemporary ethnographers would define themselves as strict positivists, it is nonetheless important to discuss positivism as foundational to any social scientific enterprise. To some extent, outlining the tenets of strict positivism may be useful in explaining what most ethnographers are not. However, before dismissing it too quickly, I should point out that, particularly with regard to the mandates of certain gatekeepers of credible research reporting, ethnography is not as far removed from its positivist principles as some of its practitioners would like to think. Postpositivist orientations 24 toward valuing empirical evidence, making efforts toward detached objectivism, and deductive reasoning continue to carry weight, even if researchers are less confident about their conclusions.
Interpretivism
Interpretivism, which issues from an acknowledgment of the constructed nature of all social reality, recognizes no single all-encompassing Truth, but rather multiple (small “t”) truths that are the products of human subjectivities. Thus, cultural and contextual specifics are critical to understanding, and inductive reasoning becomes the privileged path to making sense of unwieldy social realities. Reality, which is shaped by experience, thus becomes something to be interpreted. Such interpretivism sees human action as inherently meaningful with meanings being processual, temporal, and historically unfinished. The subjectivity of the ethnographer is quite consequential here. Under any form of interpretivism, the outcomes of researcher bias are acknowledged. Sometimes efforts are made to mitigate researchers’ subjectivities. Such techniques might involve reflexive journaling, inventorying subjectivities, and other attempts to manage and track bias (Schwandt, 2000 , p. 207n11). Yet, increasingly, interpretivist approaches accept that within ethnography the human is the research instrument and, as such, cultural, social, and personal frames of reference are inescapable.
Critical Research
The critical research paradigm focuses on the workings of power, with attention to axes including (but not limited to) race, gender, ethnicity, age, class, sexuality, and differential abilities. As opposed to the positivist stance of neutrality and detachment, critical researchers distinguish themselves by their personal and sometimes emotional investment in the welfare of the individuals and communities they work among. Critical researchers are committed to using their research to empower such communities by working with them to create meaningful social change. 25 As such, they aspire to make the processes surrounding research transparent to both the communities they work among and their various audiences. Critical perspectives emerged in connection with various social movements of the 1960s and 1970s and, accordingly, are often fashioned as a form of scholar activism. Recently, participant action and collaboration have become key methodological imperatives shaping the relationships formed around various critical research projects. Through such developments, questions regarding who initiates research, controls its direction, and owns its products have become vitally important.
Ethnographers do not just take part in the daily lives of the people they conduct research among; as a consequence of their participation, they impact people’s lives and, in turn, are implicated in them. It is therefore difficult to separate cognitive, social, and moral concerns surrounding research. All are influenced by the research paradigm(s) the ethnographer observes. Paradigmatic orientations affect the entire ethnographic process, starting with the ways research is conceived of and designed, what qualifies as data, and ultimately how such data are treated.
Through the previous discussion of paradigms and essential attributes, I have drawn attention to ethnography as a research methodology, as opposed to a method. Again, this distinction is important to my effort to differentiate ethnography from qualitative field research more generally. Nevertheless, when someone mentions doing ethnographic research, a handful of research activities (or methods) come to mind. These include having sustained contact with a community of people through participant observation, writing field notes, and (usually) interviewing. In the following sections, I give each of these research conventions additional consideration.
Participant Observation
Participant observation, as the term suggests, refers to a research disposition somewhere between full participation, just like (or as) a member of a community, and strictly observing. While participant observation is often conceptualized as a location on a continuum between these two extremes—with ideally some level of balance 26 —I believe it is better thought of as a simultaneous process that oscillates between varying degrees of participation and observation. Such oscillations occur both situationally and temporally. In the case of the latter, they might take place in the context of a particular event or more generally over the course of different research phases. Participant observation has historically been championed as providing the virtues of both an insider’s (participant) and an outsider’s (observer) perspective. As a foundation of ethnographic understanding, a discussion of this insider/outsider binary is instructive even if such neat distinctions rarely, if ever, exist in the lived world.
Whereas a recognized goal of ethnography is to grasp people’s understandings of their world, since its inception the primary means of achieving this goal has been through experiential understanding. Writing in his introduction to Argonauts , Malinowski (1922/1966, p. 5) recalled that, to “get … the hang of tribal life,”
I had to learn how to behave, and to a certain extent, I acquired “the feeling” for native good and bad manners. With this, and with the capacity of enjoying their company and sharing some of their games and amusements, I began to feel that I was indeed in touch with the natives, and this is certainly the preliminary condition of being able to carry on successful field work. (p. 8)
Yet to simply grasp the native’s point of view is often not enough. Ethnographers have long recognized that “those cultural features of a particular society that are the most deeply ingrained are the least likely to be explicated and questioned by native members themselves” (Wengle, 1988 , p. xvii). As a consequence of ethnocentrism —that is, the tendency for all people to position their own cultural beliefs and practices at the center of their worldview (i.e., to see them as “normal”)—native members of a cultural group are at times blind to many of the most salient aspects of their lifeways. 27 Thus, a flexible and situated position somewhere between an insider and an outsider is typically upheld as ideal.
As a practice, participant observation involves an inherent critique of interviewing. Although interviewing is fundamental to most ethnographic projects, advocates of participant observation are quick to point out that, if the goal is to understand behaviors and worldviews in their cultural context, interviews alone will not suffice. There is usually some disjuncture between what people do and what they say they do. At one level, this can be seen as a distinction between ideal and actual behavior. In an interview setting, people are more likely to shade their representations of behaviors toward cultural ideals. For example, studies point out the tendency among Americans to underreport the amount of alcohol they consume (Rathje & Murphy, 1992 ). Whether consciously underreported or not, this pattern is likely connected to the cultural ideal against drinking too much. Yet even in circumstances where a strong cultural ideal is not in play, people’s behaviors amount to more than what they choose or are able to tell an interviewer in the context of an interview. Native language speakers, for example, would have considerable difficulty explaining the rules to their language or how they know what they know without additional linguistic training. Even in a situation where both conditions are met (someone is aware and can explain ), an interviewee must make decisions about what to emphasize and what to ignore or gloss over. Such choices might lead them to steer clear of topics that the interviewer would find salient. 28
To return to the drinking example, in particular settings where the ability to consume a lot of alcohol is linked to status, it may be likely that quantities will be overreported. Of course, such settings are usually informal, are semiexclusive, and involve peer groups—for example, the stereotypical morning after the college fraternity party. Another advantage of participant observation over interviewing alone is that it provides access to these interior spaces. Fieldworkers achieve this by locating such spaces, gaining access (including building rapport), and, notably, spending time there. The famous Hawthorne studies on worker productivity found that people tend to alter their behavior for short periods of time under the scrutiny of a researcher or observer (Landsberger, 1958 ). Such reactivity can jeopardize ethnography’s aspirations for naturalistic inquiry. Thus, an ideal, if nearly unattainable, goal of participant observation is that the researcher becomes familiar enough within the research setting that everyday life proceeds as if he or she was not there. Factors surrounding this include duration of time in a setting, resemblance between researcher and members of the researched community, and level of participation.
Duration of Time in the Setting
The general rule is that the longer a researcher stays in “the field,” the more accustomed people become to his or her presence—not to mention the greater the understanding of what is going on. Yet this is conditional. Wolcott ( 1987 ) pointed out that, “based on any one researcher’s skill, sensitivity, problem, and setting, optimum periods of fieldwork may vary” (p. 39). Nevertheless, it is worth noting that within anthropology the Malinowski-derived standard has been a minimum of 1 year in the field.
Resemblance between Researcher and Members of the Researched Community
This resemblance includes both physical and social resemblances. Greater resemblance, in theory, facilitates “life as usual,” whereas notable differences are a perpetual reminder that there is a researcher present. Some of the most recognizable differences concern race, language proficiency, decisions regarding self-presentation, and, in certain instances, age and gender.
Level of Participation
This, in part, depends on the researcher’s aspirations—for example, a researcher may aspire to a stance that, at different times, involves full participation or minimum participation (Junker, 1960 ). At the same time, and in conjunction with the previously noted factors, the various communities researchers engage have differing levels of accessibility and inclinations toward hospitality (e.g., insisting that someone “join in”); and beyond language alone, researchers have different competencies 29 —all of which can impact their level of participation.
In sum, participant observation is simultaneously the most fundamental, complex, and uncertain method of ethnographic research. Its temporal parameters can range from strictly designated fieldwork outings—for example, a few hours in the field on a weekday afternoon—to an all-consuming living experience (24 hours a day) spanning several years. Its spatial parameters can be as narrow as a Midwest college bar (Spradley & Mann, 1975 ), as broad as multiple sites across a global landscape (Wulff, 1998 ), and as amorphous as translocal (Gupta & Ferguson, 1997 ) and virtual (Nardi, 2010 ) fields of activity. 30 While a good deal of planning goes into participant observation research projects, the combination of its ill-defined parameters and the fact that it plays out in the lived world render it difficult to forecast and, consequently, a largely improvised endeavor.
Field-Note Writing
A second principal method of ethnographic research is the creation and management of ethnographic field notes. These systematic in-the-field writings are inextricably linked to participant observation in that they serve as the primary means of recording the detailed observations and insights gleaned through such experiences. Accordingly, the quality and character of field-note writing have implications on an ethnographer’s ability to accurately and effectively report research findings. 31 Historically, field notes received little methodological attention. Like ethnography more generally, their resemblance to people’s everyday activities—particularly the act of keeping a personal journal or diary—cultivated the belief that instructions to simply “write down everything you see and hear” would suffice. In the literature that has since emerged on field-note writing, there is no consensus on a single correct method. I would advise any researcher to use the available methodological prescripts as guidelines but to develop particular routines and procedures that align with their own best writing habits as well as the specific circumstances of research. Nevertheless, a handful of best practices consistently show up in the literature and together illustrate why field-note writing and keeping a diary are not one and the same.
Schedule a significant amount of time each day or soon after each fieldwork “outing” to write field notes. Details fade with the passage of time, so do not unnecessarily delay field-note writing. In a full-immersion fieldwork situation—where participant observation comprises the entirety of one’s living experience—this practice of writing field notes (i.e., articulating and reflecting on observations and experiences) can be thought of as the major nonparticipatory endeavor that the researcher consistently engages in.
Employ jottings or “scratch notes” (Sanjek, 1990 , p. 96)—that is, quickly scribbled words or phrases, written in the context of participant observing, intended to jog one’s memory when writing. A researcher should always carry a small notebook or some equivalent jot-recording technology (e.g., a small handheld recorder). Additionally, when observing/experiencing the world with the intention of documenting it through field-note writing, it is important to rely on all one’s senses and not merely vision alone. Sounds, smells, tastes, and touches can all be powerful means to creating scenes on a page.
Organize different approaches to field-note writing categorically. For example, Emerson et al. (2011, pp. 57–79) discussed four general field-note subcategories: (a) descriptions based on concrete sensory details of physical spaces, people, objects, or actions, (b) dialogues between people, (c) characterizations portraying how a person acts and lives, and (d) narratives involving either sketches (i.e., snapshots) of a setting/character or episodes illustrated through continuous action and interaction. In all of these categories, it is important for the field-note writer to distinguish between that which is concrete and/or directly observed—for example, verbatim quotes—and that which is inferred, approximated, or logically assumed (Bailey, 2017 ). Field notes can additionally take the form of methodological notes (highlighting research techniques used and/or planned), analytic notes (periodic forays into conceptual understandings that strive to approximate professional writing 32 ), and personal notes (therapeutic and potentially revealing outlets for discussing one’s relationships, feelings, and emotions).
Ethnographic Interviews
Ethnographers typically conduct interviews as a primary method of research. However, whereas participant observation is so central to ethnography that some well-practiced scholars might be forgiven for simply—and in my view, mistakenly—equating the two, interview-based research and ethnography are distinctly different (Becker & Geer, 1957 ; Lamont & Swidler, 2014 ). Ethnographers, like most qualitative researchers, conduct interviews, but, unlike participant observation, interviews alone do not come close to approximating ethnography.
Ethnographic interviewing is distinct from what I will call general interview-based research in several ways. First, ethnographic interviews typically take place after a researcher has been in the field for some period of time. Ethnographers do not enter the field assuming they know what is most important; firsthand experience in a social arena is thought to facilitate better interview questions (O’Reilly, 2012 ). It is furthermore presumed that a level of familiarity between researcher and researched, and perhaps even mutual respect, leads to better research collaborations.
Second, ethnographers understand and at times analyze interviews as speech events—meaning that an interview is more than just a transcript of questions and answers. Contextual factors including (but not limited to) place, time, body language, fluidity of dialogue, and prior relationship between interviewer and interviewee may all have a bearing on the way an interview plays out (O’Reilly, 2012 ). In fact, an ethnographer may find as much value in what a person chooses not to talk about as in what they emphasize. Additionally, the texture of statements—such things as inflection, accent, volume, and cadence—combined with context, can often alter the literal meaning of what is said.
Finally, some ethnographers consider everyday dialogue with people in the field as a form of informal interviewing. If an interview is defined as a consciously initiated verbal exchange through which a researcher—primarily via questions and answers—learns from the people they conduct research among about a given topic, we must be cognizant of the fact that, during the course of participant observation–based fieldwork, these types of exchanges take place all the time. At what point does asking someone how to take the bus downtown or inquiring, over coffee, about why someone did not join his or her sister in visiting a relative turn into an interview? The point is, with participant observation research, these distinctions are conditional and often undefined.
Participant observation, field-note writing, and ethnographic interviewing are by no means the only research methods ethnographers employ. The data collection techniques of ethnographic research are often determined pragmatically in relation to theoretical orientations, research questions, and the availability and appropriateness of various options. Ethnographers also gather and analyze pieces of material culture, make nonparticipatory behavioral observations; record videos; take photographs; engage in community mapping; conduct surveys, genealogies, and domain analyses; and examine archival documents, censuses, and various media materials, in addition to a range of other methods. Nevertheless, participant observations, the field notes they inspire, and interviewing comprise the core practices of most ethnographic researchers.
Ethnographic Comportment
As a final framework for understanding ethnography and what distinguishes it from other forms of participant observation–based field research, I introduce the idea of ethnographic comportment as a politics of positionality, which bears on an ethnographer’s conduct and demeanor throughout the research and writing process. The critical awarenesses that underly ethnographic comportment, in many respects, are extensions of ethnography’s now-standard mandate for reflexivity. Generally speaking, reflexivity in ethnography amounts to an awareness of “one’s own role in the construction of social life as [ethnographic research] unfolds” (O’Reilly, 2012 , p. 11). It involves “a continual internal dialogue and critical self-evaluation” regarding one’s positionality, assumptions, and agendas (Berger, 2015 , p. 220). The origins of reflexivity can be traced to ethnographers’ postwar rise in self-consciousness (Nash & Wintrob, 1972 ), which was fully realized with anthropology’s 1980s postmodern turn (Clifford & Marcus, 1986 ; Marcus & Fischer, 1986 ). In the early 21st century, reflexivity is thought of as both an important aspect of ethnographic knowledge production and a means to assessing research accountability and validity. Trained ethnogra phers are well aware of this—to the point, perhaps, where reflexivity becomes embodied knowledge or a part of who we are.
Ethnographic training also includes familiarity with ethnography’s history and key debates (McGranahan, 2014 ). This history began during the colonial era at a time when, according to Kathleen Gough ( 1968 ), “Western nations were making their final push to bring practically the whole pre-industrial non-Western world under their political and economic control” (p. 401). Anthropologists, particularly, are well schooled in this history and, as a foundation of contemporary disciplinary training, debate the extent to which past ethnographers were willingly and/or unwillingly complicit in furthering it (see Lewis, 2013 ). Ethnographers working in sociology observe a similar tradition of researching marginalized urban communities (Vidich & Lyman, 2000 ) and representing them in ways, or through analytical categories, that were often not consistent with their self-understandings and/or best interests.
Training in ethnography should also incorporate considerations of the power dynamics that continue to shape ethnographic encounters (Koivunen, 2010 ; Wolfe, 1996 ). These critical awarenesses inspire sensibilities that ethnographers carry with them throughout the research enterprise. I am in no position to prescribe the exact decisions and actions that follow from such awarenesses. Does the White British ethnographer researching in Ghana meaningfully grapple with the politics surrounding the favorable attention she receives as a European in Africa, or does she simply explain that Ghanaians are nice and she had no trouble building rapport? Does she struggle with the historical implications of potentially projecting her own frames of understanding onto contemporary Abron music practices or does she simply report what she understands she is seeing and move on? The choice is up to the ethnographer; however, it should be made with some understanding of and critical reflection on the enterprise she is taking part in. To summarize, ethnographic comportment involves a historical awareness and reflexive self-awareness of one’s participation in ethnography as a research tradition. Following João de Pina-Cabral’s ( 1992 ) assertion that ethnographers match what they observe “against the accumulated knowledge of [their] discipline” (p. 6), I maintain that such knowledge increasingly includes a critical outlook on both the historical and the resonating fault lines of ethnography as practiced.
At a moment when the (mis)use of ethnography as an umbrella term for any and all qualitative research threatens its integrity, researchers who are seriously invested in ethnography are reflexive of their participation in this research tradition. Accordingly, they adopt a disposition of accountability for their role in advancing rejuvenated and/or progressive forms of ethnographic practice. Throughout the process of research, ethnographers are (self-)conscious about how they comport themselves in relation to their research and the people they are researching among; they are also conscious—albeit often abstractly—of the end product that they are working toward. Such textual awareness (Van Maanen, 2011 ) influences their decision-making throughout the various, flexible, and often unforeseeable stages of an ethnographic project. When their work is finished, they hope that both their in-the-field conduct and their written ethnography will be regarded as good (see Harrison, 2018 ) and, in the best of instances, that the latter will contribute to furthering the ethnographic tradition in positive ways.
In sum, ethnographic comportment is predicated on the idea that the embodied knowledge a researcher has accrued through disciplinary and methodological training guides them, as a form of improvised analysis, throughout the ethnographic enterprise toward the goal of producing work that is valued in its own right, (usually) by the researched community, and as part of the ethnographic tradition.
At a time when the proliferation of ethnography threatens to untether it from its core commitments and fundamental modes of inquiry, I see a pressing need to reprofessionalize ethnography by calling attention to its historical foundations, outlining its central practices and research principles, and presenting new frameworks, which I believe are helpful in grasping and gauging its contemporary significance. An awareness of ethnography’s history—its complicated engagements with colonialism and progressive humanism—should inform all efforts to move it forward. Beyond key practices like participant observation, field-note writing, and ethnographic interviewing, ethnography is marked by its attention to culture as an explanatory construct, lavish contextualization, iterative modes of data collection and analysis, empathetic engagements, and abundant storytelling. In embracing these attributes, ethnographers thoughtfully observe, reflect on, and represent the complexities of social life and culturally situated perspectives of people.
Ethnographers are not particularly adept at problem solving, in large part because the knowledge they procure, produce, and distribute is expansive, conditional, and historically unfinished. While “bucolic wise men” gather at the village store and resolve gun control debates or immigration issues in minutes, the ethnographer among them is perpetually suspicious of such quick answers. She understands that her job is to listen for meaning. She may participate—to extend the dialogue or maintain her own internal dialogue as she reflects on the grounded perspectives being shared around her. Above all else, she recognizes that people on all sides of a debate have convictions, passions, and frameworks of understanding that should be respected and that, as researchers, we should aspire to better understand. Increasingly, such patience and attention to human complexities are under threat by assembly line modes of academic production that treat time and knowledge as commodities. Yet by resisting these inclinations—and offering a counter to narrow definitions of research efficiency—ethnography secures its relevance to understanding the varied ways people live their lives and means through which they know what they know.
Future Directions
How can ethnography continue to flourish within contexts of accelerating academic production? How can it maintain its patient, thoughtful, and unfinished research practices at a time when academic value is equated with efficiency, volume of output, and tangibility of results?
Given that many people in the early 21st century engage with digital/social media technologies as aspects of their daily lives, how can ethnography best attend to the intersections between virtual and physical worlds?
In contexts of increased political and methodological conservatism, where institutional review boards require completed research designs and protocols as prerequisites to approval, how can ethnographers represent their iterative and inductive modes of research in ways that comply with institutionally mandated expectations?
As the lines between ethnography and everyday life become increasingly fuzzy, what new modes of ethnographic understanding and representation should be acknowledged and embraced?
In ethnography’s postpostmodern reformulations and trajectories, how should researchers map the borders of the field (ontologically and in terms of the various interests that ethnographic studies can serve)?
Ethnography’s foundations are in writing culture, yet, historically, ethnographers are deeply implicated in the project of literatizing nonliterate societies. Given this paradox, what nonliteral forms of ethnographic representations might a contemporary, critical, and historically informed ethnographic project take? How can we move beyond writing culture ?
Here, I am using field in both the traditional sense of fieldwork conducted within a physical place/space and in the Bourdieuian sense of a field of cultural practice (Bourdieu, 1984 ).
Ethnographies can also take the shorter form of essays and professional journal articles, as well as nonliterary forms like “films, records, museum displays, or whatever” (Geertz, 1973 , p. 19n). Recognizing this—yet in the interest of avoiding cumbersome qualifications—throughout the remainder of the chapter I treat ethnography foremost as a writing practice.
Etymologically, ethnography combines ethno , meaning “culture (or race),” and graphy, meaning “to write, record, and describe.” Thus, ethnography can be thought of as the process and product of writing, recording, and describing culture.
In addition to my own writings, there is a wealth of very good work on ethnography’s history—for example, see Darnell ( 2001 ), Jones ( 2010 ), Kuper ( 1996 ), Lassiter ( 2005 ), and Stocking ( 1983a ).
Broadly speaking, the distinction between social and cultural anthropology is based on national traditions, with the former practiced in England and the latter in the United States. More specifically, British (social) anthropology has historically stressed the interrelationships between social institutions and observes foundational figures like Malinowski and Alfred R. Radcliffe-Brown, whereas American (cultural) anthropology recognizes cultural coherences as outlined through the work of Franz Boas and Ruth Benedict (Garbarino, 1977/1983 ).
In the introduction to Argonauts of the Western Pacific , Malinowski ( 1922/1966 ) included a footnote explaining that, “according to a useful habit of the terminology of science, [he] uses the word Ethnography for the empirical and descriptive results of the science of Man, and the word Ethnology for speculative and comparative theories” (p. 9, fn).
Historically, the masculine pronouns he/him/his were used as universal references to all people—in this case falsely implying that all ethnographers were men. Rather than cluttering the text with numerous [ sic ]s, I let these pass without further comment. In instances where I offer gendered pronouns, as a general (but not exclusive) rule, I use the feminine she/her/hers. Following Margery Wolf ( 1992 ), I do not do this “to privilege the female voice but to call attention to the way in which the supposedly generic ‘he’ does in fact privilege the male voice” (p. 56).
Malinowski was certainly not the first to acknowledge the importance of “native subjectivity”—in fact, several commentators have highlighted this as an area where American anthropologists greatly outpaced their British counterparts (Bunzl, 2004 ; Darnell, 2001 ; Lassiter & Campbell, 2010 ). Indeed, cultural relativism as an anthropological movement is most prominently connected with Franz Boas and his students, Margaret Mead ( 1928/1961 ), Melville Herskovits ( 1972 ), and, most famously, Ruth Benedict ( 1934/2005 ). Yet the significance of Malinowski’s powerful dictate to understand native subjectivities—as a “goal, of which an ethnographer should never lose sight” (1922/1966, p. 25)—is illustrated by the frequency with which he has been and continues to be cited.
A short list of Malinowski’s students at the London School of Economics includes Raymond Firth, E. E. Evans-Pritchard, Hortense Powdermaker, Edmund Leach, Jomo Kenyatta, Lucy Mair, Audrey Richards, and Meyer Fortes.
Howard Becker ( 1999 ) is critical of this designation, arguing that “ ‘Chicago’ was never the unified chapel … [nor] unified school of thought” that many believe it to have been (p. 10).
These include Nel’s Anderson’s The Hobo (1923/1961), Frederick Thrasher’s The Gang ( 1927 ), Louis Wirth’s The Ghetto ( 1928 ), Harvey W. Zorbaugh’s The Gold Coast and the Slum (1929), Paul Cressey’s The Taxi-Dance Hall ( 1932 ), and E. Franklin Frazier’s The Negro Family in Chicago ( 1932 ).
For example, until 1929, the department at Chicago was known as the Department of Sociology and Anthropology. Among the (other) notable anthropologists in the department during these formative years were Boas’s students, Edward Sapir and Fay-Cooper Cole; Robert Redfield, who married Park’s daughter; and Ralph Linton, who taught classes there while affiliated with Chicago’s Field Museum (Faris, 1967 ).
Commenting on the improvisational nature of anthropological ethnography, Lisa H. Malkki ( 2007 ) suggested that sociologists approach ethnography “with a different sensibility” (p. 186, n2). Additionally, there appears to be some historical reluctance within the sociological tradition to refer to their brand of field research as ethnography. In Buford H. Junker’s ( 1960 ) seminal introduction to social science fieldwork, for example, based on extensive interviews with University of Chicago student fieldworkers, ethnography is only referenced on a few occasions. In one telling passage, Junker describes the ethnographer’s task of “start[ing] from scratch by learning the language of his esoteric people” in opposition to the sociological field worker operating “in some part of an otherwise already familiar cultural milieu” (1960, p. 70).
Malinowski ( 1922/1966 ) specifically said that “one of the first conditions of acceptable ethnographic work certainly is that it should deal with the totality of all social, cultural, and psychological aspects of a community, for they are so interwoven that not one can be understood without taking into consideration all the others” (p. xvi). This idea of anthropology as a holistic science—assuming the interconnections and mutual influences between various aspects of social life—continues to be reiterated in the introductory chapters of almost all discipline textbooks.
Several very good overviews of the qualitative research methods used in ethnography exist, including Bailey ( 2017 ), Bernard ( 1995 ), Emerson, Fretz, and Shaw ( 2011 ), Gobo ( 2008 ), Hammersley and Atkinson ( 1995 ), Pawluch, Shaffir, and Miall ( 2005 ), and Spradley ( 1980 ).
Whereas historically ethnographers thought of their work as focusing on neatly bounded cultures, usually (mis)represented as being isolated from globalizing influences, 21st century ethnographers understand their work to be focused on culture as a socially orienting concept—accordingly, the term shifts from being a noun to an adjective (e.g., cultural beliefs, cultural values, cultural processes).
This is not to suggest, as others have (see Marcus & Fischer, 1986 , p. 156), that “native” ethnographers lose their capacity for radical critique as a result of their Western anthropological training (McClaurin, 2001 ).
In making this characterization, I am building on Karen O’Reilly’s ( 2012 ) description of ethnography as an iterative–inductive process .
See Christians ( 2000 ) for a thorough discussion of these three guiding pillars surrounding qualitative research ethics.
I insert this qualification to recognize an earlier (less enlightened) period when some would argue that ethnography was used as an instrument of colonial domination (see Asad, 1973 ; Deloria, 1969 ; Gough, 1968 ).
I make this comparison based on behavior, not presumed intent. I am well aware that many people view politicians as being disingenuous. I am in no way implying that ethnographers operate with insincere intentions. Thank you to Steve Gerus for bringing this similarity to my attention.
I juxtapose this understanding of writerly against the example of an instruction manual, which as a very unwriterly text does not recognize its readers’ capacity to think on their own and therefore presents information in unimaginative ways with the intention of providing little room for alternative interpretations.
This can be found in Harrison, 2009 , pp. 1–6.
For a short summary of postpositivism, see Bailey ( 2017 ).
In particular cases, where such researchers work among more powerful groups, these commitments might be toward exposing the workings of power, thus leading toward the same ends of empowering those who are marginalized.
These in-between spaces are sometimes distinguished as observing participation and participating observation (see Bernard, 1995 ; Hammersley & Atkinson, 1995 ; Junker, 1960 ).
This is sometimes referred to as homeblindness , defined as being blind to crucial dimensions of one’s own lifeways because they are taken for granted (Czarniawska, 1997 ). While I acknowledge that ethnocentrism more typically involves putting one’s culture above others, I maintain that homeblindness is a product of ethnocentrism.
Additionally, there might be countless potential reasons for an interviewee to be less than forthcoming.
For instance, someone doing an ethnography of pickup basketball games may have easier access if he or she has a background in playing basketball.
Today, many people engage the virtual, online, social media, or networked worlds consistently throughout their daily lives. To the extent that ethnographers are interested in engaging with people in everyday settings and circumstances, it would seem reasonable and even potentially quite illuminating for ethnographers to be attentive to the intersections of online and offline activities (Lane, 2016 ).
There are several excellent books that discuss field-note writing; see, for example, H. Russell Bernard’s Research Methods in Anthropology (1995); Carol A. Bailey’s A Guide to Qualitative Field Research ( 2017 ); and Robert M. Emerson, Rachel I. Fretz, and Linda L. Shaw’s Writing Ethnographic Fieldnotes ( 2011 ). I strongly recommend that any novice researcher carry one of these books when embarking on fieldwork.
My definition of analytic notes is consistent with what Emerson et al. ( 2011 ) called in-process memos .
Amit, V. ( 2000 ). Introduction: Constructing the field. In V. Amit (Ed.), Constructing the field: Ethnographic fieldwork in the contemporary world (pp. 1–18). New York, NY: Routledge.
Google Scholar
Google Preview
Anderson, E. ( 2011 ). The cosmopolitan canopy: Race and civility in everyday life . New York, NY: Norton.
Anderson, N. ( 1923 /1961). The hobo: The sociology of the homeless man . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Asad, T. ( 1973 ). Anthropology and the colonial encounter . London, England: Ithaca Press.
Atkinson, P. ( 2017 ). Thinking ethnographically . Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Bailey C. A. ( 2017 ). A guide to qualitative field research (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Baker, L. D. ( 2010 ). Anthropology and the racial politics of culture . Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
Barnes, R. J. D. ( 2016 ). Raising the race: Black career woman redefine marriage, motherhood, and community . New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press.
Becker, H. S. ( 1999 ). The Chicago school, so-called. Qualitative Sociology, 22, 3–12.
Becker, H. S. , & Geer, B. ( 1957 ). Participant observation and interviewing: A comparison. Human Organization, 16(3), 28–32.
Benedict, R. ( 1934 /2005). Patterns of culture . Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin.
Berger, R. ( 2015 ). Now I see it, now I don’t: Researcher’s position and reflexivity in qualitative research. Qualitative Research, 15, 219–234.
Bernard, H. R. ( 1995 ). Research methods in anthropology: Qualitative and quantitative approaches (2nd ed.). Walnut Creek, CA: AltaMira Press.
Berreman, G. D. ( 1962 ). Behind many masks: Ethnography and impression management within a Himalayan village . Ithaca, NY: Society for Applied Anthropology.
Blumer, M. ( 1998 ). Chicago sociology and the empirical impulse: Its implications for sociological theorizing. In L. Tomasi (Ed.), The tradition of the Chicago school of sociology (pp. 75–88). Brookfield, VT: Ashgate.
Bourdieu, P. ( 1984 ). Distinction: A social critique of the judgement of taste . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Brand, M. ( 2007 ). Making moonshine: Thick histories in a US historically black community. Anthropology and Humanism, 32, 52–61.
Bunzl, M. ( 2004 ). Boas, Foucault, and the “native anthropologist”: Notes toward a neo-Boasian anthropology. American Anthropologist, 106, 435–442.
Christians, C. G. ( 2000 ). Ethics and politics of qualitative research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 133–155). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Clifford, J. , & Marcus, G. E. (Eds.). ( 1986 ). Writing culture: The poetics and politics of ethnography . Berkeley: University of California Press.
Cressey, P. G. ( 1932 ). The taxi-dance hall . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Czarniawska, B. ( 1997 ). Narrating the organization: Dramas of institutional identity . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Darnell, R. ( 2001 ). Invisible genealogies. A history of Americanist anthropology . Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Davis, K. C. ( 2014 ). Beyond the White negro: Empathy and anti-racist reading . Urbana: University of Illinois Press.
Deloria, V., Jr. ( 1969 ). Custer died for your sins: An Indian manifesto . New York, NY: Macmillan.
Emerson, R. M. , Fretz, R. I. , & Shaw, L. L. ( 2011 ). Writing ethnographic fieldnotes (2nd ed.). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Faris, R. E. L. ( 1967 ). Chicago sociology, 1920–1932 . San Francisco, CA: Chandler.
Fine, G. A. , & Deegan, J. G. ( 1996 ). Three principles of Serendip: Insight, chance, and discovery in qualitative research. Qualitative Studies in Education, 9, 434–447.
Forsythe, D. ( 1999 ). “ It’s just a matter of common sense”: Ethnography as invisible work. Computer Supported Cooperative Work, 8, 127–145.
Frazier, J. G. ( 1922 /1966). Preface. In B. Malinowski , Argonauts of the western Pacific (pp. v–x). London, England: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Frazier, E. F. ( 1932 ). The Negro family in Chicago . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Garbarino, M. S. ( 1977 /1983). Sociocultural theory in anthropology: A short history . Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland Press.
Geertz, C. ( 1973 ). The interpretation of cultures . New York, NY: Basic Books.
Gobo, G. ( 2008 ). Doing ethnography . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Gough, K. ( 1968 ). New proposals for anthropologists. Current Anthropology, 9, 403–435.
Gupta, A. , & Ferguson, J. ( 1997 ). Anthropological locations: Boundaries and grounds of a field science . Berkeley: University of California Press.
Hammersley, M . ( 2008 ). Questioning qualitative inquiry: Critical essays . Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Hammersley, M. , & Atkinson, P. ( 1995 ). Ethnography: Principles in practice (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Routledge.
Harrison, A. K. ( 2009 ). Hip hop underground: The integrity and ethics of racial identification . Philadelphia, PA: Temple University Press.
Harrison, A. K. ( 2014 ). Ethnography. In P. Leavy (Ed.), The Oxford handbook of qualitative research (pp. 223–253). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Harrison, A. K. ( 2018 ). Ethnography . New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Herskovits, M. ( 1972 ). Cultural relativism: Perspectives in cultural pluralism . New York, NY: Random House.
Holmes, S. M. ( 2013 ). Fresh fruit, broken bodies: Migrant farmworkers in the United States . Berkeley: University of California Press.
Ingold, T. ( 2014 ). That’s enough about ethnography! HAU: Journal of Ethnographic Theory, 4, 383–395.
Jones, J. S. ( 2010 ). Origins and ancestors: A brief history of ethnography. In J. S. Jones & S. Watt (Eds.), Ethnography in social science practice (pp. 13–27). New York, NY: Routledge.
Judd, N. M. ( 1967 ). The bureau of American ethnology: A partial history. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press.
Junker, B. H. ( 1960 ). Field work: An introduction to the social sciences . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Kazubowski-Houston, M. , & Magnat, V. ( 2017 ). Introduction to special issue: The transdisciplinary travels of ethnography. Cultural Studies ↔ Critical Methodologies, 18, 379–391. doi:10.1177/1532708617737100 10.1177/1532708617737100
Koivunen, T. ( 2010 ). Practicing power and gender in the field: Learning from interview refusals. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography, 39, 682–708.
Kuper, A. ( 1996 ). Anthropology and anthropologists: The modern British school (3rd ed.). New York, NY: Routledge.
Lamont, M. , & Swidler, A. ( 2014 ). Methodological pluralism and the possibilities and limits of interviewing. Qualitative Sociology, 37, 153–171.
Landsberger, H. A. ( 1958 ). Hawthorne revisited: Management and the worker, its critics, and developments in human relations in industry. Ithaca, NY: Humphrey.
Lane, J. ( 2016 ). The digital street: An ethnographic study of networked street life in Harlem. American Behavioral Scientist, 60, 43–58.
Lange, M. ( 2017 ). Meanings of maple: An ethnography of sugaring . Little Rock: University of Arkansas Press.
Lassiter, L. E. ( 2005 ). The Chicago guide to collaborative ethnography . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Lassiter, L. E. , & Campbell, E. ( 2010 ). What will we have ethnography do? Qualitative Inquiry, 16, 757–767.
Law, J. ( 2004 ). After method: Mess in social science research . New York, NY: Routledge.
Leach, E. R. ( 1954 ). Political systems of highland Burma: A study of Kachin social structure . London, England: Bell.
Leavy, P. ( 2009 ). Method meets art: Arts-based research practice . New York, NY: Guilford.
Lewis, H. S. ( 2013 ). In defense of anthropology: An investigation of the critique of anthropology. New Brunswick, NJ: Transaction.
Lincoln, Y. S. ( 2005 ). Institutional review boards and methodological conservatism. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (3rd ed., pp. 165–181). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Magubane, B. , & Faris, J. C. ( 1985 ). On the political relevance of anthropology. Dialectical Anthropology, 9, 91–104.
Malinowski, B. ( 1913 /1963). The family among the Australian aborigines. New York, NY: Schocken Books.
Malinowski, B. ( 1922 /1966). Argonauts of the western Pacific . London, England: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Malkki, L. H. ( 2007 ). Tradition and improvisation in ethnographic field research. In A. Cerwonka & L. H. Malkki (Eds.), Improvising theory: Process and temporality in ethnographic fieldwork (pp. 162–187). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Marcus, G. E. , & Fischer, M. M. J. ( 1986 ). Anthropology as cultural critique: An experimental moment in the human sciences . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
McClaurin, I. ( 2001 ). Theorizing a Black feminist self in anthropology: Towards an autoethnographic approach. In I. McClaurin (Ed.), Black feminist anthropology: Theory, politics, praxis, and poetics (pp. 49–76). New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press.
McGranahan, C. ( 2014 ). What is ethnography? Teaching ethnographic sensibilities without fieldwork. Teaching Anthropology, 4, 23–36.
Mead, M. ( 1952 ). The training of the cultural anthropologist. American Anthropologist, 54, 343–346.
Mead, M. ( 1928 /1961). Coming of age in Samoa . New York, NY: Morrow.
Messerschmidt, D. (Ed.). ( 1981 ). Anthropologists at home in North America: Methods and issues in the study of one’s own society . Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
Myers, J. L. ( 1923 ). W. H. R. Rivers. The Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland, 53, 14–17.
Nader, L. ( 1972 ). Up the anthropologist—perspectives gained from studying up. In D. Hymes (Ed.), Reinventing anthropology (pp. 284–311). New York, NY: Pantheon Books.
Narayan, K. ( 2012 ). Alive in the writing: Crafting ethnography in the company of Chekhov . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Nardi, B. ( 2010 ). My life as a night elf priest: An anthropological account of World of Warcraft . Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
Nash, D. , & Wintrob, R. ( 1972 ). The emergence of self-consciousness in ethnography. Current Anthropology, 13, 527–542.
O’Dell, T. , & Willim, R. ( 2011 ). Irregular ethnographies: An introduction. Ethnologia Europaea, 41, 5–13.
O’Reilly, K. ( 2012 ). Ethnographic methods (2nd ed). New York, NY: Routledge.
Park R. E. ( 1925 /1967). The city : Suggestions for the investigation of human behavior in the urban environment. In R. E. Park , E. W. Burgess , & R. D. Mckenzie (Eds.), The city (pp. 1–46). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Pawluch, D. , Shaffir, W. , & Miall, C. ( 2005 ). Doing ethnography: Studying everyday life . Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Canadian Scholars’ Press.
Pina-Cabral, J. D. ( 1992 ). Against translation: The role of the researcher in the production of ethnographic knowledge. In J. D. Pina-Cabral & J. Campbell (Eds.), Europe observed (pp. 1–23). New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan.
Radcliffe-Brown, A. R. ( 1952 ). Historical note on British social anthropology. American Anthropologist, 54, 275–277.
Rathje, W. , & Murphy, C. ( 1992 ). Rubbish! The archaeology of garbage . New York, NY: HarperCollins.
Redfield, R. ( 1953 ). Relations of anthropology to the social sciences and humanities. In A. L. Kroeber (Ed.), Anthropology today (pp. 728–738). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Richardson, L. , & St. Pierre, S. A. ( 2005 ). Writing: A method of inquiry. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (3rd ed., pp. 959–978). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Ryle. G. ( 1971 ). The thinking of thoughts: What is “Le Penseur” doing? In G. Ryle , Collected papers: Vol. II, Collected essays 1929–1968 (pp. 480–496). London, England: Hutchinson.
Sanjek, R. (Ed.). ( 1990 ). Fieldnotes: The makings of anthropology . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
Schwandt, T. A. ( 2000 ). Three epistemological stances for qualitative inquiry: Interpretivism, hermeneutics, and social constructionism. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 189–213). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Sluka, J. A. , & Robben, A. C. G. M. ( 2012 ). Fieldwork in cultural anthropology: An introduction. In A. C. G. M. Robben & J. A. Sluka (Eds.), Ethnographic fieldwork: An anthropological reader (2nd ed., pp. 1–47). Malden, MA: Wiley–Blackwell.
Spradley, J. P. ( 1980 ). Participant observation . Fort Worth, TX: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Spradley, J. P. , & Mann, B. J. ( 1975 ). The cocktail waitress: Woman’s work in a man’s world . New York, NY: Wiley.
Stocking, G. W., Jr. (Ed.). ( 1983 a). Observers observed: Essays on ethnographic fieldwork . Madison: University of Wisconsin Press.
Stocking, G. W., Jr. ( 1983 b). The ethnographer’s magic: Fieldwork in British anthropology from Tylor to Malinowski. In G. W. Stocking Jr. (Ed.), Observers observed: Essays on ethnographic fieldwork (pp. 70–120). Madison: University of Wisconsin Press.
Strathern, M. ( 1987 ). Out of context: The persuasive fictions of anthropology. Current Anthropology, 28, 251–281.
Sunderland, P. L. , & Denny, R. M. ( 2007 ). Doing anthropology in consumer research . Walnut Creek, CA: Left Coast Press.
Tedlock, B. ( 2000 ). Ethnography and ethnographic representation. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Sage handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 455–486). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Thrasher, F. M. ( 1927 ). The gang: A study of 1,313 gangs in Chicago . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Turner, E. ( 2007 ). Introduction to the art of ethnography. Anthropology and Humanism, 32, 108–116.
Tyler, S. A . (Ed.). ( 1969 ). Cognitive anthropology: Readings . New York, NY: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Urry, J. ( 1972 ). Notes and queries on anthropology and the development of field methods in British anthropology, 1870–1920. Proceedings of the Royal Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland, 45–57.
Van Maanen, J. ( 2011 ). Tales of the field: On writing ethnography . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Vidich, A. J. , & Lyman, S. M. ( 2000 ). Qualitative methods: Their history in sociology and anthropology. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 37–84). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Wax, R. H. ( 1971 ). Doing fieldwork: Warning and advice . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Wengle, J. L. ( 1988 ). Ethnographers in the field: The psychology of research . Tuscaloosa: University of Alabama Press.
White, W. ( 1929 ). I investigate lynchings. American Mercury, 16, 77–84.
Willis, P. ( 2000 ). The ethnographic imagination. Cambridge, England: Polity Press.
Wirth, L. ( 1928 ). The ghetto . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Wogan, P. ( 2004 ). Deep hanging out: Reflections on fieldwork and multisited Andean ethnography. Identities: Global Studies in Culture and Power, 11, 129–139.
Wolcott, H. F. ( 1987 ). On ethnographic intent. In G. Spindler & L. Spindler (Eds.), Interpretive ethnography of education: At home and abroad (pp. 37–57). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Wolf, M. ( 1992 ). A thrice-told tale: Feminism, postmodernism, and ethnographic responsibility . Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Wolfe, D. (Ed.) ( 1996 ). Feminist dilemmas in fieldwork . Boulder, CO: Westview Press.
Wulff, H. ( 1998 ). Ballet across borders: Career and culture in the world of dancers . Oxford, England: Berg.
Zorbaugh, H. W. ( 1929 ). The gold coast and the slum . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research
- Open access
- Published: 27 February 2019
- Volume 42 , pages 139–160, ( 2019 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Patrik Aspers 1 , 2 &
- Ugo Corte 3
592k Accesses
286 Citations
24 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
What is qualitative research? If we look for a precise definition of qualitative research, and specifically for one that addresses its distinctive feature of being “qualitative,” the literature is meager. In this article we systematically search, identify and analyze a sample of 89 sources using or attempting to define the term “qualitative.” Then, drawing on ideas we find scattered across existing work, and based on Becker’s classic study of marijuana consumption, we formulate and illustrate a definition that tries to capture its core elements. We define qualitative research as an iterative process in which improved understanding to the scientific community is achieved by making new significant distinctions resulting from getting closer to the phenomenon studied. This formulation is developed as a tool to help improve research designs while stressing that a qualitative dimension is present in quantitative work as well. Additionally, it can facilitate teaching, communication between researchers, diminish the gap between qualitative and quantitative researchers, help to address critiques of qualitative methods, and be used as a standard of evaluation of qualitative research.
Similar content being viewed by others

What is Qualitative in Research
Unsettling definitions of qualitative research, what is “qualitative” in qualitative research why the answer does not matter but the question is important.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
If we assume that there is something called qualitative research, what exactly is this qualitative feature? And how could we evaluate qualitative research as good or not? Is it fundamentally different from quantitative research? In practice, most active qualitative researchers working with empirical material intuitively know what is involved in doing qualitative research, yet perhaps surprisingly, a clear definition addressing its key feature is still missing.
To address the question of what is qualitative we turn to the accounts of “qualitative research” in textbooks and also in empirical work. In his classic, explorative, interview study of deviance Howard Becker ( 1963 ) asks ‘How does one become a marijuana user?’ In contrast to pre-dispositional and psychological-individualistic theories of deviant behavior, Becker’s inherently social explanation contends that becoming a user of this substance is the result of a three-phase sequential learning process. First, potential users need to learn how to smoke it properly to produce the “correct” effects. If not, they are likely to stop experimenting with it. Second, they need to discover the effects associated with it; in other words, to get “high,” individuals not only have to experience what the drug does, but also to become aware that those sensations are related to using it. Third, they require learning to savor the feelings related to its consumption – to develop an acquired taste. Becker, who played music himself, gets close to the phenomenon by observing, taking part, and by talking to people consuming the drug: “half of the fifty interviews were conducted with musicians, the other half covered a wide range of people, including laborers, machinists, and people in the professions” (Becker 1963 :56).
Another central aspect derived through the common-to-all-research interplay between induction and deduction (Becker 2017 ), is that during the course of his research Becker adds scientifically meaningful new distinctions in the form of three phases—distinctions, or findings if you will, that strongly affect the course of his research: its focus, the material that he collects, and which eventually impact his findings. Each phase typically unfolds through social interaction, and often with input from experienced users in “a sequence of social experiences during which the person acquires a conception of the meaning of the behavior, and perceptions and judgments of objects and situations, all of which make the activity possible and desirable” (Becker 1963 :235). In this study the increased understanding of smoking dope is a result of a combination of the meaning of the actors, and the conceptual distinctions that Becker introduces based on the views expressed by his respondents. Understanding is the result of research and is due to an iterative process in which data, concepts and evidence are connected with one another (Becker 2017 ).
Indeed, there are many definitions of qualitative research, but if we look for a definition that addresses its distinctive feature of being “qualitative,” the literature across the broad field of social science is meager. The main reason behind this article lies in the paradox, which, to put it bluntly, is that researchers act as if they know what it is, but they cannot formulate a coherent definition. Sociologists and others will of course continue to conduct good studies that show the relevance and value of qualitative research addressing scientific and practical problems in society. However, our paper is grounded in the idea that providing a clear definition will help us improve the work that we do. Among researchers who practice qualitative research there is clearly much knowledge. We suggest that a definition makes this knowledge more explicit. If the first rationale for writing this paper refers to the “internal” aim of improving qualitative research, the second refers to the increased “external” pressure that especially many qualitative researchers feel; pressure that comes both from society as well as from other scientific approaches. There is a strong core in qualitative research, and leading researchers tend to agree on what it is and how it is done. Our critique is not directed at the practice of qualitative research, but we do claim that the type of systematic work we do has not yet been done, and that it is useful to improve the field and its status in relation to quantitative research.
The literature on the “internal” aim of improving, or at least clarifying qualitative research is large, and we do not claim to be the first to notice the vagueness of the term “qualitative” (Strauss and Corbin 1998 ). Also, others have noted that there is no single definition of it (Long and Godfrey 2004 :182), that there are many different views on qualitative research (Denzin and Lincoln 2003 :11; Jovanović 2011 :3), and that more generally, we need to define its meaning (Best 2004 :54). Strauss and Corbin ( 1998 ), for example, as well as Nelson et al. (1992:2 cited in Denzin and Lincoln 2003 :11), and Flick ( 2007 :ix–x), have recognized that the term is problematic: “Actually, the term ‘qualitative research’ is confusing because it can mean different things to different people” (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :10–11). Hammersley has discussed the possibility of addressing the problem, but states that “the task of providing an account of the distinctive features of qualitative research is far from straightforward” ( 2013 :2). This confusion, as he has recently further argued (Hammersley 2018 ), is also salient in relation to ethnography where different philosophical and methodological approaches lead to a lack of agreement about what it means.
Others (e.g. Hammersley 2018 ; Fine and Hancock 2017 ) have also identified the treat to qualitative research that comes from external forces, seen from the point of view of “qualitative research.” This threat can be further divided into that which comes from inside academia, such as the critique voiced by “quantitative research” and outside of academia, including, for example, New Public Management. Hammersley ( 2018 ), zooming in on one type of qualitative research, ethnography, has argued that it is under treat. Similarly to Fine ( 2003 ), and before him Gans ( 1999 ), he writes that ethnography’ has acquired a range of meanings, and comes in many different versions, these often reflecting sharply divergent epistemological orientations. And already more than twenty years ago while reviewing Denzin and Lincoln’ s Handbook of Qualitative Methods Fine argued:
While this increasing centrality [of qualitative research] might lead one to believe that consensual standards have developed, this belief would be misleading. As the methodology becomes more widely accepted, querulous challengers have raised fundamental questions that collectively have undercut the traditional models of how qualitative research is to be fashioned and presented (1995:417).
According to Hammersley, there are today “serious treats to the practice of ethnographic work, on almost any definition” ( 2018 :1). He lists five external treats: (1) that social research must be accountable and able to show its impact on society; (2) the current emphasis on “big data” and the emphasis on quantitative data and evidence; (3) the labor market pressure in academia that leaves less time for fieldwork (see also Fine and Hancock 2017 ); (4) problems of access to fields; and (5) the increased ethical scrutiny of projects, to which ethnography is particularly exposed. Hammersley discusses some more or less insufficient existing definitions of ethnography.
The current situation, as Hammersley and others note—and in relation not only to ethnography but also qualitative research in general, and as our empirical study shows—is not just unsatisfactory, it may even be harmful for the entire field of qualitative research, and does not help social science at large. We suggest that the lack of clarity of qualitative research is a real problem that must be addressed.
Towards a Definition of Qualitative Research
Seen in an historical light, what is today called qualitative, or sometimes ethnographic, interpretative research – or a number of other terms – has more or less always existed. At the time the founders of sociology – Simmel, Weber, Durkheim and, before them, Marx – were writing, and during the era of the Methodenstreit (“dispute about methods”) in which the German historical school emphasized scientific methods (cf. Swedberg 1990 ), we can at least speak of qualitative forerunners.
Perhaps the most extended discussion of what later became known as qualitative methods in a classic work is Bronisław Malinowski’s ( 1922 ) Argonauts in the Western Pacific , although even this study does not explicitly address the meaning of “qualitative.” In Weber’s ([1921–-22] 1978) work we find a tension between scientific explanations that are based on observation and quantification and interpretative research (see also Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 ).
If we look through major sociology journals like the American Sociological Review , American Journal of Sociology , or Social Forces we will not find the term qualitative sociology before the 1970s. And certainly before then much of what we consider qualitative classics in sociology, like Becker’ study ( 1963 ), had already been produced. Indeed, the Chicago School often combined qualitative and quantitative data within the same study (Fine 1995 ). Our point being that before a disciplinary self-awareness the term quantitative preceded qualitative, and the articulation of the former was a political move to claim scientific status (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 ). In the US the World War II seem to have sparked a critique of sociological work, including “qualitative work,” that did not follow the scientific canon (Rawls 2018 ), which was underpinned by a scientifically oriented and value free philosophy of science. As a result the attempts and practice of integrating qualitative and quantitative sociology at Chicago lost ground to sociology that was more oriented to surveys and quantitative work at Columbia under Merton-Lazarsfeld. The quantitative tradition was also able to present textbooks (Lundberg 1951 ) that facilitated the use this approach and its “methods.” The practices of the qualitative tradition, by and large, remained tacit or was part of the mentoring transferred from the renowned masters to their students.
This glimpse into history leads us back to the lack of a coherent account condensed in a definition of qualitative research. Many of the attempts to define the term do not meet the requirements of a proper definition: A definition should be clear, avoid tautology, demarcate its domain in relation to the environment, and ideally only use words in its definiens that themselves are not in need of definition (Hempel 1966 ). A definition can enhance precision and thus clarity by identifying the core of the phenomenon. Preferably, a definition should be short. The typical definition we have found, however, is an ostensive definition, which indicates what qualitative research is about without informing us about what it actually is :
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives. (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 :2)
Flick claims that the label “qualitative research” is indeed used as an umbrella for a number of approaches ( 2007 :2–4; 2002 :6), and it is not difficult to identify research fitting this designation. Moreover, whatever it is, it has grown dramatically over the past five decades. In addition, courses have been developed, methods have flourished, arguments about its future have been advanced (for example, Denzin and Lincoln 1994) and criticized (for example, Snow and Morrill 1995 ), and dedicated journals and books have mushroomed. Most social scientists have a clear idea of research and how it differs from journalism, politics and other activities. But the question of what is qualitative in qualitative research is either eluded or eschewed.
We maintain that this lacuna hinders systematic knowledge production based on qualitative research. Paul Lazarsfeld noted the lack of “codification” as early as 1955 when he reviewed 100 qualitative studies in order to offer a codification of the practices (Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 :239). Since then many texts on “qualitative research” and its methods have been published, including recent attempts (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ) similar to Lazarsfeld’s. These studies have tried to extract what is qualitative by looking at the large number of empirical “qualitative” studies. Our novel strategy complements these endeavors by taking another approach and looking at the attempts to codify these practices in the form of a definition, as well as to a minor extent take Becker’s study as an exemplar of what qualitative researchers actually do, and what the characteristic of being ‘qualitative’ denotes and implies. We claim that qualitative researchers, if there is such a thing as “qualitative research,” should be able to codify their practices in a condensed, yet general way expressed in language.
Lingering problems of “generalizability” and “how many cases do I need” (Small 2009 ) are blocking advancement – in this line of work qualitative approaches are said to differ considerably from quantitative ones, while some of the former unsuccessfully mimic principles related to the latter (Small 2009 ). Additionally, quantitative researchers sometimes unfairly criticize the first based on their own quality criteria. Scholars like Goertz and Mahoney ( 2012 ) have successfully focused on the different norms and practices beyond what they argue are essentially two different cultures: those working with either qualitative or quantitative methods. Instead, similarly to Becker ( 2017 ) who has recently questioned the usefulness of the distinction between qualitative and quantitative research, we focus on similarities.
The current situation also impedes both students and researchers in focusing their studies and understanding each other’s work (Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 :239). A third consequence is providing an opening for critiques by scholars operating within different traditions (Valsiner 2000 :101). A fourth issue is that the “implicit use of methods in qualitative research makes the field far less standardized than the quantitative paradigm” (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 :9). Relatedly, the National Science Foundation in the US organized two workshops in 2004 and 2005 to address the scientific foundations of qualitative research involving strategies to improve it and to develop standards of evaluation in qualitative research. However, a specific focus on its distinguishing feature of being “qualitative” while being implicitly acknowledged, was discussed only briefly (for example, Best 2004 ).
In 2014 a theme issue was published in this journal on “Methods, Materials, and Meanings: Designing Cultural Analysis,” discussing central issues in (cultural) qualitative research (Berezin 2014 ; Biernacki 2014 ; Glaeser 2014 ; Lamont and Swidler 2014 ; Spillman 2014). We agree with many of the arguments put forward, such as the risk of methodological tribalism, and that we should not waste energy on debating methods separated from research questions. Nonetheless, a clarification of the relation to what is called “quantitative research” is of outmost importance to avoid misunderstandings and misguided debates between “qualitative” and “quantitative” researchers. Our strategy means that researchers, “qualitative” or “quantitative” they may be, in their actual practice may combine qualitative work and quantitative work.
In this article we accomplish three tasks. First, we systematically survey the literature for meanings of qualitative research by looking at how researchers have defined it. Drawing upon existing knowledge we find that the different meanings and ideas of qualitative research are not yet coherently integrated into one satisfactory definition. Next, we advance our contribution by offering a definition of qualitative research and illustrate its meaning and use partially by expanding on the brief example introduced earlier related to Becker’s work ( 1963 ). We offer a systematic analysis of central themes of what researchers consider to be the core of “qualitative,” regardless of style of work. These themes – which we summarize in terms of four keywords: distinction, process, closeness, improved understanding – constitute part of our literature review, in which each one appears, sometimes with others, but never all in the same definition. They serve as the foundation of our contribution. Our categories are overlapping. Their use is primarily to organize the large amount of definitions we have identified and analyzed, and not necessarily to draw a clear distinction between them. Finally, we continue the elaboration discussed above on the advantages of a clear definition of qualitative research.
In a hermeneutic fashion we propose that there is something meaningful that deserves to be labelled “qualitative research” (Gadamer 1990 ). To approach the question “What is qualitative in qualitative research?” we have surveyed the literature. In conducting our survey we first traced the word’s etymology in dictionaries, encyclopedias, handbooks of the social sciences and of methods and textbooks, mainly in English, which is common to methodology courses. It should be noted that we have zoomed in on sociology and its literature. This discipline has been the site of the largest debate and development of methods that can be called “qualitative,” which suggests that this field should be examined in great detail.
In an ideal situation we should expect that one good definition, or at least some common ideas, would have emerged over the years. This common core of qualitative research should be so accepted that it would appear in at least some textbooks. Since this is not what we found, we decided to pursue an inductive approach to capture maximal variation in the field of qualitative research; we searched in a selection of handbooks, textbooks, book chapters, and books, to which we added the analysis of journal articles. Our sample comprises a total of 89 references.
In practice we focused on the discipline that has had a clear discussion of methods, namely sociology. We also conducted a broad search in the JSTOR database to identify scholarly sociology articles published between 1998 and 2017 in English with a focus on defining or explaining qualitative research. We specifically zoom in on this time frame because we would have expect that this more mature period would have produced clear discussions on the meaning of qualitative research. To find these articles we combined a number of keywords to search the content and/or the title: qualitative (which was always included), definition, empirical, research, methodology, studies, fieldwork, interview and observation .
As a second phase of our research we searched within nine major sociological journals ( American Journal of Sociology , Sociological Theory , American Sociological Review , Contemporary Sociology , Sociological Forum , Sociological Theory , Qualitative Research , Qualitative Sociology and Qualitative Sociology Review ) for articles also published during the past 19 years (1998–2017) that had the term “qualitative” in the title and attempted to define qualitative research.
Lastly we picked two additional journals, Qualitative Research and Qualitative Sociology , in which we could expect to find texts addressing the notion of “qualitative.” From Qualitative Research we chose Volume 14, Issue 6, December 2014, and from Qualitative Sociology we chose Volume 36, Issue 2, June 2017. Within each of these we selected the first article; then we picked the second article of three prior issues. Again we went back another three issues and investigated article number three. Finally we went back another three issues and perused article number four. This selection criteria was used to get a manageable sample for the analysis.
The coding process of the 89 references we gathered in our selected review began soon after the first round of material was gathered, and we reduced the complexity created by our maximum variation sampling (Snow and Anderson 1993 :22) to four different categories within which questions on the nature and properties of qualitative research were discussed. We call them: Qualitative and Quantitative Research, Qualitative Research, Fieldwork, and Grounded Theory. This – which may appear as an illogical grouping – merely reflects the “context” in which the matter of “qualitative” is discussed. If the selection process of the material – books and articles – was informed by pre-knowledge, we used an inductive strategy to code the material. When studying our material, we identified four central notions related to “qualitative” that appear in various combinations in the literature which indicate what is the core of qualitative research. We have labeled them: “distinctions”, “process,” “closeness,” and “improved understanding.” During the research process the categories and notions were improved, refined, changed, and reordered. The coding ended when a sense of saturation in the material arose. In the presentation below all quotations and references come from our empirical material of texts on qualitative research.
Analysis – What is Qualitative Research?
In this section we describe the four categories we identified in the coding, how they differently discuss qualitative research, as well as their overall content. Some salient quotations are selected to represent the type of text sorted under each of the four categories. What we present are examples from the literature.
Qualitative and Quantitative
This analytic category comprises quotations comparing qualitative and quantitative research, a distinction that is frequently used (Brown 2010 :231); in effect this is a conceptual pair that structures the discussion and that may be associated with opposing interests. While the general goal of quantitative and qualitative research is the same – to understand the world better – their methodologies and focus in certain respects differ substantially (Becker 1966 :55). Quantity refers to that property of something that can be determined by measurement. In a dictionary of Statistics and Methodology we find that “(a) When referring to *variables, ‘qualitative’ is another term for *categorical or *nominal. (b) When speaking of kinds of research, ‘qualitative’ refers to studies of subjects that are hard to quantify, such as art history. Qualitative research tends to be a residual category for almost any kind of non-quantitative research” (Stiles 1998:183). But it should be obvious that one could employ a quantitative approach when studying, for example, art history.
The same dictionary states that quantitative is “said of variables or research that can be handled numerically, usually (too sharply) contrasted with *qualitative variables and research” (Stiles 1998:184). From a qualitative perspective “quantitative research” is about numbers and counting, and from a quantitative perspective qualitative research is everything that is not about numbers. But this does not say much about what is “qualitative.” If we turn to encyclopedias we find that in the 1932 edition of the Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences there is no mention of “qualitative.” In the Encyclopedia from 1968 we can read:
Qualitative Analysis. For methods of obtaining, analyzing, and describing data, see [the various entries:] CONTENT ANALYSIS; COUNTED DATA; EVALUATION RESEARCH, FIELD WORK; GRAPHIC PRESENTATION; HISTORIOGRAPHY, especially the article on THE RHETORIC OF HISTORY; INTERVIEWING; OBSERVATION; PERSONALITY MEASUREMENT; PROJECTIVE METHODS; PSYCHOANALYSIS, article on EXPERIMENTAL METHODS; SURVEY ANALYSIS, TABULAR PRESENTATION; TYPOLOGIES. (Vol. 13:225)
Some, like Alford, divide researchers into methodologists or, in his words, “quantitative and qualitative specialists” (Alford 1998 :12). Qualitative research uses a variety of methods, such as intensive interviews or in-depth analysis of historical materials, and it is concerned with a comprehensive account of some event or unit (King et al. 1994 :4). Like quantitative research it can be utilized to study a variety of issues, but it tends to focus on meanings and motivations that underlie cultural symbols, personal experiences, phenomena and detailed understanding of processes in the social world. In short, qualitative research centers on understanding processes, experiences, and the meanings people assign to things (Kalof et al. 2008 :79).
Others simply say that qualitative methods are inherently unscientific (Jovanović 2011 :19). Hood, for instance, argues that words are intrinsically less precise than numbers, and that they are therefore more prone to subjective analysis, leading to biased results (Hood 2006 :219). Qualitative methodologies have raised concerns over the limitations of quantitative templates (Brady et al. 2004 :4). Scholars such as King et al. ( 1994 ), for instance, argue that non-statistical research can produce more reliable results if researchers pay attention to the rules of scientific inference commonly stated in quantitative research. Also, researchers such as Becker ( 1966 :59; 1970 :42–43) have asserted that, if conducted properly, qualitative research and in particular ethnographic field methods, can lead to more accurate results than quantitative studies, in particular, survey research and laboratory experiments.
Some researchers, such as Kalof, Dan, and Dietz ( 2008 :79) claim that the boundaries between the two approaches are becoming blurred, and Small ( 2009 ) argues that currently much qualitative research (especially in North America) tries unsuccessfully and unnecessarily to emulate quantitative standards. For others, qualitative research tends to be more humanistic and discursive (King et al. 1994 :4). Ragin ( 1994 ), and similarly also Becker, ( 1996 :53), Marchel and Owens ( 2007 :303) think that the main distinction between the two styles is overstated and does not rest on the simple dichotomy of “numbers versus words” (Ragin 1994 :xii). Some claim that quantitative data can be utilized to discover associations, but in order to unveil cause and effect a complex research design involving the use of qualitative approaches needs to be devised (Gilbert 2009 :35). Consequently, qualitative data are useful for understanding the nuances lying beyond those processes as they unfold (Gilbert 2009 :35). Others contend that qualitative research is particularly well suited both to identify causality and to uncover fine descriptive distinctions (Fine and Hallett 2014 ; Lichterman and Isaac Reed 2014 ; Katz 2015 ).
There are other ways to separate these two traditions, including normative statements about what qualitative research should be (that is, better or worse than quantitative approaches, concerned with scientific approaches to societal change or vice versa; Snow and Morrill 1995 ; Denzin and Lincoln 2005 ), or whether it should develop falsifiable statements; Best 2004 ).
We propose that quantitative research is largely concerned with pre-determined variables (Small 2008 ); the analysis concerns the relations between variables. These categories are primarily not questioned in the study, only their frequency or degree, or the correlations between them (cf. Franzosi 2016 ). If a researcher studies wage differences between women and men, he or she works with given categories: x number of men are compared with y number of women, with a certain wage attributed to each person. The idea is not to move beyond the given categories of wage, men and women; they are the starting point as well as the end point, and undergo no “qualitative change.” Qualitative research, in contrast, investigates relations between categories that are themselves subject to change in the research process. Returning to Becker’s study ( 1963 ), we see that he questioned pre-dispositional theories of deviant behavior working with pre-determined variables such as an individual’s combination of personal qualities or emotional problems. His take, in contrast, was to understand marijuana consumption by developing “variables” as part of the investigation. Thereby he presented new variables, or as we would say today, theoretical concepts, but which are grounded in the empirical material.
Qualitative Research
This category contains quotations that refer to descriptions of qualitative research without making comparisons with quantitative research. Researchers such as Denzin and Lincoln, who have written a series of influential handbooks on qualitative methods (1994; Denzin and Lincoln 2003 ; 2005 ), citing Nelson et al. (1992:4), argue that because qualitative research is “interdisciplinary, transdisciplinary, and sometimes counterdisciplinary” it is difficult to derive one single definition of it (Jovanović 2011 :3). According to them, in fact, “the field” is “many things at the same time,” involving contradictions, tensions over its focus, methods, and how to derive interpretations and findings ( 2003 : 11). Similarly, others, such as Flick ( 2007 :ix–x) contend that agreeing on an accepted definition has increasingly become problematic, and that qualitative research has possibly matured different identities. However, Best holds that “the proliferation of many sorts of activities under the label of qualitative sociology threatens to confuse our discussions” ( 2004 :54). Atkinson’s position is more definite: “the current state of qualitative research and research methods is confused” ( 2005 :3–4).
Qualitative research is about interpretation (Blumer 1969 ; Strauss and Corbin 1998 ; Denzin and Lincoln 2003 ), or Verstehen [understanding] (Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 ). It is “multi-method,” involving the collection and use of a variety of empirical materials (Denzin and Lincoln 1998; Silverman 2013 ) and approaches (Silverman 2005 ; Flick 2007 ). It focuses not only on the objective nature of behavior but also on its subjective meanings: individuals’ own accounts of their attitudes, motivations, behavior (McIntyre 2005 :127; Creswell 2009 ), events and situations (Bryman 1989) – what people say and do in specific places and institutions (Goodwin and Horowitz 2002 :35–36) in social and temporal contexts (Morrill and Fine 1997). For this reason, following Weber ([1921-22] 1978), it can be described as an interpretative science (McIntyre 2005 :127). But could quantitative research also be concerned with these questions? Also, as pointed out below, does all qualitative research focus on subjective meaning, as some scholars suggest?
Others also distinguish qualitative research by claiming that it collects data using a naturalistic approach (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 :2; Creswell 2009 ), focusing on the meaning actors ascribe to their actions. But again, does all qualitative research need to be collected in situ? And does qualitative research have to be inherently concerned with meaning? Flick ( 2007 ), referring to Denzin and Lincoln ( 2005 ), mentions conversation analysis as an example of qualitative research that is not concerned with the meanings people bring to a situation, but rather with the formal organization of talk. Still others, such as Ragin ( 1994 :85), note that qualitative research is often (especially early on in the project, we would add) less structured than other kinds of social research – a characteristic connected to its flexibility and that can lead both to potentially better, but also worse results. But is this not a feature of this type of research, rather than a defining description of its essence? Wouldn’t this comment also apply, albeit to varying degrees, to quantitative research?
In addition, Strauss ( 2003 ), along with others, such as Alvesson and Kärreman ( 2011 :10–76), argue that qualitative researchers struggle to capture and represent complex phenomena partially because they tend to collect a large amount of data. While his analysis is correct at some points – “It is necessary to do detailed, intensive, microscopic examination of the data in order to bring out the amazing complexity of what lies in, behind, and beyond those data” (Strauss 2003 :10) – much of his analysis concerns the supposed focus of qualitative research and its challenges, rather than exactly what it is about. But even in this instance we would make a weak case arguing that these are strictly the defining features of qualitative research. Some researchers seem to focus on the approach or the methods used, or even on the way material is analyzed. Several researchers stress the naturalistic assumption of investigating the world, suggesting that meaning and interpretation appear to be a core matter of qualitative research.
We can also see that in this category there is no consensus about specific qualitative methods nor about qualitative data. Many emphasize interpretation, but quantitative research, too, involves interpretation; the results of a regression analysis, for example, certainly have to be interpreted, and the form of meta-analysis that factor analysis provides indeed requires interpretation However, there is no interpretation of quantitative raw data, i.e., numbers in tables. One common thread is that qualitative researchers have to get to grips with their data in order to understand what is being studied in great detail, irrespective of the type of empirical material that is being analyzed. This observation is connected to the fact that qualitative researchers routinely make several adjustments of focus and research design as their studies progress, in many cases until the very end of the project (Kalof et al. 2008 ). If you, like Becker, do not start out with a detailed theory, adjustments such as the emergence and refinement of research questions will occur during the research process. We have thus found a number of useful reflections about qualitative research scattered across different sources, but none of them effectively describe the defining characteristics of this approach.
Although qualitative research does not appear to be defined in terms of a specific method, it is certainly common that fieldwork, i.e., research that entails that the researcher spends considerable time in the field that is studied and use the knowledge gained as data, is seen as emblematic of or even identical to qualitative research. But because we understand that fieldwork tends to focus primarily on the collection and analysis of qualitative data, we expected to find within it discussions on the meaning of “qualitative.” But, again, this was not the case.
Instead, we found material on the history of this approach (for example, Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 ; Atkinson et al. 2001), including how it has changed; for example, by adopting a more self-reflexive practice (Heyl 2001), as well as the different nomenclature that has been adopted, such as fieldwork, ethnography, qualitative research, naturalistic research, participant observation and so on (for example, Lofland et al. 2006 ; Gans 1999 ).
We retrieved definitions of ethnography, such as “the study of people acting in the natural courses of their daily lives,” involving a “resocialization of the researcher” (Emerson 1988 :1) through intense immersion in others’ social worlds (see also examples in Hammersley 2018 ). This may be accomplished by direct observation and also participation (Neuman 2007 :276), although others, such as Denzin ( 1970 :185), have long recognized other types of observation, including non-participant (“fly on the wall”). In this category we have also isolated claims and opposing views, arguing that this type of research is distinguished primarily by where it is conducted (natural settings) (Hughes 1971:496), and how it is carried out (a variety of methods are applied) or, for some most importantly, by involving an active, empathetic immersion in those being studied (Emerson 1988 :2). We also retrieved descriptions of the goals it attends in relation to how it is taught (understanding subjective meanings of the people studied, primarily develop theory, or contribute to social change) (see for example, Corte and Irwin 2017 ; Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 :281; Trier-Bieniek 2012 :639) by collecting the richest possible data (Lofland et al. 2006 ) to derive “thick descriptions” (Geertz 1973 ), and/or to aim at theoretical statements of general scope and applicability (for example, Emerson 1988 ; Fine 2003 ). We have identified guidelines on how to evaluate it (for example Becker 1996 ; Lamont 2004 ) and have retrieved instructions on how it should be conducted (for example, Lofland et al. 2006 ). For instance, analysis should take place while the data gathering unfolds (Emerson 1988 ; Hammersley and Atkinson 2007 ; Lofland et al. 2006 ), observations should be of long duration (Becker 1970 :54; Goffman 1989 ), and data should be of high quantity (Becker 1970 :52–53), as well as other questionable distinctions between fieldwork and other methods:
Field studies differ from other methods of research in that the researcher performs the task of selecting topics, decides what questions to ask, and forges interest in the course of the research itself . This is in sharp contrast to many ‘theory-driven’ and ‘hypothesis-testing’ methods. (Lofland and Lofland 1995 :5)
But could not, for example, a strictly interview-based study be carried out with the same amount of flexibility, such as sequential interviewing (for example, Small 2009 )? Once again, are quantitative approaches really as inflexible as some qualitative researchers think? Moreover, this category stresses the role of the actors’ meaning, which requires knowledge and close interaction with people, their practices and their lifeworld.
It is clear that field studies – which are seen by some as the “gold standard” of qualitative research – are nonetheless only one way of doing qualitative research. There are other methods, but it is not clear why some are more qualitative than others, or why they are better or worse. Fieldwork is characterized by interaction with the field (the material) and understanding of the phenomenon that is being studied. In Becker’s case, he had general experience from fields in which marihuana was used, based on which he did interviews with actual users in several fields.
Grounded Theory
Another major category we identified in our sample is Grounded Theory. We found descriptions of it most clearly in Glaser and Strauss’ ([1967] 2010 ) original articulation, Strauss and Corbin ( 1998 ) and Charmaz ( 2006 ), as well as many other accounts of what it is for: generating and testing theory (Strauss 2003 :xi). We identified explanations of how this task can be accomplished – such as through two main procedures: constant comparison and theoretical sampling (Emerson 1998:96), and how using it has helped researchers to “think differently” (for example, Strauss and Corbin 1998 :1). We also read descriptions of its main traits, what it entails and fosters – for instance, an exceptional flexibility, an inductive approach (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :31–33; 1990; Esterberg 2002 :7), an ability to step back and critically analyze situations, recognize tendencies towards bias, think abstractly and be open to criticism, enhance sensitivity towards the words and actions of respondents, and develop a sense of absorption and devotion to the research process (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :5–6). Accordingly, we identified discussions of the value of triangulating different methods (both using and not using grounded theory), including quantitative ones, and theories to achieve theoretical development (most comprehensively in Denzin 1970 ; Strauss and Corbin 1998 ; Timmermans and Tavory 2012 ). We have also located arguments about how its practice helps to systematize data collection, analysis and presentation of results (Glaser and Strauss [1967] 2010 :16).
Grounded theory offers a systematic approach which requires researchers to get close to the field; closeness is a requirement of identifying questions and developing new concepts or making further distinctions with regard to old concepts. In contrast to other qualitative approaches, grounded theory emphasizes the detailed coding process, and the numerous fine-tuned distinctions that the researcher makes during the process. Within this category, too, we could not find a satisfying discussion of the meaning of qualitative research.
Defining Qualitative Research
In sum, our analysis shows that some notions reappear in the discussion of qualitative research, such as understanding, interpretation, “getting close” and making distinctions. These notions capture aspects of what we think is “qualitative.” However, a comprehensive definition that is useful and that can further develop the field is lacking, and not even a clear picture of its essential elements appears. In other words no definition emerges from our data, and in our research process we have moved back and forth between our empirical data and the attempt to present a definition. Our concrete strategy, as stated above, is to relate qualitative and quantitative research, or more specifically, qualitative and quantitative work. We use an ideal-typical notion of quantitative research which relies on taken for granted and numbered variables. This means that the data consists of variables on different scales, such as ordinal, but frequently ratio and absolute scales, and the representation of the numbers to the variables, i.e. the justification of the assignment of numbers to object or phenomenon, are not questioned, though the validity may be questioned. In this section we return to the notion of quality and try to clarify it while presenting our contribution.
Broadly, research refers to the activity performed by people trained to obtain knowledge through systematic procedures. Notions such as “objectivity” and “reflexivity,” “systematic,” “theory,” “evidence” and “openness” are here taken for granted in any type of research. Next, building on our empirical analysis we explain the four notions that we have identified as central to qualitative work: distinctions, process, closeness, and improved understanding. In discussing them, ultimately in relation to one another, we make their meaning even more precise. Our idea, in short, is that only when these ideas that we present separately for analytic purposes are brought together can we speak of qualitative research.
Distinctions
We believe that the possibility of making new distinctions is one the defining characteristics of qualitative research. It clearly sets it apart from quantitative analysis which works with taken-for-granted variables, albeit as mentioned, meta-analyses, for example, factor analysis may result in new variables. “Quality” refers essentially to distinctions, as already pointed out by Aristotle. He discusses the term “qualitative” commenting: “By a quality I mean that in virtue of which things are said to be qualified somehow” (Aristotle 1984:14). Quality is about what something is or has, which means that the distinction from its environment is crucial. We see qualitative research as a process in which significant new distinctions are made to the scholarly community; to make distinctions is a key aspect of obtaining new knowledge; a point, as we will see, that also has implications for “quantitative research.” The notion of being “significant” is paramount. New distinctions by themselves are not enough; just adding concepts only increases complexity without furthering our knowledge. The significance of new distinctions is judged against the communal knowledge of the research community. To enable this discussion and judgements central elements of rational discussion are required (cf. Habermas [1981] 1987 ; Davidsson [ 1988 ] 2001) to identify what is new and relevant scientific knowledge. Relatedly, Ragin alludes to the idea of new and useful knowledge at a more concrete level: “Qualitative methods are appropriate for in-depth examination of cases because they aid the identification of key features of cases. Most qualitative methods enhance data” (1994:79). When Becker ( 1963 ) studied deviant behavior and investigated how people became marihuana smokers, he made distinctions between the ways in which people learned how to smoke. This is a classic example of how the strategy of “getting close” to the material, for example the text, people or pictures that are subject to analysis, may enable researchers to obtain deeper insight and new knowledge by making distinctions – in this instance on the initial notion of learning how to smoke. Others have stressed the making of distinctions in relation to coding or theorizing. Emerson et al. ( 1995 ), for example, hold that “qualitative coding is a way of opening up avenues of inquiry,” meaning that the researcher identifies and develops concepts and analytic insights through close examination of and reflection on data (Emerson et al. 1995 :151). Goodwin and Horowitz highlight making distinctions in relation to theory-building writing: “Close engagement with their cases typically requires qualitative researchers to adapt existing theories or to make new conceptual distinctions or theoretical arguments to accommodate new data” ( 2002 : 37). In the ideal-typical quantitative research only existing and so to speak, given, variables would be used. If this is the case no new distinction are made. But, would not also many “quantitative” researchers make new distinctions?
Process does not merely suggest that research takes time. It mainly implies that qualitative new knowledge results from a process that involves several phases, and above all iteration. Qualitative research is about oscillation between theory and evidence, analysis and generating material, between first- and second -order constructs (Schütz 1962 :59), between getting in contact with something, finding sources, becoming deeply familiar with a topic, and then distilling and communicating some of its essential features. The main point is that the categories that the researcher uses, and perhaps takes for granted at the beginning of the research process, usually undergo qualitative changes resulting from what is found. Becker describes how he tested hypotheses and let the jargon of the users develop into theoretical concepts. This happens over time while the study is being conducted, exemplifying what we mean by process.
In the research process, a pilot-study may be used to get a first glance of, for example, the field, how to approach it, and what methods can be used, after which the method and theory are chosen or refined before the main study begins. Thus, the empirical material is often central from the start of the project and frequently leads to adjustments by the researcher. Likewise, during the main study categories are not fixed; the empirical material is seen in light of the theory used, but it is also given the opportunity to kick back, thereby resisting attempts to apply theoretical straightjackets (Becker 1970 :43). In this process, coding and analysis are interwoven, and thus are often important steps for getting closer to the phenomenon and deciding what to focus on next. Becker began his research by interviewing musicians close to him, then asking them to refer him to other musicians, and later on doubling his original sample of about 25 to include individuals in other professions (Becker 1973:46). Additionally, he made use of some participant observation, documents, and interviews with opiate users made available to him by colleagues. As his inductive theory of deviance evolved, Becker expanded his sample in order to fine tune it, and test the accuracy and generality of his hypotheses. In addition, he introduced a negative case and discussed the null hypothesis ( 1963 :44). His phasic career model is thus based on a research design that embraces processual work. Typically, process means to move between “theory” and “material” but also to deal with negative cases, and Becker ( 1998 ) describes how discovering these negative cases impacted his research design and ultimately its findings.
Obviously, all research is process-oriented to some degree. The point is that the ideal-typical quantitative process does not imply change of the data, and iteration between data, evidence, hypotheses, empirical work, and theory. The data, quantified variables, are, in most cases fixed. Merging of data, which of course can be done in a quantitative research process, does not mean new data. New hypotheses are frequently tested, but the “raw data is often the “the same.” Obviously, over time new datasets are made available and put into use.
Another characteristic that is emphasized in our sample is that qualitative researchers – and in particular ethnographers – can, or as Goffman put it, ought to ( 1989 ), get closer to the phenomenon being studied and their data than quantitative researchers (for example, Silverman 2009 :85). Put differently, essentially because of their methods qualitative researchers get into direct close contact with those being investigated and/or the material, such as texts, being analyzed. Becker started out his interview study, as we noted, by talking to those he knew in the field of music to get closer to the phenomenon he was studying. By conducting interviews he got even closer. Had he done more observations, he would undoubtedly have got even closer to the field.
Additionally, ethnographers’ design enables researchers to follow the field over time, and the research they do is almost by definition longitudinal, though the time in the field is studied obviously differs between studies. The general characteristic of closeness over time maximizes the chances of unexpected events, new data (related, for example, to archival research as additional sources, and for ethnography for situations not necessarily previously thought of as instrumental – what Mannay and Morgan ( 2015 ) term the “waiting field”), serendipity (Merton and Barber 2004 ; Åkerström 2013 ), and possibly reactivity, as well as the opportunity to observe disrupted patterns that translate into exemplars of negative cases. Two classic examples of this are Becker’s finding of what medical students call “crocks” (Becker et al. 1961 :317), and Geertz’s ( 1973 ) study of “deep play” in Balinese society.
By getting and staying so close to their data – be it pictures, text or humans interacting (Becker was himself a musician) – for a long time, as the research progressively focuses, qualitative researchers are prompted to continually test their hunches, presuppositions and hypotheses. They test them against a reality that often (but certainly not always), and practically, as well as metaphorically, talks back, whether by validating them, or disqualifying their premises – correctly, as well as incorrectly (Fine 2003 ; Becker 1970 ). This testing nonetheless often leads to new directions for the research. Becker, for example, says that he was initially reading psychological theories, but when facing the data he develops a theory that looks at, you may say, everything but psychological dispositions to explain the use of marihuana. Especially researchers involved with ethnographic methods have a fairly unique opportunity to dig up and then test (in a circular, continuous and temporal way) new research questions and findings as the research progresses, and thereby to derive previously unimagined and uncharted distinctions by getting closer to the phenomenon under study.
Let us stress that getting close is by no means restricted to ethnography. The notion of hermeneutic circle and hermeneutics as a general way of understanding implies that we must get close to the details in order to get the big picture. This also means that qualitative researchers can literally also make use of details of pictures as evidence (cf. Harper 2002). Thus, researchers may get closer both when generating the material or when analyzing it.
Quantitative research, we maintain, in the ideal-typical representation cannot get closer to the data. The data is essentially numbers in tables making up the variables (Franzosi 2016 :138). The data may originally have been “qualitative,” but once reduced to numbers there can only be a type of “hermeneutics” about what the number may stand for. The numbers themselves, however, are non-ambiguous. Thus, in quantitative research, interpretation, if done, is not about the data itself—the numbers—but what the numbers stand for. It follows that the interpretation is essentially done in a more “speculative” mode without direct empirical evidence (cf. Becker 2017 ).
Improved Understanding
While distinction, process and getting closer refer to the qualitative work of the researcher, improved understanding refers to its conditions and outcome of this work. Understanding cuts deeper than explanation, which to some may mean a causally verified correlation between variables. The notion of explanation presupposes the notion of understanding since explanation does not include an idea of how knowledge is gained (Manicas 2006 : 15). Understanding, we argue, is the core concept of what we call the outcome of the process when research has made use of all the other elements that were integrated in the research. Understanding, then, has a special status in qualitative research since it refers both to the conditions of knowledge and the outcome of the process. Understanding can to some extent be seen as the condition of explanation and occurs in a process of interpretation, which naturally refers to meaning (Gadamer 1990 ). It is fundamentally connected to knowing, and to the knowing of how to do things (Heidegger [1927] 2001 ). Conceptually the term hermeneutics is used to account for this process. Heidegger ties hermeneutics to human being and not possible to separate from the understanding of being ( 1988 ). Here we use it in a broader sense, and more connected to method in general (cf. Seiffert 1992 ). The abovementioned aspects – for example, “objectivity” and “reflexivity” – of the approach are conditions of scientific understanding. Understanding is the result of a circular process and means that the parts are understood in light of the whole, and vice versa. Understanding presupposes pre-understanding, or in other words, some knowledge of the phenomenon studied. The pre-understanding, even in the form of prejudices, are in qualitative research process, which we see as iterative, questioned, which gradually or suddenly change due to the iteration of data, evidence and concepts. However, qualitative research generates understanding in the iterative process when the researcher gets closer to the data, e.g., by going back and forth between field and analysis in a process that generates new data that changes the evidence, and, ultimately, the findings. Questioning, to ask questions, and put what one assumes—prejudices and presumption—in question, is central to understand something (Heidegger [1927] 2001 ; Gadamer 1990 :368–384). We propose that this iterative process in which the process of understanding occurs is characteristic of qualitative research.
Improved understanding means that we obtain scientific knowledge of something that we as a scholarly community did not know before, or that we get to know something better. It means that we understand more about how parts are related to one another, and to other things we already understand (see also Fine and Hallett 2014 ). Understanding is an important condition for qualitative research. It is not enough to identify correlations, make distinctions, and work in a process in which one gets close to the field or phenomena. Understanding is accomplished when the elements are integrated in an iterative process.
It is, moreover, possible to understand many things, and researchers, just like children, may come to understand new things every day as they engage with the world. This subjective condition of understanding – namely, that a person gains a better understanding of something –is easily met. To be qualified as “scientific,” the understanding must be general and useful to many; it must be public. But even this generally accessible understanding is not enough in order to speak of “scientific understanding.” Though we as a collective can increase understanding of everything in virtually all potential directions as a result also of qualitative work, we refrain from this “objective” way of understanding, which has no means of discriminating between what we gain in understanding. Scientific understanding means that it is deemed relevant from the scientific horizon (compare Schütz 1962 : 35–38, 46, 63), and that it rests on the pre-understanding that the scientists have and must have in order to understand. In other words, the understanding gained must be deemed useful by other researchers, so that they can build on it. We thus see understanding from a pragmatic, rather than a subjective or objective perspective. Improved understanding is related to the question(s) at hand. Understanding, in order to represent an improvement, must be an improvement in relation to the existing body of knowledge of the scientific community (James [ 1907 ] 1955). Scientific understanding is, by definition, collective, as expressed in Weber’s famous note on objectivity, namely that scientific work aims at truths “which … can claim, even for a Chinese, the validity appropriate to an empirical analysis” ([1904] 1949 :59). By qualifying “improved understanding” we argue that it is a general defining characteristic of qualitative research. Becker‘s ( 1966 ) study and other research of deviant behavior increased our understanding of the social learning processes of how individuals start a behavior. And it also added new knowledge about the labeling of deviant behavior as a social process. Few studies, of course, make the same large contribution as Becker’s, but are nonetheless qualitative research.
Understanding in the phenomenological sense, which is a hallmark of qualitative research, we argue, requires meaning and this meaning is derived from the context, and above all the data being analyzed. The ideal-typical quantitative research operates with given variables with different numbers. This type of material is not enough to establish meaning at the level that truly justifies understanding. In other words, many social science explanations offer ideas about correlations or even causal relations, but this does not mean that the meaning at the level of the data analyzed, is understood. This leads us to say that there are indeed many explanations that meet the criteria of understanding, for example the explanation of how one becomes a marihuana smoker presented by Becker. However, we may also understand a phenomenon without explaining it, and we may have potential explanations, or better correlations, that are not really understood.
We may speak more generally of quantitative research and its data to clarify what we see as an important distinction. The “raw data” that quantitative research—as an idealtypical activity, refers to is not available for further analysis; the numbers, once created, are not to be questioned (Franzosi 2016 : 138). If the researcher is to do “more” or “change” something, this will be done by conjectures based on theoretical knowledge or based on the researcher’s lifeworld. Both qualitative and quantitative research is based on the lifeworld, and all researchers use prejudices and pre-understanding in the research process. This idea is present in the works of Heidegger ( 2001 ) and Heisenberg (cited in Franzosi 2010 :619). Qualitative research, as we argued, involves the interaction and questioning of concepts (theory), data, and evidence.
Ragin ( 2004 :22) points out that “a good definition of qualitative research should be inclusive and should emphasize its key strengths and features, not what it lacks (for example, the use of sophisticated quantitative techniques).” We define qualitative research as an iterative process in which improved understanding to the scientific community is achieved by making new significant distinctions resulting from getting closer to the phenomenon studied. Qualitative research, as defined here, is consequently a combination of two criteria: (i) how to do things –namely, generating and analyzing empirical material, in an iterative process in which one gets closer by making distinctions, and (ii) the outcome –improved understanding novel to the scholarly community. Is our definition applicable to our own study? In this study we have closely read the empirical material that we generated, and the novel distinction of the notion “qualitative research” is the outcome of an iterative process in which both deduction and induction were involved, in which we identified the categories that we analyzed. We thus claim to meet the first criteria, “how to do things.” The second criteria cannot be judged but in a partial way by us, namely that the “outcome” —in concrete form the definition-improves our understanding to others in the scientific community.
We have defined qualitative research, or qualitative scientific work, in relation to quantitative scientific work. Given this definition, qualitative research is about questioning the pre-given (taken for granted) variables, but it is thus also about making new distinctions of any type of phenomenon, for example, by coining new concepts, including the identification of new variables. This process, as we have discussed, is carried out in relation to empirical material, previous research, and thus in relation to theory. Theory and previous research cannot be escaped or bracketed. According to hermeneutic principles all scientific work is grounded in the lifeworld, and as social scientists we can thus never fully bracket our pre-understanding.
We have proposed that quantitative research, as an idealtype, is concerned with pre-determined variables (Small 2008 ). Variables are epistemically fixed, but can vary in terms of dimensions, such as frequency or number. Age is an example; as a variable it can take on different numbers. In relation to quantitative research, qualitative research does not reduce its material to number and variables. If this is done the process of comes to a halt, the researcher gets more distanced from her data, and it makes it no longer possible to make new distinctions that increase our understanding. We have above discussed the components of our definition in relation to quantitative research. Our conclusion is that in the research that is called quantitative there are frequent and necessary qualitative elements.
Further, comparative empirical research on researchers primarily working with ”quantitative” approaches and those working with ”qualitative” approaches, we propose, would perhaps show that there are many similarities in practices of these two approaches. This is not to deny dissimilarities, or the different epistemic and ontic presuppositions that may be more or less strongly associated with the two different strands (see Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ). Our point is nonetheless that prejudices and preconceptions about researchers are unproductive, and that as other researchers have argued, differences may be exaggerated (e.g., Becker 1996 : 53, 2017 ; Marchel and Owens 2007 :303; Ragin 1994 ), and that a qualitative dimension is present in both kinds of work.
Several things follow from our findings. The most important result is the relation to quantitative research. In our analysis we have separated qualitative research from quantitative research. The point is not to label individual researchers, methods, projects, or works as either “quantitative” or “qualitative.” By analyzing, i.e., taking apart, the notions of quantitative and qualitative, we hope to have shown the elements of qualitative research. Our definition captures the elements, and how they, when combined in practice, generate understanding. As many of the quotations we have used suggest, one conclusion of our study holds that qualitative approaches are not inherently connected with a specific method. Put differently, none of the methods that are frequently labelled “qualitative,” such as interviews or participant observation, are inherently “qualitative.” What matters, given our definition, is whether one works qualitatively or quantitatively in the research process, until the results are produced. Consequently, our analysis also suggests that those researchers working with what in the literature and in jargon is often called “quantitative research” are almost bound to make use of what we have identified as qualitative elements in any research project. Our findings also suggest that many” quantitative” researchers, at least to some extent, are engaged with qualitative work, such as when research questions are developed, variables are constructed and combined, and hypotheses are formulated. Furthermore, a research project may hover between “qualitative” and “quantitative” or start out as “qualitative” and later move into a “quantitative” (a distinct strategy that is not similar to “mixed methods” or just simply combining induction and deduction). More generally speaking, the categories of “qualitative” and “quantitative,” unfortunately, often cover up practices, and it may lead to “camps” of researchers opposing one another. For example, regardless of the researcher is primarily oriented to “quantitative” or “qualitative” research, the role of theory is neglected (cf. Swedberg 2017 ). Our results open up for an interaction not characterized by differences, but by different emphasis, and similarities.
Let us take two examples to briefly indicate how qualitative elements can fruitfully be combined with quantitative. Franzosi ( 2010 ) has discussed the relations between quantitative and qualitative approaches, and more specifically the relation between words and numbers. He analyzes texts and argues that scientific meaning cannot be reduced to numbers. Put differently, the meaning of the numbers is to be understood by what is taken for granted, and what is part of the lifeworld (Schütz 1962 ). Franzosi shows how one can go about using qualitative and quantitative methods and data to address scientific questions analyzing violence in Italy at the time when fascism was rising (1919–1922). Aspers ( 2006 ) studied the meaning of fashion photographers. He uses an empirical phenomenological approach, and establishes meaning at the level of actors. In a second step this meaning, and the different ideal-typical photographers constructed as a result of participant observation and interviews, are tested using quantitative data from a database; in the first phase to verify the different ideal-types, in the second phase to use these types to establish new knowledge about the types. In both of these cases—and more examples can be found—authors move from qualitative data and try to keep the meaning established when using the quantitative data.
A second main result of our study is that a definition, and we provided one, offers a way for research to clarify, and even evaluate, what is done. Hence, our definition can guide researchers and students, informing them on how to think about concrete research problems they face, and to show what it means to get closer in a process in which new distinctions are made. The definition can also be used to evaluate the results, given that it is a standard of evaluation (cf. Hammersley 2007 ), to see whether new distinctions are made and whether this improves our understanding of what is researched, in addition to the evaluation of how the research was conducted. By making what is qualitative research explicit it becomes easier to communicate findings, and it is thereby much harder to fly under the radar with substandard research since there are standards of evaluation which make it easier to separate “good” from “not so good” qualitative research.
To conclude, our analysis, which ends with a definition of qualitative research can thus both address the “internal” issues of what is qualitative research, and the “external” critiques that make it harder to do qualitative research, to which both pressure from quantitative methods and general changes in society contribute.
Åkerström, Malin. 2013. Curiosity and serendipity in qualitative research. Qualitative Sociology Review 9 (2): 10–18.
Google Scholar
Alford, Robert R. 1998. The craft of inquiry. Theories, methods, evidence . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Alvesson, Mats, and Dan Kärreman. 2011. Qualitative research and theory development. Mystery as method . London: SAGE Publications.
Book Google Scholar
Aspers, Patrik. 2006. Markets in Fashion, A Phenomenological Approach. London Routledge.
Atkinson, Paul. 2005. Qualitative research. Unity and diversity. Forum: Qualitative Social Research 6 (3): 1–15.
Becker, Howard S. 1963. Outsiders. Studies in the sociology of deviance . New York: The Free Press.
Becker, Howard S. 1966. Whose side are we on? Social Problems 14 (3): 239–247.
Article Google Scholar
Becker, Howard S. 1970. Sociological work. Method and substance . New Brunswick: Transaction Books.
Becker, Howard S. 1996. The epistemology of qualitative research. In Ethnography and human development. Context and meaning in social inquiry , ed. Jessor Richard, Colby Anne, and Richard A. Shweder, 53–71. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Becker, Howard S. 1998. Tricks of the trade. How to think about your research while you're doing it . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Becker, Howard S. 2017. Evidence . Chigaco: University of Chicago Press.
Becker, Howard, Blanche Geer, Everett Hughes, and Anselm Strauss. 1961. Boys in White, student culture in medical school . New Brunswick: Transaction Publishers.
Berezin, Mabel. 2014. How do we know what we mean? Epistemological dilemmas in cultural sociology. Qualitative Sociology 37 (2): 141–151.
Best, Joel. 2004. Defining qualitative research. In Workshop on Scientific Foundations of Qualitative Research , eds . Charles, Ragin, Joanne, Nagel, and Patricia White, 53-54. http://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2004/nsf04219/nsf04219.pdf .
Biernacki, Richard. 2014. Humanist interpretation versus coding text samples. Qualitative Sociology 37 (2): 173–188.
Blumer, Herbert. 1969. Symbolic interactionism: Perspective and method . Berkeley: University of California Press.
Brady, Henry, David Collier, and Jason Seawright. 2004. Refocusing the discussion of methodology. In Rethinking social inquiry. Diverse tools, shared standards , ed. Brady Henry and Collier David, 3–22. Lanham: Rowman and Littlefield.
Brown, Allison P. 2010. Qualitative method and compromise in applied social research. Qualitative Research 10 (2): 229–248.
Charmaz, Kathy. 2006. Constructing grounded theory . London: Sage.
Corte, Ugo, and Katherine Irwin. 2017. “The Form and Flow of Teaching Ethnographic Knowledge: Hands-on Approaches for Learning Epistemology” Teaching Sociology 45(3): 209-219.
Creswell, John W. 2009. Research design. Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed method approaches . 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Davidsson, David. 1988. 2001. The myth of the subjective. In Subjective, intersubjective, objective , ed. David Davidsson, 39–52. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Denzin, Norman K. 1970. The research act: A theoretical introduction to Ssociological methods . Chicago: Aldine Publishing Company Publishers.
Denzin, Norman K., and Yvonna S. Lincoln. 2003. Introduction. The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In Collecting and interpreting qualitative materials , ed. Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, 1–45. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Denzin, Norman K., and Yvonna S. Lincoln. 2005. Introduction. The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In The Sage handbook of qualitative research , ed. Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, 1–32. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Emerson, Robert M., ed. 1988. Contemporary field research. A collection of readings . Prospect Heights: Waveland Press.
Emerson, Robert M., Rachel I. Fretz, and Linda L. Shaw. 1995. Writing ethnographic fieldnotes . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Esterberg, Kristin G. 2002. Qualitative methods in social research . Boston: McGraw-Hill.
Fine, Gary Alan. 1995. Review of “handbook of qualitative research.” Contemporary Sociology 24 (3): 416–418.
Fine, Gary Alan. 2003. “ Toward a Peopled Ethnography: Developing Theory from Group Life.” Ethnography . 4(1):41-60.
Fine, Gary Alan, and Black Hawk Hancock. 2017. The new ethnographer at work. Qualitative Research 17 (2): 260–268.
Fine, Gary Alan, and Timothy Hallett. 2014. Stranger and stranger: Creating theory through ethnographic distance and authority. Journal of Organizational Ethnography 3 (2): 188–203.
Flick, Uwe. 2002. Qualitative research. State of the art. Social Science Information 41 (1): 5–24.
Flick, Uwe. 2007. Designing qualitative research . London: SAGE Publications.
Frankfort-Nachmias, Chava, and David Nachmias. 1996. Research methods in the social sciences . 5th ed. London: Edward Arnold.
Franzosi, Roberto. 2010. Sociology, narrative, and the quality versus quantity debate (Goethe versus Newton): Can computer-assisted story grammars help us understand the rise of Italian fascism (1919- 1922)? Theory and Society 39 (6): 593–629.
Franzosi, Roberto. 2016. From method and measurement to narrative and number. International journal of social research methodology 19 (1): 137–141.
Gadamer, Hans-Georg. 1990. Wahrheit und Methode, Grundzüge einer philosophischen Hermeneutik . Band 1, Hermeneutik. Tübingen: J.C.B. Mohr.
Gans, Herbert. 1999. Participant Observation in an Age of “Ethnography”. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography 28 (5): 540–548.
Geertz, Clifford. 1973. The interpretation of cultures . New York: Basic Books.
Gilbert, Nigel. 2009. Researching social life . 3rd ed. London: SAGE Publications.
Glaeser, Andreas. 2014. Hermeneutic institutionalism: Towards a new synthesis. Qualitative Sociology 37: 207–241.
Glaser, Barney G., and Anselm L. Strauss. [1967] 2010. The discovery of grounded theory. Strategies for qualitative research. Hawthorne: Aldine.
Goertz, Gary, and James Mahoney. 2012. A tale of two cultures: Qualitative and quantitative research in the social sciences . Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Goffman, Erving. 1989. On fieldwork. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography 18 (2): 123–132.
Goodwin, Jeff, and Ruth Horowitz. 2002. Introduction. The methodological strengths and dilemmas of qualitative sociology. Qualitative Sociology 25 (1): 33–47.
Habermas, Jürgen. [1981] 1987. The theory of communicative action . Oxford: Polity Press.
Hammersley, Martyn. 2007. The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research & Method in Education 30 (3): 287–305.
Hammersley, Martyn. 2013. What is qualitative research? Bloomsbury Publishing.
Hammersley, Martyn. 2018. What is ethnography? Can it survive should it? Ethnography and Education 13 (1): 1–17.
Hammersley, Martyn, and Paul Atkinson. 2007. Ethnography. Principles in practice . London: Tavistock Publications.
Heidegger, Martin. [1927] 2001. Sein und Zeit . Tübingen: Max Niemeyer Verlag.
Heidegger, Martin. 1988. 1923. Ontologie. Hermeneutik der Faktizität, Gesamtausgabe II. Abteilung: Vorlesungen 1919-1944, Band 63, Frankfurt am Main: Vittorio Klostermann.
Hempel, Carl G. 1966. Philosophy of the natural sciences . Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Hood, Jane C. 2006. Teaching against the text. The case of qualitative methods. Teaching Sociology 34 (3): 207–223.
James, William. 1907. 1955. Pragmatism . New York: Meredian Books.
Jovanović, Gordana. 2011. Toward a social history of qualitative research. History of the Human Sciences 24 (2): 1–27.
Kalof, Linda, Amy Dan, and Thomas Dietz. 2008. Essentials of social research . London: Open University Press.
Katz, Jack. 2015. Situational evidence: Strategies for causal reasoning from observational field notes. Sociological Methods & Research 44 (1): 108–144.
King, Gary, Robert O. Keohane, S. Sidney, and S. Verba. 1994. Designing social inquiry. In Scientific inference in qualitative research . Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Chapter Google Scholar
Lamont, Michelle. 2004. Evaluating qualitative research: Some empirical findings and an agenda. In Report from workshop on interdisciplinary standards for systematic qualitative research , ed. M. Lamont and P. White, 91–95. Washington, DC: National Science Foundation.
Lamont, Michèle, and Ann Swidler. 2014. Methodological pluralism and the possibilities and limits of interviewing. Qualitative Sociology 37 (2): 153–171.
Lazarsfeld, Paul, and Alan Barton. 1982. Some functions of qualitative analysis in social research. In The varied sociology of Paul Lazarsfeld , ed. Patricia Kendall, 239–285. New York: Columbia University Press.
Lichterman, Paul, and Isaac Reed I (2014), Theory and Contrastive Explanation in Ethnography. Sociological methods and research. Prepublished 27 October 2014; https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124114554458 .
Lofland, John, and Lyn Lofland. 1995. Analyzing social settings. A guide to qualitative observation and analysis . 3rd ed. Belmont: Wadsworth.
Lofland, John, David A. Snow, Leon Anderson, and Lyn H. Lofland. 2006. Analyzing social settings. A guide to qualitative observation and analysis . 4th ed. Belmont: Wadsworth/Thomson Learning.
Long, Adrew F., and Mary Godfrey. 2004. An evaluation tool to assess the quality of qualitative research studies. International Journal of Social Research Methodology 7 (2): 181–196.
Lundberg, George. 1951. Social research: A study in methods of gathering data . New York: Longmans, Green and Co..
Malinowski, Bronislaw. 1922. Argonauts of the Western Pacific: An account of native Enterprise and adventure in the archipelagoes of Melanesian New Guinea . London: Routledge.
Manicas, Peter. 2006. A realist philosophy of science: Explanation and understanding . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Marchel, Carol, and Stephanie Owens. 2007. Qualitative research in psychology. Could William James get a job? History of Psychology 10 (4): 301–324.
McIntyre, Lisa J. 2005. Need to know. Social science research methods . Boston: McGraw-Hill.
Merton, Robert K., and Elinor Barber. 2004. The travels and adventures of serendipity. A Study in Sociological Semantics and the Sociology of Science . Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Mannay, Dawn, and Melanie Morgan. 2015. Doing ethnography or applying a qualitative technique? Reflections from the ‘waiting field‘. Qualitative Research 15 (2): 166–182.
Neuman, Lawrence W. 2007. Basics of social research. Qualitative and quantitative approaches . 2nd ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
Ragin, Charles C. 1994. Constructing social research. The unity and diversity of method . Thousand Oaks: Pine Forge Press.
Ragin, Charles C. 2004. Introduction to session 1: Defining qualitative research. In Workshop on Scientific Foundations of Qualitative Research , 22, ed. Charles C. Ragin, Joane Nagel, Patricia White. http://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2004/nsf04219/nsf04219.pdf
Rawls, Anne. 2018. The Wartime narrative in US sociology, 1940–7: Stigmatizing qualitative sociology in the name of ‘science,’ European Journal of Social Theory (Online first).
Schütz, Alfred. 1962. Collected papers I: The problem of social reality . The Hague: Nijhoff.
Seiffert, Helmut. 1992. Einführung in die Hermeneutik . Tübingen: Franke.
Silverman, David. 2005. Doing qualitative research. A practical handbook . 2nd ed. London: SAGE Publications.
Silverman, David. 2009. A very short, fairly interesting and reasonably cheap book about qualitative research . London: SAGE Publications.
Silverman, David. 2013. What counts as qualitative research? Some cautionary comments. Qualitative Sociology Review 9 (2): 48–55.
Small, Mario L. 2009. “How many cases do I need?” on science and the logic of case selection in field-based research. Ethnography 10 (1): 5–38.
Small, Mario L 2008. Lost in translation: How not to make qualitative research more scientific. In Workshop on interdisciplinary standards for systematic qualitative research, ed in Michelle Lamont, and Patricia White, 165–171. Washington, DC: National Science Foundation.
Snow, David A., and Leon Anderson. 1993. Down on their luck: A study of homeless street people . Berkeley: University of California Press.
Snow, David A., and Calvin Morrill. 1995. New ethnographies: Review symposium: A revolutionary handbook or a handbook for revolution? Journal of Contemporary Ethnography 24 (3): 341–349.
Strauss, Anselm L. 2003. Qualitative analysis for social scientists . 14th ed. Chicago: Cambridge University Press.
Strauss, Anselm L., and Juliette M. Corbin. 1998. Basics of qualitative research. Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
Swedberg, Richard. 2017. Theorizing in sociological research: A new perspective, a new departure? Annual Review of Sociology 43: 189–206.
Swedberg, Richard. 1990. The new 'Battle of Methods'. Challenge January–February 3 (1): 33–38.
Timmermans, Stefan, and Iddo Tavory. 2012. Theory construction in qualitative research: From grounded theory to abductive analysis. Sociological Theory 30 (3): 167–186.
Trier-Bieniek, Adrienne. 2012. Framing the telephone interview as a participant-centred tool for qualitative research. A methodological discussion. Qualitative Research 12 (6): 630–644.
Valsiner, Jaan. 2000. Data as representations. Contextualizing qualitative and quantitative research strategies. Social Science Information 39 (1): 99–113.
Weber, Max. 1904. 1949. Objectivity’ in social Science and social policy. Ed. Edward A. Shils and Henry A. Finch, 49–112. New York: The Free Press.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Financial Support for this research is given by the European Research Council, CEV (263699). The authors are grateful to Susann Krieglsteiner for assistance in collecting the data. The paper has benefitted from the many useful comments by the three reviewers and the editor, comments by members of the Uppsala Laboratory of Economic Sociology, as well as Jukka Gronow, Sebastian Kohl, Marcin Serafin, Richard Swedberg, Anders Vassenden and Turid Rødne.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Sociology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
Patrik Aspers
Seminar for Sociology, Universität St. Gallen, St. Gallen, Switzerland
Department of Media and Social Sciences, University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Patrik Aspers .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Aspers, P., Corte, U. What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research. Qual Sociol 42 , 139–160 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11133-019-9413-7
Download citation
Published : 27 February 2019
Issue Date : 01 June 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11133-019-9413-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Epistemology
- Philosophy of science
- Phenomenology
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

10 Types of Qualitative Research
- Updated on
- Aug 10, 2021
Are you looking forward to preparing a research proposal for your MPhil and PhD thesis? Research methodology constitutes an important part of a research thesis and much of your research depends on what type of method is selected. The two main types of research methodologies include qualitative research and quantitative research. Qualitative Research is one of the sought-after and popular methodologies and aims to delve deeper in a theoretical manner. In this blog, we have described some of the different types of qualitative research methods that are used in research analysis.
This Blog Includes:
What is qualitative research, when to use qualitative research, characteristics of qualitative research , ethnography, oral history, phenomenological method, grounded theory method, narrative model, historical model, focus groups, record keeping, process of observation.
Qualitative research involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data to gain a thorough understanding of a concept or a problem of research. This method of research seeks to answer a research question through the collection of evidence. There is a wide range of qualitative research methods you can choose from as per your topics. Further, this research methodology is extensively used in the fields of humanities and social sciences such as in the subjects of sociology, anthropology, history, etc. In qualitative research, the methods of data collection include surveys, observations, interviews, secondary research, etc.
When it comes to capturing precise, in-depth insights, researchers turn to qualitative research methodologies. Capturing “factual data” is quite beneficial. Here are some examples of when qualitative research should be used.
- Creating a new product or coming up with a concept.
- Investigating your product/brand or service in order to improve your marketing approach.
- Recognize your own talents and shortcomings.
- Understanding purchasing habits.
- To investigate your target audience’s reactions to marketing campaigns and other forms of communication.
- Investigating market demographics, segmentation, and client segments.
- Obtaining information on a brand, company, or product’s perception.
- Qualitative research methods often collect data on-site, where people are experiencing challenges or problems. These are real-time data, and participants are rarely taken out of their geographical areas to collect information.
- Rather than relying on a single data source, qualitative researchers generally collect various types of data, such as interviews, observations, and documents.
- This research technique aims to solve complicated problems by breaking them down into relevant inferences that are easily accessible and understood by everybody.
- Because it is a more conversational technique, people can develop confidence with the researcher, and the information gained is therefore raw and pure.
Types of Qualitative Research
Below are some of the types of qualitative research that are popular across diverse disciplines:
Ethnography is the descriptive study of people and their culture. The ethnographic model is one of the major types of qualitative research methods used in social sciences, especially in anthropology. This method of research aims to study individuals in their own habitat through the usage of methods like observations, interviews etc. This method is useful for studying both remote cultures as well as smaller communities within any particular region. Detailed ethnographic research may require the researcher to spend a long time doing fieldwork in the particular area of study, often extending to several months or even years.
Oral history is a type of qualitative research method which involves the collection of oral testimonies from people about their own lived experiences. This research method is extensively used in the field of history, to put forward alternative narratives (as opposed to the official sources) of a particular event or incident. The main method of collecting oral history is taking interviews and recording the narratives in audio, video, or textual versions. This method is useful for future researchers too since the oral testimonies are stored in an archive to make sure that these voices are not lost.
A case study involves a detailed examination of a particular person, event, or community. This is one of the types of qualitative research methods used extensively in the field of social sciences, law, business, and health. The data for the case study is obtained through diverse methods including interviews and observations. A case study is the most suitable method for gaining a total and in-depth knowledge of a particular issue.
One of the types of qualitative research methods, the phenomenological approach aims to explore the experiences of a particular phenomenon in a community or a group of people. It is the study of a particular phenomenon through interviews of people who have experienced it to find out the similarities between their experiences. Although this approach depends majorly on interviews, other sources of data collection may also be used to supplement the findings.
The grounded theory method is a very popular research method used across a large number of disciplines. It is involved in the collection, interpretation, and analysis of data. The grounded theory model uses the analyzed data to develop different theories regarding the topic of research.
The narrative model is one of the types of qualitative research methods which focuses on spoken or written words or visual representations by people. This method involves the analysis of these stories or narratives by people through engaging in questioning to ascertain particular questions or issues. This model is helpful in understanding the ways in which people represent them and their experiences to a wider audience.
The historical model is one of the unique approaches within qualitative research which is involved in the detailed study of past events in order to get a better understanding of the present and predict future events on that basis. The main objective of this model is to analyze the effects of the past on the present and thereby identify similar processes in the present to anticipate their effects in the future. Reviewing relevant literature is the main source of data for this method, although oral sources may also be used.
A focus group is another popular qualitative research approach for data collecting. A focus group typically consists of a small number of respondents (6-10) from your target market. The primary goal of the focus group is to obtain answers to the questions “why,” “what,” and “how.” One advantage of focus groups is that you do not have to engage with the group in person.
As the data source, this approach makes the use of pre-existing credible documents and comparable sources of information. This information can be utilized in future studies. This is comparable to visiting a library. There, one can go through books and other reference materials to get important facts that will most likely be employed in the research.
Qualitative Observation is a research approach that uses subjective methodologies to collect systematic information or data. Since the focus on qualitative observation is the study process of gathering information or data utilizing subjective techniques. Qualitative observation is generally used to compare and contrast quality variations. The five primary sense organs and their functioning are addressed in qualitative observation: sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing. This is not about measures or numbers, but about qualities.
Qualitative data gathering allows for the collection of non-numerical data, allowing us to investigate how decisions are made and get a deep understanding. To achieve such conclusions, the data collected should be comprehensive, rich, and complex, with discoveries emerging after a thorough examination.
Notes, films, audio recordings, pictures, and written documents are examples of qualitative data. Text analysis is a popular approach for analyzing qualitative data.
The qualitative research approach is useful for complicated thinking, which is an important feature. There are instances when a complicated explanation is necessary to obtain the best outcomes rather than simple statistics responses.
Thus, this blog summarized the major types of qualitative research methods you must know while working on your thesis. Want to pursue your PhD abroad? Reach out to our experts at Leverage Edu who can help you choose the best university as per your preferences and guide you throughout the admission process to ensure that you get successfully shortlisted. Sign up for a free career counselling session with us today!
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.

qualitative research evolution: from traditional to live
Contributors to this guide.

Erin Barber
President + Chief Client Officer

Kat Figatner
Senior Vice President, In-Person Qualitative Research
INTRODUCTION
Over the past year, the Coronavirus pandemic has changed the way market researchers conduct qualitative research . In-person focus groups , in-home interviews, and in-store shop-alongs that are synonymous with “traditional” qualitative research have been put on hold due to safety concerns. However, despite social distancing requirements and travel restrictions, businesses still need to connect personally with consumers to learn about their lives, their needs, and how they use their products and brands. Likewise, there are countless consumers nationwide ready and willing to participate in research from the safety and comfort of their homes.
The pandemic has necessitated that “traditional” or “in-person” qualitative researchers become more agile and creative with how they help businesses reach their consumers. At C+R, this has meant reframing our “in-person” qualitative team to our “live” qualitative team and capitalizing more on digital technologies such as webcams and collaborative whiteboard tools.
While online qual and digital tools are not new to us at C+R, the pandemic required us to deepen our experience with them and develop innovative new ways to transition some traditionally in-person qualitative methodologies into the online space.
the transition from “in-person” to “live” four qualitative methodologies
The transition from “in person” to live/online took place in four main qualitative methodologies:
- Focus groups/In-Depth Interviews (IDIs)
- Shop-alongs
- Ethnographies

get our emails on all things qualitative research (and market research)
Ethnographies.
Not surprising, ethnographies have also been impacted by the pandemic. For a long time, we’ve taken a hybrid approach to ethnographies – combining insights from digital ethnographies with in-person engagements to observe behaviors in context and gather a deep view into the consumers’ lifestyles and values. In pre-COVID times, these hybrid approaches often involved a split sample – participants from across the US participate online via asynchronous activities whereas in-person ethnographies are centered in select markets. But with COVID, we transitioned this to completely online, engaging with the same participants in both the asynchronous and live components to gain a deeper, holistic understanding of who they are and the role of the category and brands in their lives.
These online hybrid qual projects are primarily conducted in two ways.
- One way is for projects to be anchored in the “asynchronous” component, where the majority of the learnings come from the online board (which can include a variety of activities, projectives, usage journals, missions, etc.), and are augmented with live methods (conversations with superstar respondents over webcam to uncover deeper learnings and bring the findings to life).
- The other way is anchored in the “live” component, where an asynchronous activity is used to generate preliminary contextual information, and the majority of the learnings come from live webcam-based interviews or focus groups.
No matter the approach, a key component for success with these types of hybrid qual methodologies is to avoid overwhelming clients and participants with too many different platforms. Ideally, no matter how many qualitative methods you combine, it’s important to try sticking with one platform, or—if you must use multiple —ensure your client is familiar with at least one of the technologies.

An example of a hybrid project anchored in the asynchronous component was for a client in the financial services industry who wanted to learn more about Gen Z, both as a cohort in general and to understand their specific banking and financial needs.
- Because we are experts in the Gen Z cohort, C+R first led a grounding session for the client team, where we shared proprietary research and knowledge about the unique needs of Gen Z.
- Second, we created an immersive mobile hub/ community where, over the course of two weeks, Gen Z participants posted videos, answered questions, and shared their social media posts. To gain deeper insight into some of the learnings, we invited several ‘superstar’ participants to participate in live moderated “house parties” fun interviews where they were able to share their views on life in general and financial/banking needs and concerns specifically.
A hybrid qualitative project anchored in ‘live’ online qual was a recent project we partnered on with a beverage manufacturer. They wanted to understand the whys behind product usage occasions in order to develop marketing and communication materials to differentiate themselves from their competitors. The primary way we collected insights from consumers was via live moderated one-on- one webcam interviews. However, to glean contextual information into our respondents’ usage and motivation of the category, we asked participants to complete consumption journals online for one week prior to their interviews. The journal entries were captured on the same platform as their interview, meaning respondents (and our client) only had to log in and interact in a single platform
Remote Shop-alongs
Another in-person qualitative research method that has been changed by the pandemic is shop-alongs, where (traditionally) a moderator and client team join a participant in-store to see first-hand how the consumer shops and to dig deeper in real time into the whys behind their shopping behavior. This is a method that is so important to all shopper insights professionals and was one of the first methodologies impacted at C+R by the Coronavirus. At the beginning of the pandemic, we had just begun a traditional in-person shop-along study when, suddenly, social distancing mandates limited the number of people in stores – requiring us to quickly pivot to remote shop-alongs.
During a remote shop-along, the moderator and client ‘tag along’ with a shopper via the respondent’s smartphone, and the store’s WIFI. The smartphone’s back-facing camera allows the moderator and client to get the shopper’s perspective as while shopping in store. The moderator can ask questions in real time to delve into the whys of the consumer’s shopping habits. As with online focus groups, remote shop-alongs enable clients to draw upon a national sample of consumers, as the moderator can remain in a single physical location. The client observers can get their burning questions answered in the moment by sharing them with the moderator in the virtual backroom chat, allowing the moderator to integrate them easily into the conversation. Recently, a consumer durables manufacturer wanted consumer feedback on a special in-store display set up at a chain of national home improvement stores. Remote one- on-one shop-alongs allowed us to send consumers into the specific stores to view the display and provide feedback.
Online Focus Groups/IDIs
In many ways, moving our In-Depth Interviews and focus groups online was the easiest transition. We have been doing webcam- based IDIs for years so we didn’t have to think twice about using this methodology. However, moving focus groups online presented some unique challenges – as well as opportunities.
- One interesting challenge has been that even with webcams, non-verbal communication is limited. For example, the subtle eye movements and body positioning participants use in a facility to indicate who will speak next is absent in an online environment. This has led to countless instances of participants speaking over one another – or not speaking at all. One way a moderator can assist with this is to address the limitation up front. To ensure all voices are heard, the moderator can be more proactive by calling on respondents for responses versus a more open conversation typically found in in person focus groups.
- Another way we have addressed this limitation – as well as the time that can be eaten up by technology glitches – is to reduce the number of focus group participants. The number of participants went from six to seven in a traditional group to approximately four to five online. This allows more time for each participant to speak despite any lags that may occur.
The move of this methodology to online has also brought unique opportunities. Tools within the research platform allow respondents to individually rate and provide feedback on stimuli. Their responses are visible in real time to the moderator and client observers, helping to guide the conversation and probes. In addition, as the client team and moderator communicate via the online “backroom chat,” the moderator can seamlessly incorporate the clients’ questions into the conversation – without the disruptive knock on the door with a note to the moderator in a traditional setting. As mentioned earlier, many people are stuck at home and are eagerly looking for something to do; so there is no shortage of willing respondents for market research studies. Show rates have been as good—or better—than in-person groups where traffic and other logistical complications can prevent people from showing up to the facility on time. Likewise, without the need for a physical meeting space, clients have been able to broaden the geographic location of respondents for studies, allowing them more national representation in a study with no added costs. And, without travel between markets, fieldwork is able to be executed faster than when we’re in-person.

Virtual Workshops
One of our core competencies at C+R is leading in person workshops such as strategy sessions, activation sessions, consumer immersions, and ideation innovation sessions. The in-person version generally entails a group of clients, the C+R team and perhaps a few creative thinking Idea BuildersTM (consumers recruited for their creativity and trained in innovation). We meet at a fun offsite location for a day (or two) to dig into research insights and develop strategic business opportunities or new products, communications, or merchandising ideas based off those insights.
With clients still working from home, we pivoted to virtual workshops. These online work sessions follow the same principles as their in-person counterparts, such as having different periods of the session dedicated to divergence and convergence incorporating play and fun to inspire creativity, and connecting the workshop to the research to build consumer empathy. We’ve found that the strength and number of ideas generated are generally comparable to in-person. However, we’ve made some changes for this virtual approach. Instead of an offsite location, we use a virtual meeting space, many of which have “breakout room” functionality built in to allow for splitting a larger group into smaller teams to encourage active participation and parallel production. Online whiteboard tools enable the facilitation of fun activities to spur creative thinking and idea generation. But what about the cognitive load involved in having to learn a potentially new program on the fly? Our solution to this is to have what we call ‘drivers’ to handle all the technology with the breakout rooms so our clients solely focus on coming up with new ideas for their brand and not have to worry about learning a new platform.

Another alteration we’ve made for online workshops is that we split up sessions into a few hours per day (rather than running them for a full day), over the course of several days. Zoom Fatigue is real and must be accounted for. Breaking sessions across multiple days keeps participants engaged and able to think of new and creative ideas. And it’s easier to get clients to commit to a couple hours at a time versus giving up an entire workday. Additionally, a series of mini sessions allows for time to debrief, incubate, and iterate our process over the course of the project. Online workshops even offer some unique advantages over traditional workshops, including:
- A wider range of cross-functional teams can participate since budgets and productivity are not dictated by travel. Greater involvement from R&D, Sales, and outside agencies helps generate diverse ideas and gives everyone a chance to be involved. This often yields greater buy-in of the ideas.
- Client teams like it! Virtual ideation can create a greater comfort level among participants.
One of the first online ideations we facilitated was a virtual ideation for a casual dining chain client who urgently needed creative and fun ideas across four core business platforms to win new customers and retain existing ones. They tried to ideate internally, but the ideas fell flat. So, we created an online ideation session that included pre-session homework to spur participant thinking, an ideation session with smaller breakout periods to allow teams to generate across the four platforms, and time at the end to prioritize top ideas. To combat “Zoom fatigue,” the entire ideation session lasted just 2.5 hours; however, the client team still generated over 70 new ideas. As more business leaders experience them, virtual workshops are likely to become a widespread agile tool for maintaining and even accelerating the pace of innovation. Some marketing and innovation teams say they prefer the virtual approach and plan to continue using it even after travel restrictions are lifted because of the ease of execution and increased engagement.

Over the past year, we’ve learned a lot from expanding our traditional qual business into the online space. We’ve relied on tried-and-true technologies and experimented with new offerings to ensure we continue to help clients answer important business questions generally best answered with “traditional” qualitative methodologies. While we feel there will continue to be a need for in-person qual research, given the cost savings, greater ability to have a national sample, and comparable stats like show rates and number of ideas generated, we hypothesize that these digital approaches will remain important tools in the traditional qualitative toolbox. We’re excited to see what else we can do as the technology continues to evolve – even as we hope to get back into the field full-time as soon as possible!
Search this site

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Types of Data Analysis in Qualitative Research. Qualitative research employs different data analysis methods, each suited to specific research goals: Thematic Analysis: Identifies recurring themes or concepts within data. Content Analysis: Systematically categorizes and quantifies text or media content.
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials - case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts - that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals' lives.
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants ...
Focus Groups. Focus groups resemble qualitative interviews in that a researcher may prepare a guide in advance and interact with participants by asking them questions. But anyone who has conducted both one-on-one interviews and focus groups knows that each is unique. In an interview, usually one member (the research participant) is most active ...
Qualitative research is defined as a market research method that focuses on obtaining data through open-ended and conversational communication. This method is about "what" people think and "why" they think so. For example, consider a convenience store looking to improve its patronage.
In this Rip Out, we describe 3 different qualitative research approaches commonly used in medical education: grounded theory, ethnography, and phenomenology. Each acts as a pivotal frame that shapes the research question (s), the method (s) of data collection, and how data are analyzed. 4, 5. Go to:
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
"Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data."
About Research Methods. This guide provides an overview of research methods, how to choose and use them, and supports and resources at UC Berkeley. As Patten and Newhart note in the book Understanding Research Methods, "Research methods are the building blocks of the scientific enterprise. They are the "how" for building systematic knowledge.
The section on traditional research methods in health and social sciences comprises four parts. It is the largest section within the Handbook. Section 1 is an introduction to research approaches and it comprises four chapters. Pranee Liamputtong introduces the nature of the qualitative inquiry that health and social science researchers can use ...
To perform qualitative research, you must choose at least one research design approach that fits your topic. It is not uncommon for a researcher to employ more than one approach throughout their study. Here are five common design approaches: 1. Historical Study. A historical study is the ideal choice for studies that involve extensive ...
In Chapter 1 you read about three different approaches to social work research: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods approaches. In this chapter we examine different traditions and methods commonly utilized in qualitative approaches to research. The qualitative research literature presents a wide array of approaches: ethnography, life ...
Patricia Benner is a qualitative researcher who has been interested in how a nurse moves from being a novice to an expert nurse. She has used the case study approach extensively. She contended that case studies help us formalize experiential knowledge and thus promote quality nursing care (Benner, 1983).
INTRODUCTION. Qualitative research methods refer to techniques of investigation that rely on nonstatistical and nonnumerical methods of data collection, analysis, and evidence production. Qualitative research techniques provide a lens for learning about nonquantifiable phenomena such as people's experiences, languages, histories, and cultures.
The Origins of Design-Based Research. Qualitative design-based research (DBR) first emerged in the learning sciences field among a group of scholars in the early 1990s, with the first articulation of DBR as a distinct methodological construct appearing in the work of Ann Brown and Allan Collins ().For learning scientists in the 1970s and 1980s, the traditional methodologies of laboratory ...
Abstract. This chapter introduces ethnography as a distinct research and writing tradition. It opens with a discussion of ethnography's current fashionability within transdisciplinary academic spaces and some of the associated challenges. The next section provides a historical overview of ethnography's emergence as a professionalized ...
What is qualitative research? If we look for a precise definition of qualitative research, and specifically for one that addresses its distinctive feature of being "qualitative," the literature is meager. In this article we systematically search, identify and analyze a sample of 89 sources using or attempting to define the term "qualitative." Then, drawing on ideas we find scattered ...
Ethnography. Ethnography is the descriptive study of people and their culture. The ethnographic model is one of the major types of qualitative research methods used in social sciences, especially in anthropology. This method of research aims to study individuals in their own habitat through the usage of methods like observations, interviews etc.
In-person focus groups, in-home interviews, and in-store shop-alongs that are synonymous with "traditional" qualitative research have been put on hold due to safety concerns. ... a key component for success with these types of hybrid qual methodologies is to avoid overwhelming clients and participants with too many different platforms ...
What are the main types of qualitative approaches to research? While there are many different investigations that can be done, a study with a qualitative approach generally can be described with the characteristics of one of the following three types: Historical research describes past events, problems, issues and facts. Data are gathered from ...