

Types and Examples of Essays: The Complete List

Essays are concise pieces of writing that present information in a comprehensible, straightforward manner. The traditional structure of an essay begins with an introduction, uses topic sentences, and concludes with a conclusion that restates the thesis.
Table of Contents
Diverse essay types demand different writing abilities, such as the ability to inject the figurative language into a personal essay to make it come to life or to critically analyze a complex issue in an analytical essay in order to find a solution.
The length and format of essays also vary, with some spanning pages and others neatly fitting into just a few paragraphs. Before you are required to write these types of essays, familiarize yourself with them. You will become a skilled essayist once you comprehend how they differ and how they are similar.
In this article, we provide you with a list of the most prevalent essay types.
Types of Essays with Examples
Understanding the different types of essays that make up the majority of your high school, college, and university assignments is a smart place to start when considering how to write one.
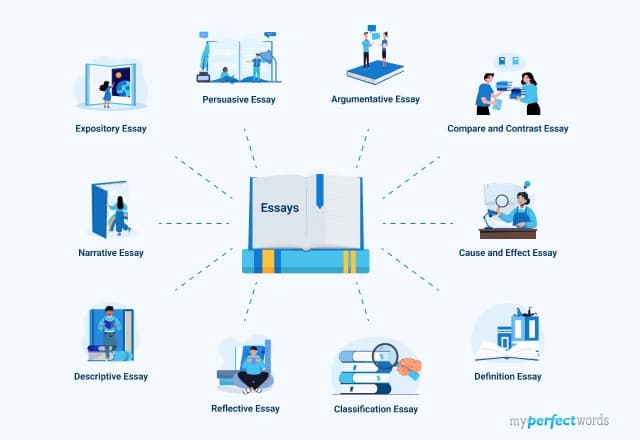
Essays can be categorized into a wide variety, but the four main types of essays are argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Let us take a detailed look at these four main types of essays with examples.
4 Major Types of Essay with Examples
The four primary methods/ types of essays that are typically required in academic settings are as follows (according to Purdue Online Writing Lab), and the majority of the essays you will ever write in your life will roughly fit into one of these categories:
The majority of the essays you will ever have to write in your existence will come under one of these four categories, which are the norm in academia.
These are four different ways to convey an essay’s idea rather than four unique essay genres. Of the nine conventional rhetorical modes, which also include techniques like classification and process analysis, these four are the most frequently employed.
1. Expository Essays
These are most likely the types of essays you may encounter and the standard essay style needed for exams.
When writing an expository essay, you will go deeper into a subject or issue to develop an idea, analyze supporting data, and then organize an “exposition” on the concept.
Depending on the writer’s objectives, expository essays can take a variety of forms including:
- Descriptive or Definition Essays
- Procedure or “How-To” Essays
- Comparison Essays
- Cause-and-Effect Essays
- Problem/Solution Essays
- Examples of Expository Essays
Watching The Thinderstoem
Over the open ocean, I observed a thunderstorm. Only thick, heavy clouds and a roiling tide could be seen at the start, and everything was quiet. I was standing on my balcony looking out toward the horizon when I heard a quiet thunderclap. The clouds began to shut over the following few minutes and reflected lightning lit up the undulating ocean. The sun was obscured by the thunderheads, casting shadows across the scene. For a very long period, there was calm.
I turned to look up just as the first thunderclap struck clearly. It shone against the sky and the water, and when I blink, I can see its outline in perfectly reversed colors. Thereafter, more. Thunder appeared to be struggling to keep up as it rumbled and stalled. Suddenly, the clouds appeared to be tearing apart, and patches of dazzling blue gleamed above the gloomy water.
I then looked down and observed the waves. Every bolt was met with a brief period of surface-spreading light. I could hear the waves smashing as they became more violent, rising high.
Then the rain started. It deluged the sea and soaked the sand all at once and in sheets. I could only see the lightning as bursts of light since the fog was so thick. The rain was so intense that it drowned out the thunder. Everything was rhythmic light and shadow, quiet and sound, and all five senses were combined into one experience.
It abruptly came to a standstill. The storm broke out. Clouds began to separate like curtains. Still falling, but much more subtly now. With the exception of one signature, it appeared as though there had never been a storm. A nearly ferociously vivid rainbow covered the sky and the lake. The horizon was once again visible.
Click here for an in-depth understanding of exploratory essays and how to write them ?????
2. Argumentative Essays
These essays are comparable to expository essays, but they are typically far more in-depth and support their arguments with well-researched qualitative and quantitative data (acquired via primary or secondary sources). An argumentative essay’s goal is to establish a viewpoint or position on a subject by offering justifications and proof.
An argumentative essay is typically written for a higher-level audience, such as high school or university. This implies that you will have to conduct some research, make some notes, and probably refer to your lecture notes.
- Examples of Argumentative Essays
Having chocolate milk in class?
I disagree that chocolate milk should no longer be served in school cafeterias. Do people believe that chocolate milk's sugar content is unhealthy, according to Chocolate Milk in School Cafeterias? They want to remove it from the dining halls. This is not a smart move.
The options available to children purchasing lunches in the cafeteria are limited. They could be limited to a single main course or veggie. They can then select chocolate milk in place of white milk. They might eat extra potato chips, cookies, donuts, and other junk food if they are unable to make a decision. Many kids just purchase junk food for lunch.
Compared to Coke or Gatorade, chocolate milk is preferable. When bringing a lunch, children must purchase a beverage; instead of purchasing milk, these children might bring a sugary beverage.
Even though chocolate milk contains some sugar, it is still preferable to other beverages. It still has vitamins and minerals, so that's a plus. Although some kids just don't like white milk, I believe it is preferable for youngsters to at least drink some milk than none at all. The American Heart Association and the American Academy of Pediatrics both say this, and I agree!
For an in-depth understanding of argumentative essays, click here. ??????
3. Descriptive Essays
As the title suggests, the focus of this essay is language in general, specifically adjectives, similes, and metaphors. The goal of these essays is to describe the topic you are requested to write about as vividly as you can. You will need to include an introduction, body, and conclusion, just like in an expository essay.
A descriptive essay, however, differs from other types of writing since it requires you to describe a specific object in great detail. The other types of essays may include description, but they typically require a little more, such as an argument, whereas a descriptive essay only provides a detailed description of something, with the thing being described serving as the main focus rather than an argument.
- Examples of Descriptive Essays
Parents' view of university education in my country
Teenagers in my nation do not work because they are too busy studying. For teenagers, playing the character of a student and a good student is paramount. Making your parents proud is crucial, as is competing for top colleges and employment.
Families and parents believe that it is crucial for kids to study very hard, very long, and without breaks in order to achieve the best grades possible. Only a small percentage of the population in my country can attend university since there are so few open spots.
Therefore, the pupils who perform best in school are the ones who attend universities. The top employment goes to students who attend the best universities. Choosing the right university will allow you to unwind.
It's crucial to make your parents happy. In the 1950s, while our nation was at war, our parents struggled mightily to rise above it. The nation was empty. Like in Japan, parents here put in long hours at work, and pupils here are expected to work hard. The family is honored for their labors. Top marks are crucial, so parents may be proud of their son's diligence.
Click here for more on descriptive essays ?????
4. Narrative Essays|
Again, a narrative essay is a more personal piece of writing where your point of view is made apparent to the reader, contrary to what the title might imply. These articles may take the form of stories or be referred to as “creative non-fiction.” In these essays, the first-person pronoun “I” is frequently used.
Narrative essays, which are frequently the closest thing to works of journalism, must also have a distinct introduction, body, and conclusion that are filled with brief language. You are probably well on your way to being a successful journalist if you are able to write a compelling narrative essay.
- Examples of Narrative Essays
Thinking in a Systems Approach
A child's death is always tragic. Only a few hours after giving birth, one of my sisters lost her first two children, twins. I learned from how my family members handled this incident that even those who were raised with the same ideas and ideals might have very diverse perspectives on the world.
My sibling was delivered early. We weren't shocked to find that her first pregnancy would not proceed to term because she arrived a month early than she should have. However, the fact that the infants would arrive two months early rather than just one upset us.
We had little expectation that they would live a long life because their prospects of survival were slim. My role in the situation was quite limited because I lived several hundred km apart, but I worried and wept with everyone else. The full extent of my sorrow for my sister and the rest of my family did not reach me until a few years later when I saw my sister at a family reunion.
That's when I realized how much hope, disappointment, and grief those two little girls' incredibly brief lives had brought to our family. At that point, I genuinely felt sad for both my sister and myself.
At about the same time, I realized that our collective perspectives on the incident varied. My mother was at one extreme and I was at the other, creating a type of polarization.
I'm a devoted Mormon, as is my mother. We both hold the same beliefs about God, including that we were all in God's presence before coming to Earth, that God has a plan for our salvation, and that if we live righteously, we can return to God. We also hold to the doctrine of foreordination, which holds that God assigns particular individuals to particular jobs on Earth.
I eventually realized that our differences stemmed from what I like to refer to as system orientation. We both practice religion, however, my mother exclusively practices religion, whilst I also practice science. She believes that religion is the only rational and consistent explanation for everything, particularly the loss of a baby.
In my worldview, which integrates religion and science, God may exist, but he need not be in charge of everything. Many events, such as infant deaths, take place within his plan without being specifically mentioned in it. Understanding and respecting my mother's viewpoints as well as my own and feeling better about them are made possible by looking at it in this way.
Click here for an in-depth look at narrative essays ?????

There are 4 main types of essays
The 7 Other Types of Essays
Using one of these four rhetorical devices may be required of you when writing an essay. You might be required to write an argumentative essay on whether or not a new college policy should be implemented.
You would convey your stance by using persuasive writing tactics in your essay, such as by outlining your opinion of the proposed legislation and how it is likely to affect society.
You can better grasp the texts you work with by having a better understanding of the four primary forms of writing. When reading an essay, try to determine the writing style the author is using by focusing on the essay’s structure, tone, vocabulary, and method of presenting the main idea.
Here we analyze the 4 types of essays available:
Personal essays
Your emphasis in a personal essay is on something that has affected you personally. It may be a current issue, a historical occurrence, or a more comprehensive examination of how many situations and events have molded you into the person you are now.
Personal essays frequently use narrative writing strategies. However, depending on the subject matter and thesis of the essay, authors may also use expository or descriptive tactics. Argumentative, comical, and college application essays are just a few examples of different genres of writing that can overlap with personal essays.
Political essays
Some of the most well-known political essays may be familiar to you from what you studied in history class. These essays are works by eminent philosophers from the past and the present that address society and ideal forms of government.
In a political essay, the author discusses the current situation and suggests solutions, occasionally using historical examples of situations or solutions that are analogous to the current one. Political essays typically fall under the categories of informative or persuasive writing.
Compare-and-contrast essays
Essays that compare and contrast two things are probably one of the essay types that students write the most. In this style of essay, the author contrasts and compares two subjects in order to highlight the main distinctions and similarities between them.
The content of compare-and-contrast essays is typically revealed through the similarities the author draws, making them expository writing assignments. When comparisons are used to persuade the reader to adopt a particular perspective, they can also be considered persuasive writing pieces.
College (application) essays
Essays you write in college may not always qualify as college essays. Actually, you’ll write all of your college essays before you enroll in a college unless you later go to graduate school or another type of specialized academic program.
A concise personal essay that emphasizes your personality traits and life experiences that make you the perfect fit for the college to which you are applying is known as a college application essay or personal statement.
Analytical essays
Essays that analyze a topic in-depth focus on its essential elements and draw conclusions after carefully analyzing these elements. An analytical essay regarding a book’s topics or an argumentative essay’s ideas can be required of you. The purpose of analytical essays, which are examples of expository writing, is to present facts by interpreting content.
An analytical essay does not attempt to persuade the reader to adopt a particular viewpoint. Instead, the author gives a piece of media, such as a short story or movie, and analyzes its theme by going over the various ways it conveys that theme.
Argumentative essays
As the name implies, you argue in an argumentative essay.
You specifically make an argument for or against a certain viewpoint. For instance, your task might be to advocate for or against your school’s rule prohibiting students from enrolling in more than two AP courses annually and to back up your arguments with facts.
You might use statistics showing a correlation between a student’s enrollment in AP courses and their typical AP test results or the amount of homework an AP course requires to support your argument that it’s a good idea.
Argumentative essays that are well-written don’t rely on emotional appeal. Instead, they use evidence—statistics, facts, and logic—to persuade readers of the validity of their ideas. Argumentative essays are typical examples of persuasive writing.
Humorous essays
As the name suggests, this sort of essay aims to make the reader laugh and be entertained. A comical essay could describe an amusing incident in the author’s life or it might be a political essay that makes political commentary through satire. A humorous essay is one that is both entertaining and academic.
Essays that are humorous frequently rely more on tactics used in narrative writing, such as metaphors and descriptive language, than they do on other essay-writing strategies. Hilarious essays frequently take the form of descriptive articles that employ hyperbole, irreverence, or quirky language to communicate a humorous perspective on the subject matter.
We hope by reading to this point, you now know how to write an essay that gets all the accolades and grades you deserve.
What are you waiting for now that you are aware of the various essay types and how to compose them? Start working on your essay right away.

How to Write Expository Essays (and Elements)

How to Write a Compelling Argumentative Essay

How to Write a Descriptive Essay (Types and Tips)

Narrative Essays: Examples and How to Write them
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We are a group of language experts, educators, and writers from all over the world who are passionate about education and want to help students succeed without putting them under stress. More About us
About us | > Contact us | > FAQ
Email Sign up

Essay Writing Guide
Types Of Essay
Explore Different Types of Essays, their Purpose, and Sub-types
11 min read
People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
Learn How to Write An Essay in Simple Steps
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
A Catalog of 500+ Essay Topics for Students
Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
Learn How to Create a Perfect Essay Outline
How to Start an Essay- A Step-by-Step Guide
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
Learn How to Write an Essay Hook, With Examples
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems
How to Make an Essay Longer: 14 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay - A Detailed Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
Are you a college or high school student ready to start on a journey through the fascinating world of essay writing ? Brace yourself because you'll encounter a variety of essay types that will challenge your writing skills and creativity.
Picture this: You're handed an assignment, a blank canvas on which to express your thoughts and ideas. But here's the catch – your teacher won't always specify the type of essay you should craft. It's up to you to solve the riddle hidden within the assignment question.
But fear not!
In this blog, we'll discuss the four most common types of essays you're likely to encounter during your academic years. While these essays may share a common foundation and structure, each possesses its own unique characteristics. Let’s get started!
- 1. Major Types of Essays In Academic Writing
- 2. Argumentative Essay
- 3. Descriptive Essay
- 4. Expository Essay
- 5. Narrative Essay
- 6. Other Essay Types
Major Types of Essays In Academic Writing
When it comes to academic writing, understanding the different types of essays is essential. Each type serves a distinct purpose and requires a specific approach. Let's explore these essay types along with their descriptions and example prompts in the table below:
Understanding these major types of essays and the skills they assess will empower you to approach your academic writing with confidence. Depending on your assignment's requirements, you'll be better equipped to choose the appropriate essay type and showcase your writing abilities effectively.
Each type offers a unique opportunity for you to express your ideas, and arguments and perfect your specific writing skills.
Here are the key types of essay formats explained in detail, along with examples to enhance your understanding.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay is an essay type that presents a well-structured argument supported by evidence and reasoning. The primary goal is to engage the reader in a discussion, provide evidence, and logically demonstrate why a particular viewpoint is more valid.
In simple words, the writer must provide evidence and remain consistent in their stance. While argumentative essays present both sides of an issue, they strongly support one perspective.
Characteristics of Argumentative Essay
- Clear Thesis: It should have a clear thesis statement to state the writer's position.
- Balanced Presentation: An argumentative essay addresses opposing views.
- Evidence: It relies on credible and relevant evidence.
- Logical Reasoning: The essay presents arguments coherently and logically.
- Persuasive Techniques: It uses persuasive techniques like ethos, pathos, and logos effectively.
- Introduction: The introduction introduces the topic and thesis, engaging the reader's interest.
- Body: The body paragraphs present arguments with supporting evidence.
- Counterargument: It addresses opposing viewpoints and refutes them.
- Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes key points and reinforces the thesis, leaving a strong impression.
Argumentative Essay Example
Before beginning the writing process, it is better to go through some expertly crafted argumentative essay examples . This approach enables you to grasp the argumentative essay outline and writing style more effectively.
Descriptive Essay
A descriptive essay is a form of writing that aims to immerse readers in a sensory-rich experience. Unlike informational or persuasive essays, its primary goal is to vividly depict a person, place, object, event, or experience. The descriptive essay must evoke the senses and emotions of the reader. In simple terms, the reader should see what you saw and feel what you felt. To make it better, you can use several literary devices such as;
- Alliteration
All of them help in making the experience and your essay better.
Key Characteristics
- Sensory Detail: Descriptive essays appeal to the five senses to create a multisensory experience.
- Vivid Imagery: They use figurative language and descriptive adjectives to bring the narrative to life.
- Emotional Connection: These essays often aim to establish an emotional bond between the reader and the subject.
- Structured Approach: They typically follow an introduction-body-conclusion structure.
- Introduction: Introduces the subject and purpose, sometimes with a thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs: Focus on specific aspects or details using sensory language and vivid descriptions.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the central theme and leaves a lasting impression.
Descriptive Essay Example
Creating a perfect descriptive essay for an assignment is not difficult if you go through some expert descriptive essay examples first.
Need more examples? Read our Descriptive Essay Examples and Writing Tips blog to get inspired!
Expository Essay
An expository essay is a type of writing that provides clear and objective explanations of a topic without expressing personal opinions. It aims to inform and educate by presenting factual information and analysis.
Therefore, it is important that you make a focused outline and stick to it throughout the process.
An expository essay incorporates a wide array of essays such as:
- Cause and effect essays
- Process essays
- Analytical essays
- Compare and contrast essays
Key Characteristics
- Objective Presentation: Expository writing maintains an impartial tone, avoiding personal biases.
- Informativeness: They focus on explaining complex ideas or processes in a straightforward manner.
- Structured: These essays follow a clear structure with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Use of Evidence: They rely on credible evidence, facts, and examples to support the topic.
- Introduction: Introduces the topic and often includes a thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs: Each paragraph focuses on a specific aspect and provides explanations and evidence.
- Conclusion: Restates the main idea and summarizes key points.
Expository Essay Example
Looking for more sample essays? Check out our Expository Essay Examples blog and take inspiration from a range of expository essays!
Narrative Essay
A narrative essay is a type of academic writing that tells a story or recounts a personal experience. Unlike other essays, its primary purpose is to engage and entertain the reader through storytelling.
- Narrative Structure: Follows a chronological sequence with an introduction, body, climax, and conclusion.
- First-Person Perspective: Typically written from the first-person point of view (e.g., "I" and "we") , sharing personal experiences and emotions.
- Vivid Description: Relies on descriptive language and imagery to create a clear picture of events, characters, and settings.
- Emotional Connection: Aims to establish an emotional bond with the reader by conveying the writer's thoughts and feelings.
- Introduction: Sets the stage and introduces the central theme or problem.
- Body: Presents events or experiences in chronological order with sensory details.
- Climax: Often includes a central event or turning point.
- Conclusion: Reflects on the narrative, offering insights, lessons, or resolution.
Narrative Essay Example
Wondering how to get your story into an interesting narrative? Learn the best way to write a perfect narrative essay with the help of expert narrative essay examples.
For more examples visit our blog on narrative essay examples .
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Other Essay Types
In addition to the major types of essays discussed earlier, there are several other specialized types that cater to specific audiences. These essays provide diverse avenues for writers to communicate their ideas effectively.
We will go through these essay types here.
Persuasive Essay
A persuasive essay is another type of academic essay. In this essay type, the writer utilizes logic and reasoning to show one’s idea is more convincing than another idea.
In writing a persuasive essay, the main aim is to persuade the reader to accept a certain point of view. The presented argument or claim must use solid evidence and sound reasoning by stating facts, examples, and quotes.
Persuasive Essay Example
Since persuasive essays are the most common type of essay, it is essential to get familiar with their writing style. For that, here is an interesting persuasive essay example that you can explore for your better understanding.
Read our persuasive essay examples blog for more samples!
Analytical Essay
An analytical essay is a type of academic essay in which the writer analyzes a topic bit by bit. Writing an analytical essay is not about convincing readers of your point of view. But wanting readers to agree with what you have written.
So, there is no need to use strong persuasive language in an analytical essay. Rather you should aim to provide enough analysis to make sure your argument is clear to the readers.
Analytical Essay Example
Let’s take a look at a sample analytical essay:
Read our analytical essay examples blog if you are looking for more sample essays!
Reflective Essay
A reflective essay type of essay requires you to examine your personal experiences through self-reflection. In the process of writing a reflective essay, you provide insight into what you have gained from those experiences.
What makes reflective essays different from other essay types is the fact that it examine the past experience from the present. Reflective essays take the reader through a journey of self-growth.
Reflective Essay Example
The following reflective essay example will help you get a clear idea of how to structure your analytical essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay
It is a form of a textual analysis essay in which the student examines and analyzes a persuasive text. It is like an essay, speech, or visual art and analyzes the rhetorical devices used in it. Writing a rhetorical analysis essay is different from writing other essays because it will be more than adding facts only.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Here is a rhetorical analysis essay example that will help you learn better.
Check out our rhetorical analysis essay examples blog for more samples!
Literary Analysis Essay
A literary analysis essay is based on close reading and analysis of a work of literature like poetry and novel. It identifies different literary factors like themes, setting, characters, setting, and the kind of language used in it. A literary analysis essay has the same 5 paragraphs as any other essay but the main subject and topic are different.
Literary Analysis Essay Example
Need help with your literary analysis essay? Below is a sample essay to help you understand better.
Summing it Up! Now you know what are the different types of essays in academic writing that you are most likely to get assigned. However, if you still find it difficult to compose your essay, leave your piece of writing to our experts.
Whether you need an argumentative essay, narrative essay, descriptive essay, or expository essay we are here to help. Our expertise extends to all types of essays, ensuring that your academic writing needs are met with precision and excellence.
Request essay help today and let our experts assist you in writing A+ grade essays within your specified timeline!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most important element in any essay.
A thesis statement is the most important part of any essay. Other than the research itself, the thesis statement is the most important part of an essay or research paper. A thesis statement summarizes the main point and essence of the argument.
What type of essay is most common at university?
Usually, university students get argumentative kinds of essays. No matter what kind of essay you write, you will need to develop an argument.
Here are some kinds of essays and the kind of arguments added to them.
- Analysis and interpretation of literary texts are discussed in literary analysis essays.
- The importance of a particular event or theory is analyzed in a history argumentative essay.
- A political theory is examined in a political argumentative essay.
Besides, there are a number of different kinds of argumentative and analysis essays.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
Types of Essays: A Comprehensive Guide to Writing Different Essay Types
When it comes to academic writing, essays are one of the most common assignments you will encounter. Essays are a way for you to showcase your understanding of a particular topic, and they come in various forms. Each type of essay has its unique characteristics, and it is essential to understand the differences between them to produce a well-written piece. In this article, we will explore the different types of essays you may encounter in your academic journey.
Types of Essays: Your Ultimate Guide to Essay Writing

Understanding Essays
Definition of essay.
An essay is a piece of writing that presents an argument or a point of view on a particular topic. It is a formal piece of writing that is usually written in the third person and is structured into paragraphs. Essays can be written on a variety of topics, ranging from literature to science, and can be of different lengths. They are often used in academic settings to assess a student’s understanding of a particular subject.
Purpose of Essay
The purpose of an essay is to persuade the reader to accept the writer’s point of view. Essays can be used to argue for or against a particular position, to explain a concept, or to analyze a text. The writer must provide evidence to support their argument and must use persuasive language to convince the reader of their position.
There are four main types of essays: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive. Each type of essay has its own unique characteristics and is written for a different purpose. Understanding the different types of essays is essential for writing a successful essay.
Types of Essays
Narrative essay.
A narrative essay is a type of essay that tells a story. It is often written in the first person point of view, and it can be either fictional or non-fictional. This type of essay allows you to express yourself in a creative and personal way.
When writing a narrative essay, it is important to have a clear and concise thesis statement that sets the tone for the rest of the essay. The thesis statement should be specific and should reflect the main point of the essay. It should also be interesting and engaging to the reader.
One of the key elements of a successful narrative essay is the use of vivid and descriptive language. This helps to create a clear picture in the reader’s mind and makes the story more engaging. Additionally, it is important to use dialogue to bring the characters to life and to show their emotions and personalities.
Another important aspect of a narrative essay is the structure. It should have a clear beginning, middle, and end, and the events should be presented in chronological order. This helps the reader to follow the story and understand the sequence of events.
Descriptive Essay
In a descriptive essay, you are required to describe something, such as an event, a person, a place, a situation, or an object. The primary objective of a descriptive essay is to provide a detailed and vivid description of the topic. By using sensory details, such as sight, sound, touch, smell, and taste, you can create a picture in the reader’s mind and make them feel as if they are experiencing the topic themselves.
When writing a descriptive essay, it is important to choose a topic that you are familiar with and have a personal connection to. This will help you to convey your emotions and feelings effectively and make your essay more engaging and interesting to the reader.
To write a successful descriptive essay, you should follow these steps:
- Choose a topic that you are passionate about and have a personal connection to.
- Brainstorm and create an outline of your essay, including the main points you want to cover and the sensory details you will use.
- Use sensory details to create a vivid and engaging picture in the reader’s mind.
- Use figurative language, such as metaphors and similes, to add depth and complexity to your descriptions.
- Use transitions to connect your ideas and create a smooth flow of information.
- Revise and edit your essay to ensure that it is well-structured, organized, and error-free.
Expository Essay
An expository essay is a type of academic writing that aims to explain, describe, or inform the reader about a particular subject. This type of essay is based on facts, evidence, and examples, and it does not require the writer’s personal opinion or feelings. Expository essays can be written in various styles, including compare and contrast, cause and effect, and problem and solution.
Compare and Contrast Essay
A compare and contrast essay is a type of expository writing that involves comparing and contrasting two or more subjects. This type of essay aims to provide the reader with a better understanding of the similarities and differences between the subjects being compared. To write a successful compare and contrast essay, you need to identify the similarities and differences between the subjects, organize your ideas, and provide supporting evidence.
Cause and Effect Essay
A cause and effect essay is a type of expository writing that explores the causes and consequences of a particular event, situation, or phenomenon. This type of essay aims to explain the reasons behind a particular occurrence and its effects on individuals, society, or the environment. To write a successful cause and effect essay, you need to identify the causes and effects of the subject, organize your ideas, and provide supporting evidence.
Problem and Solution Essay
A problem and solution essay is a type of expository writing that focuses on a particular problem and proposes a solution to it. This type of essay aims to inform the reader about a particular issue and provide a viable solution to it. To write a successful problem and solution essay, you need to identify the problem, explain its causes, propose a solution, and provide supporting evidence.
Persuasive Essay
A persuasive essay is a type of academic writing that aims to persuade the reader to accept the writer’s point of view. In this type of essay, the writer presents their argument and supports it with evidence and reasoning to convince the reader to take action or believe in a particular idea.
To write a persuasive essay, you must first choose a topic that you are passionate about and can argue convincingly. Then, you need to research the topic thoroughly and gather evidence to support your argument. You should also consider the opposing viewpoint and address it in your essay to strengthen your argument.
The structure of a persuasive essay is similar to that of other types of essays. It consists of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. In the introduction, you should grab the reader’s attention and clearly state your thesis statement. The body paragraphs should present your argument and evidence, and the conclusion should summarize your argument and restate your thesis statement.
To make your persuasive essay more effective, you can use various persuasive writing strategies, such as appealing to the reader’s emotions, using rhetorical questions, and using vivid language. You can also use statistics, facts, and examples to support your argument and make it more convincing.
Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay is a type of essay that requires you to present a well-researched and evidence-based argument on a particular topic. The aim of this essay is to convince the reader of your stance on the topic by using logical reasoning and factual evidence.
To write an effective argumentative essay, it is important to have a clear and concise thesis statement that presents your position on the topic. This statement should be supported by strong evidence, such as quotations, statistics, and expert opinions. It is also important to consider and address potential counterarguments to your position.
One key aspect of an argumentative essay is the use of logical fallacies. These are errors in reasoning that can weaken your argument and make it less convincing. Some common logical fallacies include ad hominem attacks, false dichotomies, and straw man arguments. It is important to avoid these fallacies and instead rely on sound reasoning and evidence to support your argument.
When writing an argumentative essay, it is also important to consider your audience. Your tone and language should be appropriate for your intended audience, and you should anticipate and address any potential objections or concerns they may have about your argument.
Analytical Essay
An analytical essay is a type of academic writing that involves breaking down a complex topic or idea into smaller parts to examine it thoroughly. The purpose of this essay is to provide a detailed analysis of a particular subject and to present an argument based on the evidence gathered during the research.
When writing an analytical essay, it is crucial to have a clear thesis statement that outlines the main argument of the essay. The thesis statement should be specific and concise, and it should be supported by evidence from primary and secondary sources.
To write an effective analytical essay, you should follow these steps:
- Choose a topic that interests you and that you can research thoroughly.
- Conduct research to gather relevant information and evidence to support your thesis statement.
- Create an outline to organize your ideas and arguments.
- Write an introduction that provides background information on the topic and presents your thesis statement.
- Develop body paragraphs that provide evidence to support your thesis statement.
- Write a conclusion that summarizes your main points and restates your thesis statement.
When writing an analytical essay, it is important to focus on the analysis rather than just summarizing the information. You should critically evaluate the evidence and present your own interpretation of the data.
Critical Essay
A critical essay is a type of academic writing that involves analyzing, interpreting, and evaluating a text. In a critical essay, you must make a claim about how particular ideas or themes are conveyed in a text, and then support that claim with evidence from primary and/or secondary sources.
To write a successful critical essay, you must first read the text carefully and take notes on its main ideas and themes. You should also consider the author’s purpose and audience, as well as any historical or cultural context that may be relevant to the text.
When writing your critical essay, you should follow a clear and logical structure. Begin with an introduction that provides background information on the text and your thesis statement. In the body of your essay, you should provide evidence to support your thesis, using quotes and examples from the text as well as other sources.
It is important to be critical in your analysis, examining the text in detail and considering its strengths and weaknesses. You should also consider alternative interpretations and counterarguments, and address them in your essay.
Reflective Essay
A reflective essay is a type of academic essay that requires you to analyze and interpret an academic text, such as an essay, a book, or an article. Unlike a personal experience essay, a reflective essay involves critical thinking and evaluation of the material.
In a reflective essay, you are expected to reflect on your own learning and experiences related to the material. This type of essay requires you to think deeply about the material and analyze how it relates to your own experiences and knowledge.
To write a successful reflective essay, you should follow these steps:
- Choose a topic that is relevant to the material you are reflecting on.
- Analyze the material and identify key themes and concepts.
- Reflect on your own experiences and knowledge related to the material.
- Evaluate and analyze the material and your own experiences to draw conclusions and insights.
- Write a clear and concise essay that effectively communicates your reflections and insights.
Remember that a reflective essay is not just a summary of the material, but rather an analysis and evaluation of it. Use examples and evidence to support your reflections and insights, and be sure to use proper citation and referencing to acknowledge the sources of your information.
Personal Essay
A personal essay is a type of essay that involves telling a story about yourself, your experiences, or your feelings. It is often written in the first person point of view and can be a powerful way to share your unique perspective with others.
Personal essays can be used for a variety of purposes, such as college admissions, scholarship applications, or simply to share your thoughts and experiences with a wider audience. They can cover a wide range of topics, from personal struggles and triumphs to reflections on important life events.
When writing a personal essay, it is important to keep in mind that you are telling a story. This means that you should focus on creating a narrative that is engaging and compelling for your readers. You should also be honest and authentic in your writing, sharing your true thoughts and feelings with your audience.
To make your personal essay even more effective, consider incorporating descriptive language, vivid imagery, and sensory details. This can help bring your story to life and make it more memorable for your readers.
Synthesis Essay
A synthesis essay is a type of essay that requires you to combine information from multiple sources to create a cohesive argument. This type of essay is often used in academic writing and requires you to analyze, interpret, and evaluate information from various sources to support your thesis statement.
There are two main types of synthesis essays: explanatory and argumentative. An explanatory synthesis essay aims to explain a particular topic or issue by using different sources to provide a comprehensive overview. On the other hand, an argumentative synthesis essay requires you to take a stance on a particular issue and use evidence from multiple sources to support your argument.
When writing a synthesis essay, it is important to carefully analyze and interpret each source to ensure that the information you are using is relevant and accurate. You should also consider the credibility of each source and evaluate the author’s bias or perspective.
To effectively write a synthesis essay, you should follow a clear structure that includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction should provide background information on the topic and include a clear thesis statement. The body paragraphs should each focus on a specific aspect of the topic and provide evidence from multiple sources to support your argument. The conclusion should summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement.
Review Essay
A review essay is a type of academic writing that involves analyzing and evaluating a piece of work, such as a book, movie, or article. This type of essay requires you to provide a critical assessment of the work, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses. A successful review essay should provide the reader with a clear understanding of the work being reviewed and your opinion of it.
When writing a review essay, it is important to keep in mind the following guidelines:
- Length: A review essay should be between 1,000 and 1,500 words. This length allows for a thorough analysis of the text without becoming bogged down in details. Of course, the specific length will vary depending on the nature of the text being reviewed and the desired focus of the essay.
- Structure: A review essay should follow a clear and logical structure. Start with an introduction that provides some background information on the work being reviewed and your thesis statement. The body of the essay should provide a summary of the work and a critical analysis of its strengths and weaknesses. Finally, end with a conclusion that summarizes your main points and provides your final thoughts on the work.
- Evidence: A successful review essay should be supported by evidence from the work being reviewed. This can include direct quotes or paraphrases, as well as examples that illustrate your points.
- Critical Thinking: A review essay requires you to engage in critical thinking. This means that you must evaluate the work being reviewed in a thoughtful and analytical manner, considering both its strengths and weaknesses.
Research Essay
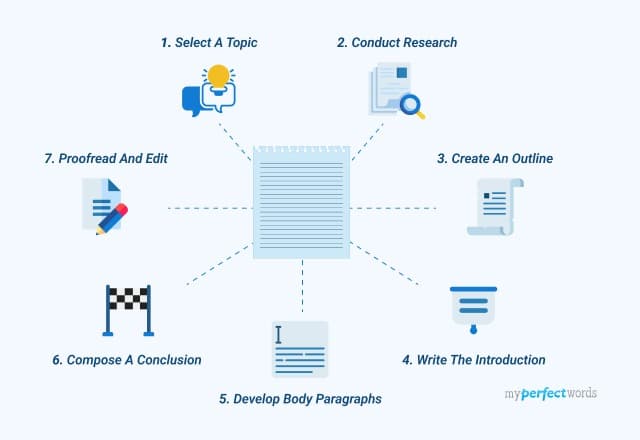
When it comes to writing a research essay, you must conduct in-depth independent research and provide analysis, interpretation, and argument based on your findings. This type of essay requires extensive research, critical thinking, source evaluation, organization, and composition.
To write a successful research essay, you must follow a specific structure. Here are some key components to include:
Introduction
The introduction should provide a brief overview of your research topic and state your thesis statement. Your thesis statement should clearly state your argument and the main points you will cover in your essay.
Literature Review
The literature review is a critical analysis of the existing research on your topic. It should provide a summary of the relevant literature, identify gaps in the research, and highlight the significance of your study.
Methodology
The methodology section should describe the methods you used to conduct your research. This may include data collection methods, sample size, and any limitations of your study.
The results section should present your findings in a clear and concise manner. You may use tables, graphs, or other visual aids to help convey your results.
The discussion section should interpret your results and provide a critical analysis of your findings. You should also discuss the implications of your research and how it contributes to the existing literature on your topic.
The conclusion should summarize your main findings and restate your thesis statement. You should also discuss the limitations of your study and suggest avenues for future research.
Report Essay
A report essay is a type of essay that presents and summarizes factual information about a particular topic, event, or issue. The purpose of a report essay is to provide readers with a clear and concise understanding of the subject matter. It is important to note that a report essay is not an opinion piece, but rather a neutral presentation of facts.
When writing a report essay, it is important to follow a structured format. The typical format includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should provide background information on the topic and state the purpose of the report. The body should present the facts in a logical and organized manner, using headings and subheadings to help readers navigate the information. The conclusion should summarize the key findings and provide any recommendations or conclusions.
One of the key elements of a report essay is research. It is essential to conduct thorough research on the topic to ensure that the information presented is accurate and reliable. This may involve reviewing academic articles, government reports, and other sources of information. It is also important to cite all sources used in the report essay using a recognized citation style, such as APA or MLA.
Informal Essay
An informal essay, also known as a familiar or personal essay, is a type of essay that is written in a personal tone and style. This type of essay is often written as a reflection or commentary on a personal experience, opinion, or observation. Informal essays are usually shorter than formal essays and are often written in a conversational style.
In an informal essay, you are free to use first-person pronouns and to express your personal opinions and feelings. However, you should still strive to maintain a clear and concise writing style and to support your arguments with evidence and examples.
Informal essays can take many forms, including personal narratives, anecdotes, and reflections on current events or social issues. They can also be humorous or satirical in nature, and may include elements of fiction or creative writing.
When writing an informal essay, it is important to keep your audience in mind and to use language and examples that will be familiar and relatable to them. You should also be aware of your tone and style, and strive to create a voice that is engaging and authentic.
Short Essay
When it comes to writing a short essay, it is essential to convey your thoughts and ideas in a concise and clear manner. Short essays are usually assigned in the range of 250-750 words, and occasionally up to 1,000 words. Therefore, it is important to focus on the most important elements of your topic.
To write a successful short essay, you should start by selecting a topic that is interesting and relevant. Once you have chosen your topic, you should conduct thorough research to gather evidence and support for your argument. This will help you to develop a clear and concise thesis statement.
When writing your short essay, it is important to structure your ideas in a logical and coherent manner. You should start with an introduction that provides background information and a clear thesis statement. The body of your essay should be structured around your main points, with each paragraph focusing on a specific idea or argument. Finally, you should conclude your essay by summarizing your main points and restating your thesis statement.
To make your short essay more engaging and impactful, you may want to consider using bullet points, tables, and other formatting techniques to convey your ideas more clearly. Additionally, you should use strong and clear language, avoiding jargon and unnecessary words.
When it comes to academic writing, a long essay is a common type of assignment that you may encounter. This type of essay typically requires you to conduct extensive research and analysis on a specific topic.
The length of a long essay can vary depending on the assignment requirements, but it is usually longer than a standard essay. In general, a long essay can range from 2,500 to 5,000 words or more.
To write a successful long essay, it is important to have a clear understanding of the topic and to conduct thorough research. This may involve reading academic articles, books, and other sources to gather information and support your arguments.
In addition to research, a long essay should also have a clear and well-structured argument. This may involve outlining your main points and supporting evidence, as well as addressing any counterarguments or potential weaknesses in your argument.
Overall, a long essay requires a significant amount of time and effort to complete. However, by following a clear structure and conducting thorough research, you can produce a well-written and persuasive essay that meets the requirements of your assignment.
Some tips for writing a successful long essay include:
- Start early to give yourself enough time to research and write
- Break down the assignment into manageable sections
- Use clear and concise language
- Provide sufficient evidence to support your arguments
- Use proper citation and referencing to avoid plagiarism
Five Paragraph Essay
If you are a student, you have likely been assigned a five-paragraph essay at some point. This type of essay is commonly used in high school and college writing classes. The five-paragraph essay is a structured format that consists of an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
The introduction paragraph is where you present your thesis statement, which is the main idea or argument that you will discuss in your essay. This paragraph should grab the reader’s attention and provide some background information about the topic. It should also include a clear thesis statement that outlines what you will be discussing in the essay.
The three body paragraphs are where you provide evidence to support your thesis statement. Each paragraph should focus on a single point that supports your thesis. You should use specific examples and evidence to back up your claims. Each paragraph should also include a transition sentence that connects it to the next paragraph.
The conclusion paragraph is where you wrap up your essay and restate your thesis statement. This paragraph should summarize the main points of your essay and leave the reader with a clear understanding of your argument. You should avoid introducing any new information in the conclusion paragraph.
Scholarship Essay
A scholarship essay is a crucial document that can help you secure financial aid for your academic pursuits. It is a written statement that highlights your qualifications, accomplishments, and goals. Scholarship essays are typically required by organizations that offer scholarships to students. The essay is meant to help the organization understand why you are deserving of the scholarship and how it will help you achieve your academic and career goals.
To write an effective scholarship essay, it is important to understand the prompt and the organization offering the scholarship. Many scholarship essay prompts are open-ended, which means that you can write about any topic that is relevant to you. However, it is important to ensure that your essay is aligned with the values and goals of the scholarship organization.
When writing a scholarship essay, it is important to be concise and clear. Use simple language and avoid jargon or technical terms that the reader may not understand. Make sure that your essay is well-structured and organized, with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. Use headings and subheadings to make your essay easy to read and navigate.
To make your scholarship essay stand out, use specific examples and anecdotes that demonstrate your qualifications and accomplishments. Use concrete details and avoid generalizations. Be honest and authentic, and avoid exaggerating or making false claims. Finally, proofread your essay carefully to ensure that it is free of errors and typos.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of academic essays?
There are four main types of academic essays: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive. Each type has its own unique purpose and structure, and it’s important to understand the differences between them in order to write effectively.
What are the parts of a standard essay?
A standard essay typically consists of three main parts: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The introduction should provide background information on the topic and include a thesis statement that outlines the main argument of the essay. The body should present evidence and support for the thesis statement, and the conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis in a new way.
Can you provide examples of different types of essays?
Sure, here are some examples of each type of essay:
- Argumentative: An essay that presents a clear argument on a controversial topic, such as gun control or abortion.
- Expository: An essay that explains or describes a topic, such as how to bake a cake or the history of the Civil War.
- Narrative: An essay that tells a story, such as a personal experience or a fictional tale.
- Descriptive: An essay that uses sensory details to paint a picture of a person, place, or thing, such as a description of a sunset or a character in a novel.
How do you write a narrative essay?
To write a narrative essay, you should first choose a topic that is meaningful to you and has a clear beginning, middle, and end. Then, you should use descriptive language and sensory details to bring the story to life for the reader. Finally, you should reflect on the experience and what you learned from it.
What are the four main types of essays?
The four main types of essays are argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive. Each type has its own unique purpose and structure, and it’s important to understand the differences between them in order to write effectively.
What are the three parts of the essay format?
The three parts of the essay format are the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. The introduction should provide background information on the topic and include a thesis statement that outlines the main argument of the essay. The body should present evidence and support for the thesis statement, and the conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis in a new way.
Last Updated on August 31, 2023

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Types of Essay
Definition of types of essay.
An essay is a short academic composition. The word “essay” is derived from a French word “essai” or “essayer,” which mean “trail.” In composition, however, an essay is a piece of non- fiction writing that talks or discusses a specific topic. Presently, essay is part of every degree program.
Each subject has specific requirements for the essays to be written. Some subjects need longer essays, while others need shorter ones, such as a five-paragraph essay. In composition, the start is made from a five-paragraph essay. Based on the requirements, there are seventeen types of essays.
- Definition Essay As the name suggests, a definition type of essay defines different things, ideas, and perceptions.
- Narrative Essay A narrative essay is a narration like a short story . It is, however, different from a short story in that it is written in an essay format.
- Descriptive Essay A descriptive essay describes something to make readers feel, smell, see, taste, or hear what is described.
- Expository Essay An expository essay exposes things in detail to make readers understand without any complications.
- Persuasive Essay A persuasive essay is meant to convince the target audience to do something or not do something.
- Argumentative Essay An argumentative essay is meant to present arguments in the favor of something. It has an additional fourth body paragraph that is meant to present opposite arguments.
- Analytical Essay An analytical essay analyzes something, such as in literature an analytical essay analyzes a piece of literature from different angles.
- Comparison and Contrast Essay A comparison and contrast essay makes either a comparison, a contrast, or both between two different or similar things.
- Cause and Effect Essay A cause and effect essay makes readers understand the cause of things, and their effects on other things.
- Critical Essay A critical essay is written on literary pieces to evaluate them on the basis of their merits or demerits.
- Process Essay A process essay outlines a process of making or breaking or doing something that readers understand fully and are able to do it after reading it.
- Synthesis Essay A synthesis essay means to synthesize different ideas to make a judgement about their merit and demerits.
- Explicatory Essay An explicatory essay is meant to explain a piece of literature. It is often written about poems , short stories, and novels .
- Rhetorical Analysis Essay A rhetorical analysis essay evaluates a speech or a piece of rhetoric on the basis of rhetorical strategies and devices used in it.
- Review Essay A review essay discusses the merits and demerits of a book and evaluates it through a review.
- Simple Essay A simple essay is just a five-paragraph essay that is written on any topic after it is specified.
- Research Essay A research essay revolves around a research question that is meant to answer some specific question through a research of the relevant literature.
Format of an Essay
Generally, a simple a five-paragraph has five paragraphs including an introduction , three body paragraphs, and a conclusion . An argumentative essay, however, has an additional paragraph which presents counter argument or opposing arguments in the same sequence. However, at the end of this paragraph, both the arguments are weighed in the favor of stronger arguments presented earlier in three body paragraphs.
The format of an argumentative essay is given below:
Function of types of essay.
An essay is a specific discussion or debate on a topic from a specific point of view . A student discusses the topic from his own specific angle. Readers not only get a glimpse of what the other aspect of the topic is, they also come to know about the tone and voice of the student writers to decide whether he has achieved a certain level of capability in writing. In literary essays, a writer becomes discusses the influence that literary piece has upon the readers about a certain point of view. Essays are also useful in winning public approval about certain political ideas.
Related posts:
- Seven Types of Ambiguity
- 6 Types of Conflicts in Literature With Examples
- 20 Major Types of Archetypes with Examples
- Four Main Types of Sonnets with Examples
- Elements of an Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Definition Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Analytical Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Cause and Effect Essay
- Critical Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Process Essay
- Explicatory Essay
- An Essay on Man: Epistle I
- Comparison and Contrast Essay
Post navigation

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,

Social Media
Facebook twitter.

4 Major Types of Essay with Examples
Writing various sorts of essays effectively has become important to academic success. Essay writing is a regular school task, a requirement on college applications, and an element of standardized tests.
Choosing the proper sort of essay to write in response to a writing prompt is crucial to answering the question correctly on examinations. Clearly, students cannot afford to be puzzled about the many forms of essays.
It’s easy to become perplexed because there are over a dozen different varieties of essays. However, rest assured that the figure is more manageable. There are four basic categories of essays, with variations accounting for the remaining.
Argumentative and Expository Essays are concerned with delivering facts and making clear arguments, but Narrative and Descriptive Essays are concerned with expressing oneself creatively and writing in an engaging manner. Argumentative essays are the most prevalent sort of essay at the university level.
You must know how to write an essay before knowing the 4 major types of Essays.
Here are the 4 Major Types of Essays for you to Learn, Once you are Clear with the Structure of an Essay.
1. narrative essay :.
The writer of a narrative essay presents a story about a real-life experience. While it may appear that narrating a tale is simple, the narrative essay requires students to think about and write about themselves.
When writing a narrative essay, authors should make the story as vivid as possible in order to engage the reader. Because narrative essays are frequently written in the first person, the reader is more engaged.
Readers will feel as if they are a part of the tale if you use “I” statements. A well-written narrative essay will also progress toward a conclusion or a personal statement.
The Christmas Cake
“First of all, let me clarify that I have grown up to be a complete amateurish in cooking. My parents performed their jobs quite efficiently and they always baked those perfect cakes for me every Christmas. That night, it was me, the inexpert chef, who took the initiative to make a Christmas cake and surprise them.
To today’s date, I’ve only made several hamburgers on my own. Unfortunately, I had no clue about baking a cake. All I knew were the ingredients that I would use throughout the process. He dived completely in-depth into the recipe reflected on a book and started to set for the Christmas cake.
Then I cleaned the kitchen first and made a huge bowl sit in front of me to mix the essentials. I was excited and tensed at the same time, as it was something I tried for the first time…”
Guidelines for Writing a Narrative Essay :
These are the most basic guidelines for writing an excellent narrative essay:
- Use conversations in your article to make it more realistic.
- When structuring the document, keep the chronological sequence in mind.
- In the first paragraph of your essay , there must be a purpose.
- To interest your readers, use highlighted descriptions and sensory data.
- All of the characters, storylines, and the beginning, or climax, must be significant.
All of these factors work together in your article to accurately depict the entire scene in front of your readers’ eyes. So, if you want to write a good narrative essay, make sure you follow these rules to the letter.
2. Descriptive Essay:
A descriptive essay, like that of a narrative essay, uses words to create a picture. A writer could describe a person, a location, an item, or even a memorable memory. This is not, however, a descriptive essay for the sake of description. The goal of a descriptive essay is to convey a deeper meaning through description.
Through the use of vivid words and sensory details, the writer should show, not tell, in a descriptive essay. The finest descriptive essays appeal to the reader’s emotions, producing a vivid effect.
“Moving up to our north cabin and spending time there had always been something that I enjoyed and looked up to. It was a nice, beautiful, and serene place. It offered a lot in terms of peace and serenity that you will not find in cities. We used to look forward to our summer vacations.
So that we can go up north and experience things that we cannot do in the city. Even though time has changed and things are not as they used to be, the memory is still fresh. The atmosphere up north was quite different than in the city. When in the cabin, I marvel at how different the atmosphere and life here are then the cities.
Life in the city is full of noise and tension. You have to get up for work, and the noise of traffic would never let you relax and enjoy nature. Only if you are lucky to have it around. Things up north were different, you can enjoy the sunshine and greenery, and there is no hustle-bustle.
The air was fresh, healthy, and clean. The nights are quiet, and you can hear the animals coming out to hunt for food. Cities are filled with polluted air. This abundance of polluted air is mainly due to the heavy traffic and factories.
The air is thick due to smoke, smog, and other types of air contaminators that no one wants to breathe in. Getting clean air in a city is next to impossible…”
Guidelines of Writing a Descriptive Essay:
- Make a decision on a certain issue. Descriptive essays that are well-written stay focused at all times.
- Gather information.
- Make a rough sketch.
- Write the first paragraph of your essay.
- Body paragraphs should be written.
- In the final paragraph, summarize the essay .
- Look for methods to make your language more lively.
3. Argumentative Essay :
An argumentative essay is a piece of writing that offers a lengthy, evidence-based case. It necessitates a solid thesis statement—a well-defined viewpoint on your subject. Your goal is to persuade the reader of your argument by providing evidence like quotes and analysis.
Argumentative essays put your abilities to investigate and convey your own point of view on a subject to the test. At the undergraduate level, this is the most prevalent style of essay—almost every paper you write will include some form of argumentation.
Students Who Study Abroad Achieve Greater Success
“Much of our learning takes place outside the classroom. We learn how to maintain budgets, forge friendships, develop business relationships, and more. Imagine extending those skills on a global level.
We would immediately cease to believe the world only contains the people and things we can see but, rather, a wide variety of opinions, customs, beliefs, and ethics. This is why every college-level student must study abroad during their undergraduate years. They will learn more in that semester abroad than in any other academic year.
According to IES Abroad, a company that encourages students to become international leaders, students who study abroad are more likely to be accepted into the graduate degree program of their choice. In fact, 90% of students who studied abroad with IES are admitted to their first or second choice for graduate school.
Imagine walking into an interview and being able to discuss preparing the most popular dish in India or organizing the best route to take from Sydney, Australia to Perth. Not only does this strike up a memorable conversation, but it also demonstrates a student’s fierce independence and determination.
All this makes someone who has studied abroad a more desirable candidate for their dream job. As if IES Abroad’s statistic above was not astounding enough, it has been proven that 97% of students who study abroad find employment within 12 months of graduation…..”
Guidelines of Writing an Argumentative Essay:
- The thesis that is well-structured. The introduction to the argument is the first step in writing an argumentative essay.
- Body Paragraphs that support the thesis statement. The essay has three body paragraphs that support the thesis’ statements.
- Arguments in opposition.
- A conclusion that is persuasive.
- Phrases that bridge the gap.
4. Expository Essay:
An expository essay is a piece of writing that provides a balanced overview of a subject. In an expository essay, the writer uses facts, data, and examples to illustrate or clarify a topic.
Expository writing includes a variety of essay types, including comparison and contrast essays, cause and effect essays, and “how to” or process essays . Expository essays do not show emotions or write in the first person since they are based on facts rather than personal feelings.
“This morning at 9 am, a school bus collided with a car at the intersection of Jones and Heard streets. There were no injuries on the school bus, but medical personnel performed checks on each student and the driver before those students were transported to their schools.
The driver of the car sustained slight, non-life-threatening injuries. He was transported to the local hospital. The accident is still under investigation at this time.
Advances in science and technology have made the use of “green” energy possible. In places where climate conditions permit, people are able to use solar energy or wind energy for power. Solar energy is the use of sunlight for energy and power.
Humans are able to harness the energy of the sun by installing solar panels on their homes or businesses . Humans have also found ways to harness the power of the wind by using wind turbines to capture wind energy. Both of these forms of “green” energy are being used more and more.
The school science fair was a success again this year! We had 15 teams participating, and they all had amazing projects. Each team consisted of two students who designed a science experiment to test a hypothesis, created a display of their experiment and results, and presented their display to the judges.
The winners this year are Sarah Jones and Mark Gordon, who hypothesized that students get into less trouble in the classroom on days when it is sunny outside.
The judges were very impressed with their data collection methods, which included asking teachers to share information on how many students earned stars at the end of each day. They correlated this information with their own data about the weather-sunny, cloudy, or rainy…”
Guidelines for Writing an Expository Essay:
- Choose the essay structure
- Start with an outline
- Verify point of view requirements
- Focus on clarity
Now that you know how to write an essay and the different types of essays, what are you waiting for? Start writing your essay today itself. Oh, do not worry about the errors and mistakes. We always have your back for that. You can close your eyes and rely on editing and proofreading services to make your essay completely immaculate.
-Isabell S.

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Narrative Essays
Narrative: The spoken or written account of connected events; a story
Narrative Introductions
The introduction of a narrative essay sets the scene for the story that follows. Interesting introductions—for any kind of writing—engage and draw readers in because they want to know more.
Since narratives tell a story and involve events, the introduction of a narrative quite often starts in the middle of the action in order to bring the reader into the story immediately, as shown in examples 1, 3, and 5 below. Other effective introductions briefly provide background for the point of the story—often the lesson learned—as in 4 below and the first example on the reverse side.
Below are some strategies for writing effective openings. Remember your introduction should be interesting and draw your reader in. It should make your audience want to read more. If it's a person , begin with a description of the person and then say why that person mattered. If it's an event , begin with the action or begin by reflecting back on why the event mattered, then go into the narrative.
- "Potter...take off!" my coach yelled as I was cracking yet another joke during practice.
- Why do such a small percentage of high school athletes play Division One sports?
- It was a cold, rainy night, under the lights on the field. I lined up the ball on the penalty line under the wet grass. After glancing up at the tied score, I stared into the goalkeeper's eyes.
- My heart pounds in my chest. My stomach full of nervous butterflies. I hear the crowd talking and names being cheered.
- Slipping the red and white uniform over my head for the first time is a feeling I will never forget.
- "No football." Those words rang in my head for hours as I thought about what a stupid decision I had made three nights before.
- "SNAP!" I heard the startling sound of my left knee before I ever felt the pain.
- According to the NCAA, there are over 400,000 student-athletes in the United States.
Narrative Story
- Unified: Ensure all actions in your story develop a central idea or argument.
- Interesting: Draw your readers into your scene(s), making them feel as if they're experiencing them first-hand.
- Coherent: Indicate changes in time, location, and characters clearly (even if your story is not chronological).
- Climactic: Include a moment (the climax) when your ending is revealed or the importance of events is made clear.
- Remember the 5 W's : Who? What? When? Where? Why?
- Write vividly : Include significant sensory information in the scene (sight, sound, touch, smell, taste) to make readers feel they are there
- Develop " Thick Descriptions "
Clifford Geertz describes thick descriptions as accounts that include not only facts but also commentary and interpretation . The goal is to vividly describe an action or scene, often through the use of metaphors, analogies, and other forms of interpretation that can emote strong feelings and images in your readers' minds.
"The flatness of the Delta made the shack, the quarters, and the railroad tracks nearby seem like some tabletop model train set. Like many Mississippi shacks, this one looked as if no one had lived there since the birth of the blues. Four sunflowers leaned alongside a sagging porch. When the front door creaked open, cockroaches bigger than pecans scurried for cover [...] walls wept with mildew."
—from Bruce Watson's Freedom Summer
Narrative Checklist
- Does the story have a clear and unifying idea? If not, what could that idea be?
- If the story doesn't include a thesis sentence, is the unifying idea of the story clear without it?
- Is the story unified, with all the details contributing to the central idea?
- Is the story arranged chronologically? If not, is the organization of ideas and events still effective and clear?
- Do the transitions show the movement from idea to idea and scene to scene?
- Are there enough details?
- Is there dialogue at important moments?
- Is there a climax to the story—moment at which the action is resolved or a key idea is revealed?
501 E. High Street Oxford, OH 45056
- Online: Miami Online
- Main Operator 513-529-1809
- Office of Admission 513-529-2531
- Vine Hotline 513-529-6400
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/emergency
1601 University Blvd. Hamilton, OH 45011
- Online: E-Campus
- Main Operator 513-785-3000
- Office of Admission 513-785-3111
- Campus Status Line 513-785-3077
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/regionals/emergency
4200 N. University Blvd. Middletown, OH 45042
- Main Operator 513-727-3200
- Office of Admission 513-727-3216
- Campus Status 513-727-3477
7847 VOA Park Dr. (Corner of VOA Park Dr. and Cox Rd.) West Chester, OH 45069
- Main Operator 513-895-8862
- From Middletown 513-217-8862
Chateau de Differdange 1, Impasse du Chateau, L-4524 Differdange Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
- Main Operator 011-352-582222-1
- Email [email protected]
- Website https://miamioh.edu/luxembourg
217-222 MacMillan Hall 501 E. Spring St. Oxford, OH 45056, USA
- Main Operator 513-529-8600
Initiatives
- Miami THRIVE Strategic Plan
- Miami Rise Strategic Plan
- Boldly Creative
- Annual Report
- Moon Shot for Equity
- Miami and Ohio
- Majors, Minors, and Programs
- Inclusive Excellence
- Employment Opportunities
- University Safety and Security
- Parking, Directions, and Maps
- Equal Opportunity
- Consumer Information
- Land Acknowledgement
- Privacy Statement
- Title IX Statement
- Report an Accessibility Issue
- Annual Security and Fire Safety Report
- Report a Problem with this Website
- Policy Library

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

12.1: Fiction and Drama - types, terms and sample essay
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 235776
WHAT ARE THE MAIN LITERARY FORMS?
The main literary forms are Fiction, Drama & Poetry .
Although each of the three major literary genres, fiction, drama, and poetry are different, they have many elements in common. For example, in all three genres, authors make purposeful use of diction (word choice), employ imagery (significant detail) and each piece of literature has its own unique tone (emotional quality). An important element that you will find in all three genres is theme, the larger meaning(s) the reader derives from the poem, story, novel or play.
Each of the literary genres is distinguished by its form: Fiction is written in sentences and paragraphs. Poetry is written in lines and stanzas. Drama is written in dialogue.
WHY IS KNOWING THEM IMPORTANT?
As you read different forms of literature you will need to know specialized vocabulary to be able to best understand, interpret, and write about what you are reading. Also, how you approach a literary text and what you focus on will depend on its literary form. For instance, fiction and drama are typically anchored by a reader’s engagement with characters while many poems do not contain a character or tell a story. Therefore, plot is often not a factor in a poem . A poem can be an impression or reflection about a person, a place, an experience or an idea.
HOW DO I APPROACH EACH FORM?
KNOW THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF FICTION:
Short Stories are usually defined as being between 2000-6000 words long. Most short stories have at least one “rounded” (developed and complex) character and any number of “flat” (less-developed, simpler) characters. Short stories tend to focus on one major source of conflict and often take place within one basic time period.
Novellas generally run between 50-150 pages, halfway between a story and a novel.
Novels don’t have a prescribed length. Because they are a longer form of fiction, an author has more freedom to work with plot and characters, as well as develop sub-plots and move freely through time. Characters can change and develop over the course of time and the theme(s) can be broader and more intricate than in shorter forms of fiction.
KNOW THE DIFFERENT TYPES AND STRUCTURE OF DRAMA:
Drama Types
Tragedy – generally serious in tone, focusing on a protagonist who experiences an eventual downfall
Comedy – light in tone, employs humor and ends happily
Satire – exaggerated and comic in tone for the purpose of criticism or ridicule
Experimental – can be light or serious in tone. It creates its own style through experimentation with language, characters, plot, etc.
Musical – can be light or serious. The majority of the dialogue is sung rather than spoken.
Drama Structure
Plays are organized into dialogue, scenes and acts. A play can be made up one act or multiple acts. Each act is divided into scenes, in which a character, or characters, come on or off stage and speak their lines. A play can have only one character or many characters. The main character is the protagonist and a character who opposes him/her is the antagonist .
The plots of plays typically follow this pattern:
- Rising Action – complications the protagonist must face, composed of any number of conflicts and crises
- Climax – the peak of the rising action and the turning point for the protagonist
- Falling Action – the movement toward a resolution
COMMONALITIES OF FICTION AND DRAMA TERMS
Both fiction and drama are typically anchored by plot and character. They also contain literary themes as well as having other elements in common, so we will look at literary terms that can be applied to both of these literary forms.
Fiction and Drama Terms
PLOT: Plot is the unfolding of a dramatic situation; it is what happens in the narrative. Be aware that writers of fiction arrange fictional events into patterns. They select these events carefully, they establish causal relationships among events, and they enliven these events with conflict. Therefore, more accurately defined, plot is a pattern of carefully selected, casually related events that contain conflict. There are two general categories of conflict: internal conflict , takes place within the minds of the characters and external conflict , takes place between individuals or between individuals and the world external to the individuals (the forces of nature, human created objects, and environments). The forces in a conflict are usually embodied by characters, the most relevant being the protagonist , the main character, and the antagonist , the opponent of the protagonist (the antagonist is usually a person but can also be a nonhuman force or even an aspect of the protagonist—his or her tendency toward evil and self-destruction for example). QUESTIONS ABOUT PLOT: What conflicts does it dramatize?
CHARACTERS: There are two broad categories of character development: simple and complex. Simple (or “flat”) characters have only one or two personality traits and are easily recognizable as stereotypes—the shrewish wife, the lazy husband, the egomaniac, etc. Complex (or “rounded”) characters have multiple personality traits and therefore resemble real people. They are much harder to understand and describe than simple characters. No single description or interpretation can fully contain them. For the characters in modern fiction, the hero has often been replaced by the antihero , an ordinary, unglamorous person often confused, frustrated and at odds with modern life. QUESTIONS ABOUT CHARACTERS: What is revealed by the characters and how they are portrayed?
THEME: The theme is an idea or point that is central to a story, which can often be summed up in a word or a few words (e.g. loneliness, fate, oppression, rebirth, coming of age; humans in conflict with technology; nostalgia; the dangers of unchecked power). A story may have several themes. Themes often explore historically common or cross-culturally recognizable ideas, such as ethical questions and commentary on the human condition, and are usually implied rather than stated explicitly.
QUESTIONS ABOUT THEME: To help identify themes ask yourself questions such as these:
SYMBOLISM: In the broadest sense, a symbol is something that represents something else. Words, for example, are symbols. But in literature, a symbol is an object that has meaning beyond itself. The object is concrete and the meanings are abstract. QUESTIONS ABOUT SYMBOLS: Not every work uses symbols, and not every character, incident, or object in a work has symbolic value. You should ask fundamental questions in locating and interpreting symbols:
SETTING: The social mores, values, and customs of the world in which the characters live; the physical world; and the time of the action, including historical circumstances.
TONE: The narrator’s predominant attitude toward the subject, whether that subject is a particular setting, an event, a character, or an idea.
POINT OF VIEW: The author’s relationship to his or her fictional world, especially to the minds of the characters. Put another way, point of view is the position from which the story is told. There are four common points of view:
- Omniscient point of view —the author tells the story and assumes complete knowledge of the characters’ actions and thoughts.
- Limited omniscient point of view —the author still narrates the story but restricts his or her revelation—and therefore our knowledge—to the thoughts of just one character.
- First person point of view —one of the characters tells the story, eliminating the author as narrator. The narration is restricted to what one character says he or she observes.
- Objective point of view —the author is the narrator but does not enter the minds of any of the characters. The writer sees them (and lets us see them) as we would in real life.
FORESHADOWING: The anticipation of something, which will happen later. It is often done subtlety with symbols or other indirect devices. We have to use inferential thinking to identify foreshadowing in some stories, and often it occurs on an almost emotional level as we're reading, leading us further into the heart of the story.
EXPOSITION : The opening portion of a story that sets the scene, introduces characters and gives background information we may need to understand the story.
INTERIOR MONOLOGUE : An extended exploration of one character's thoughts told from the inside but as if spoken out loud for the reader to overhear.
STREAM OF CONSCIOUSNESS: A style of presenting thoughts and sense impressions in a lifelike fashion, the way thoughts move freely through the mind, often chaotic or dreamlike.
IRONY: Generally irony makes visible a contrast between appearance and reality. More fully and specifically, it exposes and underscores a contrast between (1) what is and what seems to be, (2) between what is and what ought to be, (3) between what is and what one wishes to be, (4) and between what is and what one expects to be. Incongruity is the method of irony; opposites come suddenly together so that the disparity is obvious.
CLIMAX: The moment of greatest tension when a problem or complication may be resolved or, at least, confronted.
RESolution, CONCLUSION or DENOUEMENT ("untying of the knot"): Brings the problem to some sort of finality, not necessarily a happy ending, but a resolution.
Using the literary vocabulary and questions, let’s analyze a literary text.
Read the memoir, “Learning to Read,” by Jessica Powers which can be located in Chapter 1: Critical Reading in the “Faculty-Written Texts” section. Powers employs many of the elements of fiction in this autobiographical piece. When you have finished reading, answer the questions below.
Questions about plot :
- What is the main conflict in the story?
- What causes the conflict?
- Is the conflict external or internal?
- What is the turning point in the story?
- How is the main conflict resolved?
Questions about character:
- Is the main character simple or complex? Explain.
- What are the traits of the main character? Make a list.
- Does the main character change? Describe.
- What steps does she go through to change? Make a list.
- What does she learn? Describe.
- Does the main character experience an epiphany? Describe.
Questions about theme:
- What does the story show us about human behavior?
- Are there moral issues raised by the story? Describe.
- What does the story tell us about why people change?
Most Popular
How to write a position paper, how to write a hypothesis, how to write an informative essay.
3 hours ago
How To Do Footnotes
52 mins ago
How to Write a Hook

When writing a good essay, you want to capture the reader’s attention from the very first sentence to keep them focused throughout the following text. The ‘hook’ of an essay is that opening sentence – the first impression that sets the tone for the rest of your writing. It’s the bait you use to catch your readers, urging them to continue going deeper into the text. And since it is kind of an art form, you need a certain knowledge to craft perfect hooks. In the guide below we will give all the necessary details on how to make a good hook, so you better don’t skip on reading this article the whole way through.
Hooks for Essays: What Are Those?
An essay hook is essentially the first one or two sentences of your essay. Sometimes though (if it is relevant to your writing) it can even take the space of the whole first paragraph. Its main purpose is to intrigue your audience and pique their interest, compelling them to continue reading. If you are wondering why you need a well-crafted hook here are just a few reasons off the top of our heads:
- To draw in the readers
- To seamlessly connect to the broader theme or argument of your essay. Depending on the type of essay you are writing, your hook can be in the form of a question, a surprising statistic or fact, an anecdote, a quote, or even a vivid description.
- To set the tone for the rest of your writing
See, you don’t write your text just for yourself – you are doing it for your audience, whoever that might be. That’s why you need to make your reader want to stick out till the end of the text, and do that from the very beginning.
Top Hook Sentence Starters: Types and Examples
If you ask different writers, some of them might say that a rhetorical question makes a good hook, or that adding a quote is a much better way to start your writing. The thing is, all of these statements are true. There are several ways to create good hooks for argumentative essays. Choosing the one for you will depend on the audience, your writing style, and the topic of your text.
You may have seen that a lot of texts (not just essays, for that matter) start with some kind of quote, either from a book, article, a famous person, or even the writer’s relative or friend. The reason behind this is that it is rather a simple way to intrigue the reader from the very beginning.
Quotes are compact and mostly widely recognizable, and they present the main idea of your text right away. To find a fitting quote, you can explore classic literature, speeches by influential figures, research articles, or even poetry. The key is to select a quote that aligns with the essay’s subject and contributes meaningfully to the argument or narrative being constructed.

❓Rhetorical Question
A rhetorical question is a query that’s posed for its persuasive effect rather than a direct answer. By asking a question, you directly engage the reader, prompting them to consider their own stance or feelings regarding the topic at hand, thus creating a deeper personal connection between them and the text they read.
Essays that stand to benefit most from a rhetorical question as a hook are those that aim to explore moral dilemmas, provoke critical thinking, or challenge conventional beliefs. This type of hook is ideally suited for audiences who enjoy intellectual engagement and are prepared to contemplate complex issues. A well-built rhetorical question should be open-ended, avoiding simple yes or no answers, and should ideally lead seamlessly into the argument or thesis of your essay.

📊Statistic/Fact
Integrating a fact or statistic into your essay’s opening can instantly ground your reader in the reality of your topic. It offers them a tangible piece of evidence that vividly shows the importance of the issue you present. This type of hook is particularly effective in persuasive or argumentative essays where empirical evidence can support your stance right away. A compelling fact or statistic surprises (or shocks) the reader as well as provides a solid foundation for the arguments that follow. This makes it easier for your audience to appreciate the significance of your essay.

Anecdotes are brief, engaging stories showcasing a slice of life. This can help reveal the essay’s theme, making the topic relatable and memorable to the audience. An anecdote hook works exceptionally well in narrative and college application essays, or pieces designed to evoke an emotional response or deeper understanding of a universal human experience.
To make your anecdote work as a hook, you can use the STAR (Situation, Task, Action, Result) method. Using this approach, you structure your story by first setting the scene (Situation), then describing the purpose (Task), detailing what was done (Action), and, finally, revealing the outcome (Result).

🧐Common misconception
Starting with a common misconception is a dynamic way of engaging with the audience. With such a hook you can challenge their beliefs and assumptions. Using a widely held but incorrect belief, you immediately create a narrative tension that compels the reader to continue, eager to uncover the truth. This method is particularly effective in essays that aim to debunk myths, promote critical thinking, or introduce lesser-known facts about popular topics.

✍️Description
Descriptions are mostly used to transport the audience into the discussed scene or subject matter This technique involves painting a detailed picture with words and using sensory descriptions to evoke the sights, sounds, smells, tastes, and textures relevant to your essay’s topic. Description hooks are particularly effective in narrative essays, descriptive pieces, travel writing, and essays aiming to evoke a strong sense of place or atmosphere.

Jokes tend to lighten the mood especially if the topic lends itself to a humorous approach. Therefore, using it as your opening statement can spark joy or amusement in your readers, making them want to stay for a heartwarming story. This type of hook is mostly used to set a friendly and approachable tone for the piece. Note though, that your joke needs to balance humor with the serious intentions of the essay, providing an inviting entry point without undermining the piece’s overall message or purpose.

Key Steps & Tips on How to Write a Hook
Now, you know what a hook is and what types of opening sentences there can be. Overall, this knowledge is enough for you to understand how to start your essay in an attention-grabbing manner. However, we have a few notes on how you can build your writing process specifically to create a compelling hook:
- Understand Your Audience : Tailor your hook to the interests and expectations of your readers. Consider the style and level of formality that will work for your audience.
- Define the Tone of Your Essay : The overall tone of your essay is important, and the first sentence or two should also be written in the same style. Whether it’s serious, humorous, or somewhere in between, stick to the initial way of writing.
- Make it Relevant : Your first sentence needs to be relevant to your essay’s main theme or argument. After all, you don’t want to confuse your reader.
- Keep it Concise : As a hook is just an opening statement, it should be brief and impactful, setting the stage without overwhelming the audience.
- Experiment : Don’t be afraid to try different types of hooks to see what works best for your essay. After all, all texts are different.
We have also a few extra tips on how to make your first couple of sentences more authentic and gripping. For example, you can use sensory details to add depth and imagery to your words. It especially works for description hooks. Be careful with cliches and popular phrases though. Besides, don’t give away too much information in your hook – leave your readers wanting more. Have fun with it, play around with words, and maybe add puns. Writing a hook can be a creative and exciting process, so embrace it.
What Makes The Good Hooks for Essays
What fundamentally distinguishes a compelling hook from a bland one is its ability to instantly grasp the reader’s attention and seamlessly connect them to the core theme of the writing. In essence, a good hook is the one that is a) relevant and b) intriguing. And what should influence your choice of the right hook is the initial intent of the writing. Understand the purpose behind your work— to inform, persuade, entertain, or provoke thought— and you will certainly make the right choice for your first few sentences.
Sometimes though, even the most creative of writers can’t come up with a great starter on the spot. If this is your case, don’t fixate on the situation. Continue writing your essay and after it’s done come back to the introduction. This way you will already have an idea of how your essay looks like and the key points it discusses, so it will be much easier for you to pick an opening line for your writing.
It is also a good idea to reflect on the emotions or reactions you want to evoke in your readers. This will help you choose a quote or an anecdote that will adequately convey those exact feelings. And don’t tie yourself to the conventional ways of building hooks. You can always try and come up with something unique, that will fit best for your essay specifically. Experimentation, paired with a deep understanding of your intended audience and the core message of your piece, often leads to discovering that perfect starting point for your writing.
Creating a perfect hook is all about building an immediate, meaningful connection with your audience. The key lies in understanding who your readers are and what resonates with them, then carefully selecting and writing down an opening that aligns with the overall tone and theme of your essay. It doesn’t really matter whether you use a poignant quote, a compelling question, or an intriguing statistic. The right hook can transform the ordinary into the extraordinary, turning passive readers into active participants in the narrative you’re building.
What is a good hook sentence?
A good hook sentence grabs the reader’s attention, making them eager to continue reading. It can be a question, a quote, a startling fact, or any statement that provokes curiosity or emotion.
How do you write an effective hook?
To be able to write an effective hook, you need to know your audience, choose a hook that matches the tone of your essay, make it relevant to your topic, and make it concise and impactful. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different types of essay starters until you find the one that works best for your text.
What is a catchy hook for an essay?
A catchy hook is one that is memorable and engaging, often through humor, a shocking fact, or a thought-provoking question. So, be creative and think outside the box when crafting the first sentences of your essay. They will set the tone for your further writing.
How do you grab readers attention in an introduction?
The main trick to grabbing readers’ attention in an introduction is using a relevant hook sentence, that will be intriguing, and tailored to the audience’s interests or emotions. It should also connect to the main theme or argument of your essay. So, make sure you put effort into building a strong and effective starter for your essay. Because those first few sentences will determine whether your writing will be set out for success or not.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More from How to Write an Academic Assignment

12 min read

Remember Me
Is English your native language ? Yes No
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
- Essay Editor
Types of Acoustical Materials
1. introduction.
The field of acoustics is a branch of physics, concerned with the production, transmission and effects of sound. A room has been acoustically designed if it provides the necessary sound effects, as planned. What is considered a necessary sound effect varies with the particular room and its intended use. A classroom must allow good speech communication between teacher and students and between students; a concert hall may require good music and speech communication; a small office for two persons may require isolation from speech in neighboring offices. These requirements for speech and music have been discussed and formulated in various ways. For example, one requirement for a lecture hall is that a person with average voice level can be heard and understood by a listener with average hearing ability seated in any part of the room. Despite the variations in sound requirements, they can all be related to the speech and music themselves. This can be done by applying the information theory formulated by Shannon and Weaver in 1949, or using definitions by W.S. C. Williams. The information theory considers speech and music as transmissions of information and equates intelligibility with the reception of the intended message. The definitions made by Williams differentiate between speech and music and relate several attributes to them. Electroac
1.1. Purpose of the Report
These pages have been compiled with the assistance and cooperation of various manufacturers of acoustical materials with the objective of familiarizing architects, acoustical engineers, noise control engineers, and particularly interior designers with specific acoustical materials and their properties which affect their use in interior design. It is not the intent of these pages to review materials which are too numerous, too variable, or too specialized to warrant inclusion. Such materials as resilient underlay and carpet underlay are commonly used acoustical materials; however, the discussion herein of resilient materials and carpets can amply serve the same purpose and leave the detailed discussion to product descriptions. While the primary objective of these pages is to provide information on materials and their properties, it may be useful to include some rudimentary advice on the acoustical treatment of various spaces with specific guidance on recommended materials. Consequently, a section on applying these materials will be included, but it is to be clearly understood that the advice in this section is a guide only. There are very wide variables from one site to another, and the specific recommendations on materials could often be substituted by similar recommendations from the materials in these pages.
1.2. Scope of the Report
The scope of this report is to discuss the types of acoustical materials used in construction and the builders' opinions toward these products. For the purposes of this report, acoustical materials are defined as materials used in the construction or finishing of buildings to absorb or block sound. This definition encompasses a wide range of products including materials to be applied to walls or ceilings and materials used in constructing partition walls or laying a floor. The terms "absorb or block sound" are used to include changing the quality of sound by attenuating reverberation or changing the sound transmission class of a wall or floor. This definition provides the basis for determining whether a particular product can be classified as an acoustical material. Acoustical materials have had extensive use in the design and construction of buildings where acoustics is a key factor such as concert halls, theaters, and music studios. Lately, the importance of acoustics has been recognized as an integral part of the comfort and utility of a space and research has shown the significance of acoustics to human health and performance. This conclusion suggests that acoustical materials can play a role in improving the acoustic environment in existing buildings as well as in new construction. The increased application of acoustical materials is the reason for focusing on this topic today. With the wide array of products to choose from, definitive information for selecting the right product for a given application is valuable to the consumer. The development of industry standards and testing procedures for acoustical materials has produced information that can be helpful in product selection. This report seeks to compile and discuss available information to provide a general understanding of types of acoustical materials and guidance for product selection. Through a survey of Bay Area builders we encountered, an interest in builder opinion and insight into how acoustical materials are applied in the field. This will be another focus of the report in assessing the effectiveness and feasibility of various products.
2. Section 1: Absorptive Materials
Fiberglass is the most common material that is used in building absorption materials. Rigid fiberglass is made from spun glass fibers and is available in 2′ x 4′ or 4′ x 8′ rigid panels. The panels come in different thicknesses depending on the desired amount of absorption. Fiberglass panels are often used behind fabric in wall panels as a bass trap. They can also be used in a wood frame to make bass traps. Fiberglass panels are relatively inexpensive and provide a good amount of absorption across a broad range. They are lightweight so they are easy to mount to walls or ceilings. They are fragile to work with until installed and should be covered in fabric, perforated vinyl or equivalent if touched, to prevent irritation and damage to the skin. Loose fill insulation should not be used to build wall panels, it is less effective at low frequencies and poses a potential health hazard. Loose fill insulation is a totally different product and is safe for home use, just do not try to use it as wall treatment. Fiberglass should be covered by a facing material, the air gaps between the fibers are what actually resonates and provides absorption. Acoustic foam is a lightweight material that is available in several sheet sizes and thicknesses. It can be purchased with or without a paper backing. Acoustic foam is most commonly seen and used in rooms with lower SPL requirements such as home studios and vocal booths, where higher frequency absorption is needed. Although it is low in cost and can be very colorful and appealing, it typically provides less absorption than high density fiberglass or mineral wool for the same total area of coverage. Lower quality foams tend to crumble and turn to dust over time, they may also react chemically with various substances. Be sure to check the flammability rating before considering the use of foam in commercial building or public venues. High density flame rated polyurethane or melamine foam panels are available for use in industrial applications where foam is desired.
2.1. Point 1: Fiberglass Panels
The most common of all acoustical materials is the basic and versatile 1" thick or 2" thick fiberglass panel. These panels are made to absorb unwanted sound with various degrees of success. Fiberglass panels are available in a wide range of sizes and shapes. The edges are resin hardened and the most common cause of these panels is to be hung like a picture frame with a hook on the wall. The vast array of fiberglass panels makes it nearly impossible to predict their effect on a room's acoustics. Usually thicker panels are more effective on lower frequencies. Fiberglass panels are safe, light, and fairly easy to install. They can be covered with acoustical fabric or painted with latex paint to match the room's decor. Fiberglass panels are a great solution for DIY projects on a budget. This is definitely a material I would recommend for any home, garage, or project studio. The vast array of fiberglass panels makes it nearly impossible to predict their effect on a room's acoustics. Usually thicker panels are more effective on lower frequencies. Fiberglass panels are safe, light, and fairly easy to install. They can be covered with acoustical fabric or painted with latex paint to match the room's decor. Fiberglass panels are a great solution for DIY projects on a budget. This is definitely a material I would recommend for any home, garage, or project studio.
2.2. Point 2: Acoustic Foam
Absorptive materials are designed to absorb sound as it strikes the surface, as opposed to reflecting it, the overwhelming result of hard, flat building materials including drywall, concrete, and wood. When applied directly to a wall, most soft, porous acoustical materials have little effect on sound absorption below 500 Hz. However, "trapping" a layer of air behind the absorptive surface will increase low-frequency absorption. This air gap between absorptive insulation and a reflective wall is an adaptation of Helmholtz Resonators principles known as a diaphragmatic absorber, a highly effective means to absorb low frequency sound. Given time, fiberglass will conform and sag under its own weight, decreasing its low frequency absorption coefficient and rendering it less effective at absorbing low-frequency sound. This can be circumvented by selecting a thicker panel or building a frame to support the fiberglass insulation. Glass fiber absorbers can be used to successfully absorb mid and high frequency sound in the air of a room or in specific on-wall or in-wall locations using absorber panels. A common on-wall placement would be to hang 1 or more sound absorber blankets, which are functionally similar to absorber panels, and may be used in conjunction with fiberglass absorber panels. Fiberglass, if properly mounted and supported in a thicker panel or rigid material, is an effective and relatively inexpensive means to absorb sound across the frequency spectrum in rooms of any size. Acoustic foam is a synthetic material and is the most common type of absorptive material. It is lightweight and available in several different colors, patterns, shapes, and facings, and is used as an acoustical treatment or construction material with the primary objective of absorbing a broad range of sound frequencies. Photo of Auralex 2" wedge style studio foam. Studio foam is a specific type of acoustic foam marketed towards music and voice recording studio application. Most acoustic foam is of open celled polyurethane construction and offers flexibility in both application and effect. Acoustic foam is packaged in rigid panels or can be fashioned into a number of available products including ceiling tiles, wall panels, baffles, acoustical insulation, and bass traps. Foam thickness of approximately 1-4" is effective for the absorption of mid to high frequency sound. Low frequency absorption can be increased by using thicker foam and/or a foam/air space/reflective surface sandwich built into a foam panel. High frequency absorption occurs by sound wave molecular friction at the cell and wall surfaces. Absorption coefficient averages between .50 and .70 across the 125 Hz to 4000 Hz range depending on foam type and thickness. Open celled foam is pliable and functions as a diaphragmatic absorber with air movement at the rear of the panel. Although less effective at absorbing low frequency sound than the aforementioned fiberglass, foam is a flexible and low-cost material suitable for all-purpose absorption in moderate or small-sized rooms and is often applicable in mobile audio applications or control rooms.
2.3. Point 3: Perforated Wood Panels
When most people think of wood panelling, they think of a poor reflective acoustical surface. However, perforated wood panels with absorptive backings are one of the most cost-effective ways to improve room acoustics. The material provides a great acoustical surface and is often very attractive and therefore a relatively simple sell to a client. The market leader in wood acoustical panelling is probably Paxton, who make a wide range of panel types. This descriptive paper will focus on wooden perforated panels in general, as the author has little experience with the vast range of Paxton products. The panels consist of two layers: the face layer, which is a wood veneer or melamine impregnated surface, and the back layer, which is a porous open-graded fiberglass composite. These layers are bound together with glue using a two-step manufacturing process. They are pressed and then cut to size. The panels are generally quite heavy; the standard panel size is 2440x1200mm and a 16mm thick panel will weigh about 25kg.
3. Section 2: Reflective Materials
Glass wool insulation is made in a similar way, but the fibers are collected from the glass blowing process and formed into a roll blanket like a loo roll. Glass wool insulation is air and vapor permeable because its fibers are not bonded together. This allows sound to pass through it and reflect off the wall behind, creating a reflective sound. Glass wool is an excellent absorber of airborne sound and can reduce the transfer of sound from one room to another. Glass wool also has excellent thermal properties, helping to keep your room cool in summer and warm in winter. This also helps to reduce condensation on uninsulated metal roof and wall sheets, which can drip onto your stored goods. The reduced condensation will also contribute to the reduction of noise. Metal roof insulation using glass wool is normally installed as under purlin insulation on industrial buildings with metal roofs. Metal panels can be used as a reflective material for environmental noise barriers. Noise barriers are an effective solution for reflective and airborne noise. Reflective noise is reduced by placing the barrier between the source of the sound and the receiver. The denser the barrier and the more mass it has, the more airborne sound it will block. Barriers should have good sound absorption properties to reduce the level of reflected sound and also have an effective transmission loss quality in reducing airborne sound. A barrier made of metal panels or a combination of metal panels and glass wool insulation has a good transmission loss quality and is an effective absorber of environmental noise. This is ideal for reducing noise and sound transfer between different facilities in close proximity. The absorptive and reflective properties can be controlled by choosing the right barrier design for its intended purpose.
3.1. Point 1: Glass Wool Insulation
Glass wool insulation is widely used for its fire-resistant properties and incredible insulation from hot and cold temperatures. However, due to the insulation being very itchy and linked to health problems, other options are recommended to achieve an acoustical objective. Glass wool is a lump of intertwined and flexible glass fibers, which cause it to be packed tightly in blankets and other insulating products. On an acoustical level, glass fiber is very effective at reducing airborne sound, especially at higher frequencies. This is not particularly useful for music as there is a loss of energy in the insulation, and fiber absorbers are much more effective for high-frequency absorption. Glass fiber has poor absorbing properties and is only effective at low frequencies below 500Hz, where bass energy is not critical to the clarity of sound. High-frequency sound simply passes straight through the insulation and little is absorbed or reflected. Glass wool insulation is a practical option where fire resistance and temperature insulation are required, and some minor sound absorption is a bonus. However, it is not recommended for solely acoustical objectives, and there are better options available for both costs and effectiveness.
3.2. Point 2: Metal Panels
Metal panels are used in various practical and acoustical applications, such as ceiling tiles, cladding, and infill panels for raised access floors. They come in different forms and systems, some of which are designed for acoustical purposes. This report will discuss the acoustical benefits and issues related to metal panels in a broad sense. It will not delve into specific details about raised access floors or proprietary systems. Metal panels generally do not provide significant acoustical benefits in terms of sound transmission or absorption. To reduce sound transmission through a ceiling, a barrier is often placed between the sound source and the receiver. This is typically achieved by using fibrous insulation on top of the panels. While this does not greatly affect the panels themselves, the absorption provided by the ceiling helps reduce sound transmission. Glass wool insulation has been previously mentioned as a suitable option for this purpose. The performance of the panel in this scenario is evaluated based on its weight-bearing capacity. Metal panels usually have low absorption properties, resulting in a highly reflective surface. This goes against the goal of achieving good room acoustics. However, there are situations, such as service or plant rooms, where sound absorption and quality are not a concern, and a highly reflective surface is desired. In such cases, perforated metal panels can be used in combination with fibrous insulation to achieve sound absorption, with the porous absorber backed by a reflective surface. Panels that are powder coated or painted will have absorption characteristics similar to the coating, as long as they are not too thick. There are instances where metal panels need to be complemented with acoustical treatment on the reverse side, such as fire escape landings or exterior walkways. In these situations, external absorbers can be exposed to the environment, while the metal panels serve as weatherproofing elements.
4. Conclusion
If careful thought is given to frequency, amplitude, and phase material selection, a well-designed acoustical environment is possible. Our experience has shown that careful attention to material properties and placement is crucial. Careful material selection and placement will enhance user satisfaction through economical solutions. Economic solutions, however, should never sacrifice meaningful enhancement in the acoustically correct environment. Dosage recommendation is limited by the fact that the correct mix of materials depends on the specific problem and the existing environment. This simply means that correct material choice in an unsatisfactory acoustical environment can enhance user satisfaction without causing complete renovation. Repeat the patient until symptoms clear is often the approach taken toward material addition. Material addition should be done in small steps with evaluation of each room change. Stepwise changes will prove that small material changes can cause large perceived differences in the environment. In all, thoughtfully designed material selection and addition will greatly improve the relevance of user satisfaction in an acoustical environment with minimal cost.
Related articles
The children's hospital of philadelphia - 551 words.
1. Introduction The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) is a premier provider of expert pediatric healthcare services. Founded in 1855 as the nation's first pediatric hospital, CHOP provides pediatric care of the highest quality to children of every ethnic, cultural, and economic background. It is recognized both nationally and internationally for its commitment to providing comprehensive and caring services to children and their families. The entrepreneurial spirit of its founders and t ...
Practical Usages of Scientific Notation Coursework
1. Introduction Scientific notation is a way of expressing numbers that are too large or small. In this notation, arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) are simplified. This practical application can be used in our daily life. However, a lot of students have difficulties in learning scientific notation. The reason can be the teaching methods of teachers. We recommend three different teaching methods. The first is that teachers can use dynamic objects to attr ...
Ecological Consciousness, Justice and Science Essay
1. Introduction A vital scientific concept that challenges the familiar treat of environmental studies as a scientific regularity is the "ecological footprint". This is an economic term rooted in an ecological concept. It investigates the manner of human center and empire in an effort to investigate a scale measure of sustainable sociopolitical manner. The ecological consciousness is a promise for the action of education and the scientists, as well as for all social institutions that want to co ...
Tomato Plants Growing - 1536 Words | Report Example
1. Introduction Growing tomatoes is often the impetus for starting a vegetable garden, and every tomato lover dreams of growing the ultimate tomato. Choosing the best variety of tomato to grow in your climate is the first step. Another, and just as important, step is understanding the needs of the tomato plant. Here are some basic rules to grow tomatoes with healthy and productive tomato plants. How do they look? The leaves are beginning to get droopy, flowers and tomato plants are falling off ...
Qualitative and Quantitative Research in Medicine Education
1. Introduction Research is an attempt to answer questions using information. Educational research aims to systematize, transform, and develop teaching, learning, and assessment practices. It provides evidence of how educational processes occur, leads to best practices in teaching, helps to develop curricula that meet students' needs and goals effectively and efficiently, and guides other teachers' professional development. Conducting research requires competence developed through study, critic ...
Iron: Properties, Occurrence, and Uses Research Paper
1. Introduction Like iron, nickel, and cobalt are metals. They are good conductors of heat and electricity and are malleable - they can be bent and formed into different shapes easily. In addition, these elements are magnetic. Moreover, in contrast to plastics, glass, paper, and wood, iron and steel do not present any risk of fire. For these reasons, all the sorts of machinery which have changed our world over the last two centuries are made of steel - and its use is still increasing. Iron is a ...
Essay on Animals and Their Habitat
1. Introduction Abiotic components include physical conditions and the chemical nature of the surroundings of the living organisms. This factor has a major influence on the distribution of the organisms and their life activities. The important physical and chemical factors of the environment are light, heat, humidity, precipitation, atmospheric pressure, soil, water, and substances dissolved in it. The physical and chemical features of the environment are together called environmental factors. ...
Mountains Characteristics Essay (Movie Review)
1. Introduction Mountains can be of various shapes and sizes. They do not grow; they are created due to constructional or volcanic activities. It is cool and fresh at the top of the mountain, as there are many trees. They reflect the sun's rays and absorb the heat, making it always cool and fresh. We can enjoy seeing the sunrise and sunset through the mountains. The whole earth is full of beautiful things: the coast, plains, rivers, trees, flowers, and many animals that inspire us. Mountains ar ...
Financial Instruments: The Main Types Term Paper
Introduction.
Generally, in active financial markets business organizations depend on financial instruments (FI) such as bonds, and equities to help them reduce potential risks they might encounter during their operations. For instance, issues such as increasing interest rates and changes in commodity prices are more likely to affect enterprises thus they rely on the various forms of securities to reduce the impacts. Apart from the aspect of reducing potential business hazards, the FIs are useful in enabling business owners to generate the required capital. In most cases, companies trade shares to raise additional funds for their operations. The approach allows investors to own a portion of the respective business organization. Therefore, the concept of FI is an essential facet of the money market hence it is necessary to have proper knowledge about it to ensure effective financial reporting by enterprises.
The Concept of FI
The term FI refers to a form of assets that can be traded in the money market. In financial institutions, FI provides an effective and efficient flow of funds from different investors across the world. In other words, FI can be defined as either a virtual or real document that represents a legal arrangement involving any form of monetary value between two or more parties (Stolowy & Ding, 2017). In general, FI is a contract for a monetary value that can be created, modified, purchased, or even settled. In terms of the agreement, FI requires a contractual obligation between the people or institutions involved in the transactions of FI. In other words, FI encompasses a two-way commitment whereby each party must comply with the agreed conditions. For instance, assuming a company is supposed to obtain cash from investors, it will be required to provide shares for the respective financier while the individual is obligated to issue the arranged funds.
Types and Categories of FI
The FI are grouped into two broad types namely; derivative instruments, cash instruments, and foreign exchange instruments as shown in figure 1 below. Each of the categories functions differently making them unique from one another. Furthermore, the FI is categorized into two main asset classes which are debt-based FI and equity-based FI (Kańduła & Przybylska, 2021). The mentioned sets make the FI have wide functions that enable business organizations and potential investors to achieve their objectives in the money market.
Cash Instruments
Cash instruments are types of FI whose values are impacted directly by the prevailing condition of the general market. This type of FI further known as cash equivalents is categorized into additional two groups. The classes include securities and loans, and deposits which investors and business organizations can choose from depending on their needs in the financial market (Parameswaran, 2022). Generally, securities are FI that has monetary value and are mostly traded in the stock exchange market (SEM). There are a number of marketable securities that investors and business organizations can opt to purchase or buy in the money market. They include bonds, stocks, preferred shares, and debentures. When the given securities are purchased, they represent a significant portion of the publicly-traded enterprise in the SEM. In addition, the other category of cash instruments that are loans and deposits represent assets having monetary value. The cash equivalents require parties involved to have a well-formulated contractual agreement to which the participants must adhere to.
Derivate Instruments
Derivative instruments are FI that derive their values or performance from the underlying asset. Some of the underlying assets that can determine the values of derivatives include commodities such as oil, gold, and cotton. Other assets are stocks, interest rates, currencies, bonds, and market indices (Parameswaran, 2022). The mentioned items have the potential of influencing the creation of different financial derivatives in the market. Derivative instruments are classified into five main categories namely; options, future, interest rate swaps, and forwards. In most cases, the derivatives mentioned above are used for the precautionary purpose to enable business organizations and investors to manage possible risks and further facilitate the aspect of speculation in the market (Kang, 2019). Generally, the given types of derivatives fall into two broad classes known as option and lock.
A future is a contract between two parties that is buyer and seller for the purchase of an asset at a pre-determined exchange rate in the future. In most cases, the derivate is used by traders to enable them to hedge possible risks that are likely to occur. Furthermore, a future contract allows investors to speculate the forthcoming price of the underlying asset (Dungore et al., 2022). Based on the agreement, both participants are obligated to accomplish the commitment to sell or buy the given commodity.
Based on the concept of derivative instruments, an option is a FI whereby two parties agree on a given contract to undertake a transaction of an asset at an already determined price before the future date. In other words, the FI permits the owner of the asset to sell or buy the underlying asset at the specified exercise price. In this type of derivative, the buyer is limited from engaging in the buy or sell agreement. The different options include selling a call option, selling a put option, and buying a call or a put option. Generally, options are used by investors to speculate the probable prices of the underlying asset.
Swaps are types of FI mostly used by business organizations to facilitate the altercation of one cash flow with another. The agreement is made between two parties to involve in the swapping of the interest rates (Dungore et al., 2022). For instance, an investor may opt to use an interest rate swap to switch from a fixed to a variable interest rate. The FI is essential to business organizations because it allows companies to effectively revise the conditions of the debts in order to benefit the expected or even current situations of the market.
Forward contracts are FI involving an agreement between two parties to undertake the exchange of the given asset at a specified price during the end of the arrangement. In most cases, the forwards are traded over the counter (OTC) (Dungore et al., 2022). In the process of the transaction, both the buyer and seller may agree to customize the size, terms, and even procedures of settlements once the contract has been created. Its OTC feature makes the forward derivate bear a significant counterparty risk that has the potential of affecting any of the involved participants. For example, one of the participants may fail to adhere to the obligation stated in the contract. In such a situation, the affected party will be forced to take the risks.
Foreign Exchange Instruments
Generally, foreign exchange instruments are usually derivatives. These are FI that are fully represented in the foreign markets. The FI is mainly the spot markets, swaps, option, future, and forward markets. This type of FI is designed to facilitate the management of financial risks that involves foreign exchange. The aspect makes the FI an essential tool that business organizations can use to reduce the hazards they are likely to encounter following the fluctuations in currencies in the money market.
The Asset Classes of FI
Apart from the various types of FI discussed above, FI can be further classified on the basis of assets. The two main categories are debt-based FI and equity-based FI. Each of the groups presents business organizations with essential opportunities for instance; the former presents business organizations with the ability to increase their capital base for smooth operations (Kańduła & Przybylska, 2021). They include mortgages, credit cards, debentures, bonds, and lines of credit. In most cases, the mentioned FI is short-term and last for about 12 months. On the other hand, long-term debt-based FI usually takes more than a year and they are mainly cash equivalents and exotic derivatives. The latter provides investors with the capacity of legal ownership of the company offering securities in the market. In this group, the FI includes preferred stock, common stock, transferrable subscription rights, and convertible debentures. Even though both classes enable corporations to raise the necessary capital, equity-based FI provides funds for the firms over a long period of time than debt-based FI.
Importance of the FI Concept
The concept is useful, especially to investors and business organizations which operate in the money market. The topic equips individuals with adequate knowledge about the various types of FI thus making it easier to choose the best option when engaging in any contractual obligation. With such understanding, a person may opt to advice companies concerning the nature of FI to enable them to gain effectively from their usage.
Furthermore, the topic increases the individual’s perspective of FI and how business organizations through the use of various types of FI can limit or avoid the potential risks in the market. The FI concept further makes it easier to speculate the future changes in market prices which is important for making an effective and informed decision for the business. Having a proper understanding of the FI idea, it will be easier to conduct a thorough research about the performance of securities in the financial industry.
In addition, the FI concept is essential in enabling accountants to classify various forms of derivatives and cash equivalents in financial statements. When the entries are made accordingly, it allows investors to have a clear picture of the respective organization based on its financial performance in relation to both equity and debt (Havemann et al., 2020). Furthermore, the FI idea allows investors to hedge their assets effectively hence they face limited financial risks.
Furthermore, the concept of FI is important because it gives people an opportunity to understand different ways of generating capital for business operations. Since there are various options in the market, with efficient knowledge it becomes easier to choose the best alternative to raise the necessary funds.
The concept of FI enables people to understand the importance of transferring risks to the other party. For instance, an investor may opt to buy instruments such as interest-rate swaps to give them the ability to protect their businesses against losses. Based on the FI idea, it becomes easier to remain effective in the market despite the challenges a firm may encounter. The FI topic is fundamental, especially in speculating sectors that are more likely to face frequent fluctuations leading to high risks in the market.
New Areas Learned in the FI Topic
In the process of exploring the FI concept, several new pieces of information I encountered. For instance, I learned about floating rate bonds which are essential financial securities that provide various interest influenced by the coupon rate that changes based on the market interest rates. In the US, the floating rate bond is preferred by most business organizations because of its feature that allows it to increase in value depending on the current status of the market. In other words, floaters make it possible for investors to continue receiving benefits following changes in the rates. Furthermore, the securities are less affected by market volatility hence they are effective and productive. However, despite the benefits associated with investing in a floating-rate bond, the FI experiences significant limitations. For example, in terms of rates, the security offers lower rates than their counterparts the fixed-rate bonds. The aspect makes them less attractive to business organizations that are attracted to higher rates.
Relationship between the FI and Financial Reporting and Analysis
Generally, the aspect of financial reporting and analysis encompasses the recording of the monetary details in the books of account. The practice is aimed at making a comprehensive financial statement that captures all the facets of a company’s financial information. Most sources of funds for the business organization include loans and equities which are major parts of the FI. The concept of FI makes it easier for accountants to effectively classify the various FI as financial assets, liabilities, or equities. The relationship between the reporting and FI makes it easier to analyze core aspects such as bank loans, amortized cost accounting, fair value, and balance sheets. After a proper examination of the FI, the analysts are then able to provide an accurate and reliable financial statement containing the necessary details that can be used by potential investors. Furthermore, the correlation ensures the reporting provides details of possible risks that are associated with different types of FI in the market.
To sum up, the concept of FI is essential, especially for business organizations that depend on the performance of the financial market. The FI are classified into three broad categories namely; cash instruments, foreign exchange instruments, and derivatives. The various types of FI play a vital role in enabling companies to have access to adequate sources of capital. In addition, the equity-based FI allows investors to own a portion of companies that are publicly traded in the SEM. By using the FI, business organizations have the ability to reduce potential risks through hedging practices. Similarly, the companies enhance their chances of benefiting future operations following effective speculations accompanied by either sell or purchase of the underlying asset. Based on the financial details in the FI concept, it is important for people especially accountants to have adequate knowledge about the FI topic. The aspect will enable them to develop effective financial reports that capture the key types of FI and classify them accordingly.
Dungore, P. P., Singh, K., & Pai, R. (2022). An analytical study of equity derivatives traded on the NSE of India . Cogent Business & Management , 9 (1). Web.
Havemann, T., Negra, C., & Werneck, F. (2020). Blended finance for agriculture: Exploring the constraints and possibilities of combining financial instruments for sustainable transitions . Agriculture and Human Values , 37 (4), 1281-1292. Web.
Kańduła, S., & Przybylska, J. (2021). Financial instruments used by Polish municipalities in response to the first wave of COVID-19 . Public Organization Review , 21 (4), 665-686. Web.
Kang, B. J. (2019). Economic benefits of derivatives for long term investments-equity linked securities . Journal of Derivatives and Quantitative Studies . Web.
Parameswaran, S. K. (2022). Fundamentals of financial instruments: An introduction to stocks, bonds, foreign exchange, and derivatives . John Wiley & Sons.
Stolowy, H., & Ding, Y. (2017). Financial accounting and reporting: A global perspective , (5th ed.). London: South-Western Cengage Learning.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, May 10). Financial Instruments: The Main Types. https://ivypanda.com/essays/financial-instruments-the-main-types/
"Financial Instruments: The Main Types." IvyPanda , 10 May 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/financial-instruments-the-main-types/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Financial Instruments: The Main Types'. 10 May.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Financial Instruments: The Main Types." May 10, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/financial-instruments-the-main-types/.
1. IvyPanda . "Financial Instruments: The Main Types." May 10, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/financial-instruments-the-main-types/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Financial Instruments: The Main Types." May 10, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/financial-instruments-the-main-types/.
- Summary of the Article “Should We Fear Derivatives?”
- Derivatives and Derivatives Market
- Derivatives: A Contract Between a Buyer and a Seller
- Horizontal and Vertical Financial Analysis
- Navigating Turkish Market Expansion: Currency, Management, and Entry Strategies
- Impact of Debts on Returns: Discussion
- Burberry Group's Financial Reporting in 2021
- Financial Reporting for Non-Profit Organizations

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
Writing 101: The 8 Common Types of Essays. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 3 min read. Whether you're a first-time high school essay writer or a professional writer about to tackle another research paper, you'll need to understand the fundamentals of essay writing before you put pen to paper and write your first ...
Types of Essays with Examples. Understanding the different types of essays that make up the majority of your high school, college, and university assignments is a smart place to start when considering how to write one. Essays can be categorized into a wide variety, but the four main types of essays are argumentative, expository, narrative, and ...
Expository Essay. Informative Writing, Research, Clarity. Explain the causes and effects of climate change, and discuss its impact on the environment and society. Narrative Essay. Storytelling, Narrative Structure, Engagement. Describe a memorable childhood event that had a significant impact on your life.
This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people's social and cultural lives.
AI Tools to enhance your academic writing. SciSpace Copilot - AI research assistant. Literature Review. Paraphraser. AI Detector. Citation Generator. Academic writing includes different types of essays for students. This article gives a short summary of the 7 types of essays you often find in academic writing.
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
For example, if you're writing a narrative essay for a job application, you could conclude by summarizing how your experience solidified your desire to become a lawyer. 2. Descriptive essays. Descriptive essays provide a detailed description of your subject. This may be a person, place, thing or event.
Though you're likely not to encounter every single type of essay that exists, sometimes it's necessary to know about them. Learn about 15 different types here. Dictionary ... 20 Compelling Hook Examples for Essays; How to Write an Effective Thesis Statement; 5 Main Parts of an Essay: An Easy Guide to a Solid Structure;
It is a common academic assignment given to students at various educational levels. Essays can be classified into different types based on their purpose, content, and style. Here are the different types of essays with examples: Narrative Essay: A narrative essay tells a story about a real-life experience. It includes characters, a plot, and a ...
Become an essay expert with these essay examples to prepare you on your academic journey. ... Using these writing techniques, you can write many different types of essays. English author Edward Bulwer-Lytton wasn't kidding when he said, "The pen is mightier than the sword." With the right words and a well-developed argument, you can shape ...
An essay is a highly versatile, non-fictional piece of writing aimed at persuading, informing, or entertaining the reader. It can serve multiple functions, such as taking a stance on topics, disproving widely believed myths, and sharing interesting anecdotes. There are various styles and types of essay writing that can be used to serve specific functions.
An informal essay, also known as a familiar or personal essay, is a type of essay that is written in a personal tone and style. This type of essay is often written as a reflection or commentary on a personal experience, opinion, or observation. Informal essays are usually shorter than formal essays and are often written in a conversational style.
An essay is a highly versatile, non-fictional piece of writing aimed at persuading, informing, or entertaining the reader. It can serve multiple functions, such as taking a stance on topics, disproving widely believed myths, and sharing interesting anecdotes. There are various styles and types of essay writing that can be used to serve specific functions.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Examples of argumentative essay prompts. At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response. Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
Definition of Types of Essay. An essay is a short academic composition. The word "essay" is derived from a French word "essai" or "essayer," which mean "trail." In composition, however, an essay is a piece of non-fiction writing that talks or discusses a specific topic.Presently, essay is part of every degree program.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue.
An expository essay is a piece of writing that provides a balanced overview of a subject. In an expository essay, the writer uses facts, data, and examples to illustrate or clarify a topic. Expository writing includes a variety of essay types, including comparison and contrast essays, cause and effect essays, and "how to" or process essays ...
The introduction of a narrative essay sets the scene for the story that follows. Interesting introductions—for any kind of writing—engage and draw readers in because they want to know more. ... briefly provide background for the point of the story—often the lesson learned—as in 4 below and the first example on the reverse side. Below ...
Argumentative essays can be categorized into different types based on the approach and purpose of the argument. Understanding these types helps in crafting a more effective and targeted essay: Classical (Aristotelian) Argumentative Essay. Rooted in the principles of Aristotle, this type of essay presents a clear, direct argument.
Below are some samples in a few different essay lengths that are common to apps: 200 Word Essay Sample. This sample could answer the Common App prompt: Some students have a background, identity, interest, or talent that is so meaningful they believe their application would be incomplete without it. If this sounds like you, then please share ...
Drama Types. Tragedy - generally serious in tone, focusing on a protagonist who experiences an eventual downfall. Comedy - light in tone, employs humor and ends happily. Satire - exaggerated and comic in tone for the purpose of criticism or ridicule. Experimental - can be light or serious in tone.It creates its own style through experimentation with language, characters, plot, etc.
Depending on the type of essay you are writing, your hook can be in the form of a question, a surprising statistic or fact, an anecdote, a quote, or even a vivid description. ... For example, you can use sensory details to add depth and imagery to your words. It especially works for description hooks. Be careful with cliches and popular phrases ...
Types of Acoustical Materials - free essay example for studies and students. Essays & Research Papers for Free from Aithor.com ⭐ Make your own essay. 1. Introduction The field of acoustics is a branch of physics, concerned with the production, transmission and effects of sound. A room has been acoustically designed if it provides the ...
It contains thousands of paper examples on a wide variety of topics, all donated by helpful students. You can use them for inspiration, an insight into a particular topic, a handy source of reference, or even just as a template of a certain type of paper. The database is updated daily, so anyone can easily find a relevant essay example.
Examples of essay outlines. Examples of outlines for different types of essays are presented below: an argumentative, expository, and literary analysis essay. Argumentative essay outline. This outline is for a short argumentative essay evaluating the internet's impact on education. It uses short phrases to summarize each point.
Interactive example of a narrative essay. An example of a short narrative essay, responding to the prompt "Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself," is shown below. Hover over different parts of the text to see how the structure works. Narrative essay example.