Healthy Food Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on healthy food.
Healthy food refers to food that contains the right amount of nutrients to keep our body fit. We need healthy food to keep ourselves fit.
Furthermore, healthy food is also very delicious as opposed to popular thinking. Nowadays, kids need to eat healthy food more than ever. We must encourage good eating habits so that our future generations will be healthy and fit.
Most importantly, the harmful effects of junk food and the positive impact of healthy food must be stressed upon. People should teach kids from an early age about the same.


Benefits of Healthy Food
Healthy food does not have merely one but numerous benefits. It helps us in various spheres of life. Healthy food does not only impact our physical health but mental health too.
When we intake healthy fruits and vegetables that are full of nutrients, we reduce the chances of diseases. For instance, green vegetables help us to maintain strength and vigor. In addition, certain healthy food items keep away long-term illnesses like diabetes and blood pressure.
Similarly, obesity is the biggest problems our country is facing now. People are falling prey to obesity faster than expected. However, this can still be controlled. Obese people usually indulge in a lot of junk food. The junk food contains sugar, salt fats and more which contribute to obesity. Healthy food can help you get rid of all this as it does not contain harmful things.
In addition, healthy food also helps you save money. It is much cheaper in comparison to junk food. Plus all that goes into the preparation of healthy food is also of low cost. Thus, you will be saving a great amount when you only consume healthy food.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Junk food vs Healthy Food
If we look at the scenario today, we see how the fast-food market is increasing at a rapid rate. With the onset of food delivery apps and more, people now like having junk food more. In addition, junk food is also tastier and easier to prepare.
However, just to satisfy our taste buds we are risking our health. You may feel more satisfied after having junk food but that is just the feeling of fullness and nothing else. Consumption of junk food leads to poor concentration. Moreover, you may also get digestive problems as junk food does not have fiber which helps indigestion.
Similarly, irregularity of blood sugar levels happens because of junk food. It is so because it contains fewer carbohydrates and protein . Also, junk food increases levels of cholesterol and triglyceride.
On the other hand, healthy food contains a plethora of nutrients. It not only keeps your body healthy but also your mind and soul. It increases our brain’s functionality. Plus, it enhances our immunity system . Intake of whole foods with minimum or no processing is the finest for one’s health.
In short, we must recognize that though junk food may seem more tempting and appealing, it comes with a great cost. A cost which is very hard to pay. Therefore, we all must have healthy foods and strive for a longer and healthier life.
FAQs on Healthy Food
Q.1 How does healthy food benefit us?
A.1 Healthy Benefit has a lot of benefits. It keeps us healthy and fit. Moreover, it keeps away diseases like diabetes, blood pressure, cholesterol and many more. Healthy food also helps in fighting obesity and heart diseases.
Q.2 Why is junk food harmful?
A.2 Junk food is very harmful to our bodies. It contains high amounts of sugar, salt, fats, oils and more which makes us unhealthy. It also causes a lot of problems like obesity and high blood pressure. Therefore, we must not have junk food more and encourage healthy eating habits.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Healthy Food Essay 150 and 300 Words in English for Students

- Updated on
- Apr 4, 2024

Eating healthy food is important for a healthy and disease-free life. A person who eats healthy food means he/ she is taking good care of his/ her body and overall well-being. From childhood, we are told to eat healthy food, which includes green vegetables, fruits, dry fruits, dairy products, etc. On this page, we will be discussing healthy food essay 150 and 300 words for school students.
Table of Contents
- 1 Healthy Food Essay 150 Words
- 2 Essay on Healthy Food in 300 Words
- 3 10 Healthy Food Essay Lines
Quick Read: Essay on Good Habits
Healthy Food Essay 150 Words
‘Healthy food means food that is good for our physical growth and overall well-being. From an early age, we are told to eat healthy foods, ones that are rich in protein, fiber, and calcium. There are five types of healthy foods: Fruit and vegetables; starchy food; dairy products; proteins and fats.
Food is essential for growth and development, and when we talk about healthy food, it means better growth and a healthy lifestyle. Taking care of our bodies is our responsibility, and it all starts with eating healthy food.
Today, India is the largest producer of milk and pulses, and the second largest producer of rice, wheat, sugarcane, groundnut, vegetables, and fruit. The country not only sustains its 1.4 billion population with healthy food but also exports a large amount of it.
Our health is our responsibility, which can only be achieved by eating healthy food and exercising. There is a saying in sports, ‘ Your performance is determined by the type of fuel you provide to your body.’ So, let’s all live a healthy and happy life with healthy food.’
Quick Read: 200+ English Essay Topics
Essay on Healthy Food in 300 Words
‘Food is a source of energy for every living being. Even plants require food in the form of sunlight, water, and minerals from the soil. As humans, we all want to eat our favorite and most delicious food, which is mostly unhealthy. Healthy food, on the other hand, is not preferred by all, as some people don’t consider it tasty. Healthy food is known for its rich fiber and protein content. There are several benefits of eating healthy food, which are very important for our growth, body functioning and to live a sustained life.’
‘A healthy diet is generally a balanced diet of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals and vitamins. Proteins and fats are required for energy, carbohydrates support our bodily functions and physical activity, and vitamins and minerals help boost the immune system, and support normal growth and development.’
‘India is one of the largest producers of healthy foods. In India, the Northern Plains, the Central Highlands, and the coastal areas are known for their rich production of healthy and nutritious food. Uttar Pradesh is the leading producer of sugarcane and wheat, West Bengal of rice, Karnataka for coffee, and Rajasthan of millet. We are surrounded by so many natural and healthy food resources, which can help lead a healthy and sustained life.’
‘Healthy food helps maintain a good body weight. It’s all about balancing what we eat and drink with the energy we burn. Sure, filling our plates with good food is important, but watching how much we take helps too.’
‘Eating healthy food is not just advice to live a healthy life. It’s a way of life that we all must adhere to. Adding fruits, vegetables, and dairy products to our diets will help us maintain good body weight, boost our immune system, and enhance our cells and body functioning.’
10 Healthy Food Essay Lines
Here are 10 healthy food essay lines for students:
- Eating healthy food is very important for a healthy and happy life.
- We get all the important nutrients and minerals from healthy food.
- Vegetables, fruits, dairy products, and dry fruits are part of healthy food.
- Dairy products such as milk, eggs, ghee, butter, and cotton cheese are rich sources of protein.
- Healthy food keeps our mind and body fit.
- Avoiding junk food and switching to healthy food can help us live a healthier life.
- World Health Day is celebrated on April 7 every year to promote a healthy lifestyle and healthy food.
- Healthy food makes us agile and increases body functioning.
- Healthy food can help boost our immune system and digestion.
- Healthy food can uplift our mood and make us feel good.
Ans: ‘Healthy food means food that is good for our physical growth and overall well-being. From an early age, we are told to eat healthy foods, ones that are rich in protein, fiber, and calcium. There are five types of healthy foods: Fruit and vegetables; starchy food; dairy products; proteins and fats.’ ‘Food is essential for growth and development, and when we talk about healthy food, it means better growth and a healthy lifestyle. Taking care of our body is our responsibility and it all starts with eating healthy food.’
Ans: Food is a source of energy for every living being. Even plants require food in the form of sunlight, water, and minerals from the soil. As humans, we all want to eat our favourite and delicious food, which is mostly unhealthy. Healthy food, on the other hand, is not preferred by all, as some people don’t consider it tasty. Healthy food is known for its rich fiber and protein content. There are several benefits of eating healthy food, which are very important for our growth, body functioning, and living a sustained life.
Ans: ‘Healthy food helps in maintaining a good body weight It’s all about balancing what we eat and drink with the energy we burn. Sure, filling our plates with good food is important, but watching how much we take helps too. Healthy food makes us agile and increases body functioning. Healthy food can help boost our immune system and digestion. Healthy food can uplift our mood and make us feel good.
Popular Essay Topics for Students
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Shiva Tyagi
With an experience of over a year, I've developed a passion for writing blogs on wide range of topics. I am mostly inspired from topics related to social and environmental fields, where you come up with a positive outcome.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
Essays About Eating Healthy Foods: 7 Essay Examples And Topic Ideas
If you’re writing essays about eating healthy foods, here are 7 interesting essay examples and topic ideas.
Eating healthy is one of the best ways to maintain a healthy lifestyle. But we can all struggle to make it a part of our routine. It’s easier to make small changes to your eating habits instead for long-lasting results. A healthy diet is a plan for eating healthier options over the long term and not a strict diet to be followed only for the short.
Writing an essay about eating healthy foods is an exciting topic choice and an excellent way to help people start a healthy diet and change their lifestyles for the better. Tip: For help with this topic, read our guide explaining what is persuasive writing ?
1. The Definitive Guide to Healthy Eating in Real Life By Jillian Kubala
2. eating healthy foods by jaime padilla, 3. 5 benefits of eating healthy by maggie smith, 4. good food bad food by audrey rodriguez, 5. what are the benefits of eating healthy by cathleen crichton-stuart, 6. comparison between healthy food and junk food by jaime padilla, 7. nutrition, immunity, and covid-19 by ayela spiro and helena gibson-moore, essays about eating healthy foods topic ideas, 1. what is healthy food, 2. what is the importance of healthy food, 3. what does eating healthy mean, 4. why should we eat healthy foods, 5. what are the benefits of eating healthy foods, 6. why should we eat more vegetables, 7. can you still eat healthy foods even if you are on a budget.
“Depending on whom you ask, “healthy eating” may take many forms. It seems that everyone, including healthcare professionals, wellness influencers, coworkers, and family members, has an opinion on the healthiest way to eat. Plus, nutrition articles that you read online can be downright confusing with their contradictory — and often unfounded — suggestions and rules. This doesn’t make it easy if you simply want to eat in a healthy way that works for you.”
Author Jillian Kubala is a registered dietitian and holds a master’s degree in nutrition and an undergraduate degree in nutrition science. In her essay, she says that healthy eating doesn’t have to be complicated and explains how it can nourish your body while enjoying the foods you love. Check out these essays about health .
“Eating provides your body with the nourishment it needs to survive. A healthy diet supplies nutrients (such as protein, vitamins and minerals, fiber, and carbohydrates), which are important for your body’s growth, development, and maintenance. However, not all foods are equal when it comes to the nutrition they provide. Some foods, such as fruits and vegetables, are rich in vitamins and minerals; others, such as cookies and soda pop, provide few if any nutrients. Your diet can influence everything from your energy level and intellectual performance to your risk for certain diseases.”
Author Jaime Padilla talks about the importance of a healthy diet in your body’s growth, development, and maintenance. He also mentioned that having a poor diet can lead to some health problems. Check out these essays about food .
“Eating healthy is about balance and making sure that your body is getting the necessary nutrients it needs to function properly. Healthy eating habits require that people eat fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fats, proteins, and starches. Keep in mind that healthy eating requires that you’re mindful of what you eat and drink, but also how you prepare it. For best results, individuals should avoid fried or processed foods, as well as foods high in added sugars and salts.”
Author Maggie Smith believes there’s a fine line between healthy eating and dieting. In her essay, she mentioned five benefits of eating healthy foods – weight loss, heart health, strong bones and teeth, better mood and energy levels, and improved memory and brain health – and explained them in detail.
You might also be interested in our round-up of the best medical authors of all time .
“From old generation to the new generation young people are dying out quicker than their own parents due to obesity-related diseases every day. In the mid-1970s, there were no health issues relevant to obesity-related diseases but over time it began to be a problem when fast food industries started growing at a rapid pace. Energy is naturally created in the body when the nutrients are absorbed from the food that is consumed. When living a healthy lifestyle, these horrible health problems don’t appear, and the chances of prolonging life and enjoying life increase.”
In her essay, author Audrey Rodriguez says that having self-control is very important to achieving a healthy lifestyle, especially now that we’re exposed to all these unhealthy yet tempting foods that all these fast-food restaurants offer. She believes that back in the early 1970s, when fast-food companies had not yet existed and home-cooked meals were the only food people had to eat every day, trying to live a healthy life was never a problem.
“A healthful diet typically includes nutrient-dense foods from all major food groups, including lean proteins, whole grains, healthful fats, and fruits and vegetables of many colors. Healthful eating also means replacing foods that contain trans fats, added salt, and sugar with more nutritious options. Following a healthful diet has many health benefits, including building strong bones, protecting the heart, preventing disease, and boosting mood.”
In her essay, Author Cathleen Crichton-Stuart explains the top 10 benefits of eating healthy foods – all of which are medically reviewed by Adrienne Seitz, a registered and licensed dietitian nutritionist. She also gives her readers some quick tips for a healthful diet.
“In today’s generation, healthy and unhealthy food plays a big role in youths and adults. Many people don’t really understand the difference between healthy and unhealthy foods, many don’t actually know what the result of eating too many unhealthy foods can do to the body. There are big differences between eating healthy food, unhealthy food and what the result of excessively eating them can do to the body. In the ongoing battle of “healthy vs. unhealthy foods”, unhealthy foods have their own advantage.”
Author Jaime Padilla compares the difference between healthy food and junk food so that the readers would understand what the result of eating a lot of unhealthy foods can do to the body. He also said that homemade meals are healthier and cheaper than the unhealthy and pricey meals that you order in your local fast food restaurant, which would probably cost you twice as much.
“The Covid-19 pandemic has sparked both an increased clinical and public interest in the role of nutrition and health, particularly in supporting immunity. During this time, when people may be highly vulnerable to misinformation, there have been a plethora of media stories against authoritative scientific opinion, suggesting that certain food components and supplements are capable of ‘boosting’ the immune system. It is important to provide evidence-based advice and to ensure that the use of non-evidence-based approaches to ‘boost’ immunity is not considered as an effective alternative to vaccination or other recognized measures.”
Authors Ayela Spiro, a nutrition science manager, and Helena Gibson-Moore, a nutrition scientist, enlighten their readers on the misinformation spreading in this pandemic about specific food components and supplements. They say that there’s no single food or supplement, or magic diet that can boost the immune system alone. However, eating healthy foods (along with the right dietary supplements), being physically active, and getting enough sleep can help boost your immunity.

If you’re writing an essay about eating healthy foods, you have to define what healthy food is. Food is considered healthy if it provides you with the essential nutrients to sustain your body’s well-being and retain energy. Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water are the essential nutrients that compose a healthy, balanced diet.
Eating healthy foods is essential for having good health and nutrition – it protects you against many chronic non-communicable diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. If you’re writing an essay about eating healthy foods, show your readers the importance of healthy food, and encourage them to start a healthy diet.
Eating healthy foods means eating a variety of food that give you the nutrients that your body needs to function correctly. These nutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. In your essay about eating healthy foods, you can discuss this topic in more detail so that your readers will know why these nutrients are essential.
Eating healthy foods includes consuming the essential nutrients your body requires to function correctly (such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water) while minimizing processed foods, saturated fats, and alcohol. In your essay, let your readers know that eating healthy foods can help maintain the body’s everyday functions, promote optimal body weight, and prevent diseases.
Eating healthy foods comes with many health benefits – from keeping a healthy weight to preventing long-term diseases such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and cancer. So if you’re looking for a topic idea for your essay, you can consider the benefits of eating healthy foods to give your readers some useful information, especially for those thinking of starting a healthy diet.
Ever since we were a kid, we have all been told that eating vegetables are good for our health, but why? The answer is pretty simple – vegetables are loaded with the essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that our body needs. So, if you’re writing an essay about eating healthy foods, this is an excellent topic to get you started.
Of course, you definitely can! Fresh fruits and vegetables are typically the cheapest options for starting a healthy diet. In your essay about eating healthy foods, you can include some other cheap food options for a healthy diet – this will be very helpful, especially for readers looking to start a healthy diet but only have a limited amount of budget set for their daily food.
For help with this topic, read our guide explaining what is persuasive writing ?
If you’re stuck picking your next essay topic, check out our round-up of essay topics about education .

Bryan Collins is the owner of Become a Writer Today. He's an author from Ireland who helps writers build authority and earn a living from their creative work. He's also a former Forbes columnist and his work has appeared in publications like Lifehacker and Fast Company.
View all posts
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Advanced Cutoff
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Advanced Answer Key
- JEE Advanced Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Answer Key
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Result 2024
- NEET Asnwer Key 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET DU Cut off 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET DU CSAS Portal 2024
- CUET Response Sheet 2024
- CUET Result 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET PG Counselling 2024
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Healthy Food Essay
The food that we put into our bodies has a direct impact on our overall health and well-being. Eating a diet that is rich in nutritious, whole foods can help us maintain a healthy weight, prevent chronic diseases, and feel our best. It is important to make conscious, healthy food choices to support our physical and mental well-being. By incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into our diets, we can ensure that our bodies are getting the nutrients they need to thrive. Here are a few sample essays on healthy food.

100 Words Essay On Healthy Food
Healthy food is essential to maintaining a healthy and balanced lifestyle. First and foremost, healthy food is food that is nutritious and good for the body. This means that it provides the body with the vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients it needs to function properly. Healthy food can come in many forms, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Healthy food is important for maintaining a healthy body and mind. It provides the nutrients and energy the body needs to function properly and can help to prevent a wide range of health problems. So, if you want to feel your best, be sure to make healthy food a priority in your life.
200 Words Essay On Healthy Food
Healthy food is not just about what you eat – it’s also about how you eat it. For example, eating fresh, whole foods that are prepared at home with love and care is generally considered to be healthier than eating processed, pre-packaged foods that are high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats. Additionally, eating in moderation and avoiding excessive portion sizes is key to maintaining a healthy diet.
There are many reasons to eat healthy food, but the most obvious one is that it can help to prevent a wide range of health problems. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and other healthy foods can help to lower your risk of heart disease, stroke, obesity, and other chronic conditions. Additionally, healthy food can help to boost your immune system, giving your body the tools it needs to fight off illness and infection. But the benefits of healthy food go beyond just physical health. Eating well can also have a profound impact on your mental and emotional well-being. A healthy diet can help to reduce stress and anxiety, improve mood, and increase energy levels. It can also help to improve cognitive function and memory, making it easier to focus and concentrate.
500 Words Essay On Healthy Food
Healthy food is an essential aspect of a healthy lifestyle. It is not only crucial for maintaining physical health, but it can also have a significant impact on our mental and emotional well-being. Eating a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help us feel energised, focused, and happy. But for many people, eating healthy can be a challenge. In a world where fast food and processed snacks are readily available and often more convenient than cooking a meal from scratch, it can be tempting to choose unhealthy options. And with busy schedules and hectic lives, it can be difficult to find the time and energy to plan and prepare healthy meals.
However, the benefits of eating healthy far outweigh the challenges. Not only can it help us maintain a healthy weight and reduce our risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer, but it can also improve our mood, energy levels, and overall quality of life.
My Experience
As I sat down at my desk with a bag of chips and a soda for lunch again, I realised that I had been making unhealthy food choices all week. I had been so busy with work and other obligations that I hadn't taken the time to plan and prepare healthy meals. I decided then and there to make a change. I started by making a grocery list of nutritious, whole foods and meal planning for the week ahead. I also made a commitment to myself to cook at home more often instead of relying on takeout or fast food. It wasn't easy at first, but over time, I started to notice a difference in my energy levels and overall mood. I felt better physically and mentally, and I was able to maintain a healthy weight. Making healthy food choices became a priority for me, and I am now reaping the numerous benefits of a nutritious diet.
One of the key components of a healthy diet is variety. Eating a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide our bodies with the nutrients, vitamins, and minerals we need to function at our best. It's important to try to incorporate a rainbow of colours into our diets, as each colour group represents different nutrients and health benefits. For example, orange and yellow fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamin C and beta-carotene, which can support healthy skin and eyesight. Green leafy vegetables like spinach and kale are packed with antioxidants and can help support a healthy immune system. And blue and purple fruits and vegetables, like blueberries and eggplants, are high in flavonoids and can help support brain health and cognitive function.
In addition to eating a variety of fruits and vegetables, it's also important to include whole grains in our diets. Whole grains, like quinoa, brown rice, and oatmeal, are a great source of fibre, which can help keep us feeling full and satisfied. They can also help regulate our blood sugar levels, which can keep our energy levels steady and prevent unhealthy cravings.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Healthy Food Essay

Essay on Healthy Food
Food is essential for our body for a number of reasons. It gives us the energy needed for working, playing and doing day-to-day activities. It helps us to grow, makes our bones and muscles stronger, repairs damaged body cells and boosts our immunity against external harmful elements like pathogens. Besides, food also gives us a kind of satisfaction that is integral to our mental wellbeing, but there are some foods that are not healthy. Only those food items that contain nutrients in a balanced proportion are generally considered as healthy. People of all ages must be aware of the benefits of eating healthy food because it ensures a reasonably disease-free, fit life for many years.
Switching to a healthy diet doesn't have to be a one-size-fits-all approach. You don't have to be perfect, you don't have to eliminate all of your favourite foods and you don't have to make any drastic changes all at once—doing so frequently leads to straying or abandoning your new eating plan.
Making a few tiny modifications at a time is a recommended approach. Maintaining modest goals will help you achieve more in the long run without feeling deprived or overwhelmed by a very drastic diet change. Consider a healthy diet as a series of tiny, accessible actions such as including a salad in your diet once a day. You can slowly add additional healthy options as your minor modifications become habitual.
Cultivating a positive relationship with food is also crucial. Rather than focusing on what you should avoid, consider what you may include on your plate that will benefit your health such as nuts for heart-healthy, predominant fat that reduces low-density lipoprotein levels called monounsaturated fatty acids(raspberries) for fibre and especially the substances that inhibit oxidation which we call antioxidants.
Why is Healthy Food Important?
Living a healthy lifestyle has immense payback. Over time, making smart eating choices lowers your risk of cardiovascular disease, certain malignancies, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and even anxiety and depression. Daily, you will have more energy, feel better and possibly even be in a better mood.
It all boils down to how long and how good your life is. According to several surveys, A healthy diet consists of whole grains, vegetables, fruits, nuts, and fish. A higher diet of red or processed meats on the other hand doubled the chance of dying young.
Types of Healthy Food:
Following are the various types of healthy foods and their respective nutritional value:
Cereals,potatoes,bread and other root vegetables- These are the main sources of carbohydrates. The calories obtained from them enable us to do work.
Pulses, milk and milk products, eggs, bird meat, animal meat in limited quantities - these are great sources of protein. They build muscles and repair the damaged cells of our body, i.e., they are important for our immunity.
Ghee, butter, nuts and dry fruits, edible oil used in restrained quantities- These are rich sources of good fat. They provide more energy to our body than carbohydrates but should be consumed in a smaller amount.
Fresh fruits, vegetables and leafy vegetables, fish, egg, milk-these are good sources of vitamins, minerals and antioxidants are essential for normal functioning of the body. Though they are needed in small amounts, nowadays, nutrition experts prescribe their higher consumption as they help to fight lifestyle diseases like diabetes, obesity and even cancer.
Different types of healthy food when included in our daily diet in the right proportions along with water and roughage comprise a balanced diet. However, a balanced diet is not the same for all individuals considering many factors. It depends on a person’s age, gender, condition of the body-healthy or suffering from any disease and the type of work or physical activity a human does.
Benefits of Eating Healthy
Healthy food intake nourishes both our physical and mental health and helps us stay active for many years. One who break downs this broad benefit into micro-benefits will see that eating healthy:
Helps us in weight management
Makes us agile and increases our productivity
Decreases the risk of heart diseases, stroke, diabetes mellitus, poor bone density, and some cancers, etc.
Helps in uplifting mood
Improves memory
Improves digestion and appetite
Improves sleep cycle
Healthy food habits are inculcated in children by their parents early on. These habits along with the right education and physical exercise lead to an overall development of an individual which ultimately becomes the greatest resource of a country.
What is Unhealthy Food or Junk Food?
To fully understand the prominence of healthy food in our diet, we must also be aware of unhealthy food, that is, the food that we must avoid eating. These are mainly junk food items which are low in nutritional value and contain an excessive amount of salt, sugar and fats which is not healthy for a human body.
Junk food is one of the unhealthy intakes in the present day scenario. It makes us more unfit than ever before. It is high time that one realised this and adopted a healthy food habit for a sustainable lifestyle.
Steps to improve Eating Habits:
Make a detailed plan; break down the timings; kind of food to be included in each meal and keep the plan weekly and avoid making the process dull and repetitive.
Cook your food, minimise eating from outside. It helps keep the ingredients, quality and measurements in check as well as saves money.
Stock your kitchen with healthy snacks for your cravings rather than processed food so that your options are reduced to consuming unhealthy food.
Take the process slowly. You do not have to have a strict plan; ease yourself into a healthy mindset. Your mind and body will adjust gradually. Consistency is important.
Track your eating habits to understand the intake of food, items, portions etc. This motivates you to see the progress over time and make changes according to your needs.
Myths About Healthy Food:
Carrots affect eyesight: According to historic times, during World War II, there was a popular belief that eating a lot of veggies would assist maintain the pilot's eyes in good repair. In actuality, the fighter pilot's eyesight was aided by advanced technology. However, the myth has persisted since then and many parents still use this narrative to get their children to eat more veggies. Carrots are high in vitamin A and make a terrific supplement to any healthy diet, but they don't usually help you see better.
Fat-Free Food : Health foods continue to dominate grocery store shelves but it's always a good idea to look beyond the label before buying. This is especially true when it comes to "fat-free," "low-fat," and "non-fat" foods. It's generally true that anything with less fat is preferable for some dairy and meat items.
Lower fat alternatives in packaged and processed foods contain other dangerous additives as fat substitutes. Manufacturers compensate for the loss of fat in packaged cookies, for example, by adding other undesirable elements like sugar.
Protein shakes: Pre-made smoothie beverages and protein powder mixes which typically claim to contain less sugar than milkshakes, slushies and diet sodas are likely to be the popular choice among customers because of the above mentioned reason. They both have the same amount of sugar and artificial sweeteners.
However, this is not true of all pre-made protein shakes and smoothies. Many of them, particularly the plant-based mixtures, are still nutritious additions to a balanced diet. Check the nutrition label to be sure there are no added sugars or artificially sweetened mixtures.
Organic food is better: Foods that are grown organically are better for you. Nutritionists labelling a product as organic doesn't mean it's superior to non-organic foods. It's a popular misperception that organic produce is nutritionally superior to non-organic produce. Organic produce has the same caloric and nutritional value as non-organic produce since it is grown and prepared according to federal rules.

FAQs on Healthy Food Essay
1) Is sugar unhealthy?
Sugar is considered to be harmful for a healthy diet. Since it tastes so good in many foods, humans tend to increase it’s intake. It is also hidden in foods you wouldn't expect. It makes body organs fat, depresses well-being and also leads to heart diseases. However, to maintain a healthy diet, it is necessary to distinguish between natural and added sugars. Sugars are carbs that provide an essential source of energy and nourishment, nevertheless, sugar is often added to many popular dishes, which is when sugar becomes unhealthy. Natural sugars found in fruits and vegetables are regarded as healthy when consumed in moderation. Still added sugars give little nutritional benefit and contribute considerably to weight gain, compromising your healthy diet. As a result, it's critical to double-check the label.
2) What is Omega 3?
Omega-3 is the superfood of the fat group, which is particularly useful for various conditions, since the term "superfood" was coined. Omega-3 fatty acid is a medicine used in treating nutritional deficiencies. It is one of the essential nutrients with good antioxidant properties. Depression, memory loss, heart problems, joint and skin disorders and general improvement of physical and mental health and wellness are among them. Omega-3 which is abundant in fish-based diets is considered a necessary fatty acid for good health.
Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Nutrition — Persuasive Essay On Eating Healthy
Persuasive Essay on Eating Healthy
- Categories: Nutrition Persuasion
About this sample

Words: 968 |
Published: Mar 5, 2024
Words: 968 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Nursing & Health Literature

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 744 words
2 pages / 947 words
2 pages / 799 words
1 pages / 328 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Nutrition
Advocating for patients' need for basic care and comfort is pivotal in nursing practice. Healthcare professionals should ensure that patients are not harmed in the healthcare setting as it is supposed to provide healing and [...]
Healthy carob bars have gained attention as a potential substitute for traditional chocolate products. As a college student studying marketing, it is important to recognize the potential of healthy carob bars and develop a [...]
The functions and sources of minerals are important aspects of maintaining overall health and well-being. Minerals can be found in various sources, including coconut water. According to Fife (2011), coconut water has been used [...]
"History of Candy." Candy USA. https://www.candyindustry.com/articles/88357-the-future-of-candy-includes-more-consumers-who-want-to-know-whats-in-their-sweets
Fat is an essential part of our daily diet and is important for good health. There are different types of fats, some fats being healthier than other. To help make sure you stay healthy, it is important to eat unsaturated fats in [...]
A good and balanced diet has proven to have a significant effect on the physical and mental development of the child, especially in their early life. Studies have shown that good nutrition enhances school performance and [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

ReadingJunction
Ultimate hub of educational content (Essay, Speech, Debate, Festivals, Events)
Essay on Healthy Food for Students and Children in 1000 Words
December 15, 2020 by ReadingJunction 1 Comment

In this article, read about an essay on healthy food for students and children. It includes the benefits of healthy food eating, meaning, with types and examples of a nutritious, healthy diet.
Table of Contents
Essay on Healthy Food for Students and Children (1000 Words)
Every Living thing needs food to survive like a tree, animals, and humans. Food gives us strength. But power is also available only when the diet has eaten is healthy. A healthy diet is essential for a healthy life. We need to pay more attention to the nutritional value of eating than taste.
Meaning of Healthy Food
A variety of foods that give you the nutrients you need to maintain health, feel good, and have energy. And also, nutrients include protein, carbohydrates, fat, water, vitamins, and minerals. Nutrition is vital for our bodies. Being physically active and maintaining a healthy body, eating well is an excellent way to help your body stay strong and healthy.
Rice, roti, lentils, green vegetables, milk, and yogurt, etc. come inside a healthy diet. We should all eat healthy food every day. Healthy food gives us a happy life. We should also eat fruits daily in a balanced diet.
In today’s time, we are forgetting the importance of a balanced diet and going away from healthy food, because of which the risk of diabetes and obesity in children is increasing.
People are becoming more and more attracted to delicious food and are not paying attention to the quality of the food at all. Junk foods may be tasty, but they are not nutritious at all but are harmful to our health.
A lot of illnesses arise for fried and packed food. We all should not eat junk food much but should make a balanced diet a part of our daily routine.
Preserved or canned food and other such foods are entirely unhealthy for the body. Over time, it causes severe illness and serious illnesses. Children who eat junk food often lack concentration.
Also, you may have digestive problems because junk food does not contain fiber, which helps digestion. The blood sugar level is an irregularity caused by junk food. Because it contains fewer carbohydrates and protein. Also, junk food increases cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Our children love colorful food, so feed them a slice of carrot radish, whose different colors will attract them. Not only the children, but the growing people should also take a balanced diet. We should keep our meals all three times, so they must have nutritious food.
We can eat outside sometimes, but we have to eat healthy every day. We should not eat junk food more often and should eat only fresh food. Eating healthy also helps you save money. It is cheaper than junk food.
Benefits of Healthy food
With this, the cost of all those who go to prepare a healthy diet is even less. When you consume only healthy food, you will save a considerable amount. We should consume regular sugar and avoid the use of excessive sugar and limit the use of sodium (salt). It should also be iodized salt.
1. Keeps the Brain Active and Energize
Healthy food is full of nutrients, and these nutrients provide us with energy and alertness. Therefore, we remain active. So, I suggest all of you eat healthy food, do exercise every day and be healthy, as health is wealth.
2. Keeps Away From Obesity
Healthy food also saves us from obesity as it helps us in managing unnecessary weight gain.
According to W.H.O (World Health Organization)
Healthy food helps us to protect against malnutrition in all its forms, and noncommunicable diseases (NCD), including such as diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and cancer.
Keeping salt intake to less than 5 gram per day helps to prevent hypertension and reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke in the adult person. 2.5 million deaths per year are due to lack of vegetables, fruits in the diet, according to WHO, 20% of people do not use balanced diet because of cancer, 33% of people have heart attacks, and 10%, trauma. The reason for this is that, due to they take unhealthy food, 2.6 lakh people die every year.
3. Maintains Calories
It requires 1,600 to 2,400 calories per day for adult women and 2,000 to 3,000 calories per day for adult men. Within each age and gender category, the lower end of the range is for sedentary people; The high end of the scale is for active individuals.
4. Avoid Diseases
Eating unhealthy food like excessive oily, fat and spicy food may cause various types of health issues like chronic heart disease, ulcers, diarrhea and kidney failure. So, to avoid these types of health issues always eat healthy food.
5. Maintains Your Beauty
Eating healthy food keeps your skin always glowing. Eating fast food or junk food may harm your body beauty. Unhealthy oily food may cause problems like pimples and hair fall, which give you an ugly look.
Different Types of Healthy Food
Here is a list of some healthy food which you can try in your daily life to become stronger and beautiful-
Green Vegetables
Fat and calories are the least found in green vegetables. Because of which it controls obesity. It is essential to keep the body healthy and better and control obesity. Along with this, the toxins of the body come out. The more green vegetables are eaten, the better it is for health.
Along with fiber and vitamin C, the right amount of various types of antioxidants is present in the apple. If you experience hunger even after eating, then apple can be a good option for you.
Strawberries
Strawberries are a healthy diet for those who want to lose weight for the minimal amount of carbs and calories. Strawberries contain a high percentage of vitamin C, Fiber, and Manganese, which make it a healthy diet.
Milk: Excess of vitamins and minerals are present in milk. Also, milk has a high protein and fat content. Milk is considered the best source of calcium.
I would like to tell you that eggs are one of the most nutritious foods in the world. Earlier, there was a mindset about eggs that, because of high cholesterol, eggs harm health. But it is now clear from the studies that egg consumption is entirely safe.
Sheep are usually fed grass, and sheep consume a wide variety of leaves, herbs and high amounts of Omega-3 fatty acid in its meat. Therefore, it is a tasty and nutritious diet for you.
In this way, a healthy diet improves thoughts, because of which peace is established in our home, and for this peace, our country will become a society. The sage monks of our country also give importance to a balanced diet.
He lived quite a long life, and he was powerful physically, kept calm, so healthy, and a proper diet is very important for our body and mind.
Food is the first expression of every celebration in Indian culture. From birth, marriage, etc. life to death, because vitality is associated with it. This makes the mind flourish. The environment also contributes to this. Hope you liked this informative essay on healthy food for students and children.
Reader Interactions
July 29, 2021 at 3:57 pm
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Copyright Protection
All articles on this website are Copyright Protected. Copying or Using any material in any form is a serious offense.
Important Links
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions

Healthy Food Essay
Healthy food essay teaches kids the importance of eating healthy food every day. You can provide the children with BYJU’S importance of healthy food essay.
Food is a fundamental part of our life. It is the fuel that helps us go about our daily routine, and it is the meal that makes us feel good at every minute of the day. Food plays an important role in staying healthy.
The food we eat determines the health of our body, and some foods are better for our bodies than others. Healthy food contains a lot of fibre, has a low glycemic index, and is high in nutrients. Furthermore, the consumption of healthy food benefits our mental and physical health.
This short essay on healthy food helps us understand its significance, along with a healthy lifestyle.
Advantages of Healthy Food
People often consider eating healthy because it helps them look and feel better. There are many reasons to eat healthy food as it has numerous advantages. Some of the most important advantages include reducing the risk of cancer, heart disease, obesity and diabetes, which eventually improves the quality of life.
There are also people who prefer healthier options for themselves. This can be for various reasons, including not wanting to gain weight, not spending a lot of money on food that would eventually go to waste, or just because they want to make sure their diet is as healthy as possible.
A portion of healthy food can help prevent disease. Moreover, healthy foods can help keep us away from getting sick from all of the chemicals in processed and junk foods.
When we eat healthily, we stay healthy.
Healthy Food vs Junk Food
We are in an era of dominance of the fast-food industry. There is a lot of information on the internet that shows people how they can live healthier and less expensive lives. One of the ways to do this is by purchasing healthy food instead of junk food. Many restaurants and grocery stores have received backlash for their unhealthy options.
It is high time to understand the difference between healthy food vs junk food by reading the healthy food vs junk food essay available at BYJU’S and adapting ourselves to healthy eating habits.
For more essays similar to the healthy food essay and other exciting kids’ learning resources, visit BYJU’S website.
Frequently Asked Questions on Healthy Food Essay
What are the benefits of healthy food.
There are many health benefits to consuming healthy food. Some of the benefits are it helps increase metabolism, enhances the immune system, lessens inflammation associated with heart disease, reduces the risk of cancer, obesity, diabetes, blood pressure, cholesterol, helps control body weight, etc.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Essay on Importance of Healthy Food
Students are often asked to write an essay on Importance of Healthy Food in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Importance of Healthy Food
The value of healthy food.
Healthy food is essential for our bodies. It provides the necessary nutrients which help us grow, develop, and stay active.
Nutrition and Growth
Food rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins supports growth. It strengthens our immune system and helps us fight diseases.
Energy Source
Healthy food gives us energy. It helps us perform daily activities without feeling tired.
Preventing Health Issues
Eating healthy can prevent health issues like obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. It’s important to maintain a balanced diet for good health.
Remember, your health is your wealth!
Also check:
- Speech on Importance of Healthy Food
250 Words Essay on Importance of Healthy Food
The primacy of healthy food.
Healthy food plays a pivotal role in maintaining the overall well-being of individuals. It is a critical component that fuels the body, enabling it to function optimally. Consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can significantly improve physical health, mental well-being, and longevity.
Nutrition and Physical Health
A diet abundant in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains provides the body with necessary vitamins and minerals. These nutrients aid in the prevention of chronic diseases such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. For instance, dietary fiber found in whole grains aids in digestion and can prevent constipation, while omega-3 fatty acids from fish help maintain cardiovascular health.
Healthy Food and Mental Well-being
The impact of healthy food extends beyond physical health to mental well-being. Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and B vitamins have been linked to improved mood and decreased rates of depression and anxiety. Eating a balanced diet helps in maintaining brain health, enhancing memory, and improving concentration.
Longevity and Quality of Life
Consuming healthy food also contributes to longevity and a higher quality of life. Nutrient-dense foods boost immunity, reducing the risk of life-threatening diseases. They also promote healthy aging by maintaining bone health and preventing age-related macular degeneration.
In conclusion, the importance of healthy food cannot be overstated. It is integral to sustaining physical health, promoting mental well-being, and enhancing the quality of life. Therefore, embracing a balanced diet should be a priority for everyone.
500 Words Essay on Importance of Healthy Food
The pivotal role of healthy food.
The importance of healthy food cannot be overstated in the context of overall well-being and longevity. It is a fundamental pillar that supports both physical and mental health, essential for maintaining optimal body function and preventing various diseases.
The primary role of food is to provide the energy and nutrients needed by our bodies. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats ensures that we receive an array of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients. These nutrients are integral to various bodily functions, from supporting the immune system to promoting healthy skin and bone health.
For instance, calcium and vitamin D are necessary for bone health, while vitamin C boosts immunity. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish and flaxseeds, are crucial for brain function and heart health. Without a balanced diet, we risk nutrient deficiencies that can lead to various health issues, such as osteoporosis, scurvy, or cardiovascular diseases.
The connection between diet and mental health is a burgeoning area of research. Studies suggest that certain nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, and antioxidants may play a role in managing and preventing mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety. A diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats, on the other hand, has been linked to poor mental health outcomes.
Moreover, food can influence our mood and cognition. Consuming a balanced diet helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, preventing mood swings and supporting sustained mental energy throughout the day.
Healthy Food and Disease Prevention
A healthy diet is a powerful tool in disease prevention. Numerous studies have linked a healthy diet, particularly one rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, with a lower risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Moreover, obesity, a major public health issue, is largely influenced by dietary choices. Consuming a diet high in processed foods and sugars can lead to weight gain and obesity, which in turn increases the risk of numerous health problems, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers.
In conclusion, the importance of healthy food extends far beyond mere sustenance. It is a cornerstone of physical health, mental well-being, and disease prevention. As we navigate through our busy lives, it is crucial to prioritize healthy eating and understand its far-reaching implications on our overall health. In the end, the food choices we make today will significantly impact our health outcomes in the future.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Food to Relish in India
- Essay on Benefits of Healthy Food
- Essay on Plant Cell
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Healthy Food Essay (100, 150 and 500 words Essay)

Healthy food is essential for humans to nourish their bodies with proper nutrients. Educating students about healthy eating is vital and essays are a great way to learn about it. Here are 100, 150, 200, and 500-word essays that educate students about the importance of healthy eating habits.
100-word Healthy Food Essay
Healthy food is necessary to sustain life. The terms health and food go hand in hand because healthy food can contribute to both mental well-being and physical well-being. From childhood, we have been told to maintain a properly balanced diet that includes all components of food in adequate proportion.
This makes sure we get all vitamins, minerals, protein, and other nutrients from our daily meals. These nutrients nourish our bodies and keep our organs from malfunctioning. Junk foods satisfy our taste buds but are quite harmful in the long run as they fill our stomachs for a short period-and have little to no nutritional value.
150-word Healthy food essay
The proverb “Health is wealth” is indeed true because, without good health, our body won’t able to perform the simplest tasks. By choosing healthy foods, we can live a longer and more fulfilling lives. We learn about a properly balanced diet in schools that conveys the idea of getting adequate nutrition each day through our food for proper bodily function, which is quite important.
A balanced diet provides us with nutrients like protein, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and more. These nutrients are necessary to sustain life and keep our organs healthy. If we consume junk foods constantly that are high in calories, sugar, salt, our organs are at a risk of malfunctioning. These foods contain the least amount of nutrition and are not good for one’s physical health. This is why eating healthy is important because healthy foods promote our physical well-being. Junk foods have become quite popular since they require lesser time to cook and are very delicious. But we cannot avoid how they harm our health. Junk foods have high amounts of fats and carbohydrates that can lead to weight gain and other chronic diseases like diabetes, high blood pressure, heart problems, and many more.
On the other hand, eating healthy foods has a plethora of benefits. These foods contribute to not only a sound body, but also a sound mind. Nutrients like antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and protein nourish our bodies and also benefit our different organs. Fruits contain a variety of vitamins and antioxidants, plus they taste amazing. Green leafy vegetables are loaded with nutrients, while beans and lentils contain good amounts of protein.Dry fruits like almonds and walnuts are a great snacking option and are rich in the nutrient Omega-3. Also drinking water regularly helps in flushing out toxins from our body.
Hence for the overall human well-being, healthy foods play a crucial role. They can control weight gain, and make us more active and alert. They also protect us against various non-chronic and chronic diseases and adds more years to our lives by making us fit and healthy.
500-word Healthy Food Essay
Healthy food is a crucial building block for our health and overall well-being. Food is necessary to sustain life, just after water. And maintaining a healthy diet that provides us with proper nutrition is even more important.Eating is dependent on nutrition. We carry out our day-to-day activities because of the nutrition our food provides us.
It is necessary to be mindful of what we put into our bodies because food can easily make your break your overall health. In today’s busy lifestyle, junk foods have taken the upper hand because of their convenience and cheap prices. They are easy to grab on the go and are heaven for the taste buds. However, consuming them regularly can seriously harm our insides. Junk foods are notorious for containing almost no nutritional value, mostly just comprising a high amount of carbohydrates and calories. Even small portions of burgers, pizzas, and fries contain a big amount of calories. Drinks like cola contain high amounts of sugar which easily surpasses our daily instructed intake of sugar. Processed and packaged foods contain preservatives that can harm our precious health. People suffering from mental health issues also develop a habit of binge eating junk foods as a coping mechanism that goes on to severely harm their physical and mental health.
Indulging in these types of foods in limited amounts every once in a while is harmless, however, they should not become a part of our daily diet. We need to understand what kinds of foods provide us with the nutrition we need daily and inculcate them into our diet. Portion control is also very important when trying to maintain or lose weight. Also, one should avoid going on crash diets that are not sustainable in the longer run. A properly balanced meal for breakfast, lunch, and dinner is important to look and feel good inside out. Eating healthy also gives us a sense of achievement that we are taking care of our bodies. Eating nutrition-dense meals and drinking eight glasses of water a day can have a very positive effect not only on our body but also on our mental health.
In our life, if our health is not in good condition, we would slowly lose everything else. Therefore listening to our body and taking good care of it is vital. At first, most people can be unsure where to start. But there are dozens of recipes and health books online that could guide you towards a better lifestyle. Start with foods that contain high amounts of protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals like meat, beans, lentils, poultry, and fermented foods. These nourish your body with necessary nutrients and keep you full for a longer amount of time. This is also beneficial to avoid mindless snacking.
Diet and exercise go hand in hand when one speaks of maintaining good health. This is why creating a proper workout routine along with eating healthy can have a significant effect on our overall health.
Related Toppics:

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
English that goes straight to the heart
Essay on Healthy Food
An essay is a piece of writing that revolves around a particular theme and contains the academic opinions of the person writing it. A basic essay mainly consists of three parts: Introduction, Body, and Conclusion.
After reading our post, “essay on Healthy Food” you will be able to understand the importance of healthy food.
Daily Test - Attempt Now

Essay on Healthy Food (400+ Words)
Our own health is the greatest wealth, as it is a healthy body that has the potential to amass great riches. On the other hand, a wealthy individual cannot easily acquire excellent health. In today’s fast-paced world, personal time is scarce, leading people to squander most of their lives pursuing materialistic wealth in an attempt to surpass others. However, in this pursuit, they often neglect their health.
The consumption of junk food and other unhealthy items is solely driven by taste, without considering the nourishment our bodies require. The demands of life leave individuals with little time to dedicate to maintaining a proper diet. Opting for a balanced diet is crucial, as it not only reduces stress but also promotes a healthy and fulfilling life.
Healthy foods play a vital role in preserving or enhancing overall well-being. A balanced diet refers to a dietary regimen that encompasses all the necessary nutrients in appropriate proportions. This includes fluids, sufficient protein, essential fatty acids, vitamins, minerals, and calories. It is imperative to consume fresh fruits, salads, green leafy vegetables, milk, eggs, yogurt, and other nutritious foods at regular intervals to ensure the maintenance of a healthy body. Please take a moment to carefully review the provided content.
It is important to have fixed meal times and eat the right amount of food. Not eating enough can make us weak, and if we consistently eat too little, it can lead to malnourishment and weaken our immune system, potentially causing illnesses like tuberculosis, asthma, or other diseases.
It is also important to make sure that children eat enough food, as they burn a lot of calories due to their active lifestyle. They also need extra protein and fats for their growth, brain, and nerve development. However, it’s crucial not to eat too much. Eating too much for a long time can lead to various diseases such as stomach, heart, or liver problems.
Only fresh, well-washed, and well-cooked food that is free from dust and flies should be eaten. Foods containing excess fat, spices, chillis , and fried foods are harmful and should be avoided. Eating roadside food is not recommended. The last meal should be taken two or three hours before bedtime, and there should be a sufficient time gap between two meals to allow for proper digestion in the stomach.
Being healthy means more than just being free from illness or injury. It encompasses physical, mental, social, intellectual, and financial well-being. Good health is a fundamental requirement for a happy life and is nature’s greatest gift. Please read the provided content attentively. Rewrite it using simpler language and rephrase the sentences.
You Asked, We Listened – Get Free Access to All Writing Lists 😍😍

10 Famous Moral Stories
Read More »

How to Write a Report?

How to Write a letter to the Editor
Daily reading comprehension test - attempt now, discover more from english luv.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 06 December 2017
Healthy food choices are happy food choices: Evidence from a real life sample using smartphone based assessments
- Deborah R. Wahl 1 na1 ,
- Karoline Villinger 1 na1 ,
- Laura M. König ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3655-8842 1 ,
- Katrin Ziesemer 1 ,
- Harald T. Schupp 1 &
- Britta Renner 1
Scientific Reports volume 7 , Article number: 17069 ( 2017 ) Cite this article
133k Accesses
55 Citations
260 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Health sciences
- Human behaviour
Research suggests that “healthy” food choices such as eating fruits and vegetables have not only physical but also mental health benefits and might be a long-term investment in future well-being. This view contrasts with the belief that high-caloric foods taste better, make us happy, and alleviate a negative mood. To provide a more comprehensive assessment of food choice and well-being, we investigated in-the-moment eating happiness by assessing complete, real life dietary behaviour across eight days using smartphone-based ecological momentary assessment. Three main findings emerged: First, of 14 different main food categories, vegetables consumption contributed the largest share to eating happiness measured across eight days. Second, sweets on average provided comparable induced eating happiness to “healthy” food choices such as fruits or vegetables. Third, dinner elicited comparable eating happiness to snacking. These findings are discussed within the “food as health” and “food as well-being” perspectives on eating behaviour.
Similar content being viewed by others
Effects of single plant-based vs. animal-based meals on satiety and mood in real-world smartphone-embedded studies
Eating Style and the Frequency, Size and Timing of Eating Occasions: A cross-sectional analysis using 7-day weighed dietary records
Interindividual variability in appetitive sensations and relationships between appetitive sensations and energy intake
Introduction.
When it comes to eating, researchers, the media, and policy makers mainly focus on negative aspects of eating behaviour, like restricting certain foods, counting calories, and dieting. Likewise, health intervention efforts, including primary prevention campaigns, typically encourage consumers to trade off the expected enjoyment of hedonic and comfort foods against health benefits 1 . However, research has shown that diets and restrained eating are often counterproductive and may even enhance the risk of long-term weight gain and eating disorders 2 , 3 . A promising new perspective entails a shift from food as pure nourishment towards a more positive and well-being centred perspective of human eating behaviour 1 , 4 , 5 . In this context, Block et al . 4 have advocated a paradigm shift from “food as health” to “food as well-being” (p. 848).
Supporting this perspective of “food as well-being”, recent research suggests that “healthy” food choices, such as eating more fruits and vegetables, have not only physical but also mental health benefits 6 , 7 and might be a long-term investment in future well-being 8 . For example, in a nationally representative panel survey of over 12,000 adults from Australia, Mujcic and Oswald 8 showed that fruit and vegetable consumption predicted increases in happiness, life satisfaction, and well-being over two years. Similarly, using lagged analyses, White and colleagues 9 showed that fruit and vegetable consumption predicted improvements in positive affect on the subsequent day but not vice versa. Also, cross-sectional evidence reported by Blanchflower et al . 10 shows that eating fruits and vegetables is positively associated with well-being after adjusting for demographic variables including age, sex, or race 11 . Of note, previous research includes a wide range of time lags between actual eating occasion and well-being assessment, ranging from 24 hours 9 , 12 to 14 days 6 , to 24 months 8 . Thus, the findings support the notion that fruit and vegetable consumption has beneficial effects on different indicators of well-being, such as happiness or general life satisfaction, across a broad range of time spans.
The contention that healthy food choices such as a higher fruit and vegetable consumption is associated with greater happiness and well-being clearly contrasts with the common belief that in particular high-fat, high-sugar, or high-caloric foods taste better and make us happy while we are eating them. When it comes to eating, people usually have a spontaneous “unhealthy = tasty” association 13 and assume that chocolate is a better mood booster than an apple. According to this in-the-moment well-being perspective, consumers have to trade off the expected enjoyment of eating against the health costs of eating unhealthy foods 1 , 4 .
A wealth of research shows that the experience of negative emotions and stress leads to increased consumption in a substantial number of individuals (“emotional eating”) of unhealthy food (“comfort food”) 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 . However, this research stream focuses on emotional eating to “smooth” unpleasant experiences in response to stress or negative mood states, and the mood-boosting effect of eating is typically not assessed 18 . One of the few studies testing the effectiveness of comfort food in improving mood showed that the consumption of “unhealthy” comfort food had a mood boosting effect after a negative mood induction but not to a greater extent than non-comfort or neutral food 19 . Hence, even though people may believe that snacking on “unhealthy” foods like ice cream or chocolate provides greater pleasure and psychological benefits, the consumption of “unhealthy” foods might not actually be more psychologically beneficial than other foods.
However, both streams of research have either focused on a single food category (fruit and vegetable consumption), a single type of meal (snacking), or a single eating occasion (after negative/neutral mood induction). Accordingly, it is unknown whether the boosting effect of eating is specific to certain types of food choices and categories or whether eating has a more general boosting effect that is observable after the consumption of both “healthy” and “unhealthy” foods and across eating occasions. Accordingly, in the present study, we investigated the psychological benefits of eating that varied by food categories and meal types by assessing complete dietary behaviour across eight days in real life.
Furthermore, previous research on the impact of eating on well-being tended to rely on retrospective assessments such as food frequency questionnaires 8 , 10 and written food diaries 9 . Such retrospective self-report methods rely on the challenging task of accurately estimating average intake or remembering individual eating episodes and may lead to under-reporting food intake, particularly unhealthy food choices such as snacks 7 , 20 . To avoid memory and bias problems in the present study we used ecological momentary assessment (EMA) 21 to obtain ecologically valid and comprehensive real life data on eating behaviour and happiness as experienced in-the-moment.
In the present study, we examined the eating happiness and satisfaction experienced in-the-moment, in real time and in real life, using a smartphone based EMA approach. Specifically, healthy participants were asked to record each eating occasion, including main meals and snacks, for eight consecutive days and rate how tasty their meal/snack was, how much they enjoyed it, and how pleased they were with their meal/snack immediately after each eating episode. This intense recording of every eating episode allows assessing eating behaviour on the level of different meal types and food categories to compare experienced eating happiness across meals and categories. Following the two different research streams, we expected on a food category level that not only “unhealthy” foods like sweets would be associated with high experienced eating happiness but also “healthy” food choices such as fruits and vegetables. On a meal type level, we hypothesised that the happiness of meals differs as a function of meal type. According to previous contention, snacking in particular should be accompanied by greater happiness.
Eating episodes
Overall, during the study period, a total of 1,044 completed eating episodes were reported (see also Table 1 ). On average, participants rated their eating happiness with M = 77.59 which suggests that overall eating occasions were generally positive. However, experienced eating happiness also varied considerably between eating occasions as indicated by a range from 7.00 to 100.00 and a standard deviation of SD = 16.41.
Food categories and experienced eating happiness
All eating episodes were categorised according to their food category based on the German Nutrient Database (German: Bundeslebensmittelschlüssel), which covers the average nutritional values of approximately 10,000 foods available on the German market and is a validated standard instrument for the assessment of nutritional surveys in Germany. As shown in Table 1 , eating happiness differed significantly across all 14 food categories, F (13, 2131) = 1.78, p = 0.04. On average, experienced eating happiness varied from 71.82 ( SD = 18.65) for fish to 83.62 ( SD = 11.61) for meat substitutes. Post hoc analysis, however, did not yield significant differences in experienced eating happiness between food categories, p ≥ 0.22. Hence, on average, “unhealthy” food choices such as sweets ( M = 78.93, SD = 15.27) did not differ in experienced happiness from “healthy” food choices such as fruits ( M = 78.29, SD = 16.13) or vegetables ( M = 77.57, SD = 17.17). In addition, an intraclass correlation (ICC) of ρ = 0.22 for happiness indicated that less than a quarter of the observed variation in experienced eating happiness was due to differences between food categories, while 78% of the variation was due to differences within food categories.
However, as Figure 1 (left side) depicts, consumption frequency differed greatly across food categories. Frequently consumed food categories encompassed vegetables which were consumed at 38% of all eating occasions ( n = 400), followed by dairy products with 35% ( n = 366), and sweets with 34% ( n = 356). Conversely, rarely consumed food categories included meat substitutes, which were consumed in 2.2% of all eating occasions ( n = 23), salty extras (1.5%, n = 16), and pastries (1.3%, n = 14).
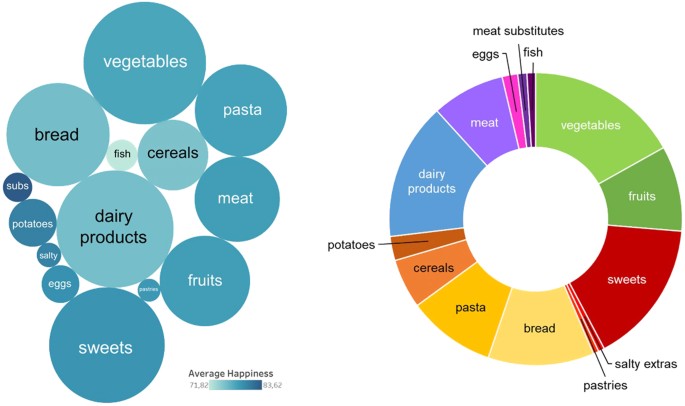
Left side: Average experienced eating happiness (colour intensity: darker colours indicate greater happiness) and consumption frequency (size of the cycle) for the 14 food categories. Right side: Absolute share of the 14 food categories in total experienced eating happiness.

Amount of experienced eating happiness by food category
To account for the frequency of consumption, we calculated and scaled the absolute experienced eating happiness according to the total sum score. As shown in Figure 1 (right side), vegetables contributed the biggest share to the total happiness followed by sweets, dairy products, and bread. Clustering food categories shows that fruits and vegetables accounted for nearly one quarter of total eating happiness score and thus, contributed to a large part of eating related happiness. Grain products such as bread, pasta, and cereals, which are main sources of carbohydrates including starch and fibre, were the second main source for eating happiness. However, “unhealthy” snacks including sweets, salty extras, and pastries represented the third biggest source of eating related happiness.
Experienced eating happiness by meal type
To further elucidate the contribution of snacks to eating happiness, analysis on the meal type level was conducted. Experienced in-the-moment eating happiness significantly varied by meal type consumed, F (4, 1039) = 11.75, p < 0.001. Frequencies of meal type consumption ranged from snacks being the most frequently logged meal type ( n = 332; see also Table 1 ) to afternoon tea being the least logged meal type ( n = 27). Figure 2 illustrates the wide dispersion within as well as between different meal types. Afternoon tea ( M = 82.41, SD = 15.26), dinner ( M = 81.47, SD = 14.73), and snacks ( M = 79.45, SD = 14.94) showed eating happiness values above the grand mean, whereas breakfast ( M = 74.28, SD = 16.35) and lunch ( M = 73.09, SD = 18.99) were below the eating happiness mean. Comparisons between meal types showed that eating happiness for snacks was significantly higher than for lunch t (533) = −4.44, p = 0.001, d = −0.38 and breakfast, t (567) = −3.78, p = 0.001, d = −0.33. However, this was also true for dinner, which induced greater eating happiness than lunch t (446) = −5.48, p < 0.001, d = −0.50 and breakfast, t (480) = −4.90, p < 0.001, d = −0.46. Finally, eating happiness for afternoon tea was greater than for lunch t (228) = −2.83, p = 0.047, d = −0.50. All other comparisons did not reach significance, t ≤ 2.49, p ≥ 0.093.
Experienced eating happiness per meal type. Small dots represent single eating events, big circles indicate average eating happiness, and the horizontal line indicates the grand mean. Boxes indicate the middle 50% (interquartile range) and median (darker/lighter shade). The whiskers above and below represent 1.5 of the interquartile range.
Control Analyses
In order to test for a potential confounding effect between experienced eating happiness, food categories, and meal type, additional control analyses within meal types were conducted. Comparing experienced eating happiness for dinner and lunch suggested that dinner did not trigger a happiness spill-over effect specific to vegetables since the foods consumed at dinner were generally associated with greater happiness than those consumed at other eating occasions (Supplementary Table S1 ). Moreover, the relative frequency of vegetables consumed at dinner (73%, n = 180 out of 245) and at lunch were comparable (69%, n = 140 out of 203), indicating that the observed happiness-vegetables link does not seem to be mainly a meal type confounding effect.
Since the present study focuses on “food effects” (Level 1) rather than “person effects” (Level 2), we analysed the data at the food item level. However, participants who were generally overall happier with their eating could have inflated the observed happiness scores for certain food categories. In order to account for person-level effects, happiness scores were person-mean centred and thereby adjusted for mean level differences in happiness. The person-mean centred happiness scores ( M cwc ) represent the difference between the individual’s average happiness score (across all single in-the-moment happiness scores per food category) and the single happiness scores of the individual within the respective food category. The centred scores indicate whether the single in-the-moment happiness score was above (indicated by positive values) or below (indicated by negative values) the individual person-mean. As Table 1 depicts, the control analyses with centred values yielded highly similar results. Vegetables were again associated on average with more happiness than other food categories (although people might differ in their general eating happiness). An additional conducted ANOVA with person-centred happiness values as dependent variables and food categories as independent variables provided also a highly similar pattern of results. Replicating the previously reported analysis, eating happiness differed significantly across all 14 food categories, F (13, 2129) = 1.94, p = 0.023, and post hoc analysis did not yield significant differences in experienced eating happiness between food categories, p ≥ 0.14. Moreover, fruits and vegetables were associated with high happiness values, and “unhealthy” food choices such as sweets did not differ in experienced happiness from “healthy” food choices such as fruits or vegetables. The only difference between the previous and control analysis was that vegetables ( M cwc = 1.16, SD = 15.14) gained slightly in importance for eating-related happiness, whereas fruits ( M cwc = −0.65, SD = 13.21), salty extras ( M cwc = −0.07, SD = 8.01), and pastries ( M cwc = −2.39, SD = 18.26) became slightly less important.
This study is the first, to our knowledge, that investigated in-the-moment experienced eating happiness in real time and real life using EMA based self-report and imagery covering the complete diversity of food intake. The present results add to and extend previous findings by suggesting that fruit and vegetable consumption has immediate beneficial psychological effects. Overall, of 14 different main food categories, vegetables consumption contributed the largest share to eating happiness measured across eight days. Thus, in addition to the investment in future well-being indicated by previous research 8 , “healthy” food choices seem to be an investment in the in-the moment well-being.
Importantly, although many cultures convey the belief that eating certain foods has a greater hedonic and mood boosting effect, the present results suggest that this might not reflect actual in-the-moment experiences accurately. Even though people often have a spontaneous “unhealthy = tasty” intuition 13 , thus indicating that a stronger happiness boosting effect of “unhealthy” food is to be expected, the induced eating happiness of sweets did not differ on average from “healthy” food choices such as fruits or vegetables. This was also true for other stereotypically “unhealthy” foods such as pastries and salty extras, which did not show the expected greater boosting effect on happiness. Moreover, analyses on the meal type level support this notion, since snacks, despite their overall positive effect, were not the most psychologically beneficial meal type, i.e., dinner had a comparable “happiness” signature to snacking. Taken together, “healthy choices” seem to be also “happy choices” and at least comparable to or even higher in their hedonic value as compared to stereotypical “unhealthy” food choices.
In general, eating happiness was high, which concurs with previous research from field studies with generally healthy participants. De Castro, Bellisle, and Dalix 22 examined weekly food diaries from 54 French subjects and found that most of the meals were rated as appealing. Also, the observed differences in average eating happiness for the 14 different food categories, albeit statistically significant, were comparable small. One could argue that this simply indicates that participants avoided selecting bad food 22 . Alternatively, this might suggest that the type of food or food categories are less decisive for experienced eating happiness than often assumed. This relates to recent findings in the field of comfort and emotional eating. Many people believe that specific types of food have greater comforting value. Also in research, the foods eaten as response to negative emotional strain, are typically characterised as being high-caloric because such foods are assumed to provide immediate psycho-physical benefits 18 . However, comparing different food types did not provide evidence for the notion that they differed in their provided comfort; rather, eating in general led to significant improvements in mood 19 . This is mirrored in the present findings. Comparing the eating happiness of “healthy” food choices such as fruits and vegetables to that of “unhealthy” food choices such as sweets shows remarkably similar patterns as, on average, they were associated with high eating happiness and their range of experiences ranged from very negative to very positive.
This raises the question of why the idea that we can eat indulgent food to compensate for life’s mishaps is so prevailing. In an innovative experimental study, Adriaanse, Prinsen, de Witt Huberts, de Ridder, and Evers 23 led participants believe that they overate. Those who characterised themselves as emotional eaters falsely attributed their over-consumption to negative emotions, demonstrating a “confabulation”-effect. This indicates that people might have restricted self-knowledge and that recalled eating episodes suffer from systematic recall biases 24 . Moreover, Boelsma, Brink, Stafleu, and Hendriks 25 examined postprandial subjective wellness and objective parameters (e.g., ghrelin, insulin, glucose) after standardised breakfast intakes and did not find direct correlations. This suggests that the impact of different food categories on wellness might not be directly related to biological effects but rather due to conditioning as food is often paired with other positive experienced situations (e.g., social interactions) or to placebo effects 18 . Moreover, experimental and field studies indicate that not only negative, but also positive, emotions trigger eating 15 , 26 . One may speculate that selective attention might contribute to the “myth” of comfort food 19 in that people attend to the consumption effect of “comfort” food in negative situation but neglect the effect in positive ones.
The present data also show that eating behaviour in the real world is a complex behaviour with many different aspects. People make more than 200 food decisions a day 27 which poses a great challenge for the measurement of eating behaviour. Studies often assess specific food categories such as fruit and vegetable consumption using Food Frequency Questionnaires, which has clear advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness. However, focusing on selective aspects of eating and food choices might provide only a selective part of the picture 15 , 17 , 22 . It is important to note that focusing solely on the “unhealthy” food choices such as sweets would have led to the conclusion that they have a high “indulgent” value. To be able to draw conclusions about which foods make people happy, the relation of different food categories needs to be considered. The more comprehensive view, considering the whole dietary behaviour across eating occasions, reveals that “healthy” food choices actually contributed the biggest share to the total experienced eating happiness. Thus, for a more comprehensive understanding of how eating behaviours are regulated, more complete and sensitive measures of the behaviour are necessary. Developments in mobile technologies hold great promise for feasible dietary assessment based on image-assisted methods 28 .
As fruits and vegetables evoked high in-the-moment happiness experiences, one could speculate that these cumulate and have spill-over effects on subsequent general well-being, including life satisfaction across time. Combing in-the-moment measures with longitudinal perspectives might be a promising avenue for future studies for understanding the pathways from eating certain food types to subjective well-being. In the literature different pathways are discussed, including physiological and biochemical aspects of specific food elements or nutrients 7 .
The present EMA based data also revealed that eating happiness varied greatly within the 14 food categories and meal types. As within food category variance represented more than two third of the total observed variance, happiness varied according to nutritional characteristics and meal type; however, a myriad of factors present in the natural environment can affect each and every meal. Thus, widening the “nourishment” perspective by including how much, when, where, how long, and with whom people eat might tell us more about experienced eating happiness. Again, mobile, in-the-moment assessment opens the possibility of assessing the behavioural signature of eating in real life. Moreover, individual factors such as eating motives, habitual eating styles, convenience, and social norms are likely to contribute to eating happiness variance 5 , 29 .
A key strength of this study is that it was the first to examine experienced eating happiness in non-clinical participants using EMA technology and imagery to assess food intake. Despite this strength, there are some limitations to this study that affect the interpretation of the results. In the present study, eating happiness was examined on a food based level. This neglects differences on the individual level and might be examined in future multilevel studies. Furthermore, as a main aim of this study was to assess real life eating behaviour, the “natural” observation level is the meal, the psychological/ecological unit of eating 30 , rather than food categories or nutrients. Therefore, we cannot exclude that specific food categories may have had a comparably higher impact on the experienced happiness of the whole meal. Sample size and therefore Type I and Type II error rates are of concern. Although the total number of observations was higher than in previous studies (see for example, Boushey et al . 28 for a review), the number of participants was small but comparable to previous studies in this field 20 , 31 , 32 , 33 . Small sample sizes can increase error rates because the number of persons is more decisive than the number of nested observations 34 . Specially, nested data can seriously increase Type I error rates, which is rather unlikely to be the case in the present study. Concerning Type II error rates, Aarts et al . 35 illustrated for lower ICCs that adding extra observations per participant also increases power, particularly in the lower observation range. Considering the ICC and the number of observations per participant, one could argue that the power in the present study is likely to be sufficient to render the observed null-differences meaningful. Finally, the predominately white and well-educated sample does limit the degree to which the results can be generalised to the wider community; these results warrant replication with a more representative sample.
Despite these limitations, we think that our study has implications for both theory and practice. The cumulative evidence of psychological benefits from healthy food choices might offer new perspectives for health promotion and public-policy programs 8 . Making people aware of the “healthy = happy” association supported by empirical evidence provides a distinct and novel perspective to the prevailing “unhealthy = tasty” folk intuition and could foster eating choices that increase both in-the-moment happiness and future well-being. Furthermore, the present research lends support to the advocated paradigm shift from “food as health” to “food as well-being” which entails a supporting and encouraging rather constraining and limiting view on eating behaviour.
The study conformed with the Declaration of Helsinki. All study protocols were approved by University of Konstanz’s Institutional Review Board and were conducted in accordance with guidelines and regulations. Upon arrival, all participants signed a written informed consent.
Participants
Thirty-eight participants (28 females: average age = 24.47, SD = 5.88, range = 18–48 years) from the University of Konstanz assessed their eating behaviour in close to real time and in their natural environment using an event-based ambulatory assessment method (EMA). No participant dropped out or had to be excluded. Thirty-three participants were students, with 52.6% studying psychology. As compensation, participants could choose between taking part in a lottery (4 × 25€) or receiving course credits (2 hours).
Participants were recruited through leaflets distributed at the university and postings on Facebook groups. Prior to participation, all participants gave written informed consent. Participants were invited to the laboratory for individual introductory sessions. During this first session, participants installed the application movisensXS (version 0.8.4203) on their own smartphones and downloaded the study survey (movisensXS Library v4065). In addition, they completed a short baseline questionnaire, including demographic variables like age, gender, education, and eating principles. Participants were instructed to log every eating occasion immediately before eating by using the smartphone to indicate the type of meal, take pictures of the food, and describe its main components using a free input field. Fluid intake was not assessed. Participants were asked to record their food intake on eight consecutive days. After finishing the study, participants were invited back to the laboratory for individual final interviews.
Immediately before eating participants were asked to indicate the type of meal with the following five options: breakfast, lunch, afternoon tea, dinner, snack. In Germany, “afternoon tea” is called “Kaffee & Kuchen” which directly translates as “coffee & cake”. It is similar to the idea of a traditional “afternoon tea” meal in UK. Specifically, in Germany, people have “Kaffee & Kuchen” in the afternoon (between 4–5 pm) and typically coffee (or tea) is served with some cake or cookies. Dinner in Germany is a main meal with mainly savoury food.
After each meal, participants were asked to rate their meal on three dimensions. They rated (1) how much they enjoyed the meal, (2) how pleased they were with their meal, and (3) how tasty their meal was. Ratings were given on a scale of one to 100. For reliability analysis, Cronbach’s Alpha was calculated to assess the internal consistency of the three items. Overall Cronbach’s alpha was calculated with α = 0.87. In addition, the average of the 38 Cronbach’s alpha scores calculated at the person level also yielded a satisfactory value with α = 0.83 ( SD = 0.24). Thirty-two of 38 participants showed a Cronbach’s alpha value above 0.70 (range = 0.42–0.97). An overall score of experienced happiness of eating was computed using the average of the three questions concerning the meals’ enjoyment, pleasure, and tastiness.
Analytical procedure
The food pictures and descriptions of their main components provided by the participants were subsequently coded by independent and trained raters. Following a standardised manual, additional components displayed in the picture were added to the description by the raters. All consumed foods were categorised into 14 different food categories (see Table 1 ) derived from the food classification system designed by the German Nutrition Society (DGE) and based on the existing food categories of the German Nutrient Database (Max Rubner Institut). Liquid intake and preparation method were not assessed. Therefore, fats and additional recipe ingredients were not included in further analyses, because they do not represent main elements of food intake. Further, salty extras were added to the categorisation.
No participant dropped out or had to be excluded due to high missing rates. Missing values were below 5% for all variables. The compliance rate at the meal level cannot be directly assessed since the numbers of meals and snacks can vary between as well as within persons (between days). As a rough compliance estimate, the numbers of meals that are expected from a “normative” perspective during the eight observation days can be used as a comparison standard (8 x breakfast, 8 × lunch, 8 × dinner = 24 meals). On average, the participants reported M = 6.3 breakfasts ( SD = 2.3), M = 5.3 lunches ( SD = 1.8), and M = 6.5 dinners ( SD = 2.0). In comparison to the “normative” expected 24 meals, these numbers indicate a good compliance (approx. 75%) with a tendency to miss six meals during the study period (approx. 25%). However, the “normative” expected 24 meals for the study period might be too high since participants might also have skipped meals (e.g. breakfast). Also, the present compliance rates are comparable to other studies. For example, Elliston et al . 36 recorded 3.3 meal/snack reports per day in an Australian adult sample and Casperson et al . 37 recorded 2.2 meal reports per day in a sample of adolescents. In the present study, on average, M = 3.4 ( SD = 1.35) meals or snacks were reported per day. These data indicate overall a satisfactory compliance rate and did not indicate selective reporting of certain food items.
To graphically visualise data, Tableau (version 10.1) was used and for further statistical analyses, IBM SPSS Statistics (version 24 for Windows).
Data availability
The dataset generated and analysed during the current study is available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Cornil, Y. & Chandon, P. Pleasure as an ally of healthy eating? Contrasting visceral and epicurean eating pleasure and their association with portion size preferences and wellbeing. Appetite 104 , 52–59 (2016).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Mann, T. et al . Medicare’s search for effective obesity treatments: Diets are not the answer. American Psychologist 62 , 220–233 (2007).
van Strien, T., Herman, C. P. & Verheijden, M. W. Dietary restraint and body mass change. A 3-year follow up study in a representative Dutch sample. Appetite 76 , 44–49 (2014).
Block, L. G. et al . From nutrients to nurturance: A conceptual introduction to food well-being. Journal of Public Policy & Marketing 30 , 5–13 (2011).
Article Google Scholar
Renner, B., Sproesser, G., Strohbach, S. & Schupp, H. T. Why we eat what we eat. The eating motivation survey (TEMS). Appetite 59 , 117–128 (2012).
Conner, T. S., Brookie, K. L., Carr, A. C., Mainvil, L. A. & Vissers, M. C. Let them eat fruit! The effect of fruit and vegetable consumption on psychological well-being in young adults: A randomized controlled trial. PloS one 12 , e0171206 (2017).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rooney, C., McKinley, M. C. & Woodside, J. V. The potential role of fruit and vegetables in aspects of psychological well-being: a review of the literature and future directions. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 72 , 420–432 (2013).
Mujcic, R. & Oswald, A. J. Evolution of well-being and happiness after increases in consumption of fruit and vegetables. American Journal of Public Health 106 , 1504–1510 (2016).
White, B. A., Horwath, C. C. & Conner, T. S. Many apples a day keep the blues away – Daily experiences of negative and positive affect and food consumption in young adults. British Journal of Health Psychology 18 , 782–798 (2013).
Blanchflower, D. G., Oswald, A. J. & Stewart-Brown, S. Is psychological well-being linked to the consumption of fruit and vegetables? Social Indicators Research 114 , 785–801 (2013).
Grant, N., Wardle, J. & Steptoe, A. The relationship between life satisfaction and health behavior: A Cross-cultural analysis of young adults. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine 16 , 259–268 (2009).
Conner, T. S., Brookie, K. L., Richardson, A. C. & Polak, M. A. On carrots and curiosity: Eating fruit and vegetables is associated with greater flourishing in daily life. British Journal of Health Psychology 20 , 413–427 (2015).
Raghunathan, R., Naylor, R. W. & Hoyer, W. D. The unhealthy = tasty intuition and its effects on taste inferences, enjoyment, and choice of food products. Journal of Marketing 70 , 170–184 (2006).
Evers, C., Stok, F. M. & de Ridder, D. T. Feeding your feelings: Emotion regulation strategies and emotional eating. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 36 , 792–804 (2010).
Sproesser, G., Schupp, H. T. & Renner, B. The bright side of stress-induced eating: eating more when stressed but less when pleased. Psychological Science 25 , 58–65 (2013).
Wansink, B., Cheney, M. M. & Chan, N. Exploring comfort food preferences across age and gender. Physiology & Behavior 79 , 739–747 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Taut, D., Renner, B. & Baban, A. Reappraise the situation but express your emotions: impact of emotion regulation strategies on ad libitum food intake. Frontiers in Psychology 3 , 359 (2012).
Tomiyama, J. A., Finch, L. E. & Cummings, J. R. Did that brownie do its job? Stress, eating, and the biobehavioral effects of comfort food. Emerging Trends in the Social and Behavioral Sciences: An Interdisciplinary, Searchable, and Linkable Resource (2015).
Wagner, H. S., Ahlstrom, B., Redden, J. P., Vickers, Z. & Mann, T. The myth of comfort food. Health Psychology 33 , 1552–1557 (2014).
Schüz, B., Bower, J. & Ferguson, S. G. Stimulus control and affect in dietary behaviours. An intensive longitudinal study. Appetite 87 , 310–317 (2015).
Shiffman, S. Conceptualizing analyses of ecological momentary assessment data. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 16 , S76–S87 (2014).
de Castro, J. M., Bellisle, F. & Dalix, A.-M. Palatability and intake relationships in free-living humans: measurement and characterization in the French. Physiology & Behavior 68 , 271–277 (2000).
Adriaanse, M. A., Prinsen, S., de Witt Huberts, J. C., de Ridder, D. T. & Evers, C. ‘I ate too much so I must have been sad’: Emotions as a confabulated reason for overeating. Appetite 103 , 318–323 (2016).
Robinson, E. Relationships between expected, online and remembered enjoyment for food products. Appetite 74 , 55–60 (2014).
Boelsma, E., Brink, E. J., Stafleu, A. & Hendriks, H. F. Measures of postprandial wellness after single intake of two protein–carbohydrate meals. Appetite 54 , 456–464 (2010).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Boh, B. et al . Indulgent thinking? Ecological momentary assessment of overweight and healthy-weight participants’ cognitions and emotions. Behaviour Research and Therapy 87 , 196–206 (2016).
Wansink, B. & Sobal, J. Mindless eating: The 200 daily food decisions we overlook. Environment and Behavior 39 , 106–123 (2007).
Boushey, C., Spoden, M., Zhu, F., Delp, E. & Kerr, D. New mobile methods for dietary assessment: review of image-assisted and image-based dietary assessment methods. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society , 1–12 (2016).
Stok, F. M. et al . The DONE framework: Creation, evaluation, and updating of an interdisciplinary, dynamic framework 2.0 of determinants of nutrition and eating. PLoS ONE 12 , e0171077 (2017).
Pliner, P. & Rozin, P. In Dimensions of the meal: The science, culture, business, and art of eating (ed H Meiselman) 19–46 (Aspen Publishers, 2000).
Inauen, J., Shrout, P. E., Bolger, N., Stadler, G. & Scholz, U. Mind the gap? Anintensive longitudinal study of between-person and within-person intention-behaviorrelations. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 50 , 516–522 (2016).
Zepeda, L. & Deal, D. Think before you eat: photographic food diaries asintervention tools to change dietary decision making and attitudes. InternationalJournal of Consumer Studies 32 , 692–698 (2008).
Stein, K. F. & Corte, C. M. Ecologic momentary assessment of eating‐disordered behaviors. International Journal of Eating Disorders 34 , 349–360 (2003).
Bolger, N., Stadler, G. & Laurenceau, J. P. Power analysis for intensive longitudinal studies in Handbook of research methods for studying daily life (ed . Mehl, M. R. & Conner, T. S.) 285–301 (New York: The Guilford Press, 2012).
Aarts, E., Verhage, M., Veenvliet, J. V., Dolan, C. V. & Van Der Sluis, S. A solutionto dependency: using multilevel analysis to accommodate nested data. Natureneuroscience 17 , 491–496 (2014).
Elliston, K. G., Ferguson, S. G., Schüz, N. & Schüz, B. Situational cues andmomentary food environment predict everyday eating behavior in adults withoverweight and obesity. Health Psychology 36 , 337–345 (2017).
Casperson, S. L. et al . A mobile phone food record app to digitally capture dietary intake for adolescents in afree-living environment: usability study. JMIR mHealth and uHealth 3 , e30 (2015).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research within the project SmartAct (Grant 01EL1420A, granted to B.R. & H.S.). The funding source had no involvement in the study’s design; the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; the writing of the report; or the decision to submit this article for publication. We thank Gudrun Sproesser, Helge Giese, and Angela Whale for their valuable support.
Author information
Deborah R. Wahl and Karoline Villinger contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Psychology, University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany
Deborah R. Wahl, Karoline Villinger, Laura M. König, Katrin Ziesemer, Harald T. Schupp & Britta Renner
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
B.R. & H.S. developed the study concept. All authors participated in the generation of the study design. D.W., K.V., L.K. & K.Z. conducted the study, including participant recruitment and data collection, under the supervision of B.R. & H.S.; D.W. & K.V. conducted data analyses. D.W. & K.V. prepared the first manuscript draft, and B.R. & H.S. provided critical revisions. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Deborah R. Wahl or Britta Renner .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary table s1, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Wahl, D.R., Villinger, K., König, L.M. et al. Healthy food choices are happy food choices: Evidence from a real life sample using smartphone based assessments. Sci Rep 7 , 17069 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17262-9
Download citation
Received : 05 June 2017
Accepted : 23 November 2017
Published : 06 December 2017
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17262-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Financial satisfaction, food security, and shared meals are foundations of happiness among older persons in thailand.
- Sirinya Phulkerd
- Rossarin Soottipong Gray
- Sasinee Thapsuwan
BMC Geriatrics (2023)
Enrichment and Conflict Between Work and Health Behaviors: New Scales for Assessing How Work Relates to Physical Exercise and Healthy Eating
- Sabine Sonnentag
- Maria U. Kottwitz
- Jette Völker
Occupational Health Science (2023)
The value of Bayesian predictive projection for variable selection: an example of selecting lifestyle predictors of young adult well-being
- A. Bartonicek
- S. R. Wickham
- T. S. Conner
BMC Public Health (2021)
Smartphone-Based Ecological Momentary Assessment of Well-Being: A Systematic Review and Recommendations for Future Studies
- Lianne P. de Vries
- Bart M. L. Baselmans
- Meike Bartels
Journal of Happiness Studies (2021)
Exploration of nutritional, antioxidative, antibacterial and anticancer status of Russula alatoreticula: towards valorization of a traditionally preferred unique myco-food
- Somanjana Khatua
- Surashree Sen Gupta
- Krishnendu Acharya
Journal of Food Science and Technology (2021)
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
12.4 Annotated Student Sample: "Healthy Diets from Sustainable Sources Can Save the Earth" by Lily Tran
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Analyze how writers use evidence in research writing.
- Analyze the ways a writer incorporates sources into research writing, while retaining their own voice.
- Explain the use of headings as organizational tools in research writing.
- Analyze how writers use evidence to address counterarguments when writing a research essay.
Introduction
In this argumentative research essay for a first-year composition class, student Lily Tran creates a solid, focused argument and supports it with researched evidence. Throughout the essay, she uses this evidence to support cause-and-effect and problem-solution reasoning, make strong appeals, and develop her ethos on the topic.
Living by Their Own Words
Food as change.
public domain text For the human race to have a sustainable future, massive changes in the way food is produced, processed, and distributed are necessary on a global scale. end public domain text
annotated text Purpose. Lily Tran refers to what she sees as the general purpose for writing this paper: the problem of current global practices in food production, processing, and distribution. By presenting the “problem,” she immediately prepares readers for her proposed solution. end annotated text
public domain text The required changes will affect nearly all aspects of life, including not only world hunger but also health and welfare, land use and habitats, water quality and availability, energy use and production, greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, economics, and even cultural and social values. These changes may not be popular, but they are imperative. The human race must turn to sustainable food systems that provide healthy diets with minimal environmental impact—and starting now. end public domain text
annotated text Thesis. Leading up to this clear, declarative thesis statement are key points on which Tran will expand later. In doing this, she presents some foundational evidence that connects the problem to the proposed solution. end annotated text
THE COMING FOOD CRISIS
public domain text The world population has been rising exponentially in modern history. From 1 billion in 1804, it doubled to approximately 2 billion by 1927, then doubled again to approximately 4 billion in 1974. By 2019, it had nearly doubled again, rising to 7.7 billion (“World Population by Year”). It has been projected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050 (Berners-Lee et al.). At the same time, the average life span also has been increasing. These situations have led to severe stress on the environment, particularly in the demands for food. It has been estimated, for example, that by 2050, milk production will increase 58 percent and meat production 73 percent (Chai et al.). end public domain text
annotated text Evidence. In this first supporting paragraph, Tran uses numerical evidence from several sources. This numerical data as evidence helps establish the projection of population growth. By beginning with such evidence, Tran underscores the severity of the situation. end annotated text
public domain text Theoretically, the planet can produce enough food for everyone, but human activities have endangered this capability through unsustainable practices. Currently, agriculture produces 10–23 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions. Greenhouse gases—the most common being carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor— trap heat in the atmosphere, reradiate it, and send it back to Earth again. Heat trapped in the atmosphere is a problem because it causes unnatural global warming as well as air pollution, extreme weather conditions, and respiratory diseases. end public domain text
annotated text Audience. With her audience in mind, Tran briefly explains the problem of greenhouse gases and global warming. end annotated text
public domain text It has been estimated that global greenhouse gas emissions will increase by as much as 150 percent by 2030 (Chai et al.). Transportation also has a negative effect on the environment when foods are shipped around the world. As Joseph Poore of the University of Oxford commented, “It’s essential to be mindful about everything we consume: air-transported fruit and veg can create more greenhouse gas emissions per kilogram than poultry meat, for example” (qtd. in Gray). end public domain text
annotated text Transition. By beginning this paragraph with her own transition of ideas, Tran establishes control over the organization and development of ideas. Thus, she retains her sources as supports and does not allow them to dominate her essay. end annotated text
public domain text Current practices have affected the nutritional value of foods. Concentrated animal-feeding operations, intended to increase production, have had the side effect of decreasing nutritional content in animal protein and increasing saturated fat. One study found that an intensively raised chicken in 2017 contained only one-sixth of the amount of omega-3 fatty acid, an essential nutrient, that was in a chicken in 1970. Today the majority of calories in chicken come from fat rather than protein (World Wildlife Fund). end public domain text
annotated text Example. By focusing on an example (chicken), Tran uses specific research data to develop the nuance of the argument. end annotated text
public domain text Current policies such as government subsidies that divert food to biofuels are counterproductive to the goal of achieving adequate global nutrition. Some trade policies allow “dumping” of below-cost, subsidized foods on developing countries that should instead be enabled to protect their farmers and meet their own nutritional needs (Sierra Club). Too often, agriculture’s objectives are geared toward maximizing quantities produced per acre rather than optimizing output of critical nutritional needs and protection of the environment. end public domain text
AREAS OF CONCERN
Hunger and nutrition.
annotated text Headings and Subheadings. Throughout the essay, Tran has created headings and subheadings to help organize her argument and clarify it for readers. end annotated text
public domain text More than 820 million people around the world do not have enough to eat. At the same time, about a third of all grains and almost two-thirds of all soybeans, maize, and barley crops are fed to animals (Barnard). According to the World Health Organization, 462 million adults are underweight, 47 million children under 5 years of age are underweight for their height, 14.3 million are severely underweight for their height, and 144 million are stunted (“Malnutrition”). About 45 percent of mortality among children under 5 is linked to undernutrition. These deaths occur mainly in low- and middle-income countries where, in stark contrast, the rate of childhood obesity is rising. Globally, 1.9 billion adults and 38.3 million children are overweight or obese (“Obesity”). Undernutrition and obesity can be found in the same household, largely a result of eating energy-dense foods that are high in fat and sugars. The global impact of malnutrition, which includes both undernutrition and obesity, has lasting developmental, economic, social, and medical consequences. end public domain text
public domain text In 2019, Berners-Lee et al. published the results of their quantitative analysis of global and regional food supply. They determined that significant changes are needed on four fronts: end public domain text
Food production must be sufficient, in quantity and quality, to feed the global population without unacceptable environmental impacts. Food distribution must be sufficiently efficient so that a diverse range of foods containing adequate nutrition is available to all, again without unacceptable environmental impacts. Socio-economic conditions must be sufficiently equitable so that all consumers can access the quantity and range of foods needed for a healthy diet. Consumers need to be able to make informed and rational choices so that they consume a healthy and environmentally sustainable diet (10).
annotated text Block Quote. The writer has chosen to present important evidence as a direct quotation, using the correct format for direct quotations longer than four lines. See Section Editing Focus: Integrating Sources and Quotations for more information about block quotes. end annotated text
public domain text Among their findings, they singled out, in particular, the practice of using human-edible crops to produce meat, dairy, and fish for the human table. Currently 34 percent of human-edible crops are fed to animals, a practice that reduces calorie and protein supplies. They state in their report, “If society continues on a ‘business-as-usual’ dietary trajectory, a 119% increase in edible crops grown will be required by 2050” (1). Future food production and distribution must be transformed into systems that are nutritionally adequate, environmentally sound, and economically affordable. end public domain text
Land and Water Use
public domain text Agriculture occupies 40 percent of Earth’s ice-free land mass (Barnard). While the net area used for producing food has been fairly constant since the mid-20th century, the locations have shifted significantly. Temperate regions of North America, Europe, and Russia have lost agricultural land to other uses, while in the tropics, agricultural land has expanded, mainly as a result of clearing forests and burning biomass (Willett et al.). Seventy percent of the rainforest that has been cut down is being used to graze livestock (Münter). Agricultural use of water is of critical concern both quantitatively and qualitatively. Agriculture accounts for about 70 percent of freshwater use, making it “the world’s largest water-consuming sector” (Barnard). Meat, dairy, and egg production causes water pollution, as liquid wastes flow into rivers and to the ocean (World Wildlife Fund and Knorr Foods). According to the Hertwich et al., “the impacts related to these activities are unlikely to be reduced, but rather enhanced, in a business-as-usual scenario for the future” (13). end public domain text
annotated text Statistical Data. To develop her points related to land and water use, Tran presents specific statistical data throughout this section. Notice that she has chosen only the needed words of these key points to ensure that she controls the development of the supporting point and does not overuse borrowed source material. end annotated text
annotated text Defining Terms. Aware of her audience, Tran defines monocropping , a term that may be unfamiliar. end annotated text
public domain text Earth’s resources and ability to absorb pollution are limited, and many current agricultural practices undermine these capacities. Among these unsustainable practices are monocropping [growing a single crop year after year on the same land], concentrated animal-feeding operations, and overdependence on manufactured pesticides and fertilizers (Hamilton). Such practices deplete the soil, dramatically increase energy use, reduce pollinator populations, and lead to the collapse of resource supplies. One study found that producing one gram of beef for human consumption requires 42 times more land, 2 times more water, and 4 times more nitrogen than staple crops. It also creates 3 times more greenhouse gas emissions (Chai et al.). The EAT– Lancet Commission calls for “halting expansion of new agricultural land at the expense of natural ecosystems . . . strict protections on intact ecosystems, suspending concessions for logging in protected areas, or conversion of remaining intact ecosystems, particularly peatlands and forest areas” (Willett et al. 481). The Commission also calls for land-use zoning, regulations prohibiting land clearing, and incentives for protecting natural areas, including forests. end public domain text
annotated text Synthesis. The paragraphs above and below this comment show how Tran has synthesized content from several sources to help establish and reinforce key supports of her essay . end annotated text
Greenhouse Gas and Climate Change
public domain text Climate change is heavily affected by two factors: greenhouse gas emissions and carbon sequestration. In nature, the two remain in balance; for example, most animals exhale carbon dioxide, and most plants capture carbon dioxide. Carbon is also captured, or sequestered, by soil and water, especially oceans, in what are called “sinks.” Human activities have skewed this balance over the past two centuries. The shift in land use, which exploits land, water, and fossil energy, has caused increased greenhouse-gas emissions, which in turn accelerate climate change. end public domain text
public domain text Global food systems are threatened by climate change because farmers depend on relatively stable climate systems to plan for production and harvest. Yet food production is responsible for up to 30 percent of greenhouse gas emissions (Barnard). While soil can be a highly effective means of carbon sequestration, agricultural soils have lost much of their effectiveness from overgrazing, erosion, overuse of chemical fertilizer, and excess tilling. Hamilton reports that the world’s cultivated and grazed soils have lost 50 to 70 percent of their ability to accumulate and store carbon. As a result, “billions of tons of carbon have been released into the atmosphere.” end public domain text
annotated text Direct Quotation and Paraphrase. While Tran has paraphrased some content of this source borrowing, because of the specificity and impact of the number— “billions of tons of carbon”—she has chosen to use the author’s original words. As she has done elsewhere in the essay, she has indicated these as directly borrowed words by placing them within quotation marks. See Section 12.5 for more about paraphrasing. end annotated text
public domain text While carbon sequestration has been falling, greenhouse gas emissions have been increasing as a result of the production, transport, processing, storage, waste disposal, and other life stages of food production. Agriculture alone is responsible for fully 10 to 12 percent of global emissions, and that figure is estimated to rise by up to 150 percent of current levels by 2030 (Chai et al.). Münter reports that “more greenhouse gas emissions are produced by growing livestock for meat than all the planes, trains, ships, cars, trucks, and all forms of fossil fuel-based transportation combined” (5). Additional greenhouse gases, methane and nitrous oxide, are produced by the decomposition of organic wastes. Methane has 25 times and nitrous oxide has nearly 300 times the global warming potential of carbon dioxide (Curnow). Agricultural and food production systems must be reformed to shift agriculture from greenhouse gas source to sink. end public domain text
Social and Cultural Values
public domain text As the Sierra Club has pointed out, agriculture is inherently cultural: all systems of food production have “the capacity to generate . . . economic benefits and ecological capital” as well as “a sense of meaning and connection to natural resources.” Yet this connection is more evident in some cultures and less so in others. Wealthy countries built on a consumer culture emphasize excess consumption. One result of this attitude is that in 2014, Americans discarded the equivalent of $165 billion worth of food. Much of this waste ended up rotting in landfills, comprised the single largest component of U.S. municipal solid waste, and contributed a substantial portion of U.S. methane emissions (Sierra Club). In low- and middle-income countries, food waste tends to occur in early production stages because of poor scheduling of harvests, improper handling of produce, or lack of market access (Willett et al.). The recent “America First” philosophy has encouraged prioritizing the economic welfare of one nation to the detriment of global welfare and sustainability. end public domain text
annotated text Synthesis and Response to Claims. Here, as in subsequent sections, while still relying heavily on facts and content from borrowed sources, Tran provides her synthesized understanding of the information by responding to key points. end annotated text
public domain text In response to claims that a vegetarian diet is a necessary component of sustainable food production and consumption, Lusk and Norwood determined the importance of meat in a consumer’s diet. Their study indicated that meat is the most valuable food category to consumers, and “humans derive great pleasure from consuming beef, pork, and poultry” (120). Currently only 4 percent of Americans are vegetarians, and it would be difficult to convince consumers to change their eating habits. Purdy adds “there’s the issue of philosophy. A lot of vegans aren’t in the business of avoiding animal products for the sake of land sustainability. Many would prefer to just leave animal husbandry out of food altogether.” end public domain text
public domain text At the same time, consumers expect ready availability of the foods they desire, regardless of health implications or sustainability of sources. Unhealthy and unsustainable foods are heavily marketed. Out-of-season produce is imported year-round, increasing carbon emissions from air transportation. Highly processed and packaged convenience foods are nutritionally inferior and waste both energy and packaging materials. Serving sizes are larger than necessary, contributing to overconsumption and obesity. Snack food vending machines are ubiquitous in schools and public buildings. What is needed is a widespread attitude shift toward reducing waste, choosing local fruits and vegetables that are in season, and paying attention to how foods are grown and transported. end public domain text
annotated text Thesis Restated. Restating her thesis, Tran ends this section by advocating for a change in attitude to bring about sustainability. end annotated text
DISSENTING OPINIONS
annotated text Counterclaims . Tran uses equally strong research to present the counterargument. Presenting both sides by addressing objections is important in constructing a clear, well-reasoned argument. Writers should use as much rigor in finding research-based evidence to counter the opposition as they do to develop their argument. end annotated text
public domain text Transformation of the food production system faces resistance for a number of reasons, most of which dispute the need for plant-based diets. Historically, meat has been considered integral to athletes’ diets and thus has caused many consumers to believe meat is necessary for a healthy diet. Lynch et al. examined the impact of plant-based diets on human physical health, environmental sustainability, and exercise performance capacity. The results show “it is unlikely that plant-based diets provide advantages, but do not suffer from disadvantages, compared to omnivorous diets for strength, anaerobic, or aerobic exercise performance” (1). end public domain text
public domain text A second objection addresses the claim that land use for animal-based food production contributes to pollution and greenhouse gas emissions and is inefficient in terms of nutrient delivery. Berners-Lee et al. point out that animal nutrition from grass, pasture, and silage comes partially from land that cannot be used for other purposes, such as producing food directly edible by humans or for other ecosystem services such as biofuel production. Consequently, nutritional losses from such land use do not fully translate into losses of human-available nutrients (3). end public domain text
annotated text Paraphrase. Tran has paraphrased the information as support. Though she still cites the source, she has changed the words to her own, most likely to condense a larger amount of original text or to make it more accessible. end annotated text
public domain text While this objection may be correct, it does not address the fact that natural carbon sinks are being destroyed to increase agricultural land and, therefore, increase greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere. end public domain text
public domain text Another significant dissenting opinion is that transforming food production will place hardships on farmers and others employed in the food industry. Farmers and ranchers make a major investment in their own operations. At the same time, they support jobs in related industries, as consumers of farm machinery, customers at local businesses, and suppliers for other industries such as food processing (Schulz). Sparks reports that “livestock farmers are being unfairly ‘demonized’ by vegans and environmental advocates” and argues that while farming includes both costs and benefits, the costs receive much more attention than the benefits. end public domain text
FUTURE GENERATIONS
public domain text The EAT– Lancet Commission calls for a transformation in the global food system, implementing different core processes and feedback. This transformation will not happen unless there is “widespread, multi-sector, multilevel action to change what food is eaten, how it is produced, and its effects on the environment and health, while providing healthy diets for the global population” (Willett et al. 476). System changes will require global efforts coordinated across all levels and will require governments, the private sector, and civil society to share a common vision and goals. Scientific modeling indicates 10 billion people could indeed be fed a healthy and sustainable diet. end public domain text
annotated text Conclusion. While still using research-based sources as evidence in the concluding section, Tran finishes with her own words, restating her thesis. end annotated text
public domain text For the human race to have a sustainable future, massive changes in the way food is produced, processed, and distributed are necessary on a global scale. The required changes will affect nearly all aspects of life, including not only world hunger but also health and welfare, land use and habitats, water quality and availability, energy use and production, greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, economics, and even cultural and social values. These changes may not be popular, but they are imperative. They are also achievable. The human race must turn to sustainable food systems that provide healthy diets with minimal environmental impact, starting now. end public domain text
annotated text Sources. Note two important aspects of the sources chosen: 1) They represent a range of perspectives, and 2) They are all quite current. When exploring a contemporary topic, it is important to avoid research that is out of date. end annotated text
Works Cited
Barnard, Neal. “How Eating More Plants Can Save Lives and the Planet.” Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine , 24 Jan. 2019, www.pcrm.org/news/blog/how-eating-more-plants-can-save-lives-and-planet. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Berners-Lee, M., et al. “Current Global Food Production Is Sufficient to Meet Human Nutritional Needs in 2050 Provided There Is Radical Societal Adaptation.” Elementa: Science of the Anthropocene , vol. 6, no. 52, 2018, doi:10.1525/elementa.310. Accessed 7 Dec. 2020.
Chai, Bingli Clark, et al. “Which Diet Has the Least Environmental Impact on Our Planet? A Systematic Review of Vegan, Vegetarian and Omnivorous Diets.” Sustainability , vol. 11, no. 15, 2019, doi: underline 10.3390/su11154110 end underline . Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Curnow, Mandy. “Managing Manure to Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions.” Government of Western Australia, Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development, 2 Nov. 2020, www.agric.wa.gov.au/climate-change/managing-manure-reduce-greenhouse-gas-emissions. Accessed 9 Dec. 2020.
Gray, Richard. “Why the Vegan Diet Is Not Always Green.” BBC , 13 Feb. 2020, www.bbc.com/future/article/20200211-why-the-vegan-diet-is-not-always-green. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Hamilton, Bruce. “Food and Our Climate.” Sierra Club, 2014, www.sierraclub.org/compass/2014/10/food-and-our-climate. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Hertwich. Edgar G., et al. Assessing the Environmental Impacts of Consumption and Production. United Nations Environment Programme, 2010, www.resourcepanel.org/reports/assessing-environmental-impacts-consumption-and-production.
Lusk, Jayson L., and F. Bailey Norwood. “Some Economic Benefits and Costs of Vegetarianism.” Agricultural and Resource Economics Review , vol. 38, no. 2, 2009, pp. 109-24, doi: 10.1017/S1068280500003142. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Lynch Heidi, et al. “Plant-Based Diets: Considerations for Environmental Impact, Protein Quality, and Exercise Performance.” Nutrients, vol. 10, no. 12, 2018, doi:10.3390/nu10121841. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Münter, Leilani. “Why a Plant-Based Diet Will Save the World.” Health and the Environment. Disruptive Women in Health Care & the United States Environmental Protection Agency, 2012, archive.epa.gov/womenandgirls/web/pdf/1016healththeenvironmentebook.pdf.
Purdy, Chase. “Being Vegan Isn’t as Good for Humanity as You Think.” Quartz , 4 Aug. 2016, qz.com/749443/being-vegan-isnt-as-environmentally-friendly-as-you-think/. Accessed 7 Dec. 2020.
Schulz, Lee. “Would a Sudden Loss of the Meat and Dairy Industry, and All the Ripple Effects, Destroy the Economy?” Iowa State U Department of Economics, www.econ.iastate.edu/node/691. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Sierra Club. “Agriculture and Food.” Sierra Club, 28 Feb. 2015, www.sierraclub.org/policy/agriculture/food. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Sparks, Hannah. “Veganism Won’t Save the World from Environmental Ruin, Researchers Warn.” New York Post , 29 Nov. 2019, nypost.com/2019/11/29/veganism-wont-save-the-world-from-environmental-ruin-researchers-warn/. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
Willett, Walter, et al. “Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT– Lancet Commission on Healthy Diets from Sustainable Food Systems.” The Lancet, vol. 393, no. 10170, 2019. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31788-4. Accessed 6 Dec. 2020.
World Health Organization. “Malnutrition.” World Health Organization, 1 Apr. 2020, www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malnutrition. Accessed 8 Dec. 2020.
World Health Organization. “Obesity and Overweight.” World Health Organization, 1 Apr. 2020, www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight. Accessed 8 Dec. 2020.
World Wildlife Fund. Appetite for Destruction: Summary Report. World Wildlife Fund, 2017, www.wwf.org.uk/sites/default/files/2017-10/WWF_AppetiteForDestruction_Summary_Report_SignOff.pdf.
World Wildlife Fund and Knorr Foods. Future Fifty Foods. World Wildlife Fund, 2019, www.wwf.org.uk/sites/default/files/2019-02/Knorr_Future_50_Report_FINAL_Online.pdf.
“World Population by Year.” Worldometer , www.worldometers.info/world-population/world-population-by-year/. Accessed 8 Dec. 2020.
Discussion Questions
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/12-4-annotated-student-sample-healthy-diets-from-sustainable-sources-can-save-the-earth-by-lily-tran
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Growth & Development
- Play & Activities
- Life Skills
- Play & Learning
- Learning & Education
- Rhymes & Songs
- Preschool Locator

How To Write An Essay On Healthy Food For Classes 1, 2 & 3

Key Points To Remember: Essay On Healthy Food For Lower Primary Classes
10 lines on healthy food for kids, a paragraph about healthy food for children, short essay on importance of eating healthy food for kids, long essay on healthy food for kids, what will your child learn from this essay on healthy food.
Essay writing is a great tool for children to develop a wide range of skills. It helps them think creatively and gives them structure and vocabulary to express themselves better. This article will look at the topic of healthy food for an essay writing assignment for classes 1, 2 and 3. This topic will give children a good understanding of eating habits and help them distinguish between healthy and unhealthy foods. It also brings about awareness in kids, which will in turn help them make better choices with their diet. So writing about healthy food can be a great way to develop your child’s writing skills along with helping them become more aware. In this article, you can find a lot of points and ideas for writing an essay about healthy foods, including short and long-form essays.
Food is an essential requirement for our body, besides water, as it provides us with the necessary nutrients required to perform our daily activities and to keep us fueled. Below you will find guidelines on how to write an essay on healthy food for children.
- Set the tone for the essay by starting with an introduction paragraph. Every paragraph following it should begin with a core idea.
- Mid sentences in the paragraphs help to support the main point.
- The next paragraph can either continue the previous idea or introduce the next idea. When discussing two different topics, it is advisable to use paragraph breaks.
- For this essay, take into account the variety of foods eaten by humans.
- Avoid picking only a specific food group or type of food because a healthy balanced diet includes a variety of food and food groups.
- List out different unhealthy foods and talk about the harms of indulging in junk food.
Here are 10 lines on healthy food suitable for an essay for classes 1 and 2. It will help kids get a better understanding of the topic.
- Our bodies need healthy meals to function properly.
- Healthy food contains all of the nutrients that our bodies require, such as protein, vitamins, lipids, and carbohydrates.
- Protein in our diet aids our bodies in the restoration of damaged or dead cells.
- Carbohydrates provide us with energy to prepare for our everyday tasks.
- Vitamins protect us from ailments and improve our bones.
- Healthy food prevents us from being dull and lethargic.
- A good diet keeps us both mentally and physically fit.
- Fruits, vegetables and grains in their natural form are healthier.
- Fried and sugary foods cannot be considered healthy.
- We should avoid junk food to stay healthy.
Here is a short paragraph about healthy food. Children can use it as a guide while writing their essays.
Eating healthy food prevents the accumulation of toxins in the body, and prevents several other issues, such as boosting cholesterol levels, early onset of obesity, and heart health issues. However, most individuals nowadays, particularly mothers, are interested in eating healthy foods. There is more awareness, especially when it comes to children. Mothers are interested in trying a range of foods throughout the week to provide helpful and healthy nutrients that will assist their kids and the rest of the family to grow. Eating healthy foods keeps the mind alert and refreshed and the body energetic throughout the day.
This section will cover a short essay outlining the significance and benefits of eating healthy food for kids. It will inform kids about the short essay format on healthy food.
Everyone has the option of being healthy. The majority of people desire to live a healthy lifestyle. Healthy nutrients are essential for raising a healthy child. Eating healthy food helps us avoid health problems. Consuming nutritious food is the only way to maintain a healthy lifestyle. We can live a disease-free life by eating high-quality, nutritional food. The correct amount of nourishment is found in a healthy balanced diet.
Carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and minerals are abundant in healthy diets and are useful in providing a well-balanced diet. Organically-grown foods are better options. Healthy food is becoming increasingly important. As pollution levels rise, there is a greater risk of contracting various diseases. So eating a balanced, nutritious meal daily will help keep you healthy.
Below is an outline of an essay on healthy food for class 3.
Food gives us the energy we need to work. A healthy diet includes the right amount of nutrients to keep our bodies in good shape. To stay active, we need to eat healthy food. A healthy diet is one of the most important aspects of human health that can be seen and felt.
Benefits Of Healthy Food
Eating healthy food has numerous advantages for humans as our physical and emotional health are influenced by what we consume. We can lower our risk of contracting diseases by eating nutritious fruits and vegetables and improving our immunity. Green vegetables, for example, aid in the maintenance of strength and vigour.
Furthermore, certain healthy foods help prevent long-term ailments such as diabetes and high blood pressure. Obesity, too, is one of the most pressing issues. Obese people tend to eat a lot of junk food. Sugar, salt, fats, and other ingredients in junk food contribute to obesity. Healthy food can help you prevent all this because it is free of harmful ingredients. It may be more expensive than junk food, but it is more wholesome. As a result, if you exclusively eat nutritious foods, you will save in the long term. Besides, good health is the best investment, isn’t it?
What Are The Types Of Healthy Foods?
Grains, legumes, vegetables, fruits, milk, eggs, and meat are all healthy foods. All of them are necessary for a well-balanced diet. All of these foods are balanced in terms of their carbohydrate, protein, fat, mineral, and vitamin content. Green leafy vegetables and organic foods are also very healthy with numerous benefits. Along with eating healthy foods, it is critical to drink enough water to assist in proper digestion.
What Are Junk Or Unhealthy Foods?
Processed food and food with large amounts of sugar are considered junk or unhealthy. Food such as burgers, pizza, and chips are considered junk. Food that contains a lot of artificial flavourings and colours is also harmful. Unhealthy food tastes nice because it contains a lot of oil and spices, but those ingredients have many ill effects. It causes a lot of ailments. Junk food is very bad for our health and makes us sluggish and inactive. If we eat such harmful foods daily, our hearts will also cease operating correctly.
Good Eating Habits
There are a few things to follow to maintain a healthy and balanced diet:
- Breakfast, lunch, and dinner are the three main meals to eat regularly.
- We can consume various types of nuts and fruits if we are hungry in between meals.
- Eat moderate amounts of food to suit your body’s needs and avoid overeating to reduce the risk of obesity, and prevent a variety of disorders.
- Avoid restricting yourself from particular foods. Avoid eating foods heavy in fat, sugar, and salt.
- Because water is so important to the human body, drink plenty of it and include it in a healthy diet.
- We benefit from a variety of healthy foods providing the body with the necessary energy to engage in all kinds of activities completely.
This essay will help your child understand the importance of eating healthy. It will also help your child distinguish between healthy and junk food to make wiser food choices even in the absence of an adult or a parent. They will also be encouraged to eat more healthy food as the essay will teach them the harms of eating a lot of junk or unhealthy food.
When children compose essays, it will help them enhance their mental abilities. As they think about everything they observe and write it down on paper, your child’s observation skills improve. As the language grows, so does their thought process. When your child thinks and writes, it improves their ability to think creatively. Your child’s character and personality development will gain a positive direction.
Essay On ‘My Favourite Food’ for Classes 1, 2 & 3 Essay On My Favourite Fruit “Mango, Apple, Strawberry & Orange” for Children Essay On The Mango For Classes 1, 2 & 3 Kids
- Essays for Class 1
- Essays for Class 2
- Essays for Class 3

Low-Stimulation Shows To Keep Your Kid Busy (For When You Need A Break!)
Summer activities and books on saving water, how to help your child become an avid reader , leave a reply cancel reply.
Log in to leave a comment

Most Popular
Jellyfish salt painting, 5 shows the entire family can enjoy together, how to make a diy rainbow cork painting , recent comments.

FirstCry Intelli Education is an Early Learning brand, with products and services designed by educators with decades of experience, to equip children with skills that will help them succeed in the world of tomorrow.

The FirstCry Intellikit `Learn With Stories` kits for ages 2-6 brings home classic children`s stories, as well as fun activities, specially created by our Early Learning Educators.
For children 6 years and up, explore a world of STEAM learning, while engaging in project-based play to keep growing minds busy!

Build a love for reading through engaging book sets and get the latest in brain-boosting toys, recommended by the educators at FirstCry Intellitots.

Our Comprehensive 2-year Baby Brain Development Program brings to you doctor-approved toys for your baby`s developing brain.

Our Preschool Chain offers the best in education across India, for children ages 2 and up.
©2024 All rights reserved
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use

Welcome to the world of Intelli!
We have some FREE Activity E-books waiting for you. Fill in your details below so we can send you tailor- made activities for you and your little one.
Parent/Guardian's Name
Child's DOB
What would you like to receive other than your Free E-book? I would like information, discounts and offers on toys, books and products I want to find a FirstCry Intellitots Preschool near me I want access to resources for my child's development and/or education

Welcome to the world of intelli!
FREE guides and worksheets coming your way on whatsapp. Subscribe Below !!
THANK YOU!!!
Here are your free guides and worksheets.
- Call us Topics in English
- Privacy Policy
- terms of use
Topics in English Topics in english to learn and fluent pronunciation and writing and facilitate conversation between you and others, whether in school, work or daily life

Healthy food essay 17 models
Healthy food essay; Healthy food essay in English with all the important and useful information where everyone seeks to know more about healthy food and how to follow a diet full of healthy food and important nutrients for the body. Everyone now prefers healthy food after research has proved the health problems that the body is exposed to because of unhealthy food. Here you will find a healthy food essay in English with all the information you want to know about healthy food.
Healthy food essay
Healthy food is one of the most important factors that play a clear and tangible role in human health. This plays an important role in preserving health in general. Some nutrients represent the major role in renewing the health of the body with its various organs.
Where we observe the tendency of some nutrients for the benefit of the body as a whole by giving him the ability to keep his internal organs intact, where eating healthy food is the largest factor in the safety of internal organs that result in an inevitable body safety as a whole and thus lead to better performance in various functions of life.
There are many guidelines to follow when eating, so that a person can have a healthy and integrated diet:
Take into account the diversity of foods eaten by humans, and avoid eating one type for long periods, as healthy food contains many species and which are included in the composition elements and vitamins important to the body, such as bread of all kinds, fish and meat, water and other balanced and healthy food.
Concentrate on eating large amounts of vegetables and fruits, because of its great importance, because it contains many elements necessary for the body, in addition to eating different types of grain.
Eat meals regularly and divide them into three main meals: breakfast, lunch, dinner. In cases where people are hungry for meals, they can eat certain types of vegetables and fruits.
Take into account the balance of foods eaten, so that it works on different types and contains more than one food element, so that the body to get all the elements of the same proportions.
Eat moderate amounts of foods and meet the body’s need for them, and avoid over-ingestion, because it works on exposure to human obesity, which in turn lead to exposure to various diseases.
Avoid depriving oneself of certain types of foods. Eating foods that contain high levels of fat, sugars and salts should be alleviated.
Drink large amounts of water, and work to make it within the healthy diet, because of its great importance to the human body.
Healthy food has many benefits to humans:
providing the body with the necessary energy, which enables him to exercise all his activities to the fullest.
Build and renew body cells by eating high-protein foods.
Strengthen and build human bones by eating foods that contain calcium.
Protect your body from the risk of getting cancer, by eating foods containing antioxidants.
The growth of the body and building it correctly and sound.
Enjoy healthy weight and ideal weight, and avoid exposure to excessive aging caused by eating unhealthy foods.
Eating healthy food not only prevents the accumulation of toxins in the body, but also prevents from several other problems such as raising the level of cholesterol in the body, causing early obesity other than the health problems that occur to the heart.
But I find that most adults today are interested in healthy food, especially mothers. I find greater awareness in them, especially when it comes to children.
I find my mother is interested in a variety of food types throughout the week to get useful and healthy nutrients that help us grow as well as the rest of the family. That’s what makes me so happy.
I love healthy food because it always makes my mind active and feel fresh. This is always reflected on my body in the ease of movement, exercising and walking.
I find it great to have healthy food in our lives. I like the media and societal interest that encourages this.
Healthy food essay 150 words
The healthy food that we grow up on since childhood helps fundamentally in building a healthy body and mind. We always find that the children of many people who are interested in sports and follow a diet adapt their children to a proper diet.
This makes them happy to adapt their children and grow up in a healthy environment. It helps them a lot because of their fitness and high physical ability. Which makes their participate in any sport in the future is easy for them.
There are also many people who like to follow a proper diet without engaging in any activities. They represent many people and I am one of them.
We only care about maintaining general health and proper form. This is due to our knowledge of the harmful effects of foods saturated with fats and carbohydrates from diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. And other diseases that affect the arteries and heart.
Therefore, we prefer to prevent this by eating healthy food, and avoiding eating fast foods, whether while out for a picnic or during vacation times. We make a proper diet an essential routine in our daily life.
Healthy food essay 200 words
my name is (..). I am (..) years old. I am studying in the (..) stage. I love eating healthy food very much. It helps in physical growth and improves body functions.
I loved eating healthy food from my grandmother. I remember I didn’t like eating healthy food that had a lot of salad. My favorite food was burgers, fries and a lot of takeaway.
But that changed after seeing my grandmother’s health and a healthy diet that made her look much younger than her age. I remember that she suggested that I try this type of food for two weeks only, and if I did not feel energetic and improved, I could stop eating it. I loved doing this experiment.
After two weeks, I remember feeling very active and the pimples disappeared from my face. I felt that my stomach muscles became more prominent. I liked a lot eating healthy food from then on .
It is good to have a motivation that helps each person to improve his physical or health condition. I was motivated to get rid of excess weight in the abdominal area and get rid of face pimples.
But of course, healthy food is more important and its benefits are more important. It strengthens bones, improves the digestive system, strengthens nerves and reduces stress and anxiety. Of course, this depends on the diet that you follow from vegetables or drinks.
Therefore, I prefer choosing the appropriate diet for your desires so that it encourages you to continue without losing your enthusiasm.
Essay about healthy food
China keeps food, tries to contain food and eat enough for our body, tries to contain food all nutrients, tries to be healthy food always, tries to be healthy food always. Such as protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins and minerals. My mother does not allow us to appoint chips or soda water, and she says that these foods, you can take the image of eating fruit juice for a shot of soda0.
Paragraph about Healthy Food
my name is (..). I am (..) years old . I study in class (..). I’m still young and I need to eat healthy food as the teacher told us to build our bodies.
The nutritionist at school passed us by and told us about the importance of eating healthy food at this stage of life, its importance in building muscle mass, and strengthening bones and nerves.
She also told us about the importance of following a proper diet in our time when we are going through a dangerous virus such as (Corona).
And the importance of raising immunity in the body. And how to maintain distance between others and the importance of sterilization and stay away from germs and microbes. All this helps to avoid infection with diseases that weaken the immune system, which increases the chance of infection with the Corona virus.
I find it wonderful to know the importance of healthy food and healthy habits since childhood, because it will grow with us and become a habit once we get used to it since our childhood.
Essay on Healthy Food
I know very well the importance of healthy food. My name is(..). We are a family of 4 people. I have a sister who is 4 years younger than me. My mom and dad take great care of us.
I learned a lot about healthy eating because my dad has diabetes. Therefore, he must follow a diet so that eating food saturated with fat does not cause him to faint.
When you grow up in a family that appreciates the diet or is forced to eat it, you will find yourself learning a lot about it. I know very well that vegetables are very useful in controlling glucose levels. I also learned that there are some types that can lead to high blood sugar levels, such as potatoes.
Therefore, I also loved eating healthy food because I knew its wonderful benefits for the body and to prevent diseases, including diabetes.
Importance of Healthy Food Essay
Eating healthy food is of great importance to the body, whether for young or old people. But it has been proven that the impact of healthy food on children in their upbringing is greater than its effect on adults.
Eating healthy foods strengthens the bones. Also, many foods that contain vegetables work to nourish the entire body, and help avoid many diseases, including obesity, diabetes, blood pressure and heart problems.
Therefore, it is great to provide a healthy diet for children from the beginning in order to build healthy bodies and avoid many diseases that may affect them in the future.
Short essay on healthy food
I love very much people who follow a healthy diet in their lives, and I love families who take care of their children at an early stage.
I find that healthy food is very important because it contains the nutrients required to maintain health, and to form a good immunity that prevents malnutrition in its various forms.
Continuous and correct follow-up of diets under medical supervision helps prevent heart disease, or diabetes which is a famous disease that may affect many because of bad eating habits.
It has also been proven that people who use healthy diets are less likely to have cancer. Therefore, the diet represents good prevention and protection in various respects.
Eating Healthy Food Essay
There is no doubt that healthy eating in the 21st century has become more prevalent, specifically in the past two years (2020, 2021).
This is due to the spread of the deadly Corona disease that affected the whole world, so many people went to follow healthy diets to maintain health and prevent infection with various diseases that affect the immune system and contribute to the infection of Corona disease.
Therefore, we find that the living conditions in the world are now different from what they were before, and there is more awareness of healthy food, and knowledge of useful varieties and types that benefit the body and keep it from many diseases, especially those affecting the respiratory system, or immune deficiency.
Importance of eating healthy food essay
There is no doubt that eating foods in the form of a healthy balanced diet, rich in minerals and vitamins, along with some regular physical activity, brings a healthy and beneficial life that many people aspire to. You will find that the weight is perfect, the memory is great, the concentration is high and the immune system is in its best condition.
Therefore, it is important for every person who aspires to achieve a healthy and strong physical condition, to maintain the consumption of a large amount of water on a daily basis, and to avoid all foods that contain oils and to stay away from sweets and alcoholic beverages. In addition to the need to maintain the amount of carbohydrates, proteins and fats that enter the body on a daily basis.
Once you follow this advice, you can get a great body and strong immunity.
Benefits of healthy food essay
Healthy food for me is to eat foods that do not contain artificial products, such as chemicals that are added to vegetables to speed up their ripening or on the fruit.
I am also interested in the source of the meat that I eat, the method of raising it, and the age of the animal. It is important that it be healthy and not injected with chemicals to speed up the growth process.
Such things, when I make sure that they are not present in my food, I can then say that it is healthy, useful and sound food.
I like very much to choose the foods that I eat where the calories are equal to the requirements of my body. I care a lot about reducing carbohydrates and eating a small amount in my meals so that it is not affected in one way or another.
Healthy food essay for grade 9
Undoubtedly, I agree with the saying of a healthy mind in a healthy body, although I tend to study more and do not like exercise a lot, but I am very familiar with the importance of a healthy body, and the impact of a healthy diet.
Therefore, I follow a healthy diet, so that I can maintain my fitness and energy to help me perform my duties and the activities that I do.
All the meals I eat are healthy and useful and contain all the ingredients that my body needs. Therefore, I pay great attention to eating vegetables in abundance and drinking water whenever I can, and eating meals that contain proteins, fibers and minerals on a regular basis, and between each meal I eat fruit meals that help in burning.
I like a lot for breakfast, a piece of fat-free cheese, with a healthy salad. An hour after breakfast I like to eat pear fruit, after that I can eat any vegetables if I feel hungry until the next meal.
At lunch I eat a piece of meat without a lot of starches, only half a small piece of bread. Then I eat yogurt to help digestion and burn. After an hour, I eat a pear, and if I feel hungry, I eat a plate of salad.
After that, have dinner, a plate of cheese or an egg, or a bottle of milk with fruits. This is the last meal an hour before bed.
This is a diet that I follow with a nutritionist and it changes according to the weight and calories I burn in the day.
Healthy food essay 150 words grade 9
The dental body needs a variety of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, water, and minerals in order to grow and function in a healthy and healthy manner, avoiding many risks and staying healthy.
Therefore, proper healthy nutrition is important for everyone, in addition to exercising on a regular basis, and maintaining a healthy weight that is commensurate with the physical mass of your body.
Many diseases can affect you if you use the wrong diet for long periods, such as stomach ulcers, digestive problems and many diseases that occur as a result of weak immunity, such as colds, infections and digestive problems.
Therefore, when eating a healthy and proper diet, many diseases can be avoided as a result of raising the immune system, and the availability of many minerals and vitamins that make the body function properly and in a regular and natural manner, without any defect in the functions of the body.
Which makes you in an excellent psychological and physical condition that helps you to spend your normal life in an excellent manner without any fatigue or health problems affecting you.
Healthy food essay grade 10
There is no doubt that a healthy diet is necessary and important for those in the educational stage in grade 10, as well as for those who are older or younger.
It is useful in the early stages of life because it helps to grow, build muscle mass, improve fitness and physical ability. Therefore, eating a healthy diet is a good and useful thing, in addition to the body getting all the minerals, vitamins and fiber that the body needs.
It is also preferable to exercise for half an hour a day along with healthy food. This will help improve the overall shape, get rid of any body fat, stimulate the heart, and get rid of insomnia and stress.
Many of the benefits that we get from following a healthy diet in addition to exercising.
Eating healthy food leads to a healthy life essay
There is no doubt that eating healthy food leads to a healthy life free of pain, resulting from inflammation of the nerves, or weight gain, and other things that occur as a result of eating unhealthy foods that contain a lot of starches and sugars.
Therefore, when you follow a healthy and proper diet that is proportional to your body mass, this results in a significant improvement in physical fitness and endurance, and many symptoms from the body and nerves disappear.
Also, healthy food has a very good effect on the external and internal appearance. Where eating vegetables helps to maintain the shape of youth, and gives the skin luster and softness, and prevents from many diseases.
Eating healthy food also helps in the regular functioning of the digestive system and prevents hemorrhoids and other cancers. Therefore, eating healthy food is necessary, important and beneficial to the body, regardless of the age of the person. In addition to doing a little exercise regularly.
Healthy food essay 100 words
Healthy food is one of the important and necessary things that God created to help us grow and build our bodies in a healthy and sound manner.
Where God created every plant, herb, fruit, animal and bird, so that we can obtain from it a specific nutritional value that our body needs.
Because man has not been able to adapt and manufacture industrial products that give the same nutritional value and important elements found in healthy food, therefore, eating a lot of healthy food plays an important and continuous role in human life.
And the more technology and science develop around us, the more we know the importance of eating these foods and the extent of their impact on the body, and the amount of nutrients we need from these foods. So I follow a daily schedule with healthy food.
So we have provided information about Healthy food essay .To read more you can access the following link :
- Healthy food topic in English
- Health is better than wealth
- English essay
About admin
Related articles.

Essays On My Hobby 2 Models

Essay on old age home

Essay on farmer
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Essay on Healthy food in English
Food is what we eat to have the energy to work. Food can be of two types- healthy and unhealthy food.
Unhealthy food is junk food like burgers, pizza or chips. This food tastes good because a lot of oil and spices are in it but we get many diseases because of it. This food is harmful to our body because we get lazy and inactive. Our heart also stops working properly if we eat such unhealthy food regularly.
On the other hand, healthy food is that in which there is a high number of vitamins and minerals. Vitamins are very important to live a healthy life because it keeps our body fit. They also provide nutrients. Some of the nutrients are iron, calcium, fibre, etc. Our bodies do not get developed properly if we do not eat healthy food. Healthy food also saves us from many diseases and also helps us to heal from any injury.
Healthy food is important both for our body and mind. We must eat vegetables and fruits in a large amount because they provide all the nutrients to us. Green vegetables have iron and fruits like peaches, banana has potassium and strawberries. Oranges keep our teeth healthy. We must also drink milk daily because it has calcium which makes our bones strong.
People who eat healthy food remain fit in their old age and live longer. We must remember that health is wealth. Nature gives us healthy food. Food made at home is always healthy. For a balance of our mind and body, we need healthy food regularly.
Table of Contents
Question on healthy food
Why healthy food is important.
Healthy food is important both for our body and mind. We must eat vegetables and fruits in a large amount because they provide all the nutrients to us. Green vegetables have iron and fruits like peaches, banana has potassium and strawberries. Oranges keep our teeth healthy.
What is healthy food essay?
Healthy food which contain balanced nutrition. Balance diet and exercise are important for a healthy life.
What are 5 benefits of healthy eating?
Reduced cancer risk, Diabetes management, Better mood, Improved memory and Strong bones and teeth.
Related Posts:
- Random Compound Word Generator
- 2 Minute Speech On My Favorite Food In English
- Of Friendship Essay | Summary by Francis Bacon
- Random University Name Generator
- 1 Minute Speech on Junk Food In English
- Goblin Market Poem by Christina Rossetti Summary, Notes and Line by Line Explanation in English


Transforming food systems for sustainable healthy diets: a global imperative
Purnima menon, deanna olney.

Poor diets have wide-ranging impacts, from malnutrition to noncommunicable diseases accounting for more than 73 percent of deaths globally. On the other hand, improving diets could save lives. So, what are healthy diets, and how should we be transforming food systems to achieve them?
Healthy diets provide the nutrients needed for an active, healthy life. They include a diversity of foods — fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, whole grains, and animal-source foods, and have limited sugar, salt and fat.
While it’s clear that healthy diets are needed to prevent malnutrition and disease, for many people around the world, healthy diets are often not desirable, affordable, accessible, or available. The reasons are complex and interconnected. Through our work on diets and food environments in low- and middle-income countries, for example, we see that people are increasingly eating cheap and unhealthy ultra-processed foods as a result of changing lifestyles coupled with intensive advertising and marketing campaigns. By contrast, many nutritious foods are increasingly unaffordable and are often inaccessible for many people, especially marginalized populations.
In addition, food systems need to increasingly take climate change and environmental constraints into account. It has been estimated that food systems produce one-third of global greenhouse gas emissions and often negatively affect land quality, water use, and biodiversity. In turn, climate change and natural resource degradation harm our food supply and the nutritional content of crops.
Improving diets, and reducing their impact on the environment, therefore, are global imperatives that require us to tackle health and sustainability as two sides of the same coin. The High Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition underscores the need for a comprehensive approach that places healthy diets at the core, while embracing economic growth, social equity, and environmental sustainability.
Prioritizing diets as a critical entry point for tackling all forms of malnutrition allows us to consider the wide range of possible policies and actions to meet realistic, measurable goals for food systems transformation.
In our newly released Global Food Policy Report on “ Food Systems for Healthy Diets and Nutrition ,” we emphasize the need for sustainable healthy diets and provide evidence-based recommendations on ways to make the foods that form these diets more desirable, affordable, accessible, and available.
This holistic approach recognizes the interplay between dietary patterns, food environments, production and policies, together with broader societal and environmental factors.
Optimal dietary intake involves consuming adequate quantities from diverse food groups while avoiding overconsumption of unhealthy foods. Achieving this will require policies and actions adapted to each country context, that focus on improving supply, food environments, and demand. Further leveraging food systems to achieve nutrition and health outcomes will require linking actions around food systems to improve diets with complementary systems like health and social protection.
For example, we need solutions like behavior change communication coupled with social assistance programs that can address some of the primary barriers to sustainable healthy diets and help directly shift consumer preferences toward healthier food choices. We also need to address well-known challenges around the commercial production and marketing of ultra-processed and other unhealthy foods, as well as increasing the supply of diverse, safe, and affordable nutritious food like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and animal source foods.
Changes in food environments such as using regulations and laws to support healthy food environments are critical in this regard. Affordability is an important aspect that requires us to promote pro-poor economic growth, realigning agricultural policies to support nutrient-dense foods, and improving infrastructure and logistics to lower the relative cost of healthy foods and improve their accessibility and availability.
This agenda will require coordinating the actions of diverse stakeholders and navigating different interests. Trade-offs need to be identified and negotiated across health, economic, sustainability, and development goals.
We also need to address remaining data gaps to inform programs and policies and to measure impact. Despite substantial efforts, publicly available information on dietary intake patterns, drivers of food choice, food environments, and environmental impacts remains insufficient.
Last, but not least, we need a strong and sustained global commitment to facilitating sustainable healthy diets. Although global commitments on nutrition are strong, the strategies, financing, and accountability mechanisms required for the world to meet Sustainable Development Goal 2 on malnutrition are lagging behind. In order to get there, we need to identify successes and learn from failures.
The future of the world's most vulnerable people hinges on our ability to make significant progress in ensuring healthy diets. It's time to prioritize this agenda.

Senior Director, Food and Nutrition Policy, CGIAR and the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI)

Director of the Nutrition, Diets and Health Unit at the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI)
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added
- Search the site GO Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
7 Superfoods To Add to Your Morning Smoothie
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_37732-ChelseaRaeBourgeois-a4e243f355204324a681466b9f56040d.jpeg)
Moyo Studio / Getty Images
Smoothies are a blended combination of fresh ingredients that can serve as a nourishing snack or part of a well-balanced breakfast. The beverage offers many potential health benefits, especially with nutrient-dense ingredients like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Some of these foods are considered "superfoods," a term for natural foods that offer a very high amount of nutrients and subsequent health benefits.
The vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in your average smoothie can help improve digestion, hydration, and energy levels. Incorporating superfoods into your smoothies, like leafy greens, Greek yogurt, and chia seeds, can make your beverage even more energizing, satiating, and flavorful.
Smoothies are highly customizable, meaning you can tailor them to fit your taste preferences, nutritional needs, and health goals.
Goji Berries
nataliaspb / Getty Images
These small, red fruits offer a tangy-sweet flavor and a wide range of nutrients, making them a popular superfood. Goji berries are a good source of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support immune function, healthy skin, mood, and eyesight. They contain many bioactive compounds, including high levels of zeaxanthin and beta-carotene, which research has linked to anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and antimicrobial properties.
For instance, 5 tablespoons (tbsp) of goji berries contain 7,500 IU of vitamin A, or about 250% of the Daily Value (DV). Vitamin A is important for maintaining eye, teeth, and skin health, among other bodily functions.
You can typically buy goji berries in powdered or dried forms. They pair well with other fresh fruits, including bananas, blueberries, and strawberries. Add almond milk or yogurt to help balance out the tart taste with a touch of creaminess.
Erika Bunea / Getty Images
Hemp seeds are tiny in size but dense in nutrition. The seeds are an excellent source of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which help fight inflammation. They're also a complete protein, meaning they contain all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own.
Three tbsp of hemp seeds provide 9 grams (g) of protein, or 18% of the DV. Protein is essential for repairing and growing muscle. Plus, it makes for a satiating smoothie addition, helping you feel fuller for longer.
Hemp seeds are also a good source of fiber, supporting healthy digestion and a balanced gut microbiome (the diverse bacteria in your gastrointestinal tract). Three tablespoons of hemp seeds provide 1.2 g of fiber, or 4% of the DV. This can help boost the fiber content of your smoothie and add texture to the drink.
Leafy Greens
Johner Images / Getty Images
Leafy green vegetables, like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard , are rich in several vitamins and minerals that support many functions in the body—making them a valuable addition to a well-balanced diet.
Although each green's nutrient profile is slightly different, research has generally linked leafy greens to benefits related to eye, heart, and immune health. Plus, leafy greens are especially rich in vitamin K, which is key in optimizing bone health. Their high antioxidant content can help fight oxidative stress and reduce the risk of chronic disease.
You can blend most greens into your smoothie seamlessly for a boost of nutrients. Pair with a sweet fruit like berries, mango, or pineapple—you'll get the benefits without noticing a difference in taste.
Elizaveta Antropova / Getty Images
Almonds can be a great addition to many smoothie varieties. The tree nuts are rich in healthy fats, protein, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
One ounce (oz) of almonds (about 23 nuts) provides 6 g of protein, or 12% of the DV, and 14 g of fat, or 18% of the DV. However, most of the fats in almonds are unsaturated fats, which can help lower your LDL (bad) cholesterol and reduce your heart disease risk—especially when you eat these fats instead of saturated fats.
Almonds' protein and fat content also balance out the carbohydrates in a fruit smoothie, helping promote better blood sugar control and satiety between meals. As your body digests the carbs from the fruit and dairy ingredients, it must also digest the fat and protein from the almonds, creating more controlled changes in blood glucose levels.
Almonds have a nutty flavor and pair well with various tastes and textures. Adding whole almonds to the blender can give your smoothie a thicker texture, enhancing your smoothie experience.
Westend61 / Getty Images
Chia seeds offer multiple health benefits, making them a powerful smoothie ingredient. The seeds are small in size but incredibly nutrient-dense. They are a good source of antioxidants, fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and protein.
One ounce of chia seeds provides nearly 10 g of fiber, or 35% of the DV. Fiber helps regulate your blood sugar levels and maintain your gastrointestinal health. Chia seeds' omega-3 content can also help reduce inflammation related to chronic disease.
Chia seeds have a mild, nutty flavor that pairs well with most fruits, veggies, and proteins. Mix them into a smoothie or use them as a topping on a smoothie bowl for added nutrients and texture.
Greek Yogurt
AlexPro9500 / Getty Images
Research has linked high-protein diets to various health benefits—like weight loss, muscle growth, and improved metabolism—leading many people to look for ways to boost their protein intake . Greek yogurt is a convenient and efficient way to increase the protein content of a smoothie, as 3/4 cups of plain, low-fat Greek yogurt contains 15 g of protein, or 30% of the DV.
Greek yogurt also contains probiotics , which help support a healthy gut microbiome. Research shows that the gut plays a pivotal role in overall health, influencing disease risk, mood, and more.
You can add plain Greek yogurt to most smoothie recipes. It pairs well with almost any fruit and adds a creamy texture to the blended beverage.
Olesia Shadrina / Getty Images
Avocados are often highlighted as a superfood. They're rich in monounsaturated fatty acids, fiber , and plant sterols, which promote cardiovascular health, weight management efforts, better cognitive function, and gastrointestinal health.
For instance, one avocado contains 9 g of fiber , or 30% of the DV. It also provides 13 g of monounsaturated fatty acids.
Avocados are an excellent source of healthy fats and add a creamy texture to smoothies. However, their flavor is almost undetectable when blended with other ingredients. Avocados pair well with various flavors and textures, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and more.
Foods To Limit
All foods can be included in a well-balanced diet in moderation. However, some ingredients may detract from the positive effect that smoothies can have on your immediate and long-term health.
For example, be mindful of added sugars and artificial sweeteners . Experts recommend limiting added sugars—such as those from processed sweeteners or sweetened juices—to less than 10% of your total daily calories.
Consuming artificial sweeteners may alter the gut microbiome and cause gastrointestinal upset in some people. Natural sweeteners like honey or agave nectar still contribute to your added sugar intake but may be easier to digest.
Here are a few tips:
- Consider the serving sizes of your ingredients. Too much sugar —even from fruit—in one sitting can cause a rapid blood sugar spike.
- When possible, opt for plain yogurt with whole fruits instead of flavored yogurts. Unlike, many flavored yogurts, this combination has no added sugar and is high in fiber.
- Avoid adding flavored syrups as they are typically a high source of added sugar and offer no nutritional benefits.
How To Make a Smoothie
Making a smoothie is relatively simple, especially if you can prep your ingredients beforehand. To make a refreshing smoothie, follow these steps:
- Assemble your ingredients: First, choose a liquid base, such as milk, coconut milk, almond milk , water, or fruit juice. Then, choose a combination of fruits, vegetables, seeds, and other solid ingredients you think will go well together. The more solid ingredients you include, the thicker your smoothie will be.
- Measure your ingredients: Portion each ingredient to your desired serving size. This will help you stay aware of the nutrition profile of your smoothie.
- Choose a sweetener: If whole food ingredients aren’t sweet enough for your liking, you can add a sweetener like agave nectar, honey, pure sugar, or artificial sweeteners. Artificial sweeteners may cause gastrointestinal distress in some people, and excessive added sugars, even through natural sources, may result in elevated blood sugars.
- Blend: Add the measured ingredients to your blender and blend until smooth. Test for consistency, and then continue to blend if needed. The longer you blend, the thinner the liquid will be. You can also thicken the consistency by adding a few ice cubes.
The possibilities are endless when it comes to smoothie recipes. You can get as creative as you like. For example:
- Avocados pair well with leafy greens and strawberries to make a green smoothie with a tangy-sweet flavor.
- Goji berries can enhance most berry smoothies, especially when combined with nutrient-dense almonds or chia seeds.
- Greek yogurt can fit into most smoothie recipes.
- Chocolate protein powder and fruit can make a milkshake-like beverage.
A Quick Review
Superfoods are nutrient-dense foods that can positively affect overall health. Superfood smoothies are an excellent way to enhance your intake of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants and cover any nutrient deficiencies caused by gaps in your diet.
Incorporating superfoods like leafy greens, chia seeds, avocados, and almonds into your smoothie can support a healthy immune system, heart, digestive tract, skin, and brain, among other benefits.
There are endless combinations of smoothie ingredients; you can tailor your health-boosting beverage to your taste and texture preferences.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/HannahHarper-9f98c29c5ce447759e025349c7a94dc2.jpg)
Vidović BB, Milinčić DD, Marčetić MD, et al. Health benefits and applications of goji berries in functional food products development: A review . Antioxidants (Basel) . 2022;11(2):248. doi:10.3390/antiox11020248
U.S. Department of Agriculture: FoodData Central. Goji berries, dried .
MedlinePlus. Vitamin A .
Farinon B, Molinari R, Costantini L, Merendino N. The seed of industrial hemp ( Cannabis sativa L.): Nutritional quality and potential functionality for human health and nutrition . Nutrients . 2020;12(7):1935. doi:10.3390/nu12071935
U.S. Department of Agriculture: FoodData Central. Seeds, hemp seed, hulled .
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Daily value on the nutrition and supplement fact labels .
MedlinePlus. Protein in diet .
Barber TM, Kabisch S, Pfeiffer AFH, Weickert MO. The health benefits of dietary fibre . Nutrients . 2020;12(10):3209. doi:10.3390/nu12103209
Li N, Wu X, Zhuang W, et al. Green leafy vegetable and lutein intake and multiple health outcomes . Food Chem . 2021;360:130145. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130145
Sim M, Lewis JR, Prince RL, et al. The effects of vitamin K-rich green leafy vegetables on bone metabolism: A 4-week randomised controlled trial in middle-aged and older individuals . Bone Rep . 2020;12:100274. doi:10.1016/j.bonr.2020.100274
Hossain A, Khatun MA, Islam M, Huque R. Enhancement of antioxidant quality of green leafy vegetables upon different cooking method . Prev Nutr Food Sci . 2017;22(3):216-222. doi:10.3746/pnf.2017.22.3.216
Barreca D, Nabavi SM, Sureda A, et al. Almonds ( Prunus Dulcis Mill. D. A. Webb): A source of nutrients and health-promoting compounds . Nutrients . 2020;12(3):672. doi:10.3390/nu12030672
U.S. Department of Agriculture: FoodData Central. Nuts, almonds .
MedlinePlus. Monounsaturated fats .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diabetes meal planning .
Grancieri M, Martino HSD, Gonzalez de Mejia E. Chia Seed (Salvia hispanica L.) as a source of proteins and bioactive peptides with health benefits: A review . Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf . 2019;18(2):480-499. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12423
Pereira da Silva B, Kolba N, Stampini Duarte Martino H, Hart J, Tako E. Soluble extracts from chia seed ( Salvia hispanica L.) affect brush border membrane functionality, morphology and intestinal bacterial populations in vivo ( Gallus gallus ) . Nutrients . 2019;11(10):2457. doi:10.3390/nu11102457
Moon J, Koh G. Clinical evidence and mechanisms of high-protein diet-induced weight loss . J Obes Metab Syndr . 2020;29(3):166-173. doi:10.7570/jomes20028
U.S. Department of Agriculture: FoodData Central. Yogurt, Greek, low fat milk, plain.
Zhang YJ, Li S, Gan RY, Zhou T, Xu DP, Li HB. Impacts of gut bacteria on human health and diseases . Int J Mol Sci . 2015;16(4):7493-519. doi:10.3390/ijms16047493
Dias SS, de Souza Vergílio D, Pereira AM, et al. Probiotic Greek yogurt: effect of the addition of prebiotic fat substitutes on the physicochemical characteristics, probiotic survival, and sensory acceptance . J Dairy Res . 2021;88(1):98-104. doi:10.1017/S0022029921000121
Dreher ML, Cheng FW, Ford NA. A comprehensive review of Hass avocado clinical trials, observational studies, and biological mechanisms. Nutrients . 2021;13(12):4376. doi:10.3390/nu13124376
U.S. Department of Agriculture: FoodData Central. Avocados, raw, California .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Get the facts: Added sugars .
Hosseini A, Barlow GM, Leite G, et al. Consuming artificial sweeteners may alter the structure and function of duodenal microbial communities . iScience . 2023;26(12):108530. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.108530
Related Articles
- Share full article
Advertisement
‘Delicious, Easy, Healthy and Affordable’
Yasmin Fahr’s new recipe for one-pot chicken meatballs with greens is already proving to be a weeknight winner.

By Melissa Clark

My family and I have just returned from a weekend in rural Pennsylvania, where we spend every Memorial Day weekend hanging out with good friends, eating enormous platters of grilled meat and veggies, and enjoying the mixed choir of tree frogs and bullfrogs that populate the lake. More reliably than any calendar, that throaty, flirty chorus announces that summer is finally (if unofficially) here.
Back in Brooklyn, there’s a whole other chorale going on: bass-crazy car speakers, anxious sirens, laughter from the neighbor kids as they cover their stoops in chalk art. Hark, summer has arrived here, too!
All of this is nature’s cue to shift into a lighter and more laid-back mode of cooking. Maybe the tomatoes haven’t quite peaked yet, but the farmers’ market already boasts greens in profusion, notably the piles of rainbow chard with their red and yellow stems. I’m excited to put some to good use in Yasmin Fahr’s one-pot chicken meatballs with greens .
Her recipe is fiendishly clever. After browning the meatballs, she smothers them under a mound of greens seasoned with sliced lemons and cumin, and then covers the pot to let it steam. The greens wilt, the meatballs cook through and the lemons release their juice into the savory pan drippings. It’s a colorful, fuss-free meal to rock us into the season.
Featured Recipe
One-Pot Chicken Meatballs With Greens
View Recipe →
Another Yasmin creation I can’t wait to make this week is her garlic shrimp with crispy chickpeas , an ebullient mash-up of shrimp scampi and gambas al ajillo , liberally seasoned with smoked paprika. The chickpeas are sizzled in a hot skillet until crunchy, and then doused in wine and simmered until tender. Shrimp are folded in along with lemon and parsley for zip and freshness. Be sure to cook this with a wine you’d want to drink with your meal — it really does make a difference!
We also have a new meatless recipe from Hetty “Tofu Whisperer” Lui McKinnon: her lemongrass tofu with broccoli . This speedy dish gets its intense flavor from the chopped lemongrass used in a marinade that doubles as a pan sauce. Marinate the tofu the day before if you’re planning ahead, but the dish would also work perfectly with a 10-minute soak. Seared broccoli florets and onion slices add texture, vegetable heft and a delightfully smoky char.
Another tantalizing option — this time starring the ever charismatic duo of chicken and rice — is Kay Chun’s arroz con pollo verde . It’s a Peruvian dish made with an emerald green cilantro purée spiked with jarred aji amarillo (a hot yellow pepper paste). A can of soft, pillowy hominy stirred into the rice mix adds an earthy flavor and textural contrast.
Or maybe you’d like to dive right into the deep end of summer with a no-cook recipe. Dan Pelosi has your hot-weather remedy, a marinated antipasto salad made from your favorite salty snacks. It’s got olives, salami, provolone cheese and canned artichoke hearts, all anchored in a tangy butter bean and cherry tomato salad. Serve it with crusty bread and put it on repeat for an easygoing meal that will get you through the whole season.
To me, the perfect summer dessert has loads of warm, bubbling fruit that I can top with scoops of ice cream that melt into a lush and creamy sauce. Crisps are the Platonic ideal of this, particularly Yossy Arefi’s gorgeous, ruby-hued rhubarb crisp with its nubby brown butter topping.
And as always, you’ll want to subscribe to access all these smart recipes and scads more (to the tune of tens of thousands more). If you need any technical help, the sharp folks at [email protected] are there for you. And I’m at [email protected] if you want to say hi.
That’s all for now. See you on Wednesday.
Melissa Clark has been writing her column, A Good Appetite , for The Times’s Food section since 2007. She creates recipes for New York Times Cooking, makes videos and reports on food trends. She is the author of 45 cookbooks, and counting. More about Melissa Clark
More on Food and Dining
Keep tabs on dining trends, restaurant reviews and recipes..
Breezy and adaptable, we’ve rounded up 100 easy summer recipes that can be on the table in 30 minutes or less.
Taquería El Califa de León, in Mexico City, became the first Mexican taco stand to win a Michelin star. Since then, it has been deluged with customers and fame .
Leaner than farmed fish and far more flavorful, wild salmon is in season now. Here’s how to cook and savor it .
At some restaurants, the “family meal” tradition of serving workers before customers is getting new life as a perk, a motivator and a teaching tool.
Eating in New York City
Pete Wells, our restaurant critic, ranked his top 100 restaurants in New York City .
One family has owned Totonno’s, the beloved Coney Island pizzeria, through fire, flood and a pandemic. Now the business is up for sale .
Mads Refslund’s creative ideas at the Brooklyn restaurant ILIS can be dreamily seductive, Wells writes , even if the execution isn’t always as compelling.
A Times food editor documented the high, the low and the mid from a week’s worth of TikTok restaurant suggestions.

Why climate change is still the greatest threat to human health
Polluted air and steadily rising temperatures are linked to health effects ranging from increased heart attacks and strokes to the spread of infectious diseases and psychological trauma.
People around the world are witnessing firsthand how climate change can wreak havoc on the planet. Steadily rising average temperatures fuel increasingly intense wildfires, hurricanes, and other disasters that are now impossible to ignore. And while the world has been plunged into a deadly pandemic, scientists are sounding the alarm once more that climate change is still the greatest threat to human health in recorded history .
As recently as August—when wildfires raged in the United States, Europe, and Siberia—World Health Organization Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said in a statement that “the risks posed by climate change could dwarf those of any single disease.”
On September 5, more than 200 medical journals released an unprecedented joint editorial that urged world leaders to act. “The science is unequivocal,” they write. “A global increase of 1.5°C above the pre-industrial average and the continued loss of biodiversity risk catastrophic harm to health that will be impossible to reverse.”
Despite the acute dangers posed by COVID-19, the authors of the joint op-ed write that world governments “cannot wait for the pandemic to pass to rapidly reduce emissions.” Instead, they argue, everyone must treat climate change with the same urgency as they have COVID-19.
Here’s a look at the ways that climate change can affect your health—including some less obvious but still insidious effects—and why scientists say it’s not too late to avert catastrophe.
Air pollution
Climate change is caused by an increase of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in Earth’s atmosphere, mostly from fossil fuel emissions. But burning fossil fuels can also have direct consequences for human health. That’s because the polluted air contains small particles that can induce stroke and heart attacks by penetrating the lungs and heart and even traveling into the bloodstream. Those particles might harm the organs directly or provoke an inflammatory response from the immune system as it tries to fight them off. Estimates suggest that air pollution causes anywhere between 3.6 million and nine million premature deaths a year.
For Hungry Minds
“The numbers do vary,” says Andy Haines , professor of environmental change and public health at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and author of the recently published book Planetary Health . “But they all agree that it’s a big public health burden.”

People over the age of 65 are most susceptible to the harmful effects of air pollution, but many others are at risk too, says Kari Nadeau , director of the Sean N. Parker Center for Allergy and Asthma Research at Stanford University. People who smoke or vape are at increased risk, as are children with asthma.
Air pollution also has consequences for those with allergies. Carbon dioxide increases the acidity of the air, which then pulls more pollen out from plants. For some people, this might just mean that they face annoyingly long bouts of seasonal allergies. But for others, it could be life-threatening.
“For people who already have respiratory disease, boy is that a problem,” Nadeau says. When pollen gets into the respiratory pathway, the body creates mucus to get rid of it, which can then fill up and suffocate the lungs.
Even healthy people can have similar outcomes if pollen levels are especially intense. In 2016, in the Australian state of Victoria, a severe thunderstorm combined with high levels of pollen to induce what The Lancet has described as “the world’s largest and most catastrophic epidemic of thunderstorm asthma.” So many residents suffered asthma attacks that emergency rooms were overwhelmed—and at least 10 people died as a result.
Climate change is also causing wildfires to get worse, and wildfire smoke is especially toxic. As one recent study showed, fires can account for 25 percent of dangerous air pollution in the U.S. Nadeau explains that the smoke contains particles of everything that the fire has consumed along its path—from rubber tires to harmful chemicals. These particles are tiny and can penetrate even deeper into a person’s lungs and organs. ( Here’s how breathing wildfire smoke affects the body .)
Extreme heat
Heat waves are deadly, but researchers at first didn’t see direct links between climate change and the harmful impacts of heat waves and other extreme weather events. Haines says the evidence base has been growing. “We have now got a number of studies which has shown that we can with high confidence attribute health outcomes to climate change,” he says.

Most recently, Haines points to a study published earlier this year in Nature Climate Change that attributes more than a third of heat-related deaths to climate change. As National Geographic reported at the time , the study found that the human toll was even higher in some countries with less access to air conditioning or other factors that render people more vulnerable to heat. ( How climate change is making heat waves even deadlier .)
That’s because the human body was not designed to cope with temperatures above 98.6°F, Nadeau says. Heat can break down muscles. The body does have some ways to deal with the heat—such as sweating. “But when it’s hot outside all the time, you cannot cope with that, and your heart muscles and cells start to literally die and degrade,” she says.
If you’re exposed to extreme heat for too long and are unable to adequately release that heat, the stress can cause a cascade of problems throughout the body. The heart has to work harder to pump blood to the rest of the organs, while sweat leeches the body of necessary minerals such as sodium and potassium. The combination can result in heart attacks and strokes .
Dehydration from heat exposure can also cause serious damage to the kidneys, which rely on water to function properly. For people whose kidneys are already beginning to fail—particularly older adults—Nadeau says that extreme heat can be a death sentence. “This is happening more and more,” she says.
Studies have also drawn links between higher temperatures and preterm birth and other pregnancy complications. It’s unclear why, but Haines says that one hypothesis is that extreme heat reduces blood flow to the fetus.
Food insecurity
One of the less direct—but no less harmful—ways that climate change can affect health is by disrupting the world’s supply of food.
You May Also Like

2024 hurricane season forecasted to be record-breaking year

The U.S. plans to limit PFAS in drinking water. What does that really mean?

Here’s what extreme heat does to the body
Climate change both reduces the amount of food that’s available and makes it less nutritious. According to an Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) special report , crop yields have already begun to decline as a result of rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events. Meanwhile, studies have shown that increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can leech plants of zinc, iron, and protein—nutrients that humans need to survive.

Malnutrition is linked to a variety of illnesses, including heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. It can also increase the risk of stunting, or impaired growth , in children, which can harm cognitive function.
Climate change also imperils what we eat from the sea. Rising ocean temperatures have led many fish species to migrate toward Earth’s poles in search of cooler waters. Haines says that the resulting decline of fish stocks in subtropic regions “has big implications for nutrition,” because many of those coastal communities depend on fish for a substantial amount of the protein in their diets.
This effect is likely to be particularly harmful for Indigenous communities, says Tiff-Annie Kenny, a professor in the faculty of medicine at Laval University in Quebec who studies climate change and food security in the Canadian Arctic. It’s much more difficult for these communities to find alternative sources of protein, she says, either because it’s not there or because it’s too expensive. “So what are people going to eat instead?” she asks.
Infectious diseases
As the planet gets hotter, the geographic region where ticks and mosquitoes like to live is getting wider. These animals are well-known vectors of diseases such as the Zika virus, dengue fever, and malaria. As they cross the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Nadeau says, mosquitoes and ticks bring more opportunities for these diseases to infect greater swaths of the world.
“It used to be that they stayed in those little sectors near the Equator, but now unfortunately because of the warming of northern Europe and Canada, you can find Zika in places you wouldn’t have expected,” Nadeau says.
In addition, climate conditions such as temperature and humidity can impact the life cycle of mosquitoes. Haines says there’s particularly good evidence showing that, in some regions, climate change has altered these conditions in ways that increase the risk of mosquitos transmitting dengue .
There are also several ways in which climate change is increasing the risk of diseases that can be transmitted through water, such as cholera, typhoid fever, and parasites. Sometimes that’s fairly direct, such as when people interact with dirty floodwaters. But Haines says that drought can have indirect impacts when people, say, can’t wash their hands or are forced to drink from dodgier sources of freshwater.
Mental health
A common result of any climate-linked disaster is the toll on mental health. The distress caused by drastic environmental change is so significant that it has been given its own name— solastalgia .

Nadeau says that the effects on mental health have been apparent in her studies of emergency room visits arising from wildfires in the western U.S. People lose their homes, their jobs, and sometimes their loved ones, and that takes an immediate toll. “What’s the fastest acute issue that develops? It’s psychological,” she says. Extreme weather events such as wildfires and hurricanes cause so much stress and anxiety that they can lead to post-traumatic stress disorder and even suicide in the long run.
Another common factor is that climate change causes disproportionate harm to the world’s most vulnerable people. On September 2, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) released an analysis showing that racial and ethnic minority communities are particularly at risk . According to the report, if temperatures rise by 2°C (3.6°F), Black people are 40 percent more likely to live in areas with the highest projected increases in related deaths. Another 34 percent are more likely to live in areas with a rise in childhood asthma.
Further, the effects of climate change don’t occur in isolation. At any given time, a community might face air pollution, food insecurity, disease, and extreme heat all at once. Kenny says that’s particularly devastating in communities where the prevalence of food insecurity and poverty are already high. This situation hasn’t been adequately studied, she says, because “it’s difficult to capture these shocks that climate can bring.”
Why there’s reason for hope
In recent years, scientists and environmental activists have begun to push for more research into the myriad health effects of climate change. “One of the striking things is there’s been a real dearth of funding for climate change and health,” Haines says. “For that reason, some of the evidence we have is still fragmentary.”
Still, hope is not lost. In the Paris Agreement, countries around the world have pledged to limit global warming to below 2°C (3.6°F)—and preferably to 1.5°C (2.7°F)—by cutting their emissions. “When you reduce those emissions, you benefit health as well as the planet,” Haines says.
Meanwhile, scientists and environmental activists have put forward solutions that can help people adapt to the health effects of climate change. These include early heat warnings and dedicated cooling centers, more resilient supply chains, and freeing healthcare facilities from dependence on the electric grid.
Nadeau argues that the COVID-19 pandemic also presents an opportunity for world leaders to think bigger and more strategically. For example, the pandemic has laid bare problems with efficiency and equity that have many countries restructuring their healthcare facilities. In the process, she says, they can look for new ways to reduce waste and emissions, such as getting more hospitals using renewable energy.
“This is in our hands to do,” Nadeau says. “If we don’t do anything, that would be cataclysmic.”
Related Topics
- AIR POLLUTION
- WATER QUALITY
- NATURAL DISASTERS
- PUBLIC HEALTH
- CLIMATE CHANGE

This summer's extreme weather is a sign of things to come

This African lake may literally explode—and millions are at risk

We got rid of BPA in some products—but are the substitutes any safer?

How the additives in your vaccines rev up your immune system

Long COVID can destroy your ability to exercise. Now we know why.
- Environment
- Paid Content
- Photography
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Destination Guide
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Bobbie Thomas shares her summer must-haves — all for 50% off
- Share this —

- Watch Full Episodes
- Read With Jenna
- Inspirational
- Relationships
- TODAY Table
- Newsletters
- Start TODAY
- Shop TODAY Awards
- Citi Concert Series
- Listen All Day
Follow today
More Brands
- On The Show
- TODAY Plaza
Poppi prebiotic soda brand faces class-action lawsuit over gut health claims

All is not bright and cheery with colorful prebiotic soda brand Poppi.
A California woman has filed a class-action complaint against the brand over what she says is false advertising of its prebiotic functionality.
The lawsuit was filed in the U.S. District Court in the Northern District of California on May 29 by San Francisco resident Kristin Cobbs. The plaintiff says she purchased Poppi products on multiple occasions because they were labeled and marketed as a prebiotic soda made “For a Healthy Gut,” noting the brand’s slogan was “Be Gut Happy. Be Gut Healthy.” (The slogan could no longer be found on Poppi’s website at the time of publication.)
Cobbs says she bought sodas in March 2024 both in-store and online, noting one can of Poppi soda contains two grams of fiber. According to the filing, that’s an amount “too low to cause meaningful gut health benefits” for someone who drinks just one can.
“Accordingly, a consumer would need to drink more than four Poppi sodas in a day to realize any potential health benefits from its prebiotic fiber,” the lawsuit claims, adding one would need to drink at least that many, daily, for 21 consecutive days to even potentially see results. The document adds that “even if a consumer were to do this, Poppi’s high sugar content would offset most, if not all, of these purported gut health benefits.”
The Poppi website states that each can of its soda has, at most, five grams of sugar and contains agave inulin and apple cider vinegar , which are said to work both as a prebiotic and probiotic.
The lawsuit further cites research from 2022 that found consuming 7.5 grams of agave inulin daily for three weeks did not result in any meaningful prebiotic benefit .
The plaintiff said she “reasonably relied” on Poppi’s representations when she decided to buy the brand’s sodas, adding she would not have made the purchase if she knew “those representations were not true.” Cobbs is seeking monetary relief for herself and all others similarly situated.
Representatives for Poppi did not immediately respond to TODAY.com’s request for comment.
The brand denied the lawsuit’s claims in a statement to The Associated Press .
“We are on a mission to revolutionize soda for the next generation of soda drinkers, and we have diligently innovated to provide a tasting experience that millions of people have come to enjoy,” a representative for the brand said. “We believe the lawsuit is baseless, and we will vigorously defend against these allegations.”
What is prebiotic soda?
To understand what Cobbs’ lawsuit is claiming, it's important to understand what prebiotic soda is and what health benefits it may offer.
Natalie Rizzo, registered dietitian and nutrition editor for TODAY.com, says probiotic soda is typically seltzer water that has been enriched with inulin , a fiber that is derived from chicory root that has prebiotic properties.
“Prebiotics are a type of fiber that serve as food for probiotics (the healthy gut microorganisms),” Rizzo says. “Eating prebiotics helps probiotics thrive, which promotes gut health.”
Probiotics are a combination of live bacteria and yeast that are beneficial for gut health, which also supports the immune system and aids in digestion. Feeding probioticsa with prebiotics has been proven by scientific research to be beneficial for your health.
“Probiotics play a role in a variety of bodily functions, such as digestion, absorbing nutrients and immune function, Rizzo says, adding that they also contribute to the prevention and treatment of certain diseases, like irritable bowel disease, UTIs, cystic fibrosis and certain cancers. They even help with dental health . “For all of these reasons, maintaining a healthy and balanced gut microbiome is important.”
Is Poppi actually good for you?
While it has been proven that prebiotics are good for gut health, prebiotic sodas are another story. Experts are divided on whether or not these soft drinks are beneficial in the way they claim.
“The term prebiotic was only coined in 1995 , and the research on prebiotics is still in its infancy,” Rizzo says. “Studies show that prebiotics are beneficial for the gut, but the research uses varying doses and strains, so it’s difficult to know how much prebiotics you really need and what strains are the most beneficial.”
Rizzo notes that Poppi’s estimated two grams of prebiotics in each can may not offer significant health benefits, adding that most of the research uses at least four grams per day . “With all of that said, it’s hard to say if the prebiotics in Poppi are making a huge dent in your gut health,” she says.
While its gut health claims may be exaggerated, Poppi offers other health benefits. A 12-ounce can of Poppy contains five grams of sugar, which is lower than most popular soda brands such as Coca-Cola, whose 12-ounce can contains 10.83 grams of sugar , and Dr Pepper, which has 38 grams of sugar per 12 ounces.
If you’re a prebiotic superfan wondering what to do, though, Rizzo suggests improving your prebiotic consumption for your gut health by turning to the produce section .
“Prebiotics naturally exist in common foods such as asparagus , garlic, onion, Jerusalem artichoke, wheat, honey, banana, barley, tomato, rye, soybean, cow’s milk, peas and beans,” Rizzo says. “Your best bet is to include these foods in your diet with probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, sauerkraut and tempeh.”
The internet bubbles over
As soon as news of Cobbs’ lawsuit hit the internet, TikTok exploded like a can of soda shaken in a paint mixer. Online reactions to the news range from shock and despair to jokes, dubbing the drama “ Poppi-gate .”
“Olipop watching Poppi get sued,” wrote one user on X, showing a meme of Octavia Spencer relishing in someone else’s misfortune in the movie, “Ma.”
“I’ma use whatever settlement we get in the Poppi class action to buy more Poppi,” wrote another die-hard fan on X.
“No one talk to me, I just found out my fave ‘healthy’ soda is being sued for false marketing,” reads one TikTok video shared by @thehustle.co.
“Wait so is Poppi cancelled?” asks @shelbya28 in her TikTok video , soda in hand. “Is it actually bad for me or is it just not as healthy as they claimed?”
“I just like them ‘cause they taste good and they’re not soda,” says @aarmanijones_ in her video , remarking that she plans on continuing to drink them anyway. “You don’t wanna see me without my Poppi.”
Washington, D.C. native Joseph Lamour is a lover of food: its past, its present and the science behind it. With food, you can bring opposites together to form a truly marvelous combination, and he strives to take that sentiment to heart in all that he does.

6 things to know before serving cheese, according to experts

Sonic is selling its new fries for just $1 all month long

Costco exec responds to rumors its hot dog combo price will increase

Krispy Kreme is giving away doughnuts and deals for National Doughnut Day

A timeline of the lawsuits Panera is facing over its Charged Lemonade

What is the true history of the California roll? The sushi has a fishy origin story

Jet Tila sometimes felt ‘confused’ about his Asian identity as a kid. Food helped him embrace it
Amazon Prime members can now score free Grubhub delivery nationwide

6 food and drink companies embracing florals for spring

Taco Bell drops The Big Cheez-It Crunchwrap Supreme and Tostada

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500+ Words Essay on Healthy Food. Healthy food refers to food that contains the right amount of nutrients to keep our body fit. We need healthy food to keep ourselves fit. Furthermore, healthy food is also very delicious as opposed to popular thinking. Nowadays, kids need to eat healthy food more than ever. We must encourage good eating habits ...
500 Words Essay on Healthy Food Introduction. The importance of healthy food cannot be overstated, particularly in today's fast-paced, convenience-oriented world where processed and fast foods have become a staple in many diets. Consuming a well-balanced, nutritious diet is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing chronic ...
Healthy Food Essay 150 Words. 'Healthy food means food that is good for our physical growth and overall well-being. From an early age, we are told to eat healthy foods, ones that are rich in protein, fiber, and calcium. There are five types of healthy foods: Fruit and vegetables; starchy food; dairy products; proteins and fats.
In her essay, she mentioned five benefits of eating healthy foods - weight loss, heart health, strong bones and teeth, better mood and energy levels, and improved memory and brain health - and explained them in detail. You might also be interested in our round-up of the best medical authors of all time. 4.
100 Words Essay On Healthy Food. Healthy food is essential to maintaining a healthy and balanced lifestyle. First and foremost, healthy food is food that is nutritious and good for the body. This means that it provides the body with the vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients it needs to function properly. Healthy food can come in many forms ...
October 14, 2021 by Prasanna. Healthy Food Essay: Food is fundamental for our body for various reasons. It furnishes us with the energy required for working, playing, and doing everyday exercises. It assists us with developing, makes our bones and muscles solid, fixes harmed body cells, and lifts our insusceptibility against outer unsafe ...
Essay on Healthy Food. Food is essential for our body for a number of reasons. It gives us the energy needed for working, playing and doing day-to-day activities. It helps us to grow, makes our bones and muscles stronger, repairs damaged body cells and boosts our immunity against external harmful elements like pathogens.
Furthermore, writing about healthy food topics can raise awareness about the importance of making informed dietary decisions and promote healthier eating habits. When choosing a healthy food essay topic, consider your interests, the audience you are writing for, and the available resources for research.
500 Words Essay on Healthy Food Habits Introduction. Food, one of the essential elements of life, plays a significant role in our health, growth, and development. Healthy food habits are not just about following a diet; they are about making lifestyle changes that contribute to overall wellbeing. The Importance of Healthy Food Habits
This essay will explore the benefits of eating healthy, the impact of unhealthy eating habits, and the ways in which individuals can be persuaded to make healthier food choices. By understanding the significance of healthy eating and the potential consequences of neglecting it, we can take proactive steps to improve our overall well-being.
500+ Words Essay on Healthy Food. Before starting your daily activity, you must have food. Food is essential for our body besides water. Eating healthy food gives you the required nutrients you need to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Your daily food should have carbohydrates, proteins, water, vitamins, fat and minerals.
Essay on Healthy Food for Students and Children (1000 Words) Every Living thing needs food to survive like a tree, animals, and humans. Food gives us strength. But power is also available only when the diet has eaten is healthy. A healthy diet is essential for a healthy life. We need to pay more attention to the nutritional value of eating than ...
Healthy Food Essay - Eating healthy is a great lifestyle. Read the short essay on healthy food, available at BYJU'S. Also, the benefits of healthy food essay is available in PDF format.
250 Words Essay on Importance of Healthy Food The Primacy of Healthy Food. Healthy food plays a pivotal role in maintaining the overall well-being of individuals. It is a critical component that fuels the body, enabling it to function optimally. Consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can significantly improve physical health ...
Here are 100, 150, 200, and 500-word essays that educate students about the importance of healthy eating habits. 100-word Healthy Food Essay. Healthy food is necessary to sustain life. The terms health and food go hand in hand because healthy food can contribute to both mental well-being and physical well-being.
10 Points on Healthy Food Essay. This section will include a healthy food essay 200 words, describing the significance and benefits of feeding children nutritious foods. This healthy food essay for kids will teach children the importance of healthy foods. Here are ten lines about eating well that would work well in a class 1 or 2 essay.
Summary. Healthy eating has many benefits, such as reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. A person may also boost their mood and gain more energy by maintaining ...
Essay on Healthy Food (400+ Words) Our own health is the greatest wealth, as it is a healthy body that has the potential to amass great riches. On the other hand, a wealthy individual cannot easily acquire excellent health. In today's fast-paced world, personal time is scarce, leading people to squander most of their lives pursuing ...
Supporting this perspective of "food as well-being", recent research suggests that "healthy" food choices, such as eating more fruits and vegetables, have not only physical but also mental ...
Throughout the essay, Tran has created headings and subheadings to help organize her argument and clarify it for readers. end annotated text. ... Socio-economic conditions must be sufficiently equitable so that all consumers can access the quantity and range of foods needed for a healthy diet. Consumers need to be able to make informed and ...
Here are 10 lines on healthy food suitable for an essay for classes 1 and 2. It will help kids get a better understanding of the topic. Our bodies need healthy meals to function properly. Healthy food contains all of the nutrients that our bodies require, such as protein, vitamins, lipids, and carbohydrates.
Healthy food essay 100 words. Healthy food is one of the important and necessary things that God created to help us grow and build our bodies in a healthy and sound manner. Where God created every plant, herb, fruit, animal and bird, so that we can obtain from it a specific nutritional value that our body needs.
Essay on Healthy food in English - Food is what we eat to have the energy to work. Food can be of two types- healthy and unhealthy food. On the other hand, healthy food is that in which there is a high number of vitamins and minerals. Vitamins are very important to live a healthy life because it keeps our body fit. They also provide nutrients. Some of the nutrients are iron, calcium, fibre ...
The concept of a healthy diet is not a static definition; over the years, it has been molded to scientific knowledge. Recently, international organizations have updated their concept of a healthy diet, defining it as one that promotes all dimensions of health and individual well-being; has low environmental pressure and impact; is accessible, affordable, safe, and equitable; and is also ...
In our newly released Global Food Policy Report on " Food Systems for Healthy Diets and Nutrition ," we emphasize the need for sustainable healthy diets and provide evidence-based recommendations on ways to make the foods that form these diets more desirable, affordable, accessible, and available. This holistic approach recognizes the ...
Almonds can be a great addition to many smoothie varieties. The tree nuts are rich in healthy fats, protein, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds with antioxidant and anti ...
Melissa Clark has been writing her column, A Good Appetite, for The Times's Food section since 2007. She creates recipes for New York Times Cooking, makes videos and reports on food trends. She ...
The author of the new cookbook "Food is Love" and former "Chopped" winner is one of the many chefs amplifying Indian cuisine in the United States. Though Indian eateries only make up about ...
Air pollution is detrimental to human health. Malnutrition is linked to a variety of illnesses, including heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. It can also increase the risk of stunting, or ...
A California woman has filed a class-action complaint against the brand over what she says is false advertising of its prebiotic functionality. The lawsuit was filed in the U.S. District Court in ...