Essay on Biodiversity for Students and Children
500+ words essay on biodiversity.
Essay on Biodiversity – Biodiversity is the presence of different species of plants and animals on the earth. Moreover, it is also called biological diversity as it is related to the variety of species of flora and fauna. Biodiversity plays a major role in maintaining the balance of the earth.

Furthermore, everything depends upon the biological diversity of different plants and animals. But due to some reasons, biodiversity is decreasing day by day. If it does not stop then our earth could no longer be a place to live in. Therefore different measures help in increasing the biodiversity of the earth.

Methods to Increase Biodiversity
Building wildlife corridors- This means to build connections between wildlife spaces. In other words, many animals are incapable to cross huge barriers. Therefore they are no able to migrate the barrier and breed. So different engineering techniques can make wildlife corridors. Also, help animals to move from one place to the other.
Set up gardens- Setting up gardens in the houses is the easiest way to increase biodiversity. You can grow different types of plants and animals in the yard or even in the balcony. Further, this would help in increasing the amount of fresh air in the house.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Protected areas- protected areas like wildlife sanctuaries and zoo conserve biodiversity. For instance, they maintain the natural habitat of plants and animals. Furthermore, these places are away from any human civilization. Therefore the ecosystem is well maintained which makes it a perfect breeding ground for flora and fauna. In our country, their various wildlife sanctuaries are build that is today spread over a vast area. Moreover, these areas are the only reason some of the animal species are not getting extinct. Therefore the protected areas should increase all over the globe.
Re-wilding – Re-wilding is necessary to avert the damage that has been taking place over centuries. Furthermore, the meaning of re-wilding is introducing the endangered species in the areas where it is extinct. Over the past years, by various human activities like hunting and cutting down of trees the biodiversity is in danger. So we must take the necessary steps to conserve our wildlife and different species of plants.
Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is extremely important to maintain the ecological system. Most Noteworthy many species of plants and animals are dependent on each other.
Therefore if one of them gets extinct, the others will start getting endangered too. Moreover, it is important for humans too because our survival depends on plants and animals. For instance, the human needs food to survive which we get from plants. If the earth does not give us a favorable environment then we cannot grow any crops. As a result, it will no longer be possible for us to sustain on this planet.
Biodiversity in flora and fauna is the need of the hour. Therefore we should take various countermeasures to stop the reduction of endangering of species. Furthermore, pollution from vehicles should decrease. So that animals can get fresh air to breathe. Moreover, it will also decrease global warming which is the major cause of the extinction of the species.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Biodiversity in 500 Words for Students

- Updated on
- Dec 7, 2023

Essay on Biodiversity: Biodiversity refers to the variety of animals and plants in the world or a specific area. Even in today’s modern world where so many technological advances have taken place, we still rely on our natural environment and resources to survive, A healthy and vibrant ecosystem is not disturbed by human activities. We humans are the largest consumers of natural resources, and you know what? We are also a real threat to the natural environment? Biodiversity is not just about a variety of animal and plant species, but, also offers us water, climate, disease control, nutrition cycle, oxygen release, etc. According to one report released by the United Nations, around 10 lakh plant and animal species are on the verge of extinction. The worst thing is that this number is almost at a doubling rate.
Also Read: Essay on 5g Technology
Check out all the latest updates on all board exams 2024
Why is Biodiversity Important?
Biodiversity supports all life forms on earth. To understand the importance of biodiversity, we don’t need to think or act like a biologist. All we need is a holistic understanding.
- Biodiversity promotes resilience and stability in our ecosystem. If there is any natural disturbance in the environment, a diverse ecosystem will be able to survive and recover better.
- Fields like agriculture, forestry, and medicine completely rely on biodiversity. We get genetic resources from biodiversity, which is essential for agriculture and medicine fields.
- A healthy biodiversity environment means healthy humans. The medicinal drugs we use are derived from plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- In many parts of the world, biodiversity is an integral part of cultural identity. Indigenous tribes are connected with their natural environment and species.
- Forest areas and oceans play an important role in regulating global temperature and storing carbon dioxide.
- Our environment is constantly changing and the species around it also need to adapt to for to survive. Therefore, genetic diversity within species is also important.
- Natural activities like soil formation, nutrient cycling, water purification, etc, are all dependent on biodiversity.
Also Read: NCERT Solutions Class 9 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
What is Biodiversity Loss?
Biodiversity loss means the global extinction of various species, resulting in the loss of biological diversity. One of the main factors responsible for biodiversity loss is the conversion of natural habitats into agricultural and urban areas. Cutting down forests and using the land for commercial activities results in destroying the livelihood of all the species in the region. Other factors responsible for biodiversity loss are listed below.
- Overexploitation
- Climate change
- Global trade and transportation
- Emerging diseases
- Pollution
Also Read: Essay on Save Environment
What is Biodiversity Conservation?
Biodiversity conservation refers to the preservation of species, natural resources, and habitats from the rate of extinction. To achieve the goals of biodiversity conservation, effective management, and sustainable practices are required.
- Biodiversity conservation includes protected areas like biodiversity hotspots, national parks, and wildlife sanctuaries.
- One of the most effective ways to conserve biodiversity is rehabilitation and restoring degraded habitats is crucial.
- Promoting sustainable practices in agriculture, forestry, and other resource-dependent activities is essential for the conservation of biodiversity.
- Encouraging the participation of local and indigenous communities can be one solution to achieving the goals of biodiversity conservation. Indigenous and local knowledge can contribute to effective conservation strategies.
Also Read: Essay on Junk Food
Quotes on Biodiversity
Here are some popular quotes on biodiversity. Feel free to add them to your writing topics related to the natural environment.
- ‘Look closely at nature. Every species is a masterclass, exclusively adapted to the particular environment in which it has survived. Who are we to destroy or even diminish biodiversity?’ – E O Wilson
- ‘Biodiversity is our most valuable but least appreciated resource.’ – E O Wilson
- ‘Biodiversity is the greeted treasure we have. It’s diminishment is to be prevented at all cost.’ – Thomas Eisner
- ‘Animal protection is education to humanity.’ – Albert Schweitzer
- ‘Only beautiful animals or ugly people wear fur.’ – Unknown
- ‘Babies and animals are the mirrors of the nature.’ – Epicurus
Also Read: Essay on Globalization
Ans: Biodiversity refers to the variety of plants and animals in our natural environment or a particular region. Biodiversity supports all life forms on earth. To understand the importance of biodiversity, we don’t need to think or act like a biologist. All we need is a holistic understanding. Biodiversity promotes resilience and stability in our ecosystem. If there is any natural disturbance in the environment, a diverse ecosystem will be able to survive and recover better. Fields like agriculture, forestry, and medicine completely rely on biodiversity. We get genetic resources from biodiversity, which is essential for agriculture and medicine fields.
Ans: Biodiversity conservation refers to the preservation of species, natural resources, and habitats from the rate of extinction. To achieve the goals of biodiversity conservation, effective management, and sustainable practices are required.
Ans: Some of the popular biodiversity hotspots in India are the Himalayas, Indo-Burma, Western Ghats & Sundaland.
Related Articles
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu .
Shiva Tyagi
With an experience of over a year, I've developed a passion for writing blogs on wide range of topics. I am mostly inspired from topics related to social and environmental fields, where you come up with a positive outcome.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Advanced Cutoff
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Advanced Answer Key
- JEE Advanced Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2024
- CAT 2024 College Predictor
- TS ICET 2024 Results
- AP ICET Counselling 2024
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Result 2024
- NEET Asnwer Key 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET DU Cut off 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET DU CSAS Portal 2024
- CUET Response Sheet 2024
- CUET Result 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET PG Counselling 2024
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Biodiversity Essay
Broadly speaking, biodiversity, also known as biological diversity, refers to various types of plants and animals on Earth. The process of continuous biodiversity conservation is essential right now. A greater level of biodiversity is necessary to maintain the harmony of the natural environment. Here are a few sample essays on biodiversity.
100 Words Essay On Biodiversity
200 words essay on biodiversity, 500 words essay on biodiversity.

The term "biodiversity" is used to describe the variety of plants, animals, and other species found in an environment. All of them have a significant impact on preserving the planet's healthy ecosystem. In order to sustain the health of the ecosystem and human life, it is critical to maintain a high degree of biodiversity.
However, maintaining biodiversity is getting more challenging due to the increasing air, water, and land pollution on our planet. A number of plant and animal species have gone extinct as a result of the quick environmental changes brought on by the aforementioned causes of biodiversity loss.
By encouraging individuals to adopt more environmentally friendly behaviours and practises and to build a more peaceful and sympathetic relationship with the environment, it is possible to preserve biodiversity.
‘Bio’, which stands for life, and ‘diversity’, which means variety, make up the phrase "biodiversity." The diversity of life on Earth is referred to as biodiversity. Living species include all types of plants, animals, microorganisms, and fungus.
Benefits Of Biodiversity
Community engagement to protect biodiversity is crucial. Biodiversity has several economic advantages.
Many parts of the world benefit economically from biodiversity. The tourism and recreation industries are facilitated by biodiversity. National Parks and Natural Reserves gain a lot from it.
The best locations for ecotourism, photography, art, cinematography, and literary works are in forests, animal reserves, and sanctuaries.
Biodiversity is essential for maintaining the gaseous composition of the atmosphere, breaking down waste, and removing contaminants.
Biodiversity helps in improving soil quality.
Types Of Biodiversity
Genetic Biodiversity | Genetic diversity refers to the variance in genes and genotypes within a species, such as how each individual human differs from the others in appearance.
Species Biodiversity | The variety of species found in a habitat or an area is known as species diversity. It is the diversity of life that is seen in a community. Ecosystem Biodiversity | The diversity of plant and animal species that coexist and are linked by food webs and food chains is referred to as ecological biodiversity.
The biological diversity of many plants and animals is essential to everything. However, biodiversity is declining daily for a number of causes. Our planet could no longer be a place to live if it doesn't stop. Thus, several strategies help in boosting the earth's biodiversity. The three main threats to biodiversity today are habitat loss, hunting, and poaching. At an alarming rate, humans are destroying forests, grasslands, reefs and other natural areas.
Hundreds of species that live in these habitats are therefore vanishing every year. Due to population decline caused by illegal hunting and poaching, several species are put under even more stress.
Importance Of Biodiversity
Maintaining biodiversity is crucial for the health of the ecological system. Many species of plants and animals are dependent on each other. As a result, if one becomes extinct, the others will begin to become vulnerable. Additionally, as both plants and animals are necessary for human existence, it is crucial for us as well. For instance, in order to exist, humans require food, which we obtain from plants. We cannot produce any crops if the soil does not provide a conducive climate. As a result, we won't be able to live sustainably on this planet.
Biodiversity in both flora and fauna is essential today. Therefore, to prevent the decrease in species in danger, we need to implement a number of interventions. Furthermore, vehicle pollution should decrease. So that both humans and animals can get fresh air to breathe. Moreover, it will also decrease global warming which is the major cause of the extinction of the species.
How To Preserve Biodiversity
The basic goal of biodiversity conservation is to protect life on earth, all species, the ecosystem, and a healthy environment for all time so that it will continue to be healthy for future generations. The maintenance of the food chain, the provision of a healthy habitat for many animals, including people, and the promotion of our sustainable development all depend heavily on biodiversity conservation.
Here are some ways you can preserve biodiversity:
Set Up Gardens | The simplest approach to increase biodiversity is to build gardens inside of homes. In the yard or even on the balcony, you may grow a variety of plants. Additionally, this would contribute to bringing in more fresh air within the house.
Plant Local Flowers, Fruits And Vegetables | Plant a variety in your backyard or a hanging garden using the native plants, fruits, and vegetables of your region. Nurseries are excellent places to learn about caring for and preserving plants.
3 R’s | Reduce your consumption, reuse what you can, recycle before throwing away.
Since humans consume the majority of biodiversity resources, it is primarily their duty to maintain and safeguard biodiversity in order to save the environment. The diversity of species, the health of the ecosystem, the state of the environment, and the continued viability of life on earth are crucial. By maintaining and safeguarding species, ecosystems, and natural resources, biodiversity conservation can be achieved for the sustainability of a healthy planet. Some rare species can be saved with the help of law enforcement.
All living species are interconnected and can be negatively impacted by one disturbance and therefore maintaining biodiversity is crucial for human survival. Inadequate biodiversity protection puts human life, as well as the lives of plants, animals, and the environment, at danger. As a result, we must make every effort to preserve our biodiversity.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in

Essay On Biodiversity [300-500 words]
Essay On Biodiversity: The earth is the only known planet having the existence of life on it. Besides, life has manifested in different forms such as animals, birds, plants, microorganisms etc. Among these broad categories, Each one has its variety. This diversity is called Biodiversity.
In other words, Biodiversity refers to the presence of different species of plants, animals, insects, and reptiles on the earth. It is one of the essential parts of the ecosystem that help in running the life cycle effortlessly.
Short Essay On Biodiversity | 250-300 Words
Introduction- Biodiversity or biological diversity refers to the presence of different species of plants and animals on the earth. A lot of reasons can be described for the biodiversity on earth such as geological positions, temperatures, climatic conditions and genetic changes etc. Biodiversity is considered a vital part of the life cycle on Earth.
Importance- There is a very thin line between biodiversity and ecology. One can not exist without the second. We can conclude that these two terms refer to the same intention. Hence, biodiversity is very important in maintaining the ecological balance as living things on the planet are interdependent.
If one species is decreased in number or eliminated from the environment, other species have to face negative effects because of that. Moreover, we humans are dependent on plants and animals. Thus our life is also dependent on biodiversity. If it damages, we will have to face the results.
✔ Essay On Pollution
✔ Essay On Global Warming

Conservation- After understanding the importance of biodiversity, it is clear that a threat to biodiversity is a threat to the existence of life on Earth. Hence, it becomes very important to protect and conserve biodiversity to protect the ecology and ourselves. We can take the following steps to conserve biodiversity.
- Setting up home gardens to grow different types of plants.
- Using organic agricultural methods to save microorganisms
- Discouraging the practice of deforestation
- Encouraging the practice of Afforestation
- Prevention of smuggling of animals and their body parts
- Prevention of smuggling of plants, trees and byproducts
- Feeding the stray animals
Conclusion- Biodiversity is not only important for us but it is extremely important for the existence of life on the planet. The present scenario is not in our favour means we are under threat of damaged biodiversity. That is why preserving biodiversity is the need of the hour.
500+ Words Essay On Biodiversity
Introduction.
Nature has created diverse forms of life such as plants, animals, insects, microorganisms etc. This diversification is known as biodiversity or biological diversity. Biodiversity is not uniformly dispersed over the planet and it is found more in the forests and locations undisturbed by humans.
Nature’s intelligence is very sophisticated to understand. It has designed everything so well that despite having no similarities living beings are interdependent to survive. Biodiversity is one of the essential parts of the ecosystem that help in running the life cycle effortlessly. That is the reason that biodiversity holds a huge significance for each organism whether it is a plant, animal or human being.
Biodiversity & Survival
Biodiversity is the most critical factor in executing the life cycle and maintaining the balance of the earth as living things are interdependent. If one life form is lowered or eliminated from the environment, other life forms have to encounter adverse effects because of that.
Moreover, we humans are dependent on plants and animals. Thus our life is also dependent on biodiversity. If it damages, we will have to face the results. Thus it can endanger the existence of life on Earth. Furthermore, there are many studies have been conducted on the effect of change on biodiversity and the outcomes were shocking.
The Threats!
There are lots of threats to biodiversity. First of all, a constant change in the climate is endangering many species. Some of them are on the ledge of extinction. Second, we humans are clearing out forests for various purposes that expells wild animals of their homes and eventually, they die of the lack of food and shelter.
Third, pollution and chemicals discharged into the water bodies cause many aquatic animals to die which also decreases the amount of biodiversity on Earth. Fourth, the smuggling of rare plants, trees, animals, their skin, their bones and other byproducts is one of the most critical threats to biodiversity.
How to Increase Biodiversity
We have lost a large amount of biodiversity in the past time and the adverse effects can be identified. Now, it is time to find a solution to increase biodiversity to restore the ecological balance. We can do it by taking various steps and initiatives. We need to eliminate the reasons responsible for the decrease in biodiversity.
Apart from that, we need to put effort to build a perfect planet to live in. We can do the following things to help biodiversity
Biodiversity & Sustainable Development
Sustainable development refers to “ the development which meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. ” But we are gradually losing our biodiversity. Then how would sustainable development be possible?
The decrease in biodiversity will lead to the scarcity of several natural resources. The conservation of biodiversity is a game changer for sustainable development. Hence, we can conclude that sustainable development is not possible without the conservation of biodiversity.
✔ Essay On Sustainable Development
✔ Essay On Climate Change
To sum it up, One of the reasons for the execution of life on the earth is biodiversity. It is important to restore biodiversity on the planet. For this to happen, humans must take control of their actions against the ecosystem. It is time to protect the earth’s flora and fauna to witness sustainable development.

What does It mean By “Biodiversity”?
Biodiversity refers to the presence of different species of plants and animals on the planet.
When is International Day for Biological Diversity celebrated?
22 May is celebrated as the international day for biological diversity.
What are the types of Biodiversity?
There are three types of biodiversity: 1. Genetic Biodiversity – Genetic diversity is the variation in genes and genotypes within a species, 2. Species Biodiversity – Species Diversity is the variety of species within a habitat or a region. 3. Ecosystem Biodiversity – Ecological biodiversity refers to the variations in the plant and animal species living together.
latest Essays
- Essay On 5G Technology In India
Essay On Chandrayaan 3 For Students
Essay on english language [short & long].
- Essay On Summer Vacation In 150 Words
Summer Season Essay for students
- Essay On Summer Vacation For Students
- Essay on Visit to a Zoo for Students
- Essay on Good Manners [Short & Long]
- Essay on Childhood Memories [With Headings]
- Essay On Mother [Short & Long]
- Essay on Village Life In English
- My Village Essay In English
- Short Essay on APJ Abdul Kalam
- Essay On Sports In 250 Words
- Essay On Water Pollution in 150 Words
- Essay on Save Environment For Future Generations
- Essay On Cleanliness in 150 Words
- Essay On Water Conservation In 200 Words
- 100 Words Essay On Friendship
- Essay On Deforestation In 250 Words

Related Posts


Essay on Biodiversity 1000+ Words
Biodiversity, short for biological diversity, is a remarkable tapestry of life that blankets our planet. It encompasses the variety of living organisms, ecosystems, and habitats that make Earth a vibrant and thriving place. In this essay, we will delve into the importance of biodiversity, the threats it faces, and why we should protect it.
The Marvelous World of Biodiversity
Imagine a world without colorful flowers, buzzing bees, towering trees, or majestic tigers. Biodiversity is what makes our world so diverse and beautiful. It includes everything from tiny microbes in the soil to the largest whales in the ocean. Earth’s rich biodiversity provides us with essential resources, from food to medicine, and enriches our lives in countless ways.
The Benefits of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is not just about pretty landscapes and exotic animals; it plays a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth. It helps maintain a stable and healthy environment. For instance, forests with diverse tree species are better at absorbing carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. Biodiversity also supports pollinators like bees and butterflies, which are essential for our food supply. The more diverse our ecosystems, the more resilient they are to threats like diseases and extreme weather.
Food and Medicine
Biodiversity is the foundation of our food system. Different plant and animal species provide us with a wide range of foods, from fruits and vegetables to grains and meats. Moreover, many of the medicines we rely on come from plants and animals. For example, the bark of the willow tree gave us aspirin, and the Madagascar periwinkle plant provides a lifesaving medicine for cancer patients. Protecting biodiversity ensures that we have a diverse and healthy diet and access to essential medicines.
Cultural and Recreational Value
Biodiversity isn’t just about science and survival; it also enriches our cultures and leisure activities. Many indigenous communities around the world have deep cultural connections to the land and its diverse species. Biodiversity inspires art, literature, and music. Imagine a world without the fascinating stories of animals like the African elephant or the enchanting songs of birds like the nightingale. Biodiversity enhances our quality of life in ways we might not even realize.
Threats to Biodiversity
Despite its immense value, biodiversity is under threat. Human activities, such as deforestation, pollution, overfishing, and habitat destruction, are driving many species to the brink of extinction. Climate change, fueled by the burning of fossil fuels, poses another significant threat. Rising temperatures can disrupt ecosystems and push species out of their habitats. These threats not only endanger the creatures themselves but also disrupt the delicate balance of our planet.
Conservation Efforts
The good news is that people around the world are working hard to protect biodiversity. Conservation organizations, scientists, and governments are implementing measures to safeguard endangered species and preserve critical habitats. National parks and wildlife reserves provide safe havens for countless plants and animals. Additionally, there are international agreements like the Convention on Biological Diversity aimed at preserving biodiversity on a global scale.
What You Can Do
You, as a young environmental advocate, can also play a crucial role in protecting biodiversity. You can start by learning more about the species and ecosystems in your area. Participate in local conservation efforts, like planting trees or cleaning up parks. Reduce your environmental footprint by conserving water, reducing waste, and using energy-efficient appliances. Spread the word about the importance of biodiversity to inspire others to take action.
Conclusion of Essay on Biodiversity
In conclusion, biodiversity is a precious gift that we must cherish and protect. It sustains life on Earth, provides us with essential resources, and enriches our cultures and enjoyment of the natural world. However, it faces serious threats from human activities and climate change. By understanding the importance of biodiversity and taking action to conserve it, we can ensure a healthier and more vibrant planet for future generations. Let us celebrate the wonders of biodiversity and work together to safeguard the incredible diversity of life on Earth.
Also Check: Simple Guide on How To Write An Essay
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Biodiversity Essay

Essay on Biodiversity
Biodiversity is a term made up of two words - Bio meaning Life, and Diversity meaning Variety. The term biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth. Plants, animals, microbes, and fungi are all examples of living species on the planet.
Types of Biodiversity
Genetic Biodiversity- Genetic diversity is the variation in genes and genotypes within a species, e.g., every human looks different from the other.
Species Biodiversity- Species Diversity is the variety of species within a habitat or a region. It is the biodiversity observed within a community.
Ecosystem Biodiversity- Ecological biodiversity refers to the variations in the plant and animal species living together and connected by food chains and food webs.
Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is an integral part of cultural identity. Human cultures co-evolve with their environment and conservation is a priority for cultural identity. Biodiversity is used for Medicinal purposes.
Many plants and animals are used for medicinal purposes, like vitamins and painkillers. It contributes to climate stability. It helps in controlling the effects of climate change and managing greenhouse gases.
Biodiversity provides more food resources. It supplies many vital ecosystems, such as creating and maintaining soil quality, controlling pests, and providing habitat for wildlife. Biodiversity has a relationship with Industry. Biological sources provide many Industrial materials including rubber, cotton, leather, food, paper, etc.
There are many economic benefits of Biodiversity. Biodiversity also helps in controlling pollution. Biodiversity helps in forming a healthy ecosystem. Biodiversity also acts as a source of recreation. Along with other factors, biodiversity helps in improving soil quality.
Long Essay on Biodiversity
There are many economic benefits of Biodiversity. Biodiversity is a source of economic wealth for many regions of the world. Biodiversity facilitates Tourism and the Recreational industry. Natural Reserves and National Parks benefit a lot from it. Forest, wildlife, biosphere reserve, sanctuaries are prime spots for ecotourism, photography, painting, filmmaking, and literary works.
Biodiversity plays a vital role in the maintenance of the gaseous composition of the atmosphere, breakdown of waste material, and removal of pollutants.
Conservation of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is very important for human existence as all life forms are interlinked with each other and one single disturbance can have multiple effects on another. If we fail to protect our biodiversity, we can endanger our plants, animals, and environment, as well as human life. Therefore, it is necessary to protect our biodiversity at all costs. Conservation of Biodiversity can be done by educating the people to adopt more environment-friendly methods and activities and develop a more harmonious and empathetic nature towards the environment. The involvement and cooperation of communities are very important. The process of continuous protection of Biodiversity is the need of the hour.
The Government of India, along with 155 other nations, has signed the convention of Biodiversity at the Earth Summit to protect it. According to the summit, efforts should be made in preserving endangered species.
The preservation and proper management methods for wildlife should be made. Food crops, animals, and plants should be preserved. Usage of various food crops should be kept at a minimum. Every country must realize the importance of protecting the ecosystem and safeguarding the habitat.
The Government of India has launched the Wild Life Protection Act 1972 to protect, preserve, and propagate a variety of species. The Government has also launched a scheme to protect national parks and sanctuaries. There are 12 countries - Mexico, Columbia, Peru, Brasil, Ecuador, Democratic Republic of Congo, Madagascar, India, China, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Australia, in which Mega Diversity Centres are located. These countries are tropical and they possess a large number of the world’s species.
Various hotspots have been made to protect the vegetation. There are various methods for conserving biodiversity.
If biodiversity conservation is not done efficiently, each species would eventually become extinct due to a lack of appetite and hunger. This scenario has been a big issue for the last few decades, and many unique species have already become extinct. As a result of a lack of biodiversity protection, several species are still on the verge of extinction.

FAQs on Biodiversity Essay
1. What are the three types of Biodiversity?
Biodiversity is referred to as the variability that exists between the living organisms from different sources of nature, such as terrestrial, marine, and other aquatic ecosystems. Biodiversity has three levels, which are genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. This is also considered as the type of ecosystem.
2. What is Biodiversity and why is it important?
Biodiversity is responsible for boosting the productivity of the ecosystems in which every species, no matter how small, has an important role to play. For example, a greater variety of crops can be obtained from a plant species which is in large numbers. If species diversity is in a greater amount, then it ensures natural sustainability for all life forms.
3. What is the connection between Biodiversity and the Food Chain?
If a single species goes extinct from the food chain, it will have an impact on the species that survive on it, putting them on the verge of extinction.
4. How are human beings affecting biodiversity?
Pollution- Pollution not only affects human beings, but also affects our flora and fauna, and we should control the pollution to conserve our biodiversity.
Population- Population control is a must to maintain a balance in our ecological system. Humans contribute to pollution by bursting crackers and by not following all the traffic rules.
5. How does Deforestation affect biodiversity?
Deforestation- Trees are very important for survival. They help in balancing out the ecosystem. Deforestation leads to the destruction of habitat. Deforestation should be stopped to protect our animals and plants. Deforestation not only removes vegetation that is important for removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, but it also emits greenhouse gases.
- About Project
- Testimonials
Business Management Ideas

Essay on Biodiversity
List of short and long essays on biodiversity, biodiversity essay for kids and school students, essay on biodiversity – essay 1 (150 words), essay on biodiversity: types, importance and conclusion – essay 2 (250 words), essay on biodiversity: with threats and importance – essay 3 (300 words), essay on biodiversity: introduction, importance, decline and steps – essay 4 (400 words), essay on biodiversity – essay 5 (500 words), biodiversity essay for competitive exam and upsc civil services exam, essay on biodiversity: with conclusion – essay 6 (600 words), essay on biodiversity: facts, importance and preservation – essay 7 (750 words), essay on biodiversity in india – essay 8 (1000 words).
Introduction:
Biodiversity also known as biological diversity is the variables that exist among several species living in the ecosystem. These living organisms include marine, terrestrial and aquatic life. Biodiversity aims to understand the positions these organisms occupy in the broader ecosystem.
Importance of Biodiversity:
When there is biodiversity in our ecosystem it translates to a greener environment. This is because plant life thrives in a balanced ecosystem. This invariably affects humans as we consume plants for our survival. Also, a healthy ecosystem can help to reduce the risk of diseases and the way we respond to them.
Increasing Biodiversity:
Some changes could be encouraged to improve biodiversity in our environment.
Some of them are:
1. Stopping penetration of invasive alien species.
2. Using sustainable agricultural methods.
3. Having protected areas for spices to thrive.
4. Having an organic maintenance culture for fertilizers.
Conclusion:
To make the world a safe place for all organisms, we must maintain good health in all the ecosystems. This is the benefit of paying attention to biodiversity.
Diversity is the hallmark of nature. Things exist in different forms which creates diversity. Biodiversity is a significant and desirable variation in plant and animal existence on the surface of the earth. The variation exists due to genetics, species and the ecosystem or the habitat. Biodiversity is an important aspect in the world because it enables the survival and sustainability of living things on earth.
Types of Biodiversity:
The variation in living things has resulted in different types of biodiversity depending on the certain variables. Genetic diversity is due to the genetic components shared by living organisms. The species that have similar genes diverge and they develop differently thus creating biodiversity. Species diversity occurs when a habitat comprises different kinds of living things. Ecological diversity is through the interaction of living things that share common sources of energy in an ecosystem which contributes to biodiversity.
The existence of living things in an ecosystem and the functioning of the ecosystem contribute to the relevance of biodiversity in nature. Through biodiversity, living organisms are able to acquire food and other important resources to sustain their lives. The climate and environmental changes are regulated because of biodiversity. The culture is enriched through biodiversity as it involves existence of several groups of species and people in one environment.
All the three types of biodiversity are important to the existence of living organisms. The ecosystem is the hallmark of diversity because it helps to sustain the lives of diverse living things.
Biodiversity is the variability or the diversity of the different species of life forms. The planet earth is habitat for a wide variety of flora and fauna like plants, animals and other life forms.
What is Biodiversity?
Biodiversity or Biological diversity refers to the variety and variability of living beings on planet earth and it is the degree of variation of life. It represents the wealth of biological assets available on earth and encompasses microorganism, plants, animals and ecosystems such as coral reefs, forests, rainforests, deserts etc.
Threats to Biodiversity:
The growing population, industrialization, technology, etc., all are impacting biodiversity. The increased human activities have been reducing the natural area for plants, animals and other living things. A number of plants and animals have gone extinct because of increased deforestation and other factors. Growing pollution, causing global warming and climate change, is a big threat to biodiversity. The decline in biodiversity would in turn lead to imbalance in the ecosystem and would become a threat to the human race as well as other living organisms.
Different plants and animals are dependent on others to live and keep the natural surroundings in a balanced state. For example, human beings are dependent on various plants and animals for their food, shelter, safety, clothes etc. Similarly, every living species is dependent on some other species. It is, therefore, important to preserve biodiversity in our planet in order to maintain the ecological balance.
Protecting Biodiversity:
As we know, the biodiversity loss is a serious threat for human race, we all should work for maintaining biodiversity, and find out solutions to reduce the biodiversity decline. Since, air pollution and deforestation are major threats to biodiversity, these are the first things that need to be controlled. Government should frame stricter laws and organizations should sensitize people to be concerned about it and contribute their bit.
Biodiversity, also referred to as the biological diversity refers to the diversified form of plants and animals that exists in our planet . It also denotes each and every aspect of the ecosystem such as micro-organisms, coral reefs, rainforests, deserts, forests etc.,
A good balance in biodiversity supports human race and humans on the other hand must ensure to save biodiversity. This essay is going to talk about the importance of biodiversity and the role of human beings in safeguarding the ecosystem.
There are more than 300,000 species of flora that has been identified and there should be many more unidentified varieties. Similarly there must be infinite variety of other species in our Earth and these together form a perfect natural protection for the human race. Biodiversity supports human race in different ways.
Few of them are listed below:
1. Some of the species capture and stores energy and releases it back in the atmosphere for human consumption.
2. Some biological species help in decomposing organic materials and thus acts as a natural recycling agent.
3. Plants and trees help in reducing pollution and maintain the purity of atmospheric air.
4. It is from the biological resources that humans receive food and shelter.
5. The astonishing beauty of biodiversity is the base for tourism industry to flourish.
Decline in Biodiversity:
The Earth’s biodiversity is undergoing a severe decline and this is a great threat to the human race. There are several factors that lead to the decline in biological species, the most significant one being the behavior of human beings.
1. Human beings destroy forests to build houses and offices. Through deforestation humans are actually destroying the natural habitat of many plants and animals.
2. All new scientific inventions are causing harm to the environment. We cannot even find some species of birds today because of the increase in noise pollution.
3. Global warming is another reason for the decline in biodiversity. Some species require specific climate to survive and when the climatic conditions change continuously these species either migrate or become extinct. Decline in the number of coral reefs are a perfect example.
Steps to Be Taken:
The Government and different voluntary organizations must act upon immediately to create awareness among people on environmental issues and its consequences. It is also the responsibility of every common man to save mother Earth by maintaining a rich biodiversity .
If proper care is not taken, the biodiversity of Earth may become extinct one day and if it happens then, humans have to find another planet to live. It’s better to act now before it gets too late.
Biodiversity can be said to mean the extreme importance of a very wide variety of animals and plants that are resident on the planet earth or in a particular habitat. It is very necessary to maintain the level of biodiversity on the earth so that the environmental harmony can be balanced. Biological diversity is another name for biodiversity and is widely the variability or diversity of all the different species of animals and plants on this planet. Having a very high biodiversity is extremely essential to help maintain the surroundings in a state of harmony. Biodiversity can be loosely defined as a variety of fauna and flora that are available in a specific habitat or the planet earth. Biodiversity is largely originated from the terms – species diversity and species richness.
Biodiversity is mainly a united view of the biological varieties. A lot of other words and terms have been at one time or another used to explain diversity. Some of these terms include taxonomic diversity (this comes from a species diversity point of view), ecological diversity (this comes from an ecosystem diversity point of view), morphological diversity (this comes from a genetic diversity point of view) and functional diversity (this comes from the point of view of the functions of the species). Biodiversity gives quite a uniform view of the above discussed biological varieties.
Biological diversity is quite important because its helps maintain the ecological balance in a system. Different animals and plants depend on one another to fulfill all of their needs. For example, we human beings depend on various animals and plants for our clothes, shelter and food. Other species also do the same and depend on a variety of other species to sustain them and provide them with the basics. Biodiversity and its beautiful richness ensure that the earth is fit enough for the survival of each and every one of the organism living on the earth. However, the ever increasing pollution is negatively affecting biodiversity. Quite a lot of animals and plants have gone into extinction as a result of this pollution and a lot more are going to become extinct if proper care is not taken and the pollution of the environment continues to exponentially and this would cause a sharp decline in the biodiversity.
We human beings have to understand how important the maintenance of the immensely rich biodiversity is. Smokes from vehicles causes a high rate of air pollution and this causes harm to a lot of species. The level of pollution in the atmosphere has to be put under control. Water bodies like seas, oceans and rivers are polluted by the release of industrial wastes into the. These wastes are very harmful to the marine organism and life in the water bodies. There is therefore a need to try as much as possible to dispose industrial wastes through other means and methods that do not harm the environment. The industrial wastes can be primarily treated before being disposed into the water properly and safely.
When you are a biology student biodiversity is one of the most important words you can learn. Not only that but it also becomes your lives calling to maintain it. But let’s not get ahead of ourselves before we can understand why it is important, we need to understand what it is.
This term refers to the many different life forms that inhabit the earth at this moment, this includes bacteria, plants, animals and humans and it also refers to their shared environment. Life has manifested itself in many different forms we do not know why exactly but we are certain that they all exist and depend on each other for survival.
Why is biodiversity important?
The answer to this question is more important than just simply stating what biodiversity is. My personal experience as a student has thought me that I learn best when I have an example so I will give you an example of the importance of biodiversity.
The famous Yellowstone Park is a natural reserve and national park but before it was declared as such it was just another forest that man wanted to hunt in. The geographical region had many wolfs inhabiting its plains, for generations they were hunted until they became extinct in the region. After a while, the coyotes began to reproduce as they hade more space and they started hunting the small mammals, which lead to a decrease in the population of eagles in the area but the most significant change came because of the deer. After fifty years of no wolfs in the park the number of roe deer rose and since they had no natural predators, they no longer feared open grasslands. That’s when they started grazing extensively which depleted the grass on the shore of the Yellow stone river and this, in turn, made the soil loos. The river began to take away a lot of soil and to deposit it in other places flooding certain areas while at the same time causing droughts to happen in other places.
Biologists came to the park with a wish to restore its wolf population and after a decade of planning and working they restored one pack to the park. The pack soon made the deer go back to the forest so they could be harder to hunt, the coyote’s population dropped because they couldn’t compete with the wolf, that led to the increase of small rodents which let to the return of carnivores’ grate birds. But above all the grazing on the river edge stopped and after a few years, the Yellowstone river returned to its natural flow.
This story is completely true and I love to use it as an example of the importance of maintaining biodiversity. There are many regions in the world that have similar problems and if we do not do our best to conserve biodiversity, we could be looking at similar or even worst natural catastrophes.
People tend to mass produce and they do this with most things. They will destroy a forest of many thousands of life forms to make a plantation with one single plant, the same is true of animal farming. With our need to be productive all the time we lose sight of the small things that make the system function as whole. Even though an insignificant thing as a bug or a wolf pack might seem the least important for our daily lives once we take them out of the picture, we see that the balance and wealth biodiversity gives to the planet is not something that can be easily compensated.
The genetic, species and ecosystem variability of flora and fauna on earth are known as Biodiversity. For painting what exactly is Biodiversity, we need a large canvas beyond imagination. Such is the volume of the subject. But, the actual meaning and terms are still not clear.
Keeping it very simple and to the point, the term ‘Biodiversity’ comprises of two words. The first word is Bio, and the other one is Diversity. Bio means the forms of life and Diversity means mixture or variety. So, when both the words combine they form a definition like this ‘Biodiversity means various and mixed forms of life on earth.’ The variety of life forms on earth includes plants and animals and their natural habitat.
Facts about Biodiversity:
Digging into the term ‘Biodiversity’ more generously makes us realize that we have over 10,000 species of birds on earth. The amazing number blows everyone’s mind. Insects have a different counting, and their species are in millions. Plants are also a part of this biological system, and hence there are more than 20,000 species of plants.
Even after so many species of plants, animals and insects have specified there are still over millions of species which are not known by anyone. These species cannot be counted under any head as they don’t pursue an identity. The actual picture says that earth is home to almost 50 million species or even more than that. These facts do not conclude the point because one or the other day there may be many new species evolving.
Biodiversity is essential for survival. The importance of Biodiversity not only related to plants, animals and natural habitat. But it also provides us so many natural products such as fibre and timber and the fresh water to carry out our daily lives. Therefore we need to understand the importance of Biodiversity.
1. The natural and organic resources:
In the happiness of living our lives, we often forget that Biodiversity is a part of nature. We should protect it no matter whatever be the limitations. Mother Nature has provided us with enough resources which are the Biological Resources. These include wood, medicines, food, etc., which are direct blessings of Biological System or by-product of the Biological Systems. Herbs and plants play a vital role in producing medicines. They may get their final touch from the pharmaceutical companies, but the original source is plants which are again a part of Biodiversity.
2. Biodiversity provides fibres:
It is important to know that wool, jute, palms, etc., use to produce various types of fibres after processing which are again part of the Biological Systems. So, if biodiversity does not persist how people will have access to these fibres? Flax plants use for the production of linen, which is extensively using for making clothes. Similarly, Corchorus plants and Agave plants are using for the production of Jute and sisal respectively. These fibres are no doubt essential for the cloth industry. Therefore it becomes our duty to maintain the Biodiversity.
3. Powerful benefits of Biodiversity:
People may not be aware of the importance, but there are many spiritual benefits of biodiversity. Our folk dances, mythology, and history have a deep link with the Biodiversity in one or the other way. Everyone enjoys or experience the Biodiversity in a different format. Biological diversity also contributes to attracting tourists, especially flora and fauna, which is a rare phenomenon in cities. Therefore it is our ethical duty to preserve Biodiversity.
Preserve Biodiversity:
There are different ways in which we can preserve our Biological environment. Biodiversity should be protected by following these ways.
i. People should stop the process of hunting and poaching the animals. They are a part of Biodiversity.
ii. Protection of endangered species and their surroundings.
iii. We need to curb pollution for protecting Biodiversity.
iv. The explosive growth of population is a threat to Biodiversity. So, to maintain the biological balance, we need to have the population growth under control. Otherwise, people will be exploiting natural resources unethically for survival.
All steps must be taken to protect biodiversity. Things may seem difficult in the initial stages but practicing them will lead to genuine results. Creating awareness on environmental issues and the negative impact of the loss of biodiversity will let people understand the inevitable need for biodiversity conservation.
It is our responsibility to protect the endangered species of plant and animals. If one wants to reach their destination, then it is imperative to take the first step. Without taking a step forward, things will never change on their own. To make a better tomorrow, we need to take steps for preserving our very own Biodiversity.
Biodiversity is a term used to refer the different forms of life on the Earth. It also includes the variety of species in the ecosystem. There is an uneven distribution of the biodiversity on the Earth due to the extreme variation of temperatures in different regions. For instance, it is more in regions near the equator due to warm climatic conditions. However, near the pole, the extreme cold and unfavourable weather conditions do not support a majority of life forms. Additionally, changes in climatic conditions on the Earth over a period of time have also led to the extinction of a number of species.
Biodiversity is often defined at different levels depending upon the category of species. For example, taxonomic diversity is used to measure the species diversity level of different forms of life on the Earth. Ecological diversity is a broader term used for the ecosystem diversity. Similarly, functional diversity is a type used to measure diversity based on their feeding mechanisms along with other functions of species within a population.
Distribution:
There is an uneven distribution of biodiversity on the Earth. In fact, it increases from pole to equator. The climatic conditions of a region decide the presence of different species in an area. Not all species can survive in all weather conditions. Moreover, lower altitudes have a high concentration of species as compared to higher altitudes.
The importance of biodiversity does not only lie in the survival of various species of the earth. There is social, cultural as well as the economic importance of it as well. Biodiversity is of extreme importance to maintain the balance of nature. It is vital to maintaining the food chain as well. One species may be the food for another species and various species are linked to each other through this food chain. Apart from this, there is scientific importance of the biodiversity as well. The research and breeding programmes involve the variety of species. If these species cease to exist then such programmes shall not be possible.
Also, most of the drugs and medicine which are vital for the cure of many diseases are also made from many plants and animals. For instance, penicillin is a fungus through which the penicillin antibiotic is extracted.
Another important importance of biodiversity is that it provides food to all including human beings. All the food we consume is either derived from plants or animals such as fishes and other marine animals. They are also the source of new crops, pesticides and source material for agricultural practices.
Biodiversity is also important for industrial use. We get many products such as fur, honey, leather and pearls from animals. Moreover, we get timber for plants which are the basis of the paper we use in our everyday life. Tea, coffee and other drinks along with dry fruits and our regular fruits and vegetables, all are obtained from the various plants.
There is cultural and religious importance of many species as well. Many plants and animals are worshipped in different cultures and religions such as Ocitnum sanctum (Tulsi) which is a plant worshipped by Hindus.
Biodiversity in India:
India ranks among the top 12 nations which have a rich heritage of biodiversity. There are about 350 different species of mammals along with 12000 different species of birds which are found in India. Additionally, there are around 50000 species of insects which have their habitat in our country. There are a wide variety of domestic animals such as cows and buffaloes along with marine life which is found in India. Moreover, India is a land of 10 different biographical regions which include islands, Trans Himalayas, Desert, Western Ghats, Gangetic Plain, Semi-arid zone, Northeastern zone, Deccan Plateau, Coastal islands and the Western Ghats.
The Gradual Decrease:
Not all species which existed in the ancient times exist today as well. For example, dinosaurs used to exist on our planet in older times. But they were not able to adapt to the changing environmental conditions which led to their extinction from the Earth. Similarly, there are many other species which are on the verge of extinction due to the urbanisation and modernisation of the world. With the increase in population, there has been a constant need to reduce the forest areas and make way for new cities. This has led to the reduction in forests which are the natural habitat for many wild animals and plants. Due to this many wild plants have become extinct and there has been an increase in the man-animal conflict as well. Hence there has been a need to conserve the biodiversity so as to maintain the balance of nature.
Initiatives for the Conservation of Biodiversity:
There have been initiatives by the governments all over the world to conserve the existing biodiversity on the earth. For example, there are dedicated national parks which earmark the area for wild animals and plants and reduce human intervention in their lives. There are various wildlife conservation programmes in place to protect the vulnerable and endangered species. For example, Project Tiger is one such measure in place to increase the population of tigers in our country.
There are also many laws in place which make the hunting of endangered and vulnerable animals a punishable offence. At the international level, UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) and IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) have also initiated many programmes in order to preserve various species.
It is not possible for the human to live all alone on the Earth. Various other life forms are equally important and play their roles in the mutual survival of the various species on the Earth. Each one of species has its own set of contribution for the environment. Already many species have become extinct as they were not able to survive in the changing weather conditions. Hence it is our duty to ensure that our activities do not affect the other flora and fauna on the planet. Although there are a number of steps taken by the government so as to preserve the various life forms, we should also contribute individually towards this cause. If we do not act today, we may yet again witness the extinction of the vulnerable biodiversity which may further disturb the balance of nature.
Biodiversity , Ecosystem , Environment
Get FREE Work-at-Home Job Leads Delivered Weekly!

Join more than 50,000 subscribers receiving regular updates! Plus, get a FREE copy of How to Make Money Blogging!
Message from Sophia!
Like this post? Don’t forget to share it!
Here are a few recommended articles for you to read next:
- Essay on Noise Pollution
- Essay on Deforestation
- Essay on Environmental Pollution
- Essay on Acid Rain
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Billionaires
- Donald Trump
- Warren Buffett
- Email Address
- Free Stock Photos
- Keyword Research Tools
- URL Shortener Tools
- WordPress Theme
Book Summaries
- How To Win Friends
- Rich Dad Poor Dad
- The Code of the Extraordinary Mind
- The Luck Factor
- The Millionaire Fastlane
- The ONE Thing
- Think and Grow Rich
- 100 Million Dollar Business
- Business Ideas
Digital Marketing
- Mobile Addiction
- Social Media Addiction
- Computer Addiction
- Drug Addiction
- Internet Addiction
- TV Addiction
- Healthy Habits
- Morning Rituals
- Wake up Early
- Cholesterol
- Reducing Cholesterol
- Fat Loss Diet Plan
- Reducing Hair Fall
- Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss
Internet Marketing
- Email Marketing
Law of Attraction
- Subconscious Mind
- Vision Board
- Visualization
Law of Vibration
- Professional Life
Motivational Speakers
- Bob Proctor
- Robert Kiyosaki
- Vivek Bindra
- Inner Peace
Productivity
- Not To-do List
- Project Management Software
- Negative Energies
Relationship
- Getting Back Your Ex
Self-help 21 and 14 Days Course
Self-improvement.
- Body Language
- Complainers
- Emotional Intelligence
- Personality
Social Media
- Project Management
- Anik Singal
- Baba Ramdev
- Dwayne Johnson
- Jackie Chan
- Leonardo DiCaprio
- Narendra Modi
- Nikola Tesla
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Sandeep Maheshwari
- Shaqir Hussyin
Website Development
Wisdom post, worlds most.
- Expensive Cars
Our Portals: Gulf Canada USA Italy Gulf UK
Privacy Overview

Short Essay: Biodiversity
Writing a short essay on biodiversity involves discussing the complex web of life that includes and sustains all organisms on Earth. Biodiversity encompasses species diversity, ecosystem diversity, and genetic diversity within species, each contributing uniquely to the resilience and productivity of natural systems. Whether you’re a student, educator, or simply a concerned citizen wanting to articulate the importance of biodiversity, here’s a straightforward guide to help you craft a concise and impactful essay.
Table of Contents
Title and Introduction
Title : Choose a concise and descriptive title that directly references biodiversity, such as “The Crucial Role of Biodiversity in Sustaining Life on Earth.”
Introduction : Start with an engaging opening to draw in the reader. This could be a surprising statistic, a question, or an anecdote illustrating the interaction between different species. Briefly define biodiversity and state your thesis, outlining the main points you will cover, such as the value of biodiversity, threats to it, and strategies for its conservation.
Body of the Essay
Understanding Biodiversity :
- Paragraph 1 : Discuss what biodiversity is. Explain the three levels of biodiversity: genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. Describe how these levels interact to support the functioning of ecosystems.
- Paragraph 2 : Illustrate the importance of biodiversity. You can discuss its role in ecosystem services such as pollination, water purification, and nutrient cycling, which are essential for the survival of humans and other species.
Threats to Biodiversity :
- Paragraph 3 : Identify and explain major threats to biodiversity such as habitat destruction, climate change, pollution, invasive species, and overexploitation. Use specific examples to show how these threats impact biodiversity at different levels.
Conservation Efforts :
- Paragraph 4 : Describe current strategies for biodiversity conservation. Highlight successful examples of wildlife conservation, protected areas, legal frameworks, and community-based conservation efforts. Discuss the role of international agreements like the Convention on Biological Diversity.
Summarize the key points discussed in the body of the essay. Reinforce the thesis by emphasizing the critical role of biodiversity in sustaining life on Earth and the urgent need to protect it. Conclude with a call to action, encouraging readers to participate in or support biodiversity conservation efforts. This could involve lifestyle changes, supporting environmental organizations, or advocating for policy changes.
Biodiversity Essay Example #1
Biodiversity, a contraction of “biological diversity,” refers to the variety and variability among living organisms and the ecological complexes in which they occur. This encompasses diversity within species, between species, and of ecosystems. It forms the web of life of which we are an integral part and upon which we so fully depend.
Biodiversity is crucial for human well-being and is directly linked to several aspects of human life, including food security, health, and ecological services such as pollination, water purification, and climate regulation. The natural variety of plants and animals provides a genetic library from which crops, medicines, and other materials can be derived. For instance, a significant percentage of pharmaceutical products are derived from natural sources.
The threats to biodiversity are increasing at an alarming rate, largely due to human activities. Habitat destruction, overexploitation, pollution, invasive species, and climate change are the primary drivers of biodiversity loss. Deforestation for agriculture and urban development leads to habitat fragmentation, which is detrimental to wildlife. Overfishing and hunting have decimated populations of various species, while pollution and climate change alter and destroy the natural habitats that organisms depend on for survival.
Conservation of biodiversity is essential for maintaining the natural balance and health of ecosystems. Various strategies can be employed to protect biodiversity, including establishing protected areas such as national parks and wildlife reserves, enforcing laws that prohibit poaching, and regulating and reducing pollutants that harm ecosystems. Additionally, restoration ecology can help restore degraded ecosystems, and community involvement in conservation efforts ensures sustainable practices at the local level.
In conclusion, the protection and promotion of biodiversity are critical to sustaining the natural environment for the benefit of all life on Earth, including humans. It is imperative that collective actions are taken at the global, national, and local levels to conserve biodiversity and promote sustainability for future generations.

Biodiversity Essay Example #2
Biodiversity, the term used to describe the vast variety of life on Earth, encompasses not only the many species that exist but also their genetic diversity and the complex ecosystems they form. The importance of biodiversity cannot be overstated, as it is crucial to ecosystem productivity, resilience, and the overall stability of our planet’s environmental systems.
Understanding the significance of biodiversity starts with recognizing its role in providing essential services that support human life. These include food production, water purification, oxygen production, and disease control. For instance, diverse insect populations help pollinate plants, including many food crops, while different species of bacteria and fungi break down organic material, keeping soils fertile and productive.
However, biodiversity is under threat from numerous human activities. Habitat destruction, driven by logging, agriculture, and urban expansion, is perhaps the most significant threat, as it leads to the fragmentation and loss of critical habitats for many species. Pollution, from industrial, agricultural, and domestic sources, also severely affects biodiversity by altering and contaminating the environments in which species live. Overexploitation through activities like hunting, fishing, and trade in wildlife products drives many species to the brink of extinction, while climate change compounds these threats by altering temperature and weather patterns at a rate that species cannot adapt to quickly enough.
In response to these threats, conservation efforts are more critical than ever. Protecting areas of significant biodiversity by creating reserves and parks is one of the most effective conservation strategies. These protected areas provide safe havens for species and preserve functioning ecosystems that can continue to provide essential services. Laws and regulations at both the national and international levels are crucial in managing human impacts on wildlife. Policies that promote sustainable resource use and reduce pollution are equally important.
Furthermore, the role of local communities should not be underestimated in biodiversity conservation. Indigenous peoples and local communities often have a deep understanding of their local ecosystems and can offer valuable insights into sustainable management practices. Empowering these communities to manage their natural resources can lead to more effective and sustainable conservation outcomes.
In conclusion, the preservation of biodiversity is not just beneficial but necessary for the health and sustainability of our planet. It requires a concerted effort from all sectors of society, including governments, NGOs, the private sector, and local communities. By working together, we can ensure that our natural world remains diverse and robust, capable of supporting future generations in the same way it supports us today.
Biodiversity Essay Example #3
Biodiversity encompasses the variety of life forms on Earth, including different species, their genetic variations, and the ecosystems in which they inhabit. This diversity not only enriches the planet but also provides vital services that sustain human life. From food and medicine to ecosystem services like climate regulation and flood protection, biodiversity plays an essential role in human welfare.
The significance of biodiversity extends beyond practical benefits. It contributes to the health of the planet, ensuring that ecosystems function effectively and can recover from a variety of shocks. For instance, diverse plant species can improve soil fertility and help stabilize the climate by capturing carbon dioxide. Similarly, a variety of animals can ensure natural pest control and pollination, which are crucial for agricultural productivity.
Despite its importance, biodiversity faces significant threats primarily due to human activities. Habitat destruction is the most pervasive, driven by agricultural expansion, urban development, and deforestation. This not only reduces the areas where species can live but also fragments the remaining habitats, making it difficult for species to survive and interact. Pollution is another major threat, affecting air, water, and soil quality and thus the health and survival of species. Overexploitation through hunting, fishing, and trade depletes species faster than their natural recovery rates. Additionally, climate change alters temperature and weather patterns, disrupting the delicate balance of many ecosystems.
Conservation efforts are vital to mitigate these threats. Establishing protected areas such as wildlife reserves and marine parks is a direct method to safeguard habitats. Legal frameworks and regulations can help control the exploitation of natural resources and manage pollution. Furthermore, restoring damaged ecosystems can help revive biodiversity levels and ecosystem services.
Engaging local and indigenous communities in conservation efforts is also crucial. These communities often have a profound connection with and understanding of their environments, making them invaluable in managing and protecting biodiversity. Education and awareness campaigns can empower communities and the broader public, leading to more sustainable behaviors and attitudes towards nature.
In summary, maintaining biodiversity is essential for the well-being of the planet and all who live on it. The collective efforts of global cooperation, local action, and enhanced public awareness are necessary to preserve this invaluable natural resource for future generations. The challenge is significant, but the benefits of a rich and vibrant biodiversity are worth striving for, ensuring a healthy planet and a sustainable future.
Final Writing Tips
- Be Concise : Given the limited length of a short essay, focus on the most essential information. Each paragraph should have a clear point that supports the thesis.
- Use Credible Sources : Support your arguments with data and examples from reputable sources such as scientific studies, government reports, and respected conservation organizations.
- Visual Aids : If applicable, include charts, graphs, or images that help illustrate key points about biodiversity loss and conservation.
- Objective Tone : Maintain an academic tone that reflects an objective consideration of the topic. While personal passion about the subject is valuable, the arguments should remain grounded in verified information.
- Proofread : Review your essay for grammatical errors and ensure that your arguments flow logically. A well-organized essay makes a stronger impact.
About Mr. Greg
Mr. Greg is an English teacher from Edinburgh, Scotland, currently based in Hong Kong. He has over 5 years teaching experience and recently completed his PGCE at the University of Essex Online. In 2013, he graduated from Edinburgh Napier University with a BEng(Hons) in Computing, with a focus on social media.
Mr. Greg’s English Cloud was created in 2020 during the pandemic, aiming to provide students and parents with resources to help facilitate their learning at home.
Whatsapp: +85259609792
[email protected]

ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Biodiversity.
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living species on Earth, including plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi. While Earth’s biodiversity is so rich that many species have yet to be discovered, many species are being threatened with extinction due to human activities, putting the Earth’s magnificent biodiversity at risk.
Biology, Ecology
grasshoppers
Although all of these insects have a similar structure and may be genetic cousins, the beautiful variety of colors, shapes, camouflage, and sizes showcase the level of diversity possible even within a closely-related group of species.
Photograph by Frans Lanting

Biodiversity is a term used to describe the enormous variety of life on Earth. It can be used more specifically to refer to all of the species in one region or ecosystem . Bio diversity refers to every living thing, including plants, bacteria, animals, and humans. Scientists have estimated that there are around 8.7 million species of plants and animals in existence. However, only around 1.2 million species have been identified and described so far, most of which are insects. This means that millions of other organisms remain a complete mystery.
Over generations , all of the species that are currently alive today have evolved unique traits that make them distinct from other species . These differences are what scientists use to tell one species from another. Organisms that have evolved to be so different from one another that they can no longer reproduce with each other are considered different species . All organisms that can reproduce with each other fall into one species .
Scientists are interested in how much biodiversity there is on a global scale, given that there is still so much biodiversity to discover. They also study how many species exist in single ecosystems, such as a forest, grassland, tundra, or lake. A single grassland can contain a wide range of species, from beetles to snakes to antelopes. Ecosystems that host the most biodiversity tend to have ideal environmental conditions for plant growth, like the warm and wet climate of tropical regions. Ecosystems can also contain species too small to see with the naked eye. Looking at samples of soil or water through a microscope reveals a whole world of bacteria and other tiny organisms.
Some areas in the world, such as areas of Mexico, South Africa, Brazil, the southwestern United States, and Madagascar, have more bio diversity than others. Areas with extremely high levels of bio diversity are called hotspots . Endemic species — species that are only found in one particular location—are also found in hotspots .
All of the Earth’s species work together to survive and maintain their ecosystems . For example, the grass in pastures feeds cattle. Cattle then produce manure that returns nutrients to the soil, which helps to grow more grass. This manure can also be used to fertilize cropland. Many species provide important benefits to humans, including food, clothing, and medicine.
Much of the Earth’s bio diversity , however, is in jeopardy due to human consumption and other activities that disturb and even destroy ecosystems . Pollution , climate change, and population growth are all threats to bio diversity . These threats have caused an unprecedented rise in the rate of species extinction . Some scientists estimate that half of all species on Earth will be wiped out within the next century. Conservation efforts are necessary to preserve bio diversity and protect endangered species and their habitats.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
March 11, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

Biodiversity Explained: Facts, Myths, and the Race to Protect It

By MJ Altman on January 4, 2023

A baby sloth hangs in a tree at the Bosque da Ciência in Manaus, Brazil. PHOTO: Michael Dantas/United Nations Foundation
As ecosystems and habitats degrade and disappear worldwide, biodiversity — the interconnectedness of all forms of life on our planet — is in jeopardy. In light of a new global agreement to protect our lands, ocean, and waters, explore what biodiversity really means and what it will take to preserve life on Earth.
From microscopic fungi to mega forests, “biodiversity” is the collective term for the variety of life on Earth in all its forms. It is 4.5 billion years of evolution, embodied.
Biodiversity is responsible for our food, our soil, our water, our weather, even the air we breathe. Yet despite being a crucial foundation for our collective future, biodiversity is often lost amid conversations on climate change — until recently.
In December 2022, leaders from nearly 200 nations adopted a landmark UN agreement to reverse nature’s rapid decline before it’s too late. Known as the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework , it calls for protecting 30% of the planet’s land, ocean, and inland waters and includes 23 other targets to help restore and protect ecosystems and endangered species worldwide.
Here are 12 things you should know:
1. Biodiversity is more than just the total number of species on Earth.
“It is actually more complex than that,” Dr. Thomas Lovejoy, the late ecologist, told the United Nations Foundation in 2018. “It’s about the genetic diversity within species, the diversity of habitats, and the large biological units known as biomes.”
This includes the interactions that occur between species within ecosystems – primordial relationships that shape our environment in countless, often unseen ways.
“Without biological diversity, there is no other life on Earth — including our own,” he explained. “Even though we are often oblivious to it, this diversity of life is what provides clean water, oxygen, and all other things that end up being part of our diet, as well as clothing and shelter. It provides a lot of psychological benefits too, which are not much appreciated.”
2. We’re only just beginning to understand biodiversity’s influence and importance in our lives.
Earth’s many ecosystems rely on a delicate, complicated, and fascinating tangle of life that, in many ways, remains a mystery. In fact, the term “biological diversity” wasn’t introduced to the scientific community until 1980 in a research paper on species loss by Dr. Lovejoy. Scientists still haven’t identified all forms of life on the planet. New species are discovered every year.

A harbor seal swims through kelp off the coast of Southern California's Channel Islands. Seals are among the thousands of species that rely on kelp forests for food and shelter. PHOTO: Shutterstock/Joe Belanger
Take kelp, for example. These undersea forests provide sustenance and shelter for marine species like chinook salmon, which, in turn, serve as a staple food for orcas. And kelp also absorb excess carbon dioxide, which can help mitigate climate change.
3. The planet’s biodiversity holds enormous, untapped potential for medical and scientific breakthroughs.
Lovejoy described each species on the planet as a unique set of solutions for a particular set of biological problems. “Whoever would have thought a bacterium from a Yellowstone hot spring would revolutionize forensic and diagnostic medicine, make the human genome project possible, and confer benefits in the trillion-dollar range?” he wrote as a Senior Fellow at the United Nations Foundation, citing a previously unknown and seemingly inconsequential microbe discovered in 1966 that revolutionized genetic testing and immunization development, including the COVID-19 vaccine.

A flowering plant grows from a tree in the Amazon Rainforest, near the research station known as Camp 41 north of Manaus, Brazil. PHOTO: Michael Dantas/United Nations Foundation
Today, one-fourth of all modern medicines are derived from tropical plants, and 70% of all cancer drugs are natural or bio-inspired products. In the past decade, researchers in Nova Scotia found a soil fungus that can disarm antibiotic-resistant bacteria — a discovery that could transform the fields of medicine and agriculture. The possibilities for discovery and innovation are monumental.
4. Climate change and biodiversity are interconnected.
Climate change is causing biodiversity loss, and biodiversity loss is causing climate change. Here’s how: Destroying and degrading ecosystems releases more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than burning fossil fuels.
Meanwhile, the consequences of burning fossil fuels — rising global temperatures, an increase in wildfires, and ocean acidification, to name a few — are threatening habitats and wildlife alike. In late 2019 and early 2020, for example, more than 60,000 koalas were killed by wildfires in Australia so massive that nearly 3 billion animals died or were displaced as a result. Earlier this year, the Australian government officially listed koalas as an endangered species.
At COP 27 last year, world leaders reached a historic agreement to create a “loss and damage” fund to support communities that are already feeling climate change’s disastrous impact, including biodiversity loss and its impact on livelihoods.

More than 60,000 koalas were killed by wildfires in Australia in late 2019 and early 2020. Increased wildfires and subsequent habitat loss are just one of the consequences of climate change. PHOTO: Patrick Kavanagh
5. Biodiversity can help us adapt to climate change.
The UN considers biodiversity our strongest natural defense against climate change. Land and ocean ecosystems currently absorb 60% of human-caused emissions , and they are the planet’s only way of storing massive amounts of carbon dioxide. Coastal wetlands, for example, protect against storm surges and flooding during extreme weather while also storing carbon dioxide and creating oxygen.
According to a joint estimate by the UN Development Programme and the Government of Papua New Guinea, every dollar invested in environmental protection generates more than $2,500 in so-called ecosystem services — water regulation, coastal protection, carbon storage, and other invisible functions that nature provides. It’s one of the reasons that Papua New Guinea launched the first-ever national, independent Biodiversity and Climate Fund to protect its status as one of just 17 “megadiverse” countries.
6. Less biodiversity means a higher risk of disease.
For decades, the scientific community has warned that biodiversity loss increases the spread of infectious disease . Why? Because extinction upsets the ecosystem in unpredictable ways, and the destruction of natural habitats increases interaction between humans and wildlife. Biodiversity essentially acts as a barrier between humans and animal-borne disease.
Species that tend to survive logging, farming, mining, wildlife trade and consumption, and other human activities behind widespread biodiversity loss are often “vectors of disease” like mice and mosquitoes, which host pathogens that are able to make the jump to humans. It’s one of the reasons why cases of Lyme disease in the northeast United States have spiked in recent decades: With fewer mammals to prey on, ticks are increasingly seeking out people. In fact, roughly 75% of emerging infectious diseases are zoonotic .
It’s also why researchers like Dr. Alessandra Nava and her team of virus hunters at Brazil’s Fiocruz Amazônia are tracking the spread of disease in bats, monkeys, and rodents in the world’s largest rainforest. Their goal is to stay a step ahead of future pandemics by better understanding the pathogens contained within the jungle’s creatures before they come in contact with humans — encounters that become more likely as the human footprint expands.
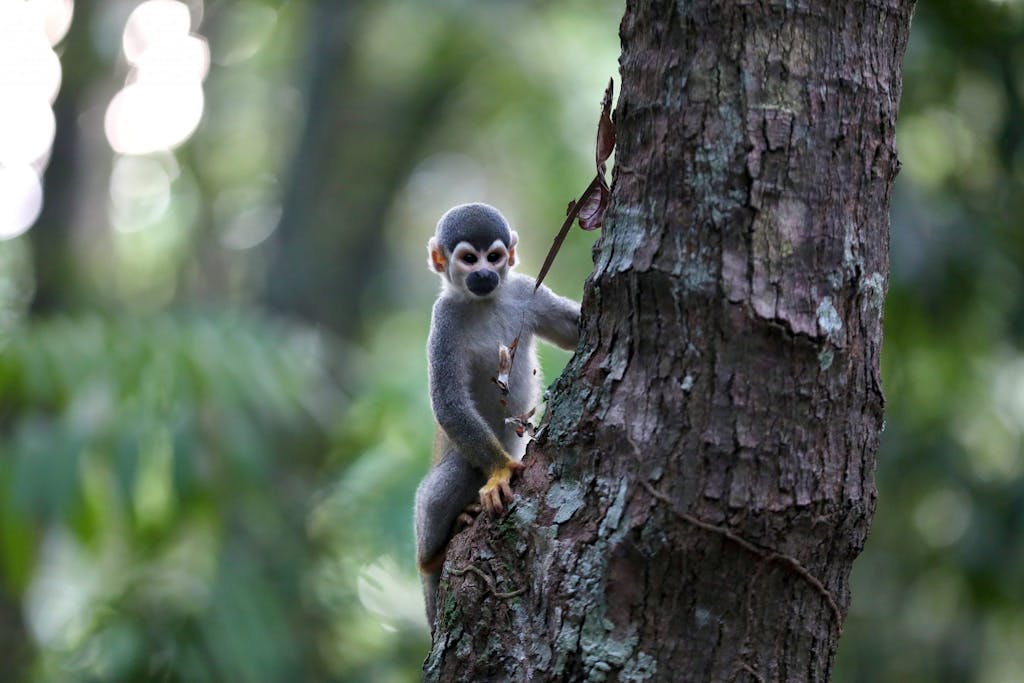

A golden-backed squirrel monkey at the Bosque da Ciência, a rainforest park in Manaus, Brazil. PHOTO: Michael Dantas/United Nations Foundation
7. Biodiversity on land depends on biodiversity in water.
Maintaining the ocean’s ecological balance is crucial for protecting biodiversity on land, as well as maintaining our ability to feed future generations. The ocean plays a vital role in regulating the planet’s weather and water and the air we breathe. It is also the planet’s largest source of protein , feeding more than 3 billion people every day who rely on fish as a staple food.
Yet the ocean remains a vastly unexplored ecological frontier. While scientists have identified 200,000 marine species , the actual number is estimated to be in the millions. Unsustainable fishing practices, pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction are threatening creatures that may vanish before we even knew they existed.
8. Our planet’s biodiversity is on the brink.
Some 1 million species are threatened with extinction right now. That’s more than any other time in history, and they’re disappearing at a rate that is 1,000 times the norm. The culprit is the way most humans consume, produce, travel, and live.
A 2019 UN report found that we have altered 75% of the planet’s terrestrial environment, 40% of its marine environment, and 50% of streams and rivers. Nearly three-fourths of our freshwater resources are devoted to crop or livestock production, which often means using pesticides, fertilizers, fuels, and antibiotics that pollute our rivers, streams, seas, and soil. Every day we are destroying habitats and degrading massive amounts of soil and water through industrial manufacturing and agriculture while jeopardizing precious natural resources that could be lost forever in our lifetime; in the past two decades, we’ve lost half of the planet’s coral reefs . Deforestation in the Amazon rainforest hit a record high last year; some 18% is gone already, with scientists warning that we’re approaching a tipping point toward potential collapse .
9. Sustainability is the only way forward.
Such irresponsible production and consumption of our natural resources come at a catastrophic cost. We are destroying our planet at an unprecedented rate and losing a vast number of plants, animals, insects, and marine life in the process — to the detriment of our own future. Humanity’s health and well-being are dependent on a biodiverse planet.
Fortunately, examples are emerging of a greener, more sustainable way of doing business. Circular economic models are becoming more common as companies realize the economic and environmental value of reducing, reusing, and recycling their supply chain. At the same time, more citizens are demanding sustainable sourcing and socially just labor practices from their consumer goods. In 2022, the founder of the outdoor retailer Patagonia announced plans to invest all of the company’s profits toward combating climate change . “If we have any hope of a thriving planet — much less a business — 50 years from now, it is going to take all of us doing what we can with the resources we have,” Yvon Chouinard wrote .

Along Brazil’s Rio Negro, fourth-generation logger Roberto Brito de Mendonça stands in the dining lodge of his community’s ecotourism lodge. He retired from the family business to help start the operation, which includes a newly built classroom named in honor of Dr. Lovejoy. PHOTO: Michael Dantas/United Nations Foundation
10. Indigenous communities are crucial.
For thousands of years, Indigenous communities have served as the planet’s most effective environmental stewards. Today, according to the UN, Indigenous people manage more than 20% of the planet’s land and 80% of its biodiversity. “For us, it is not a passion, or a job,” Hindou Ibrahim of the Mbororo tribe in Chad, an SDG (Sustainable Development Goal) Advocate and Indigenous rights activist, told the UN last year. “It is our way of living. And that’s what we have done for all generations.”
In 2015, the UN created the Local Communities and Indigenous Peoples Platform to ensure their formal participation in global negotiations on climate change.
11. Conservation is critical.
One of our most promising solutions is preservation. Restoring degraded ecosystems alone could provide up to one-third of the climate mitigation needed to keep the Earth from warming too far above pre-industrial levels. This means creating protected areas, curbing extractive capitalism, and restoring the planet’s enormous amount of degraded land.
People across the globe are leading efforts to do just that. One inspiring example is Rita Mesquita, who expanded the amount of protected rainforest in Brazil by 76% during her time in the country’s Ministry of the Environment. Today, she oversees programs that encourage residents and visitors alike in Manaus to interact with the surrounding Amazon rainforest.
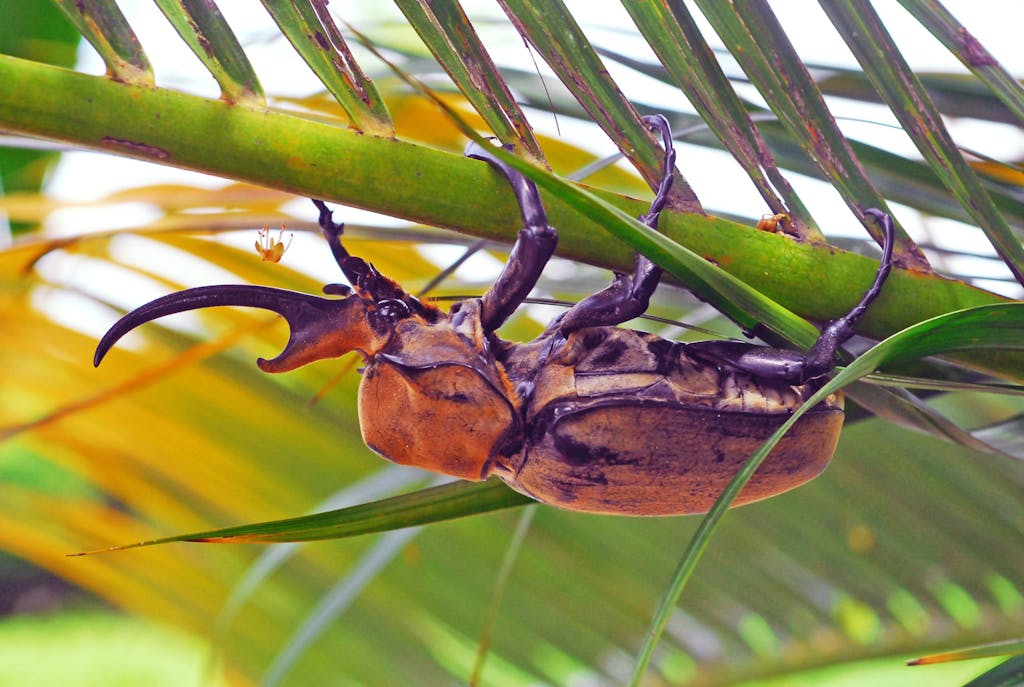

A Rhinoceros Beetle in Costa Rica’s National Park Tortuguero. The rhino beetle is one of the strongest insects in the world with relation to its body size, but because its tropical lowland habitat has been deforested and overcut, it is struggling to survive. PHOTO: GRID-Arendal/Peter Prokosch
12. We need cooperation — and revolution — at all levels.
We need partnerships among countries, communities, consumers, and corporations. And we’re seeing signs of progress every day. In fact, at COP 27, the Governments of Brazil, Democratic Republic of Congo, and Indonesia announced an alliance to protect their respective rainforests. Their historic agreement could pave the way for more multilateral action and impact. Coming just a month later, the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework represents an enormous and long-awaited step toward halting extinction rates that some scientists are calling an existential crisis akin to climate change.
A huge part of the solution to the biodiversity challenge will be transforming how we approach the natural world and our place within it. As Dr. Lovejoy told the UN Foundation in 2018 , “There needs to be a major shift in perception from thinking of nature as something with a fence around it in the middle of an expansive, human-dominated landscape … to thinking about embedding our aspirations in nature.”
Share on Mastodon

Why is biodiversity important?
Biodiversity is essential for the processes that support all life on Earth, including humans. Without a wide range of animals, plants and microorganisms, we cannot have the healthy ecosystems that we rely on to provide us with the air we breathe and the food we eat. And people also value nature of itself.
Some aspects of biodiversity are instinctively widely valued by people but the more we study biodiversity the more we see that all of it is important – even bugs and bacteria that we can’t see or may not like the look of. There are lots of ways that humans depend upon biodiversity and it is vital for us to conserve it. Pollinators such as birds, bees and other insects are estimated to be responsible for a third of the world’s crop production. Without pollinators we would not have apples, cherries, blueberries, almonds and many other foods we eat. Agriculture is also reliant upon invertebrates – they help to maintain the health of the soil crops grow in. Soil is teeming with microbes that are vital for liberating nutrients that plants need to grow, which are then also passed to us when we eat them. Life from the oceans provides the main source of animal protein for many people.
Trees, bushes and wetlands and wild grasslands naturally slow down water and help soil to absorb rainfall. When they are removed it can increase flooding. Trees and other plants clean the air we breathe and help us tackle the global challenge of climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide. Coral reefs and mangrove forests act as natural defences protecting coastlines from waves and storms.
Many of our medicines, along with other complex chemicals that we use in our daily lives such as latex and rubber, also originate from plants. Spending time in nature is increasingly understood to lead to improvements in people’s physical and mental health. Simply having green spaces and trees in cities has been shown to decrease hospital admissions, reduce stress and lower blood pressure.
Further reading
Plural valuation of nature matters for environmental sustainability and justice by Berta Martin-Lopez, Social-Ecological Systems Institute, Faculty of Sustainability, Leuphana University of Lüneburg, Germany
Climate change and biodiversity
Human activities are changing the climate. Science can help us understand what we are doing to habitats and the climate, but also find solutions.
Email updates
We promote excellence in science so that, together, we can benefit humanity and tackle the biggest challenges of our time.
Subscribe to our newsletters to be updated with the latest news on innovation, events, articles and reports.
What subscription are you interested in receiving? (Choose at least one subject)
50 Latest Biodiversity IELTS Topics
- Unlimited Task 1 checks Get all the feedback you need to keep improving your charts and letters.
- Unlimited Task 2 checks Practice and perfect your skills with essays.
- Personalized suggestions Know how to boost your score.
- Detailed mistakes analysis Get instant feedback. Spot every mistake.
- Topic ideas generator Get topic-specific ideas to enhance your writing.
- Vocabulary helper Get the right words for any topic.
- Progress tracking Track your writing improvements.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Biology library
Course: biology library > unit 30.
- Conservation and the race to save biodiversity
- Protecting biodiversity: the power of the individual
Protecting biodiversity: local and global policies
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
Video transcript
Site Navigation
‘life in the ocean touches everyone’: u.s. rolls out first national ocean biodiversity strategy.

Coral Reef at Palmyra Atoll. Credit USFWS.
Roughly 2 million species live in the world’s ocean. But scientists have only described a mere 10% of them. With extinctions on the rise and biodiversity threatened worldwide, many species are in danger of vanishing before researchers can identify them or fully grasp the benefits they provide.
The National Ocean Biodiversity Strategy calls for a stronger, more unified and inclusive approach to ocean conservation. Written by a team led by the Smithsonian and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the strategy was announced by the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy June 3. It represents the first nationwide strategy aimed at changing course to save marine life and all the services it provides to people. The plan seeks to improve scientists’ ability to gather and share knowledge and use that knowledge for more effective protections.
“We are confronting biodiversity loss and its implications for human well-being, alongside the challenges posed by climate change and social inequity,” said Ellen Stofan, Under Secretary for Science and Research at the Smithsonian. “But we hold the power to overcome these obstacles with a united, society-wide effort to preserve nature and its benefits.”
The prosperity and health of the U.S. is inextricably tied to the ocean and its life. The ocean contributes nearly $400 billion to the U.S. economy every year and provides 2.4 million jobs according to NOAA , including fishing, shipping, tourism and energy. And the nation’s ocean waters are vast: The total ocean territory under U.S. management—known as the “U.S. Exclusive Economic Zone”—covers an area larger than all 50 states combined. Much of this prosperity comes from the ocean’s diverse species and habitats.
“Life in the ocean touches everyone,” said Gabrielle Canonico, leader of the U.S. Marine Biodiversity Observation Network at NOAA and co-chair of the team that wrote the strategy. “Every other breath we take comes from the oxygen produced by microscopic ocean plants, and more than a billion people worldwide rely on food from the ocean as their primary source of protein. But these and other benefits will degrade with biodiversity loss, with dire consequences especially for frontline communities .”
Critical gaps remain in the nation’s protection and even knowledge of ocean life. The knowledge scientists do possess about the ocean is often scattered, with many organizations gathering information in different formats that are difficult to share. Many smaller organisms, including those that cause disease, are barely studied at all. Scientists suspect these neglected species contain secrets vital to keeping coral reefs and fisheries thriving and the ocean’s plankton pumping atmospheric carbon into the deep sea. The strategy addresses this challenge with plans to strengthen the nation’s ocean observing system and the information pipeline that delivers knowledge to those who need it.
“We are advancing frontier technologies for biodiversity science and understanding,” said Sarah Kapnick, NOAA chief scientist. “But it is critical that we come together around the use of evidence-based metrics and indicators for decision making in ocean spaces, and for monitoring, reporting and verification to ensure that investments in conservation or development deliver the desired outcomes while minimizing negative impacts to ocean life.”
“Biodiversity is the beating heart of the ocean that supports society , but it’s in trouble ,” said Emmett Duffy, the other co-chair of the strategy’s writing team and chief scientist of MarineGEO at the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center . “ This strategy is our best chance yet to turn the tide . We need to implement it to reach a future where people and the rest of nature thrive together by join ing forces and leverag ing the power of people and technology to understand the living ocean ecosystem.”
The National Ocean Biodiversity Strategy outlines a threefold plan to create a more inclusive, evidence-based network of protection in U.S. ocean waters and the Great Lakes:
- Coordinate ocean research and conservation across the U.S. As a first step, the strategy would bring together federal agencies with ocean-related missions to engage stakeholders, including states, Tribes and local communities, toward co-designed solutions. A key part of this process is documenting the economic and cultural values of the ocean, to reveal the hidden costs of degrading nature and include them properly in economic decision making across government and private sectors.
- Strengthen the information pipeline. The U.S. has a wealth of existing data on ocean life, but much of it is inaccessible to policymakers and managers who are making decisions on the ground. The strategy calls for stronger support of centralized, open-source databases that everyone with a stake in the ocean’s health can find and use. This also requires revamping the neglected field of taxonomy to reveal undiscovered species and harnessing new technologies to track biodiversity, such as environmental DNA (“eDNA”), satellites and artificial intelligence.
- Protect, conserve, restore and sustainably use ocean biodiversity. The strategy’s success hinges on partnerships with all key stakeholders—states, Tribes, local communities, NGOs and the private sector, including commercial and recreational fishers. The strategy calls for listening sessions as a critical starting point for collaborations built on trust. As each group’s needs and contributions are understood, managers can use their continually improving biodiversity knowledge to co-create protection measures that work over the long term, with the benefit of community input.
Lead authors Duffy and Canonico emphasize that this strategy is a first step—a high-level roadmap to a more sustainable ocean. An implementation plan is currently in development to outline specific actions tailored to region s communit ies based on feedback collected through engagement with stakeholder s .
The full strategy is available on the Office of Science and Technology Policy website . For photos or to speak with one of the authors, contact Kristen Goodhue at [email protected] .
SI-119-2024
Kristen Goodhue
443-482-2325
- News Releases
- Media Contacts
- Photos and Video
- Fact Sheets
- Visitor Stats
- Secretary and Admin Bios
- Filming Requests
Media Events
Newsdesk RSS Research News RSS

Kelp & Sardines, Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
share this!
June 3, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
'Life in the ocean touches everyone': US rolls out first national ocean biodiversity strategy
by Smithsonian
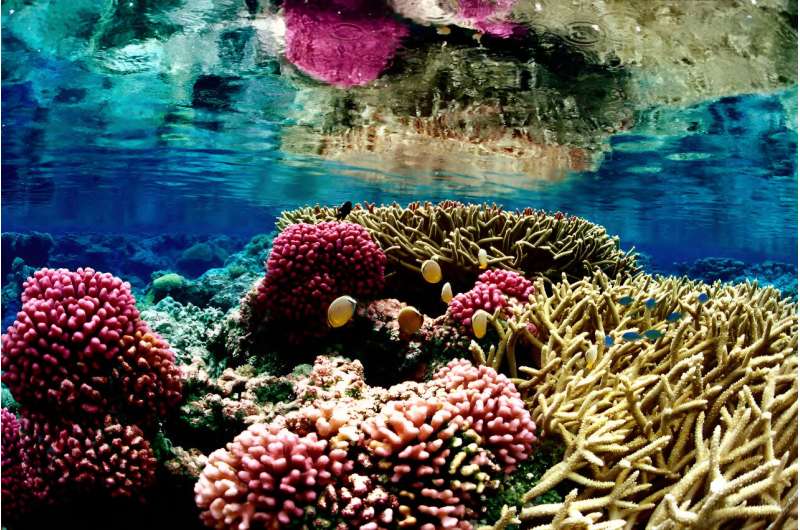

Roughly 2 million species live in the world's oceans. But scientists have only described a mere 10% of them. With extinctions on the rise and biodiversity threatened worldwide, many species are in danger of vanishing before researchers can identify them or fully grasp the benefits they provide.
The National Ocean Biodiversity Strategy calls for a stronger, more unified and inclusive approach to ocean conservation . Written by a team led by the Smithsonian and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the strategy was announced by the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy on June 3.
It represents the first nationwide strategy aimed at changing course to save marine life and all the services it provides to people. The plan seeks to improve scientists' ability to gather and share knowledge and use that knowledge for more effective protection.
"We are confronting biodiversity loss and its implications for human well-being, alongside the challenges posed by climate change and social inequity," said Ellen Stofan, Under Secretary for Science and Research at the Smithsonian. "But we hold the power to overcome these obstacles with a united, society-wide effort to preserve nature and its benefits."
The prosperity and health of the U.S. is inextricably tied to the ocean and its life. The ocean contributes nearly $400 billion to the U.S. economy every year and provides 2.4 million jobs according to NOAA, including fishing, shipping, tourism and energy.
And the nation's ocean waters are vast: The total ocean territory under U.S. management—known as the "U.S. Exclusive Economic Zone"—covers an area larger than all 50 states combined. Much of this prosperity comes from the ocean's diverse species and habitats.
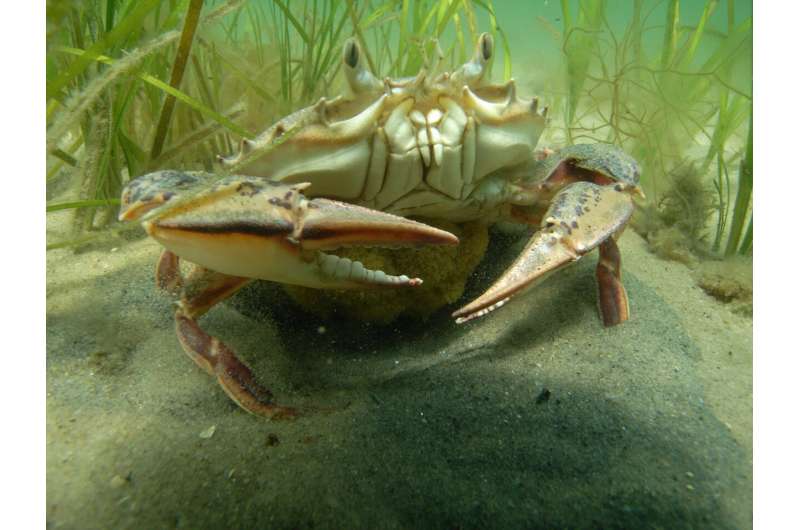

"Life in the ocean touches everyone," said Gabrielle Canonico, leader of the U.S. Marine Biodiversity Observation Network at NOAA and co-chair of the team that wrote the strategy.
"Every other breath we take comes from the oxygen produced by microscopic ocean plants, and more than a billion people worldwide rely on food from the ocean as their primary source of protein. But these and other benefits will degrade with biodiversity loss , with dire consequences especially for frontline communities."
Critical gaps remain in the nation's protection and even knowledge of ocean life. The knowledge scientists do possess about the ocean is often scattered, with many organizations gathering information in different formats that are difficult to share. Many smaller organisms, including those that cause disease, are barely studied at all.
Scientists suspect these neglected species contain secrets vital to keeping coral reefs and fisheries thriving and the ocean's plankton pumping atmospheric carbon into the deep sea. The strategy addresses this challenge with plans to strengthen the nation's ocean observing system and the information pipeline that delivers knowledge to those who need it.
"We are advancing frontier technologies for biodiversity science and understanding," said Sarah Kapnick, NOAA chief scientist. "But it is critical that we come together around the use of evidence-based metrics and indicators for decision-making in ocean spaces, and for monitoring, reporting, and verification to ensure that investments in conservation or development deliver the desired outcomes while minimizing negative impacts to ocean life."
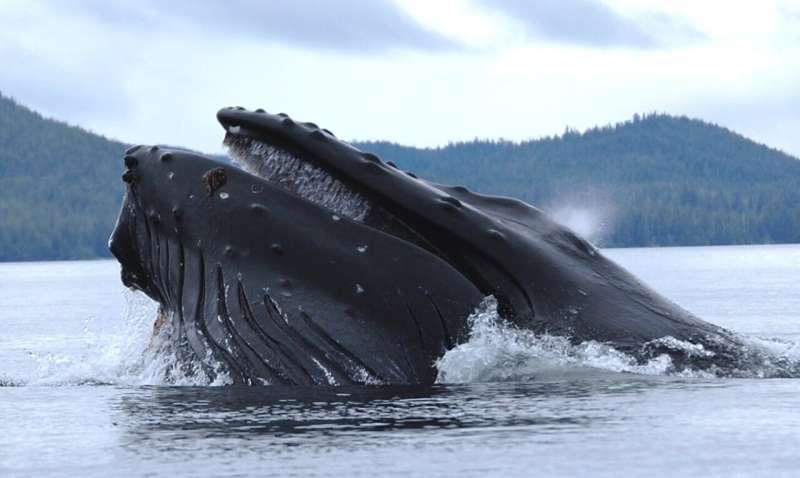

"Biodiversity is the beating heart of the ocean that supports society, but it's in trouble," said Emmett Duffy, the other co-chair of the strategy's writing team and chief scientist of MarineGEO at the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center . "This strategy is our best chance yet to turn the tide. We need to implement it to reach a future where people and the rest of nature thrive together by joining forces and leveraging the power of people and technology to understand the living ocean ecosystem."
The National Ocean Biodiversity Strategy outlines a three-fold plan to create a more inclusive, evidence-based network of protection in U.S. ocean waters and the Great Lakes:
- Coordinate ocean research and conservation across the U.S: As a first step, the strategy would bring together federal agencies with ocean-related missions to engage stakeholders, including states, Tribes and local communities, toward co-designed solutions. A key part of this process is documenting the economic and cultural values of the ocean, to reveal the hidden costs of degrading nature and include them properly in economic decision making across both government and private sectors.
- Strengthen the information pipeline: The U.S. has a wealth of existing data on ocean life, but much of it is inaccessible to policymakers and managers who are making decisions on the ground. The strategy calls for stronger support of centralized, open-source databases that everyone with a stake in the ocean's health can find and use. This also requires revamping the neglected field of taxonomy to reveal undiscovered species and harnessing new technologies to track biodiversity, such as environmental DNA ("eDNA"), satellites and artificial intelligence.
- Protect, conserve, restore and sustainably use ocean biodiversity: The strategy's success hinges on partnerships with all key stakeholders—states, Tribes, local communities, NGOs and the private sector, including commercial and recreational fishers. The strategy calls for listening sessions as a critical starting point for collaborations built on trust. As each group's needs and contributions are understood, managers can use their continually improving biodiversity knowledge to co-create protection measures that work over the long term, with the benefit of community input.
Lead authors Duffy and Canonico both emphasize that this strategy is a first step—a high-level roadmap to a more sustainable ocean. An implementation plan is currently in development to outline specific actions tailored to regions and communities based on feedback collected through engagement with stakeholders.
Provided by Smithsonian
Explore further
Feedback to editors

A protein that enables smell in ants—and stops cell death
26 minutes ago
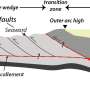
Cascadia Subduction Zone, one of Earth's top hazards, comes into sharper focus

New research finds lake under Mars ice cap unlikely

Research team uses CRISPR/Cas9 to alter photosynthesis for the first time

First ever report of two ancient ape species cohabiting in Miocene Europe 11 million years ago
Researchers discover Earth and space share the same turbulence
44 minutes ago

DNA in the feces of snow leopards shows alpine cats eat plants

Study suggests evolutionary basis for male risk-taking behaviors
Study adds new sea cucumber species to the research toolbox

Wildfire smoke reached 99% of US lakes in 2019–2021: Study introduces 'lake-smoke day' metric
2 hours ago
Relevant PhysicsForums posts
The secrets of prof. verschure's rosetta stones.
21 hours ago
Is it possible to transform an electric thunderstorm into an EMP storm?
Jun 4, 2024
Jacchia Atmospheric Model
Jun 3, 2024
Iceland warming up again - quakes swarming
Mount ibu, indonesia erupts.
May 29, 2024
Adirondack Mountains and earthquakes
May 23, 2024
More from Earth Sciences
Related Stories

A plan to protect the biodiversity of US waters
Feb 21, 2024
Equity must be considered in ocean governance to achieve global targets by 2030, researchers say
May 15, 2024

Transformation of ocean management is underway, study finds
May 9, 2024

Climate-smart marine spatial planning in Antarctica can be a model for the global ocean
May 22, 2024
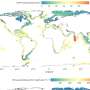
Seaweed forests are an overlooked component of oceanic carbon storage, study finds
Tagged turtles and 3D ocean current maps reveal loggerheads' navigation mechanisms
Dec 13, 2023
Recommended for you
Scientists develop new method to estimate electrical parameters of regular pulse bursts in lightning
4 hours ago
Coming in from the cold: Study reveals widespread negative experiences for women in polar research
Jun 6, 2024

Faster alerts for California megaquakes: Early-warning system gets major upgrade
Fighting fires from space in record time: How AI could prevent a repeat of Australia's devastating wildfires
Jun 5, 2024
Microsoft unveils Aurora, an AI-based weather forecasting system that can also predict air pollution levels
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Aspects, Importance and Issues of Biodiversity Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Importance of biodiversity, aspects of biodiversity, reference list.
Biological diversity, also known as biodiversity, is the variety and variability among living organisms and the ecological complexes in which they occur.
This diversity is evidenced by differences in the morphology of living organisms which make them suitably adapted to various ecosystems. The following paragraphs discuss the importance of biodiversity on our planet and some of the different aspects of biodiversity.
As mentioned above, biodiversity is important because ecosystems that support life on earth have various characteristics that make them only suitable for specific species. Each organism has a specific role to play in an ecosystem.
The human species derive multiple benefits from a diverse biological ecosystem that we can not imagine how life would be sustained without biodiversity.
Natural products from plants and animals are used by human beings to provide food, medicine extracts such as penicillin, fertilizers, and pesticides. Plants and trees use carbon dioxide giving out oxygen which is used by human beings.
Diversity in plants and animals form the basis for scientific inquiry into different realms such as evolutionary science, anatomy, and ecology.
Last but not least biodiversity is beautiful, many recreational facilities benefit from biodiversity; hence biodiversity is often the subject of aesthetic interest (Wilson, 2008, p. 32s).
Loss of biodiversity will have a disastrous effect on the human species. Food security will be compromised in case of species become extinct; this will lead to malnutrition and eventually death.
Trees are a cheap energy source for many poor communities in developing countries around the world. Loss of trees will make such communities vulnerable to disease and malnutrition due to lack of heat to cook food and boil water.
Continued deforestation and destruction of water bodies will decrease the amount of clean water that is needed to support life.
Oxygen levels will decrease drastically leading to increased levels of carbon dioxide gas which will cause severe breathing conditions eventually death (Wilson, 2008, p. 57).
Aspects of biodiversity fall under three major categories namely genetic diversity, species diversity, and ecological diversity. Genetic diversity is a term used to refer to the dissimilitude of organisms of the same species. Species diversity is used to refer to dissimilitude of organisms in a given region.
Species diversity presents the richness of a variety of species on a single region. Ecological diversity is a variety of biological communities or ecosystems in a given area (Wilson, 2008, p. 53).
For example varieties of biological communities that interact with one another and with their physical and chemical environments.
All the aspects of biodiversity promote better species which are more resilient to diseases; genetic biodiversity reduces relatedness within the same species in a given region such as colonies ensuring long term survival of species.
Species diversity ensures better utilization of available resources in an ecosystem thus maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
Ecological diversity ensures better coordination of species in their physical and environmental locations (Wilson, 2008, p. 64). Thus most species have been successfully conserved by biological diversity.
As discussed above, biodiversity is essential. It is particularly important in the sustenance of species. Species are preserved by their interrelation.
Evidence of the dependence of man on biodiversity is everywhere, but the most useful benefit of biodiversity is the provision of oxygen and clean water which enables all the organisms to thrive on earth without which there could be no life.
Wilson, E. (2008). Biodiversity. California. Barnes & Noble.
- Natural Selection and Biodiversity
- Biodiversity, Its Importance and Benefits
- National Biodiversity Strategy
- Bio Diversity and Future of Our World
- Mescaline Peyote: Origins, Effects, and Uses
- The Diffusion of a Cell
- Genetic Experimentation and Development
- A Study of “Escherichia Coli”
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, March 13). Aspects, Importance and Issues of Biodiversity. https://ivypanda.com/essays/biodiversity-issues/
"Aspects, Importance and Issues of Biodiversity." IvyPanda , 13 Mar. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/biodiversity-issues/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Aspects, Importance and Issues of Biodiversity'. 13 March.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Aspects, Importance and Issues of Biodiversity." March 13, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/biodiversity-issues/.
1. IvyPanda . "Aspects, Importance and Issues of Biodiversity." March 13, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/biodiversity-issues/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Aspects, Importance and Issues of Biodiversity." March 13, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/biodiversity-issues/.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Perspective
- Open access
- Published: 05 June 2024
Research needs on the biodiversity–ecosystem functioning relationship in drylands
- Fernando T. Maestre 1 ,
- Lucio Biancari 2 , 3 ,
- Ning Chen 4 , 5 ,
- Mario Corrochano-Monsalve 4 , 6 ,
- G. Darrel Jenerette 4 , 7 ,
- Corey Nelson 4 ,
- Kaarina N. Shilula 4 , 8 &
- Yelyzaveta Shpilkina 4
npj Biodiversity volume 3 , Article number: 12 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
359 Accesses
15 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Biodiversity
- Community ecology
- Ecosystem ecology
Research carried out in drylands over the last decade has provided major insights on the biodiversity–ecosystem functioning relationship (BEFr) and about how biodiversity interacts with other important factors, such as climate and soil properties, to determine ecosystem functioning and services. Despite this, there are important gaps in our understanding of the BEFr in drylands that should be addressed by future research. In this perspective we highlight some of these gaps, which include: 1) the need to study the BEFr in bare soils devoid of perennial vascular vegetation and biocrusts, a major feature of dryland ecosystems, 2) evaluating how intra-specific trait variability, a key but understudied facet of functional diversity, modulate the BEFr, 3) addressing the influence of biotic interactions on the BEFr, including plant–animal interactions and those between microorganisms associated to biocrusts, 4) studying how differences in species–area relationships and beta diversity are associated with ecosystem functioning, and 5) considering the role of temporal variability and human activities, both present and past, particularly those linked to land use (e.g., grazing) and urbanization. Tackling these gaps will not only advance our comprehension of the BEFr but will also bolster the effectiveness of management and ecological restoration strategies, crucial for safeguarding dryland ecosystems and the livelihoods of their inhabitants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Multiple elements of soil biodiversity drive ecosystem functions across biomes
The supply of multiple ecosystem services requires biodiversity across spatial scales
Experimental impacts of grazing on grassland biodiversity and function are explained by aridity
Introduction.
Drylands are broadly defined as those areas with an aridity index (precipitation/potential evapotranspiration) below 0.65 1 . They host a biota that must cope with environments characterized by the scarcity of resources such as water and soil nutrients, highly variable and in some cases extreme climatic conditions, and recurrent disturbances such as droughts 2 . Contrary to the belief that these harsh environmental conditions should restrict biodiversity (e.g., the environmental filtering theory 3 ), drylands host unique landscapes and biota (Fig. 1 ) that have fascinated explorers and scientists for centuries 4 , 5 , 6 . As an example, drylands show a high diversity of plant leaf functional traits mirroring that observed across the rest of terrestrial ecosystems (the so–called drylands functional paradox 7 ). Other remarkable findings are that dryland vegetation has been found to contribute disproportionately to observed global productivity increases over the last decades 8 , and that iconic dryland megafauna, such as elephants, not only are fundamental for the development of local communities but also contribute to soil carbon sequestration 9 . These discoveries have helped to increase awareness among scientists and the general public of the importance of drylands and their biodiversity for sustaining life on our planet as we know it, and for mitigating the impacts of ongoing climate change.

Drylands areas are marked in dark gray in the map. Photo credits (from left to right and from the upper to the lower part of the figure): Raychel Sanner on Unsplash , Leo Barco, Fernando T. Maestre, Azzedine Rouichi on Unsplash , NEOM on Unsplash , Explore with Joshua on Unsplash , Rabah Al Shammary on Unsplash , David Vives on Unsplash , Markus Blüthner on Unsplash , Leon Pauleikhoff on Unsplash , sutirta budiman on Unsplash , and Megan Clark on Unsplash .
A key topic of biodiversity research over the last 30 years has been to understand the functional consequences of biodiversity, and in particular the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning (BEFr hereafter) 10 , 11 . This body of work has, among other aspects, shown that increases in both species richness and functional diversity enhance key ecosystem functions such as productivity across a wide range of ecosystems, has revealed the mechanisms behind the BEFr, and has shown that diversity effects increase through time 10 . While most of the initial research on this topic was carried out in non–dryland environments, over the last decade dryland research has made fundamental contributions to our understanding of the BEFr. These include, among others, the first empirical evidence at the global scale of positive links between plant 12 and microbial 13 diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality (EMF), assessing how multiple biodiversity facets (taxonomic, functional, and phylogenetic) jointly affect EMF globally 14 , and highlighting how functional diversity maximizes EMF across drylands worldwide 15 .
In recent years, BEF research is moving from demonstrating that biodiversity matters for ecosystem functioning to understanding the context–dependency of the BEFr and to explicitly account for the inherent complexity of dealing with multi–taxa and multi–trophic ecosystems that change both in space and time. This includes evaluating how the BEFr is modulated by other biotic and abiotic factors 16 , how it changes through time 17 and depends on the functions being considered 18 , or how diversity across multiple taxa and trophic levels impact the BEFr 19 . Despite increased research efforts over the years, some of these emerging topics have not been addressed in drylands yet or are just starting to be explored 20 , 21 .
Here we discuss some emerging and understudied questions about the BEFr in drylands (Fig. 2 ). We do not pretend to provide an in–depth review of all the relevant topics surrounding the BEFr, but rather to highlight a few key knowledge gaps that, in our opinion, need to be addressed by future research to better understand this relationship in drylands. In doing so, we can not only deepen our understanding of the BEFr, but also propel research efforts aimed at conserving biodiversity and effectively managing ecosystem services vital for supporting the livelihoods of over 2 billion people residing in dryland regions, which cover more than 41% of the Earth’s surface 22 .

These include addressing the BEFr in bare soils and evaluating the influences of various factors such as biotic interactions, trait variations, species–area relationships, beta diversity, and human activities on the BEFr. The numbers correspond with the order in which these gaps are presented in the abstract and the main text. The arrows show connections between the different gaps, and aim to highlight how advances in our understanding of a given topic can contribute to fill other gaps in our understanding of the BEFr.
Bare soils, a key but understudied feature of dryland ecosystems
Bare soils, which cover approximately 35 million km 2 worldwide 23 , are a common and distinctive feature of drylands (Box 1 ). Dryland ecosystems are typically characterized by discrete plant patches surrounded by a matrix of bare ground devoid of perennial vegetation (Fig. 3 ), which may or not contain biocrusts (communities of mosses, lichens, cyanobacteria, and other microorganisms living in the soil surface that are prevalent in global drylands; see ref. 24 for a formal definition and Supplementary Fig. 1 for examples). Despite their global extent, bare soils have been largely overlooked in the BEFr literature compared to vegetated areas 10 , 11 , 25 .

The figure shows examples of bare soils with ( A ) and without ( B ) well-developed biocrusts. See Supplementary Fig. 1 for close-up examples of the types of biocrusts that can be found in drylands. Photo credits: Andrea Castillo-Monroy ( A ) and Juan Gaitán ( B ).
Bare soils are highly exposed to abiotic factors because they lack the buffering effect of vegetation or biocrusts 26 . In this sense, these areas represent an excellent opportunity to explore BEFr under extreme edaphoclimatic conditions, which are forecasted to extend in future decades 27 , and can shed light on mechanisms that can be relevant for understanding ecosystem responses to climate change in non–dryland environments 28 .
Our understanding of the BEFr in bare soils is significantly limited when compared to our extensive knowledge of soils with vegetation, and to a lesser degree, biocrusts 29 . We could hypothesize that a very plastic BEFr can occur in these areas, with a microbiome adapted to an efficient –but also fast– use of scarce resources resulting in great metabolic pulses linked to rainfall events 30 . A very specialized microbiota might be necessary for doing so. However, we lack sufficient data to generalize whether a higher or a lower diversity is needed in bare soils to maintain ecosystem functioning. The bare soil microbiome might contain a rich batch of genes associated with efficient resource use and resistance genotypes, of which a majority are probably not available in public datasets 31 . In the absence of vegetation, microbially mediated modifications of soil properties and their influence on nutrient cycling could become even more relevant 32 . We have very limited field data regarding nutrient transformation rates in these areas. Some studies suggest intense leaks of nitrogen in gaseous forms in arid environments 33 , 34 , but the role of biodiversity in influencing such emissions remains almost unknown and represents a key topic for future research.
Understanding the BEFr of bare soils can also be helpful to enhance the success of ecological restoration initiatives. Gaining insights into the intricacies of the BEFr in bare soils would provide valuable knowledge to determine whether a given bare soil has the microbial species and interactions needed to maintain nutrient cycling 35 , which is essential for the survival of tree/shrub/grass plantations and thus to support essential functions and services.
Box 1 What are bare soils in drylands?
Expanses of open ground dotted with sparse vegetation are a common feature of dryland ecosystems (Fig. 1 ). This spatial heterogeneity typically gives rise to soil microsites with varying biodiversity and functioning 2 , 29 , 70 . Here, we broadly define three microsites that are commonly found in drylands worldwide as: i) soils influenced by the canopy and nutrient inputs of perennial vegetation, ii) bare soils inhabited by biocrusts (typically found in plant interspaces, see Figs. 3 and S1 ), and iii) bare soils, which are those not directly influenced by aboveground parts of perennial vegetation nor harboring developed biocrusts. Investigations of soil biodiversity and their relationship to ecosystem functioning in drylands tend to focus on soils influenced by perennial phototrophs (vegetation and biocrusts), while bare soils have typically been understudied.
Accounting for understudied facets of functional diversity
Functional traits represent the physical, chemical, physiological, structural, phenological, or behavioral attributes of organisms that have an impact on their performance, overall fitness and contribution to ecosystem processes 36 , 37 . They are commonly used to characterize community responses to environmental changes and to measure how shifts in communities affect ecosystem functions 36 , 37 . As such, the study of functional traits can help us better understand the mechanisms underlying the BEFr 36 and holds particular significance in drylands owing to the distinct features of these ecosystems. These include a greater plant functional diversity and a higher evenness in the distribution of plant functional traits compared to other biomes 7 . Indeed, the importance of functional diversity for the BEFr in drylands has been already demonstrated using multiple spatial scales and taxa 38 , 39 .
Intra–specific trait variability has been shown to play a substantial role in shaping the response of certain plant functional traits to aridity in drylands 38 , 40 , and its role in maintaining ecosystem functioning is being increasingly recognized 41 . However, there is a lack of studies addressing the impact of such variability in the BEFr in drylands and thus it is largely unknown how the loss of intra–specific trait variability could affect the functioning of these ecosystems. Such loss can have important functional consequences, as genetic erosion and the loss of phenotypic diversity could result in a decrease of ecosystem functioning without losing species from an ecosystem 42 .
Research on the ecological roles of functional diversity in general, and on the BEFr in particular, has largely focused on the study of plants (see ref. 43 and references therein). Being crucial for ecosystem functioning, plants mainly operate within a single trophic level, and thus an excessive dependence on plant traits tends to overlook the intricacies and significance of functional diversity across multiple trophic levels 44 . The analysis of functional traits of biocrusts is receiving increasing attention over the years 39 , 45 , 46 , whereas comparatively less emphasis has been placed on exploring the functional traits of animals 44 . Furthermore, no previous study has, to our knowledge, assessed how the functional diversity of biocrusts and animals impact the BEFr in drylands, and thus the role of the functional diversity (vs. taxonomic diversity) of these important organisms for the maintenance of ecosystem functioning in drylands is unknown. This is thus an important knowledge gap to be covered by future studies.
Biotic interactions, critical drivers of dryland ecosystem structure
Species in drylands are adapted to exist at the edge of environmental conditions suitable for life 2 . The distribution of these organisms is subject to biotic interactions, which largely influence the structure and functioning of these ecosystems 7 , 47 . For example, many dryland species depend on positive biotic interactions for their persistence in stressful water–limited environments 48 , 49 . Further, observed positive effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning lie on the basis of a positive balance between negative (e.g., competition) and positive (e.g., facilitation and mutualism) interactions 50 . Understanding the influence of biotic interactions on the BEFr is crucial as species interactions may be more prone to rapid shifts due to the increased frequency and magnitude of extreme events in drylands 51 .
Some key questions remain to be elucidated regarding plant–animal interactions and the BEFr that are particularly important in drylands. We know very little about how interactions between plants and soil fauna affect ecosystem functioning and the BEFr in these areas, but they will likely play an important role. For example, in Neotropical savannas, the composition and diversity of soil epigeic fauna have been found to influence litter decomposition rates 52 . It is also known that the release of organic compounds by roots, among other functions, serve to attract beneficial soil invertebrates and disrupt harmful bacteria communication, ultimately fostering plant growth across diverse ecosystems 53 . This area strongly warrants future research attention, together with the study of the relationships between pollinator diversity and ecosystem functioning in drylands, which remain inadequately understood 54 .
Within drylands, biocrusts are biodiversity/functional hotspots that provide a variety of services such as nutrient inputs, stabilization, and alteration of hydrological properties of the soils they inhabit 24 , 55 . Despite their recognized importance and the growing interest in biocrust BEFr research 29 , investigations into the role of biotic interactions within biocrusts or how these interactions might influence the BEFr in drylands are limited 47 . Recent advances in the microbial ecology of biocrusts have provided evidence that microbe–microbe interactions can influence the BEFr in drylands. For example, the formation of biocrusts typically depends on mutualistic resource trading relationships between pioneer cyanobacteria and soil diazotrophic bacteria during the initial colonization of bare soils to provide nutrient inputs required for the biomass necessary to stabilize soils for further colonization 56 , 57 . Conversely, a newly described predatory bacterium ( Candidatus ‘Cyanoraptor togatus’) preys preferentially on specific biocrust–associated cyanobacteria 58 , disrupting the spatial organization of biocrust and creating niches for less abundant –but predation–resistant– biocrust pioneer species, such as those found in the family Coleofasciculaceae (formerly Microcoleus steenstrupii ) 59 . These biotic interactions fundamentally impact biodiversity and functional traits in biocrust communities at the cm scale, which, given the extent of biocrusts across global drylands 24 , are likely to contribute significantly to ecosystem functioning.
A comprehensive exploration of microbial interactions governing soil processes and how they contribute to the BEFr in drylands can certainly enhance our comprehension of biocrust responses to global change drivers. Predicted climate change will likely have a large effect on biocrusts and the interactions within their constituents, as it has already been shown that temperature and precipitation patterns have differential effects on biogeographical predominance of pioneer soil microbes linked to biocrust formation 60 . Determining whether fundamental microbial interactions can persist under increased frequency and magnitude of extreme events will be key in determining the distribution and functioning of biocrusts in a rapidly changing world. Doing so could not only potentially indicate environmental thresholds that could predict sudden changes in ecosystem functioning as biotic interactions shift, but also aid with the development of soil conservation and restoration strategies in a more arid world.
Incorporating spatial scale
While much success in BEFr research has been made in plot–scale studies, a need remains to move beyond individual plots to identify landscape interactions with the BEFr 61 , 62 . This is especially true in drylands because spatial heterogeneity is extensive in these environments 2 , 7 and the BEFr may be affected by the distribution of habitat patches and environmental gradients throughout a landscape 63 .
While variation across scales has been considered in detail for biodiversity, we need better approaches for connecting this research to ecosystem functioning. For example, species–area relationships have been considered one of the few “laws” of ecology 64 but this relationship has had only limited connections to ecosystem functioning 62 . How differences in species–area relationships are associated with ecosystem functioning remain a key question for future BEFr research in drylands. In another example, extensive research has been directed to characterizing beta diversity, or the turnover of species among locations 65 . In contrast to the extensive research on BEFr with plot–scale diversity, more research is needed to characterize how variation in beta diversity affects ecosystem functioning 66 , 67 .
Through the consideration of scale, the spatial heterogeneity characterizing dryland landscapes should be a key component of landscape controls on the BEFr. Dryland BEFr should vary throughout a landscape in response to variation in water availability, nutrients, and community assemblages, and is likely to be affected by the connectivity among locations and the isolation of habitats 63 , 68 . How the movement of materials and organisms among habitats (e.g., isolated plant patches) can affect the BEFr is an important frontier for future research 69 . Finally, landscape heterogeneity may reflect self–organization of ecological interactions, which can affect both biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Two prominent dryland examples, the generation of islands of fertility 70 and of fairy circles 71 , both reflect an organization of species and ecosystem dynamics that may affect the BEFr.
Accounting for temporal variability and humans
The structure and functioning of drylands is largely impacted by temporal changes in key resources such as water 2 . Thus it is not surprising to see the large body of conceptual and empirical research aiming to understand the ecological roles of rainfall pulses, which are inherently temporally variable in drylands 30 , 72 , 73 . Some studies have addressed how biodiversity, alone and in interaction with other abiotic and biotic factors, impacts ecosystem stability in drylands 20 , 74 . However, there are still large uncertainties regarding the role that the BEFr plays in the temporal dynamics of these ecosystems, which should be addressed by future research. Key questions to be addressed include: i) evaluating temporal changes in the BEFr at different scales, from rainfall pulses to decadal drought as well as directional changes associated with ongoing warming, ii) explicitly considering both contemporaneous and legacy effects 75 of temporal variability on the BEFr, and iii) addressing the role of rare places and rare events (“hotspots and hot moments” sensu ref. 76 ) on the BEFr.
Another key control on the BEFr in drylands that we should also explicitly consider is the role of human activities, both present and past, which can vary across spatial and temporal scales and have pronounced effects on the structure and functioning of drylands 77 , 78 , 79 . Spanning agricultural practices, from irrigated crops to grazing, development, from urbanization to nutrient pollution, and natural resource management, from fire prevention to restoration, human activities generate novel ecosystems that are likely to have distinct BEFr from theoretically “natural” ecosystems. For example, changes in grazing pressure could modify the effect that plant and herbivore diversity have on the provision of multiple ecosystem services 21 . However, more studies are needed to elucidate the effect of herbivore species replacement (e.g., increasing domestic livestock instead of wild herbivores or vice versa) and on how the diversity (both taxonomic and functional) and complementarity of herbivores affect ecosystem functioning 21 . Studying BEFr in dryland urban environments is also a topic of particular interest. There is a renewed interest and efforts for greening dryland cities to mitigate the impacts of climate change and to increase their livability 80 . These efforts would undoubtedly benefit from studies aiming to understand how the taxonomical and functional diversity of trees and shrubs in urban parks and streets impact water use, evapotranspiration, carbon sequestration, the biodiversity of other taxa, and human wellbeing. Such research holds significant potential to optimize the advantages of greening initiatives while concurrently mitigating water consumption, which is increasingly constrained in drylands globally due to climate change and mismanagement 81 . The imprint of historic land use by humans also has a lasting effect on soil conditions; for example, agricultural activities more than 1000 years in the past have influenced current patterns of desert species assemblages and soil conditions 82 . A better understanding of legacy effects from human activities could also inform future forecasts for drylands, as recently illustrated with the use of climatic legacies for predicting the future distribution of dryland forests 83 .
United Nations Environment Programme. World Atlas of Desertification . https://wedocs.unep.org/20.500.11822/42137 (1992).
Whitford, W. G. Ecology of Desert Systems . (Academic Press, 2002).
Keddy, P. A. Assembly and response rules: two goals for predictive community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 3 , 157–164 (1992).
Article Google Scholar
Shreve, F. The desert vegetation of North America. Bot. Rev. 8 , 195–246 (1942).
Keast A., Crocker R. L., Christian C. S. (Eds). Biogeography and Ecology in Australia . (Dr. W. Junk, 1959).
Hegazy, A. & Lovett-Doust, J. Plant Ecology in the Middle East . (Oxford University Press, 2016).
Maestre, F. T. et al. Biogeography of global drylands. New Phytol. 231 , 540–558 (2021).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Wang, S. et al. Drylands contribute disproportionately to observed global productivity increases. Sci. Bull. 68 , 224–232 (2023).
Sandhage-Hofmann, A., Linstädter, A., Kindermann, L., Angombe, S. & Amelung, W. Conservation with elevated elephant densities sequesters carbon in soils despite losses of woody biomass. Glob. Chang. Biol. 27 , 4601–4614 (2021).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Tilman, D., Isbell, F. & Cowles, J. M. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 45 , 471–493 (2014).
Ali, A. Biodiversity–ecosystem functioning research: Brief history, major trends and perspectives. Biol. Conserv. 285 , 110210 (2023).
Maestre, F. T. et al. Plant species richness and ecosystem multifunctionality in global drylands. Science 335 , 214–218 (2012).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Delgado-Baquerizo, M. et al. Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 7 , 10541 (2016).
Le Bagousse-Pinguet, Y. et al. Phylogenetic, functional, and taxonomic richness have both positive and negative effects on ecosystem multifunctionality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 116 , 8419–8424 (2019).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gross, N. et al. Functional trait diversity maximizes ecosystem multifunctionality. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 1 , 0132–0132 (2017).
Gottschall, F. et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of abiotic and biotic properties explain biodiversity–ecosystem‐functioning relationships. Ecol. Monogr . 92 , e01490 (2022).
Meyer, S. T. et al. Effects of biodiversity strengthen over time as ecosystem functioning declines at low and increases at high biodiversity. Ecosphere 7 , e01619 (2016).
Geert Hiddink, J., Wynter Davies, T., Perkins, M., Machairopoulou, M. & Neill, S. P. Context dependency of relationships between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning is different for multiple ecosystem functions. Oikos 118 , 1892–1900 (2009).
Eisenhauer, N. et al. A multitrophic perspective on biodiversity–ecosystem functioning research. Adv. Ecol. Res. 61 , 1–54 (2019).
García-Palacios, P., Gross, N., Gaitán, J. & Maestre, F. T. Climate mediates the biodiversity-ecosystem stability relationship globally. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 115 , 8400–8405 (2018).
Maestre, F. T. et al. Grazing and ecosystem service delivery in global drylands. Science 378 , 915–920 (2022).
Reynolds, J. F. et al. Global desertification: Building a science for dryland development. Science 316 , 847–851 (2007).
Song, X.-P. et al. Global land change from 1982 to 2016. Nature 560 , 639–643 (2018).
Weber, B. et al. What is a biocrust? A refined, contemporary definition for a broadening research community. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 97 , 1768–1785 (2022).
Guerra, C. A. et al. Blind spots in global soil biodiversity and ecosystem function research. Nat. Commun. 11 , 3870 (2020).
Biancari, L., Aguiar, M. R. & Cipriotti, P. A. Grazing impact on structure and dynamics of bare soil areas in a Patagonian grass-shrub steppe. J. Arid Environ. 179 , 104197 (2020).
Huang, J., Yu, H., Guan, X., Wang, G. & Guo, R. Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 6 , 166–171 (2016).
Grünzweig, J. M. et al. Dryland mechanisms could widely control ecosystem functioning in a drier and warmer world. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 6 , 1064–1076 (2022).
Bowker, M. A., Maestre, F. T. & Escolar, C. Biological crusts as a model system for examining the biodiversity–ecosystem function relationship in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 42 , 405–417 (2010).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Collins, S. L. et al. A multiscale, hierarchical model of pulse dynamics in arid-land ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 45 , 397–419 (2014).
Chen, Y., Neilson, J. W., Kushwaha, P., Maier, R. M. & Barberán, A. Life-history strategies of soil microbial communities in an arid ecosystem. ISME J. 15 , 649–657 (2021).
Philippot, L., Chenu, C., Kappler, A., Rillig, M. C. & Fierer, N. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 22 , 226–239 (2023).
Krichels, A. H. et al. Rapid nitrate reduction produces pulsed NO and N2O emissions following wetting of dryland soils. Biogeochemistry 158 , 233–250 (2022).
Andrews, H. M. et al. Wetting-induced soil CO2 emission pulses are driven by interactions among soil temperature, carbon, and nitrogen limitation in the Colorado Desert. Glob. Chang. Biol. 29 , 3205–3220 (2023).
Jiao, S., Peng, Z., Qi, J., Gao, J. & Wei, G. Linking bacterial-fungal relationships to microbial diversity and soil nutrient cycling. mSystems 6 , e01052–20 (2021).
Debouk, H., de Bello, F. & Sebastià, M.-T. Functional trait changes, productivity shifts and vegetation stability in mountain grasslands during a short-term warming. PLoS One 10 , e0141899 (2015).
Nock, C. A., Vogt, R. J. & Beisner, B. E. Functional Traits . In: eLS. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd (Ed.) (2016).
Gross, N. et al. Uncovering multiscale effects of aridity and biotic interactions on the functional structure of Mediterranean shrublands. J. Ecol. 101 , 637–649 (2013).
Concostrina-Zubiri, L. et al. Species‐specific effects of biocrust‐forming lichens on soil properties under simulated climate change are driven by functional traits. New Phytol. 230 , 101–115 (2021).
Siefert, A. et al. A global meta-analysis of the relative extent of intraspecific trait variation in plant communities. Ecol. Lett. 18 , 1406–1419 (2015).
Jónsdóttir, I. S. et al. Intraspecific trait variability is a key feature underlying high Arctic plant community resistance to climate warming. Ecol. Monogr. 93 , e1555 (2023).
Des Roches, S. et al. The ecological importance of intraspecific variation. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2 , 57–64 (2017).
Cadotte, M. W., Carscadden, K. & Mirotchnick, N. Beyond species: functional diversity and the maintenance of ecological processes and services. J. Appl. Ecol. 48 , 1079–1087 (2011).
Schleuning, M., García, D. & Tobias, J. A. Animal functional traits: Towards a trait‐based ecology for whole ecosystems. Funct. Ecol. 37 , 4–12 (2023).
Mallen-Cooper, M. & Eldridge, D. J. Laboratory-based techniques for assessing the functional traits of biocrusts. Plant Soil 406 , 131–143 (2016).
Soliveres, S. & Eldridge, D. J. Dual community assembly processes in dryland biocrust communities. Funct. Ecol. 34 , 877–887 (2020).
Maestre, F. T. et al. Do biotic interactions modulate ecosystem functioning along stress gradients? Insights from semi-arid plant and biological soil crust communities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 365 , 2057–2070 (2010).
Mazía, N. et al. The sign and magnitude of tree-grass interaction along a global environmental gradient: Positive and negative interactions along an aridity index gradient. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 25 , 1510–1519 (2016).
Vega-Álvarez, J., García-Rodríguez, J. A. & Cayuela, L. Facilitation beyond species richness. J. Ecol. 107 , 722–734 (2019).
Flombaum, P. & Sala, O. E. Higher effect of plant species diversity on productivity in natural than artificial ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 105 , 6087–6090 (2008).
McCluney, K. E. et al. Shifting species interactions in terrestrial dryland ecosystems under altered water availability and climate change. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 87 , 563–582 (2012).
Inkotte, J. et al. Linking soil biodiversity and ecosystem function in a Neotropical savanna. Appl. Soil Ecol. 169 , 104209 (2022).
Briones, M. J. I. The serendipitous value of soil fauna in ecosystem functioning: The unexplained explained. Front. Environ. Sci. 6 , 149 (2018).
Katumo, D. M. et al. Pollinator diversity benefits natural and agricultural ecosystems, environmental health, and human welfare. Plant Diversity 44 , 429–435 (2022).
Eldridge, D. J. et al. The pervasive and multifaceted influence of biocrusts on water in the world’s drylands. Glob. Chang. Biol. 26 , 6003–6014 (2020).
Couradeau, E., Giraldo-Silva, A., De Martini, F. & Garcia-Pichel, F. Spatial segregation of the biological soil crust microbiome around its foundational cyanobacterium, Microcoleus vaginatus , and the formation of a nitrogen-fixing cyanosphere. Microbiome 7 , 55 (2019).
Nelson, C., Giraldo-Silva, A., Warsop Thomas, F. & Garcia-Pichel, F. Spatial self-segregation of pioneer cyanobacterial species drives microbiome organization in biocrusts. ISME Commun. 2 , 114 (2022).
Bethany, J., Johnson, S. L. & Garcia-Pichel, F. High impact of bacterial predation on cyanobacteria in soil biocrusts. Nat. Commun. 13 , 4835 (2022).
Moreira, C., Fernandes, V., Giraldo-Silva, A., Roush, D. & Garcia-Pichel, F. Coleofasciculaceae, a monophyletic home for the Microcoleus steenstrupii complex and other desiccation-tolerant filamentous cyanobacteria. J. Phycol. 57 , 1563–1579 (2021).
Garcia-Pichel, F., Loza, V., Marusenko, Y., Mateo, P. & Potrafka, R. M. Temperature drives the continental-scale distribution of key microbes in topsoil communities. Science 340 , 1574–1577 (2013).
Brose, U. & Hillebrand, H. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in dynamic landscapes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 371 , 20150267 (2016).
Qiu, J. & Cardinale, B. J. Scaling up biodiversity-ecosystem function relationships across space and over time. Ecology 101 , e03166 (2020).
Spiesman, B. J., Stapper, A. P. & Inouye, B. D. Patch size, isolation, and matrix effects on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in a landscape microcosm. Ecosphere 9 , e02173 (2018).
Lawton, J. H. Are there general laws in ecology? Oikos 84 , 177 (1999).
Tuomisto, H. A diversity of beta diversities: straightening up a concept gone awry. Part 1. Defining beta diversity as a function of alpha and gamma diversity. Ecography 33 , 2–22 (2010).
Hammill, E. et al. Landscape heterogeneity strengthens the relationship between β-diversity and ecosystem function. Ecology 99 , 2467–2475 (2018).
Wang, S. et al. Biotic homogenization destabilizes ecosystem functioning by decreasing spatial asynchrony. Ecology 102 , e03332 (2021).
Okin, G. S. et al. Connectivity in dryland landscapes: shifting concepts of spatial interactions. Front. Ecol. Environ. 13 , 20–27 (2015).
Harvey, E. et al. A general meta‐ecosystem model to predict ecosystem functions at landscape extents. Ecography 11 , e06790 (2023).
Ochoa-Hueso, R. et al. Soil fungal abundance and plant functional traits drive fertile island formation in global drylands. J. Ecol. 106 , 242–253 (2018).
Guirado, E. et al. The global biogeography and environmental drivers of fairy circles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 120 , e2304032120 (2023).
Noy-Meir, I. Desert ecosystems: Environment and producers. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 4 , 25–51 (1973).
Reynolds, J. F., Kemp, P. R., Ogle, K. & Fernández, R. J. Modifying the ‘pulse–reserve’ paradigm for deserts of North America: precipitation pulses, soil water, and plant responses. Oecologia 141 , 194–210 (2004).
Zuo, X. et al. Dominant species determine grazing effects on the stability of herbaceous community production at multiple scales in drylands. J. Appl. Ecol. 60 , 1917–1928 (2023).
Ye, J.-S., Delgado-Baquerizo, M., Soliveres, S. & Maestre, F. T. Multifunctionality debt in global drylands linked to past biome and climate. Glob. Chang. Biol. 25 , 2152–2161 (2019).
Bernhardt, E. S. et al. Control points in ecosystems: Moving beyond the hot spot hot moment concept. Ecosystems 20 , 665–682 (2017).
Maestre, F. T. On the importance of patch attributes, environmental factors and past human impacts as determinants of perennial plant species richness and diversity in Mediterranean semiarid steppes: Determinants of species richness and diversity in semiarid steppes. Divers. Distrib. 10 , 21–29 (2004).
Felipe-Lucia, M. R. et al. Land-use intensity alters networks between biodiversity, ecosystem functions, and services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 117 , 28140–28149 (2020).
Delgado-Baquerizo, M. et al. Human impacts and aridity differentially alter soil N availability in drylands worldwide. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 25 , 36–45 (2016).
FAO. Urban Forestry and Urban Greening in Drylands - Improving Resilience, Health, and Wellbeing of Urban Communities. A Background Document for the Green Urban Oases Programme . Rome. https://doi.org/10.4060/cc2065en (2022).
Stringer, L. C. et al. Climate change impacts on water security in global drylands. One Earth 4 , 851–864 (2021).
Hall, S. J. et al. Legacies of prehistoric agricultural practices within plant and soil properties across an arid ecosystem. Ecosystems 16 , 1273–1293 (2013).
Guirado, E. et al. Climate legacies drive the current distribution and future restoration potential of dryland forests. Nat. Plants 8 , 879–886 (2022).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Emilio Guirado for his help in crafting Fig. 1 . F.T.M. acknowledges support by the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) and the KAUST Climate and Livability Initiative. M.C.-M. holds a Postdoctoral Margarita Salas contract from the Ministerio de Universidades of Spain funded through the NextGenerationEU initiative of the European Union. N.C. appreciated helpful discussion with Zhengwei Ren of Lanzhou University and was supported by the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación of Spain (PCI2021-122103-2B), by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (lzujbky-2021-ey16), and by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32271620). C.N. is supported by Juan de la Cierva postdoctoral fellowship funded by the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación of Spain (FJC2021-046473-I). L.B. is sponsored by a postdoctoral fellowship of Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCyT Argentina, PICT 2019-2645). K.S. acknowledges support from a Learn Africa predoctoral fellowship funded by the Gender Equality Unit of the University of Alicante.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Environmental Sciences and Engineering, Biological and Environmental Science and Engineering Division, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology, Thuwal, 23955-6900, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Fernando T. Maestre
IFEVA, Universidad de Buenos Aires, CONICET, Facultad de Agronomía, Av. San Martín 4453, Buenos Aires, C1417DSE, Argentina
Lucio Biancari
Cátedra de Ecología, Departamento de Recursos Naturales y Ambiente, Facultad de Agronomía, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Av. San Martín 4453, Buenos Aires, C1417DSE, Argentina
Instituto Multidisciplinar Para el Estudio del Medio “Ramon Margalef”, Universidad de Alicante, Carretera de San Vicente del Raspeig s/n, 03690, San Vicente del Raspeig, Spain
Ning Chen, Mario Corrochano-Monsalve, G. Darrel Jenerette, Corey Nelson, Kaarina N. Shilula & Yelyzaveta Shpilkina
State Key Laboratory of Herbage Improvement and Grassland Agro-ecosystems, College of Ecology, Lanzhou University, No.222, Tianshui South Road, Lanzhou, Gansu, 730000, China
Departamento de Genética, Antropología Física y Fisiología Animal, Facultad de Ciencia y Tecnología, Universidad del País Vasco (UPV/EHU), Leioa, Spain
Mario Corrochano-Monsalve
Department of Botany and Plant Sciences, University of California, Riverside, CA, USA
G. Darrel Jenerette
Departamento de Ecología, Universidad de Alicante, Carretera de San Vicente del Raspeig s/n, 03690, San Vicente del Raspeig, Spain
Kaarina N. Shilula
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
F.T.M. planned the perspective, with inputs from L.B., N.C., M.C-M., G.D.J., C.N., K.N. S. & Y.S. F.T.M. led the writing of the manuscript and revised the manuscript to account for reviewer´s comments; L.B., N.C., M.C-M., G.D.J., C.N., K.N. S. & Y.S. contributed to the writing of the manuscript. All co-authors jointly revised the final draft.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Fernando T. Maestre .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary material, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Maestre, F.T., Biancari, L., Chen, N. et al. Research needs on the biodiversity–ecosystem functioning relationship in drylands. npj biodivers 3 , 12 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44185-024-00046-6
Download citation
Received : 20 November 2023
Accepted : 05 April 2024
Published : 05 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s44185-024-00046-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
The University of Chicago The Law School
College essays and diversity in the post-affirmative action era, sonja starr’s latest research adds data, legal analysis to discussion about race in college admissions essays.

Editor’s Note: This story is part of an occasional series on research projects currently in the works at the Law School.
The Supreme Court’s decision in June 2023 to bar the use of affirmative action in college admissions raised many questions. One of the most significant is whether universities should consider applicants’ discussion of race in essays. The Court’s decision in Students for Fair Admissions (SFFA) v. Harvard did not require entirely race-blind admissions. Rather, the Court explicitly stated that admissions offices may weigh what students say about how race affected their lives. Yet the Court also warned that this practice may not be used to circumvent the bar on affirmative action.
Many university leaders made statements after SFFA suggesting that they take this passage seriously, and that it potentially points to a strategy for preserving diversity. But it’s not obvious how lower courts will distinguish between consideration of “race-related experience” and consideration of “race qua race.” Sonja Starr, Julius Kreeger Professor of Law & Criminology at the Law School, was intrigued by the implication of that question, calling the key passage of the Court’s opinion the “essay carveout.”
“Where is the line?” she wrote in a forthcoming article, the first of its kind to discuss this issue in depth in the post- SFFA era. “And what other potential legal pitfalls could universities encounter in evaluating essays about race?”
To inform her paper’s legal analysis, Starr conducted empirical analyses of how universities and students have included race in essays, both before and after the Court’s decision. She concluded that large numbers of applicants wrote about race, and that college essay prompts encouraged them to do so, even before SFFA .
Some thought the essay carveout made no sense. Justice Sonia Sotomayor called it “an attempt to put lipstick on a pig” in her dissent. Starr, however, disagrees. She argues that universities are on sound legal footing relying on the essay carveout, so long as they consider race-related experience in an individualized way. In her article, Starr points out reasons the essay carveout makes sense in the context of the Court’s other arguments. However, she points to the potential for future challenges—on both equal protection and First Amendment grounds—and discusses how colleges can survive them.
What the Empirical Research Showed
After SFFA , media outlets suggested that universities would add questions about race or identity in their admissions essays and that students would increasingly focus on that topic. Starr decided to investigate this speculation. She commissioned a professional survey group to recruit a nationally representative sample of recent college applicants. The firm queried 881 people about their essay content, about half of whom applied in 2022-23, before SFFA , and half of whom submitted in 2023-24.
The survey found that more than 60 percent of students in non-white groups wrote about race in at least some of their essays, as did about half of white applicants. But contrary to what the media suggested, there were no substantial changes between the pre-and post- SFFA application cycles.
Starr also reviewed essay prompts that 65 top schools have used over the last four years. She found that diversity and identity questions—as well as questions about overcoming adversity, which, for example, provide opportunities for students to discuss discrimination that they have faced—are common and have increased in frequency both before and after SFFA.
A Personally Inspired Interest
Although Starr has long written about equal protection issues, until about two years ago, she would have characterized educational admissions as a bit outside her wheelhouse. Her research has mostly focused on the criminal justice system, though race is often at the heart of it. In the past, for example, she has assessed the role of race in sentencing, the constitutionality of algorithmic risk assessment instruments in criminal justice, as well as policies to expand employment options for people with criminal records.
But a legal battle around admissions policies at Fairfax County’s Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology—the high school that Starr attended—caught her attention. Starr followed the case closely and predicted that “litigation may soon be an ever-present threat for race-conscious policymaking” in a 2024 Stanford Law Review article on that and other magnet school cases.
“I got really interested in that case partly because of the personal connection,” she said. “But I ended up writing about it as an academic matter, and that got me entrenched in this world of educational admissions questions and their related implications for other areas of equal protection law.”
Implications in Education and Beyond
Starr’s forthcoming paper argues that the essay carveout provides a way for colleges to maintain diversity and stay on the right side of the Court’s decision.
“I believe there’s quite a bit of space that’s open for colleges to pursue in this area without crossing that line,” she said. “I lay out the arguments that colleges can put forth.”
Nevertheless, Starr expects future litigation targeting the essay carveout.
“I think we could see cases filed as soon as this year when the admissions numbers come out,” she said, pointing out that conservative legal organizations, such as the Pacific Legal Foundation, have warned that they’re going to be keeping a close eye on admissions numbers and looking for ways that schools are circumventing SFFA .
Starr envisions her paper being used as a resource for schools that want to obey the law while also maintaining diversity. “The preservation of diversity is not a red flag that something unconstitutional is happening,” she said. “There are lots of perfectly permissible ways that we can expect diversity to be maintained in this post- affirmative action era.”
Starr’s article, “Admissions Essays after SFFA ,” is slated to be published in Indiana Law Journal in early 2025.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500+ Words Essay on Biodiversity. Essay on Biodiversity - Biodiversity is the presence of different species of plants and animals on the earth. Moreover, it is also called biological diversity as it is related to the variety of species of flora and fauna. Biodiversity plays a major role in maintaining the balance of the earth.
Essay on Biodiversity: Biodiversity refers to the variety of animals and plants in the world or a specific area. Even in today's modern world where so many technological advances have taken place, we still rely on our natural environment and resources to survive, A healthy and vibrant ecosystem is not disturbed by human activities.
Introduction to Biodiversity. Biodiversity encompasses the array of life on Earth, spanning species, ecosystems, and genetic resources crucial for sustaining the planet. In a delicate ecological balance, each component plays a unique role, contributing to the stability and resilience of our shared environment.
The term "biodiversity" is used to describe the variety of plants, animals, and other species found in an environment. All of them have a significant impact on preserving the planet's healthy ecosystem. In order to sustain the health of the ecosystem and human life, it is critical to maintain a high degree of biodiversity. However, maintaining ...
Essay On Biodiversity: The earth is the only known planet having the existence of life on it. Besides, life has manifested in different forms such as animals, birds, plants, microorganisms etc. Among these broad categories, Each one has its variety. This diversity is called Biodiversity. In other words, Biodiversity refers to the presence of ...
Human beings get so many benefits from biodiversity. These services may include food, wood, nitrogen fixation, pollination, and beauty. Other services include maintenance of climate and life, prevention of overflow of water and famine, natural bug's control, and even spiritual enrichment.
Essay on Biodiversity 1000+ Words. Biodiversity, short for biological diversity, is a remarkable tapestry of life that blankets our planet. It encompasses the variety of living organisms, ecosystems, and habitats that make Earth a vibrant and thriving place. In this essay, we will delve into the importance of biodiversity, the threats it faces ...
Biodiversity Essay. Biodiversity is a term made up of two words - Bio meaning Life, and Diversity meaning Variety. The term biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth. Plants, animals, microbes, and fungi are all examples of living species on the planet.
Biodiversity is the description of the natural state of the planet. It is not something that humans can create, they can only manage it. Biodiversity is an important aspect of the earth's ecosystem. It is extremely unfortunate that mankind will realize this when it is already too late. The most urgent problem right now is to maintain the ...
Essay on Biodiversity - Essay 1 (150 Words) Introduction: Biodiversity also known as biological diversity is the variables that exist among several species living in the ecosystem. These living organisms include marine, terrestrial and aquatic life. Biodiversity aims to understand the positions these organisms occupy in the broader ecosystem.
Benefits of Biodiversity. To start with, biodiversity provides most of the food that humans and other living beings use for their survival. Humans feed on a wide array of living organisms like animals, plants, fish and others, which provide holistic nutritional value to them. Likewise, predators depend on other animals for food while plants ...
The first essay is a long essay on the biodiversity of 400-500 words. This long essay about biodiversity is suitable for students of class 7, 8, 9 and 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants. The second essay is a short essay on biodiversity of 150-200 words. These are suitable for students and children in class 6 and below.
Writing an essay on biodiversity provides an opportunity to explore the complexity of life forms, their interactions, and the significance of preserving this rich tapestry of biological diversity. To effectively write an essay on biodiversity, it is crucial to approach the topic with a multidisciplinary perspective. Biodiversity encompasses a ...
Biodiversity is a term used to describe the enormous variety of life on Earth. It can be used more specifically to refer to all of the species in one region or ecosystem. Bio diversity refers to every living thing, including plants, bacteria, animals, and humans. Scientists have estimated that there are around 8.7 million species of plants and animals in existence.
From microscopic fungi to mega forests, "biodiversity" is the collective term for the variety of life on Earth in all its forms. It is 4.5 billion years of evolution, embodied. Biodiversity is responsible for our food, our soil, our water, our weather, even the air we breathe. Yet despite being a crucial foundation for our collective future ...
Why is biodiversity important? Biodiversity is essential for the processes that support all life on Earth, including humans. Without a wide range of animals, plants and microorganisms, we cannot have the healthy ecosystems that we rely on to provide us with the air we breathe and the food we eat. And people also value nature of itself.
To write an effective diversity essay, include vulnerable, authentic stories about your unique identity, background, or perspective. Provide insight into how your lived experience has influenced your outlook, activities, and goals. If relevant, you should also mention how your background has led you to apply for this university and why you're ...
Essay on Biodiversity: Biodiversity is the presence of different species of plants and animals on the earth, which means it's crucial that we take care of these precious creatures and preserve their habitats so they can thrive in today's world. This Essay on Biodiversity on the importance of biodiversity will teach you about the vital role ...
Biodiversity is measured in terms of attributes that explore the quality of nature; richness and evenness of the living organisms within an ecological niche. Biodiversity, Its Importance and Benefits. Apart from that, the paper is going to speculate on the most and least diverse species in the local area.
50 Latest Biodiversity IELTS Topics. Get a band score and detailed report instantly. Check your IELTS essays right now! Read more ». Problem and Solution. The influence of human beings on the world's ecosystem is leading to the extinction of species and loss of biodiversity.
Protecting biodiversity: local and global policies. Policy making plays a crucial role in protecting biodiversity. Since organisms do not adhere to human-made borders, conservation efforts need to be local, regional, national, and international. While economic factors often overshadow conservation, long-term environmental effects are starting ...
Roughly 2 million species live in the world's ocean. But scientists have only described a mere 10% of them. With extinctions on the rise and biodiversity threatened worldwide, many species are in danger of vanishing before researchers can identify them or fully grasp the benefits they provide. The National Ocean Biodiversity Strategy calls for a stronger, more unified and inclusive approach ...
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
Roughly 2 million species live in the world's oceans. But scientists have only described a mere 10% of them. With extinctions on the rise and biodiversity threatened worldwide, many species are in ...
Introduction. Biological diversity, also known as biodiversity, is the variety and variability among living organisms and the ecological complexes in which they occur. This diversity is evidenced by differences in the morphology of living organisms which make them suitably adapted to various ecosystems. The following paragraphs discuss the ...
Research carried out in drylands over the last decade has provided major insights on the biodiversity-ecosystem functioning relationship (BEFr) and about how biodiversity interacts with other ...
Editor's Note: This story is part of an occasional series on research projects currently in the works at the Law School. The Supreme Court's decision in June 2023 to bar the use of affirmative action in college admissions raised many questions. One of the most significant is whether universities should consider applicants' discussion of race in essays. The Court's decision in Students ...