Trends and patterns in digital marketing research: bibliometric analysis
- Original Article
- Published: 12 August 2021
- Volume 10 , pages 158–172, ( 2022 )

Cite this article

- Zahra Ghorbani 1 ,
- Sanaz Kargaran 1 ,
- Ali Saberi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8839-6772 2 ,
- Manijeh Haghighinasab 1 ,
- Seyedh Mahboobeh Jamali ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8728-5827 3 &
- Nader Ale Ebrahim ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7091-4439 4
2052 Accesses
21 Citations
11 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
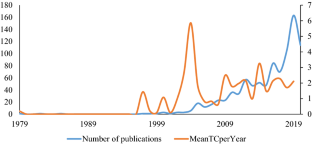
In today’s digital era, the importance of digital marketing has increased from one year to another as a way of providing novel properties for informing, engaging, and selling services and products to clients. The research’s aim is to investigate trends and patterns in the area of digital marketing research from 1979 to June 2020 through a bibliometric analysis technique. A total of 924 articles published were obtained from the Scopus database for the analysis. In this paper, we examine variant bar charts including the year of publication, writer, publication, keyword, and country to provide more insights. Results indicated that digital marketing research steadily increased during the study period and the maximum publications occurred in the year 2019 that reach to 163 documents. The trend of publications is still growing. The top 20 documents based on the times cited per year (TCpY) were qualitatively analyzed. The largest number of multiple (MCP) and single (SCP) publications was from the USA, followed by the UK and China. The top 20 most repeated authors’ keywords out of 1909 with their trends illustrated. The “real-time bidding”, “machine learning”, “big data”, “social media marketing”, and “influencer marketing” are the emerging keywords in the digital Marketing area. This bibliometric study generally provides the whole image of the field and suggests that researchers focus on novel areas to add new findings and knowledge in the literature if they conduct digital marketing research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Way Forward for Sustainable Digital Marketing: A Bibliometric Analysis
26 years left behind: a historical and predictive analysis of electronic business research

Bibliometric Analysis Based on Scientific Mapping in the Use of Digital Marketing Strategies
Abedini, A., R. Rahman, H.S. Naeini, and N. Ale Ebrahim. 2017. The 100 most cited papers in’industrial design’: A bibliometric analysis. Exacta – EP, São Paulo 15 (3): 515–526.
Aghaei Chadegani, A., H. Salehi, M. Yunus, H. Farhadi, M. Fooladi, M. Farhadi, and N. Ale Ebrahim. 2013. A comparison between two main academic literature collections: Web of Science and Scopus databases. Asian Social Science 9 (5): 18–26.
Google Scholar
Aksnes, D.W. 2003. Characteristics of highly cited papers. Research Evaluation 12 (3): 159–170.
Article Google Scholar
Ale Ebrahim, S., A. Ashtari, M.Z. Pedram, N. Ale Ebrahim, and A. Sanati-Nezhad. 2020. Publication trends in exosomes nanoparticles for cancer detection. International Journal of Nanomedicine 15: 4453.
Aria, M., and C. Cuccurullo. 2017. Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics 11 (4): 959–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007 .
Barnes, S.J., and E. Scornavacca. 2004. Mobile marketing: The role of permission and acceptance. International Journal of Mobile Communications 2 (2): 128–139.
Baumgartner, H., and R. Pieters. 2003. The structural influence of marketing journals: A citation analysis of the discipline and its subareas over time. Journal of Marketing 67 (2): 123–139.
Bethu, S., V. Sowmya, B.S. Babu, G.C. Babu, and Y.J.N. Kumar. 2018. Data science: Identifying influencers in social networks. Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences 6 (1): 215–228.
Bharadwaj, V., P. Chen, W. Ma, C. Nagarajan, et al. 2012. Shale: An efficient algorithm for allocation of guaranteed display advertising. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, 1195–1203. https://doi.org/10.1145/2339530.2339718 .
Brodie, R.J., and B. Juric. 2018. Customer engagement: Developing an innovative research that has scholarly impact. Journal of Global Scholars of Marketing Science 28 (3): 291–303.
Cai, H., K. Ren, W. Zhang, K. Malialis, J. Wang, Y. Yu, and D. Guo. 2017. Real-time bidding by reinforcement learning in display advertising. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the Tenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, 661–670. https://doi.org/10.1145/3018661.3018702 .
Cavallo, R., R.P. McAfee, and S. Vassilvitskii. 2015. Display advertising auctions with arbitrage. ACM Transactions on Economics and Computation (TEAC) 3 (3): 1–23.
Diodato, V. 1994. Dictionary of bibliometrics psychology press . Binghamton: The Haworth Press.
Ferreira, M.P. 2011. A bibliometric study on Ghoshal's managing across borders. Multinational Business Review 19 (4): 357–375.
Ferreira, M.P., J.C. Santos, M.I.R. de Almeida, and N.R. Reis. 2014. Mergers & acquisitions research: A bibliometric study of top strategy and international business journals, 1980–2010. Journal of Business Research 67 (12): 2550–2558.
Fierro, I., D.A. Cardona Arbelaez, and J. Gavilanez. 2017. Digital marketing: A new tool for international education. Pensamiento & Gestión 42: 241–260.
Franceschini, F., and D. Maisano. 2011. Regularity in the research output of individual scientists: An empirical analysis by recent bibliometric tools. Journal of Informetrics 5 (3): 458–468.
Fujita, M., P. Harrigan, and G. Soutar. 2017. A netnography of a university’s social media brand community: Exploring collaborative co-creation tactics. Journal of Global Scholars of Marketing Science 27 (2): 148–164.
Ghanbari Baghestan, A., H. Khaniki, A. Kalantari, M. Akhtari-Zavare, E. Farahmand, E. Tamam, and M. Danaee. 2019. A crisis in “open access”: Should communication scholarly outputs take 77 years to become open access? SAGE Open 9 (3): 2158244019871044.
Ghosh, A., P. McAfee, K. Papineni, and S. Vassilvitskii. 2009. Bidding for representative allocations for display advertising. Paper presented at the International workshop on internet and network economics, 208–219.
Ghosh, A., B.I.P. Rubinstein, S. Vassilvitskii, and M. Zinkevich. 2009. Adaptive bidding for display advertising. Paper presented at the 18th International World Wide Web Conference, WWW 2009, Madrid, 251–260.
Gordhamer, S. 2009. Ways social media is changing business. New York: Mashable . Retrieved from http://Mashable.ComMedia-Business/2009/09/22/Social-Media-Business/ .
Guercini, S., P.M. Bernal, and C. Prentice. 2018. New marketing in fashion e-commerce. Journal of Global Fashion Marketing 9 (1): 1–8.
Han, S.-L., T. Thao Nguyen, and V. Anh Nguyen. 2016. Antecedents of intention and usage toward customers’ mobile commerce: Evidence in Vietnam. Journal of Global Scholars of Marketing Science 26 (2): 129–151.
Hay, A.M., and K.S. Beavon. 1979. Periodic marketing: A preliminary graphical analysis of the conditions for part time and mobile marketing. Tijdschrift Voor Economische En Sociale Geografie 70 (1): 27–34.
Järvinen, J., and H. Karjaluoto. 2015. The use of Web analytics for digital marketing performance measurement. Industrial Marketing Management 50: 117–127.
Jayawardhena, C., A. Kuckertz, H. Karjaluoto, and T. Kautonen. 2009. Antecedents to permission based mobile marketing: an initial examination. European Journal of Marketing 43 (3/4): 473–499.
Kalantari, A., A. Kamsin, H.S. Kamaruddin, N.A. Ebrahim, A. Gani, A. Ebrahimi, and S. Shamshirband. 2017. A bibliometric approach to tracking big data research trends. Journal of Big Data 4 (1): 1–18.
Kamal, Y. (2016). Study of trend in digital marketing and evolution of digital marketing strategies. International Journal of Engineering Science 6 (5): 5300–5302.
Kaplan, A.M., and M. Haenlein. 2010. Users of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of Social Media. Business Horizons 53 (1): 59–68.
Kargaran, S., M. J. Pour, and H. Moeini. 2017. Successful customer knowledge management implementation through social media capabilities. VINE Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems, 47 (3): 353–371.
Karjaluoto, H., and T. Alatalo. 2007. Consumers’ attitudes towards and intention to participate in mobile marketing. International Journal of Services Technology and Management 8 (2–3): 155–173.
Khodabandelou, R., N. Aleebrahim, A. Amoozegar, and G. Mehran. 2019. Revisiting three decades of educational research in Iran: A bibliometric analysis. Iranian Journal of Comparative Education 2 (1): 1–21.
Kim, J. 2018. Social dimension of sustainability: From community to social capital. Journal of Global Scholars of Marketing Science 28 (2): 175–181.
Kim, E.Y., and K. Yang. 2018. Self-service technologies (SSTs) streamlining consumer experience in the fashion retail stores: The role of perceived interactivity. Journal of Global Fashion Marketing 9 (4): 287–304.
Ko, E. 2019. Bridging Asia and the world: Global platform for the Interface between marketing and management . New York: Elsevier.
LABS, X. 2017. How is big data influencing digital marketing strategy? Retrieved from https://www.xcubelabs.com/blog/how-is-big-data-influencing-digital-marketing-strategy/ .
Lamberton, C., and A.T. Stephen. 2016. A thematic exploration of digital, social media, and mobile marketing: Research evolution from 2000 to 2015 and an agenda for future inquiry. Journal of Marketing 80 (6): 146–172.
Levy, S., and Y. Gvili. 2015. How credible is e-word of mouth across digital-marketing channels?: The roles of social capital, information richness, and interactivity. Journal of Advertising Research 55 (1): 95–109.
Li, S., J.Z. Li, H. He, P. Ward, and B.J. Davies. 2011. WebDigital: A Web-based hybrid intelligent knowledge automation system for developing digital marketing strategies. Expert Systems with Applications 38 (8): 10606–10613.
Maghami, M.R., M.E. Rezadad, N.A. Ebrahim, and C. Gomes. 2015. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of solar hydrogen generation literature from 2001 to 2014. Scientometrics 105 (2): 759–771.
Martín-Consuegra, D., M. Faraoni, E. Díaz, and S. Ranfagni. 2018. Exploring relationships among brand credibility, purchase intention and social media for fashion brands: A conditional mediation model. Journal of Global Fashion Marketing 9 (3): 237–251.
Nerur, S.P., A.A. Rasheed, and V. Natarajan. 2008. The intellectual structure of the strategic management field: An author co-citation analysis. Strategic Management Journal 29 (3): 319–336.
Perlich, C., B. Dalessandro, R. Hook, O. Stitelman, T. Raeder, and F. Provost. 2012. Bid optimizing and inventory scoring in targeted online advertising. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, 804–812. https://doi.org/10.1145/2339530.2339655 .
Poushter, J., C. Bishop, and H. Chwe. 2018. Social media use continues to rise in developing countries but plateaus across developed ones. Retrieved from https://www.pewresearch.org/global/2018/06/19/social-media-use-continues-to-rise-in-developing-countries-but-plateaus-across-developed-ones/ .
Ramos-Rodríguez, A.R., and J. Ruíz-Navarro. 2004. Changes in the intellectual structure of strategic management research: A bibliometric study of the Strategic Management Journal, 1980–2000. Strategic Management Journal 25 (10): 981–1004.
Ren, K., W. Zhang, K. Chang, Y. Rong, Y. Yu, and J. Wang. 2017. Bidding machine: Learning to bid for directly optimizing profits in display advertising. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 30 (4): 645–659.
Ren, K., W. Zhang, Y. Rong, H. Zhang, Y. Yu, and J. Wang. 2016. User response learning for directly optimizing campaign performance in display advertising. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 25th acm international on conference on information and knowledge management, 679–688. https://doi.org/10.1145/2983323.2983347 .
Saura, J.R., P. Palos-Sánchez, and L.M. Cerdá Suárez. 2017. Understanding the digital marketing environment with KPIs and web analytics. Future Internet 9 (4): 76.
Shafique, M. 2013. Thinking inside the box? Intellectual structure of the knowledge base of innovation research (1988–2008). Strategic Management Journal 34 (1): 62–93.
Taiminen, H.M., and H. Karjaluoto. 2015. The usage of digital marketing channels in SMEs. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development 22 (4): 633–651. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSBED-05-2013-0073 .
Taylor, C.R., Y.-N. Cho, C.M. Anthony, and D.B. Smith. 2018. Photoshopping of models in advertising: A review of the literature and future research agenda. Journal of Global Fashion Marketing 9 (4): 379–398.
Van Eck, N.J., and L. Waltman. 2010. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84 (2): 523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3 .
Wang, J., W. Zhang, and S. Yuan. 2016. Display advertising with real-time bidding (RTB) and behavioural targeting. arXiv:1610.03013 .
Weinberg, T. 2009. The new community rules: Marketing on the social web. Journal of Applied Communications 96(2): 11.
Whiting, A., and D. Williams. 2013. Why people use social media: A uses and gratifications approach. Qualitative Market Research 16 (4): 362–369.
Willett, P. 2007. A bibliometric analysis of the Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling 26 (3): 602–606.
Woodside, A.G., and P. Bernal Mir. 2019. Clicks and purchase effects of an embedded, social-media, platform endorsement in internet advertising. Journal of Global Scholars of Marketing Science 29 (3): 343–357.
Yang, Z., Y. Shi, and B. Wang. 2015. Search engine marketing, financing ability and firm performance in E-commerce. Procedia Computer Science 55: 1106–1112.
Yin, C., S. Ding, and J. Wang. 2019. Mobile marketing recommendation method based on user location feedback. Human-Centric Computing and Information Sciences 9 (1): 1–17.
Yodel, G. 2017. What is influencer marketing. Huffington Post . https://www.huffpost.com/entry/what-is-influcner-marketing_b_10778128#:~:text=Influencer%20marketing%20is%20simply%20the,the%20character%20of%20a%20brand.&text=Anyone%20with%20internet%20access%20can,well%20enough%2D%20become%20an%20influencer .
Yuan, S., J. Wang, and X. Zhao. 2013. Real-time bidding for online advertising: measurement and analysis. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the Seventh International Workshop on Data Mining for Online Advertising.
Zarrella, D. 2009. The social media marketing book . Sebastopol: O’Reilly Media Inc.
Zhang, M., and N. Dholakia. 2018. Conceptual framing of virtuality and virtual consumption research. Journal of Global Scholars of Marketing Science 28 (4): 305–319.
Zhang, W., Y. Rong, J. Wang, T. Zhu, and X. Wang. 2016. Feedback control of real-time display advertising. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the Ninth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, 407–416. https://doi.org/10.1145/2835776.2835843 .
Zhang, W., and J. Wang. 2015. Statistical arbitrage mining for display advertising. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 1465–1474. https://doi.org/10.1145/2783258.2783269 .
Zhang, W., Yuan, S., and Wang, J. (2014). Optimal real-time bidding for display advertising. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, 1077–1086. https://doi.org/10.1145/2623330.2623633 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Social Science and Economics Department, Alzahra University, Vanak, Tehran, Iran
Zahra Ghorbani, Sanaz Kargaran & Manijeh Haghighinasab
Farabi Campus, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran
Ministry of Education District 7, Eshragh Institute, Tehran, Iran
Seyedh Mahboobeh Jamali
Research and Technology Department, Alzahra University, Vanak, Tehran, Iran
Nader Ale Ebrahim
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Zahra Ghorbani .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ghorbani, Z., Kargaran, S., Saberi, A. et al. Trends and patterns in digital marketing research: bibliometric analysis. J Market Anal 10 , 158–172 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41270-021-00116-9
Download citation
Revised : 14 December 2020
Accepted : 31 May 2021
Published : 12 August 2021
Issue Date : June 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41270-021-00116-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Digital marketing
- Electronic commerce marketing
- Search engine marketing
- Bibliometric
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, a systematic literature review: digital marketing and its impact on smes.
Journal of Indian Business Research
ISSN : 1755-4195
Article publication date: 20 February 2023
Issue publication date: 3 March 2023
This study aims to analyze the available literature on the use of digital marketing and its impact on small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). This study identifies the use of digital marketing practices and its impact on SMEs.
Design/methodology/approach
A systematic literature review has been conducted on digital marketing, and its implementation in SMEs. The impact of digital marketing on SMEs performance is observed over the past 12 years through the resources which are undertaken for the study, namely, Science Direct, Scopus, Springer, IEEE Explorer, ACM Digital Library, Engineering Village, ISI Web of Knowledge database is used to search the research publications on the selected topic.
Although some SME firms use digital marketing, their impact is not similar where we can recommend a fixed strategy for applying digital marketing. This review provides an insight into how digital marketing has evolved over the period of time and how SMEs are adopting it for their sustenance.
Practical implications
This study will give theoretical analysis of various benefits received by SMEs because of digital marketing in the different capacities helping organizations to uplift their productivity. Mind mapping will give the idea of impact of SMEs on their various performances in rural as well as in the urban areas. This study will give further scope for digital marketers to approach those industries specifically at rural parts of the nation for bringing change into their marketing operations and also for increasing turnover by the use of digital marketing.
Originality/value
Research on the use of digital marketing by SMEs firms is still at the embryonic stage in India. This study is a pioneering effort to review the use of digital marketing in SMEs and identify research priorities for scholars and practitioners.
- Literature review
- Digital marketing
- Small and medium enterprises
- Impact on SMEs
Jadhav, G.G. , Gaikwad, S.V. and Bapat, D. (2023), "A systematic literature review: digital marketing and its impact on SMEs", Journal of Indian Business Research , Vol. 15 No. 1, pp. 76-91. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIBR-05-2022-0129
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2023, Emerald Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.7(12); 2021 Dec

How digital marketing evolved over time: A bibliometric analysis on scopus database
Mohammad faruk.
a Department of Business Administration, Bangladesh Army International University of Science and Technology, Cumilla, Bangladesh
Mahfuzur Rahman
b Department of Marketing, Comilla University, Cumilla, Bangladesh
Shahedul Hasan
c East Delta University, Chattogram, Bangladesh
Associated Data
Data will be made available on request.
Nowadays, a large number of customers are spending their time on social and digital media for a variety of purposes ranging from information searching to the final purchase of products. Responding to this shift, marketers are spending a significant part of the advertising budget on digital marketing. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to review articles on digital marketing to identify top themes, determine the current status of research in digital marketing and indicate how influential works have shaped it. This research has reviewed 925 papers published between 2000 and 2019 in Scopus by applying bibliometrics analysis. These results show that on average 2.18 authors have contributed to every single paper on digital marketing and the collaboration index is 2.71. The top contributing countries in the digital marketing field are USA, India and UK. The study also identifies three dominant clusters in digital marketing research, e.g., 1) strategic planning with digital marketing 2) mobile marketing with apps development and 3) dealing with demographic profiles of customers.
Bibliometric analysis; Digital marketing; 4th industrial revolution; Scopus database.
1. Introduction
It is reported that, in December 1995, internet users were only 16 million. On the other hand, in June 2019, the number increased to 4,536 million which cover 58.8% of the total world population that amounting to 7.71 billion ( Busca and Bertrandias, 2020 ). It is estimated that everyday people spend, on average, 6 h and 42 min online and by 2021, 73% of e-commerce sales will be generated through the mobile platform ( Mandal, 2017 ). Moreover, the 4 th industrial revolution has begun with the invention of web 4.0, the internet of things (IoT), blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics and 4g/5g internet speed ( Kerren, 2014 ). These technological inventions have significantly affected the lifestyle of consumers and the way marketers communicate with their customers. In 2004, Facebook came into the market, followed by many other social networking sites in later years. People had accepted these social media at an exponential rate affecting the way people communicated and interacted with each other.
After the induction of world wide web technology, people have become used to the virtual world. When people (e.g., customers) shifted to the internet or virtual marketplace, marketers focused their marketing attention on this market. Consumers are spending more time on social media for a variety of purposes ranging from brand information searching to the final purchase of products. Consumers’ shifting from traditional media to digital media enables marketers to reach, notify, engage, sell to, study about and provide services to the targeted audience more effectively and efficiently. Responding to this fundamental shifting of consumers from traditional to digital media, marketers are continuously trying to grab the opportunity by devising product, price, place and promotion strategies for this marketplace. Therefore, scholars have investigated different aspects of digital marketing (DM).
While reviewing the literature, it is noticed very few research studies were focused on identifying and analyzing the development of themes and clusters in this arena by applying bibliometric analysis ( Ghorbani et al., 2021 ; Kim et al., 2019 ; León-Castro et al., 2021 ). Ghorbani et al. (2021) conducted a bibliometric analysis to identify key trends and patterns in the field of DM by investigating 924 research articles published in the Scopus database. However, given the importance of digital marketing, more systematic literature reviews are necessary for this field. Kim et al. (2019) undertook a bibliometric analysis that was more focused on digital marketing communication (DMC) and hence, studies other than DMC were ignored. León-Castro et al. (2021) covered only a web of science database to run a bibliometric analysis on digital marketing, but the keywords focused on more specific aspects of DM such as “influencer”, “ewom”, “youtube”, “instagram” and “facebook”.
However, finding out how scholarly works on digital marketing practice and theory have been developed over time and contributed to DM literature is limited. Analyzing which journals, countries and authors are contributing more in the field of digital marketing was also nascent. The authors have exactly taken the endeavour to address these issues. Since this study will analyze all the major scholarly articles that are published in the Scopus database, it will pave the way for future researchers who intend to research digital marketing.
Considering the limitations of the past studies on DM, the study has been undertaken to serve several purposes such as a) to identify the evolution of DM literature over time by applying a bibliometric analysis; b) to assess and synthesize 925 Scopus papers and offer future research directions in the field of DM.
The significant contribution of this study includes identifying which are the journals and authors that contributed the most in the development of digital marketing. It also contributes by explaining the emergent themes in DM along with identifying the most cited journals in this sector. Moreover, the co-citation networks that exist between most cited researches and the schools of thought that exist in co-citation networks have also been investigated thoroughly.
This paper is organized into several parts. The following section contains a literature review followed by the research methodology. The next section includes results and discussion from the bibliometric analysis of the articles published in Scopus between 2000 and 2019. The final part of the paper includes the conclusion and implications from theoretical and practical perspectives along with limitations and future research directions.
2. Literature review
With the advent of social media and development in the web and mobile apps technologies, communication has become much easier than that of past decades ( Khomenko et al., 2020 ). Since modern customers are spending their time in digital media, marketers have also developed strategies and tactics to reach them through these media. Therefore, a significant amount of scholarly research had been conducted on different aspects such as search engine optimization, social media marketing, affiliate marketing, content marketing, video marketing and many others ( Jimenez, 2020 ). This study presents an intensive analysis of scholarly works done and published by scholars from different countries on this revolutionary field of marketing between 2000 to 2019. Digital marketing opens up new opportunities for reaching, informing, and engaging consumers, as well as providing and selling goods and services. Digital marketing is projected to remain at the forefront of the technological transition in the future ( Ko, 2019 ; Lamberton and Stephen, 2016 ; Martín-Consuegra et al., 2018 ). Millions of people's daily lives have been transformed by digital marketing through social and mobile media, which has expanded into popular social media practices and often leads to the formation of customer relationships ( Fujita et al., 2017 ; Han et al., 2016 ; Kim, 2018 ; Woodside and Mir, 2019 ).
As more marketing researchers and professionals have dedicated themselves to digital technologies, the speed of transition has quickened. The digital marketing model has changed from selling unique goods and services to marketing campaigns that are introduced across digital platforms to now make use of digital resources. Social media has existed for over the past decade for several different purposes such as blogging, video and photography/photo-sharing using mobile phones ( Fujita et al., 2017 ; Han et al., 2016 ; Kim, 2018 ). Virtual technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) seem to be replacing traditional approaches to marketing suggesting new territory for marketing researchers to pursue ( Brodie and Juric, 2018 ; Guercini et al., 2018 ; Kim and Yang, 2018 , J. Kim et al., 2018 ; Taylor and Costello, 2017 ; Zhang and Dholakia, 2018 ).
Marketers soon noticed the networking advantages of social networks like Facebook, YouTube, Twitter, Instagram, Snapchat, Pinterest, and LinkedIn, and invested $51.3 billion on global social network ads in 2017, up 55.4% from 2016 ( Cooper, 2020 ). The amount spent on digital ads is expected to rise 17.7% in 2018, accounting for $273 billion (44%) of the $629 billion spent on advertising globally ( McNair, 2018 ). In 2017, mobile ad spending rose by 39%, and it is projected to rise by another 27% in 2018, accounting for 55% of all digital ad spending ( Magna Global, 2017 ). The growing concentration of advertising dollars demonstrates digital marketing's effectiveness in targeting audiences and achieving growth goals such as increased revenue, brand recognition, consumer loyalty, lead generation, and lower customer acquisition and service costs ( Labrecque et al., 2013 ; Lamberton and Stephen, 2016 ; Tuten, 2020 ).
The way businesses market themselves is changing as a result of social media, posing new obstacles as well as opportunities ( Arora and Sanni, 2019 ; Dwivedi et al., 2015 , 2017 ; Hossain et al., 2019 ; Nisar et al., 2018 ; Wang and Herrando, 2019 ). Digital marketing, whether used inappropriately or by unskilled practitioners, may harm businesses ( Aswani et al., 2018 ). As a result, businesses must gain social media expertise ( Braojos-Gomez et al., 2015 ). Companies should focus on aligning their digital marketing strategies with their overall business goals ( Tafesse and Wien, 2018 ; Thorpe, 2018 ). When used strategically, social media marketing may lead to increased consumer satisfaction and perceived value ( Chen and Lin, 2019 ; Pacauskas et al., 2018 ), co-creation ( Kamboj et al., 2018 ; Zhang et al., 2017 ), brand loyalty ( Laroche et al., 2013 ; Shanahan et al., 2019 ) and positive attitude ( Laroche et al., 2013 ).
Furthermore, social media has opened up new avenues for marketers to obtain audience experience by researching online user-generated content, electronic word of mouth (eWOM) conversations ( Chang et al., 2019 ; Liu et al., 2019 ; Xu et al., 2017 ), and online communities ( Chang et al., 2019 ; Habibi et al., 2014 ; Liu et al., 2018 ). Consumer reviews are a large part of social media, and they throw up questions about content accuracy, credibility, usefulness, and validity ( Ismagilova et al., 2017 ; Kapoor et al., 2018 ; Singh et al., 2017 ). Consumer preferences and purchasing habits can be affected by online feedback, which can affect a company's results ( Ismagilova et al., 2020 ; Kawaf and Istanbulluoglu, 2019 ; Shareef et al., 2018 ; Yerasani et al., 2019 ).
A variety of factors can influence digital marketing activities and practices. Some research, for example, looked at the impact of new laws on digital marketing ( Hemsley, 2018 ; Sposit, 2019 ). Furthermore, social media marketing research has begun to concentrate on developing markets, where the adoption rate of social media marketing is lower than the developed countries ( Christino et al., 2019 ; Liu et al., 2019 ). Some businesses in these developing countries continue to rely on conventional media for product and service ads because they are more trustworthy than social media platforms ( Ali et al., 2016 ; Olanrewaju et al., 2020 ). Therefore, this article aims at assessing different paradigms of published articles on DM and finding out how these studies evolved. In addition, finding out what are the dominant themes in this area of research is also a concern of this paper.
3. Methodology
Bibliometric analysis along with a citation and co-citation analysis presents a powerful way to analyze the patterns and characteristics of already published papers in any scholarly field. It may also help to find out the school of thought, if any, in any specific area of study ( Mandal, 2017 ; Christie, 2008 ). The bibliometric analysis takes the objective philosophy and employs a quantitative investigation method on written documents (i.e., journals, books, websites). Citation and co-citation analysis focus on finding out the emergent themes in specific areas of study, the impact of different journals and different schools of thought ( Nyagadza, 2020 ). Going beyond merely counting and collating citations, previous studies have pointed out the nature and course of development of a discipline to assess which journals and authors have created value to other researchers by collaboration.
Bibliometric studies, such as citation and co-citation analyses, are useful for delving into the trends and characteristics of what has been written, making it easier to explore, organize, and articulate work done in a particular discipline ( Diodato, 1994 ; Ferreira et al., 2014 ). Bibliometric analyses can help to guide collection growth, define institutional scholarship strengths and citation/co-citation trends, and identify possible schools of thought in a discipline ( Lewis and Alpi, 2017 ). For a comprehensive investigation of written source documents (e.g., academic journal papers and books), bibliometric research uses citation and co-citation analyses as an analytical tool for inspecting part or the entirety of a scholarly discipline ( Diodato, 1994 ; Ferreira et al., 2014 ; Nerur et al., 2008 ; Ramos-Rodríguez and Ruíz-Navarro, 2004 ; Shafique, 2013 ).
The researchers have adopted objectivist research philosophy since it focuses on quantitative methods of analysis and bibliometric analysis is a powerful quantitative tool to analyze published documents in any scholarly area ( Diodato and Gellatly, 2013 ). The authors have mined the bibliometric data from the Scopus database with the keyword “Digital Marketing”. Digital marketing is the common keyword across different papers, however, articles with other related keywords such as “social networking online”, “social media sales”, “electronic commerce”, “data mining”, “information systems” were considered. Scopus database was selected by the authors since they had authorized access to this database only. Hence analysis on other prominent databases such as Web of Science can be considered in future research.
After loading the dataset, it is observed that it contains 935 articles in total starting from 1982. However, the authors have applied the “publication year” filtering strategy and kept the data from 2000 to 2019. This period is chosen since the proliferation of the internet began in the 21st century. In the case of “document type”, all types of documents (i.e., article, book, book chapter, conference paper, conference review, editorial, short survey, note review) were considered. All types of documents were considered since the author had applied only one keyword “digital marketing” for retrieving data and it only produced 935 articles. In addition, the authors wanted to investigate the theoretical and practical development of digital marketing throughout every scholarly research field and understand the relationship among them. Other studies also applied a similar technique to represent the whole DM research ( Ghorbani et al., 2021 ). About “total citation”, the full range of citations from 0 to 305 were considered since the authors wanted to consider both highly cited articles and lowly cited articles and this helps to identify the difference between good work and mediocre research work. In addition, about “source by Bradford Law Zones”, all the sources were considered. This filtration has produced 925 papers finally which are to be analyzed. After retrieving the data from the Scopus database, with the help of the bibliometrics package of R programming, the data were analyzed.
4. Results and discussion
4.1. summary statistics.
This chapter presents analysis and findings from bibliometric analysis of 925 documents related to digital marketing published between 2000 and 2019. Table 1 presents the summary findings from the analysis. The documents that were published in this period in the Scopus database received 5.076 citations on average. The higher average citations per document indicate a speedy growth of scholarly papers in the field of DM. The results also showed that 2015 unique authors have contributed to the digital marketing field in this period, who got impressions of 2359 times. In addition, single-author documents counted as 262. On average, 2.18 authors contributed to completing each document while every single author contributed to at least 0.459 documents. Documents per author counted to 0.459 while co-authors per document are 2.55. This signifies that in the development of digital marketing, a good amount of research studies are done in collaboration with other authors which is again confirmed in the collaboration index of 2.71. However, a significant amount of single-author articles are also undertaken.
Table 1
Summary statistics.
4.2. Performance analysis
Figure 1 showed the key trends in annual scientific production in the DM field. The timeline can be broadly divided into two main decades with varying trends in annual publications. Although research on digital marketing and related topics had begun as early as 2000, digital marketing studies were almost overlooked by the researchers during the first decade (2000–2010). Therefore, the actual proliferation commenced after 2010 meaning in the second decade (2010–2020) and as time passes, research in this domain has grown exponentially. This growth can be attributed to the increasing number of internet and social media users in the 2000s ( Ghorbani et al., 2021 ). When we see the research development from the perspective of Pareto's law, in only 4 years' time period (2016–2019), 70% (648) of the research papers were published in Scopus on digital marketing. Contemporary studies are found to focus more on marketing science issues accompanied by modern information technology tools and techniques such as artificial intelligence, big data, deep learning etc.

Annual scientific production in digital marketing.
4.3. Relationship between authors, keywords and sources
Figure 2 contained three field analyses showing the relationship between authors, keywords and sources where the left column contained the name of authors, the middle column contained keywords and the right column contained the journal name. This confirms that most of the authors have considered digital marketing as their keyword. However, “social media marketing”, “internet”, “machine learning”, “web 2.0”, “social networks”, “customer relationship management”, “Facebook”, “Twitter” and many others closely related keywords with digital marketing had also been used in different research articles. A new trend is represented by social media for companies that strive to communicate with their customers using both online and offline media. For example, popular social media sites like Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and corporate blogs are increasingly used by the Fortune 500 companies in their marketing communication campaigns ( Markos-Kujbus and Gati, 2012 ). Previous researchers who used digital marketing as their keyword also found to include the above-listed keywords. But this is also clear from the data that focus on digital marketing is higher than any other keywords. The reason for this consideration can be justified with the proliferation of the use of digital marketing compared to other semantic terminologies which can also be used to mean the same thing. Almost every journal contributed equally, although some journals such as Journal of Direct, Data and Digital Marketing Practice, are pioneering the advancement in this field. Although mobile marketing is a powerfully dominant domain of digital marketing ( Cheng et al., 2013 ), this area is yet to be explored. Therefore, future researchers can contribute to this domain.

Three field analyses in digital marketing.
4.4. Performance of academic journals
To identify the most contributing journals, Figure 3 showed that the “Journal of Direct Data and Digital Marketing Practice” had the highest contribution in this domain. This journal solely published 46 research papers within the specified period amounted to almost 5% of the total publications. However, this journal of Springer has last published articles in June 2016 and till then it is not being published anymore. That means the top-most contributing journal is out of the market and thereby creating a gap in the field and providing other journals to fill the gap. “Journal of Digital and Social Media Marketing” has published 10 papers and “Journal of Marketing Education” has also contributed 10 papers in this domain. Moreover, another critical point to be noted here, the Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing is not on the top contributing list, although this journal is contributing significantly in the domain with its strong editorial board.

Most contributing journal in digital marketing.
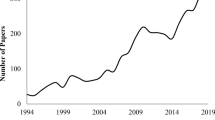
4.5. Source growth of digital marketing over time
As we explained earlier in this paper, “Journal of Direct Data and Digital Marketing Practice” had contributed the most in the digital marketing research area. However, the contribution of this journal has decreased significantly in recent times (see Figure 4 ). On the contrary, the contribution of sources like the “International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering” is increasing exponentially. Adobe Research, Amity University, Yonsei University are found to be the most contributing parties in the scholarly publications on digital marketing. However, other universities such as Chaoyang University of Technology, Jaypee Business School, and the University of Florida have also kept significant contributions in this domain.

Source growth of digital marketing over time.
4.6. Contribution by countries
In the case of the contribution of different countries in scholarly works on digital marketing, the bibliometric analysis found that the USA had contributed the most (223 papers). Surprisingly researchers from India have achieved the second position in contributing to this emerging field of study (187 papers). However, this is a powerful point that in the case of MCP or author collaboration with the authors from other countries, the USA ranked 1st while the UK ranked 2nd. India's authors have not secured the second position in this area. In addition, the UK has kept a significant amount of contribution and other countries such as Indonesia, Spain, Korea, Portugal, Brazil, and France's contributions are average.
As the contribution from the USA, UK and India are the most, theoretically, this is expected that collaboration among researchers in these countries would be the highest. This expectation is confirmed with this Figure 5 . As a country Australia does not have many contributions, however, different authors from this country have collaborated significantly with authors from other countries. From a continental analytical point of view, it is observed that North America and Europe contributed the most followed by Asia. However, South America and Africa are completely void of any kind of notable contribution. This can be attributed to the economic and demographic development of the countries. Most of the countries in South America and Africa are not developed as other contributing countries. Another interesting insight is also observed in this analysis, which is the “North-South gap”. Countries located north of the equator are observed to contribute more than the countries located south of the equator.

Authors' collaboration around the world.
4.7. Bibliographic links of academic journals
This bibliometric analysis identified 3 dominant research clusters in digital marketing, as illustrated in Figure 6 . Each cluster has a significant amount of difference from other clusters. As identified with the analysis, the biggest cluster in digital marketing is about strategic planning with digital marketing. Another dominant research domain in digital marketing focuses on mobile marketing with apps development. In addition, the third cluster on digital marketing concentrates especially on dealing with demographic profiles of customers along with website marketing metrics. In addition, the word-cloud analysis expresses which keyword was discussed the most in these 925 papers published from 2000 to 2019 in Scopus. Digital marketing is the central word which is accompanied by other dominant keywords such as commerce, marketing, social networking online, social media sales and internet. Another amazing insight generated from this cluster analysis, e.g., three clusters represents three different facets of marketing; the green-coloured cluster represents societal and humane aspects of marketing while the red- coloured cluster represents the fundamental philosophical and strategic aspects of marketing (i.e., consumer behaviour, strategic planning, information management, social media, public relations) and the blue coloured cluster represents the recent development of digital marketing because of the proliferation of extensive data generation (i.e., database management, data mining, artificial management). But here one inconsistency can be noticed that theoretically big data analytics should fall in the blue coloured cluster but here it falls in the red coloured cluster and the authors are unable to explain the reason for this which can also be considered as a limitation of the article. Although digital marketing has received its importance after the advent of social media after 2000, it is considered in the red coloured cluster. That means digital marketing must be considered as the fundamental part of marketing and it must be given its due importance from the implicational aspect while the theory and philosophy remain the same.

Cluster analysis in digital marketing research.
5. Conclusion and implications
The bibliometric study provides a comprehensive picture of specific research fields and enables researchers to focus on unique areas to add new results and knowledge to the literature ( Ghorbani et al., 2021 ). In summary, this can be firmly claimed that the growth in the field of DM research has started in 2014. Three dominant themes of study have been developed including a strategic framework, mobile marketing and apps development and demographic analysis with web analytics. As a country, USA, UK and India contributed the most to this development. In the last half-decade, digital marketing has evolved as a buzzword. Revolution has been created by electronic commerce in business by transforming the physical aspect of delivery to the virtual aspect of marketing and selling. Digital marketing has become an integral part of any marketing and sales strategy ( Bhojaraja and Muniraju, 2018 ).
Analysis of the DM literature through bibliometric analysis will assist both the academicians and practitioners in various ways. First of all, this study will inform academic researchers and digital marketers regarding the evolution, trends and history of digital marketing. This paper will also inform about the most researched domains under DM, hence, enables researchers to identify research gaps to be filled by further studies in the future. The analysis shows that digital marketing is the single most keyword used in most of the studies. The other areas along with DM should also be investigated including consumer behaviour, social networks, machine learning, big data, advertising, mobile marketing, web 2.0, branding and so forth. Secondly, the study shows that research on DM has received tremendous focus since 2010 due to the growth of the internet and social media. As social media allure customers to speak for the brands, global companies increasingly focus on digital marketing as an effective tool of brand communication ( Bhuyan and Rahman, 2014 ). Thus, digital marketers should ensure the best use of digital media in brand communication. Third, the analysis reveals that DM literature is the most prevalent in the countries like USA, UK and India. Future researchers should focus on other parts of the world especially the developing countries regarding the prospects of digital marketing.
Finally, there are three dominant clusters are identified from the analysis. Strategic planning with digital marketing is the largest cluster suggesting the significant domain for both researchers and policymakers. After happening the latest technological revolution in businesses, digital marketing has become more prominent and widely practised. The methods of traditional marketing are completely replaced by those of digital marketing. Nowadays, marketers are forced to use the internet and digital technology for selling and promoting their products and services. Therefore, both the prospects and challenges of digital marketing must be properly detected and analyzed by marketers to set the best marketing plan and communication goals ( Bhojaraja and Muniraju, 2018 ). Mobile marketing with apps development is another domain identified from the cluster analysis. The rate of smartphone penetration and mobile applications is going up day by day due to availability and affordability. Therefore, markers should adopt mobile marketing such as banner ads on apps, SMS marketing and so forth to reach the target customers. The last research cluster is demographic profiles of customers along with website marketing metrics. The outcomes of marketing investment can easily be measured using digital marketing metrics. The effectiveness and quality of online content can also be evaluated and audited with the help of digital marketing ( Bhojaraja and Muniraju, 2018 ).
5.1. Limitations of the study and future research direction
This study does not include the major works indexed in another significant database (i.e. web of science), which is the major limitation of the study. In addition to that, documents were explored using the only keyword “Digital Marketing”, hence, other relevant keywords were not considered. Only one keyword is chosen to keep the analysis simple and to make it easier for the authors to interpret the analysis. Hence, further researches can be conducted to get a more holistic view by considering other strongly related keywords such as “online marketing”, “social media marketing”, “email marketing”, “affiliate marketing” and “mobile marketing”.
In future, how big data analytics and artificial intelligence are going to affect the digital marketing landscape can be explored. How marketing research has been shaped in the digital marketing field can also be an interesting pathway to pursue future research. Why USA, UK and India have contributed the most, on the other hand, why Canada, Australia, Germany, Russia, France and others are lagging in contributing to this field should also be analyzed.
Declarations
Author contribution statement.
All authors listed have significantly contributed to the development and the writing of this article.

Funding statement
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Data availability statement
Declaration of interests statement.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
No additional information is available for this paper.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Md. Abul Kalam Azad, Associate Professor, BTM, Islamic University of Technology for helping to retrieve the (.bib) data file from the Scopus database.
- Ali Z., Shabbir M.A., Rauf M., Hussain A. To assess the impact of social media marketing on consumer perception. Int. J. Acad. Res. Account. Finance. Manag. Sci. 2016; 6 (3):69–77. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arora A.S., Sanni S.A. Ten years of ‘social media marketing’ research in the Journal of Promotion Management: research synthesis, emerging themes, and new directions. J. Promot. Manag. 2019; 25 (4):476–499. [ Google Scholar ]
- Aswani R., Kar A.K., Ilavarasan P.V., Dwivedi Y.K. Search engine marketing is not all gold: insights from Twitter and SEO Clerks. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018; 38 (1):107–116. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bhojaraja, Muniraju D.M. Challenges and opportunities in digital marketing. IAETSD J. Adv. Res. Appl. Sci. 2018; 5 (1) [ Google Scholar ]
- Bhuyan M., Rahman S.M. Social media as a tool of brand communication in Bangladesh: problems and Prospects. DIU J. Human. Soc. Sci. 2014; 2 [ Google Scholar ]
- Braojos-Gomez J., Benitez-Amado J., Llorens-Montes F.J. How do small firms learn to develop a social media competence? Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2015; 35 (4):443–458. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brodie R.J., Juric B. Customer engagement: developing an innovative research that has scholarly impact. J. Glob. Scholars Mark. Sci. 2018; 28 (3):291–303. [ Google Scholar ]
- Busca L., Bertrandias L. A framework for digital marketing research: investigating the four cultural eras of digital marketing. J. Interact. Market. 2020; 49 :1–19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chang Y.-C., Ku C.-H., Chen C.-H. Social media analytics: extracting and visualizing Hilton hotel ratings and reviews from TripAdvisor. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019; 48 :263–279. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen S.-C., Lin C.-P. Understanding the effect of social media marketing activities: the mediation of social identification, perceived value, and satisfaction. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change. 2019; 140 :22–32. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cheng X., Liu J., Dale C. Understanding the characteristics of internet short video sharing: a YouTube-based measurement study. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2013; 15 (5):1184–1194. [ Google Scholar ]
- Christie D. Extracting data off the internet. Teach. Stat. 2008; 30 (1):23–25. [ Google Scholar ]
- Christino J.M.M., Silva T.S., Cardozo E.A.A., de Pádua Carrieri A., de Paiva Nunes P. Understanding affiliation to cashback programs: an emerging technique in an emerging country. J. Retailing Consum. Serv. 2019; 47 :78–86. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper P. 2020. 43 Social Media Advertising Stats that Matter to Marketers in 2020. https://blog.hootsuite.com/social-media-advertising-stats/ Retrieved from. [ Google Scholar ]
- Diodato V. The Haworth Press; Binghamton: 1994. Dictionary of Bibliometrics Psychology Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Diodato V.P., Gellatly P. Routledge; 2013. Dictionary of Bibliometrics. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dwivedi Y.K., Kapoor K.K., Chen H. Social media marketing and advertising. Market. Rev. 2015; 15 (3):289–309. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dwivedi Y.K., Rana N.P., Alryalat M.A.A. Affiliate marketing: an overview and analysis of emerging literature. Market. Rev. 2017; 17 (1):33–50. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ferreira M.P., Santos J.C., de Almeida M.I.R., Reis N.R. Mergers & acquisitions research: a bibliometric study of top strategy and international business journals, 1980–2010. J. Bus. Res. 2014; 67 (12):2550–2558. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fujita M., Harrigan P., Soutar G. A netnography of a university’s social media brand community: exploring collaborative co-creation tactics. J. Glob. Scholars Mark. Sci. 2017; 27 (2):148–164. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ghorbani Z., Kargaran S., Saberi A., Haghighinasab M., Jamali S.M., Ale Ebrahim N. Trends and patterns in digital marketing research: bibliometric analysis. J. Market. Anal. 2021:1–15. [ Google Scholar ]
- Guercini S., Bernal P.M., Prentice C. New marketing in fashion e-commerce. J. Glob. Fashion Market. 2018; 9 (1):1–8. [ Google Scholar ]
- Habibi M.R., Laroche M., Richard M.-O. Brand communities based in social media: how unique are they? Evidence from two exemplary brand communities. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2014; 34 (2):123–132. [ Google Scholar ]
- Han S.-L., Thao Nguyen T.P., Anh Nguyen V. Antecedents of intention and usage toward customers’ mobile commerce: evidence in Vietnam. J. Glob. Scholars Mark. Sci. 2016; 26 (2):129–151. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hemsley M. Why the General Data Protection Regulation is likely to disrupt core digital marketing channels in Europe. J. Digit. Soc. Media Market. 2018; 6 (2):137–142. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hossain T.M.T., Akter S., Kattiyapornpong U., Dwivedi Y.K. Multichannel integration quality: a systematic review and agenda for future research. J. Retailing Consum. Serv. 2019; 49 :154–163. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ismagilova E., Dwivedi Y.K., Slade E., Williams M.D. Springer; 2017. Electronic Word of Mouth (eWOM) in the Marketing Context: A State-Of-The-Art Analysis and Future Directions. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ismagilova E., Slade E.L., Rana N.P., Dwivedi Y.K. The effect of electronic word of mouth communications on intention to buy: a meta-analysis. Inf. Syst. Front. 2020; 22 (5):1203–1226. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jimenez M.M. MARCOMBO; 2020. Marketing Digital. [S.l.] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kamboj S., Sarmah B., Gupta S., Dwivedi Y. Examining branding co-creation in brand communities on social media: applying the paradigm of Stimulus-Organism-Response. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018; 39 :169–185. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kapoor K.K., Tamilmani K., Rana N.P., Patil P., Dwivedi Y.K., Nerur S. Advances in social media research: past, present and future. Inf. Syst. Front. 2018; 20 (3):531–558. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kawaf F., Istanbulluoglu D. Online fashion shopping paradox: the role of customer reviews and facebook marketing. J. Retailing Consum. Serv. 2019; 48 :144–153. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kerren l. Understanding digital marketing: marketing strategies for engaging the digital generation. Choice Rev. Online. 2014; 52 (5):52–2647. [ Google Scholar ]
- Khomenko L., Saher L., Polcyn J. Analysis of the marketing activities in the blood service: bibliometric analysis. Health Econ. Manag. Rev. 2020; 1 (1):20–36. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim E.Y., Yang K. Self-service technologies (SSTs) streamlining consumer experience in the fashion retail stores: the role of perceived interactivity. J. Glob. Fashion Market. 2018; 9 (4):287–304. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim J. Social dimension of sustainability: from community to social capital. J. Glob. Scholars Mark. Sci. 2018; 28 (2):175–181. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim J., Kang S., Lee K.H. Evolution of digital marketing communication: bibliometric analysis and network visualization from key articles. J. Bus. Res. 2019 [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim J., Kang S., Taylor C.R. Technology driven experiences from mobile direct to virtual reality. J. Glob. Scholars Mark. Sci. 2018; 28 (1):96–102. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ko E. Bridging Asia and the world: global platform for the Interface between marketing and management. J. Bus. Res. 2019; 99 :350–353. [ Google Scholar ]
- Labrecque L.I., vor dem Esche J., Mathwick C., Novak T.P., Hofacker C.F. Consumer power: evolution in the digital age. J. Interact. Market. 2013; 27 (4):257–269. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamberton C., Stephen A.T. A thematic exploration of digital, social media, and mobile marketing: research evolution from 2000 to 2015 and an agenda for future inquiry. J. Market. 2016; 80 (6):146–172. [ Google Scholar ]
- Laroche M., Habibi M.R., Richard M.-O. To be or not to be in social media: how brand loyalty is affected by social media? Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2013; 33 (1):76–82. [ Google Scholar ]
- León-Castro M., Rodríguez-Insuasti H., Montalván-Burbano N., Victor J.A. In: Proceedings of the Marketing and Smart Technologies. Rocha Á., Reis J.L., Peter M.K., Cayolla R., Loureiro S., Bogdanovic Z., editors. 2021. Bibliometrics and Science Mapping of Digital Marketing; pp. 95–107. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lewis D.M., Alpi K.M. Bibliometric network analysis and visualization for serials librarians: an introduction to Sci2. Ser. Rev. 2017; 43 (3–4):239–245. [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu L., Lee M.K.O., Liu R., Chen J. Trust transfer in social media brand communities: the role of consumer engagement. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018; 41 :1–13. [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu S., Perry P., Gadzinski G. The implications of digital marketing on WeChat for luxury fashion brands in China. J. Brand Manag. 2019; 26 (4):395–409. [ Google Scholar ]
- Magna Global . 2017. Magna Advertising Forecasts winter Update. https://www.magnaglobal.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/MAGNA-Global-Forecast_Winter-Update_Final.pdf Retrieved from. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mandal P. Understanding digital marketing strategy. Int. J. Scient. Res. Manag. 2017 [ Google Scholar ]
- Markos-Kujbus E., Gati M. ECREA 2012 - 4th European Communication Conference. 24–27. 2012. Social media's new role in marketing communication and its opportunities in online strategy building. Istanbul, Turkey. [ Google Scholar ]
- Martín-Consuegra D., Faraoni M., Díaz E., Ranfagni S. Exploring relationships among brand credibility, purchase intention and social media for fashion brands: a conditional mediation model. J. Glob. Fashion Market. 2018; 9 (3):237–251. [ Google Scholar ]
- McNair C. 2018. Global Ad Spending. https://www.emarketer.com/content/global-ad-spending Retrieved from. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nerur S.P., Rasheed A.A., Natarajan V. The intellectual structure of the strategic management field: an author co-citation analysis. Strat. Manag. J. 2008; 29 (3):319–336. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nisar T.M., Prabhakar G., Patil P.P. Sports clubs’ use of social media to increase spectator interest. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018; 43 :188–195. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nyagadza B. Search engine marketing and social media marketing predictive trends. J. Digital Media Policy. 2020 [ Google Scholar ]
- Olanrewaju A.-S.T., Hossain M.A., Whiteside N., Mercieca P. Social media and entrepreneurship research: a literature review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020; 50 :90–110. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pacauskas D., Rajala R., Westerlund M., Mäntymäki M. Harnessing user innovation for social media marketing: case study of a crowdsourced hamburger. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018; 43 :319–327. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramos-Rodríguez A.-R., Ruíz-Navarro J. Changes in the intellectual structure of strategic management research: a bibliometric study of the Strategic Management Journal, 1980–2000. Strat. Manag. J. 2004; 25 (10):981–1004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shafique M. Thinking inside the box? Intellectual structure of the knowledge base of innovation research (1988–2008) Strat. Manag. J. 2013; 34 (1):62–93. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shanahan T., Tran T.P., Taylor E.C. Getting to know you: social media personalization as a means of enhancing brand loyalty and perceived quality. J. Retailing Consum. Serv. 2019; 47 :57–65. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shareef M.A., Mukerji B., Alryalat M.A.A., Wright A., Dwivedi Y.K. Advertisements on Facebook: identifying the persuasive elements in the development of positive attitudes in consumers. J. Retailing Consum. Serv. 2018; 43 :258–268. [ Google Scholar ]
- Singh J.P., Irani S., Rana N.P., Dwivedi Y.K., Saumya S., Kumar Roy P. Predicting the “helpfulness” of online consumer reviews. J. Bus. Res. 2017; 70 :346–355. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sposit N. Adapting to digital marketing regulations: the impact of the General Data Protection Regulation on individualised, behaviour-based marketing techniques. J. Digit. Soc. Media Market. 2019; 6 (4):341–348. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tafesse W., Wien A. Implementing social media marketing strategically: an empirical assessment. J. Market. Manag. 2018; 34 (9–10):732–749. [ Google Scholar ]
- Taylor C.R., Costello J.P. What do we know about fashion advertising? A review of the literature and suggested research directions. J. Glob. Fashion Market. 2017; 8 (1):1–20. [ Google Scholar ]
- Thorpe H. Creating an integrated digital marketing strategy: using cross-channel data to build intelligent strategies. J. Digit. Soc. Media Market. 2018; 6 (1):28–39. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tuten T.L. Sage; 2020. Social media Marketing. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang Y., Herrando C. Does privacy assurance on social commerce sites matter to millennials? Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019; 44 :164–177. [ Google Scholar ]
- Woodside A.G., Mir P.B. Clicks and purchase effects of an embedded, social-media, platform endorsement in internet advertising. J. Glob. Scholars Mark. Sci. 2019; 29 (3):343–357. [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu X., Wang X., Li Y., Haghighi M. Business intelligence in online customer textual reviews: understanding consumer perceptions and influential factors. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2017; 37 (6):673–683. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yerasani S., Appam D., Sarma M., Tiwari M.K. Estimation and maximization of user influence in social networks. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019; 47 :44–51. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang M., Dholakia N. Conceptual framing of virtuality and virtual consumption research. J. Glob. Scholars Mark. Sci. 2018; 28 (4):305–319. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang M., Guo L., Hu M., Liu W. Influence of customer engagement with company social networks on stickiness: mediating effect of customer value creation. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2017; 37 (3):229–240. [ Google Scholar ]
Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.
Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.
Use imagination to make the most of generative AI
Lending standards can be too tight for too long, research finds
US voters exhibit ‘flexible morals’ when confronting misinformation
Credit: Anton Vierietin / Shutterstock
Ideas Made to Matter
Digital marketing trends for 2022
Beth Stackpole
Jul 13, 2022
The advent of digital tools has upended age-old processes in marketing and advertising. Digital marketing technology is now a requirement for identifying, attracting, and retaining customers in an omnichannel world.
A new e-book from the MIT Initiative on the Digital Economy highlights learnings from the 2022 MIT Chief Marketing Officer Summit held this spring. The topline message to marketing executives: Add data, analytics, and algorithms to better reach socially-linked modern consumers.
Here are MIT Sloan researchers’ top digital marketing trends for 2022:
Social consumers in broad digital and social media networks
Today’s consumers make brand decisions based on a very broad set of digitally connected networks, from Facebook to WhatsApp, and the mix is constantly in flux.
Since social consumers are influenced by what social network peers think about different products and services (a trend called “ social proof ”), marketers must employ granular analysis to really understand the role of social media in marketing, according to IDE director Sinan Aral.
Aral examined 71 different products in 25 categories purchased by 30 million people on WeChat and found significantly positive effects from inserting social proof into an ad, although the effectiveness varied. For example, Heineken had a 271% increase in the click-through rate, while Disney’s interactions rose by 21%. There were no brands for which social proof reduced the effectiveness of the ads, Aral said.
Video analytics on TikTok, YouTube, and other social media
TikTok influencers loom large, especially with Gen Z. The problem is whether or not those viral influencer videos actually translate beyond attention into sales.
Research shows that engagement and product appearance isn’t the crucial factor — it’s more about whether the product is complementary or well-synched to the video ad. And the effect is more pronounced for “product purchases that tend to be more impulsive, hedonic, and lower-priced,” according to research conducted by Harvard Business School assistant professor Jeremy Yang while he was a PhD student at MIT.
Measuring consumer engagement with machine learning
Call it the “chip and dip” challenge: Marketers have long grappled with how to bundle goods, finding the right consumer products to combine for co-purchase from a huge assortment. With billions of options, this research is exacting and massive in scale, and data analysis can be daunting.
Researcher Madhav Kumar, a PhD candidate at MIT Sloan, developed a machine learning-based framework that churns through thousands of field scenarios to identify successful and less successful product pairs.
“The optimized bundling policy is expected to increase revenue by 35%,” he said.
Using machine learning to forecast outcomes
Most marketers are concerned about retention and revenue, but without good forecasts, decisions about effective marketing interventions can be arbitrary, said Dean Eckles, social and digital experimentation research group lead at IDE. Instead, update customer targeting through use of AI and machine learning to forecast outcomes more quickly and accurately.
In collaboration with the Boston Globe, IDE researchers took a statistical machine learning approach to analyze the results of a discount offer on customer behavior after the first 90 days. The short-term surrogate prediction was just as accurate as a prediction made after 18 months.
“There’s a lot of value to applying statistical machine learning to predict long-term and hard-to-measure outcomes,” Eckles said.
Adding “good friction” to reduce AI bias
Digital marketers talk frequently about reducing customer “friction” points by using AI and automation to ease the customer experience. But many marketers don’t understand bias is a very real factor with AI, said Renée Richardson Gosline, lead for the Human/AI Interface Research Group at IDE. Instead of getting swept up in “frictionless fever,” marketers must think about when and where friction can actually play a positive role.
“Use friction to interrupt the automatic and potentially uncritical use of algorithms,” Gosline said. “Using AI in a way that’s human-centered as opposed to exploitative will be a true strategic advantage” for marketing.
Read the 2022 MIT CMO Summit Report
Related Articles

More From Forbes
Achieving growth: overcoming the obstacles of digital marketing.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Founder of Anthony Media Group .
The digital marketing landscape has experienced a meteoric rise and rapid evolution in recent years, reshaping how businesses engage with their audiences.
An exponential expansion of tools and techniques—from the advent of search engine optimization (SEO) and pay-per-click (PPC) advertising to the proliferation of social media platforms and the emergence of influencer marketing (a market worth $21 billion )—are all becoming industrywide standards.
The Promise Of Scaling
In today's increasingly competitive digital world , scaling is crucial for digital marketing businesses. Scaling involves expanding the reach and impact of marketing efforts and developing to meet changing trends and consumer behaviors. Effective scaling strategies include:
• Diversifying marketing channels.
• Optimizing processes for efficiency.
Google Chrome Gets Third Emergency Update In A Week As Attacks Continue
Japanese fans are puzzled that yasuke is in ‘assassin’s creed shadows’, forbes releases 2024 30 under 30 asia list.
• Embracing innovative technologies.
• Fostering a dynamic and adaptable organizational culture.
One of the most significant advantages of scaling is the potential for increased revenue streams. By scaling strategically, companies can enter new markets and benefit from economies of scale, resulting in growth in revenue generation. Companies can also strengthen their market position, leading to improved brand awareness and credibility. Such recognition attracts new customers and fortifies customer loyalty, positioning the brand as a leader in its industry.
The Challenges Of Scaling Digital Marketing Companies
1. talent acquisition and retention.
Scaling a digital marketing company can be challenging, especially when recruiting and retaining talented employees. I've noticed the rapidly growing field of digital marketing has resulted in an increased demand for skilled professionals who deeply understand emerging technologies and changing consumer behavior. The need for such qualified individuals has intensified the competition among companies, making attracting and retaining top-tier talent difficult.
In my experience, a company's success depends on its ability to offer competitive compensation packages, professional development opportunities and a work culture that aligns with the values of the digital age.
To achieve this, companies must cultivate an environment that fosters innovation, encourages creative thinking and provides avenues for continual growth. Additionally, providing autonomy, recognizing achievements and fostering a collaborative atmosphere is critical in nurturing a motivated and valued workforce.
For example, my approach centers on fostering a stress-free environment for employees, whether through face-to-face or digital interactions, including our remote work setup. I prioritize providing resources and support to help maintain a healthy work-life balance and manage stress effectively. Communication is key, and I aim for it to be enriching, transparent and empathetic.
As Nikola Tesla is believed to have said, "The most important product of a creative mind is an invention." I recommend company leaders value and celebrate innovative ideas, aiming to build bridges of trust and encouragement within your team, keeping everyone focused on your shared objectives and moving toward better solutions.
2. Successful Integration Of Technology
The potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to transform marketing strategies is immense, as it can automate repetitive tasks, improve campaign performance and provide detailed insights. AI's ability to leverage vast datasets enables enhanced audience segmentation, personalized targeting and predictive analytics, making it an essential component of any scaling strategy. In fact, 98% of marketers are already using AI.
However, the integration of AI and other cutting-edge tools requires a delicate balance. Challenges arise in seamlessly incorporating these technologies into existing systems while ensuring a cohesive workflow and minimizing disruption to ongoing operations. Businesses often require assistance in integrating new AI-powered platforms or tools, as compatibility issues, data migration challenges and the need for upskilling or reskilling the workforce may arise.
Incorporating AI with existing processes requires careful planning, robust training programs and a strategic phased approach to implementation to minimize potential disruptions and maximize the benefits of AI.
Success lies in having a comprehensive strategy that aligns these innovations with the company's goals. Make sure to thoughtfully select AI-driven solutions and create a culture of adaptability and learning.
3. Data Security And Privacy Concerns
Data has become a cornerstone for strategic decision-making and targeted outreach. As businesses use data to refine their marketing strategies and cultivate customer relationships, navigating the web of data security and privacy regulations is crucial.
Adhering to evolving regulations and compliance standards requires a proactive approach to securing sensitive information, ensuring ethical data-handling practices and strengthening consumer trust.
Make sure you have a comprehensive understanding of regulatory frameworks like GDPR and CCPA . Maneuvering these intricacies involves adhering to legal requirements and fostering a data ethics and accountability culture. Implement robust data protection measures, incorporating privacy-by-design principles into marketing strategies and empowering stakeholders with comprehensive training.
For example, at my company, we prioritize a culture of data ethics and accountability. We achieve this through regular training on ethical data practices, robust data governance, transparency and ethical decision-making. These efforts ensure our employees handle data responsibly and ethically. We approach our responsibilities with integrity and respect, recognizing the significance of data and treating it accordingly.
4. Market Saturation And Competition
While it is important to recognize the saturation point, it does not mean the end of the road for companies. To distinguish oneself, try strategies like targeting niche-specific segments, creating unique value propositions or utilizing innovative technologies to redefine customer experiences.
Focusing on quality, authenticity and consistency in content and interactions can help you stand out amid the noise and foster deeper connections. By prioritizing innovation and adopting a customer-centric approach, businesses can overcome saturation challenges and carve a distinct position.
For example, at my company, one strategy we've found to be effective is reviewing and ensuring that our messaging, tone and content quality are consistent across all platforms, reinforcing our brand identity. We focus on providing value and building genuine relationships, avoiding overly promotional content.
As markets evolve and consumer behaviors continuously shift, it becomes essential to have a meticulous strategy that adapts to changes. To succeed, companies must remain adaptable, constantly evaluating and improving their methods to capitalize on opportunities and navigate challenges. By fostering a culture of innovation and responsiveness, coupled with a strategic outlook, businesses can truly unlock the potential for sustainable growth in the expansive realm of digital marketing.
Forbes Business Council is the foremost growth and networking organization for business owners and leaders. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Search for: Search
- Get Free Newsletters
New $90 Million Project to Create Digital Research Hub Focused on K-12 Education
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)

The National Science Foundation has awarded Rice University $90 million to build what is being described as a first-of-its-kind education research hub that will leverage data from an array of major digital learning platforms currently serving tens of millions of students.
The university recently announced the investment as its largest ever federal research grant. OpenStax at Rice, a major publisher of open education resources, will build the research and development hub known as SafeInsights .
The project will focus on producing “research-informed insights about teaching and learning for educators, institutions and learning platforms to use to create tailored programs, pedagogies and policies that will equip learners to thrive.”
“Just like there are bigger telescopes that let astronomers see deeper into the night, SafeInsights’ goal is to have this large student population that will enable researchers to see deeper into the student learning experience,” Slavinsky said in an interview.
The SafeInsights hub will take five years to build, he said, with early research projects b eginning in 16 to 18 months, and full-scale research operations starting in 2029.
School districts’ commitment to seeking and using research-based educational strategies is uneven at best. Many district officials complain that academic and other scientifically based research is too abstract, disconnected from their work, and outdated to be of practical use in their decision-making.
When surveyed recently by EdWeek Market Brief on what sorts of research they value most when choosing products and services, district and school leaders were much more likely to point to data on student outcomes, or product usage data than they were rigorous, experimental research.
Data Security in Focus
At $90 million, the award is NSF’s largest investment in research and development infrastructure for education at a national scale, the university said.
In the past, education research has been hampered by small study groups and short time frames, but the recent boom in digital learning can provide researchers with a plethora of data needed to better understand academic outcomes, Slavinsky said.
SafeInsights’ goal is to have this large student population that will enable researchers to see deeper into the student learning experience. J.P. Slavinsky, Executive Director, SafeInsights
And research will not be limited to only STEM (science, technology, engineering, and math) areas. Schools, education companies, and researchers participating in SafeInsights will bring their own research agenda, Slavinsky said.
Protecting student data is a major concern within school districts, particularly as schools’ and students’ reliance on technology has steadily grown.
The data collected as part of the new project will remain secure, Slavinsky said. No student information will be revealed to researchers.
Instead, researchers will submit their inquiries to SafeInsights, and the research hub will have the data in question analyzed where it is originally stored — by schools or on a digital platform — and provide researchers with aggregate results.
The research and development project will be a central hub for 80 partners and collaborating institutions. That number is expected to grow, Slavinsky said.
“One of the great things about SafeInsights is that it is very scalable,” he said. “And we want to build this community, so we can get a better and better picture of the students and the teachers we’re trying to help.”
Follow EdWeek Market Brief on Twitter @EdMarketBrief or connect with us on LinkedIn .
Image credit Stockyarder/DigitalVision/Getty
- When Districts Say They Value ‘Research,’ What Do They Mean?
- Need a Partner to Research Your Product? Here Are 5 Questions to Ask
- The Bar for Evidence That Education Companies Are Asked to Meet
- What’s the Value of Research to School Districts, and Education Companies?
Most Popular
- New $90 Million Project to Create Digital Research Hub Focused on K-12 Education May 14, 2024
- Rhode Island District Looks to Assess Course Quality; Pa. System Seeks World Languages Program May 14, 2024
Related Posts
Ftc takes action against chegg for alleged data breaches, school-to-work issues are surging in state legislatures, former bush education official to head digital learning initiative, schedule a tour.
Username or Email address *
Remember me
Lost your password?
Digital twins: The art of the possible in product development and beyond
Industrial companies around the world rely on digital tools to turn ideas into physical products for their customers. These tools have become increasingly more powerful, flexible, and sophisticated since the 1960s and 1970s, when computers first began replacing drawing boards in design offices. Today, product life-cycle management (PLM) has become engineers’ first language: PLM systems help companies to capture, codify, process, and communicate product knowledge across their organizations.
About the authors
This article is a collaborative effort by Mickael Brossard , Sebastien Chaigne, Jacomo Corbo, Bernhard Mühlreiter , and Jan Paul Stein, representing views from McKinsey’s Operations Practice.
Yet as engineering tools have become more capable, the demands placed upon them have also increased. Product functions are increasingly delivered through a combination of hardware and software. Sensors and communications capabilities allow products to offer more features and to respond more effectively to changing operating conditions and user requirements. Advanced, adaptable user interfaces have simplified the operation of complex and sophisticated machines.
Evolving business models are also blurring the boundaries between design and use. Customers expect the performance and functionality of products to improve during their life cycle, enabled by over-the-air software updates or the ability to unlock new features as needed. Many products operate as part of an ecosystem of related products and services. Increasingly, customers are not buying products outright, but paying for the capabilities they provide on a per-use or subscription basis.
The birth of the digital twin
These changing requirements have triggered a transformation in digital product representation and the creation of a new tool: the digital twin. Digital twins combine and build upon existing digital engineering tools, incorporating additional data sources, adding advanced simulation and analytics capabilities, and establishing links to live data generated during the product’s manufacture and use. A conventional PLM system uses one digital model to represent each variant of a product. A digital twin, by contrast, may have one model for each individual product, which is continually updated using data collected during the product’s life cycle.
The digital-twin approach can be applied to products, manufacturing processes, or even entire value chains. In this article, we will focus on their application to products, specifically to product design.
Digital twins offer multiple potential benefits for product-based companies and users. They can aid design optimization, reduce costs and time to market, and accelerate the organization’s response to new customer needs. Digital twins can also be a critical enabler of new revenue streams, such as remote maintenance and support offerings and “as a service” business models.
Based on the experience of companies that have already adopted the approach, we estimate that digital-twin technologies can drive a revenue increase of up to 10 percent, accelerate time to market by as much as 50 percent, and improve product quality by up to 25 percent. Digital-twin technology is becoming a significant industry. Current estimates indicate that the market for digital twins in Europe alone will be around €7 billion by 2025, with an annual growth rate of 30 to 45 percent. 1 Infinium; MarketsandMarkets; MarkNTel Advisors; Meticulous Market Research; Mordor Intelligence; SBIS; Technavio, last accessed April 2020.
Digital twins in practice
Companies in many different industries are already capturing real value by applying digital twins to product development , manufacturing, and through-life support (exhibit).
An automotive OEM, for example, has used the digital-twin approach to create a concept configurator for early phase development . The start of the development process is especially challenging for complex products because the various stakeholder groups, such as sales, engineering, and finance, may have different or even contradictory product requirements. The OEM now balances these trade-offs using a digital concept configurator that allows for simultaneous evaluation of customer requirements, technical concepts, and product costs. When a technical concept within a system or subsystem of the product is changed, the implications for meeting customer requirements or product cost targets become immediately transparent.
Would you like to learn more about our work in Product Digital Twins ?
Using the configurator within cross-functional development teams has helped the OEM to reallocate 5 to 15 percent of a new vehicle’s material costs to the attributes that drive the most customer value. Applying the approach to select customer-facing components has allowed the company to optimize costs and customer value simultaneously, improving the contribution margin of those parts by 5 to 10 percent. As a further benefit, the configurator helped the team reduce the time taken to reach agreement on changes by 20 percent, thus accelerating time to market.
Digital twins are even being used to replicate systems in complex mission scenarios. Using this approach, one aerospace and defense player has cut the time required to develop advanced products by 30 to 40 percent. The digital twin also aids discussion with customers during the development process, helping the company validate and improve its designs.
In the consumer electronics sector, a company is using product digital twins to boost quality and supply chain resilience . It stores detailed information on the content of its products, including the exact source of individual components. In the event of quality issues during production or early failures in the field, the company can trace problems back to specific supplier facilities, then take appropriate action to prevent reoccurrence of the issue. An automotive supplier uses the same approach to trace quality deviations in its production through to the upstream supply chain, and in the process has reduced scrap by 20 percent.
Digital twins are increasingly being used to improve future product generations . An electric-vehicle (EV) manufacturer, for example, uses live data from more than 80 sensors to track energy consumption under different driving regimes and in varying weather conditions. Analysis of that data allows it to upgrade its vehicle control software, with some updates introduced into new vehicles and others delivered over the air to existing customers.
Developers of autonomous-driving systems , meanwhile, are increasingly developing their technology in virtual environments. The training and validation of algorithms in a simulated environment is safer and cheaper than real-world tests. Moreover, the ability to run numerous simulations in parallel has accelerated the testing process by more than 10,000 times. Incorporating sensor data from real-world vehicles into these tests helps companies improve the veracity of their simulations and identify blind spots in the virtual test database.

The mainstreaming of additive manufacturing
A company in the renewable-energy sector is using a digital twin to automate, accelerate, and improve the engineering of hydroelectric turbines . Using the machine learning system to evaluate the likely performance of the new designs allowed it to rate more than a million different designs in seconds rather than the hours required for conventional computational flow dynamics (CFD) analysis. The winning geometry delivers the maximum theoretical performance, significantly higher than what is achievable by conventional optimization methods. Moreover, by using machine learning, the overall end-to-end design cycle time was cut in half compared with the conventional approach.
Digital twins in three dimensions
Digital twins can take many different forms. Organizations that want to take advantage of digital-twin technologies must select an appropriate form that will enhance its technical and business objectives. The design of a digital twin can vary across three dimensions (exhibit).
The first dimension encompasses the value chain steps that the digital twin will cover. An engineering twin covers value chain steps similar to those covered by conventional PLM systems, ranging from product definition to detailed engineering. A production twin replicates a product throughout the manufacturing process, incorporating data such as the components, materials, and process parameters used, as well as the results of tests and quality checks. A service twin incorporates data collected from the product in use, such as operating modes, performance, diagnostic information, and maintenance history. The most sophisticated digital twins span multiple parts of the value chain, allowing in-service data to optimize manufacturing processes or future design iterations.
The second dimension is the scope of the digital twin. A product may consist of several major systems, multiple subsystems, and hundreds or thousands of hardware and software components. Some digital twins cover only one or several components, for example, those that simulate the flow of liquids through a pipe. Others cover a full product, for example, those that simulate a car’s crash characteristics. Given the limitations of computing power, generally, the narrower the scope of a digital twin, the more precise its virtual replica will be. In contrast, full-product digital twins often need to abstract or simplify certain product behaviors to remain manageable.
The final dimension of a digital twin is its degree of sophistication . The simplest digital twins consist of various sources of data relating to a product, often from sources that have few or no links with one another. The second level of sophistication uses traditional simulation tools to perform analyses of design performance and integrate the various sources through a PLM system or similar platform.
At the third level of sophistication, a digital twin will use predictive or prescriptive analytics, as well as machine learning technology to run automated simulation refinements and yield new insights. This allows design and manufacturing teams to make informed decisions based upon direct results and performances.
At the last level of sophistication, digital twins use predictions of component failure rates or performance variations to react to changing environments and manipulate the real-world counterpart in a closed-loop setup. This approach might be used in a condition monitoring system, for example, where sensor data and simulations are combined to make inferences and predictions about the state and behavior of a specific product, and might allow a machine to compensate for wear or variations in operating conditions by adjusting parameters in real time.
Companies in other sectors are also starting to use digital twins to derive deeper insights into customer behaviors and preferences . For example, white-goods manufacturers can use data from in-service products to identify the most and least used features. That can inform future product development decisions, such as deleting rarely used features or revising the user interface to make the features more accessible.
The adoption of digital twins is currently gaining momentum across industries, as companies aim to reap the benefits of various types of digital twins. Given the many different shapes and forms of digital twins (see sidebar, “Digital twins in three dimensions”), and the different starting points of each organization, a clear strategy is needed to help prioritize where to focus digital-twin development and what steps to take to capture the most value.
How to start and succeed on your digital-twin journey
Embarking on a digital-twin journey can look daunting at first sight, especially since the breadth and depth of use cases can span the entire corporate landscape, including product portfolio choices, business model design, R&D, manufacturing, and through-life support.
This versatility can also be a strength, however, as it allows companies to start small and expand the scope, sophistication, and value-chain coverage of their digital-twin projects over time. The experience of companies that have applied digital twins in their own product operations leads to a few simple rules that can greatly increase your odds of success.
Define your aspirations
Be aware of digital-twin best practices. Do your homework and seek out perspectives on best practices and future trends in digital-twin technology. Assess and prioritize the elements of your vision. Evaluate the potential of digital-twin-related opportunities and prioritize them into an implementation road map.
Be clear about the business case. Quantify the value offered by different digital-twin opportunities and determine the minimum level of model sophistication required to generate that value. Successful projects focus on short development times and rapid ROI.
Test the waters by prototyping select use cases. Run a series of hackathons (possibly supported by digital-twin specialists) to assess your capabilities’ baseline, develop solution prototypes, refine, and adjust the initial concepts. This step calibrates the approach and prevents you from losing time and resources by attempting an impossible plan. It is part of a broader value assurance move aimed at bringing the entire project to a successful conclusion.
Know your strengths
Perform a maturity assessment. Understand your current digital product development capabilities along six main dimensions: development methodologies, PLM governance, data strategy, business processes, system complexity, and collaboration. Understanding the areas where you are most advanced and where you are lagging behind will help prioritize areas of investment for a balanced implementation of a digital twin and its use cases.
Access to appropriate talent and capabilities can make or break a digital-twin initiative. Many organizations need to develop additional expertise in areas such as advanced simulation and modeling or data analytics for user experience design.
Plan a step-by-step, agile implementation
Invest several months in developing a minimum viable product (MVP). Incubate a cross-functional, agile team dedicated to bringing priority use cases to life and building digital capabilities in the process. The MVP is now the must-do approach to maximize value gains from the start rather than waiting until the program is finalized before experiencing the first benefits.
Perform an MVP retrospective to pivot or persevere. Derive lessons from the first MVP phase to confirm your digital-twin aspirations or pivot them based on the findings (for example, the validity of use cases, complexity of implementation, and maturity of the organization). This is the second value assurance move that enables you to further calibrate the implementation plan and revise the scope to avoid generating sunk costs.
Scale up the digital-twin initiative and accelerate ROI. Optimize and standardize implementation based on insights from the MVP phase. Define an (internal or external) recruiting and capability-building strategy. Build an operating model to enable rapid scaling of successful approaches. The most advanced organizations typically consider digital-twin technologies a core strategic capability.
By following these simple best practices, you will be able to reap the benefits of digital twins in a scalable, progressive way. Are you ready?
Mickael Brossard is a partner in McKinsey’s Paris office, where Sebastien Chaigne is an associate partner; Jacomo Corbo is a partner in the London office; Bernhard Mühlreiter is a partner in the Vienna office; and Jan Paul Stein is an associate partner in the Munich office.
The authors wish to thank Roberto Argolini, Elia Berteletti, Kimberly Borden, Akshay Desai, Hannes Erntell, Alessandro Faure Ragani, Anna Herlt, Mark Huntington, Mithun Kamat, Michele Manzo, and Alessandro Mattozzi for their contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Full-potential procurement: Lessons amid inflation and volatility

Product sustainability: Back to the drawing board

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Our search for relevant literature focuses on four marketing journals: International Journal of Research in Marketing, Marketing Science, Journal of Marketing Research, and Journal of Marketing, focusing on articles published between 2000 to 2016.We started at Web of Science and searched for articles with the keywords "digital" or "online ...
Despite particular research conducted on the issues related to digital marketing and marketing analytics, additional attention is needed to study the revolution and potentially disruptive nature of these domains (Petrescu and Krishen 2021, 2022).Considering the substantial impact of digital marketing and marketing analytics in the current competitive and demanding business landscape, the ...
The digital marketing discipline is facing growing fragmentation; the proliferation of different subareas of research impedes the accumulation of knowledge. ... Thus, our aim is to provide an integrative framework for research in digital marketing derived from the historical analysis of the Internet. Using practice theory and institutional ...
as 'the Digital Transformation' of marketing, widely accepted and investigated by both. practitioners and a cademics. Digital advertiseme nts, e-commerce, mobile services, just to name. a few ...
We broadly divide the nine studies into three themes: (1) Impact of social media (including studies that focus on Facebook, Snapchat, or Twitter) and text mining analyses, (2) Insights from survey-based data (in the context of healthcare and data marketing industry), and (3) New technologies and emerging research areas as summarized in Fig. 2.The next section offers a brief overview of the ...
Abstract The aim of this study is to explore the contemporary digital marketing. strategies and tools and the role played by these in various marketing activities or. areas. The study also ...
In today's digital era, the importance of digital marketing has increased from one year to another as a way of providing novel properties for informing, engaging, and selling services and products to clients. The research's aim is to investigate trends and patterns in the area of digital marketing research from 1979 to June 2020 through a bibliometric analysis technique. A total of 924 ...
This research complements prior studies on digital marketing and sheds some light on these gaps. Therefore, the main aim of this article is to assess how digital marketing tactics can impact a company and to examine how SMEs can use digital media to enhance brand awareness outside the domestic market.
Digital marketing is the process of advertising of products or services of companies using dig ital. technologies available o n internet including mobile phones, display advertising, and any o ...
Notwithstanding the body of research on the characteristics and benefits of content marketing as a digital marketing strategy, ... Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing: 1: 3: Journal of Consumer Behavior: 1: 4: Journal of Interactive Advertising: 1: 5: International Journal of Advertising: 1: 6, 8, 13: Industrial Marketing Management: 3: 9:
For example, Lamberton and Stephen reviewed and synthesized 160 articles on digital, social media, and mobile marketing published during the period from 2000 to 2015, while Salo's review of 40 studies assessed the advances in social media marketing research in the industrial marketing field. Notwithstanding their usefulness, these reviews: (a ...
This article takes a quasi-historical perspective on digital and social media marketing. It traces digital marketing from its roots in direct and interactive marketing to the present day. The article suggests a broad view of digital marketing to encompass customer co-creation and engagement.
The impact of digital marketing on SMEs performance is observed over the past 12 years through the resources which are undertaken for the study, namely, Science Direct, Scopus, Springer, IEEE Explorer, ACM Digital Library, Engineering Village, ISI Web of Knowledge database is used to search the research publications on the selected topic ...
1. Introduction. These days, digital marketing has become part of people's daily lives around the world. As of January 2021, there were 4.66 billion internet users worldwide—59.5% of the global population (Statista, Citation 2021).Vietnam alone has 70.3% of the population using the Internet, an increase of 0.8% over the same period last year.
Although research on digital marketing and related topics had begun as early as 2000, digital marketing studies were almost overlooked by the researchers during the first decade (2000-2010). Therefore, the actual proliferation commenced after 2010 meaning in the second decade (2010-2020) and as time passes, research in this domain has grown ...
A new e-book from the MIT Initiative on the Digital Economy highlights learnings from the 2022 MIT Chief Marketing Officer Summit held this spring. The topline message to marketing executives: Add data, analytics, and algorithms to better reach socially-linked modern consumers. Here are MIT Sloan researchers' top digital marketing trends for 2022:
Digital marketing is one of the most popular and powerful ways to generate awareness, interest and sales for your products or services. As the name implies, digital marketing is conducted via ...
Digital marketing is a form of marketing that leverages the internet and digital technologies, such as computers and mobile devices, to connect with customers. More than running a sponsored Instagram ad to drive sales, it's a set of practices that interacts with customers at every stage of the buying journey. Digital marketing strategy includes ...
• Analyse the different forms, approaches, and applications of digital marketing. • To research how digital marketing has affected consumer behavior. Scope of the study 1. The study sheds light on the effectiveness of digital marketing for businesses from a consumer standpoint. 2. The survey provides information on the types and formats of ...
The research tries to find out how machine learning impacts the digital marketing scene in India. We aim to increase the existing knowledge on machine learning and its resourcefulness in digital marketing (Kaplan & Haenlein, 2019; Vinish et al., 2021) which served as the motivation and need for the study. We try and find the solutions for the ...
The digital marketing landscape has experienced a meteoric rise and rapid evolution in recent years, reshaping how businesses engage with their audiences. An exponential expansion of tools and ...
The National Science Foundation has awarded Rice University $90 million to build what is being described as a first-of-its-kind education research hub that will leverage data from an array of major digital learning platforms currently serving tens of millions of students.. The university recently announced the investment as its largest ever federal research grant.
An automotive OEM, for example, has used the digital-twin approach to create a concept configurator for early phase development.The start of the development process is especially challenging for complex products because the various stakeholder groups, such as sales, engineering, and finance, may have different or even contradictory product requirements.
The major objective of the research was to uncover the relationship between digital marketing tools and strategic firm marketing. Details like how they can contribute to lead generation and the ...
The estimated total pay for a Marketing Digital is $82,438 per year in the United States area, with an average salary of $62,705 per year. These numbers represent the median, which is the midpoint of the ranges from our proprietary Total Pay Estimate model and based on salaries collected from our users.
Based on the company's Monday demonstration, GPT-4o will effectively turn ChatGPT into a digital personal assistant that can engage in real-time, spoken conversations.
According to previous research "When technology works on a personal level, it creates an endearing bond with the users, when marketers tap into such a bond, the potential for customer value creation is enormous" (Kumar et al., 2019, p. 137).Advanced and innovative AI-powered marketing solutions can rapidly adapt to the changing needs of businesses and come up with communications and ...