
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download

Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- Last modified on: 2 months ago
- Reading Time: 8 Minutes

Table of Contents
[Download] Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
Here we are providing case study or passage-based questions for class 6 science chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits.
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
An electric bulb has a filament that is connected to the terminals. The two terminals of filament are fixed with two thick wires provides support to it. These terminals are fixed in such a manner that they do not touch each other. 1. Where is the filament fixed in the electric bulb? (a) Near the positive terminal (b) Near the negative terminal (b) In the middle (d) None of the above is correct 2. Filament is (a) a thin wire that gives off light when bulb is switched on (b) fixed to two thick wires which provides support to it (c) Both the above are correct (d) None of these is correct 3. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct? (a) The two terminals of a bulb are fixed in such a way that they do not touch each other. (b) The two terminals of a bulb are fixed in such a way that they touch each other. (c) The two terminals of a bulb are connected to the same terminal of the electric cell. (d) None of the above is correct
Related Posts
What is case study question for class 6 science.
Case study or passage-based questions in class 6 Science typically require students to read a given scenario or passage and answer questions based on the information provided. These questions assess students’ comprehension, analytical thinking, and application of scientific concepts. Here is an example of case study or passage-based questions for class 6 Science:
Passage: Rahul conducted an experiment to investigate how different liquids affect the rusting of iron nails. He placed four iron nails in four separate beakers containing water, vinegar, oil, and saltwater. After one week, he observed the nails and recorded his observations.
a) What is the purpose of Rahul’s experiment?
b) Compare and contrast the appearance of the iron nails in each beaker after one week.
Best Ways to Prepare for Case Study Questions
To develop a strong command on class 6 Science case study questions, you can follow these steps:
- Read the textbook and study materials: Familiarize yourself with the concepts and topics covered in your class 6 Science curriculum. Read the textbook thoroughly and take notes on important information.
- Practice analyzing case studies: Look for case studies or passages related to class 6 Science topics. Analyze the given information, identify key details, and understand the context of the situation.
- Develop comprehension skills: Focus on improving your reading comprehension skills. Practice reading passages or articles and try to summarize the main points or extract relevant information. Pay attention to details, vocabulary, and the overall structure of the passage.
- Understand scientific concepts: Ensure that you have a solid understanding of the scientific concepts discussed in class. Review the fundamental principles and theories related to each topic.
- Make connections: Try to connect the information provided in the case study to the concepts you have learned in class. Identify any cause-effect relationships, patterns, or relevant scientific principles that apply to the situation.
- Practice critical thinking: Develop your critical thinking skills by analyzing and evaluating the information given in the case study. Think logically, consider multiple perspectives, and draw conclusions based on the evidence provided.
- Solve practice questions: Look for practice questions or sample case study questions specifically designed for class 6 Science. Solve these questions to apply your knowledge, practice your analytical skills, and familiarize yourself with the format of case study questions.
- Seek clarification: If you come across any challenging concepts or have doubts, don’t hesitate to ask your teacher for clarification. Understanding the underlying principles will help you tackle case study questions effectively.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Class 6 Science Case Study Question
Case study question class 6 science (cbse / ncert board).
Class 6 Science Case Study Question and Answer: CBSE / NCERT Board Class 6 Science Case Study Question prepared by expert Science Teacher. Students can learn Case Based Question / Paragraph Type Question for NCERT Class 6 Science.
There are total 16 chapter Food Where Does It Come From, Components of Food, Fibre to Fabric, Sorting Materials Into Groups, Separation of Substances, Changes Around Us, Getting to Know Plants, Body Movements, The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings, Motion and Measurement of Distances, Light Shadows and Reflection, Electricity and Circuits, Fun with Magnets, Water, Air Around Us, Garbage In Garbage Out.
For any problem during learning any Case or any doubts please comment us. We are always ready to help You.
CBSE Class 6 Science Case Study Question
Chapter 1 Food Where Does It come From Case Study Question
Chapter 2 Components of Food Case Study Question
Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric Case Study Question
Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups Case Study Question
Chapter 5 Separation of Substances Case Study Question
Chapter 6 Changes Around Us Case Study Question
Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants Case Study Question
Chapter 8 Body Movements Case Study Question
Chapter 9 The Living Organisms – Characteristics and Habitats Case Study Question
Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances Case Study Question
Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection Case Study Question
Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Case Study Question
Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Case Study Question
Chapter 14 Water Case Study Question
Chapter 15 Air Around Us Case Study Question
Chapter 16 Garbage In Garbage Out Case Study Question
What is Case Study Question?
Ans. At case Study there will one paragraph and on the basis of that concept some question will made. Students have to solve that question.
How many marks will have at case based question?
Most of time 5 questions will made from each case. There will 1 or 2 marks for each question.
Important links:
- Lakhmir Singh Class 6 Book Solution
- NCERT Solution Class 6 Science
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits are given below. Our notes are designed by the subject experts and are as per the NCERT guidelines. These notes include all the important points of the chapter in detailed way, so you can refer to this whenever required. Study Path provides CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 12 that are easy to understand and also free downloadable PDF format, so students can practice it for their studies and get good marks in their examinations.
Electricity and Circuits Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 12
Introduction to Electricity and Circuits
Electricity has become so common that sometimes we forget its immense applications.
Advantages of Electricity:
- Light in our houses, offices, roads etc. even past sunset
- To operate pumps which in turn have a lot of applications
- Electrical appliances like refrigerator, fans etc.
- Building houses, installing equipment etc.
- Current is the flow of particles in a particular direction. E.g air currents that cause winds or water currents.
- When particles flow in an electric circuit to produce electricity, it is called an electric current.
Electric current
The flow of electric charges in a circuit is called an electric current. The direction is taken from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the battery in an external circuit.
Electric Cell
- It is a small cylindrical structure which helps in operating the devices.
- A small metal cap is placed on one side and a metal disc is present on the other side.
- All cells have two terminals: Positive and Negative.
- The metal cap and metal disc are positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the electric cell respectively.
- Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy inside a cell. When the chemicals are exhausted, the cell stops working.

- An electric wire is a conducting path in an electric circuit, through which current flows.
- It is usually made out of a metal that is a good conductor of electricity.

Electric Bulb and its working
- The outer covering is glass and the base is metallic.
- The part of the bulb which glows is called Filament and is made up of tungsten.
- The filament is attached to two wires. One of the wires is connected to the metal case at the base and the other wire is connected to the metal wire at the centre of the base.
- Base of the bulb and metal tip are the terminals of the bulb and they do not touch each other.

Electric circuit
- A closed-loop path, which the current takes is known as an electric circuit.
- When the path of the circuit is closed, current flows through it.
- When there is a break in the path (switch is open) then, the circuit is open and not conducting so the current does not flow.
Consider an electric cell and a bulb. The terminals of the cell are connected to the terminals of the bulb by the means of electric wires. Such an arrangement of cell and bulb is called an Electric Circuit . The circuit is said to be complete in this case because of which electricity will flow and the bulb will glow.
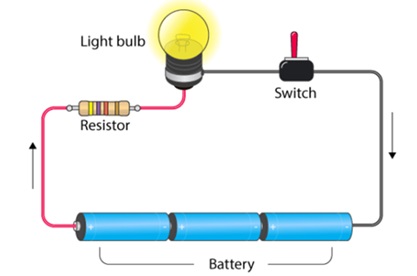
Electric switches
Switch is an integral part of an electric circuit. It is a simple device which breaks or completes a circuit. When the switch is ‘on’, the circuit is complete. When the switch is ‘off’, current does not flow in the circuit. So an electric appliance will only work if the switch is ‘on’.

Conductors and insulators
- Any material that allows the electric current to pass through it is called as the conductor. Eg: metals like copper
- Materials that do not allow the free flow of current through it are known as bad conductors or insulators E.g.: Rubber, plastic
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12 – Free PDF Download
Our Class 6 Revision Notes will provide a quick glimpse of the chapter and improve the learning experience. We have made these revision notes keeping the convenience of students in mind so that it proves more effective. You can easily read these Class 6 notes just by clicking on the chapter names provided above.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity And Circuits
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 12 is provided below for the reference of CBSE Class 6 science students. Those interested can check the full NCERT solutions for Science Chapter 12 here
January 16, 2024

Table of Contents
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 12
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 12: NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 on Electricity and Circuits provides answers and explanations for filling in the blanks, true or false, circuit diagrams, and descriptive questions. These solutions assist in grasping the concepts covered in the chapter. The chapter addresses topics such as electric cells, bulbs, circuits, switches, conductors, insulators, and offers examples of both.
The solutions of Chapter 12 in NCERT presents accurate solutions, aiding students in efficiently completing homework and preparing for exams. It ensures comprehensive coverage of all concepts in the chapter. Class 6 is a crucial stage, forming the foundation for future academic years. Hence, students aiming for good Science scores should diligently practice CBSE Sample Papers.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 1
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Overview
The NCERT Solutions for Chapter 12 of Class 6 Science provide a thorough exploration of electricity and circuits. This chapter elucidates the principles of electricity, various electrical devices, electrical circuits, conductors, switches, insulators, and more.
Comprising a total of five sub-topics, the chapter initiates with a general introduction to the mentioned concepts, progressing to explain electric cells, circuits, switches, and related topics. The chapter summary and technical terms provided at the end contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the concepts.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 offer a concise solution for student comprehension. These solutions are accessible online in PDF format, allowing students to download them without any charges.

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 2
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity And Circuits
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity And Circuits are provided here with simple step-by-step explanations.
1. Fill in the blanks:
(i) A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called —.
(ii) An electric cell has ——— terminals.
(i) A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called a switch.
(ii) An electric cell has two terminals.
2. Mark ‘True’ or ‘False’ for the following statements:
( a) Electric current can flow through metal.
(b) Instead of metal wires, a jute string can be used to make a circuit.
(c) Electric current can pass through a sheet of thermocol.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 3
3. Explain why the bulb would not glow in the arrangement shown in Fig.

Ans: The bulb will not light since the circuit is broken due to the insulator in the middle.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 12 PDF Download
4. Complete the drawing shown in Fig, to indicate where the free ends of the two wires should be joined to make the bulb glow.

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 13
5. What is the purpose of using an electric switch? Name some electrical gadgets that have switches built into them.
Ans: A switch is a basic device that completes or breaks a circuit in an electric circuit. Electric fans, electric irons, toasters, and other electric appliances need switches.
6. Would the bulb glow after completing the circuit shown in Fig in the Q.4 if instead of a safety pin we use an eraser?
Ans: No, because the eraser is an insulator.
7. Would the bulb glow in the circuit shown in Fig. in Question 04?
Ans: No, the bulb will not glow.
8. Using the “conduction tester” on an object it was found that the bulb begins to glow. Is that objected to by a conductor or an insulator? Explain.
Ans: Because electricity can only pass through a conductor and not through an insulator, that object is called a conductor. The bulb will not glow unless the thing is a conductor.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 4
9. Why should an electrician use rubber gloves while repairing an electric switch at your home?
Ans: Rubber gloves are used as insulators. This prevents the electrician from being electrocuted. That is why, when repairing an electric switch, an electrician wears rubber gloves.
10. The handles of the tools like screwdrivers and pliers used by electricians for repair work usually have plastic or rubber covers on them. Can you explain why?
Ans: Plastic and rubber are both poor electrical conductors. As a result, they protect from electric shock.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Topic Wise Explanation
Chapter 12 of Class 6 Science is divided into 5 sections. Here’s a breakdown of each topic.
Introduction
The 12th Science class for grade 6 starts by introducing the concept of electricity and circuits. It begins by highlighting the importance of electricity in our daily lives and the devices that rely on it.
Electric Cell:
This part of Class 6 Science Chapter 12 delves into the electric cell concept. It explains the working of various electric cells, their structure, and the warning signs on them. Once students grasp how these cells work, they can proceed to experiments. There are two do-it-yourself activities for students to try at home. The first involves understanding the structure of a torch bulb. Students can take out the bulb, examine its various parts, and observe how the filament produces light with the help of an electric cell.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 16
Bulb Connected to an Electric Cell:
In the subsequent section of electricity and circuits in Class 6, students learn how to light a torch bulb using an electric cell. This part provides a step-by-step guide on successfully carrying out this process.
Students can take two electric wires of different colors, strip off their plastic covering to expose their metal cores, and then connect one end of the exposed metal part to the cell and the other end to the bulb. They can use an electrician’s tape to secure them. Students can experiment by switching the wires and note down the results for later discussion.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 8
Electric Circuit:
As the name suggests, this chapter in NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 12 offers a comprehensive understanding of electrical circuits. Building on the previous experiment, students already learned the basics of an electrical circuit when they lit a torch bulb with an electric cell.
In the prior experiment, they established an electrical circuit by connecting the electric cell to a torch bulb. They created a clear path for electricity to flow between two terminals of electric cells. Class 6 Science Chapter 12 also provides a do-it-yourself project to enhance students’ understanding of a basic electrical circuit.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 15
Electric Switch:
Class 6 Science Chapter 12 then explains the concept of an electric switch. Electric switches are crucial in an electrical circuit as they regulate the flow of electricity within that circuit.
This section includes an activity that students can do to deepen their understanding of electric switches. The activity involves using household materials like ThermoCol or a wooden board, paper clips, safety pins, etc., to create a circuit and an electric switch.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 14
Electric Conductors and Insulators:
Electricity and Circuits Class 6 NCERT Solutions cover various conductors and insulators. This topic starts with an example from the previous experiment, discussing how metal serves as a good conductor of electricity.
Following that, NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 progress to a detailed discussion about different objects and their ability to conduct electricity. Afterward, students learn about insulators, how they work, and their significance in an electrical circuit.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11
Benefits of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 offer numerous benefits to students, aiding in their understanding of the subject matter. Here are some detailed benefits:
1. Comprehensive Coverage : The solutions provide a comprehensive coverage of the topics included in Chapter 12 of Class 6 Science, ensuring that students grasp all essential concepts related to electricity and circuits.
2. Clarity and Explanation: The solutions offer clear and detailed explanations for each question and concept. This clarity helps students in understanding the underlying principles, making the learning process more effective.
3. Structured Format: NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 are presented in a structured format, following the sequence of topics in the textbook. This structure aids in organized learning and helps students navigate through the content systematically.
4. Guidance in Various Question Types: The solutions cover a variety of question types, including fill in the blanks, true or false, circuit diagrams, and descriptive questions. This variety prepares students for different question formats they might encounter in exams.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 7
5. Exam Preparation: The solutions serve as an invaluable resource for exam preparation. Students can use them to practice and assess their knowledge, ensuring they are well-prepared for assessments and examinations.
6. Time-Saving: The solutions are presented in a concise and clear manner, saving students time that might be otherwise spent searching for explanations. This efficiency is crucial, especially when students are revising or completing assignments.
7. Free of Cost: NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 are available free of charge. This accessibility ensures that financial constraints do not hinder students from accessing crucial study materials.
8. Consistency with NCERT Curriculum: Since the solutions are based on the NCERT curriculum, they align perfectly with the content taught in Class 6 Science. This consistency ensures that students focus on the relevant material outlined by the educational board.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 9
How to Prepare With NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12
Here’s a detailed guide on how to effectively prepare for NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 using these solutions:
1. Read the Chapter Thoroughly: Before diving into the solutions, read Chapter 12 of Class 6 Science thoroughly. Understand the basic concepts related to electricity and circuits. Take note of key terms, definitions, and examples provided in the chapter.
2. Take Notes: While reading the chapter, take concise notes summarizing important points. These notes can serve as quick revision materials later on.
3. Refer to Solutions Step by Step: Use the solutions step by step. For each question, try to solve it on your own first. Afterward, refer to the solutions to check your answers and understand the correct approach.
4. Practice Regularly: Regular practice is key to mastering any subject. Set aside dedicated time for practicing questions from NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12. Consistent practice enhances retention and understanding.
5. Collaborate with Peers: Discussing concepts and problem-solving approaches with classmates can provide fresh perspectives and enhance your understanding. Collaborative learning can be beneficial in grasping difficult concepts.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 6
6. Stay Consistent: Consistency is crucial for effective preparation. Allocate regular study sessions, avoid cramming, and stay committed to your study plan.
7. Review and Revise: Periodically review the entire chapter and revisit the solutions. This helps reinforce what you’ve learned and ensures better retention. Create a revision schedule to cover the chapter multiple times before exams.
8. Focus on Conceptual Understanding: Instead of memorizing answers, focus on understanding the underlying concepts. This approach ensures a more profound and sustainable grasp of the subject matter.
9. Solve Previous Years’ Questions: If available, solve previous years’ questions from Class 6 Science exams. This practice helps you become familiar with the question patterns and enhances your problem-solving skills.
10. Seek Clarification for Doubts: If you encounter difficulties or have doubts about any concept, seek clarification from your teacher, classmates, or online resources. Understanding the basics is crucial for advanced learning.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 FAQs
A fused bulb in Class 6 refers to a light bulb that has a broken filament, causing it to stop working.
In Class 6, a torch is a portable hand-held light source powered by batteries.
Electric current in Class 6 can be defined as a flow of electric charge, typically through a conductor, creating a pathway for the movement of electrons.
In Class 6, a switch is a device that opens or closes an electric circuit, controlling the flow of electric current.
An electric cell in Class 6 is a device that produces electric energy through chemical reactions, commonly used to power various electronic devices.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Body Movements
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 3 Playing With Numbers

.st1{display:none} Related Articles
- Tamil Nadu 10th Toppers List 2024 OUT Check School Wise Toppers List
- NCERT Solutions of Class 10 English First Flight Chapter 1 A Letter to God
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English Footprints without Feet Chapter 1 A Triumph of Surgery
- NCERT Solutions of Class 10 English First Flight Chapter 2 Nelson Mandela: Long Walk to Freedom
- CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes Chapter 15 Statistics
- Roots of x2-11x-28=0, How to Solve Quadratic Equations? Find Solution
- Tamil Nadu 10th Supplementary Exam 2024
- Algae: Classification, Types, Benifits, and Facts
- Eye Diseases: Introduction and Types
- Karnataka SSLC Result 2024 OUT Anytime on This Date Check Details
Book a Trial With Our Experts
Hey there! We receieved your request
Stay Tuned as we are going to contact you within 1 Hour
Thank you for registering.
One of our academic counsellors will contact you within 1 working day.

Click to Chat
- 1800-5470-145
- +91 7353221155
- Login | Register
- My Classroom
- My Self Study Packages
- Batch Discussion
- My Forum Activity
- Refer a Friend
- Edit Profile
- Add Question
- Add Paragraph
- Search Coupon
Use Coupon: CART20 and get 20% off on all online Study Material
Complete Your Registration (Step 2 of 2 )

Register Now and Win Upto 25% Scholorship for a Full Academic Year !
Enter your details.

Registration done!
Sit and relax as our customer representative will contact you within 1 business day
Mobile Verification
OTP to be sent to Change
- Junior Hacker
- Junior Hacker New
- Self Study Packages
- JEE Advanced Coaching
- 1 Year Study Plan
- Rank Predictor
- Paper Pattern
- Important Books
- Sample Papers
- Past Papers
- Preparation Tips
- Latest News
- JEE Main Exams
- Online Coaching
- Branch Predictor
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Past Year Papers
- Math Preparation Tips
- IIT JEE Exam Details
- JEE Syllabus
- IIT JEE Toppers Tips
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 11
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 9
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 8
- IIT JEE Preparation Time Table
- IIT JEE Online Coaching
- Correspondence Course For IIT JEE
- IIT JEE Coaching after 10th
- IIT JEE Coaching For Foundation Classes
- JEE Coaching Institutes
- IIT JEE Coaching in Kota
- IIT JEE Coaching Institutes In Kota
- BITSAT Examination
- View complete IIT JEE Section
- View All Engineering Exams
- Top Engineering Colleges
- Top Engineering Branches
- Engineering Exam Calendar
- NEET Entrance Exam
- NEET Online Coaching
- NEET Preparation Tips
- Participating States
- AIIMS Examination
- AIIMS Online Coaching
- View all Medical Exams
- Top Medical Colleges
- Medical Exam Coaching
- Best Medical Coaching In Kota
- Medical Exam Calendar
- NTSE Examination
- Notifications
- Application
- Important Dates
- Eligibility
- Study Material
- KVPY Examination
- Olympiads Examination
- Indian National Mathematics Olympiad
- Physics Olympiad
- Chemistry Olympiad
- Biology Olympiad
- Olympiads Sample Papers
- INMO Papers
- CBSE School Exams
- Solutions for Board Exam
- JEE Advanced
- Karnataka CET
- Manipal UGET
- NCERT Class 12 Solutions
- NCERT Class 11 Solutions
- NCERT Class 10 Solutions
- NCERT Class 9 Solutions
- NCERT Class 8 Solutions
- NCERT Class 7 Solutions
- NCERT Class 6 Solutions
- List of JEE Main & JEE Advanced Books
- R.D. Sharma Solutions PDFâ
- Concepts of Physics by HC Verma for JEE
- HC Verma Solutions Part 1
- HC Verma Solutions Part 2
- Most Scoring Topics in IIT JEE
- IIT JEE Entrance Exam
- Discuss with Colleagues and IITians
- Engineering Entrance Exams
- Branch Ranking of IIT
- Discuss with Askiitians Tutors
- NEET (AIPMT)
- Marks and Rank in IIT JEE
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- AIEEE Entrance Exam
- Electric Current
- Wave Motion
- Modern Physics
- Thermal Physics
- Electromagnetic Induction
- General Physics
- Electrostatics
- Wave Optics
- Physical Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Trigonometry
- Analytical Geometry
- Differential Calculus
- Integral Calculus
- Magical Mathematics
- Online Tutoring
- View complete NRI Section
- View Complete Study Material
- View Complete Revision Notes
- Ahmadi (FAIPS)
- Khaitan (Carmel School)
IIT JEE Courses

One Year IIT Programme
- Super Premium LIVE Classes
- Top IITian Faculties
- 955+ hrs of Prep
- Test Series & Analysis

Two Year IIT Programme
- 1,835+ hrs of Prep

Crash Course
- LIVE + Pre Recorded Sessions
- 300+ hrs of Prep
NEET Courses

One Year NEET Programme
- Top IITian & Medical Faculties
- 900+ hrs of Prep

Two Year NEET Programme
- 1,820+ hrs of Prep

- LIVE 1-1 Classes
- Personalized Sessions
- Design your own Courses
- Personalized Study Materials
School Board
Live online classes, class 11 & 12.
- Class 11 Engineering
- Class 11 Medical
Class 9 & 10
Class 6, 7 & 8, test series, jee test series.
- 2 Year Jee Test Series
- 1 Year Jee Test Series
NEET test series
- 2 Year NEET Test Series
- 1 Year NEET Test Series
C.B.S.E test series
- 11 Engineering
- 12 Engineering
Complete Self Study Packages
Full course.
- 2 year NEET
- Chemistry 11th & 12th
- Maths 11th & 12th
- Physics 11th & 12th
- Biology 11th & 12th
- View Complete List
For class 12th
- Chemistry class 12th
- Maths class 12th
- Physics class 12th
- Biology class 12 th
For class 11th
- Chemistry class 11th
- Maths class 11th
- Physics class 11th
- Biology class 11th
Revision Notes on Electricity and Circuits
Introduction to electricity and circuits.
Electricity has become so common that sometimes we forget its immense applications.
Advantages of Electricity:
Light in our houses, offices, roads etc. even past sunset
To operate pumps which in turn have a lot of applications
Electrical appliances like refrigerator, fans etc.
Building houses, installing equipment etc.

Fig 1: Refrigerator {Electric Appliance}
Electric Cell and Electric Bulb
Features of an Electric Cell:
It is a small cylindrical structure which helps in operating the devices.
A small metal cap is placed on one side and a metal disc is present on the other side.
All cells have two terminals: Positive and Negative.
The metal cap and metal disc are positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the electric cell respectively.
Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy inside a cell. When the chemicals are exhausted, the cell stops working.

Fig 2: Electric Cell
Features of an Electric Bulb:
The outer covering is glass and the base is metallic.
The part of the bulb which glows is called Filament and is made up of tungsten.
The filament is attached to two wires. One of the wires is connected to the metal case at the base and the other wire is connected to the metal wire at the centre of the base.
Base of the bulb and metal tip are the terminals of the bulb and they do not touch each other.

Fig 3: Electric Bulb
An Electric Circuit
Consider an electric cell and a bulb. The terminals of the cell are connected to the terminals of the bulb by the means of electric wires. Such an arrangement of cell and bulb is called an Electric Circuit . The circuit is said to be complete in this case because of which electricity will flow and the bulb will glow.
One should be careful while setting up an electric circuit. It should be done under supervision.
Electric Switch
Switch is an integral part of an electric circuit. It is a simple device which breaks or completes a circuit. When the switch is ‘on’, the circuit is complete. When the switch is ‘off’, current does not flow in the circuit. So an electric appliance will only work if the switch is ‘on’.

Fig 4: Switch on and off respectively
Electric Conductors and Insulators:
Conductors - Materials that allow electricity to flow through them easily.
Insulators - Materials that do not allow electricity to pass through them.
Human body is a conductor, so touch a current carrying wire is detrimental and so insulating it prevents from an electric shock.
Some examples of conductors are: Metals like copper, Iron
Some examples of insulators are: Rubber, Plastic

Fig 5: Danger Sign
This sign is used in areas which are near electric junctions as a warning.
TOP Your EXAMS!
Upto 50% scholarship on live classes, course features.
- Video Lectures
- Revision Notes
- Previous Year Papers
- Study Planner
- NCERT Solutions
- Discussion Forum
- Test paper with Video Solution
Book Free demo of askIITians Live class
View courses by askiitians.

Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Ask question.
Get your questions answered by the expert for free

Your Question has been posted!
You will get reply from our expert in sometime.
We will notify you when Our expert answers your question. To View your Question
POST QUESTION
Select the tag for question.

Revision Notes on Separation of Substances On a...
Getting to Know Plants CBSE Class 6 Science...
Revision Notes on The living organisms and their...
Revision Notes on Luminous Objects and...
Revision Notes on Garbage In, Garbage Out Dealing...
Revision Notes on Water Introduction: It is common...
Components of Food CBSE Class 6 Science Revision...
Revision Notes on Changes Around Us Everything...
Revision Notes on Food: Where Does It Come From...
Revision Notes on Air around Us The invisible...
Revision Notes on Fibre to Fabric Variety in...
Revision Notes on Motion and Measurement of...
Revision Notes on Fun with Magnets What are...
Revision Notes on Sorting Materials into Groups...
Body Movements CBSE Class 6 Science Revision Notes...
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits

CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits - Free PDF Download
Class 6 Science explains fascinating concepts to young minds. They learn many new things and find exciting new facts about different topics. The 12 th chapter of the Class 6 NCERT Science book focuses on explaining current, electricity, and circuits. This chapter will introduce the children to the world of electricity and circuits. After finishing answering the exercise questions, you can proceed to solve the Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions .
All these questions have been developed following the concepts delivered in this chapter. The questions will hold a higher level in terms of concepts. You will find what other questions can be formed and asked in the exams. Download these NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions and complete your preparation of this chapter. Resolve all your doubts by referring to the solution provided in the same file. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions, they can download Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions for other chapters:
Study Important Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 – Electricity and Circuit
Very Short Answer Questions: 1 Mark
Choose the correct answer from the options given.
1. An electric cell has _____________ terminals.
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
Ans: Option - b.
2. An electric cell has a
a) Positive and negative terminal
b) Two positive terminals
c) Two negative terminals
d) None of the above
Ans: Option - a.
3. An electric cell
a) Uses electricity
b) Uses light
c) Produces electricity
Ans: Option - c.
4. An electric cell uses ___________ to produce electricity.
a) Electricity
b) Heat
c) Light
d) Chemicals
Ans: Option - c.
5. An electric cell does not produce electricity when
a) Chemicals inside get completely used up
b) The terminals are not connected properly
c) Both of the above
Short Answer Questions: 3 Marks
1. How does a light bulb produce light?
Ans: A thin wire like structure known as filament is present inside the bulb. When we switch on the bulb, electricity passes through filament causing it to heat up and glow to produce light. In this process the electric energy changes into light energy.
2. What is an electric circuit?
Ans: The closed path in which electric current flows is called an electric circuit. Generally, an electric circuit consists of wire, battery, switch and an appliance which needs electricity to work. The current in the electric circuit flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. The switch is used to break the flow of the current when the appliance is not in use.
3. How does a bulb fuse?
Ans: Inside the bulb there is a thin wire like structure called filament. Filament is made of substances having a low melting point. Filament gets heated and emits light when we switch on the bulb. But when there is excess flow of current through the filament it melts down due to excessive heat. This causes fusing of the bulb.
4. Explain the role of a switch in a circuit. What is it made up of?
Ans: An electric switch is a circuit component that can be used to control the flow of electricity through the circuit. It has the ability to both complete and break the circuit. A conducting substance is used to make the switch. The circuit is complete and power flows through it when the switch is in the "ON" position. The circuit is broken and power cannot flow through it while the switch is in the "OFF" position.
5. Label the parts in the following diagram. Indicate the positive and negative terminals.
Long Answer Questions: 5 Marks
1. Differentiate between conductors and insulators.
Ans: The differences between conductors and insulators are as follows:
2. In the following diagram explain whether the bulb will glow in each of the cases.
Ans: a) The bulb will glow as the circuit is complete.
b) The bulb will not glow as the circuit is incomplete.
c) The bulb will not glow as the circuit is incomplete.
d) The bulb will not glow as both wires are connected only to the negative terminal of the cell.
e) The bulb will not glow as both wires from the bulb are connected only to the positive terminal of the cell.
f) The bulb will glow as the circuit is complete.
Electricity and Circuits: NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Summary
You might have come across the term ‘current’ in other chapters of different subjects. A current represents a flow of anything. It can be water, a substance, or wind. Anything that flows can be explained as a current. People flocking in a busy station by forming a line can also be considered as an example of human current. This chapter will explain what a current is and it is defined in the context of electricity. The Important Questions on Electricity and Circuits for Class 6 will be based on these concepts. These questions will also be answered by the top teachers.
Let us check what the chapter will cover and what kind of questions you will find in this file.
Students will learn what current means. They will also learn how the flow of electrons is considered to be an electric current. An electric current has a set of features that you should learn from this chapter. This is when you will develop the foundation of concepts based on electricity. Using this foundation, you will then proceed to learn new advanced concepts in the higher classes related to this chapter.
You will learn how an electric current is formed and flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal when connected to a battery. For the first time, you will learn what a circuit means. Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions will be based on those new concepts of this chapter. Make sure you study them well to answer these questions easily. On proceeding further, you will come to know about an electric cell and how it works to generate electricity when connected to a circuit. Certain factors determine the flow of current from one terminal to the other. Find out how an electric cell gets exhausted from use.
In the next section of the chapter, you will study how an electric bulb is connected to a circuit and how it glows using the electric current flowing in it. The various components of the electric circuit along with the bulb will be described and the Important Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 will be based on this topic. Learn how an electric bulb functions when connected to a live circuit. You will also come to know different kinds of wires used in a circuit and what materials are used to make them. Delve deeper into the chapter and learn more about conductors, insulators, keys, switches, resistors, etc.
Why Should You Prefer Studying Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions?
Vedantu has prepared a set of NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions to provide the following benefits to the students.
Suggestions Related to Possible Questions from this Chapter
The important questions can be followed to find the possible questions a teacher can ask in an exam. Apart from the exercise questions, this list of questions will work as a suggestive set for students to solve and prepare the chapter well.

Best Ways to Approach and Answer Conceptual Questions
The Electricity and Circuits Class 6 Important Questions will also suggest how to approach and answer conceptual questions. Even if you have properly understood the prime concepts of this chapter, you will need assistance to form answers in the best way possible so that you can fetch good marks in the exams.
Doubt Clarification
The more you study and solve questions based on a chapter, the better your concepts will be cleared. Your understanding level will increase and you will become more efficient in clarifying doubts on your own. Hence, studying these Important Questions on Electricity and Circuits for Class 6 along with answers will help you understand the concepts perfectly.
Important Related Links for CBSE 6 Science
Reviewing all the crucial questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits provides students with a solid grasp of the chapter's topics. The extra and important questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits engage in a concept-focused discussion encompassing all chapter themes. This question-and-answer method proves time-saving during exam prep, offering an efficient way to revise the chapter and enhance understanding. Practising these important questions streamlines preparation and boosts confidence for the upcoming exams.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits
1. What is an Electric Current?
The electrical charges flowing through a conductor from the positive end to the negative end of a battery is called an electric current. As per the answers of Class 6 Science Ch 12 Important Questions, an electric current is produced when there is a difference in potential between the two terminals.
2. Why Should You Choose Vedantu for Downloading NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Important Questions?
Vedantu has always been the leading choice for Class 6 students to find important questions related to the Science chapters. These conceptual questions and answers help students to develop their knowledge regarding electricity and circuits.
3. What is class 6 Science chapter 12 about?
Class 6 Science chapter 12 is about Electricity and Electric circuits. When you read this chapter, you come to know about various things related to electric current or electricity. This is a major necessity for mankind for their day to day activities and if you are curious to know about how electric current is produced or how it flows throughout your house etc then you will find this chapter interesting. Focus on the concepts in order to do well in exams.
4. What do you mean by electric circuit?
Electric current needs a path to flow. This well-structured path designed for the flow of electric current is called the electric circuit. This path usually consists of a source of current that is a cell or battery. The circuit is made of conducting materials like copper wire and there is a switch to start or stop the flow of current and there are other parts too that are attached to the circuit which helps in conduction and measurement of the flowing current.
5. What is a fuse?
A fuse is an electric object that is attached to the electric circuit in order to stop the excess flow of current or to detach the circuit when needed. This works by stopping the current flow in case of urgency that would help to prevent any kind of short circuit. It is a useful electric appliance that must be connected to all households or places that have an electric connection. To know more, solve the important questions by visiting the page Important questions for Class 6 Science and download a free PDF of the same.
6. What is the difference between insulator and conductor?
Insulators and conductors are terms related to electricity. Insulators are those materials that restrict the electric current to flow through them. They are made of non-conducting materials that cause resistance to the flow of current. But conductors are just the opposite. These are materials that allow the electric current to flow through them. They are mostly used in making electric wires, circuits, filaments etc. To know more and practice questions students can download the vedantu app.
7. Why does the bulb give light?
An electric bulb is an illuminating device that lights up when the switch is connected. Now this happens due to the thin filament that is present inside the bulb. This is a delicate conducting material and is connected to thick wires which further connects to the current source. When current flows through the wires and is passed on to the filament, it gets heated up and results in the bulb glowing and produces light.
Chapter wise Important Questions for CBSE Class 6 Science
Cbse study materials.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
These NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Questions and Answers are prepared by our highly skilled subject experts to help students while preparing for their exams.
Electricity and Circuits NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12
Class 6 science chapter 12 electricity and circuits textbook exercise questions and answers.
Question 1. Fill in the blanks: a. A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called …………………. b. An electric cell has …………………. terminals. Answer: a. switch b. two
Question 2. Mark ‘True’ or ‘False’ for the following statements: a. Electric current can flow through metals. b. Instead of metal wires, a jute string can be used to make a circuit. c. Electric current can pass through a sheet of thermocol. Answer: a. True b. False c. False

Question 5. What is the purpose of using an electric switch? Name some electrical gadgets that have switches built into them. Answer: An electrical switch is used to open the circuit or to close the circuit due to which electrical gadgets start or stop. Electrical switch is used in many electrical gadgets such as: television, washing machine, electrical mixer, toaster, heater, etc.
Question 6. Would the bulb glow after completing the circuit shown in figure of Question 4, if instead of safety pin we use an eraser? Answer: No, since eraser is an insulator so it does not allow the current to pass through it. Hence, the bulb will not glow.

Question 8. Using the “conduction tester” on an object it was found that the bulb begins to glow. Is that object a conductor or an insulator? Explain. Answer: If the object is a good conductor of electricity, then current will pass through conduction tester and the bulb will glow. Hence, the object will be a conductor of electricity.
Question 9. Why should an electrician use rubber gloves while repairing an electric switch at your home? Explain. Answer: Our body is a good conductor of electricity and rubber is an insulator. During repairing work, if the body comes in contact with current carrying wire then there will not be any accident as rubber does not allow the passage of current through it. Hence, electrician should use rubber gloves while repairing an electric switch.
Question 10. The handles of the tools like screwdrivers and pliers used by electricians for repair work usually have plastic or rubber covers on them. Can you explain why? Answer: Plastic or rubber is an insulator which does not allow electric current to pass through it. The handles of the tools like screwdrivers and pliers used by electricians for repair have covering of plastic or rubber so that electric current may not pass through these tools to the body of the electrician to harm him.
NCERT Extended Learning Activities And Projects
Question 1. Imagine there were no electric supply for a month. How would that affect your day-to-day activities and others in your family? Present your imagination in the form of a story or a play. If possible stage the play written by you or your friends in school. Hint: Do it yourself.
Question 2. For your friends, you may set up a game “How steady is your hand?”. You will need a cell, an electric bulb, a metal key, two iron nails (about 5 cm in length), about one and a half metre long thick metal wire (with its plastic insulation scraped off) and few pieces of connecting wires. Fix two nails nearly one metre apart on a wooden board so that these can be used as a hook. Fix the wire between the nails after inserting it through the loop of the key. Connect one end of this wire to a bulb and a cell. Connect the other terminal of the cell to the key with a wire. Ask your friend to move the loop along the straight wire without touching it. Glowing of the bulb would indicate that the loop of the key has touched the wire. Hint: Do it yourself.
Question 3. Read and find out about Alessandro Volta who invented the electric cell. You may also find out about Thomas Alva Edison who invented the electric bulb. Hint: Do it yourself.
Objective: To make an electric bulb light up using an electric cell. Materials Required: Bulb, cell and connecting wire. Procedure:
- Take four lengths of electric wire with differently coloured plastic coverings.
- Remove a little of the plastic covering from each length of wire at the ends. This would expose the metal wires at the ends of each length.
- Fix the exposed parts of the wires to the cell and the bulb as shown in figure below.

- You can stick the wires to the bulb with the tape used by electricians. Use rubber bands or tape to fix the wires to the cell.
- Now, connect the wires fixed to the bulb with those attached to the cell in six different ways as has been shown below. For each arrangement, find out whether the bulb glows or not.

Observations: You connected one terminal of the electric cell to the other terminal through wires passing to and from the electric bulb. Note that in the arrangements shown in Fig. (a) and (f), the two terminals of the electric cell were connected to the two terminals of the bulb. Such an arrangement is an example of a closed electric circuit.
Conclusion: The electric circuit provides a complete path for electricity to pass (current to flow) between the two terminals of the electric cell. The bulb glows only when current flows through the circuit.
- Electric bulb: Electric bulb is the electrical device which converts electrical energy into light and heat energy.
- Filament: Filament is a thin wire in the bulb which is made up of tungsten metal and is used to emit light in the bulb. The Filament gets heated due to electric current. This heat is then converted into light.
Objective: To study the structure of a torch bulb. Material Required: A torch bulb. Procedure:
- Take out the bulb from a torch.
- Observe the bulb from outside and also from inside with a magnifying glass.
- List the various parts you could see.
Observations: The torch bulb consists of the following parts:
- Metal casing having grooves in the lower part.
- A small spiral of thin wire called filament is present.
- Two slightly thicker wires in the upper ends of the wires support the filament.
- The lower end of the one of the thicker wire is connected to the metal casing and that of the other wire to the metal tip at the bottom of the bulb.
- The metal tip and the metal casing are fixed in such a way that they do not touch each other.

Electric switch: Electric switch is a device by which an electric circuit can be easily completed or broken. The switch is ‘ON’ in a closed circuit and ‘OFF’ in an open circuit.
Objective: To make a simple and easy switch to use in our circuit. Materials Required: Two drawing pins, a safety pin (or a paper clip), two wires and a small sheet of thermocol or a wooden board. Procedure:
- Insert a drawing pin into the ring at one end of the safety pin and fix it on the thermocol sheet as shown in the figure.
- Make sure that the safety pin can be rotated freely.
- Now, fix the other drawing pin on the thermocol sheet in a way that the free end of the safety pin can touch it.
- The safety pin fixed in this way would be your switch in this activity.

- Now, make a circuit by connecting an electric cell and a bulb with this switch as shown. Rotate the safety pin so that its free end touches the other drawing pin and observe.
- Now, move the safety pin away and observe again.
Observations:
- The safety pin covered the gap between the drawing pins when you made it touch the two of them. In this position the switch is said to be ‘on’. Since the material of the safety pin allows the current to pass through it, the circuit was complete. Hence, the bulb glows.
- On the other hand, the bulb did not glow when the safety pin was not in touch with the other drawing pin. The circuit was not complete as there was a gap between the two drawing pins. In this position, the switch is said to be ‘off’.
Conductors: Conductors are the materials which allow the electric current to pass through them. Mostly metals are good conductors of electricity. Insulators: Insulators are the materials which do not allow the electric current to pass through them. Rubber and wood are insulators.
Objective: To find out which object is a conductor and which is an insulator. Materials Required: Three pieces of wire, a small torch bulb, a thick sheet of cardboard or wood, sticky tape, pencil cell and objects such as metal spoon, eraser, peel of wood, etc. Procedure:
- Connect a pencil cell to the socket which holds a small torch bulb.
- Attach clips to the bare ends of both wires.
- Hold various objects between the two clips.
- Observe if the bulb glows or not. Record your observations.

- The bulb does not glow when the free ends of the wires are in contact with some of the materials you have tested. This means that these materials do not allow the electric current to pass through them.
- On the other hand, some materials allow electric current to pass through them, which is indicated by the glowing bulb.
Conclusion: Materials which allow electric current to pass through them are conductors of electricity. Insulators do not allow electric current to pass through them.
Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Additional Important Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. How much voltage is given by a single dry cell? Answer: 1.5 volts.
Question 2. Name the two types of circuits. Answer: Open circuit and closed circuit are the two types of circuits.
Question 3. Name two terminals that all electric cells contain. Answer: Positive terminal and negative terminal.
Question 4. What is the work of an electric cell? Answer: An electric cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
Question 5. Define battery. Answer: The combination of two or more than two cells is called a battery.
Question 6. What is the work of a filament in a bulb? Answer: A filament gets heated and emits light in the bulb.
Question 7. What is a solar cell? Answer: A solar cell is a device which converts solar energy into electrical energy.
Question 8. Write one use of insulators. Answer: Insulators are used in making switchboards, handles of testers, screwdrivers, etc.
Question 9. Name a device which is used to ‘open’ or ‘close’ a circuit. Answer: Switch.
Question 10. How does an electric cell produce electricity? Answer: An electric cell produces electricity from chemicals stored inside it.
Question 11. Is electricity pollution free and a useful form of energy? Answer: Yes.
Question 12. Which terminal of the cell does have a metal cap? Answer: Positive terminal.
Question 13. In a cell, the carbon rod is surrounded by which mixture? Answer: Manganese dioxide and powdered charcoal.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Write two advantages of a dry cell. Answer: Two advantages of a dry cell are:
- It converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
- It is light in weight and small in
Question 2. What is the difference between a conductor and an insulator? Answer: A conductor allows the passage of current through it whereas an insulator does not allow the passage of current through it.
Question 3. How does a bulb start glowing with an electric cell? Answer: When the electric cell is connected with conducting wire and the wire ends are connected to the bulb, the bulb glows immediately.
Question 4. If you touch an electric wire carrying current you get a shock, but if on the same wire, the birds sit they do not get any shock/current. Give reason. Answer: When we hold the wire carrying current then the circuit is closed and the current flows from our body and enters the earth but the birds sitting on the same wire do not get any current as the circuit is not complete. If the bird touches the earth wire, it will die due to electric shock.
Question 5. What is a switch? When we switch on an electrical appliance, what changes are we making to the circuit? Answer: The switch is a simple device which is used to open or close a circuit. When the switch is turned on, the gap in the circuit is closed and a complete circuit is made. Due to complete circuit, electricity starts flowing in the circuit and electrical appliance will now start working.

Question 7. Describe the positive and negative terminals of a cell. Answer: The metal cap of the cell is considered as positive terminal. It is indicated by sign (+). The metal disc or the container of the cell is the negative terminal. It is indicated by sign (-).
Question 8. What is a fused bulb? Why it does not glow? Answer: Bulb has a small filament inside it. If the filament of a bulb is broken, then such a bulb with broken filament is called fused bulb. The broken filament cannot complete the circuit. As a result, current cannot flow through the filament and fused bulb does not glow.
Question 9. What are the essential components or elements of an electric circuit? Answer: The essential components or elements of an electric circuit are:
- Electric sources (cell, battery).
- Electric appliances (a device for using the electric current).
- Conductor (for providing a path for the flow of current).
- Switch or key (for opening and closing the circuit).
Long Answer Type Questions

Question 2. What is a torch? How does it work? Answer: A torch is a portable electric lamp which uses two or more cells to light a small bulb. A torch contains a simple electric circuit. In a torch, two (or more) cells are connected to a torch bulb through a sliding switch. When the torch is needed to provide light, we close the sliding switch by pushing it forward so that the circuit is completed and the bulb lights up.
Question 3. What are the differences between conductors and insulators? Answer:
Question 4. Define the following terms: (a) Dry cell and (b) Secondary cell. Answer: a. Dry cell: An electric cell is used to operate objects like calculators and phones. It is a small source of electricity or electric current. It is also known as a pencil cell or dry cell. A dry cell has two terminals. One side that has a small circular metal cap is the positive terminal. It is marked with positive (+) sign. The other side has a flat metal plate behaves like the negative terminal and is marked with a negative (-) sign.
There are some chemicals inside a cell. These chemicals react to produce electricity. When the chemicals get used up, the cell stops producing electricity and the appliance stops functioning. These electric cells then . have to be replaced by new cells.
b. Secondary cell: Secondary cells are the cells that provide electrical energy to the gadget as a result of chemical reactions taking place in them. In these cells, electrical energy can be stored in the form of chemical energy and the stored chemical energy can be reconverted into electrical energy. Such cells are also called rechargeable cells. Lead accumulator and nickel- iron accumulators are two examples of secondary cells. They are mainly used in mobile phones, laptops and car batteries.
Question 5. What is the importance of electricity in our life? Answer: We use a variety of things in our day-to-day life that run on electricity such as fans, lights, televisions, radio, refrigerator and computer. Electricity makes it possible to light our homes, roads, offices, markets and factories even after sunset. This helps us to continue working at night. In the field of communication, electricity is also used as a medium for the transmission of signals. The different fields of our life which depend on electricity are rather wide.
Question 6. Mention the precautions that are advised while handling electric appliances. Answer: While handling electric appliances, the following precautions need to be taken.
- Do not operate an electric appliance or switch with wet hands.
- While using electric appliances, always wear rubber soled footwear. Rubber being a bad conductor of electricity prevents current from passing through our body.
- In case of a fire caused by electric spark, make sure that we should not throw water on electric appliances. Always use an extinguisher to put out electrical fires.
Picture-Based Questions

NCERT Solution for Class 6 Science Chapter 12
NCERT Solution for Class 6 Science Chapter 12: Electricity and Circuits, Download English, and Hindi Medium PDF Solutions for Academic Session 2020-2021.
Other Subjects of Ncert Class 6
NCERT Textbooks, e-Content, and Study Materials are Copyright of The National Council of Educational Research and Training . CBSE/ICSE/NIOS & Other Education Board's e-Contents are wholly owned by respective States Governments or the Ministry of Education, India . We do not claim any type of ownership of these materials nor commercially promote them. Please contact us before taking any legal action, we will remove all links related to the copyright owner.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science are available for everyone to download in PDF format so that students can review this document whenever they want. These provide in-depth solutions and information about each an every chapter in NCERT science textbook for class 6.
As CBSE 6th Class Science textbook consists of 16 chapters as the total, Class 6 science NCERT Solutions are the best study material to read. The book is designed specifically to cover up the CBSE syllabus as a whole.
- Chapter 1 Food Where Does It Come From
- Chapter 2 Components of Food
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups
- Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
- Chapter 6 Changes Around Us
- Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
- Chapter 8 Body Movements
- Chapter 9 The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
- Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
- Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection
- Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
- Chapter 14 Water
- Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- Chapter 16 Garbage In Garbage Out
NCERT Solutions NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science PDF Download

Science is a subject that paves the way for everyone to get ready for various medical and engineering competitive exams. You never know what profession you might opt for after completing your 12th. Thus, it is important to have your basics covered in all the subjects. Particularly in science, as this is one of the subjects that can also be useful in day to day life. We have provided chapter by chapter overview below for your understanding.
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food Where Does it Come From?
Chapter 1 of NCERT textbook deals with a variety of sources of food which is available and we consume every day. The chapter begins with an activity that introduces the food that we eat daily and makes the students aware of the food they eat daily. Furthermore, the chapter discusses all the food sources and materials that turn into plants. This chapter categorizes foods that come from plants and animals.
Class 6 Science Chapter 2 Components of Foods
The components of foods which is chapter 2 explain the comparison of food that we eat and the proportion of certain foods. Along with this, this chapter explains the effects of various food components in our body and how to develop a balanced diet. The chapter starts by introducing the different foods that we eat daily like rice, Chapati, salad, sabzi, etc. This chapter also introduces to various terms like carbohydrates, nutrients, fats, proteins, etc.
Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
This chapter explains students the process of preparing cloth from raw materials that are available from animals and plants. This chapter will further take you to plant fabrics, fabrics and other processes of preparing fabric from fibers. The chapter starts with an activity of identifying various types of fabrics. As you move forward concepts such as natural, synthetic fibers are introduced in the chapter. Then it continues with plant fibers like jute and cotton and their cleaning and refining process along with the extraction is explained in this chapter.
Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Sorting Materials into Groups
Sorting different materials into groups is an interesting chapter as it teaches how to classify the objects and materials around you. This concept can further help you deal with various complex issues of elements and animals. The chapter also helps in awareness of the objects that are around us by observing their size and shape.
Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
This chapter of NCERT textbook of class 6 takes you through different ways and needs to separate the substances by having their original properties intact. This procedure of separation is explained with the help of processes like filtration, decantation, churning, etc. As you move forward in the chapter, it deals with various methods for separating substances. Each of these methods is described with the help of an activity or an example.
Class 6 Science Chapter 6 Changes Around Us
The NCERT solutions for class 6 science can be helpful for students to solve all the questions given in the exercise and understand them. This chapter explains the changes that are happening around us and their various effects and types. This will immensely help in learning the changes that are based on these similarities. The chapter also explains about different activities that can help you classify the changes that are irreversible or reversible.
Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
This chapter introduces to various types of parts in a plant. This can be helpful to understand the differences in plants of various kinds. Along with this, the chapter introduces to the world of shrubs, herbs, and trees through different activities. This helps students observe the different plants and based on this classify them. There is a section later on in the chapter that explains parts of root, stem, flower, and leaf.
Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Body Movements
Chapter 8 in NCERT science textbook for class 6 explains different types of movements in the body of human beings and animals. This chapter also takes you through various processes where parts of the body are involved. In section 1, the movements of the human body and joints are explained. In this, different kinds of joints like a hinge joint, pivot joint, socket joint, and fixed joints are explained. Furthermore, this chapter discusses the function and location of these joints and other important details are discussed in this chapter.
Class 6 Science Chapter 9 The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
This chapter takes you through different environments in which an organism sustains. Also, it explains why a particular type of animal is found in that particular region. Furthermore, this chapter dwells into the surroundings of the organisms and where they live. They focus on listing of desert, forest, sea, mountains or another area through an activity. The primary concept of this activity is to understand various types of surroundings in which an animal resides.
Class 6 Science Chapter 10 Measurements and Motions of Distance
This chapter begins with the evolution of the history of transport and then gradually explains various methods of measurement used for measuring different tools. It also deals with standard units and measurements that are followed throughout the globe.
Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light, Reflections and Shadows
This is a very basic and conceptual chapter that helps students understand the complexities associated with shadows, light, and reflections in higher grades. There are important topics like no-emitting and light emitting objects, their applications and nature, and their properties which are discussed in chapter 11 of NCERT science textbook.
Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Circuits and Electricity
This chapter takes you through different concepts of electricity, electric circuit, electrical devices, switch, insulators, and conductors. This chapter also explains various electric cells their attachments and terminals, connecting an electric cell to an electric bulb, how to make an electric circuit, connections, and components of an electric switch, etc. Furthermore, this chapter includes examples, diagrams, and illustrations of the topics connected to our day to day life.
Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
This chapter explains the discovery of magnets along with various types of magnetic and nonmagnetic materials, properties and their various applications. The chapter begins with a beautiful story on the discovery of magnets. As you move forward the chapter discusses the various magnetic and nonmagnetic materials. You will also learn about the examples, definitions of materials that turn into nonmagnetic and magnetic materials. You will a better understanding of magnets after going through this chapter.
Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Water
This chapter is all the misuse, use, conservation, and sources of water. This chapter will help create awareness about water amongst the students. The chapter starts with an activity that explains the quantity of water used by us every day. Furthermore, students will have to involve a thought process on the daily usage of water and whether this much amount is necessary or not.
Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us
This chapter discusses the air that is around us and it’s different composition. This chapter starts with the question, ‘Is the air present around us everywhere?’ There are many activities in this chapter that will discuss ed vacuum.
Class 6 Science Chapter 16 Garbage In, Garbage Out
This is an interesting chapter in the textbook that talks about waste management at a very initial level. The main topics that will be discussed in this chapter are thought and throw, dealing with the garbage, vermicomposting, how to recycle paper and plastic, and many more.
NCERT solutions for class 6 science helps all the students in reviewing the chapter at their own comfort. Students can also share this article with friends and help them also understand these concepts better.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- CBSE Notes For Class 6
- Class 6 Science Notes
- Chapter 12: Electricity And Circuits
Electricity and Circuits Class 6 Notes - Chapter 12
According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 9.
The Electric Cell
- Current is the flow of particles in a particular direction. For example, air currents that cause winds or water currents.
- When particles flow in an electric circuit to produce electricity, it is called an electric current.
Electric Current
The flow of electric charges in a circuit is called an electric current. The direction is taken from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the battery in an external circuit.
For more information on the Flow of Current, watch the below video
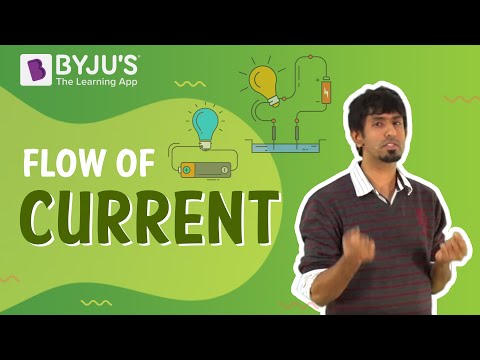
To know more about Electric Current, visit the link below;
Electric Cell
- A cell is a source of electric power created inside by internal chemical reactions.
- When the chemicals inside the cell are exhausted, the cell needs to be replaced by a new one.
- Cells have two terminals: a positive and a negative terminal. In order for current to flow, the positive terminal must be connected to the negative terminal, and this polarity must be maintained.

To know more about Electric Cell, visit the link below;
Bulb Connected to an Electric Cell
- An electric wire is a conducting path in an electric circuit through which current flows.
- It is usually made out of a metal that is a good conductor of electricity.

Electric Bulb, and its Working
- It consists of a thin wire that glows due to the passage of current. This is known as the filament.
- An electric circuit provides a closed path for the current to flow. The terminals of the bulb are connected by wires to the electric cell.
- Sometimes the bulb does not glow as the filament gets fused (breaks) due to overheating.

An Electric Circuit
Electric circuit.
- A closed-loop path, which the current takes, is known as an electric circuit.
- When the path of the circuit is closed, current flows through it.
- When there is a break in the path (the switch is open), then the circuit is open and not conducting, so the current does not flow.
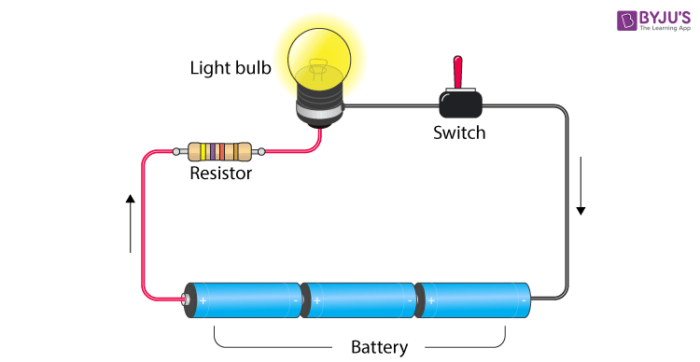
To know more about Circuit Component, visit the link below;
Circuit Component
An Electric Switch
Electric switches.
- Devices that are used to connect the circuit or break it.
- When the switch is connected, we call it ON, and when it’s not in contact (or open) with the circuit, the switch is OFF.
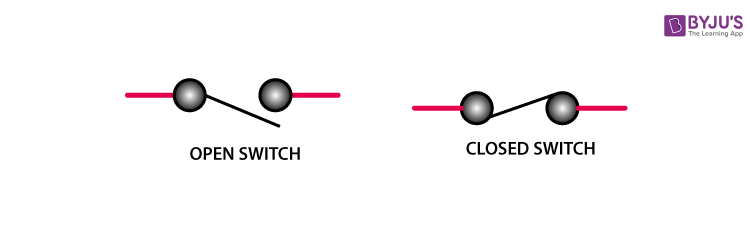
To know more about Electricity and Circuit, visit the link below;
Electricity and Circuit – Conductors and Insulators
Conductors and insulators
- Any material that allows the electric current to pass through it is called the conductor. For example, metals like copper
- Materials that do not allow the free flow of current through them are known as bad conductors or insulators. For example, rubber and plastic
For more information on Electricity, watch the below video
Learn more about Electricity and Circuits from the topics given below:
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
What is the flow of current.
Current flow basically means the flow of electric charges with respect to time.
What is an electric cell?
An electric cell is a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
Who invented electricity?
Benjamin Franklin had one of the greatest scientific minds of his time. He was interested in many areas of science, and made many discoveries. In the mid-1700s, he became interested in electricity.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits with Answers
We have compiled the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits with Answers Pdf free download covering the entire syllabus. Practice MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science with Answers on a daily basis and score well in exams. Refer to the Electricity and Circuits Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation.
Electricity and Circuits Class 6 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option.
Question 1. The material present inside the bulb that glows on heating is called (a) cell (b) switch (c) filament (d) thick wire
Answer: (c) filament

Question 2. Which of these is a conductor? (a) Rubber (b) Mica (c) Copper (d) Wood
Answer: (c) Copper

Question 3. Our body is (a) a good conductor of electricity (b) sometimes good and sometimes bad conductor (c) bad conductor of electricity (d) none of these
Answer: (a) a good conductor of electricity
Question 4. Combination of two or more cells is called (a) battery (b) cell (c) bulb (d) circuit
Answer: (a) battery
Question 5. Rubber is (a) a semiconductor (b) a conductor (c) an insulator (d) None of these
Answer: (c) an insulator
Question 6. A device that breaks the circuit is called: (a) switch (b) filament (c) bulb (d) battery
Answer: (a) switch
Question 7. A bulb has (a) two terminals and two filaments (b) two terminals and a filament (c) multiple terminals and single filament (d) single terminal and a filament
Answer: (b) two terminals and a filament
Question 8. The filament of a bulb is made up of (a) tungsten (b) platinum (c) aluminium (d) chromium
Answer: (a) tungsten
Question 9. Which of the following is an insulator? (a) Bakelite (b) Aluminium (c) Tap water (d) Moist air
Answer: (a) Bakelite
Question 10. A bulb lights up only in (a) a closed circuit (b) an open circuit (c) in both (d) series connection
Answer: (a) a closed circuit
Question 11. Which of the following is a non-conductor or electricity? (a) Battery (b) Rubber glove (c) Metal spoon (d) Coin
Answer: (b) Rubber glove
Question 12. Filament of a torch bulb is (a) a metal case (b) metal tip at the centre of the base (c) two thick wires (d) a thin wire
Answer: (d) a thin wire
Question 13. A dry cell has (a) two terminals (b) one terminal (c) three terminals (d) none of these
Answer: (a) two terminals
Question 14. A bulb whose filament is broken is called (a) fused (b) glowing (c) conductor (d) none of these
Answer: (a) fused
Question 15. The thin wire that gives off light is called (a) current (b) filament (c) bulb (d) cell
Answer: (b) filament
Question 16. The direction of flow of an electric current in a conducting wire is from: (a) negative to positive (b) positive to negative (c) sometimes positive and sometimes negative
Answer: (b) positive to negative
Question 17. Lead of pencil is (a) an insulator (b) a semiconductor (c) a conductor (d) none of these
Answer: (c) a conductor
Question 18. A filament with low melting point is used in (a) fuse (b) electric bulb (c) electric iron (d) electric heater
Answer: (a) fuse
Question 19. An electrician wears a rubber glove while doing electrical repairs to (a) save electricity (b) prevent himself from shock (c) just make fun (d) keep away from getting dirty
Answer: (b) prevent himself from shock
Question 20. Glass is (a) a conductor (b) an insulator (e) both conductor and insulator (d) semiconductor
Answer: (b) an insulator
Question 21. Battery is the combination of two or more (a) cells (b) bulbs (c) circuits (d) none of these
Answer: (a) cells
Question 22. Graphite is a/an (a) insulator (b) conductor (c) both of these (d) none of these
Answer: (b) conductor
Question 23. Plastic is a/an (a) insulator (b) conductor (c) both of these (d) none of these
Answer: (a) insulator
Question 24. The bulb lights up only when (a) the cell, bulb and the wires make a closed circuit. (b) there is a gap in the electrical path. (c) the path starts and ends up at the same terminal of the cell. (d) the cell, bulb and wires make an open circuit.
Answer: (a) the cell, bulb and the wires make a closed circuit.
Question 25. Thin wire in the bulb that gives off light is (a) cell (b) battery (c) filament (d) circuit
Question 26. The direction of current in a conducting wire is (a) positive to negative terminal (b) negative to positive terminal (c) may vary (d) none of these
Answer: (a) positive to negative terminal
Question 27. Which of the following will make a closed circuit? (a) Eraser (b) Metal Key (c) Bulb (d) Battery
Answer: (b) Metal Key
Question 28. A device that breaks the circuit is called (a) filament (b) switch (c) bulb (d) battery
Answer: (b) switch
Question 29. The materials which allow electric current to pass through them are (a) conductors (b) insulators (c) semi-conductors (d) None of these
Answer: (a) conductors
Question 30. A circuit may have (a) only one bulb (b) only two bulbs (c) only three bulbs (d) any number of bulbs
Answer: (d) any number of bulbs
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1. Gases used in electric bulbs are ………………. gases.
Answer: inert
Question 2. A cell converts ………………. energy into ………………. energy.
Answer: chemical; electric
Question 3. The combination of two or more cells in a specific order is called a ……………….
Answer: battery
Question 4. A ………………. is a device which makes or breaks the circuit.
Answer: switch
Question 5. A closed path made for the flow of electric current is called ……………….
Answer: circuit
Question 6. Our body is a good ………………. of electricity.
Answer: conductor
Question 7. Substances through which an electric current can pass are called ……………….
Answer: conductors
Question 8. Substances through which an electric current cannot pass are called ……………….
Answer: insulators
Question 9. We use a ………………. to test the conductivity of a material, i.e., whether it is a conductor or an insulator.
Answer: conduction tester
Question 10. Electrical charges that build up on the surface of object being rubbed is called ………………. electricity.
Answer: static
Question 11. There is a thin wire inside the bulb which emits light is called ………………. of the bulb.
Answer: filament
Question 12. ………………. and ………………. are used for covering electrical wires, plug tops, switches and other electrical appliances.
Answer: Rubber; plastics
Question 13. Air is ……………….
Answer: an insulator
Question 14. An electric current flows from terminal of the electric cell to its ………………. terminal.
Answer: positive, negative
Question 15. A bulb in which the ………………. is broken is called a bulb.
Answer: filament; fused
Question 16. ………………… is a useful form of energy.
Answer: Electricity
Question 17. ………………… cell does not contain any liquid chemical.
Answer: Dry
Question 18. The metal cap is the ………………… terminal of electric cell.
Answer: positive
Question 19. A single dry cell gives a voltage of ………………… volts.
Answer: 1.5
Question 20. In ………………… circuit current flows from the positive terminal to its negative terminal.
Answer: closed
Question 21. No ………………… flows in an open circuit.
Answer: current
Question 22. A ………………… works by opening and closing a gap in an electric circuit.
Question 23. In a torch two cells are connected to a torch bulb through …………………
Answer: sliding switch
Question 24. Cotton and jute are …………………
Question 25. Silver and copper are …………………
True or False
Question 1. Electricity is a form of energy.
Answer: True
Question 2. In an electric cell, the side with the metal cap is the negative terminal.
Answer: False
Question 3. The electric cell produces electric current.
Question 4. Gases filled inside the bulb are nitrogen, argon, krypton, etc.
Question 5. Electricity can pass through thermocol.
Question 6. A fused bulb does not glow.
Question 7. When we rub an object with something, it acquires charge.
Question 8. Our body is a bad conductor of electricity.
Question 9. Both electric cells and the bulbs have one terminal each.
Question 10. In an open circuit, electricity cannot flow.
Question 11. Electric switches, plugs, sockets, etc., are made of conductors.
Question 12. Light bulb was invented by Thomas Alva Edison.
Question 13. In a circuit, electric current flows from positive terminal to negative terminal.
Question 14. Air is a bad conductor of electricity.
Question 15. Rubber glove is an example of non-conductor of electricity.
Question 16. Electricity flows in an open electric circuit.
Question 17. The black rod in a dry cell is lead rod.
Question 18. Conductors do not allow the electric current to pass through them.
Question 19. The circuit in which electrical contact at any point is broken is called on open electric circuit.
Question 20. An electric cell has four terminals.
Question 21. Handle of an electrician’s screw driver is made of insulator.
Question 22. Thin wire in an electric bulb is called filament.
Question 23. The current flows in closed circuit from +ve to -ve terminal of the cell.
Question 24. Dry cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
Match the following
Hope the information shed above regarding NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 6 Science Electricity and Circuits MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, feel free to reach us so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
CBSE Class 6 Science Revision Notes Chapter 12
Home » CBSE » CBSE Class 6 Science Revision Notes Chapter 12

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Revision Notes – Electricity and Circuits
Electricity in Science is defined as the flow of electrons through a circuit. It is crucial to understanding the concept of electrical conduction through a circuit. Chapter 12 of CBSE Class 6 Science explains these concepts in detail. The electrical components required for a circuit are also described. It lists the different types of electrical conductors and insulators. The chapter goes on to explain the additional effects of electricity, including the effects of heating, lighting, and magnetism.
Quick Links
Extramarks’ Revision Notes for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12 are written in an easy-to-understand language for students to revise quickly and effectively before their examinations. Students can access these notes from the website at their convenience.
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12
Access class 6 science chapter 12 – electricity and circuits notes.
Definition of Electricity
Electricity is the movement of charges (electrons) or electrical power through a suitable medium. For example, the wires used in homes. Electric currents can be produced by batteries, generators, inverters, dry or electric cells, or by converting other energy sources.
Electric Circuit:
A closed path known as an electric circuit delivers a constant flow of electrons or electric current from a source of voltage to the machinery in use. The term “current flow” refers to the movement of electricity in a circuit from one terminal of a power source, such as a cell, to another. The starting terminal is typically regarded as positive and the ending terminal as negative. A simple circuit consists of two wires connecting a bulb to a battery. As long as the battery is not dead and the bulb is not fused, it will begin to glow.
A circuit diagram is a representation of this current flow path or circuit using various symbols and notation for various components.
Open and Closed Circuits
When the path taken by an electrical current from one termin
al to its opposite terminal is uninterrupted and continuous, it is referred to as a closed circuit. However, if the same path is broken somewhere along the way, it is referred to as an open circuit.
Electrical Components
- Wire: Wires are electrical conductors that connect two or more electrical components and allow current to flow. The wires are typically made of metals that are effective electrical conductors. The type of metal and wire size are chosen based on the application.
- Bulb: It is a filament inside a glass case that is connected to two terminals and heats up when an electric current flows through it and emits light. Typically, tungsten wire coils are used to create the filament wire. The two terminals between which the filament is located receive the electricity.
- Electric Cell or Dry Cell: It is a particular type of apparatus that captures chemical energy and transforms it into electrical energy that can be applied to various tasks. Positive and negative terminals make up its two terminals. Charges move from the negative to the positive terminal inside a cell, whereas the opposite occurs outside the cell.
- Battery: A battery is a collection of two or more cells connected in series.
- Switch: An electrical circuit uses this device to allow or restrict the steady flow of current. When activated, it creates a conducting medium between two gaps in a circuit, allowing the circuit to function. . When turned off, it breaks the circuit by removing the conducting medium from its gap.
An electric torch is made up of a battery, an LED (Light Emitting Diode) bulb, and the above-mentioned parts altogether.
Electrical Conductors and Insulators
The materials that permit the flow of electricity through them are known as electrical conductors. All metals fall into the category of excellent electrical conductors. The only non-metal that conducts electricity is carbon, which can be tested by laying wires across a pencil’s two ends.
On the other hand, materials that do not permit the flow of electric currents are referred to as insulators or poor conductors. Some examples of insulators include plastic, rubber, dry wood, PVC, etc.
Effects of Electricity
The passage of an electric current through a material is accompanied by a number of additional effects, some of which can be put to other uses or result in energy losses. Some of these effects are discussed below.
- Heating Effect: When an electric current passes through a conductor, heat is generated due to the conductor’s resistance to the flowing current. Electric heaters, ovens, and other devices use this effect to generate heat.
- Lighting Effect: When an electric current passes through the filament of an electric bulb, the thin wire glows as a result of the current flow.
- Magnetic Effect: When an electric current is passed through the coil, the metal becomes magnetic. Electromagnets make use of the magnetic effect. An electromagnet is a magnet made up of a piece of iron or steel surrounded by a coil.
- Chemical Effect: A solution ionises and breaks down into ions when an electric current flows through it. This chemical action is used in electroplating and electrolysis.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. what is an electric circuit.
Electricity is defined as the flow of electrons or charges through a suitable medium of conduction, typically the wires that come from batteries, cells, or generators. A closed path of conduction known as an electric circuit enables a constant flow of electrons from one end of the current source to the other terminal end of the apparatus being used.
2. What are the various components of the electric circuit?
The following elements are necessary for an electric circuit to function properly so that electrons or charges can flow continuously through the medium of conduction. A cell, a device that transforms chemical energy into electrical energy, or a battery, which is a combination of cells, is one of the components. A switch is used to open or close the function of the circuit. Other components include wires used for conduction.
3. What are electric conductors and insulators?
To generate electricity, charge moves from one terminal end of the current source to the other. Conductors are the components in a circuit that permit the flow of current through them. All metals, carbon, and nonmetals, are recognised as being good electrical conductors because electrons pass through them with ease. Insulators, or poor electrical conductors, are objects that do not allow electrons to pass through them. For example, rubber.
4. What are the effects of electricity?
The passage of electric charges through a medium is usually accompanied by some effects. These effects are caused by electricity and are used for other purposes that help in the completion of various tasks. The different effects of electricity include the heating effect, which is used in electric heaters for iron, the lighting effect, which is used in light bulbs and other similar objects, and the magnetic effect, which is used in the field of electromagnetics.
CBSE Related Links

- School Guide
- Class 12 Syllabus
- Class 12 Revision Notes
- Maths Notes Class 12
- Physics Notes Class 12
- Chemistry Notes Class 12
- Biology Notes Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- RD Sharma Solutions Class 12
- Class 11 Political Science Notes: Political Theory - An Introduction
- CBSE Class 9 Political Science Revision Notes
- Freedom| Class 11 Political Science Notes
- Class 10 Political Science Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Political Science Previous Year Question Paper
- Federalism Political Science Class 11 Notes
- Citizen and Nation Class 11 Political Science Notes
- Harm Principle| Class 11 Polity Notes
- NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Political Science Chapter-1 The Constitution
- Rights in the Indian Constitution Class 11 Polity Notes
- John Rawls Theory of Justice Class 11 Polity Notes
- Kinds of Rights| Class 11 Polity Notes
- Enforcement of Safety Laws| Class 8 Polity Notes
- Chapter 4: Social Justice Class 11 Political Science Notes
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Political Science Set 2 with Solutions
- Class 11 Polity Notes: Special Provisions to some States
- Analyse the Functions of Consumer Protection Council
- Election and Representation Class 11 Polity Notes
- Oil Prices and the Global Economy - Cause & Impact
The Protection of Global Commons| Class 12 Political Science Notes
The concept of ‘global commons’ refers to natural resources and regions that lie outside the political reach of any one nation-state and are considered common areas shared by all. These include the Earth’s atmosphere, outer space, Antarctica, and the high seas. The protection of these areas is crucial due to their universal importance and vulnerability to exploitation and environmental degradation. This article explores the various dimensions of global commons, the challenges in their protection, and the role of international law and organizations in safeguarding these vital resources.
Table of Content
Understanding Global Commons
Challenges in protecting global commons, international laws and agreements, role of international organizations, case studies, future perspectives and challenges.
Global commons encompass those parts of the planet that are not owned by any single entity but are shared among nations and peoples. These include:
- The High Seas : Areas of oceans not covered by national jurisdiction, beyond the Exclusive Economic Zone (200 nautical miles from a nation’s coast).
- The Atmosphere : The blanket of gases surrounding the Earth, crucial for climate regulation and life support.
- Antarctica : Governed by the Antarctic Treaty System, it is a landmass devoted to peace and science.
- Outer Space : Including celestial bodies and the orbital environments around Earth.
- Biodiversity : While not limited to commons, the diversity of ecosystems, species, and genes is vital for sustainability and is shared globally.
The protection of global commons faces numerous challenges:
- The tragedy of the Commons : This concept illustrates how individual users acting independently according to their self-interest can deplete or spoil shared resources, even against everyone’s long-term best interests.
- Jurisdictional Issues : Global commons often exist beyond the jurisdiction of any single country, making enforcement of laws challenging.
- Environmental Degradation : Pollution, overfishing, and the impacts of climate change are significant issues affecting the health of global commons.
- Economic Pressures : Economic imperatives often drive nations and corporations to exploit these resources unsustainably.
Several international laws and agreements have been established to protect global commons, including:
- The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) : Governs the use of the oceans and aims to protect the marine environment.
- The Antarctic Treaty (1959) : Establishes Antarctica as a scientific preserve and bans military activity on the continent.
- The Outer Space Treaty (1967) : Bans the placement of nuclear weapons in space and limits the use of celestial bodies to peaceful purposes.
- The Montreal Protocol (1987) : A successful environmental treaty that phases out the production of numerous substances responsible for ozone depletion.
International organizations play a crucial role in the governance and protection of global commons:
- The United Nations (UN) : Through various bodies like the UNEP and the International Maritime Organization, the UN spearheads initiatives to protect and manage the global environment.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) : While primarily focused on trade, the WTO also deals with environmental issues related to trade.
- The International Whaling Commission (IWC) : Works to regulate whaling and promote whale conservation globally.
- The Amazon Rainforest : Often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth”, the Amazon is a critical global common for biodiversity and carbon sequestration. Efforts to protect it involve international cooperation and regulations.
- The Arctic : Climate change is making the Arctic more accessible to navigation and exploitation. The region is governed by the Arctic Council, which includes countries like the USA, Canada, Russia, and others.
The future of global commons protection lies in enhancing international cooperation, improving compliance with international laws, and integrating sustainability into economic and social policies. Challenges like geopolitical conflicts, economic disparities, and technological advancements continue to impact the effectiveness of global commons governance.
The protection of global commons is essential for maintaining global stability and ensuring sustainable development. While significant progress has been made through international treaties and organizations, ongoing vigilance, cooperation, and adaptability are required to address the evolving challenges faced by global commons. By understanding the importance and vulnerabilities of these shared resources, we can better appreciate the necessity of their protection for future generations.
FAQs on Class 12 Political Science Notes Chapter Chapter 6 The Protection of Global Commons
What are the global commons.
Global commons refer to natural resources and areas that are not owned by any single country or entity but are shared among nations. These include the high seas, the atmosphere, outer space, and Antarctica.
Why is the protection of global commons considered challenging?
Protecting global commons is challenging for the following reasons: Jurisdictional ambiguities : Since these areas do not fall under the sovereignty of any one nation, it’s challenging to enforce regulations. Varied national interests : Countries often have conflicting interests and priorities, which can complicate negotiations and enforcement of international agreements.
How does the Tragedy of the Commons relate to global commons?
The Tragedy of the Commons principle is highly relevant to global commons, as their shared nature means that without cooperative management, they are at risk of over-exploitation and degradation, leading to long-term negative outcomes for all.
What role do international treaties play in the protection of global commons?
International treaties are crucial in the management and protection of global commons. They provide a framework for cooperation and legal standards for usage that all signatory nations agree to follow. Examples include: The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) for the oceans. The Antarctic Treaty for Antarctica. The Outer Space Treaty for celestial bodies and outer space. These treaties help to establish guidelines and rules that are designed to prevent the overuse and ensure the sustainability of these resources.
Can global commons be effectively protected without international cooperation?
It is highly unlikely that global commons can be protected without robust international cooperation. Since these areas do not fall within the jurisdiction of any single nation, no one country can effectively manage or protect them alone.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Chapterwise-Notes-Class-12
- School Learning
- School Polity
- Social Science
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
[Download] Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Here we are providing case study or passage-based questions for class 6 science chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits. Case Study/Passage Based Questions Passage-1 An electric bulb has a filament that is connected to the terminals. The two terminals of filament are fixed … Continue reading Case Study ...
CBSE Class 6 Science Case Study Question and Answer for all Chapter 1 to 16. Class 6 Students can learn Case Type Question from here. 100% FREE Exercise & Practice for CBSE, NCERT and ICSE ... Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Case Study Question. Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Case Study Question.
13. Give one difference between a cell and a battery. Answer: A cell produces electricity by chemical reactions taking place in it whereas battery is made up of two or more cells joined together. 14. Write any two uses of electric cells. Answer: It is used in alarm clocks and wrist watches.
Access Answers to NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits. Multiple Choice Questions: 1. Choose from the options a, b, c and d given in fig 12.1, which shows the correct direction of the current.
Class 6 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits. Multiple Choice Questions. 1. Choose from the options a, b, c and d given in Fig. 12.1, the figure which shows the correct direction of the current. Ans: The correct answer is option (b).
Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Textbook Questions and Answers. EXERCISES. Question 1: Fill in the blanks: (a) A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called a ________. (b) An electric cell has ________ terminals. Answer: (a) A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called switch. (b) An electric cell has two terminals.
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 12 - Free PDF Download. Our Class 6 Revision Notes will provide a quick glimpse of the chapter and improve the learning experience. We have made these revision notes keeping the convenience of students in mind so that it proves more effective. You can easily read these Class 6 notes just by ...
Get free NCERT Solutions for Science Class 6 Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits solved by experts. Available here are Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits Exercises Questions with Solutions and detail explanation for your practice before the examination ... NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self ...
The NCERT solutions for class 6th Science chapter 12 include a detailed discussion about the basics of electrical circuits, switches, and electrical cells. It begins with a general introduction, followed by the working principles of electrical cells, and its architecture. This chapter further provides an idea about electrical circuits and switches.
The NCERT Solutions for Chapter 12 of Class 6 Science provide a thorough exploration of electricity and circuits. This chapter elucidates the principles of electricity, various electrical devices, electrical circuits, conductors, switches, insulators, and more. Comprising a total of five sub-topics, the chapter initiates with a general ...
Fig 5: Danger Sign. This sign is used in areas which are near electric junctions as a warning. Get Revision Notes of Class 6th Science Chapter 12 Electricity and circuits to score good marks in your Exams. Our notes of Chapter 12 Electricity and circuits are prepared by Maths experts in an easy to remember format, covering all syllabus of CBSE ...
CBSE Class 6 Science Important Questions Chapter 12 - Electricity and Circuits - Free PDF Download. Class 6 Science explains fascinating concepts to young minds. They learn many new things and find exciting new facts about different topics. The 12th chapter of the Class 6 NCERT Science book focuses on explaining current, electricity, and circuits.
Objective: To study the structure of a torch bulb. Material Required: A torch bulb. Procedure: ... Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Additional Important Questions and Answers. ... In case of a fire caused by electric spark, make sure that we should not throw water on electric appliances. ...
Answer: When two or more cells are joined together, it is called a battery. Question 3. Give any difference between a cell and a battery. Answer: A cell has only one plate as a positive and only one plate as a negative electrode, while a battery, which is a combination of cells in a series, can have many plates. Question 4.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits. 1. Fill in the blanks: 2. Mark 'True' or 'False' for the following statements: (a) Electric current can flow through metals. (b) Instead of metal wires, a jute string can be used to make a circuit. (c) Electric current can pass through a sheet of thermocol.
Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Question Answer - Electricity and Circuits. Science introduces and elaborates new concepts and ideas to students. Science teaches students to be curious and develop critical and scientific methods to reach logical conclusions. Science is interesting and stimulating. It also opens up new opportunities for a lot of ...
The NCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 12 starts with an introduction to electricity and circuits in general. It discusses the importance of electricity in our daily lives and mentions some devices that rely on it to function. There are a total of five subsections in Chapter 12. They are discussed topic-wise in detail as follows:
NCERT Solution for Class 6 Science Chapter 12: Electricity and Circuits, Download English, and Hindi Medium PDF Solutions for Academic Session 2020-2021.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science. Chapter 1 Food Where Does It Come From. Chapter 2 Components of Food. Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric. Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups. Chapter 5 Separation of Substances. Chapter 6 Changes Around Us. Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants.
Electricity and Circuits Class 6 Notes - Chapter 12. The Electric Cell Bulb Connected to an Electric Cell An Electric Circuit An Electric Switch Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits. According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 9.
Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Extra Questions and Answers Electricity and Circuits. ... In case of short circuit or a spark in a switch, put the main switch off immediately with the help of a plastic or wooden stick. In case of fire in electric wires, never use water to extinguish it. First switch off the mains, then use dry sand to extinguish the ...
The bulb lights up only when. (a) the cell, bulb and the wires make a closed circuit. (b) there is a gap in the electrical path. (c) the path starts and ends up at the same terminal of the cell. (d) the cell, bulb and wires make an open circuit. Answer. Question 25. Thin wire in the bulb that gives off light is.
Chapter 12 of CBSE Class 6 Science explains these concepts in detail. The electrical components required for a circuit are also described. It lists the different types of electrical conductors and insulators. The chapter goes on to explain the additional effects of electricity, including the effects of heating, lighting, and magnetism.
Case Studies. The Amazon Rainforest: Often referred to as the "lungs of the Earth", the Amazon is a critical global common for biodiversity and carbon sequestration. Efforts to protect it involve international cooperation and regulations. ... FAQs on Class 12 Political Science Notes Chapter Chapter 6 The Protection of Global Commons
2024 AP Exam Dates. The 2024 AP Exams will be administered in schools over two weeks in May: May 6-10 and May 13-17. AP coordinators are responsible for notifying students when and where to report for the exams. Early testing or testing at times other than those published by College Board is not permitted under any circumstances.