Essay Papers Writing Online
A comprehensive guide to essay writing.

Essay writing is a crucial skill that students need to master in order to succeed academically. Whether you’re a high school student working on a history paper or a college student tackling a critical analysis essay, having a solid understanding of the essay writing process is essential.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the essential tips and tricks that will help you improve your essay writing skills. From generating ideas and organizing your thoughts to crafting a strong thesis statement and polishing your final draft, we’ve got you covered.
Not only that, but we’ll also provide you with useful templates that you can use as a framework for your essays. These templates will help you structure your writing, stay focused on your main argument, and ensure that your essay flows smoothly from one point to the next.

The Ultimate Essay Writing Guides
Essay writing can be a challenging task for many students, but with the right guidance and tips, you can improve your writing skills and produce high-quality essays. In this ultimate guide, we will provide you with valuable advice, tricks, and templates to help you excel in your essay writing endeavors.
1. Understand the Prompt: Before you start writing your essay, make sure you fully understand the prompt or question. Analyze the requirements and key points that need to be addressed in your essay.
2. Create an Outline: Organize your ideas and thoughts by creating a detailed outline for your essay. This will help you structure your arguments and ensure a logical flow of information.
3. Research Thoroughly: Conduct extensive research on your topic to gather relevant information and evidence to support your arguments. Use credible sources and cite them properly in your essay.
4. Write Clearly and Concisely: Avoid using jargon or complex language in your essay. Write in a clear and concise manner to convey your ideas effectively to the reader.
5. Proofread and Edit: Before submitting your essay, make sure to proofread and edit it carefully. Check for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and ensure that your essay flows cohesively.
By following these ultimate essay writing guides, you can enhance your writing skills and produce outstanding essays that will impress your instructors and peers. Practice regularly and seek feedback to continuously improve your writing abilities.
Tips for Crafting an A+ Essay

1. Understand the Assignment: Before you start writing, make sure you fully understand the assignment guidelines and requirements. If you have any doubts, clarify them with your instructor.
2. Conduct Thorough Research: Gather relevant sources and information to support your arguments. Make sure to cite your sources properly and use credible sources.
3. Create a Strong Thesis Statement: Your thesis statement should clearly outline the main point of your essay and guide your readers on what to expect.
4. Organize Your Ideas: Create an outline to organize your thoughts and ensure a logical flow of ideas in your essay.
5. Write Clearly and Concisely: Use clear, concise language and avoid unnecessary jargon or complex sentences. Be direct and to the point.
6. Revise and Edit: Always proofread your essay for grammar and spelling errors. Revise your work to ensure coherence and clarity.
7. Seek Feedback: Ask a peer or instructor to review your essay and provide constructive feedback for improvement.
8. Use Proper Formatting: Follow the formatting guidelines provided by your instructor, such as font size, margins, and citation style.
9. Stay Focused: Keep your essay focused on the main topic and avoid going off on tangents. Stick to your thesis statement.
10. Practice, Practice, Practice: The more you practice writing essays, the better you will get at it. Keep practicing and refining your writing skills.
Tricks to Improve Your Writing Skills

Improving your writing skills can be a challenging but rewarding process. Here are some tricks to help you become a better writer:
1. Read widely: Reading a variety of genres and styles can help you develop your own voice and writing style.
2. Practice regularly: The more you write, the better you will become. Set aside time each day to practice writing.
3. Get feedback: Share your writing with others and ask for constructive criticism. Feedback can help you identify areas for improvement.
4. Study grammar and punctuation: Good writing requires a solid understanding of grammar and punctuation rules. Take the time to study and practice these essential skills.
5. Edit and revise: Writing is a process, and editing is an important part of that process. Take the time to edit and revise your work to improve clarity and coherence.
6. Experiment with different writing techniques: Try experimenting with different writing techniques, such as using metaphors, similes, or descriptive language, to enhance your writing.
7. Stay inspired: Find inspiration in the world around you. Whether it’s nature, art, or literature, draw inspiration from your surroundings to fuel your writing.
By following these tricks and practicing regularly, you can improve your writing skills and become a more confident and effective writer.
Step-by-Step Essay Writing Templates
When it comes to writing an essay, having a clear and structured template can be incredibly helpful. Here are some step-by-step essay writing templates that you can use to guide you through the process:
- Introduction: Start your essay with a hook to grab the reader’s attention. Provide some background information on the topic and end with a thesis statement that outlines the main argument of your essay.
- Body Paragraphs: Each body paragraph should focus on a single point that supports your thesis. Start with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph, provide evidence to support your point, and then analyze the evidence to show how it relates back to your thesis.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points of your essay and restate your thesis in a new way. Avoid introducing new information in the conclusion and instead focus on tying together all the points you have made throughout the essay.
Expert Advice for Writing Top-Notch Essays
When it comes to writing a top-notch essay, it’s essential to follow expert advice to ensure your work stands out. Here are some key tips to help you elevate your writing:
1. Start with a strong thesis statement that clearly outlines your main argument.
2. Conduct thorough research to support your points with credible sources.
3. Organize your thoughts logically and ensure your essay flows smoothly from one point to the next.
4. Use a variety of sentence structures and vocabulary to keep your writing engaging.
5. Proofread and edit your essay carefully to eliminate errors and refine your arguments.
By following these expert tips, you can take your essay writing skills to the next level and produce work that is both informative and compelling.
Resources to Enhance Your Essay Writing Process
When it comes to improving your essay writing skills, there are a variety of resources available to help you enhance your process. Here are some valuable resources that can aid you in becoming a more effective and efficient writer:
- Writing Guides: There are countless writing guides and books that offer tips, tricks, and strategies for improving your writing skills. Whether you’re looking to enhance your grammar, structure, or argumentation, these guides can provide valuable insights.
- Online Writing Communities: Joining online writing communities can be a great way to connect with other writers, receive feedback on your work, and engage in writing challenges and prompts. Websites like Writing.com and Wattpad are popular platforms for writers to share their work and receive critiques.
- Writing Workshops and Courses: Participating in writing workshops and courses can help you hone your craft and develop your writing skills. Whether you prefer in-person workshops or online courses, there are many options available to suit your needs and schedule.
- Writing Apps and Tools: Utilizing writing apps and tools can streamline your writing process and help you stay organized. Tools like Grammarly can assist with grammar and spelling checks, while apps like Scrivener can help you organize your research and ideas.
- Libraries and Writing Centers: Visiting your local library or university writing center can provide access to valuable resources, such as writing guides, research materials, and writing tutors who can offer personalized feedback and support.
By taking advantage of these resources, you can enhance your essay writing process and become a more skilled and confident writer.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, tips and techniques for crafting compelling narrative essays.

How to Write an Essay
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Essay Writing Fundamentals
How to prepare to write an essay, how to edit an essay, how to share and publish your essays, how to get essay writing help, how to find essay writing inspiration, resources for teaching essay writing.
Essays, short prose compositions on a particular theme or topic, are the bread and butter of academic life. You write them in class, for homework, and on standardized tests to show what you know. Unlike other kinds of academic writing (like the research paper) and creative writing (like short stories and poems), essays allow you to develop your original thoughts on a prompt or question. Essays come in many varieties: they can be expository (fleshing out an idea or claim), descriptive, (explaining a person, place, or thing), narrative (relating a personal experience), or persuasive (attempting to win over a reader). This guide is a collection of dozens of links about academic essay writing that we have researched, categorized, and annotated in order to help you improve your essay writing.
Essays are different from other forms of writing; in turn, there are different kinds of essays. This section contains general resources for getting to know the essay and its variants. These resources introduce and define the essay as a genre, and will teach you what to expect from essay-based assessments.
Purdue OWL Online Writing Lab
One of the most trusted academic writing sites, Purdue OWL provides a concise introduction to the four most common types of academic essays.
"The Essay: History and Definition" (ThoughtCo)
This snappy article from ThoughtCo talks about the origins of the essay and different kinds of essays you might be asked to write.
"What Is An Essay?" Video Lecture (Coursera)
The University of California at Irvine's free video lecture, available on Coursera, tells you everything you need to know about the essay.
Wikipedia Article on the "Essay"
Wikipedia's article on the essay is comprehensive, providing both English-language and global perspectives on the essay form. Learn about the essay's history, forms, and styles.
"Understanding College and Academic Writing" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
This list of common academic writing assignments (including types of essay prompts) will help you know what to expect from essay-based assessments.
Before you start writing your essay, you need to figure out who you're writing for (audience), what you're writing about (topic/theme), and what you're going to say (argument and thesis). This section contains links to handouts, chapters, videos and more to help you prepare to write an essay.
How to Identify Your Audience
"Audience" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This handout provides questions you can ask yourself to determine the audience for an academic writing assignment. It also suggests strategies for fitting your paper to your intended audience.
"Purpose, Audience, Tone, and Content" (Univ. of Minnesota Libraries)
This extensive book chapter from Writing for Success , available online through Minnesota Libraries Publishing, is followed by exercises to try out your new pre-writing skills.
"Determining Audience" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
This guide from a community college's writing center shows you how to know your audience, and how to incorporate that knowledge in your thesis statement.
"Know Your Audience" ( Paper Rater Blog)
This short blog post uses examples to show how implied audiences for essays differ. It reminds you to think of your instructor as an observer, who will know only the information you pass along.
How to Choose a Theme or Topic
"Research Tutorial: Developing Your Topic" (YouTube)
Take a look at this short video tutorial from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill to understand the basics of developing a writing topic.
"How to Choose a Paper Topic" (WikiHow)
This simple, step-by-step guide (with pictures!) walks you through choosing a paper topic. It starts with a detailed description of brainstorming and ends with strategies to refine your broad topic.
"How to Read an Assignment: Moving From Assignment to Topic" (Harvard College Writing Center)
Did your teacher give you a prompt or other instructions? This guide helps you understand the relationship between an essay assignment and your essay's topic.
"Guidelines for Choosing a Topic" (CliffsNotes)
This study guide from CliffsNotes both discusses how to choose a topic and makes a useful distinction between "topic" and "thesis."
How to Come Up with an Argument
"Argument" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
Not sure what "argument" means in the context of academic writing? This page from the University of North Carolina is a good place to start.
"The Essay Guide: Finding an Argument" (Study Hub)
This handout explains why it's important to have an argument when beginning your essay, and provides tools to help you choose a viable argument.
"Writing a Thesis and Making an Argument" (University of Iowa)
This page from the University of Iowa's Writing Center contains exercises through which you can develop and refine your argument and thesis statement.
"Developing a Thesis" (Harvard College Writing Center)
This page from Harvard's Writing Center collates some helpful dos and don'ts of argumentative writing, from steps in constructing a thesis to avoiding vague and confrontational thesis statements.
"Suggestions for Developing Argumentative Essays" (Berkeley Student Learning Center)
This page offers concrete suggestions for each stage of the essay writing process, from topic selection to drafting and editing.
How to Outline your Essay
"Outlines" (Univ. of North Carolina at Chapel Hill via YouTube)
This short video tutorial from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill shows how to group your ideas into paragraphs or sections to begin the outlining process.
"Essay Outline" (Univ. of Washington Tacoma)
This two-page handout by a university professor simply defines the parts of an essay and then organizes them into an example outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL Online Writing Lab)
Purdue OWL gives examples of diverse outline strategies on this page, including the alphanumeric, full sentence, and decimal styles.
"Outlining" (Harvard College Writing Center)
Once you have an argument, according to this handout, there are only three steps in the outline process: generalizing, ordering, and putting it all together. Then you're ready to write!
"Writing Essays" (Plymouth Univ.)
This packet, part of Plymouth University's Learning Development series, contains descriptions and diagrams relating to the outlining process.
"How to Write A Good Argumentative Essay: Logical Structure" (Criticalthinkingtutorials.com via YouTube)
This longer video tutorial gives an overview of how to structure your essay in order to support your argument or thesis. It is part of a longer course on academic writing hosted on Udemy.
Now that you've chosen and refined your topic and created an outline, use these resources to complete the writing process. Most essays contain introductions (which articulate your thesis statement), body paragraphs, and conclusions. Transitions facilitate the flow from one paragraph to the next so that support for your thesis builds throughout the essay. Sources and citations show where you got the evidence to support your thesis, which ensures that you avoid plagiarism.
How to Write an Introduction
"Introductions" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page identifies the role of the introduction in any successful paper, suggests strategies for writing introductions, and warns against less effective introductions.
"How to Write A Good Introduction" (Michigan State Writing Center)
Beginning with the most common missteps in writing introductions, this guide condenses the essentials of introduction composition into seven points.
"The Introductory Paragraph" (ThoughtCo)
This blog post from academic advisor and college enrollment counselor Grace Fleming focuses on ways to grab your reader's attention at the beginning of your essay.
"Introductions and Conclusions" (Univ. of Toronto)
This guide from the University of Toronto gives advice that applies to writing both introductions and conclusions, including dos and don'ts.
"How to Write Better Essays: No One Does Introductions Properly" ( The Guardian )
This news article interviews UK professors on student essay writing; they point to introductions as the area that needs the most improvement.
How to Write a Thesis Statement
"Writing an Effective Thesis Statement" (YouTube)
This short, simple video tutorial from a college composition instructor at Tulsa Community College explains what a thesis statement is and what it does.
"Thesis Statement: Four Steps to a Great Essay" (YouTube)
This fantastic tutorial walks you through drafting a thesis, using an essay prompt on Nathaniel Hawthorne's The Scarlet Letter as an example.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement" (WikiHow)
This step-by-step guide (with pictures!) walks you through coming up with, writing, and editing a thesis statement. It invites you think of your statement as a "working thesis" that can change.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement" (Univ. of Indiana Bloomington)
Ask yourself the questions on this page, part of Indiana Bloomington's Writing Tutorial Services, when you're writing and refining your thesis statement.
"Writing Tips: Thesis Statements" (Univ. of Illinois Center for Writing Studies)
This page gives plentiful examples of good to great thesis statements, and offers questions to ask yourself when formulating a thesis statement.
How to Write Body Paragraphs
"Body Paragraph" (Brightstorm)
This module of a free online course introduces you to the components of a body paragraph. These include the topic sentence, information, evidence, and analysis.
"Strong Body Paragraphs" (Washington Univ.)
This handout from Washington's Writing and Research Center offers in-depth descriptions of the parts of a successful body paragraph.
"Guide to Paragraph Structure" (Deakin Univ.)
This handout is notable for color-coding example body paragraphs to help you identify the functions various sentences perform.
"Writing Body Paragraphs" (Univ. of Minnesota Libraries)
The exercises in this section of Writing for Success will help you practice writing good body paragraphs. It includes guidance on selecting primary support for your thesis.
"The Writing Process—Body Paragraphs" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
The information and exercises on this page will familiarize you with outlining and writing body paragraphs, and includes links to more information on topic sentences and transitions.
"The Five-Paragraph Essay" (ThoughtCo)
This blog post discusses body paragraphs in the context of one of the most common academic essay types in secondary schools.
How to Use Transitions
"Transitions" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill explains what a transition is, and how to know if you need to improve your transitions.
"Using Transitions Effectively" (Washington Univ.)
This handout defines transitions, offers tips for using them, and contains a useful list of common transitional words and phrases grouped by function.
"Transitions" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
This page compares paragraphs without transitions to paragraphs with transitions, and in doing so shows how important these connective words and phrases are.
"Transitions in Academic Essays" (Scribbr)
This page lists four techniques that will help you make sure your reader follows your train of thought, including grouping similar information and using transition words.
"Transitions" (El Paso Community College)
This handout shows example transitions within paragraphs for context, and explains how transitions improve your essay's flow and voice.
"Make Your Paragraphs Flow to Improve Writing" (ThoughtCo)
This blog post, another from academic advisor and college enrollment counselor Grace Fleming, talks about transitions and other strategies to improve your essay's overall flow.
"Transition Words" (smartwords.org)
This handy word bank will help you find transition words when you're feeling stuck. It's grouped by the transition's function, whether that is to show agreement, opposition, condition, or consequence.
How to Write a Conclusion
"Parts of An Essay: Conclusions" (Brightstorm)
This module of a free online course explains how to conclude an academic essay. It suggests thinking about the "3Rs": return to hook, restate your thesis, and relate to the reader.
"Essay Conclusions" (Univ. of Maryland University College)
This overview of the academic essay conclusion contains helpful examples and links to further resources for writing good conclusions.
"How to End An Essay" (WikiHow)
This step-by-step guide (with pictures!) by an English Ph.D. walks you through writing a conclusion, from brainstorming to ending with a flourish.
"Ending the Essay: Conclusions" (Harvard College Writing Center)
This page collates useful strategies for writing an effective conclusion, and reminds you to "close the discussion without closing it off" to further conversation.
How to Include Sources and Citations
"Research and Citation Resources" (Purdue OWL Online Writing Lab)
Purdue OWL streamlines information about the three most common referencing styles (MLA, Chicago, and APA) and provides examples of how to cite different resources in each system.
EasyBib: Free Bibliography Generator
This online tool allows you to input information about your source and automatically generate citations in any style. Be sure to select your resource type before clicking the "cite it" button.
CitationMachine
Like EasyBib, this online tool allows you to input information about your source and automatically generate citations in any style.
Modern Language Association Handbook (MLA)
Here, you'll find the definitive and up-to-date record of MLA referencing rules. Order through the link above, or check to see if your library has a copy.
Chicago Manual of Style
Here, you'll find the definitive and up-to-date record of Chicago referencing rules. You can take a look at the table of contents, then choose to subscribe or start a free trial.
How to Avoid Plagiarism
"What is Plagiarism?" (plagiarism.org)
This nonprofit website contains numerous resources for identifying and avoiding plagiarism, and reminds you that even common activities like copying images from another website to your own site may constitute plagiarism.
"Plagiarism" (University of Oxford)
This interactive page from the University of Oxford helps you check for plagiarism in your work, making it clear how to avoid citing another person's work without full acknowledgement.
"Avoiding Plagiarism" (MIT Comparative Media Studies)
This quick guide explains what plagiarism is, what its consequences are, and how to avoid it. It starts by defining three words—quotation, paraphrase, and summary—that all constitute citation.
"Harvard Guide to Using Sources" (Harvard Extension School)
This comprehensive website from Harvard brings together articles, videos, and handouts about referencing, citation, and plagiarism.
Grammarly contains tons of helpful grammar and writing resources, including a free tool to automatically scan your essay to check for close affinities to published work.
Noplag is another popular online tool that automatically scans your essay to check for signs of plagiarism. Simply copy and paste your essay into the box and click "start checking."
Once you've written your essay, you'll want to edit (improve content), proofread (check for spelling and grammar mistakes), and finalize your work until you're ready to hand it in. This section brings together tips and resources for navigating the editing process.
"Writing a First Draft" (Academic Help)
This is an introduction to the drafting process from the site Academic Help, with tips for getting your ideas on paper before editing begins.
"Editing and Proofreading" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page provides general strategies for revising your writing. They've intentionally left seven errors in the handout, to give you practice in spotting them.
"How to Proofread Effectively" (ThoughtCo)
This article from ThoughtCo, along with those linked at the bottom, help describe common mistakes to check for when proofreading.
"7 Simple Edits That Make Your Writing 100% More Powerful" (SmartBlogger)
This blog post emphasizes the importance of powerful, concise language, and reminds you that even your personal writing heroes create clunky first drafts.
"Editing Tips for Effective Writing" (Univ. of Pennsylvania)
On this page from Penn's International Relations department, you'll find tips for effective prose, errors to watch out for, and reminders about formatting.
"Editing the Essay" (Harvard College Writing Center)
This article, the first of two parts, gives you applicable strategies for the editing process. It suggests reading your essay aloud, removing any jargon, and being unafraid to remove even "dazzling" sentences that don't belong.
"Guide to Editing and Proofreading" (Oxford Learning Institute)
This handout from Oxford covers the basics of editing and proofreading, and reminds you that neither task should be rushed.
In addition to plagiarism-checkers, Grammarly has a plug-in for your web browser that checks your writing for common mistakes.
After you've prepared, written, and edited your essay, you might want to share it outside the classroom. This section alerts you to print and web opportunities to share your essays with the wider world, from online writing communities and blogs to published journals geared toward young writers.
Sharing Your Essays Online
Go Teen Writers
Go Teen Writers is an online community for writers aged 13 - 19. It was founded by Stephanie Morrill, an author of contemporary young adult novels.
Tumblr is a blogging website where you can share your writing and interact with other writers online. It's easy to add photos, links, audio, and video components.
Writersky provides an online platform for publishing and reading other youth writers' work. Its current content is mostly devoted to fiction.
Publishing Your Essays Online
This teen literary journal publishes in print, on the web, and (more frequently), on a blog. It is committed to ensuring that "teens see their authentic experience reflected on its pages."
The Matador Review
This youth writing platform celebrates "alternative," unconventional writing. The link above will take you directly to the site's "submissions" page.
Teen Ink has a website, monthly newsprint magazine, and quarterly poetry magazine promoting the work of young writers.
The largest online reading platform, Wattpad enables you to publish your work and read others' work. Its inline commenting feature allows you to share thoughts as you read along.
Publishing Your Essays in Print
Canvas Teen Literary Journal
This quarterly literary magazine is published for young writers by young writers. They accept many kinds of writing, including essays.
The Claremont Review
This biannual international magazine, first published in 1992, publishes poetry, essays, and short stories from writers aged 13 - 19.
Skipping Stones
This young writers magazine, founded in 1988, celebrates themes relating to ecological and cultural diversity. It publishes poems, photos, articles, and stories.
The Telling Room
This nonprofit writing center based in Maine publishes children's work on their website and in book form. The link above directs you to the site's submissions page.
Essay Contests
Scholastic Arts and Writing Awards
This prestigious international writing contest for students in grades 7 - 12 has been committed to "supporting the future of creativity since 1923."
Society of Professional Journalists High School Essay Contest
An annual essay contest on the theme of journalism and media, the Society of Professional Journalists High School Essay Contest awards scholarships up to $1,000.
National YoungArts Foundation
Here, you'll find information on a government-sponsored writing competition for writers aged 15 - 18. The foundation welcomes submissions of creative nonfiction, novels, scripts, poetry, short story and spoken word.
Signet Classics Student Scholarship Essay Contest
With prompts on a different literary work each year, this competition from Signet Classics awards college scholarships up to $1,000.
"The Ultimate Guide to High School Essay Contests" (CollegeVine)
See this handy guide from CollegeVine for a list of more competitions you can enter with your academic essay, from the National Council of Teachers of English Achievement Awards to the National High School Essay Contest by the U.S. Institute of Peace.
Whether you're struggling to write academic essays or you think you're a pro, there are workshops and online tools that can help you become an even better writer. Even the most seasoned writers encounter writer's block, so be proactive and look through our curated list of resources to combat this common frustration.
Online Essay-writing Classes and Workshops
"Getting Started with Essay Writing" (Coursera)
Coursera offers lots of free, high-quality online classes taught by college professors. Here's one example, taught by instructors from the University of California Irvine.
"Writing and English" (Brightstorm)
Brightstorm's free video lectures are easy to navigate by topic. This unit on the parts of an essay features content on the essay hook, thesis, supporting evidence, and more.
"How to Write an Essay" (EdX)
EdX is another open online university course website with several two- to five-week courses on the essay. This one is geared toward English language learners.
Writer's Digest University
This renowned writers' website offers online workshops and interactive tutorials. The courses offered cover everything from how to get started through how to get published.
Writing.com
Signing up for this online writer's community gives you access to helpful resources as well as an international community of writers.
How to Overcome Writer's Block
"Symptoms and Cures for Writer's Block" (Purdue OWL)
Purdue OWL offers a list of signs you might have writer's block, along with ways to overcome it. Consider trying out some "invention strategies" or ways to curb writing anxiety.
"Overcoming Writer's Block: Three Tips" ( The Guardian )
These tips, geared toward academic writing specifically, are practical and effective. The authors advocate setting realistic goals, creating dedicated writing time, and participating in social writing.
"Writing Tips: Strategies for Overcoming Writer's Block" (Univ. of Illinois)
This page from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign's Center for Writing Studies acquaints you with strategies that do and do not work to overcome writer's block.
"Writer's Block" (Univ. of Toronto)
Ask yourself the questions on this page; if the answer is "yes," try out some of the article's strategies. Each question is accompanied by at least two possible solutions.
If you have essays to write but are short on ideas, this section's links to prompts, example student essays, and celebrated essays by professional writers might help. You'll find writing prompts from a variety of sources, student essays to inspire you, and a number of essay writing collections.
Essay Writing Prompts
"50 Argumentative Essay Topics" (ThoughtCo)
Take a look at this list and the others ThoughtCo has curated for different kinds of essays. As the author notes, "a number of these topics are controversial and that's the point."
"401 Prompts for Argumentative Writing" ( New York Times )
This list (and the linked lists to persuasive and narrative writing prompts), besides being impressive in length, is put together by actual high school English teachers.
"SAT Sample Essay Prompts" (College Board)
If you're a student in the U.S., your classroom essay prompts are likely modeled on the prompts in U.S. college entrance exams. Take a look at these official examples from the SAT.
"Popular College Application Essay Topics" (Princeton Review)
This page from the Princeton Review dissects recent Common Application essay topics and discusses strategies for answering them.
Example Student Essays
"501 Writing Prompts" (DePaul Univ.)
This nearly 200-page packet, compiled by the LearningExpress Skill Builder in Focus Writing Team, is stuffed with writing prompts, example essays, and commentary.
"Topics in English" (Kibin)
Kibin is a for-pay essay help website, but its example essays (organized by topic) are available for free. You'll find essays on everything from A Christmas Carol to perseverance.
"Student Writing Models" (Thoughtful Learning)
Thoughtful Learning, a website that offers a variety of teaching materials, provides sample student essays on various topics and organizes them by grade level.
"Five-Paragraph Essay" (ThoughtCo)
In this blog post by a former professor of English and rhetoric, ThoughtCo brings together examples of five-paragraph essays and commentary on the form.
The Best Essay Writing Collections
The Best American Essays of the Century by Joyce Carol Oates (Amazon)
This collection of American essays spanning the twentieth century was compiled by award winning author and Princeton professor Joyce Carol Oates.
The Best American Essays 2017 by Leslie Jamison (Amazon)
Leslie Jamison, the celebrated author of essay collection The Empathy Exams , collects recent, high-profile essays into a single volume.
The Art of the Personal Essay by Phillip Lopate (Amazon)
Documentary writer Phillip Lopate curates this historical overview of the personal essay's development, from the classical era to the present.
The White Album by Joan Didion (Amazon)
This seminal essay collection was authored by one of the most acclaimed personal essayists of all time, American journalist Joan Didion.
Consider the Lobster by David Foster Wallace (Amazon)
Read this famous essay collection by David Foster Wallace, who is known for his experimentation with the essay form. He pushed the boundaries of personal essay, reportage, and political polemic.
"50 Successful Harvard Application Essays" (Staff of the The Harvard Crimson )
If you're looking for examples of exceptional college application essays, this volume from Harvard's daily student newspaper is one of the best collections on the market.
Are you an instructor looking for the best resources for teaching essay writing? This section contains resources for developing in-class activities and student homework assignments. You'll find content from both well-known university writing centers and online writing labs.
Essay Writing Classroom Activities for Students
"In-class Writing Exercises" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page lists exercises related to brainstorming, organizing, drafting, and revising. It also contains suggestions for how to implement the suggested exercises.
"Teaching with Writing" (Univ. of Minnesota Center for Writing)
Instructions and encouragement for using "freewriting," one-minute papers, logbooks, and other write-to-learn activities in the classroom can be found here.
"Writing Worksheets" (Berkeley Student Learning Center)
Berkeley offers this bank of writing worksheets to use in class. They are nested under headings for "Prewriting," "Revision," "Research Papers" and more.
"Using Sources and Avoiding Plagiarism" (DePaul University)
Use these activities and worksheets from DePaul's Teaching Commons when instructing students on proper academic citation practices.
Essay Writing Homework Activities for Students
"Grammar and Punctuation Exercises" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
These five interactive online activities allow students to practice editing and proofreading. They'll hone their skills in correcting comma splices and run-ons, identifying fragments, using correct pronoun agreement, and comma usage.
"Student Interactives" (Read Write Think)
Read Write Think hosts interactive tools, games, and videos for developing writing skills. They can practice organizing and summarizing, writing poetry, and developing lines of inquiry and analysis.
This free website offers writing and grammar activities for all grade levels. The lessons are designed to be used both for large classes and smaller groups.
"Writing Activities and Lessons for Every Grade" (Education World)
Education World's page on writing activities and lessons links you to more free, online resources for learning how to "W.R.I.T.E.": write, revise, inform, think, and edit.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1924 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,556 quotes across 1924 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt
Asking analytical questions, introductions, what do introductions across the disciplines have in common, anatomy of a body paragraph, transitions, tips for organizing your essay, counterargument, conclusions.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write the Most Common Supplemental College Essays: A Complete Guide
Note: This post focuses on supplemental essays. If you want advice on the Common App prompts, check out our guide to the Common App essays .
Your grades are in, your test scores have been sent, and recommendation letters have been uploaded…but there’s one last component of your college applications left: the essays. For many students, essays are the final and most daunting hurdle to clear before hitting submit.
Your essays, however, are your opportunity to tell admissions officers how you want them to remember you. Maybe you didn’t do so well on the SAT, or maybe you got a lower grade than you hoped for in Honors Chemistry, but you can’t change your grades or scores.
The essays, however, are entirely in your control. There is so much freedom to tell your story and what makes you unique. Our mission at CollegeVine is to make the essay-writing as stress-free as possible. Read on for our tips and tricks on writing a college essay that will give you the best chance at getting that thick envelope!
Content overview:
- Why this college?
- Why this major?
- Elaborate on an extracurricular activity or work experience.
- Discuss a community you belong to that has impacted who you are today.
- Crafting the essay
- Avoiding pitfalls
Want to learn more about Supplemental Essays? Check out one of our popular recorded live streams on this topic.
Common Types of College Essays
Colleges will find a hundred different ways to ask a question, but most of the time, the prompt boils down to one of the following common essay themes.
Common Essay #1: Why this college?
Students’ most common mistake on a “Why this college?” essay is lack of specificity; in particular, some students will list attributes that can apply to multiple schools, which is what you want to avoid at all costs.
When it comes to a “Why this college?” essay, you need to discuss qualities and programs specific to that school. It is not enough to merely list or name-drop, however. Instead, talk about why this item is important to you. Here’s how this plays out:
What not to do:
I want to go to the University of Southern California because it is a highly ranked school in Los Angeles. In addition, I like its Cosmic Writers Club, as well as the Incubate USC program. I am especially excited about the abundant film resources.
Why the previous response doesn’t work:
There are many reasons you want to avoid a response like this. Let’s start with the first sentence: replace the school’s name with UCLA and the accuracy doesn’t suffer. What this means is that the sentence is not specific enough to USC. In addition, you never want to state, or even imply, that you’re applying to a school due to prestige or ranking.
The exception for the previous rule is if a school is ranked highly for a specific program of interest. For example, if you want to pursue creative writing and a school has the number one creative writing program in the country, you can mention this because it is a quality specific to that school. A school’s overall prestige, however, should not be mentioned in your essay.
Why else doesn’t this response work? Let’s look at the second sentence. The writer does well to mention specific programs within USC. However, the response fails to discuss why they liked these programs or how they would benefit from having access to them.
What to write instead:
As someone with a lasting love for writing and a blossoming passion for entrepreneurship, I was so excited to find a large urban school like the University of Southern California that would give me the resources to pursue both. From classes with award-winning authors—amongst them Professor T. Boyle, whose environmental fiction works are similar to those I hope to someday publish—to clubs like the Cosmic Writers Club, which unites author hopefuls, USC offers more resources than I could ever exhaust in my journey to publish my first book.
On the business side, USC is known for fostering the type of creativity and innovation needed in pursuing start-ups. In particular, I was so excited to learn of the Incubate USC program, a unique mothership of ideas that nurtures the creativity of students. With the help of this program, I would be able to pursue my growing interest in the world of start-up ventures.
Why the previous response works:
This response not only mentions programs and resources specific to USC, but it shows how the student would take advantage of these opportunities. In addition, this response portrays passion and ambition, infusing elements of the student’s personality while still staying focused on answering the prompt.
Other things to keep in mind:
- The first time you say the school’s name, you should write it out. After that, you can abbreviate.
- Avoid writing what every other applicant is going to write. For example, every NYU applicant is going to mention NYU’s location in New York City. Unless you have a unique twist on this, you should skip it.
- Don’t mention frivolous things like dorms or dining halls. Your reasons for liking a school should be more substantial.
- Do your research. For example, don’t say you’ve always wanted to go to a city if you’re writing an essay for a rural school.
- Do not copy and paste your “Why this college?” essay and simply change the school name. Many non-Harvard admissions officers have received essays from students about why they want to go to Harvard. If your “Why this college?” essay is so general that you can copy and paste it, your reasoning will not impress admissions officers.
For more tips on writing this essay, see our complete guide to the “Why this college?” essay , including a real sample essay.
Common Essay #2: Why this major?
One of the most important things to remember is that admissions officers are not looking for a résumé. This is not to say you can’t discuss your activities and how they culminated a passion for a specific major. The challenge, however, is to use these activities to tell a story rather than a mere list of achievements.
How do you do this? Share your thought processes. Many times it is the thoughts surrounding an activity more than the activity itself that will show the reader your journey to choosing a major.
Other tips:
- Don’t ever say that your reason for choosing a major is money-making potential. If you want to mention life beyond college, then talk about how this major will help you achieve your dreams. If your dream is to produce a feature-length film and a film major will help you get there, say that. But don’t say your dream is to be a rich film producer.
- Undeclared? That’s totally okay. Just be sure to list a couple potential majors, and explain your interest in those. Under no circumstances should you say you have absolutely no idea, as that will make you look like you don’t care. For more tips, see our post on how to write the “Why this major?” essay if you’re undecided .
For more tips on writing this essay, see our complete guide to the “Why this major?” essay , including a real sample essay.
Common Essay 3: Elaborate on an extracurricular activity or work experience.
Is there an activity or work experience in your application that you have more to say about? Maybe there’s a story behind it that you want to tell. Some questions to consider are:
- How did you become interested in this extracurricular?
- What is your role in the activity or work experience?
- Why do you do it?
- Have you experienced growth within the activity over time?
There are endless angles you can pursue here, but your essay should, in short, show your motivation behind participating in a certain activity or job.
What you don’t want to do, however, is simply restate something that’s been said elsewhere. If you have already spotlighted an activity in another essay for a given college, don’t write about the same activity. Your goal here is to share new information and your breadth of experiences.
As with the “Why Major?” prompt, it is more powerful to share a story with the reader rather than to detail the activity itself.
For more tips on writing this essay, see our complete guide to the Extracurricular Activity essay , including a real sample essay.
Common Essay 4: Discuss a community you belong to that has impacted who you are today.
“Community” can mean many things, so there are many possible approaches to this prompt. Some applicants respond with a community they’re linked to through culture, and others through sports or a club.
One thing you can emphasize is personal growth—or other aspects of who you are as a person—that has come from belonging to this community. The majority of the essay should, in fact, center around how being part of this group has changed or impacted who you are as a person.
What to avoid:
- Do not discriminate against other communities in your response.
- Try not to talk about your community in broad terms, but instead focus on your place within this community.
- Avoid using the essay as a chance to complain. If you choose to talk about challenges in a certain community, find a way to give your essay a sense of resolution. This can consist even of talking about how you’ve grown as a person or learned how to confront these obstacles in a productive way.
Writing the Essay
Phase 1: ideation.
Highlights of this section:
- Thinking of an idea
- Portraying individuality
- Staying true to yourself
- General tips and tricks
Now that you’re familiar with some of the most common types of essay prompts, let’s dive into the ideation process. Here are some questions that it’s good to ask yourself when you’re just starting out, particularly when the prompt deviates from the more straightforward archetypes above:
- What makes you unique?
- What is your story?
- Is there something you weren’t able to say in your application that you think admissions officers should know?
- Did you mention something earlier in your application that you want to elaborate on?
Remember that your essays, and application in general, should read like a portfolio in which all components are complementary without being redundant. If the application is like a drawing, then the essays should contribute to creating one coherent image without sketching the same line more than once or leaving gaps in the drawing.
Don’t shy away from being quirky! The more you present yourself as your own unique person, the more likely the admissions officer is to remember you. Take the following cases, for instance:
- A football player who scores a winning touchdown in the last five seconds of the game.
- A football player who knits scarves for residents of a retirement home in his free time.
In the first case, telling this story doesn’t do anything to differentiate this football player from others. However, the second story portrays a unique student with two interests the reader might not otherwise have paired together. Individuality is the goal here.
Of course, don’t exaggerate , lie, or pretend to be someone you’re not. In particular, don’t write something just because you think the admissions officer wants to hear it. They have read enough applications to separate the genuine voices from the insincere. As such, your only job is to put your true self on the page!
Here are some other things to keep in mind while brainstorming college essay topics:
- Narratives will always be more successful because they engage the reader emotionally. They are also an easy way to demonstrate how you’ve changed and grown over time.
- If you have already emphasized something in your application, don’t dedicate an essay to it unless can share an entirely new perspective. When in doubt, choose a new topic.
- Your essay doesn’t have to be about something rare and incredible. You don’t have to have started a company or traveled the world to write a solid essay. In fact, some of the strongest essays have taken a simple, perhaps even everyday occurrence, and portrayed it in a beautiful way that shows a unique way of thinking.
- Be sure to answer all aspects of the prompt while still giving the reader insight into who you are. It’s very easy to speak about some topics in third-person or broad terms (example: “What is your idea of success?”). Don’t do this. Instead, find a way to link the prompt to your own life.
Overall, think of the essays as a way to let the admissions officer get to know you on a personal level. Humanize yourself.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.
Phase 2: Crafting the Essay
- Show, don’t tell.
- Perfecting the first and last sentence
- What does the essay say about me?
You have likely heard this next tip a hundred times throughout high school, but it’s vital to writing a strong essay: show, don’t tell . The whole point of essays is to give insight into who you are and how you think. Can you effectively do that if you’re merely listing off things that happened? Nope. Let’s take a lot at two examples:
- An example of telling: The cat ran out the door, and I got scared.
- An example of showing: The doorbell rang, accompanied by the creak of the mailbox as the mailman slipped the day’s envelopes inside. I ran downstairs and threw the door open, knowing today was the day I was going to hear back. My excitement made me oblivious, though, and it wasn’t until I saw a blur of dark fur dash through the open door that I realized my mistake.
The second example takes the facts and turns it into a story. It gives the reader a sense of anticipation as well as a character to identify with and root for. That’s what “show, don’t tell” does for your essay.
Now let’s talk about the two most important parts of your essay: the first sentence and the last sentence.
Your first sentence’s job is to hook the reader. Aim for a first sentence that surprises, even slightly jars, the reader to wake them up and get their full focus on your essay. Here are some examples:
- It wasn’t supposed to be blue.
- Was the car meant to sound like that?
In both cases, the writer has intentionally withheld information, providing just enough to leave the reader wanting to know the rest of the story. What isn’t supposed to be blue? What happens next?
As for the last sentence, its job is to resolve the essay, leaving the reader with a sense of peace and finality. Give the reader one last great impression to remember you by. Here’s an example:
“I’ve learned to hold my failures close; not so close that they burden me, per say, but just
close enough that they can guide me as I journey onward.”
This sentence works because it gives the reader a sense that, though the story continues on in the form of the narrator’s ongoing journey, the story on the page has been resolved. It feels peaceful.
Now then, after you’ve completed your first draft, the next thing you want to do is ask yourself the following question : What three things about me can the reader get from reading this essay? If you’re having trouble answering this question, then the essay needs to share more about you. Otherwise, you’re ready for revision!
Phase 3: Revision
- Careless errors
- Staying under the word limit
- Getting a second opinion
You’ve done the hard work. You came up with a brilliant idea and poured your heart and soul into the writing. Now comes the tedious part: revision.
Most importantly, college essays need to be absolutely devoid of grammatical or spelling mistakes . You don’t want to give your admissions officer the impression that you didn’t care enough to proofread, especially after all of your hard work.
Another aspect that tends to frustrate students is the word limit. If you’ve made it under the word limit, great! If not, here are some methods of cutting down.
- Example: In visiting your campus, it occurred to me that the method with which you schedule your classes is ideal because…
- This can be cut down to: The way you schedule your classes is ideal because…
- Most times phrases such as “I think,” “I believe,” “it seems,” and other similar wording is not necessary and simply takes up extra space. Use your judgement, but generally, these phrases get the boot.
- Keep an eye out for the word “that.” This can almost always be cut.
- If you use a long hyphen (—), no space is needed between words. This will bring your word count down. Don’t get too hyphen happy, though!
If the above tips are not enough to get you below the word limit, you may need to remove entire paragraphs. If a paragraph does not drive the story forward, or is unnecessary in understanding the progression of the story, you may want to remove it.
Once your essay is mistake-free and below the word limit, your next task is to send it to at least three trusted individuals. Ask them the following questions to guide their suggestions:
- Does it make sense?
- Does it sound like me?
- What does it say about me? (Check that this aligns with what you want it to say about you).
Take note of their responses and decide what changes you want to implement. Be receptive, but remember to stay true to yourself and your vision.
Avoiding Pitfalls:
- Avoid discussion of taboo subjects or things that can be perceived as controversial. Everyone is entitled to their own views, but you don’t want to chance saying something controversial that your reader might disagree with.
- Never appear discriminatory in any way. Colleges tend to be vastly left-wing and progressive.
- Don’t turn in work that isn’t your own. When does accepting another person’s edits become plagiarism? If they are rewriting entire sentences in their own words, it is no longer your own work.
- Avoid clichés! It is okay to write about a common experience (like a sports injury or service trip), but only if you have a unique take on them. Don’t write on a popular topic if you will simply describe the same lesson that everyone else learned.
- Don’t write your essay directly into the application text box or it may not save your work. Write it in a separate document and copy and paste it later. Then, double check that the format is correct.
At the end of the day, your essays should just leave the reader thinking: I want to have a conversation with this student. You want to show that you’re an multifaceted, mature person with an interesting story to tell. At CollegeVine, we’re rooting for you all the way—go get writing!
Want help with your college essays to improve your admissions chances? Sign up for your free CollegeVine account and get access to our essay guides and courses. You can also get your essay peer-reviewed and improve your own writing skills by reviewing other students’ essays.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

A Complete Essay Format Guide
25 June, 2020
11 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
So, you’ve crafted your essay. Congratulations! The hard part is truly over. Now comes the time to choose the proper essay format. It is no longer about your content, but rather about the way you arrange it. You do it to meet your school’s requirements.
In this guide, we will focus on common formatting styles:
- APA essay format;
- MLA essay format;
- Harvard format essay, and
- Chicago essay format.
So, without further ado, let’s get right to business.
What is an Essay Format?
An essay format is the structure and the general guidelines of an essay that keep its content organized and well-structured.
The primary purpose of the college essay format is to help the readers follow main ideas behind the content without stumbling upon its structure. It is not a daunting task to deal with. It is a great way to organize your thoughts for the target audience to understand what you were trying to say in the first place.
Moreover, at least 10% of your grade depends on the proper essay format . Thus, it is in your best interests to stick to the guidelines and use correct essay format.
And it is also true in case you want to get into a college of your dream. Half of the success is in proper college application essay format. So, don’t miss your chance!
Educational institutions require different essay formats. Therefore, to get the highest grades, one must know the difference between types of essay formats and follow the guidelines when working on a piece.
In just a bit, you will find out the difference between the APA, Chicago, Harvard, and MLA format for essays.
Types of Essay Formats
Here are four most common types of essay formats, as we have mentioned above.
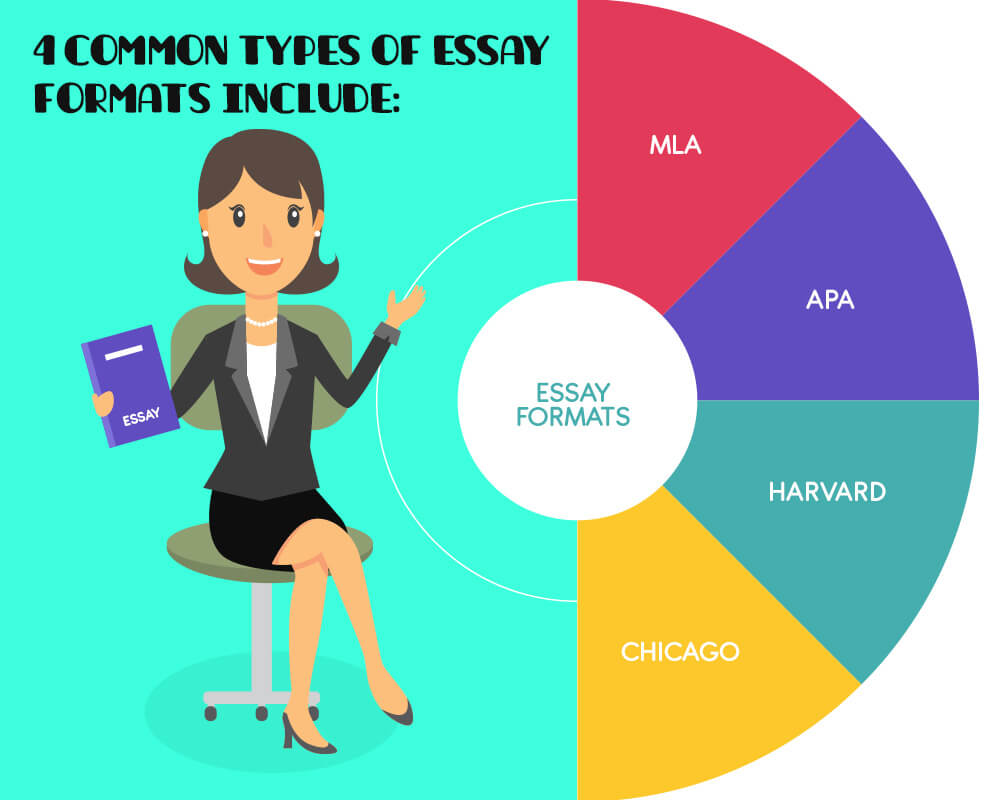
They all have their specifics, and each school has its own requirements. However, MLA remains the top essay format. We don’t say that it’s the best essay writing format. However, it is the most popular one.
And unless you have clear instructions on what essay format to use in your paper, you’d rather opt for an MLA format essay.
The essay format style has nothing to do with the complexity of your paper. The argumentative essay format at your school depends on the preferences of your tutors, not on the academic level of the paper. So, don’t fall victim to this silly idea.
How to Format a College Essay

To get the highest grade, a student has to know how to format an essay in accordance with these requirements. Here’s an example of how essay formats might differ.
The Difference Between MLA and APA Essay Formats
We’ll give more details on each of these essay formats later in the guide, but for now, let’s see what differences one should know about when it comes to these two formats.
- The list of works used in the paper is called differently in APA and MLA formats (“ References ” and “ Works cited ” respectively). And even though both of them list works used in the essay alphabetically, with MLA, the name of the author is written in full, while with the APA, only the first letter of his name is mentioned following the last name.
- In general, APA essay format is mostly used in papers on social studies , while the MLA essay format is typically the top choice for other subjects .
- Finally, in case you are adding citations inside the text and mention the author within the quote, MLA essay format requires you to add a number of the page you found the quote on at the end of the sentence while in case of the APA essay format you need to mention the year . Here is an APA format essay example with the quote: “Bill Gates (1985) stated that young people would have no problem finding a good job as long as they view computers as tools.”
These might seem like insignificant differences. Yet, when it comes to grading your paper, the tutor will look closely at each of these essay format requirements to see how well you did your homework.
Now that you understand the differences between MLA and APA essay formats let’s go into specifics of each one of them.
How to Write an Essay in MLA Format
The basic guidelines for the MLA essay format are the following:
- Font : Times New Roman
- Size of the font : 12pt
- Margins : 1-inch margin on all the sides of the pape
- Header : Each page should have a header that will contain the author’s last name and a page number
- Alignment : To the left-hand side
- Spacing : Double
- Indentation : Yes, at the beginning of each paragraph
- Title : The title comes on the first page at the same font size as the rest of the text, only aligned to the center of the page.
- Footnotes : Not required
When explaining to you how to start an essay in MLA format, we have to mention that every piece begins with a heading. Place it in the upper right corner, and make sure to include the following facts into it:
- Your first and last name;
- Your tutor’s (or professor’s) name;
- The course you’re taking;
Here is a good MLA essay format example of the headline:
“Mark Snow Jonathan Brown Psychology September 24, 2018.”
If you need more information on the MLA essay format , check our recent guide on this topic.
How to Write an Essay in APA Format
This essay format is also quite common. Its main requirements include but are not limited to:
- Margins : 1-inch margin on all the sides of the paper
- Header : Each page should have a header that will contain the title of the paper and a page number. Note that in this essay format the title cannot exceed 50 characters.
- Title : The title comes on the first page at the same font size as the rest of the text. With it, according to this essay format guidelines, a student must mention his full name and the educational establishment he is currently studying at.
In this case, the APA essay format example of the cover page will look like this:
“Foreign Language Education: How to Teach English to Adults” Mark Snow Yale University”
To find more details on this essay format, please read our complete guide to APA essay format .
Chicago Style Essay Format
Requirements for this essay format include but are not limited to:
- Font : Times New Roman (unless your tutor specified a different one)
- Font size : 12pt
- Margins : 1-inch margins on sides, top, and bottom;
- Header : Each page should have a page number at the top right corner and your last name. Don’t put a number on the title page.
- Indentation : 1/2″ indent for paragraph beginnings
- Footnotes : Required
A title page in case of this essay format starts with a title of your paper placed ¼ page down from the top. Then ½ page down from top comes your full name followed by the course number, the name of the professor and due date at the bottom of the page. You should write each of these points in separate lines with double spacing.
Take a look at this essay format example of a cover page if you need brighter examples to clarify the subject.

Harvard Format
Last but not least is the Harvard essay format . Here are the requirements for this essay writing format:
- Font : Times New Roman or Arial
- Header : Each page should have a short version of the paper’s title and a page number in the top right corner with exactly five spaces in between them.
- Alignment : To the left-hand side.
The cover page in the Harvard essay format is very specific.
The title of your essay should be capitalized and written ½ page down. Then you have to go three lines down to place the author of the work (no capitalization here). From there, you have to go four more lines down to mention the class you are taking first and the tutor’s full name in the next line. Finally, this essay format requires you to specify the name of the educational establishment, its location, and the due date in the following lines.
It doesn’t matter what paper you are writing using this essay format. The structure stays the same.
Here is an example of the compare and contrast essay format. Feast your eyes on it:

Essay Outline Format
Apart from sticking to the requirements of these essay formats, students should also pay close attention to following the essay writing guidelines when it comes to its outline.
Thus, the scholarship essay format, as well as the persuasive essay format, are only considered correct if the text contains all the essential components.
Any essay should have the following structure.

Related Posts: Essay outline | Research Paper outline
Over to You
These are four common essay formats every student should know. Use this guide as a cheat sheet whenever needed.
And in case you don’t want to deal with essay formats, you can always trust us with this important task. Our Online Essay Writer service is your best choice when it comes to excellent essay writing services and perfect essay format.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
Essay Writing Guide
Essay Writing
Last updated on: Jun 8, 2023
How to Write an Essay - A Complete Guide with Examples
By: Nova A.
13 min read
Reviewed By: Rylee W.
Published on: Jan 1, 2019

Are you finding yourself staring at a blank page, unsure of where to begin when it comes to writing an essay?
Do you struggle with organizing your thoughts and expressing your ideas effectively?
You're not alone!
Many students face challenges when it comes to essay writing, but fear not!
In this comprehensive guide, we will help you in writing impactful essays with confidence. From choosing a compelling topic to crafting a well-structured argument, we'll take you step-by-step through the essay writing process.
So, get ready to become a skilled essay writer in no time!

On this Page
Pre-Writing Process: Preparation and Planning
Building a strong foundation is key to crafting a stellar essay. The pre-writing process sets the stage for your essay by focusing on preparation and planning.
Understand the Essay Prompt or Topic
Before diving into the writing process, it is crucial to choose and thoroughly understand the essay topic .
Carefully read and analyze the requirements, instructions, and any specific guidelines provided.
Identify the key components of the prompt, such as:
- The main question or issue to be addressed
- The scope of the topic
- Any specific requirements for the essay
Choose the Type of Essay
The next step is to decide which type of essay you need to write. Choosing the correct type of essay is an important step toward your successful essay.
Here are the main types of essays in which every academic essay can be categorized.
- Descriptive Essay - A descriptive essay discusses the topic in detail so that it becomes easy to understand for the reader.
- Narrative Essay - A narrative essay is a narration of a story in the form of an essay.
- Persuasive Essay - A persuasive essay convinces the reader to accept your perspective about the essay topic.
- Expository Essay - An expository essay explains and clarifies the topic with great details and examples.
Knowing what type of essay you are required to write can help you choose the topic and draft the essay. Here are the other types of essays that you should also be familiar with.
- Argumentative essay
- Analytical essay
- Cause and effect essay
- Classification essay
- Synthesis essay
- Compare and Contrast Essay
Conduct Thorough Research
Once you have a clear understanding of the essay prompt, it's time to gather relevant information through research.
Utilize various sources such as scholarly articles and academic databases to gather information that will support your arguments.
Also decide what type of formatting and citation styles you need for your essay. Generally, the following are some common college essay writing styles for students:
- APA (American Psychological Association) - An Author-Date citation style designed for psychology and social science discipline.
- MLA (Modern Language Association) - An Author-Page number citation style designed for language and humanities disciplines.
- CMS (Chicago Manual of Style) - A Notes-bibliography or Author-Date citation style, also known as Turabian Style. It is applicable to both scientific and non-scientific disciplines.
Create an Outline to Structure Your Essay
An outline acts as a skeleton for your essay, providing a structured framework to guide your writing. It helps you with how to write essay format questions and ensure that your essay flows logically and coherently.
Start by organizing your main ideas or subtopics into sections or paragraphs. Then, under each main idea, list the supporting points, evidence, or examples you will include.
Wondering how to write an outline for an essay ? Here is a 5 paragraph essay outline structure.
Writing Process: Crafting Your Essay
The writing process includes engaging introduction, body and conclusion. Let’s get through the step by step for crafting each section.
Write the Introduction
An introduction paragraph is the first paragraph of your essay. The purpose of the introduction is to inform your reader about the topic that you will discuss in the essay.
If you are thinking how to write an essay introduction, here is what an engaging introduction includes:
Engaging Hook
To capture the reader's attention from the start, consider using a compelling hook .
This can be a thought-provoking question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an intriguing anecdote.
The goal is to create curiosity and make the reader eager to continue reading.
Background Information
After grabbing the reader's attention, provide some context or background information related to your essay topic.
This will help the reader understand the significance and relevance of the subject matter.
It can include historical context, relevant statistics, or an overview of the current state of affairs.
Thesis Statement
Conclude the introduction with a clear and concise thesis statement that encapsulates the main argument or purpose of your essay.
The thesis statement should reflect the stance you will be taking and provide a roadmap for the subsequent body paragraphs.
Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs are the linking paragraphs between the conclusion and introduction.
All the information, examples, facts, and details about the topic in this section ultimately support your thesis statement.
Topic Sentences and Supporting Arguments
In each body paragraph, start with a topic sentence that introduces the main point or argument.
Each topic sentence should be clear and specific, guiding the reader on what to expect in the paragraph.
Follow up with supporting arguments or ideas that expand on the topic sentence and provide evidence or examples to support your claims.
Using Evidence and Examples
To strengthen your arguments, include relevant evidence, examples, or data. This could be in the form of research findings, expert opinions, real-life scenarios, or personal experiences.
Ensure that the evidence directly supports your claims and helps convince the reader of your point of view.
Use Clear Transitions
Maintain a logical flow within and between paragraphs by using clear transitions.
Transitions help connect ideas and create a smooth transition from one point to another. This ensures that your essay is cohesive and easy to follow.
Use transition words and phrases such as "furthermore," "in addition," "on the other hand," and "in contrast" to signal shifts in ideas and create a seamless reading experience.
Conclusion
The conclusion is the last paragraph that summarizes the main theme of the essay and its outcomes. It should include:
Summarize Key Points
In the conclusion, provide a brief summary of the key points discussed in the body paragraphs. Remind the reader of the main arguments and evidence presented throughout the essay.
Restate the Thesis Statement
Reiterate the thesis statement but rephrase it or present it in a slightly different manner. This helps reinforce the central message and reminds the reader of the main focus of the essay.
Call-to-Action/ Impression
End the conclusion with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action. This could be a reflection on the broader implications of the topic, a suggestion for further research, or a call to action.
Post-Writing Process: Editing and Refining
After writing your essay, make sure you:
Proofread for Grammar and Spelling Errors
After completing the initial draft of your essay, it's crucial to thoroughly proofread it for any grammatical, spelling, or punctuation errors.
This step ensures that your writing is clear, polished, and professional.
Check for Clarity and Coherence
Read through your essay with a critical eye, examining the flow of ideas and the logical progression of arguments.
Ensure that each paragraph and sentence contributes to the overall coherence of the essay.
Look for any gaps in information or abrupt transitions and revise accordingly to enhance the clarity and readability of your essay.


Essay Checklist
Writing an essay requires careful attention to various aspects, ranging from content to structure, grammar, and formatting.
Use the following checklist to ensure that your essay meets the necessary requirements and is of high quality.
How to Write an Essay - Examples
There are several different categories of essays, each with its unique requirements. Each essay presents different information in different ways.
Here are some useful how-to-write essay samples for different types of essays that will help you write your essay.
HOW TO WRITE AN ACADEMIC ESSAY - EXAMPLE
HOW TO WRITE AN ARGUMENTATIVE ESSAY - EXAMPLE
HOW TO WRITE A NARRATIVE ESSAY - EXAMPLE
HOW TO WRITE A DESCRIPTIVE ESSAY - EXAMPLE
How to Write an Essay About Yourself
Tips for Effective Essay Writing
Writing an essay can be a challenging task, but with the right approach, you can create a compelling and well-crafted piece of work.
Here are some tips to help you improve your essay-writing skills:
- Understand the essay prompt: Carefully read and comprehend the essay prompt to ensure your essay stays focused.
- Plan and outline your essay: Create a clear outline to provide structure and coherence to your essay.
- Conduct thorough research: Gather reliable information from credible sources to support your arguments.
- Develop a strong thesis statement: Craft a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your writing.
- Write clear and concise paragraphs: Focus each paragraph on a single main idea and use concise language.
- Use evidence and examples: Support your claims with evidence, examples, and proper citations.
- Revise and edit: Review for clarity, coherence, grammar, and formatting errors.
- Seek feedback: Get input from others to gain valuable insights and suggestions for improvement.
- Practice writing regularly: Regular practice helps improve your writing skills and style.
- Manage your time: Take breaks and allocate time effectively for each stage of the writing process.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing an Essay
As a beginner, there are high chance that you make mistakes while writing your essay. However, you can avoid them by working on some basics.
Below we have mentioned some common errors made by the non-natives.
- Using passive voice
- Adding complex sentences
- Adding improper or no transitional sentences
- Plagiarism
- Failing to follow the assignment instructions
- Ignoring pronoun subjective-objective agreement
- Improper or missing citation references
- Citing unreliable resources
You can also check this detailed video guide on what to avoid while writing an essay!
Make sure you avoid these mistakes to make your piece of writing impactful. However, if you are not sure about your essay writing skills, getting professional help is a good idea.
Let expert writers at 5StarEssays.com assist you with “ write my essay for me ” worries!
Get professional help with your essays and research papers to achieve academic success.
Contact us now to experience the difference our essay writing service can make. Don't wait, start writing exceptional essays today!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do i start writing an essay.
To start writing an essay, begin by understanding the essay prompt or topic. Conduct research to gather relevant information and develop a clear thesis statement. Create an outline to organize your thoughts and structure your essay.
What are the 5 parts of an essay?
The five parts of an essay include:
- Introduction
- Body Paragraphs
- Transitions
- References or Bibliography

Marketing, Literature
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- The Art of Effective Writing: Thesis Statements Examples and Tips

- Writing a 500 Word Essay - Easy Guide

- What is a Topic Sentence - An Easy Guide with Writing Steps & Examples

- A Complete Essay Outline - Guidelines and Format

- 220 Best Transition Words for Essays

- Essay Format: Detailed Writing Tips & Examples

- How to Write a Conclusion - Examples & Tips

- Essay Topics: 100+ Best Essay Topics for your Guidance

- How to Title an Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide for Effective Titles

- How to Write a Perfect 1000 Word Essay

- How To Make An Essay Longer - Easy Guide For Beginners

- Learn How to Start an Essay Effectively with Easy Guidelines

- Types of Sentences With Examples

- Hook Examples: How to Start Your Essay Effectively

- Essay Writing Tips - Essential Do’s and Don’ts to Craft Better Essays

- How To Write A Thesis Statement - A Step by Step Guide

- Art Topics - 200+ Brilliant Ideas to Begin With

- Writing Conventions and Tips for College Students

People Also Read
- ieee citation guide
- college application essay format
- exemplification essay
- debate topics
- poetry writing
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved

- Test Preparation
- College & High School

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.
Buy new: .savingPriceOverride { color:#CC0C39!important; font-weight: 300!important; } .reinventMobileHeaderPrice { font-weight: 400; } #apex_offerDisplay_mobile_feature_div .reinventPriceSavingsPercentageMargin, #apex_offerDisplay_mobile_feature_div .reinventPricePriceToPayMargin { margin-right: 4px; } $14.99 $ 14 . 99 FREE delivery Monday, May 20 on orders shipped by Amazon over $35 Ships from: Amazon.com Sold by: Amazon.com
Return this item for free.
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method
Save with Used - Good .savingPriceOverride { color:#CC0C39!important; font-weight: 300!important; } .reinventMobileHeaderPrice { font-weight: 400; } #apex_offerDisplay_mobile_feature_div .reinventPriceSavingsPercentageMargin, #apex_offerDisplay_mobile_feature_div .reinventPricePriceToPayMargin { margin-right: 4px; } $2.54 $ 2 . 54 $3.99 delivery May 20 - 24 Ships from: Goodwill of Colorado Sold by: Goodwill of Colorado

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Follow the author

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player

The Complete College Essay Handbook: A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing the Personal Statement and the Supplemental Essays Paperback – July 19, 2021
Purchase options and add-ons.
Want to write memorable college application essays in less time, with less stress? This book will guide you through the process, with hands-on activities, practical tips, and tons of real application essays—personal statements and supplemental essays—by real students!
Finally—the book you’ve been waiting for! The Complete College Essay Handbook demystifies the entire college essay writing process with easy-to-follow directions and hands-on activities that have worked for hundreds of students. Maschal, a former admissions officer, and Wood, a professional writer and writing teacher, draw on their combined expertise to help students craft a successful set of application essays for every school on their list. Supplemental essays in particular can seem overwhelming—some schools ask students to write as many as six essays in addition to the personal statement. Maschal and Wood identify four types of supplemental essays, walking students through how to write each one and then how to recycle these essays for other schools.
The Complete College Essay Handbook walks students through:
- What makes an essay stand out, drawing on sample essays by real students to illustrate main points
- Brainstorming activities to find the best topics for the personal statement and supplemental essays
- How to write the two central components of every application essay: scene and reflection
- Editing and revision—including techniques to cut down or expand an essay to hit the word limit
- The four types of supplemental essays and how to decode the different essay prompts, using actual essay questions
- The strategy behind a well-rounded set of application essays
The Complete College Essay Handbook is a no-frills, practical guide that will give students the confidence and know-how they need to craft the best essays for every single school on their list—in less time and with less stress.
This book is for students, high school teachers and counselors, parents, and anyone else who wants to help students through the college essay writing process.
- Print length 212 pages
- Language English
- Publication date July 19, 2021
- Dimensions 6 x 0.48 x 9 inches
- ISBN-10 173731598X
- ISBN-13 978-1737315988
- See all details

Frequently bought together

Customers who bought this item also bought

Product details
- Publisher : 1 (July 19, 2021)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 212 pages
- ISBN-10 : 173731598X
- ISBN-13 : 978-1737315988
- Item Weight : 11.7 ounces
- Dimensions : 6 x 0.48 x 9 inches
- #437 in College Guides (Books)
- #567 in College Entrance Test Guides (Books)
About the author
Brittany maschal.
Dr. Brittany Maschal is the founder of Brittany Maschal Consulting, LLC, an educational consulting firm that works with students applying to college and graduate school.
Brittany has held positions in admissions and student services at the University of Pennsylvania at Penn Law and The Wharton School; Princeton University (undergraduate) and the Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs; and the Johns Hopkins University-Paul H. Nitze School of Advanced International Studies (SAIS). She has served on admissions committees with American Councils for International Education and International Research and Exchanges Board; as an invited speaker to numerous community programs in the US and abroad; and as an alumni interviewer and admissions representative for the Graduate School of Education at the University of Pennsylvania. Brittany was also an Executive Board member and Membership Director of the Penn GSE Alumni Association.
Brittany received her doctorate in higher education from the George Washington University in 2012. Prior, she attended the University of Pennsylvania for her master’s, and the University of Vermont for her bachelor’s degree—a degree she obtained in three years. Brittany is a member of the Independent Educational Consultants Association and a member of the Professional Association of Resume Writers and Career Coaches.
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
Reviews with images

- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the complete ib extended essay guide: examples, topics, and ideas.
International Baccalaureate (IB)

IB students around the globe fear writing the Extended Essay, but it doesn't have to be a source of stress! In this article, I'll get you excited about writing your Extended Essay and provide you with the resources you need to get an A on it.
If you're reading this article, I'm going to assume you're an IB student getting ready to write your Extended Essay. If you're looking at this as a potential future IB student, I recommend reading our introductory IB articles first, including our guide to what the IB program is and our full coverage of the IB curriculum .
IB Extended Essay: Why Should You Trust My Advice?
I myself am a recipient of an IB Diploma, and I happened to receive an A on my IB Extended Essay. Don't believe me? The proof is in the IBO pudding:
If you're confused by what this report means, EE is short for Extended Essay , and English A1 is the subject that my Extended Essay topic coordinated with. In layman's terms, my IB Diploma was graded in May 2010, I wrote my Extended Essay in the English A1 category, and I received an A grade on it.
What Is the Extended Essay in the IB Diploma Programme?
The IB Extended Essay, or EE , is a mini-thesis you write under the supervision of an IB advisor (an IB teacher at your school), which counts toward your IB Diploma (learn more about the major IB Diploma requirements in our guide) . I will explain exactly how the EE affects your Diploma later in this article.
For the Extended Essay, you will choose a research question as a topic, conduct the research independently, then write an essay on your findings . The essay itself is a long one—although there's a cap of 4,000 words, most successful essays get very close to this limit.
Keep in mind that the IB requires this essay to be a "formal piece of academic writing," meaning you'll have to do outside research and cite additional sources.
The IB Extended Essay must include the following:
- A title page
- Contents page
- Introduction
- Body of the essay
- References and bibliography
Additionally, your research topic must fall into one of the six approved DP categories , or IB subject groups, which are as follows:
- Group 1: Studies in Language and Literature
- Group 2: Language Acquisition
- Group 3: Individuals and Societies
- Group 4: Sciences
- Group 5: Mathematics
- Group 6: The Arts
Once you figure out your category and have identified a potential research topic, it's time to pick your advisor, who is normally an IB teacher at your school (though you can also find one online ). This person will help direct your research, and they'll conduct the reflection sessions you'll have to do as part of your Extended Essay.
As of 2018, the IB requires a "reflection process" as part of your EE supervision process. To fulfill this requirement, you have to meet at least three times with your supervisor in what the IB calls "reflection sessions." These meetings are not only mandatory but are also part of the formal assessment of the EE and your research methods.
According to the IB, the purpose of these meetings is to "provide an opportunity for students to reflect on their engagement with the research process." Basically, these meetings give your supervisor the opportunity to offer feedback, push you to think differently, and encourage you to evaluate your research process.
The final reflection session is called the viva voce, and it's a short 10- to 15-minute interview between you and your advisor. This happens at the very end of the EE process, and it's designed to help your advisor write their report, which factors into your EE grade.
Here are the topics covered in your viva voce :
- A check on plagiarism and malpractice
- Your reflection on your project's successes and difficulties
- Your reflection on what you've learned during the EE process
Your completed Extended Essay, along with your supervisor's report, will then be sent to the IB to be graded. We'll cover the assessment criteria in just a moment.

We'll help you learn how to have those "lightbulb" moments...even on test day!
What Should You Write About in Your IB Extended Essay?
You can technically write about anything, so long as it falls within one of the approved categories listed above.
It's best to choose a topic that matches one of the IB courses , (such as Theatre, Film, Spanish, French, Math, Biology, etc.), which shouldn't be difficult because there are so many class subjects.
Here is a range of sample topics with the attached extended essay:
- Biology: The Effect of Age and Gender on the Photoreceptor Cells in the Human Retina
- Chemistry: How Does Reflux Time Affect the Yield and Purity of Ethyl Aminobenzoate (Benzocaine), and How Effective is Recrystallisation as a Purification Technique for This Compound?
- English: An Exploration of Jane Austen's Use of the Outdoors in Emma
- Geography: The Effect of Location on the Educational Attainment of Indigenous Secondary Students in Queensland, Australia
- Math: Alhazen's Billiard Problem
- Visual Arts: Can Luc Tuymans Be Classified as a Political Painter?
You can see from how varied the topics are that you have a lot of freedom when it comes to picking a topic . So how do you pick when the options are limitless?

How to Write a Stellar IB Extended Essay: 6 Essential Tips
Below are six key tips to keep in mind as you work on your Extended Essay for the IB DP. Follow these and you're sure to get an A!
#1: Write About Something You Enjoy
You can't expect to write a compelling essay if you're not a fan of the topic on which you're writing. For example, I just love British theatre and ended up writing my Extended Essay on a revolution in post-WWII British theatre. (Yes, I'm definitely a #TheatreNerd.)
I really encourage anyone who pursues an IB Diploma to take the Extended Essay seriously. I was fortunate enough to receive a full-tuition merit scholarship to USC's School of Dramatic Arts program. In my interview for the scholarship, I spoke passionately about my Extended Essay; thus, I genuinely think my Extended Essay helped me get my scholarship.
But how do you find a topic you're passionate about? Start by thinking about which classes you enjoy the most and why . Do you like math classes because you like to solve problems? Or do you enjoy English because you like to analyze literary texts?
Keep in mind that there's no right or wrong answer when it comes to choosing your Extended Essay topic. You're not more likely to get high marks because you're writing about science, just like you're not doomed to failure because you've chosen to tackle the social sciences. The quality of what you produce—not the field you choose to research within—will determine your grade.
Once you've figured out your category, you should brainstorm more specific topics by putting pen to paper . What was your favorite chapter you learned in that class? Was it astrophysics or mechanics? What did you like about that specific chapter? Is there something you want to learn more about? I recommend spending a few hours on this type of brainstorming.
One last note: if you're truly stumped on what to research, pick a topic that will help you in your future major or career . That way you can use your Extended Essay as a talking point in your college essays (and it will prepare you for your studies to come too!).
#2: Select a Topic That Is Neither Too Broad nor Too Narrow
There's a fine line between broad and narrow. You need to write about something specific, but not so specific that you can't write 4,000 words on it.
You can't write about WWII because that would be a book's worth of material. You also don't want to write about what type of soup prisoners of war received behind enemy lines, because you probably won’t be able to come up with 4,000 words of material about it. However, you could possibly write about how the conditions in German POW camps—and the rations provided—were directly affected by the Nazis' successes and failures on the front, including the use of captured factories and prison labor in Eastern Europe to increase production. WWII military history might be a little overdone, but you get my point.
If you're really stuck trying to pinpoint a not-too-broad-or-too-narrow topic, I suggest trying to brainstorm a topic that uses a comparison. Once you begin looking through the list of sample essays below, you'll notice that many use comparisons to formulate their main arguments.
I also used a comparison in my EE, contrasting Harold Pinter's Party Time with John Osborne's Look Back in Anger in order to show a transition in British theatre. Topics with comparisons of two to three plays, books, and so on tend to be the sweet spot. You can analyze each item and then compare them with one another after doing some in-depth analysis of each individually. The ways these items compare and contrast will end up forming the thesis of your essay!
When choosing a comparative topic, the key is that the comparison should be significant. I compared two plays to illustrate the transition in British theatre, but you could compare the ways different regional dialects affect people's job prospects or how different temperatures may or may not affect the mating patterns of lightning bugs. The point here is that comparisons not only help you limit your topic, but they also help you build your argument.
Comparisons are not the only way to get a grade-A EE, though. If after brainstorming, you pick a non-comparison-based topic and are still unsure whether your topic is too broad or narrow, spend about 30 minutes doing some basic research and see how much material is out there.
If there are more than 1,000 books, articles, or documentaries out there on that exact topic, it may be too broad. But if there are only two books that have any connection to your topic, it may be too narrow. If you're still unsure, ask your advisor—it's what they're there for! Speaking of advisors...

Don't get stuck with a narrow topic!
#3: Choose an Advisor Who Is Familiar With Your Topic
If you're not certain of who you would like to be your advisor, create a list of your top three choices. Next, write down the pros and cons of each possibility (I know this sounds tedious, but it really helps!).
For example, Mr. Green is my favorite teacher and we get along really well, but he teaches English. For my EE, I want to conduct an experiment that compares the efficiency of American electric cars with foreign electric cars.
I had Ms. White a year ago. She teaches physics and enjoyed having me in her class. Unlike Mr. Green, Ms. White could help me design my experiment.
Based on my topic and what I need from my advisor, Ms. White would be a better fit for me than would Mr. Green (even though I like him a lot).
The moral of my story is this: do not just ask your favorite teacher to be your advisor . They might be a hindrance to you if they teach another subject. For example, I would not recommend asking your biology teacher to guide you in writing an English literature-based EE.
There can, of course, be exceptions to this rule. If you have a teacher who's passionate and knowledgeable about your topic (as my English teacher was about my theatre topic), you could ask that instructor. Consider all your options before you do this. There was no theatre teacher at my high school, so I couldn't find a theatre-specific advisor, but I chose the next best thing.
Before you approach a teacher to serve as your advisor, check with your high school to see what requirements they have for this process. Some IB high schools require your IB Extended Essay advisor to sign an Agreement Form , for instance.
Make sure that you ask your IB coordinator whether there is any required paperwork to fill out. If your school needs a specific form signed, bring it with you when you ask your teacher to be your EE advisor.
#4: Pick an Advisor Who Will Push You to Be Your Best
Some teachers might just take on students because they have to and aren't very passionate about reading drafts, only giving you minimal feedback. Choose a teacher who will take the time to read several drafts of your essay and give you extensive notes. I would not have gotten my A without being pushed to make my Extended Essay draft better.
Ask a teacher that you have experience with through class or an extracurricular activity. Do not ask a teacher that you have absolutely no connection to. If a teacher already knows you, that means they already know your strengths and weaknesses, so they know what to look for, where you need to improve, and how to encourage your best work.
Also, don't forget that your supervisor's assessment is part of your overall EE score . If you're meeting with someone who pushes you to do better—and you actually take their advice—they'll have more impressive things to say about you than a supervisor who doesn't know you well and isn't heavily involved in your research process.
Be aware that the IB only allows advisors to make suggestions and give constructive criticism. Your teacher cannot actually help you write your EE. The IB recommends that the supervisor spends approximately two to three hours in total with the candidate discussing the EE.
#5: Make Sure Your Essay Has a Clear Structure and Flow
The IB likes structure. Your EE needs a clear introduction (which should be one to two double-spaced pages), research question/focus (i.e., what you're investigating), a body, and a conclusion (about one double-spaced page). An essay with unclear organization will be graded poorly.
The body of your EE should make up the bulk of the essay. It should be about eight to 18 pages long (again, depending on your topic). Your body can be split into multiple parts. For example, if you were doing a comparison, you might have one third of your body as Novel A Analysis, another third as Novel B Analysis, and the final third as your comparison of Novels A and B.
If you're conducting an experiment or analyzing data, such as in this EE , your EE body should have a clear structure that aligns with the scientific method ; you should state the research question, discuss your method, present the data, analyze the data, explain any uncertainties, and draw a conclusion and/or evaluate the success of the experiment.
#6: Start Writing Sooner Rather Than Later!
You will not be able to crank out a 4,000-word essay in just a week and get an A on it. You'll be reading many, many articles (and, depending on your topic, possibly books and plays as well!). As such, it's imperative that you start your research as soon as possible.
Each school has a slightly different deadline for the Extended Essay. Some schools want them as soon as November of your senior year; others will take them as late as February. Your school will tell you what your deadline is. If they haven't mentioned it by February of your junior year, ask your IB coordinator about it.
Some high schools will provide you with a timeline of when you need to come up with a topic, when you need to meet with your advisor, and when certain drafts are due. Not all schools do this. Ask your IB coordinator if you are unsure whether you are on a specific timeline.
Below is my recommended EE timeline. While it's earlier than most schools, it'll save you a ton of heartache (trust me, I remember how hard this process was!):
- January/February of Junior Year: Come up with your final research topic (or at least your top three options).
- February of Junior Year: Approach a teacher about being your EE advisor. If they decline, keep asking others until you find one. See my notes above on how to pick an EE advisor.
- April/May of Junior Year: Submit an outline of your EE and a bibliography of potential research sources (I recommend at least seven to 10) to your EE advisor. Meet with your EE advisor to discuss your outline.
- Summer Between Junior and Senior Year: Complete your first full draft over the summer between your junior and senior year. I know, I know—no one wants to work during the summer, but trust me—this will save you so much stress come fall when you are busy with college applications and other internal assessments for your IB classes. You will want to have this first full draft done because you will want to complete a couple of draft cycles as you likely won't be able to get everything you want to say into 4,000 articulate words on the first attempt. Try to get this first draft into the best possible shape so you don't have to work on too many revisions during the school year on top of your homework, college applications, and extracurriculars.
- August/September of Senior Year: Turn in your first draft of your EE to your advisor and receive feedback. Work on incorporating their feedback into your essay. If they have a lot of suggestions for improvement, ask if they will read one more draft before the final draft.
- September/October of Senior Year: Submit the second draft of your EE to your advisor (if necessary) and look at their feedback. Work on creating the best possible final draft.
- November-February of Senior Year: Schedule your viva voce. Submit two copies of your final draft to your school to be sent off to the IB. You likely will not get your grade until after you graduate.
Remember that in the middle of these milestones, you'll need to schedule two other reflection sessions with your advisor . (Your teachers will actually take notes on these sessions on a form like this one , which then gets submitted to the IB.)
I recommend doing them when you get feedback on your drafts, but these meetings will ultimately be up to your supervisor. Just don't forget to do them!

The early bird DOES get the worm!
How Is the IB Extended Essay Graded?
Extended Essays are graded by examiners appointed by the IB on a scale of 0 to 34 . You'll be graded on five criteria, each with its own set of points. You can learn more about how EE scoring works by reading the IB guide to extended essays .
- Criterion A: Focus and Method (6 points maximum)
- Criterion B: Knowledge and Understanding (6 points maximum)
- Criterion C: Critical Thinking (12 points maximum)
- Criterion D: Presentation (4 points maximum)
- Criterion E: Engagement (6 points maximum)
How well you do on each of these criteria will determine the final letter grade you get for your EE. You must earn at least a D to be eligible to receive your IB Diploma.
Although each criterion has a point value, the IB explicitly states that graders are not converting point totals into grades; instead, they're using qualitative grade descriptors to determine the final grade of your Extended Essay . Grade descriptors are on pages 102-103 of this document .
Here's a rough estimate of how these different point values translate to letter grades based on previous scoring methods for the EE. This is just an estimate —you should read and understand the grade descriptors so you know exactly what the scorers are looking for.
Here is the breakdown of EE scores (from the May 2021 bulletin):
How Does the Extended Essay Grade Affect Your IB Diploma?
The Extended Essay grade is combined with your TOK (Theory of Knowledge) grade to determine how many points you get toward your IB Diploma.
To learn about Theory of Knowledge or how many points you need to receive an IB Diploma, read our complete guide to the IB program and our guide to the IB Diploma requirements .
This diagram shows how the two scores are combined to determine how many points you receive for your IB diploma (3 being the most, 0 being the least). In order to get your IB Diploma, you have to earn 24 points across both categories (the TOK and EE). The highest score anyone can earn is 45 points.
Let's say you get an A on your EE and a B on TOK. You will get 3 points toward your Diploma. As of 2014, a student who scores an E on either the extended essay or TOK essay will not be eligible to receive an IB Diploma .
Prior to the class of 2010, a Diploma candidate could receive a failing grade in either the Extended Essay or Theory of Knowledge and still be awarded a Diploma, but this is no longer true.
Figuring out how you're assessed can be a little tricky. Luckily, the IB breaks everything down here in this document . (The assessment information begins on page 219.)
40+ Sample Extended Essays for the IB Diploma Programme
In case you want a little more guidance on how to get an A on your EE, here are over 40 excellent (grade A) sample extended essays for your reading pleasure. Essays are grouped by IB subject.
- Business Management 1
- Chemistry 1
- Chemistry 2
- Chemistry 3
- Chemistry 4
- Chemistry 5
- Chemistry 6
- Chemistry 7
- Computer Science 1
- Economics 1
- Design Technology 1
- Design Technology 2
- Environmental Systems and Societies 1
- Geography 1
- Geography 2
- Geography 3
- Geography 4
- Geography 5
- Geography 6
- Literature and Performance 1
- Mathematics 1
- Mathematics 2
- Mathematics 3
- Mathematics 4
- Mathematics 5
- Philosophy 1
- Philosophy 2
- Philosophy 3
- Philosophy 4
- Philosophy 5
- Psychology 1
- Psychology 2
- Psychology 3
- Psychology 4
- Psychology 5
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 1
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 2
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 3
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 1
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 2
- Visual Arts 1
- Visual Arts 2
- Visual Arts 3
- Visual Arts 4
- Visual Arts 5
- World Religion 1
- World Religion 2
- World Religion 3

What's Next?
Trying to figure out what extracurriculars you should do? Learn more about participating in the Science Olympiad , starting a club , doing volunteer work , and joining Student Government .
Studying for the SAT? Check out our expert study guide to the SAT . Taking the SAT in a month or so? Learn how to cram effectively for this important test .
Not sure where you want to go to college? Read our guide to finding your target school . Also, determine your target SAT score or target ACT score .

As an SAT/ACT tutor, Dora has guided many students to test prep success. She loves watching students succeed and is committed to helping you get there. Dora received a full-tuition merit based scholarship to University of Southern California. She graduated magna cum laude and scored in the 99th percentile on the ACT. She is also passionate about acting, writing, and photography.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
The Ultimate Narrative Essay Guide for Beginners

A narrative essay tells a story in chronological order, with an introduction that introduces the characters and sets the scene. Then a series of events leads to a climax or turning point, and finally a resolution or reflection on the experience.
Speaking of which, are you in sixes and sevens about narrative essays? Don’t worry this ultimate expert guide will wipe out all your doubts. So let’s get started.
Table of Contents
Everything You Need to Know About Narrative Essay
What is a narrative essay.
When you go through a narrative essay definition, you would know that a narrative essay purpose is to tell a story. It’s all about sharing an experience or event and is different from other types of essays because it’s more focused on how the event made you feel or what you learned from it, rather than just presenting facts or an argument. Let’s explore more details on this interesting write-up and get to know how to write a narrative essay.
Elements of a Narrative Essay
Here’s a breakdown of the key elements of a narrative essay:
A narrative essay has a beginning, middle, and end. It builds up tension and excitement and then wraps things up in a neat package.
Real people, including the writer, often feature in personal narratives. Details of the characters and their thoughts, feelings, and actions can help readers to relate to the tale.
It’s really important to know when and where something happened so we can get a good idea of the context. Going into detail about what it looks like helps the reader to really feel like they’re part of the story.
Conflict or Challenge
A story in a narrative essay usually involves some kind of conflict or challenge that moves the plot along. It could be something inside the character, like a personal battle, or something from outside, like an issue they have to face in the world.
Theme or Message
A narrative essay isn’t just about recounting an event – it’s about showing the impact it had on you and what you took away from it. It’s an opportunity to share your thoughts and feelings about the experience, and how it changed your outlook.
Emotional Impact
The author is trying to make the story they’re telling relatable, engaging, and memorable by using language and storytelling to evoke feelings in whoever’s reading it.
Narrative essays let writers have a blast telling stories about their own lives. It’s an opportunity to share insights and impart wisdom, or just have some fun with the reader. Descriptive language, sensory details, dialogue, and a great narrative voice are all essentials for making the story come alive.
The Purpose of a Narrative Essay
A narrative essay is more than just a story – it’s a way to share a meaningful, engaging, and relatable experience with the reader. Includes:
Sharing Personal Experience
Narrative essays are a great way for writers to share their personal experiences, feelings, thoughts, and reflections. It’s an opportunity to connect with readers and make them feel something.
Entertainment and Engagement
The essay attempts to keep the reader interested by using descriptive language, storytelling elements, and a powerful voice. It attempts to pull them in and make them feel involved by creating suspense, mystery, or an emotional connection.
Conveying a Message or Insight
Narrative essays are more than just a story – they aim to teach you something. They usually have a moral lesson, a new understanding, or a realization about life that the author gained from the experience.
Building Empathy and Understanding
By telling their stories, people can give others insight into different perspectives, feelings, and situations. Sharing these tales can create compassion in the reader and help broaden their knowledge of different life experiences.
Inspiration and Motivation
Stories about personal struggles, successes, and transformations can be really encouraging to people who are going through similar situations. It can provide them with hope and guidance, and let them know that they’re not alone.
Reflecting on Life’s Significance
These essays usually make you think about the importance of certain moments in life or the impact of certain experiences. They make you look deep within yourself and ponder on the things you learned or how you changed because of those events.
Demonstrating Writing Skills
Coming up with a gripping narrative essay takes serious writing chops, like vivid descriptions, powerful language, timing, and organization. It’s an opportunity for writers to show off their story-telling abilities.
Preserving Personal History
Sometimes narrative essays are used to record experiences and special moments that have an emotional resonance. They can be used to preserve individual memories or for future generations to look back on.
Cultural and Societal Exploration
Personal stories can look at cultural or social aspects, giving us an insight into customs, opinions, or social interactions seen through someone’s own experience.
Format of a Narrative Essay
Narrative essays are quite flexible in terms of format, which allows the writer to tell a story in a creative and compelling way. Here’s a quick breakdown of the narrative essay format, along with some examples:
Introduction
Set the scene and introduce the story.
Engage the reader and establish the tone of the narrative.
Hook: Start with a captivating opening line to grab the reader’s attention. For instance:
Example: “The scorching sun beat down on us as we trekked through the desert, our water supply dwindling.”
Background Information: Provide necessary context or background without giving away the entire story.
Example: “It was the summer of 2015 when I embarked on a life-changing journey to…”
Thesis Statement or Narrative Purpose
Present the main idea or the central message of the essay.
Offer a glimpse of what the reader can expect from the narrative.
Thesis Statement: This isn’t as rigid as in other essays but can be a sentence summarizing the essence of the story.
Example: “Little did I know, that seemingly ordinary hike would teach me invaluable lessons about resilience and friendship.”
Body Paragraphs
Present the sequence of events in chronological order.
Develop characters, setting, conflict, and resolution.
Story Progression : Describe events in the order they occurred, focusing on details that evoke emotions and create vivid imagery.
Example : Detail the trek through the desert, the challenges faced, interactions with fellow hikers, and the pivotal moments.
Character Development : Introduce characters and their roles in the story. Show their emotions, thoughts, and actions.
Example : Describe how each character reacted to the dwindling water supply and supported each other through adversity.
Dialogue and Interactions : Use dialogue to bring the story to life and reveal character personalities.
Example : “Sarah handed me her last bottle of water, saying, ‘We’re in this together.'”
Reach the peak of the story, the moment of highest tension or significance.
Turning Point: Highlight the most crucial moment or realization in the narrative.
Example: “As the sun dipped below the horizon and hope seemed lost, a distant sound caught our attention—the rescue team’s helicopters.”
Provide closure to the story.
Reflect on the significance of the experience and its impact.
Reflection : Summarize the key lessons learned or insights gained from the experience.
Example : “That hike taught me the true meaning of resilience and the invaluable support of friendship in challenging times.”
Closing Thought : End with a memorable line that reinforces the narrative’s message or leaves a lasting impression.
Example : “As we boarded the helicopters, I knew this adventure would forever be etched in my heart.”
Example Summary:
Imagine a narrative about surviving a challenging hike through the desert, emphasizing the bonds formed and lessons learned. The narrative essay structure might look like starting with an engaging scene, narrating the hardships faced, showcasing the characters’ resilience, and culminating in a powerful realization about friendship and endurance.
Different Types of Narrative Essays
There are a bunch of different types of narrative essays – each one focuses on different elements of storytelling and has its own purpose. Here’s a breakdown of the narrative essay types and what they mean.
Personal Narrative
Description : Tells a personal story or experience from the writer’s life.
Purpose: Reflects on personal growth, lessons learned, or significant moments.
Example of Narrative Essay Types:
Topic : “The Day I Conquered My Fear of Public Speaking”
Focus: Details the experience, emotions, and eventual triumph over a fear of public speaking during a pivotal event.
Descriptive Narrative
Description : Emphasizes vivid details and sensory imagery.
Purpose : Creates a sensory experience, painting a vivid picture for the reader.
Topic : “A Walk Through the Enchanted Forest”
Focus : Paints a detailed picture of the sights, sounds, smells, and feelings experienced during a walk through a mystical forest.
Autobiographical Narrative
Description: Chronicles significant events or moments from the writer’s life.
Purpose: Provides insights into the writer’s life, experiences, and growth.
Topic: “Lessons from My Childhood: How My Grandmother Shaped Who I Am”
Focus: Explores pivotal moments and lessons learned from interactions with a significant family member.
Experiential Narrative
Description: Relays experiences beyond the writer’s personal life.
Purpose: Shares experiences, travels, or events from a broader perspective.
Topic: “Volunteering in a Remote Village: A Journey of Empathy”
Focus: Chronicles the writer’s volunteering experience, highlighting interactions with a community and personal growth.
Literary Narrative
Description: Incorporates literary elements like symbolism, allegory, or thematic explorations.
Purpose: Uses storytelling for deeper explorations of themes or concepts.
Topic: “The Symbolism of the Red Door: A Journey Through Change”
Focus: Uses a red door as a symbol, exploring its significance in the narrator’s life and the theme of transition.
Historical Narrative
Description: Recounts historical events or periods through a personal lens.
Purpose: Presents history through personal experiences or perspectives.
Topic: “A Grandfather’s Tales: Living Through the Great Depression”
Focus: Shares personal stories from a family member who lived through a historical era, offering insights into that period.
Digital or Multimedia Narrative
Description: Incorporates multimedia elements like images, videos, or audio to tell a story.
Purpose: Explores storytelling through various digital platforms or formats.
Topic: “A Travel Diary: Exploring Europe Through Vlogs”
Focus: Combines video clips, photos, and personal narration to document a travel experience.
How to Choose a Topic for Your Narrative Essay?
Selecting a compelling topic for your narrative essay is crucial as it sets the stage for your storytelling. Choosing a boring topic is one of the narrative essay mistakes to avoid . Here’s a detailed guide on how to choose the right topic:
Reflect on Personal Experiences
- Significant Moments:
Moments that had a profound impact on your life or shaped your perspective.
Example: A moment of triumph, overcoming a fear, a life-changing decision, or an unforgettable experience.
- Emotional Resonance:
Events that evoke strong emotions or feelings.
Example: Joy, fear, sadness, excitement, or moments of realization.
- Lessons Learned:
Experiences that taught you valuable lessons or brought about personal growth.
Example: Challenges that led to personal development, shifts in mindset, or newfound insights.
Explore Unique Perspectives
- Uncommon Experiences:
Unique or unconventional experiences that might captivate the reader’s interest.
Example: Unusual travels, interactions with different cultures, or uncommon hobbies.
- Different Points of View:
Stories from others’ perspectives that impacted you deeply.
Example: A family member’s story, a friend’s experience, or a historical event from a personal lens.
Focus on Specific Themes or Concepts
- Themes or Concepts of Interest:
Themes or ideas you want to explore through storytelling.
Example: Friendship, resilience, identity, cultural diversity, or personal transformation.
- Symbolism or Metaphor:
Using symbols or metaphors as the core of your narrative.
Example: Exploring the symbolism of an object or a place in relation to a broader theme.
Consider Your Audience and Purpose
- Relevance to Your Audience:
Topics that resonate with your audience’s interests or experiences.
Example: Choose a relatable theme or experience that your readers might connect with emotionally.
- Impact or Message:
What message or insight do you want to convey through your story?
Example: Choose a topic that aligns with the message or lesson you aim to impart to your readers.
Brainstorm and Evaluate Ideas
- Free Writing or Mind Mapping:
Process: Write down all potential ideas without filtering. Mind maps or free-writing exercises can help generate diverse ideas.
- Evaluate Feasibility:
The depth of the story, the availability of vivid details, and your personal connection to the topic.
Imagine you’re considering topics for a narrative essay. You reflect on your experiences and decide to explore the topic of “Overcoming Stage Fright: How a School Play Changed My Perspective.” This topic resonates because it involves a significant challenge you faced and the personal growth it brought about.
Narrative Essay Topics
50 easy narrative essay topics.
- Learning to Ride a Bike
- My First Day of School
- A Surprise Birthday Party
- The Day I Got Lost
- Visiting a Haunted House
- An Encounter with a Wild Animal
- My Favorite Childhood Toy
- The Best Vacation I Ever Had
- An Unforgettable Family Gathering
- Conquering a Fear of Heights
- A Special Gift I Received
- Moving to a New City
- The Most Memorable Meal
- Getting Caught in a Rainstorm
- An Act of Kindness I Witnessed
- The First Time I Cooked a Meal
- My Experience with a New Hobby
- The Day I Met My Best Friend
- A Hike in the Mountains
- Learning a New Language
- An Embarrassing Moment
- Dealing with a Bully
- My First Job Interview
- A Sporting Event I Attended
- The Scariest Dream I Had
- Helping a Stranger
- The Joy of Achieving a Goal
- A Road Trip Adventure
- Overcoming a Personal Challenge
- The Significance of a Family Tradition
- An Unusual Pet I Owned
- A Misunderstanding with a Friend
- Exploring an Abandoned Building
- My Favorite Book and Why
- The Impact of a Role Model
- A Cultural Celebration I Participated In
- A Valuable Lesson from a Teacher
- A Trip to the Zoo
- An Unplanned Adventure
- Volunteering Experience
- A Moment of Forgiveness
- A Decision I Regretted
- A Special Talent I Have
- The Importance of Family Traditions
- The Thrill of Performing on Stage
- A Moment of Sudden Inspiration
- The Meaning of Home
- Learning to Play a Musical Instrument
- A Childhood Memory at the Park
- Witnessing a Beautiful Sunset
Narrative Essay Topics for College Students
- Discovering a New Passion
- Overcoming Academic Challenges
- Navigating Cultural Differences
- Embracing Independence: Moving Away from Home
- Exploring Career Aspirations
- Coping with Stress in College
- The Impact of a Mentor in My Life
- Balancing Work and Studies
- Facing a Fear of Public Speaking
- Exploring a Semester Abroad
- The Evolution of My Study Habits
- Volunteering Experience That Changed My Perspective
- The Role of Technology in Education
- Finding Balance: Social Life vs. Academics
- Learning a New Skill Outside the Classroom
- Reflecting on Freshman Year Challenges
- The Joys and Struggles of Group Projects
- My Experience with Internship or Work Placement
- Challenges of Time Management in College
- Redefining Success Beyond Grades
- The Influence of Literature on My Thinking
- The Impact of Social Media on College Life
- Overcoming Procrastination
- Lessons from a Leadership Role
- Exploring Diversity on Campus
- Exploring Passion for Environmental Conservation
- An Eye-Opening Course That Changed My Perspective
- Living with Roommates: Challenges and Lessons
- The Significance of Extracurricular Activities
- The Influence of a Professor on My Academic Journey
- Discussing Mental Health in College
- The Evolution of My Career Goals
- Confronting Personal Biases Through Education
- The Experience of Attending a Conference or Symposium
- Challenges Faced by Non-Native English Speakers in College
- The Impact of Traveling During Breaks
- Exploring Identity: Cultural or Personal
- The Impact of Music or Art on My Life
- Addressing Diversity in the Classroom
- Exploring Entrepreneurial Ambitions
- My Experience with Research Projects
- Overcoming Impostor Syndrome in College
- The Importance of Networking in College
- Finding Resilience During Tough Times
- The Impact of Global Issues on Local Perspectives
- The Influence of Family Expectations on Education
- Lessons from a Part-Time Job
- Exploring the College Sports Culture
- The Role of Technology in Modern Education
- The Journey of Self-Discovery Through Education
Narrative Essay Comparison
Narrative essay vs. descriptive essay.
Here’s our first narrative essay comparison! While both narrative and descriptive essays focus on vividly portraying a subject or an event, they differ in their primary objectives and approaches. Now, let’s delve into the nuances of comparison on narrative essays.
Narrative Essay:
Storytelling: Focuses on narrating a personal experience or event.
Chronological Order: Follows a structured timeline of events to tell a story.
Message or Lesson: Often includes a central message, moral, or lesson learned from the experience.
Engagement: Aims to captivate the reader through a compelling storyline and character development.
First-Person Perspective: Typically narrated from the writer’s point of view, using “I” and expressing personal emotions and thoughts.
Plot Development: Emphasizes a plot with a beginning, middle, climax, and resolution.
Character Development: Focuses on describing characters, their interactions, emotions, and growth.
Conflict or Challenge: Usually involves a central conflict or challenge that drives the narrative forward.
Dialogue: Incorporates conversations to bring characters and their interactions to life.
Reflection: Concludes with reflection or insight gained from the experience.
Descriptive Essay:
Vivid Description: Aims to vividly depict a person, place, object, or event.
Imagery and Details: Focuses on sensory details to create a vivid image in the reader’s mind.
Emotion through Description: Uses descriptive language to evoke emotions and engage the reader’s senses.
Painting a Picture: Creates a sensory-rich description allowing the reader to visualize the subject.
Imagery and Sensory Details: Focuses on providing rich sensory descriptions, using vivid language and adjectives.
Point of Focus: Concentrates on describing a specific subject or scene in detail.
Spatial Organization: Often employs spatial organization to describe from one area or aspect to another.
Objective Observations: Typically avoids the use of personal opinions or emotions; instead, the focus remains on providing a detailed and objective description.
Comparison:
Focus: Narrative essays emphasize storytelling, while descriptive essays focus on vividly describing a subject or scene.
Perspective: Narrative essays are often written from a first-person perspective, while descriptive essays may use a more objective viewpoint.
Purpose: Narrative essays aim to convey a message or lesson through a story, while descriptive essays aim to paint a detailed picture for the reader without necessarily conveying a specific message.
Narrative Essay vs. Argumentative Essay
The narrative essay and the argumentative essay serve distinct purposes and employ different approaches:
Engagement and Emotion: Aims to captivate the reader through a compelling story.
Reflective: Often includes reflection on the significance of the experience or lessons learned.
First-Person Perspective: Typically narrated from the writer’s point of view, sharing personal emotions and thoughts.
Plot Development: Emphasizes a storyline with a beginning, middle, climax, and resolution.
Message or Lesson: Conveys a central message, moral, or insight derived from the experience.
Argumentative Essay:
Persuasion and Argumentation: Aims to persuade the reader to adopt the writer’s viewpoint on a specific topic.
Logical Reasoning: Presents evidence, facts, and reasoning to support a particular argument or stance.
Debate and Counterarguments: Acknowledge opposing views and counter them with evidence and reasoning.
Thesis Statement: Includes a clear thesis statement that outlines the writer’s position on the topic.
Thesis and Evidence: Starts with a strong thesis statement and supports it with factual evidence, statistics, expert opinions, or logical reasoning.
Counterarguments: Addresses opposing viewpoints and provides rebuttals with evidence.
Logical Structure: Follows a logical structure with an introduction, body paragraphs presenting arguments and evidence, and a conclusion reaffirming the thesis.
Formal Language: Uses formal language and avoids personal anecdotes or emotional appeals.
Objective: Argumentative essays focus on presenting a logical argument supported by evidence, while narrative essays prioritize storytelling and personal reflection.
Purpose: Argumentative essays aim to persuade and convince the reader of a particular viewpoint, while narrative essays aim to engage, entertain, and share personal experiences.
Structure: Narrative essays follow a storytelling structure with character development and plot, while argumentative essays follow a more formal, structured approach with logical arguments and evidence.
In essence, while both essays involve writing and presenting information, the narrative essay focuses on sharing a personal experience, whereas the argumentative essay aims to persuade the audience by presenting a well-supported argument.
Narrative Essay vs. Personal Essay
While there can be an overlap between narrative and personal essays, they have distinctive characteristics:
Storytelling: Emphasizes recounting a specific experience or event in a structured narrative form.
Engagement through Story: Aims to engage the reader through a compelling story with characters, plot, and a central theme or message.
Reflective: Often includes reflection on the significance of the experience and the lessons learned.
First-Person Perspective: Typically narrated from the writer’s viewpoint, expressing personal emotions and thoughts.
Plot Development: Focuses on developing a storyline with a clear beginning, middle, climax, and resolution.
Character Development: Includes descriptions of characters, their interactions, emotions, and growth.
Central Message: Conveys a central message, moral, or insight derived from the experience.
Personal Essay:
Exploration of Ideas or Themes: Explores personal ideas, opinions, or reflections on a particular topic or subject.
Expression of Thoughts and Opinions: Expresses the writer’s thoughts, feelings, and perspectives on a specific subject matter.
Reflection and Introspection: Often involves self-reflection and introspection on personal experiences, beliefs, or values.
Varied Structure and Content: Can encompass various forms, including memoirs, personal anecdotes, or reflections on life experiences.
Flexibility in Structure: Allows for diverse structures and forms based on the writer’s intent, which could be narrative-like or more reflective.
Theme-Centric Writing: Focuses on exploring a central theme or idea, with personal anecdotes or experiences supporting and illustrating the theme.
Expressive Language: Utilizes descriptive and expressive language to convey personal perspectives, emotions, and opinions.
Focus: Narrative essays primarily focus on storytelling through a structured narrative, while personal essays encompass a broader range of personal expression, which can include storytelling but isn’t limited to it.
Structure: Narrative essays have a more structured plot development with characters and a clear sequence of events, while personal essays might adopt various structures, focusing more on personal reflection, ideas, or themes.
Intent: While both involve personal experiences, narrative essays emphasize telling a story with a message or lesson learned, while personal essays aim to explore personal thoughts, feelings, or opinions on a broader range of topics or themes.

A narrative essay is more than just telling a story. It’s also meant to engage the reader, get them thinking, and leave a lasting impact. Whether it’s to amuse, motivate, teach, or reflect, these essays are a great way to communicate with your audience. This interesting narrative essay guide was all about letting you understand the narrative essay, its importance, and how can you write one.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score

COMMENTS
Tips for Crafting an A+ Essay. 1. Understand the Assignment: Before you start writing, make sure you fully understand the assignment guidelines and requirements. If you have any doubts, clarify them with your instructor. 2. Conduct Thorough Research: Gather relevant sources and information to support your arguments.
Revised on July 23, 2023. An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph, giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold. You'll sometimes be asked to submit an essay outline as a separate ...
The essay writing process consists of three main stages: Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline. Writing: Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion. Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling ...
Harvard College Writing Center 2 Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt When you receive a paper assignment, your first step should be to read the assignment
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
How to Prepare to Write an Essay. Before you start writing your essay, you need to figure out who you're writing for (audience), what you're writing about (topic/theme), and what you're going to say (argument and thesis). This section contains links to handouts, chapters, videos and more to help you prepare to write an essay.
Next, let's make sure you understand the different types of college essays. You'll most likely be writing a Common App or Coalition App essay, and you can also be asked to write supplemental essays for each school. Each essay has a prompt asking a specific question. Each of these prompts falls into one of a few different types.
Strategies for Essay Writing--Complete. description. Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt. description. Asking Analytical Questions. description. Thesis. description. Introductions. description. What Do Introductions Across the Disciplines Have in Common? description. Anatomy Of a Body Paragraph. description. Transitions.
Step 2: Pick one of the things you wrote down, flip your paper over, and write it at the top of your paper, like this: This is your thread, or a potential thread. Step 3: Underneath what you wrote down, name 5-6 values you could connect to this. These will serve as the beads of your essay.
For more tips on writing this essay, see our complete guide to the Extracurricular Activity essay, including a real sample essay. Common Essay 4: Discuss a community you belong to that has impacted who you are today. "Community" can mean many things, so there are many possible approaches to this prompt.
Along with Emily Perry, PhD. Paige teaches QuillBot writers about grammar rules and writing conventions. She has a BA in English, which she received by reading and writing a lot of fiction. That is all she knows how to do. Writing an essay doesn't have to suck. Learn how to write a killer essay fast with the tools and tricks outlined in our ...
Making an all-state team → outstanding achievement. Making an all-state team → counting the cost of saying "no" to other interests. Making a friend out of an enemy → finding common ground, forgiveness. Making a friend out of an enemy → confront toxic thinking and behavior in yourself.
Step 4: Add Depth with Subpoints. To add depth and clarity to your essay, incorporate subpoints under each main point. These subpoints provide more specific details, evidence, or examples that support your main ideas. They help to further strengthen your arguments and make your essay more convincing.
The basic guidelines for the MLA essay format are the following: Font: Times New Roman. Size of the font: 12pt. Margins: 1-inch margin on all the sides of the pape. Header: Each page should have a header that will contain the author's last name and a page number. Alignment: To the left-hand side.
Plan and outline your essay: Create a clear outline to provide structure and coherence to your essay. Conduct thorough research: Gather reliable information from credible sources to support your arguments. Develop a strong thesis statement: Craft a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your writing.
The Complete College Essay Handbook demystifies the entire college essay writing process with easy-to-follow directions and hands-on activities that have worked for hundreds of students. Maschal, a former admissions officer, and Wood, a professional writer and writing teacher, draw on their combined expertise to help students craft a successful ...
References and bibliography. Additionally, your research topic must fall into one of the six approved DP categories, or IB subject groups, which are as follows: Group 1: Studies in Language and Literature. Group 2: Language Acquisition. Group 3: Individuals and Societies. Group 4: Sciences. Group 5: Mathematics.
This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people's social and cultural lives.
Purpose: Reach the peak of the story, the moment of highest tension or significance. Elements: Turning Point: Highlight the most crucial moment or realization in the narrative. Example: "As the sun dipped below the horizon and hope seemed lost, a distant sound caught our attention—the rescue team's helicopters.".
Most vocational school programs can be completed within several months to two years. The short duration allows students to enter the workforce and start earning a living sooner than they would by attending a traditional four-year college. Compared to four-year colleges, vocational school programs are also often much more affordable.