Skip to content
Read the latest news stories about Mailman faculty, research, and events.

Departments
We integrate an innovative skills-based curriculum, research collaborations, and hands-on field experience to prepare students.
Learn more about our research centers, which focus on critical issues in public health.
Our Faculty
Meet the faculty of the Mailman School of Public Health.
Become a Student
Life and community, how to apply.
Learn how to apply to the Mailman School of Public Health.
Content Analysis
Content analysis is a research tool used to determine the presence of certain words, themes, or concepts within some given qualitative data (i.e. text). Using content analysis, researchers can quantify and analyze the presence, meanings, and relationships of such certain words, themes, or concepts. As an example, researchers can evaluate language used within a news article to search for bias or partiality. Researchers can then make inferences about the messages within the texts, the writer(s), the audience, and even the culture and time of surrounding the text.
Description
Sources of data could be from interviews, open-ended questions, field research notes, conversations, or literally any occurrence of communicative language (such as books, essays, discussions, newspaper headlines, speeches, media, historical documents). A single study may analyze various forms of text in its analysis. To analyze the text using content analysis, the text must be coded, or broken down, into manageable code categories for analysis (i.e. “codes”). Once the text is coded into code categories, the codes can then be further categorized into “code categories” to summarize data even further.
Three different definitions of content analysis are provided below.
Definition 1: “Any technique for making inferences by systematically and objectively identifying special characteristics of messages.” (from Holsti, 1968)
Definition 2: “An interpretive and naturalistic approach. It is both observational and narrative in nature and relies less on the experimental elements normally associated with scientific research (reliability, validity, and generalizability) (from Ethnography, Observational Research, and Narrative Inquiry, 1994-2012).
Definition 3: “A research technique for the objective, systematic and quantitative description of the manifest content of communication.” (from Berelson, 1952)
Uses of Content Analysis
Identify the intentions, focus or communication trends of an individual, group or institution
Describe attitudinal and behavioral responses to communications
Determine the psychological or emotional state of persons or groups
Reveal international differences in communication content
Reveal patterns in communication content
Pre-test and improve an intervention or survey prior to launch
Analyze focus group interviews and open-ended questions to complement quantitative data
Types of Content Analysis
There are two general types of content analysis: conceptual analysis and relational analysis. Conceptual analysis determines the existence and frequency of concepts in a text. Relational analysis develops the conceptual analysis further by examining the relationships among concepts in a text. Each type of analysis may lead to different results, conclusions, interpretations and meanings.
Conceptual Analysis
Typically people think of conceptual analysis when they think of content analysis. In conceptual analysis, a concept is chosen for examination and the analysis involves quantifying and counting its presence. The main goal is to examine the occurrence of selected terms in the data. Terms may be explicit or implicit. Explicit terms are easy to identify. Coding of implicit terms is more complicated: you need to decide the level of implication and base judgments on subjectivity (an issue for reliability and validity). Therefore, coding of implicit terms involves using a dictionary or contextual translation rules or both.
To begin a conceptual content analysis, first identify the research question and choose a sample or samples for analysis. Next, the text must be coded into manageable content categories. This is basically a process of selective reduction. By reducing the text to categories, the researcher can focus on and code for specific words or patterns that inform the research question.
General steps for conducting a conceptual content analysis:
1. Decide the level of analysis: word, word sense, phrase, sentence, themes
2. Decide how many concepts to code for: develop a pre-defined or interactive set of categories or concepts. Decide either: A. to allow flexibility to add categories through the coding process, or B. to stick with the pre-defined set of categories.
Option A allows for the introduction and analysis of new and important material that could have significant implications to one’s research question.
Option B allows the researcher to stay focused and examine the data for specific concepts.
3. Decide whether to code for existence or frequency of a concept. The decision changes the coding process.
When coding for the existence of a concept, the researcher would count a concept only once if it appeared at least once in the data and no matter how many times it appeared.
When coding for the frequency of a concept, the researcher would count the number of times a concept appears in a text.
4. Decide on how you will distinguish among concepts:
Should text be coded exactly as they appear or coded as the same when they appear in different forms? For example, “dangerous” vs. “dangerousness”. The point here is to create coding rules so that these word segments are transparently categorized in a logical fashion. The rules could make all of these word segments fall into the same category, or perhaps the rules can be formulated so that the researcher can distinguish these word segments into separate codes.
What level of implication is to be allowed? Words that imply the concept or words that explicitly state the concept? For example, “dangerous” vs. “the person is scary” vs. “that person could cause harm to me”. These word segments may not merit separate categories, due the implicit meaning of “dangerous”.
5. Develop rules for coding your texts. After decisions of steps 1-4 are complete, a researcher can begin developing rules for translation of text into codes. This will keep the coding process organized and consistent. The researcher can code for exactly what he/she wants to code. Validity of the coding process is ensured when the researcher is consistent and coherent in their codes, meaning that they follow their translation rules. In content analysis, obeying by the translation rules is equivalent to validity.
6. Decide what to do with irrelevant information: should this be ignored (e.g. common English words like “the” and “and”), or used to reexamine the coding scheme in the case that it would add to the outcome of coding?
7. Code the text: This can be done by hand or by using software. By using software, researchers can input categories and have coding done automatically, quickly and efficiently, by the software program. When coding is done by hand, a researcher can recognize errors far more easily (e.g. typos, misspelling). If using computer coding, text could be cleaned of errors to include all available data. This decision of hand vs. computer coding is most relevant for implicit information where category preparation is essential for accurate coding.
8. Analyze your results: Draw conclusions and generalizations where possible. Determine what to do with irrelevant, unwanted, or unused text: reexamine, ignore, or reassess the coding scheme. Interpret results carefully as conceptual content analysis can only quantify the information. Typically, general trends and patterns can be identified.
Relational Analysis
Relational analysis begins like conceptual analysis, where a concept is chosen for examination. However, the analysis involves exploring the relationships between concepts. Individual concepts are viewed as having no inherent meaning and rather the meaning is a product of the relationships among concepts.
To begin a relational content analysis, first identify a research question and choose a sample or samples for analysis. The research question must be focused so the concept types are not open to interpretation and can be summarized. Next, select text for analysis. Select text for analysis carefully by balancing having enough information for a thorough analysis so results are not limited with having information that is too extensive so that the coding process becomes too arduous and heavy to supply meaningful and worthwhile results.
There are three subcategories of relational analysis to choose from prior to going on to the general steps.
Affect extraction: an emotional evaluation of concepts explicit in a text. A challenge to this method is that emotions can vary across time, populations, and space. However, it could be effective at capturing the emotional and psychological state of the speaker or writer of the text.
Proximity analysis: an evaluation of the co-occurrence of explicit concepts in the text. Text is defined as a string of words called a “window” that is scanned for the co-occurrence of concepts. The result is the creation of a “concept matrix”, or a group of interrelated co-occurring concepts that would suggest an overall meaning.
Cognitive mapping: a visualization technique for either affect extraction or proximity analysis. Cognitive mapping attempts to create a model of the overall meaning of the text such as a graphic map that represents the relationships between concepts.
General steps for conducting a relational content analysis:
1. Determine the type of analysis: Once the sample has been selected, the researcher needs to determine what types of relationships to examine and the level of analysis: word, word sense, phrase, sentence, themes. 2. Reduce the text to categories and code for words or patterns. A researcher can code for existence of meanings or words. 3. Explore the relationship between concepts: once the words are coded, the text can be analyzed for the following:
Strength of relationship: degree to which two or more concepts are related.
Sign of relationship: are concepts positively or negatively related to each other?
Direction of relationship: the types of relationship that categories exhibit. For example, “X implies Y” or “X occurs before Y” or “if X then Y” or if X is the primary motivator of Y.
4. Code the relationships: a difference between conceptual and relational analysis is that the statements or relationships between concepts are coded. 5. Perform statistical analyses: explore differences or look for relationships among the identified variables during coding. 6. Map out representations: such as decision mapping and mental models.
Reliability and Validity
Reliability : Because of the human nature of researchers, coding errors can never be eliminated but only minimized. Generally, 80% is an acceptable margin for reliability. Three criteria comprise the reliability of a content analysis:
Stability: the tendency for coders to consistently re-code the same data in the same way over a period of time.
Reproducibility: tendency for a group of coders to classify categories membership in the same way.
Accuracy: extent to which the classification of text corresponds to a standard or norm statistically.
Validity : Three criteria comprise the validity of a content analysis:
Closeness of categories: this can be achieved by utilizing multiple classifiers to arrive at an agreed upon definition of each specific category. Using multiple classifiers, a concept category that may be an explicit variable can be broadened to include synonyms or implicit variables.
Conclusions: What level of implication is allowable? Do conclusions correctly follow the data? Are results explainable by other phenomena? This becomes especially problematic when using computer software for analysis and distinguishing between synonyms. For example, the word “mine,” variously denotes a personal pronoun, an explosive device, and a deep hole in the ground from which ore is extracted. Software can obtain an accurate count of that word’s occurrence and frequency, but not be able to produce an accurate accounting of the meaning inherent in each particular usage. This problem could throw off one’s results and make any conclusion invalid.
Generalizability of the results to a theory: dependent on the clear definitions of concept categories, how they are determined and how reliable they are at measuring the idea one is seeking to measure. Generalizability parallels reliability as much of it depends on the three criteria for reliability.
Advantages of Content Analysis
Directly examines communication using text
Allows for both qualitative and quantitative analysis
Provides valuable historical and cultural insights over time
Allows a closeness to data
Coded form of the text can be statistically analyzed
Unobtrusive means of analyzing interactions
Provides insight into complex models of human thought and language use
When done well, is considered a relatively “exact” research method
Content analysis is a readily-understood and an inexpensive research method
A more powerful tool when combined with other research methods such as interviews, observation, and use of archival records. It is very useful for analyzing historical material, especially for documenting trends over time.
Disadvantages of Content Analysis
Can be extremely time consuming
Is subject to increased error, particularly when relational analysis is used to attain a higher level of interpretation
Is often devoid of theoretical base, or attempts too liberally to draw meaningful inferences about the relationships and impacts implied in a study
Is inherently reductive, particularly when dealing with complex texts
Tends too often to simply consist of word counts
Often disregards the context that produced the text, as well as the state of things after the text is produced
Can be difficult to automate or computerize
Textbooks & Chapters
Berelson, Bernard. Content Analysis in Communication Research.New York: Free Press, 1952.
Busha, Charles H. and Stephen P. Harter. Research Methods in Librarianship: Techniques and Interpretation.New York: Academic Press, 1980.
de Sola Pool, Ithiel. Trends in Content Analysis. Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1959.
Krippendorff, Klaus. Content Analysis: An Introduction to its Methodology. Beverly Hills: Sage Publications, 1980.
Fielding, NG & Lee, RM. Using Computers in Qualitative Research. SAGE Publications, 1991. (Refer to Chapter by Seidel, J. ‘Method and Madness in the Application of Computer Technology to Qualitative Data Analysis’.)
Methodological Articles
Hsieh HF & Shannon SE. (2005). Three Approaches to Qualitative Content Analysis.Qualitative Health Research. 15(9): 1277-1288.
Elo S, Kaarianinen M, Kanste O, Polkki R, Utriainen K, & Kyngas H. (2014). Qualitative Content Analysis: A focus on trustworthiness. Sage Open. 4:1-10.
Application Articles
Abroms LC, Padmanabhan N, Thaweethai L, & Phillips T. (2011). iPhone Apps for Smoking Cessation: A content analysis. American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 40(3):279-285.
Ullstrom S. Sachs MA, Hansson J, Ovretveit J, & Brommels M. (2014). Suffering in Silence: a qualitative study of second victims of adverse events. British Medical Journal, Quality & Safety Issue. 23:325-331.
Owen P. (2012).Portrayals of Schizophrenia by Entertainment Media: A Content Analysis of Contemporary Movies. Psychiatric Services. 63:655-659.
Choosing whether to conduct a content analysis by hand or by using computer software can be difficult. Refer to ‘Method and Madness in the Application of Computer Technology to Qualitative Data Analysis’ listed above in “Textbooks and Chapters” for a discussion of the issue.
QSR NVivo: http://www.qsrinternational.com/products.aspx
Atlas.ti: http://www.atlasti.com/webinars.html
R- RQDA package: http://rqda.r-forge.r-project.org/
Rolly Constable, Marla Cowell, Sarita Zornek Crawford, David Golden, Jake Hartvigsen, Kathryn Morgan, Anne Mudgett, Kris Parrish, Laura Thomas, Erika Yolanda Thompson, Rosie Turner, and Mike Palmquist. (1994-2012). Ethnography, Observational Research, and Narrative Inquiry. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University. Available at: https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=63 .
As an introduction to Content Analysis by Michael Palmquist, this is the main resource on Content Analysis on the Web. It is comprehensive, yet succinct. It includes examples and an annotated bibliography. The information contained in the narrative above draws heavily from and summarizes Michael Palmquist’s excellent resource on Content Analysis but was streamlined for the purpose of doctoral students and junior researchers in epidemiology.
At Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, more detailed training is available through the Department of Sociomedical Sciences- P8785 Qualitative Research Methods.
Join the Conversation
Have a question about methods? Join us on Facebook
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
Content Analysis | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
Published on 5 May 2022 by Amy Luo . Revised on 5 December 2022.
Content analysis is a research method used to identify patterns in recorded communication. To conduct content analysis, you systematically collect data from a set of texts, which can be written, oral, or visual:
- Books, newspapers, and magazines
- Speeches and interviews
- Web content and social media posts
- Photographs and films
Content analysis can be both quantitative (focused on counting and measuring) and qualitative (focused on interpreting and understanding). In both types, you categorise or ‘code’ words, themes, and concepts within the texts and then analyse the results.
Table of contents
What is content analysis used for, advantages of content analysis, disadvantages of content analysis, how to conduct content analysis.
Researchers use content analysis to find out about the purposes, messages, and effects of communication content. They can also make inferences about the producers and audience of the texts they analyse.
Content analysis can be used to quantify the occurrence of certain words, phrases, subjects, or concepts in a set of historical or contemporary texts.
In addition, content analysis can be used to make qualitative inferences by analysing the meaning and semantic relationship of words and concepts.
Because content analysis can be applied to a broad range of texts, it is used in a variety of fields, including marketing, media studies, anthropology, cognitive science, psychology, and many social science disciplines. It has various possible goals:
- Finding correlations and patterns in how concepts are communicated
- Understanding the intentions of an individual, group, or institution
- Identifying propaganda and bias in communication
- Revealing differences in communication in different contexts
- Analysing the consequences of communication content, such as the flow of information or audience responses
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
- Unobtrusive data collection
You can analyse communication and social interaction without the direct involvement of participants, so your presence as a researcher doesn’t influence the results.
- Transparent and replicable
When done well, content analysis follows a systematic procedure that can easily be replicated by other researchers, yielding results with high reliability .
- Highly flexible
You can conduct content analysis at any time, in any location, and at low cost. All you need is access to the appropriate sources.
Focusing on words or phrases in isolation can sometimes be overly reductive, disregarding context, nuance, and ambiguous meanings.
Content analysis almost always involves some level of subjective interpretation, which can affect the reliability and validity of the results and conclusions.
- Time intensive
Manually coding large volumes of text is extremely time-consuming, and it can be difficult to automate effectively.
If you want to use content analysis in your research, you need to start with a clear, direct research question .
Next, you follow these five steps.
Step 1: Select the content you will analyse
Based on your research question, choose the texts that you will analyse. You need to decide:
- The medium (e.g., newspapers, speeches, or websites) and genre (e.g., opinion pieces, political campaign speeches, or marketing copy)
- The criteria for inclusion (e.g., newspaper articles that mention a particular event, speeches by a certain politician, or websites selling a specific type of product)
- The parameters in terms of date range, location, etc.
If there are only a small number of texts that meet your criteria, you might analyse all of them. If there is a large volume of texts, you can select a sample .
Step 2: Define the units and categories of analysis
Next, you need to determine the level at which you will analyse your chosen texts. This means defining:
- The unit(s) of meaning that will be coded. For example, are you going to record the frequency of individual words and phrases, the characteristics of people who produced or appear in the texts, the presence and positioning of images, or the treatment of themes and concepts?
- The set of categories that you will use for coding. Categories can be objective characteristics (e.g., aged 30–40, lawyer, parent) or more conceptual (e.g., trustworthy, corrupt, conservative, family-oriented).
Step 3: Develop a set of rules for coding
Coding involves organising the units of meaning into the previously defined categories. Especially with more conceptual categories, it’s important to clearly define the rules for what will and won’t be included to ensure that all texts are coded consistently.
Coding rules are especially important if multiple researchers are involved, but even if you’re coding all of the text by yourself, recording the rules makes your method more transparent and reliable.
Step 4: Code the text according to the rules
You go through each text and record all relevant data in the appropriate categories. This can be done manually or aided with computer programs, such as QSR NVivo , Atlas.ti , and Diction , which can help speed up the process of counting and categorising words and phrases.
Step 5: Analyse the results and draw conclusions
Once coding is complete, the collected data is examined to find patterns and draw conclusions in response to your research question. You might use statistical analysis to find correlations or trends, discuss your interpretations of what the results mean, and make inferences about the creators, context, and audience of the texts.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Luo, A. (2022, December 05). Content Analysis | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/content-analysis-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked
How to do thematic analysis | guide & examples, data collection methods | step-by-step guide & examples, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods.
- What is content analysis?
Last updated
20 March 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
When you're conducting qualitative research, you'll find yourself analyzing various texts. Perhaps you'll be evaluating transcripts from audio interviews you've conducted. Or you may find yourself assessing the results of a survey filled with open-ended questions.
Streamline content analysis
Bring all your qualitative research into one place to code and analyze with Dovetail
Content analysis is a research method used to identify the presence of various concepts, words, and themes in different texts. Two types of content analysis exist: conceptual analysis and relational analysis . In the former, researchers determine whether and how frequently certain concepts appear in a text. In relational analysis, researchers explore how different concepts are related to one another in a text.
Both types of content analysis require the researcher to code the text. Coding the text means breaking it down into different categories that allow it to be analyzed more easily.
- What are some common uses of content analysis?
You can use content analysis to analyze many forms of text, including:
Interview and discussion transcripts
Newspaper articles and headline
Literary works
Historical documents
Government reports
Academic papers
Music lyrics
Researchers commonly use content analysis to draw insights and conclusions from literary works. Historians and biographers may apply this approach to letters, papers, and other historical documents to gain insight into the historical figures and periods they are writing about. Market researchers can also use it to evaluate brand performance and perception.
Some researchers have used content analysis to explore differences in decision-making and other cognitive processes. While researchers traditionally used this approach to explore human cognition, content analysis is also at the heart of machine learning approaches currently being used and developed by software and AI companies.
- Conducting a conceptual analysis
Conceptual analysis is more commonly associated with content analysis than relational analysis.
In conceptual analysis, you're looking for the appearance and frequency of different concepts. Why? This information can help further your qualitative or quantitative analysis of a text. It's an inexpensive and easily understood research method that can help you draw inferences and conclusions about your research subject. And while it is a relatively straightforward analytical tool, it does consist of a multi-step process that you must closely follow to ensure the reliability and validity of your study.
When you're ready to conduct a conceptual analysis, refer to your research question and the text. Ask yourself what information likely found in the text is relevant to your question. You'll need to know this to determine how you'll code the text. Then follow these steps:
1. Determine whether you're looking for explicit terms or implicit terms.
Explicit terms are those that directly appear in the text, while implicit ones are those that the text implies or alludes to or that you can infer.
Coding for explicit terms is straightforward. For example, if you're looking to code a text for an author's explicit use of color, you'd simply code for every instance a color appears in the text. However, if you're coding for implicit terms, you'll need to determine and define how you're identifying the presence of the term first. Doing so involves a certain amount of subjectivity and may impinge upon the reliability and validity of your study .
2. Next, identify the level at which you'll conduct your analysis.
You can search for words, phrases, or sentences encapsulating your terms. You can also search for concepts and themes, but you'll need to define how you expect to identify them in the text. You must also define rules for how you'll code different terms to reduce ambiguity. For example, if, in an interview transcript, a person repeats a word one or more times in a row as a verbal tic, should you code it more than once? And what will you do with irrelevant data that appears in a term if you're coding for sentences?
Defining these rules upfront can help make your content analysis more efficient and your final analysis more reliable and valid.
3. You'll need to determine whether you're coding for a concept or theme's existence or frequency.
If you're coding for its existence, you’ll only count it once, at its first appearance, no matter how many times it subsequently appears. If you're searching for frequency, you'll count the number of its appearances in the text.
4. You'll also want to determine the number of terms you want to code for and how you may wish to categorize them.
For example, say you're conducting a content analysis of customer service call transcripts and looking for evidence of customer dissatisfaction with a product or service. You might create categories that refer to different elements with which customers might be dissatisfied, such as price, features, packaging, technical support, and so on. Then you might look for sentences that refer to those product elements according to each category in a negative light.
5. Next, you'll need to develop translation rules for your codes.
Those rules should be clear and consistent, allowing you to keep track of your data in an organized fashion.
6. After you've determined the terms for which you're searching, your categories, and translation rules, you're ready to code.
You can do so by hand or via software. Software is quite helpful when you have multiple texts. But it also becomes more vital for you to have developed clear codes, categories, and translation rules, especially if you're looking for implicit terms and concepts. Otherwise, your software-driven analysis may miss key instances of the terms you seek.
7. When you have your text coded, it's time to analyze it.
Look for trends and patterns in your results and use them to draw relevant conclusions about your research subject.
- Conducting a relational analysis
In a relational analysis, you're examining the relationship between different terms that appear in your text(s). To do so requires you to code your texts in a similar fashion as in a relational analysis. However, depending on the type of relational analysis you're trying to conduct, you may need to follow slightly different rules.
Three types of relational analyses are commonly used: affect extraction , proximity analysis , and cognitive mapping .
Affect extraction
This type of relational analysis involves evaluating the different emotional concepts found in a specific text. While the insights from affect extraction can be invaluable, conducting it may prove difficult depending on the text. For example, if the text captures people's emotional states at different times and from different populations, you may find it difficult to compare them and draw appropriate inferences.
Proximity analysis
A relatively simpler analytical approach than affect extraction, proximity analysis assesses the co-occurrence of explicit concepts in a text. You can create what's known as a concept matrix, which is a group of interrelated co-occurring concepts. Concept matrices help evaluate and determine the overall meaning of a text or the identification of a secondary message or theme.
Cognitive mapping
You can use cognitive mapping as a way to visualize the results of either affect extraction or proximity analysis. This technique uses affect extraction or proximity analysis results to create a graphic map illustrating the relationship between co-occurring emotions or concepts.
To conduct a relational analysis, you must start by determining the type of analysis that best fits the study: affect extraction or proximity analysis.
Complete steps one through six as outlined above. When it comes to the seventh step, analyze the text according to the relational analysis type they've chosen. During this step, feel free to use cognitive mapping to help draw inferences and conclusions about the relationships between co-occurring emotions or concepts. And use other tools, such as mental modeling and decision mapping as necessary, to analyze the results.
- The advantages of content analysis
Content analysis provides researchers with a robust and inexpensive method to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze a text. By coding the data, you can perform statistical analyses of the data to affirm and reinforce conclusions you may draw. And content analysis can provide helpful insights into language use, behavioral patterns, and historical or cultural conventions that can be valuable beyond the scope of the initial study.
When content analyses are applied to interview data, the approach provides a way to closely analyze data without needing interview-subject interaction, which can be helpful in certain contexts. For example, suppose you want to analyze the perceptions of a group of geographically diverse individuals. In this case, you can conduct a content analysis of existing interview transcripts rather than assuming the time and expense of conducting new interviews.
What is meant by content analysis?
Content analysis is a research method that helps a researcher explore the occurrence of and relationships between various words, phrases, themes, or concepts in a text or set of texts. The method allows researchers in different disciplines to conduct qualitative and quantitative analyses on a variety of texts.
Where is content analysis used?
Content analysis is used in multiple disciplines, as you can use it to evaluate a variety of texts. You can find applications in anthropology, communications, history, linguistics, literary studies, marketing, political science, psychology, and sociology, among other disciplines.
What are the two types of content analysis?
Content analysis may be either conceptual or relational. In a conceptual analysis, researchers examine a text for the presence and frequency of specific words, phrases, themes, and concepts. In a relational analysis, researchers draw inferences and conclusions about the nature of the relationships of co-occurring words, phrases, themes, and concepts in a text.
What's the difference between content analysis and thematic analysis?
Content analysis typically uses a descriptive approach to the data and may use either qualitative or quantitative analytical methods. By contrast, a thematic analysis only uses qualitative methods to explore frequently occurring themes in a text.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Emotions
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Culture
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Law and Politics
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Oncology
- Medical Toxicology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Games
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business History
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Methodology
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Theory
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Politics and Law
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

19 Content Analysis
Lindsay Prior, School of Sociology, Social Policy, and Social Work, Queen's University
- Published: 02 September 2020
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
In this chapter, the focus is on ways in which content analysis can be used to investigate and describe interview and textual data. The chapter opens with a contextualization of the method and then proceeds to an examination of the role of content analysis in relation to both quantitative and qualitative modes of social research. Following the introductory sections, four kinds of data are subjected to content analysis. These include data derived from a sample of qualitative interviews ( N = 54), textual data derived from a sample of health policy documents ( N = 6), data derived from a single interview relating to a “case” of traumatic brain injury, and data gathered from fifty-four abstracts of academic papers on the topic of “well-being.” Using a distinctive and somewhat novel style of content analysis that calls on the notion of semantic networks, the chapter shows how the method can be used either independently or in conjunction with other forms of inquiry (including various styles of discourse analysis) to analyze data and also how it can be used to verify and underpin claims that arise from analysis. The chapter ends with an overview of the different ways in which the study of “content”—especially the study of document content—can be positioned in social scientific research projects.
What Is Content Analysis?
In his 1952 text on the subject of content analysis, Bernard Berelson traced the origins of the method to communication research and then listed what he called six distinguishing features of the approach. As one might expect, the six defining features reflect the concerns of social science as taught in the 1950s, an age in which the calls for an “objective,” “systematic,” and “quantitative” approach to the study of communication data were first heard. The reference to the field of “communication” was nothing less than a reflection of a substantive social scientific interest over the previous decades in what was called public opinion and specifically attempts to understand why and how a potential source of critical, rational judgment on political leaders (i.e., the views of the public) could be turned into something to be manipulated by dictators and demagogues. In such a context, it is perhaps not so surprising that in one of the more popular research methods texts of the decade, the terms content analysis and communication analysis are used interchangeably (see Goode & Hatt, 1952 , p. 325).
Academic fashions and interests naturally change with available technology, and these days we are more likely to focus on the individualization of communications through Twitter and the like, rather than of mass newspaper readership or mass radio audiences, yet the prevailing discourse on content analysis has remained much the same as it was in Berleson’s day. Thus, Neuendorf ( 2002 ), for example, continued to define content analysis as “the systematic, objective, quantitative analysis of message characteristics” (p. 1). Clearly, the centrality of communication as a basis for understanding and using content analysis continues to hold, but in this chapter I will try to show that, rather than locate the use of content analysis in disembodied “messages” and distantiated “media,” we would do better to focus on the fact that communication is a building block of social life itself and not merely a system of messages that are transmitted—in whatever form—from sender to receiver. To put that statement in another guise, we must note that communicative action (to use the phraseology of Habermas, 1987 ) rests at the very base of the lifeworld, and one very important way of coming to grips with that world is to study the content of what people say and write in the course of their everyday lives.
My aim is to demonstrate various ways in which content analysis (henceforth CTA) can be used and developed to analyze social scientific data as derived from interviews and documents. It is not my intention to cover the history of CTA or to venture into forms of literary analysis or to demonstrate each and every technique that has ever been deployed by content analysts. (Many of the standard textbooks deal with those kinds of issues much more fully than is possible here. See, for example, Babbie, 2013 ; Berelson, 1952 ; Bryman, 2008 , Krippendorf, 2004 ; Neuendorf, 2002 ; and Weber, 1990 ). Instead, I seek to recontextualize the use of the method in a framework of network thinking and to link the use of CTA to specific problems of data analysis. As will become evident, my exposition of the method is grounded in real-world problems. Those problems are drawn from my own research projects and tend to reflect my academic interests—which are almost entirely related to the analysis of the ways in which people talk and write about aspects of health, illness, and disease. However, lest the reader be deterred from going any further, I should emphasize that the substantive issues that I elect to examine are secondary if not tertiary to my main objective—which is to demonstrate how CTA can be integrated into a range of research designs and add depth and rigor to the analysis of interview and inscription data. To that end, in the next section I aim to clear our path to analysis by dealing with some issues that touch on the general position of CTA in the research armory, especially its location in the schism that has developed between quantitative and qualitative modes of inquiry.
The Methodological Context of Content Analysis
Content analysis is usually associated with the study of inscription contained in published reports, newspapers, adverts, books, web pages, journals, and other forms of documentation. Hence, nearly all of Berelson’s ( 1952 ) illustrations and references to the method relate to the analysis of written records of some kind, and where speech is mentioned, it is almost always in the form of broadcast and published political speeches (such as State of the Union addresses). This association of content analysis with text and documentation is further underlined in modern textbook discussions of the method. Thus, Bryman ( 2008 ), for example, defined CTA as “an approach to the analysis of documents and texts , that seek to quantify content in terms of pre-determined categories” (2008, p. 274, emphasis in original), while Babbie ( 2013 ) stated that CTA is “the study of recorded human communications” (2013, p. 295), and Weber referred to it as a method to make “valid inferences from text” (1990, p. 9). It is clear then that CTA is viewed as a text-based method of analysis, though extensions of the method to other forms of inscriptional material are also referred to in some discussions. Thus, Neuendorf ( 2002 ), for example, rightly referred to analyses of film and television images as legitimate fields for the deployment of CTA and by implication analyses of still—as well as moving—images such as photographs and billboard adverts. Oddly, in the traditional or standard paradigm of CTA, the method is solely used to capture the “message” of a text or speech; it is not used for the analysis of a recipient’s response to or understanding of the message (which is normally accessed via interview data and analyzed in other and often less rigorous ways; see, e.g., Merton, 1968 ). So, in this chapter I suggest that we can take things at least one small step further by using CTA to analyze speech (especially interview data) as well as text.
Standard textbook discussions of CTA usually refer to it as a “nonreactive” or “unobtrusive” method of investigation (see, e.g., Babbie, 2013 , p. 294), and a large part of the reason for that designation is because of its focus on already existing text (i.e., text gathered without intrusion into a research setting). More important, however (and to underline the obvious), CTA is primarily a method of analysis rather than of data collection. Its use, therefore, must be integrated into wider frames of research design that embrace systematic forms of data collection as well as forms of data analysis. Thus, routine strategies for sampling data are often required in designs that call on CTA as a method of analysis. These latter can be built around random sampling methods or even techniques of “theoretical sampling” (Glaser & Strauss, 1967 ) so as to identify a suitable range of materials for CTA. Content analysis can also be linked to styles of ethnographic inquiry and to the use of various purposive or nonrandom sampling techniques. For an example, see Altheide ( 1987 ).
The use of CTA in a research design does not preclude the use of other forms of analysis in the same study, because it is a technique that can be deployed in parallel with other methods or with other methods sequentially. For example, and as I will demonstrate in the following sections, one might use CTA as a preliminary analytical strategy to get a grip on the available data before moving into specific forms of discourse analysis. In this respect, it can be as well to think of using CTA in, say, the frame of a priority/sequence model of research design as described by Morgan ( 1998 ).
As I shall explain, there is a sense in which CTA rests at the base of all forms of qualitative data analysis, yet the paradox is that the analysis of content is usually considered a quantitative (numerically based) method. In terms of the qualitative/quantitative divide, however, it is probably best to think of CTA as a hybrid method, and some writers have in the past argued that it is necessarily so (Kracauer, 1952 ). That was probably easier to do in an age when many recognized the strictly drawn boundaries between qualitative and quantitative styles of research to be inappropriate. Thus, in their widely used text Methods in Social Research , Goode and Hatt ( 1952 ), for example, asserted that “modern research must reject as a false dichotomy the separation between ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’ studies, or between the ‘statistical’ and the ‘non-statistical’ approach” (p. 313). This position was advanced on the grounds that all good research must meet adequate standards of validity and reliability, whatever its style, and the message is well worth preserving. However, there is a more fundamental reason why it is nonsensical to draw a division between the qualitative and the quantitative. It is simply this: All acts of social observation depend on the deployment of qualitative categories—whether gender, class, race, or even age; there is no descriptive category in use in the social sciences that connects to a world of “natural kinds.” In short, all categories are made, and therefore when we seek to count “things” in the world, we are dependent on the existence of socially constructed divisions. How the categories take the shape that they do—how definitions are arrived at, how inclusion and exclusion criteria are decided on, and how taxonomic principles are deployed—constitute interesting research questions in themselves. From our starting point, however, we need only note that “sorting things out” (to use a phrase from Bowker & Star, 1999 ) and acts of “counting”—whether it be of chromosomes or people (Martin & Lynch, 2009 )—are activities that connect to the social world of organized interaction rather than to unsullied observation of the external world.
Some writers deny the strict division between the qualitative and quantitative on grounds of empirical practice rather than of ontological reasoning. For example, Bryman ( 2008 ) argued that qualitative researchers also call on quantitative thinking, but tend to use somewhat vague, imprecise terms rather than numbers and percentages—referring to frequencies via the use of phrases such as “more than” and “less than.” Kracauer ( 1952 ) advanced various arguments against the view that CTA was strictly a quantitative method, suggesting that very often we wished to assess content as being negative or positive with respect to some political, social, or economic thesis and that such evaluations could never be merely statistical. He further argued that we often wished to study “underlying” messages or latent content of documentation and that, in consequence, we needed to interpret content as well as count items of content. Morgan ( 1993 ) argued that, given the emphasis that is placed on “coding” in almost all forms of qualitative data analysis, the deployment of counting techniques is essential and we ought therefore to think in terms of what he calls qualitative as well as quantitative content analysis. Naturally, some of these positions create more problems than they seemingly solve (as is the case with considerations of “latent content”), but given the 21st-century predilection for mixed methods research (Creswell, 2007 ), it is clear that CTA has a role to play in integrating quantitative and qualitative modes of analysis in a systematic rather than merely ad hoc and piecemeal fashion. In the sections that follow, I will provide some examples of the ways in which “qualitative” analysis can be combined with systematic modes of counting. First, however, we must focus on what is analyzed in CTA.
Units of Analysis
So, what is the unit of analysis in CTA? A brief answer is that analysis can be focused on words, sentences, grammatical structures, tenses, clauses, ratios (of, say, nouns to verbs), or even “themes.” Berelson ( 1952 ) gave examples of all of the above and also recommended a form of thematic analysis (cf., Braun & Clarke, 2006 ) as a viable option. Other possibilities include counting column length (of speeches and newspaper articles), amounts of (advertising) space, or frequency of images. For our purposes, however, it might be useful to consider a specific (and somewhat traditional) example. Here it is. It is an extract from what has turned out to be one of the most important political speeches of the current century.
Iraq continues to flaunt its hostility toward America and to support terror. The Iraqi regime has plotted to develop anthrax and nerve gas and nuclear weapons for over a decade. This is a regime that has already used poison gas to murder thousands of its own citizens, leaving the bodies of mothers huddled over their dead children. This is a regime that agreed to international inspections then kicked out the inspectors. This is a regime that has something to hide from the civilized world. States like these, and their terrorist allies, constitute an axis of evil, arming to threaten the peace of the world. By seeking weapons of mass destruction, these regimes pose a grave and growing danger. They could provide these arms to terrorists, giving them the means to match their hatred. They could attack our allies or attempt to blackmail the United States. In any of these cases, the price of indifference would be catastrophic. (George W. Bush, State of the Union address, January 29, 2002)
A number of possibilities arise for analyzing the content of a speech such as the one above. Clearly, words and sentences must play a part in any such analysis, but in addition to words, there are structural features of the speech that could also figure. For example, the extract takes the form of a simple narrative—pointing to a past, a present, and an ominous future (catastrophe)—and could therefore be analyzed as such. There are, in addition, several interesting oppositions in the speech (such as those between “regimes” and the “civilized” world), as well as a set of interconnected present participles such as “plotting,” “hiding,” “arming,” and “threatening” that are associated both with Iraq and with other states that “constitute an axis of evil.” Evidently, simple word counts would fail to capture the intricacies of a speech of this kind. Indeed, our example serves another purpose—to highlight the difficulty that often arises in dissociating CTA from discourse analysis (of which narrative analysis and the analysis of rhetoric and trope are subspecies). So how might we deal with these problems?
One approach that can be adopted is to focus on what is referenced in text and speech, that is, to concentrate on the characters or elements that are recruited into the text and to examine the ways in which they are connected or co-associated. I shall provide some examples of this form of analysis shortly. Let us merely note for the time being that in the previous example we have a speech in which various “characters”—including weapons in general, specific weapons (such as nerve gas), threats, plots, hatred, evil, and mass destruction—play a role. Be aware that we need not be concerned with the veracity of what is being said—whether it is true or false—but simply with what is in the speech and how what is in there is associated. (We may leave the task of assessing truth and falsity to the jurists). Be equally aware that it is a text that is before us and not an insight into the ex-president’s mind, or his thinking, or his beliefs, or any other subjective property that he may have possessed.
In the introductory paragraph, I made brief reference to some ideas of the German philosopher Jürgen Habermas ( 1987 ). It is not my intention here to expand on the detailed twists and turns of his claims with respect to the role of language in the “lifeworld” at this point. However, I do intend to borrow what I regard as some particularly useful ideas from his work. The first is his claim—influenced by a strong line of 20th-century philosophical thinking—that language and culture are constitutive of the lifeworld (Habermas, 1987 , p. 125), and in that sense we might say that things (including individuals and societies) are made in language. That is a simple justification for focusing on what people say rather than what they “think” or “believe” or “feel” or “mean” (all of which have been suggested at one time or another as points of focus for social inquiry and especially qualitative forms of inquiry). Second, Habermas argued that speakers and therefore hearers (and, one might add, writers and therefore readers), in what he calls their speech acts, necessarily adopt a pragmatic relation to one of three worlds: entities in the objective world, things in the social world, and elements of a subjective world. In practice, Habermas ( 1987 , p. 120) suggested all three worlds are implicated in any speech act, but that there will be a predominant orientation to one of them. To rephrase this in a crude form, when speakers engage in communication, they refer to things and facts and observations relating to external nature, to aspects of interpersonal relations, and to aspects of private inner subjective worlds (thoughts, feelings, beliefs, etc.). One of the problems with locating CTA in “communication research” has been that the communications referred to are but a special and limited form of action (often what Habermas called strategic acts). In other words, television, newspaper, video, and Internet communications are just particular forms (with particular features) of action in general. Again, we might note in passing that the adoption of the Habermassian perspective on speech acts implies that much of qualitative analysis in particular has tended to focus only on one dimension of communicative action—the subjective and private. In this respect, I would argue that it is much better to look at speeches such as George W Bush’s 2002 State of the Union address as an “account” and to examine what has been recruited into the account, and how what has been recruited is connected or co-associated, rather than use the data to form insights into his (or his adviser’s) thoughts, feelings, and beliefs.
In the sections that follow, and with an emphasis on the ideas that I have just expounded, I intend to demonstrate how CTA can be deployed to advantage in almost all forms of inquiry that call on either interview (or speech-based) data or textual data. In my first example, I will show how CTA can be used to analyze a group of interviews. In the second example, I will show how it can be used to analyze a group of policy documents. In the third, I shall focus on a single interview (a “case”), and in the fourth and final example, I will show how CTA can be used to track the biography of a concept. In each instance, I shall briefly introduce the context of the “problem” on which the research was based, outline the methods of data collection, discuss how the data were analyzed and presented, and underline the ways in which CTA has sharpened the analytical strategy.
Analyzing a Sample of Interviews: Looking at Concepts and Their Co-associations in a Semantic Network
My first example of using CTA is based on a research study that was initially undertaken in the early 2000s. It was a project aimed at understanding why older people might reject the offer to be immunized against influenza (at no cost to them). The ultimate objective was to improve rates of immunization in the study area. The first phase of the research was based on interviews with 54 older people in South Wales. The sample included people who had never been immunized, some who had refused immunization, and some who had accepted immunization. Within each category, respondents were randomly selected from primary care physician patient lists, and the data were initially analyzed “thematically” and published accordingly (Evans, Prout, Prior, Tapper-Jones, & Butler, 2007 ). A few years later, however, I returned to the same data set to look at a different question—how (older) lay people talked about colds and flu, especially how they distinguished between the two illnesses and how they understood the causes of the two illnesses (see Prior, Evans, & Prout, 2011 ). Fortunately, in the original interview schedule, we had asked people about how they saw the “differences between cold and flu” and what caused flu, so it was possible to reanalyze the data with such questions in mind. In that frame, the example that follows demonstrates not only how CTA might be used on interview data, but also how it might be used to undertake a secondary analysis of a preexisting data set (Bryman, 2008 ).
As with all talk about illness, talk about colds and flu is routinely set within a mesh of concerns—about causes, symptoms, and consequences. Such talk comprises the base elements of what has at times been referred to as the “explanatory model” of an illness (Kleinman, Eisenberg, & Good, 1978 ). In what follows, I shall focus almost entirely on issues of causation as understood from the viewpoint of older people; the analysis is based on the answers that respondents made in response to the question, “How do you think people catch flu?”
Semistructured interviews of the kind undertaken for a study such as this are widely used and are often characterized as akin to “a conversation with a purpose” (Kahn & Cannell, 1957 , p. 97). One of the problems of analyzing the consequent data is that, although the interviewer holds to a planned schedule, the respondents often reflect in a somewhat unstructured way about the topic of investigation, so it is not always easy to unravel the web of talk about, say, “causes” that occurs in the interview data. In this example, causal agents of flu, inhibiting agents, and means of transmission were often conflated by the respondents. Nevertheless, in their talk people did answer the questions that were posed, and in the study referred to here, that talk made reference to things such as “bugs” (and “germs”) as well as viruses, but the most commonly referred to causes were “the air” and the “atmosphere.” The interview data also pointed toward means of transmission as “cause”—so coughs and sneezes and mixing in crowds figured in the causal mix. Most interesting, perhaps, was the fact that lay people made a nascent distinction between facilitating factors (such as bugs and viruses) and inhibiting factors (such as being resistant, immune, or healthy), so that in the presence of the latter, the former are seen to have very little effect. Here are some shorter examples of typical question–response pairs from the original interview data.
(R:32): “How do you catch it [the flu]? Well, I take it its through ingesting and inhaling bugs from the atmosphere. Not from sort of contact or touching things. Sort of airborne bugs. Is that right?” (R:3): “I suppose it’s [the cause of flu] in the air. I think I get more diseases going to the surgery than if I stayed home. Sometimes the waiting room is packed and you’ve got little kids coughing and spluttering and people sneezing, and air conditioning I think is a killer by and large I think air conditioning in lots of these offices.” (R:46): “I think you catch flu from other people. You know in enclosed environments in air conditioning which in my opinion is the biggest cause of transferring diseases is air conditioning. Worse thing that was ever invented that was. I think so, you know. It happens on aircraft exactly the same you know.”
Alternatively, it was clear that for some people being cold, wet, or damp could also serve as a direct cause of flu; thus: Interviewer: “OK, good. How do you think you catch the flu?”
(R:39): “Ah. The 65 dollar question. Well, I would catch it if I was out in the rain and I got soaked through. Then I would get the flu. I mean my neighbour up here was soaked through and he got pneumonia and he died. He was younger than me: well, 70. And he stayed in his wet clothes and that’s fatal. Got pneumonia and died, but like I said, if I get wet, especially if I get my head wet, then I can get a nasty head cold and it could develop into flu later.”
As I suggested earlier, despite the presence of bugs and germs, viruses, the air, and wetness or dampness, “catching” the flu is not a matter of simple exposure to causative agents. Thus, some people hypothesized that within each person there is a measure of immunity or resistance or healthiness that comes into play and that is capable of counteracting the effects of external agents. For example, being “hardened” to germs and harsh weather can prevent a person getting colds and flu. Being “healthy” can itself negate the effects of any causative agents, and healthiness is often linked to aspects of “good” nutrition and diet and not smoking cigarettes. These mitigating and inhibiting factors can either mollify the effects of infection or prevent a person “catching” the flu entirely. Thus, (R:45) argued that it was almost impossible for him to catch flu or cold “cos I got all this resistance.” Interestingly, respondents often used possessive pronouns in their discussion of immunity and resistance (“my immunity” and “my resistance”)—and tended to view them as personal assets (or capital) that might be compromised by mixing with crowds.
By implication, having a weak immune system can heighten the risk of contracting colds and flu and might therefore spur one to take preventive measures, such as accepting a flu shot. Some people believe that the flu shot can cause the flu and other illnesses. An example of what might be called lay “epidemiology” (Davison, Davey-Smith, & Frankel, 1991 ) is evident in the following extract.
(R:4): “Well, now it’s coincidental you know that [my brother] died after the jab, but another friend of mine, about 8 years ago, the same happened to her. She had the jab and about six months later, she died, so I know they’re both coincidental, but to me there’s a pattern.”
Normally, results from studies such as this are presented in exactly the same way as has just been set out. Thus, the researcher highlights given themes that are said to have emerged from the data and then provides appropriate extracts from the interviews to illustrate and substantiate the relevant themes. However, one reasonable question that any critic might ask about the selected data extracts concerns the extent to which they are “representative” of the material in the data set as a whole. Maybe, for example, the author has been unduly selective in his or her use of both themes and quotations. Perhaps, as a consequence, the author has ignored or left out talk that does not fit the arguments or extracts that might be considered dull and uninteresting compared to more exotic material. And these kinds of issues and problems are certainly common to the reporting of almost all forms of qualitative research. However, the adoption of CTA techniques can help to mollify such problems. This is so because, by using CTA, we can indicate the extent to which we have used all or just some of the data, and we can provide a view of the content of the entire sample of interviews rather than just the content and flavor of merely one or two interviews. In this light, we must consider Figure 19.1 , which is based on counting the number of references in the 54 interviews to the various “causes” of the flu, though references to the flu shot (i.e., inoculation) as a cause of flu have been ignored for the purpose of this discussion. The node sizes reflect the relative importance of each cause as determined by the concept count (frequency of occurrence). The links between nodes reflect the degree to which causes are co-associated in interview talk and are calculated according to a co-occurrence index (see, e.g., SPSS, 2007 , p. 183).
What causes flu? A lay perspective. Factors listed as causes of colds and flu in 54 interviews. Node size is proportional to number of references “as causes.” Line thickness is proportional to co-occurrence of any two “causes” in the set of interviews.
Given this representation, we can immediately assess the relative importance of the different causes as referred to in the interview data. Thus, we can see that such things as (poor) “hygiene” and “foreigners” were mentioned as a potential cause of flu—but mention of hygiene and foreigners was nowhere near as important as references to “the air” or to “crowds” or to “coughs and sneezes.” In addition, we can also determine the strength of the connections that interviewees made between one cause and another. Thus, there are relatively strong links between “resistance” and “coughs and sneezes,” for example.
In fact, Figure 19.1 divides causes into the “external” and the “internal,” or the facilitating and the impeding (lighter and darker nodes). Among the former I have placed such things as crowds, coughs, sneezes, and the air, while among the latter I have included “resistance,” “immunity,” and “health.” That division is a product of my conceptualizing and interpreting the data, but whichever way we organize the findings, it is evident that talk about the causes of flu belongs in a web or mesh of concerns that would be difficult to represent using individual interview extracts alone. Indeed, it would be impossible to demonstrate how the semantics of causation belong to a culture (rather than to individuals) in any other way. In addition, I would argue that the counting involved in the construction of the diagram functions as a kind of check on researcher interpretations and provides a source of visual support for claims that an author might make about, say, the relative importance of “damp” and “air” as perceived causes of disease. Finally, the use of CTA techniques allied with aspects of conceptualization and interpretation has enabled us to approach the interview data as a set and to consider the respondents as belonging to a community, rather than regarding them merely as isolated and disconnected individuals, each with their own views. It has also enabled us to squeeze some new findings out of old data, and I would argue that it has done so with advantage. There are other advantages to using CTA to explore data sets, which I will highlight in the next section.
Analyzing a Sample of Documents: Using Content Analysis to Verify Claims
Policy analysis is a difficult business. To begin, it is never entirely clear where (social, health, economic, environmental) policy actually is. Is it in documents (as published by governments, think tanks, and research centers), in action (what people actually do), or in speech (what people say)? Perhaps it rests in a mixture of all three realms. Yet, wherever it may be, it is always possible, at the very least, to identify a range of policy texts and to focus on the conceptual or semantic webs in terms of which government officials and other agents (such as politicians) talk about the relevant policy issues. Furthermore, insofar as policy is recorded—in speeches, pamphlets, and reports—we may begin to speak of specific policies as having a history or a pedigree that unfolds through time (think, e.g., of U.S. or U.K. health policies during the Clinton years or the Obama years). And, insofar as we consider “policy” as having a biography or a history, we can also think of studying policy narratives.
Though firmly based in the world of literary theory, narrative method has been widely used for both the collection and the analysis of data concerning ways in which individuals come to perceive and understand various states of health, ill health, and disability (Frank, 1995 ; Hydén, 1997 ). Narrative techniques have also been adapted for use in clinical contexts and allied to concepts of healing (Charon, 2006 ). In both social scientific and clinical work, however, the focus is invariably on individuals and on how individuals “tell” stories of health and illness. Yet narratives can also belong to collectives—such as political parties and ethnic and religious groups—just as much as to individuals, and in the latter case there is a need to collect and analyze data that are dispersed across a much wider range of materials than can be obtained from the personal interview. In this context, Roe ( 1994 ) demonstrated how narrative method can be applied to an analysis of national budgets, animal rights, and environmental policies.
An extension of the concept of narrative to policy discourse is undoubtedly useful (Newman & Vidler, 2006 ), but how might such narratives be analyzed? What strategies can be used to unravel the form and content of a narrative, especially in circumstances where the narrative might be contained in multiple (policy) documents, authored by numerous individuals, and published across a span of time rather than in a single, unified text such as a novel? Roe ( 1994 ), unfortunately, was not in any way specific about analytical procedures, apart from offering the useful rule to “never stray too far from the data” (p. xii). So, in this example, I will outline a strategy for tackling such complexities. In essence, it is a strategy that combines techniques of linguistically (rule) based CTA with a theoretical and conceptual frame that enables us to unravel and identify the core features of a policy narrative. My substantive focus is on documents concerning health service delivery policies published from 2000 to 2009 in the constituent countries of the United Kingdom (that is, England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland—all of which have different political administrations).
Narratives can be described and analyzed in various ways, but for our purposes we can say that they have three key features: they point to a chronology, they have a plot, and they contain “characters.”
All narratives have beginnings; they also have middles and endings, and these three stages are often seen as comprising the fundamental structure of narrative text. Indeed, in his masterly analysis of time and narrative, Ricoeur ( 1984 ) argued that it is in the unfolding chronological structure of a narrative that one finds its explanatory (and not merely descriptive) force. By implication, one of the simplest strategies for the examination of policy narratives is to locate and then divide a narrative into its three constituent parts—beginning, middle, and end.
Unfortunately, while it can sometimes be relatively easy to locate or choose a beginning to a narrative, it can be much more difficult to locate an end point. Thus, in any illness narrative, a narrator might be quite capable of locating the start of an illness process (in an infection, accident, or other event) but unable to see how events will be resolved in an ongoing and constantly unfolding life. As a consequence, both narrators and researchers usually find themselves in the midst of an emergent present—a present without a known and determinate end (see, e.g., Frank, 1995 ). Similar considerations arise in the study of policy narratives where chronology is perhaps best approached in terms of (past) beginnings, (present) middles, and projected futures.
According to Ricoeur ( 1984 ), our basic ideas about narrative are best derived from the work and thought of Aristotle, who in his Poetics sought to establish “first principles” of composition. For Ricoeur, as for Aristotle, plot ties things together. It “brings together factors as heterogeneous as agents, goals, means, interactions, circumstances, unexpected results” (p. 65) into the narrative frame. For Aristotle, it is the ultimate untying or unraveling of the plot that releases the dramatic energy of the narrative.
Characters are most commonly thought of as individuals, but they can be considered in much broader terms. Thus, the French semiotician A. J. Greimas ( 1970 ), for example, suggested that, rather than think of characters as people, it would be better to think in terms of what he called actants and of the functions that such actants fulfill within a story. In this sense, geography, climate, and capitalism can be considered characters every bit as much as aggressive wolves and Little Red Riding Hood. Further, he argued that the same character (actant) can be considered to fulfill many functions, and the same function may be performed by many characters. Whatever else, the deployment of the term actant certainly helps us to think in terms of narratives as functioning and creative structures. It also serves to widen our understanding of the ways in which concepts, ideas, and institutions, as well “things” in the material world, can influence the direction of unfolding events every bit as much as conscious human subjects. Thus, for example, the “American people,” “the nation,” “the Constitution,” “the West,” “tradition,” and “Washington” can all serve as characters in a policy story.
As I have already suggested, narratives can unfold across many media and in numerous arenas—speech and action, as well as text. Here, however, my focus is solely on official documents—all of which are U.K. government policy statements, as listed in Table 19.1 . The question is, How might CTA help us unravel the narrative frame?
It might be argued that a simple reading of any document should familiarize the researcher with elements of all three policy narrative components (plot, chronology, and character). However, in most policy research, we are rarely concerned with a single and unified text, as is the case with a novel; rather, we have multiple documents written at distinctly different times by multiple (usually anonymous) authors that notionally can range over a wide variety of issues and themes. In the full study, some 19 separate publications were analyzed across England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland.
Naturally, listing word frequencies—still less identifying co-occurrences and semantic webs in large data sets (covering hundreds of thousands of words and footnotes)—cannot be done manually, but rather requires the deployment of complex algorithms and text-mining procedures. To this end, I analyzed the 19 documents using “Text Mining for Clementine” (SPSS, 2007 ).
Text-mining procedures begin by providing an initial list of concepts based on the lexicon of the text but that can be weighted according to word frequency and that take account of elementary word associations. For example, learning disability, mental health, and performance management indicate three concepts, not six words. Using such procedures on the aforementioned documents gives the researcher an initial grip on the most important concepts in the document set of each country. Note that this is much more than a straightforward concordance analysis of the text and is more akin to what Ryan and Bernard ( 2000 ) referred to as semantic analysis and Carley ( 1993 ) has referred to as concept and mapping analysis.
So, the first task was to identify and then extract the core concepts, thus identifying what might be called “key” characters or actants in each of the policy narratives. For example, in the Scottish documents, such actants included “Scotland” and the “Scottish people,” as well as “health” and the “National Health Service (NHS),” among others, while in the Welsh documents it was “the people of Wales” and “Wales” that figured largely—thus emphasizing how national identity can play every bit as important a role in a health policy narrative as concepts such as “health,” “hospitals,” and “well-being.”
Having identified key concepts, it was then possible to track concept clusters in which particular actants or characters are embedded. Such cluster analysis is dependent on the use of co-occurrence rules and the analysis of synonyms, whereby it is possible to get a grip on the strength of the relationships between the concepts, as well as the frequency with which the concepts appear in the collected texts. In Figure 19.2 , I provide an example of a concept cluster. The diagram indicates the nature of the conceptual and semantic web in which various actants are discussed. The diagrams further indicate strong (solid line) and weaker (dashed line) connections between the various elements in any specific mix, and the numbers indicate frequency counts for the individual concepts. Using Clementine , the researcher is unable to specify in advance which clusters will emerge from the data. One cannot, for example, choose to have an NHS cluster. In that respect, these diagrams not only provide an array in terms of which concepts are located, but also serve as a check on and to some extent validation of the interpretations of the researcher. None of this tells us what the various narratives contained within the documents might be, however. They merely point to key characters and relationships both within and between the different narratives. So, having indicated the techniques used to identify the essential parts of the four policy narratives, it is now time to sketch out their substantive form.
Concept cluster for “care” in six English policy documents, 2000–2007. Line thickness is proportional to the strength co-occurrence coefficient. Node size reflects relative frequency of concept, and (numbers) refer to the frequency of concept. Solid lines indicate relationships between terms within the same cluster, and dashed lines indicate relationships between terms in different clusters.
It may be useful to note that Aristotle recommended brevity in matters of narrative—deftly summarizing the whole of the Odyssey in just seven lines. In what follows, I attempt—albeit somewhat weakly—to emulate that example by summarizing a key narrative of English health services policy in just four paragraphs. Note how the narrative unfolds in relation to the dates of publication. In the English case (though not so much in the other U.K. countries), it is a narrative that is concerned to introduce market forces into what is and has been a state-managed health service. Market forces are justified in terms of improving opportunities for the consumer (i.e., the patients in the service), and the pivot of the newly envisaged system is something called “patient choice” or “choice.” This is how the story unfolds as told through the policy documents between 2000 and 2008 (see Table 19.1 ). The citations in the following paragraphs are to the Department of Health publications (by year) listed in Table 19.1 .
The advent of the NHS in 1948 was a “seminal event” (2000, p. 8), but under successive Conservative administrations, the NHS was seriously underfunded (2006, p. 3). The (New Labour) government will invest (2000) or already has (2003, p. 4) invested extensively in infrastructure and staff, and the NHS is now on a “journey of major improvement” (2004, p. 2). But “more money is only a starting point” (2000, p. 2), and the journey is far from finished. Continuation requires some fundamental changes of “culture” (2003, p. 6). In particular, the NHS remains unresponsive to patient need, and “all too often, the individual needs and wishes are secondary to the convenience of the services that are available. This ‘one size fits all’ approach is neither responsive, equitable nor person-centred” (2003, p. 17). In short, the NHS is a 1940s system operating in a 21st-century world (2000, p. 26). Change is therefore needed across the “whole system” (2005, p. 3) of care and treatment.
Above all, we must recognize that we “live in a consumer age” (2000, p. 26). People’s expectations have changed dramatically (2006, p. 129), and people want more choice, more independence, and more control (2003, p. 12) over their affairs. Patients are no longer, and should not be considered, “passive recipients” of care (2003, p. 62), but wish to be and should be (2006, p. 81) actively “involved” in their treatments (2003, p. 38; 2005, p. 18)—indeed, engaged in a partnership (2003, p. 22) of respect with their clinicians. Furthermore, most people want a personalized service “tailor made to their individual needs” (2000, p. 17; 2003, p. 15; 2004, p. 1; 2006, p. 83)—“a service which feels personal to each and every individual within a framework of equity and good use of public money” (2003, p. 6).
To advance the necessary changes, “patient choice” must be and “will be strengthened” (2000, p. 89). “Choice” must be made to “happen” (2003), and it must be “real” (2003, p. 3; 2004, p. 5; 2005, p. 20; 2006, p. 4). Indeed, it must be “underpinned” (2003, p. 7) and “widened and deepened” (2003, p. 6) throughout the entire system of care.
If “we” expand and underpin patient choice in appropriate ways and engage patients in their treatment systems, then levels of patient satisfaction will increase (2003, p. 39), and their choices will lead to a more “efficient” (2003, p. 5; 2004, p. 2; 2006, p. 16) and effective (2003, p. 62; 2005, p. 8) use of resources. Above all, the promotion of choice will help to drive up “standards” of care and treatment (2000, p. 4; 2003, p. 12; 2004, p. 3; 2005, p. 7; 2006, p. 3). Furthermore, the expansion of choice will serve to negate the effects of the “inverse care law,” whereby those who need services most tend to get catered to the least (2000, p. 107; 2003, p. 5; 2006, p. 63), and it will thereby help in moderating the extent of health inequalities in the society in which we live. “The overall aim of all our reforms,” therefore, “is to turn the NHS from a top down monolith into a responsive service that gives the patient the best possible experience. We need to develop an NHS that is both fair to all of us, and personal to each of us” (2003, p. 5).
We can see how most—though not all—of the elements of this story are represented in Figure 19.2. In particular, we can see strong (co-occurrence) links between care and choice and how partnership, performance, control, and improvement have a prominent profile. There are some elements of the web that have a strong profile (in terms of node size and links), but to which we have not referred; access, information, primary care, and waiting times are four. As anyone well versed in English healthcare policy would know, these elements have important roles to play in the wider, consumer-driven narrative. However, by rendering the excluded as well as included elements of that wider narrative visible, the concept web provides a degree of verification on the content of the policy story as told herein and on the scope of its “coverage.”
In following through on this example, we have moved from CTA to a form of discourse analysis (in this instance, narrative analysis). That shift underlines aspects of both the versatility of CTA and some of its weaknesses—versatility in the sense that CTA can be readily combined with other methods of analysis and in the way in which the results of the CTA help us to check and verify the claims of the researcher. The weakness of the diagram compared to the narrative is that CTA on its own is a somewhat one-dimensional and static form of analysis, and while it is possible to introduce time and chronology into the diagrams, the diagrams themselves remain lifeless in the absence of some form of discursive overview. (For a fuller analysis of these data, see Prior, Hughes, & Peckham, 2012 ).
Analyzing a Single Interview: The Role of Content Analysis in a Case Study
So far, I have focused on using CTA on a sample of interviews and a sample of documents. In the first instance, I recommended CTA for its capacity to tell us something about what is seemingly central to interviewees and for demonstrating how what is said is linked (in terms of a concept network). In the second instance, I reaffirmed the virtues of co-occurrence and network relations, but this time in the context of a form of discourse analysis. I also suggested that CTA can serve an important role in the process of verification of a narrative and its academic interpretation. In this section, however, I am going to link the use of CTA to another style of research—case study—to show how CTA might be used to analyze a single “case.”
Case study is a term used in multiple and often ambiguous ways. However, Gerring ( 2004 ) defined it as “an intensive study of a single unit for the purpose of understanding a larger class of (similar) units” (p. 342). As Gerring pointed out, case study does not necessarily imply a focus on N = 1, although that is indeed the most logical number for case study research (Ragin & Becker, 1992 ). Naturally, an N of 1 can be immensely informative, and whether we like it or not, we often have only one N to study (think, e.g., of the 1986 Challenger shuttle disaster or of the 9/11 attack on the World Trade Center). In the clinical sciences, case studies are widely used to represent the “typical” features of a wider class of phenomena and often used to define a kind or syndrome (as in the field of clinical genetics). Indeed, at the risk of mouthing a tautology, one can say that the distinctive feature of case study is its focus on a case in all of its complexity—rather than on individual variables and their interrelationships, which tends to be a point of focus for large N research.
There was a time when case study was central to the science of psychology. Breuer and Freud’s (2001) famous studies of “hysteria” (originally published in 1895) provide an early and outstanding example of the genre in this respect, but as with many of the other styles of social science research, the influence of case studies waned with the rise of much more powerful investigative techniques—including experimental methods—driven by the deployment of new statistical technologies. Ideographic studies consequently gave way to the current fashion for statistically driven forms of analysis that focus on causes and cross-sectional associations between variables rather than ideographic complexity.
In the example that follows, we will look at the consequences of a traumatic brain injury (TBI) on just one individual. The analysis is based on an interview with a person suffering from such an injury, and it was one of 32 interviews carried out with people who had experienced a TBI. The objective of the original research was to develop an outcome measure for TBI that was sensitive to the sufferer’s (rather than the health professional’s) point of view. In our original study (see Morris et al., 2005 ), interviews were also undertaken with 27 carers of the injured with the intention of comparing their perceptions of TBI to those of the people for whom they cared. A sample survey was also undertaken to elicit views about TBI from a much wider population of patients than was studied via interview.
In the introduction, I referred to Habermas and the concept of the lifeworld. Lifeworld ( Lebenswelt ) is a concept that first arose from 20th-century German philosophy. It constituted a specific focus for the work of Alfred Schutz (see, e.g., Schutz & Luckman, 1974 ). Schutz ( 1974 ) described the lifeworld as “that province of reality which the wide-awake and normal adult simply takes-for-granted in an attitude of common sense” (p. 3). Indeed, it was the routine and taken-for-granted quality of such a world that fascinated Schutz. As applied to the worlds of those with head injuries, the concept has particular resonance because head injuries often result in that taken-for-granted quality being disrupted and fragmented, ending in what Russian neuropsychologist A. R. Luria ( 1975 ) once described as “shattered” worlds. As well as providing another excellent example of a case study, Luria’s work is also pertinent because he sometimes argued for a “romantic science” of brain injury—that is, a science that sought to grasp the worldview of the injured patient by paying attention to an unfolding and detailed personal “story” of the individual with the head injury as well as to the neurological changes and deficits associated with the injury itself. In what follows, I shall attempt to demonstrate how CTA might be used to underpin such an approach.
In the original research, we began analysis by a straightforward reading of the interview transcripts. Unfortunately, a simple reading of a text or an interview can, strangely, mislead the reader into thinking that some issues or themes are more important than is warranted by the contents of the text. How that comes about is not always clear, but it probably has something to do with a desire to develop “findings” and our natural capacity to overlook the familiar in favor of the unusual. For that reason alone, it is always useful to subject any text to some kind of concordance analysis—that is, generating a simple frequency list of words used in an interview or text. Given the current state of technology, one might even speak these days of using text-mining procedures such as the aforementioned Clementine to undertake such a task. By using Clementine , and as we have seen, it is also possible to measure the strength of co-occurrence links between elements (i.e., words and concepts) in the entire data set (in this example, 32 interviews), though for a single interview these aims can just as easily be achieved using much simpler, low-tech strategies.
By putting all 32 interviews into the database, several common themes emerged. For example, it was clear that “time” entered into the semantic web in a prominent manner, and it was clearly linked to such things as “change,” “injury,” “the body,” and what can only be called the “I was.” Indeed, time runs through the 32 stories in many guises, and the centrality of time is a reflection of storytelling and narrative recounting in general—chronology, as we have noted, being a defining feature of all storytelling (Ricoeur, 1984 ). Thus, sufferers both recounted the events surrounding their injury and provided accounts as to how the injuries affected their current life and future hopes. As to time present, much of the patient story circled around activities of daily living—walking, working, talking, looking, feeling, remembering, and so forth.
Understandably, the word and the concept of “injury” featured largely in the interviews, though it was a word most commonly associated with discussions of physical consequences of injury. There were many references in that respect to injured arms, legs, hands, and eyes. There were also references to “mind”—though with far less frequency than with references to the body and to body parts. Perhaps none of this is surprising. However, one of the most frequent concepts in the semantic mix was the “I was” (716 references). The statement “I was,” or “I used to” was, in turn, strongly connected to terms such as “the accident” and “change.” Interestingly, the “I was” overwhelmingly eclipsed the “I am” in the interview data (the latter with just 63 references). This focus on the “I was” appears in many guises. For example, it is often associated with the use of the passive voice: “I was struck by a car,” “I was put on the toilet,” “I was shipped from there then, transferred to [Cityville],” “I got told that I would never be able …,” “I was sat in a room,” and so forth. In short, the “I was” is often associated with things, people, and events acting on the injured person. More important, however, the appearance of the “I was” is often used to preface statements signifying a state of loss or change in the person’s course of life—that is, as an indicator for talk about the patient’s shattered world. For example, Patient 7122 stated,
The main (effect) at the moment is I’m not actually with my children, I can’t really be their mum at the moment. I was a caring Mum, but I can’t sort of do the things that I want to be able to do like take them to school. I can’t really do a lot on my own. Like crossing the roads.
Another patient stated,
Everything is completely changed. The way I was … I can’t really do anything at the moment. I mean my German, my English, everything’s gone. Job possibilities is out the window. Everything is just out of the window … I just think about it all the time actually every day you know. You know it has destroyed me anyway, but if I really think about what has happened I would just destroy myself.
Each of these quotations, in its own way, serves to emphasize how life has changed and how the patient’s world has changed. In that respect, we can say that one of the major outcomes arising from TBI may be substantial “biographical disruption” (Bury, 1982 ), whereupon key features of an individual’s life course are radically altered forever. Indeed, as Becker ( 1997 , p. 37) argued in relation to a wide array of life events, “When their health is suddenly disrupted, people are thrown into chaos. Illness challenges one’s knowledge of one’s body. It defies orderliness. People experience the time before their illness and its aftermath as two separate entities.” Indeed, this notion of a cusp in personal biography is particularly well illustrated by Luria’s patient Zasetsky; the latter often refers to being a “newborn creature” (Luria, 1975 , pp. 24, 88), a shadow of a former self (p. 25), and as having his past “wiped out” (p. 116).
However, none of this tells us about how these factors come together in the life and experience of one individual. When we focus on an entire set of interviews, we necessarily lose the rich detail of personal experience and tend instead to rely on a conceptual rather than a graphic description of effects and consequences (to focus on, say, “memory loss,” rather than loss of memory about family life). The contents of Figure 19.3 attempt to correct that vision. Figure 19.3 records all the things that a particular respondent (Patient 7011) used to do and liked doing. It records all the things that he says he can no longer do (at 1 year after injury), and it records all the consequences that he suffered from his head injury at the time of the interview. Thus, we see references to epilepsy (his “fits”), paranoia (the patient spoke of his suspicions concerning other people, people scheming behind his back, and his inability to trust others), deafness, depression, and so forth. Note that, although I have inserted a future tense into the web (“I will”), such a statement never appeared in the transcript. I have set it there for emphasis and to show how, for this person, the future fails to connect to any of the other features of his world except in a negative way. Thus, he states at one point that he cannot think of the future because it makes him feel depressed (see Figure 19.3 ). The line thickness of the arcs reflects the emphasis that the subject placed on the relevant “outcomes” in relation to the “I was” and the “now” during the interview. Thus, we see that factors affecting his concentration and balance loom large, but that he is also concerned about his being dependent on others, his epileptic fits, and his being unable to work and drive a vehicle. The schism in his life between what he used to do, what he cannot now do, and his current state of being is nicely represented in the CTA diagram.
The shattered world of Patient 7011. Thickness of lines (arcs) is proportional to the frequency of reference to the “outcome” by the patient during the interview.
What have we gained from executing this kind of analysis? For a start, we have moved away from a focus on variables, frequencies, and causal connections (e.g., a focus on the proportion of people with TBI who suffer from memory problems or memory problems and speech problems) and refocused on how the multiple consequences of a TBI link together in one person. In short, instead of developing a narrative of acting variables, we have emphasized a narrative of an acting individual (Abbott, 1992 , p. 62). Second, it has enabled us to see how the consequences of a TBI connect to an actual lifeworld (and not simply an injured body). So the patient is not viewed just as having a series of discrete problems such as balancing, or staying awake, which is the usual way of assessing outcomes, but as someone struggling to come to terms with an objective world of changed things, people, and activities (missing work is not, for example, routinely considered an outcome of head injury). Third, by focusing on what the patient was saying, we gain insight into something that is simply not visible by concentrating on single outcomes or symptoms alone—namely, the void that rests at the center of the interview, what I have called the “I was.” Fourth, we have contributed to understanding a type, because the case that we have read about is not simply a case of “John” or “Jane” but a case of TBI, and in that respect it can add to many other accounts of what it is like to experience head injury—including one of the most well documented of all TBI cases, that of Zatetsky. Finally, we have opened up the possibility of developing and comparing cognitive maps (Carley, 1993 ) for different individuals and thereby gained insight into how alternative cognitive frames of the world arise and operate.
Tracing the Biography of a Concept
In the previous sections, I emphasized the virtues of CTA for its capacity to link into a data set in its entirety—and how the use of CTA can counter any tendency of a researcher to be selective and partial in the presentation and interpretation of information contained in interviews and documents. However, that does not mean that we always must take an entire document or interview as the data source. Indeed, it is possible to select (on rational and explicit grounds) sections of documentation and to conduct the CTA on the chosen portions. In the example that follows, I do just that. The sections that I chose to concentrate on are titles and abstracts of academic papers—rather than the full texts. The research on which the following is based is concerned with a biography of a concept and is being conducted in conjunction with a Ph.D. student of mine, Joanne Wilson. Joanne thinks of this component of the study more in terms of a “scoping study” than of a biographical study, and that, too, is a useful framework for structuring the context in which CTA can be used. Scoping studies (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005 ) are increasingly used in health-related research to “map the field” and to get a sense of the range of work that has been conducted on a given topic. Such studies can also be used to refine research questions and research designs. In our investigation, the scoping study was centered on the concept of well-being. Since 2010, well-being has emerged as an important research target for governments and corporations as well as for academics, yet it is far from clear to what the term refers. Given the ambiguity of meaning, it is clear that a scoping review, rather than either a systematic review or a narrative review of available literature, would be best suited to our goals.
The origins of the concept of well-being can be traced at least as far back as the 4th century bc , when philosophers produced normative explanations of the good life (e.g., eudaimonia, hedonia, and harmony). However, contemporary interest in the concept seemed to have been regenerated by the concerns of economists and, most recently, psychologists. These days, governments are equally concerned with measuring well-being to inform policy and conduct surveys of well-being to assess that state of the nation (see, e.g., Office for National Statistics, 2012 )—but what are they assessing?
We adopted a two-step process to address the research question, “What is the meaning of ‘well-being’ in the context of public policy?” First, we explored the existing thesauri of eight databases to establish those higher order headings (if any) under which articles with relevance to well-being might be cataloged. Thus, we searched the following databases: Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature, EconLit, Health Management Information Consortium, Medline, Philosopher’s Index, PsycINFO, Sociological Abstracts, and Worldwide Political Science Abstracts. Each of these databases adopts keyword-controlled vocabularies. In other words, they use inbuilt statistical procedures to link core terms to a set lexis of phrases that depict the concepts contained in the database. Table 19.2 shows each database and its associated taxonomy. The contents of Table 19.2 point toward a linguistic infrastructure in terms of which academic discourse is conducted, and our task was to extract from this infrastructure the semantic web wherein the concept of well-being is situated. We limited the thesaurus terms to well-being and its variants (i.e., wellbeing or well being). If the term was returned, it was then exploded to identify any associated terms.
To develop the conceptual map, we conducted a free-text search for well-being and its variants within the context of public policy across the same databases. We orchestrated these searches across five time frames: January 1990 to December 1994, January 1995 to December 1999, January 2000 to December 2004, January 2005 to December 2009, and January 2010 to October 2011. Naturally, different disciplines use different words to refer to well-being, each of which may wax and wane in usage over time. The searches thus sought to quantitatively capture any changes in the use and subsequent prevalence of well-being and any referenced terms (i.e., to trace a biography).
It is important to note that we did not intend to provide an exhaustive, systematic search of all the relevant literature. Rather, we wanted to establish the prevalence of well-being and any referenced (i.e., allied) terms within the context of public policy. This has the advantage of ensuring that any identified words are grounded in the literature (i.e., they represent words actually used by researchers to talk and write about well-being in policy settings). The searches were limited to abstracts to increase the specificity, albeit at some expense to sensitivity, with which we could identify relevant articles.
We also employed inclusion/exclusion criteria to facilitate the process by which we selected articles, thereby minimizing any potential bias arising from our subjective interpretations. We included independent, stand-alone investigations relevant to the study’s objectives (i.e., concerned with well-being in the context of public policy), which focused on well-being as a central outcome or process and which made explicit reference to “well-being” and “public policy” in either the title or the abstract. We excluded articles that were irrelevant to the study’s objectives, those that used noun adjuncts to focus on the well-being of specific populations (i.e., children, elderly, women) and contexts (e.g., retirement village), and those that focused on deprivation or poverty unless poverty indices were used to understand well-being as opposed to social exclusion. We also excluded book reviews and abstracts describing a compendium of studies.
Using these criteria, Joanne Wilson conducted the review and recorded the results on a template developed specifically for the project, organized chronologically across each database and timeframe. Results were scrutinized by two other colleagues to ensure the validity of the search strategy and the findings. Any concerns regarding the eligibility of studies for inclusion were discussed among the research team. I then analyzed the co-occurrence of the key terms in the database. The resultant conceptual map is shown in Figure 19.4.
The position of a concept in a network—a study of “well-being.” Node size is proportional to the frequency of terms in 54 selected abstracts. Line thickness is proportional to the co-occurrence of two terms in any phrase of three words (e.g., subjective well-being, economics of well-being, well-being and development).
The diagram can be interpreted as a visualization of a conceptual space. So, when academics write about well-being in the context of public policy, they tend to connect the discussion to the other terms in the matrix. “Happiness,” “health,” “economic,” and “subjective,” for example, are relatively dominant terms in the matrix. The node size of these words suggests that references to such entities is only slightly less than references to well-being itself. However, when we come to analyze how well-being is talked about in detail, we see specific connections come to the fore. Thus, the data imply that talk of “subjective well-being” far outweighs discussion of “social well-being” or “economic well-being.” Happiness tends to act as an independent node (there is only one occurrence of happiness and well-being), probably suggesting that “happiness” is acting as a synonym for well-being. Quality of life is poorly represented in the abstracts, and its connection to most of the other concepts in the space is very weak—confirming, perhaps, that quality of life is unrelated to contemporary discussions of well-being and happiness. The existence of “measures” points to a distinct concern to assess and to quantify expressions of happiness, well-being, economic growth, and gross domestic product. More important and underlying this detail, there are grounds for suggesting that there are in fact a number of tensions in the literature on well-being.
On the one hand, the results point toward an understanding of well-being as a property of individuals—as something that they feel or experience. Such a discourse is reflected through the use of words like happiness, subjective , and individual . This individualistic and subjective frame has grown in influence over the past decade in particular, and one of the problems with it is that it tends toward a somewhat content-free conceptualization of well-being. To feel a sense of well-being, one merely states that one is in a state of well-being; to be happy, one merely proclaims that one is happy (cf., Office for National Statistics, 2012 ). It is reminiscent of the conditions portrayed in Aldous Huxley’s Brave New World , wherein the rulers of a closely managed society gave their priority to maintaining order and ensuring the happiness of the greatest number—in the absence of attention to justice or freedom of thought or any sense of duty and obligation to others, many of whom were systematically bred in “the hatchery” as slaves.
On the other hand, there is some intimation in our web that the notion of well-being cannot be captured entirely by reference to individuals alone and that there are other dimensions to the concept—that well-being is the outcome or product of, say, access to reasonable incomes, to safe environments, to “development,” and to health and welfare. It is a vision hinted at by the inclusion of those very terms in the network. These different concepts necessarily give rise to important differences concerning how well-being is identified and measured and therefore what policies are most likely to advance well-being. In the first kind of conceptualization, we might improve well-being merely by dispensing what Huxley referred to as “soma” (a superdrug that ensured feelings of happiness and elation); in the other case, however, we would need to invest in economic, human, and social capital as the infrastructure for well-being. In any event and even at this nascent level, we can see how CTA can begin to tease out conceptual complexities and theoretical positions in what is otherwise routine textual data.
Putting the Content of Documents in Their Place
I suggested in my introduction that CTA was a method of analysis—not a method of data collection or a form of research design. As such, it does not necessarily inveigle us into any specific forms of either design or data collection, though designs and methods that rely on quantification are dominant. In this closing section, however, I want to raise the issue as to how we should position a study of content in our research strategies as a whole. We must keep in mind that documents and records always exist in a context and that while what is “in” the document may be considered central, a good research plan can often encompass a variety of ways of looking at how content links to context. Hence, in what follows, I intend to outline how an analysis of content might be combined with other ways of looking at a record or text and even how the analysis of content might be positioned as secondary to an examination of a document or record. The discussion calls on a much broader analysis, as presented in Prior ( 2011 ).
I have already stated that basic forms of CTA can serve as an important point of departure for many types of data analysis—for example, as discourse analysis. Naturally, whenever “discourse” is invoked, there is at least some recognition of the notion that words might play a part in structuring the world rather than merely reporting on it or describing it (as is the case with the 2002 State of the Nation address that was quoted in the section “Units of Analysis”). Thus, for example, there is a considerable tradition within social studies of science and technology for examining the place of scientific rhetoric in structuring notions of “nature” and the position of human beings (especially as scientists) within nature (see, e.g., work by Bazerman, 1988 ; Gilbert & Mulkay, 1984 ; and Kay, 2000 ). Nevertheless, little, if any, of that scholarship situates documents as anything other than inert objects, either constructed by or waiting patiently to be activated by scientists.
However, in the tradition of the ethnomethodologists (Heritage, 1991 ) and some adherents of discourse analysis, it is also possible to argue that documents might be more fruitfully approached as a “topic” (Zimmerman & Pollner, 1971 ) rather than a “resource” (to be scanned for content), in which case the focus would be on the ways in which any given document came to assume its present content and structure. In the field of documentation, these latter approaches are akin to what Foucault ( 1970 ) might have called an “archaeology of documentation” and are well represented in studies of such things as how crime, suicide, and other statistics and associated official reports and policy documents are routinely generated. That, too, is a legitimate point of research focus, and it can often be worth examining the genesis of, say, suicide statistics or statistics about the prevalence of mental disorder in a community as well as using such statistics as a basis for statistical modeling.
Unfortunately, the distinction between topic and resource is not always easy to maintain—especially in the hurly-burly of doing empirical research (see, e.g., Prior, 2003 ). Putting an emphasis on “topic,” however, can open a further dimension of research that concerns the ways in which documents function in the everyday world. And, as I have already hinted, when we focus on function, it becomes apparent that documents serve not merely as containers of content but also very often as active agents in episodes of interaction and schemes of social organization. In this vein, one can begin to think of an ethnography of documentation. Therein, the key research questions revolve around the ways in which documents are used and integrated into specific kinds of organizational settings, as well as with how documents are exchanged and how they circulate within such settings. Clearly, documents carry content—words, images, plans, ideas, patterns, and so forth—but the manner in which such material is called on and manipulated, and the way in which it functions, cannot be determined (though it may be constrained) by an analysis of content. Thus, Harper’s ( 1998 ) study of the use of economic reports inside the International Monetary Fund provides various examples of how “reports” can function to both differentiate and cohere work groups. In the same way. Henderson ( 1995 ) illustrated how engineering sketches and drawings can serve as what she calls conscription devices on the workshop floor.
Documents constitute a form of what Latour ( 1986 ) would refer to as “immutable mobiles,” and with an eye on the mobility of documents, it is worth noting an emerging interest in histories of knowledge that seek to examine how the same documents have been received and absorbed quite differently by different cultural networks (see, e.g., Burke, 2000 ). A parallel concern has arisen with regard to the newly emergent “geographies of knowledge” (see, e.g., Livingstone, 2005 ). In the history of science, there has also been an expressed interest in the biography of scientific objects (Latour, 1987 , p. 262) or of “epistemic things” (Rheinberger, 2000 )—tracing the history of objects independent of the “inventors” and “discoverers” to which such objects are conventionally attached. It is an approach that could be easily extended to the study of documents and is partly reflected in the earlier discussion concerning the meaning of the concept of well-being. Note how in all these cases a key consideration is how words and documents as “things” circulate and translate from one culture to another; issues of content are secondary.
Studying how documents are used and how they circulate can constitute an important area of research in its own right. Yet even those who focus on document use can be overly anthropocentric and subsequently overemphasize the potency of human action in relation to written text. In that light, it is interesting to consider ways in which we might reverse that emphasis and instead to study the potency of text and the manner in which documents can influence organizational activities as well as reflect them. Thus, Dorothy Winsor ( 1999 ), for example, examined the ways in which work orders drafted by engineers not only shape and fashion the practices and activities of engineering technicians but also construct “two different worlds” on the workshop floor.
In light of this, I will suggest a typology (Table 19.3 ) of the ways in which documents have come to be and can be considered in social research.
While accepting that no form of categorical classification can capture the inherent fluidity of the world, its actors, and its objects, Table 19.3 aims to offer some understanding of the various ways in which documents have been dealt with by social researchers. Thus, approaches that fit into Cell 1 have been dominant in the history of social science generally. Therein, documents (especially as text) have been analyzed and coded for what they contain in the way of descriptions, reports, images, representations, and accounts. In short, they have been scoured for evidence. Data analysis strategies concentrate almost entirely on what is in the “text” (via various forms of CTA). This emphasis on content is carried over into Cell 2–type approaches, with the key differences being that analysis is concerned with how document content comes into being. The attention here is usually on the conceptual architecture and sociotechnical procedures by means of which written reports, descriptions, statistical data, and so forth are generated. Various kinds of discourse analysis have been used to unravel the conceptual issues, while a focus on sociotechnical and rule-based procedures by means of which clinical, police, social work, and other forms of records and reports are constructed has been well represented in the work of ethnomethodologists (see Prior, 2011 ). In contrast, and in Cell 3, the research focus is on the ways in which documents are called on as a resource by various and different kinds of “user.” Here, concerns with document content or how a document has come into being are marginal, and the analysis concentrates on the relationship between specific documents and their use or recruitment by identifiable human actors for purposeful ends. I have pointed to some studies of the latter kind in earlier paragraphs (e.g., Henderson, 1995 ). Finally, the approaches that fit into Cell 4 also position content as secondary. The emphasis here is on how documents as “things” function in schemes of social activity and with how such things can drive, rather than be driven by, human actors. In short, the spotlight is on the vita activa of documentation, and I have provided numerous example of documents as actors in other publications (see Prior, 2003 , 2008 , 2011 ).
Content analysis was a method originally developed to analyze mass media “messages” in an age of radio and newspaper print, well before the digital age. Unfortunately, CTA struggles to break free of its origins and continues to be associated with the quantitative analysis of “communication.” Yet, as I have argued, there is no rational reason why its use must be restricted to such a narrow field, because it can be used to analyze printed text and interview data (as well as other forms of inscription) in various settings. What it cannot overcome is the fact that it is a method of analysis and not a method of data collection. However, as I have shown, it is an analytical strategy that can be integrated into a variety of research designs and approaches—cross-sectional and longitudinal survey designs, ethnography and other forms of qualitative design, and secondary analysis of preexisting data sets. Even as a method of analysis, it is flexible and can be used either independent of other methods or in conjunction with them. As we have seen, it is easily merged with various forms of discourse analysis and can be used as an exploratory method or as a means of verification. Above all, perhaps, it crosses the divide between “quantitative” and “qualitative” modes of inquiry in social research and offers a new dimension to the meaning of mixed methods research. I recommend it.
Abbott, A. ( 1992 ). What do cases do? In C. C. Ragin & H. S. Becker (Eds.), What is a case? Exploring the foundations of social inquiry (pp. 53–82). Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
Google Scholar
Google Preview
Altheide, D. L. ( 1987 ). Ethnographic content analysis. Qualitative Sociology, 10, 65–77.
Arksey, H. , & O’Malley, L. ( 2005 ). Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Sociological Research Methodology, 8, 19–32.
Babbie, E. ( 2013 ). The practice of social research (13th ed.) Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Bazerman, C. ( 1988 ). Shaping written knowledge. The genre and activity of the experimental article in science . Madison: University of Wisconsin Press.
Becker, G. ( 1997 ). Disrupted lives. How people create meaning in a chaotic world . London, England: University of California Press.
Berelson, B. ( 1952 ). Content analysis in communication research . Glencoe, IL: Free Press.
Bowker, G. C. , & Star, S. L. ( 1999 ). Sorting things out. Classification and its consequences . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Braun, V. , & Clarke, V. ( 2006 ). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 3, 77–101.
Breuer, J. , & Freud, S. ( 2001 ). Studies on hysteria. In L. Strachey (Ed.), The standard edition of the complete psychological works of Sigmund Freud (Vol. 2). London, England: Vintage.
Bryman, A. ( 2008 ). Social research methods (3rd ed.). Oxford, England: Oxford University Press.
Burke, P. ( 2000 ). A social history of knowledge. From Guttenberg to Diderot . Cambridge, MA: Polity Press.
Bury, M. ( 1982 ). Chronic illness as biographical disruption. Sociology of Health and Illness, 4, 167–182.
Carley, K. ( 1993 ). Coding choices for textual analysis. A comparison of content analysis and map analysis. Sociological Methodology, 23, 75–126.
Charon, R. ( 2006 ). Narrative medicine. Honoring the stories of illness . New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Creswell, J. W. ( 2007 ). Designing and conducting mixed methods research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Davison, C. , Davey-Smith, G. , & Frankel, S. ( 1991 ). Lay epidemiology and the prevention paradox. Sociology of Health & Illness, 13, 1–19.
Evans, M. , Prout, H. , Prior, L. , Tapper-Jones, L. , & Butler, C. ( 2007 ). A qualitative study of lay beliefs about influenza. British Journal of General Practice, 57, 352–358.
Foucault, M. ( 1970 ). The order of things. An archaeology of the human sciences . London, England: Tavistock.
Frank, A. ( 1995 ). The wounded storyteller: Body, illness, and ethics . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Gerring, J. ( 2004 ). What is a case study, and what is it good for? The American Political Science Review, 98, 341–354.
Gilbert, G. N. , & Mulkay, M. ( 1984 ). Opening Pandora’s box. A sociological analysis of scientists’ discourse . Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
Glaser, B. G. , & Strauss, A. L. ( 1967 ). The discovery of grounded theory. Strategies for qualitative research . New York, NY: Aldine de Gruyter.
Goode, W. J. , & Hatt, P. K. ( 1952 ). Methods in social research . New York, NY: McGraw–Hill.
Greimas, A. J. ( 1970 ). Du Sens. Essays sémiotiques . Paris, France: Ėditions du Seuil.
Habermas, J. ( 1987 ). The theory of communicative action: Vol.2, A critique of functionalist reason ( T. McCarthy , Trans.). Cambridge, MA: Polity Press.
Harper, R. ( 1998 ). Inside the IMF. An ethnography of documents, technology, and organizational action . London, England: Academic Press.
Henderson, K. ( 1995 ). The political career of a prototype. Visual representation in design engineering. Social Problems, 42, 274–299.
Heritage, J. ( 1991 ). Garkfinkel and ethnomethodology . Cambridge, MA: Polity Press.
Hydén, L-C. ( 1997 ). Illness and narrative. Sociology of Health & Illness, 19, 48–69.
Kahn, R. , & Cannell, C. ( 1957 ). The dynamics of interviewing. Theory, technique and cases . New York, NY: Wiley.
Kay, L. E. ( 2000 ). Who wrote the book of life? A history of the genetic code . Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Kleinman, A. , Eisenberg, L. , & Good, B. ( 1978 ). Culture, illness & care, clinical lessons from anthropologic and cross-cultural research. Annals of Internal Medicine, 88, 251–258.
Kracauer, S. ( 1952 ). The challenge of qualitative content analysis. Public Opinion Quarterly, Special Issue on International Communications Research (1952–53), 16, 631–642.
Krippendorf, K. ( 2004 ). Content analysis: An introduction to its methodology (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Latour, B. ( 1986 ). Visualization and cognition: Thinking with eyes and hands. Knowledge and Society, Studies in Sociology of Culture, Past and Present, 6, 1–40.
Latour, B. ( 1987 ). Science in action. How to follow scientists and engineers through society . Milton Keynes, England: Open University Press.
Livingstone, D. N. ( 2005 ). Text, talk, and testimony: Geographical reflections on scientific habits. An afterword. British Society for the History of Science, 38, 93–100.
Luria, A. R. ( 1975 ). The man with the shattered world. A history of a brain wound ( L. Solotaroff , Trans.). Harmondsworth, England: Penguin.
Martin, A. , & Lynch, M. ( 2009 ). Counting things and counting people: The practices and politics of counting. Social Problems, 56, 243–266.
Merton, R. K. ( 1968 ). Social theory and social structure . New York, NY: Free Press.
Morgan, D. L. ( 1993 ). Qualitative content analysis. A guide to paths not taken. Qualitative Health Research, 2, 112–121.
Morgan, D. L. ( 1998 ). Practical strategies for combining qualitative and quantitative methods. Qualitative Health Research, 8, 362–376.
Morris, P. G. , Prior, L. , Deb, S. , Lewis, G. , Mayle, W. , Burrow, C. E. , & Bryant, E. ( 2005 ). Patients’ views on outcome following head injury: A qualitative study, BMC Family Practice, 6, 30.
Neuendorf, K. A. ( 2002 ). The content analysis guidebook . Thousand Oaks: CA: Sage.
Newman, J. , & Vidler, E. ( 2006 ). Discriminating customers, responsible patients, empowered users: Consumerism and the modernisation of health care, Journal of Social Policy, 35, 193–210.
Office for National Statistics. ( 2012 ). First ONS annual experimental subjective well-being results . London, England: Office for National Statistics. Retrieved from http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/dcp171766_272294.pdf
Prior, L. ( 2003 ). Using documents in social research . London, England: Sage.
Prior, L. ( 2008 ). Repositioning documents in social research. Sociology. Special Issue on Research Methods, 42, 821–836.
Prior, L. ( 2011 ). Using documents and records in social research (4 vols.). London, England: Sage.
Prior, L. , Evans, M. , & Prout, H. ( 2011 ). Talking about colds and flu: The lay diagnosis of two common illnesses among older British people. Social Science and Medicine, 73, 922–928.
Prior, L. , Hughes, D. , & Peckham, S. ( 2012 ) The discursive turn in policy analysis and the validation of policy stories. Journal of Social Policy, 41, 271–289.
Ragin, C. C. , & Becker, H. S. ( 1992 ). What is a case? Exploring the foundations of social inquiry . Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
Rheinberger, H.-J. ( 2000 ). Cytoplasmic particles. The trajectory of a scientific object. In Daston, L. (Ed.), Biographies of scientific objects (pp. 270–294). Chicago, IL: Chicago University Press.
Ricoeur, P. ( 1984 ). Time and narrative (Vol. 1., K. McLaughlin & D, Pellauer, Trans.). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Roe, E. ( 1994 ). Narrative policy analysis, theory and practice . Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
Ryan, G. W. , & Bernard, H. R. ( 2000 ). Data management and analysis methods. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 769–802). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Schutz, A. , & Luckman, T. ( 1974 ). The structures of the life-world (R. M. Zaner & H. T. Engelhardt, Trans.). London, England: Heinemann.
SPSS. ( 2007 ). Text mining for Clementine . 12.0 User’s Guide. Chicago, IL: SPSS.
Weber, R. P. ( 1990 ). Basic content analysis . Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Winsor, D. ( 1999 ). Genre and activity systems. The role of documentation in maintaining and changing engineering activity systems. Written Communication, 16, 200–224.
Zimmerman, D. H. , & Pollner, M. ( 1971 ). The everyday world as a phenomenon. In J. D. Douglas (Ed.), Understanding everyday life (pp. 80–103). London, England: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
What Is Qualitative Content Analysis?
Qca explained simply (with examples).
By: Jenna Crosley (PhD). Reviewed by: Dr Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | February 2021
If you’re in the process of preparing for your dissertation, thesis or research project, you’ve probably encountered the term “ qualitative content analysis ” – it’s quite a mouthful. If you’ve landed on this post, you’re probably a bit confused about it. Well, the good news is that you’ve come to the right place…
Overview: Qualitative Content Analysis
- What (exactly) is qualitative content analysis
- The two main types of content analysis
- When to use content analysis
- How to conduct content analysis (the process)
- The advantages and disadvantages of content analysis
1. What is content analysis?
Content analysis is a qualitative analysis method that focuses on recorded human artefacts such as manuscripts, voice recordings and journals. Content analysis investigates these written, spoken and visual artefacts without explicitly extracting data from participants – this is called unobtrusive research.
In other words, with content analysis, you don’t necessarily need to interact with participants (although you can if necessary); you can simply analyse the data that they have already produced. With this type of analysis, you can analyse data such as text messages, books, Facebook posts, videos, and audio (just to mention a few).
The basics – explicit and implicit content
When working with content analysis, explicit and implicit content will play a role. Explicit data is transparent and easy to identify, while implicit data is that which requires some form of interpretation and is often of a subjective nature. Sounds a bit fluffy? Here’s an example:
Joe: Hi there, what can I help you with?
Lauren: I recently adopted a puppy and I’m worried that I’m not feeding him the right food. Could you please advise me on what I should be feeding?
Joe: Sure, just follow me and I’ll show you. Do you have any other pets?
Lauren: Only one, and it tweets a lot!
In this exchange, the explicit data indicates that Joe is helping Lauren to find the right puppy food. Lauren asks Joe whether she has any pets aside from her puppy. This data is explicit because it requires no interpretation.
On the other hand, implicit data , in this case, includes the fact that the speakers are in a pet store. This information is not clearly stated but can be inferred from the conversation, where Joe is helping Lauren to choose pet food. An additional piece of implicit data is that Lauren likely has some type of bird as a pet. This can be inferred from the way that Lauren states that her pet “tweets”.
As you can see, explicit and implicit data both play a role in human interaction and are an important part of your analysis. However, it’s important to differentiate between these two types of data when you’re undertaking content analysis. Interpreting implicit data can be rather subjective as conclusions are based on the researcher’s interpretation. This can introduce an element of bias , which risks skewing your results.
2. The two types of content analysis
Now that you understand the difference between implicit and explicit data, let’s move on to the two general types of content analysis : conceptual and relational content analysis. Importantly, while conceptual and relational content analysis both follow similar steps initially, the aims and outcomes of each are different.
Conceptual analysis focuses on the number of times a concept occurs in a set of data and is generally focused on explicit data. For example, if you were to have the following conversation:
Marie: She told me that she has three cats.
Jean: What are her cats’ names?
Marie: I think the first one is Bella, the second one is Mia, and… I can’t remember the third cat’s name.
In this data, you can see that the word “cat” has been used three times. Through conceptual content analysis, you can deduce that cats are the central topic of the conversation. You can also perform a frequency analysis , where you assess the term’s frequency in the data. For example, in the exchange above, the word “cat” makes up 9% of the data. In other words, conceptual analysis brings a little bit of quantitative analysis into your qualitative analysis.
As you can see, the above data is without interpretation and focuses on explicit data . Relational content analysis, on the other hand, takes a more holistic view by focusing more on implicit data in terms of context, surrounding words and relationships.
There are three types of relational analysis:
- Affect extraction
- Proximity analysis
- Cognitive mapping
Affect extraction is when you assess concepts according to emotional attributes. These emotions are typically mapped on scales, such as a Likert scale or a rating scale ranging from 1 to 5, where 1 is “very sad” and 5 is “very happy”.
If participants are talking about their achievements, they are likely to be given a score of 4 or 5, depending on how good they feel about it. If a participant is describing a traumatic event, they are likely to have a much lower score, either 1 or 2.
Proximity analysis identifies explicit terms (such as those found in a conceptual analysis) and the patterns in terms of how they co-occur in a text. In other words, proximity analysis investigates the relationship between terms and aims to group these to extract themes and develop meaning.
Proximity analysis is typically utilised when you’re looking for hard facts rather than emotional, cultural, or contextual factors. For example, if you were to analyse a political speech, you may want to focus only on what has been said, rather than implications or hidden meanings. To do this, you would make use of explicit data, discounting any underlying meanings and implications of the speech.
Lastly, there’s cognitive mapping, which can be used in addition to, or along with, proximity analysis. Cognitive mapping involves taking different texts and comparing them in a visual format – i.e. a cognitive map. Typically, you’d use cognitive mapping in studies that assess changes in terms, definitions, and meanings over time. It can also serve as a way to visualise affect extraction or proximity analysis and is often presented in a form such as a graphic map.
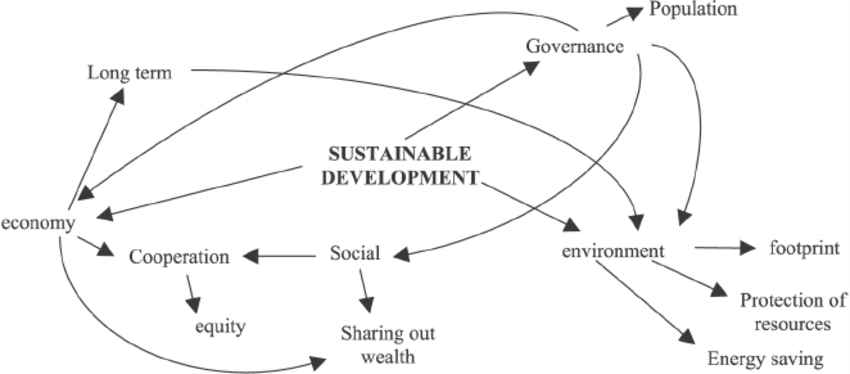
To recap on the essentials, content analysis is a qualitative analysis method that focuses on recorded human artefacts . It involves both conceptual analysis (which is more numbers-based) and relational analysis (which focuses on the relationships between concepts and how they’re connected).
Need a helping hand?
3. When should you use content analysis?
Content analysis is a useful tool that provides insight into trends of communication . For example, you could use a discussion forum as the basis of your analysis and look at the types of things the members talk about as well as how they use language to express themselves. Content analysis is flexible in that it can be applied to the individual, group, and institutional level.
Content analysis is typically used in studies where the aim is to better understand factors such as behaviours, attitudes, values, emotions, and opinions . For example, you could use content analysis to investigate an issue in society, such as miscommunication between cultures. In this example, you could compare patterns of communication in participants from different cultures, which will allow you to create strategies for avoiding misunderstandings in intercultural interactions.
Another example could include conducting content analysis on a publication such as a book. Here you could gather data on the themes, topics, language use and opinions reflected in the text to draw conclusions regarding the political (such as conservative or liberal) leanings of the publication.

4. How to conduct a qualitative content analysis
Conceptual and relational content analysis differ in terms of their exact process ; however, there are some similarities. Let’s have a look at these first – i.e., the generic process:
- Recap on your research questions
- Undertake bracketing to identify biases
- Operationalise your variables and develop a coding scheme
- Code the data and undertake your analysis
Step 1 – Recap on your research questions
It’s always useful to begin a project with research questions , or at least with an idea of what you are looking for. In fact, if you’ve spent time reading this blog, you’ll know that it’s useful to recap on your research questions, aims and objectives when undertaking pretty much any research activity. In the context of content analysis, it’s difficult to know what needs to be coded and what doesn’t, without a clear view of the research questions.
For example, if you were to code a conversation focused on basic issues of social justice, you may be met with a wide range of topics that may be irrelevant to your research. However, if you approach this data set with the specific intent of investigating opinions on gender issues, you will be able to focus on this topic alone, which would allow you to code only what you need to investigate.
Step 2 – Reflect on your personal perspectives and biases
It’s vital that you reflect on your own pre-conception of the topic at hand and identify the biases that you might drag into your content analysis – this is called “ bracketing “. By identifying this upfront, you’ll be more aware of them and less likely to have them subconsciously influence your analysis.
For example, if you were to investigate how a community converses about unequal access to healthcare, it is important to assess your views to ensure that you don’t project these onto your understanding of the opinions put forth by the community. If you have access to medical aid, for instance, you should not allow this to interfere with your examination of unequal access.

Step 3 – Operationalise your variables and develop a coding scheme
Next, you need to operationalise your variables . But what does that mean? Simply put, it means that you have to define each variable or construct . Give every item a clear definition – what does it mean (include) and what does it not mean (exclude). For example, if you were to investigate children’s views on healthy foods, you would first need to define what age group/range you’re looking at, and then also define what you mean by “healthy foods”.
In combination with the above, it is important to create a coding scheme , which will consist of information about your variables (how you defined each variable), as well as a process for analysing the data. For this, you would refer back to how you operationalised/defined your variables so that you know how to code your data.
For example, when coding, when should you code a food as “healthy”? What makes a food choice healthy? Is it the absence of sugar or saturated fat? Is it the presence of fibre and protein? It’s very important to have clearly defined variables to achieve consistent coding – without this, your analysis will get very muddy, very quickly.

Step 4 – Code and analyse the data
The next step is to code the data. At this stage, there are some differences between conceptual and relational analysis.
As described earlier in this post, conceptual analysis looks at the existence and frequency of concepts, whereas a relational analysis looks at the relationships between concepts. For both types of analyses, it is important to pre-select a concept that you wish to assess in your data. Using the example of studying children’s views on healthy food, you could pre-select the concept of “healthy food” and assess the number of times the concept pops up in your data.
Here is where conceptual and relational analysis start to differ.
At this stage of conceptual analysis , it is necessary to decide on the level of analysis you’ll perform on your data, and whether this will exist on the word, phrase, sentence, or thematic level. For example, will you code the phrase “healthy food” on its own? Will you code each term relating to healthy food (e.g., broccoli, peaches, bananas, etc.) with the code “healthy food” or will these be coded individually? It is very important to establish this from the get-go to avoid inconsistencies that could result in you having to code your data all over again.
On the other hand, relational analysis looks at the type of analysis. So, will you use affect extraction? Proximity analysis? Cognitive mapping? A mix? It’s vital to determine the type of analysis before you begin to code your data so that you can maintain the reliability and validity of your research .
How to conduct conceptual analysis
First, let’s have a look at the process for conceptual analysis.
Once you’ve decided on your level of analysis, you need to establish how you will code your concepts, and how many of these you want to code. Here you can choose whether you want to code in a deductive or inductive manner. Just to recap, deductive coding is when you begin the coding process with a set of pre-determined codes, whereas inductive coding entails the codes emerging as you progress with the coding process. Here it is also important to decide what should be included and excluded from your analysis, and also what levels of implication you wish to include in your codes.
For example, if you have the concept of “tall”, can you include “up in the clouds”, derived from the sentence, “the giraffe’s head is up in the clouds” in the code, or should it be a separate code? In addition to this, you need to know what levels of words may be included in your codes or not. For example, if you say, “the panda is cute” and “look at the panda’s cuteness”, can “cute” and “cuteness” be included under the same code?
Once you’ve considered the above, it’s time to code the text . We’ve already published a detailed post about coding , so we won’t go into that process here. Once you’re done coding, you can move on to analysing your results. This is where you will aim to find generalisations in your data, and thus draw your conclusions .
How to conduct relational analysis
Now let’s return to relational analysis.
As mentioned, you want to look at the relationships between concepts . To do this, you’ll need to create categories by reducing your data (in other words, grouping similar concepts together) and then also code for words and/or patterns. These are both done with the aim of discovering whether these words exist, and if they do, what they mean.
Your next step is to assess your data and to code the relationships between your terms and meanings, so that you can move on to your final step, which is to sum up and analyse the data.
To recap, it’s important to start your analysis process by reviewing your research questions and identifying your biases . From there, you need to operationalise your variables, code your data and then analyse it.

5. What are the pros & cons of content analysis?
One of the main advantages of content analysis is that it allows you to use a mix of quantitative and qualitative research methods, which results in a more scientifically rigorous analysis.
For example, with conceptual analysis, you can count the number of times that a term or a code appears in a dataset, which can be assessed from a quantitative standpoint. In addition to this, you can then use a qualitative approach to investigate the underlying meanings of these and relationships between them.
Content analysis is also unobtrusive and therefore poses fewer ethical issues than some other analysis methods. As the content you’ll analyse oftentimes already exists, you’ll analyse what has been produced previously, and so you won’t have to collect data directly from participants. When coded correctly, data is analysed in a very systematic and transparent manner, which means that issues of replicability (how possible it is to recreate research under the same conditions) are reduced greatly.
On the downside , qualitative research (in general, not just content analysis) is often critiqued for being too subjective and for not being scientifically rigorous enough. This is where reliability (how replicable a study is by other researchers) and validity (how suitable the research design is for the topic being investigated) come into play – if you take these into account, you’ll be on your way to achieving sound research results.
Recap: Qualitative content analysis
In this post, we’ve covered a lot of ground – click on any of the sections to recap:
If you have any questions about qualitative content analysis, feel free to leave a comment below. If you’d like 1-on-1 help with your qualitative content analysis, be sure to book an initial consultation with one of our friendly Research Coaches.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...

You Might Also Like:

14 Comments
If I am having three pre-decided attributes for my research based on which a set of semi-structured questions where asked then should I conduct a conceptual content analysis or relational content analysis. please note that all three attributes are different like Agility, Resilience and AI.
Thank you very much. I really enjoyed every word.
please send me one/ two sample of content analysis
send me to any sample of qualitative content analysis as soon as possible
Many thanks for the brilliant explanation. Do you have a sample practical study of a foreign policy using content analysis?
1) It will be very much useful if a small but complete content analysis can be sent, from research question to coding and analysis. 2) Is there any software by which qualitative content analysis can be done?
Common software for qualitative analysis is nVivo, and quantitative analysis is IBM SPSS
Thank you. Can I have at least 2 copies of a sample analysis study as my reference?
Could you please send me some sample of textbook content analysis?
Can I send you my research topic, aims, objectives and questions to give me feedback on them?
please could you send me samples of content analysis?
Yes please send
really we enjoyed your knowledge thanks allot. from Ethiopia
can you please share some samples of content analysis(relational)? I am a bit confused about processing the analysis part
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Privacy Policy

Home » Content Analysis – Methods, Types and Examples
Content Analysis – Methods, Types and Examples
Table of Contents

Content Analysis
Definition:
Content analysis is a research method used to analyze and interpret the characteristics of various forms of communication, such as text, images, or audio. It involves systematically analyzing the content of these materials, identifying patterns, themes, and other relevant features, and drawing inferences or conclusions based on the findings.
Content analysis can be used to study a wide range of topics, including media coverage of social issues, political speeches, advertising messages, and online discussions, among others. It is often used in qualitative research and can be combined with other methods to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular phenomenon.
Types of Content Analysis
There are generally two types of content analysis:
Quantitative Content Analysis
This type of content analysis involves the systematic and objective counting and categorization of the content of a particular form of communication, such as text or video. The data obtained is then subjected to statistical analysis to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between different variables. Quantitative content analysis is often used to study media content, advertising, and political speeches.
Qualitative Content Analysis
This type of content analysis is concerned with the interpretation and understanding of the meaning and context of the content. It involves the systematic analysis of the content to identify themes, patterns, and other relevant features, and to interpret the underlying meanings and implications of these features. Qualitative content analysis is often used to study interviews, focus groups, and other forms of qualitative data, where the researcher is interested in understanding the subjective experiences and perceptions of the participants.
Methods of Content Analysis
There are several methods of content analysis, including:
Conceptual Analysis
This method involves analyzing the meanings of key concepts used in the content being analyzed. The researcher identifies key concepts and analyzes how they are used, defining them and categorizing them into broader themes.
Content Analysis by Frequency
This method involves counting and categorizing the frequency of specific words, phrases, or themes that appear in the content being analyzed. The researcher identifies relevant keywords or phrases and systematically counts their frequency.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing the content of two or more sources to identify similarities, differences, and patterns. The researcher selects relevant sources, identifies key themes or concepts, and compares how they are represented in each source.
Discourse Analysis
This method involves analyzing the structure and language of the content being analyzed to identify how the content constructs and represents social reality. The researcher analyzes the language used and the underlying assumptions, beliefs, and values reflected in the content.
Narrative Analysis
This method involves analyzing the content as a narrative, identifying the plot, characters, and themes, and analyzing how they relate to the broader social context. The researcher identifies the underlying messages conveyed by the narrative and their implications for the broader social context.
Content Analysis Conducting Guide
Here is a basic guide to conducting a content analysis:
- Define your research question or objective: Before starting your content analysis, you need to define your research question or objective clearly. This will help you to identify the content you need to analyze and the type of analysis you need to conduct.
- Select your sample: Select a representative sample of the content you want to analyze. This may involve selecting a random sample, a purposive sample, or a convenience sample, depending on the research question and the availability of the content.
- Develop a coding scheme: Develop a coding scheme or a set of categories to use for coding the content. The coding scheme should be based on your research question or objective and should be reliable, valid, and comprehensive.
- Train coders: Train coders to use the coding scheme and ensure that they have a clear understanding of the coding categories and procedures. You may also need to establish inter-coder reliability to ensure that different coders are coding the content consistently.
- Code the content: Code the content using the coding scheme. This may involve manually coding the content, using software, or a combination of both.
- Analyze the data: Once the content is coded, analyze the data using appropriate statistical or qualitative methods, depending on the research question and the type of data.
- Interpret the results: Interpret the results of the analysis in the context of your research question or objective. Draw conclusions based on the findings and relate them to the broader literature on the topic.
- Report your findings: Report your findings in a clear and concise manner, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions. Provide details about the coding scheme, inter-coder reliability, and any limitations of the study.
Applications of Content Analysis
Content analysis has numerous applications across different fields, including:
- Media Research: Content analysis is commonly used in media research to examine the representation of different groups, such as race, gender, and sexual orientation, in media content. It can also be used to study media framing, media bias, and media effects.
- Political Communication : Content analysis can be used to study political communication, including political speeches, debates, and news coverage of political events. It can also be used to study political advertising and the impact of political communication on public opinion and voting behavior.
- Marketing Research: Content analysis can be used to study advertising messages, consumer reviews, and social media posts related to products or services. It can provide insights into consumer preferences, attitudes, and behaviors.
- Health Communication: Content analysis can be used to study health communication, including the representation of health issues in the media, the effectiveness of health campaigns, and the impact of health messages on behavior.
- Education Research : Content analysis can be used to study educational materials, including textbooks, curricula, and instructional materials. It can provide insights into the representation of different topics, perspectives, and values.
- Social Science Research: Content analysis can be used in a wide range of social science research, including studies of social media, online communities, and other forms of digital communication. It can also be used to study interviews, focus groups, and other qualitative data sources.
Examples of Content Analysis
Here are some examples of content analysis:
- Media Representation of Race and Gender: A content analysis could be conducted to examine the representation of different races and genders in popular media, such as movies, TV shows, and news coverage.
- Political Campaign Ads : A content analysis could be conducted to study political campaign ads and the themes and messages used by candidates.
- Social Media Posts: A content analysis could be conducted to study social media posts related to a particular topic, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, to examine the attitudes and beliefs of social media users.
- Instructional Materials: A content analysis could be conducted to study the representation of different topics and perspectives in educational materials, such as textbooks and curricula.
- Product Reviews: A content analysis could be conducted to study product reviews on e-commerce websites, such as Amazon, to identify common themes and issues mentioned by consumers.
- News Coverage of Health Issues: A content analysis could be conducted to study news coverage of health issues, such as vaccine hesitancy, to identify common themes and perspectives.
- Online Communities: A content analysis could be conducted to study online communities, such as discussion forums or social media groups, to understand the language, attitudes, and beliefs of the community members.
Purpose of Content Analysis
The purpose of content analysis is to systematically analyze and interpret the content of various forms of communication, such as written, oral, or visual, to identify patterns, themes, and meanings. Content analysis is used to study communication in a wide range of fields, including media studies, political science, psychology, education, sociology, and marketing research. The primary goals of content analysis include:
- Describing and summarizing communication: Content analysis can be used to describe and summarize the content of communication, such as the themes, topics, and messages conveyed in media content, political speeches, or social media posts.
- Identifying patterns and trends: Content analysis can be used to identify patterns and trends in communication, such as changes over time, differences between groups, or common themes or motifs.
- Exploring meanings and interpretations: Content analysis can be used to explore the meanings and interpretations of communication, such as the underlying values, beliefs, and assumptions that shape the content.
- Testing hypotheses and theories : Content analysis can be used to test hypotheses and theories about communication, such as the effects of media on attitudes and behaviors or the framing of political issues in the media.
When to use Content Analysis
Content analysis is a useful method when you want to analyze and interpret the content of various forms of communication, such as written, oral, or visual. Here are some specific situations where content analysis might be appropriate:
- When you want to study media content: Content analysis is commonly used in media studies to analyze the content of TV shows, movies, news coverage, and other forms of media.
- When you want to study political communication : Content analysis can be used to study political speeches, debates, news coverage, and advertising.
- When you want to study consumer attitudes and behaviors: Content analysis can be used to analyze product reviews, social media posts, and other forms of consumer feedback.
- When you want to study educational materials : Content analysis can be used to analyze textbooks, instructional materials, and curricula.
- When you want to study online communities: Content analysis can be used to analyze discussion forums, social media groups, and other forms of online communication.
- When you want to test hypotheses and theories : Content analysis can be used to test hypotheses and theories about communication, such as the framing of political issues in the media or the effects of media on attitudes and behaviors.
Characteristics of Content Analysis
Content analysis has several key characteristics that make it a useful research method. These include:
- Objectivity : Content analysis aims to be an objective method of research, meaning that the researcher does not introduce their own biases or interpretations into the analysis. This is achieved by using standardized and systematic coding procedures.
- Systematic: Content analysis involves the use of a systematic approach to analyze and interpret the content of communication. This involves defining the research question, selecting the sample of content to analyze, developing a coding scheme, and analyzing the data.
- Quantitative : Content analysis often involves counting and measuring the occurrence of specific themes or topics in the content, making it a quantitative research method. This allows for statistical analysis and generalization of findings.
- Contextual : Content analysis considers the context in which the communication takes place, such as the time period, the audience, and the purpose of the communication.
- Iterative : Content analysis is an iterative process, meaning that the researcher may refine the coding scheme and analysis as they analyze the data, to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Reliability and validity : Content analysis aims to be a reliable and valid method of research, meaning that the findings are consistent and accurate. This is achieved through inter-coder reliability tests and other measures to ensure the quality of the data and analysis.
Advantages of Content Analysis
There are several advantages to using content analysis as a research method, including:
- Objective and systematic : Content analysis aims to be an objective and systematic method of research, which reduces the likelihood of bias and subjectivity in the analysis.
- Large sample size: Content analysis allows for the analysis of a large sample of data, which increases the statistical power of the analysis and the generalizability of the findings.
- Non-intrusive: Content analysis does not require the researcher to interact with the participants or disrupt their natural behavior, making it a non-intrusive research method.
- Accessible data: Content analysis can be used to analyze a wide range of data types, including written, oral, and visual communication, making it accessible to researchers across different fields.
- Versatile : Content analysis can be used to study communication in a wide range of contexts and fields, including media studies, political science, psychology, education, sociology, and marketing research.
- Cost-effective: Content analysis is a cost-effective research method, as it does not require expensive equipment or participant incentives.
Limitations of Content Analysis
While content analysis has many advantages, there are also some limitations to consider, including:
- Limited contextual information: Content analysis is focused on the content of communication, which means that contextual information may be limited. This can make it difficult to fully understand the meaning behind the communication.
- Limited ability to capture nonverbal communication : Content analysis is limited to analyzing the content of communication that can be captured in written or recorded form. It may miss out on nonverbal communication, such as body language or tone of voice.
- Subjectivity in coding: While content analysis aims to be objective, there may be subjectivity in the coding process. Different coders may interpret the content differently, which can lead to inconsistent results.
- Limited ability to establish causality: Content analysis is a correlational research method, meaning that it cannot establish causality between variables. It can only identify associations between variables.
- Limited generalizability: Content analysis is limited to the data that is analyzed, which means that the findings may not be generalizable to other contexts or populations.
- Time-consuming: Content analysis can be a time-consuming research method, especially when analyzing a large sample of data. This can be a disadvantage for researchers who need to complete their research in a short amount of time.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Cluster Analysis – Types, Methods and Examples

Discriminant Analysis – Methods, Types and...

MANOVA (Multivariate Analysis of Variance) –...

Documentary Analysis – Methods, Applications and...

ANOVA (Analysis of variance) – Formulas, Types...

Graphical Methods – Types, Examples and Guide
- Open access
- Published: 19 April 2024
A scoping review of continuous quality improvement in healthcare system: conceptualization, models and tools, barriers and facilitators, and impact
- Aklilu Endalamaw 1 , 2 ,
- Resham B Khatri 1 , 3 ,
- Tesfaye Setegn Mengistu 1 , 2 ,
- Daniel Erku 1 , 4 , 5 ,
- Eskinder Wolka 6 ,
- Anteneh Zewdie 6 &
- Yibeltal Assefa 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 487 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
901 Accesses
Metrics details
The growing adoption of continuous quality improvement (CQI) initiatives in healthcare has generated a surge in research interest to gain a deeper understanding of CQI. However, comprehensive evidence regarding the diverse facets of CQI in healthcare has been limited. Our review sought to comprehensively grasp the conceptualization and principles of CQI, explore existing models and tools, analyze barriers and facilitators, and investigate its overall impacts.
This qualitative scoping review was conducted using Arksey and O’Malley’s methodological framework. We searched articles in PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and EMBASE databases. In addition, we accessed articles from Google Scholar. We used mixed-method analysis, including qualitative content analysis and quantitative descriptive for quantitative findings to summarize findings and PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR) framework to report the overall works.
A total of 87 articles, which covered 14 CQI models, were included in the review. While 19 tools were used for CQI models and initiatives, Plan-Do-Study/Check-Act cycle was the commonly employed model to understand the CQI implementation process. The main reported purposes of using CQI, as its positive impact, are to improve the structure of the health system (e.g., leadership, health workforce, health technology use, supplies, and costs), enhance healthcare delivery processes and outputs (e.g., care coordination and linkages, satisfaction, accessibility, continuity of care, safety, and efficiency), and improve treatment outcome (reduce morbidity and mortality). The implementation of CQI is not without challenges. There are cultural (i.e., resistance/reluctance to quality-focused culture and fear of blame or punishment), technical, structural (related to organizational structure, processes, and systems), and strategic (inadequate planning and inappropriate goals) related barriers that were commonly reported during the implementation of CQI.
Conclusions
Implementing CQI initiatives necessitates thoroughly comprehending key principles such as teamwork and timeline. To effectively address challenges, it’s crucial to identify obstacles and implement optimal interventions proactively. Healthcare professionals and leaders need to be mentally equipped and cognizant of the significant role CQI initiatives play in achieving purposes for quality of care.
Peer Review reports
Continuous quality improvement (CQI) initiative is a crucial initiative aimed at enhancing quality in the health system that has gradually been adopted in the healthcare industry. In the early 20th century, Shewhart laid the foundation for quality improvement by describing three essential steps for process improvement: specification, production, and inspection [ 1 , 2 ]. Then, Deming expanded Shewhart’s three-step model into ‘plan, do, study/check, and act’ (PDSA or PDCA) cycle, which was applied to management practices in Japan in the 1950s [ 3 ] and was gradually translated into the health system. In 1991, Kuperman applied a CQI approach to healthcare, comprising selecting a process to be improved, assembling a team of expert clinicians that understands the process and the outcomes, determining key steps in the process and expected outcomes, collecting data that measure the key process steps and outcomes, and providing data feedback to the practitioners [ 4 ]. These philosophies have served as the baseline for the foundation of principles for continuous improvement [ 5 ].
Continuous quality improvement fosters a culture of continuous learning, innovation, and improvement. It encourages proactive identification and resolution of problems, promotes employee engagement and empowerment, encourages trust and respect, and aims for better quality of care [ 6 , 7 ]. These characteristics drive the interaction of CQI with other quality improvement projects, such as quality assurance and total quality management [ 8 ]. Quality assurance primarily focuses on identifying deviations or errors through inspections, audits, and formal reviews, often settling for what is considered ‘good enough’, rather than pursuing the highest possible standards [ 9 , 10 ], while total quality management is implemented as the management philosophy and system to improve all aspects of an organization continuously [ 11 ].
Continuous quality improvement has been implemented to provide quality care. However, providing effective healthcare is a complicated and complex task in achieving the desired health outcomes and the overall well-being of individuals and populations. It necessitates tackling issues, including access, patient safety, medical advances, care coordination, patient-centered care, and quality monitoring [ 12 , 13 ], rooted long ago. It is assumed that the history of quality improvement in healthcare started in 1854 when Florence Nightingale introduced quality improvement documentation [ 14 ]. Over the passing decades, Donabedian introduced structure, processes, and outcomes as quality of care components in 1966 [ 15 ]. More comprehensively, the Institute of Medicine in the United States of America (USA) has identified effectiveness, efficiency, equity, patient-centredness, safety, and timeliness as the components of quality of care [ 16 ]. Moreover, quality of care has recently been considered an integral part of universal health coverage (UHC) [ 17 ], which requires initiatives to mobilise essential inputs [ 18 ].
While the overall objective of CQI in health system is to enhance the quality of care, it is important to note that the purposes and principles of CQI can vary across different contexts [ 19 , 20 ]. This variation has sparked growing research interest. For instance, a review of CQI approaches for capacity building addressed its role in health workforce development [ 21 ]. Another systematic review, based on random-controlled design studies, assessed the effectiveness of CQI using training as an intervention and the PDSA model [ 22 ]. As a research gap, the former review was not directly related to the comprehensive elements of quality of care, while the latter focused solely on the impact of training using the PDSA model, among other potential models. Additionally, a review conducted in 2015 aimed to identify barriers and facilitators of CQI in Canadian contexts [ 23 ]. However, all these reviews presented different perspectives and investigated distinct outcomes. This suggests that there is still much to explore in terms of comprehensively understanding the various aspects of CQI initiatives in healthcare.
As a result, we conducted a scoping review to address several aspects of CQI. Scoping reviews serve as a valuable tool for systematically mapping the existing literature on a specific topic. They are instrumental when dealing with heterogeneous or complex bodies of research. Scoping reviews provide a comprehensive overview by summarizing and disseminating findings across multiple studies, even when evidence varies significantly [ 24 ]. In our specific scoping review, we included various types of literature, including systematic reviews, to enhance our understanding of CQI.
This scoping review examined how CQI is conceptualized and measured and investigated models and tools for its application while identifying implementation challenges and facilitators. It also analyzed the purposes and impact of CQI on the health systems, providing valuable insights for enhancing healthcare quality.
Protocol registration and results reporting
Protocol registration for this scoping review was not conducted. Arksey and O’Malley’s methodological framework was utilized to conduct this scoping review [ 25 ]. The scoping review procedures start by defining the research questions, identifying relevant literature, selecting articles, extracting data, and summarizing the results. The review findings are reported using the PRISMA extension for a scoping review (PRISMA-ScR) [ 26 ]. McGowan and colleagues also advised researchers to report findings from scoping reviews using PRISMA-ScR [ 27 ].
Defining the research problems
This review aims to comprehensively explore the conceptualization, models, tools, barriers, facilitators, and impacts of CQI within the healthcare system worldwide. Specifically, we address the following research questions: (1) How has CQI been defined across various contexts? (2) What are the diverse approaches to implementing CQI in healthcare settings? (3) Which tools are commonly employed for CQI implementation ? (4) What barriers hinder and facilitators support successful CQI initiatives? and (5) What effects CQI initiatives have on the overall care quality?
Information source and search strategy
We conducted the search in PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and EMBASE databases, and the Google Scholar search engine. The search terms were selected based on three main distinct concepts. One group was CQI-related terms. The second group included terms related to the purpose for which CQI has been implemented, and the third group included processes and impact. These terms were selected based on the Donabedian framework of structure, process, and outcome [ 28 ]. Additionally, the detailed keywords were recruited from the primary health framework, which has described lists of dimensions under process, output, outcome, and health system goals of any intervention for health [ 29 ]. The detailed search strategy is presented in the Supplementary file 1 (Search strategy). The search for articles was initiated on August 12, 2023, and the last search was conducted on September 01, 2023.
Eligibility criteria and article selection
Based on the scoping review’s population, concept, and context frameworks [ 30 ], the population included any patients or clients. Additionally, the concepts explored in the review encompassed definitions, implementation, models, tools, barriers, facilitators, and impacts of CQI. Furthermore, the review considered contexts at any level of health systems. We included articles if they reported results of qualitative or quantitative empirical study, case studies, analytic or descriptive synthesis, any review, and other written documents, were published in peer-reviewed journals, and were designed to address at least one of the identified research questions or one of the identified implementation outcomes or their synonymous taxonomy as described in the search strategy. Based on additional contexts, we included articles published in English without geographic and time limitations. We excluded articles with abstracts only, conference abstracts, letters to editors, commentators, and corrections.
We exported all citations to EndNote x20 to remove duplicates and screen relevant articles. The article selection process includes automatic duplicate removal by using EndNote x20, unmatched title and abstract removal, citation and abstract-only materials removal, and full-text assessment. The article selection process was mainly conducted by the first author (AE) and reported to the team during the weekly meetings. The first author encountered papers that caused confusion regarding whether to include or exclude them and discussed them with the last author (YA). Then, decisions were ultimately made. Whenever disagreements happened, they were resolved by discussion and reconsideration of the review questions in relation to the written documents of the article. Further statistical analysis, such as calculating Kappa, was not performed to determine article inclusion or exclusion.
Data extraction and data items
We extracted first author, publication year, country, settings, health problem, the purpose of the study, study design, types of intervention if applicable, CQI approaches/steps if applicable, CQI tools and procedures if applicable, and main findings using a customized Microsoft Excel form.
Summarizing and reporting the results
The main findings were summarized and described based on the main themes, including concepts under conceptualizing, principles, teams, timelines, models, tools, barriers, facilitators, and impacts of CQI. Results-based convergent synthesis, achieved through mixed-method analysis, involved content analysis to identify the thematic presentation of findings. Additionally, a narrative description was used for quantitative findings, aligning them with the appropriate theme. The authors meticulously reviewed the primary findings from each included material and contextualized these findings concerning the main themes1. This approach provides a comprehensive understanding of complex interventions and health systems, acknowledging quantitative and qualitative evidence.
Search results
A total of 11,251 documents were identified from various databases: SCOPUS ( n = 4,339), PubMed ( n = 2,893), Web of Science ( n = 225), EMBASE ( n = 3,651), and Google Scholar ( n = 143). After removing duplicates ( n = 5,061), 6,190 articles were evaluated by title and abstract. Subsequently, 208 articles were assessed for full-text eligibility. Following the eligibility criteria, 121 articles were excluded, leaving 87 included in the current review (Fig. 1 ).
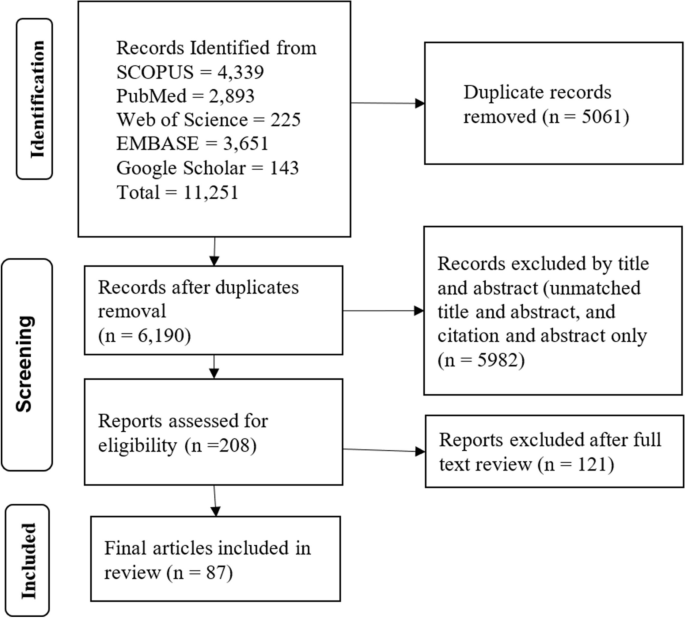
Article selection process
Operationalizing continuous quality improvement
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI) is operationalized as a cyclic process that requires commitment to implementation, teamwork, time allocation, and celebrating successes and failures.
CQI is a cyclic ongoing process that is followed reflexive, analytical and iterative steps, including identifying gaps, generating data, developing and implementing action plans, evaluating performance, providing feedback to implementers and leaders, and proposing necessary adjustments [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 ].
CQI requires committing to the philosophy, involving continuous improvement [ 19 , 38 ], establishing a mission statement [ 37 ], and understanding quality definition [ 19 ].
CQI involves a wide range of patient-oriented measures and performance indicators, specifically satisfying internal and external customers, developing quality assurance, adopting common quality measures, and selecting process measures [ 8 , 19 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 39 , 40 ].
CQI requires celebrating success and failure without personalization, leading each team member to develop error-free attitudes [ 19 ]. Success and failure are related to underlying organizational processes and systems as causes of failure rather than blaming individuals [ 8 ] because CQI is process-focused based on collaborative, data-driven, responsive, rigorous and problem-solving statistical analysis [ 8 , 19 , 38 ]. Furthermore, a gap or failure opens another opportunity for establishing a data-driven learning organization [ 41 ].
CQI cannot be implemented without a CQI team [ 8 , 19 , 37 , 39 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 ]. A CQI team comprises individuals from various disciplines, often comprising a team leader, a subject matter expert (physician or other healthcare provider), a data analyst, a facilitator, frontline staff, and stakeholders [ 39 , 43 , 47 , 48 , 49 ]. It is also important to note that inviting stakeholders or partners as part of the CQI support intervention is crucial [ 19 , 38 , 48 ].
The timeline is another distinct feature of CQI because the results of CQI vary based on the implementation duration of each cycle [ 35 ]. There is no specific time limit for CQI implementation, although there is a general consensus that a cycle of CQI should be relatively short [ 35 ]. For instance, a CQI implementation took 2 months [ 42 ], 4 months [ 50 ], 9 months [ 51 , 52 ], 12 months [ 53 , 54 , 55 ], and one year and 5 months [ 49 ] duration to achieve the desired positive outcome, while bi-weekly [ 47 ] and monthly data reviews and analyses [ 44 , 48 , 56 ], and activities over 3 months [ 57 ] have also resulted in a positive outcome.
Continuous quality improvement models and tools
There have been several models are utilized. The Plan-Do-Study/Check-Act cycle is a stepwise process involving project initiation, situation analysis, root cause identification, solution generation and selection, implementation, result evaluation, standardization, and future planning [ 7 , 36 , 37 , 45 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 53 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 ]. The FOCUS-PDCA cycle enhances the PDCA process by adding steps to find and improve a process (F), organize a knowledgeable team (O), clarify the process (C), understand variations (U), and select improvements (S) [ 55 , 71 , 72 , 73 ]. The FADE cycle involves identifying a problem (Focus), understanding it through data analysis (Analyze), devising solutions (Develop), and implementing the plan (Execute) [ 74 ]. The Logic Framework involves brainstorming to identify improvement areas, conducting root cause analysis to develop a problem tree, logically reasoning to create an objective tree, formulating the framework, and executing improvement projects [ 75 ]. Breakthrough series approach requires CQI teams to meet in quarterly collaborative learning sessions, share learning experiences, and continue discussion by telephone and cross-site visits to strengthen learning and idea exchange [ 47 ]. Another CQI model is the Lean approach, which has been conducted with Kaizen principles [ 52 ], 5 S principles, and the Six Sigma model. The 5 S (Sort, Set/Straighten, Shine, Standardize, Sustain) systematically organises and improves the workplace, focusing on sorting, setting order, shining, standardizing, and sustaining the improvement [ 54 , 76 ]. Kaizen principles guide CQI by advocating for continuous improvement, valuing all ideas, solving problems, focusing on practical, low-cost improvements, using data to drive change, acknowledging process defects, reducing variability and waste, recognizing every interaction as a customer-supplier relationship, empowering workers, responding to all ideas, and maintaining a disciplined workplace [ 77 ]. Lean Six Sigma, a CQI model, applies the DMAIC methodology, which involves defining (D) and measuring the problem (M), analyzing root causes (A), improving by finding solutions (I), and controlling by assessing process stability (C) [ 78 , 79 ]. The 5 C-cyclic model (consultation, collection, consideration, collaboration, and celebration), the first CQI framework for volunteer dental services in Aboriginal communities, ensures quality care based on community needs [ 80 ]. One study used meetings involving activities such as reviewing objectives, assigning roles, discussing the agenda, completing tasks, retaining key outputs, planning future steps, and evaluating the meeting’s effectiveness [ 81 ].
Various tools are involved in the implementation or evaluation of CQI initiatives: checklists [ 53 , 82 ], flowcharts [ 81 , 82 , 83 ], cause-and-effect diagrams (fishbone or Ishikawa diagrams) [ 60 , 62 , 79 , 81 , 82 ], fuzzy Pareto diagram [ 82 ], process maps [ 60 ], time series charts [ 48 ], why-why analysis [ 79 ], affinity diagrams and multivoting [ 81 ], and run chart [ 47 , 48 , 51 , 60 , 84 ], and others mentioned in the table (Table 1 ).
Barriers and facilitators of continuous quality improvement implementation
Implementing CQI initiatives is determined by various barriers and facilitators, which can be thematized into four dimensions. These dimensions are cultural, technical, structural, and strategic dimensions.
Continuous quality improvement initiatives face various cultural, strategic, technical, and structural barriers. Cultural dimension barriers involve resistance to change (e.g., not accepting online technology), lack of quality-focused culture, staff reporting apprehensiveness, and fear of blame or punishment [ 36 , 41 , 85 , 86 ]. The technical dimension barriers of CQI can include various factors that hinder the effective implementation and execution of CQI processes [ 36 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 ]. Structural dimension barriers of CQI arise from the organization structure, process, and systems that can impede the effective implementation and sustainability of CQI [ 36 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 ]. Strategic dimension barriers are, for example, the inability to select proper CQI goals and failure to integrate CQI into organizational planning and goals [ 36 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 90 ].
Facilitators are also grouped to cultural, structural, technical, and strategic dimensions to provide solutions to CQI barriers. Cultural challenges were addressed by developing a group culture to CQI and other rewards [ 39 , 41 , 80 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 90 , 91 , 92 ]. Technical facilitators are pivotal to improving technical barriers [ 39 , 42 , 53 , 69 , 86 , 90 , 91 ]. Structural-related facilitators are related to improving communication, infrastructure, and systems [ 86 , 92 , 93 ]. Strategic dimension facilitators include strengthening leadership and improving decision-making skills [ 43 , 53 , 67 , 86 , 87 , 92 , 94 , 95 ] (Table 2 ).
Impact of continuous quality improvement
Continuous quality improvement initiatives can significantly impact the quality of healthcare in a wide range of health areas, focusing on improving structure, the health service delivery process and improving client wellbeing and reducing mortality.
Structure components
These are health leadership, financing, workforce, technology, and equipment and supplies. CQI has improved planning, monitoring and evaluation [ 48 , 53 ], and leadership and planning [ 48 ], indicating improvement in leadership perspectives. Implementing CQI in primary health care (PHC) settings has shown potential for maintaining or reducing operation costs [ 67 ]. Findings from another study indicate that the costs associated with implementing CQI interventions per facility ranged from approximately $2,000 to $10,500 per year, with an average cost of approximately $10 to $60 per admitted client [ 57 ]. However, based on model predictions, the average cost savings after implementing CQI were estimated to be $5430 [ 31 ]. CQI can also be applied to health workforce development [ 32 ]. CQI in the institutional system improved medical education [ 66 , 96 , 97 ], human resources management [ 53 ], motivated staffs [ 76 ], and increased staff health awareness [ 69 ], while concerns raised about CQI impartiality, independence, and public accountability [ 96 ]. Regarding health technology, CQI also improved registration and documentation [ 48 , 53 , 98 ]. Furthermore, the CQI initiatives increased cleanliness [ 54 ] and improved logistics, supplies, and equipment [ 48 , 53 , 68 ].
Process and output components
The process component focuses on the activities and actions involved in delivering healthcare services.
Service delivery
CQI interventions improved service delivery [ 53 , 56 , 99 ], particularly a significant 18% increase in the overall quality of service performance [ 48 ], improved patient counselling, adherence to appropriate procedures, and infection prevention [ 48 , 68 ], and optimised workflow [ 52 ].
Coordination and collaboration
CQI initiatives improved coordination and collaboration through collecting and analysing data, onsite technical support, training, supportive supervision [ 53 ] and facilitating linkages between work processes and a quality control group [ 65 ].
Patient satisfaction
The CQI initiatives increased patient satisfaction and improved quality of life by optimizing care quality management, improving the quality of clinical nursing, reducing nursing defects and enhancing the wellbeing of clients [ 54 , 76 , 100 ], although CQI was not associated with changes in adolescent and young adults’ satisfaction [ 51 ].
CQI initiatives reduced medication error reports from 16 to 6 [ 101 ], and it significantly reduced the administration of inappropriate prophylactic antibiotics [ 44 ], decreased errors in inpatient care [ 52 ], decreased the overall episiotomy rate from 44.5 to 33.3% [ 83 ], reduced the overall incidence of unplanned endotracheal extubation [ 102 ], improving appropriate use of computed tomography angiography [ 103 ], and appropriate diagnosis and treatment selection [ 47 ].
Continuity of care
CQI initiatives effectively improve continuity of care by improving client and physician interaction. For instance, provider continuity levels showed a 64% increase [ 55 ]. Modifying electronic medical record templates, scheduling, staff and parental education, standardization of work processes, and birth to 1-year age-specific incentives in post-natal follow-up care increased continuity of care to 74% in 2018 compared to baseline 13% in 2012 [ 84 ].
The CQI initiative yielded enhanced efficiency in the cardiac catheterization laboratory, as evidenced by improved punctuality in procedure starts and increased efficiency in manual sheath-pulls inside [ 78 ].
Accessibility
CQI initiatives were effective in improving accessibility in terms of increasing service coverage and utilization rate. For instance, screening for cigarettes, nutrition counselling, folate prescription, maternal care, immunization coverage [ 53 , 81 , 104 , 105 ], reducing the percentage of non-attending patients to surgery to 0.9% from the baseline 3.9% [ 43 ], increasing Chlamydia screening rates from 29 to 60% [ 45 ], increasing HIV care continuum coverage [ 51 , 59 , 60 ], increasing in the uptake of postpartum long-acting reversible contraceptive use from 6.9% at the baseline to 25.4% [ 42 ], increasing post-caesarean section prophylaxis from 36 to 89% [ 62 ], a 31% increase of kangaroo care practice [ 50 ], and increased follow-up [ 65 ]. Similarly, the QI intervention increased the quality of antenatal care by 29.3%, correct partograph use by 51.7%, and correct active third-stage labour management, a 19.6% improvement from the baseline, but not significantly associated with improvement in contraceptive service uptake [ 61 ].
Timely access
CQI interventions improved the time care provision [ 52 ], and reduced waiting time [ 62 , 74 , 76 , 106 ]. For instance, the discharge process waiting time in the emergency department decreased from 76 min to 22 min [ 79 ]. It also reduced mean postprocedural length of stay from 2.8 days to 2.0 days [ 31 ].
Acceptability
Acceptability of CQI by healthcare providers was satisfactory. For instance, 88% of the faculty, 64% of the residents, and 82% of the staff believed CQI to be useful in the healthcare clinic [ 107 ].
Outcome components
Morbidity and mortality.
CQI efforts have demonstrated better management outcomes among diabetic patients [ 40 ], patients with oral mucositis [ 71 ], and anaemic patients [ 72 ]. It has also reduced infection rate in post-caesarean Sect. [ 62 ], reduced post-peritoneal dialysis peritonitis [ 49 , 108 ], and prevented pressure ulcers [ 70 ]. It is explained by peritonitis incidence from once every 40.1 patient months at baseline to once every 70.8 patient months after CQI [ 49 ] and a 63% reduction in pressure ulcer prevalence within 2 years from 2008 to 2010 [ 70 ]. Furthermore, CQI initiatives significantly reduced in-hospital deaths [ 31 ] and increased patient survival rates [ 108 ]. Figure 2 displays the overall process of the CQI implementations.
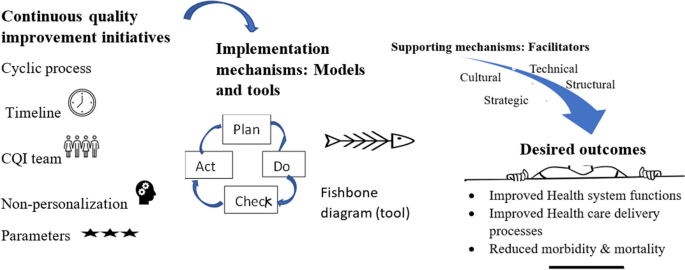
The overall mechanisms of continuous quality improvement implementation
In this review, we examined the fundamental concepts and principles underlying CQI, the factors that either hinder or assist in its successful application and implementation, and the purpose of CQI in enhancing quality of care across various health issues.
Our findings have brought attention to the application and implementation of CQI, emphasizing its underlying concepts and principles, as evident in the existing literature [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 39 , 40 , 43 , 45 , 46 ]. Continuous quality improvement has shared with the principles of continuous improvement, such as a customer-driven focus, effective leadership, active participation of individuals, a process-oriented approach, systematic implementation, emphasis on design improvement and prevention, evidence-based decision-making, and fostering partnership [ 5 ]. Moreover, Deming’s 14 principles laid the foundation for CQI principles [ 109 ]. These principles have been adapted and put into practice in various ways: ten [ 19 ] and five [ 38 ] principles in hospitals, five principles for capacity building [ 38 ], and two principles for medication error prevention [ 41 ]. As a principle, the application of CQI can be process-focused [ 8 , 19 ] or impact-focused [ 38 ]. Impact-focused CQI focuses on achieving specific outcomes or impacts, whereas process-focused CQI prioritizes and improves the underlying processes and systems. These principles complement each other and can be utilized based on the objectives of quality improvement initiatives in healthcare settings. Overall, CQI is an ongoing educational process that requires top management’s involvement, demands coordination across departments, encourages the incorporation of views beyond clinical area, and provides non-judgemental evidence based on objective data [ 110 ].
The current review recognized that it was not easy to implement CQI. It requires reasonable utilization of various models and tools. The application of each tool can be varied based on the studied health problem and the purpose of CQI initiative [ 111 ], varied in context, content, structure, and usability [ 112 ]. Additionally, overcoming the cultural, technical, structural, and strategic-related barriers. These barriers have emerged from clinical staff, managers, and health systems perspectives. Of the cultural obstacles, staff non-involvement, resistance to change, and reluctance to report error were staff-related. In contrast, others, such as the absence of celebration for success and hierarchical and rational culture, may require staff and manager involvement. Staff members may exhibit reluctance in reporting errors due to various cultural factors, including lack of trust, hierarchical structures, fear of retribution, and a blame-oriented culture. These challenges pose obstacles to implementing standardized CQI practices, as observed, for instance, in community pharmacy settings [ 85 ]. The hierarchical culture, characterized by clearly defined levels of power, authority, and decision-making, posed challenges to implementing CQI initiatives in public health [ 41 , 86 ]. Although rational culture, a type of organizational culture, emphasizes logical thinking and rational decision-making, it can also create challenges for CQI implementation [ 41 , 86 ] because hierarchical and rational cultures, which emphasize bureaucratic norms and narrow definitions of achievement, were found to act as barriers to the implementation of CQI [ 86 ]. These could be solved by developing a shared mindset and collective commitment, establishing a shared purpose, developing group norms, and cultivating psychological preparedness among staff, managers, and clients to implement and sustain CQI initiatives. Furthermore, reversing cultural-related barriers necessitates cultural-related solutions: development of a culture and group culture to CQI [ 41 , 86 ], positive comprehensive perception [ 91 ], commitment [ 85 ], involving patients, families, leaders, and staff [ 39 , 92 ], collaborating for a common goal [ 80 , 86 ], effective teamwork [ 86 , 87 ], and rewarding and celebrating successes [ 80 , 90 ].
The technical dimension barriers of CQI can include inadequate capitalization of a project and insufficient support for CQI facilitators and data entry managers [ 36 ], immature electronic medical records or poor information systems [ 36 , 86 ], and the lack of training and skills [ 86 , 87 , 88 ]. These challenges may cause the CQI team to rely on outdated information and technologies. The presence of barriers on the technical dimension may challenge the solid foundation of CQI expertise among staff, the ability to recognize opportunities for improvement, a comprehensive understanding of how services are produced and delivered, and routine use of expertise in daily work. Addressing these technical barriers requires knowledge creation activities (training, seminar, and education) [ 39 , 42 , 53 , 69 , 86 , 90 , 91 ], availability of quality data [ 86 ], reliable information [ 92 ], and a manual-online hybrid reporting system [ 85 ].
Structural dimension barriers of CQI include inadequate communication channels and lack of standardized process, specifically weak physician-to-physician synergies [ 36 ], lack of mechanisms for disseminating knowledge and limited use of communication mechanisms [ 86 ]. Lack of communication mechanism endangers sharing ideas and feedback among CQI teams, leading to misunderstandings, limited participation and misinterpretations, and a lack of learning [ 113 ]. Knowledge translation facilitates the co-production of research, subsequent diffusion of knowledge, and the developing stakeholder’s capacity and skills [ 114 ]. Thus, the absence of a knowledge translation mechanism may cause missed opportunities for learning, inefficient problem-solving, and limited creativity. To overcome these challenges, organizations should establish effective communication and information systems [ 86 , 93 ] and learning systems [ 92 ]. Though CQI and knowledge translation have interacted with each other, it is essential to recognize that they are distinct. CQI focuses on process improvement within health care systems, aiming to optimize existing processes, reduce errors, and enhance efficiency.
In contrast, knowledge translation bridges the gap between research evidence and clinical practice, translating research findings into actionable knowledge for practitioners. While both CQI and knowledge translation aim to enhance health care quality and patient outcomes, they employ different strategies: CQI utilizes tools like Plan-Do-Study-Act cycles and statistical process control, while knowledge translation involves knowledge synthesis and dissemination. Additionally, knowledge translation can also serve as a strategy to enhance CQI. Both concepts share the same principle: continuous improvement is essential for both. Therefore, effective strategies on the structural dimension may build efficient and effective steering councils, information systems, and structures to diffuse learning throughout the organization.
Strategic factors, such as goals, planning, funds, and resources, determine the overall purpose of CQI initiatives. Specific barriers were improper goals and poor planning [ 36 , 86 , 88 ], fragmentation of quality assurance policies [ 87 ], inadequate reinforcement to staff [ 36 , 90 ], time constraints [ 85 , 86 ], resource inadequacy [ 86 ], and work overload [ 86 ]. These barriers can be addressed through strengthening leadership [ 86 , 87 ], CQI-based mentoring [ 94 ], periodic monitoring, supportive supervision and coaching [ 43 , 53 , 87 , 92 , 95 ], participation, empowerment, and accountability [ 67 ], involving all stakeholders in decision-making [ 86 , 87 ], a provider-payer partnership [ 64 ], and compensating staff for after-hours meetings on CQI [ 85 ]. The strategic dimension, characterized by a strategic plan and integrated CQI efforts, is devoted to processes that are central to achieving strategic priorities. Roles and responsibilities are defined in terms of integrated strategic and quality-related goals [ 115 ].
The utmost goal of CQI has been to improve the quality of care, which is usually revealed by structure, process, and outcome. After resolving challenges and effectively using tools and running models, the goal of CQI reflects the ultimate reason and purpose of its implementation. First, effectively implemented CQI initiatives can improve leadership, health financing, health workforce development, health information technology, and availability of supplies as the building blocks of a health system [ 31 , 48 , 53 , 68 , 98 ]. Second, effectively implemented CQI initiatives improved care delivery process (counselling, adherence with standards, coordination, collaboration, and linkages) [ 48 , 53 , 65 , 68 ]. Third, the CQI can improve outputs of healthcare delivery, such as satisfaction, accessibility (timely access, utilization), continuity of care, safety, efficiency, and acceptability [ 52 , 54 , 55 , 76 , 78 ]. Finally, the effectiveness of the CQI initiatives has been tested in enhancing responses related to key aspects of the HIV response, maternal and child health, non-communicable disease control, and others (e.g., surgery and peritonitis). However, it is worth noting that CQI initiative has not always been effective. For instance, CQI using a two- to nine-times audit cycle model through systems assessment tools did not bring significant change to increase syphilis testing performance [ 116 ]. This study was conducted within the context of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people’s primary health care settings. Notably, ‘the clinics may not have consistently prioritized syphilis testing performance in their improvement strategies, as facilitated by the CQI program’ [ 116 ]. Additionally, by applying CQI-based mentoring, uptake of facility-based interventions was not significantly improved, though it was effective in increasing community health worker visits during pregnancy and the postnatal period, knowledge about maternal and child health and exclusive breastfeeding practice, and HIV disclosure status [ 117 ]. The study conducted in South Africa revealed no significant association between the coverage of facility-based interventions and Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI) implementation. This lack of association was attributed to the already high antenatal and postnatal attendance rates in both control and intervention groups at baseline, leaving little room for improvement. Additionally, the coverage of HIV interventions remained consistently high throughout the study period [ 117 ].
Regarding health care and policy implications, CQI has played a vital role in advancing PHC and fostering the realization of UHC goals worldwide. The indicators found in Donabedian’s framework that are positively influenced by CQI efforts are comparable to those included in the PHC performance initiative’s conceptual framework [ 29 , 118 , 119 ]. It is clearly explained that PHC serves as the roadmap to realizing the vision of UHC [ 120 , 121 ]. Given these circumstances, implementing CQI can contribute to the achievement of PHC principles and the objectives of UHC. For instance, by implementing CQI methods, countries have enhanced the accessibility, affordability, and quality of PHC services, leading to better health outcomes for their populations. CQI has facilitated identifying and resolving healthcare gaps and inefficiencies, enabling countries to optimize resource allocation and deliver more effective and patient-centered care. However, it is crucial to recognize that the successful implementation of Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI) necessitates optimizing the duration of each cycle, understanding challenges and barriers that extend beyond the health system and settings, and acknowledging that its effectiveness may be compromised if these challenges are not adequately addressed.
Despite abundant literature, there are still gaps regarding the relationship between CQI and other dimensions within the healthcare system. No studies have examined the impact of CQI initiatives on catastrophic health expenditure, effective service coverage, patient-centredness, comprehensiveness, equity, health security, and responsiveness.
Limitations
In conducting this review, it has some limitations to consider. Firstly, only articles published in English were included, which may introduce the exclusion of relevant non-English articles. Additionally, as this review follows a scoping methodology, the focus is on synthesising available evidence rather than critically evaluating or scoring the quality of the included articles.
Continuous quality improvement is investigated as a continuous and ongoing intervention, where the implementation time can vary across different cycles. The CQI team and implementation timelines were critical elements of CQI in different models. Among the commonly used approaches, the PDSA or PDCA is frequently employed. In most CQI models, a wide range of tools, nineteen tools, are commonly utilized to support the improvement process. Cultural, technical, structural, and strategic barriers and facilitators are significant in implementing CQI initiatives. Implementing the CQI initiative aims to improve health system blocks, enhance health service delivery process and output, and ultimately prevent morbidity and reduce mortality. For future researchers, considering that CQI is context-dependent approach, conducting scale-up implementation research about catastrophic health expenditure, effective service coverage, patient-centredness, comprehensiveness, equity, health security, and responsiveness across various settings and health issues would be valuable.
Availability of data and materials
The data used and/or analyzed during the current study are available in this manuscript and/or the supplementary file.
Shewhart WA, Deming WE. Memoriam: Walter A. Shewhart, 1891–1967. Am Stat. 1967;21(2):39–40.
Article Google Scholar
Shewhart WA. Statistical method from the viewpoint of quality control. New York: Dover; 1986. ISBN 978-0486652320. OCLC 13822053. Reprint. Originally published: Washington, DC: Graduate School of the Department of Agriculture, 1939.
Moen R, editor Foundation and History of the PDSA Cycle. Asian network for quality conference Tokyo. https://www.deming.org/sites/default/files/pdf/2015/PDSA_History_Ron_MoenPdf . 2009.
Kuperman G, James B, Jacobsen J, Gardner RM. Continuous quality improvement applied to medical care: experiences at LDS hospital. Med Decis Making. 1991;11(4suppl):S60–65.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Singh J, Singh H. Continuous improvement philosophy–literature review and directions. Benchmarking: An International Journal. 2015;22(1):75–119.
Goldstone J. Presidential address: Sony, Porsche, and vascular surgery in the 21st century. J Vasc Surg. 1997;25(2):201–10.
Radawski D. Continuous quality improvement: origins, concepts, problems, and applications. J Physician Assistant Educ. 1999;10(1):12–6.
Shortell SM, O’Brien JL, Carman JM, Foster RW, Hughes E, Boerstler H, et al. Assessing the impact of continuous quality improvement/total quality management: concept versus implementation. Health Serv Res. 1995;30(2):377.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lohr K. Quality of health care: an introduction to critical definitions, concepts, principles, and practicalities. Striving for quality in health care. 1991.
Berwick DM. The clinical process and the quality process. Qual Manage Healthc. 1992;1(1):1–8.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Gift B. On the road to TQM. Food Manage. 1992;27(4):88–9.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Greiner A, Knebel E. The core competencies needed for health care professionals. health professions education: A bridge to quality. 2003:45–73.
McCalman J, Bailie R, Bainbridge R, McPhail-Bell K, Percival N, Askew D et al. Continuous quality improvement and comprehensive primary health care: a systems framework to improve service quality and health outcomes. Front Public Health. 2018:6 (76):1–6.
Sheingold BH, Hahn JA. The history of healthcare quality: the first 100 years 1860–1960. Int J Afr Nurs Sci. 2014;1:18–22.
Google Scholar
Donabedian A. Evaluating the quality of medical care. Milbank Q. 1966;44(3):166–206.
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US). 2001. 2, Improving the 21st-century Health Care System. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK222265/ .
Rubinstein A, Barani M, Lopez AS. Quality first for effective universal health coverage in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet Global Health. 2018;6(11):e1142–1143.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Agency for Healthcare Reserach and Quality. Quality Improvement and monitoring at your fingertips USA,: Agency for Healthcare Reserach and Quality. 2022. Available from: https://qualityindicators.ahrq.gov/ .
Anderson CA, Cassidy B, Rivenburgh P. Implementing continuous quality improvement (CQI) in hospitals: lessons learned from the International Quality Study. Qual Assur Health Care. 1991;3(3):141–6.
Gardner K, Mazza D. Quality in general practice - definitions and frameworks. Aust Fam Physician. 2012;41(3):151–4.
PubMed Google Scholar
Loper AC, Jensen TM, Farley AB, Morgan JD, Metz AJ. A systematic review of approaches for continuous quality improvement capacity-building. J Public Health Manage Pract. 2022;28(2):E354.
Hill JE, Stephani A-M, Sapple P, Clegg AJ. The effectiveness of continuous quality improvement for developing professional practice and improving health care outcomes: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2020;15(1):1–14.
Candas B, Jobin G, Dubé C, Tousignant M, Abdeljelil AB, Grenier S, et al. Barriers and facilitators to implementing continuous quality improvement programs in colonoscopy services: a mixed methods systematic review. Endoscopy Int Open. 2016;4(02):E118–133.
Peters MD, Marnie C, Colquhoun H, Garritty CM, Hempel S, Horsley T, et al. Scoping reviews: reinforcing and advancing the methodology and application. Syst Reviews. 2021;10(1):1–6.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
McGowan J, Straus S, Moher D, Langlois EV, O’Brien KK, Horsley T, et al. Reporting scoping reviews—PRISMA ScR extension. J Clin Epidemiol. 2020;123:177–9.
Donabedian A. Explorations in quality assessment and monitoring: the definition of quality and approaches to its assessment. Health Administration Press, Ann Arbor. 1980;1.
World Health Organization. Operational framework for primary health care: transforming vision into action. Geneva: World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF); 2020 [updated 14 December 2020; cited 2023 Nov Oct 17]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240017832 .
The Joanna Briggs Institute. The Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewers’ Manual :2014 edition. Australia: The Joanna Briggs Institute. 2014:88–91.
Rihal CS, Kamath CC, Holmes DR Jr, Reller MK, Anderson SS, McMurtry EK, et al. Economic and clinical outcomes of a physician-led continuous quality improvement intervention in the delivery of percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Manag Care. 2006;12(8):445–52.
Ade-Oshifogun JB, Dufelmeier T. Prevention and Management of Do not return notices: a quality improvement process for Supplemental staffing nursing agencies. Nurs Forum. 2012;47(2):106–12.
Rubenstein L, Khodyakov D, Hempel S, Danz M, Salem-Schatz S, Foy R, et al. How can we recognize continuous quality improvement? Int J Qual Health Care. 2014;26(1):6–15.
O’Neill SM, Hempel S, Lim YW, Danz MS, Foy R, Suttorp MJ, et al. Identifying continuous quality improvement publications: what makes an improvement intervention ‘CQI’? BMJ Qual Saf. 2011;20(12):1011–9.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sibthorpe B, Gardner K, McAullay D. Furthering the quality agenda in Aboriginal community controlled health services: understanding the relationship between accreditation, continuous quality improvement and national key performance indicator reporting. Aust J Prim Health. 2016;22(4):270–5.
Bennett CL, Crane JM. Quality improvement efforts in oncology: are we ready to begin? Cancer Invest. 2001;19(1):86–95.
VanValkenburgh DA. Implementing continuous quality improvement at the facility level. Adv Ren Replace Ther. 2001;8(2):104–13.
Loper AC, Jensen TM, Farley AB, Morgan JD, Metz AJ. A systematic review of approaches for continuous quality improvement capacity-building. J Public Health Manage Practice. 2022;28(2):E354–361.
Ryan M. Achieving and sustaining quality in healthcare. Front Health Serv Manag. 2004;20(3):3–11.
Nicolucci A, Allotta G, Allegra G, Cordaro G, D’Agati F, Di Benedetto A, et al. Five-year impact of a continuous quality improvement effort implemented by a network of diabetes outpatient clinics. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(1):57–62.
Wakefield BJ, Blegen MA, Uden-Holman T, Vaughn T, Chrischilles E, Wakefield DS. Organizational culture, continuous quality improvement, and medication administration error reporting. Am J Med Qual. 2001;16(4):128–34.
Sori DA, Debelew GT, Degefa LS, Asefa Z. Continuous quality improvement strategy for increasing immediate postpartum long-acting reversible contraceptive use at Jimma University Medical Center, Jimma, Ethiopia. BMJ Open Qual. 2023;12(1):e002051.
Roche B, Robin C, Deleaval PJ, Marti MC. Continuous quality improvement in ambulatory surgery: the non-attending patient. Ambul Surg. 1998;6(2):97–100.
O’Connor JB, Sondhi SS, Mullen KD, McCullough AJ. A continuous quality improvement initiative reduces inappropriate prescribing of prophylactic antibiotics for endoscopic procedures. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94(8):2115–21.
Ursu A, Greenberg G, McKee M. Continuous quality improvement methodology: a case study on multidisciplinary collaboration to improve chlamydia screening. Fam Med Community Health. 2019;7(2):e000085.
Quick B, Nordstrom S, Johnson K. Using continuous quality improvement to implement evidence-based medicine. Lippincotts Case Manag. 2006;11(6):305–15 ( quiz 16 – 7 ).
Oyeledun B, Phillips A, Oronsaye F, Alo OD, Shaffer N, Osibo B, et al. The effect of a continuous quality improvement intervention on retention-in-care at 6 months postpartum in a PMTCT Program in Northern Nigeria: results of a cluster randomized controlled study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017;75(Suppl 2):S156–164.
Nyengerai T, Phohole M, Iqaba N, Kinge CW, Gori E, Moyo K, et al. Quality of service and continuous quality improvement in voluntary medical male circumcision programme across four provinces in South Africa: longitudinal and cross-sectional programme data. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(8):e0254850.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wang J, Zhang H, Liu J, Zhang K, Yi B, Liu Y, et al. Implementation of a continuous quality improvement program reduces the occurrence of peritonitis in PD. Ren Fail. 2014;36(7):1029–32.
Stikes R, Barbier D. Applying the plan-do-study-act model to increase the use of kangaroo care. J Nurs Manag. 2013;21(1):70–8.
Wagner AD, Mugo C, Bluemer-Miroite S, Mutiti PM, Wamalwa DC, Bukusi D, et al. Continuous quality improvement intervention for adolescent and young adult HIV testing services in Kenya improves HIV knowledge. AIDS. 2017;31(Suppl 3):S243–252.
Le RD, Melanson SE, Santos KS, Paredes JD, Baum JM, Goonan EM, et al. Using lean principles to optimise inpatient phlebotomy services. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67(8):724–30.
Manyazewal T, Mekonnen A, Demelew T, Mengestu S, Abdu Y, Mammo D, et al. Improving immunization capacity in Ethiopia through continuous quality improvement interventions: a prospective quasi-experimental study. Infect Dis Poverty. 2018;7:7.
Kamiya Y, Ishijma H, Hagiwara A, Takahashi S, Ngonyani HAM, Samky E. Evaluating the impact of continuous quality improvement methods at hospitals in Tanzania: a cluster-randomized trial. Int J Qual Health Care. 2017;29(1):32–9.
Kibbe DC, Bentz E, McLaughlin CP. Continuous quality improvement for continuity of care. J Fam Pract. 1993;36(3):304–8.
Adrawa N, Ongiro S, Lotee K, Seret J, Adeke M, Izudi J. Use of a context-specific package to increase sputum smear monitoring among people with pulmonary tuberculosis in Uganda: a quality improvement study. BMJ Open Qual. 2023;12(3):1–6.
Hunt P, Hunter SB, Levan D. Continuous quality improvement in substance abuse treatment facilities: how much does it cost? J Subst Abuse Treat. 2017;77:133–40.
Azadeh A, Ameli M, Alisoltani N, Motevali Haghighi S. A unique fuzzy multi-control approach for continuous quality improvement in a radio therapy department. Qual Quantity. 2016;50(6):2469–93.
Memiah P, Tlale J, Shimabale M, Nzyoka S, Komba P, Sebeza J, et al. Continuous quality improvement (CQI) institutionalization to reach 95:95:95 HIV targets: a multicountry experience from the Global South. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):711.
Yapa HM, De Neve JW, Chetty T, Herbst C, Post FA, Jiamsakul A, et al. The impact of continuous quality improvement on coverage of antenatal HIV care tests in rural South Africa: results of a stepped-wedge cluster-randomised controlled implementation trial. PLoS Med. 2020;17(10):e1003150.
Dadi TL, Abebo TA, Yeshitla A, Abera Y, Tadesse D, Tsegaye S, et al. Impact of quality improvement interventions on facility readiness, quality and uptake of maternal and child health services in developing regions of Ethiopia: a secondary analysis of programme data. BMJ Open Qual. 2023;12(4):e002140.
Weinberg M, Fuentes JM, Ruiz AI, Lozano FW, Angel E, Gaitan H, et al. Reducing infections among women undergoing cesarean section in Colombia by means of continuous quality improvement methods. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(19):2357–65.
Andreoni V, Bilak Y, Bukumira M, Halfer D, Lynch-Stapleton P, Perez C. Project management: putting continuous quality improvement theory into practice. J Nurs Care Qual. 1995;9(3):29–37.
Balfour ME, Zinn TE, Cason K, Fox J, Morales M, Berdeja C, et al. Provider-payer partnerships as an engine for continuous quality improvement. Psychiatric Serv. 2018;69(6):623–5.
Agurto I, Sandoval J, De La Rosa M, Guardado ME. Improving cervical cancer prevention in a developing country. Int J Qual Health Care. 2006;18(2):81–6.
Anderson CI, Basson MD, Ali M, Davis AT, Osmer RL, McLeod MK, et al. Comprehensive multicenter graduate surgical education initiative incorporating entrustable professional activities, continuous quality improvement cycles, and a web-based platform to enhance teaching and learning. J Am Coll Surg. 2018;227(1):64–76.
Benjamin S, Seaman M. Applying continuous quality improvement and human performance technology to primary health care in Bahrain. Health Care Superv. 1998;17(1):62–71.
Byabagambi J, Marks P, Megere H, Karamagi E, Byakika S, Opio A, et al. Improving the quality of voluntary medical male circumcision through use of the continuous quality improvement approach: a pilot in 30 PEPFAR-Supported sites in Uganda. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(7):e0133369.
Hogg S, Roe Y, Mills R. Implementing evidence-based continuous quality improvement strategies in an urban Aboriginal Community Controlled Health Service in South East Queensland: a best practice implementation pilot. JBI Database Syst Rev Implement Rep. 2017;15(1):178–87.
Hopper MB, Morgan S. Continuous quality improvement initiative for pressure ulcer prevention. J Wound Ostomy Cont Nurs. 2014;41(2):178–80.
Ji J, Jiang DD, Xu Z, Yang YQ, Qian KY, Zhang MX. Continuous quality improvement of nutrition management during radiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nurs Open. 2021;8(6):3261–70.
Chen M, Deng JH, Zhou FD, Wang M, Wang HY. Improving the management of anemia in hemodialysis patients by implementing the continuous quality improvement program. Blood Purif. 2006;24(3):282–6.
Reeves S, Matney K, Crane V. Continuous quality improvement as an ideal in hospital practice. Health Care Superv. 1995;13(4):1–12.
Barton AJ, Danek G, Johns P, Coons M. Improving patient outcomes through CQI: vascular access planning. J Nurs Care Qual. 1998;13(2):77–85.
Buttigieg SC, Gauci D, Dey P. Continuous quality improvement in a Maltese hospital using logical framework analysis. J Health Organ Manag. 2016;30(7):1026–46.
Take N, Byakika S, Tasei H, Yoshikawa T. The effect of 5S-continuous quality improvement-total quality management approach on staff motivation, patients’ waiting time and patient satisfaction with services at hospitals in Uganda. J Public Health Afr. 2015;6(1):486.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Jacobson GH, McCoin NS, Lescallette R, Russ S, Slovis CM. Kaizen: a method of process improvement in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med. 2009;16(12):1341–9.
Agarwal S, Gallo J, Parashar A, Agarwal K, Ellis S, Khot U, et al. Impact of lean six sigma process improvement methodology on cardiac catheterization laboratory efficiency. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;85:S119.
Rahul G, Samanta AK, Varaprasad G A Lean Six Sigma approach to reduce overcrowding of patients and improving the discharge process in a super-specialty hospital. In 2020 International Conference on System, Computation, Automation and Networking (ICSCAN) 2020 July 3 (pp. 1-6). IEEE
Patel J, Nattabi B, Long R, Durey A, Naoum S, Kruger E, et al. The 5 C model: A proposed continuous quality improvement framework for volunteer dental services in remote Australian Aboriginal communities. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2023;51(6):1150–8.
Van Acker B, McIntosh G, Gudes M. Continuous quality improvement techniques enhance HMO members’ immunization rates. J Healthc Qual. 1998;20(2):36–41.
Horine PD, Pohjala ED, Luecke RW. Healthcare financial managers and CQI. Healthc Financ Manage. 1993;47(9):34.
Reynolds JL. Reducing the frequency of episiotomies through a continuous quality improvement program. CMAJ. 1995;153(3):275–82.
Bunik M, Galloway K, Maughlin M, Hyman D. First five quality improvement program increases adherence and continuity with well-child care. Pediatr Qual Saf. 2021;6(6):e484.
Boyle TA, MacKinnon NJ, Mahaffey T, Duggan K, Dow N. Challenges of standardized continuous quality improvement programs in community pharmacies: the case of SafetyNET-Rx. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2012;8(6):499–508.
Price A, Schwartz R, Cohen J, Manson H, Scott F. Assessing continuous quality improvement in public health: adapting lessons from healthcare. Healthc Policy. 2017;12(3):34–49.
Gage AD, Gotsadze T, Seid E, Mutasa R, Friedman J. The influence of continuous quality improvement on healthcare quality: a mixed-methods study from Zimbabwe. Soc Sci Med. 2022;298:114831.
Chan YC, Ho SJ. Continuous quality improvement: a survey of American and Canadian healthcare executives. Hosp Health Serv Adm. 1997;42(4):525–44.
Balas EA, Puryear J, Mitchell JA, Barter B. How to structure clinical practice guidelines for continuous quality improvement? J Med Syst. 1994;18(5):289–97.
ElChamaa R, Seely AJE, Jeong D, Kitto S. Barriers and facilitators to the implementation and adoption of a continuous quality improvement program in surgery: a case study. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2022;42(4):227–35.
Candas B, Jobin G, Dubé C, Tousignant M, Abdeljelil A, Grenier S, et al. Barriers and facilitators to implementing continuous quality improvement programs in colonoscopy services: a mixed methods systematic review. Endoscopy Int Open. 2016;4(2):E118–133.
Brandrud AS, Schreiner A, Hjortdahl P, Helljesen GS, Nyen B, Nelson EC. Three success factors for continual improvement in healthcare: an analysis of the reports of improvement team members. BMJ Qual Saf. 2011;20(3):251–9.
Lee S, Choi KS, Kang HY, Cho W, Chae YM. Assessing the factors influencing continuous quality improvement implementation: experience in Korean hospitals. Int J Qual Health Care. 2002;14(5):383–91.
Horwood C, Butler L, Barker P, Phakathi S, Haskins L, Grant M, et al. A continuous quality improvement intervention to improve the effectiveness of community health workers providing care to mothers and children: a cluster randomised controlled trial in South Africa. Hum Resour Health. 2017;15(1):39.
Hyrkäs K, Lehti K. Continuous quality improvement through team supervision supported by continuous self-monitoring of work and systematic patient feedback. J Nurs Manag. 2003;11(3):177–88.
Akdemir N, Peterson LN, Campbell CM, Scheele F. Evaluation of continuous quality improvement in accreditation for medical education. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20(Suppl 1):308.
Barzansky B, Hunt D, Moineau G, Ahn D, Lai CW, Humphrey H, et al. Continuous quality improvement in an accreditation system for undergraduate medical education: benefits and challenges. Med Teach. 2015;37(11):1032–8.
Gaylis F, Nasseri R, Salmasi A, Anderson C, Mohedin S, Prime R, et al. Implementing continuous quality improvement in an integrated community urology practice: lessons learned. Urology. 2021;153:139–46.
Gaga S, Mqoqi N, Chimatira R, Moko S, Igumbor JO. Continuous quality improvement in HIV and TB services at selected healthcare facilities in South Africa. South Afr J HIV Med. 2021;22(1):1202.
Wang F, Yao D. Application effect of continuous quality improvement measures on patient satisfaction and quality of life in gynecological nursing. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(6):6391–8.
Lee SB, Lee LL, Yeung RS, Chan J. A continuous quality improvement project to reduce medication error in the emergency department. World J Emerg Med. 2013;4(3):179–82.
Chiang AA, Lee KC, Lee JC, Wei CH. Effectiveness of a continuous quality improvement program aiming to reduce unplanned extubation: a prospective study. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22(11):1269–71.
Chinnaiyan K, Al-Mallah M, Goraya T, Patel S, Kazerooni E, Poopat C, et al. Impact of a continuous quality improvement initiative on appropriate use of coronary CT angiography: results from a multicenter, statewide registry, the advanced cardiovascular imaging consortium (ACIC). J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2011;5(4):S29–30.
Gibson-Helm M, Rumbold A, Teede H, Ranasinha S, Bailie R, Boyle J. A continuous quality improvement initiative: improving the provision of pregnancy care for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander women. BJOG: Int J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;122:400–1.
Bennett IM, Coco A, Anderson J, Horst M, Gambler AS, Barr WB, et al. Improving maternal care with a continuous quality improvement strategy: a report from the interventions to minimize preterm and low birth weight infants through continuous improvement techniques (IMPLICIT) network. J Am Board Fam Med. 2009;22(4):380–6.
Krall SP, Iv CLR, Donahue L. Effect of continuous quality improvement methods on reducing triage to thrombolytic interval for Acute myocardial infarction. Acad Emerg Med. 1995;2(7):603–9.
Swanson TK, Eilers GM. Physician and staff acceptance of continuous quality improvement. Fam Med. 1994;26(9):583–6.
Yu Y, Zhou Y, Wang H, Zhou T, Li Q, Li T, et al. Impact of continuous quality improvement initiatives on clinical outcomes in peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int. 2014;34(Suppl 2):S43–48.
Schiff GD, Goldfield NI. Deming meets Braverman: toward a progressive analysis of the continuous quality improvement paradigm. Int J Health Serv. 1994;24(4):655–73.
American Hospital Association Division of Quality Resources Chicago, IL: The role of hospital leadership in the continuous improvement of patient care quality. American Hospital Association. J Healthc Qual. 1992;14(5):8–14,22.
Scriven M. The Logic and Methodology of checklists [dissertation]. Western Michigan University; 2000.
Hales B, Terblanche M, Fowler R, Sibbald W. Development of medical checklists for improved quality of patient care. Int J Qual Health Care. 2008;20(1):22–30.
Vermeir P, Vandijck D, Degroote S, Peleman R, Verhaeghe R, Mortier E, et al. Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. Int J Clin Pract. 2015;69(11):1257–67.
Eljiz K, Greenfield D, Hogden A, Taylor R, Siddiqui N, Agaliotis M, et al. Improving knowledge translation for increased engagement and impact in healthcare. BMJ open Qual. 2020;9(3):e000983.
O’Brien JL, Shortell SM, Hughes EF, Foster RW, Carman JM, Boerstler H, et al. An integrative model for organization-wide quality improvement: lessons from the field. Qual Manage Healthc. 1995;3(4):19–30.
Adily A, Girgis S, D’Este C, Matthews V, Ward JE. Syphilis testing performance in Aboriginal primary health care: exploring impact of continuous quality improvement over time. Aust J Prim Health. 2020;26(2):178–83.
Horwood C, Butler L, Barker P, Phakathi S, Haskins L, Grant M, et al. A continuous quality improvement intervention to improve the effectiveness of community health workers providing care to mothers and children: a cluster randomised controlled trial in South Africa. Hum Resour Health. 2017;15:1–11.
Veillard J, Cowling K, Bitton A, Ratcliffe H, Kimball M, Barkley S, et al. Better measurement for performance improvement in low- and middle-income countries: the primary Health Care Performance Initiative (PHCPI) experience of conceptual framework development and indicator selection. Milbank Q. 2017;95(4):836–83.
Barbazza E, Kringos D, Kruse I, Klazinga NS, Tello JE. Creating performance intelligence for primary health care strengthening in Europe. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):1006.
Assefa Y, Hill PS, Gilks CF, Admassu M, Tesfaye D, Van Damme W. Primary health care contributions to universal health coverage. Ethiopia Bull World Health Organ. 2020;98(12):894.
Van Weel C, Kidd MR. Why strengthening primary health care is essential to achieving universal health coverage. CMAJ. 2018;190(15):E463–466.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
The authors received no fund.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Public Health, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
Aklilu Endalamaw, Resham B Khatri, Tesfaye Setegn Mengistu, Daniel Erku & Yibeltal Assefa
College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Bahir Dar University, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia
Aklilu Endalamaw & Tesfaye Setegn Mengistu
Health Social Science and Development Research Institute, Kathmandu, Nepal
Resham B Khatri
Centre for Applied Health Economics, School of Medicine, Grifth University, Brisbane, Australia
Daniel Erku
Menzies Health Institute Queensland, Grifth University, Brisbane, Australia
International Institute for Primary Health Care in Ethiopia, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Eskinder Wolka & Anteneh Zewdie
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AE conceptualized the study, developed the first draft of the manuscript, and managing feedbacks from co-authors. YA conceptualized the study, provided feedback, and supervised the whole processes. RBK provided feedback throughout. TSM provided feedback throughout. DE provided feedback throughout. EW provided feedback throughout. AZ provided feedback throughout. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Aklilu Endalamaw .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable because this research is based on publicly available articles.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Endalamaw, A., Khatri, R.B., Mengistu, T.S. et al. A scoping review of continuous quality improvement in healthcare system: conceptualization, models and tools, barriers and facilitators, and impact. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 487 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10828-0
Download citation
Received : 27 December 2023
Accepted : 05 March 2024
Published : 19 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10828-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Continuous quality improvement
- Quality of Care
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Content analysis is a research method used to identify patterns in recorded communication. To conduct content analysis, you systematically collect data from a set of texts, which can be written, oral, or visual: Books, newspapers and magazines. Speeches and interviews. Web content and social media posts. Photographs and films.
Theme names are very descriptive and include verbs, adverbs and adjectives ... Content analysis, as in all qualitative analysis, is a reflective process. There is no "step 1, 2, 3, done!" linear progression in the analysis. ... Graneheim U.H., Lundman B. Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: concepts, procedures, and measures to ...
Content analysis is a research tool used to determine the presence of certain words, themes, or concepts within some given qualitative data (i.e. text). Using content analysis, researchers can quantify and analyze the presence, meanings, and relationships of such certain words, themes, or concepts.
Step 1: Select the content you will analyse. Based on your research question, choose the texts that you will analyse. You need to decide: The medium (e.g., newspapers, speeches, or websites) and genre (e.g., opinion pieces, political campaign speeches, or marketing copy)
In summative content analysis, a descriptive approach is taken, identifying and quantifying words or content in order to describe their context. ... We encourage pharmacy educators to ask questions suited for qualitative research and to consider the use of content analysis as a qualitative research method for discovering meaning in their data ...
Content analysis is a research method that helps a researcher explore the occurrence of and relationships between various words, phrases, themes, or concepts in a text or set of texts. ... Content analysis typically uses a descriptive approach to the data and may use either qualitative or quantitative analytical methods. By contrast, a thematic ...
Abstract. This paper describes the research process - from planning to presentation, with the emphasis on credibility throughout the whole process - when the methodology of qualitative content analysis is chosen in a qualitative study. The groundwork for the credibility initiates when the planning of the study begins.
These are essentially descriptive research uses of content analysis. Krippendorff (2013) states that authors of content analyses often use study findings as an evidence base for making abductive arguments. An abductive argument links an observation with a hypothesis that accounts for or explains the observation (Reichertz, 2010). In abductive ...
Abstract. This chapter offers an inclusive definition of content analysis. This helps in clarifying some key terms and concepts. Three approaches to content analysis are introduced and defined briefly: basic content analysis, interpretive content analysis, and qualitative content analysis. Long-standing differences between quantitative and ...
Abstract. In this chapter, the focus is on ways in which content analysis can be used to investigate and describe interview and textual data. The chapter opens with a contextualization of the method and then proceeds to an examination of the role of content analysis in relation to both quantitative and qualitative modes of social research.
Hsieh and Shannon (2005) present three types of content analysis, any of which could be used in a qualitative descriptive study. Conventional content analysis is used in studies that aim to describe a phenomenon where exiting research and theory are limited. Data are collected from open-ended questions, read word for word, and then coded.
Descriptive research methods. Descriptive research is usually defined as a type of quantitative research, though qualitative research can also be used for descriptive purposes. The research design should be carefully developed to ensure that the results are valid and reliable.. Surveys. Survey research allows you to gather large volumes of data that can be analyzed for frequencies, averages ...
If the goal of the analysis is the reduction and description of a dataset in relation to a research question about manifest content, further analysis is unnecessary and may even be counterproductive. It would be unhelpful for data reduction purposes to have an identical code for a distinct concept in multiple places.
Qualitative content analysis is one of the several qualita- tive methods currently available for analyzing data and inter - preting its meaning (Schreier, 2012). As a research method, it represents a systematic and objective means of describing and quantifying phenomena (Downe-Wamboldt, 1992; Schreier, 2012).
Content analysis is a qualitative analysis method that focuses on recorded human artefacts such as manuscripts, voice recordings and journals. Content analysis investigates these written, spoken and visual artefacts without explicitly extracting data from participants - this is called unobtrusive research. In other words, with content ...
The methodological bases: systematic literature reviews and content analysis. Literature reviews are primarily qualitative synthesis that provide critical tools for understanding a topic's discourse especially, in a climate of increasing, and often deviant and contradictory, research output .Literature reviews serve as a research-orienting device to identify trends, gaps, intersections ...
Content analysis and thematic analysis as qualitative descriptive approaches. According to Sandelowski and Barroso research findings can be placed on a continuum indicating the degree of transformation of data during the data analysis process from description to interpretation.The use of qualitative descriptive approaches such as descriptive phenomenology, content analysis, and thematic ...
Content analysis is a research method used to analyze and interpret the characteristics of various forms of communication, such as text, images, or audio. It involves systematically analyzing the content of these materials, identifying patterns, themes, and other relevant features, and drawing inferences or conclusions based on the findings.
The next step is to develop codes that are descriptive labels for the condensed meaning units (Table 3). Codes concisely describe the condensed meaning unit and are tools to help researchers reflect on the data in new ways. ... Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: concepts, procedures, and measures to achieve trustworthiness. Nurse ...
Quantitative content analysis is always describing a positivist manifest content analysis, in that the nature of truth is believed to be objective, observable, and measurable. Qualitative research, which favors the researcher's interpretation of an individual's experience, may also be used to analyze manifest content.
Qualitative research collects data qualitatively, and the method of analysis is also primarily qualitative. This often involves an inductive exploration of the data to identify recurring themes, patterns, or concepts and then describing and interpreting those categories. Of course, in qualitative research, the data collected qualitatively can ...
They are used for provision of descriptive knowledge and understandings of the phenomenon under study. However, the method underpinning directed qualitative content analysis is insufficiently delineated in international literature. ... Qualitative content analysis (QCA) is a research approach for the description and interpretation of textual ...
The growing adoption of continuous quality improvement (CQI) initiatives in healthcare has generated a surge in research interest to gain a deeper understanding of CQI. However, comprehensive evidence regarding the diverse facets of CQI in healthcare has been limited. Our review sought to comprehensively grasp the conceptualization and principles of CQI, explore existing models and tools ...
The research methodology used is descriptive and qualitative research with framework analysis, which means framework analysis techniques. This analysis technique is carried out by conceptualizing the system through a structure that describes the connection between one variable and another in a systematic and detailed manner.
Qualitative description (QD) is a label used in qualitative research for studies which are descriptive in nature, particularly for examining health care and nursing-related phenomena (Polit & Beck, 2009, 2014).QD is a widely cited research tradition and has been identified as important and appropriate for research questions focused on discovering the who, what, and where of events or ...