
Direct and Indirect Speech: Useful Rules and Examples
Are you having trouble understanding the difference between direct and indirect speech? Direct speech is when you quote someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. This can be a tricky concept to grasp, but with a little practice, you’ll be able to use both forms of speech with ease.

Direct and Indirect Speech
When someone speaks, we can report what they said in two ways: direct speech and indirect speech. Direct speech is when we quote the exact words that were spoken, while indirect speech is when we report what was said without using the speaker’s exact words. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I love pizza,” said John. Indirect speech: John said that he loved pizza.
Using direct speech can make your writing more engaging and can help to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion. However, indirect speech can be useful when you want to summarize what someone said or when you don’t have the exact words that were spoken.
To change direct speech to indirect speech, you need to follow some rules. Firstly, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb. Secondly, you need to change the pronouns and adverbs in the reported speech to match the new speaker. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will go to the park,” said Sarah. Indirect speech: Sarah said that she would go to the park.
It’s important to note that when you use indirect speech, you need to use reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked” to indicate who is speaking. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is it?” asked Tom. Indirect speech: Tom asked what time it was.
In summary, understanding direct and indirect speech is crucial for effective communication and writing. Direct speech can be used to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion, while indirect speech can be useful when summarizing what someone said. By following the rules for changing direct speech to indirect speech, you can accurately report what was said while maintaining clarity and readability in your writing.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech
When it comes to reporting speech, there are two ways to go about it: direct and indirect speech. Direct speech is when you report someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. Here are some of the key differences between direct and indirect speech:
Change of Pronouns
In direct speech, the pronouns used are those of the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the pronouns have to be changed to reflect the perspective of the reporter. For example:
- Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John.
- Indirect speech: John said he was going to the store.
In the above example, the pronoun “I” changes to “he” in indirect speech.
Change of Tenses
Another major difference between direct and indirect speech is the change of tenses. In direct speech, the verb tense used is the same as that used by the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the verb tense may change depending on the context. For example:
- Direct speech: “I am studying for my exams,” said Sarah.
- Indirect speech: Sarah said she was studying for her exams.
In the above example, the present continuous tense “am studying” changes to the past continuous tense “was studying” in indirect speech.
Change of Time and Place References
When reporting indirect speech, the time and place references may also change. For example:
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” said Tom.
- Indirect speech: Tom said he would meet you at the park the next day.
In the above example, “tomorrow” changes to “the next day” in indirect speech.
Overall, it is important to understand the differences between direct and indirect speech to report speech accurately and effectively. By following the rules of direct and indirect speech, you can convey the intended message of the original speaker.
Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
When you need to report what someone said in your own words, you can use indirect speech. To convert direct speech into indirect speech, you need to follow a few rules.
Step 1: Remove the Quotation Marks
The first step is to remove the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text. This is because indirect speech does not use the exact words of the speaker.
Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a Linker
To indicate that you are reporting what someone said, you need to use a reporting verb such as “said,” “asked,” “told,” or “exclaimed.” You also need to use a linker such as “that” or “whether” to connect the reporting verb to the reported speech.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I love ice cream,” said Mary.
- Indirect speech: Mary said that she loved ice cream.
Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb
When you use indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb.
- Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store.
Step 4: Change the Pronouns
You also need to change the pronouns in the reported speech to match the subject of the reporting verb.
- Direct speech: “Are you busy now?” Tina asked me.
- Indirect speech: Tina asked whether I was busy then.
By following these rules, you can convert direct speech into indirect speech and report what someone said in your own words.
Converting Indirect Speech Into Direct Speech
Converting indirect speech into direct speech involves changing the reported speech to its original form as spoken by the speaker. Here are the steps to follow when converting indirect speech into direct speech:
- Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb used in the indirect speech. This will help you determine the tense of the direct speech.
- Change the pronouns: The next step is to change the pronouns in the indirect speech to match the person speaking in the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “She said that she was going to the store,” the direct speech would be “I am going to the store,” if you are the person speaking.
- Change the tense: Change the tense of the verbs in the indirect speech to match the tense of the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “He said that he would visit tomorrow,” the direct speech would be “He says he will visit tomorrow.”
- Remove the reporting verb and conjunction: In direct speech, there is no need for a reporting verb or conjunction. Simply remove them from the indirect speech to get the direct speech.
Here is an example to illustrate the process:
Indirect Speech: John said that he was tired and wanted to go home.
Direct Speech: “I am tired and want to go home,” John said.
By following these steps, you can easily convert indirect speech into direct speech.
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct and indirect speech are two ways to report what someone has said. Direct speech reports the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech reports the meaning of what was said. Here are some examples of both types of speech:
Direct Speech Examples
Direct speech is used when you want to report the exact words spoken by someone. It is usually enclosed in quotation marks and is often used in dialogue.
- “I am going to the store,” said Sarah.
- “It’s a beautiful day,” exclaimed John.
- “Please turn off the lights,” Mom told me.
- “I will meet you at the library,” said Tom.
- “We are going to the beach tomorrow,” announced Mary.
Indirect Speech Examples
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, is used to report what someone said without using their exact words. It is often used in news reports, academic writing, and in situations where you want to paraphrase what someone said.
Here are some examples of indirect speech:
- Sarah said that she was going to the store.
- John exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
- Mom told me to turn off the lights.
- Tom said that he would meet me at the library.
- Mary announced that they were going to the beach tomorrow.
In indirect speech, the verb tense may change to reflect the time of the reported speech. For example, “I am going to the store” becomes “Sarah said that she was going to the store.” Additionally, the pronouns and possessive adjectives may also change to reflect the speaker and the person being spoken about.
Overall, both direct and indirect speech are important tools for reporting what someone has said. By using these techniques, you can accurately convey the meaning of what was said while also adding your own interpretation and analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is direct and indirect speech?
Direct and indirect speech refer to the ways in which we communicate what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, using quotation marks to indicate that you are quoting someone. Indirect speech, on the other hand, involves reporting what someone has said without using their exact words.
How do you convert direct speech to indirect speech?
To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb, such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.” For example, “I love ice cream,” said Mary (direct speech) can be converted to “Mary said that she loved ice cream” (indirect speech).
What is the difference between direct speech and indirect speech?
The main difference between direct speech and indirect speech is that direct speech uses the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. Direct speech is usually enclosed in quotation marks, while indirect speech is not.
What are some examples of direct and indirect speech?
Some examples of direct speech include “I am going to the store,” said John and “I love pizza,” exclaimed Sarah. Some examples of indirect speech include John said that he was going to the store and Sarah exclaimed that she loved pizza .
What are the rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech?
The rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech include changing the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb and use appropriate reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.”
What is a summary of direct and indirect speech?
Direct and indirect speech are two ways of reporting what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions and introduce a reporting verb.
You might also like:
- List of Adjectives
- Predicate Adjective
- Superlative Adjectives
Related Posts:

This website is AMNAZING
MY NAAMEE IS KISHU AND I WANTED TO TELL THERE ARE NO EXERCISES AVAILLABLEE BY YOUR WEBSITE PLEASE ADD THEM SSOON FOR OUR STUDENTS CONVIENCE IM A EIGHT GRADER LOVED YOUR EXPLABATIO
sure cries l miss my friend

17 Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Conversion

Understanding direct and indirect speech conversion rules is crucial for clear and accurate communication. We will explore these rules with detailed examples to master this aspect of the English language in an easy way.
Have you ever found yourself confused about how to accurately report someone else’s speech or statements? If so, you’re not alone. Direct and indirect speech, also known as reported speech, can be tricky to navigate.
But fear not! In this article, we will explore the world of direct and indirect speech conversion rules, guiding you through the intricacies of transforming spoken words into written form.
Let’s now discover the Direct and Indirect Speech Rules in this informative article.
What is Direct Speech or Narration?
Direct speech is a form of reporting that presents someone’s exact words without any alterations. It is commonly enclosed in quotation marks, allowing readers to see the speaker’s statements precisely as they were uttered. For example:
Direct Speech: Riya says, “I shall not go to school.”
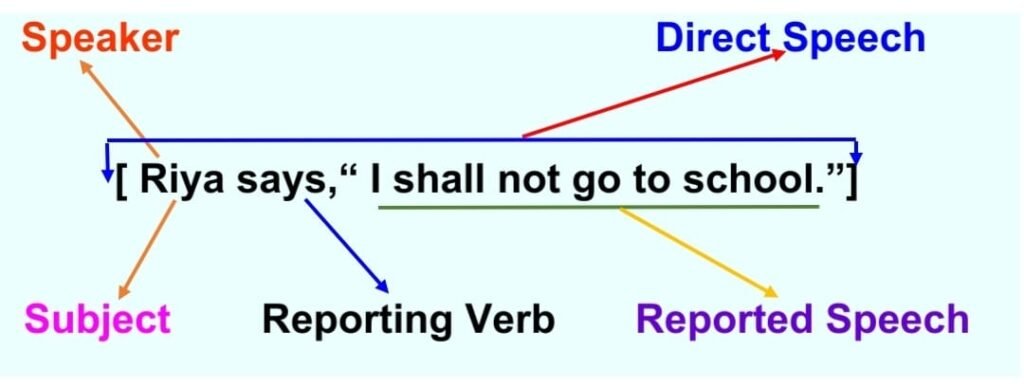
“I shall not go to school. ” – are actual words of Riya. So, it is in the Quotation Marks / Inverted Comma (“ ”) . This format of a sentence with commas and Quotation Marks / Inverted Commas is called Direct Speech where ‘Riya’ is the subject or speaker, ‘ says’ is the reporting verb, and ‘ I shall not go to school’ is called reported speech.
What is Indirect Speech or Narration?
Indirect speech , on the other hand, involves paraphrasing someone’s words and reporting them indirectly, without using quotation marks. It requires a few changes in structure, such as tense and pronoun shifts. Let’s convert the previous example of direct speech into indirect speech:
Indirect Speech: Riya says that she will not go to school.
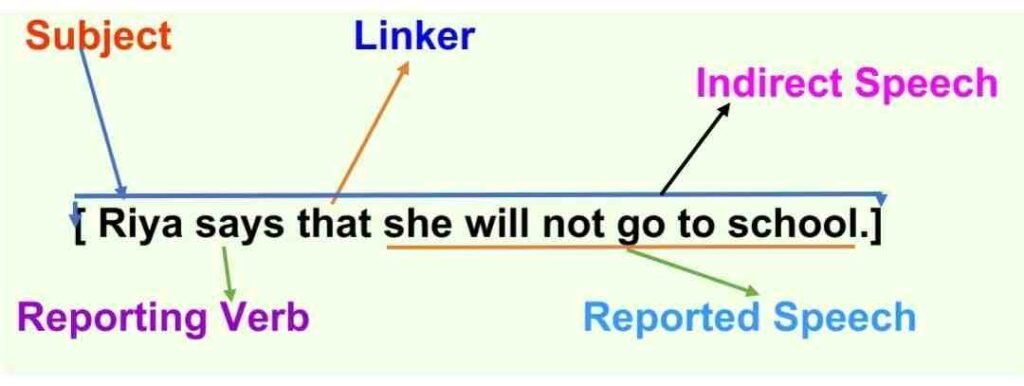
Similarly, we can report the above-mentioned sentence without quoting Riya’s actual words but keeping the meaning the same. This Format of the sentence is called Indirect Speech . In this format, no Comma and no Quotation Mark / Inverted Comma are used. Only Full Stop ( . ) is used at the end of the sentence.
People also ask
Direct and Indirect Speech General Rules
Now, learn the general rules of direct and indirect speech with numerous examples to enhance your language skills. Understand the subtleties of transforming statements, questions, and commands from one form to another effortlessly.
A. Direct and Indirect Speech (Reporting Verbs) Rules
Different reporting verbs are used to introduce indirect speech. The choice of reporting verb can convey the speaker’s attitude towards the reported speech.
Changes in reporting verbs according to tense are one of the most important rules for converting direct speech into indirect speech.
Remember: If the reporting verbs are in the presen t or future tense, the tense of the verb in the reported speech is not changed .
Remember: If the reporting verbs are in the past t ense, the tense of the verb in the reported speech will be in the corresponding past tense.
Here are some commonly used reporting verbs:
Rule 1: Reporting verbs ‘Say’ and ‘Tell’
“Say” and “tell” are two frequently used reporting verbs. “Say” is generally followed by the reported speech, while “tell” is followed by the indirect object (the person being addressed).
Direct: He says , “I am your friend.”
Indirect: He says that he is your friend.
Direct: He said to me, “I’m going to the store.”
Indirect: She told me that he was going to the store.
Rule 2: Reporting Verb ‘Ask’ and ‘Inquire’
When reporting questions , “ask” and “inquire” are commonly employed reporting verbs.
Direct: He said to me, “Where are you going?”
Indirect: He asked where I was going.
Direct: She said , “When will the concert start?”
Indirect: She inquired , “When will the concert start?”
Rule 3: Reporting Verb Request, Advise, Order, and Beg
To report imperative sentences, “Request”, “Advise”, “Order”, and “beg” are often used.
Direct: He said to me, “Go home at once”
Indirect: He ordered me to go home at once.
Direct: She said , “Do not run in the sun”
Indirect: She advised not to run in the sun.”
B. Direct and Indirect Speech ( Tenses ) Rules
The second most important rule is the changes of Tenses for converting direct speech to indirect speech
When transforming direct speech into indirect speech, there are specific rules to follow regarding tense changes:
Rule 4: Reporting Verb Present Tense:
If the Reporting Verb is in the Present Tense, there is no change in the tense in the Reported Verb when Direct Speech is converted into Indirect Narration.
Direct: Arnab says , “The room is dark.”
Indirect: Arnab says that the room is dark.
Direct: Arnab says , “The room was dark.”
Indirect: Arnab says that the room was dark.
Direct: Arnab says , “I shall finish the work.”
Indirect: Arnab says that he will finish the work.
Rule 5: Reporting Verb Future Tense:
If the Reporting Verb is in the Future Tense, there is no change in the tense in the Reported Verb when Direct Speech is converted into Indirect Narration.
Direct: Arnab will say , “The room is dark.”
Indirect: Arnab will say that the room is dark.
Direct: Arnab will say , “The room was dark.”
Indirect: Arnab will say that the room was dark.
Direct: Arnab will say , “I shall finish the work.”
Indirect: Arnab will say that he will finish the work.
Rule 6: Reporting Verb Past Tense:
If the Reporting verb of the Direct Narration is in the Past Tense, the Present Tense of the Verb in the Reported Speech of Direct Narration is changed into the corresponding Past Tense in Indirect Narration.
Direct Speech: Rohan said , “She works hard.”
Indirect Speech: Rohan said that she worked hard.
Direct Speech: Rohan said , “She is singing a song.”
Indirect Speech: Rohan said that she was singing a song.
Direct Speech: The guest said shouting, “We have arrived .”
Indirect Speech: The guest shouted that they had arrived .
Direct Speech: My sister said , “It has been raining hard for 3 days”.
Indirect Speech: My sister said that it had been raining hard for 3 days.
Direct Speech: Father said , “I visited the Taj yesterday.”
Indirect Speech: Father said that he had visited the Taj the previous day.
Direct Speech: The boys said , “They were traveling in the park.”
Indirect Speech: The boys said that they had been traveling in the park.
Direct Speech: The reporters commented, “The Kohinoor had been lost long ago”.
Indirect Speech: The reporters commented that the Kohinoor had been los t long ago.
D i rect Speech: Jyotsna said , “ She had been doing the work for 3 hours”.
Indirect Speech: Jyotsna said that she had been doing the work for 3 hours.
Rule: 7 Direct Indirect Speech (Universal Truth or Habitual Fact) Rules.
The Tense of the Verb remains unchanged in Indirect Narration in cases of General Statements of Facts , Universal Truths , Commonplace Occurrences , and Habitual or Repeated Actions . No real change occurs in these cases. Only there will be present Tense alone.
Direct: The boy said to his mother, “ The sun rises in the East”.
Indirect: The boy told his mother that the sun rises in the East. [ Universal Truth ]
Direct: The monk answered , “ Man is mortal”.
Indirect: The monk answered that man is mortal. [ Universal Truth ]
Direct: The teacher told the students, “ Perseverance always leads to success.”
Indirect: The teacher told the students that perseverance always leads to success.
3. Direct and Indirect Speech ( Changing of Pronouns) Rules
There are certain rules to follow regarding the changes of pronouns from direct speech to indirect speech:
Rule 8: Personal Pronouns
First person.
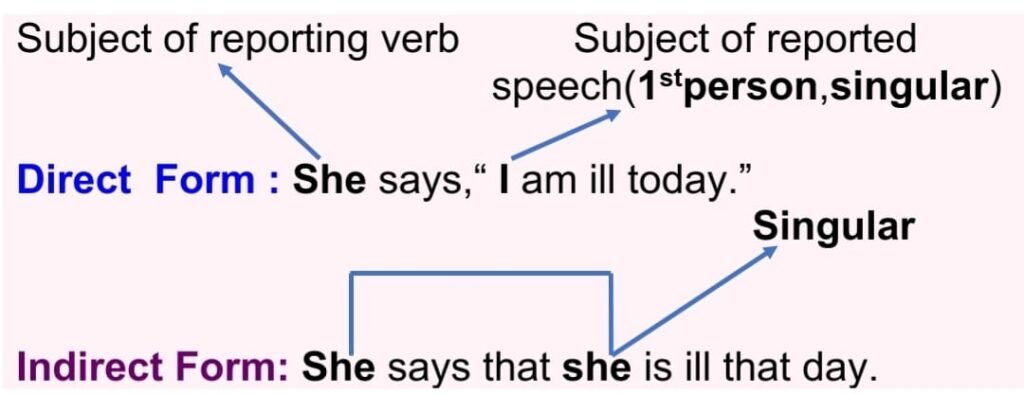
(a) If the subject of the reported speech of direct form is in the first person, the subject of the reported speech will be replaced by the subject of the reporting verb in indirect form, but the number must be the same. [ singular > singular and plural > plural ]
Direct: She says, “ I am ill today.”
Indirect: She says that she is ill that day.
Second Person
(b) If the subject of the reported speech in the Direct Form is in the second person, the subject of the reported speech will be replaced by the object of the reporting verb in the indirect form, but the number must be the same. [ singular > singular and plural > plural ]
Direct: He says to me , ” You can do this work.”
Indirect: He tells me that I can do that work.

Third Person
(c) If the subject of the reported speech of Direct Form is in the third person, there will be no change in the person of the Indirect Form.
Direct: I said, “ He will not wait for his friend.”
Indirect: I said that he would not wait for his friend.

Changing pronouns Chart
Rule 9: demonstrative pronouns.
In the case of demonstrative pronouns, replace them with appropriate pronouns in indirect speech.
Direct: “ This is my book,” she said.
Indirect: She said that it was her book.
4. Direct and Indirect Speech (Punctuation and Quotation Marks ) Rules
Understanding how to punctuate and use quotation marks correctly is crucial when dealing with direct and indirect speech. Here are some guidelines:
Rule 10: Comma and Reporting Verb
When introducing indirect speech with a reporting verb, use a comma to separate the reporting verb from the reported speech.
Example: She said, “I’ll be there on time.”
Rule 11: Question Mark to Full Stop
If the direct speech is a question, change the question mark to a full stop when converting to indirect speech.
Direct: He asked, “Are you coming to the party?”
Indirect: He asked if I was coming to the party.
Rule 12: Exclamation Mark to Full Stop
In cases where the direct speech has an exclamation mark, replace it with a full stop in indirect speech.
Direct: She exclaimed, “What a beautiful day!”
Indirect: She exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
Direct to Indirect speech (Modals and Conditional Sentences) Rules
Indirect speech involving modals and conditional sentences requires careful attention to maintain accuracy:
Rule 13: Modals in Indirect Speech
When dealing with modals like can, could, will, would, may, might, shall, should, must, etc., use the appropriate past form in indirect speech.
Direct: She said , “I can swim.”
Indirect: She said that she could swim.
Rule 14: Conditional Sentences in Indirect Speech
In indirect speech, conditional sentences undergo specific changes, especially when they involve “will” or “would.”
Direct: He said , “I will help you.”
Indirect: He said that he would help me.
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules: (Modifying Words – Time, Place, Manner)
Adding modifying words or phrases can alter the meaning of the reported speech:
Rule 15: Reporting with Adverbs of Time
When using adverbs of time in indirect speech, adjust them to match the new timeframe.
Direct: “I will come tomorrow,” she said.
Indirect: She said that she would come the next day.
Rule 16: Reporting with Adverbs of Place
Similar to adverbs of time, adverbs of place need modification in indirect speech.
Direct: ” I live here,” he said.
Indirect: He said that he lived there.
Rule 17: Reporting with Adverbs of Manner
We can also use Adverbs of manner in indirect speech, requiring appropriate adjustments.
Direct: “He ran quickly,” she said.
Indirect: She said that he ran quickly.
Time, Place, Manner, Distance, and Direction Chart
In Indirect Narration, words denoting Time, Place, Manner, Distance, and Direction used in the quoted speech are correspondingly changed to conform to the point of view of the Reporter. Thus, the sense of nearness is changed into that of Distance, and so on.
Place Chart
Manner chart, distance chart, direction chart, direct and indirect speech advanced rules.
It is necessary to know about the Direct Indirect Speech Advanced Rules to change the mode of narration from direct to indirect speech of different sentences. All five sentences of Direct Indirect Speech Conversion Rules are shown with proper examples below.
A. Assertive Sentence Conversion Rules
To convert Assertive sentences into indirect speech the following rules are applied.
(a) No comma and Inverted comma in Indirect Speech, only full stop at the end.
(b) Reporting Verbs changed from Direct Speech to Indirect Speech ; ‘say – say’, ‘says – says’, ‘said – said’, ‘said to – told’, ‘say to – tell’, ‘says to – tells’.
(c) Connective ‘that’ added before Reported Speech in indirect Narration.
Direct: He said to me, “I am ill.”
Indirect: He told me that he was ill.
B. Interrogative sentences Conversion rules
Forming indirect speech with questions necessitates some adjustments:
Reporting Yes/No Questions
When reporting yes/no questions, use “if” or “whether” and invert the subject and auxiliary verb in indirect speech.
Direct: “Will you be there?” he asked.
Indirect: He asked if I would be there.
Reporting Wh-Questions
For reporting wh-questions, maintain the question word and adjust the word order in indirect speech.
(a) ‘Tell’ and ‘say’ in Direct Narration are changed to ‘ask’, ‘enquire of’, ‘question’, ‘want to know’ etc. in Indirect Narration. (b) In place of introductory ‘that’. ‘if’ or ‘whether’ should be used. (c) In Indirect Narration a full stop (.) must be put in place of a question mark(?) at the end of the sentence. (d) In Direct Narration the Reported Speech begins with W-word or how, in Indirect Narration the same Wh-word or how is retained.
Direct: “Where are you going?” she asked.
Indirect: She asked where I was going.
Direct: The teacher said to me, “Why are you late?”
Indirect: The teacher asked me why I was late.
C. Imperative Sentences Conversion rules
The indirect speech also involves reporting imperatives, which are commands, requests, or advice:
Reporting Commands
When reporting commands, use the reporting verb “tell” and change the imperative verb to the corresponding infinitive.
Direct: The teacher said, “Open your books.”
Indirect: The teacher told the students to open their books.
Reporting Requests
For reporting requests, employ the reporting verb “ask” and convert the imperative verb to the corresponding infinitive.
Direct: She said, “Please help me with this.”
Indirect: She asked for help with that.
(a) Reporting verbs of Direct Speech changed into order or command, advise, or request according to sense in Indirect Speech. (b) ‘To’ is placed before Reported speech in Indirect Narration; for the negative imperative sentence ‘not to’ is used. (c) ‘not to’ can also be replaced by ‘forbid’, or ‘prohibit’. (d) ‘Let’ implies ‘suggestion’ or ‘proposal’; Reporting verb will be ‘suggest’ or ‘propose’ in Indirect Speech. ‘that’ is used before Reported speech in Indirect Narration (e) ‘Let’ without ‘suggestion’ or ‘proposal’; Reporting verb will be ‘tell’, or ‘wish’ according to sense in Indirect Speech. ‘that’ is used before Reported speech in Indirect Narration.
Direct: Mother said to me, “Don’t run in the sun.”
Indirect: Mother advised me not to run in the sun.
Direct: She said to me, “Let us go for a picnic.”
Indirect: She suggested that we should go for a picnic.
D. Optative Sentence Conversion rules
The following rules are used to change an optative sentence from direct speech to indirect speech
(a) Reporting verbs changed to ‘ wish ’, ‘ pray ’, and ‘ bless ’ in Indirect Speech.
(b) Linker, ‘ that ’ is placed before Reported speech in Indirect Narration.
Direct: The monk said to me, “ May God bless you.”
Indirect: The monk wished that God might bless me.
E. Exclamatory Sentences Conversion rules
(a) The reporting verb is changed into exclaim (in joy), exclaim (in grief), cried out (in sorrow), pray, wish, etc. (b) Examinations are turned into statements. (c) Interjections (Alas, Oh, Hurrah) are omitted. (d) ‘What’, and ‘How’ used in exclamation should be replaced by great, great, very, very much, and big.
Direct: The boys said, “Hurrah! we have won the match.”
Indirect: The boy exclaimed in joy that they had won the match.
Solved Exercises Direct and Indirect Speech
Change the following sentences into indirect speech.
Q: Ratan said to Anita, “I don’t like your brother”.
Ans: Ratan told Anita that she did not like her brother.
Q: The hermit said to the boys, “God is present everywhere.”
Ans: The hermit told the boys that God is present everywhere.
Q: :He said to you, “You shouldn’t play in my garden.”
Ans: He told you that you should not play in his garden.
Q: The class teacher said to the students. “The inspector will visit our school today.”
Ans: The class teacher told the students that the inspector would visit their school that day.
Q: He said to me, “I don’t believe you.”
Ans: He told me that he didn’t believe me.
Q: She said to her son, “I’ve often told you not to play with fire.”
Ans: She told her son that she had often told him not to play with fire.
Q: Sitesh said to Lina, “I want you to go to Patna with me.”
Ans: Sitesh told Lina that he wanted her to go to Patna with him.
Q: “We can’t be quite happy in life,” he said.
Ans: He said that they couldn’t be quite happy in life.
Q: He said, “The Muslims bury their dead.”
He said that the Muslims bury their dead.
Q: “You’ve overcooked the steak again, Mary”, he said.
Ans: He told Mary that she had overcooked the steak again.
Q: Ramen said to Bina, “I’m going to your house this, week.”
Ans: Ramen told Bina that he was going to her house that week.
Q: He said, “We will discuss this tomorrow.”
Ans: He said that they would discuss that the next day
Turn the following sentences into direct speech.
Q: He said to me, “You are wicked; so I shall not mix with you.”
Ans: He told me that I was wicked; so he would not mix with me.
Q: He said to you, “I was much struck by your eloquence.”
Ans: He told you that he had been much struck by your eloquence.
Q: We remarked, “God is gracious.”
Ans: We remarked that God is gracious.
Q: I said to my mother, “I shall always obey you.”
Ans: I told my mother that I should always obey her.
Q: He said to Gopal, “You were a mere boy when I saw you last.”
Ans: He told Gopal that he was a mere boy when he had seen him last.
Q: I said to him, “The sky is blue.”
Ans: I told him that the sky is blue.
Q: He said to me, “You will feel the consequences.”
Ans: He told me that I should feel the consequences.
Q: She said to you, “I am not angry with you.”
Ans: She told you that she was not angry with you.
Q: I said to them, “You have done wrong.”
Ans: I told them that they had done wrong.
Q: He said, “I visit the temple every day.”
Ans: He said that he visited the temple every day.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): Direct and Indirect Speech
Q : what is the key difference between direct and indirect speech.
Ans: The main difference lies in the quoting style. Direct speech involves repeating someone’s exact words, while indirect speech reports what was said without quoting verbatim.
FAQ 2: Is it always necessary to backshift the tense in indirect speech?
Ans: While backshifting is common, some exceptions exist, especially in cases where the statement’s truth remains constant.
FAQ 3: How do I handle multiple speakers in indirect speech?
Ans: When reporting multiple speakers, use appropriate reporting verbs and introduce each person’s dialogue in a logical sequence.
FAQ 4: Can I mix direct and indirect speech in the same sentence?
Ans: Combining direct and indirect speech in a sentence is possible, but it requires precision to avoid confusion.
FAQ 5: What are some reporting verbs commonly used in indirect speech?
Ans: Reporting verbs like “said,” “told,” “asked,” “claimed,” and “explained” are frequently employed.
FAQ 6: How can I ensure my writing maintains a natural flow when switching between direct and indirect speech?
Ans: Focus on maintaining consistency in style and verb tense to ensure a smooth transition between direct and indirect speech.
FAQ 7: How do I identify direct and indirect speech in a sentence?
Ans: Direct speech is usually enclosed within quotation marks and directly quotes someone’s words. Indirect speech, on the other hand, reports those words without quotation marks, often using reporting verbs like “said,” “told,” “asked,” etc.
FAQ 8: Can reporting verbs change the meaning of indirect speech?
Ans: Yes, the choice of reporting verbs can convey the speaker’s attitude or emotions towards the reported speech. Different reporting verbs can modify the meaning slightly.
FAQ 9: What are the common reporting verbs for indirect speech?
Ans: Common reporting verbs for indirect speech include “say,” “tell,” “ask,” “inquire,” “explain,” “describe,” and more.
FAQ 10: How do I change tenses in indirect speech?
Ans: The tense in indirect speech is generally shifted back one step. For example, present simple becomes past simple, present continuous becomes past continuous, and so on.
FAQ 11: Is it essential to use quotation marks in indirect speech?
Ans: No, quotation marks are not used in indirect speech as they report the speech without directly quoting it.
FAQ 12: Can you give an example of indirect speech in narratives?
Ans: Certainly! In the story, he said, “I love you,” to which she replied that she loved him too.
FAQ 14: Can we omit the reporting verb in indirect speech?
Ans: It is possible to omit the reporting verb in some cases, especially in informal contexts, but including it adds clarity and structure to the reported speech.
FAQ 15: Do all tenses change in indirect speech?
Ans: Most tenses change in indirect speech, but the changes depend on the context and the tense of the original statement.
FAQ 16: Can you provide more examples of direct and indirect speech transformations?
Ans: Certainly! Here are a few more examples:
Direct: “I am reading a book,” she said. Indirect: She said that she was reading a book.
Direct: “We have completed the project,” they exclaimed. Indirect: They exclaimed that they had completed the project.
FAQ 17: How can I practice using direct and indirect speech effectively?
Ans: Practice by converting direct speech to indirect speech and vice versa using various reporting verbs, tenses, and pronouns. Additionally, read books or articles and identify the reported speech used by the authors.
Related posts:
Direct and Indirect speech, Rules, Chart and Exercises
Direct and Indirect speech are ways of narrating the speech of someone to some other person following certain rules. This article covers its types, rules, examples and some exercises on the same.

Table of Contents
Direct and Indirect Speech: In English Grammar, direct and Indirect speech are used in instances when we wish to repeat or convey a speech or statement of some other person. Both direct and indirect speech describes what a third person said or conveyed in the past. Indirect speech is more commonly employed unless it’s a direct quotation, which is consistently enclosed in double quotation marks. Whereas indirect speech is used when you want to convey someone’s statement using your own precise words. It’s worth highlighting that indirect speech is consistently expressed using verbs like “said,” “told,” or “asked.”
Direct and Indirect Speech
There are two types of reported speech in English grammar, they are Direct and Indirect speech. Both speech conveys the speech or statement which was told by some other person. To explain any event, action or scenario we generally convey the sentences quoted by someone in the form of direct and indirect speech. In order to clearly differentiate and make people understand easily, we have detailed the two types of reported speech with examples and exercises below.
Direct Speech
Direct speech is the mode of expression that directly presents the words spoken or quoted by a third person. Generally, direct speech is written inside quotation marks (“”). The quotation is used to differentiate the speech of the third person that has happened in the past. Thus direct speech conveys statements or conversations of someone in the past tense but quoted inside the quotation marks in the present or future tense.
- Kiran said, “I am doing my work.”
- They said, ” We will go for the function.”
- He asked,”Can I make this?”
Indirect Speech
Indirect Speech is used when we convey what someone said in our own words without repeating the actual text of that person. Instead of using quotation marks, the conjunction word, ‘that’ is used. Thus speaker’s words and sentences are reframed into our own words in Indirect speech. Some examples of indirect speech are:
- Direct speech: Kiran said, “I am doing my work.”
- Indirect speech: Kiran said that she is doing her work.
- Direct speech: They said, ” We will go for the function.”
- Indirect speech: They said that they would go to the function.
- Direct speech: He asked, “Can I make this?”
- Indirect speech: He asked whether he can make that.
Rules for Direct and Indirect Speech
There are certain rules and regulations followed while converting a simple direct speech into indirect speech. Certain factors such as Verbs, Tenses, Modals, time, place, and pronouns are also considered while changing. The following are the rules applied when you convert direct speech to indirect speech in English grammar.
Rule-1 : Direct To Indirect Speech Conversion – Reporting Verb
The reporting verb is an important factor to note when changing a direct to an indirect sentence. When the reporting verb is past tense, then the verb inside the quotation is also changed to past when changing a sentence from direct to indirect speech. Examples:
- Direct: He said,’ I am sad.’
- Indirect: He said that he was sad.
An exception is for cases like a universal truth, the tenses remain the same.
- Teena said” The sun rises in the east”.
- Teena said that the sun rises in the east.
If the reporting verb is in present/future tense, then the tense remains the same as in direct speech.
- Direct: She says/will say, ‘I am coming.’
- Indirect: She says/will say she is coming.
Rule 2: Direct Speech to Indirect Speech Conversion – Tenses
If the sentences inside quotes in direct speech are present tense, it is changed to past tense when changed to indirect speech. The rule in the following table is applied while changing tenses from direct speech to reported speech.
Examples of change in Tenses
Rule 4: Direct to Indirect speech Conversion Interrogative sentences
If a sentence starts with a question word like what, when, and why in direct speech, the question word itself acts as the joining class.
- Direct speech: “Where do you live ?” Asked the boy.
- Indirect Speech: The boy enquired where I lived.
Rule 5: Direct to Indirect Speech Conversion Change in Modals
Modal verbs are those verbs that are preceded by another verb, which is the main verb. Can, May, and Must are some examples of Modals. Modals that won’t change are Could, would, should, ought to, might. While changing direct to indirect speech, the Modals change as below:
- Can become could
- May becomes Might
- Must becomes had to (or) would have to
- Direct: She said,” She can sing.”
- Indirect: She said that she could sing.
- Direct: She said,” I should cook the lunch”
- Indirect: She said that she should cook the lunch.
Rule 6: Direct to Indirect speech conversion – pronoun
The first person in Direct speech changes as per the subject of the speech
- Direct: He said, “I am in grade sixth.”
- Indirect: He said that he was in grade sixth.
The second person of Direct speech changes as per the object of the indirect speech.
- Direct: She says to them, “You have achieved your goal.”
- Indirect: She tells them that they have achieved their goal.
If the third person is mentioned in the Direct speech, it does not change in reported speech.
- Direct: He says, “She sings well.”
- Indirect: He says that she sings well.
Rule 7: Direct to indirect speech conversion – Request, Command, Wish and Exclamation.
The imperative words in direct speech change into Infinitives in indirect speech.
- Direct: She said to her ‘Please remove it’.
- Indirect: She requested her to remove that.
Exclamation
- Direct: She said, ‘Alas! I am undone.
- Indirect: She exclaimed sadly that she was broke.
Rule 8: Direct to indirect speech conversion – punctuations
In Direct speech, the words spoken must start with(“) and ends with(.) inside the double inverted commas. All symbols such as question marks, full stops or exclamatory marks should be placed inside the quotes.
- They said. “We are the best”
- She asked, “Can I come with You?”
- He uttered, “Keep Quiet!”
Rule 9: Direct to indirect speech conversion – Change of time
While converting direct speech to Indirect speech, there are certain words to be noted that cannot be used as such in indirect speech. These words get modified into new words which are enlisted below:
- Now becomes Then
- Ago becomes before
- Thus becomes So
- Today becomes That day
- Tomorrow becomes the next day
- Yesterday becomes the day before
- This becomes that
- These become those
- Come becomes go
- Hence becomes thence
- Next week or next month becomes the following week or month
- Direct: He says/will say, ‘My girlfriend came yesterday.’
- Indirect: He says/will say that his girlfriend had come the day before.
Rules for Converting Indirect Speech into Direct Speech:
The following rules should be followed while converting an indirect speech to direct speech:
- Use the reporting verb such as (say, said to) in its correct
- Put a comma before the statement and the first letter of the statement should be in capital
- Insert question marks, quotation marks, exclamation marks and full stops, based on the mood of the
- Remove the conjunctions like (that, too, if or wh ether) wherever necessary .
- Where the reporting verb is in the past tense in indirect, change it to present tense in the direct
- Change the past perfect tense either into the present perfect tense or past tense, as necessary .
Direct and Indirect Speech – Some Exercises
The following are some exercises that students can practice while preparing for their revision tests or board exams.
Q.1. Find out the correct indirect speech for the given sentence.
She said,’ I have cooked this meal.’
- She said that she cooked this meal
- She said that she had cooked that meal.
- She said that I cooked that meal.
- She said that she had cooked this meal.
Answer (2) She said that she had cooked that meal.
Q.2. Choose the correct sentence.
Sanjay said, ‘What a beautiful painting it is’.
- Sanjay exclaimed wonderfully that the painting was very beautiful.
- Sanjay exclaimed with wonder that the painting was very beautiful.
Answer (4) Sanjay exclaimed with wonder that the painting was very beautiful.
Q.3. The correct indirect speech for She asked, “What is the cost of these books?”
- She enquired what was the cost of those books.
- She inquired what was the cost of these books.
- She enquired what is the cost of those books.
- She questioned what was the cost of those books.
Answer (1) She enquired what was the cost of those books.
Q.4. The man said, ‘Oh God! I missed the train today.’
- The man cried that he missed the train that day.
- The man exclaimed in grief that he missed the train today.
- The man said that oh God! he missed that day.
- The man exclaimed with sorrow that he missed the train that day.
Answer (4) The man exclaimed with sorrow that he missed the train that day.
Sharing is caring!
Direct and Indirect speech-FAQs
Q1. what are direct and indirect speech in english.
Ans. Direct speech is a speech that describes what a third person has conveyed or quoted in a direct manner. Generally, direct speech is written inside quotation marks ("").Indirect Speech is used when we convey what someone said in our own words without repeating the actual text of that person.
Q2. In which speech conjunctions are used and what is the purpose?
Ans. The conjunctions are used in Indirect speech. The speaker's words and sentences are reframed into our own words in Indirect speech using conjuctions as connecting words.
Q3. What are modals and what is the significance of using modals?
Ans. Modal verbs are those verbs that are preceded by another verb, which is the main verb. Can, May, and Must are some examples of Modals. While converting direct to indirect speech Can becomes could, May becomes Might, Will becomes Would. Modals that won’t change are Could, would, should, ought to, might.
As Team Lead- Content Writer, I take on leadership within our content creation team, overseeing the development of error-free educational content. My primary responsibility is to produce and analyse high-quality content educating and informing the aspirants about upcoming government exams published on our website. I have more than 6 years experience in content writing wherein 3.5 years of experience in ed-tech content writing.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2023-24
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2023-24
- CBSE Class 12 English Syllabus 2023-24
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2023-24
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus 2023-24
CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2023-24
- CBSE Class 10 English Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 SST Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Hindi Syllabus
Exam Date 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- NEET Exam Date 2024
- JEE Mains Exam Date 2024
- NEET 2024 Notification
- NEET Age Limit 2024
Latest Posts
Important exams.
- JEE Mains 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- NIMCET 2024
- AP EAMCET 2024
- TS EAMCET 2024
- AP ECET 2024
- TS ECET 2024
- TS PGECET 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- AP Polycet 2024
- TS Polycet 2024
- JEECUP 2024
- Bihar Polytechnic 2024
- Jharkhand Polytechnic 2024
- Responsible Disclosure Program
- Cancellation & Refunds
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy

Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
English grammar direct and indirect speech rules, what is direct and indirect speech.
We often have to give information about what people say or think. In order to do this, we can use direct or quoted speech or indirect or reported speech .
Direct Speech
Saying exactly what someone has said is called direct speech (sometimes called quoted speech).
For example:
- She said, “Today’s lesson is on presentations.” Or “Today’s lesson is on presentations,” she said.
Indirect speech
Indirect speech (sometimes called reported speech or Narration ), doesn’t use quotation marks to enclose what the person said and it doesn’t have to be word for word. Thus, in indirect speech, we convey the speaker’s message in our own words.
- Direct Speech: He said, “I’m going to the cinema”.
- Indirect Speech: He said that he was going to the cinema.
Reported Speech Tenses Change Chart
Reported speech does not go back a tense if it is already in the past perfect (there is no further back it can go), and some modal verbs also do not change.
Direct and Indirect speech Examples for Tense
1. Simple Present to Simple Past
- Direct: He said, “The boy goes home.” Indirect: He said that the boy went home.
2. Present Continuous to Past Continuous
- Direct: Ram said, “I am reading a book.” Indirect: Ram said that he was reading a book.
3. Present Perfect to Past Perfect
- Direct: The girl said, “I have lost my pen.” Indirect: The girl said that she had lost her pen.
4. Present Perfect Continuous to Past Perfect Continuous
- Direct: He said, “Ram has been going.” Indirect: He said that Ram had been going.
5. Past Indefinite to Past Perfect
- Direct: Mother said, “I bought a watch for you.”
- Indirect: Mother said that she had bought a watch for him.
6. Past Continuous to Past Perfect Continuous
- Direct: Raju said, “I was repairing a car.” Indirect: Raju said that he had been repairing a car.
7. Future Tense (shall/will) to future in the Past (should/would)
- Direct: The teacher said, “I shall give you notes.” Indirect: The teacher said that he would give them notes.
8. Conditional to Perfect Conditional Direct:
- Direct: He said, “If I had the money I could buy the car.” Indirect: She said that if he had the money he could have bought the car.
9. Past Perfect Tense: No Change
- Direct: She said, “I had gone to Bhagalpur.” Indirect: She said that she had gone to Bhagalpur.
10. Auxiliary Verbs (would, should, might, could, ought, must) — No Change
- Direct: He said, “I would like to take milk.” Indirect: He said that he would like to take milk.
- Direct: The boy said, “The teacher could have solved it in no time.” Indirect: The boy said that the teacher could have solved it in no time.
- Direct: He said, “The boy must apologise to the teacher.” Indirect: He said that the boy must apologise to the teacher.
Changes of Interrogative Sentences
- Toni said, “What is Luna doing?” Toni asked me what Luna was doing.
- Luna said, “Will she come for lunch?” Luna asked if she would come for lunch.
- The boy asked, “ Wh ere do you stay?” The boy inquired where I stayed
Things are slightly more complicated with imperatives
Time and place references.
- I went to the theatre last night . He said he had gone to the theatre the night before .
- I’m having a party next weekend . He said he was having a party the next weekend .
- I’m staying here until next week . He said he was staying there until the following week.
- I came over from London 3 years ago . He said he had come over from London 3 years before.
When verbs don’t follow the rules?
- You’ve invited someone for dinner at your house, and the phone rings. It’s them! They say:
- (on the phone) “I’m sorry, but I think I’m going to be a bit late. There’s a lot of traffic.”
- After you finish speaking on the phone, you say to someone else:
- That was Juan. He said he thinks he’s going to be late because there’s a lot of traffic.
Another example:
- A friend says to you: “Maria’s ill. She’ s got chickenpox!”
- You say to someone else: Laura said that Maria’ s ill. She’ s got chickenpox.
- However, the following day you see Maria at the beach. You’re surprised and say to her:
- Laura said that you were ill. She said you had chickenpox.
This has to change to the past because it isn’t true . Maria obviously isn’t ill .
- A friend is telling you about the horrible weather: “It started raining heavily when I left work.” (This is where things get confusing):
- He said it had started raining heavily when he had left work (it sounds horrible and the sentence is almost nothing but verbs).
- He said it had started raining heavily when he left work (is wrong because it means it was already raining when he left work)
- He said it started raining heavily when he left work (is the best version because it is accurate, short, and there is no confusion because of the time context)
Generally speaking, the past simple and continuous don’t always need to be changed if:
Rules for Universal Truth, Habitual Facts, etc.
- Direct: My friend said, “I am an early riser.” Indirect: My friend said that he is an early riser.
- Direct: Father said, “Man is the only animal that cooks his food.” Indirect: Father said that man is the only animal that cooks his food.
- Direct: The teacher said, “Honesty is the best policy.” Indirect: The teacher said that honesty is the best policy.
- Direct: The teacher said, “The earth moves around the sun.” Indirect: The teacher said that the earth moves around the sun.
- Direct: Sarla said, “When Ram was reading Sham was writing.” Indirect: Sarla said that when Ram was reading Sham was writing.
- Direct: The teacher said, “Akbar died in 1605 AD.” Indirect: The teacher said that Akbar died in 1605 AD.
- Direct: The speaker said, “Gentlemen, I will tell you what is going there.” Indirect: The speaker told his audience (those present) that he would tell them what was going there
- Direct: He said, “I hope, friends, you will support me.” Indirect: He said that he hoped they would support him.
- Direct: He said, “I would rather she played.” Indict: He said that he would rather she played.
- Direct: He said, “If I were rich, I would settle in Mumbai. Indirect: He said that if he were rich, he would settle in Mumbai.
- Direct: He said. “When we lived/were living in Chennai, we often visited Rameshwarm” Indirect: He said that when they lived/ were living in Chennai, they often visited / had visite Rameshwarm
Rules for the Change of Pronouns
If the direct speech has a pronoun, its person is changed, when necessary, to refer in the indirect to the same individual as it does in the direct.
- Soni said, “ I am a good girl.” Soni said that she was a good girl.
- I told them, “ You have finished your work.” I told them that they had finished their work.
- He said, “ She is in Delhi.” He said that she was in Delhi.
- Direct: He said, “I can cross this river.” Indirect: He said that he could cross that river.
- Direct: You said. “I can cross this river.” Indirect: You said that you could cross that river.
- Direct: I said, “I can cross this river.” Indirect: I said that I could cross that river.
You also need to be careful with personal pronouns . They need to be changed according to the situation. You need to know the context.
For example , there is possible confusion when you try to change reported speech to direct speech:
- She said she ’d been waiting for hours. (Is ‘ she ‘ one person or two different people?)
- I told them they would have to ask permission. (Are we talking about two groups of people or only one?)
- Types of Verbs
- Types of Adjectives
- Types of Noun
- Participles
- Phrases and Clauses
- Parts of Speech
- Parts of a Sentence
- Determiners
- Parallelism
- Direct & Indirect Speech
- Modal Verbs
- Relative Clauses
- Nominalisation
- Substitution & Ellipsis
- Demonstratives
- Pronoun Reference
- Confusing Words
- Online Grammar Quizzes
- Printable Grammar Worksheets
- Courses to purchase
- Grammar Book
- Grammar Blog
- Direct & Indirect Speech
Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct and indirect speech grammar rules vary so you need to understand them. We'll start by looking at what each one is. Note that indirect speech is also commonly knows as reported speech.
Definition of Direct Speech
Direct speech is when the words are given in exactly the way that the speaker said them. So in other words they are quoted with no change .
When presenting direct speech, the words are usually placed in quotation marks, with a comma after say(s) / said if it is used to present the speech. Say (s) / said can also be placed at the end of the quotation, in which case a comma comes before it.
Examples of Direct Speech:
- He said, "Don't take the car without asking me".
- John says, "I will help you with your work".
- "We are prepared to revise the law if we can", they said.
- The teacher said, "You must wear the proper uniform".
Definition of Indirect Speech
Indirect speech is also known as reported speech . You may also see it referred to as indirect discourse or indirect narration .
Indirect speech is the reporting of what someone else said in your own words but without changing the meaning of what was said.
Reporting verbs are used to present indirect speech. The common ones are:
- say(s)/said (that)
- told me (that)
That is in brackets as it can be omitted from the sentence, whether spoken or written.

Examples of Indirect Speech:
- He said (that) he would definitely buy it.
- Sheila told me (that) I had to come back in the afternoon.
- The council said (that) they will try and clear the rubbish.
- She told me (that) she was feeling unwell.
So the key difference between direct and indirect speech is that with direct speech the exact words are quoted but in indirect speech it is your own words .
Direct speech is fairly simple to use and understand as it involves just repeating what was said. There is not much to get confused about with the grammar, apart from getting say(s)/said correct.
But indirect or reported speech is more difficult so we will look at that in more detail now.
View more examples of direct and indirect speech >>
Direct and Indirect Speech Conversion
With direct and indirect speech, there are three main things you need to be aware of when converting one to the other:
- Changes in Tense
- Changes in Person and Pronouns
- Changes in Time Phrases
Changing Tenses
The tense of verbs when moving from direct to indirect speech do not necessarily change because if the circumstances of what someone said is the same, then it may be reported as that. For example:
- "I am feeling tired" (= Direct Speech )
- Present Continuous
- She said she is feeling tired (= Indirect Speech )
However, as we are reporting what was said in the past, we often change the tense. This rule for this is related to backshifting, which means shifting back a tense. So the present will go back to the past. Some modals also change.
Here are examples using the previous examples of indirect speech, showing you how they look like in direct speech:
Direct Speech
- "I want to meet you later".
- "You have to come back in the afternoon"
- "We like it a lot"
- "I have been mowing the lawn"
Indirect Speech
- He said he wanted to meet me later.
- Sheila told me I had to come back in the afternoon.
- They said they liked it a lot.
- He said he had been mowing the lawn.
There are more details on the site about changing tenses in indirect / reported speech:
Learn more about changing tenses >>
Changing Pronouns
Pronouns in indirect speech also need to be changed from what they were in the indirect speech, as well as of course adapting the first pronoun to fit the person who said the statement:
- " I want to meet you later".
- " You have to come back in the afternoon"
- " We like it a lot"
- " I have been walking with my wife"
- He said he had been walking with his wife.
Changing Time Phrases
You may also need to change phrases referring to time, though this depends on the context and when you are reporting the speech.
With these examples you have to assume the speech is being reported at a time in the future so the phrases such as 'yesterday' or 'tomorrow' would not makes sense any more in terms of the reported speech.
- She said, "I saw her yesterday ".
- He said, "He will bring the book tomorrow ".
- She said, "I'm going to London today ".
- He said, "We need your assistance now ".
- She said that she had seen her the day before .
- He said that he would bring the book the next day .
- She said she was going to London that day .
- He said they needed my assistance then .
Imperatives
Some different rules apply when turning direct speech using imperatives or commands into indirect speech. Check out the rules here:
Rules for Reported Speech Imperatives >>
More on Reported Speech:

Reported Speech Imperatives: Reporting commands in indirect speech
Reported speech imperatives, also known as reported commands, follow a slightly different structure to normal indirect speech. We use imperatives to give orders, advice, or make requests.

Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
In these examples of direct and indirect speech you are given a sentence in direct speech which is then connected to indirect speech.

Reported Speech Quiz - Practice forming indirect speech
This reported speech quiz gives you the chance to practice converting direct speech to reported speech, also known as indirect speech. This involves backshifting with the tenses.

Reported Speech Tenses Chart: How to convert tenses
Reported speech tenses may differ from the tense of the direct speech. The general rule for tenses in reported speech is that it changes to the past tense. This is called backshifting.
Sign up for free grammar tips, quizzes and lessons, straight into your inbox
New! Comments
Any questions or comments about the grammar discussed on this page?
Post your comment here.

Grammar Rules
Subscribe to grammar wiz:, grammar ebook.

This is an affiliate link
Recent Articles
When to Use the Definite Article: "The"
Mar 23, 24 05:49 PM

Who or Whom Quiz: Multiple Choice
Mar 15, 24 04:22 AM
Difference between Who and Whom in Relative Clauses
Mar 14, 24 12:14 PM
Important Pages
Online Quizzes Courses Blog
Connect with Us
Search Site
Privacy Policy / Disclaimer / Terms of Use
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
English Grammar & Vocabulary
Lessons & Practice Tests
Direct and Indirect Speech – Rules and Examples
13th June 2020 By Edify English Leave a Comment
Any word spoken by a speaker can be written in two different ways. Those two are direct and indirect speech. Direct Speech is when the speaker’s actual words are quoted and these words are put in inverted commas (“…..”) while Indirect Speech is when the speaker’s words are said indirectly with the same meaning without repeating the exact words. For Example, the statement in direct speech She said to me, “I am going to the park” changes into She told me that she was going to the park in indirect speech.

Basic Changes while changing from Direct speech to indirect speech
- The comma ( , )after the reporting verb is removed and the conjunction that is added in the indirect speech.
- If the direct speech contains ‘said to’ , it will be converted into ‘told’ in the indirect speech.
- The quotation marks (Inverted commas) are to be removed in the indirect speech.
- I becomes He/ She
- We becomes they
- You becomes He / She/ They
- Me becomes Him/ he r (Depending on the gender in the direct speech)
- My becomes His/ Her .
- Our becomes their
- Us becomes them
- Your becomes His/ her/ their .
Rules in changing a sentence from Direct and Indirect Speech
- Rule 1: The Verb in the simple present tense in the direct speech changes into the simple past tense in indirect speech
Example: He said to me, “I am happy” becomes He told me that he was happy
(The verb in the direct speech ‘am’ is converted into ‘was’.)
- Rule 2: The verb in the simple past tense becomes past perfect tense in indirect speech.
Example: He said to me, “I was happy” changes into He told me that he had been happy
- Rule 3: A present continuous tense in direct speech becomes past continuous tense in indirect speech.
Example: The peon said, “The professor is teaching in that classroom” changes into The peon said that the professor was teaching in that classroom.
- Rule 4: If the direct speech contains present perfect tense, it changes into the past perfect tense in indirect speech.
Example: She said, “I have passed the test” becomes She said that she had passed the test.
- Rule 5: If the direct speech contains a statement talking about a universal truth or a factual statement, there will be no change of tense in indirect speech.
Example: The teacher said, “The sun rises in the East” becomes The teacher said that the sun rises in the east in indirect speech.
Example: Samuel said, “I know the university’s address.” and the indirect speech for that is Samuel said that he knows the university’s address
Rules for converting Interrogatory sentences
- Rule 6: While converting interrogative sentences, the verb ‘said to’ becomes ‘asked’ and if/ whether will come in the place of ‘that’. The connecting word ‘that’ will not be used in indirect speech. Also, the interrogation mark (?) is not repeated in the indirect speech.
Example: He said to her, “Will you marry me?” changes into He asked her whether she would marry him in the indirect speech.
Rules for Converting Imperative Sentences
- Rule 7: During the conversion of imperative sentences, the verb “said to” is changed into ordered, advised, requested, suggested, proposed, etc. depending on the situation. Also, the connecting word ‘that’ is not used. Instead of that, ‘ to’ is used before the reporting verb.
Example: My father said to me, “prepare well for your examination” . It can be converted to My father advised me to prepare well for my examination.
Rules for Converting Exclamatory Sentences
- Rule 8: For exclamatory sentences, the verb is converted into: exclaimed with joy or sorrow or with surprise, wished, prayed, applauded,/ etc. The exclamatory words and the exclamation are not mentioned anymore in the indirect speech. For example,
Example: The coach said, “Hurrah! we won the match!” is changed as The coach exclaimed with joy that we had won the match.
These are the changes in helping verbs while changing from Direct and Indirect Speech
Note: There is no change in the helping verbs “would, should, could, might, had” in the direct speech and they remain the s ame in indirect speech as well.
Changes in Time and Place
Cha nges in pronoun s
The changes in pronouns in indirect speech depends on the subject and the object of the reporting verb.
- Rule 1: The first person of reported speech changes based on the subject of the reporting verb.
Example: She said, “I watched a movie” can be converted into She said that she had watched a movie . Hence, the first person in the direct speech “I” has become “she” based on the subject.
Had there been “he” instead of “she”, the first person in reported speech changes accordingly into “he”.
- Rule 2: The second person in reported speech changes based on the object of the reporting verb.
Example: She said to me, “You watched a movie” can be converted into She told me that I had watched a movie.
- Rule 3 : The third person in the reported speech remains unchanged.
Example: I said to her, “He will play Chess” can be converted into I told her that he would play Chess.
Stay tuned for more examples of direct and indirect speech.
For an extensive material on tenses, Click here
Follow us on Facebook

Share this:
Subscribe to blog via email.
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.

Direct And Indirect Speech Complete Rules
We often convey a message or give information about what someone said, thought or felt to somebody else. In order to do this you can use the grammar structure named direct or quoted speech, or indirect or reported speech. Indeed this structure can be a source of confusion for ESL learners because they mix it with active and passive voice . Read the whole article to know about direct and indirect speech rules.

To learn more about direct and indirect speech click here.
Initially we will look at direct and indirect speech, then look at how to convert speech from direct to indirect or vice-versa.
Direct Speech / Quoted Speech Saying or quoting exactly what someone has said is called direct speech (sometimes called quoted speech) Here what a person says appears within quotation marks (“…”) a nd should be word for word.
- She said, “Today’s lesson is about direct and indirect speech.” or
- “Today’s lesson is about direct and indirect speech.”, she said.
Indirect Speech / Reported Speech Saying or reporting what someone said without quoting his exact words is called indirect speech. Here we don’t use quotation marks to enclose what the person said and does not have to be word for word.
- He said that yesterday’s lesson was about direct and indirect speech.
Reporting Verb The verb in the first part of sentence (i.e. say, said, tell, admit, complain, explain remind, reply think, hope, offer, refuse etc.) before the statement of a person in sentence is called reporting verb.
How to Change Direct Speech into Indirect Speech?
Rule 1. (Adverbs of Time and Place)
If the reported sentence contains an expression of time, you must change it to fit in with the time of reporting, and adverb of nearness should be put into those of distance.
- Today => y esterday/ that day
- This evening => t hat evening
- These (days) => those (days)
- Now => then
- (A week) ago => (a week) before
- Last weekend => the previous weekend
- Here => there
- Here after => there after
- Next (week) => the following (week)/ a week after
- Tomorrow => the next/following day
- Thus => so
- Last night => the previous night
- Yesterday => the day before / the previous day
- Hither => thither
- Hence => thence
Note: If something is said and reported at the same time, then the time expression can remain the same.
- He told me today, “ I will go to Karachi tomorrow.”
- He told me today he would go to Karachi tomorrow.
- She told me this week, “ we gave our exam last week.”
- She told me this week, they had given their exam last wee.
Rule 2. Tenses
A) If the reporting verb is in present or future (i.e say, says or will say) then don’t change the tense that you can find within the quotation marks.
- He says,”I was a fool then.”
- He says that he was a fool then.
- I will say, “ He loves his mom.”
- I will say that he loves his mom.
B) If reporting verb is in the past tense. the tense of the verbs in the reported speech or indirect speech must be generally changed. This is because when we use reported speech, we are usually talking about a time in the past (because obviously the person who spoke originally spoke in the past). The verbs therefore usually have to be in the past too.
- He said,”I am going to the cinema.”
- He said he was going to the cinema.
Tense Change As a rule when you report something someone has said you go back a tense. Present Simple › Past simple
- She said, ”it is cold,”
- She said it was cold.
Present continuous › Past continuous
- She said, “I’m teaching Math online.”
- She said she was teaching Math online.
Present perfect › Past perfect
- She said, “I’ve lived in Pakistan since 1999.”
- She said she had lived in Pakistan since 1999.
Present perfect continuous › Past perfect continuous
- She said, “I’ve been teaching English for seven years.”
- She said she had been teaching English for seven years.
Past simple › Past perfect
- She said, “I taught active and passive yesterday.”
- She said she had taught active and passive yesterday.
Past continuous › Past perfect continuous
- She said, “I was teaching the lesson.”
- She said she had been teaching the lesson.
Past perfect › Past perfect
- She said, “The lesson had already started when he arrived.”
- NO CHANGE – She said the lesson had already started when he arrived.
Past perfect continuous › Past perfect continuous
- She said, “I’d already been teaching for five minutes.”
- NO CHANGE – She said she’d already been teaching for five minutes.
Modal verb forms also sometimes change: Will › would
- She said, “I’ll teach English online tomorrow.”
- She said she would teach English online tomorrow.
Can › could
- She said, “I can teach English online.”
- She said she could teach English online.
Must › had to
- She said, “I must have a computer to teach English online.”
- She said she had to have a computer to teach English online.
Shall › › should/ would
- She said, “What shall we learn today?”
- She asked what we should learn today.
- He said, ”I shall appreciate it.”
- He said he would appreciate it.
May › might
- She said, “May I open a new browser?”
- She asked if she might open a new browser.
Note – There is no change to; could, would, should, might and ought to.
- “I might go to the cinema”, he said.
- He said he might go to the cinema.
Rule 3. (After wish, would rather, had better , it is time)
- Ali said, ”I wish they were in Pakistan.”
- Ali said he wished they were in Pakistan.
- Hussain said, “ I would rather fly.”
- Hussain said he would rather fly.
- Zahra said, ” they had better go.”
- Zahra said they had better go.
- Ahmed said, “It is time I got up.”
- Ahmed said it was time he got up.
If indirect speech the words within quotation marks talk of a universal truth or habitual action or when a sentence is made and reported at the same time and the fact is still true then the tense inside the quotation marks is not changed at all.
- He said,”My name is Ali.”
- He said his name was Ali Or He said his name is Ali.
- The teacher said,” the sun rises in the east.”
- The teacher said that the sun rises in the east.
- Shazia said, “ I am thirsty.”
- Shazia said she is thirsty.
You can also use the present tense if you are talking about a future event.
- She said,”next week’s lesson is on reported speech.”
- She said next week’s lesson will be on reported speech.
Rule 6. (Pronouns)
We have to change the pronouns to keep the same meaning of a sentence.
- Ali said, “ We are the best players.”
- Ali said they were the best players.
Note: Sometimes we have to use a noun instead of a pronoun, otherwise the new sentence is confusing consider the examples below:
- Mohammad said, “He killed them.”
- Mohammad said that the man had killed them.
(If we only make mechanical changes, then the new sentence can have different meaning)
- Mohammad said he had killed them. (Mohammad himself killed them)
Rule 7. Reported Speech In If-Clauses.
- Hussain: “If I tidied my room, my dad would be happy.”
- Hussain said that if he tidied his room, his dad would be happy.
- Teacher: “If you concentrate, you will learn about direct and indirect speech.”
- Teacher said if we concentrate we would learn about direct and indirect speech.
Rule 8. Reported Speech of Time-Clauses.
- Ali: “When I was staying in Quetta I met my best friend.” –
- He said that when he was staying in Quetta he met his best friend.
Rule 9. Reported Speech of Interrogative Sentences 1. Remove the quotation marks and question mark in the interrogative sentence. 2. Use ‘if’ or ‘whether’ if the sentence inside the quotation marks begins with a helping verb (Auxiliary verb). 3. Use the given interrogative word (what, when, where, why, who, whom, whose, which, now etc.) if it does not begin with the helping verb. 4. Don‘t use ‘that’ 5. Changing the reporting verb (say, said) into ‘ask, want to know wonder or inquire’ in its correct tense. 6. Omit helping verb like ‘do, does, did’. But don’t omit them when they are with ‘not’.
- Said I to my teacher,” won’t you help me to learn about direct and indirect speech complete rules?”
- I asked my teacher if he would not help me to learn about direct and indirect speech complete rules.
- “ How often do you go to the cinema?” Ali said to Ahmed,
- Ali asked Ahmed how often he went to the cinema.
- “Where have you been?” he said.
- He asked me where I had been.
- “What time did it start?” he said.
- He wanted to know what time it had started.
- “Why won’t he do it?” she said.
- She wondered why he wouldn’t do it.
Rule 10. Reported Speech of Yes/ No Questions
In yes/no questions we use if or whether in questions. If is more common and whether is more formal.
- “Will you go?” she asked me.
- She asked me if/whether I would go.
- “Did he buy a car?” she said.
- She wondered if/whether he had bought a car.
Rule 11. Reported Speech of Commands and Requests
1. Remove the quotation mark in an Imperative sentence. 2. Use ‘to’ if it is an affirmative sentence. (without don‘t) 3. Use ‘not to’ if the sentence begins without Don‘t. 4. Don‘t use ‘that’ 5. Omit the word ‘please’. Use the word ‘request’ instead of ‘say’. 6. If the direct speech contains a request or a command, the reporting verb (say, said) change to tell, request, order, command etc. in its correct tense. 7. The commands, requests and advice mostly have the same form in English: verb + object + infinitive (advise, ask, beg, forbid, order, persuade, recommend, tell, urge, warn etc.).
- “Get up!” he said.
- He warned me to get up.
- “Please, revise for the test,” he said.
- He requested me to revise for the test.
- “Bring me a cup of tea” said Zahra to Sara.
- Zahrs asked Sara to bring her a cup of tea.
Negative: + object + not + infinitive.
- “Don’t hesitate,” he said.
- He persuaded me not to hesitate.
- “Don’t smoke,” the doctor warned my father.
- The doctor warned my father not to smoke.
Rule 12. Reported Speech of Advice If it contains advice the reporting verb changes into advised.
- “Put on your coat,” I said.
- I advised him to put on his coat.
Rule 13. Reported Speech of Exclamatory Sentences
1. Change the exclamatory sentence into statement or assertive 2. Remove the quotation marks and exclamatory mark. 3. Use the conjunction ‘that’ 4. Omit the interjections such as Oh, O, Alas, how, what, hurrah. 5. Add the word ‘very’ to the adjective or adverb if necessary. 6. If the verb is not given, use ‘Be’ form verb (is, was, are, were, am) in its correct tense according to the subject. 7. Change the reporting verb (say, said) to ‘exclaim joyfully’ 8. Use ‘exclaim’ sorrowfully for sorrowful incidents.
- She said ,” Wow, What a beautiful car that is!”
- She exclaimed joyfully that was a verb beautiful car.
- He said,” Alas! I have missed the paper.”
- He exclaimed sorrowfully that he had missed the paper.
Rule 14. Use of ‘That’ in Reported Speech
In reported speech, the word that is often used, however it is optional. We recommend you no to use it because in some cases we don’t use ‘That’ in reported speech like: question, command request and order, so its better not to use it.
- He told me that he lived in Hazara Town.
- He told me he lived in Hazara Town.
Rule 15. Punctuation in Direct Speech
In direct speech, various punctuation conventions are used to separate the quoted words from the rest of the text: this allows a reader to follow what’s going on. Here are the basic rules: A) We use inverted commas (also called quotation marks, quotes or speech marks) to indicate direct speech. Double quotes (“) are preferred in American English, while single quotes (‘) are more common in British English:
- “I’m coming home late tonight,” she said. (American English)
- ‘I’m coming home late tonight,’ she said. (British English)
B) Every time a new speakers says something, you should start a new paragraph:
- “They think it’s a more respectable job,” said Ali.
- “I don’t agree,” I replied.
C) There should be a comma, full stop, question mark, or exclamation mark at the end of a piece of speech. This is placed inside the closing inverted comma or commas.
- He asked, “ Can I go outside?”
- She shouted, “ Sit down!”
- We said, “ They are wrong.”
D) If the direct speech is broken up by information about who is speaking, you need a comma (or a question mark or exclamation mark) to end the first piece of speech and a full stop or another comma before the second piece (before the inverted comma or commas):
- “You’re right,” he said. “It feels strange.”
- “Thinking back,” she said, “he didn’t expect to win.”
- “No!” he cried. “You can’t leave now!”
Conclusion: I hope that the points that I have mentioned above about direct and indirect speech may prove beneficial for people learning English. All you need to do is to understand the crucial rules of direct and indirect speech, and don’t mix it with passive and active voice.
Check out Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises With Answers
If you would like to know more about direct or quoted speech, or indirect or reported speech, check out more in the book below.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
Related posts
Reduction of an adjective clause to an adjective phrase, indirect speech of imperative sentences, 12 kinds of verbs in english, 20 comments.
hello! I’m Abdullah and I want to ask a question related to indirect and direct speech.what would be the indirect sentence of this this speech: “I fell fed up” says trevor
Hello dear Abdullah. When the reporting verb (He says)is in simple present tense, then we don’t go one tense back,so the statement won’t be changed in this case and remains the same in reported speech.
Helo ,,pls let me know about one thing…if there is no object in reporting speech and “you” is used in reporting speech ,,in which pronoun v have to change “you”,,???
Tashakkur, bisyar malumati bud 🙂
You are welcome dear Raza.
This article is beneficial…thnkxx
You are welcome.
Very helpful thank you soooo muchhhh
I want a clarification for the following sentence. “Would you post this letter when you go out?”she said. She asked if I would post that letter when I go out . OR She asked if I would post that letter when I went out.
Change the narration. 1.’I must leave at once’ I said,’because i must not be late’ 2 .Tariq said the police could not prove that the man had been murdered .
very helpful understanding direct and indirect speech thank you very soooooo muuuuccccchhhh
You are welcome Mr. Moueez
Thank you . It’s really helpful
Welcome dear.
Useful article thank you.
Hope it is useful and informative.
Tomorrow is my English exam and this page is very helpful
Thank you Rahema. We always try to help people enhance their skills in four models: Listening, Speaking, Reading and writing.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- _Grammar Rules
- __Parts of Speech
- _Vocabulary
- __One Word Substitution
- __Etymology
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for all Tenses (with Examples) | Narration Change Rules for All Tenses

- Practical Tips
- Spoken English

Direct To Indirect Speech: Complete Rules With Examples

Direct and indirect speech is often a confusing topic for English learners. The basic idea is this:
- In direct speech, we quote a person’s exact words. For example, Meera said, “I can speak English fluently.”
- In indirect speech, we do not quote the person’s exact words but provide a summary of what was said. For example, Meera said that she could speak English fluently.
The critical difference is that direct speech uses the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech summarizes what was said. While the definition is simple, the challenge for English language learners is using the proper tenses when converting a phrase from direct to indirect and vice versa.
Why Should You Learn Direct To Indirect Speech Rules?
There are several occasions – in your professional and personal – where you might need to describe an action or event to others. For example, you might have to repeat the team leader’s instructions to your teammates at the workplace. In this scenario, you convert your team leader’s direct to indirect speech.
Knowing conversion rules can help you present or describe the event correctly without making any grammatical errors or spoken English blunders.
In this post, we walk you through the rules of converting direct to indirect speech, helping you speak English fluently online and offline.
How To Use Direct Speech?
The rule is simple: Use direct speech when you want to repeat what someone says as it is, and ensure that the spoken text is sandwiched between quotation (speech) marks.
John said, “I want to learn to speak English fluently.”
It’s common to see the direct speech in newspaper articles and books. For example,
The District Collector announced, “The Chief Minister will inaugurate the city centre next week.”
As you can notice, in direct speech, we use the verb say (said in the past tense) to denote what was spoken. You can also use related verbs like ‘asked,’ ‘replied,’ ‘told,’ ‘informed,’ ‘shouted,’ etc.
How To Use Indirect Speech?
Indirect speech is also reported speech, as we use it to inform/repeat what someone else said. Using the two examples above, we can convert it into indirect speech as follows:
John said that he wanted to learn to speak English fluently.
The District Collector announced that the Chief Minister would inaugurate the city centre the week after.
Another example,
Direct Speech: “I feel cold.”
Indirect Speech: She says that she feels cold.
If you notice these examples carefully, you can see that the tense changes when converting from direct to indirect speech. To illustrate this point, in the following example, direct speech is in the present simple tense, while indirect speech is written in the simple past tense.
Direct Speech: “I live in the city centre.”
Indirect Speech: He said he lived in the city centre.
Tense Change Rules: Direct To Indirect Speech
Similarly, other tenses follow similar rules when changing from direct to indirect speech. Use the following table to help you better understand the tense change rules:
Modal Verbs: Direct To Indirect Speech
When converting direct to indirect speech, you must change modal verbs accordingly. Here are a few examples to help you understand better:
Changing Time Expressions: Direct To Indirect Speech
Sometimes it becomes necessary to change the time expressions when converting from direct to indirect speech. A few examples,
- Direct speech: Sheila said, “I am meeting my brother tomorrow.”
- Indirect speech: Sheila said that she was meeting her brother the following day.
Here are a few examples of other typical time expressions and how they change:
Changing Place Expressions: Direct To Indirect Speech
Like time expressions, you might also have to change words representing places when reporting indirect speech. For example,
- Direct speech: “It’s raining here.”
- Indirect speech: She said that it was raining there.
Here are a few examples of other common place expressions and how they change:
However, the place words only change when you report something from a different location.
Over To You
Now that you’ve seen the rules to convert direct to indirect speech, it’s time to put them into practice. The most efficient way to improve English speaking is to practice what you’ve learned. Join online English-speaking practice classes to gain confidence and mastery in your daily conversations.
Recent Posts
Como usar uma calculadora martingale para melhorar suas estratégias de opções binárias, 35 positive words to describe your best female friend, 20 stylish and popular idioms related to success, how can you teach your child to speak english at home, 40 different ways to say happy birthday.
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- August 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
Related Posts

Broadening Your Vocabulary: Unlocking 40 Altern...

Using Instagram To Learn English: Top 10 Accoun...

50 Commonly Used English Abbreviations For Text...

Never Miss a Blog
Enter your Email ID below to get our insightful blogs into your inbox.

Onlymyenglish.com
Learn English
Direct and Indirect Speech
Table of Contents
What is Speech (Narration):
If we want to describe the speech of some other people with other people in our own words, that speech is called a Reported speech or Narration.
Types of Speech
In the English language, there are certain ways to express the spoken words between two people.
The speech has two main types, Direct speech , and Indirect speech , respectively.
These two ways of narration of spoken words are also called Direct and Indirect speech, also known as Direct and Indirect narrations.
Direct and indirect speech is majorly used in any conversations, scripts, or any biographies, etc. where one or more than one person converses with each other.
Direct speech:
It is also called straight speech or quoted speech, which is spoken or written directly in the text by the speaker, writer, or the first person, who is going to speak with anyone with him.
The spoken statements of the speaker normally come under the inverted commas notation, and a speaker who speaks these sentences may come like “he said/he said that.”
The speaker’s words or statements are mentioned in a single phrase pattern or direct discussion.
Indirect speech:
An Indirect speech is also called a reported speech, or secondary speech means the speech, which has spoken indirectly.
It is simply an overlook statement that is used to say about the incident that has happened in the past time.
The actual words of the speaker changed into the past tense and the sentence, and hence the reported speech of the direct speech does not come inside the inverted commas.
Reporting speech:
A person who is going to report the speech or a speech that comes in the first part of the direct speech is called a reporting speech.
- He says , “He cooks food”.
Reported speech:
Reported speech is a speech that is always in an inverted comma or quotation marks.
It is a second part of the direct speech sentence.
- He says, “He cooks food.”
Reporting verb:
The verb, which is used in a reporting speech to report something in a direct speech, is called a reporting verb.
- Zoya said , “I want to go there.”
Reported verb:
The verb which comes inside the reported speech is called reported verb, respectively.
- Zoya said, “I want to go there.”
As we start writing any direct and indirect conversation, we often use reported verbs like “say, tell, ask, inform, instruct, claim, suggest, enquire, etc.”
These reported verbs, whenever used in direct or indirect speech, change into the past simple form like said, told, asked, informed, instructed, claimed, suggested, enquired, etc.
But the verbs used in a speech between the inverted commas will remain as it is.
Examples of direct and indirect speech:
- Indirect speech: John said that she was looking so beautiful.
- Indirect : He said that he was not a culprit.
- Indirect : He said that she was working on that project.
- Indirect : The teacher asked if he completed his homework.
- Indirect : She says that she is an artist.
- Indirect : Sam told me that he was not coming with me.
- Indirect : He says that she is working on that project.

Some basic rules for converting direct speech into indirect speech:
Rule 1 : “no inverted commas.”.
The reported speech does not come into inverted commas or quotation in an indirect speech.
Example: Direct: He said, “I have completed my assignments yesterday.”
Indirect: He said that he had completed his assignments the previous day.
Rule 2: use of “that” conjunction
Using the conjunction word “that” in-between the reporting speech and reported speech in an indirect speech.
Example:
- He said, “I have completed my assignment yesterday.”
- He said that he had completed his assignment the previous day.
Rule 3: Change of tense
While writing a direct speech into an indirect speech, we have to change the tense of the reported speech because whatever we are writing in indirect speech has already happened in the past timing.
- If the tense of a reporting speech of direct speech is in the present tense or future tense , then the tense of the reported speech in indirect speech will not change. It may be in the present tense, past tense, or future tense, respectively.
- Indirect : He says that he is going to school. (no change in tense)
- Indirect : She says that she will not come with me. (no change in tense)
- Indirect : He says that he wrote a letter. (no change in tense)
If the tense of the reporting verb of direct speech is in the past tense, then the tense will change according to these criteria.
For the present tense:
Simple present tense will change into simple past tense..
Direct: He said, “They come to meet me.”
Indirect: He said that they came to meet him.
Present continuous tense will change into past continuous tense.
Direct: She said, “They are coming to meet me.”
Indirect: She said that they were coming to meet her.
Present perfect tense will change into past perfect tense.
Direct: He said, “They have come to meet me.”
Indirect: He said that they had come to meet him.
Present perfect continuous tense will change into past perfect continuous tense.
Direct: She said, “They have been coming to meet me.”
Indirect: She said that they had been coming to meet her.
For the past tense:
Simple past tense will change into the past perfect tense.
Direct: He said, “They came to meet me.”
Indirect: He said that they had come to meet him.
Past continuous tense will change into past perfect continuous tense.
Direct: She said, “They were coming to meet me.”
Indirect: She said that they had been coming to meet her.
Past perfect tense and past perfect continuous tense will remain the same.
Direct: He said, “They had come to meet me.”
Direct: She said, “They had been coming to meet me.”
For the future tense:
There are no changes in the future tense sentences; only shall/will may change into would, can change into could.
- Direct: She said, “Can you come tomorrow.”
Indirect: She said that could he come on the next day
- Direct: He said, “I will never forgive you.”
Indirect: He said that he would never forgive me.
Rule 4: Changing the pronoun
The pronoun used as an indirect subject speech sometimes needs to be changed accordingly in indirect speech as of the reported verb of the direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the first person in reported speech changes based on the subject of the reporting speech in a direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the second person in reported speech changes based on the report’s object in a direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the third person remains the same in the reported speech.
- Direct: He said, “ I am going to school.”
- Indirect: He said that he is going to school.
- Direct: She says, “ I will not come with you .”
- Indirect: She says that she will not come with me .
- Direct: They said, “ we are eating our tiffin box.”
- Indirect: They said that they were eating their tiffin box.
Rule 5: Changing the time
The mentioned time (not the timing) in a direct speech sentence will have to change in indirect speech like now becomes then, tomorrow becomes the next day, yesterday becomes the previous day, today becomes that day, later becomes soon.
- Direct: He told, “He is coming from Tokyo today .”
- Indirect: He told me that he was coming from Tokyo that day .
- Direct: She asked, “Will the parcel reach by tomorrow or not?”
- Indirect: She asked whether the parcel will reach by the next day or not.
- Direct: “The teacher has given some assignments yesterday ”, he reminds me.
- Indirect: He reminds me that the teacher had given some assignments on the previous day.
Conversion of statements from direct speech into Indirect speech:
Assertive sentences:.
Assertive sentences are simple statements that may be affirmative or negative.
If we are going to convert assertive sentences from direct speech into indirect speech, we have to replace “said” with “told” sometimes.
Here, the subject in direct speech refers to someone in his talk.
- Direct: He said to me, “she is working on this project.”
Indirect: He told me that she was working on that project.
- Direct: She said to me, “I’m going for a long drive.”
Indirect: She told me that she was going for a long drive.
Imperative sentences:
Imperative sentences are statements that deliver a command, order, request, appeal, or advice.
It depends on the speaker, how he delivers the message to the other person.
- Sit properly!
- Stand by my side!
- Come closer!
While converting these types of sentences cum statements from direct speech to indirect speech, we have to check the type of sentence, whether it is a command, order, request, or else.
- Direct: The teacher said to me, “Sit properly!”
Indirect: The teacher ordered me to sit properly.
- Direct: The Boss said to an office boy, “Bring one coffee for me.”
Indirect: The Boss commanded an office boy to bring a coffee for him.
Indirect: The teacher requested me to sit properly.
- Direct: The bartender said to me, “try this drink.”
Indirect: The bartender advised me to try that drink.
Interrogative sentences:
An interrogative sentence is a sentence which interrogates or ask questions.
Each interrogative sentence ends with an interrogative sign or a question mark sign “?”.
- What is your name?
- Can you do me a favor?
- Why are you laughing in the classroom?
While writing interrogative sentences from direct speech into indirect speech,
- the reporting verb “said” in the direct speech is changed into “asked” in the indirect speech because it asks the question to another person.
- If any reporting verb comes first in the reporting speech, then “If” is used despite “that.”
- In a reporting speech, if any wh-type question words are present, then no other words will be used, and the sentence ends with a full stop sign instead of a question mark.
- Indirect: He asked me what was my name.
- Indirect: She asked if he could do her a favor.
- Indirect: The teacher asked him why he was laughing in the classroom.
Exclamatory sentences:
Exclamatory sentences are those sentences that show emotions, feelings and ends with an exclamation mark!
- Congratulations! You have a baby girl.
- I am extremely sorry for your loss!
- Most welcome!
If any interjection comes in an exclamation sentence, then the exclamation sign removes in an indirect speech, and an exclamatory sentence gets converted into an assertive sentence.
The replacement of reporting verb “said” with exclaimed with (great wonder, sorrow, joy) exclaimed (joyfully, sorrowfully)
Replace with very or very great , if words like how or what comes at the beginning of the reported speech.
- Indirect: He exclaimed with joy that I had a baby girl.
- Indirect: She exclaimed with sorrow that she felt sorry for my loss.
- Indirect: They exclaimed with joy that most welcome.
You might also like

Question Tag
Informal letter format in english, articles in english grammar, subordinate clause types and examples.

12th English Grammar | Class 12 English Grammar

Present Perfect Continuous Tense: Definition, Examples, Formula, Structure & Rules
- --> Try Free Downloads
- Computer Science & Applications
- General Paper 1
- Human Resource Management
- Library And Information Science
- Political Science
- Biotechnology (BT)
- Biological Sciences (BL)
- Mathematical Statistics (MS)
- Mathematics (MA)
- Physics (PH)
- Geology (GG)
- Chemistry (CY)
- Economics (EN)
- Chemical Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Life Sciences
- Mathematical Sciences
- Physical Sciences
- General Aptitude
- JEE Advanced
- Computer Science And IT
- Electronics And Communication
- RRB Group D
- SSC GD Constable
- Choose Exam Goal
- About Eduncle
- Announcements
Speak With a Friendly Mentor.
- My Wishlist
- Subscribe Exams
- Try Free Downloads

Government Jobs
- Articles (53)
- Products (0)
- Reviews

Eduncle posted an Article
Direct and indirect speech rules with examples for competitive exams.
- Share(4525)
- 23 Comments

Competition is getting harder day by day in every competitive exam like SSC , IBPS and other Government Exams .One should be having command on all sections to score more and ace the exam. There are certain topics which are common in almost every competitive exam.
Here, we have tried to cover Direct and Indirect Speech through this blog. We are providing rules, example and exercise to help you with this topic.
Reported Speech is also known as Direct and Indirect Speech or Narration. In Indirect Speech, we convey the speaker’s message in our own words. Thus, the message can be conveyed in 2 ways.
- Direct Speech
- Indirect Speech
Direct speech is known as repeating the exact words spoken and Indirect speech is known as reporting the words.
But the question occurs how to report or how to use Indirect speech? There are certain rules to make changes in a sentence from Direct to Indirect speech. Read the complete blog to know more.
- Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
Below, we are sharing the rules to make changes from Direct to Indirect speech. The changes of Direct and Indirect speech depend on some factors like modals, reporting verb, place, time, tense, pronoun etc. You can check the complete information of changes in Direct and Indirect speech.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Modals:
Look to the Direct and Indirect Speech examples with answers using modals.
- He said, “I can cook food.”
He said that he could cook food.
- They said, “We may go to Canada.”
They said that they might go to Canada.
- She said, “I must finish the work on time.”
She said that she had to finish the work on time.
Modals that remain unchanged are: Should, might, could, would, ought to.
- Kanika said, “I ought to avoid junk food.”
Kanika said that she ought to avoid junk food.
Changes as per Reporting Verb
According to the reporting verb, changes are made in the direct sentence or the sentence in inverted commas.
If the reporting verb is in the past tense, then the direct sentence is changed in its past tense. The tense of direct speech remains unchanged when the reporting verb is in the present or future tense. If the direct sentence contains the universal truth, then it remains unchanged in the Indirect Speech.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Reporting Verb
Below, we are providing Direct and Indirect Speech examples using reporting verb changes .
- Navin said, “He is young.”
Navin said that he was young.
- Isha says, “I am pretty.”
Isha says that she is pretty.
- Rohan will say, “I am tall.”
Rohan will say that he is tall.
- They said, “The sun rises in the east.”
They said that the sun rises in the east.
Changes as per Tense
In the below table, we are sharing how tense changes into Indirect speech.
Direct and Indirect speech exercises for Tense
Check the Direct and Indirect speech examples for tense using the above table. Changes will always be made according to the given table only.
- Heena said, “I walk.”
Heena said that she walked.
- Deepak said, “I am having tea.”
Deepak said that he was having tea.
- Ayesha said, “Honey has left for school.”
Ayesha said that Honey had left for school.
- Vidisha said, “Ananya took pasta.”
Vidisha said that Ananya had taken pasta.
- They told, “We were living in Paris.”
They told that they had been living in Paris.
- Ramesh said, “I will go to Sri Lanka.”
Ramesh said that he would go to Sri Lanka.
- Aishwarya Said, “They will be watering plants.”
Aishwarya said that they would be watering plants.
Changes in Place and Time
Words are changed in an Indirect Speech to replace nearness from distance. In the table, we are sharing some words which are changed in Indirect speech.
Changes of Interrogative Sentences
Here, we are sharing certain rules of Direct and Indirect speech for interrogative sentences conversions.
The reporting verb said/said to is changed in asked, demanded, ordered, enquired as per the nature of the sentence. While a sentence starts with reporting verb then at the conversion time if /whether is used as the joining clause. In case the sentence starts from “Wh” question word, then no extra conjunction is used.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Interrogative Sentences
We are applying the above rules in the given exercise below to make changes in Direct and Indirect speech.
- Ravi said, “What is Heena doing?”
Ravi asked me what Heena was doing.
- Esha said, “Will she come for lunch?”
Esha asked if she would come for lunch.
- The boy asked, “Where do you stay?”
The boy inquired where I stayed
Changes of Pronouns
While making the changes from Direct and Indirect speech, one should be having knowledge of rules of changes in pronouns.
The first person in reported speech changes according to the subject of reporting speech. In Reported Speech change of the second person depends on the object of reporting speech. The third person remains unchanged.
You can check the table for the changes in pronoun.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Changes in Pronoun
- Vidya said, “I am a good girl.”
Vidya said that she was a good girl.
- I told them, “You have finished your work.”
I told them that they had finished their work.
- He said, “She is in Delhi.”
He said that she was in Delhi.
So, aspirants in order not to leave any questions from this topic, you must go through all the information, rules and exercise given in this blog.
If you find the article useful, must share it with your friends who are preparing for competitive exams.
We try to provide you with the best information. So, stay connected for more updates regarding competitive exam preparations. Keep learning folks.
- Direct and Indirect Speech
- Reported Speech
- Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise
- Direct and Indirect Speech Examples
- Direct and Indirect Speech for Competitive Exams
You Might Also Like

Charankalisetti
- Likes ( 0 )

Hello Charankalisetti, Greetings from Eduncle! Thanks for the kind words and appreciation! We value your generous feedback. For more such updates, Kindly stay tuned with Eduncle.
Sagar batra
Thanks eduncle for solving these query thanks ♥️♥️♥️
Hello Sonia, Greetings from Eduncle! Thanks for the kind words and appreciation! We value your generous feedback. For more such updates, Kindly stay tuned with Eduncle.
Nandita singh
It's very useful....thank u for this information ??❤️
Hello Nandita, Greetings from Eduncle! Thanks for the kind words and appreciation! We value your generous feedback. For more such updates, Kindly stay tuned with Eduncle.
Very very very very helpful site, Actually, I need something like it to revise my grammar and thanks a lot.Good job?, keep it up ??
Sameer ansari
It's very helpful for us and our final exam is also coming.
Perumandla anusha
Really very useful .... liked it a lot by this we can improve our knowledge too. could u please post punctuations?
- Likes ( 1 )
Hello Perumandla, Greetings from Eduncle! Thanks for the kind words and appreciation! We value your generous feedback. For more such updates, Kindly stay tuned with Eduncle.
It's very useful
Hello Charan, Greetings from Eduncle! Thanks for the kind words and appreciation! We value your generous feedback. For more such updates, Kindly stay tuned with Eduncle.
Thank you, nice information
Hello Tanmayi, Greetings from Eduncle! Thanks for the kind words and appreciation! We value your generous feedback. For more such updates, Kindly stay tuned with Eduncle.
Apurwa singh
Hello Apurwa Greetings from Eduncle! Thanks for the kind words and appreciation! We value your generous feedback. For more such updates, Kindly stay tuned with Eduncle.
Gershan pradhan
It helps everyone ???
Hello Gershan, Greetings from Eduncle! Thanks for the kind words and appreciation! We value your generous feedback. For more such updates, Kindly stay tuned with Eduncle.

Do You Want Better RANK in Your Exam?
Start Your Preparations with Eduncle’s FREE Study Material
- Updated Syllabus, Paper Pattern & Full Exam Details
- Sample Theory of Most Important Topic
- Model Test Paper with Detailed Solutions
- Last 5 Years Question Papers & Answers
Sign Up to Download FREE Study Material Worth Rs. 500/-
I agree to the Terms and Conditions
I agree to receive exam notifications via WhatsApp.
Wait Wait Wait... !
We Have Something Special for YOU
Download FREE Study Material Designed by Subject Experts & Qualifiers
Want Enhanced Learning Experience For Exam Preparation?
- Ask Your Doubts and Get Them Answered by Exam Experts & Students' Community Members Across India
- Regular Guidance, Mentorship & Study Tips by Eduncle Experts
- Quality Content with More Than 300 Courses in Multiple Exams Curated by Experts
Enter your mobile number to get the download link.

Learning & Teaching App
Skyrocket Your Chances to RANK HIGHER in the Exam
Time management is very much important in IIT JAM. The eduncle test series for IIT JAM Mathematical Statistics helped me a lot in this portion. I am very thankful to the test series I bought from eduncle.
Eduncle served as my guiding light. It has a responsive doubt solving team which solves & provides good solutions for your queries within 24 hours. Eduncle Mentorship Services guides you step by step regarding your syllabus, books to be used to study a subject, weightage, important stuff, etc.
The General Aptitude part of Eduncle study materials were very good and helpful. Chapters of the Earth Science were also very satisfactory.
The study material of Eduncle helps me a lot. The unit wise questions and test series were helpful. It helped me to clear my doubts. When I could not understand a topic, the faculty support too was good. Thanks Eduncle.
I recommend Eduncle study material & services are best to crack UGC-NET exam because the material is developed by subject experts. Eduncle material consists a good no. of ques with online test series & mock test papers.
I am truly Statisfied with study material of Eduncle.com for English their practise test paper was really awsome because it helped me to crack GSET before NET. Thanks Team of eduncle.
Request a Call back
Let Our Mentors Help You With the Best Guidance

We have Received Your Query
Are you sure you want to Unfollow ?

How can we assist you?

Oops! You Can’t Unfollow Your Default Category.

Your profile has been successfully submitted
Kindly give us 1 - 3 week to review your profile. In case of any query, write to us at [email protected]
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for All Tenses
Change in tense in indirect speech.
Change in tense in indirect speech! The tense of the reported speech changed at the time when we are reporting what someone said or thought in the past. This change in tense of the reported speech because of the reporting verb that we usually put in the past tense (They asked, he said, he told me, they enquired, etc.), so the speech being reported must be changed as well. We use an appropriate tense that may be different from the one used in the original statement. The change in tense in the reported speech is called back shifting. For example
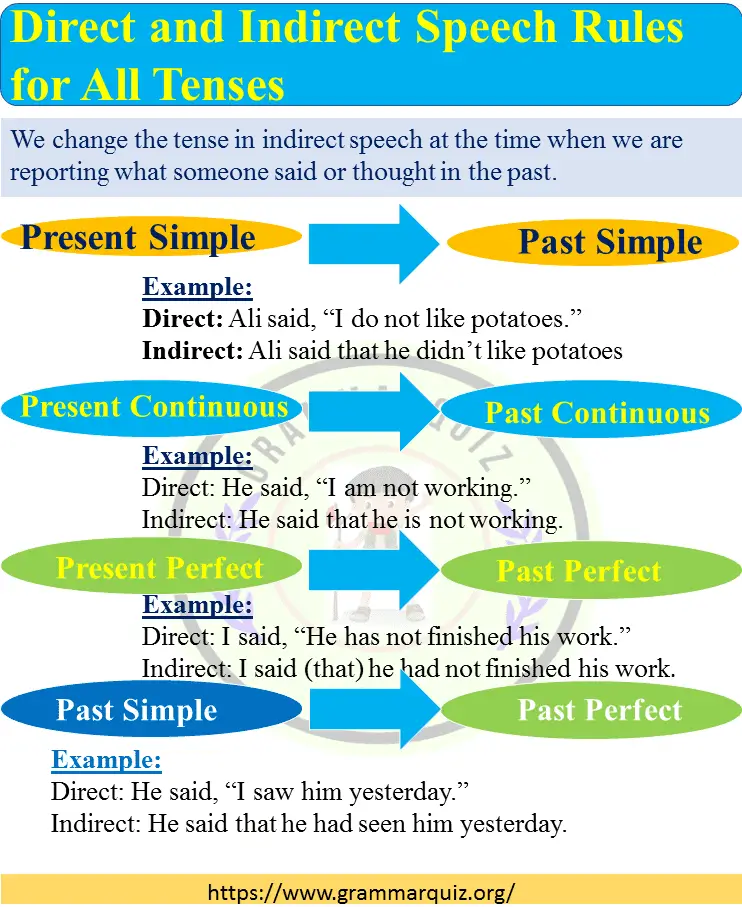
Change in Tense In Indirect Speech (Present Simple Becomes Past Simple)
- Direct: Our teacher said, “India is more extensive than Pakistan.”
- Indirect: Our teacher said that India is more extensive than Pakistan. (This situation is still valid, so we don’t change the tense to the past simple)
- Direct: Asama said to me, “I come to this park daily.”
- Indirect: Asma told me that she came to that park daily.
- Direct: Ali said, “I do not like potatoes.”
- Indirect: Ali said that he didn’t like potatoes
- Direct: My friend said , “ I don’t like my new house.”
- Indirect: My friend said that he didn’t like his new house.
- Direct: His sister says, “I don’t waste my time.”
- Indirect: His sister says that she doesn’t waste her time.
Change in Tense In Indirect Speech ( Present Continuous Becomes Past Continuous)
- Direct: Ahmad said, “I am watching TV now.”
- Indirect: Ahmad said that he was watching TV then.
- Direct: He said, “I am not working.”
- Indirect: He said that he is not working.
- Direct: ‘Ahmad and Saleem are looking at you.’
- Indirect: He told me that Ahmad and Saleem were looking at me.
- Direct: Abdul said, “I am bringing the book now.”
- Indirect: Abdul said that he was bringing the book then.
Present Perfect Becomes Past Perfect
- Direct: The children said, “I have seen him here.”
- Indirect: The children said that they had seen him there.
- Direct: I said, “He has not finished his work.”
- Indirect: I said (that) he had not finished his work.
- Direct: The girl said. “The police have caught the thief.”
- Indirect: The girl said that the police had caught the thief.
Present Perfect Continuous Becomes Past Perfect Continuous
- Direct: Usman said, “I have been studying since morning.”
- Indirect: Usman said that he had been studying since morning.
- Direct: The students said, “We have been studying for three hours.”
- Indirect: The students said that they had been studying for three hours.
- Direct: Karim said, “I have been visiting this museum for three years.”
- Indirect: Karim said that he had been visiting that museum for three years.
Past Simple Becomes Past Perfect
Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous, past perfect and past perfect continuous remain unchanged in indirect speech .
- Direct: Kamran said, “I had not seen him yet.”
- Indirect: Kamran said that I had not seen him yet.
- Direct: Asma said. “She had cooked the dinner.”
- Indirect: Asma said she had cooked the dinner.
Unreal Past Tenses in Indirect Speech
- Direct: “I wish I didn’t have to take the paper.” said the student
- Indirect: The student said he wished he didn’t have to take the paper.
- Direct: “It’s time you began planning your holidays.” Akram said to me
- Indirect: Akram told me that it was time I began planning my holidays.
Reporting Without Change of Tense
- Direct: She said, “I like eating mangoes.”
- Indirect: She said that she likes eating mangoes.
- Direct: Ann said to him, “Your dress looks beautiful.”
- Indirect: Ann told him that his dress looks beautiful.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
1290+ easy words that end in s (s ending words list), 530 cool words that start with f (easy f words list in english), imperative sentences definition structure and examples, 50 examples of simple sentences in english, 50 examples of interrogative sentences (interrogative examples), watch past tense and past participle: watch verb forms v1 v2 v3, what are declarative sentences definition, structure, and examples, 30 interrogative sentences examples in english.
Active and Passive Voice
- Adverb Clauses
Conditional Sentences
- Direct and Indirect Speech
- Example Sentences
- Irregular Verbs Forms
- Modal Verbs
- Parts-of-Speech
- Phrasal Verbs
- Phrases and Clauses
- Regular Verbs Forms
- Sentence Types & Examples
- Subject-Verb Agreement
Grammar Quiz
This is a free blog designed to help you improve your English grammar. This blog requires no registration to use any of our online activities, exercises, and tests.
Popular Categories
Direct & Indirect Speech
Parts of Speech
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Copyright 2024 © Grammar Quiz | All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Disclaimer | About

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Reported Speech /
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules & Examples [Download Exercise PDF]
- Updated on
- Dec 14, 2023

Owing to the nuances of the systems involved, English may be a very difficult language to master. But once you get hold of the fundamentals, you can be a pro. It’s these rules that will help you create a solid base. And we all know what these fundamentals are and what every language’s base is. It’s grammar , indeed. The rest of the journey becomes much easier once you get a good grip on the grammar. So, today, we’re going to talk about one of those basic rules, an important part of English grammar , i.e., Direct and Indirect Speech rules and examples.
MUST READ! Reported Speech: Definition, Rules, Usage with Examples, Tips, Exercises for Students
What is Direct and Indirect Speech?
First and foremost, you need to note that both Direct and Indirect Speech are an extended body of Reported Speech. To elaborate, you can refer to them as Reported Speech as well. So, let’s see how direct and indirect speech are different from each other in terms of usage from the description below.
Also Check: 50 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises
6 Important Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
Now, comes the most tricky yet crucial stage of mastering this grammatical tool, which is learning in depth about all the Direct and Indirect Speech rules. It will not only aid you in dealing with a Reported speech at the school level but will also ease your preparation routine whenever you choose to take up a competitive exam or an English proficiency test in the future.
1. Rules for Changing Direct Speech to Indirect Speech
The rules for changing a direct speech into indirect is the easiest amongst the other guidelines you would find hereon. After all, you can achieve an Indirect speech sentence only by following these general rules:
- Remove the quotation marks and the “ said ” or “ told ” from the direct speech.
- Change the pronouns and possessive adjectives according to the speaker and the reporting verb.
- Change the tense of the verb according to the time of the reporting verb.
Although, these were the rules you would require to follow almost wherever you use a reported speech. But, there is more to Direct and Indirect speech rules than meets the eye.
Also Read: Best English Grammar Books: To Master Your Proficiency
2. Rules for Changing Reported Speech Interrogative
Just like the above-mentioned, to change the reported speech of questions or interrogative sentences you need to keep these changes in mind:
- Change the yes/no question into a statement with “ if ” or “ whether .”
- Change the wh-question into a statement with a wh-word .
3. Rules of Changes in Tenses
Next comes the task of knowing what would be the impact on tense under the direct and indirect speech rules. So, here you go:
Let’s check the following examples for a better understanding of the changes in tenses under the umbrella of reported speech:
Direct : Reema says, “I am going out.” Indirect : Reema says that she is going out.
Direct : Ramesh said, “Honesty is the best policy.” Indirect : Ramesh said that honesty is the best policy.
Direct : Vishnu said, “India gained independence in 1947.” Indirect : Vishnu said that India gained independence in 1947.
Direct : Akshat will say, “I want a slice of cake.” Indirect : Akshat will say that he wants a slice of cake.
Direct : Reena said, “I am writing a novel.” Indirect : Reena said that she was writing a novel.
Direct : Ayushi said, “I was working on my project.” Indirect : Ayushi said that she had been working on her project.
Also Read: Figures of Speech with Examples, PDF
4. Modals Rules in Reported Speech
Whereas, the rules for changes in Modals of reported speech go in the following manner:
Examples of Changes in Modal:
Direct : “I can speak five languages.”
Indirect : He said that he could speak five languages.
Direct : “I may go to London next week.”
Indirect : She said that she might go to London next week.
5. Changes in Pronouns
So far, you must have observed that multiple changes are going on when you change direct speech to Indirect speech. But did you note the change in subjects, or to be more specific changes of pronouns in the process? If not, then check the following table and learn it to use it effortlessly.
6. Changes in Time and Place
Last but not the final rule under the realm of reported speech, you would be required; to make these changes in time and places while transitioning from direct to indirect speech:
👉 Now : Then
👉 Here : There
👉 Today : That day
👉 Tonight : That Night
👉 Tomorrow : The next day
👉 Yesterday : The last day
👉 Last week : The previous week
👉 This : That
👉 Ago : Before
👉 Thus : So
👉 Hither : Thither
👉 Come : Go
👉 Hence : Thence
👉 Next : Following
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise PDF
You can also explore exciting reads on Tenses here!
This was all about the Direct and Indirect Speech rules and more. Hope you understand the concept and where it’s used. You can also follow Leverage Edu for more exciting and informative blogs.
Harshita is a creative writer cum literature enthusiast in pursuit to extend her learnings of overseas and Indian education sectors to the masses, through her well-curated articles. You may also find her emerging in prose writing or reading Toni Morrison when not writing stuff related to education.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out

Narration Change in Future Tense
Back to: Direct and Indirect Speech (Narration)
Examples of narration change in simple future tense, future continuous, future perfect and future perfect continuous are given below –
Table of Contents
Direct and Indirect Speech Future Simple Tense Examples
If reported verb is in Past Tense, and reported speech is in Future Indefinite Tense, will changes into would & shall changes into should .
Direct and Indirect Speech Future Continuous Tense Examples
If verb is in Past Tense, and reported speech is in Future Continuous Tense, will be changes into would be & shall be changes into should be .
Direct and Indirect Speech Future Perfect Tense Examples
If verb is in Past Tense, and reported speech is in Future Perfect Tense, will have changes into would have & shall have changes into should have .
Direct and Indirect Speech Future Perfect Continuous Tense Examples
If verb is in Past Tense, and reported speech is in Future Perfect Continuous Tense, will have been changes into would have been & shall have been changes into should have been .
- Our Sponsors
Rules for Converting Direct to Indirect Speech
- Direct and Indirect Speech , English Grammar
Introduction: Converting direct speech to indirect speech requires following certain rules to convey the meaning accurately while adjusting pronouns, verbs, tenses, and other elements. In this chapter, we will explore the essential rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech, enabling you to effectively report what someone has said.
The main part of the topic:
- 1.Changes in Pronouns: When converting direct speech to indirect speech, pronouns usually change according to the perspective of the reporting speaker. Here are the general rules:
a) First-person pronouns:
- “I” changes to “he/she” or the person’s name.
- “We” changes to “they.”
b) Second-person pronouns:
- “You” changes to “he/she” or the person’s name.
c) Third-person pronouns:
- No change is required if the reported speech refers to the same person or people.
- If the reported speech refers to a different person or people, pronouns need adjustment.
- 2.Changes in Verbs: Verbs in reported speech often undergo changes in tense, mood, and verb form. Here are the general rules:
a) Tense changes:
- Present simple in direct speech changes to past simple in indirect speech.
- Present continuous changes to past continuous.
- Present perfect changes to past perfect.
b) Modal verbs:
- Modal verbs like “can,” “could,” “may,” “might,” “will,” “would,” “shall,” and “should” can undergo changes according to the context and reported speech.
- 3.Changes in Adverbs of Time and Place: Adverbs of time and place often require adjustment when converting direct speech to indirect speech. Here are the general rules:
a) Adverbs of time:
- Words like “now,” “today,” “tomorrow,” “yesterday,” etc., usually change according to the context and become words like “then,” “that day,” “the following day,” “the previous day,” etc.
b) Adverbs of place:
- Words like “here” and “this” may change to “there” and “that” respectively, depending on the context.
Examples: Direct Speech: “I am going to the park,” she said. Indirect Speech: She said that she was going to the park.
Direct Speech: “Can you help me with my homework?” he asked. Indirect Speech: He asked if he could help with his homework.
Key Takeaways:
- 1.Pronouns in reported speech may change based on the perspective of the reporting speaker.
- 2.Verbs often undergo tense and form changes when converting from direct to indirect speech.
- 3.Adverbs of time and place require adjustments to maintain accuracy in indirect speech.
- 4.Modal verbs may require changes depending on the context and reported speech.
Join the discussion Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Read also...
Coherence: Importance, Techniques &Examples in English Grammar
- 22 min read

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Converting Direct to Indirect Speech. 1. Eliminate the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text. 2. Retain the tense of the reporting verb and add the word "that" after it. 3. Change the tense of the verb in the reported speech, if needed. 4. Change the pronouns accordingly.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech. Change of Pronouns. Change of Tenses. Change of Time and Place References. Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech. Step 1: Remove the Quotation Marks. Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a Linker. Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb. Step 4: Change the Pronouns.
B. Direct and Indirect Speech (Tenses) Rules. The second most important rule is the changes of Tenses for converting direct speech to indirect speech. When transforming direct speech into indirect speech, there are specific rules to follow regarding tense changes: Rule 4: Reporting Verb Present Tense:
Rule 2: Direct Speech to Indirect Speech Conversion - Tenses. If the sentences inside quotes in direct speech are present tense, it is changed to past tense when changed to indirect speech. The rule in the following table is applied while changing tenses from direct speech to reported speech. Direct Speech. Indirect Speech.
Indirect Speech for all Tenses - Rules. The verb in the first part of the sentence (e.g., he said, she said) is called a reporting verb. The second part of the sentence, enclosed in inverted commas or quotation marks, is called a reported speech. For converting direct speech into indirect speech, the tense of the reported speech is changed.
Direct and Indirect speech Examples for Tense. 1. Simple Present to Simple Past. Direct: He said, "The boy goes home.". Indirect: He said that the boy went home. 2. Present Continuous to Past Continuous. Direct: Ram said, "I am reading a book.". Indirect: Ram said that he was reading a book.
3. The tenses of direct speech do not change if the reporting verb is in future tense or present tense. Direct to indirect speech example: Direct: She says/will say, „she is going‟ Indirect: She says/will say she is going. Rule 2 - Direct Speech to Indirect Speech conversion - Present Tense. Present Perfect Changes to Past Perfect.
Direct and indirect speech grammar rules vary so you need to understand them. We'll start by looking at what each one is. Note that indirect speech is also commonly knows as reported speech. ... Reported speech tenses may differ from the tense of the direct speech. The general rule for tenses in reported speech is that it changes to the past tense.
Direct and indirect speech: an overview of the rules. When the reporting verb is in the past tense, all present tenses in the direct speech will change into the corresponding past tenses. For example, the simple present will become simple past. He said, 'I want to go.'. He said that he wanted to go.
The shift to indirect speech leads to changes in the tense, depending on whether the verb is in the present tense or in the past tense. If the introductory verb is in the present tense, the tense (or modal) does not change. "I'm sorry." → He says he is sorry. "I hate driving" → He says he hates driving.
Rule 2: The verb in the simple past tense becomes past perfect tense in indirect speech. Example: He said to me, "I was happy" changes into He told me that he had been happy. Rule 3: A present continuous tense in direct speech becomes past continuous tense in indirect speech. Example: The peon said, "The professor is teaching in that ...
Rule 4. If indirect speech the words within quotation marks talk of a universal truth or habitual action or when a sentence is made and reported at the same time and the fact is still true then the tense inside the quotation marks is not changed at all. He said,"My name is Ali.".
Direct - John says, "I don't smoke." Indirect - John says that he doesn't smoke. Direct - She has said to me, "You help me whenever I am in trouble." Indirect - She has told me I help her whenever she is in trouble. Direct - I say to her, "Do you agree with me?" Indirect - I ask het if/whether she agrees with me. Direct - You say to me, "Don't you read ...
The tenses of direct speech do not change if the reporting verb is in the future tense or present tense. Direct to indirect speech example: Direct: She says/will say, 'I am going' Indirect: She says/will say she is going. Rule 2 - Direct Speech to Indirect Speech conversion - Present Tense Present Perfect Changes to Past Perfect.
If you notice these examples carefully, you can see that the tense changes when converting from direct to indirect speech. To illustrate this point, in the following example, direct speech is in the present simple tense, while indirect speech is written in the simple past tense. Direct Speech: "I live in the city centre."
To change exclamatory sentences into Indirect Speech using direct indirect rules, follow the following rules along with the above-mentioned rules: In case, there is an interjection i.e., alas, aha, hurray, aha etc in the reported speech, then they are omitted along with the sign of exclamation using reported speech rules.
Zoya said, "I want to go there."; Reported verb: The verb which comes inside the reported speech is called reported verb, respectively. Zoya said, "I want to go there."; As we start writing any direct and indirect conversation, we often use reported verbs like "say, tell, ask, inform, instruct, claim, suggest, enquire, etc.". These reported verbs, whenever used in direct or ...
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules . Below, we are sharing the rules to make changes from Direct to Indirect speech. The changes of Direct and Indirect speech depend on some factors like modals, reporting verb, place, time, tense, pronoun etc. You can check the complete information of changes in Direct and Indirect speech.
Unreal Past Tenses in Indirect Speech. Unreal past tenses after sooner or would rather, wish, and it is time do not change. Direct: "I wish I didn't have to take the paper." said the student. Indirect: The student said he wished he didn't have to take the paper. Direct: "It's time you began planning your holidays.".
Let's check the following examples for a better understanding of the changes in tenses under the umbrella of reported speech: Direct: Reema says, "I am going out.". Indirect: Reema says that she is going out. Direct: Ramesh said, "Honesty is the best policy.". Indirect: Ramesh said that honesty is the best policy.
Direct and Indirect Speech Future Simple Tense Examples. If reported verb is in Past Tense, and reported speech is in Future Indefinite Tense, will changes into would & shall changes into should. Direct Speech. Indirect Speech. Shakespeare said, "I will write another drama tomorrow.". Shakespeare said that he would write another drama the ...
The shift to indirect discourse leads to changes in the tense, depending on whether the verb is in the present tense or in the past tense. If the introductory verb is in the present tense, the tense (or modal) does not change. "I'm sorry." → He says he is sorry. "I hate driving" → He says he hates driving.
The main part of the topic: 1.Changes in Pronouns: When converting direct speech to indirect speech, pronouns usually change according to the perspective of the reporting speaker. Here are the general rules: a) First-person pronouns: "I" changes to "he/she" or the person's name. "We" changes to "they.". b) Second-person pronouns: