Home » JavaScript Tutorial » JavaScript Assignment Operators

JavaScript Assignment Operators
Summary : in this tutorial, you will learn how to use JavaScript assignment operators to assign a value to a variable.
Introduction to JavaScript assignment operators
An assignment operator ( = ) assigns a value to a variable. The syntax of the assignment operator is as follows:
In this syntax, JavaScript evaluates the expression b first and assigns the result to the variable a .
The following example declares the counter variable and initializes its value to zero:
The following example increases the counter variable by one and assigns the result to the counter variable:
When evaluating the second statement, JavaScript evaluates the expression on the right-hand first ( counter + 1 ) and assigns the result to the counter variable. After the second assignment, the counter variable is 1 .
To make the code more concise, you can use the += operator like this:
In this syntax, you don’t have to repeat the counter variable twice in the assignment.
The following table illustrates assignment operators that are shorthand for another operator and the assignment:
Chaining JavaScript assignment operators
If you want to assign a single value to multiple variables, you can chain the assignment operators. For example:
In this example, JavaScript evaluates from right to left. Therefore, it does the following:
- Use the assignment operator ( = ) to assign a value to a variable.
- Chain the assignment operators if you want to assign a single value to multiple variables.
JS Tutorial
Js versions, js functions, js html dom, js browser bom, js web apis, js vs jquery, js graphics, js examples, js references, javascript assignment, javascript assignment operators.
Assignment operators assign values to JavaScript variables.
Shift Assignment Operators
Bitwise assignment operators, logical assignment operators, the = operator.
The Simple Assignment Operator assigns a value to a variable.
Simple Assignment Examples
The += operator.
The Addition Assignment Operator adds a value to a variable.
Addition Assignment Examples
The -= operator.
The Subtraction Assignment Operator subtracts a value from a variable.
Subtraction Assignment Example
The *= operator.
The Multiplication Assignment Operator multiplies a variable.
Multiplication Assignment Example
The **= operator.
The Exponentiation Assignment Operator raises a variable to the power of the operand.
Exponentiation Assignment Example
The /= operator.
The Division Assignment Operator divides a variable.
Division Assignment Example
The %= operator.
The Remainder Assignment Operator assigns a remainder to a variable.
Remainder Assignment Example
Advertisement
The <<= Operator
The Left Shift Assignment Operator left shifts a variable.
Left Shift Assignment Example
The >>= operator.
The Right Shift Assignment Operator right shifts a variable (signed).
Right Shift Assignment Example
The >>>= operator.
The Unsigned Right Shift Assignment Operator right shifts a variable (unsigned).
Unsigned Right Shift Assignment Example
The &= operator.
The Bitwise AND Assignment Operator does a bitwise AND operation on two operands and assigns the result to the the variable.
Bitwise AND Assignment Example
The |= operator.
The Bitwise OR Assignment Operator does a bitwise OR operation on two operands and assigns the result to the variable.
Bitwise OR Assignment Example
The ^= operator.
The Bitwise XOR Assignment Operator does a bitwise XOR operation on two operands and assigns the result to the variable.
Bitwise XOR Assignment Example
The &&= operator.
The Logical AND assignment operator is used between two values.
If the first value is true, the second value is assigned.
Logical AND Assignment Example
The &&= operator is an ES2020 feature .
The ||= Operator
The Logical OR assignment operator is used between two values.
If the first value is false, the second value is assigned.
Logical OR Assignment Example
The ||= operator is an ES2020 feature .
The ??= Operator
The Nullish coalescing assignment operator is used between two values.
If the first value is undefined or null, the second value is assigned.
Nullish Coalescing Assignment Example
The ??= operator is an ES2020 feature .
Test Yourself With Exercises
Use the correct assignment operator that will result in x being 15 (same as x = x + y ).
Start the Exercise

COLOR PICKER

Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, do not hesitate to send us an e-mail:
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.
- Skip to main content
- Select language
- Skip to search
- Assignment operators
An assignment operator assigns a value to its left operand based on the value of its right operand.
The basic assignment operator is equal ( = ), which assigns the value of its right operand to its left operand. That is, x = y assigns the value of y to x . The other assignment operators are usually shorthand for standard operations, as shown in the following definitions and examples.
Simple assignment operator which assigns a value to a variable. The assignment operation evaluates to the assigned value. Chaining the assignment operator is possible in order to assign a single value to multiple variables. See the example.
Addition assignment
The addition assignment operator adds the value of the right operand to a variable and assigns the result to the variable. The types of the two operands determine the behavior of the addition assignment operator. Addition or concatenation is possible. See the addition operator for more details.
Subtraction assignment
The subtraction assignment operator subtracts the value of the right operand from a variable and assigns the result to the variable. See the subtraction operator for more details.
Multiplication assignment
The multiplication assignment operator multiplies a variable by the value of the right operand and assigns the result to the variable. See the multiplication operator for more details.
Division assignment
The division assignment operator divides a variable by the value of the right operand and assigns the result to the variable. See the division operator for more details.

Remainder assignment
The remainder assignment operator divides a variable by the value of the right operand and assigns the remainder to the variable. See the remainder operator for more details.
Exponentiation assignment
This is an experimental technology, part of the ECMAScript 2016 (ES7) proposal. Because this technology's specification has not stabilized, check the compatibility table for usage in various browsers. Also note that the syntax and behavior of an experimental technology is subject to change in future version of browsers as the spec changes.
The exponentiation assignment operator evaluates to the result of raising first operand to the power second operand. See the exponentiation operator for more details.
Left shift assignment
The left shift assignment operator moves the specified amount of bits to the left and assigns the result to the variable. See the left shift operator for more details.
Right shift assignment
The right shift assignment operator moves the specified amount of bits to the right and assigns the result to the variable. See the right shift operator for more details.
Unsigned right shift assignment
The unsigned right shift assignment operator moves the specified amount of bits to the right and assigns the result to the variable. See the unsigned right shift operator for more details.
Bitwise AND assignment
The bitwise AND assignment operator uses the binary representation of both operands, does a bitwise AND operation on them and assigns the result to the variable. See the bitwise AND operator for more details.
Bitwise XOR assignment
The bitwise XOR assignment operator uses the binary representation of both operands, does a bitwise XOR operation on them and assigns the result to the variable. See the bitwise XOR operator for more details.
Bitwise OR assignment
The bitwise OR assignment operator uses the binary representation of both operands, does a bitwise OR operation on them and assigns the result to the variable. See the bitwise OR operator for more details.
Left operand with another assignment operator
In unusual situations, the assignment operator (e.g. x += y ) is not identical to the meaning expression (here x = x + y ). When the left operand of an assignment operator itself contains an assignment operator, the left operand is evaluated only once. For example:
Specifications
Browser compatibility.
- Arithmetic operators
Document Tags and Contributors
- JavaScript basics
- JavaScript first steps
- JavaScript building blocks
- Introducing JavaScript objects
- Introduction
- Grammar and types
- Control flow and error handling
- Loops and iteration
- Expressions and operators
- Numbers and dates
- Text formatting
- Regular expressions
- Indexed collections
- Keyed collections
- Working with objects
- Details of the object model
- Iterators and generators
- Meta programming
- A re-introduction to JavaScript
- JavaScript data structures
- Equality comparisons and sameness
- Inheritance and the prototype chain
- Strict mode
- JavaScript typed arrays
- Memory Management
- Concurrency model and Event Loop
- References:
- ArrayBuffer
- AsyncFunction
- Float32Array
- Float64Array
- GeneratorFunction
- InternalError
- Intl.Collator
- Intl.DateTimeFormat
- Intl.NumberFormat
- ParallelArray
- ReferenceError
- SIMD.Bool16x8
- SIMD.Bool32x4
- SIMD.Bool64x2
- SIMD.Bool8x16
- SIMD.Float32x4
- SIMD.Float64x2
- SIMD.Int16x8
- SIMD.Int32x4
- SIMD.Int8x16
- SIMD.Uint16x8
- SIMD.Uint32x4
- SIMD.Uint8x16
- SharedArrayBuffer
- StopIteration
- SyntaxError
- Uint16Array
- Uint32Array
- Uint8ClampedArray
- WebAssembly
- decodeURI()
- decodeURIComponent()
- encodeURI()
- encodeURIComponent()
- parseFloat()
- Array comprehensions
- Bitwise operators
- Comma operator
- Comparison operators
- Conditional (ternary) Operator
- Destructuring assignment
- Expression closures
- Generator comprehensions
- Grouping operator
- Legacy generator function expression
- Logical Operators
- Object initializer
- Operator precedence
- Property accessors
- Spread syntax
- async function expression
- class expression
- delete operator
- function expression
- function* expression
- in operator
- new operator
- void operator
- Legacy generator function
- async function
- for each...in
- function declaration
- try...catch
- Arguments object
- Arrow functions
- Default parameters
- Method definitions
- Rest parameters
- constructor
- element loaded from a different domain for which you violated the same-origin policy.">Error: Permission denied to access property "x"
- InternalError: too much recursion
- RangeError: argument is not a valid code point
- RangeError: invalid array length
- RangeError: invalid date
- RangeError: precision is out of range
- RangeError: radix must be an integer
- RangeError: repeat count must be less than infinity
- RangeError: repeat count must be non-negative
- ReferenceError: "x" is not defined
- ReferenceError: assignment to undeclared variable "x"
- ReferenceError: deprecated caller or arguments usage
- ReferenceError: invalid assignment left-hand side
- ReferenceError: reference to undefined property "x"
- SyntaxError: "0"-prefixed octal literals and octal escape seq. are deprecated
- SyntaxError: "use strict" not allowed in function with non-simple parameters
- SyntaxError: "x" is a reserved identifier
- SyntaxError: JSON.parse: bad parsing
- SyntaxError: Malformed formal parameter
- SyntaxError: Unexpected token
- SyntaxError: Using //@ to indicate sourceURL pragmas is deprecated. Use //# instead
- SyntaxError: a declaration in the head of a for-of loop can't have an initializer
- SyntaxError: applying the 'delete' operator to an unqualified name is deprecated
- SyntaxError: for-in loop head declarations may not have initializers
- SyntaxError: function statement requires a name
- SyntaxError: identifier starts immediately after numeric literal
- SyntaxError: illegal character
- SyntaxError: invalid regular expression flag "x"
- SyntaxError: missing ) after argument list
- SyntaxError: missing ) after condition
- SyntaxError: missing : after property id
- SyntaxError: missing ; before statement
- SyntaxError: missing = in const declaration
- SyntaxError: missing ] after element list
- SyntaxError: missing formal parameter
- SyntaxError: missing name after . operator
- SyntaxError: missing variable name
- SyntaxError: missing } after function body
- SyntaxError: missing } after property list
- SyntaxError: redeclaration of formal parameter "x"
- SyntaxError: return not in function
- SyntaxError: test for equality (==) mistyped as assignment (=)?
- SyntaxError: unterminated string literal
- TypeError: "x" has no properties
- TypeError: "x" is (not) "y"
- TypeError: "x" is not a constructor
- TypeError: "x" is not a function
- TypeError: "x" is not a non-null object
- TypeError: "x" is read-only
- TypeError: More arguments needed
- TypeError: can't access dead object
- TypeError: can't define property "x": "obj" is not extensible
- TypeError: can't redefine non-configurable property "x"
- TypeError: cyclic object value
- TypeError: invalid 'in' operand "x"
- TypeError: invalid Array.prototype.sort argument
- TypeError: invalid arguments
- TypeError: invalid assignment to const "x"
- TypeError: property "x" is non-configurable and can't be deleted
- TypeError: setting getter-only property "x"
- TypeError: variable "x" redeclares argument
- URIError: malformed URI sequence
- Warning: -file- is being assigned a //# sourceMappingURL, but already has one
- Warning: 08/09 is not a legal ECMA-262 octal constant
- Warning: Date.prototype.toLocaleFormat is deprecated
- Warning: JavaScript 1.6's for-each-in loops are deprecated
- Warning: String.x is deprecated; use String.prototype.x instead
- Warning: expression closures are deprecated
- Warning: unreachable code after return statement
- JavaScript technologies overview
- Lexical grammar
- Enumerability and ownership of properties
- Iteration protocols
- Transitioning to strict mode
- Template literals
- Deprecated features
- ECMAScript 2015 support in Mozilla
- ECMAScript 5 support in Mozilla
- ECMAScript Next support in Mozilla
- Firefox JavaScript changelog
- New in JavaScript 1.1
- New in JavaScript 1.2
- New in JavaScript 1.3
- New in JavaScript 1.4
- New in JavaScript 1.5
- New in JavaScript 1.6
- New in JavaScript 1.7
- New in JavaScript 1.8
- New in JavaScript 1.8.1
- New in JavaScript 1.8.5
- Documentation:
- All pages index
- Methods index
- Properties index
- Pages tagged "JavaScript"
- JavaScript doc status
- The MDN project

JAVASCRIPT ASSIGNMENT OPERATORS
In this tutorial, you will learn about all the different assignment operators in javascript and how to use them in javascript.
Assignment Operators
In javascript, there are 16 different assignment operators that are used to assign value to the variable. It is shorthand of other operators which is recommended to use.
The assignment operators are used to assign value based on the right operand to its left operand.
The left operand must be a variable while the right operand may be a variable, number, boolean, string, expression, object, or combination of any other.
One of the most basic assignment operators is equal = , which is used to directly assign a value.
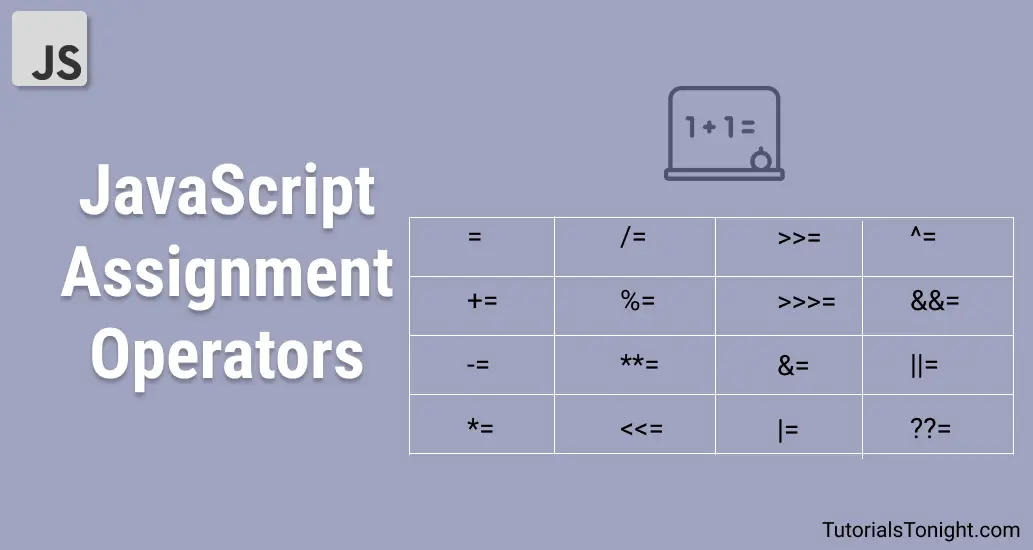
Assignment Operators List
Here is the list of all assignment operators in JavaScript:
In the following table if variable a is not defined then assume it to be 10.
Assignment operator
The assignment operator = is the simplest value assigning operator which assigns a given value to a variable.
The assignment operators support chaining, which means you can assign a single value in multiple variables in a single line.
Addition assignment operator
The addition assignment operator += is used to add the value of the right operand to the value of the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
On the basis of the data type of variable, the addition assignment operator may add or concatenate the variables.
Subtraction assignment operator
The subtraction assignment operator -= subtracts the value of the right operand from the value of the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
If the value can not be subtracted then it results in a NaN .
Multiplication assignment operator
The multiplication assignment operator *= assigns the result to the left operand after multiplying values of the left and right operand.
Division assignment operator
The division assignment operator /= divides the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
Remainder assignment operator
The remainder assignment operator %= assigns the remainder to the left operand after dividing the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Exponentiation assignment operator
The exponential assignment operator **= assigns the result of exponentiation to the left operand after exponentiating the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Left shift assignment
The left shift assignment operator <<= assigns the result of the left shift to the left operand after shifting the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Right shift assignment
The right shift assignment operator >>= assigns the result of the right shift to the left operand after shifting the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Unsigned right shift assignment
The unsigned right shift assignment operator >>>= assigns the result of the unsigned right shift to the left operand after shifting the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Bitwise AND assignment
The bitwise AND assignment operator &= assigns the result of bitwise AND to the left operand after ANDing the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Bitwise OR assignment
The bitwise OR assignment operator |= assigns the result of bitwise OR to the left operand after ORing the value of left operand by the value of the right operand.
Bitwise XOR assignment
The bitwise XOR assignment operator ^= assigns the result of bitwise XOR to the left operand after XORing the value of the left operand by the value of the right operand.
Logical AND assignment
The logical AND assignment operator &&= assigns value to left operand only when it is truthy .
Note : A truthy value is a value that is considered true when encountered in a boolean context.
Logical OR assignment
The logical OR assignment operator ||= assigns value to left operand only when it is falsy .
Note : A falsy value is a value that is considered false when encountered in a boolean context.
Logical nullish assignment
The logical nullish assignment operator ??= assigns value to left operand only when it is nullish ( null or undefined ).
AI Creations

Javascript Loops and Functions
Get Unstuck
Assignment with a Returned Value
If you'll recall from our discussion about Storing Values with the Assignment Operator , everything to the right of the equal sign is resolved before the value is assigned. This means we can take the return value of a function and assign it to a variable.
Assume we have pre-defined a function sum that adds two numbers together, then:
will call the sum function, which returns a value of 17 and assigns it to the ourSum variable.

COMMENTS
Second thing is assigning y to x, and so on. Assigning is not return (it's not a function, and in JS it doesn't have C++ syntax to overload operator's behavior). return is sth more complex then assignment. return construct is not only returning a value, but is closing current context causing it to be destroyed. Also it's closing any parent ...
The assignment (=) operator is used to assign a value to a variable or property. The assignment expression itself has a value, which is the assigned value. ... Return value. The value of y. Exceptions. ... Note that the implication of the above is that, contrary to popular misinformation, JavaScript does not have implicit or undeclared ...
4.Call PutValue(Result(1), Result(3)). 5.Return Result(3). Basically when you make (foo.bar = foo.bar) the actual assignment ( Step 4.) has no effect because PutValue will only get the value of the reference and will place it back, with the same base object. The key is that the assignment operator returns ( Step 5) the value obtained in the ...
An assignment operator ( =) assigns a value to a variable. The syntax of the assignment operator is as follows: let a = b; Code language: JavaScript (javascript) In this syntax, JavaScript evaluates the expression b first and assigns the result to the variable a. The following example declares the counter variable and initializes its value to zero:
Well organized and easy to understand Web building tutorials with lots of examples of how to use HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SQL, Python, PHP, Bootstrap, Java, XML and more. ... The Addition Assignment Operator adds a value to a variable. Addition Assignment Examples. let x = 10;
This chapter describes JavaScript's expressions and operators, including assignment, comparison, arithmetic, bitwise, logical, string, ternary and more. At a high level, an expression is a valid unit of code that resolves to a value. There are two types of expressions: those that have side effects (such as assigning values) and those that ...
An assignment operator assigns a value to its left operand based on the value of its right operand.. Overview. The basic assignment operator is equal (=), which assigns the value of its right operand to its left operand.That is, x = y assigns the value of y to x.The other assignment operators are usually shorthand for standard operations, as shown in the following definitions and examples.
If you'll recall from our discussion about Storing Values with the Assignment Operator, everything to the right of the equal sign is resolved before the value is assigned.This means we can take the return value of a function and assign it to a variable. Assume we have defined a function sum which adds two numbers together.. ourSum = sum (5, 12);. Calling the sum function with the arguments of ...
In this tutorial, you will learn about all the different assignment operators in javascript and how to use them in javascript. Assignment Operators. In javascript, there are 16 different assignment operators that are used to assign value to the variable. It is shorthand of other operators which is recommended to use.
Assignment with a Returned Value. If you'll recall from our discussion about Storing Values with the Assignment Operator , everything to the right of the equal sign is resolved before the value is assigned. This means we can take the return value of a function and assign it to a variable. Assume we have pre-defined a function sum that adds two ...
This is because the assignment operator returns the value that is assigned. First, b is set to 5. Then the a is also set to 5 — the return value of b = 5, a.k.a. right operand of the assignment. As another example, the unique exponentiation operator has right-associativity, whereas other arithmetic operators have left-associativity.
This means we can take the return value of a function and assign it to a variable. Assume we have pre-defined a function sum which adds two numbers together, then: will call sum function, which ...
You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You switched accounts on another tab or window.
Description. Logical OR assignment short-circuits, meaning that x ||= y is equivalent to x || (x = y), except that the expression x is only evaluated once. No assignment is performed if the left-hand side is not falsy, due to short-circuiting of the logical OR operator. For example, the following does not throw an error, despite x being const: js.
Are there any practical uses of the assignment operator's return value that could not be trivially rewritten? Generally speaking, no. The idea of having the value of an assignment expression be the value that was assigned means that we have an expression which may be used for both its side effect and its value , and that is considered by many ...
The void operator evaluates an expression and discards its return value. typeof. The typeof operator determines the type of a given object. +. The unary plus operator converts its operand to Number type. -. The unary negation operator converts its operand to Number type and then negates it. ~.
The destructuring assignment syntax is a JavaScript expression that makes it possible to unpack values from arrays, or properties from objects, into distinct variables. ... You cannot use them with compound assignment operators such as += or *=. ... Destructuring can make working with an array return value more concise. In this example, f ...
The return type is important for chaining operations. Consider the following construction: a = b = c;. This should be equal to a = (b = c), i.e. c should be assigned into b and b into a. Rewrite this as a.operator= (b.operator= (c)). In order for the assignment into a to work correctly the return type of b.operator= (c) must be reference to the ...
Most typically, it is used in object methods, where this refers to the object that the method is attached to, thus allowing the same method to be reused on different objects. The value of this in JavaScript depends on how a function is invoked (runtime binding ), not how it is defined. When a regular function is invoked as a method of an object ...
The multiplication assignment (*=) operator performs multiplication on the two operands and assigns the result to the left operand. ... JavaScript. General-purpose scripting language. HTTP. Protocol for transmitting web resources. ... Reduce of empty array with no initial value; TypeError: setting getter-only property "x" TypeError: X.prototype ...