Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., ai + human expertise – a paradigm shift..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai....
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
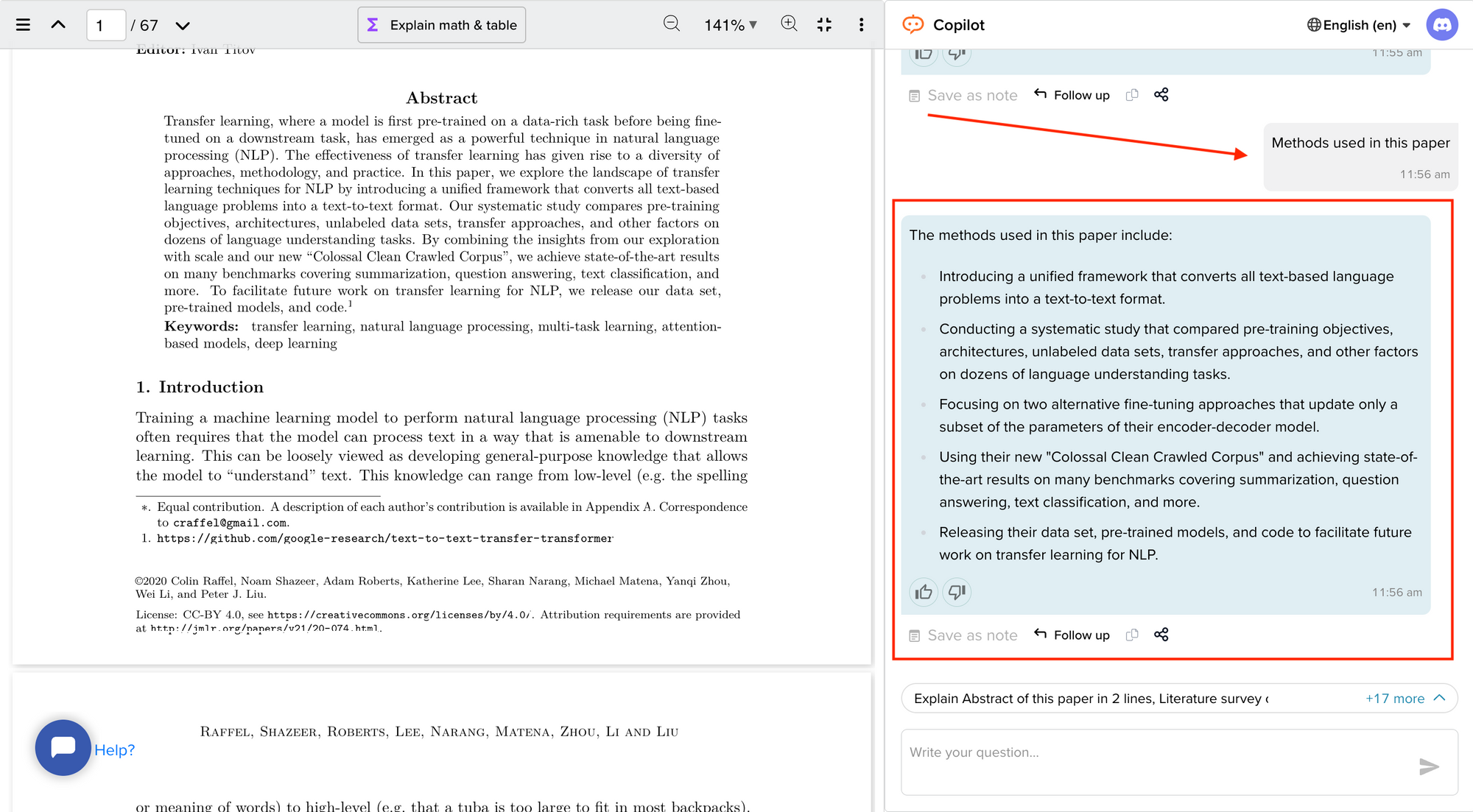
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .

You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- अन्वेषण करें हमारे बारे में समुदाय विविध लेख श्रेणियाँ
- श्रेणियाँ (categories) खोजें
- विकिहाउ के बारे में
- लॉग इन/ खाता बनाएं
- शिक्षा और संचार
कैसे एक शोधपत्र (Research Paper) लिखें
इस आर्टिकल के सहायक लेखक (co-author) हमारी बहुत ही अनुभवी एडिटर और रिसर्चर्स (researchers) टीम से हैं जो इस आर्टिकल में शामिल प्रत्येक जानकारी की सटीकता और व्यापकता की अच्छी तरह से जाँच करते हैं। wikiHow's Content Management Team बहुत ही सावधानी से हमारे एडिटोरियल स्टाफ (editorial staff) द्वारा किये गए कार्य को मॉनिटर करती है ये सुनिश्चित करने के लिए कि सभी आर्टिकल्स में दी गई जानकारी उच्च गुणवत्ता की है कि नहीं। यहाँ पर 8 रेफरेन्स दिए गए हैं जिन्हे आप आर्टिकल में नीचे देख सकते हैं। यह आर्टिकल १,३६,९३२ बार देखा गया है।
स्कूल की ऊंची कक्षाओं में पढ़ने के दौरान और कॉलेज पीरियड में हमेशा ही, आपको शोध-पत्र तैयार करने के लिए कहा जाएगा। एक शोध-पत्र का इस्तेमाल वैज्ञानिक, तकनीकी और सामाजिक मुद्दों की ख़ोज-बीन और पहचान में किया जा सकता है। यदि शोध-पत्र लेखन का आपका यह पहला अवसर है, तो बेशक कुछ डरावना भी लग सकता है, पर मस्तिष्क को अच्छी तरह से संयोजित और एकाग्र करें, तो आप खुद के लिए इस प्रक्रिया को आसान बना सकते हैं। शोध-पत्र तो स्वयं नहीं लिख जाएगा, पर आप इस प्रकार से योजना बना सकते हैं, और ऐसी तैयारी कर सकते हैं कि लेखन व्यावहारिक रूप में खुद-ब-खुद जेहन में उतरता चला जाए।
अपने विषयवस्तु का चयन

- आम तौर पर, वेबसाइट जिनके नाम के अंत में .edu, .gov, या .org होता है, ऎसी सूचनाएं रखती हैं जिन्हें इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है। ऐसा इसलिए है कि ये वेबसाइट स्कूलों, सरकार या उन संगठनों की होती हैं जो आपके विषय से सम्बंधित हैं।
- अपनी खोज का प्रश्न बार-बार बदलें ताकि आपके विषय पर अलग-अलग तरह के खोज परिणाम मिलें। अगर कुछ भी मिलता नज़र न आये तो ऐसा हो सकता है कि आपकी खोज का प्रश्न अधिकाँश लेखों के शीर्षक से मेल नहीं खा रहा है जो आपके विषय पर हैं।

- ऐसे डेटाबेस ढूंढ़िए जो आपके विषय को ही सम्मिलित करते हों। उदहारण के लिए PsycINFO एक ऐसा डेटाबेस है जो कि केवल मनोविज्ञान और समाजशास्त्र के क्षेत्र में ही विद्वानों द्वारा किये काम को सम्मिलित करता है। एक सामान्य खोज के मुकाबले यह आपको अपने अनुरूप शोध सामग्री पाने में मदद करेगा। [२] X रिसर्च सोर्स
- पूछताछ के एकाधिक खोज-बॉक्स या केवल केवल एक ही प्रकार के स्रोत वाले आर्काइव के साथ अधिकाँश अकादमिक डेटाबेस आपको ये सुविधा देते हैं कि आप बेहद विशिष्ट सूचना मांग सकें (जैसे केवल जर्नल आलेख या केवल समाचार पत्र)। इस सुविधा का लाभ उठाकर जितने अधिक खोज बॉक्स आप इस्तेमाल कर सकते हैं उतना करें।
- अपने विभाग के पुस्तकालय जाएँ और लाइब्रेरियन से अकादमिक डेटाबेस, जिनकी सदस्यता ली गयी है, की पूरी सूची और उनके पासवर्ड ले लें।

एक रूपरेखा का निर्माण

- रूपरेखा बनाने और शोधपत्र लिखने का काम आखिरकार आसान करने के लिए टीका-टिप्पणी का काम गहनता से कीजिये। जिस चीज़ के महत्वपूर्ण होने का आपको ज़रा भी अंदेशा हो या जो आपके शोधपत्र में इस्तेमाल हो सकता है, उसकी निशानदेही कर लीजिए।
- जैसे-जैसे आप अपने शोध में महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सों को चिन्हित करते जाएँ, अपनी टिप्पणी और नोट जोड़ते जाएँ कि इन्हें आप अपने शोध-पत्र में कहाँ इस्तेमाल करेंगे। अपने विचारों को लिखना जैसे-जैसे वे आते जाएँ, आपके शोधपत्र लेखन को कहीं आसान बना देगा और ऎसी सामग्री के रूप में रहेगा जिसे आप सन्दर्भ के लिए फिर-फिर इस्तेमाल कर सकें।

- हर उद्धरण या विषय जिसे आपने चिन्हित किया है उसे अलग-अलग नोट कार्ड पर लिखने की कोशिश कीजिए। इस तरह से आप अपने कार्डों को मनचाहे ढंग से पुनर्व्यवस्थित कर सकेंगे।
- अपने नोट का रंगों में कोड बना लें, ताकि वे आसान हो जाएँ। अलग-अलग स्रोतों से जो भी नोट आप ले रहे हैं, उन्हें सूची बद्ध कर लें, और फिर सूचना के अलग-अलग वर्गों को अलग-अलग रंगों में चिन्हित कर लें। उदाहरण के लिए, जो कुछ भी आप किसी विशेष किताब या जर्नल से ले रहे हैं उन्हें एक कागज़ पर लिख लें ताकि नोट्स को सुगठित किया जा सके, और फिर जो कुछ भी चरित्रों से सम्बंधित है उसे हरे से चिन्हित करें, कथानक से जुड़े सबकुछ को नारंगी रंग में चिन्हित करें, आदि-आदि।

- एक तार्किक शोधपत्र विवादित विषयों पर एक पक्ष लेता है और एक दृष्टिकोण के लिए तर्क प्रस्तुत करता है। मुद्दे पर एक तर्कसंगत प्रतिपक्ष के साथ बहस की जानी चाहिए।
- एक विश्लेषणात्मक शोधपत्र किसी महत्त्वपूर्ण विषय पर नए सिरे से दृष्टिपात करता है। विषय आवश्यक नहीं है कि विवादित हो, पर आपको अपने पाठकों को सहमत करना पड़ेगा कि आपके विचारों में गुणवत्ता है। यह महज आपके शोध से विचारों की उबकाई भर नहीं, बल्कि अपने उन विशिष्ट अद्वितीय विचारों की प्रस्तुति है जिन्हें आपने गहन शोध से सीखा है।

- थीसिस विकसित करने का आसान तरीका है कि उसे एक प्रश्न के रूप में ढालिए जिसका आपका निबंध उत्तर देगा। वह मुख्य प्रश्न या हाइपोथीसिस क्या है जिसको आप अपने शोधपत्र में प्रमाणित करना चाहते हैं? उदाहरण के लिए आपकी थीसिस का प्रश्न हो सकता है, “मानसिक बीमारियों के इलाज की सफलता को सांस्कृतिक स्वीकृति कैसे प्रभावित करती है?” यह प्रश्न आपकी थीसिस क्या होगी उसे निर्धारित कर सकता है – इस प्रश्न के लिए आपका जो भी उत्तर होगा, वही आपका थीसिस-कथन होगा।
- शोधपत्र के सभी तर्कों को दिए बिना या उसकी रूपरेखा बताये बिना ही आपकी थीसिस को आपके शोध के मुख्य विचार को व्यक्त करना होगा। यह एक सरल कथन होना चाहिए, न कि कई सहायक वाक्यों का एक समूह, आपका बाक़ी शोधपत्र तो इस काम के लिए है ही!

- जब आप अपने मुख्य विचारों की रूप-रेखा बनाएं, उनको एक विशिष्ट क्रम में रखना अहम है। अपने सबसे मज़बूत तर्कों को निबंध के सबसे पहले और सबसे अंत में रखिये। जबकि ज्यादा औसत बिन्दुओं को निबंध के बीचोंबीच या अंत की तरफ रखिये।
- सबसे मुख्य बिन्दुओं को एक ही पैराग्राफ में समेटना ज़रूरी नहीं है, विशेष करके अगर आप एक अपेक्षाकृत लंबा शोधपत्र लिख रहे हैं। प्रमुख विचारों को जितने पैराग्राफ में आप ज़रूरी समझें फैलाकर लिख सकते हैं।

- अपनी हर बात को साक्ष्यों से पुष्ट करें। क्योंकि यह एक शोधपत्र है इसलिए ऐसी टिप्पणी न करें जिसकी पुष्टि सीधे आपके शोध के तथ्यों से न हो।
- अपने शोध में पर्याप्त व्याख्याएं दीजिये। बिना तथ्यों के अपने मत के बखान का विलोम बगैर किसी व्याख्या के बिना तथ्यों को देना होगा। यद्यपि आप निश्चित ही पर्याप्त प्रमाण देना चाहते हैं, तो भी जहां भी संभव हो अपनी टिप्पणी जोड़ते हुए यह सुनिश्चित कीजिए कि शोधपत्र पर आपकी मौलिक और विशिष्ट छाप हो।
- बहुत सारे सीधे लम्बे उद्धरण देने से बचें। यद्यपि आपका निबंध शोध पर आधारित है, फिर भी महत्वपूर्ण बात यह है कि आपको अपने विचार प्रस्तुत करने हैं। जिस उद्धरण का आप इस्तेमाल करना चाहते हैं, जब तक वह बेहद अनिवार्य न हो, उसे अपने ही शब्दों में व्यक्त और विश्लेषित करने की कोशिश कीजिए।
- अपने पेपर में साफ़-सुथरे और संतुलित गति से एक बिंदु से दूसरे तक जाने का प्रयास करें। निबंध में स्वछन्द तारतम्य और प्रवाह होना चाहिए, इसके बजाय कि अनाड़ी की तरह रुक-रुक कर क्रम टूटे और फिर अचानक शुरू हो जाए। यह ध्यान रखें कि लेख के मुख्य भाग वाला हर पैरा अपने बाद वाले से जाकर मिलता हो।

- आपके निष्कर्ष का लक्ष्य, साधारण शब्दों में, इस प्रश्न का उत्तर देना है, “तो क्या?” ध्यान रखें कि पाठक आख़िरकार महसूस करे कि उसे कुछ प्राप्त हुआ है।
- कई कारणों से अच्छा नुस्खा तो यह है कि, निष्कर्ष को भूमिका के पहले लिख लिया जाये। पहली बात तो यह है कि जब प्रमाण आपके दिमाग में ताज़ा हों तो निष्कर्ष लिखना ज्यादा आसान होता है। उससे भी बड़ी बात यह है, सलाह दी जाती है कि आप निष्कर्ष में अपने सबसे चुनिन्दा शब्द और भाषा का मजबूती से इस्तेमाल करें और फिर उन्हीं विचारों को भिन्न शब्दों में अपेक्षाकृत कम वेग के साथ भूमिका में रख दें, न कि इसका उल्टा करें; यह पाठकों पर ज्यादा स्थायी प्रभाव छोड़ेगा।

- MLA फॉर्मेट को विशेष रूप से साहित्यिक शोध-पत्रों के लिए इस्तेमाल किया जाता है और इसमें ‘उद्धृत सामग्री’ की एक सूची अंत में जोड़नी होती है, इस विधि में अंतरपाठीय उद्धरण प्रयोग किये जाते हैं।
- APA फॉर्मेट का इस्तेमाल सामाजिक विज्ञान के क्षेत्र में शोधपत्रों के लिए शोधकर्त्ताओं द्वारा किया जाता है, और इसमें भी अंतरपाठीय उद्धरण देने होते हैं। इसमें निबंध का अंत “सन्दर्भ” पृष्ठ के साथ होता है, और इसमें मुख्य भाग के पैराग्राफों के बीच में अनुच्छेद शीर्षक का प्रयोग भी किया जा सकता है।
- शिकागो फोर्मटिंग को प्रमुखतः ऐतिहासिक शोधपत्रों के लिए इस्तेमाल किया जाता है और इसमें अंतरपाठीय उद्धरण के स्थान पर पृष्ठ के नीचे फुटनोट का प्रयोग होता है और साथ में एक ‘उद्धृत सामग्री’ और सन्दर्भों का पृष्ठ जुड़ता है। [७] X रिसर्च सोर्स

- अपने पेपर का सम्पादन यदि खुद आपने किया है, तो उस पर वापस आने से पहले कम से कम तीन दिन प्रतीक्षा कीजिए। अध्ययन दिखाते हैं कि, लेख समाप्त करने के बाद भी दो-तीन दिन तक यह आपके जेहन में ताज़ा बना रहता है, और इसलिए ज्यादा संभावना यह रहेगी कि आम तौर पर आप जिन बुनियादी त्रुटियों को पकड़ पाते, उन्हें भी अपनी सरसरी नज़र में नजरअंदाज कर जाएँगे।
- दूसरों के द्वारा संपादन को महज इसलिए नजरअंदाज न करें कि उनसे आपका काम बढ़ जाएगा। अगर वे आपके पेपर के किसी अंश को दोबारा लिखे जाने की सलाह दे रहे हों तो उनके इस आग्रह का संभवतया उचित कारण है। अपने पेपर के सघन सम्पादन पर समय दीजिए। [८] X रिसर्च सोर्स

- रिसर्च के दौरान महत्वपूर्ण थीम, प्रश्नों और केन्द्रीय मुद्दों को ढूँढ़ें।
- यह समझने की कोशिश करें कि, आप वास्तव में निर्दिष्ट रूप में किस चीज़ का अन्वेषण करना चाहते हैं, इसके बजाय कि पेपर में ढेर सारे व्यापक विचारों को ठूस दिया जाए।
- ऐसा करने के लिये अंतिम क्षण तक प्रतीक्षा मत कीजिए।
- अपने असाइंमेंट को समयानुसार पूरा करना सुनिश्चित कीजिए।
संबंधित लेखों

- ↑ http://www.infoplease.com/homework/t3sourcesofinfo.html
- ↑ http://www.ebscohost.com/academic
- ↑ http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/552/03/
- ↑ http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/544/02/
- ↑ http://www.indiana.edu/~wts/pamphlets/thesis_statement.shtml
- ↑ http://libguides.jcu.edu.au/content.php?pid=83923&sid=3619280
- ↑ http://writing.yalecollege.yale.edu/why-are-there-different-citation-styles
- ↑ http://professionalonlineediting.com/how-to-edit-your-essay-or-research-paper-fast.asp
विकीहाउ के बारे में

- प्रिंट करें
यह लेख ने कैसे आपकी मदद की?
सम्बंधित लेख.

- हमें कॉन्टैक्ट करें
- यूज़ करने की शर्तें (अंग्रेजी में)
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
हमें फॉलो करें

Literature Review (rough draft)
Demographic Variables
Age. According to McClean and Beak (2012), research findings have shown that for the majority of crimes where a firearm is used, the offender is mainly in the middle to late adolescence after which there is a sharp and permanent drop. This is referred to as the age-crime-curve and has been developed based on the major parameters for measuring violent crime among them; self-reporting, victimization, and conviction data. Studies have also shown that there is a variation in the age-crime-curve depending on the type of crime. A specific study into violent crimes with a man as the perpetrator showed that the peak for violent crimes using a firearm was at a lesser age as compared to property crimes (Mclean & Beak, 2012). The research findings were based on rapid evidence assessment designed to study evidence based factors whereby results are based on 53 studies and 7 databases . At the age of 40, the rate of violent crime was half its peak and at zero at the age of 65. Research findings however, pointed to the fact that the factors identified within the research were associated with predictive of repeat violent behavior.
Gender. There is strong evidence that suggests there is more male firearm using offenders than females and thus, research has been more focused towards further exploring this phenomenon. Men compared to women commit many more criminal acts. While women in crime have criminal careers of less than a year and have a likelihood of one crime instance using a firearm, men, on the other hand, have the longest criminal histories and have the likelihood of recidivating into violent crime (Mclean & Beak, 2012; Hoskin, 2011).
The article is meant to investigate if their exists any relationship between firearm possession and gun-related suicides and homicidesnot just within the USA but in the entire world. Results for the research in Miami showed that males and young adults aged between 10 and 24 are at an increased risk of using a gun in homicide than their female counterparts (Stroebe, 2013). In the same research, it is further elaborate that, the only factor that differentiates frequency of violent offenders using firearm and frequency of non-violent offenders was gender, and men had the higher likelihood of being in the frequency violent using firearm offending group. The study is a combination of quantitative and qualitative because it embraces other case studies in methodology section and statistical data useful in making decisions. Each of the case study provides different results for observations made during varying time limits over the years.The data indicates that sucide cases that happened during the observation period were not all that were gun related. That impies that gun is just but one cause of sucide but not the overall cause since, cases associated to it were minimal.
Ethnicity. Studies into race/ethnicity in violent crimes using firearms suggests that Blacks are more likely to possess, use, and be victims of a firearm crime as compared to the other races/ethnic groups in the American community (Stroebe, 2013; Males, 2015). According to Males (2015) research utilizing victimization data and official data from police crime records suggested that it is more likely for a black male to use and be the victim of violence where a firearm is used. While blacks are at an increased risk of using a gun in a violent crime, whites are the least likely with Hispanics at the middle.
Other Demographic Variables. Other demographic factors in the use of a firearm in violent crime include education level, employment history, socio-economic status, and violent recidivism (Mclean & Beak, 2012). Low education and unemployment have been shown, through a study of Danish birth cohort, to be typical among firearm-using violent offenders (Willits, Broidy & Denman, 2012).Primarily, the study by Willits, Broidy and Denman (2012) was done to examine the degree to which person, incident, and structural characteristics predict firearm usage in violent crimes. The data that was used in this particular study was drawn from consenus of 2000 and official crime data come from the Albuquerque Police Department (APD). Three variables were adopted in the study namely, person variables, incident variables, and structural variables.Person variables were charactirised by data made up of age, gender, and race.Where the ages involved were less than 18 years and 18 to 25 years. Incident variables assumed time between 8 pm to 2 am. The research adopted a descriptive statistiucs methodology in explaining violent incidents. The results from the research elaborate that 67% of violent incidents were made of male offenders while, 20% involved male and female offenders. In addition, 44 % of incidents were made of male victims and 133% was made by bothe male and female victims. Finally, it is clear from the research that crime offenders and victims have shared incident characteristics that firearm crimes tend to share and they can be identified for creation of policies that would assist curb such incidences.
Legal Issues/Previous arrests or previous behavior
Previously Carrying a Weapon. A study by Valle and Glover (2012)on the effects of weapon carrying, either legally or illegally, in 57 American cities showed that individuals were more likely to use firearm in violent crime. Research proposal was exploratory because their has been mass shootings within America that have elicited mixed reactions from commentators and attracted political debates. Participants for the survey were drawn from each of the 57 cities. Thus, analysis would by comparison of groups in different cities with more strict gun and ammunition regulations compared to cities with less restrictive regulations of guns and ammunition. Results show that in cities with laws allowing gun carrying, even though incidences of gun violence are higher, rates of robbery, including robbery with violence, are very minimal. Further statistics show that for individuals who previously carried weapons, they are more likely to be involved in firearm violence including homicide by a 20-30%.
Runaways are a major factor in gun violence and in particular, mass shooting. Runaways in the recent years, in the US, have been a major cause of gun violence, particularly to children, not factoring in incidences that are motivated by terror. Exposure to runaways has been mainly in homes, in schools, and in other community public areas. Since 2010, runaway firearm violence has contributed about 1% of the total homicide cases in the United States.
Threats against others
According to Hemenway and Solnick (2015) a study was conducted to determine the relative effectiveness of SDGU in preventing injury and property loss in America. Research findings from the study show that threats towards and against others are a contributing factor towards the use of a firearm in violence. The study adopted data from National Crime Victimization Survey for 2007–2011 whereby quantitative multivariate analyses that was controlled took course. The results are fascinating in that over 14,000 incidents in which the victim was present, only 127 which amounts to 0.9% were involved in SDGU . The conclusion drawn from the study is that SDGU is not uniquely beneficial in reduction of the likelihood of injury or property loss when compared to other protective action.Hemenway & Solnick (2015) argue that a firearm is more likely to be used in threatening others and more so in states where gun ownership is loosely controlled. On the reverse, threats victims using guns for self-defense are less likely to be injured, even though researchers found not a significant difference to probability to be injured as compared to victims using other protective measures.
Gun use in fighting is more pronounced within gangs in the United States. In a study of 2,792 gun-using violent offenders, 6.8% were members of various gangs (Willits et al., 2012). The research was conducted by New Mexico Statistical Analysis Center (NM SAC) to exame the extent to which person, incident, and structural characteristics predict firearm usage in violent crimes. Data for testing 8 hypothesis that were developed for the research were obtained from Official crime data coming from the Albuquerque Police Department (APD). Moreover, search into gang involvement showed that guns were their primary weapon of choice in gang-to-gang fights. Research shows that being a gang member increases the risk of firearm violence across gender where both males and females by virtue of being a gang member have equal and higher risks to using a firearm in violence. In non-gang related fights, research has shown that it’s more likely for a gun-owner to use it primarily for the purpose of intimidating the other.
Juvenile Justice/Conduct Disorder history
According to Swanson et al. (2015), conduct disorder and history of the same condition is a contributory factor towards the use of a firearm in the perpetration of the violent crimes. Their research shows that persons with a history of conduct disorder are more likely to use a gun in aggressive behavior. However, the actual use of a firearm in an act of violence depends on access to a firearm either at home or through illegal channels. In addition, the likelihood of using a firearm in aggressive behavior was higher among males, younger persons, married, and persons living in outlying areas of a metropolitan rather in within city centers.
Other legal issues/previous behavior problems
Other legal issues that are cited as factors promoting the use of firearms in aggressive behavior are recidivism. Studies show that, generally, for a group of violent firearm-using offenders, half are usually recidivists.
Willits et al. (2012) argue that there is research evidence showing that the possibility of aggressive behavior using a firearm increases with each subsequent violent offense. However, the peak of recidivism is highest during mid-adolescence and gradually tails off in late adolescence, similar to the age-crime-curve. Research findings show that men with long criminal careers, regardless of the type of crime are at an increased risk of engaging in aggressive behavior using a firearm (Kasprzak, 2013). Similar, an individual with a history of crime is more likely to engage in violent recidivism.
- Deviant peers
Deviant peer groups have been argued to be a cause of antisocial behavior, especially at a young age. Data from a national survey of state prison inmates was used in to calculation of the proportion of offenders, incarcerated for crimes committed with firearms in 13 which were categorized to have the least restrictions on firearm purchase and possession laws, who would have been prohibited if their states had stricter gun laws; and second the determination of the source of gun acquisition for offenders who were not legally permitted to purchase and possess firearms.In addition, research shows that deviant peer can be used to predict violent offending. One study comparing violent offenders and general offenders found that such groups exhibited antisocial behavior and it suggested antisocial behavior can be used to predict chronic offending but not violent firearm using aggressive behavior (Vittes, Vernick & Webster, 2013). For adults involved in violent crime, deviant peers were only cited as being a contributory factor towards non-recidivism and violent recidivists, with those with, or have had deviant peers being violent recidivists. Finally, the results showed that 3 in 10 gun offenders were legal gun possesors and they would not have been lincensed to own the guns if their states had more strict prohibitions on purchasing a firearm.
- Dysfunctional families
Domestic abuse incidents
Various factors related to originating from dysfunctional families have been shown to have contributory roles towards predicting the use of a firearm in aggressive behavior. Domestic abuse, especially at a young age, for instance, has been shown through research to predict violent behavior, with possible firearm usage for the purpose of preventing through intimidation or simply stopping any resistance. However, research has not shown any significant difference between domestic abuse and engagement in violent behavior using a firearm. A study comparing adolescents arrested due to violent behavior with adolescents arrested for non-violent offenses showed no significance difference between through who experienced domestic abuse and those who didn’t. However, research has shown that persons who have experienced domestic abuse in the hands of their parents or guardians are at an increased risk of being recidivists (Stroebe, 2013; Males, 2015).
- Mental illness
Research provides little population-level evidence to indicate that persons who have been diagnosis with mental illness are more likely to commune gun crimes (Metzl & MacLeish, 2015). According to Metzl & MacLeish (2015), less than 3-5% of crimes in the US involve persons with mental illness, and the percentage for those who have been diagnosed with mental illness and their use a gun in a crime is even lower. Based on data from gun homicide, fewer than 5% of the 120,000 gun-related killing between 2001 and 2010 were by persons who had been diagnosed with mental illness.
Inpatient at psychiatric facility
There is little if any statistical data related to an inpatient at a psychiatric facility for the basic reason that, firearms and weapons, in general, are prohibited in these facilities and inpatients have limited access to firearms. Nevertheless, research has shown that persons with serious mental illness and thus, have been admitted to a psychiatric facility are three times more likely to commit acts of violence using firearms. The number of persons with serious mental illness in the US per year is on average 2.9% making it a very small number.
Threats or acts of self-harm
Suicidal tendencies, in particular, are considered a major factor in predicting the use of a firearm in aggressive behavior. According to Swanson et al. (2015), suicides accounted for on average 61% of all firearm-related deaths in the US in 2014. However, the specific link between self-harm and violent crime is contentious among various researchers. Some researchers argue that persons with mental illness and exhibiting suicidal tendencies are at a greater risk of using a firearm in aggressive behavior in the periods between psychotic episodes and psychiatric hospitalization.
- Narcotics/substance abuse/alcohol abuse
Drug and alcohol abuse in earlier ages is argued to be related to violent offending as well as recidivism. Research has shown that substance and alcohol abuse in early years, especially before 11 years is a factor towards predicting future violence. Adolescents who are classified as frequent drinkers are 2.4 times more likely to engage in violent crime as compared to their light to non-drinking counterparts (Sevigny & Allen, 2015; Mclean & Beak, 2012). For adult substance and alcohol users, the link between drug usage and violent crime is mixed. While some studies show that drug use and violent behavior have a significant relationship for both men and women, others show that drug abuse is only a contributory factor and leads to violent behavior when combined with other factors (Chen & Wu, 2016).
Nevertheless, none of the studies seems to have a direct link between drug abuse and use of a firearm, simply violent behavior with no clear use of a firearm. However, researchers conclude that substance abuse should be factored in gun-crime control initiatives (Sevigny & Allen, 2015; Chen & Wu, 2016).
Chen, D., & Wu, L. T. (2016). Association between substance use and gun-related behaviors. Epidemiologic reviews , mxv013.
Hemenway, D. & Solnick, S.J. (2015). The epidemiology of self-defense gun use: Evidence from the National Crime Victimization Surveys 2007-2011. Preventive Medicine . 79: 22-27.
Hoskin, A. (2011). Household gun prevelence and rates of violent crime: A test of competing gun theories. Criminal Justice Studies, 125-136.
Kasprzak, J. (2013). Scope of illegal Possession of Weapons in Poland and Character Study of a Perpetrator of this Crime. Internal Security , 147-158.
Males, M. (2015). Age, Poverty, Homicide, and Gun Homicide Is Young Age or Poverty Level the Key Issue? SAGE Open, 1-12. DOI: 10.1177/2158244015573359
Mclean, F. & Beak, K. (2012). Factors associated with serious or persistent violent offending: Findings from a rapid evidence assessment . National Policing Improvement Agency
Metzl, J. M., & MacLeish, K. T. (2015). Mental Illness, Mass Shootings, and the Politics of American Firearms. American Journal of Public Health , 105 (2), 240–249. doi.10.2105/AJPH.2014.302242
Sevigny, E. L., & Allen, A. (2015). Gun carrying among drug market participants: evidence from incarcerated drug offenders. Journal of quantitative criminology , 31 (3), 435-458.
Stroebe, W. (2013). Firearm possession and violent death: A critical review, Aggression and Violent Behavior. doi.10.1016/j.avb.2013.07.025
Swanson, J.W., Sampson, N.A., Petukhova, M.V., Zaslavsky, A.M., Appelbaum, P.S., Swartz, M.S. & Kessler, R.C. (2015). Guns, Impulsive Angry Behavior, and Mental Disorders: Results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R), Behavioral Sciences and the Law . DOI: 10.1002/bsl.2172
Valle, J. &. (2012). Revisiting Licensed Handgun Carrying: Personal Protection or Interpersonal Liability? American Journal of Criminal Justice , 580-601.
Vittes, K. A., Vernick, J. S., & Webster, D. W. (2013). Legal Status and Source of Offenders’ Firearms In States With the Least Stringent Criteria for Gun Ownership. Injury Prevention 19 .1, 26-31.
Willits, D., Broidy, L. & Denman, K. (2012). Predictors of Firearm Usage in Violent Crimes: Assessing the Importance of Individual, Situational, and Contextual Factors , New Mexico Statistical Analysis Center.
INSTANT PRICE
Get an instant price. no signup required.

We respect your privacy and confidentiality!
Share the excitement and get a 15% discount
Introduce your friends to The Uni Tutor and get rewarded when they order!
Refer Now >

FREE Resources
- APA Citation Generator
- Harvard Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- MLA Referencing Generator
- Oscola Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- Turabian Citation Generator
New to this Site? Download these Sample Essays
- Corporate Law Thesis
- Political Philosophy
- Legal Writing Rules
- Sample Philosophy Thesis
Send me free samples >
How The Order Process Works
- Order Your Work Online
- Tell us your specific requirements
- Pay for your order
- An expert will write your work
- You log in and download your work
- Order Complete
Amazing Offers from The Uni Tutor Sign up to our daily deals and don't miss out!

Contact Us At
- e-mail: info@theunitutor.com
- tel: +44 20 3286 9122

Brought to you by SiteJabber

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2002-2024 - The Uni Tutor - Custom Essays. 10347001, info@theunitutor.com, +44 20 3286 9122 , All Rights Reserved. - Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
The Uni Tutor : We are a company registered in the United Kingdom. Registered Address London, UK , London , England , EC2N 1HQ


25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

कैसे लिखे सबसे अच्छा आर्टिकल?
- Updated on
- दिसम्बर 2, 2022
Article writing in Hindi बहुत ही आसान होता है, परंतु जब हम उसे लिखने बैठते हैं, तो हमें समझ नहीं आता कि क्या लिखें और क्या नहीं! जब हम बोलते हैं तब हमारी बातों पर हमारा कंट्रोल नहीं होता, हम बहुत सारी बातें बोलते हैं। परंतु जब लिखने की बात आती है तब हम वही बातें लिखते हैं जो बहुत जरूरी होती है। ठीक उसी तरह आर्टिकल लिखने मतलब होता है कि कम से कम शब्दों में ज्यादा से ज्यादा और जानकारी के बारे में बताना। जब हम बातें करते हैं तो हमें सामने वाले चेहरे को देखकर पता चलता है कि हम जो बोल रहे हैं वह उसे समझ आ रहा है या नहीं, परंतु जब लिखने के बाद आती है तब हमें इस बात का पता नहीं चलता।
यदि आप पैराग्राफ राइटिंग इन हिंदी लिखना चाहते हैं तो इस लिंक पर क्लिक करें: Paragraph writing in Hindi
आर्टिकल लेखन क्या है?
आर्टिकल लेखन एक ऐसा तरीका है जिसमें हम किसी भी विषय के बारे में लिखकर उसकी जानकारी या उसके बारे में बता सकते है। उसे हिंदी में ‘ लेख ‘ कहा जाता है। Article writing in Hindi का मतलब होता है कि किसी भी विषय पर ज्यादा से ज्यादा जानकारी देना। आर्टिकल राइटिंग दो प्रकार के होते हैं-
- पहला प्रकार- जिसके हर शब्द का अपना एक अलग ही महत्व होता है।
- दूसरा प्रकार- किसी भी आर्टिकल में उस विषय की जानकारी को सरल और साधारण भाषा में समझाया गया हो।
आर्टिकल लेखन के उद्देश्य
एक लेख निम्नलिखित उद्देश्यों को ध्यान में रखकर लिखा जाना चाहिए-
- इसे विषय या रुचि के विषय को अग्रभूमि में लाना चाहिए।
- लेख में सभी आवश्यक जानकारी पर चर्चा होनी चाहिए।
- इसे पाठकों को सिफारिशें करनी चाहिए या सुझाव देना चाहिए।
- यह पाठकों पर प्रभाव डालने और उन्हें सोचने पर मजबूर करने के योग्य होना चाहिए।
- लेख में लोगों, स्थानों, उभरती चुनौतियों और तकनीकी प्रगति सहित विषयों की एक विस्तृत श्रृंखला शामिल होनी चाहिए।
आर्टिकल लेखन फॉर्मेट
आप जो कुछ भी लिखना चाहते हैं, आपके लिए यह महत्वपूर्ण है कि आप पहले लेख की संरचना को जानें और फिर उसके अनुसार विवरण का उल्लेख करें। मुख्य रूप से 3 खंडों में विभाजित- शीर्षक, बायलाइन और मुख्य भाग , आइए हम लेख लेखन प्रारूप पर एक नज़र डालते हैं जिसे आपको अपनी जानकारी लिखते समय ध्यान में रखना चाहिए।
शीर्षक या उप शीर्षक
पहली बात जिस पर ध्यान दिया जाना चाहिए और लेख लेखन में सबसे महत्वपूर्ण घटक शीर्षक/शीर्षक है। पाठकों का ध्यान आकर्षित करने के लिए यह आवश्यक है कि लेख को 5 से 6 शब्दों से अधिक का आकर्षक शीर्षक दिया जाए।
बायलाइन या लेखक का नाम
शीर्षक के नीचे एक बाइलाइन आती है जिसमें उस लेखक का नाम होता है जिसने लेख लिखा है। यह हिस्सा लेखक को वास्तविक श्रेय अर्जित करने में मदद करता है जिसके वे हकदार हैं।
लेख का मुख्य भाग
मुख्य भाग में एक लेख की मुख्य सामग्री होती है। कहानी लेखन हो या लेख लेखन, यह पूरी तरह से लेखक पर निर्भर करता है कि वह रचना की लंबाई और उन पैराग्राफों की संख्या तय करे जो जानकारी को एम्बेड करेंगे। आम तौर पर, एक लेख में 3 या 4 पैराग्राफ होते हैं, जिसमें पहला पैराग्राफ पाठकों को यह बताता है कि लेख किस बारे में होगा और सभी आवश्यक जानकारी। दूसरे और तीसरे पैराग्राफ में विषय की जड़ को शामिल किया जाएगा और यहां सभी प्रासंगिक डेटा, केस स्टडी और आंकड़े प्रस्तुत किए गए हैं। इसके बाद, चौथा पैराग्राफ उस लेख को समाप्त करेगा जहां समस्याओं के समाधान, जैसा कि दूसरे और तीसरे मार्ग (यदि कोई हो) में प्रस्तुत किया गया है, पर चर्चा की जाएगी।
ऑटिकल कैसे लिखा जाता है?
जब भी आप किसी भी टॉपिक पर आर्टिकल लिखते हैं तो आपको बहुत सारी बातों को ध्यान रखना पड़ता है जो आपके लिखने की क्षमता को कई गुना ज्यादा निखरता हैं इसलिए ऑटिकल लिखने के लिए नीचे दिए गए जानकारी को ध्यान से पढ़े जो आपको ऑटिकल लिखने में कई ज्यादा मदद करेंगा।
सोचकर लिखना सीखें
यह Article writing in Hindi का सबसे महत्वपूर्ण अंग और सबसे पहला भाग है कि आप किसी भी टॉपिक में कोई भी ऑटिकल लिखते है तो सिर्फ एक विचार को ध्यान में रखकर ना लिखे बल्कि उस पूरे समाज और सभी लोगों के लिए लिखें जो आपके इस ऑटिकल का फायदा मिल सकें। और इमेजिनेशन ही एक ऐसी चीज है जिसे आप हर तरह का सीन क्रिएट कर सकते हैं इमेजिनेशन के जरिये ही आप अपने अंदर ही अंदर आर्टिकल का एक बेतरीन स्ट्रक्चर तैयार कर सकते है जो आपके रीडर्स को आपका पूरा आर्टिकल पढ़ने के लिए उत्साहित करता है।
शांत वातावरण
अक्सर आपने फिल्मों में देखा और पढ़ा होगा कि अगर कोई लिखता है तो वह एक ऐसा वातावरण देखते है जहाँ शाति हो और वहाँ वे अपनी लिखने की कौशल को एक बेहतर लेखन शैली पर लेकर जा सकें। ऐसा इसलिए ताकि वह किसी भी तरीके से डिस्टर्ब न हो ताकि वह अपनी इमेजिनेशन पर पूरी तरह से केंद्रित रह सकें क्योंकि हमारा मन बहुत चंचल हैं और अगर कोई हमें डिस्टर्ब कर देता है तो हम उस इमेजिनेशन से एक दम बहार आ जाते है औऱ फिर से उसपर केंद्रित होने में काफ़ी समय लग सकता है इसलिए हमेशा एक अच्छा और बेहतरीन ऑटिकल लिखने के पहले शांत वातावरण की जरूरत होती है।
एक शब्द का इस्तेमाल बार-बार ना करें
ऑटिकल लिखते समय इस बात का हमेशा आपको ध्यान रखना है कि आप किसी भी शब्द को एक से ज्यादा बार अपने ऑटिकल में इस्तेमाल नहीं करें। अब इसका मुख्या कारण यानी ऐसा करने से आपके रीजर्स ऑटिकल पढ़ते पढ़ते बोर हो जाते है जिसके बाद उस ऑटिकल में ज्यादा संख्या में व्यू नहीं आते हैं। इसलिए एक जैसे शब्दों का प्रयोग न करके उसके जैसे समान अर्थ वाले शब्दों का प्रयोग करें जिसे रीडर्स को यह न लगे कि वह बार-बार की की लाइन पढ़ रहा है।।
ज़ीरो से लिखना शुरू करें
आर्टिकल लिखते समय आपको नहीं पता होता कि आपका यह ऑटिकल दुनिया के किन कौने में कौन से व्यक्ति द्वारा पढ़ा जा रहा है। इसलिए आपने ऑटिकल में जब भी आप किसी भी टॉपिक के बारे में बताएं तो इस बात को ध्यान में रखकर लिखें जिसको पढ़कर उस टॉपिक के बारे में किसी भी रीडर में मन में अधूरी जानकारी ना रहें। इसलिए आपको अपने आर्टिकल को बिल्कुल ज़ीरो से लिखना चाहिए ताकि हर वर्ग का व्यक्ति बहुत आसनी से समझ सकें क्योंकि जब आपके लिखे गए तथ्य लोगों के समझ नही आते तो वह आपके आर्टिकल को छोड़कर चले जाते है।
अपने अनुभव के साथ लिखें
अगर आप किसी एक ऐसे विषय पर लिख रहे हैं जिसमे आपका अपना कोई पर्सनल अनुभव हैं तो आपको उसी आधार पर अपने आर्टिकल को लिखना चाहिए। क्योंकि हम सब की एक जैसी समस्याएं होती हैं और रीडर्स उस समय सबसे ज्यादा आर्टिकल को पढ़ने के लिए उत्साहित होता है जब उसे लगता है कि उसकी समस्या भी बिल्कुल ऐसी है और फिर वह उनका हल जाने के लिए अंत तक आर्टिकल पढ़ता है।
आर्टिकल लिखने का सही तरीका
Article writing in Hindi सरल और साधारण भाषा में होना चाहिए। ताकि उसे एक बार पढ़ना शुरू करें तो अंत तक उसे पूरा पढ़ कर ही रखें।आर्टिकल पढ़ने वाले के लिए लाभदायक होना चाहिए ताकि उसके हर सवालों के जवाब उसके अंदर उसे मिल जाए। इसलिए आर्टिकल लिखने से पहले उसके फॉर्मेट के बारे में हमें पता होना चाहिए। आर्टिकल लिखने की शुरुआत कैसी करनी चाहिए? कहां पर किस बारे में बताना चाहिए ?आर्टिकल को पूरा कैसे करना चाहिए ?उसके अंदर कौनसी-कौनसी बातों का उल्लेख करना चाहिए? ऐसे कई सारी बातों का ध्यान में रखकर आर्टिकल आप शानदार रूप से लिख सकते हैं। Article writing in Hindi को तीन भाग में विभाजित किया गया है:
लेख लेखन उद्घाटन अनुभाग
लेख लेखन कार्रवाई अनुभाग, लेख लेखन समापन अनुभाग.
यदि आप informal letter in Hindi के बारे में जानकारी चाहते हैं तो दिए गए लिंक पर क्लिक करें।
आर्टिकल लेखन की शुरुआत सरल और आसान भाषा से होनी चाहिए। आर्टिकल के अंदर कहीं जाने वाली बातों का उल्लेख करना चाहिए। सीधे-सीधे बातों को पेश न करके उसे रोचक वाले शब्दों से उद्घाटन करना चाहिए। इमैजिनेशन जैसे शब्दों का इस्तेमाल करके आर्टिकल को पढ़ने पर मजबूर करने वाले शब्दों का प्रयोग करें। अपने कई बार देखा होगा न्यूज़ में कुछ ऐसे शब्दों का प्रयोग होता है जिससे हम न्यूज़ को देखने के लिए व्याकुल हो जाते हैं।
उदाहरण के तौर पर,” गौर से देखिए इस मासूम बच्ची को”, यह शब्द सुनते ही हमारा पूरा ध्यान न्यूज़ की तरफ केंद्रित हो जाता है। हमें वह न्यूज़ को देखने पर मजबूर कर देता है। ठीक उसी तरह हमारे आर्टिकल में भी कुछ ऐसे शब्दों का प्रयोग करके हम रीडर्स को अपनी तरफ आकर्षित कर सकते हैं। किसी भी बात को समझाने के लिए सीधे-सीधे ना बताकर, रोचक वाले शब्दों का इस्तेमाल करके अपने आर्टिकल को आकर्षित बना सकते हैं।
यह सबसे अहम विमाग होता है। जिसमें हम उन बातों का उल्लेख करता है , जिसके लिए रीडर आर्टिकल को पढ़ने के लिए आया होता है। इसलिए यह एक्शन पार्ट कहलाता है। इसके अंदर रीडर्स के सवालों के जवाब के बारे में लिखा जाता है।
उदाहरण के लिए-
- डॉक्टर कैसे बने
- डॉक्टर के लिए कौन सी पढ़ाई करनी चाहिए
- डॉक्टर के लिए कौन सा कोर्स करना चाहिए
- डॉक्टर के लिए टॉप कॉलेज
- डॉक्टर के लिए टॉप सरकारी कॉलेज
- डॉक्टर के लिए कितने साल की पढ़ाई होती है
- डॉक्टर की पढ़ाई के बाद क्या करना चाहिए
- ऐसे कई सारे सवालों का जवाब आर्टिकल के अंदर उल्लेख होना चा
इन सभी सवालों का जवाब देकर आप रीडर को अपनी तरफ आकर्षित कर सकते हैं। आर्टिकल लेखन हमेशा सरल और साधारण वाक्य और भाषा में होना चाहिए। आर्टिकल को अलग-अलग उदाहरण के साथ समझा भी सकते हैं।
जितना आर्टिकल राइटिंग का ओपनिंग सेक्शन जरूरी होता है ठीक उतना ही आर्टिकल राइटिंग का समापन विभाग भी उतना ही जरूरी होता है। आर्टिकल राइटिंग क्लोजिंग सेक्शन में आप पूरे आर्टिकल के ओवरव्यू के बारे में बताते हैं। इसके अंदर कुछ महत्वपूर्ण बातों के बारे में समझा सकते हैं। समापन विभाग तुरंत खत्म ना करें उसके अंदर थोड़ी-थोड़ी रोचक वाले शब्दों का प्रयोग करके आकर्षित बनाएं ताकि रीडर अंत तक पूरा आर्टिकल पढ़ें। Article Writing in Hindi इस प्रकार तीन हिस्सों में बांट सकते हैं। अगर आप यह तीन हिस्सों में अच्छे से आर्टिकल लिखेंगे तो आप रीडर को अपनी तरफ आकर्षित कर सकते हैं। आर्टिकल राइटिंग को बेहतर बनाने के लिए उसके अंदर राइटिंग स्किल होना बहुत ही जरूरी है। राइटिंग स्किल से आप अपने आर्टिकल को और भी बेहतर बना सकते हैं।
आर्टिकल राइटिंग के लिए स्टेप बाय स्टेप गाइड
प्रारूप जानने के बाद, आइए लेख लिखने की प्रक्रिया में शामिल 5 सरल चरणों पर एक नजर डालते हैं:-
चरण 1: अपने लक्षित दर्शकों को खोजें
किसी भी विषय पर लिखने से पहले, लेखक के लिए यह महत्वपूर्ण है कि वह पहले उन श्रोताओं की पहचान करे जो लेख लक्षित करता है। यह लोगों, बच्चों, छात्रों, किशोरों, युवा वयस्कों, मध्यम आयु वर्ग, बुजुर्ग लोगों, व्यवसायी लोगों, सेवा वर्ग आदि का एक विशेष समूह हो सकता है। आप जिस भी समूह के लोगों के लिए लिखना चुनते हैं, उस विषय का चयन करें जो प्रत्यक्ष या अप्रत्यक्ष रूप से हो। उनके जीवन को प्रभावित करता है या प्रासंगिक जानकारी फैलाता है।
उदाहरण के लिए, यदि लेख माता-पिता पर केंद्रित है, तो आप बाल मनोविज्ञान, बच्चे के दैनिक पोषण आहार आदि के बारे में लिख सकते हैं। स्वर और भाषा भी लेख लेखन में उपयुक्त श्रोताओं से मेल खाना चाहिए।
चरण 2: एक विषय और एक आकर्षक शीर्षक चुनें
अपने लक्षित दर्शकों को चुनने के बाद, लेख लेखन में दूसरा महत्वपूर्ण कदम अपनी रचना के लिए एक उपयुक्त विषय चुनना है। यह एक विचार देता है कि आपको लेख के साथ कैसे प्रक्रिया करनी चाहिए। विषय का चयन करने के बाद, उसके लिए एक दिलचस्प शीर्षक के बारे में सोचें।
उदाहरण के लिए, यदि आप छात्रों को उपलब्ध विभिन्न एमबीए विशेषज्ञताओं से अवगत कराना चाहते हैं, तो आप लिख सकते हैं – ” एमबीए विशेषज्ञता के बारे में आपको जो कुछ भी जानने की आवश्यकता है “।
चरण 3: रिसर्च कुंजी है
अपने लक्षित दर्शकों, विषय और लेख के शीर्षक का चयन करने के परिणामस्वरूप, लेख लेखन में शोध सबसे महत्वपूर्ण चीज है। लेख में शामिल की जाने वाली सभी सूचनाओं को जानने के लिए ढेर सारे लेख, आंकड़े, तथ्य और डेटा, और नए शासी कानून (यदि कोई हों) पढ़ें। इसके अतिरिक्त, डेटा की प्रामाणिकता की जांच करें, ताकि आप कुछ भी पुराना न बताएं। लेख लिखने के साथ आगे बढ़ने से पहले, बुलेट पॉइंट्स और कीवर्ड्स में लेख का एक रफ ड्राफ्ट या रूपरेखा तैयार करें ताकि आप महत्वपूर्ण जानकारी से न चूकें।
चरण 4: लिखें और प्रूफरीड
एक बार जब आप सभी तथ्य और डेटा एकत्र कर लेते हैं, तो अब आप अपना लेख लिखना शुरू कर सकते हैं। जैसा कि चर्चा की गई है, लेख को एक परिचयात्मक पैराग्राफ के साथ शुरू करें, उसके बाद एक वर्णनात्मक और एक समापन पैराग्राफ। आपके द्वारा सब कुछ लिखने के बाद, अपने पूरे लेख को प्रूफरीड करना और यह जांचना उचित है कि कहीं कोई व्याकरण संबंधी त्रुटि तो नहीं है। एक पाठक के रूप में, जब आप एक छोटी सी गलती भी देखते हैं तो यह एक बड़ा मोड़ बन जाता है। साथ ही, सुनिश्चित करें कि सामग्री किसी अन्य वेबसाइट से कॉपी नहीं की गई है।
चरण 5: चित्र और इन्फोग्राफिक्स जोड़ें
लोगों को पढ़ने के लिए अपनी सामग्री को और अधिक आकर्षक बनाने के लिए, आप कुछ इन्फोग्राफिक्स भी शामिल कर सकते हैं। छवियों को जोड़ने से लेख और भी आकर्षक हो जाता है और यह अधिक प्रभावशाली साबित होता है। इस प्रकार आपके लेख लेखन के उद्देश्य को सफल बनाते हैं!
आर्टिकल राइटिंग के उदाहरण
- महिला सशक्तिकरण
यत्र नार्यस्तु पूज्यन्ते रमन्ते तत्र देवताः। यत्रैतास्तु न पूज्यन्ते सर्वास्तत्राफलाः क्रियाः।। जब बात महिलाओं की आती है तो सबसे पहले इसी श्लोक को याद किया जाता है। हम सब औरत को देवी का रुप मानते है, आत्मविश्वास, अनुभव, रचनात्मकता से परिपूर्ण वास्तविकता में यहीं एक औरत की पहचान है। पारंपरिक समाज और चार दिवारों तक सीमित रहने वाली औरत आज देश कि राष्ट्रीय आय में अपनी भूमिका निभा रही है। महिलाएं आर्थिक कारकों के कारण उद्यमिता में प्रवेश करती हैं जो उन्हें अपने दम पर आगे बढ़ाती हैं। भारतीय महिलाएं, जिन्हें बेहतर माना जाता है लेकिन वे समाज में समान भागीदार नहीं हैं। महिलाओं की उद्यमीता में लिंग अंतर बहुत मायने रखता है। जिसके कारण बहुत सी परेशानीयों का सामना करना पड़ता है। आईआईटी, दिल्ली द्वारा किए सर्वेक्षण के अनुसार संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका और कनाडा में छोटे व्यवसाय का एक तिहाई महिलाएं है। एशियाई देशों में कुल कार्यबल का 40 प्रतिशत हिस्सा महिलाओं का है। भारत में महिलाएं अपने परिवार से बहुत भावनात्मक रूप से जुड़ी हुई हैं। घर के काम, बच्चों परिवार के सदस्यों की देखभाल करने में व्यस्त रहती है। ऐसे में उनके पास अपने लिए कुछ करने ंका समय कहां बचता है। दुसरी समस्या है हमारा पुरुष प्रधान समाज। महिलओं के साथ पुरुषों के बराबर व्यवहार नहीं किया जाता है। व्यवसाय में उनके प्रवेश के लिए परिवार के प्रमुख की मुजूरी की आवश्यकता होती है। पारंपरिक रूप से उद्यमिता को पुरुषों कि निगरानी में रखा गया है जो महिलाओं के विकास में रूकावट हैं। महिला साक्षरता को लेकर आंकडे बदल रहे है। भारतीय समाजों में प्रचलित परंपराएं और रीति-रिवाज एक बोझ बन जाते है। भारत में महिलाएं स्वभाव से कमजोर, शर्मीली और सौम्य है। ऐसे में शिक्षा, प्रशिक्षण और वित्तीय सहायता की कमी उनकी क्षमता में कमी कर देती है। चूंकि महिलाएं मार्केटिंग, डिस्ट्रीब्यूशन और मनी कलेक्शन के लिए इधर-उधर भाग दौड़ नहीं कर सकती हैं, इसलिए उन्हें निर्भर रहना पड़ता है। लेकिन इन सबके बाद भी उन्होंने अपनी पहचान पा ली है जैसे- अखिला श्रीनिवासन, प्रबंध निदेशक, श्रीराम इनवेस्टमेंट लि., चंदा कोचर, कार्यकारी निदेशक, आईसीआईसीआई बैंक, एकता कपूर, क्रिएटिव डायरेक्टर, बालाजी टेलीफिल्म्स लि., ज्योति नाइक, अध्यक्ष, लिज्जत पापड., किरण मजूमदार शॉ, अध्यक्ष और प्रबंध निदेशक, बायोकॉन लि, ललिता डी गुप्ते, जेएमडी, आईसीआईसीआई बैंक , नैना लाल किडवार, डिप्टी सीईओ, प्रीता रेड्डी, प्रबंध निदेशक, अपोलो अस्पताल, प्रिया पॉल, अध्यक्ष, एपीजे पार्क होटल राजश्री पैथी, अध्यक्ष, राश्री शुगर्स एंड केमिकल्स लि
छात्रों के लिए कोविड-19 पर लेख लेखन
कोविड-19 ने मानव जीवन के सभी वर्गों को प्रभावित किया है। जबकि इसने सभी उद्योग क्षेत्रों को प्रभावित किया, इसका शिक्षा पर बड़ा प्रभाव पड़ा। रात के भीतर कक्षाओं को ऑफलाइन से ऑनलाइन कर दिया गया था, लेकिन इससे छात्रों में भ्रम की स्थिति पैदा हो गई, खासकर उन छात्रों के लिए जो कॉलेजों में प्रवेश करने वाले थे। स्थिति बेहतर होने की उम्मीद में छात्रों ने एक साल का अंतराल भी लिया। जबकि दुनिया भर में टीकाकरण के कारण स्कूल और कॉलेज खुल रहे हैं, अभी भी कई चुनौतियाँ हैं।
COVID-19 को समझना, यह कैसे फैलता है, और खुद को कैसे सुरक्षित रखना है, यह सबसे महत्वपूर्ण चीजें हैं जो स्कूल के फिर से खुलते ही सबसे पहले सीखी जानी चाहिए। छात्रों को उन नियमों को जानना चाहिए जिनका वे पालन करने जा रहे हैं और स्कूल कक्षा में कोविड-19 सुरक्षा नियमों का पालन करने के लाभ। बच्चों को समझाना बहुत मुश्किल है क्योंकि हो सकता है कि मासूम दिमाग वर्तमान परिस्थितियों से परिचित न हो।
कोविड-19 के संपर्क में आने के जोखिम से बचने के लिए हर छात्र और स्कूल फैकल्टी को हर समय इन नियमों का पालन करना चाहिए। छात्रों को हर समय हैंड सैनिटाइटर साथ रखना होगा। छात्रों को कभी भी अपने हाथों पर छींक नहीं देनी चाहिए, बल्कि उन्हें इसे अपनी कोहनी से ढंकना चाहिए, या एक ऊतक या रूमाल का उपयोग कर सकते हैं। छात्रों को सूचित करें कि वे अपनी आंख, नाक और मुंह को बार-बार न छुएं। चूंकि आंखों और नाक को छूने से वायरस फैलने की संभावना बहुत अधिक है। यदि छात्र और शिक्षक इन बुनियादी नियमों का पालन करते हैं, तो प्रसार को रोका जा सकता है और स्कूल फिर से खुल सकते हैं।
एक अच्छा लेख लिखने के लिए टिप्स
कुछ ही समय में एक उत्कृष्ट लेख लिखने में आपकी मदद करने के लिए बहुत सारे उपयोगी संकेतों के साथ चरण-दर-चरण मार्गदर्शिका यहां दी गई है:
- सभी विचारों की सूची बनाना और उन्हें संभाल कर रखना
- सभी प्रकार के विकर्षणों को दूर करना
- विषय पर कुशलता से शोध करना
- इसे सरल और कम जटिल रखना
- अपने विचारों को बुलेट पॉइंट्स में लिखने का प्रयास करें
- पहला मसौदा लिखने के बाद संपादित करें
- एक टाइमर सेट करें
लेख लेखन में सामान्य गलतियों से बचना चाहिए
त्रुटियों की संभावना अब बढ़ जाती है जब आप लेख लेखन के चरणों और लेख लेखन प्रारूप को समझते हैं। सामान्य भूलों के कुछ उदाहरण निम्नलिखित हैं:
- तथ्यों या उद्धरणों या इसी तरह के मामलों का उपयोग नहीं करना
- ऐसे स्वर का उपयोग करना जो बहुत औपचारिक हो
- इसका अर्थ जाने बिना कठिन शब्दावली का प्रयोग करना
- अपने लेख के लिए आकर्षक शीर्षक का उपयोग नहीं करना
- जानकारी को विभाजित करने के लिए अनुच्छेदों का उपयोग नहीं करना
- व्यक्तिगत विचार या राय व्यक्त नहीं करना
ध्यान रखने योग्य बातें
- लेखों के विषय अद्वितीय और प्रासंगिक होने चाहिए
- लेख पर ध्यान देना चाहिए
- यह दिलचस्प होना चाहिए
- इसे पढ़ना आसान होना चाहिए
- एक लेख लिखने का मुख्य लक्ष्य खोजें। लक्ष्य सूचना, मनोरंजन, और सलाह प्रदान करने या तुलना करने आदि से कुछ भी हो सकता है।
- शीर्षक आकर्षक, स्पष्ट और दिलचस्प होना चाहिए
- परिचय या प्रारंभिक पैराग्राफ अत्यधिक चौकस होना चाहिए। अपने शब्दावली कौशल का प्रयोग करें या शुरुआत के लिए कुछ प्रश्नवाचक शब्दों का उपयोग करने का प्रयास करें
- स्पष्ट कथनों का प्रयोग करें और अभिकथन करें
- दोहराव और शीर्ष तर्क और कारणों से बचें
- अनुच्छेद लेखन की शैली का उपयोग करें और सामग्री को विशिष्ट और स्पष्ट रूप से लिखें
- उन बिंदुओं का उपयोग करने से बचें जो केवल आपकी रुचि रखते हैं और आम जनता के लिए नहीं
- अपने लेख लेखन को हमेशा एक अच्छे और तार्किक नोट पर समाप्त करें
आर्टिकल लेखन टॉपिक्स
क्या आपको एक लेख लिखना है जो अभी चलन में है और आपको बेहतर स्कोर करने में मदद करेगा या आपको बेहतर अभ्यास करने में मदद करेगा? लेख लेखन के लिए समसामयिक विषयों की सूची इस प्रकार है:
- ग्लोबल वार्मिंग
- पर्यावरण प्रदूषण
- इंटरनेट का प्रभाव
- शिक्षा और फिल्में
- शिक्षा में खेलों का महत्व
- योग और माइंड हीलिंग
- मानसिक स्वास्थ्य का महत्व
- समाज में शिक्षा का महत्व
- शिक्षा के महत्व पर लेख
- ग्लोबल वार्मिंग पर निबंध
- इंटरनेट पर निबंध
- जीवन में मेरा उद्देश्य पर निबंध
- शिक्षा प्रणाली पर निबंध
- लोकतंत्र पर निबंध
- करियर लक्ष्य निबंध कैसे लिखें?
- डिजिटल इंडिया पर निबंध
आशा करते हैं कि आपको Article Writing in Hindi ब्लॉग अच्छा लगा होगा । यदि आप विदेश में पढ़ाई करना चाहते हैं, तो हमारे Leverage Edu एक्सपर्ट्स के साथ 30 मिनट का फ्री सेशन 1800 572 000 पर कॉल कर बुक करें।
Team Leverage Edu
प्रातिक्रिया दे जवाब रद्द करें
अगली बार जब मैं टिप्पणी करूँ, तो इस ब्राउज़र में मेरा नाम, ईमेल और वेबसाइट सहेजें।
Contact no. *
17 comments
Mujhe v article writing skill sikhna h ? Plss help 🙏(Blogging)
दिलशद जी, आर्टिकल लिखने के लिए आपको बहुत सारी बातों को ध्यान रखना पड़ता है जैसे सोचकर लिखे, एक शब्द का इस्तेमाल बार-बार ना करें, एक आकर्षक शीर्षक चुनें आदि।
बहुत सुन्दर जानकारी आर्टिकल लेखन के लिए।
आपका धन्यवाद
बहुत-बहुत आभार
आर्टिकल लेखन क्या है? इसके बारे में जानने के लिए आप हमारी साइट पर जाकर ब्लॉग्स पढ़ सकते हैं।
Article Writing in Hindi में लेखन से जुड़ी महत्वपूर्ण जानकारियां दी गई है।
आपका धन्यवाद, इसी तरह https://leverageedu.com/ पर बने रहें।
GOOD KNOWLDGE
धन्यवाद, आप ऐसे ही हमारी वेबसाइट पर बने रहिए।
धन्यवाद, आप ऐसे ही हमारी वेबसाइट पर आते रहिए।
Artical likhna chahate hai but ise kaise aur kis topic pr likhe
आप हमारा आर्टिकल पढ़ सकते हैं।
Mai article likhna chati hu
हिंदी में ऑटिकल लिखने के लिए आप हमारी टीम के साथ जुड़ सकते हैं।

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.

How to write book review in Hindi with example- पुस्तक समीक्षा कैसे लिखें
अगर आप कोई ऐसी वेबसाइट खोलने की सोच रहे हैं जो किताबों पर आधारित है या किसी भी freelancer वेबसाइट पर book reviewer बनना चाहते हैं तो यह वेबसाइट आपके लिए ही है । आप इस पोस्ट में विस्तारपूर्वक जानेंगे कि how to write book review in Hindi यानि कि हिंदी में पुस्तक समीक्षा कैसे करें ? इस पोस्ट के माध्यम से आप आसानी से किसी भी book का review Hindi में कर सकते हैं ।
प्राचीन समय से ही किताबों की महत्ता विश्व समाज में सर्वोपरि रही है । पहले लोग किताबों के बारे में लोगों से सुन सुन कर , फिर किताब को पढ़ते थे । परन्तु , आज के digital दुनिया में लोग इंटरनेट पर किताबों के reviews खोजते हैं । इसके अलावा कई ऐसे publishers हैं जो अपनी किताब का review कराते हैं ताकि उन्हें सही मूल्यांकन का पता चल सकें । यह freelancing के अंतर्गत आता है ।
ऐसे में अगर आप किसी भी वजह या profession के लिए पुस्तक समीक्षा सीखना चाहते हैं तो how to write book review in Hindi का यह पोस्ट आपके लिए बहुत ही ज्यादा हेल्पफुल रहेगा । इसलिए इसे अंत तक पढ़ें और अगर आपको यह हेल्पफुल लगे तो शेयर जरुर करें । तो चलिए जानते हैं book review format in Hindi –
Book review क्या है ?

Book review एक पुस्तक का विश्लेषण है जिसमें इसके विषय, खूबियां, कमियां और संदर्भ शामिल हैं । इसमें किताब का संक्षिप्त सारांश, लेखक के पृष्ठभूमि की जानकारी, किताब का विषय और कंटेंट का evaluation किया जाता है ।
अपने विद्यार्थी दौर में आपने अपने हिंदी / इंगलिश शिक्षक से बुक रिव्यू करने का होमवर्क अवश्य पाया होगा या पा रहे होंगे । तो ऐसे में आप किताब के बारे में क्या राय रखते हैं या आपको किताब कैसी लगी , यही नहीं लिख सकते । सही मायनों में पुस्तक समीक्षा यह नहीं है । पुस्तक समीक्षा करते वक्त आपको निम्नलिखित बातों का ध्यान रखना चाहिए –
- किताब का short summary ( सारांश )
- लेखक की पृष्ठभूमि
- किताब का टॉपिक
- Content का critical evaluation
अगर आप ऊपर दिए इन 4 बिंदुओं को ध्यान में रखकर book review in Hindi करते हैं तो वह सही मायनों में पुस्तक समीक्षा होगी । आगे आप इस how to write book review in Hindi पोस्ट में उदाहरण के माध्यम से भी जानेंगे कि पुस्तक समीक्षा कैसे करें ?
How to write book review in Hindi
चलिए आपके प्रश्न book review kaise kare का उत्तर देते हैं । इसके पहले आप यह instagram infographic देख सकते हैं जिससे कि आपको इस पोस्ट के बारे में संक्षेप में idea हो जाएगा ।
अगर आप सच में एक expert book reviewer बनना चाहते हैं तो आपको सबसे पहले ढेर सारी किताबें पढ़ना चाहिए । आप किसी भी भाषा की किताबें पढ़कर काफी कुछ सीख सकते हैं इसलिए सबसे पहले पढ़ें ।
How to write book review in Hindi के लिए यह helpful infographic –

1. किताब की short summary लिखें
किसी भी किताब की समीक्षा करते समय , शुरुआत में उसकी short summary अवश्य लिखें । इससे लेखकों को उस किताब के content के बारे में थोड़ा idea हो जाता है कि वे किताब में क्या पढ़ेंगे । परन्तु , ध्यान रखें कि आपको इस summary में अपने reviews चाहे वो positive हों या negative , नहीं लिखना है । इसके साथ ही इस short summary में spoilers लिखने से बचें ।
अगर आप किताब के असली climax और अंत को शुरुआत में ही उजागर कर देंगे , तो readers के गुस्से का सामना आपको करना पड़ सकता है । इसलिए पाठकों के किताब पढ़ने के मज़े को बिल्कुल भी खराब न करें । इसके अलावा एक expert book reviewer की तरह किताब की समीक्षा करें ।
2. किताब के plus points को बताएं
book review in Hindi को लिखने के लिए short summary से शुरुआत करें । इसके बाद आपको बुक के बारे में short introduction देते हुए plus points बताना है । यह हमेशा ध्यान रखें कि समीक्षा के शुरुआत में कभी भी negative points को लिखने से बचें । किताब की अच्छाइयों को बताते हुए आप इन बिंदुओं का उत्तर दे सकते हैं –
- किताब में आपका सबसे पसंदीदा किरदार कौन था ?
- क्या किताब के सभी किरदार जीवंत ( real ) लग रहे थे ?
- क्या कोई पुस्तक पढ़ते समय आगे की कहानी को guess कर सकता है ?
- क्या आपको कहानी बांधे रखती है ?
- किताब में कौनसा भाग आपको सबसे अच्छा लगा ?
- क्या किताब ने आपकी भावनाओं से खेलने की कोशिश की ? जैसे हसना , रोना या दुखी होना इत्यादि ।
- आपको कौनसा dialogue सबसे रोचक लगा ?
3. किताब के negative points को लिखें
किताब के Good points को लिखने के बाद आपको उन points को लिखना चाहिए , जो आपको किताब के बारे में अच्छा न लगा हो । इसमें आप सभी negative points को लिख सकते हैं । Book review करते समय हमेशा critical रहें और ईमानदारी दिखाएं । आपकी किताब समीक्षा किसी भी पुस्तक के sales को घटा या बढ़ा सकती है इसलिए plz be honest !
Negative points को लिखते समय भी आप निम्न बिंदुओं पर गौर करें –
- क्या कहानी का main character पाठकों को entertain कर पाएगा या वह अपनी भूमिका सही से निभा पाया ?
- क्या आपको कहानी का अंत उबाऊपन लगा ? अगर हां तो क्यों ?
- क्या यह किताब / कहानी अपने main theme या topic से न्याय कर पाई ?
इन बिंदुओं को आप विस्तार से अपने किताब के नकारात्मक समीक्षा वाले भाग में लिख सकते हैं । इस तरह आप आसानी से और बेहतरीन तरीके से किताब के नकारात्मक पक्ष को भी पाठकों के समक्ष रख सकते हैं ।
4. अपने समीक्षा को round up करें
जिस तरह से आपने पूरी कहानी या किताब के कंटेंट को शुरुआत में summarise किया था ठीक उसी तरह आपको अपने book reviews को भी round up करना है । इसमें आप overall experience के बारे में बात करते हुए book recommendation भी कर सकते हैं । उदाहरण के तौर पर – यह किताब किसे पसंद आएगी ? क्या यह teenage बच्चो के पढ़ने लायक है ?
इसकेे अलावा आप ऐसी ही किसी अन्य किताब से compare भी कर सकते हैं । पर ध्यान रखें कि आप जिस भी अन्य किताब से compare करें , कम ही लिखें । ऐसा न लगे कि आप साथ ही किसी अन्य किताब की भी marketing कर रहे हों ।
5. किताब को rate करें
अगर आप जिस भी किताब का book review कर रहे हैं , उसका rating भी कर दें तो यह bonus point साबित होगा और आपके रीडर्स भी यह decide कर सकेंगे कि उन्हें यह पुस्तक पढ़नी है या नहीं । आप चाहें तो किताब के overall experience को 5 या 10 में से star दे सकते हैं ।
इस तरह आप समझ गए होंगे कि पुस्तक समीक्षा कैसे लिखें । पुस्तक समीक्षा को लिखने के लिए यह जरूरी 5 बिंदुओं को ध्यान में अवश्य रखें और बुक रिव्यू लिखना शुरू करें ।
How to write book review in Hindi – Examples
अगर आप How to write book review in Hindi का एक बेहतरीन Example तलाश रहे हैं , तो Femina वेबसाइट पर छपे Animal farm Hindi book review की पुस्तक समीक्षा को पढ़ सकते हैं । इसे पढ़कर आप सही मायने में किसी पुस्तक की समीक्षा कर सकते हैं ।
इसके अलावा भी अगर आप विद्यार्थी हैं तो learncbse पर इस पोस्ट को पढ़ सकते हैं जिसमें ढेरों पुस्तक समीक्षाएं मौजूद है । इसे आप पढ़कर अपने स्कूली परीक्षाओं में लिख भी सकते हैं ।
पुस्तक समीक्षा के लिए क्या Qualification हैं ?
पुस्तक समीक्षा करने के लिए कोई specific qualification की जरूरत तो नहीं है , फिर भी अगर आप एक expert book reviewer बनना चाहते हैं तो हिंदी / इंगलिश विषय में स्नातक या स्नातकोत्तर तक की पढ़ाई कर सकते हैं । इससे आपकी हिंदी या अंग्रेजी भाषा पर काफी अच्छी पकड़ हो जाएगी , जो आपको पुस्तक समीक्षा में काफी मदद करेगा ।
इसके अलावा भी आप पुस्तक समीक्षा लिखने से पहले इन बिंदुओं पर ध्यान दें –
- ज्यादा से ज्यादा किताबों को पढ़ें
- किताबों का मुफ्त में रिव्यू करना शुरू करें
- ऊपर बताए गए guidelines को ध्यान में रखकर ही book review करें
- Book review करते समय ईमानदारी दिखाएं और हमेशा रीडर्स की भलाई के बारे में सोचें
- अपनी इंटरनेट पर online presence बनाएं और सभी बुक रिव्यूज को अपने ब्लॉग पर रखें
- किसी खास genre की पुस्तक समीक्षा करने के लिए specialist बनें
- अपने सबसे बेहतरीन समीक्षाओं को इकट्ठा करें और जरूरत पड़ने पर clients को दिखाएं
- किसी बेहतरीन book community का हिस्सा जरूर बनें
- किसी भी बुक लॉन्च के एक महीने पहले से ही उस पुस्तक की समीक्षा की तैयारी करें
अगर आप ऊपर बताए गए सभी बिंदुओं पर ध्यान देकर book review in Hindi करते हैं तो आप आसानी से इस फील्ड में expert बन सकते हैं ।
Book review करने के लिए websites
अगर आप पुस्तक समीक्षा करने के लिए तैयार और eligible हैं तो आप content writing के अंतर्गत नीचे दिए वेबसाइट्स पर आने लिए जॉब ढूंढ सकते हैं ।
- writer fulbooks
- Kirkus Media
- Online Book Club
How to write book review in Hindi – Conclusion
अगर आप किसी भी पुस्तक की समीक्षा लिखना चाहते हैं या कर रहे हैं तो यह पोस्ट आपके लिए काफी लाभदायक साबित होगा । इसे आप पूरा पढ़ें और पोस्ट में लिखें बिंदुओं को पुस्तक समीक्षा करते समय अवश्य ध्यान में रखें । How to write book reviews in Hindi का यह पोस्ट अगर आपको पसंद आया हो तो शेयर अवश्य करें ताकि अन्य लोगों को भी फायदा हो ।
- Review meaning in Hindi
- Literature review meaning in Hindi
- Amish Tripathi Books in Hindi
- Motivational Books in Hindi
- Atomic Habits Book Summary in Hindi
- Best Osho Books in Hindi
- Human Psychology Books in Hindi
इसके साथ ही आप पोस्ट के बारे में नीचे कॉमेंट कर सकते हैं । हम इस वेबसाइट पर पुस्तक समीक्षा भी करते हैं , तो आपको किस पुस्तक की समीक्षा चाहिए उसे भी कमेंट के जरिए अवश्य बताएं ।
I have always had a passion for writing and hence I ventured into blogging. In addition to writing, I enjoy reading and watching movies. I am inactive on social media so if you like the content then share it as much as possible .
Related Posts
Escrow account meaning in hindi – एस्क्रो अकाउंट क्या है, personality development course free in hindi – पर्सनैलिटी डेवलपमेंट, iso certificate क्या होता है आईएसओ सर्टिफिकेट के फायदे और उपयोग.
Women emporment and bharat in hindi review
We’ll review this one in near future.
Very nicely written article, lot to learn from this. Good job they are very helpful for hindi review of books.
very nice content . thank you sir
Thanks Pramod, keep visiting.
Leave A Reply Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar

Writing Tips Oasis - A website dedicated to helping writers to write and publish books.
पुस्तक समीक्षा कैसे लिखें
By Smitha Abraham
उत्कट पाठक सामान्यतः इसमें रुचि लेते हैं कि जो पुस्तकें उन्होंने पढ़ी हैं उनके संबंध में अन्य पाठक क्या राय रखते हैं। ऐसे पाठक उन पुस्तक समीक्षाओं को पढ़ना पसंद करेंगे जो एक निष्पक्ष बोध उपलब्ध करेगी कि यह पुस्तक किस संबंध में है। यह निबंध आपको दर्शाएगा कि पुस्तक समीक्षा कैसे लिखते हैं।
पुस्तक के संबंध में कुछ वाक्य लिखिए
पहला नियम है पुस्तक की कहानी को कभी भी प्रकट नहीं करना। पाठकों की कल्पना के लिए कुछ छोड़ दीजिए। पुस्तक में होने वाली घटनाओं के विस्तृत विवरण से बचना अच्छा है। यदि पुस्तक त्रयी या किसी श्रृंखला का अंश है, तब आप इसका, और यदि आप सोचते हैं कि कि इसका आनंद लेने के लिए श्रृंखला की अन्य पुस्तकों को पढ़ना आवश्यक है, उल्लेख कर सकते हैं।
उस चीज की चर्चा कीजिए जिसने आपको इस पुस्तक में आकर्षित किया था
अपने-आप से पूछिए कि आपको इस पुस्तक में सबसे आकर्षक क्या लगा था। जो आपको आकर्षक लगा था वह पात्र, कथानक चा विषय-वस्तु में से कुछ भी या कोई और चीज हो सकती है। कहानी, और जिस तरह से इसे कहा गया है उस पर अपने अनुभव तथा सोच पर ध्यान केंद्रित कीजिए। आप स्वयं से निम्नलिखित प्रश्न पूछ सकते हैं और तदनुसार अपने उत्तरों पर आधारित एक समीक्षा लिख सकते हैं:
- आपकी पसंद का पात्र कौन था और क्यों?
- क्या पात्र आपको वास्तविक लगे थे?
- क्या कथानक में अनिश्चय/रोमांस या कोई ऐसी चीज थी जिसने आपको आकर्षित किया था?
- क्या पुस्तक ने आपको हँसाया या रुलाया था?
- दृश्य कैसे लिखे गए थे? वे किस प्रकार के दृश्य थे? उदाहरण के लिए आनंदपूर्ण दृश्य, रोमांटिक दृश्य, रहस्यात्मक दृश्य, इत्यादि।
- कथानक ने कैसा आकार लिया था? क्या कथानक ने आपके चित्त को आकर्षित किया था?
- क्या आपको संवाद पसंद आए थे? क्या कोई ऐसे संवाद थे जिनसे आप प्रेरित हुए थे?
- पुस्तक में समायोजन कैसा था? क्या यह ऊष्णतापूर्ण रोमांस था, या पागलपन भरे अभियान के लिए कोई विदेशी ठिकाना था? उदाहरण के लिए, कोई पर्वतीय क्षेत्र आसन्न संकट सूचित कर सकता है। वातावरण में व्याप्त गुलाबों की सुगंध रोमांस का सुझाव दे सकती है। किसी अस्पताल का प्रतीक्षा कक्ष विपदा सूचित करता है।
- किस तरह की शब्दावली का प्रयोग किया गया था? उदाहरण के लिए उत्तर प्रदेश के ग्रामीण व्यक्तियों के द्वारा प्रयोग की गई भाषा इसी राज्य के शहरी क्षेत्रों में रहने वाले व्यक्तियों से अलग सुनाई देगी।
पुस्तक के संबंध में किसी ऐसी चीज का उल्लेख कीजिए जो आपको पसंद नहीं आई थी
जहाँ आपको पुस्तक के अधिकांश अंश अच्छे लगे होंगे, कुछ ऐसा भी हो सकता है जो आपको पसंद नहीं आया हो। यह कहानी का अंत, जिस तरह से पात्रों से व्यवहार किया गया था, विषय-वस्तु, संवाद या समायोजन, कुछ भी हो सकता है। इसका वर्णन कीजिए।
अपनी पुस्तक समीक्षा का समापन कीजए
अपनी समीक्षा का सारांश यह उल्लेख करते हुए दीजिए कि किस प्रकार के पाठकों को यह पुस्तक आकर्षित करती है। यह युवा पाठक हो सकते हैं, वयस्क पाठक हो सकते हैं, नाटक, रोमांस, अनिश्चय, रहस्य या किसी अन्य विधा के कट्टर अनुगामी हो सकते हैं। यदि आप इस पुस्तक की आपके द्वारा पढ़ी गई किसी अन्य पुस्तक के साथ तुलना कर सकते हैं, तब उसे भी सम्मिलित कर लीजिए।
पुस्तक का मूल्यांकन कीजिए
पुस्तक का मूल्यंकन उपलब्ध कीजिए, उदाहरण के लिए, पाँच या दस में से स्कोर। यह पाठकों को एक अच्छी अवधारणा देगा कि पुस्तक को पढ़ा जाए या नहीं।
यहाँ पुस्तक समीक्षा की एक रूप रेखा दी गई है। इसे आप अपने विचारों तथा रुचि के अनुसार बना सकते हैं।
- एक रूपरेखा तैयार कीजिए
अपने नोट्स पढ़िए और अपनी समीक्षा का उद्देश्य लिखने के लिए उनके साथ मिलान कीजिए।
- प्रारूप लिखिए
अपने नोट्स मथिए और एक परिचय, मध्य तथा निष्कर्ष सम्मिलित कीजिए।
- प्रारूप का सुधार कीजिए
आपने जो लिखा है उसे फिर से पढ़िए, कछ समय व्यतीत होने दीजिए। तब वापस अपनी समीक्षा पर जा कर स्पष्टता, सामंजस्यता तथा व्याकरण, इत्यादि की जाँच कीजिए। [author] [author_image timthumb=’on’]https://writingtipsoasis.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/Smitha-Abraham.jpg[/author_image] [author_info]I’m Smitha Abraham. I love traveling in my flights of imagination and use these flights to craft short stories and poetry. I am a budding writer from India. My passions are reading, creative writing, listening to music, learning new languages, meeting new people, getting acquainted with different cultures and traveling. Authors like Isabel Allende, Gabriel Garcia Marquez, Carlos Ruiz Zafón, genres like magic realism, historical romance, and writing styles that are imaginative and flow effortlessly fascinate me. I love to unwind with a book curled up on a sofa or by gazing at the stars by the sea shore. I am a nature lover and spending time admiring the sunset and sunrise is relaxing for me.[/author_info] [/author]
What We Guarantee
- No Plagiarism
- On Time Delevery
- Privacy Policy
- Complaint Resolution
Constant customer Assistance
Finished Papers
Write my essay for me frequently asked questions
Abletricks.Com
Tips And Tricks
रिव्यू लिखकर पैसे कमाए – Review Likhe Aur Paise Kamaye in Hindi
October 30, 2018 by Tricks King 2 Comments
रिव्यु (Review) लिखकर पैसे कमाए (Review Likhe Aur Paise Kamaye) ऑनलाइन रिव्यु लिखे और पैसे कमाए, घर बैठे पैसे कमाने का तरीका।

Table of Contents
रिव्यू लिखकर पैसे कमाए (Review Likhe Aur Paise Kamaye in Hindi )
यदि आप लिखने के शौकीन है और आप अच्छा लिख लेते है तो यह लेख आपके लिए ही है, आप इससे घर बैठे अच्छी खासी कमाई कर सकते है। इसके लिए आपको किसी भी तरह का कोई निवेश करने की आवश्यकता है। हम यहां पे बात कर रहे है, रिव्यु लिख कर पैसे कमाने की। क्या आप जानते है रिव्यु (Review) किसे कहते है.. आइये पहले इस बारे में थोडा जान लेते है।
रिव्यु (Review) जिसे हम हिंदी में समीक्षा कह सकते है, रिव्यु लिखना यानी की गुण-दोष निरूपण करना है। रिव्यु लिखे और पैसे कमाए.. आइये इसका मतलब समजते है। इस आर्टिकल के अनुसार “रिव्यु लिखे (Review Likhe) पैसे कमाए” का मतलब.. प्रोडक्ट के गुण-दोष के बारे में लिखना और पैसे कमाना है। आपको बता दे की आप इस काम से भी काफी अच्छी कमाई कर सकते है, कई लोग यह काम पार्टटाइम के तौर पर करते है, आप भी कर सकते है।
आप कई बार देखते होंगे, जब आप इन्टरनेट पर किसी प्रोडक्ट के बारे में सर्च करते है तो आपको उस प्रोडक्ट के निचे ऐसे कई रिव्यु लिखे दिखते होंगे, बस इसी तरह के रिव्यु आपको लिखने है जिसके बदले में आपको पैसे दिए जायेंगे। जानकारी के लिए हम आपको बता दे की आपको 1 रिव्यु लिखने के 40 रुपये मिलते है, यदि आप 10 रिव्यु लिखते है तो आपको 400 रुपये मिलेंगे। आप इस तरह जितने ज्यादा रिव्यु लिखेंगे उतने ज्यादा पैसे कमा सकते है।
अब आप यह सोच रहे होंगे की आप यह काम कहां करेंगे अर्थात आप यह काम इन्टरनेट पर कहां करेंगे..आइये इस बारे में आगे जानते है, रिव्यु लिखे (Review Likhe) पैसे कमाए पूरी जानकारी।
रिव्यु लिखकर पैसे कमाए (Review Likhe Aur Paise Kamaye in Hindi )
इन्टरनेट पर ऐसी बहुत सी वेबसाइट्स मौजूद है जो रिव्यु लिखने का काम प्रदान करती है और उसके बदले में पैसे देती है। यहां पर हम आपको एक ऐसी ही वेबसाइट के बारे में बताने जा रहे है, जो आपको रिव्यु लिखने का काम देती है और उसके बदले में पैसे देती है, आइये इसके बारे में विस्तार से जानते है।
Mouthshut वेबसाइट से पैसे कमाए
यह वेबसाइट एक बहुत ही अच्छी वेबसाइट है, इस वेबसाइट पर अकाउंट बनाने के बाद आपको रिव्यु लिखने का काम दिया जाता है। यहां पर आप अपनी पसंद के किसी भी प्रोडक्ट के ऊपर रिव्यु लिख सकते है, क्योंकि इस वेबसाइट पे ऐसे लाखो प्रोडक्ट उपलब्ध है, जिसके ऊपर आप रिव्यु लिख सकते है और अच्छी खासी कमाई कर सकते है।
Note : इस काम के लिए आपकी इंग्लिश भाषा में काफी अच्छी पकड़ होनी चाहिए क्योंकि आपको प्रोडक्ट के रिव्यु इंग्लिश भाषा में लिखने है और वो रिव्यु आपको कहीं से भी कॉपी नहीं करना है बल्कि वो रिव्यु आपका खुद का लिखा होना चाहिए। यदि आप किसी का लिखा हुवा रिव्यु कॉपी पेस्ट करते है तो आपको पैसे नहीं मिलेंगे।
Mouthshut वेबसाइट पे अकाउंट कैसे बनाए
सबसे पहले आपको https://www.mouthshut.com इस वेबसाइट पे जाना होगा। उसके बाद ऊपर दिए हुए आप्शन में से Free Sign Up आप्शन पे क्लिक करे।
अब एक पेज खुलेगा उसमे आप फेसबुक द्वारे या जीमेल अकाउंट द्वारे अपना अकाउंट बना सकते है, या फिर आप अन्य ईमेल द्वारे भी अपना अकाउंट बना सकते है।
यदि आप फेसबुक अकाउंट द्वारे अपना अकाउंट बनाना चाहते है तो Sign in with facebook पे क्लिक करे। या यदि जीमेल अकाउंट द्वारे अपना अकाउंट बनाना चाहते है तो Sign in with Google पे क्लिक करे। या यदि किसी अन्य ईमेल अकाउंट द्वारे अपना अकाउंट बनाना चाहते है तो निचे दिए हुए Sign Up with Email आप्शन पे क्लिक करे। आप इसपे बहुत ही आसानी से अपना अकाउंट बना सकते है।
अब मान लेते है की इसमें आपने इस वेबसाइट पे अपना अकाउंट बना लिया है, आइये अब आगे की प्रोसेस के बारे में जानते है। Mouthshut.Com इस वेबसाइट से पैसे कैसे कमाए, इस बारे में।
Mouthshut.Com वेबसाइट से पैसे कैसे कमाए
अब आपको उस वेबसाइट पे लॉग इन करना है, यदि आप लॉग इन है तो आगे बढे। अब ऊपर दिए हुए विकल्प में से Write Your Review बटन पे क्लिक करे। अब एक सर्च आप्शन खुलेगा उसमे आपको जिस भी प्रोडक्ट का रिव्यु लिखना उस प्रोडक्ट का नाम लिख कर सर्च करना है। उसके बाद एक पेज खुलेगा उसमे आपको प्रोडक्ट के ऊपर रिव्यु लिखना है और सब होने के बाद Submit Review पे क्लिक करना है।
प्रोडक्ट रिव्यु कैसे लिखे (Review Likhe Aur Paise Kamaye in Hindi)
- सबसे पहले यह बाताये की आप उस प्रोडक्ट को लाइक करते है या नहीं, Yes Or No में बताये।
- उसके बाद उस प्रोडक्ट को अपने अनुभव के हिसाब से Star Rating दे।
- उसके बाद अपने अनुभव के हिसाब से टाइटल लिखे।
- उसके बाद उसके निचे के बॉक्स में वह प्रोडक्ट कैसा है, उस प्रोडक्ट के बारे में आपका अनुभव लिखे।
- उसके बाद यदि आपके पास कोई फोटो है तो वह अपलोड करे, यदि नहीं है तो रहने दे।
- उसके बाद निचे दिए विकल्पों में आप अपने हिसाब से आप्शन सिलेक्ट कर सकते है।
- उसके बाद अन्तः में आपको Submit Review पे क्लिक करना है।
- अब आपके द्वारा सबमिट किये गए रिव्यु की जांच की जायेगी, इसके लिए 48 घंटों का समय भी लग सकता है। उसके बाद आपका रिव्यु अप्प्रोव किया जाएगा। जब आपका लिखा रिव्यु अप्प्रोव हो जाता है तब आपके इस वेबसाइट के अकाउंट में कुछ MS Point क्रेडिट किये जाते है।
इसमें 1 MS Point एक रुपया के बराबर होता है, जब आपके अकाउंट में 500 MS Point जमा हो जाते है तब आपको बैंक डिटेल्स अपडेट करनी होती है। आपको बता दे की, इसका पेमेंट हर महीने 1 से 10 तारीख तक बैंक अकाउंट में मिल जाता है।
यह भी जरुर पढ़े :
- iWriter से पैसे कैसे कमाए
- बिना पैसा लगाए पैसा कमाए
- फेसबुक पैसे कैसे कमाती है
- गूगल से लाखो रुपये कमाए
- फ्लिपकार्ट से पैसे कमाए
Tags : Online Colleges, Degree Course, Classes, Salary, Review Money, Personal, Car, Motor Loan Insurance, Online Money Making Tips.
Related keyword : रिव्यु (Review) लिखकर पैसे कमाए (Review Likhe Aur Paise Kamaye) ऑनलाइन रिव्यु लिखे और पैसे कमाए, घर बैठे पैसे कमाने का तरीका।
दोस्तों, यदि आपको “ रिव्यू लिखकर पैसे कमाए ” यह जानकारी उपयोगी लगे तो इसे अपने दोस्तों में एवं परिचित लोगों में शेयर जरुर करे तथा इस आर्टिकल से रिलेटेड आपका कोई भी सुझाव या सवाल हो तो आप निचे कमेंट बॉक्स में कमेंट करके हमें पुछ सकते है।
ये आर्टिकल भी जरुर पढ़े :
इस तरह की रोचक खबरे प्राप्त करने के लिए हमारे फेसबुक पेज को लाइक जरुर करे और इस लेख को Social sites पर Share करना ना भूले।
Share this:
About Tricks King
यह, एबलट्रिक्स डॉट कॉम के लिए नौकरी, शिक्षा और टेक्नोलॉजी से संबंधित लेख लिखते हैं. इन्हें पढ़ने-लिखने और नई नई जानकारी हासिल करने का बहुत शौक है. यह लंबे समय से एबलट्रिक्स डॉट कॉम के साथ जुड़े हुए है.
October 31, 2018 at 3:32 AM
Nice information, keep it up.
October 31, 2018 at 3:33 AM
Keep visiting..
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Privacy policy
Please do not share any of your personal information on this website. Such as bank related information, Aadhaar number, PAN number, mobile number, etc.
If you find anything wrong on this website, then you tell us through the comment, we will try to correct it as soon as possible.
Useful Links
- Request a call back
- Write For Us
Well-planned online essay writing assistance by PenMyPaper
Writing my essays has long been a part and parcel of our lives but as we grow older, we enter the stage of drawing critical analysis of the subjects in the writings. This requires a lot of hard work, which includes extensive research to be done before you start drafting. But most of the students, nowadays, are already overburdened with academics and some of them also work part-time jobs. In such a scenario, it becomes impossible to write all the drafts on your own. The writing service by the experts of PenMyPaper can be your rescuer amidst such a situation. We will write my essay for me with ease. You need not face the trouble to write alone, rather leave it to the experts and they will do all that is required to write your essays. You will just have to sit back and relax. We are offering you unmatched service for drafting various kinds for my essays, everything on an online basis to write with. You will not even have to visit anywhere to order. Just a click and you can get the best writing service from us.
Customer Reviews
Estelle Gallagher
How to Order Our Online Writing Services.
There is nothing easier than using our essay writer service. Here is how everything works at :
- You fill out an order form. Make sure to provide us with all the details. If you have any comments or additional files, upload them. This will help your writer produce the paper that will exactly meet your needs.
- You pay for the order with our secure payment system.
- Once we receive the payment confirmation, we assign an appropriate writer to work on your project. You can track the order's progress in real-time through the personal panel. Also, there is an option to communicate with your writer, share additional files, and clarify all the details.
- As soon as the paper is done, you receive a notification. Now, you can read its preview version carefully in your account. If you are satisfied with our professional essay writing services, you confirm the order and download the final version of the document to your computer. If, however, you consider that any alterations are needed, you can always request a free revision. All our clients can use free revisions within 14 days after delivery. Please note that the author will revise your paper for free only if the initial requirements for the paper remain unchanged. If the revision is not applicable, we will unconditionally refund your account. However, our failure is very unlikely since almost all of our orders are completed issue-free and we have 98% satisfied clients.
As you can see, you can always turn to us with a request "Write essay for me" and we will do it. We will deliver a paper of top quality written by an expert in your field of study without delays. Furthermore, we will do it for an affordable price because we know that students are always looking for cheap services. Yes, you can write the paper yourself but your time and nerves are worth more!

Customer Reviews
Frequently Asked Questions

Compare Properties
How does this work.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Read more: https://researchersquest.wordpress.com/2021/10/11/easy-method-to-write-literature-review-in-research-paper/Subscribe to my Youtube ChannelIf you e...
This is PART 1 video on establishing the base for review of literature. It includes explanations with examples on how you can search for papers and articles ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
In this video- literature review in hindi, I discussed- what is literature review what are the sources available for literature review. literature review in...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
Okay - with the why out the way, let's move on to the how. As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter.
Literature review को हिंदी में साहित्य समीक्षा कहते हैं । आप जिस चीज की जांच कर रहे हैं और जो आपके विषय क्षेत्र में पहले ही जांच की जा चुकी है, के ...
한국어: 리포트 쓰는 방법. 日本語: 研究論文を書く. सभी लेखकों को यह पृष्ठ बनाने के लिए धन्यवाद दें जो १,३६,७३८ बार पढ़ा गया है।. कैसे एक शोधपत्र (Research Paper) लिखें ...
Literature Review (rough draft) Demographic Variables. Age. According to McClean and Beak (2012), research findings have shown that for the majority of crimes where a firearm is used, the offender is mainly in the middle to late adolescence after which there is a sharp and permanent drop. This is referred to as the age-crime-curve and has been ...
The video is presenting the tips and tricks to write the literature review without reading the complete research paper word to word. In this video, it is dem...
ऑटिकल लिखते समय इस बात का हमेशा आपको ध्यान रखना है कि आप किसी भी शब्द को एक से ज्यादा बार अपने ऑटिकल में इस्तेमाल नहीं करें। अब इसका ...
How to write book review in Hindi. 1. किताब की short summary लिखें. किसी भी किताब की समीक्षा करते समय , शुरुआत में उसकी short summary अवश्य लिखें । इससे लेखकों को उस किताब के ...
The articles reviewed in this congoceptual review paper have been downloaded from google, google scholar, emerald data base, International Journal Of Scientific Research and Management and various other journals and sources. In total 55 articles published in between 2006-2015 have been chosen for review. IV. Review of literature
Writing Tips Oasis - A website dedicated to helping writers to write and publish books.
Pay For Essay Writer Help. Level: University, College, Master's, High School, PHD, Undergraduate, Entry, Professional. ID 12417. Review Category. 1753. Finished Papers. Free essays. Job Application Letter Kaise Likhe, Disobey A Lawful Order Article 92, Homework Leading To Depression, New York Public Library Homework Help, Resume Styles Or ...
Following are the concepts discussed in this video:What is literature review,literature review in research methodology in hindiliterature review in urduliter...
For Sale. ,485,000. Essay Kaise Likhe In Hindi, Example Of A Research Literature Review, Resume Wizard Program, Expository Editor Services Us, Mentoring Phd Thesis, Painting And Decorating Business Plan Free, Popular Literature Review Ghostwriters Websites For University. 4.9 stars - 1387 reviews.
रिव्यु लिखकर पैसे कमाए (Review Likhe Aur Paise Kamaye in Hindi). इन्टरनेट पर ऐसी बहुत सी वेबसाइट्स मौजूद है जो रिव्यु लिखने का काम प्रदान करती है और उसके बदले में पैसे देती है ...
Application Letter Kaise Likhe, Writing Essay On Your Family, Purpose Of A Cover Letter For Resume, Cover Letter Examples For Custodian Jobs, How To Write A Cnclusion For A Persuuasive Essay, Writing A Descriptive Essay On A Person, Esl Analysis Essay Editor Site For School. ID 12011. amlaformulatorsschool. 4.7 stars - 1189 reviews.
This video contains the complete outline of how to write a literature review for any kind of research or review paper, dissertation, research proposal, and s...
First, you have to sign up, and then follow a simple 10-minute order process. In case you have any trouble signing up or completing the order, reach out to our 24/7 support team and they will resolve your concerns effectively. User ID: 407841. Essay on Healthcare.
Telegram Channel- https://t.me/successclassesa1