

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Education /
Business Studies Class 12 Project: Marks Distribution, Topics, and More
- Updated on
- Jan 16, 2024

Looking for a Class 12 Business Project? CBSE has mandated students to prepare a project as part of the Class 12 Business Studies syllabus wherein they can conduct their own research, gather primary or secondary data and make inferences out of the results in a presentable way. If you are struggling to make a nice project and want to have good guidance, read on to find everything you need to know about the Business Studies class 12 project and BST project class 12 on marketing management , principles of management, stock exchange and more.
This Blog Includes:
- CBSE BST Project Class 12 2023-24: Marks Distribution
CBSE Class 12 BST Project Topics 2023-24
Marketing management, elements of business environment , principles of management project in business studies, stock exchange, important guidelines, cbse bst project class 12 2023-24 : marks distribution.
The revised Business Studies Class 12 syllabus 2022-23 allotted 20 marks to the project work. Take a look at the distribution of marks for Class 12 Business Studies Project 2023-24:
Click here to download the official CBSE Class 12 Business Project Topics
Here are the best BST project class 12 topics:
- Elements of Business Environment
- Consumer Protection
Also Read: Controlling Class 12: Important Revision Notes
For this BST project class 12 on Marketing Management, The students can consider the following products and conduct research to gather information about the various aspects concerning the marketing of the product. Some of the most prominent and sought-after products are mentioned in the table below:
The students can choose either of the aforementioned or any of the products permissible by the teacher for their Business Studies Project. Taking any one of the products into consideration, the students will have to gather information on the following parameters.
- Profit margin in percentage to the manufacturer, wholesaler and retailer
- Packaging of the product
- Selling price to the consumer
- Promotion or marketing of the product
- Identify the USP
- Type/category of product
- Grading and standardization
- Channels of distribution
Also Read: Courses & Career Options in Commerce without Maths
In this topic of the Business Studies class 12 project, given below are the important elements of the business environment:
- Changes witnessed in packaging and economic impact over the last few years in relation to products like fruits and vegetables, plastic/wooden furniture, milk, reuse of packages, packages as a means of advertisement, etc.
- Reasons behind the changes in “ Coca Cola and Fanta in the 70s decade to Thums up and Campa Cola in the 80s decade to Pepsi and Cola in the 90s. ”
- Changes in the patterns of export and import of different products.
- The law, effects and implementation of the anti-plastic campaign.
- Social factors affecting acceptance and rejection of an identified product (atta maker, dishwasher)
- Effect of changes in the technological environment on employee behaviour.
Also Read: Top 20 Career Options in Commerce with Maths Stream
Under this subject of the Business Studies class 12 project, the students are required to visit any departmental store, fast food outlet or any industrial unit and perceive if applications like Fayol’s General Principles of Management or F.W. Taylor’s Scientific Management Techniques are applied or not. For clarification, have a look at the principles and techniques advocated by both the administrative gurus:
Also Read: Commerce Subjects in Class 12 [Download Updated PDF]
The students who opt for the third option in the business studies class 12 project will have to learn various aspects of the stock market, monitor the stock market trends and how calculate profit or loss in relation to stock. Through this topic, the students will be able to learn about the capital market and the sources of business finance along with a deep understanding of the concepts used in the stock exchange. Business Studies class 12 project will expect the students to work on the following parameters:
- Create a brief report on the history of stock exchanges in India.
- Prepare a hypothetical portfolio with a sum of INR 50,000 in any 5 top companies over a period of 20 working days.
- Identify the reasons for fluctuations in prices, for example, change of seasons, strikes and accidents, political environment, the spread of an epidemic, international events, etc.
- Find the value of the investments and update the portfolio accordingly through various graphical representations.
Also Read: Business Studies Class 11 Syllabus, Exam Pattern & More
Here are the official CBSE guidelines for the Class 12 Business Studies project:
- The entire project must be completed between 25 to 30 pages
- It is compulsory for class 12th students that the project must be handwritten
- The project must be clubbed inside a neat and tidy transparent folder
- Cover Page: Student information, School name and year
- Index (List of Contents)
- Acknowledgement and Preface
- Introduction
- Topic with a Unique Title/Heading
- List of activities and planning done to gather information about the project (If any)
- Observations from the places of visit
- Conclusions
- Photographs (if any)
- Teacher’s remarks
- Signature of the teachers
Related Reads
Ans: The official CBSE guidelines for the Class 12 Business Studies project are: 1. The entire project must be completed between 25 to 30 pages 2. It is compulsory for class 12th students that the project must be handwritten 3. The project must be clubbed inside a neat and tidy transparent folder 4. While crafting your project, you must follow this specified format: -Cover Page: Student information -School name and year -Index (List of Contents) -Acknowledgement and Preface -Introduction -Topic with a Unique Title/Heading -List of activities and planning done to gather information about the project (If any) -Observations from the places of visit -Conclusions -Photographs (if any) -Appendix -Teacher’s remarks -Signature of the teachers
Ans: The business studies project is an important part of the Class 12 business studies curriculum and is of a total of 20 marks.
Ans: There are a total of 12 chapters in Class 12 business studies.
Ans: To crack your business studies exam, you must practice sample papers and previous year exam papers of business studies as well as master the basic concepts of every chapter.
We hope that this blog covered every single aspect essential for you to know about the Business Studies class 12 project. Connect with us at Leverage Edu and we will help you choose the right course and university after 12th that goes well with your dream of becoming one of the future business leaders . Book your 30 minutes of free career counselling now! For more on NCERT study materials and school education , follow Leverage Edu now!!
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
Hi Muskan, Thanks for your feedback!
Hi Muskan, Thanks for your feedback! We hope this may interest you https://leverageedu.com/blog/accounts-project-class-12/
It help me a lot😊thanks for sharing this project with us😊
It’s too good and easy to prepare…… Thanks a lot it’s very helpful
Hey Shreya!
We are happy to help! If you want similar content then subscribe to our newsletter!
Thank you, for sharing such informative blog. It seems very interesting and very informative. It helped a lot, keep sharing…!!
Thank you for your comment!

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Chapter 11 - Marketing
- NCERT Solutions

Class 12 NCERT Solutions Business Studies - Marketing - Free PDF Download
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 by Vedantu gives students a great opportunity to get access to the best study material available. NCERT Solutions is the best choice for promising marks in various examinations related to Class 12 Chapter 11 Marketing. Currently, when there is a wide range of online materials available, our NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies can be recognized as the best platform to get reliable notes and can vouch for quality content. Even students who usually find it difficult to grasp concepts can sit back and use this to witness a drastic change.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 Marketing is beneficial for students while preparing for the CBSE Class 12 Business Studies examinations. NCERT Solutions for Business Studies Chapter 11 Marketing in PDF format includes solutions to all the questions asked in the chapter, that will surely help students to understand the concepts of each and every topic in a better way. The solution presents a clear picture of what the market is and its functioning. To get a precise understanding of the chapter, download NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chapter 11 Marketing free PDF through the PDF link given below.
Topics Covered In Business Studies Chapter 11 Marketing
Introduction to Marketing
Features of Marketing
Marketing Management
Marketing Management Philosophies (Production Concept, Product Concept, The Marketing Concept, The Selling Concept, The Societal Marketing Concept)
Functions of Marketing
Role of Marketing
Marketing Mix Elements (Product, Price, Place, And Promotion)
Advertising
Physical Distribution
Personal Selling
Related Chapters
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 – Marketing
Very Short Questions
1. Explain the advantages of branding to marketers of goods and services.
Ans: Branding entails giving a product a distinct name, sign, symbol, or term for identification. The following are the benefits of branding for marketers.
i) Branding allows a company to differentiate its product from the products of other companies.
ii) It makes product advertising easier. Only after a product has been given a brand can it be advertised and thus attract customers. It is illegal to promote a product with a generic name.
iii) Through effective branding, manufacturers can foster product loyalty and habituation. As a result, the company can profit from this and charge a different price for its product.
iv) It aids in the establishment of a foundation if a new product is to be launched. This is because it is expected that if a new product is launched under a good and established brand, it will receive a good boost and benefit from the brand's reputation.
2. List the characteristics of a good brand name.
Ans: The following characteristics define a good brand name.
i) The name should be brief and simple to spell, pronounce, and remember. Ponds, Rin, and so on.
ii) A brand should suggest the product's benefits or qualities while also fitting its functions. As an example, consider the words Boost, Fair & Lovely.
iii) The name should be distinct while also being adaptable to packaging and labeling requirements. It should also be adaptable to different advertising mediums and languages.
iv) A brand name should be adaptable and able to accommodate new products introduced under the brand.
v) It must be distinguishable and legally protectable.
3. What is the societal concept of marketing?
Ans: According to the societal concept of marketing, organizations must identify the market's and target consumers' needs and efficiently deliver the desired results. The organization should identify not only the market's immediate needs, but also the consumers' long-term well-being. Thus, in addition to customer satisfaction, organizations should strive for ecological, ethical, and social goals such as pollution, resource scarcity, and so on.
4. List the characteristics of convenience products.
Ans: Convenience products are those that are purchased frequently, quickly, and with minimal time and effort. A convenience product has the following characteristics.
i) Such products are easily accessible in convenient locations, requiring little time and effort.
ii) Convenience products are frequently consumed and have a steady demand. In general, essential commodities are classified as convenience products.
iii) They are available in small quantities at low and consistent prices.
iv) There is a lot of competition in the market for such products. As a result, these products will require extensive advertising.
5. Enlist the advantages of packaging of a customer product.
Ans: The process of developing and designing a product's container is referred to as packaging. The following are the benefits of good packaging.
i) It allows a product to be distinguished and identified from other products.
ii) It serves as a marketing tool. The use of colors, pictures, and symbols in packaging aids in attracting customers.
iii) Appropriate packaging adds to the ease of handling the product.
iv) It aids in the protection of the product's quality from any type of damage. It aids in the prevention of spoilage, breakage, and other damage, particularly during storage and transportation.
6. What are the limitations of advertising as a promotional tool? Enlist.
Ans: The limitations of advertising as a promotional tool are as follows.
i) It lacks personal communication and thus is less powerful.
ii) Evaluating the effectiveness of the advertisement is extremely difficult.
iii) Advertisements are pre-packaged and cannot be customized to meet the needs of different consumer groups.
iv) Advertising effectiveness is low because there may be numerous advertisements.
7. List five shopping products purchased by you or your family during the last few months.
Ans: The following shopping items were purchased.
i) Clothes
ii) Jewelry
iii) Television
iv) Shoes
v) Household goods
Short Questions
1. What is marketing? What functions does it play with the process of exchange of goods and services? Explain.
Ans: Marketing is the process by which buyers and sellers interact with one another in order to purchase and sell goods and services. Previously, different approaches to marketing's definition were taken. It is also sometimes called as a process which occurs post-production involving the purchase of the final products, and other times as a pre-production process involving the merchandising (designing) of the product. In reality, marketing is said to be a much broader concept. It includes all of the activities involved in the exchange of goods and services between producers and consumers. These are the functions that fall under the purview of marketing. It entails product planning, design, packaging and labeling, standardization, branding, warehousing, transportation, advertising, pricing, and distribution. It also includes activities that are carried out even after the product has been sold, such as maintaining customer relations and gathering feedback. As a result, marketing plays an important role in the exchange of goods as well as services.
2. Distinguish between the product concept and production concept of marketing.
Ans: The difference between two concepts of marketing are mentioned below:
3. Product is a bundle of utilities? Do you agree? Comment.
Ans: When a customer decides to purchase a product, his or her primary focus is on the utility that he or she will receive from using it. A customer seeks various levels of satisfaction from a product. A product's benefits can be classified into three types: functional benefits, psychological benefits, and social benefits. For example, when a consumer buys a car, it provides him with functional utility as a mode of transportation. In addition, having purchased a car provides him with a psychological benefit in the form of pride and self-esteem. It also comes with a social benefit in the form of peer acceptance. As a result, a product is said to be a bundle of utilities, and a buyer values all such utilities when purchasing a product.
4. What are industrial products? How are they different from consumer products? Explain.
Ans: Industrial products are those that are used as inputs in the manufacture of other goods. These items are not intended for final consumption; rather, they are used as raw materials and inputs by manufacturers in the production of consumer goods. Machines, tools, and so on are examples of industrial products. In contrast, consumer products are those that are used by the ultimate customers for their personal consumption. Consumer goods include items such as toothpaste, edible oil, furniture, and so on. The distinctions between industrial and consumer products are highlighted in the following points.
5. Distinguish between convenience products and shopping products.
Ans: The difference between convenience products and shopping products is given below:
6. 'Products is a mixture of tangible and intangible attributes'. Discuss.
Ans: In general, a product is a tangible asset with physical characteristics. For example, we consider a motorcycle or a laptop to be products. However, when it comes to marketing a product, it is important to consider not only the physical or tangible attributes of the product, but also certain intangible attributes. That is, a consumer's decision to buy a product is influenced not only by its tangible characteristics, but also by certain intangible characteristics. In other words, a consumer buys a product for reasons other than its functional utility, such as brand recognition, reputation, social satisfaction, and so on. When a person buys a laptop, he looks for intangible attributes such as guarantee, brand, and so on, in addition to the physical attributes and functional utility of the model, size, features, and so on. As a result, a product is a combination of tangible as well as intangible attributes.
7. Describe the functions of labelling in the marketing of products.
Ans: Labeling plays an important role in product packaging during the marketing process. Labeling essentially provides information about the product in the form of a tag (in the case of unbranded local products such as rice, wheat, and so on) or graphics (such as a lady applying cream on face for a face cream). Labeling serves several functions, the most important of which are as follows.
i) Contents and Description of Use: The primary function of labeling is to provide information about the product's use, application, warnings, content, and so on. For example, the contents of a shampoo bottle are written on the bottle, along with warnings such as "keep away from children under the age of 10." Similarly, a picture of noodles describing its appearance can be found on food products such as Maggie Cuppa Mania. Along with this, the ingredients and method of preparation are specified.
ii) Identification and Distinction: A label makes it easier to identify a product. It assists consumers in differentiating their preferred products from others. In a potato chip product, for example, a man eating potato chips is imprinted for identification. A label also contains useful information such as the manufacturer's name or address, net weight, maximum retail price, batch number, and so on.
iii) Standardization and Evaluation: A label also aids in the determination of a product's grade. This allows marketers to categorize the product into different categories based on specific qualities or features. For example, a face-cream brand may be divided into three categories: oily skin, dry skin, and normal skin.
iv) Encourages Production: An appealing label also aids marketers in promoting the product. It aids in attracting new customers to the product. For example, the label for Maggi Noodles reads, "Taste bhi, Health bhi." In this case, the label is crucial in highlighting the product and promoting its sale.
v) Information Necessary for Law: The label also provides and mentions the information that is required by law to be included. On a packet of tobacco, for example, it says, 'chewing tobacco is harmful to your health.'
8. Discuss the role of intermediaries in the distribution of consumer non-durable products.
Ans: Intermediaries are crucial in the distribution of consumer nondurables. They facilitate the movement of goods from the point of manufacture to the point of consumption. In the case of nondurables, the intermediaries perform the following functions.
i) Arrangement: An intermediary receives goods from a variety of sources. He then categorizes these items into homogeneous groups based on characteristics such as size, quality, and so on. For example, an electronic goods seller may receive a supply of various electronic goods (TV, washing machine, etc.) and then sort them according to their functions.
ii) Collection: An intermediary keeps a large stock of goods on hand to ensure an easy flow of supply. For example, an electronic goods seller may keep a large stock of each type of electronic item.
iii) Allocation and Packing: This function entails dividing larger stock into smaller units. For example, each electronic item and its spare parts are packed separately.
iv) Creating Variety: An intermediary obtains various goods from various sources and assembles them in a single location. As a result, it keeps a wide range of goods. He obtains the products and then sells them in various combinations as desired by the customers. Most people, for example, prefer a television and a video player together. As a result, the retailer can sell a mix of the two.
v) Promotion of Product: They help the manufacturers with their promotional efforts. Manufacturers, for example, use advertising to promote their product. Intermediaries can help this process by displaying banners and other advertisements. For example, an electronic goods retailer may display banners highlighting the features of various products.
vi) Mediation: Middlemen are responsible for negotiating a deal that will satisfy both the producers and the consumers. They negotiate the price, quality, quantity, and so on for an efficient transfer of ownership that meets the needs of both parties.
vii) Bearing Risk: Intermediaries buy goods from manufacturers and keep them in their possession until the final sale. During the process, they are vulnerable to fluctuations in demand, price, spoilage, and so on. Assume a retailer purchases a large number of air conditioners. However, after a few months, winter arrives, and demand for air conditioners decreases. As a result, the stock remains unsold, and the retailer suffers a loss.
9. Explain the factors determining choice of channels of distribution.
Ans: One of the most important marketing decisions is deciding which channel of distribution to use. The following factors influence channel selection.
(i) Product Category: The channel of distribution chosen is determined by the type of product produced. It is critical to determine whether the product is perishable or non-perishable, whether it is an industrial or consumer product, whether its unit value is high or low, and the product's degree of complexity. For example, if a product is perishable, short channels should be used rather than long ones. Likewise, if a product has a low unit value, a longer channel is preferred. Similarly, consumer goods are distributed via long channels, whereas industrial goods are distributed via short channels.
ii) The Company's Characteristics: The two most important characteristics of a company that influence channel selection are its financial strength and the level of control it desires over intermediaries. Shorter channels necessitate more funds than longer channels, but they also provide greater control over the channel's members (intermediaries). As a result, companies that are financially strong or want to have more control over the distribution channel choose shorter distribution channels.
iii) Factors of Competition: The degree of competition and the channels chosen by other competitors influence the distribution channel selection. Depending on its policies, a company may choose to use the same channel as its competitors or a different channel. For example, if a company's competitors choose to sell through a retail store, the company may do the same, or it may choose a different channel, such as direct selling.
iv) Environmental Aspects: Environmental factors such as economic constraints and legal policies all play a role in channel of distribution selection. For example, the requirement of complex legal formalities at each stage of distribution encourages companies to choose shorter distribution channels.
v) Market Elements: Other factors influencing channel selection include market size, geographical concentration of buyers, quantity demanded, and so on. Shorter channels, for example, are used when potential buyers are concentrated in a small geographical area. In contrast, if the buyers are spread out over a larger area, longer distribution channels may be used.
10. Explain briefly the components of physical distribution.
Ans: Physical distribution is the movement of goods from the point of manufacture to the point of consumption. The components of physical distribution are as follows.
i) Processing of Order: Order processing consists of several steps, including order placement, transmission of the order by intermediaries to the manufacturer, inventory maintenance as needed, delivery of goods, and so on. Because all of these processes take time, a physical distribution system should be designed to ensure quick and accurate order processing. In summary, order processing speed and accuracy are directly related to customer satisfaction. Fast and accurate order processing leads to higher levels of customer satisfaction.
ii) Transportation of Products: The physical movement of goods from the point where they are manufactured to the point where they are consumed is referred to as product transportation. Transporting goods from the point of production to the point of consumption is required to make them physically available to consumers.
iii) Warehousing: The process of storing manufactured goods prior to the final act of sale is known as warehousing. If we suppose that a company has a lot of warehouses then it indicates that the company will be able to provide goods at various locations more quickly and also on time. However, maintaining warehouses comes with its own set of expenses. As a result, a company must weigh the relative benefits and costs of warehousing and strike a balance between the two as needed.
iv) Maintenance of Inventory: Inventory is kept on hand by the companies to ensure that products are delivered on time. Inventory maintenance, like warehousing, has a positive relationship with customer service. However, inventory maintenance comes at a cost because a large amount of capital remains locked up in the stock until it is sold. As a result, the companies must strike a balance between customer service and cost.
11. Define advertising. What are its main features? Explain.
Ans: Advertising is a marketing technique that is used to promote a product. Companies use advertising to attract customers to their products and persuade them to buy them. Newspapers, magazines, television, and other forms of advertising are common. The following are some of the most important aspects of advertising.
(i) Cost Involved: Advertising is not free. It is a form of paid promotion. The costs of advertising will be borne by the sponsors.
ii) Impersonal Mode: Advertising is a form of impersonal communication. In other words, there is no direct interaction between the customer and the advertiser. As a result, it lacks personality and creates a monologue.
iii) Specific Sponsor: There are always a few individuals or sponsors who take on the responsibility of designing it and bearing the associated costs.
12. Discuss the role of 'sales promotion' as an element of promotion mix.
Ans: Sales promotion refers to the incentives provided to buyers in order to persuade them to purchase the product. It included activities such as providing discounts, gifts, and free samples, among others. These activities supplement the company's other promotional efforts, such as advertising and direct selling. They are increasingly attracting customers and persuading them to buy the product right away. Such activities are especially beneficial during the launch of a new product. They provide a temporary boost to sales. Discounts are given by selling the product at a lower price than the listed price, for example. Quantity gifts are given away as freebies (such as 20 percent extra or buy 2, get 1 free). When a new brand is launched, free samples are distributed in the form of small packets. Companies use such incentives to attract more customers and increase sales.
Long Questions
1. Define marketing. How is it different from selling? Discuss.
Ans: Marketing is the process by which buyers and sellers interact with one another in order to purchase and sell goods and services. It includes a variety of activities such as product planning, design, packaging and labeling, pricing, and distribution, as well as after-sales services such as customer relations and feedback collection. Selling, on the other hand, refers to the activities that are undertaken to promote the sale of goods and services. These promotional activities can take the form of advertising, publicity, and so on. The product is converted into cash during the selling process. In this sense, selling can be considered a subset of marketing.
2. What is the marketing concept? How does it help in the effective marketing of goods and services?
Ans: The marketing management concept places a premium on customer satisfaction. It believes that customer satisfaction is critical to the success of any business. In the long run, any organization can only survive and maximize profits if it identifies and effectively addresses customer needs. This concept refers to the fact that people purchase a product in order to meet a specific need (social need, functional need and psychological need, etc). Any organization must strive to identify and meet such needs in an efficient manner. That is, all decisions must be made based on the needs and requirements of the customers. An organization works and sells based on what the customer wants rather than what it has. The following are the pillars of the marketing concept.
i. All marketing efforts must be directed toward a specific market segment or group of customers. Organizations must clearly identify the target customer's needs and requirements.
ii. It should create products and services that meet the needs of its customers
iii. It should not only work independently toward customer satisfaction, but it should also strive to satisfy customers better than its competitors.
iv. Profit is at the heart of all marketing efforts. The marketing concept aids in the efficient marketing of goods and services. Marketing goods and services would be more effective and efficient if all marketing activities were directed toward customer satisfaction. Selling would not be a problem if production, pricing, design, and other decisions were based on the needs of the customers. For example, if customers want dual-sim mobile phones with high-resolution cameras, GPS, and other features, the company manufactures them. Similarly, the company's other decisions, such as pricing, branding, and so on, are based on the needs of the customers.
3. What is marketing mix? What are its main elements? Explain.
Ans: The marketing mix is the collection of marketing tools used to achieve the various marketing objectives. The market offering is critical in the marketing process. To put it another way, for effective marketing, a company must decide on various aspects of a product, such as its size, quality, and location of sale, among others. A variety of factors influence such decisions. Some of them are under the firm's control. The firm, for example, has control over decisions regarding packaging, branding, pricing, advertising, and so on. However, there are some uncontrollable factors that influence a firm's decision making. For example, government policies and bank credit policies are beyond the firm's control. To achieve marketing objectives, a company continuously modifies the various controllable factors. These elements are known as marketing tools and serve as the pillars of marketing. A company selects the best combination of alternative marketing tools from which to develop a market offeringThe marketing mix is a collection of marketing tools that a company employs to achieve its marketing objectives.
The following are the components of the marketing mix.
1. Product: A product is any good or service that adds value and meets a customer's needs. A car, toothpaste, soap, teacher services, and so on are all examples of products. In marketing, a product refers not only to the physical product, but also to the satisfaction of the customer's various needs and utilities. Consumption of a product, for example, benefits a consumer by satisfying functional needs, social needs, and psychological needs. Such advantages are also included in the product. A product also includes after-sales services such as collecting feedback and resolving customer complaints, among other things. A product's design, quality, features, labeling, branding, and packaging are all important considerations.
2. Price: The price is the amount of money paid by customers to obtain a product. The price of a product influences its demand. When the price of a product rises, so does its demand, and vice versa. Marketers must thoroughly examine the various factors that influence price in order to determine an appropriate price for the product. When determining a price, for example, the target customers, pricing policy followed by competitors, firm objectives, and so on must all be considered. The price should be set in such a way that customers consider it to be in line with the value of the product. Appropriate discounts and incentive schemes must also be determined.
3. Location: In addition to product and pricing decisions, a company must consider the product's availability to its target customers. A company must choose the right dealers or intermediaries for the distribution of its goods. Other critical decisions include inventory management, warehousing, storage, and transportation of goods.
4. Promotion: Promotional activities are those that inform customers about the availability of a product, its features, qualities, and so on. In order to persuade customers to purchase the product Organizations engage in a wide range of promotional activities, including advertising, sales techniques, personal selling, and so on. An organization must carefully select the medium of promotion and then take the necessary actions. For example, the organization must decide which sales techniques, such as discounts, free gifts, sales, and so on, to employ.
5. What are the factors affecting the determination of the price of a product or service?
Ans: The price of a product is the amount of money paid by customers to obtain it, and this price influences its demand. As a result, pricing is critical in the marketing of goods. A company's revenue and profits are affected by the price it charges for its product. Furthermore, pricing serves as a competitive tool. Firms that produce similar substitutable products compete on the basis of price. As a result, firms must place a premium on proper product pricing. Marketers must thoroughly examine the various factors that influence price in order to determine an appropriate price for the product. The following are the elements that influence the price of a product or service.
1. Cost of Product: The cost of the product is a major factor in determining the price. It includes the costs associated with the product's production, distribution, and sale. Product costs can be divided into three broad categories: fixed costs, variable costs, and semi-variable costs. Fixed costs are those that do not change in proportion to the amount of output produced. In order to produce a good, a company, for example, incurs costs for the purchase of machinery, land, and so on. These are one-time expenses. Variable costs, on the other hand, vary directly in proportion to the volume of production. That is, as output increases, so does the variable cost. Variable costs include things like labor and raw materials. Semi-variable costs vary with output level but not directly proportionally. Payments made to intermediaries for the sale of goods, for example, is a semi-variable cost. In general, firms set the price of a product so that it covers all of its costs. Furthermore, they hope to make a profit above and beyond the costs they incur. As a result, firms decide on a price that takes into account both the cost and the profit factor.
2. Demand for the Product: A company must consider the demand for its product when determining the price. The elasticity of demand is important in this context. The proportionate change in demand caused by a given proportionate change in price is referred to as demand elasticity. The demand is said to be elastic if it changes by a larger proportion due to a small proportionate change in price. That is, demand is said to be elastic if a small price increase (or decrease) results in a relatively large price decrease (or increase). In this case, the firm cannot charge a higher price because it would cause a significant drop in demand. Demand, on the other hand, is said to be inelastic if a change in price has little effect on it. In this case, the firm has the option of charging a higher price because, even at a higher price, demand would not fall significantly. As a result, the price of goods with elastic demand is generally lower than the price of goods with inelastic demand.
3. Degree of Competition in the Market: In broad, the lower the price that a company can charge for its product, the higher the market competition. This is because, in a high-competition environment, a firm that attempts to charge a high price will lose customers to competitors. On the other hand, if a company's product has little competition, it can charge a higher price.
4. Government Regulations: To protect the general public's interests, the government may intervene in price determination at times. In the case of essential commodities, for example, the government can set a maximum price that can be charged.
5. Pricing Objectives: Each firm has different pricing objectives that it considers when determining a price. Some of the pricing objectives are as follows.
i. Profit Maximisation: Profit maximization is the goal of every business. If, on the other hand, the firm's goal is to maximize profits in the short run, it may make a decision to charge a higher price in order to increase revenue. If, on the other hand, the firm's goal is to maximize profit in the long run, it will charge a lower price in order to gain a larger market share and benefit from higher sales.
ii. Acquiring Market Share: If a company wants to expand its market share, it will charge a lower price to attract a larger number of customers to its product.
iii. Surviving Competition: In the face of fierce competition, a company will keep its product's price low. This is related to the reasons that if it charges a higher price, it will lose customers to competitors.
iv. Quality Focus: If a company focuses on improving product quality, it will charge a higher price to cover the additional costs.
6. Method of Marketing: The firm's marketing methods, such as distribution, advertisement, customer service, branding, and so on, also have an impact on price determination. For example, if the company uses a lot of advertising to promote the product, it will charge a higher price.
6. What do you mean by channels of distribution? What functions do they play in the distribution of goods and services? Explain.
Ans: Individuals, institutions, and agents who facilitate the distribution process are referred to as distribution channels. As a product's potential consumers are dispersed across a larger geographical area, it becomes more difficult for the producers or manufacturers to directly contact the customers in order to sell their products. Distribution channels are crucial in this case. They facilitate the movement of goods from the point of manufacture to the point of consumption. For example, it would be difficult for a sugar manufacturer in Punjab to contact customers in other parts of the country. To make the process easier, it would sell its product to wholesalers, who would then sell it to retailers. Finally, the product is sold to the customers by the retailers. Furthermore, channels of distribution reduce consumers' efforts by providing a variety of goods and services in a convenient single location. A customer, for example, can purchase a wide range of goods at a retail store. Thus, the term "channels of distribution" refers to the group of people, agents, and organizations that facilitating the exchange or transfer of goods and services from the producer to the consumer Distribution channels serve the following purposes.
1. Arrangement: An intermediary receives goods from a variety of sources. However, the goods received vary in size, quality, and features. Based on their characteristics, the intermediary arranges or sorts these goods into homogeneous groups.
2. Collection: A middleman gathers and retains a large stock of goods to ensure a continuous and smooth supply flow.
3. Allocation and Packing: A middleman divides the goods into small, marketable units. It repacks the goods into handy packets.
4. Creating Variety: An intermediary obtains various goods from various sources and assembles them in a single location. As a result, it keeps a wide range of goods. A grocer, for example, keeps a wide variety of products for sale.
5. Product Promotion: They help manufacturers with their product promotion efforts. Manufacturers, for example, use advertising to promote their product. Intermediaries can help this process by displaying banners and other advertisements.
6. Mediation: On the one hand, middlemen interact with producers, and on the other, with customers. As a result, they serve as a conduit between producers and customers. They bargain over price, quality, and other issues, and work to meet the needs of both parties.
7. Risk-bearing: Intermediaries purchase goods from producers and keep them in their possession until the final sale. During the process, they are vulnerable to fluctuations in demand, price, spoilage, and so on. Assume a retailer purchases a large quantity of sugar. However, as time passes, the price of sugar rises, reducing demand. As a result, the retailer may suffer a loss as the stock remains unsold.
7. Explain the major activities involved in the physical distribution of products.
Ans: Once the product has been manufactured, packaged, promoted, branded, and priced, it must be made available to consumers. That is, they must be transported from where they are produced to where they will be consumed. Physical distribution of products refers to the physical movement of products from the point of manufacture to the point of consumption. It entails the four major activities listed below.
1. Processing of Order: The most important aspect of the buyer-seller relationship is the processing of orders and the delivery of goods. Order processing consists of several steps, including order placement, transmission of the order by intermediaries to the manufacturer, inventory maintenance as needed, delivery of goods, and so on. All of these processes take time. The physical distribution system should be designed in such a way that orders are processed quickly and correctly. In general, order processing speed and accuracy are directly related to customer satisfaction. Consumers are more satisfied when orders are processed quickly and accurately. As a result, a proper order processing system is critical.
2. Transportation of Products: The physical movement of goods from the point where they are manufactured to the point where they are consumed is referred to as product transportation. A product's potential customers are dispersed across a large geographical area. They must be transported from the point of production to the point of consumption in order for the goods to be physically available to them. Sales cannot take place unless the products are physically transported and made available at the point of consumption.
3. Warehousing: There is a time lag between the act of production and the act of sale or consumption in most cases. This means that the goods must be properly stored and sorted before being sold. Warehousing refers to the process of storing and sorting products. Proper warehousing ensures efficiency in product delivery and sale, which leads to higher customer satisfaction. For example, warehousing allows a company to keep products in stock and ensure timely delivery of goods as needed. However, maintaining warehouses comes with its own set of expenses. As a result, a company must weigh the relative benefits and costs of warehousing and strike a balance between the two as needed.
4. Maintenance of Inventory: Maintaining a stock of products is what inventory entails. Inventory is kept on hand by the companies to ensure that products are delivered on time. Inventory and customer service are inextricably linked. Maintaining a higher inventory allows a company to ensure timely delivery of goods to customers and, as a result, improve customer service. However, inventory maintenance comes at a cost because a large amount of capital remains locked up in the stock until it is sold. As a result, the companies must strike a balance between customer service and cost. The decision to keep inventory is influenced by a variety of factors, including how well the distribution system responds to orders and deliveries, the cost of keeping the inventory, the firm's objectives, and so on. The company must choose an appropriate inventory while considering the various costs and benefits involved.
8. Expenditure on advertising is a social waste' Do you agree? Discuss.
Ans: Advertising expenditure is frequently regarded as a social waste. Advertising is criticized for increasing the company's costs unnecessarily, undermining social values, and exacerbating, building up consumer needs and desires for a variety of products. However, proponents of advertising argue that advertising through increased sales reduces costs and aids the growth process. The following considerations aid in determining whether advertising is a waste of time.
1. Higher Cost: Advertisement costs add to the overall cost of the business. Companies, in turn, pass on the increased costs to customers in the form of higher prices. Advertisement supporters, on the other hand, argue that it lowers the per unit cost of production. This is related to the reasons that advertising can attract a larger number of customers to the product, implying an increase in demand for the product. Manufacturers increase production in response to increased demand. As production increases, the per unit cost of production decreases. As a result, even though advertising costs add to the cost, this increase in cost can be offset by a decrease in per unit cost due to increased demand and production.
2. Weakens Social Values: One of the most common criticisms leveled at advertising is that it undermines social values and instead promotes materialism in society. Advertisement draws customers' attention to new products and encourages them to buy them. Customers are dissatisfied with their current situation as they gain more knowledge about the availability of new products. In the process, they frequently end up purchasing items that they do not even need. However, such a cycle of dissatisfaction and product acquisition never ends, and materialism grows. Advertisements, on the other hand, are said to merely inform buyers about the availability of various products, and that the final decision to purchase the product is left to the consumer. Customers' knowledge is increased and they are kept informed as a result of advertising.
3. Creates Confusion: Customers are said to be confused by a large number of advertisements for similar products. For example, advertisements for various hair oils claim that using their product will result in healthy and long hair. With so many advertisements, the consumer becomes perplexed as to which product of which brand should be purchased. Ad supporters, on the other hand, disagree with this criticism and argue that advertisements provide consumers with a choice. After considering various factors such as price, style, quality, and so on, consumers can make an informed decision for themselves.
4. Promotes Inferior Goods: It is argued that both superior and inferior quality products are advertised. Advertisement can also be used to increase demand for inferior goods. Such a claim, however, is only partially correct. This is due to the fact that quality is a relative concept. What one consumer considers to be inferior may be considered superior by another. Advertisements promote a wide range of products, and consumers buy them if they meet their needs.
5. Objectionable Advertisements: Advertisements, it is said, frequently undermine social values and are in poor taste. The language, images, and content of advertisements may not always appeal to the general public. For example, women in male-oriented products (such as shaving creams, deodorants, and so on) are frequently chastised. In response, some argue that good or bad taste is a subjective phenomenon that varies from person to person. What is acceptable to one person may be offensive to another. As a result, while advertising expenditure is criticized, the criticisms are not entirely accurate. On the one hand, they can be abused and have drawbacks, but on the other hand, one cannot deny the benefits of advertising.
9. Distinguish between advertising and personal selling.
Ans: Advertising is a faceless, paid form of communication used by marketers to promote their products and services. Personal selling, on the other hand, entails the seller communicating directly with potential customers. That is, it entails direct face-to-face communication between sellers and customers for the purpose of product sale. The distinctions between advertising and personal selling are highlighted in the following points.
Application Based Questions
1. As marketing manager of a big hotel located at an important tourist destination, what societal concerns would be faced by you and what steps would you plan to take to take care of these concerns? Discuss.
Rainwater harvesting
Solar geyser use
waste recycling
proper drainage
use of CNG-powered vehicles
2. Suppose you are the marketing vice president of an insurance company, planning to design a new mediclaim policy for senior citizens. What information would you like to collect to perform this task and how will you collect such information? Discuss.
Senior citizen's age
Income
Medical information
Working or not working
3. What shopping products have been purchased by you/your family in the last six months. Make a list and specify what factors influenced the purchase of each of these products.
Ans:
Washing Machine: Brand, Price, Specifications, and Warranty
Dress Material: Cost and Fashion
Price, quality, comfort, and design of a cot bed
Sandal: cost, brand, size, and material
4. What information is generally placed on the package of a food product. Design a label for one of the food products of your choice.
Product name
Brand
Price
Manufacturing date and expiration date
Weight
Ingredients used
Directions for use
FPO mark
Preservatives used
5. For buyers of consumer durable products, what ‘customer care services’ would you plan as a manager of a firm marketing a new brand of motorcycle. Discuss.
Monthly Payments
Exchange Offer
Free Servicing
Case Problem
Nokia takes a four-lane road to consumers.
NEW DELHI: After having grabbed a king-size 79% share of the Rs 15,000- crore mobile handset market in India, Nokia India has found a new way of connecting people. The mobile handset manufacturer has embarked upon a brand new retail strategy that is based on a classification of its consumers into four major groups that separates people in terms of usage, income level and lifestyle. The classification is based on an extensive survey – the Nokia Segmentation Study — that was carried over two years involving 42,000 consumers from 16 countries. It studied the impact lifestyle choices and attitudes have on the mobile devices consumers buy and how they use them. The strategy, which was announced globally in June last year, is being unfolded in India now. While the nitty-gritty of the new strategy is still being worked out, it is likely that the company would follow separate marketing strategies for the four different segments. The advertising campaigns could be different for the segments. Nokia’s entire product portfolio has now been realigned towards these four groups to address the specific needs of each. The first of these segments Live, aimed at first time users whose basic need is to stay in touch with voice as the main driver, would have basic handsets low on features and price. “These may be functional phones but the target group for these phones range from SEC C (low socioeconomic class) to SEC A1+ (very high socioeconomic class) markets,” says Nokia India marketing head Devinder Kishore. The second segment Connect looks at more evolved users who look for more functionality and features and connectivity. Accordingly, phones in this segment would have GPRS, camera and music capabilities. The next two categories, Achieve and Explore, are aimed at high-end users and have Nokia’s top-end handsets. For example, Achieve segment looks at enterprise users who need to have business functionalities in their phones. Nokia’s new E-series has been put under this segment with handsets having QWERTY keyboards and full Internet capabilities. Aimed at high-end lifestyle users, Explore would be the most prominent segment for the company in the coming years. Says Nokia India multimedia business director Vineet Taneja, “This segment would see the most vibrant growth in the coming year. It will look at five different areas – applications, imaging, mobile TV, music and gaming. We are fast developing the ecosystem to support these areas.” Nokia acquired music solution and content provider LoudEye and GPS solution provider Gate5. It is all slated to launch its most high-profile handset, which boasts of having a 5 megapixel camera and GPS capabilities apart from iPod quality music, in February. Says Taneja, “There is increasing demand for convergence and multiple functionalities in high-end handsets. The N-series will try to address that.” Nokia feels that the new platform strategy wherein different handsets are launched under a platform, like the N-Series, will become a status and style statement and drive numbers.
Questions
1. Identify the four market segments that Nokia plans to address as per the news report above.
Ans: Live, Connect, Achieve, and Discover
2. What is the basis of classification of the market used by the company?
Ans: SEC Socio-Economic Class, Usage, and Way of Life
3. What do you mean by realignment of product portfolio? Illustrate this from the case above.
Ans: Product portfolio realignment refers to the development of a portfolio in relation to the needs. The four different handsets are planned to meet the needs of various customers.
4. Identify the points that can be highlighted in marketing campaigns for each segment.
Model
Performance
Technology
User-Friendliness
5. What are the different considerations in the mind of consumers of each segment while purchasing mobile phones as given in the above case?
First Segment: Mobile users for the first time. The primary consideration in this case is price.
Second Segment: Users who think about features and functionality. Both features and price are important considerations in this case.
Third Segment: High-end customers. The main considerations here are its uniqueness and functionalities.
Marketing Class 12 NCERT Solutions- Free PDF Download
Free PDF study material is available for download from our website and app. Students can grab this opportunity and start their learning now itself. Our NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies consists of clear solutions to all NCERT textbook questions along with other forms of fun worksheets. The study material consists of questions ranging from MCQs to Long answers. Answers are organized conveniently, be it a tabular form or even a simple point. The notes are all thoroughly revised and error-free.
Students can completely rely on this single source which gives them adequate information regarding the subject. Students can find all kinds of explanations regarding the chapter in NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Business Studies
Chapter 11 - marketing.
Chapter 11 Marketing is a significant topic for students, both theoretically and practically. Apart from academics, marketing is an important aspect to be discussed for aspiring entrepreneurs. Some of the concepts cleared in NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies include branding, labelling, convenience products, packaging, advertising, etc. Beginners at times may find it tough to realize the functioning behind these broad terms. However, if he/she goes through these study materials, it's sure that they can pick up almost all the concepts in no time and the rest of them in subsequent reading. Topics like consumer rights, societal concepts, packaging, designing, etc are covered in NCERT Solutions.
Business Studies Class 12 Chapter-wise Marks Weightage
The weightage of marks expected from Chapter 11 Marketing ranges between 10-15 with the chances of many long answers. So this chapter isn't a one that is supposed to be skipped. Students need to thoroughly learn this chapter to ensure good marks in examination, for which NCERT Solutions will be always backing you.
Some of the long answers expected from this portion are:
What is a marketing concept and how does it help in the productive marketing of goods and services?
Explain how branding helps in creating product differentiation. State if it is useful in the marketing of goods and services.
Why Are NCERT Solutions Marketing Class 12 Business Studies Important?
At the end of using these notes, students will get an image regarding the functioning of markets and other related aspects for sure.
As all kinds of questions and topics are covered, students need not waste their time searching for multiple books or notes
The quality solutions provided enables students to cultivate a very good base in answering questions accurately.
The speed of writing and reading is naturally increased through the various activities scripted in our NCERT Solutions.
- Students get the ability to think and analyze a situation or question from a practical point of view at the end.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 - Marketing provides a comprehensive and insightful understanding of marketing concepts and strategies. These solutions cover essential topics like market segmentation, branding, advertising, and distribution channels, equipping students with the knowledge to excel in the dynamic business environment. The practical examples and case studies in these solutions enhance students' analytical and problem-solving skills, fostering a strategic approach to marketing decisions. By engaging with these solutions, learners can develop a deeper appreciation for the role of marketing in business success and gain valuable insights into consumer behavior and market trends. Overall, NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 empower students to excel in the field of marketing and contribute effectively to the business world.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Chapter 11 - Marketing
1. What are the Advantages of the Packaging of Consumer Products?
Packaging can be defined as the process of beautifying a container or a cover as per the needs of a product. It's advantages are:
As various designs and colours are used, it acts as a source of attraction for the consumers.
Consumers can easily differentiate products with the help of packaging.
The product is prevented from various kinds of damage and spoiling.
Details regarding the product are listed on the packaging which gives a sense of transparency to the consumers.
2. Explain the Societal Concept of Marketing.
The societal concept of marketing can be explained as the concept wherein different organizations identify the need or purpose of markets along with targeting the consumers attracted to those markets. This concept enables the delivery of products efficiently to the customers along with good and services.
This kind of marketing comes with the responsibility of protecting customer values and desires. Consumers must always be a priority for this concept to work out. Long term understanding between various organizations and markets are also important for this concept.
3. State any two advantages of branding to marketers of goods and services.
There are multiple advantages of branding for marketers of goods and services. The two main advantages are:
Branding facilitates the goods or services to stand out and have a unique identity of their own so that it reaches out to more and more people and ultimately has loyal buyers.
Whenever the marketer aims at launching a new product or service, he already has his base set with that unique brand of his.
4. How does branding help in differential pricing?
The more unique, popular or reputed a brand is, the more loyal buyers it tends to have. Hence these brands have the freedom to manipulate the prices of similar products as their customers know that the brand will not compromise in terms of the quality of their products or services. Hence we see such differences in prices of similar goods or services of different brands, the most reputed ones having premium prices.
5. Is branding important?
Yes, branding is really important, especially in today’s market. It is crucial as it not only creates a good impression on buyers but also informs your customers and clients about what to expect from your business. It is a method of distinguishing yourself from competitors and clarifying what you provide that makes you the better choice. For more information on this subject, you can visit the Vedantu website or the app.
6. How to master Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11?
Remind yourself of the fundamentals of this chapter.
Get an in-depth understanding of this chapter.
Do not mug up and understand the logic behind each concept.
Try answering NCERT questions.
Determine which topics you are comfortable with and which need more practice. If you are having trouble understanding a topic, you can seek the help of Vedantu to clear your doubts.
7. Is Chapter 11 Class 12 Business Studies easy?
Class 12 is less difficult than Class 11, but the syllabus is more extensive. Also, because you will be preparing for higher education, it is important to study and perform well in your Class 12 exams, as these will have an impact on your university selection process. The fundamental concepts must be thoroughly understood, and various exercises must be performed. Chapter 11 is an easy and interesting concept, while all the solutions are available free of cost on Vedantu.
CBSE Study Materials
Jee study materials, neet study materials.
myCBSEguide
- Marketing Management class 12...
- Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
CBSE class 12 Business Studies Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies in PDF are available for free download in myCBSEguide mobile app. The best app for CBSE students now provides Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies latest chapter wise notes for quick preparation of CBSE board exams and school based annual examinations. Class 12 Business Studies notes on chapter 11 Marketing Management are also available for download in CBSE Guide website.
CBSE Guide Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
CBSE guide notes are the comprehensive notes which covers the latest syllabus of CBSE and NCERT. It includes all the topics given in NCERT class 12 Business Studies text book. Users can download CBSE guide quick revision notes from myCBSEguide mobile app and my CBSE guide website.
12 Business Studies notes Chapter 11 Marketing Management
Download CBSE class 12th revision notes for chapter 11 Marketing Management in PDF format for free. Download revision notes for Marketing Management class 12 Notes and score high in exams. These are the Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies prepared by team of expert teachers. The revision notes help you revise the whole chapter 11 in minutes. Revision notes in exam days is one of the best tips recommended by teachers during exam days.
Download Revision Notes as PDF
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes CHAPTER – 11 Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
MEANING OF SOME IMPORTANT TERMS:
• Needs = basic human requirements. Essential items necessary or fundamental to human existence.
• Wants= desire for a particular product. Tend to be “satisfier specific”.
• Demand- willingness to buy is backed by purchasing power
• Utility – want satisfying power of a product.
• What can be marketed:
• A product = • bundle of utility not confined to physical products but can refer to other things of value such as services, ideas, place. It refers to anything that satisfies a need or want.
• may be tangible or intangible(i.e. goods and services)
• even people can be marketed • Customers= people or organizations that seek satisfaction of their wants. • “Marketers‟ = • Anyone taking a more active role in the process of exchange is called a marketer. Normally it is the seller. But in certain situations, it may also be the buyer. This may be in the situation of rare supply.
• Sellers as marketer are the deliverers or providers of satisfaction. They makes available products or services and offers them to customers with an intention of satisfying customer needs and wants. They can be divided into:
• Goods marketers (such as Hindustan Lever)
• Services marketers (such as Indian Airlines)
• Others marketing experiences (such as Walt Disney) or places (like tourist destinations). • Marketing activities =activities carried on by the marketers to facilitate exchange of goods and services between the producers and the users of such products. • Market is:
• Place where buyers and sellers meet and conduct buying and selling activities. It does not necessarily mean a geographical place(e.g. conduct of business thro telephone, mail or internet)
• The other ways in which this term is being used is in the context of a product market (cotton market, gold or share market), geographic market (national and international market), type of buyers (consumer market and industrial market) and the quantity of goods transacted (retail market and wholesale market).
• In the modern marketing sense, it refers to a set of actual or potential buyers of a product or service i.e. all customers who share a particular need or want and are able to buy the product (also referred to as target markets)
Important Features of Marketing
1. Needs and wants: Satisfaction of the needs and wants of individuals and organizations.
2. Creating a market offering: Complete offer for a product of service.
3. Customer value: greatest benefit or value for the money.
4 . Exchange mechanism: Exchange of products/services for money/for something of value to them.
Meaning and concept of Marketing Management
Marketing management means management of the marketing functions. It is the process of organizing, directing and controlling the activities related to marketing of goods and services to satisfy customers’ needs & achieve organizational goals.
The process of Marketing involves:
i. Choosing a target market
ii. Getting, keeping as well as growing the customer
• that is, ensure that the target customers purchase the firm‘s product, ensure that they keep their customers satisfied with the products and attract new customers so that the firm can grow.
iii. Create, develop and communicate superior values to the customers.
Functions of Marketing/Marketing activities
Gathering And Analyzing Market Information:
• systematic investigation of facts
• SWOT analysis
• Necessary to identify needs
• Decisions can be wrt. Identifying customer needs and wants, identifying buying motives, choice of a brand name, packaging and media used for promotion.
• Data is available both from primary as well as secondary sources.
Marketing planning : • Aim = to develop a complete marketing plan so that the marketing objectives can be achieved. • It also must specify the action programs . • E.g if a marketer aims at enhancing his market share in the country in the next three years, then his marketing plan should include various important aspects like plan for increasing level of production, promotion of products etc.
Product designing and development: • Involves decisions regarding the product to be manufactured and it‘s attributes such as its quality considerations, packaging, models and variations to be introduced etc.. • Done by anticipating customer needs and developing new products or improving existing products to satisfy these needs.
Standardization and grading: • Standardization = Process of setting certain standards for a product on the basis of its desired qualities. E.g. ISI mark for electrical goods. • Grading = Division of products into classes made up of units possessing similar features such as for agricultural products
Packaging and labeling: • Packaging‘ refers to designing a package (that is a wrapper or a container) for a product. • Packaging protects the products from damage , risks of spoilage, breakage and leakage. It also makes buying convenient for customers and serves as a promotional tool. • Labeling = designing a label to be put on the package. It may vary from a simple tag to complex graphics.
Branding • Whether to sell the product in its generic name or in a Brand name. • Helps in differentiation, builds customer loyalty and promote its sale. • Decision = whether each product will have a separate brand name or the same brand name to be used for all products.
Concepts & Philosophies of Marketing
1. PRODUCTION CONCEPT = In the earlier days of the industrial revolution, the number of producers were limited, → limited supply of industrial products → not able to match demand . So, anyone who was able to produce goods could easily find buyers for the same.
2. PRODUCT CONCEPT= With passage of time, the supply improved→ customers started looking for products that were superior in performance, quality and features.
3. SELLING CONCEPT= increase in scale of production→ competition among the sellers → Product quality and availability alone did not ensure survival as a large number of firms were now selling products of similar quality.
4. MARKETING CONCEPT : Implies that a firm can achieve its goals by identifying needs of the customer and satisfying them better than the competitors. Customer satisfaction is the precondition for realizing the firm’s goal and objectives,
5. SOCIAL MARKETING CONCEPT : Under this concept customer satisfaction is supplemented by social welfare. Some products bring harmful effect on environment so these should not be supplied. It pays attention to the social, ethical and ecological aspects of marketing. Raman, Joginder, John, Iqbal and Shreya are friends. They are operating different business. Each one has his/her own concept regarding operating their business. Raman believes in producing products at a large scale. Thereby decreasing the average cost of the products and selling it’s at a reasonable price.
Meaning and Concept of Marketing and Selling
Marketing is a wide term. It refers to a large set of activities of which selling is just one part. A marketer before making the sale does a lot of other activities such as planning the type, design of the product, the price and selecting the distribution outlets at which the same would be available.
Selling: refers to the sale of goods or service through publicity, promotion and salesmanship. The title of the product is transferred from seller to buyer. The entire focus in selling is to covert the product into cash.
Difference between Selling & Marketing
Marketing Mix
There are a large number of factors that affect marketing decisions. They can be classified as:
• Non-controllable factors and Controllable factors: To be successful, a firm needs to take sound decisions wrt controllable factors while keeping the environmental factors in mind.
To develop marketing tools, marketing managers use the above mentioned controllable factors and the set of marketing tools that a firm uses to pursue its marketing objectives in the target market is described as Marketing Mix. Success of a market offer will depend upon how well these ingredients are mixed to create superior value for customers and simultaneously achieve their sales and profit objective. Thus, an ideal marketing mix would need: • Producing satisfying products • Offered to buyers at a reasonable price • Conveniently available • About which communication is offered
Marketing mix refers to ingredients or the tools or the variables which the marketeer mixes in order to interact with a particular market.
11.8.1 Elements of Marketing Mix
The four main elements of marketing mix as classified by MCcarthy are:
A. Product B. Price C. Place/Physical Distribution D. Promotion
Elements/4 Ps of Marketing Mix
4. Place Mix: Physical distribution: Various decisions regarding distribution of products.
• Channels of distribution: Whether wholesalers, retailers are to be used or not.
• Physical movement of the products from producer to consumers.
• Storage, transportation, managing inventory (stock) etc.
i) Branding:
The process used to create a distinct identity of a product. It is the process of using a name, term, symbol or design individually or in some combination to identify a product.
Brand : Name, term, sign, design or some combination of the above used to identify the products of the seller and to differentiate them from those of competitors .
Qualities of a Good Brand Name
1. Short, easy to pronounce, spell and remember(Rin, Vim, Ponds)
2. Suggest product benefits and quality (Genteel, Boost)
3. Distinctive (Zodiac, Safari)
4. adaptable to packing or labeling requirements, to different advertising media and to different languages.
5. Versatile to accommodate new products(Maggi)
6. Capable of being registered and protected legally
7. Have staying power(should not get outdated easily.
Advantages of Branding-
Advantages to the marketers:
1. Enables product differentiation:.
• Distinguishes the firms products from that of its competitors, thus secures and controls its markets.
2. Helps in advertising and display programmes:
• Without a brand, the advertiser can only create an awareness about the generic product and not be sure of the sale of his brand.
3. Differential pricing:
• As when customers like and become used to a brand, they would agree to pay a little more for it than the competing product
4. Ease in introduction of a new product
minimizes selling costs – enjoys the reflected glory of the brand.
Advantages to Customers:
1. Helps in product identification:
• If customer is satisfied with a brand, he will not make a close inspection every time.
2. Ensures quality:
• deviation in quality, customers can have a recourse to the manufacturer/marketer. ↑ confidence and level of satisfaction of customers
3. Status symbol:
• Because of their quality, customers feel proud of suing them and so ↑ level of satisfaction of customers
2. (ii) Packaging: Act of designing and producing the container or wrapper of a product. Good packaging often helps in selling the product so it is called a silent salesman.
Levels of Packaging
1. Primary Package: refers to the product’s immediate container e.g. toffee in a wrapper, a match box.
2. Secondary Package : refers to additional layers of protection that are kept till the product is ready for use e.g. a Colgate toothpaste usually comes in a card board box.
Functions of Packaging
1. Product Identification : Packaging helps in identification of the product.
2. Product Protection: The main function of the packing is to provide protection to the product from dirt, insects and breakage.
3. Convenience: It provides convenience in carriage, stocking and in consumption.
4. Product Promotion: Packaging simplifies the work of sales promotion.
Advantages of Packaging
• Rising Standards Of Health And Sanitation – As chances of adulteration in such goods are minimized
• Self-Service Outlets – so some of the traditional role assigned to personal selling w.r.t promotion has gone to packaging.
• Innovational Opportunities – innovation on packaging used to market products e.g. tetra packs for milk.
• Product differentiation – colour, size, material etc of packaging makes a difference in perception of customers about the quality of the product.
3 . Labelling :
Labelling means putting identification marks on the package. Label is a carrier of information & provides information like – name of the product, name of the manufacturer, contents of the product, expiry and manufacturing date, general information for use, weight etc. Labels perform following functions:
1. Identify the product: It helps the customers to identify the product from the various types available. For example: We can easily identify a Cadbury chocolate from the various chocolates by purple colour of its label.
2. Describe the product and specify its contents:
5. Providing information required by law: There is legal compulsion to print batch no., contents, max retail price, weight/volume on all the products and statutory warning on the packet of cigarettes, “Smoking is injuries of health”: In case of hazard on/poisonous material appropriate safety warnings need to be put.
II P-PRICE MIX:
Meaning and concept of Price: Sum of values that consumers exchange for the benefit of having or using the product Price may therefore be defined as the amount of money paid by a buyer (or received by a seller) in consideration of the purchase of a product or a service
Normally expressed in monetary terms. Decisions include decisions wrt basic price, discounts to be offered etc
Factors determining price determination:
1. Pricing Objectives
(a) to maximise profits in the short term-tend to charge maximum price.
(b) Obtain large share of the market i.e., by maximising sales it will charge lower price.
(c) Firm is operating in the competitive market it may charge low price for it.
2. Product cost:
• Price should include all costs and also include a fair return for undertaking the marketing effort and risk.
• Includes costs of producing, distributing and selling the product.
• Costs sets the floor price – the minimum level / lower limit at which the product may be sold. • Price should recover Total costs (Fixed costs/overheads + Variable costs+ Semi-variable costs) in the long run, but in certain circumstances(introduction of a new product/entry into a new market) product price may not cover all the costs for a short while.
3. Utility and demand:
• Utility provided by the product and the demand of a product set the upper limit of price that a buyer would be willing to pay for a product.
• Buyers pay to the point where the utility of the demand is more than or eequal to the utility derived from it.
• Law of demand = consumers purchase more at a lesser price.
• Elasticity of demand = responsiveness of demand to change in prices of a product. Demand = elastic if a small change in price results in a large change in quantity demanded.
• If demand is inelastic, firm can fix higher prices.
4. Competition in Market : Prices of competitors need to be considered before fixing prices.
5. Government Policies: Products regulated by government pricing regulations need to be priced as per government policies.
III. P-Place Mix/Physical Distribution Mix
A set of decisions needs to be taken to make the product available to customers for purchase and consumption.
• The marketer needs to make sure that the product is available at the right quantity, at the right time and at the right place.
• It requires development of:
• Channels of distribution
• Physical distribution of products.
Components of physical distribution-
1. Order Processing: Accurate & speedy order processing leads to profit & goodwill & vice versa.
2. Transportation: Add value of the goods by moving them to the place where they are required.
3. Inventory control: Additional demand can be met in less time, the need for inventory will also be low.
4. Ware housing: Need arises to fill the gap between the time when the product is produced & time when it is required for consumption.
Channels of Distribution
• Includes a series of firms/ individuals/ people/institutions/merchants and functionaries who form a network which helps in the transfer of title to a product from the producer to the end consumer.
• They help to overcome time, place and possession gaps that separate the goods and services from those who need/want them from those who want them
Types of Channels:
Direct Channel — Manufacturer-Customer. Eg. mail order, internet, door to door selling.
Indirect Channel —
1. Manufacturer-Retailer-Customer.
Usually used for specialty goods like expensive watches, appliances, Cars( Maruti Udyog) etc.
2. Manufacture-wholesaler-Retailer-customer.
Usually used for consumer goods like soaps , salt etc.
3. Manufacture → Agent → Wholesaler → Retailer → Customer
Factors Determining Choice of Channels of Distribution
IV. P-Promotion Mix
Tools/Elements of Promotion Mix
1. Advertising: Most commonly used tool of promotion. It is an impersonal form to communication, which is paid by the marketers (sponsors) to promote goods and services. Common mediums are newspaper, magazine, television & radio.
Role or Importance of Advertising
1. Paid Form –sponsorer has to bear the costs of communicating with the prospective buyer.
2. Impersonality – no direct face to face contact between prospects and advertisers. Creates a monologue and not a dialogue.
3. Identified Sponsor –undertaken by an identified individual who makes the advertising effort and bears the costs of it.
4. Mass Reach – large number of people over a large geographical area can be reached.
5. Enhancing Customer Satisfaction And Confidence – creates confidence and prospective buyers feel more comfortable and assured about the product quality
6. Expressiveness – due to development in art, computer designs and graphics, special effect can be created that makes simple products and messages look attractive.
7. Economy- because of its wide reach, overall cost of advertising gets spread over a wide audience and per unit cost of reach ↓.
Objections against Advertising: Though advertising is one of the most frequently used medium of promotion of goods & services but it attracts a lot of criticism/objections against it, which are as follows: 1. Increased Product Price: Which is ultimately added to product cost, manufacturers pass this cost to ultimate customers. 2. Confusion to Customers: The number of advertisements shown for a single product having different brands confuse the customers and it becomes very difficult for them to make choice. 3. Encouraging sale of Inferior Products: In many cases some product features are over emphasized. 4. Advertisement of Bad Tastes: Events, models degrade the human dignity. 5. Undermines Social Values and Promotes Materialism: It induces the customers to buy more and more products. Because of emphasis on materialism, social relationships are distorted which brings social disorder. In the changed economic environment of globalisation, advertising is considered as an important tool of marketing. It helps a firm in effectively communicating with its target market, increasing the sale and thereby reducing the per unit cost of production. It is not a social waste rather it adds value to the social cause by giving a boost to production and generating employment.
2. Personal Selling Personal selling consists of contacting prospective buyers of product personally i.e face to face interaction between seller and buyer for the purpose of sale.
Features of the Personal Selling
1. Personal contact is established under personal selling.
2. Oral conversation.
3. Quick solution of queries.
4. Receipt of additional information.
1. Physical qualities: Tidy appearance, good posture, cheerful smile etc
2. Psychological qualities: good nature with Empathy and ego drive,
3. Technical quality: Full technical knowledge about the product,
4. Good communication skills – Polite, tactful, having good manners etc
5. Honesty,
6. Courtesy,
7. Persistent- must not give up as one additional argument can close a sale.
Merits of Sales Promotion:
1. Attention Value: Attract attention of people through use of incentives. 2. Useful In New Product Launch: Sales promotion tools induce people to break away from their regular buying behavior and try new products. 3. Synergy in Total Promotional Efforts: Sales promotion activities add to the overall effectiveness of the promotional efforts (advertising and personal selling) of a firm.
• Limitations Of Sales Promotion – if used frequently: a. Reflects Crisis: A firm that frequently relies on sales promotion activities may give the impression that it is unable to manage its sales and there are no takers for its products. b. Spoils Product Image: Consumers may feel that the products are not of good quality or are not appropriately priced.
1. Product Combination: Offering another product as gift along with the purchase of a product.
2. Istant draws and assigned gift: Scratch a card and instantly win a prize with the purchase of a TV, T. Shirt, Refrigerator etc.
3. Q uantity Gift: Offering extra quantity of the product e.g., Buy three LUX soaps and get one free.
4. Refunds: Refunding a part of price paid by customer on production of some proof of purchase. e.g Rs 2 off on presentation of empty pack of Ruffle lays
5. Sampling : Offer of free samples of the product to potential customers. Generally used at the time of introduction of a product.
Public Relations
“The Chartered Institute of Public Relations” defines Public Relations as a strategic management function that adds value to an organization by helping it to manage its reputation Public relations covers a wide range of tactics, usually involve providing
information to independent media sources in the hope of gaining favorable coverage. It also involves a mix of promoting specific products, services and events and promoting the overall brand of an organization, which is an ongoing tact. Public Relation tools include:
1. Press Release: A press release is an announcement of an event, performance, or other newsworthy item that is issued to the press by a public relations professional of an organization. It is written in the form of a story with an attractive heading so that the media quickly grasp and circulates the message through newspaper/radio/television/internet.
2. Press Kits: It is a comprehensive package of information outlining a company’s products and services most frequently sent to members of the press. It includes
• A brief company biography.
• Information of senior management.
• Comments from customers.
• Reprints of newspaper and magazine articles.
• Photos of products.
3. Brochures: It is a booklet published by the organization which contains the organization’s background, its ethics, vision, mission, its past, present and future projects, its CISP, etc. E.g.: brochure given to new employees to give them a gist of the organization.
4. Newsletter: It is a printed publication produced at regular intervals focusing on a particular set of people. The content of a newsletter is presented in a writing style that is less formal and letter-like. For example, a newsletter published by a college consists of information about activities conducted during a particular period, special achievements by students or teachers, etc.
5. Events and Press support: Special events are acts of news development. The ingredients are time, place, people, activities, drama, showmanship; one special event may have many subsidiary events, such as luncheons, banquets, contests, speeches, and many others as part of the buildup.
6. Conferences and Seminars: Conferences and seminars are conducted for making people aware about the organization. For example travel companies generally call prospective clients and offer travel packages. The members are contacted through telephones and asked to attend seminar.
7. Websites: A website acts as a window for the outside world to know an organization. So it is designed not just to serve as a resource for members, but also to present a positive message to non-members who are browsing through.
ROLE OF ‘PR’ IN AN ORIGINATION
(i) Smooth functioning of business and achievement of objectives. (ii) Building corporate image that affects favorably on its products. Up keep of parks, gardens, sponsoring sports activities etc.
- CBSE Revision notes (PDF Download) Free
- CBSE Revision notes for Class 12 Business Studies PDF
- CBSE Revision notes Class 12 Business Studies – CBSE
- CBSE Revisions notes and Key Points Class 12 Business Studies
- Summary of the NCERT books all chapters in Business Studies class 12
- Short notes for CBSE class 12th Business Studies
- Key notes and chapter summary of Business Studies class 12
- Quick revision notes for CBSE board exams
CBSE Class-12 Revision Notes and Key Points
Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies. CBSE quick revision note for class-12 Business Studies, Chemistry, Math’s, Biology and other subject are very helpful to revise the whole syllabus during exam days. The revision notes covers all important formulas and concepts given in the chapter. Even if you wish to have an overview of a chapter, quick revision notes are here to do if for you. These notes will certainly save your time during stressful exam days.
- Revision Notes for class-12 Physics
- Revision Notes for class-12 Chemistry
- Revision Notes for class-12 Mathematics
- Revision Notes for class-12 Biology
- Revision Notes for class-12 Accountancy
- Revision Notes for class-12 Economics
- Revision Notes for class-12 Business Studies
- Revision Notes for class-12 Computer Science
- Revision Notes for class-12 Informatics Practices
- Revision Notes for class-12 English Core
- Revision Notes for class-12 History
- Revision Notes for class-12 Physical Education
To download Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies, sample paper for class 12 Physics, Chemistry, Biology, History, Political Science, Economics, Geography, Computer Science, Home Science, Accountancy, Business Studies and Home Science; do check myCBSEguide app or website. myCBSEguide provides sample papers with solution, test papers for chapter-wise practice, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar solutions, quick revision notes for ready reference, CBSE guess papers and CBSE important question papers. Sample Paper all are made available through the best app for CBSE students and myCBSEguide website.
- Nature and Significance of Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Principles of Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Business Environment class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Planning class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Organizing class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Staffing class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Directing class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Controlling class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Financial Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Financial Markets class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Consumer Protection class 12 Notes Business Studies
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
Leave a comment.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
NCERT Books and Solutions for all classes
Marketing Management Class 12 Notes
Please refer to the Marketing Management Class 12 Notes for Business Studies given below. These revision notes and important question answers have been prepared based on the latest NCERT book for Class 12 Business Studies. Our teachers have developed these short notes and Important Questions Class 12 Business Studies as per the latest syllabus for Grade 12 Business Studies issued by CBSE. Read these notes and important questions to get better marks in examinations
Class 12 Business Studies Marketing Management
Marketing Management
Marketing: Definition Marketing is a social process by which individual groups obtain what they need and want through creating offerings and freely exchanging products and services of value with others. – Philip Kotler
Marketing management is “the art and science of choosing target markets and getting, keeping, and growing customers through creating, delivering, and communicating superior customer value”.
Discuss about Marketing
Market: Definition A market consists of all the potential customers who have both the ability and willingness to buy a product or service to satisfy their needs or wants
Features of marketing • It seeks to provide what individuals or groups need or want • A market offering is created by the marketer. • It adds value to a product by increasing its utility • It is facilitated through the exchange mechanism
What can be Marketed? ❖ Physical product ❖ Services ❖ Ideas ❖ Persons ❖ Place ❖ Experience ❖ Properties ❖ Events ❖ Information ❖ Organizations
Functions of Marketing 1. Gathering and analysing market information is done to know the taste and preference of the target market. 2. Marketing planning is needed to meet the marketing objectives of the firm effectively and efficiently. 3. Product designing and development is carried out to make the product innovative and attractive. 4. Packaging and labeling are needed for product protection, product identification and product differentiation. 5. Branding helps to create a unique identity of the products. 6. Customer support services help to create a good image of the marketer in the eyes of consumers. 7. Pricing of product is a crucial decision as it may greatly influence the demand for a product. 8. Promotion helps to boost the sales of a product. 9. Physical distribution ensures the availability of the product at the right place, at the right time and in right condition so as to facilitate its purchase. 10. Transportation creates place utility through movement of goods from the production of goods to the place of distribution. 11. Warehousing creates time utility by providing for the storage during the time gap between the production and distribution of goods . 12. Standardization helps to produce goods as per predetermined specifications and grading facilitates their classification into groups on the basis of some criterion like quality, size etc.
Marketing Management Philosophies/Concepts
Product: Definition A product is anything of value i.e. a product or service offered to a market to satisfy needs or wants.
Important product decisions include • Determining its layout, features, quality, design etc. • Branding • Labelling • Packaging
A Product includes • Physical product • After sale services • Handling grievances • Replacement of parts etc.
Types of utilities offered by a product 1. Functional utility 2. Psychological utility 3. Social utility
Packaging: Definition Packaging is the process of designing a suitable wrapper or container for a product.
Importance of Packaging • Rising standards of health and sanitation • Useful in self service outlets • Innovative packaging adds value to a product • Facilitates product differentiation
Levels of Packaging • Primary package refers to the immediate container of a product. • Secondary packaging refers to the additional protection provided besides primary package. • Transportation packaging refers further packaging that helps in storage, identification of transportation of the product.
Functions of Packaging • Helps in product identification • Provides protection to the product • Facilitates the use of product • Assists in promotion of the product
Primary Market
Primary Market: Definition • Primary market is also known as new issue market as the securities are issued for the first time by the companies through this market. Primary Market is a segment of capital market.
Features of Primary Market • It is the new issue market. • Only buying of securities takes place. • Prices of the securities are determined by the company. • It involves dealings between the company and investors. • There is no fixed location of primary market.
Instruments of Primary Market • Shares • Debentures • Bonds
Methods of Floatation in Primary Market 1. Offer through Prospectus (The company approaches the members of the general public directly by issuing a prospectus) 2. Offer For Sale (The company approaches members of the general public indirectly through intermediaries like issuing houses, stock brokers etc.) 3. Private Placement (The company can raise finance by allotting securities to selective individuals and institutions only) 4. e-IPOs (The investors may subscribe to the securities of a company online) 5. Rights Issue (It is a pre-emptive right given only to the existing shareholders to subscribe to the securities of the company as per its terms and conditions)
Secondary Market: Secondary Market: Definition It is a market for old or existing securities It is a segment of capital market.
Features of Secondary Market / Stock Exchanges • It is the market for old/existing securities. • Both buying and selling of securities takes place. • Prices of the securities are determined by the forces of demand and supply. • It involves dealings between two investors. • Stock exchanges exist at fixed location
Money Market
Definition of Money Market The money market is a market for short term debt instruments whose period of maturity is upto one year. It is a segment of financial market.
Features of Money Market • It is a market for short term funds. • The main participants are institutional investors. • Since the cost of securities may be high, investment in the money market may require huge capital outlay. • The money market enjoys high liquidity as The Discount Finance House of India works as a compulsory market maker for it. • The instruments in money market carry low risk as the expected return is low on
Instruments In Money Market
Stock Exchange
Stock Exchange: Definition According To Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act 1956, “Stock Exchange means any body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, constituted for the purpose of assisting, regulating or controlling the business of buying and selling or dealings in securities.”
Functions of Stock Exchange ✔ Ensures liquidity and marketability of existing securities by a providing a ready and continuous market for the sale and purchase of securities. ✔ Helps in determining the prices of the securities through the forces of demand and supply. ✔ It promotes the habit of saving and investment among the general public. ✔ It provides a legal framework for fair and safe dealings. ✔ It helps the companies in raising finance thus facilitating capital formation and economic growth. It provides scope for healthy speculation in a controlled and restricted way.
Some important Definition
Dematerialization: Definition Dematerialization refers to the process of holding securities in electronic form.
Depository: Definition Depository is the organization with which an investor has to open a D-Mat account to hold securities in electronic form.
In India there are two depositories: 1. National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) 2. Central Depository Services Limited (CDSL) The depository participant serves as a link between the investor and the depository i.e. either NSDL or CDSL.
Screen Based Trading: Definition Screen-based trading refers to the process of buying or selling securities on-line.
Advantages of Screen-based Trading ✔ As the investors get an access to the stock market during real time, there is complete transparency and in the dealings. ✔ It provides a common platform for exchange of securities thereby increasing the efficient transactions by saving time, effort and money. ✔ This virtual market has a very wide reach hence it increases its liquidity.
Steps In The Trading And Settlement Procedure 1. The investor approaches a registered broker or sub-broker for trading. The investor has to sign a broker-client agreement and a client registration form. • The investor has to furnish certain details and information about himself including PAN number which is mandatory, date of birth, bank account details, income details etc. • A broker acts as an intermediary between the buyers and sellers. • After the completion of the above formalities, the broker opens a trading account in the name of the investor. 2. The investor has to open a demat account with a depository participant and a bank account for trading transactions in cash. 3. The investor then places an order to buy or sell shares with the broker: • By giving clear instructions about the desired quantity and price. • The broker will then make the investor aware about the feasibility of the order. • The broker will issue an order confirmation slip to the investor. 4. The broker will then execute the order through screen based trading by considering the best available deal. 5. The broker will issue a trade confirmation slip to the investor. 6. Within 24 hours after the deal is executed the broker issues a contract note. • A contract note contains details about the deal i.e. the number of securities bought/sold, price, date and time of transaction etc. • The contract note includes a unique order code generated by the stock exchange for that transaction. • A contract note is a legal which may be used to settle the claims between the investor and the broker. 7. Since the settlement cycle is T +2 therefore, within two days of receiving the Contract Note, the investor has to pay cash or deliver shares sold as the case may be. The broker can then forward it to the exchange. This is called pay-in-day. 8. On the T+2 day, cash will be paid or shares will be delivered as the case may be by the exchange to the other broker. This is called pay-out-day. Then, in case of sale of shares, the broker has to make the payment to the investor within 24 hours. 9. However, in the case of purchase of securities, the amount will be transferred electronically to the investor’s demat account.
Securities And Exchange Board Of India (Sebi) The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the regulator for the securities market in India. 1. It was established in the year 1988 by the Government of India. It was to function under the overall administrative control of Ministry of Finance of the Government of India. 2. It was given statutory powers on 30th January 1992 through an ordinance. 3. The ordinance was later on replaced by an Act of Parliament known as the SEBI Act, 1992.
The Organization Structure of SEBI • The various activities undertaken by SEBI are now divided into five operational departments. • Each department is headed by an executive director. • The head office of SEBI is located at Mumbai. • Besides, regional offices have been set up in Kolkata, Chennai and Delhi to attend to consumers complaints and maintain liaison with the issuers, intermediaries and stock exchanges in the concerned regions. • SEBI has also formed Primary Market Advisory Committee and Secondary Market Advisory Committee to assist in the process of SEBI’S policies formation. • These two committees consist of the market players, the investor’s association recognized by SEBI and the eminent persons in the capital market.
Objectives of SEBI 1. To prevent trading malpractice in these securities markets. 2. To protect the rights and interest of investors, and to guide and educate them. 3. To regulate and develop a code of conduct and fair practices by intermediaries like brokers, merchant bankers, etc. with a view to making them competitive and professional. 4. To regulate stock exchanges and the securities market to promote their orderly functioning.
Purpose and Role of SEBI SEBI has to be responsive to the needs of three groups, which constitue the market namely: • The issuers of securities so as to provide them a platform for raising capital in an easy, effective and efficient manner. • The investors so as to protect their interests in securities by keeping them abreast about the developments through true and appropriate information. • The market intermediaries in order to provide them a framework so as to enable them to perform their functions effectively and efficiently.
Objectives of Advisory Committees Formed by SEBI 1. To advise SEBI on matters relating to regulation of intermediaries for ensuring investor protection in the primary market. 2. To advise SEBI on issues related to development of primary market in India. 3. To advise SEBI on matters required to be taken by for changes in legal framework to introduce simplification and transparency in the primary market. 4. To advise SEBI on disclosure requirements for companies. 5. To advise the board in matters relating to the development and regulation of secondary market in the country.
Functions Of Sebi
Protective Functions of SEBI • SEBI prohibits fraudulent and unfair trade practices in the securities market • Promotion of fair practices and code of conduct in securities market • Undertaking steps for investor protection • Controlling insider trading and imposing penalties for such malpractices. The Preamble of the Securities and Exchange Board of India describes the basic functions of the Securities and Exchange Board of India as “…to protect the interests of investors in securities and to promote the development of, and to regulate the securities market and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto”
Developmental Functions of SEBI 1. Ensuring training of intermediaries of securities market 2. Conducting research and publishing information useful to all market participants 3. Facilitating flexibility in the working of capital markets.
Regulatory Functions of SEBI ✔ Registration and regulation of brokers, sub-brokers and other players in the financial market. ✔ Registration of collective investment schemes and Mutual Funds. ✔ Conducting enquiries and audits of stock exchanges & intermediaries. ✔ Regulation portfolio exchanges, underwriters, merchant bankers and the dealings in the stock exchanges. ✓ Regulation of takeover bids by the companies
Case Study Marketing Management Class 12 Business Studies
Question. Meca Ltd. a reputed automobile manufacturer needs Rupees ten crores as additional capital to expand its business. Atul Jalan, the CEO of the company wanted to raise funds through equity. On the other hand the Finance Manager, Nimi Sahdev said that the public issue may be expensive on account of various mandatory and non-mandatory expenses. Therefore, it was decided to allot the securities to institutional investors. Name the method through which the company decided to raise additional capital. Ans. Private placement is method through which the company decided to raise additional capital .
Question. These days, the development of a country is also judged by its system of transferring finance from the sector where it is in surplus to the sector where it is needed most. To give strength to the economy, SEBI is undertaking measures to develop the capital market. In addition to this there is another market in which unsecured and short-term debt instruments are actively traded everyday. These markets together help the savers and investors in directing the available funds into their most productive investment opportunity. 1. Name the function being performed by the market in the above case. 2. Also, explain briefly three other functions performed by this market. Ans. 1. Mobilisation of funds is the function being performed by the financial market in the above case. It performs the allocative function by mobilisation of savings and channelising them into the most productive avenues. 2. The other three functions being performed by the financial market are outlined below: ✔ It helps to determine the price for the financial asset in a particular financial market through the market forces of demand and supply. ✔ It provides liquidity to the financial assets by providing ready markets wherein the securities can be easily converted into cash or vice versa. ✔ It provides a common platform for exchange of securities thereby reducing the cost of transactions by saving time, effort and money spent by the buyers and sellers in locating each other.
Question. These days, the development of a country is also judged by its system of transferring finance from the sector where it is in surplus to the sector where it is needed the most. To give strength to the economy, SEBI is undertaking measures to develop the capital market. In addition to this, there is another market in which unsecured and short-term debt instruments are actively traded every day. These markets together help the savers and investors in directing the available funds into their most productive investment opportunity. 1. Name the function being performed by the market in the above case. 2. Name the market segment other than the capital market segment in which unsecured and short-term debt instrument are traded. Also, give any three points of difference between the two Ans. 1. Mobilization of funds is the function being performed by the financial market in the above case. It performs the allocative function by mobilization of savings and channelizing them into the most productive avenues. 2. Money market is the other segment of market.
Question. ABC Ltd. issued prospectus for the subscription of its shares for Rs. 500 crores in 2008. The issue was oversubscribed by 20 times. The company issued shares to all the applicants on pro-rata basis. Later SEBI inspected the prospectus and found some misleading statement about the management of the company in it. SEBI imposed a penalty of Rs. 5 crores and banned its three executive directors for dealing in securities market for three years. Identify the function and its type performed by SEBI in the above case. Ans. Protective function has been performed by SEBI in the above case. And the type of Protective function is Prohibition of fraudulent and unfair trade practices.
Question. “Unicon Securities Pvt. Ltd” was established to deal in securities. It was registered as a stock broker with National Stock Exchange (NSE) and Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) to trade in securities listed at these exchanges. It is also a depository participant with CDSL and NSDL. In the first three years, it developed its business successfully. After that the composition of Board of Directors changed. Some customers complained to the customer care centre of the company that shares purchased by them and for which the payment has been duly made, were not transferred to their D’mat Accounts by “Unicon securities Pvt. Ltd” . The executive of customer care centre promised the aggrieved customers that their shares will be transferred to their respective D’mat Accounts very soon. But the company delayed the matter and didn’t transfer the shares of the customers to their D’mat Accounts. This eroded investors confidence and multiplied, their grievances. 1. Identify the step of trading procedure in a stock exchange which has not been followed by “Unicon Securities Pvt. Ltd” . 2. Name the Apex statutory body of capital market to whom customer can complain to redress their grievances. 3. Write two values not followed by Unicon Security Pvt. Ltd . Answer: 1. The step of trading procedure in a stock exchange which has not been followed by “Unicon Securities Pvt. Ltd” is settlement i.e. the delivery of shares through the D’mat Account of the broker to D’mat account of the investors. 2. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the Apex statutory body of capital market to whom customer can complain to redress their grievances. 3. The two values not followed by Unicon Security Pvt. Ltd are’: ✔ Truthfulness ✔ Fair practices
Question. Reshu’s father has gifted her the shares of a large cement company with which he had been working. The securities were in physical form. She already has a bank account and does not possess any other forms of securities. She wished to sell the shares and approached a registered broker for the purpose. Mention one mandatory detail which she will have to provide with the broker. Ans. Reshu will have to give her Permanent Account Number (PAN) to the broker as it is mandatory as per law.

Related Posts:

Related Posts

Important Questions for NCERT Class 12 Economics

Notes And Questions NCERT Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance

Important Questions For NCERT Class 12 Economics Production Function and Returns to Factor
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free

Class 12 Business Studies Assignments
We have provided below free printable Class 12 Business Studies Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 12 Business Studies . These Assignments for Grade 12 Business Studies cover all important topics which can come in your standard 12 tests and examinations. Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 12 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable Assignments for Business Studies Class 12 with solutions and answers. All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Business Studies Class 12. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Business Studies class 12 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 12 Business Studies Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Business Studies Class 12 Assignments Pdf Download
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 12 Business Studies . Students and teachers can download and save all free Business Studies assignments in Pdf for grade 12th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 12 important questions and answers for Business Studies as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 12 Business Studies and CBSE Assignments for Business Studies Class 12 will be really helpful for standard 12th students to prepare for the class tests and school examinations. Class 12th students can easily free download in Pdf all printable practice worksheets given below.
Topicwise Assignments for Class 12 Business Studies Download in Pdf

Advantages of Class 12 Business Studies Assignments
- As we have the best and largest collection of Business Studies assignments for Grade 12, you will be able to easily get full list of solved important questions which can come in your examinations.
- Students will be able to go through all important and critical topics given in your CBSE Business Studies textbooks for Class 12 .
- All Business Studies assignments for Class 12 have been designed with answers. Students should solve them yourself and then compare with the solutions provided by us.
- Class 12 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Business Studies chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf
- Class 12 Business Studies question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 12 Business Studies students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free assignments for Business Studies Class 12 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 12 Business Studies chapter-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Business Studies in Grade 12, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here topic-wise Business Studies Grade 12 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best collection of question bank and practice tests for Class 12 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 12 Mathematics Application Of Integrals Assignments

Class 12 Physical Education Assignments

Class 12 Biology Assignments
- List of Commerce Articles
Marketing Concept
Concept of marketing - class 12 business studies, what is marketing concept.
Marketing concept is a set of strategies that the firms adopt where they analyse the needs of their customers and implement strategies to fulfil those needs which will result in an increase in sales, profit maximisation and also beat the existing competition.
The marketing concept has been widely used by companies all over the world in the present age, but the situation was not the same earlier. As per this concept, it is said that for an organisation to satisfy the objectives of the organisation, the needs and wants of the customer should be satisfied. This theory was first mentioned in Adam Smith’s book “The Wealth of Nations” in 1776 but came into widespread use only 200 years later.
Therefore, marketing can be said as a process of acquiring customers and maintaining relations with them and at the same time matching needs and wants with the services or product offered by the organisation, which ensures that the organisation will become profitable.
What are Needs, Wants and Demand
Marketing concept focuses on the needs, wants and demands of customers. Let us understand them in brief.
Needs are basic requirements that enable a healthy and active life. If needs are not fulfilled, it will result in the dysfunction of the system, which can result in disability or death. It can be objective as well as physical as in need of food, water and shelter.
Wants are something that is desired by the person. These are not required for day to day functioning. Wants are not necessary for basic survival and are mostly moulded by cultural influence.
3. Demands:
When the needs and wants are supported by an ability to pay, it becomes a demand.
Types of Marketing Concept
Five types of marketing concepts are as follows:
1. Production Concept
2. Product Concept
3. Selling concept
4. Marketing concept
5. Societal marketing concept
Production Concept
This concept was based on the assumption that customers are primarily interested in products which are accessible and affordable. This concept was introduced at a time when business was focused mainly on production. It says that a business will be able to lower costs by producing more quantity or mass production of goods.
Solely focusing on producing goods may lead to the firm deviating from its objective.
Product Concept
The product concept is based on the assumption that customers will be more inclined towards products that are offering more quality, innovative features and top-level performance.
In this type of marketing concept, a business focuses on creating high-quality products and refining it every time in order to develop a better and improved product.
Selling Concept
While the previous two concepts focused on production, the selling concept is focused on selling. It believes that customers will be buying products only when the product is aggressively marketed by the company. It does not focus on building relationships with customers, and ensuring customer satisfaction is also not deemed necessary.
A marketing concept places the centre of focus on the customer. All the activities that are undertaken by an organisation are done keeping the customer in mind. The organisations are more concerned about creating value propositions for the customers, which will differentiate them from the competition.
Societal Marketing Concept
This is the fifth and most advanced form of the marketing concept. Here the focus is on needs and wants of the customer as well as ensuring the safety of the customer and society first. It believes in giving back to society and making the world a better place for all human beings.
This was all about the different marketing concepts. For more such interesting concepts, stay tuned to BYJU’S.
Important Topics for Commerce students:
- What is a Balance Sheet?
- Partnership Deed
- What is Goodwill?
- Treatment of Goodwill
- What Is Partnership
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Good and interesting
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Commerce Aspirant » Business Studies Class 12 » Functions of Marketing Class 12 Notes
Functions of Marketing Class 12 Notes
There are various activities involved in marketing management and these are also called the Functions of Marketing Management Class 12. A detailed explanation of all the functions is given below.
Functions of Marketing Management Class 12
Gathering and analysing market information.
To satisfy the customers we need to find out what their wants and needs are. To find out the needs and wants it is important and imperative to gather the information and analyse it properly. This information can be in form of feedback from existing customers or in the form of surveys from potential customers. The survey is done to find out what lies as an opportunity for the organization. Analysing the information is also important to find out what all firm’s qualities the customers like i.e. strengths and what qualities would they like to change i.e. weaknesses or potential improvements. Threats are also found through surveys and feedback and tracking environmental changes and trends. With the betterment of technology each day, surveys and feedback have become easy as they have turned online by adding an option for rating the company’s product and services by giving them stars, through Google forms etc.
Marketing Planning
As per Functions of Marketing Class 12 Making marketing plans is very important because it is not possible to grow without having a plan for the future. When we know where we want to go then only it will be possible to reach there. So to fill the gap between the present position and the future expected to position it is important to make plans. Marketing plans can be like this- a firm which has a market share of 10% and it wants to increase its market share in the next 2 years by 5%. A proper plan will help in achieving the objectives.
Product Designing and Development under Functions of Marketing Management
When the market information is gathered and properly analysed then a proper plan is laid out, and then comes the designing of the product or service which be built according to the needs and wants of the customers. A good design helps in attracting customers and will give a competitive edge. Product design includes decisions related to size, shape, style etc.
Standardization and Grading under Functions of Marketing Management
One of the important Functions of Marketing Class 12 is Standardization and grading. Standardization means determining some standard or specifications related to the size, shape colour, quality etc of goods so that they will be produced according to these predetermined specifications. This helps the consumer in being assured about the product and they need not check the qualities they are looking for again and again. For example: when a consumer will buy an Amul product, says Amul choco minis, then they will be assured of the same quality product in each box.
Grading, on the other hand, is done for distinguishing between various products of the same brand with differences in quality, colour, size, shape or any other characteristic. For example, there are three categories of Amul milk. Amul tazza, amul shakti and amul gold. This grading is done based on the fat content in each variety.
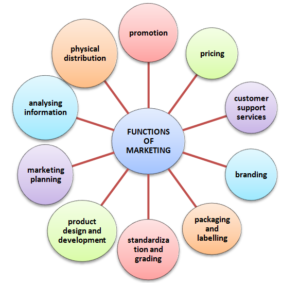
Packaging and labelling
Packaging for a product and labelling a product so that it can be put up on a package are equally important. Packaging is important from a point of view of any breakage, damage, leakage or destruction of the product. It also helps in handling the product in a better way. It can be in the form of bottles, plastic covers, canisters, wooden boxes etc. While labelling will help a product to get identified in the market very easily. Such as McDonald’s will get easily identified by the customers in comparison to some other new brands in the market.
Branding under Functions of Marketing Management
Branding is also a very important decision and function in marketing management class 12. It helps in deciding whether the product will be sold under its generic name or will have a brand name. a brand name helps the product to get easily identified and also helps in building product loyalty. For example, a pen can be sold as a simple pen without a brand name or it can be sold as Elkos, Goldex, Rotomac etc. this will help the customers to buy the product next time with ease.
Customer Support Service
Customer support service means providing customers with after-sales service and helping them in solving their queries and grievances. This helps in creating brand loyalty and getting repeat sales of the product. These services can include maintenance services, technical services credit services etc.
Pricing of product
Price means the amount that the customer will have to pay in order to get the product. It is a very important function in marketing management class 12 for the success of the product. It is beneficial in increasing the demand for the product by offering better quality products than the competitors at a lower price. Price includes various aspects such as the cost involved, profit margin etc.
Promotion under Functions of Marketing Management
Promotion of the product means creating awareness of the product by persuading people to purchase the product. There are various methods through which promotion can be done. These methods include advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, publicity etc.
Physical Distribution
It is also an important function of marketing class 12 because it involves decisions regarding the selection of the channel of distribution. There are various channels of distribution such as direct and indirect channels. It also involves decisions regarding storage, warehousing, managing inventory, transportation of goods etc.
Transportation of goods is also part of the physical movement of goods and this depends on the type of good, the cost involved and target market location etc. Warehousing is also important because sometimes there is a time gap between the production of goods and their sale and thus keeping the products in a safe place is important.
Also, it is very important for maintaining the smooth flow of products in the market without creating a gap between demand and supply.
function in marketing management class 12 concludes that marketing can’t work in isolation it is a combination of so many activities that a firm does to satisfy the needs and wants of the consumers with their product.
BST Chapter 11 – Marketing
- Marketing Management
- Marketing Management Philosophies
- Functions of marketing
- Marketing mix
- Products – Classification of Products
- Packaging – Levels , Functions & Importance
- Pricing – Factors affecting Price of a Product or Service
- Components of Physical Distribution
- Channels of Distribution
- Advertising – Benefits, Limitations, Objections
- Personal selling
- Sales promotion
- Publicity – Characteristics and Objectives
- Economics Class 12 Notes
- Business Studies Class 12 Notes
- Accountancy Class 12 Notes
- Economics Class 12 MCQs
- Business Studies Class 12 MCQs
- Accountancy Class 12 MCQs
Sandeep garg Class 12 Solutions
Unit Number 319, Vipul Trade Centre, Sohna Road, Gurgaon, Sector 49, Gurugram, Haryana-122028, India
- +91-9667714335
- [email protected]
Class 11 Notes
- Economics Class 11 Notes
- Accountancy Class 11 Notes
Class 11 MCQs
- Economics Class 11 MCQs
- Business Studies Class 11 MCQs
Class 12 Notes
Class 12 MCQs

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

28.23: Assignment- Marketing Mix Examples
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 45631
Open Pedagogy Assignments are assignments in which students use their agency and creativity to create knowledge artifacts that can support their own learning, their classmates’ learning, and the learning of students around the world. (See this peer-reviewed article for more details.) The assignment on this page is aligned to the learning outcomes of Introduction to Business and we’ve identified the module where the reading appears. All of the assignments can be created with a cell phone camera or any video recording device, Google or Word documents, and your learning management system.
Learning Objectives
- Give examples of the marketing mix
In the Marketing Function module, we cover the 4Ps: Products, Promotion, Place, and Price. Even if you haven’t had experience with marketing, you have a lot of experience as a customer. What is the marketing mix of one of your favorite brand? Think of the marketing mix as a recipe that can be adjusted—through small adjustments or dramatic changes—to support broader company goals.
Using your cell phone or any other recording device, create a short video about the 4Ps of one of your favorite products. You don’t have to edit or create a professional-grade film. You’ve most likely have done this type of recording already on social media, so feel free to use the same informal conversational tone.
Do an internet search for a product of your choice. Research for areas of their website where they mention details about their products, promotions, places, and price. Think of your audience as fellow students who are interested to learn about these ideas because they want to learn important marketing concepts. In your video, you can address the following:
- What are some interesting points on the website about the product?
- What are their promotions? What’s the price? Where can you find the product?
- If you have had experience with the company of your choice, and you feel comfortable sharing your experience, tell your audience what worked or didn’t work for you about their marketing. What can they improve?
A Note To Teachers: For this assignment, the first term students will be creating the videos, and then the next term’s students can respond to the videos. After you have two terms of examples, use the best three from the batch as examples and start the process over again. Using the videos as starting points for OL discussion boards may work as well. If you are using the Salty Paws Case Study, you could refer back to that assignment as guidance for your students who may be learning these concepts for the first time.
Contributors and Attributions
- Open Pedagogy Assignment: Marketing Mix Examples . Authored by : Lumen Learning . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Bihar Board
SRM University
Jac 12th result 2024.
- TS Board Result 2024
- Punjab Board Result 2024
- JAC Board Result 2024
- WB Board Result 2024
- UK Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
ISC Class 12 Mass Media & Communication Syllabus 2024-25: Download Class 12th Mass Communiation Syllabus 2025 PDF
Isc class 12 mass media & communication syllabus 2025: here, students can find the cisce board class 12th mass media and communication syllabus 2024-25 for students of the current academic session. also, get a free pdf download link of the detailed syllabus here..

ISC Class 12 Mass Media & Communication Syllabus 2025: The CISCE Board Class 12th Mass Media and Communication Syllabus 2024-25 has been provided in this article along with the PDF download link of the same. The curriculum has been specifically designed by the board authorities and revised as per the needs and requirements of the current generation. We have brought to you the revised syllabus provided by the board, and hence all of you can be carefree while referring to the syllabus presented here. Also, get to know about the marking distribution, exam pattern, course structure laid down by the board, and much more.
ISC Class 12 Mass Media & Communication Syllabus 2025
Isc class 12 mass media and communication project work syllabus .
- Any two projects from the topics covered in the theory syllabus have to be picked by students.
- Project work can include any of the following:
- Script writing
- Documentary/ video
- Book review/ film review/ posters/ advertisements/ cartoon strip
- Advertisement campaign, social media campaign
- Case study
- The project work is of total 30 marks
- 15 marks are based on the internal evaluation done by teachers
- The rest 15 marks are based on evaluation by Visiting Examiner
ISC Class 12 Mass Media & Communication List of Suggested Assignments for Project Work
- Develop a script for radio advertisement on any one social issue of your choice. The duration of the advertisement should not be more than 30 seconds. You are also expected to develop a suitable jingle.
- Develop a short comic story. You can choose maximum 4 characters to build the story. The cartoons should be drawn by yourself in your own way. Write suitable dialogues. Colouring of the comics is optional. The story should not be more than five scenes or 15 drawings. candidates can submit them pasted in a chart or book. No software should be used for this assignment.
- Produce a one hour documentary on the topic “Life in School”. The documentary must contain video clips from various activities conducted in school as well as general school life such as recess and dismissal. There must be at least one interview with a student and one with a member of staff. Narration must be clear and fit with the visual matter. Any recording not in English must have subtitles.
- Develop an advertising campaign on any issue related to the conservation of the environment. You can choose any non-electronic media for the campaign. For example, pamphlets, placards, leaflets, etc. Prepare a report of the detailed process along with pictures of the campaign.
- Create a power point presentation showcasing the various Graduation courses a student can apply for after the completion of school. The PPT must contain statistical data regarding employment rates of adults who have completed the courses, number and type of jobs which make use of the courses as well as difficulty of the courses. Pie charts and bar graphs may be used. Reasons must be given why the courses should be taken as well as what advantages certain courses have over others.
- Choose a social media campaign. Follow it for a week. Do a detailed analysis of the campaign in terms of its strategy, followers, comments/ likes, sharing and development over time.
- Use any camera or mobile phone with video facility to create a 1-5-minute fiction story on a topic of your choice.
- Write a detailed review of a film from any one of the following genres: Fantasy/ Sci-fi, comedy, musical
Also Check:
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- PSEB 12ਵੀਂ ਟਾਪਰ ਸੂਚੀ 2024
- 12th, 8th ਨਤੀਜਾ 2024 PSEB
- jac.jharkhand.gov.in Class 12 Result 2024
- Uttarakhand Board Result at Jagran Josh
- UK Board 12th Toppers 2024
- JAC 12th Toppers 2024
- HBSE 12th Result 2024
- AP SSC Results 2024 Manabadi by Jagran Josh
- AP SSC Topper List 2024
Latest Education News
[DECLARED] JAC 12th Result 2024 Released: Check Jharkhand Board Class 12 Results Out at jac.jharkhand.gov.in, jacresult.com, Check Online by Roll Number, Pass Percentage and Topper's List
GJU Admit Card 2024 OUT at gjuonline.ac.in, Check Download Link
HBSE Result 2024: Check हरियाणा बोर्ड Result Online at bseh.org.in
HBSE 12th Result 2024: Check हरियाणा बोर्ड Class 12 Result Online at bseh.org.in
International Workers Day 2024: List of Countries that Celebrate Labor Day on 1st May, Check Here
Optical Illusion Vision Test: Find the pair of glasses in the picture in 6 seconds!
UPPSC Medical Officer Eligibility 2024: Check Age Limit, Qualification and Nationality
"Sathyabama Shines Bright with Unprecedented Success in Placements!: Excellence Day 2024"
UPMRC Admit Card 2024 OUT at lmrcl.com: Download UP Metro Call Letter Here
Labour Day 2024: Are Banks, Offices And Schools Closed On May 1? Check The Complete List Here
UPSC IES ISS Salary 2024: Check In Hand Pay, Job Profile, Perks and Allowances
PSEB 12th, 8th Result 2024 Analysis: 93.04 Pass out in Class 12, Check 12th 8th Result Details Here
Today’s School Assembly Headlines (01 May): 26th Chief Of Naval Staff, Nepal Investment Summit 2024, Ammunition Cum Torpedo Cum Missile Barge and Other News in English
India T20 World Cup Squad 2024: Complete List of Team Players and Name
TSCB Admit Card 2024 Out For 156 Clerk, MTS and Other posts at tscbank.nic.in: Direct Link to Hall Ticket
Personality Test: Your Sitting Positions Reveals Your Hidden Personality Traits
CGCRI Apprentice Recruitment 2024: Applications Invited For Various Posts, Check Eligibility
India T20 World Cup 2024 Squad: टी20 ताज के लिए भारत ने बनाई ‘विराट’ टीम, किस रोल में कौन देखें यहां
Kerala SSLC, Plus 2 Results Date and Time Confirmed, 10th Results on May 8, DHSE Plus 2 Results on May 9
NIOS 12th Business Studies Syllabus 2023-2024: Download Class 12 Business Studies Syllabus PDF
Great Salt Lake wetlands endangered by inland port project, environmentalists say
The project was expanded to almost 9,000 acres by the utah inland port authority..
(Trent Nelson | The Salt Lake Tribune) Weber County property slated for an inland port on Friday, April 5, 2024.
Environmentalists were worried when the Weber County Commission approved a 903-acre inland port industrial project on sensitive wetlands and bird habitat on the eastern shore of the Great Salt Lake.
“You shouldn’t be intentionally subsidizing development next to a globally important bird area,” Deeda Seed, with the Center for Biological Diversity, told The Tribune at the time. “You also shouldn’t be building on the shores of the Great Salt Lake.”
The proposed project is part of a new approach that the entity, originally formed in 2018 to develop the northwest part of Salt Lake City into an international port , is taking. Along with a branding redesign, the Utah Inland Port Authority (UIPA) is less about ports and more about “building a better statewide logistics system.” Cities with industrial or manufacturing plans that are approved as port projects can secure additional funding through UIPA’s $60 million infrastructure bank or through the creation of tax differential funds.
“For us, we’re just saying any place where we can create that access point,” Inland Port Authority executive director BEN Hart previously told The Tribune , “where we can either offload truck to rail or whatever, something that’s multimodal, that’s kind of our definition.”
He hopes the agency pursues more projects that bring “advanced manufacturing and “clean technology” jobs.“
T he commission recently expanded the project to almost 9,000 acres, although many residents spoke out against the project.
“You’re taking ... this pristine land,” a Davis County resident said at the meeting, “[and] turning it into another parking lot for trucks, with developers who are going to be subsidized.”
UIPA also has a wetlands policy in the works. On Monday morning at the Utah Inland Port Authority’s board meeting at the Utah Capitol, Hart took a few minutes to address the proposed Weber County project.
“We’re not going to beat around the bush, there are a lot of wetlands in this area,” Hart said, “and we take seriously our responsibility to make sure that those wetlands are protected.”
He noted that the land in Weber County already allowed for industrial use and the Inland Port Authority would not change that. “What the port does bring is additional protections for existing wetlands and the lake; in addition to additional protections the inland port also brings funding,” he said.
Much of the area is currently open, agricultural land with some ephemeral ponds and birds. Compass Minerals and Westinghouse Electric Company also operate in the quiet corner of Weber County.
On Monday, Seed delivered a letter with 1,515 signatures asking the Inland Port Authority to complete traffic and independent wetland studies to “fully assess the impact to the ecosystem, along with a Human Health Risk Assessment” before handing over public resources.
“Significant public harm will be caused by paving over, destroying and impairing thousands of acres of Great Salt Lake’s biological wetlands,” Seed told the authority, “and to add insult to injury, taxpayer dollars will be used to subsidize this destruction.”
She also noted that the project would be wedged between the Harold S. Crane and Ogden Bay Waterfowl Management Areas.
Rhonda Anderson-Lauritzen, a resident of Hooper, told the port authority board she frequents the Ogden Bay Waterfowl Management Area near her home. “But I only go in for half of the year because all of the entrances are closed to all foot traffic. I emphasize this is such a sensitive area that you’re not allowed to even walk in there.”
From March through July 31 parts of the management area are closed for wildlife production, according to the Utah Division of Wildlife Resources wildlife recreation access map.
(Trent Nelson | The Salt Lake Tribune) Brent Davis and Deeda Seed lead a tour of Weber County property slated for an inland port on Friday, April 5, 2024.
If birds in the area are sensitive to human footsteps, Anderson-Lauritzen wondered how increased truck traffic and lights would impact populations.
“Given the close proximity to the Great Salt Lake, care will need to be taken from the beginning to ensure water-wise construction, wildlife-friendly lighting practices, and traffic considerations that minimize impacts to the surrounding area,” the draft proposal states. It also notes that roads will likely need to be constructed and improved.
Many are skeptical of the environmental protection claims and point to the loss of habitat in Salt Lake City’s northwest quadrant.
“In Salt Lake City promises were made about ‘sustainable development’ but instead giant pollution-inducing warehouses are being built and wetlands are paved over,” residents of Weber County wrote in a letter sent to the Weber County Commissioners on April 16. “They are six years into this project, and although a Traffic Study, Human Health Risk Assessment and Community Impact Study were agreed to, none of these studies have been completed.”
The Utah Inland Port Authority will formally discuss the proposed Weber County Inland Port Project in May.

Donate to the newsroom now. The Salt Lake Tribune, Inc. is a 501(c)(3) public charity and contributions are tax deductible
Weber State University takes Utah nurse to next level in life, career.
How one byu student is helping her peers combat perfectionism and other mental health challenges, stowaway cat from utah shipped to california in amazon returns package, opinion: skepticism is healthy — but in medicine, it can be dangerous, new film fuses art and indigenous voices to spotlight great salt lake’s plight, featured local savings.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For this BST project class 12 on Marketing Management, The students can consider the following products and conduct research to gather information about the various aspects concerning the marketing of the product. Some of the most prominent and sought-after products are mentioned in the table below: Adhesives: Mobile Phones: Inverters:
Very Short Answer Questions NCERT Business Studies Solutions Class 12 Chapter 11. Q.1 State any two advantages of branding to marketers of goods and services. The advantages of branding to marketers of goods and services are as follows: 1. It enables a firm to distinguish its product from the competitor firm.
The Class 12 Revision Notes Chapter 11 comprise explanations of the different elements of the marketing mix, its classification into different categories, the factors that affect price determination, the types of distribution channels, and the tools of promotion mix like sales promotion, personal selling, publicity, and advertising.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 - Marketing. Very Short Questions. 1. Explain the advantages of branding to marketers of goods and services. Ans: Branding entails giving a product a distinct name, sign, symbol, or term for identification. The following are the benefits of branding for marketers.
CBSE Class-12 Revision Notes and Key Points. Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies. CBSE quick revision note for class-12 Business Studies, Chemistry, Math's, Biology and other subject are very helpful to revise the whole syllabus during exam days. The revision notes covers all important formulas and concepts given in the chapter.
Gathering and analysing market information is done to know the taste and preference of the target market. 2. Marketing planning is needed to meet the marketing objectives of the firm effectively and efficiently. 3. Product designing and development is carried out to make the product innovative and attractive. 4.
So, go ahead and check the Important Notes for Class 12 Business Studies Marketing. Points to Remember. 1. Market It refers to the 'set of potential and actual buyers of a product or service'. 2. Customer It refers to the people or organisations that seek satisfaction of their needs and wants. 3.
According to JF Pyle, "Marketing is that phase of business activity through which the human wants are satisfied by the exchange of goods and services.". 5. Features of Marketing. (i) Need and want (ii) Creating a market offering. (iii) Customer value (iv) Exchange Mechanism. 6.
MARKETING (SUBJECT CODE 812) Blue Print for Sample Question Paper for Class XII (Session 2020-2021) Max. Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 60 PART A - EMPLOYABILITY SKILLS (10 MARKS): UNIT NO. NAME OF THE UNIT OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS TOTAL QUESTIONS 1 MARK EACH 2 MARKS EACH 1Communication Skills-IV 1 1 2.
812- MARKETING Class XI & XII - 2021-2022. This course will empower the students to gain insights into what marketing practitioners actually do and the decisions they have to make in day to day marketing. This course is an effort to taught marketing in more creative and visual way with the coverage of advances in new technology and the social ...
Class 12 Assignments. We have provided below free printable Class 12 Business Studies Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 12 Business Studies. These Assignments for Grade 12 Business Studies cover all important topics which can come in your standard 12 tests and examinations.
8 likes • 5,911 views. K. KushShah65. Marketing Management of the product- BACKPACKS USP- Expandable backpacks and durable. Education. 1 of 20. Download now. Download to read offline. Business Studies Project Marketing Management Class 12 CBSE - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Marketing concept is a set of strategies that the firms adopt where they analyse the needs of their customers and implement strategies to fulfil those needs which will result in an increase in sales, profit maximisation and also beat the existing competition. The marketing concept has been widely used by companies all over the world in the ...
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Case Studies - Marketing. Marketing is a social process of identifying needs and wants and satisfying them through created market offering by giving something of value to the customer with the help of an exchange mechanism. Important Features of Marketing. Needs and wants. The needs and wants of the target ...
7.Philosophies/Concepts of Marketing Management. (i)Production concept Consumers prefer products which are widely available at an affordable price. (ii)Product concept Consumers prefer products with superior quality, performance and features. (iii)Selling concept Firms believe that aggressive selling and promotional efforts will convince a ...
812 marketing xii - Download as a PDF or view online for free ... Upload. 812 marketing xii • 3 likes • 1,437 views. K. kushmanchanda2 Follow. class 12 marketing support material helpful for sudies Read less. Read more. Education. Report. Share. Report. Share. 1 of 129. Download now Download to read offline. ... Assignment 1 (marketing).doc ...
It is also an important function of marketing class 12 because it involves decisions regarding the selection of the channel of distribution. There are various channels of distribution such as direct and indirect channels. It also involves decisions regarding storage, warehousing, managing inventory, transportation of goods etc.
The subject for this assignment should be the organization and products and/or services you identified for the Marketing Plan, Parts 1 and 2 Assignments. When you submit this assignment, you should submit it as a complete marketing plan, including all your work from Marketing Plan Assignments, Parts 1 and 2. All elements of your marketing plan ...
4: Marketing Strategy. Expand/collapse global location. 4.23: Assignment- Marketing Plan, Part I. Page ID. Lumen Learning. Lumen Learning. Student Instructions: Complete the following information about the organization and products and/or services you will focus on as you develop a complete marketing plan throughout the course.
28: Module 13- Marketing Function. 28.23: Assignment- Marketing Mix Examples. Expand/collapse global location. 28.23: Assignment- Marketing Mix Examples. Page ID. Open Pedagogy Assignments are assignments in which students use their agency and creativity to create knowledge artifacts that can support their own learning, their classmates ...
ISC Class 12th Mass Media & Communication Syllabus 2024 - 2025: Get here detailed ICSE Board Class 12 Mass Media and Communication Syllabus chapter-wise, marking scheme, weightage, paper pattern ...
Former President Donald Trump sits in Manhattan criminal court with his legal team ahead of the start of jury selection in New York, Monday, April 15, 2024.
Utah high school removes class assignment on student essay titled 'It Is So Hard to Be Trans' What Utah football player Aaron Lowe's parents said to the man who killed their son
Editor's note: This story discusses sexual assault. If you need to report or discuss a sexual assault in Utah, you can call the Rape and Sexual Assault Crisis Line at 801-736-4356. The National ...
More than 1,000 people signed a petition asking the Utah Inland Port Authority to pause before providing funding to an industrial project on wetlands near the Great Salt Lake.