

How to use the PhD title and all the little doctorate “rules”
There are many conventions in the academic world that can make it difficult to navigate the PhD title. The PhD title is awarded to those who have completed a doctoral degree but, not many people know how to use it once they have it.
This article will go through everything you need to know about using the PhD title and when you can start using it.
The “rules” are relatively simple and can be broken as they are not officially set in stone – other than when you can officially call yourself a doctor.
There is no one correct answer but it may be misleading if you use the PhD title incorrectly. Here are the recommendations for effective communication.
It very much depends on the setting. Here are some examples of how I would use my PhD titles awarded to me after my PhD degree.
How do you Write PhD correctly after a name? Is it ph d or phd?
It can be confusing to know exactly how to write PhD after your name. Which bits are capitalised? Is there a ‘.’ In the middle?
When writing a name with a PhD after it, the correct way to do so is to use “PhD” or “Ph.D. or Ph.D”
Depending on the preference of the individual, either form can be used.
However, if the individual has a business card that states their degree in full, then the more formal “Doctor of Philosophy” should be used.
It is important to note that using “PhD” without any periods is incorrect; this abbreviation should only be used in informal contexts such as emails or text messages. I tend to use PhD in my YouTube videos and some people have pointed out that this is incorrect…
Following the individual’s preferred format will ensure that their name and credentials are properly represented.
Should you use Dr as well as PhD?
Some people like to use Dr and PhD in their official titles. There are a couple of important points that you need to know about markers and academic titles.
- A person can have more than one marker in their name. For example my full title is Dr Andrew Stapleton, PhD, MChem.
- The doctor title at the front can be used as a variant to the PhD at the end.
It can be a little bit ambiguous if I was to use Dr Andrew Stapleton, PhD as there are two markers. This could mean that I have two PhD’s, it could mean that I have a PhD and a medical doctorate, or it could just be that I want to use both the doctor and the PhD tags for the one degree.
However, in my experience, I still like to use the doctor title at the front and the PhD tag at the end of my name for official purposes.
Academics would rarely use the PhD suffix in everyday communication. They would much rather just use the doctor title.
What is the proper title for a PhD?
The proper title for a PhD is Doctor of Philosophy. However, some teachers and professors like to be referred to without their official title.
If you are not sure about how your professor, lecturer, or friend with a PhD wishes to be officially addressed you can ask them.
Most of the time, I like to refer to my colleagues with their doctor title for official purposes, but I do not include the PhD at the end of their name. That is much better suited to a business card.
Your lecture may wish to be referred to as:
- Dr [last name]
- Dr [first name]
Asking them in the early stages of your relationship is the best way to work out which one they prefer.
If in doubt, always go for the more formal name and nomenclature.
When can you start to use your PhD title after your doctorate?
When you have earned your PhD, you can start using your title immediately. Although, it can be a little bit confusing as to when you have actually passed your PhD. Is it when you have submitted your dissertation? Is it when you have received the comments back?
The University of Adelaide says that you can use it from your conferral date:
Students can be conferred on one of five dates during the year and for PhD students the conferral date will be the first available following the completion of all the academic requirements of your degree, including final thesis lodgement and the disbursement of any outstanding financial obligations to the University.
I started using my PhD title as soon as my confirmation letter arrived at my house. It was the first letter from the University that referred to me as Dr Stapleton. It was incredibly excited.
Generally, it is acceptable to use the title “Dr.” both professionally and socially but socially, people very rarely use it – at least in Australia. But you should never use it if you are a PhD student, PhD candidate or enrolled in a PhD program without a previous PhD qualification.
I do use it in professional settings but it always makes me feel a little bit awkward.
However, there may be some restrictions for certain settings. For example, if have a research degree resulting in a doctor title and you are working in a medical setting – some institutions do not like you to use Dr as it can confuse patients into thinking that you have a medical degree.
Instead, they ask that you use the PhD tag at the end of your name rather than the doctoral title for official and professional communications.
What is the correct way to write PhD?
When writing about someone’s PhD, the correct way is to write the term in full and capitalize each letter.
This should be done for all academic degrees, not just PhDs.
For example, it would be “Doctor of Philosophy” or “PhD” instead of “Ph.D.”, “Dr.”, or “DPhil”.
Additionally, it is common to mention the field of study in which the degree was earned if known, such as “Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics”. It is also good practice to include the institution that granted the degree if it is a recognized one.
When writing about someone’s PhD, use proper capitalization and include relevant information like field of study and institution if known to ensure accuracy.
How do you put a PhD in a title?
Putting a PhD in a title is not as complicated as it may sound.
Generally speaking, the proper way to list a PhD in an academic or professional setting is by writing “Dr.” before the name, followed by the person’s full name and the appropriate abbreviations for their degree.
For example, if John Smith has earned a doctorate in psychology, his credentials would be listed as “Dr. John Smith, Ph.D.”
In some cases, such as when addressing someone formally in speech or on a business card, it may also be acceptable to list their credentials as “John Smith, Ph.D.”
Depending on context and personal preference, some people may also choose to list their higher degrees after their names by writing out the entire degree instead of just its abbreviation.
For example, John Smith could choose to write his full title as “John Smith, Doctor of Psychology”
However, I have not seen this in real academic life.
Should the font size of Ph.D. be the same as someone’s name?
The question of whether the font size of a Ph.D. should be the same as someone’s name is an interesting one.
On one hand, it could be argued that the Ph.D. deserves to be highlighted and therefore should be given a larger font size than someone’s name to denote its importance.
On the other, it could be argued that this would not be necessary or appropriate, and that treating everyone equally regardless of their title or degree is more important.
It depends on context and usage – if both names appear in the same document then they should likely have the same font size; however, if one appears in a formal setting such as a diploma or certificate, then it may make sense to give it a larger font size than someone’s name to emphasize its importance and significance.
Ph.Ds (or PhDs) are an important academic achievement and should be respected accordingly but without going overboard by giving them overly large fonts sizes which can take away from rather than add to their importance.
Wrapping up – doctoral title rules
this article has been over everything you need to know that using the PhD title properly and effectively.
The doctor title can be used in place of the PhD and for incredibly formal communications, such as a business email or card, you can use both.
However, sometimes using both can cause confusion as to whether or not there is a reason first using both the doctor and PhD tags. Nonetheless, many people still use both.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

AP Style Academic Degrees
Home » AP Style » AP Style Academic Degrees
Sometimes it is necessary to establish the credentials of a subject in your text. When you need to do this, the AP Stylebook prefers you to write out the title of a degree in a phrase and to avoid using an abbreviation. For example,
- Correct: John Smith, who has a doctorate in astronomy, showed us constellations in the night sky.
- Wrong: John Smith, who has a Ph.D. in astronomy, showed us constellations in the night sky.
Bachelor Degree or Bachelor’s Degree?
AP Style states that you should use an apostrophe in bachelor’s degree and master’s degree. For example,
- Correct: I have two bachelor’s degrees and one master’s degree.
- Wrong: I have two bachelors degrees and one masters degree.
- Wrong: I have two bachelor degrees and one master degree.
An associate degree, however, does not use an apostrophe. For example,
- Correct: I received my associate degree before my bachelor’s.
- Wrong: I received my associate’s degree.
There is also no apostrophe in Bachelor of Arts, Master of Science, etc.
- Correct: I have a Bachelor of Arts in Linguistics.
- Wrong: I have a Bachelor’s of Arts in Linguistics.
Abbreviation of AP Style Academic Degrees
Use such abbreviations as B.S., M.S., LL.D., J.D., and Ph.D. only when you need to identify many individuals by degree on first reference and doing so in the AP Style academic degrees preferred way would be cumbersome. You should use abbreviations like these only after full names, never after just a last name.
When an academic abbreviation is used after a full name, commas should set it off. For example,
- Charles Smith, Ph.D., will present tonight’s lecture.
You should never precede a name with a courtesy title for an academic degree and then also follow it with the abbreviation for the degree in the same reference. For example,
- Wrong: Dr. Smith, Ph.D., will present tonight’s lecture.
- Correct: Dr. Smith will present tonight’s lecture.
- Correct: Charles Smith, Ph.D., will present tonight’s lecture.
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.
From admission to dissertation. Tips on making the PhD journey happy, productive and successful

How To Write PhD? Is it ph d or phd
How do you write phd correctly after a name is it ph d or phd, here are the steps to write phd correctly:.
- Firstly, “P” must be in a capital case.
- Secondly, “h” is in small case with no space after “P”
- Thirdly, use period/full-stop after “h”
- Fourthly, Write “D” in capital case.
- Fifthly, keep Period after “D”
- Finally, the correct way to write is Ph.D .
- Or, It can be also written as PhD in a sentence.
- As per APA style, write Ph. D
- As per Chicago style, write PhD
- As per MLA style, write it as Ph. D.
For example this is how to write PhD title after your name: Dr.John Mathew, Ph.D. You can write PhD after name on your business cards, resumes, CV’s or identity cards or on nameplates etc. Some have confusion with the use of comma and full stops while writing PhD title after name. Here is my indepth review how to write out properly PhD.
Writing a PhD title after name
Use capital “p” and “d” in the word ph.d..
You must write ‘P’ as capital and ‘D’ as capital letters. Though there is no strict rule on how to use capital and small letters, many of them do this way. Both letters which I have just mentioned must be written in Capital because those letters are the heart of the abbreviationPh.D. There is no other way of writing. Even if you search the whole world and ask many people and read many books, this is how PhD title is written. Sometimes there are possibilities that both letters are written in small letters by mistake. You need to correct instantly if such is the case. Otherwise, it looks awkward when someone looks at it or reads it. Usually, mistaken words are clearly observed than that of rightly written ones.
Use small letter ‘h’ in the word Ph.D.
The letter ‘h’ is what written small letter in this 3 letter word is. We write it in a small letter after name because this letter ‘h’ is in the middle of the word Ph.D. Here also don’t write mistake by using capital letters. This is the reason why many people write a PhD title after the name wrongly. They are confused about where to use capital letters and were not to use small letters. I suggest you practice all the letters in one or other way.
Why do we write a PhD title after the name?
We write a PhD title after the name to know that one has completed his doctoral studies and it is a sign of knowledge and status. We write a Ph.D. even for other purposes. For example, if someone is working in a university, it is mandatory that his qualification must be known to all the students and as well as the staff. This is why we write the Ph.D. title after the name. Not only in the university but also to the competent authorities who come for an inspection to the university must know the status of the faculty profiles. So the title Ph.D. is written after every faculty name as a title.
Should we use bold letters
I say a big no. You cannot write bold and fashioned way while writing PhD title after your name. As you write you must make it look similar along with the name without any difference. There is no way that you must write the Ph.D. title in bold fonts. This way, it looks very odd for those who look. Instead of reading your name, they will read Ph.D. firstly. So there is a chance of not remembering your name. So never use bold fonts while writing PhD title after your name.
Should we use Italic Letters
Again it is a big no. Do be too creative while writing a Ph.D. after your name. The use of italics is a big mistake. Do not use such writing in italics. Every time you use italic, again it looks very different from the original name adjacent to it.
Is Ph.D. a title after your name?
Do you think it is a PhD title or just a status? It is both status and title. Though in my personal opinion it is not a title, many call it as a title. But if you ask me I would tell it is a status word that is symbolically represented a matter of qualification. This is only my personal opinion about the title of Ph.D. So if at all you have some doubts about how this title arose as a part of history, you must read a vast number of history books about the Ph.D. title. It all requires for you to understand that a Ph.D. is not a title finally and just a resemblance of qualification.
Is it good to put PhD after title in your identity cards?
No, you must not use the title Ph.D. after your name in any type of identity card. These cards are existing irrespective of your qualification. This is meant to identify you as you are. There is no necessity what you have achieved. There is no need for knowing your qualifications. So in any type of identity card which is issued by the government like passport and voter card etc, you cannot use such title after your name. But there is one exception that the identity card at university or college or at job area must be given with Ph.D. title. If you ever need expert help with writing your Doctoral level papers, go to WriteMyPaperHub and send your request to write my PhD thesis for me .
Should we use the subject name when using a Ph.D. with the name?
This thought is quite awkward. But I must still mention this. There are some who use the subject name after the Ph.D. title along with the name. Like for example Dr. Luke, Ph.D. in Linguistics. Using this way is quite reasonable if there are some important debates or international meetups. Otherwise, I don’t suggest such type of writing after your name.
What happens if you don’t use a Ph.D. after your name?
If you do not use the Ph.D. title after your name, people around you won’t know that you are a doctoral research fellow. So it is very important to let them know it. You can only use this if at all there are some students around you or any known people. If there are unknown people around you, then there is no way that it is mandatory to use a Ph.D. after your name. Anyhow, I say that there is no danger of not using Ph.D. after your name.
Should comma be addded before or after PhD
Yes, a comma is a mandatory thing to be added after Ph.D. This is a rule. Otherwise, it is mixed combined with your original name. It will become part of your name. So comma is good after your name. I have already given the example above on how to put a comma after your name. But let me give here one more example as a matter of understanding. Dr.Mohima, Ph.D. If you see the name, for example, there is a comma used after the name to separate Ph.D. from it. So try to put a comma. But never use another punctuation mark as such full stop or colon after your name. I have seen people using other punctuation marks like semicolon after name and then they write the title Ph.D. Some don’t use at all. All such things are mistakes. Use the only comma after your name always.
Can we write Dr instead of Ph.D. after the name?
Writing a doctor instead of a Ph.D. means a different thing. So you cannot use such way. As this is not the right format. ‘Dr’ is used at the beginning of the name as another title. But after the name, it must be a Ph.D. and not ‘Dr’
Should we write a Ph.D. at all after one’s name that is too long?
Sometimes it so happens that your name is too long to write Ph.D. after it. During this trouble, you must cut out some part of the name and type PhD as a title after your name. There is no other way to do it. Usually, longs name are common in some countries like Germany and India. But in the USA we have shorter names. Whatever may be the length, you must try to use the most used name and eliminate the rest of the name. This way you can use the title Ph.D. comfortable after your name. Always try to use the same name. Don’t change the name or cut your name in different ways on different days. These will again a problem to your recognition.
Should we write phd or ph d on business card, welcome banners during functions?
On welcome banners and business cards, it is very important to mention the title Ph.D. This will be more serious if you do not use the Ph.D. title after the name. There are many people watching that public banner. If you do not write the title after the name, you are disrespecting the guest totally. So be aware of using the title ofPh.D. whenever you have public functions or welcome banners or during some important meetings. This is a sign that others should treat the guest better than the other out there.
Should the font size of Ph.D. be the same as someone’s name?
The name and the title Ph.D. must be in the same size. There must not be unusual differences. Font sizes matter a lot. Don’t use wrong font size or awkward fonts while using your title Ph.D. after your name. The best font could be like Ariel, Lato, Times New Roman, etc. These fonts will look better as a Ph.D. title after your name. Initially, there is some confusion about using the right font. But once you learn the size usage, you are comfortable using them rightly. Even when you write manually, you can easily write with similar size throughout. This requires a good amount of practice to write the Ph.D. title after your name with good font limitations.
Popular posts that others are reading now::
- Age Limit For PhD in the USA. Little known restriction for PhD, USA.
- How many words per page in apa style format
- How to do PhD in Harvard University
- Number of phds per country
- Why is PhD not Dph| What does PhD stand for| Funny
Syam Prasad Reddy T
Hello, My name is Syam, Asst. Professor of English and Mentor for Ph.D. students worldwide. I have worked years to give you these amazing tips to complete your Ph.D. successfully. Having put a lot of efforts means to make your Ph.D. journey easier. Thank you for visiting my Ph.D. blog.

You May Also Like

What must be the Age limit for PhD in Norway

Age limit for PhD in Germany

Age limit for PhD in Europe

How to Correctly Use the Titles Dr. & PhD With a Name

How to Reference a Person With a PhD
When someone has earned a Doctor of Philosophy, or Ph.D., degree, that person is subsequently referred to as “doctor” in formal speech. The same is true of a person who is a medical doctor, psychologist, dentist or veterinarian. In formal speech, that person should be referred to as “doctor.” However, the rules are different in written form when addressing someone who is called “doctor” in formal speech. In written form, the titles “Dr.” and “Ph.D.” are not interchangeable.
Determine the Type of Doctor
First, you should identify what type of doctor you are addressing. Doctors of medicine and psychology, doctors of dentistry and doctors of veterinary medicine must be addressed differently in comparison to academic doctors who have earned a Doctor of Philosophy doctoral degree. Be advised that there are different types of doctoral degrees. A Doctor of Philosophy degree is just one kind of doctoral degree. There’s also, for example, a Doctor of Education doctoral degree and a Doctor of Psychology doctoral degree. The titles associated with the various doctoral degrees are not interchangeable. Only a person who has earned a Doctor of Philosophy degree should be addressed as Ph.D.
Addressing a Doctor in Writing
Place the title of “Dr.” before the name of a person who is a doctor of medicine or psychology, doctor of dentistry, or doctor of veterinary medicine. For example Dr. George Ross. Always write the word “doctor” in its abbreviated form when it goes before the person’s name. Never write, for example, Doctor George Ross. Do not combine the title of “Dr.” with any other title even if the person could appropriately be addressed by a different title. Never write, for example, “Dr. George Ross, Ph.D.,” even if the person is a medical doctor who has also earned a Doctor of Philosophy degree. Pick one title. Do not use the “Dr.” title when referring to someone who is solely an academic doctor.
Put a comma followed by the title “Ph.D.” after the name of a person who has earned a Doctor of Philosophy doctoral degree. For example Stacey Childs, Ph.D. Do not combine the title of “Ph.D.” with any other title even if the person could appropriately be addressed by a different title. For instance, even if the person being addressed is a doctor of medicine who has also earned a Ph.D., never write, for example, Dr. Stacey Childs, Ph.D. Pick one title. Do not use the “Ph.D.” title when referring to someone who not earned a Doctor of Philosophy doctoral degree.
Related Articles
How to sign your name when you have a bachelor of science in criminal ....

Proper Way to Notate College Degrees

How to Address a DVM

Different Types of Doctoral Degrees

How to Address Multiple Ladies in a Letter

The Difference Between a Doctoral Degree and a Ph.D.

The Difference Between a PhD & DLitt

Doctorate Degrees That Don't Require a Dissertation
- The Emily Post Institute: What are some professional titles to know?
Maya Austen began freelance writing in 2009. She has written for many online publications on a wide variety of topics ranging from physical fitness to amateur astronomy. She's also an author and e-book publisher. Austen has a Bachelor of Arts in communications from the New England Institute of Art and currently lives in Boston, Mass.
How to Write PhD

How to Write PhD – Once you’ve completed your doctorate (PhD), you’ll want to put this achievement at the top of your resume envelope. The problem is how to put this academic milestone to good use if you decide to explore new career opportunities in business or discovered that you truly enjoy academic research.
Writers often use Ph.D. after their names to boost their credibility and professionalism, but what does it mean when the abbreviation doesn’t immediately follow your name?
Table of Contents
How do you Write PhD correctly after a name? Is it ph d or phd?
Here are the steps to write phd correctly:.
- Firstly, “P” must be in a capital case.
- Secondly, “h” is in small case with no space after “P”
- Thirdly, use period/full-stop after “h”
- Fourthly, Write “D” in capital case.
- Fifthly, keep Period after “D”
- Finally, the correct way to write is Ph.D .
- Or, It can be also written as PhD in a sentence.
- As per APA style, write Ph. D
- As per Chicago style, write PhD
- As per MLA style, write it as Ph. D.
For example this is how to write PhD title after your name: Dr.John Mathew, Ph.D. You can write PhD after name on your business cards, resumes, CV’s or identity cards or on nameplates etc. Some have confusion with the use of comma and full stops while writing PhD title after name. Here is my indepth review how to write out properly PhD.
Writing a PhD title after name
Use capital “p” and “d” in the word ph.d..
You must write ‘P’ as capital and ‘D’ as capital letters. Though there is no strict rule on how to use capital and small letters, many of them do this way. Both letters which I have just mentioned must be written in Capital because those letters are the heart of the abbreviationPh.D. There is no other way of writing. Even if you search the whole world and ask many people and read many books, this is how PhD title is written. Sometimes there are possibilities that both letters are written in small letters by mistake. You need to correct instantly if such is the case. Otherwise, it looks awkward when someone looks at it or reads it. Usually, mistaken words are clearly observed than that of rightly written ones.
Use small letter ‘h’ in the word Ph.D.
The letter ‘h’ is what written small letter in this 3 letter word is. We write it in a small letter after name because this letter ‘h’ is in the middle of the word Ph.D. Here also don’t write mistake by using capital letters. This is the reason why many people write a PhD title after the name wrongly. They are confused about where to use capital letters and were not to use small letters. I suggest you practice all the letters in one or other way.
Why do we write a PhD title after the name?
We write a PhD title after the name to know that one has completed his doctoral studies and it is a sign of knowledge and status. We write a Ph.D. even for other purposes. For example, if someone is working in a university, it is mandatory that his qualification must be known to all the students and as well as the staff. This is why we write the Ph.D. title after the name. Not only in the university but also to the competent authorities who come for an inspection to the university must know the status of the faculty profiles. So the title Ph.D. is written after every faculty name as a title.
Should we use bold letters
I say a big no. You cannot write bold and fashioned way while writing PhD title after your name. As you write you must make it look similar along with the name without any difference. There is no way that you must write the Ph.D. title in bold fonts. This way, it looks very odd for those who look. Instead of reading your name, they will read Ph.D. firstly. So there is a chance of not remembering your name. So never use bold fonts while writing PhD title after your name.
Should we use Italic Letters
Again it is a big no. Do be too creative while writing a Ph.D. after your name. The use of italics is a big mistake. Do not use such writing in italics. Every time you use italic, again it looks very different from the original name adjacent to it.
Is Ph.D. a title after your name?
Do you think it is a PhD title or just a status? It is both status and title. Though in my personal opinion it is not a title, many call it as a title. But if you ask me I would tell it is a status word that is symbolically represented a matter of qualification. This is only my personal opinion about the title of Ph.D. So if at all you have some doubts about how this title arose as a part of history, you must read a vast number of history books about the Ph.D. title. It all requires for you to understand that a Ph.D. is not a title finally and just a resemblance of qualification.
Is it good to put PhD after title in your identity cards?
No, you must not use the title Ph.D. after your name in any type of identity card. These cards are existing irrespective of your qualification. This is meant to identify you as you are. There is no necessity what you have achieved. There is no need for knowing your qualifications. So in any type of identity card which is issued by the government like passport and voter card etc, you cannot use such title after your name. But there is one exception that the identity card at university or college or at job area must be given with Ph.D. title. If you ever need expert help with writing your Doctoral level papers, go to WriteMyPaperHub and send your request to write my PhD thesis for me .
Should we use the subject name when using a Ph.D. with the name?
This thought is quite awkward. But I must still mention this. There are some who use the subject name after the Ph.D. title along with the name. Like for example Dr. Luke, Ph.D. in Linguistics. Using this way is quite reasonable if there are some important debates or international meetups. Otherwise, I don’t suggest such type of writing after your name.
What happens if you don’t use a Ph.D. after your name?
If you do not use the Ph.D. title after your name, people around you won’t know that you are a doctoral research fellow. So it is very important to let them know it. You can only use this if at all there are some students around you or any known people. If there are unknown people around you, then there is no way that it is mandatory to use a Ph.D. after your name. Anyhow, I say that there is no danger of not using Ph.D. after your name.
Should comma be addded before or after PhD
Yes, a comma is a mandatory thing to be added after Ph.D. This is a rule. Otherwise, it is mixed combined with your original name. It will become part of your name. So comma is good after your name. I have already given the example above on how to put a comma after your name. But let me give here one more example as a matter of understanding. Dr.Mohima, Ph.D. If you see the name, for example, there is a comma used after the name to separate Ph.D. from it. So try to put a comma. But never use another punctuation mark as such full stop or colon after your name. I have seen people using other punctuation marks like semicolon after name and then they write the title Ph.D. Some don’t use at all. All such things are mistakes. Use the only comma after your name always.
Can we write Dr instead of Ph.D. after the name?
Writing a doctor instead of a Ph.D. means a different thing. So you cannot use such way. As this is not the right format. ‘Dr’ is used at the beginning of the name as another title. But after the name, it must be a Ph.D. and not ‘Dr’
Should we write a Ph.D. at all after one’s name that is too long?
Sometimes it so happens that your name is too long to write Ph.D. after it. During this trouble, you must cut out some part of the name and type PhD as a title after your name. There is no other way to do it. Usually, longs name are common in some countries like Germany and India. But in the USA we have shorter names. Whatever may be the length, you must try to use the most used name and eliminate the rest of the name. This way you can use the title Ph.D. comfortable after your name. Always try to use the same name. Don’t change the name or cut your name in different ways on different days. These will again a problem to your recognition.
Should we write phd or ph d on business card, welcome banners during functions?
On welcome banners and business cards, it is very important to mention the title Ph.D. This will be more serious if you do not use the Ph.D. title after the name. There are many people watching that public banner. If you do not write the title after the name, you are disrespecting the guest totally. So be aware of using the title ofPh.D. whenever you have public functions or welcome banners or during some important meetings. This is a sign that others should treat the guest better than the other out there.
Should the font size of Ph.D. be the same as someone’s name?
The name and the title Ph.D. must be in the same size. There must not be unusual differences. Font sizes matter a lot. Don’t use wrong font size or awkward fonts while using your title Ph.D. after your name. The best font could be like Ariel, Lato, Times New Roman, etc. These fonts will look better as a Ph.D. title after your name. Initially, there is some confusion about using the right font. But once you learn the size usage, you are comfortable using them rightly. Even when you write manually, you can easily write with similar size throughout. This requires a good amount of practice to write the Ph.D. title after your name with good font limitations.
10 tips for writing a PhD thesis
Writing up a PhD can often take place in a frenzy of activity in the last few months of your degree study, after years of hard work. But there are some steps that you can take to increase your chances of success.
- Do not be daunted by the task of “writing up”. Work on the text as your PhD takes shape, remember that all writers need editing, and help yourself by using these basic tips to make life easier. Read what great writers say about how to write before you start, and take their advice to heart. There is no dark art to clear, concise work; it is mostly a result of editing, and editing again. Above all, keep Elmore Leonard’s advice in mind: “If it reads like writing…rewrite it.”
- Plan the structure of your thesis carefully with your supervisor. Create rough drafts as you go so that you can refine them as you become more focused on the write-up. Much of writing comprises rewriting so be prepared to rework each chapter many times. Even Ernest Hemingway said: “The first draft of everything is shit.”
- Academic writing does not have to be dry. Inject some flair into your work. Read advice on writing and remember George Orwell’s words in Why I Write : “Never use the passive where you can use the active”; and Mark Twain’s on adjectives: “When you catch an adjective, kill it.” If you prefer, Stephen King said: “The road to hell is paved with adverbs.”
- Do not write up in chronological order. Work on each chapter while it is fresh in your mind or pertinent to what you are doing at that moment, but come back to it all later and work it up into a consistent, coherent piece, restructuring sections where necessary.
- Think carefully about your writing. Write your first draft, leave it and then come back to it with a critical eye. Look objectively at the writing and read it closely for style and sense. Look out for common errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement and inconsistency. If you are too involved with the text to be able to take a step back and do this, then ask a friend or colleague to read it with a critical eye. Remember Hemingway’s advice: “Prose is architecture, not interior decoration.” Clarity is key.
- Most universities use a preferred style of references. Make sure you know what this is and stick to it. One of the most common errors in academic writing is to cite papers in the text that do not then appear in the bibliography. All references in your thesis need to be cross-checked with the bibliography before submission. Using a database during your research can save a great deal of time in the writing-up process. Helpful software includes EndNote or Paperpile. Managing your bibliography from day one may seem obsessive but it will save you a great deal of time and stress by the end of the PhD process.
- Use a house style. Professional publications such as Times Higher Education use a house style guide to ensure consistency in spelling. For example, do not use both -ise spellings and -ize spellings, stick to British spelling and be consistent when referring to organisations or bodies. Because dictionaries vary in their use of hyphenation, use one dictionary and stick to it throughout the writing process. If you consult the New Oxford Dictionary for Writers and Editors , you will note the extraordinary number of words with alternative spellings. It can also be a very useful guide to preferred spellings, use of italicisation and foreign phrases.
- Take care when quoting from other sources. Ensure you note whether the italic emphasis is in the original and take careful notes when you are collecting quotes for your thesis. Transcribe them accurately to save work later and keep original spellings (even if they differ from your chosen style) to ensure fidelity to your source.
- Think about plagiarism. If you are quoting from works, quote from them accurately and paraphrase where necessary for your argument. This is where careful note-taking and use of references is invaluable and will help you to avoid even inadvertently plagiarising another work.
- Remember that your thesis is your chance to present your work in the best possible light. Consider your opening paragraphs, entice your reader with your writing and above all be clear about your hypothesis and your conclusion. Append material where it adds value but not where it merely bulks out your work. Consider your reader at all times. This is your chance to showcase your work.
If you stick to these simple rules, your writing will be clear and jargon-free. Above all, take to heart Orwell’s advice: “Never use a foreign phrase, a scientific word, or a jargon word if you can think of an everyday English equivalent.”
In the academic world, having a PhD after your name means you have been awarded a prestigious three-year doctoral degree from a university or college. A Ph.D. is a Doctor of Philosophy degree and can be earned in a variety of subjects.

- Writing Tips
http://www.btb.termiumplus.gc.ca

Liens de la barre de menu commune
- Contactez-nous
- Rechercher dans Canada.ca
Liens vers une langue non officielle
- Español
Accueil > TERMIUM Plus ® > Writing Tips > Search for entries starting with P > PhD, Ph.D., Dr.
Liens institutionnels
Bureau de la traduction, portail linguistique du canada, termium plus ®, outils d'aide à la rédaction , développer/réduire.
- Chroniques de langue
- Clefs du français pratique
- Dictionnaire des cooccurrences
- Juridictionnaire
- Le guide du rédacteur
- Le Rouleau des prépositions
- Les mots du droit
- Lexique analogique
- Favourite Articles
- HyperGrammar2
- Peck's English Pointers
- The Canadian Style
- Word Tailoring
- Pacific Daylight Time
- Pacific Standard Time
- parallel between
- parallelism in headings
- parallelism with correlative conjunctions
- parallelism with items in a series
- parallel to
- parallel with
- Paralympic Winter Games
- parentheses
- participle phrase
- particular to
- passive voice
- past history
- past tradition
- peculiar to
- perfectly legitimate
- period of time
- permanent resident
- perpendicular to
- perpendicular with
- Persian (1)
- Persian (2)
- personal pronouns
- personification
- perspective (from the)
- phosphorous
- planning in advance
- plurals of compounds
- plurals of family names
- possessive with gerunds
- practicable
- practically
- predict in advance
- preference for
- preference in
- prefer one to the other
- preoccupied about
- preoccupied by
- preoccupied with
- preplanning
- prepositional phrase
- prepositions
- prerequisite
- present with
- preside over
- preventable
- prevent from
- preventible
- previously listed
- previously listed above
- Prince Edward Island
- Prince Edward Islander
- proceed against
- proceed with
- prohibit from
- pronoun agreement: collective nouns
- pronoun agreement: compound antecedents with and
- pronoun agreement: compound antecedents with or
- pronoun agreement: gender
- pronoun agreement: indefinite pronouns
- pronoun agreement: number
- pronoun agreement: person
- property owner
- proportional(y)
- proportionate(ly)
- provide a description
- provide against
- provide for
- provide with
- public service: capitalization rules (Linguistic recommendation from the Translation Bureau)
- punctuation: spacing
- pursuance (in)
- put in place
- put into place
Divulgation proactive

Avis important
L'outil Writing Tips a été archivé et ne sera plus mis à jour jusqu'à son retrait définitif.
Pour obtenir notre contenu le plus à jour, veuillez consulter Writing Tips Plus , un outil combinant le contenu des outils Writing Tips et The Canadian Style . N'oubliez pas de modifier vos favoris!
La zone de recherche et les fonctionnalités
Phd, ph.d., dr..
In English, PhD can be written with or without periods; both are correct. The trend today is to drop periods with abbreviations of academic degrees. However, many sources, including the Canadian Oxford Dictionary , still recommend the use of periods: Ph.D.
When you are addressing a person with a doctoral degree, it is considered more polite to use the title Dr. or the academic abbreviation PhD with the person’s name, instead of the simple courtesy titles Mr. or Ms.
Note: Do not use both the title and the degree. If the degree is listed after the name, the title is not used before the name.
- Chris Cameron, PhD.
- Dr. Chris Cameron
© Services publics et Approvisionnement Canada, 2024 TERMIUM Plus ® , la banque de données terminologiques et linguistiques du gouvernement du Canada Outils d'aide à la rédaction – Writing Tips Un produit du Bureau de la traduction
PhD Writing – How to Structure the Perfect Dissertation
- Post author By Dennis Piper
- Post date December 16, 2021
Source: https://unsplash.com/photos/zUf39GDNyzU
A good piece of writing is born out of a clear thought process. A process wherein information flows naturally toward a purpose.
The challenge we experience in writing is the result of our efforts in untangling obscurities in our minds. This holds true for all types of writings as we always have a reason (or more) for presenting information, even if we are oblivious to it.
Writing a dissertation, in essence, is formulating an argument. A cogent argument is a clear and well-structured set of statements that support a conclusion. Creating an outline for your dissertation or thesis helps you objectify your argument to assess its validity before investing any time in writing it. For an arduous academic project like this, it saves you a lot of time and effort over the course of months.
Dissertation Outline
A dissertation outline can be thought of as an intellectual scaffolding that supports the construction of your theoretical framework. It is a high-level structure that helps you visualize what you want to convey and keep track of your thoughts and progress.
Creating an outline is necessary because it helps you connect the information to form a coherent and logical statement. It’s a rough sketch that allows you to experiment with ideas before committing to anything and shows you where you need to go, which makes the process a much better experience. But before we delve deeper into how to create a good outline, let’s briefly overview the components that are included in a dissertation.
The Common Structure of a Dissertation
As with any other academic paper, the structure of a dissertation can vary depending on its type and nature. In addition, different universities might have slightly different approaches but the core elements usually remain the same. However, before finalizing your structure, we recommend that you check in with your institution to make sure you’ll follow their specific requirements.
A typical dissertation is made up of 8 sections:
- Front Matter – This section typically includes all the pages that come before the introduction. It contains the title page, acknowledgments, abstract, table of contents, list of tables and figures, list of abbreviations, and glossary;
- Introduction – As the name suggests, the introductory section sets up the topic and justifies the purpose and relevance of the research. It provides a road map of what’s to be expected in the main body of the paper;
- Literature Review – This section takes a look at the existing studies in the space of the dissertation’s subject. Here, the author reviews the existing sources and provides a theoretical background and critical assessment to form a clear basis for his or her research;
- Methodology – This section lays out how the research has been designed and conducted. It includes the methods of data collection and analysis to answer the research questions.
- Results – the results chapter is about presenting the raw findings. It does not include any interpretation of the findings or their analysis in relation to the research questions or the literature;
- Discussion – This chapter is where the results are interpreted to infer meaningful findings. The author then compares and related the findings to the literature to show if they align or are at odds with each other and hypotheses are set forth to explain why that’s the case.
- Conclusion – The conclusion addresses the main research questions and binds together the paper’s various parts to present the reader with the author’s central argument and ultimate finding;
- End Matter – This last section contains the reference list and appendices.
How to Create a Dissertation Outline
Choose a Topic and Form a Thesis
Before you start writing an outline, you should have a clear idea about the argument or thesis you want to present. If you haven’t already, you should do a fair amount of diligent research surrounding the topic to gather enough information to develop an angle or viewpoint. This process includes brainstorming ideas and evaluating them to form a statement that you are comfortable with. If you are struggling to come up with or choose between competing ideas, there are some thesis writing services that can help you.
Break Down Your Argument
After settling on your initial thesis and overall argument, you need to break it down into different components and organize them in a way that serves that argument. This is perhaps the most difficult part as there are lots of ways it can be done. First, try to identify different criteria for classifying your material. This helps you categorize the various ideas and sources in your mind into groups sharing similar features. By scribbling them down, you get a better idea of how you want to go about the main structure of the body of your dissertation.
Design Your Methodology
This is where you need to determine how you’re going to gather your data and information, how you are going to analyze that data, what tools or materials you’re going to use, and what your reasons are for choosing these methods. Try to provide enough detail that you paint a clear picture of how things need to proceed later on when you’re doing the actual research. Specify if your data should be quantitative or qualitative. Are you going to use secondary data or do you plan to collect the data yourself? Are you going to use surveys, interviews, or observation? Details like these give you clarity and a better understanding of whether or not you’ve made the right choices.
Major Points for Each Component
The next step is to write the points you want to make for each of the components you determined earlier. While doing so, make sure that everything is coherent and closely related to your thesis. As the best essay writing service puts it, this step is not about listing the things we know about the topic, rather, it’s about connecting the dots to build an argument and assess and identify the potential defects and flaws.
Sometimes, we find that we need to rearrange the supporting points to improve the validity of the argument. Logically, some subjects may need to precede others to facilitate the flow of information. Sorting these levels of information can even help inform the thesis and lead to changes in the initial assumptions.
After arranging the points in a logical order, your dissertation outline is almost finished. You just need to review the points to see if there’s a need for more analysis and evidence. After that, you have everything you need to start writing. Keep in mind that the outline is not set in stone. It’s a guideline designed to give you direction and you can adjust or deviate from it as you move forward. It’s also recommended that you take note of each reference in your studies from day one as it can get complicated and cumbersome in later stages of your dissertation.


Tips for writing a PhD dissertation: FAQs answered
From how to choose a topic to writing the abstract and managing work-life balance through the years it takes to complete a doctorate, here we collect expert advice to get you through the PhD writing process
Campus team
Additional links.

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
A diy guide to starting your own journal, universities, ai and the common good, artificial intelligence and academic integrity: striking a balance, create an onboarding programme for neurodivergent students.
Embarking on a PhD is “probably the most challenging task that a young scholar attempts to do”, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith in their practical guide to dissertation and thesis writing. After years of reading and research to answer a specific question or proposition, the candidate will submit about 80,000 words that explain their methods and results and demonstrate their unique contribution to knowledge. Here are the answers to frequently asked questions about writing a doctoral thesis or dissertation.
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
Whatever the genre of the doctorate, a PhD must offer an original contribution to knowledge. The terms “dissertation” and “thesis” both refer to the long-form piece of work produced at the end of a research project and are often used interchangeably. Which one is used might depend on the country, discipline or university. In the UK, “thesis” is generally used for the work done for a PhD, while a “dissertation” is written for a master’s degree. The US did the same until the 1960s, says Oxbridge Essays, when the convention switched, and references appeared to a “master’s thesis” and “doctoral dissertation”. To complicate matters further, undergraduate long essays are also sometimes referred to as a thesis or dissertation.
The Oxford English Dictionary defines “thesis” as “a dissertation, especially by a candidate for a degree” and “dissertation” as “a detailed discourse on a subject, especially one submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of a degree or diploma”.
- Ten platinum rules for PhD supervisors
- Fostering freedom in PhD students: how supervisors can shape accessible paths for doctoral research
- Lessons from students on effective research supervision
The title “doctor of philosophy”, incidentally, comes from the degree’s origins, write Dr Felix, an associate professor at Mahidol University in Thailand, and Dr Smith, retired associate professor of education at the University of Sydney , whose co-authored guide focuses on the social sciences. The PhD was first awarded in the 19th century by the philosophy departments of German universities, which at that time taught science, social science and liberal arts.
How long should a PhD thesis be?
A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words ( 100 to 300 pages in length ) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) – from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion.
The structure of a dissertation will vary depending on discipline (humanities, social sciences and STEM all have their own conventions), location and institution. Examples and guides to structure proliferate online. The University of Salford , for example, lists: title page, declaration, acknowledgements, abstract, table of contents, lists of figures, tables and abbreviations (where needed), chapters, appendices and references.
A scientific-style thesis will likely need: introduction, literature review, materials and methods, results, discussion, bibliography and references.
As well as checking the overall criteria and expectations of your institution for your research, consult your school handbook for the required length and format (font, layout conventions and so on) for your dissertation.
A PhD takes three to four years to complete; this might extend to six to eight years for a part-time doctorate.
What are the steps for completing a PhD?
Before you get started in earnest , you’ll likely have found a potential supervisor, who will guide your PhD journey, and done a research proposal (which outlines what you plan to research and how) as part of your application, as well as a literature review of existing scholarship in the field, which may form part of your final submission.
In the UK, PhD candidates undertake original research and write the results in a thesis or dissertation, says author and vlogger Simon Clark , who posted videos to YouTube throughout his own PhD journey . Then they submit the thesis in hard copy and attend the viva voce (which is Latin for “living voice” and is also called an oral defence or doctoral defence) to convince the examiners that their work is original, understood and all their own. Afterwards, if necessary, they make changes and resubmit. If the changes are approved, the degree is awarded.
The steps are similar in Australia , although candidates are mostly assessed on their thesis only; some universities may include taught courses, and some use a viva voce. A PhD in Australia usually takes three years full time.
In the US, the PhD process begins with taught classes (similar to a taught master’s) and a comprehensive exam (called a “field exam” or “dissertation qualifying exam”) before the candidate embarks on their original research. The whole journey takes four to six years.
A PhD candidate will need three skills and attitudes to get through their doctoral studies, says Tara Brabazon , professor of cultural studies at Flinders University in Australia who has written extensively about the PhD journey :
- master the academic foundational skills (research, writing, ability to navigate different modalities)
- time-management skills and the ability to focus on reading and writing
- determined motivation to do a PhD.

How do I choose the topic for my PhD dissertation or thesis?
It’s important to find a topic that will sustain your interest for the years it will take to complete a PhD. “Finding a sustainable topic is the most important thing you [as a PhD student] would do,” says Dr Brabazon in a video for Times Higher Education . “Write down on a big piece of paper all the topics, all the ideas, all the questions that really interest you, and start to cross out all the ones that might just be a passing interest.” Also, she says, impose the “Who cares? Who gives a damn?” question to decide if the topic will be useful in a future academic career.
The availability of funding and scholarships is also often an important factor in this decision, says veteran PhD supervisor Richard Godwin, from Harper Adams University .
Define a gap in knowledge – and one that can be questioned, explored, researched and written about in the time available to you, says Gina Wisker, head of the Centre for Learning and Teaching at the University of Brighton. “Set some boundaries,” she advises. “Don’t try to ask everything related to your topic in every way.”
James Hartley, research professor in psychology at Keele University, says it can also be useful to think about topics that spark general interest. If you do pick something that taps into the zeitgeist, your findings are more likely to be noticed.
You also need to find someone else who is interested in it, too. For STEM candidates , this will probably be a case of joining a team of people working in a similar area where, ideally, scholarship funding is available. A centre for doctoral training (CDT) or doctoral training partnership (DTP) will advertise research projects. For those in the liberal arts and social sciences, it will be a matter of identifying a suitable supervisor .
Avoid topics that are too broad (hunger across a whole country, for example) or too narrow (hunger in a single street) to yield useful solutions of academic significance, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith. And ensure that you’re not repeating previous research or trying to solve a problem that has already been answered. A PhD thesis must be original.
What is a thesis proposal?
After you have read widely to refine your topic and ensure that it and your research methods are original, and discussed your project with a (potential) supervisor, you’re ready to write a thesis proposal , a document of 1,500 to 3,000 words that sets out the proposed direction of your research. In the UK, a research proposal is usually part of the application process for admission to a research degree. As with the final dissertation itself, format varies among disciplines, institutions and countries but will usually contain title page, aims, literature review, methodology, timetable and bibliography. Examples of research proposals are available online.
How to write an abstract for a dissertation or thesis
The abstract presents your thesis to the wider world – and as such may be its most important element , says the NUI Galway writing guide. It outlines the why, how, what and so what of the thesis . Unlike the introduction, which provides background but not research findings, the abstract summarises all sections of the dissertation in a concise, thorough, focused way and demonstrates how well the writer understands their material. Check word-length limits with your university – and stick to them. About 300 to 500 words is a rough guide – but it can be up to 1,000 words.
The abstract is also important for selection and indexing of your thesis, according to the University of Melbourne guide , so be sure to include searchable keywords.
It is the first thing to be read but the last element you should write. However, Pat Thomson , professor of education at the University of Nottingham , advises that it is not something to be tackled at the last minute.
How to write a stellar conclusion
As well as chapter conclusions, a thesis often has an overall conclusion to draw together the key points covered and to reflect on the unique contribution to knowledge. It can comment on future implications of the research and open up new ideas emanating from the work. It is shorter and more general than the discussion chapter , says online editing site Scribbr, and reiterates how the work answers the main question posed at the beginning of the thesis. The conclusion chapter also often discusses the limitations of the research (time, scope, word limit, access) in a constructive manner.
It can be useful to keep a collection of ideas as you go – in the online forum DoctoralWriting SIG , academic developer Claire Aitchison, of the University of South Australia , suggests using a “conclusions bank” for themes and inspirations, and using free-writing to keep this final section fresh. (Just when you feel you’ve run out of steam.) Avoid aggrandising or exaggerating the impact of your work. It should remind the reader what has been done, and why it matters.
How to format a bibliography (or where to find a reliable model)
Most universities use a preferred style of references , writes THE associate editor Ingrid Curl. Make sure you know what this is and follow it. “One of the most common errors in academic writing is to cite papers in the text that do not then appear in the bibliography. All references in your thesis need to be cross-checked with the bibliography before submission. Using a database during your research can save a great deal of time in the writing-up process.”
A bibliography contains not only works cited explicitly but also those that have informed or contributed to the research – and as such illustrates its scope; works are not limited to written publications but include sources such as film or visual art.
Examiners can start marking from the back of the script, writes Dr Brabazon. “Just as cooks are judged by their ingredients and implements, we judge doctoral students by the calibre of their sources,” she advises. She also says that candidates should be prepared to speak in an oral examination of the PhD about any texts included in their bibliography, especially if there is a disconnect between the thesis and the texts listed.
Can I use informal language in my PhD?
Don’t write like a stereotypical academic , say Kevin Haggerty, professor of sociology at the University of Alberta , and Aaron Doyle, associate professor in sociology at Carleton University , in their tongue-in-cheek guide to the PhD journey. “If you cannot write clearly and persuasively, everything about PhD study becomes harder.” Avoid jargon, exotic words, passive voice and long, convoluted sentences – and work on it consistently. “Writing is like playing guitar; it can improve only through consistent, concerted effort.”
Be deliberate and take care with your writing . “Write your first draft, leave it and then come back to it with a critical eye. Look objectively at the writing and read it closely for style and sense,” advises THE ’s Ms Curl. “Look out for common errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement and inconsistency. If you are too involved with the text to be able to take a step back and do this, then ask a friend or colleague to read it with a critical eye. Remember Hemingway’s advice: ‘Prose is architecture, not interior decoration.’ Clarity is key.”
How often should a PhD candidate meet with their supervisor?
Since the PhD supervisor provides a range of support and advice – including on research techniques, planning and submission – regular formal supervisions are essential, as is establishing a line of contact such as email if the candidate needs help or advice outside arranged times. The frequency varies according to university, discipline and individual scholars.
Once a week is ideal, says Dr Brabazon. She also advocates a two-hour initial meeting to establish the foundations of the candidate-supervisor relationship .
The University of Edinburgh guide to writing a thesis suggests that creating a timetable of supervisor meetings right at the beginning of the research process will allow candidates to ensure that their work stays on track throughout. The meetings are also the place to get regular feedback on draft chapters.
“A clear structure and a solid framework are vital for research,” writes Dr Godwin on THE Campus . Use your supervisor to establish this and provide a realistic view of what can be achieved. “It is vital to help students identify the true scientific merit, the practical significance of their work and its value to society.”
How to proofread your dissertation (what to look for)
Proofreading is the final step before printing and submission. Give yourself time to ensure that your work is the best it can be . Don’t leave proofreading to the last minute; ideally, break it up into a few close-reading sessions. Find a quiet place without distractions. A checklist can help ensure that all aspects are covered.
Proofing is often helped by a change of format – so it can be easier to read a printout rather than working off the screen – or by reading sections out of order. Fresh eyes are better at spotting typographical errors and inconsistencies, so leave time between writing and proofreading. Check with your university’s policies before asking another person to proofread your thesis for you.
As well as close details such as spelling and grammar, check that all sections are complete, all required elements are included , and nothing is repeated or redundant. Don’t forget to check headings and subheadings. Does the text flow from one section to another? Is the structure clear? Is the work a coherent whole with a clear line throughout?
Ensure consistency in, for example, UK v US spellings, capitalisation, format, numbers (digits or words, commas, units of measurement), contractions, italics and hyphenation. Spellchecks and online plagiarism checkers are also your friend.

How do you manage your time to complete a PhD dissertation?
Treat your PhD like a full-time job, that is, with an eight-hour working day. Within that, you’ll need to plan your time in a way that gives a sense of progress . Setbacks and periods where it feels as if you are treading water are all but inevitable, so keeping track of small wins is important, writes A Happy PhD blogger Luis P. Prieto.
Be specific with your goals – use the SMART acronym (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and timely).
And it’s never too soon to start writing – even if early drafts are overwritten and discarded.
“ Write little and write often . Many of us make the mistake of taking to writing as one would take to a sprint, in other words, with relatively short bursts of intense activity. Whilst this can prove productive, generally speaking it is not sustainable…In addition to sustaining your activity, writing little bits on a frequent basis ensures that you progress with your thinking. The comfort of remaining in abstract thought is common; writing forces us to concretise our thinking,” says Christian Gilliam, AHSS researcher developer at the University of Cambridge ’s Centre for Teaching and Learning.
Make time to write. “If you are more alert early in the day, find times that suit you in the morning; if you are a ‘night person’, block out some writing sessions in the evenings,” advises NUI Galway’s Dermot Burns, a lecturer in English and creative arts. Set targets, keep daily notes of experiment details that you will need in your thesis, don’t confuse writing with editing or revising – and always back up your work.
What work-life balance tips should I follow to complete my dissertation?
During your PhD programme, you may have opportunities to take part in professional development activities, such as teaching, attending academic conferences and publishing your work. Your research may include residencies, field trips or archive visits. This will require time-management skills as well as prioritising where you devote your energy and factoring in rest and relaxation. Organise your routine to suit your needs , and plan for steady and regular progress.
How to deal with setbacks while writing a thesis or dissertation
Have a contingency plan for delays or roadblocks such as unexpected results.
Accept that writing is messy, first drafts are imperfect, and writer’s block is inevitable, says Dr Burns. His tips for breaking it include relaxation to free your mind from clutter, writing a plan and drawing a mind map of key points for clarity. He also advises feedback, reflection and revision: “Progressing from a rough version of your thoughts to a superior and workable text takes time, effort, different perspectives and some expertise.”
“Academia can be a relentlessly brutal merry-go-round of rejection, rebuttal and failure,” writes Lorraine Hope , professor of applied cognitive psychology at the University of Portsmouth, on THE Campus. Resilience is important. Ensure that you and your supervisor have a relationship that supports open, frank, judgement-free communication.
If you found this interesting and want advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the THE Campus newsletter .
Authoring a PhD Thesis: How to Plan, Draft, Write and Finish a Doctoral Dissertation (2003), by Patrick Dunleavy
Writing Your Dissertation in Fifteen Minutes a Day: A Guide to Starting, Revising, and Finishing Your Doctoral Thesis (1998), by Joan Balker
Challenges in Writing Your Dissertation: Coping with the Emotional, Interpersonal, and Spiritual Struggles (2015), by Noelle Sterne
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
Global perspectives: navigating challenges in higher education across borders, how to help young women see themselves as coders, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, authentic assessment in higher education and the role of digital creative technologies, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site

Should I Write Ph.D. or PhD? (Complete Guide)
As some of you are probably aware, the kind of English used on my side of the pond (England) is sometimes a bit different to the English used in the land of burgers and Trump.
Some words are spelt differently. But others just have a few bits of grammar difference.
Today, I want to look at the difference between Ph.D. and PhD. We’ll look at which one is correct, what it stands for, and why it’s a bit odd that it stands for that.
Should I Write Ph.D. Or PhD?
It is correct to write both Ph.D. and PhD. Which one is best to use depends on where you are in the world. In Great Britain, they tend to use Ph.D. In the United States of America, they prefer to use Ph.D.

What Does Ph.D. Or PhD Stand For?
Let’s try to understand what Ph.D. stands for.
It stands for two things. And it doesn’t stand for one or the other, it stands for both of them at the same time.
The first thing is “Doctor of Philosophy” and the second is “Philosophiae Doctor”. As the eagle-eyed among you may have noticed, “Philosophiae” is not English. It’s in Latin.
This goes back to the days when the only people who needed university were high thinkers and philosophers.
Why Americans And Brits Disagree On Ph.D. Or PhD
This could help us to understand why Brits prefer PhD but Americans prefer Ph.D.
Perhaps, according to the Brits, it stands for “Philosophiae Doctor”. But, according to the Americans, it stands for “Doctor or Philosophy”.
After all, the Brits do have a habit of trying to sound smarter. But, whichever one you use, people on both sides should know what you’re saying.
Why Ph.D. Or PhD Is A Bit Strange
Now, I want you all to understand how strange it is to call anyone with a PhD a “doctor of Philosophy”.
Let’s say someone gets a Ph.D. in history.
Well, first of all, is she really a doctor? If you break your leg, she’s not the first person you’ll go to for help.
But not only that, she studied history, not philosophy. So, she’s called a doctor of philosophy despite not being a doctor and not having studied history.
Yet, for some reason, we still call her a “Doctor of philosophy”.
Where Does The Word “Doctor” Come From?
When most of us hear the word “Doctor”, we think of someone who makes us better when we’re sick. And there may be a few of you who think of a skinny man who travels through time in a Police Box.
But originally, “Doctor” was Latin for teacher. Through time, you were able to get a “PhD” in more things than just philosophy.
And, if you wanted to become what we think of as a “Doctor”, you would need to have a “doctorate” in medicine.
Technically, “Doctor” would be the wrong word . But it’s become so common, it’s managed to “common” itself enough to become the right word.
How To Get A Ph.D. Or PhD
Now I’m afraid you can’t just walk into a university and walk out with a PhD. There are steps you need to take before you get there.
First of all, you will need to do a Bachelor’s degree. This is the degree you do when you first enter university. There are some jobs where a bachelors is enough.
Let’s be honest here, most of the time you spend doing a bachelor is just having fun.
If you want to, you can then progress onto doing a master’s degree. This is a bit more high level, and you tend to need to work for it.
Once you have your bachelors you may decide to go on to get a PhD. If you go for this, you will be officially able to call yourself an intellectual.
What Kind Of Word Is Ph.D. Or PhD?
There are three ideas for what kind of word Ph.D. is. I’ll tell you all of them and let you make up your own mind.
A PhD is something you have. You work towards it, and once you’ve handed in all of your papers, you get a PhD.
A PhD is also something you are. If you have a PhD, you might say “I’m a PhD.”
It can also be a title, similar to “Sir” or “OBE”.
If your name is James Smith, and you are PhD, your name and title could be, Mr James Smith PhD.
How To Address Someone With A Ph.D. Or PhD
Talking of this man called James Smith, there are several ways to address and introduce him.
- If you have a Ph.D., you are allowed to call yourself “Doctor” even if you don’t have a PhD in medicine. Therefore, if he wants, James could be called Dr Smith.
- Maybe he doesn’t want to be confused for a medical doctor but still wants to show off his Ph.D. In that case, we can call him James Smith PhD.
- But, like many with a Ph.D., he may not want to mention it unless it’s important. If he’s one of these people, we should just call him Mr Smith.
Ph.D. Or PhD Vs Doctorate
Asking “What’s the difference between a PhD and a doctorate?” is a bit like asking what the difference is between an apple and a fruit.
Just like an apple is a kind of fruit, a PhD is a kind of doctorate. However, it’s not the only doctorate there is.
Here are some forms of doctorate you may want to know.
Doctor of philosophy. But now also means Doctor of something there isn’t a doctorate for.
Doctorate in business.
Doctorate in engineering.
Doctorate in education
Doctor of medicine.
If you were wondering whether you should write “PhD” or “Ph.D.”, you can write either, both are grammatically correct, and both are very common terms that mean the same thing.
The only slight difference is that “PhD” is more common in England and “Ph.D.” is more common in America. This is perhaps because the British believe it stands for “philosophiae doctor” but Americans see it as “Doctor of Philosophy”.
But, no matter whether you use “PhD” or “Ph.D.”, to have one, you neither need to be a doctor nor study philosophy. All you need to do is stay in university for long enough to be able to get yourself a PhD. Then, you can become a PhD, and your title will be PhD.
You may also like: DSc Degree vs. PhD Degree – What’s the Difference? 9 Correct Ways to Write PhD Title on a Business Card

Martin holds a Master’s degree in Finance and International Business. He has six years of experience in professional communication with clients, executives, and colleagues. Furthermore, he has teaching experience from Aarhus University. Martin has been featured as an expert in communication and teaching on Forbes and Shopify. Read more about Martin here .
- “At University” Or “In University” – Easy Preposition Guide
- James’s or James’? (Correct Possessive Form)
- Is It “Doctor’s Appointment” or “Doctors appointment”?
- Universities or University’s or Universities’? (Easy Guide)
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
PhD Dissertation Outline: Creating a Roadmap to Success

A good PhD dissertation outline is as important to your dissertation as a map is to get you to your destination. Imagine for instance you’re trying to drive to a specific place to attend a party you’ve been looking forward to. You know the address, but you don’t have a map or a driving app. You get there eventually, but it takes a lot longer that it should have and stresses you so much that you’re in a bad mood when you get there. The party ends up being a bust.
This is similar to trying to write an academic paper, especially a PhD dissertation, without using an outline.
Why you need a PhD dissertation outline
When you do your PhD, outlines become the driving app for your academic paper, giving you direction so you know what’s in front of you. This is especially important for a PhD dissertation because of its physical length and the amount of time you will need to live with it. Successful PhD dissertation writing requires a laser focus, and an outline makes a great navigator.
There are many advantages of creating a PhD dissertation outline 1,2 :
- Organize your project – Using an PhD dissertation outline will help you organize your thoughts and your work. If you have an idea or find a bit of information to include in a different section, simply write a note in the appropriate place to remind yourself.
- Stay on task – Like the driving app, a PhD dissertation structure keeps you on the proper road and minimizes distractions. When writing without keeping in mind your PhD dissertation structure, it’s easy to find yourself in the weeds.
- Increase productivity – A PhD dissertation outline keeps you aware of what you have to do, allows you to set goals, and be more productive.
- Save time – This is a major advantage in PhD dissertation writing. The faster you can successfully complete your dissertation process, the more money you’ll save, and the sooner you can get on with the rest of your life.
- Reduce anxiety – The effective use of a good PhD dissertation outline will give you control over this massive project. You’ll be more confident that you can successfully complete your PhD dissertation.
How to write a PhD dissertation outline
So, now that you’re convinced that you need a PhD dissertation outline, where do you start? A few general steps will get you on the right road 3 :
- Select an appropriate topic: This one might seem obvious, but it is often a very difficult decision to make. The topic will guide the approach and research methodology. Although the research question will probably be tweaked along the way, not choosing a relevant topic at the start will result in chaos later on.
- Review other dissertations on your topic: This will give you an idea about what your PhD dissertation structure will look like.
- Draft a research problem: The research problem is the core of your dissertation and will guide your methodology and thus strongly influence your PhD dissertation structure.
- Get input from your advisor/supervisor: Seek advice from your supervisor on some PhD thesis outline examples and take advantage of any assistance they provide to help you choose wisely. This will help keep you on the right road
PhD dissertation structure
Doctoral dissertations typically have five standard chapters, although your university might have a specific required structure. Here is a brief description of the typical five-chapter PhD dissertation format 3 .
Chapter 1: Introduction – This section provides an overview of the dissertation including its topic, purpose, and relevance. Typically, the general subject area is discussed and narrowed down to the research topic. Then, the research questions are posed, and the methodology is presented. Chapter 2: Literature Review – A comprehensive survey and synthesis of existing studies on the research topic, the literature review demonstrates the research gap and sets the context for the research question. Depending on the topic, theory may also be explored. Existing methodologies used to address this topic are also discussed. Chapter 3: Methodology – In this section, the methodology and materials used to collect and analyze the research data are presented in enough detail to demonstrate the validity of the method and allow the research to be duplicated by others. Chapter 4: Results – The research findings are reported in this section and presented in relation to the research question. Relevant visuals such as tables and figures are typically included here to communicate the findings effectively. C hapter 5: Discussion – In a five-chapter format, this is the final chapter in a PhD dissertation format. In this chapter, the findings are discussed and interpreted in light of the research question. Bits from all the chapters are synthesized to completely address the research question.
An additional chapter is sometimes added that includes conclusions, recommendations, and suggestions for future research.
Tips for creating your PhD dissertation outline 3,4
Finally, here are some quick and useful tips for your PhD thesis outline journey.
- Use the structure to complete the outline – Carefully think about each chapter and write down questions and information you will need.
- Create your outline early – Keep it up to date through your early research and advisor meetings.
- Be flexible – Changes will need to be made to your outline as you progress.
- Be detailed – You never know when a small piece of information you jotted down in your outline will save you time and anxiety.
- Keep in close contact with your PhD dissertation advisor/supervisor – Make sure to share your outline. You may just save yourself a lot of time and misery if major changes need to be made.
- Stay calm – Changes will come from different committee members. Remember, they are just trying to strengthen your work.
- Statistics Solutions. The benefit of outlining. https://www.statisticssolutions.com/the-benefits-of-outlining/ [Accessed 14 July 2022].
- PapersOwl. How To Create An Outline For A Dissertation? https://papersowl.com/blog/outline-for-dissertation [Accessed 14 July 2022].
- Research.com. What Is A University Dissertation: Structure, Challenges & Writing Tips. https://research.com/research/what-is-a-university-dissertation [Accessed 14 July 2022].
- Docformats.com. Dissertation Outline Templates. https://www.docformats.com/dissertation-outline-templates/ [Accessed 14 July 2022].
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How to Write a Research Paper Outline: Simple Steps for Researchers
- Good Publication Practices: 6 Essential Steps for Publication Success
- How to Choose and Use Keywords in Research Papers
- Supplementary Materials in Research: 5 Tips for Authors
Paperpal Partners with the American Accounting Association for a Smooth Author Submission Journey
How to write a research paper summary, you may also like, ai in education: it’s time to change the..., publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how..., 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., 8 most effective ways to increase motivation for..., how to make your thesis supervision work for..., how to write a conclusion for research papers..., ethical research practices for research with human subjects, 5 reasons for rejection after peer review, what is peer review: importance and types of....
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | Guide, Examples, & Template
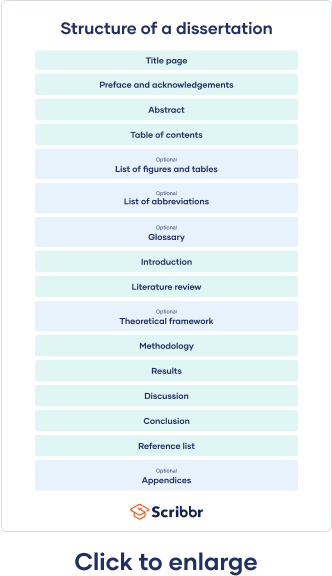
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program.
Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you’ve ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating to know where to begin.
Your department likely has guidelines related to how your dissertation should be structured. When in doubt, consult with your supervisor.
You can also download our full dissertation template in the format of your choice below. The template includes a ready-made table of contents with notes on what to include in each chapter, easily adaptable to your department’s requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
- In the US, a dissertation generally refers to the collection of research you conducted to obtain a PhD.
- In other countries (such as the UK), a dissertation often refers to the research you conduct to obtain your bachelor’s or master’s degree.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Dissertation committee and prospectus process, how to write and structure a dissertation, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your dissertation, free checklist and lecture slides.
When you’ve finished your coursework, as well as any comprehensive exams or other requirements, you advance to “ABD” (All But Dissertation) status. This means you’ve completed everything except your dissertation.
Prior to starting to write, you must form your committee and write your prospectus or proposal . Your committee comprises your adviser and a few other faculty members. They can be from your own department, or, if your work is more interdisciplinary, from other departments. Your committee will guide you through the dissertation process, and ultimately decide whether you pass your dissertation defense and receive your PhD.
Your prospectus is a formal document presented to your committee, usually orally in a defense, outlining your research aims and objectives and showing why your topic is relevant . After passing your prospectus defense, you’re ready to start your research and writing.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
The structure of your dissertation depends on a variety of factors, such as your discipline, topic, and approach. Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an overall argument to support a central thesis , with chapters organized around different themes or case studies.
However, hard science and social science dissertations typically include a review of existing works, a methodology section, an analysis of your original research, and a presentation of your results , presented in different chapters.
Dissertation examples
We’ve compiled a list of dissertation examples to help you get started.
- Example dissertation #1: Heat, Wildfire and Energy Demand: An Examination of Residential Buildings and Community Equity (a dissertation by C. A. Antonopoulos about the impact of extreme heat and wildfire on residential buildings and occupant exposure risks).
- Example dissertation #2: Exploring Income Volatility and Financial Health Among Middle-Income Households (a dissertation by M. Addo about income volatility and declining economic security among middle-income households).
- Example dissertation #3: The Use of Mindfulness Meditation to Increase the Efficacy of Mirror Visual Feedback for Reducing Phantom Limb Pain in Amputees (a dissertation by N. S. Mills about the effect of mindfulness-based interventions on the relationship between mirror visual feedback and the pain level in amputees with phantom limb pain).
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you. In some cases, your acknowledgements are part of a preface.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150 to 300 words long. Though this may seem very short, it’s one of the most important parts of your dissertation, because it introduces your work to your audience.
Your abstract should:
- State your main topic and the aims of your research
- Describe your methods
- Summarize your main results
- State your conclusions
Read more about abstracts
The table of contents lists all of your chapters, along with corresponding subheadings and page numbers. This gives your reader an overview of your structure and helps them easily navigate your document.
Remember to include all main parts of your dissertation in your table of contents, even the appendices. It’s easy to generate a table automatically in Word if you used heading styles. Generally speaking, you only include level 2 and level 3 headings, not every subheading you included in your finished work.
Read more about tables of contents
While not usually mandatory, it’s nice to include a list of figures and tables to help guide your reader if you have used a lot of these in your dissertation. It’s easy to generate one of these in Word using the Insert Caption feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
Similarly, if you have used a lot of abbreviations (especially industry-specific ones) in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
In addition to the list of abbreviations, if you find yourself using a lot of highly specialized terms that you worry will not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary. Here, alphabetize the terms and include a brief description or definition.
Read more about glossaries
The introduction serves to set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance. It tells the reader what to expect in the rest of your dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving the background information needed to contextualize your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of your research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your research questions and objectives
- Outline the flow of the rest of your work
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant. By the end, the reader should understand the what, why, and how of your research.
Read more about introductions
A formative part of your research is your literature review . This helps you gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic.
Literature reviews encompass:
- Finding relevant sources (e.g., books and journal articles)
- Assessing the credibility of your sources
- Critically analyzing and evaluating each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g., themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps) to strengthen your overall point
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing sources. Your literature review should have a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear justification for your own research. It may aim to:
- Address a gap in the literature or build on existing knowledge
- Take a new theoretical or methodological approach to your topic
- Propose a solution to an unresolved problem or advance one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework. Here, you define and analyze the key theories, concepts, and models that frame your research.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to critically assess its credibility. Your methodology section should accurately report what you did, as well as convince your reader that this was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- The overall research approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative ) and research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment )
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Any tools and materials you used (e.g., computer programs, lab equipment)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses , or themes, but avoid including any subjective or speculative interpretation here.
Your results section should:
- Concisely state each relevant result together with relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Briefly state how the result relates to the question or whether the hypothesis was supported
- Report all results that are relevant to your research questions , including any that did not meet your expectations.
Additional data (including raw numbers, full questionnaires, or interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix. You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results. Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is your opportunity to explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research question. Here, interpret your results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. Refer back to relevant source material to show how your results fit within existing research in your field.
Some guiding questions include:
- What do your results mean?
- Why do your results matter?
- What limitations do the results have?
If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your dissertation’s conclusion should concisely answer your main research question, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your central argument and emphasizing what your research has contributed to the field.
In some disciplines, the conclusion is just a short section preceding the discussion section, but in other contexts, it is the final chapter of your work. Here, you wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you found, with recommendations for future research and concluding remarks.
It’s important to leave the reader with a clear impression of why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known? Why is your research necessary for the future of your field?
Read more about conclusions
It is crucial to include a reference list or list of works cited with the full details of all the sources that you used, in order to avoid plagiarism. Be sure to choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your dissertation. Each style has strict and specific formatting requirements.
Common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA , but which style you use is often set by your department or your field.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
Your dissertation should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents such as interview transcripts or survey questions can be added as appendices, rather than adding them to the main body.
Read more about appendices
Making sure that all of your sections are in the right place is only the first step to a well-written dissertation. Don’t forget to leave plenty of time for editing and proofreading, as grammar mistakes and sloppy spelling errors can really negatively impact your work.
Dissertations can take up to five years to write, so you will definitely want to make sure that everything is perfect before submitting. You may want to consider using a professional dissertation editing service , AI proofreader or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect prior to submitting.
After your written dissertation is approved, your committee will schedule a defense. Similarly to defending your prospectus, dissertation defenses are oral presentations of your work. You’ll present your dissertation, and your committee will ask you questions. Many departments allow family members, friends, and other people who are interested to join as well.
After your defense, your committee will meet, and then inform you whether you have passed. Keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality; most committees will have resolved any serious issues with your work with you far prior to your defense, giving you ample time to fix any problems.
As you write your dissertation, you can use this simple checklist to make sure you’ve included all the essentials.
Checklist: Dissertation
My title page includes all information required by my university.
I have included acknowledgements thanking those who helped me.
My abstract provides a concise summary of the dissertation, giving the reader a clear idea of my key results or arguments.
I have created a table of contents to help the reader navigate my dissertation. It includes all chapter titles, but excludes the title page, acknowledgements, and abstract.
My introduction leads into my topic in an engaging way and shows the relevance of my research.
My introduction clearly defines the focus of my research, stating my research questions and research objectives .
My introduction includes an overview of the dissertation’s structure (reading guide).
I have conducted a literature review in which I (1) critically engage with sources, evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, (2) discuss patterns, themes, and debates in the literature, and (3) address a gap or show how my research contributes to existing research.
I have clearly outlined the theoretical framework of my research, explaining the theories and models that support my approach.
I have thoroughly described my methodology , explaining how I collected data and analyzed data.
I have concisely and objectively reported all relevant results .
I have (1) evaluated and interpreted the meaning of the results and (2) acknowledged any important limitations of the results in my discussion .
I have clearly stated the answer to my main research question in the conclusion .
I have clearly explained the implications of my conclusion, emphasizing what new insight my research has contributed.
I have provided relevant recommendations for further research or practice.
If relevant, I have included appendices with supplemental information.
I have included an in-text citation every time I use words, ideas, or information from a source.
I have listed every source in a reference list at the end of my dissertation.
I have consistently followed the rules of my chosen citation style .
I have followed all formatting guidelines provided by my university.
Congratulations!
The end is in sight—your dissertation is nearly ready to submit! Make sure it's perfectly polished with the help of a Scribbr editor.
If you’re an educator, feel free to download and adapt these slides to teach your students about structuring a dissertation.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation Binding and Printing | Options, Tips, & Comparison
- Example of a dissertation abstract
- Figure and Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Purpose and structure of an advisory report
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Shorten your abstract or summary
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Ph.D. Handbook
- OU Homepage
- The University of Oklahoma

- Undergraduate Program
- Information for M.A. Students
- Rhetoric and Writing Studies
- Resources and Forms
- Awards and Funding
- Publications
- News and Events
- Mark Allen Everett Poetry Series
- First-Year Composition
- Support the Department of English
Contact Information
Dr. Roxanne Mountford , Chair of the Department of English: [email protected]
Brenda Mackey , Office Manager: [email protected]
First-Year Composition : [email protected]
The doctoral degree is awarded for excellence in research scholarship. It signifies the attainment of independently acquired and comprehensive learning attesting to general professional competence. The doctoral degree requires at least 90 post-baccalaureate hours, including both formal coursework and hours of research.
All Ph.D. students are expected to choose two research areas, one primary and one secondary, in which to focus their coursework and writing. Students will design these areas of study in close consultation with the chair of their committee. These areas of study may be selected from well-established fields of national literature and/or historical periods (e.g., British, American, Native American, post-colonial Anglophone, medieval, early modern, Eighteenth, Nineteenth or Twentieth century), Rhetoric and Writing Studies, theoretical approaches (feminism/gender studies, critical race/ethnicity studies, Marxism, poststructuralism), media studies (film, graphic novel), more recent areas of scholarly interest (transnational literatures, new kinds of interdisciplinary studies, digital humanities). The committee must consist of a committee chair, an outside member, and at least two other members of the English graduate faculty.
The faculty are committed to preparing graduate students through preparation in coursework, mentoring, and professional development. Students have published their work in prominent journals and presented at national and local conferences. Teaching assistantships are competitive with peer institutions, and financial assistance for dissertation completion and conference travel is available through the department, the College of Arts and Sciences, and the Graduate College. The department has been successful in helping students find tenure-track positions and other employment in the field.
Admissions Requirements:
- Prospective graduate students must submit an application for admission and official transcripts to the Office of Admissions .
- A $50 non-refundable application processing fee is required of all applicants for admission to the University of Oklahoma.
- The English Department deadline for applying to the Graduate Program for the Fall term is January 5th. New students are not accepted into the graduate programs during the Spring or Summer terms.
- To be considered for admission into the Ph.D. program, we require the following: a Grade Point Average of 3.5 or better on a 4.00 scale in graduate work already completed; and an M.A. in English or in a closely related field. A student with a slightly lower G.P.A. may be considered if the application is otherwise very strong. Candidates are admitted on a competitive basis.
- A Financial Aid Services packet, and information about eligibility for financial aid, can be obtained from the Office of Financial Aid at (405) 325-4521.
Application Requirements (to be submitted with online application):
- Three (3) Letters of Reference: On your online application, you will be asked to provide emails for three references who will be contacted by the University with a request for a letter of recommendation. Your recommenders should comment specifically upon (1) your qualifications as a graduate student (literary judgment, writing ability, originality, diligence) and, if you are applying for Graduate Teaching Assistantship (GTA), (2) your qualifications as a prospective teacher (ability to organize, enthusiasm, responsibility, objectivity). If possible, referees should use the online reference system, but if they prefer, they may send hardcopy letters directly to the Office of Graduate Admissions (731 Elm Avenue, Room 318 Norman, OK 73019).
- Official Transcripts: These should be sent directly to the Office of Graduate Admissions (731 Elm Avenue, Room 318 Norman, OK 73019). Unofficial transcripts may also be uploaded to your online application.
- Statement of Goals in Graduate education: This should include your reasons for the choice of Field of Specialization and be 250-500 words. Upload this statement to your online application.
- Critical Writing Sample: It should be no more than 25 pages, appropriate to program and area. Uploaded to your online application.
Teaching Assistantships:
- Teaching Assistantships with stipends of $16,404 are available on a competitive basis for up to five years at the Ph.D. level. Prospective students interested in teaching assistantship support should indicate that on the application.
- Two weeks before the beginning of the first semester, all students who receive teaching appointments will also participate in a workshop to help them prepare for their courses, covering topics such as reading assignments, writing assignments, paper grading, and classroom strategy.
- Students awarded graduate teaching assistantship (GTA) positions will typically teach one to two composition courses each semester under the supervision of the First Year Composition Office (FYC).
- After a student has completed coursework and passed the Ph.D. General Exams, dissertation research can be supported with a $1000 increase in the assistantship stipend for one year.
Dissertation Fellowships:
- Ph.D. students working on their dissertations are eligible to apply for a one-year dissertation fellowship, which will provide them financial support without any teaching duties.
- Students applying will need to demonstrate that substantial work on the dissertation is already completed, and that they have a clear plan for a writing schedule for the rest of the chapters.
- Students awarded fellowships will be expected not to take on any additional work responsibilities so that they can concentrate on research and writing.
- For more information, see the Awards and Funding page.
- Initial advisement should occur just prior to the beginning of the fall and spring semesters. In your admission letter you are informed of the name of the assigned faculty member from the Graduate Committee who will be your adviser for the first semester or year. As soon as possible, students should seek an advisor from among the faculty in their area of study. Until the student has found a permanent adviser, he or she should seek advisement from the assigned adviser and the Director of Graduate Studies.
- During the first several weeks of the first semester in the program, new graduate students will meet collectively with the faculty and advanced students for an Orientation session and Q&A.
- After the student has chosen a faculty member to serve as adviser, the adviser will thereafter help the student construct a coherent plan of study according to the regulations of the Graduate College and the structure of the Ph.D. program.
- A plan of study will be prepared by the student and the Adviser, and approved by the Director of Graduate Studies, before enrollment for the second semester.
LCS Ph.D. Program Requirements
- ENGL 5113 Teaching College Composition Proseminar (3 Credits)
- ENGL 5313 Literary Criticism Proseminar (3 Credits)
- 7 Seminars (21 Credits)
- ENGL 6880 PhD Exam Hours (3 Credits)
- ENGL 6980 PhD Dissertation Hours (30 Credits)
Total Credits = 60 Hours + 30 Hours at the MA level = 90 Hours
*If a student has gone through our MA program and remained in our program to pursue a PhD, that student would not be required to retake either the ENGL 5113 Teaching Proseminar (3 Credits) or the ENGL 5313 Literary Criticism Proseminar (3 Credits). Instead, that student can take an additional 2 seminars as Proseminars in the first year by completing a Proseminar contract with the instructor. Contact the Graduate Director, Dr. Amit R. Baishya ( [email protected] ) for that form.
RWS Ph.D. Program Requirements
- ENGL 5403 Introduction to Rhetoric and Writing Studies Proseminar (3 Credits)
- ENGL 6103 Research Methods in Rhetoric and Writing Proseminar (3 Credits)
- 6 Additional Seminars (18 Credits)
*If a student has gone through our MA program in RWS and remained in our program to pursue a PhD in that area, that student would not be expected to retake the required courses again. Instead, the student can take any other seminars to replace the required courses. In the first year at the PhD level, the student may take two of those seminars as Proseminars. The student would complete a Proseminar contract with the instructor. Contact the Graduate Director, Dr. Amit R. Baishya ( [email protected] ) for that form.
UPDATE: A new exam structure will go into effect in the 2021-2022 academic year. Students completing their exams in 2020-2021 may choose between the traditional exam structure or the new exam structure.
New Exam Structure (effective 2021-2022)
Rhetoric and Writing Studies- Revised Doctoral Exam Structure
Literary and Cultural Studies- Revised Doctoral Exam Structure
Traditional Exam Structure (phased out by 2021-2022)
Ph.D. Exam Committee :
The exam committee should be composed of at least 3 faculty members of the English Department and one external member. These members should be submitted to the Graduate College via the Advisory Conference Report form. In addition to the Advisory Conference Report form, students must complete a General Examination Application form the semester before they intend to take their exams.
2 Reading Lists :
- Primary list: 50 entries
- Secondary list: 30 entries
Students will compose 2 reading lists to prepare for their General Examination. The first list is connected to their primary area of interest and the second is for their secondary field. Lists should be determined in consultation with the PhD Exam Committee, particularly with the guidance of the Committee Chair.
Questions :
The student provides questions for the exam in consultation with the Committee. The student will provide three questions for the primary list and two for the secondary list. The Committee chooses two questions, one for each area, from the list provided by the student.
Written Requirement:
- 2 take home essays
- First Essay will be on the Primary list and should be 15-20 pages
- Second Essay will be on the Secondary list and should be 10-15 pages
Oral Requirement (Oral Defense of the PhD Written Exams) :
The student writes and defends the exam essays in the fourth semester at the PhD level. Sometimes students will wait until the beginning of the fifth semester to take the exam. Students should not take their exams any later than early fall of the fifth semester to remain on track.
After successfully passing their PhD exams, students will sign up for dissertation credits and tuition waivers (usually five credits/semester- sometimes they will need to take more or fewer credits depending on how long they are in the program to make a full 30 Credits. Details can be discussed with Brenda Mackey, Graduate Coordinator).
Typically students will complete and defend their dissertation two or three years after passing their exams.
Written Requirement
Students will write a dissertation in consultation with their Dissertation Committee, particularly their Dissertation Chair.
Oral Requirement (Oral Defense of the Dissertation)
It is important that students successfully defend their dissertation before running out of tuition waivers. Contact Brenda Mackey ( [email protected] ) for details.
The forms needed to complete this dissertation can be found at the Graduate College website.
Language Requirements :
One language at reading proficiency level.
- Two undergraduate courses in the language (must have received at least a B in each class)
- A translation exam offered by the Department of Modern Languages or other appropriate department.
- A graduate level reading class offered in Modern Languages (this class is offered each summer and only Spanish or French are offered).
- Native proficiency
*Before the department informs the Graduate College that a graduate student has met the requirement for language proficiency, the student’s chair must determine whether the student has met the necessary proficiency level for the student’s particular area and research project. Some fields require greater language proficiency than the first three options above may allow for.
**The graduate level reading course does not count for the degree credits nor do any other language courses taken during degree time count for credits toward the degree. Students can petition the graduate college for extra waivers to take language classes.
With permission, students may avail themselves of all three options. However, these options will only be approved in exceptional circumstances.
- Directed Readings (3 Credits): When a student cannot proceed with their main course of study without taking a directed reading, the student and their chair can petition the graduate committee for permission to replace a seminar with a directed reading. Students may petition to take up to one directed reading at the M.A. level and one directed reading at the Ph.D. level. The student and faculty must also fill out a directed reading contract specifying required assignments, readings, and meetings.
- Students may take up to one graduate 4000 level course (3 Credits) when that course is truly necessary for the student’s course of study with the approval of the graduate committee and the student’s chair. This course must result in a 20+ page research paper. Students may petition to take up to one 4000 level course at the M.A. level and one at the Ph.D. level.
- Students may take up to one graduate level seminar (3 Credits) in another department when that course is truly necessary for the student’s course of study with the approval of the graduate committee and the student’s chair. Students may petition to take up to one seminar in another department at the M.A. level and one at the Ph.D. level.
- Each graduate student will be evaluated formally and collectively at the end of each academic year during a meeting of the faculty. The annual evaluation of each current graduate student will be an occasion for a careful (re)assessment of his or her scholastic progress, accomplishments, and prospects of continuation in the program. Students are evaluated upon their timely progress in the program and the quality of their work.
- In the spring semester, students will submit a self-assessment to their Adviser on the Annual Student Progress Report (ASPR), sent through email by Sara Knight, with the required information for that academic year. The Adviser will submit the ASPR with his or her written evaluation of the student’s work based on a review of the student's grades, performance in courses, and timely progress toward degree. At the end of the Spring semester, the full graduate faculty meet to discuss each student’s performance and consider whether or not the student’s progress is satisfactory or unsatisfactory.
- If a student's annual evaluation indicates that he or she is not making satisfactory progress in the program, the Graduate Committee will review the case and make an official recommendation to the Graduate College. If a student receives an “Unsatisfactory” on an annual review, thereafter, he or she will be evaluated every semester. The Graduate College automatically disenrolls students who receive two “Unsatisfactory” reports. Unless there are extenuating circumstances approved by the advisor, students are automatically disenrolled by the Department if their cumulative GPA falls below 3.0.
Revised policies and practices to be implemented for Spring 2022 and subsequent graduates:
4 weeks prior to the last day of finals (and at least 10 working days prior to the defense): Deadline to submit a reading copy of the dissertation to the committee and to submit the Report of Reading Copy Submission and Request for Authority to Defend to the Graduate College.
- Explanation: Students will now be required to submit a full reading copy to the committee and to report to the Graduate College that they have done so as part of the process of requesting authority to defend.
3 weeks prior to the last day of finals (and at least 5 working days prior to the defense): Deadline for committee members to sign the Report of Reading Copy Submission and Request for Authority to Defend .
- Explanation: Committee members will affirm that they received the reading copy as reported by the student and will provide their assessment of whether the thesis or dissertation is ready to defend. The timeline provides committee members with one week (5 working days) to make this assessment.
2 weeks (10 working days) prior to the last day of finals: Deadline to defend the thesis or dissertation.
- Explanation: This deadline allows the student to spend one week making limited revisions and still graduate during the current semester. Academic units may wish to encourage or require earlier defenses if more extensive revisions tend to be needed, or to encourage committees to provide feedback earlier in the process- talk to your advisor about their requirements.
1 week (5 working days) prior to the last day of finals: Deadline to submit the thesis or dissertation to SHAREOK in order to graduate during the current academic term.
- Explanation: A large proportion of theses and dissertations require formatting adjustments or other corrections after initial submission to SHAREOK. This deadline allows these issues to be resolved by the end of the semester for graduation and timely degree clearance.
Two additional changes in policy and practice will accompany these timelines.
- The Request for Degree Check will be due during the first two weeks of the semester. This will enable the grad college to identify and address any potential barriers to graduation early in the semester and facilitate processing of the Request for Authority to Defend once all signatures are received. The Request for Degree Check is easy to submit, and there is no penalty for requesting a degree check but not graduating that semester. In addition, requiring it early in the semester will encourage students and committees to confer about the plan for completion.
- The grad college will enforce the requirement to enroll in the subsequent semester if degree completion requirements are not met in accordance with the above timelines. Students will be eligible to graduate without repeating the defense if they submit their thesis or dissertation to SHAREOK within 60 calendar days after the defense, but they will be required to enroll in the following semester if their submission occurs after the final day of classes. (The grad college will continue to entertain petitions to waive the enrollment requirement if serious exigent circumstances are present, but the grad college will not approve petitions in the absence of such circumstances.)

- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- OU Job Search
- Accreditation
- Legal Notices
- Resources & Offices
- OU Report It!
English Social Media

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When writing a name with a PhD after it, the correct way to do so is to use "PhD" or "Ph.D. or Ph.D". Depending on the preference of the individual, either form can be used. However, if the individual has a business card that states their degree in full, then the more formal "Doctor of Philosophy" should be used.
Abbreviation of AP Style Academic Degrees. Use such abbreviations as B.S., M.S., LL.D., J.D., and Ph.D. only when you need to identify many individuals by degree on first reference and doing so in the AP Style academic degrees preferred way would be cumbersome. You should use abbreviations like these only after full names, never after just a ...
Firstly, "P" must be in a capital case. Secondly, "h" is in small case with no space after "P". Thirdly, use period/full-stop after "h". Fourthly, Write "D" in capital case. Fifthly, keep Period after "D". Finally, the correct way to write is Ph.D. Or, It can be also written as PhD in a sentence. As per APA style, write Ph.
49. Actually both are correct. I could easily find both on my NOAD, and there are plenty of pages on the net where you find it written as "PhD". The OALD gives an interesting distinction, stating that Ph.D. is especially North American English. Now, being a non-native speaker, I can only rely on official sources to state who uses what, but ...
Addressing a Doctor in Writing. Place the title of "Dr." before the name of a person who is a doctor of medicine or psychology, doctor of dentistry, or doctor of veterinary medicine. For example Dr. George Ross. Always write the word "doctor" in its abbreviated form when it goes before the person's name. Never write, for example ...
Here are the steps to write PhD correctly: Firstly, "P" must be in a capital case. Secondly, "h" is in small case with no space after "P". Thirdly, use period/full-stop after "h". Fourthly, Write "D" in capital case. Fifthly, keep Period after "D". Finally, the correct way to write is Ph.D.
Writing a doctoral thesis—the culmination of years of research work—can be a daunting endeavor. But learning from those who have already tackled this task can help you make the process a little smoother. Science Careers asked recent graduates and current students to reflect on their experiences and what did—and didn't—work for them.
Most importantly, while writing your thesis, be sure to take care of yourself. Eat well, exercise, and get plenty of sleep so you're at your best when you sit down every day to write. This is the home stretch of your Ph.D., and you want to make sure you cross the finish line energized and ready for the next step.
You'll need to write a research proposal if you're submitting your own project plan as part of a PhD application. A good PhD proposal outlines the scope and significance of your topic and explains how you plan to research it. It's helpful to think about the proposal like this: if the rest of your application explains your ability to do a PhD ...
PhD, Ph.D., Dr. In English, PhD can be written with or without periods; both are correct. The trend today is to drop periods with abbreviations of academic degrees. However, many sources, including the Canadian Oxford Dictionary, still recommend the use of periods: Ph.D.. When you are addressing a person with a doctoral degree, it is considered more polite to use the title Dr. or the academic ...
How to Create a Dissertation Outline. Choose a Topic and Form a Thesis. Before you start writing an outline, you should have a clear idea about the argument or thesis you want to present. If you haven't already, you should do a fair amount of diligent research surrounding the topic to gather enough information to develop an angle or viewpoint.
A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words ( 100 to 300 pages in length) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) - from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion. The structure of a dissertation will vary depending on discipline (humanities, social ...
Graduate School Writing Samples Bernhard Nickel · [email protected] July 10, 2022 ... and you can't work out the details without actually trying to write the paper. Once you've spent a lot of time writing the paper, you'll be in a position to outline. (See also the section on Workflow below.)
A PhD is a terminal academic degree students typically pursue when they're interested in an academic or research career. A PhD is the highest possible academic degree a student can obtain. PhD stands for "Doctor of Philosophy," which refers to the immense knowledge a student gains when earning the degree. While you can actually get a PhD in ...
The only slight difference is that "PhD" is more common in England and "Ph.D." is more common in America. This is perhaps because the British believe it stands for "philosophiae doctor" but Americans see it as "Doctor of Philosophy". But, no matter whether you use "PhD" or "Ph.D.", to have one, you neither need to be a ...
minimum of ten days for all members of the thesis committee to review the thesis. Step 1: Prepare the content of your presentation. The content of your presentation is the mirror of your thesis ...
At 100+ pages, writing a PhD thesis paralyzes the bravest student. Breaking writer's block for PhD students is possible and easy. Keep reading to know how. One of the most important and ...
A PhD dissertation outline is vital to write your thesis systematically. When you do your PhD, outlines make the task of writing the thesis easier and more productive. So, check out these quick and useful tips to create a strong PhD dissertation structure.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
The assessment of a PhD by Publication is generally very similar to the assessment of a traditional dissertation. It involves the submission of a written document that contains both the published academic papers and a narrative the explains how the papers together make an original contribution to advancing knowledge.
Oral Requirement (Oral Defense of the PhD Written Exams): The student writes and defends the exam essays in the fourth semester at the PhD level. Sometimes students will wait until the beginning of the fifth semester to take the exam. ... The student and faculty must also fill out a directed reading contract specifying required assignments ...
To start with challenge one: being, by now, a bit 'over' the PhD. I have written elsewhere on this blog about how unproductive last year - post-PhD year 1 - was in terms of writing and sending off papers developed out of my PhD research. In the midst of the year full of work, kids, work, life and more work there seemed to be space to ...
Humanities PhD: how do you make a writing out of your notes? It might sound like a very basic question, but I've found not every PhD candidate does it the same. Once you have done all the reading and the note taking from existing literature, how do you actually write something out of it? How do you make and articulate sentences out of isolated ...
PhD student of Mathematics, Department of Mathematics, Foo Baz University, BB, August 2011 - March 2015. Edit: To make it clearer: you can put "work experience", "studies" and "academic degrees" in different sections of your CV. That way it will be clear, that you have been a PhD student for a long time, but your highest archivement it your ...