Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


Determinants of Profitability of Commercial Banks in Ethiopia

Related Papers
Publisher ijmra.us UGC Approved
The purpose of this study is to investigate determinants of banks profitability in CBE by using time series data of CBE from year 1983 to 2012. The study used quantitative research approach and secondary financial data are analyzed by using multiple linear regression models for the bank profitability measures: Return on Asset (ROA). OLS method was applied to investigate the impact of bank size, managerial efficiency, liquidity, credit risk, real GDP growth rate, and annual inflation rate on major bank profitability measure i.e., (ROA) separately. The empirical results shows that bank specific factors; bank size, managerial efficiency, credit risk and macroeconomic factors; level of GDP and annual inflation rate have a strong influence on the profitability of banks. The empirical study shows that, all explanatory variables in this study have negative effect on the profitability measure except GDP and inflation rate. In addition to this, without liquidity all explanatory variables are statistically significant. Finally, the researcher have made conclusions and recommendations based on the analyzed results.
Enyew Alemaw Mesfin
This study examines the bank-specific, industry-specific and macroeconomic factors that affect bank profitability of nine commercial banks in Ethiopia, during the period of 2007-2016. To this end, the study adopts a quantitative method of research approach and 9 sample commercial banks were purposively selected from 18 banks operating in Ethiopia. Random effect regression model was run to analyze the raw data collected through audited financial statements. The findings of the study show that capital adequacy, leverage, liquidity, and ownership have statistically significant and positive relationship with banks' profitability. On the other hand, operational efficiency GDP, inflation and interest rate have a negative and statistically significant relationship with banks' profitability. However, the relationship between bank size and number of branch is found to be statistically insignificant. Therefore, Ethiopian commercial banks should not only be worried about internal structures and rules, but they have to give attention for both the internal and the macroeconomic variables together in fashioning out plans to pick up their performance.
mohamed waritu
Addis Ababa university
Belayneh Hailegeorgis
The aim of this study is to examine the impact of bank-specific, industryspecific and macroeconomic determinants of Ethiopian commercial banks profitability. The study applied the balanced panel data of seven Ethiopian commercial banks that covers the period 2001- 2010. The paper used Ordinary Least Square (OLS) technique to investigate the impact of capital, size, loan, deposits, noninterest income, noninterest expense, credit risk, market concentration, economic growth, inflation and saving interest rate on major profitability indicator i.e., return on asset (ROA). The estimation results show that all bank-specific determinants, with the exception of saving deposit, significantly affect commercial banks profitability in Ethiopia. Market concentration is also a significant determining factor of profitability. Finally, with regard to macroeconomic variables, only economic growth exhibits a significant relationship with banks’ profitability. The results of the study are of value to both academics and policy makers.
Tilahun mihretu
Dawit Belete
Both internal and external determinants of Bank profitability affect the profitability of Private Commercial Banks in Ethiopia. This study identifies bank specific, industry specific and macroeconomic factors that determine the profitability of Ethiopian private commercial banks. Six private commercial banks have been the subject for the study ranging from 2004/2005 to 2014/2015. The bank's Audited financial statement, National Bank of Ethiopia and Ministry of finance and Economic Cooperation has been the main source for the study and the panel analysis has been carried out to obtain the result for this empirical study. The study used ROA as a Dependent variable and capital adequacy, operational efficiency, liquidity, income diversification, concentration, GDP, inflation and money supply as independent variables. The empirical results showed that capital, operational efficiency, income diversification, concentration and money supply have significant relationship with profitabili...
Plaxedes Gochero
With the objective to establish determinants and effects of profitability in Zimbabwean commercial banks for the period 2009 to 2013 a Generalized Least Squares method was used on pooled panel data of 11 commercial banks over 5 years to solve for heteroskedasticity. Employing RoA as a proxy for profits, Net interest Income and Expenses are highly significant at the 1 % level of significance with positive and negative coefficients respectively implying that operational efficiency and product diversification are vital for profitability. Inflation, Liquidity, Financial Structure and Asset Composition are weakly significant at the 10 % level of significance while Deposit Composition was found to be statistically insignificant. Legislators have well vested interest in implementing policies aimed at stabilisation and efficiency in the banking sector. For one to formulate an effective policy that strikes a balance between the two there’s need to understand the determinants of bank profitab...
SAMUEL ALEMU
A Thesis Submitted to The Department of Accounting and Finance Presented in the Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Degree of Masters of Science (Accounting and Finance)
Copernican Journal of Finance and Accounting
Endalew Tarfa
The healthiness of the banks is critical because they are highly fragile, vulnerable and closely integrated with other sectors. One way of testing the healthiness of the banks is through the measure of their profitability. Profitability is the primary objective of any business including commercial banks. Profitable banks can withstand any negative shocks and stabilize the whole financial sector. The main objective of this study was to analyze the determinants of the profitability of commercial banks in Ethiopia. To achieve this objective a secondary source balanced panel data of ten years from nine commercial banks were used, and internal determinants; business mix indicators, risk aversion index, management efficiency, liquidity risk, bank size, and external determinants; ownership, market concentration, and GDP, were regressed against return on asset by using the pooled OLS technique. Results indicated that internal determinants were more important than external factors. Thus busi...
ketema sime
The study was attempted to investigate determinants of financial performance of commercial banks in Ethiopian by using secondary data. The data were obtained from audited financial statements of five sampled commercial banks for the period of 1997 to 2017 and National Bank of Ethiopia. The study used return on assets (ROA) and return on equity (ROE) as dependent financial performance variable. Moreover, the study used bank specific variables as explanatory variables. Both descriptive statistics and econometrics model specifically fixed effects estimation were used to analyze the relationships of dependent variable with explanatory variables. The major findings of the study shows that bank specific determinants were very important in explaining financial performance of commercial banks. The management efficiency, customer deposit to total asset ratio, capital adequacy ratio, loan to deposit ratio were positively and significantly related to bank’s financial performance. The study ...
RELATED PAPERS
Sri Nurhidayah
Journal of Applied Oral Science
Celso Caldeira
LÊ THỊ MỸ HOA
Robert J Bunker
Charlotte Trinquet du Lys
Jeong-Yeol Han
Journal of the Optical Society of America A
Barbara Dosher
World Water Policy
Nevo Chinedu
Majalah Kedokteran UKI
Dhanu Arianto
Sebastian Goraj
Katalin Tolnai
Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology
Corrie Erasmus
Journal of Education, Society and Behavioural Science
William Onu
Erika Paulina Rodríguez Yebra
Journal of Animal Science
Johanna Vilkki
Romanian journal of morphology and embryology = Revue roumaine de morphologie et embryologie
Anca Zanfirescu
MOHAMED DJEMEL
Tony Brinkley
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences
melinda noer
Quaderns de prehistòria i arqueologia de Castelló
Gerard Clausell
Ömer Sinan Aksoy
Devi Fatimatu Zahra dan Gita Indah
PAI Ekstensi STAIB 22'23
Turkish Journal of Botany
Tuğba Ekici Ertuğrul
UMinho Editora eBooks
Ricardo Resende
Social Science Research Network
Vasil Penchev
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Open access
- Published: 05 September 2022
Deposit mobilization and its determinants: evidence from commercial banks in Ethiopia
- Nesru Kasim Banke ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8106-7554 1 &
- Mekonnen Kumlachew Yitayaw ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6076-1774 1
Future Business Journal volume 8 , Article number: 32 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
25k Accesses
2 Citations
Metrics details
Deposit mobilization is the most important service and an integral part of banking operations. In Ethiopia, mobilizing savings through intense deposit collection has been regarded as the major task of banking. However, managing deposits is impossible without understanding and controlling the factors that influence them. Thus, this study examined the bank-specific and macroeconomic determinants of deposit mobilization in Ethiopian banking sectors using balanced panel data of 14 commercial banks from 2011 to 2020. Secondary data sources from sampled commercial bank audited financial statements were used to achieve the stated objective. A quantitative approach and explanatory design were employed. The model result demonstrated that loan to deposit ratio, capital adequacy, economic growth, inflation, population growth, and political stability have a negative and statistically significant effect on commercial bank deposit mobilization. On the other hand, the bank's profitability has a positive and statistically significant impact on commercial bank deposit growth. The study suggests that Ethiopian commercial banks need to improve deposit mobilization by paying more attention to internal factors controlled by management, while keeping in mind the influence of the overall economic and political dynamic. This study provides useful insights for bank managers, owners, analysts, policymakers, depositors, and other stakeholders on the deposit growth of commercial banks and its determinants. Meanwhile, academic researchers and students may use the findings and suggestions to conduct a study in the banking area. Unlike the previous studies, the present study examined the effect of population growth and political stability on deposit mobilization and contributes to the limited stock of existing knowledge in the area.
Introduction
An efficient financial system is essential for sustainable economic growth and building a dynamic economic system, and countries with well-developed financial institutions tend to grow faster [ 53 ]. In developing countries where the banking industry dominates the financial sector, such as Ethiopia, commercial banks are the primary controllers of the financial system, performing financial intermediation, and their effective and efficient operation plays a vital role in accelerating economic growth [ 2 ]. As a result, the banking system serves as the backbone of financial intermediation by mobilizing and channeling financial resources to the economy [ 13 ].
Banks play an intermediary function in a contemporary economy by mobilizing funds from savers (those with surplus income) and then lending them to investors, both individuals and businesses (deficit units) [ 5 , 61 ]. Granting loans and advances, which is the primary source of income for banks, is usually attainable if the banks have amassed adequate deposits from the available market [ 54 ]. Thus, deposits are a vital source of funds for banking operations and are regarded as the essential resource for commercial banks in meeting the needs of banking systems' financial resources [ 54 , 46 ].
Deposit mobilization is an important source of working capital for banks and is of paramount importance to the banking industry as the size of deposits mobilized by the general public through current, savings, fixed deposits, time deposits, and other specialized systems critical to the bank's success [ 28 , 66 ]. The government has also urged banks to make all possible efforts to mobilize additional deposits, which can only speed up banks' pace of lending activities from surplus units to deficit units for the economy's development [ 23 ]. Since a deposit is considered a low-cost source of working capital, the bank's ability to lend more and its success is highly reliant on deposit mobilization [ 28 ].
In economic theory, banks are generally regarded as oligopolistic institutions with high competition [ 34 ]. However, in this highly competitive business, the bank's capacity to mobilize sufficient cash from the public through various schemes will depend on the systems employed [ 21 ]. Deposit mobilization is as important to banks as oxygen is to humans. Banks and other financial institutions may fail to meet their business objectives if they do not have enough deposits (Viswanadham, et al. [ 66 ]. The survival of the banking industry was heavily reliant on deposit growth [ 3 ]. Banks must be able to raise enough deposits to keep the economy running smoothly [ 34 ]. Although deposits are the most important source of operating capital for banks, mobilizing adequate deposits is impossible without first recognizing and controlling the factors that influence them 2 ]. Thus, the issue of bank deposit growth and the factors that influence it is critical to the financial sector of emerging countries like Ethiopia.
Several studies like Bista and Basnet [ 17 ], Alemu [ 3 ], Thisaranga and Ariyasena [ 59 ], Abiodun et al. [ 1 ], Yakubu and Abokor [ 70 ], Ayene [ 9 ], Islam et al. [ 38 ], Azolibe [ 11 ],Tarekegn [ 57 ], and Erna and Ekki [ 24 ], examined various external and internal factors that influence deposit growth and found inconsistent results. However, there are still discrepancies in many studies across continents, countries, and periods in identifying which factors have a major impact and the direction of those impacts. Furthermore, studies in Ethiopia have not considered the impact of population growth and political stability on deposit mobilization, and with the composition of the variables considered in this study. Thus, the purpose of this study was to fill this gap by investigating the determinants of deposit mobilization in Ethiopia and contributes to the existing empirical evidence.
The findings of the study demonstrated that loan to deposit ratio, capital adequacy, economic growth, inflation, population growth, and political stability have a significant negative effect on commercial bank deposit mobilization. On the other hand, the bank's profitability has a significant positive impact on commercial bank deposit growth. The results of the study will provide valuable input for banks’ managers and policy makers in developing sound policies and strategies to enhance deposit mobilization.
The remainder of the study is organized as follows. Section " Literature reviews " discusses the relevant literature reviewed. Section " Data and methodology " presents the data and methodology used in the study. Section " Results and discussions " indicates the results and discussions and Section " Conclusions " comprises of conclusions, recommendations, and directions for future studies.
Literature reviews
Banks are one of the profitable financial institutions that offer banking and other financial services to their customers by accepting deposits from the depositors and providing loans to the borrowers [ 38 , 51 ]. Thus, deposits become the most important financial resource for commercial banks to meet the financial needs of their customers, and it requires them to mobilize and accumulate enough deposit amounts [ 46 ]. As a result, the financial resources of banking systems are primarily provided by customer deposits. The going concern of every commercial bank is highly dependent on deposits collected from customers [ 46 ]. Deposit mobilization is the process of mobilizing funds by financial institutions from the surplus units to the deficit units to create better opportunities for productive investment [ 12 , 39 ]. A bank's lending capacity is highly dependent on its ability to attract deposits, making it the ultimate source of bank profit and growth [ 9 , 20 ]. However, deposit mobilization should encourage customers to deposit cash in the bank or have new customers come and open an account in the bank [ 61 ]. To be competitive in the banking sector, banks need to have a sufficient share of the deposit market. Deposit mobilization is ineffective unless you know and control the factors that influence it. Thus, it is worthwhile to study determinant factors of deposit mobilization. Empirical evidence documented that the influence factors may be categorized as bank-specific and macroeconomic factors, [ 11 , 38 , 70 ]. Thus, we discussed further the variables considered in the study and how they influence bank deposit mobilization in Ethiopia.
Factors Affecting Deposits mobilization of Commercial Banks
In general, the determinants of bank deposits are divided into micro and macroeconomic aspects. Microeconomic factors are bank-specific variables, but Macroeconomic variables are those, when manipulated, are capable of achieving the nation’s macroeconomic objectives [ 1 , 4 , 10 , 69 , 70 ].
Firm-specific factors
Profitability (roa).
Osei [ 49 ] documented that profitability is an important factor determining rural banks' deposit mobilization. Bhalla [ 15 ] explained Return on Asset (ROA) as a ratio used to measure the company's efficiency in using its assets to generate profit. It reflects the management's ability to utilize the banks financial and real investment resources to generate profits [ 35 ]. Consequently, the more efficient company will generate a higher profit level from a given level of total assets than its less efficient competitor [ 15 ]. Thus, higher profit is considered a positive signal or soundness of the bank, making it easier for such banks to attract other deposits [ 25 ]. Alemu [ 3 ], Tarekegn [ 57 ], Getachew [ 31 ], and Erna and Ekki [ 24 ] found that a bank's profitability has a positive effect on the growth of banks deposit. Since the depositor confidence will increase if the commercial banks are profitable and have adequate asset returns, banks should sustain their profitability to increase their deposit amount.
Profitability has a significant positive effect on deposit mobilization.
Loan to deposit ratio (Bank's liquidity)
Loan to deposit ratio (LTD) can be defined as a measure of bank liquidity, which reflects the proportion of customers’ deposits that have been given out in the form of loans [ 29 , 71 ]. It refers to a bank’s ability to execute its commitments at any time, including repaying customer deposits or making a payment on the client's order [ 67 ] The greater this ratio is, the less liquid the bank is, resulting in a decline in client deposits due to the bank's limited capacity to reimburse depositors. When a bank fails to pay its depositors, it faces liquidity risk, which causes other depositors not to deposit in that particular bank [ 45 ]. Amene [ 4 ] and Awole [ 8 ] found a negative impact of bank liquidity on commercial bank deposits growth. However, Finger & Hesse [ 25 ] stated that the bank's liquidity situation plays a significant role in determining banks deposit growth and higher liquidity buffers tend to signal greater bank soundness, which could be a factor favoring deposit demand. Studies by Ünvan and Yakubu [ 63 ], and Turhani and Hoda [ 60 ] also documented that there is a positive relationship between bank liquidity and deposit.
LTD ratio has a significant negative effect on deposit mobilization
Capital adequacy
Capital adequacy is the level of capital that banks must hold to enable them to withstand credit, market, and operational risks they are exposed to Tarekegn [ 57 ]. Bank capital plays an important role in maintaining the security of banks and the security of the banking system in general [ 44 ] to prevent unexpected losses that banks may face. It turns out that the availability of large amounts of capital increases the risk absorption capacity of banks (Berger and Bouwman [ 14 ] and liquidity creation capability [ 22 ]. Thus, banks having a higher capital ratio may not necessarily need to mobilize more deposits, “the crowding out of deposits” [ 33 ]. Ünvan and Yakubu [ 63 ], Amene [ 4 ] and Turhani and Hoda [ 60 ] also revealed that capital adequacy affects bank deposits negatively. However, the study conducted by Tarekegn [ 57 ] established a positive relationship between capital adequacy and band deposit.
Capital adequacy has a significant negative effect on deposit mobilization.
Macroeconomic factors
Inflation is described as a general and sustained rise in prices of goods and services in the economy [ 57 ], and Usman and Adejare [ 64 ]. Inflation affects bank deposits in two ways. First, it reduces the purchasing power of money and thus leads to high living costs. This means that households can hardly buy with disposable income and therefore may have little or no deposit in a bank. Second, in situations where hyperinflation occurs, i.e., Cash or bank savings are worthless (Azolibe [ 11 ] because the purchasing power of money is so much less than the sudden and excessive runaway price increases in the economy. Therefore, people may choose to convert deposits and cash into storage commodities in anticipation of future price increases and the possibility that they will not be able to deposit money in banks. Namazi and Salehi [ 46 ] also argued that when the inflation rate increases, the actual yield rate of money and assets decreases,therefore, deposits are no longer attractive. The effect of inflation on deposits is significantly negative. Maturu [ 43 ], Abiodun, et al. [ 1 ], Orok et al. [ 48 ], Muluken [ 45 ], Larbi-Siaw and Lawer [ 40 ], and Ostadi and Sarlak [ 50 ] have also documented the negative effect of inflation on the commercial bank deposits. However, Thisaranga and Ariyasena [ 59 ], Ukinamemen [ 62 ] and Athukorala & Sen [ 6 ] revealed that the rate of inflation has a positive impact on saving.
Inflation has a significant negative effect on deposit mobilization.
Gross domestic product is the market value of all goods and services produced in a country over one year and are one of the primary indicators used to measure economic performance (Azolibe [ 11 ]. According to Stanford [ 56 ], changes in real GDP per capita over time are often understood as a measure of changes in the average standard of living. Logically, if households and firms desire to hold more money, deposits will increase. Thus, the relationship between income and deposits is positive, that is, as the income of the society increases, the commercial bank's deposits increase. Empirical studies conducted by Hassan [ 36 ], Adem [ 2 ], Mashamba et al. [ 42 ], and Stanford [ 56 ] also revealed that GDP has a positive influence on the volume of commercial bank deposit. Whereas Yakubu, and Abokor [ 70 ] and Bikker and Gerritsen [ 16 ] found a significant negative effect of GDP on bank deposits. Islam et al. [ 38 ] also documented that the GDP growth rate has a negative but insignificant effect on the bank's deposit growth rate.
GDP growth has a significant positive effect on deposit mobilization
Population growth
Acquiring deposits and advancing the credit objectives of banks cannot be attained without the good banking habits of the people (Varman [ 65 ]. Thus, the deposit amount depends on the number of deposit account holders. Hibret [ 37 ] also argued that population growth would mean an increase in the functional labor force that would attract investment, create wealth and positively affect overall economic growth, as a result, the deposit will grow because the more number populations tend to have more number of income generator and saver. Thus, Hibret [ 37 ] revealed that population growth had a positive and significant impact on deposits. Teshome [ 58 ] also found a positive relationship between population growth and bank deposit. However, Legass et al. [ 41 ] and Cincotta and Engelman [ 19 ] documented the negative effect of population growth on deposit growth as rapid population growth produces large proportions of children relative to the labor force, resulting in high costs and retard household savings.
Population growth has a significant positive effect on deposit mobilization.
Political stability
The country's economic, social and political factors may affect the propensity for depositors to place funds in the banking system, and banks' success in their operation mainly depends on the environment where the business is undertaken (Finger and Hesse [ 25 ]. Political stability encourages investment and promotes economic growth, thereby increasing the profitability of a business [ 55 ]. Political stability in democratic regimes is positively related to economic freedom indicators because greater economic freedom positively influences investment and economic growth [ 30 ]. However, conflicts and political instability can lead to a greater risk of systemic banking crisis and low bank deposits. [ 52 ] emphasized that conflicts weaken the performance of the financial sector and deteriorate banks’ ability to sustain financial intermediation role. Political instability could increase the volatility of bank deposits [ 7 ]. [ 32 ] found that the Syrian conflict deeply affected the banking sector by causing deposit and assets runs, and raising non-performing loan.
Political stability has a significant positive effect on deposit mobilization.
Conceptual framework
Conceptual framework helps to clearly identify the variables used in the study and shows how particular variables are connected with each other in the study. The conceptual framework presented both internal and external variables used in this study and the independent variable in Fig. 1 below.
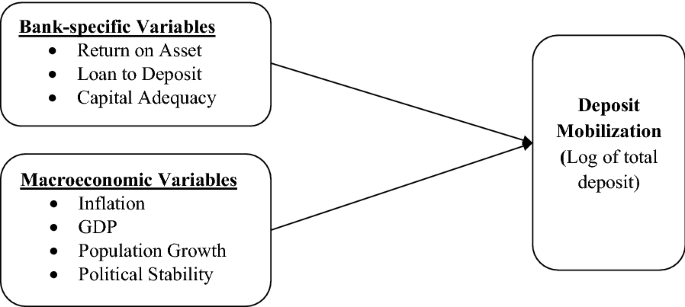
Data and methodology
The purpose of this study was to investigate the factors that influence commercial bank deposit mobilization in Ethiopia. This study used a quantitative approach to determine the determinants that influence commercial bank deposit mobilization in light of the inquiry about the purpose, the theories developed, and the quantitative character of the data. This study used an explanatory research approach to investigate the cause and impact of links between bank deposit mobilization and their determining factors.
From the total population of 18 commercial banks in Ethiopia, 14 commercial banks with a long period of audited financial data from 2011 to 2020 are selected as a sample. The analysis relied on secondary data, which included the yearly financial reports, primarily balance sheets and income statements, of the commercial banks under consideration. The data was a balanced panel data set that captured both cross-sectional and time-series behaviors at the same time.
Methods of data analysis
The data was analyzed using both descriptive measurements and econometric instruments in the study. The preceding contains simple descriptive approaches such as mean, maximum, minimum, standard deviations, and others that enable a higher knowledge of the current situation and examine the data's common patterns.
The descriptive analysis was supported by the study's use of econometric models to determine cause and effect between the explanatory and dependent variables. The Fixed Effect Model was used in the study to identify determinants that have a significant influence on commercial bank deposit mobilization in Ethiopia.
Robustness tests examine how well the estimated effect of the baseline model holds up when the specification of other plausible alternative models is systematically changed. [ 47 ] define resilience as the degree to which an additional robustness test model that modifies the model specification logically supports the estimated effect of interest from the baseline model. The accuracy of all estimation techniques is dependent on certain assumptions [ 27 ]. Before fully accepting and interpreting our regression result, we attempt to verify the fulfilment of fundamental hypotheses such as no perfect collinearity (multicollinearity test), homoskedasticity (heteroskedasticity test), and model specification (Hausman test) in our manuscript. All of the preceding diagnostic tests demonstrate the reliability of our regression result.
Definition and measurements of variables
Dependent variable.
Deposit mobilization (Natural log of total deposit) was used as a dependent variable in this study. Deposit mobilization is one of the most important functions of the banking industry because it is a critical source of working capital for the bank, and the amount of deposits mobilized from the public through current, savings, fixed, and recurring accounts, as well as other specialized schemes, is critical to the bank's fruitful operation [ 66 ]. The government has also directed banks from time to time to make all possible efforts to mobilize new deposits, which can only speed up the pace of lending activities by banks from the surplus units to deficit units for the development of the economy [ 23 ]. In this study, logarithm of total deposit is used as a proxy for deposit mobilization and used by Firdawek [ 26 ] and Teshome [ 58 ]. It demonstrated the size of deposits obtained from the general population by banks.
Independent variables
The explanatory variables employed in this study to determine the deposit mobilization of Ethiopian commercial banks are bank-specific factors (such as profitability, liquidity, and capital adequacy ratio) and macroeconomics factors (such as inflation rate, GDP Growth, political stability and population growth) (Table 1 ). These variables are used in various combinations and have been identified as important factors in determining bank deposit mobilization in a variety of studies [ 70 , 11 , 18 , 57 , 68 , 71 ].
To determine the effect of explanatory variables on Commercial Bank deposit mobilization, the following econometric model was developed:
where DM is the Deposit Mobilization, LTD is the Liquidity, CA is the Capital Adequacy, ROA is the Return on Asset, GDP is the GDP growth and INF is the Inflation, PS is the Political Stability, and PG is the Population Growth and i is the i th Banks, t is the time, β 1 to β 7 are the coefficients for each explanatory variables in the model, ε it is the error term.
Result and discussion
Descriptive analysis.
The dependent variable is deposit mobilization measured by the Log of total deposits. According to Table 2 , the average value of log of deposit mobilization is 4.031, equal to 10,739.9 Ethiopian Birr, which is the average deposit mobilized by sampled commercial banks from the public during the study period. The maximum and minimum log of deposits mobilized during the study period were 5.855 (716,143.4 Ethiopian Birr) and 2.42 (263 Ethiopian Birr), respectively, with the standard deviation value of 0.598 in its natural logarithm implying that Commercial Banks in the sample varied in the amount of deposit mobilized during the study period.
Regarding explanatory variables, the average liquidity value was 0.620 with a minimum value of 0.142 and a maximum value of 1.029. A standard deviation of 0.112 indicated the existence of variation in the liquidity level of sampled commercial banks in Ethiopia. Profitability has an average value of 0.025 with a minimum value of − 0.005 and maximum value of 0.052, and a standard deviation of 0.007, which indicates that there are banks that incurred negative returns from their investment in assets during the study period. The average value of capital adequacy is 0.2015 with a minimum value of 0.056 and maximum value of 0.9252, and a standard deviation of 0.1152, which indicates the presence of variation in the capital adequacy of sampled banks. Likewise, the average value of the GDP growth rate is 9.129, with a minimum value of 6.056 and a maximum value of 11.17 during the study period. The average inflation rate value was 14.791, with a minimum value of 6.628 and a maximum of 33.23 during the study period. Population growth has an average value of 2.758 with a minimum value of 2.579 and a maximum value of 2.879, which indicated that the country's average population growth was consistent during the study period. Finally, the average value of political stability is − 1.464 with a minimum value of − 1.679 and a maximum value of − 1.279, which indicates the presence of political instability in the country.
Diagnostic tests
The results of the diagnostic tests performed to validate that the data satisfies the basic assumptions of the classical linear regression model are shown in this section.

Test for multicollinearity
The Variance Inflation Factor was used to test the multicollinearity assumption (VIF). The result shows that a VIF average of 1.80 indicates that there is no multicollinearity (Table 3 ).
Test for heteroskedasticity; var(ut) = σ 2 < ∞
The result of the Breusch-Pagan / Cook-Weisberg test for heteroscedasticity revealed that the variance of residuals is homoscedastic, implying that there is no heteroscedasticity within the model, as the ( p -value = 0.1691) was greater than 0.05 (Table 4 ).
Model Specification test
The Hausman test was used in the study to select the most convenient estimating method (fixed or random effect). The fixed effect regression model is more appropriate for the study than the random effect model, according to the Hausman test, as the ( p -value = 0.0005) is less than 0.05 as of Table 5 .
Fixed effect model results
Table 6 shows the model results for identifying the factors of commercial banks' deposit mobilization in Ethiopia. The model’s variables explained almost 47.5% of the overall variation in deposit mobilization scores, indicating a reasonably good fit. This means that the factors in the model explained almost 47.5% of the overall variation in the bank's deposit mobilization.
According to the model results profitability has a positive and statistically significant impact on bank deposit mobilization, which demonstrated that by keeping other factors constant; an increase in banks profitability by one percent will increase the banks’ deposit mobilization by 7.078. The result is consistent with the earlier expectation that the higher profit is considered a positive flag or soundness of the bank, which could make it easier for banks to attract more deposits [ 25 ] and in line with the findings of Alemu 3 , Tarekegn [ 57 ], Getachew [ 31 ], Osei [ 49 ] and Erna and Ekki [ 24 ] found that bank's profitability has a positive effect on the growth of banks deposit.
The study results show that, bank liquidity measured by loan to deposit ratio has a negative and statistically significant impact on bank deposit mobilization. Keeping all other variables constant, a 1% increase in loan to deposit ratio reduces customer deposit by 0.369. Theoretically, the higher this ratio, the less liquid the bank is, resulting in a decline in client deposits due to the bank’s limited ability to reimburse depositors. The result confirms previous expectations that a high ratio puts the bank at high risk of not repaying deposit money to clients, and that depositors may perceive the bank as poorly managed and less secure to deposit with. The findings are consistent with those of Muluken [ 45 ], Amene [ 4 ], and Awole [ 8 ], who discovered a negative impact of bank liquidity on bank deposits, as opposed to those of Ünvan and Yakubu [ 63 ] and Turhani and Hoda [ 60 ], who found a positive relationship between bank liquidity and deposit.
The capital adequacy ratio has a negative and statistically significant impact on bank deposit mobilization, revealing that a rise in bank capital adequacy by one percent results in a 0.785 decrease in bank deposit mobilization when all other factors remain unchanged. The result is in line with the prior expectation that banks having a higher capital ratio may not necessarily mobilize more deposits, "the crowding out of deposits" [ 33 ], and consistent with the findings of Ünvan and Yakubu [ 63 ], Amene [ 4 ] and Turhani and Hoda [ 60 ] who revealed capital adequacy affects banks deposit negatively as an increase in bank capital adequacy may not necessarily translate into deposit growth. However, the result is against the findings of Tarekegn [ 57 ], who established a positive relationship between capital adequacy and bank deposit.
Regarding the macroeconomic variables inflation has a negative and statistically significant impact on bank deposits. This result is in line with previous expectations that when inflation rate increase, purchasing power of the money would decrease and a huge amount of money would be required to consume or to do a business which leads to a decrease in deposit mobilization. Higher inflation causes savers to save less as a result, deposits are no longer attractive and the impact of inflation on deposits is significantly negative [ 46 ]. The result is in line with the findings of Abiodun et al. [ 1 ], Maturu [ 43 ], Orok et al. [ 48 ], Larbi-Siaw and Lawer [ 40 ], and Ostadi and Sarlak [ 50 ] found a negative impact of inflation on the commercial bank deposits. However, it is against the findings of Thisaranga and Ariyasena [ 59 ], Ukinamemen [ 62 ], and Athukorala & Sen [ 6 ] who revealed positive impact of inflation on saving.
The model result appeared that GDP growth has a negative and statistically significant influence on bank deposit mobilization at a 5% level. The outcome showed that an increase in GDP leads to lower bank deposit mobilization, which was contrary to expectations. The result is supported by the findings of Yakubu and Abokor [ 70 ], Islam et al. [ 38 ], and Bikker and Gerritsen [ 16 ] found a negative effect of GDP on bank deposits. However, it is against the findings of Hassan [ 36 ], Adem [ 2 ], and Mashamba et al. [ 42 ] found that GDP has a positive influence on the volume of commercial bank deposits.
Population growth has a negative and statistically significant impact on bank deposit mobilization, demonstrating that an increase in population leads to a decrease deposit mobilization, contrary to what was previously expected. The result is consistent with the finding of Legass et al. [ 41 ] and Cincotta and Engelman [ 19 ] found a negative impact of population growth on deposit growth as rapid population growth produces large extents of children relative to the labor force which may result in high cost and impede family savings. However, the result is against the findings of Teshome [ 58 ] and Hibret [ 37 ] found a positive relationship between population growth and bank deposit.
At long last, contrary to the prior expectations, political stability has a negative and statistically significant impact on deposit mobilization. The findings demonstrated that political soundness had a detrimental effect on commercial banks' deposit mobilization in Ethiopia. It can be contended that under stable political conditions, investors favor spending their cash on other venture opportunities instead of keeping it in a bank, resulting in a decrease in bank deposit mobilization. The result is against the finding of [ 55 ], who documented that political stability promotes economic growth, thereby increasing profitability and their deposit.
Conclusion and recommendations
The banking sector is one of Ethiopia's fastest-growing industries, and it is critical to the country's economic development. Recognizing the fundamental factors influencing deposits is critical for banks in developing viable deposit mobilization policies and procedures. Based on a test of 14 commercial banks, this study inspected both firm-specific variables and macroeconomic variables affecting deposit mobilization in Ethiopia from 2011 to 2020.
The study's findings show that loan to deposit ratio, capital adequacy, economic growth, inflation, population growth, and political stability all had a negative and statistically significant impact on commercial banks’ deposit mobilization in Ethiopia over the study period. However, a bank's profitability has a positive and statistically significant impact on deposit growth, implying that the higher the profitability, the more deposits are mobilized.
The study provided the following operational and policy suggestions to improve commercial bank deposits based on the findings.
Banks should mobilize more deposits by managing their liquidity because a lack of liquidity can put an end to a bank's efforts to mobilize deposits and, in the worst-case scenario, cause it to collapse. As profitability has a positive and significant effect on deposit mobilization; the management ought to work to improve the bank's profitability by reducing costs and utilizing invested asset efficiently. The country has to ensure its political stability to increase the activities of commercial banks as well as to boost its deposit mobilization effort. Moreover, the government has to educate the citizens about family planning and saving to reduce the negative effect of larger family with poor saving habit on deposit mobilization.
The study is also recommended for further study: As the present study identifies only limited bank-specific and macroeconomic variables due to the data availability, there have to be further researches that include more bank-specific, regulatory, and macroeconomic and governance variables that affect the deposit growth of Ethiopian commercial banks. A study can be also carried out using other deposit measurement ratios such as deposit to total asset and bank deposit growth rate which are not considered in this study.
Availability of data and materials
The data will be made available upon request.
Abbreviations
Consumer price index
- Deposit mobilization
Gross domestic product
Loan to deposit
Not applicable
Return on asset
Variance inflation factor
Abiodun AE, Ogundipe AT, Musa-Agboneni O (2021) Deposit determinants and domestic currency deposits in Nigeria (2000–2018)
Adem SB (2015) Determinants of commercial bank deposits in Ethiopia: a case of commercial bank of Ethiopia. Degree of Master Thesis, Addis Ababa University
Alemu FM (2021) Drivers of deposit mobilization in private commercial banks of Ethiopia. J Invest Manag 10(4):56–61
Google Scholar
Amene DH (2017) Determinants of deposit in Ethiopian private commercial banks. MSc. Addis Ababa University
Anthony O (2012) Bank savings and bank credits in Nigeria: Determinants and impact on economic growth. Int J Econ Financ Issues 2(3):357–372
Athukorala PC, Sen K (2004) The determinants of private saving in India. World Dev 32(3):491–503
Article Google Scholar
Attila J (2022) Does bank deposits volatility react to political instability in developing countries? Finance Res Lett 49:103126
Awole B (2016) Determinants of commercial banks' deposit growth. Addis Ababa University
Ayene GY (2020) Determinants of deposit mobilization in the case of commercial bank of Ethiopia selected branches. Eur J Bus Manag 12(13):39–50
Ayodeji EA, Ajala RB (2019) Capital market performance and sectoral output growth in Nigeria (1984–2016). J Adv Soci Sci Humanit 5(9):1033–1062
Azolibe CB (2019) Macroeconomic dynamics, bank-specific factors, and deposit mobilization of the Nigerian banking sector. Asian J Econ, Busin Account 12(2):1–16
Banson FAK, Sey E, Sakoe J (2012) The Role of Mobile Deposit in Deposit Mobilization in Ghana. Asian J Busin Manag Sci, 1–18
Bello YA (2005) Banking system consolidation in Nigeria and some regional experiences: challenges and prospects
Berger AN, Bouwman CH (2017) Bank liquidity creation, monetary policy, and financial crises. J Financ Stab 30:139–155
Bhalla VK (2006) Financial management and policy-text and cases. Ind J Econ 342:455
Bikker JA, Gerritsen DF (2018) Determinants of interest rates on time deposits and savings accounts: macro factors, bank risk, and account features. Int Rev Financ 18(2):169–216
Bista RB, Basnet P (2022) Measuring determinants of time deposit in the commercial banks in Nepal. ARRUS J Soc Sci Human 2(1):13–25
Boadi EK, Li Y, Lartey VC (2015) Determinants of bank deposits in Ghana: does interest rate liberalization matter? Mod Econ 6(09):990
Cincotta RP, Engelman R (1997) Economics and rapid change: the influence of population growth
Devinaga R (2010) Theoretical framework of profitability as applied to commercial bank in Malaysia, Multimedia University, Faculty of Business and Law, Melaka. Malaysia Eur J Econo, Finance, Administrat Sci
Digaria HA (2011) Deposit mobilization. MAEER s MIT school of management, PUNE, 411038
Distinguin I, Roulet C, Tarazi A (2013) Bank regulatory capital and liquidity: evidence from US and European publicly traded banks. J Bank Finance 37(9):3295–3317
Eriemo NO (2014) Macroeconomic determinants of bank deposits in Nigeria. J Econ Sustain Develop 5(10):357–372
Erna R, Ekki S (2004) Factors affecting Mudaraba deposits in Indonesia. Mudaraba, Indonesia: Evid Iran World Appl Sci J 11(1):653–661
Finger MH, Hesse MH (2009) Lebanon-determinants of commercial bank deposits in a regional financial center. International Monetary Fund
Firdawek T (2019) Determinants of deposit in Ethiopian private commercial banks (Doctoral dissertation, Addis Ababa Science and Technology University).
Fox J, Weisberg S (2002) Robust regression. An R and S-Plus companion to applied regression, 91
Garo G (2015) Determinants of deposit mobilization and related costs of commercial banks in Ethiopia. A research project paper submitted to the department of management college of business and economics
Gebre, T. (2019). Determinants of Private commercial banks’ deposit growth in Ethiopia. Degree of Master Thesis, Addis Ababa University .
Georgiou MN, Kyriazis N, Economou EML (2015) Democracy, political stability, and economic performance. Panel Data Anal 2(1):1–18
Getachew K (2017) Determinants of commercial banks deposit mobilization in Ethiopia (Doctoral dissertation, St. Mary's University)
Gobat J, Kostial MK (2016) Syria’s conflict economy. International Monetary Fund Working Paper 16/123, Washington DC
Gorton G, Winton A (2017) Liquidity provision, bank capital, and the macroeconomy. J Money, Credit, Bank 49(1):5–37
Gunasekara HU, Kumari P (2018) Factors affecting for deposit mobilization in Sri Lanka. Int Rev Manag Mark 8(5):30
Hassan MK, Bashir AHM (2003) Determinants of Islamic banking profitability. In 10th ERF annual conference, Morocco, December (Vol. 7, pp. 2–31)
Hassan OM (2016) Effect of interest rate on commercial bank deposits in Nigeria (2000–2013), May. In Proceeding of the First American Academic Research Conference on Global Business, Economics, Finance and Social Sciences (AAR16 New York Conference)
Hibret B (2015) Determinate of commercial bank" s Deposit Growth in Ethiopia: case study on the commercial bank. MSc, AAU
Islam SN, Ali MJ, Wafik A (2019) Determinants of deposit mobilization of private commercial banks: evidence from Bangladesh. Int J Bus Manag Invent (IJBMI) 8(10):26–33
Iswarya MR (2015) A study on consumer awareness of modern banking Services in THENI (DT). Int J Commer Bus Manag 4:823–831
Larbi-Siaw O, Lawer PA (2015) Determinants of bank deposits in Ghana: a cointegration approach. Asian J Econ Emp Resear 2(1):1–7
Legass HA, Shikur AA, Ahmed OM (2021) Determinants of commercial banks deposit growth evidence from ethiopian commercial banks
Mashamba T, Magweva R, Gumbo LC (2014) Analyzing the relationship between Banks' deposit interest rate and deposit mobilisation: Empirical evidence from Zimbabwean commercial banks (1980–2006)
Maturu B (2021) What ails bank deposit mobilization and credit creation in Kenya? (No. 54). KBA Centre for Research on Financial Markets and Policy Working Paper Series
Moh’d Al-Tamimi KA, Obeidat SF (2013) Determinants of capital adequacy in commercial banks of Jordan an empirical study. Dirassat J Econ Issue 4(2):267–280
Muluken D (2017) Determinants of deposit mobilization in private commercial banks of Ethiopia (Doctoral dissertation, St. Mary's University)
Namazi M, Salehi M (2010) The role of inflation in financial repression: evidence of Iran. World Appl Sci J 11(6):653–661
Neumayer E, Plümper T (2017) Robustness tests for quantitative research. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Book Google Scholar
Orok AB, Okoi IO, Essien A (2018) Inflation and deposit mobilization in deposit money banks: the Nigerian perspective. Int J Publ Administr Manag Resear 4(4):109–121
Osei LK (2016) Determinants of rural banks deposit mobilization in Ghana (Doctoral dissertation, Doctoral dissertation)
Ostadi H, Sarlak A (2014) Effective factors on the absorption of bank deposits to increase the relative share of Isfahan Sepah Bank. Int J Acad Res Econ Manag Sci 3(4):139–149
Rao ND (1975) Deposit mobilisation by co-operative banks: a comparison with scheduled commercial banks. Economic and Political Weekly, 1098–1100
Rother MB, Pierre MG, Lombardo D, Herrala R, Toffano MP, Roos ME, Manasseh MK (2016) The economic impact of conflicts and the refugee crisis in the Middle East and North Africa. International Monetary Fund
Salami GO, Oluseyi AA (2013) Impact of financial sector development on the Nigerian economic growth. Am J Bus Manag 2(4):347–356
Selvaraj N, Balaji Kumar P (2015) A study on the deposit mobilization pattern of the Dindigul district central co-operative bank limited. J Tourism Hospit 4(138):2167–269
Shabbir G, Anwar M, Adil S (2016) Corruption, political stability and economic growth. Pakistan Devel Rev, https://doi.org/10.30541/v55i4I-IIpp.689-702
Stanford J (2008) A "How-To" Guide: Finding and Interpreting GDP Statistics. Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives
Tarekegn G (2018) Determinants of deposit mobilization in Ethiopian commercial banks. Horn Afr J Bus Econ (HAJBE) 1(1):67–76
Teshome F (2017) Determinants of commercial banks deposit in Ethiopia. Degree of Master Thesis, Addis Ababa University.
Thisaranga KDIU, Ariyasena DLMNK (2021) Effect of camel model on bank performance: with special reference to listed commercial banks in Sri Lanka
Turhani A, Hoda H (2016) The determinative factors of deposits behavior in banking system in Albania (Jan 2005–Dec 2014). Acad J Interd Stud 5(2):246–246
Tuyishime R, Memba F, Mbera Z (2015) The effects of deposits mobilization on financial performance in commercial banks in Rwanda. A case of equity bank Rwanda limited. Int J Small Bus Entrepr Res 3(6):44–71
Ukinamemen AA (2010) The determinants of commercial bank deposits in Nigeria 1989–2007: A Study of Union Bank of Nigeria Plc. NnamdiAzikiwe University
Ünvan YA, Yakubu IN (2020) Do bank-specific factors drive bank deposits in Ghana? J Comput Appl Math 376:112827
Usman OA, Adejare AT (2013) Inflation and capital market performance: the Nigerian outlook. J Emerg Trends Econ Manag Sci 5(1):93–99
Varman M (2005) Impact of self-help groups on formal banking habits. Economic and political weekly, 1705–1713
Viswanadham P, Yirgalem T, Medanit B (2015) The effect of location and information technology on banks deposit mobilization status in Ethiopia: empirical evidence on private commercial banks in Adama Town. International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), 6–14
Vodova PK (2016) Bank liquidity and profitability in the Polish banking sector. Sci J Bielsko-Biala Sch Financ Law 20(1):19–33.
Voon-Choong Y, Hway-Boom O, Kok-Thim C, Yueh-Sin A (2010) Factors affecting banks’ risk exposure: evidence from Malaysia. Eur J Econ Finance Adm Sci 19:121–122
Wubitu E (2012) Factors determining commercial bank deposit: an empirical study on commercial bank of Ethiopia. MSc project paper: Addis Ababa University
Yakubu IN, Abokor AH (2020) Factors determining bank deposit growth in Turkey: an empirical analysis. Rajagiri Manag J. https://doi.org/10.1108/RAMJ-05-2020-0017
Yitayaw MK (2021) Firm-specific and macroeconomic determinants of commercial banks liquidity in Ethiopia: Panel data approach. Cog Bus Manag 8(1):1956065
Download references
Acknowledgments
We declare that there is no fund received in publishing this paper.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Accounting and Finance, College of Business & Economics, Haramaya University, P.O. Box: 138, Dire Dawa, Ethiopia
Nesru Kasim Banke & Mekonnen Kumlachew Yitayaw
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
MK compiled, summarized, and analyzed the data. MK and NK both made contributions to the research hypothesis and design. NK drafted the manuscript and finally reviewed the content. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nesru Kasim Banke .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate..
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
We declare that there is no conflict of interest in publishing this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations'' (in PDF at the end of the article below the references; in XML as a back matter article note).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Banke, N.K., Yitayaw, M.K. Deposit mobilization and its determinants: evidence from commercial banks in Ethiopia. Futur Bus J 8 , 32 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-022-00144-6
Download citation
Received : 17 June 2022
Accepted : 15 August 2022
Published : 05 September 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-022-00144-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bank-specific
- Commercial bank
- Determinants
- Macroeconomic

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The least is commercial bank of Ethiopia with 3.58. The elements The elements of CAMEL is earning quality that measu res the ability of the financial institutions to generate returns on the asset
This research examines the impact of digitization on commercial bank profitability in Ethiopia, using return on equity as a proxy for profitability. The study selected nine commercial banks operating in Ethiopia between 2018 and 2021 using secondary data and a purposive sampling technique.
IN COMMERCIAL BANKS OF ETHIOPIA: THE CASE OF COMMERCIAL BANK OF ETHIOPIA (CBE) By BIRUK TESFAYE KEBEDE SGS/0467/2009A A Thesis Submitted to St. Mary's University, School of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Business Administration (General MBA Concentration) June, 2018 Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
The Bank of Ethiopia provided central and commercial banking services to the country (Mauri, 2010). The Italian invasion in 1935 brought the demise of one of the earliest initiatives in African banking. During the Italian occupation, Italian banks were active in Ethiopia. In 1963, the Ethiopian government split the State Bank of Ethiopia (est ...
NBE confirmed that mobile banking service is stared in late 2013 by Zemen Bank S.C and followed by Commercial Bank of Ethiopia in 2014. Therefore, this study attempts to see the practices of mobile banking services, and identify the challenges and opportunities of the adoption of mobile banking in Ethiopia.
This research project focuses on identifying the impacts of core banking and service quality on customer satisfaction in commercial bank of Ethiopia Bishoftu branch. The main objective of this project is to assess the impact of core banking and services quality on customer satisfaction in commercial bank of Ethiopia.
A commercial bank is a type of financial intermediary and a type of bank. Commercial banking is also known as business banking. It is a bank that provides checking accounts, savings accounts, and money market accounts and that accepts time deposits. Commercial banks play a vital role in the economy for two reasons: they provide a major source
A cross-sectional research design was used to investigate the relationship and impacts of the variables. A sample was drawn from managers and senior staff, who engage in planning and monitoring activities. ... Otherwise, as the annual report of the Commercial Bank of Ethiopia disclosed the typical reasons for an inefficient organization and the ...
Commercial Bank of Ethiopia has more than 1,200 branches in Ethiopia and CBE-BIRR is taking advantage of this huge number of networked branches to recruit new agents and customers. Currently commercial bank of Ethiopia had 3,211 CBE-BIRR agents, 589,071 CBE-BIRR customers and mobilized 2.5 million birr (CBE annual report, June 2018).
ASSESSMENT OF CREDIT ANALYSIS AND PROCESSING (In case of Commercial Bank Of Ethiopia Bishoftu Branch) An Research proposal submitted to the school of graduate studies of Rift Valley University in partial fulfillment of the requirement for BA Degree in Accounting RIFT VALLEY UNIVERSITY - BISHOFTU CAMPUS Department of Accounting NAME HANA GUTA ...
Bank of Ethiopia took over the commercial activities of the Bank of Abysinia and was authorized to issue notes and coins. (www.nbe.gov.et) The Ethiopian Monetary and Banking law that came into force in 1963 separated the function of commercial and central banking creating National Bank of Ethiopia and give birth to commercial Bank of Ethiopia.
Deposit mobilization is the most important service and an integral part of banking operations. In Ethiopia, mobilizing savings through intense deposit collection has been regarded as the major task of banking. However, managing deposits is impossible without understanding and controlling the factors that influence them. Thus, this study examined the bank-specific and macroeconomic determinants ...
The purpose of the study would be seek to conduct the internal auditing practice of commercial bank of Ethiopia Toba branch. The general objective of this study was assessing internal auditing practice of commercial bank Ethiopia of Toba branch. In order to achieve the stated objective the researcher use qualitative and qualitative method.
and entitled as "Analysis of credit risk management systems and practice in commercial banks of Ethiopia: A case study of Commercial Bank of Ethiopia, HQ" The first chapter covered the background to the study, thus a general introduction, statement of the problem, research questions and objectives of the study. It also entails
This study tried to assess the lending practice of commercial bank of Ethiopia in case of main branch. 1.3. Statement of the Problem Loans are the most important asset held banks, lending provides the bulk of bank income. It is equally true that bank loans, as they are profitable, equally risky. Bank loans fluctuate and
The specific objectives are: 1. To assess if there is an impact relationship between Loan to total asset and loan loss provisions with the performance of commercial Banks. 2. To assess if there is an impact relationship between credit administration (cost per loan) and the performance of commercial Banks. 3.
commercial bank of Ethiopia played on economic growth for a period of 32 years from1981-2012. The researcher used different statistical and ... 5% and 10% significance level mostly in this research 5% significant level is used. The multiple linear regressions model for REALGDP PRO ASS DEPO INVES RANDC and LADV shown on ...
Commercial Bank of Ethiopia/CBE/, Wolaita Sodo Branch BIRHANU ALEMU GEBRE Lecturer of Accounting and Finance in Wolaita Sodo University ... Research Journal of Finance and Accounting www.iiste.org ISSN 2222-1697 (Paper) ISSN 2222-2847 (Online) DOI: 10.7176/RJFA Vol.10, No.3, 2019 78 properly manage the their loan. Absence of proper loans ...
Semantic Scholar extracted view of "ASSESSMENT OF CREDIT RISK MANAGEMENT PRACTICE IN COMMERCIAL BANK OF ETHIOPIA (CBE'S)." by Gebrewahd Tesfay. ... Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature, based at the Allen Institute for AI. Learn More. About