

Federalists and Anti-Federalists
The Federalist and Anti-Federalist factions developed during the Constitutional Convention of 1787.

Alexander Hamilton was a prominent leader of the Federalist faction. Image Source: Wikipedia.
Federalists and Anti-Federalists Summary
The Federalists and Anti-Federalists were two factions that emerged in American politics during the Philadelphia Convention of 1787 . The original purpose of the Convention was to discuss problems with the government under the Articles of Confederation and find reasonable solutions. Instead of updating the Articles, the delegates replaced the Articles with something entirely new — the Constitution of the United States. Despite the development of the Constitution, there was disagreement. The people who favored the Constitution became known as Federalists. Those who disagreed, or even opposed it, were called Anti-Federalists. Anti-Federalists argued the Constitution failed to provide details regarding basic civil rights — a Bill of Rights — while Federalists argued the Constitution provided significant protection for individual rights. After the Constitution was adopted by the Convention, it was sent to the individual states for ratification. The ensuing debate between the Federalists and Anti-Federalists that followed remains of the great debates in American history, and eventually led to the ratification of the United States Constitution.

Quick Facts About Federalists
- The name “Federalists” was adopted by people who supported the ratification of the new United States Constitution.
- Federalists favored a strong central government and believed the Constitution provided adequate protection for individual rights.
- The group was primarily made up of large property owners, merchants, and businessmen, along with the clergy, and others who favored consistent law and order throughout the states.
- Prominent Federalists were James Madison , Alexander Hamilton , and John Jay .
- During the debate on the Constitution, the Federalists published a series of articles known as the “Federalists Papers” that argued for the passage of the Constitution.
- The Federalists eventually formed the Federalist Party in 1791 .
Quick Facts About Anti-Federalists
- Anti-Federalists had concerns about a central government that had too much power.
- They favored the system of government under the Articles of Confederation but were adamant the Constitution needed a defined Bill of Rights.
- The Anti-Federalists were typically small farmers, landowners, independent shopkeepers, and laborers.
- Prominent Anti-Federalists were Patrick Henry , Melancton Smith, Robert Yates, George Clinton , Samuel Bryan, and Richard Henry Lee .
- The Anti-Federalists delivered speeches and wrote pamphlets that explained their positions on the Constitution. The pamphlets are collectively known as the “Anti-Federalist Papers.”
- The Anti-Federalists formed the Democratic-Republican Party in 1792 .
Significance of Federalists and Anti-Federalists
The Federalists and Anti-Federalists are important to the history of the United States because their differences over the United States Constitution led to its ratification and the adoption of the Bill of Rights — the first 10 Amendments .
Learn More About Federalists and Anti-Federalists on American History Central
- Federalist No. 1
- Federalist No. 2
- Federalist No. 3
- Alexander Hamilton’s Speech to the New York Convention
- Articles of Confederation
- Presidency of George Washington — Study Guide
- Written by Randal Rust
Home — Essay Samples — Government & Politics — Political Participation — Anti Federalists vs. Federalists
Anti Federalists Vs. Federalists
- Categories: Political Participation
About this sample

Words: 1554 |
Published: Jul 17, 2018
Words: 1554 | Pages: 3 | 8 min read
The essay analyzes the ideological and historical conflict between the Federalists and Anti-Federalists in the early years of the United States. This division emerged in the aftermath of the Revolutionary War when the country faced economic challenges due to the war's cost and resulting debt. Anti-Federalists, primarily from rural areas, opposed the development of a strong federal government and instead advocated for power to remain with state and local governments. On the other hand, Federalists, often wealthy individuals from larger urban areas, supported a stronger national government and the ratification of the Constitution as a means to manage post-Revolution debt and tensions effectively.
The essay draws parallels between this historical division and contemporary political divides, such as Democrats vs. Republicans, highlighting how differing socioeconomic groups tended to align with one side or the other. It emphasizes the economic and political context of the time, where the Articles of Confederation proved insufficient in governing the young nation.
The essay also discusses the role of key figures like Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson, as well as the debates surrounding the ratification of the Constitution, leading to the inclusion of the Bill of Rights. It highlights the Federalists' belief in the necessity of a strong national government while preserving state sovereignty.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Government & Politics

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 721 words
2 pages / 928 words
2 pages / 780 words
2 pages / 939 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Democracy is a system of government in which power is vested in the people, who rule either directly or through freely elected representatives. Direct democracy and representative democracy are two forms of democracy [...]
Political socialization is the ‘procedure by which people learn and habitually disguise a political focal point confining their view of how power is masterminded and how their general surroundings is and ought to be composed; [...]
"Strawberry and Chocolate wants to signify how political and social ideas can be changed through compassion and acceptance, and as Shields (2004, p.242) argues, “through a postmodern process of image making”. As we see the [...]
I’d be lying if I said my parents didn’t influence my political ideology. I believe any young man or woman our age would be lying if they said that their parents didn’t have any sort of influence on their political ideologies. [...]
This essay will discuss globalization which is a process that refers to international integration among countries, economies, regions, and individuals in order to create a global network. Examples of globalization which occur in [...]
Countries spend millions of dollars both trying to boost and, also to monitor their favorability in the international politics. This essay will compare and contrast political participation and political communication in the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
MA in American History : Apply now and enroll in graduate courses with top historians this summer!
- AP US History Study Guide
- History U: Courses for High School Students
- History School: Summer Enrichment
- Lesson Plans
- Classroom Resources
- Spotlights on Primary Sources
- Professional Development (Academic Year)
- Professional Development (Summer)
- Book Breaks
- Inside the Vault
- Self-Paced Courses
- Browse All Resources
- Search by Issue
- Search by Essay
- Become a Member (Free)
- Monthly Offer (Free for Members)
- Program Information
- Scholarships and Financial Aid
- Applying and Enrolling
- Eligibility (In-Person)
- EduHam Online
- Hamilton Cast Read Alongs
- Official Website
- Press Coverage
- Veterans Legacy Program
- The Declaration at 250
- Black Lives in the Founding Era
- Celebrating American Historical Holidays
- Browse All Programs
- Donate Items to the Collection
- Search Our Catalog
- Research Guides
- Rights and Reproductions
- See Our Documents on Display
- Bring an Exhibition to Your Organization
- Interactive Exhibitions Online
- About the Transcription Program
- Civil War Letters
- Founding Era Newspapers
- College Fellowships in American History
- Scholarly Fellowship Program
- Richard Gilder History Prize
- David McCullough Essay Prize
- Affiliate School Scholarships
- Nominate a Teacher
- Eligibility
- State Winners
- National Winners
- Gilder Lehrman Lincoln Prize
- Gilder Lehrman Military History Prize
- George Washington Prize
- Frederick Douglass Book Prize
- Our Mission and History
- Annual Report
- Contact Information
- Student Advisory Council
- Teacher Advisory Council
- Board of Trustees
- Remembering Richard Gilder
- President's Council
- Scholarly Advisory Board
- Internships
- Our Partners
- Press Releases
History Resources

The United States Constitution: Federalists v. Anti-Federalists
By tim bailey, unit objective.
This unit is part of Gilder Lehrman’s series of Common Core State Standards–based teaching resources. These units were developed to enable students to understand, summarize, and analyze original texts of historical significance. Through a step-by-step process, students will acquire the skills to analyze any primary or secondary source material.
Today students will participate as members of a critical thinking group and "read like a detective" in order to analyze the arguments made by the Federalists in favor of ratifying the new US Constitution.
Introduction
Tell the students that after the Constitutional Convention of 1787 in Philadelphia, the nation’s new Constitution had to be ratified by the states. The debate over ratification became very heated, especially in New York. This led to a spirited exchange of short essays between the Federalists, who promoted the new Constitution, and the Anti-Federalists, who put forward a variety of objections to the proposed new government. Today we will be closely reading excerpts from four of the Federalist Papers in order to discover what the Federalists’ positions and arguments were. Although the Federalist Papers were written anonymously under the pen name "Publius," historians generally agree that the essays were written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay.
- Federalist Papers #1, #10, #51, and #84 (excerpts) . Source: The full text of all the Federalist Papers are available online at the Library of Congress.
- US Constitution, 1787 . Source: Charters of Freedom , National Archives and Records Administration, www.archives.gov/exhibits/charters
- Overhead projector or other display
The students will encounter vocabulary that they do not know. There are words in eighteenth-century essays that many adults do not know the meaning of either. It would be overwhelming to give the definition for every unknown word as well as self-defeating when we are trying to get the students to be more independent learners. One benefit of having the students work in groups is that they can reason out the meanings of words in context together. If the students are truly stuck on a word that is critical to the passage, you can open up a class discussion. As a last resort, you can provide the meaning.
First, a caution: do not reveal too much to the students about the arguments presented by either the Federalists or Anti-Federalists. The point is to let the students discover them through careful reading of the text and discussion with their classmates. They will then construct their own arguments based on the text. Depending on the length of the class period or other factors, this lesson may carry over into tomorrow as well.
- Divide the class into groups of three to five students. These will be the "critical thinking groups" for the next several days.
- Discuss the information in the introduction. The students need to at least be familiar with the failure of the Articles of Confederation, the Constitutional Convention, and the writing of the US Constitution.
- Hand out the four excerpts from Federalist Papers #1, #10, #51, and #84. If possible have a copy up on a document projector so that everyone can see it and you can refer to it easily.
- "Share read" the Federalist Papers with the students. This is done by having the students follow along silently while the teacher begins reading aloud. The teacher models prosody, inflection, and punctuation. The teacher then asks the class to join in with the reading after a few sentences while the teacher continues to read along with the students, still serving as the model for the class. This technique will support struggling readers as well as English language learners (ELL).
- Answers will vary, but in the end the students should conclude that groups interested in "the rights of the people" more often end up as "tyrants."
- Answers will vary, but in the end the students should conclude that the "effects" include "a division of society," and the remedy is the formation of "a republic."
- Answers will vary, but in the end the students should conclude that "such devices [separation of powers] should be necessary to control the abuses of government" and "you must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to control itself."
- Answers will vary, but in the end they should conclude that "the Constitution is itself, in every rational sense, and to every useful purpose, A BILL OF RIGHTS . . ."
- Wrap-up: Discuss final conclusions and clarify points of confusion. We want students to be challenged, not overwhelmed.
Today students will participate as members of a critical thinking group and "read like a detective" in order to analyze the arguments made by the Anti-Federalists in opposition to ratifying the new US Constitution.
Review the background information from the last lesson. Today we will be closely reading excerpts from four of the Anti-Federalist Papers in order to discover just what the Anti-Federalists’ positions and arguments were. Although the Anti-Federalists’ essays were written anonymously under various pen names, most famously "Brutus," historians generally agree that among the authors of the Anti-Federalist essays were Robert Yates, Samuel Bryan, George Clinton, and Richard Henry Lee.
- Anti-Federalist Papers #1, #9, #46, and #84 (excerpts) . Source: Morton Borden, ed. The Antifederalist Papers (East Lansing: Michigan State University Press, 1965). Unlike the Federalist Papers, the essays by Anti-Federalists were not conceived of as a unified series. Thus historians have imposed different numbering systems as they compiled various essays; the numbers used here are Morton Borden’s chronology.
- US Constitution, 1787
- Overhead projector or other display method
As in the previous lesson, encourage students to reason out the meanings of words they do not know. If the students are truly stuck on a word that is critical to the passage, you can open up a class discussion. As a last resort, you can provide the meaning.
- Students should sit with their critical thinking groups from the last lesson.
- Discuss the information in the introduction.
- Hand out the four excerpts from Anti-Federalist Papers #1, #9, #46, and #84. If possible have a copy up on a document projector so that everyone can see it and you can refer to it easily.
- "Share read" the Anti-Federalist Papers with the students.
- Answers will vary, but in the end the students should conclude that the "Aristocracy" and "Lawyers" are out to deceive "The People" in order to "satiate their voracious stomachs with the golden bait."
- Answers will vary, but in the end the students should conclude that this Anti-Federalist Paper is a satire and that the evidence includes statements such as "totally incapable of thinking or acting" and "have power over little else than yoking hogs."
- Answers will vary, but in the end the students should conclude that "the Congress are therefore vested with the supreme legislative powers" and "undefined, unbounded and immense power."
- Answers will vary but in the end they should conclude that "but rulers have the same propensities as other men, they are likely to use the power with which they are vested, for private purposes" and "grand security to the rights of the people is not to be found in this Constitution."
The students will deeply understand the major arguments concerning the ratification of the US Constitution. This understanding will be built upon close analysis of the Federalist Papers and Anti-Federalist Papers. The students will demonstrate their understanding in both writing and speaking.
Tell the students that now they get to apply their knowledge and understanding of the Federalist and Anti-Federalist arguments. They will need to select a debate moderator from within their group and divide the remaining students into Federalists and Anti-Federalists. As a group they will write questions based on the issues presented in the primary documents. They will also script responses from both sides based solely on what is written in the documents. This is not an actual debate but rather a scripted presentation for the sake of making arguments that the authors of these documents would have made in a debate format. In the next lesson the groups will present their debates for the class.
- Federalist Papers #1, #10, #51, and #84 (excerpts)
- Anti-Federalist Papers #1, #9, #46, and #84 (excerpts)
Students will be sitting with the same critical thinking group as in the previous two lessons. All of the students should have copies of the excerpts from the Federalist Papers and the Anti-Federalist Papers as well as the United States Constitution as reference materials.
- Tell the students that they need to choose one person to be a debate moderator and then divide the rest of the group into Federalists and Anti-Federalists.
- Inform the students that they will be writing a script for a debate based on the issues raised in the primary documents that you have been studying. This script is to be written as a team effort, and everyone in the group will have a copy of the final script.
- The teacher will provide three questions that all groups must address during the debate. However, the students should add another two to four questions that can be answered directly from the primary source material.
- It is important that the students portraying both the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists use the actual text from the documents to make their arguments.
- What is your position on a bill of rights being added to the Constitution?
- How would you address concerns about the "powers of government" under this new Constitution?
- Can you explain why this Constitution is or is not in the best interests of our nation as a whole?
- Students can then construct their own questions to be directed to either side with the opportunity for rebuttal from the other side.
- Remind the students again that everyone needs to work on the script and the responses must be taken directly from the text of the documents introduced in class.
- Wrap-up: If students have time, let them rehearse their presentations for the next lesson.
The students will demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of the Federalist and Anti-Federalist arguments. This is not an actual debate but a scripted presentation making arguments that the authors of these documents would have made in a debate format.
Students will be sitting with the same critical thinking groups as in the previous three lessons. All of the students should have copies of the excerpts from the Federalist Papers and the Anti-Federalist Papers as well as the United States Constitution as reference materials.
- Tell the students that they will be presenting the debates between the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists that they scripted in the last lesson.
- The Moderator should begin the debate by introducing both sides and setting out the protocol for the "debate." (Actually watching a clip of a debate might be helpful as well.)
- In evaluating the student work you should measure the following: Did the students effectively address all three mandatory questions using text-based evidence? Did the additional questions developed by the students address pertinent issues? Were all of the students in a group involved in the process?
- Wrap-up: As time allows, have students debrief the last four lessons and what they learned.
- OPTIONAL: If you believe that you need to evaluate more individualized understanding of the issues presented over the past four lessons you can have students write a short essay addressing the three mandatory questions that they were given as a group.
Stay up to date, and subscribe to our quarterly newsletter.
Learn how the Institute impacts history education through our work guiding teachers, energizing students, and supporting research.
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Federalist Papers
By: History.com Editors
Updated: June 22, 2023 | Original: November 9, 2009

The Federalist Papers are a collection of essays written in the 1780s in support of the proposed U.S. Constitution and the strong federal government it advocated. In October 1787, the first in a series of 85 essays arguing for ratification of the Constitution appeared in the Independent Journal , under the pseudonym “Publius.” Addressed to “The People of the State of New York,” the essays were actually written by the statesmen Alexander Hamilton , James Madison and John Jay . They would be published serially from 1787-88 in several New York newspapers. The first 77 essays, including Madison’s famous Federalist 10 and Federalist 51 , appeared in book form in 1788. Titled The Federalist , it has been hailed as one of the most important political documents in U.S. history.
Articles of Confederation
As the first written constitution of the newly independent United States, the Articles of Confederation nominally granted Congress the power to conduct foreign policy, maintain armed forces and coin money.
But in practice, this centralized government body had little authority over the individual states, including no power to levy taxes or regulate commerce, which hampered the new nation’s ability to pay its outstanding debts from the Revolutionary War .
In May 1787, 55 delegates gathered in Philadelphia to address the deficiencies of the Articles of Confederation and the problems that had arisen from this weakened central government.
A New Constitution
The document that emerged from the Constitutional Convention went far beyond amending the Articles, however. Instead, it established an entirely new system, including a robust central government divided into legislative , executive and judicial branches.
As soon as 39 delegates signed the proposed Constitution in September 1787, the document went to the states for ratification, igniting a furious debate between “Federalists,” who favored ratification of the Constitution as written, and “Antifederalists,” who opposed the Constitution and resisted giving stronger powers to the national government.
The Rise of Publius
In New York, opposition to the Constitution was particularly strong, and ratification was seen as particularly important. Immediately after the document was adopted, Antifederalists began publishing articles in the press criticizing it.
They argued that the document gave Congress excessive powers and that it could lead to the American people losing the hard-won liberties they had fought for and won in the Revolution.
In response to such critiques, the New York lawyer and statesman Alexander Hamilton, who had served as a delegate to the Constitutional Convention, decided to write a comprehensive series of essays defending the Constitution, and promoting its ratification.
Who Wrote the Federalist Papers?
As a collaborator, Hamilton recruited his fellow New Yorker John Jay, who had helped negotiate the treaty ending the war with Britain and served as secretary of foreign affairs under the Articles of Confederation. The two later enlisted the help of James Madison, another delegate to the Constitutional Convention who was in New York at the time serving in the Confederation Congress.
To avoid opening himself and Madison to charges of betraying the Convention’s confidentiality, Hamilton chose the pen name “Publius,” after a general who had helped found the Roman Republic. He wrote the first essay, which appeared in the Independent Journal, on October 27, 1787.
In it, Hamilton argued that the debate facing the nation was not only over ratification of the proposed Constitution, but over the question of “whether societies of men are really capable or not of establishing good government from reflection and choice, or whether they are forever destined to depend for their political constitutions on accident and force.”
After writing the next four essays on the failures of the Articles of Confederation in the realm of foreign affairs, Jay had to drop out of the project due to an attack of rheumatism; he would write only one more essay in the series. Madison wrote a total of 29 essays, while Hamilton wrote a staggering 51.

Federalist Papers Summary
In the Federalist Papers, Hamilton, Jay and Madison argued that the decentralization of power that existed under the Articles of Confederation prevented the new nation from becoming strong enough to compete on the world stage or to quell internal insurrections such as Shays’s Rebellion .
In addition to laying out the many ways in which they believed the Articles of Confederation didn’t work, Hamilton, Jay and Madison used the Federalist essays to explain key provisions of the proposed Constitution, as well as the nature of the republican form of government.
'Federalist 10'
In Federalist 10 , which became the most influential of all the essays, Madison argued against the French political philosopher Montesquieu ’s assertion that true democracy—including Montesquieu’s concept of the separation of powers—was feasible only for small states.
A larger republic, Madison suggested, could more easily balance the competing interests of the different factions or groups (or political parties ) within it. “Extend the sphere, and you take in a greater variety of parties and interests,” he wrote. “[Y]ou make it less probable that a majority of the whole will have a common motive to invade the rights of other citizens[.]”
After emphasizing the central government’s weakness in law enforcement under the Articles of Confederation in Federalist 21-22 , Hamilton dove into a comprehensive defense of the proposed Constitution in the next 14 essays, devoting seven of them to the importance of the government’s power of taxation.
Madison followed with 20 essays devoted to the structure of the new government, including the need for checks and balances between the different powers.
'Federalist 51'
“If men were angels, no government would be necessary,” Madison wrote memorably in Federalist 51 . “If angels were to govern men, neither external nor internal controls on government would be necessary.”
After Jay contributed one more essay on the powers of the Senate , Hamilton concluded the Federalist essays with 21 installments exploring the powers held by the three branches of government—legislative, executive and judiciary.
Impact of the Federalist Papers
Despite their outsized influence in the years to come, and their importance today as touchstones for understanding the Constitution and the founding principles of the U.S. government, the essays published as The Federalist in 1788 saw limited circulation outside of New York at the time they were written. They also fell short of convincing many New York voters, who sent far more Antifederalists than Federalists to the state ratification convention.
Still, in July 1788, a slim majority of New York delegates voted in favor of the Constitution, on the condition that amendments would be added securing certain additional rights. Though Hamilton had opposed this (writing in Federalist 84 that such a bill was unnecessary and could even be harmful) Madison himself would draft the Bill of Rights in 1789, while serving as a representative in the nation’s first Congress.

HISTORY Vault: The American Revolution
Stream American Revolution documentaries and your favorite HISTORY series, commercial-free.
Ron Chernow, Hamilton (Penguin, 2004). Pauline Maier, Ratification: The People Debate the Constitution, 1787-1788 (Simon & Schuster, 2010). “If Men Were Angels: Teaching the Constitution with the Federalist Papers.” Constitutional Rights Foundation . Dan T. Coenen, “Fifteen Curious Facts About the Federalist Papers.” University of Georgia School of Law , April 1, 2007.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Anti-Federalist vs. Federalist

In U.S. history, anti-federalists were those who opposed the development of a strong federal government and the ratification of the Constitution in 1788, preferring instead for power to remain in the hands of state and local governments. Federalists wanted a stronger national government and the ratification of the Constitution to help properly manage the debt and tensions following the American Revolution . Formed by Alexander Hamilton , the Federalist Party, which existed from 1792 to 1824, was the culmination of American federalism and the first political party in the United States. John Adams, the second president of the United States, was the first and only Federalist president.
Comparison chart
Anti-federalist vs. federalist debate.
The American Revolution was a costly war and left the colonies in an economic depression . The debt and remaining tensions—perhaps best summarized by a conflict in Massachusetts known as Shays' Rebellion —led some founding political members in the U.S. to desire for more concentrated federal power. The thought was that this concentrated power would allow for standardized fiscal and monetary policy and for more consistent conflict management.
However, a more nationalistic identity was the antithesis of some founding political members' ideals for the developing states. A more centralized American power seemed reminiscent of the monarchical power of the English crown that had so recently and controversially been defeated. The potential consequences of centralized fiscal and monetary policy were especially frightening for some, reminding them of burdensome and unfair taxation. Anti-federalists were closely tied to rural landowners and farmers who were conservative and staunchly independent.
The most important parts of this debate were decided in the 1700s and 1800s in U.S. history, and the Federalist Party dissolved centuries ago, but the battles between federalist and anti-federalist ideologies continue into the present day in left and right wing American politics . To better understand the history behind this ongoing ideological debate, watch the following video from author John Green's U.S. history Crash Course series.
Articles of Confederation
Prior to the Constitution, there was the Articles of Confederation, a 13-articled agreement between the 13 founding states that covered issues of state sovereignty, (theoretical) equal treatment of citizenry, congressional development and delegation, international diplomacy, armed forces, fund raising, supermajority lawmaking, the U.S.-Canadian relationship, and war debt.
The Articles of Confederation was a very weak agreement on which to base a nation—so weak, in fact, that the document never once refers to the United States of America as being part of a national government, but rather "a firm league of friendship" between states. This is where the concept of the "United States"—i.e., a group of roughly and ideologically united, individually ruling bodies—comes from in the naming of the country. The Articles of Confederation took years for the 13 states to ratify, with Virginia being the first to do so in 1777 and Maryland being the last in 1781.
With the Articles of Confederation, Congress became the only form of federal government, but it was crippled by the fact that it could not fund any of the resolutions it passed. While it could print money, there was no solid regulation of this money, which led to swift and deep depreciation . When Congress agreed to a certain rule, it was primarily up to the states to individually agree to fund it, something they were not required to do. Though Congress asked for millions of dollars in the 1780s, they received less than 1.5 million over the course of three years, from 1781 to 1784.
This inefficient and ineffective governance led to economic woes and eventual, if small scale, rebellion. As George Washington 's chief of staff, Alexander Hamilton saw firsthand the problems caused by a weak federal government, particularly those which stemmed from a lack of centralized fiscal and monetary policies. With Washington's approval, Hamilton assembled a group of nationalists at the 1786 Annapolis Convention (also known as the "Meeting of Commissioners to Remedy Defects of the Federal Government"). Here, delegates from several states wrote a report on the conditions of the federal government and how it needed to be expanded if it was to survive its domestic turmoil and international threats as a sovereign nation.
Constitution
In 1788, the Constitution replaced the Articles of Confederation, greatly expanding the powers of the federal government. With its current 27 amendments, the U.S. Constitution remains the supreme law of the United States of America, allowing it to define, protect, and tax its citizenry. Its development and relatively quick ratification was perhaps just as much the result of widespread dissatisfaction with a weak federal government as it was support for the constitutional document.
Federalists, those who identified with federalism as part of a movement, were the main supporters of the Constitution. They were aided by a federalist sentiment that had gained traction across many factions, uniting political figures. This does not mean there was no heated debate over the Constitution's drafting, however. The most zealous anti-federalists, loosely headed by Thomas Jefferson, fought against the Constitution's ratification, particularly those amendments which gave the federal government fiscal and monetary powers.
A sort of ideological war raged between the two factions, resulting in the Federalist Papers and the Anti-Federalist Papers , a series of essays written by various figures—some anonymously, some not—for and against the ratification of the U.S. Constitution.
Ultimately, anti-federalists greatly influenced the document, pushing for strict checks and balances and certain limited political terms that would keep any one branch of the federal government from holding too much power for too long. The Bill of Rights , the term used for the first 10 amendments of the Constitution, are especially about personal, individual rights and freedoms; these were included partly to satisfy anti-federalists.
Prominent Anti-Federalists and Federalists
Among anti-federalists, some of the most prominent figures were Thomas Jefferson and James Monroe . Jefferson was often considered a leader among the anti-federalists. Other prominent anti-federalists included Samuel Adams , Patrick Henry , and Richard Henry Lee .
Alexander Hamilton, a former chief of staff to George Washington, was a proponent of a strong federal government and founded the Federalist Party. He helped oversee the development of a national bank and a taxation system. Other prominent federalists of the time included John Jay and John Adams .
Other figures, such as James Madison , greatly supported Hamilton's federalist intentions for a constitution and national identity, but disagreed with his fiscal policies and were more likely to side with anti-federalists on matters of money. Without Madison's influence, which included acceptance of anti-federalists' desire for a bill of rights, it is unlikely that the U.S. Constitution would have been ratified.
Quotes From Anti-Federalists and Federalists
- "One can hardly expect the state legislatures to take enlightened views on national affairs." —James Madison, Federalist
- "You say that I have been dished up to you as an Anti-Federalist, and ask me if it be just. My opinion was never worthy enough of notice to merit citing; but, since you ask it, I will tell it to you. I am not a Federalist, because I never submitted the whole system of my opinions to the creed of any party of men whatever, in religion, in philosophy, in politics, or in anything else, where I was capable of thinking for myself. Such an addiction is the last degradation of a free and moral agent. If I could not go to heaven but with a party, I would not go there at all. Therefore, I am not of the party of Federalists." —Thomas Jefferson, Anti-Federalist
- "...that if we are in earnest about giving the Union energy and duration, we must abandon the vain project of legislating upon the States in their collective capacities; we must extend the laws of the federal government to the individual citizens of America; we must discard the fallacious scheme of quotas and requisitions, as equally impracticable and unjust." —Alexander Hamilton in Federalist Paper No. 23
- "Congress, or our future lords and masters, are to have power to lay and collect taxes, duties, imposts, and excises. Excise is a new thing in America, and few country farmers and planters know the meaning of it." —A Farmer and Planter (pseudonym) in Anti-Federalist Paper No. 26
- "Nothing is more certain than the indispensable necessity of government, and it is equally undeniable, that whenever and however it is instituted, the people must cede to it some of their natural rights in order to vest it with requisite powers." —John Jay in Federalist Paper No. 2
- "This being the beginning of American freedom, it is very clear the ending will be slavery, for it cannot be denied that this constitution is, in its first principles , highly and dangerously oligarchical; and it is every where agreed, that a government administered by a few, is, of all governments, the worst." —Leonidas (pseudonym) in Anti-Federalist Paper No. 48
- "It is, that in a democracy, the people meet and exercise the government in person: in a republic, they assemble and administer it by their representatives and agents. A democracy, consequently, must be confined to a small spot. A republic may be extended over a large region." —James Madison in Federalist Paper No. 14
- 7 quotes from the Federalist Papers - Constitution Center
- American Federalism: Past, Present, and Future - Issues of Democracy
- Anti-Federalists - U.S. History
- Quotes from The Essential Anti-Federalist Papers (PDF) by Bill Bailey
- Federalism - U.S. History
- Federalists - U.S. History
- Thomas Jefferson Exhibition - Library of Congress
- Thomas Jefferson on the New Constitution - Encyclopedia Britannica
- Wikipedia: Articles of Confederation
- Wikipedia: Timeline of drafting and ratification of the United States Constitution
- Wikipedia: U.S. Constitution
- Wikipedia: United States Bill of Rights#The Anti-Federalists
- Wikipedia: Anti-Federalism
- Wikipedia: Federalism in the United States
- Wikipedia: Federalist#United States
- Wikipedia: Federalist Era
- Wikipedia: Federalist Party
Related Comparisons

Share this comparison via:
If you read this far, you should follow us:
"Anti-Federalist vs Federalist." Diffen.com. Diffen LLC, n.d. Web. 28 Mar 2024. < >
Comments: Anti-Federalist vs Federalist
- Joe Biden vs Donald Trump
- Revolutionary War vs Civil War
- Democracy vs Republic
- Abraham Lincoln vs George Washington
- Left Wing vs Right Wing
- Conservative vs Liberal
- Democrat vs Republican
- Democrat vs Libertarian
Edit or create new comparisons in your area of expertise.
Stay connected
© All rights reserved.
- Lesson Plans
- Teacher's Guides
- Media Resources
The Federalist and Anti-federalist Debates on Diversity and the Extended Republic
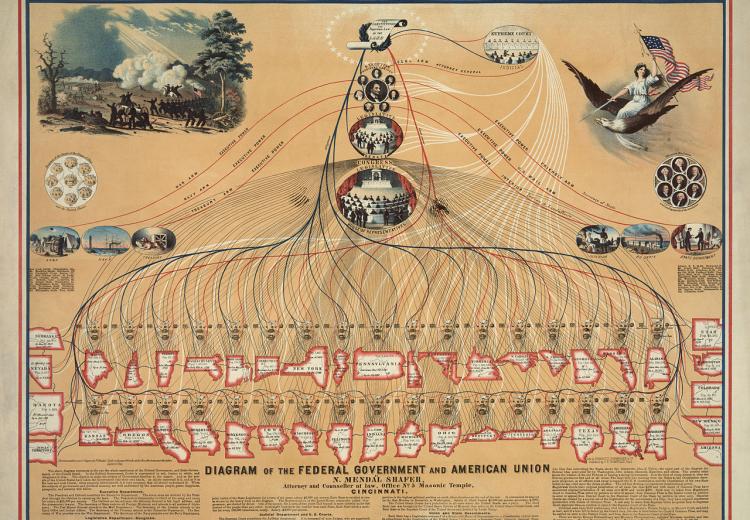
Diagram of the US Federal Government and American Union, 1862.
Wikimedia Commons
In September of 1787, the delegates to the Convention in Philadelphia presented their work to the American public for ratification. The proposed Constitution marked a clear departure from the Articles of Confederation, which had essentially established a federal “league of friendship” between thirteen sovereign and largely independent states. Under the newly proposed plan of government, the union between the states would be strengthened under a national government that derived its authority—at least in part—directly from the American people rather than purely from the state legislatures. And under the new Constitution, the people would be represented equally in the House, regardless of the state in which they lived—unlike the Articles of Confederation, according to which the Continental Congress equally represented the states . In other words, the proposed Constitution would make the United States a nation of one people rather than a loose confederation of states.
In this unit, students will examine the arguments of Anti-federalists and Federalists to learn what their compromises would mean for the extended republic that would result from the new Constitution. They will become familiar with some of the greatest thinkers on both sides of the argument and their reasons for opposing or supporting the Constitution. They will learn why Anti-federalists believed that a large nation could not long preserve liberty and self-government. They will also learn why Federalists such as James Madison believed that a large nation was vital to promote justice and the security of rights for all citizens, majority and minority alike. Finally, students will see the seriousness of the question as one that both sides believed would determine the happiness, liberty, and safety of future generations of Americans.
Guiding Questions
What are the merits of the Anti-federalist argument that an extended republic will lead to the destruction of liberty and self-government?
Was James Madison correct when he claimed that a republican government over an extended territory was necessary to both preserve the Union and secure the rights of citizens?
Learning Objectives
Understand what Anti-federalists meant by the terms “extended republic” or “consolidated republic.”
Articulate the problems the Anti-federalists believed would arise from extending the republic over a vast territory.
Evaluate the nature and purpose of representation and the competing arguments regarding the short and long-term outcomes of these decisions.
Evaluate the argument that a large republic would result in an abuse of power by those holding elected office.
Evaluate the merits of a “pure democracy” and a representative republic.
Construct an argument as to which perspective regarding the size of a government and republic has proved true in the U.S. today.
Curriculum Details
The proposed Constitution, and the change it wrought in the nature of the American Union, spawned one of the greatest political debates of all time. In addition to the state ratifying conventions, the debates also took the form of a public conversation, mostly through newspaper editorials, with Anti-federalists on one side objecting to the Constitution, and Federalists on the other supporting it. Writers from both sides tried to persuade the public that precious liberty and self-government, hard-earned during the late Revolution, were at stake in the question.
Anti-federalists such as the Federal Farmer, Centinel, and Brutus argued that the new Constitution would eventually lead to the dissolution of the state governments, the consolidation of the Union into “one great republic” under an unchecked national government, and as a result the loss of free, self-government. Brutus especially believed that in such an extensive and diverse nation, nothing short of despotism “could bind so great a country under one government.” Federalists such as James Madison (writing as Publius) countered that it was precisely a large nation, in conjunction with a well-constructed system of government, which would help to counter the “mortal disease” of popular governments: the “dangerous vice” of majority faction. In an extended republic, interests would be multiplied, Madison argued, making it difficult for a majority animated by one interest to unite and oppress the minority. If such a faction did form, a frame of government that included “auxiliary precautions” such as separation of powers and legislative checks and balances would help to prevent the “factious spirit” from introducing “instability, injustice, and confusion … into the public councils.”
Review each lesson plan. Locate and bookmark suggested materials and links from EDSITEment-reviewed websites. Download and print out selected documents and duplicate copies as necessary for student viewing.
- Text Document for Lesson 1, Activity 1
- Text Document for Lesson 1, Activity 2
- Text Document for Lesson 2, Activity 1
- Text Document for Lesson 2, Activity 2
These Text Documents contain excerpted versions of the documents used in the activities, as well as questions for students to answer.
Analyzing primary sources — If students need practice in analyzing primary source documents, excellent resource materials are available at The Learning Page from the Library of Congress and Educator Resources from the National Archives .
Lesson Plans in Curriculum
Lesson 1: anti-federalist arguments against "a complete consolidation".
This lesson focuses on the chief objections of the Anti-federalists, especially The Federal Farmer (Richard Henry Lee), Centinel, and Brutus, regarding the extended republic. Students become familiar with the larger issues surrounding this debate, including the nature of the American Union, the difficulties of uniting such a vast territory with a diverse multitude of regional interests, and the challenges of maintaining a free republic as the American people moved toward becoming a nation rather than a mere confederation of individual states.
Lesson 2: The Federalist Defense of Diversity and "Extending the Sphere"
This lesson involves a detailed analysis of Alexander Hamilton’s and James Madison’s arguments in favor of the extended republic in The Federalist Nos. 9, 10 and 51. Students consider and understand in greater depth the problem of faction in a free republic and the difficulty of establishing a government that has enough power to fulfill its responsibilities, but which will not abuse that power and infringe on liberties of citizens.
Related on EDSITEment
Advanced placement u.s. history lessons, the federalist debates: balancing power between state and federal governments, commemorating constitution day, the constitutional convention of 1787.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
My Thesis Statement. The Federalists and Anti-Federalist groups created a new, successful frame of government, which we use today, 227 years after it was written. It is my belief that it was these two groups who allowed the government of America to become as it is today, with rights of the individual that cannot be infringed upon, and with a ...
“Federalists, Anti-Federalists, and the US Constitution” By Denver Brunsman, Associate Professor of History, The George Washington University When the Constitutional Convention ended on September 17, 1787, the work of ratifying the US Constitution immediately began.
The Federalists and Anti-Federalists were two factions that emerged in American politics during the Philadelphia Convention of 1787. The original purpose of the Convention was to discuss problems with the government under the Articles of Confederation and find reasonable solutions. Instead of updating the Articles, the delegates replaced the ...
Read Summary. Anti Federalist vs. Federalists started after the Revolutionary war and the Americans had to figure out a way to get themselves out of economic depression because the war was costly and left many colonies in debt. Anti-federalists were those who opposed the development of a strong federal government and the Constitution in 1788 ...
Hand out the four excerpts from Anti-Federalist Papers #1, #9, #46, and #84. If possible have a copy up on a document projector so that everyone can see it and you can refer to it easily. "Share read" the Anti-Federalist Papers with the students. The teacher now asks the students a critical analysis question for each of the Anti-Federalist Papers.
The Federalist Papers was a collection of essays written by John Jay, James Madison, and Alexander Hamilton in 1788. The essays urged the ratification of the United States Constitution, which had been debated and drafted at the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787. The Federalist Papers is considered one of the most significant ...
The Federalist Papers are a collection of essays written in the 1780s in support of the proposed U.S. Constitution and the strong federal government it advocated. In October 1787, the first in a ...
Anti-Federalist vs. Federalist. In U.S. history, anti-federalists were those who opposed the development of a strong federal government and the ratification of the Constitution in 1788, preferring instead for power to remain in the hands of state and local governments. Federalists wanted a stronger national government and the ratification of ...
Anti-Federalists in Massachusetts, Virginia and New York, three crucial states, made ratification of the Constitution contingent on a Bill of Rights. In Massachusetts, arguments between the Federalists and Anti-Federalists erupted in a physical brawl between Elbridge Gerry and Francis Dana. Sensing that Anti-Federalist sentiment would sink ...
The Federalist and Anti-federalist Debates on Diversity and the Extended Republic. In September of 1787, the delegates to the Convention in Philadelphia presented their work to the American public for ratification. The proposed Constitution marked a clear departure from the Articles of Confederation, which had essentially established a federal ...