HIGH SCHOOL
- ACT Tutoring
- SAT Tutoring
- PSAT Tutoring
- ASPIRE Tutoring
- SHSAT Tutoring
- STAAR Tutoring

GRADUATE SCHOOL
- MCAT Tutoring
- GRE Tutoring
- LSAT Tutoring
- GMAT Tutoring
- AIMS Tutoring
- HSPT Tutoring
- ISAT Tutoring
- SSAT Tutoring
Search 50+ Tests
Loading Page
math tutoring
- Elementary Math
- Pre-Calculus
- Trigonometry
science tutoring
Foreign languages.
- Mandarin Chinese
elementary tutoring
- Computer Science
Search 350+ Subjects
- Video Overview
- Tutor Selection Process
- Online Tutoring
- Mobile Tutoring
- Instant Tutoring
- How We Operate
- Our Guarantee
- Impact of Tutoring
- Reviews & Testimonials
- Media Coverage
- About Varsity Tutors
Common Core: High School - Geometry : Rotations and Reflections of Rectangles, Parallelograms, Trapezoids, and Regular Polygons: CCSS.Math.Content.HSG-CO.A.3
Study concepts, example questions & explanations for common core: high school - geometry, all common core: high school - geometry resources, example questions, example question #1 : rotations and reflections of rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and regular polygons: ccss.math.content.hsg co.a.3.
Determine whether the statement is true or false:
The following image can be divided multiple ways to result in a reflected image.

Looking at the statement and the image given, it is seen that the object is a trapezoid.
A trapezoid has two bases of differing lengths and two side pieces of equal length in this particular case.
For an object to be divided into images that can be reflected onto one another, the images must be identically mirrored.
To identify the possible solutions, draw the lines of symmetry.

Only one line of symmetry could be drawn to allow for two images of the trapezoid to be reflected over that line. The trapezoid cannot be divided in any other way that will result in a reflected image.
Therefore, the original statement is false.
Example Question #24 : Congruence
Given a hexagon, how many lines of symmetry exist?
Recall that a hexagon is a six sided figure. Now recall that a line of symmetry creates two mirrored, identical figures which is also known as a reflection.
Knowing these two pieces of information draw the image of the hexagon and the lines of symmetry

Counting up these lines results 6 lines of symmetry.
Therefore, the answer is 6.
Example Question #25 : Congruence
A cylinder is composed of two circular bases. For one base to be carried onto the other, what geometric transformation must occur?
Rotation and Translation
All of the answers are correct.
Translation
Since a cylinder is composed of two, identical circular bases that are separated by the height of the cylinder, the transformation that must occur to have one carried onto the other is a translation. Recall that a translation is the sliding of an object without changing its size or shape. Therefore, for the one base to be carried onto the other, translation is the geometric transformation that must occur.
Example Question #4 : Rotations And Reflections Of Rectangles, Parallelograms, Trapezoids, And Regular Polygons: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsg Co.A.3
If the rectangle is reflected across the x-axis, what is the resulting image?

None of the other answers.

In order to create the resulting image of a reflection first recall what a reflection is.
Reflection: To flip the orientation of an object over a specific line or function.
In this specific situation the line of reflection is the x-axis.
The original image is,
This is the correct answer.
Example Question #26 : Congruence
Given a trapezoidal based prism how can one base be carried onto the other?
None of the answers.
Since a trapezoidal based prism is composed of two, identical trapezoidal bases that are separated by the height of the prism, the transformation that must occur to have one base carried onto the other is a translation. Recall that a translation is the sliding of an object without changing its size or shape. Therefore, for the one base to be carried onto the other, translation is the geometric transformation that must occur.
Reflections and rotations never result in the same image.
To determine whether the statement is true or false, identify any example that would make the statement false.
"Reflections and rotations never result in the same image."
Imagine a square that exists in quadrant two. When this image is reflected across the y-axis it is still a square that is now in quadrant one. When the square from quadrant two is rotated around the origin, it results in the same image in quadrant one. Therefore, it is possible for a reflection and rotation to result in the same image.
Thus, the statement "Reflections and rotations never result in the same image." is false.
Example Question #7 : Rotations And Reflections Of Rectangles, Parallelograms, Trapezoids, And Regular Polygons: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsg Co.A.3

To rotate the rectangular object around the origin, first recall the definition for a rotation and origin.

Looking at the original image and making one 90 degree rotation around the origin results in the following.

When rotating, the bottom right point will become the bottom left point, the top right point becomes the bottom right point, the left bottom point becomes the top left point, and the left top point becomes the top right point.

Example Question #8 : Rotations And Reflections Of Rectangles, Parallelograms, Trapezoids, And Regular Polygons: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsg Co.A.3

Looking at the original image and making one rotation around the origin results in the following.
When rotating, the bottom right point will become the bottom left point, the top right point becomes the bottom right point, the left bottom point becomes the top left point, and the left top point becomes the top right point. The visual representation for this rotation is as follows.

Example Question #9 : Rotations And Reflections Of Rectangles, Parallelograms, Trapezoids, And Regular Polygons: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsg Co.A.3

Example Question #10 : Rotations And Reflections Of Rectangles, Parallelograms, Trapezoids, And Regular Polygons: Ccss.Math.Content.Hsg Co.A.3

Report an issue with this question
If you've found an issue with this question, please let us know. With the help of the community we can continue to improve our educational resources.
DMCA Complaint
If you believe that content available by means of the Website (as defined in our Terms of Service) infringes one or more of your copyrights, please notify us by providing a written notice (“Infringement Notice”) containing the information described below to the designated agent listed below. If Varsity Tutors takes action in response to an Infringement Notice, it will make a good faith attempt to contact the party that made such content available by means of the most recent email address, if any, provided by such party to Varsity Tutors.
Your Infringement Notice may be forwarded to the party that made the content available or to third parties such as ChillingEffects.org.
Please be advised that you will be liable for damages (including costs and attorneys’ fees) if you materially misrepresent that a product or activity is infringing your copyrights. Thus, if you are not sure content located on or linked-to by the Website infringes your copyright, you should consider first contacting an attorney.
Please follow these steps to file a notice:
You must include the following:
A physical or electronic signature of the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf; An identification of the copyright claimed to have been infringed; A description of the nature and exact location of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright, in \ sufficient detail to permit Varsity Tutors to find and positively identify that content; for example we require a link to the specific question (not just the name of the question) that contains the content and a description of which specific portion of the question – an image, a link, the text, etc – your complaint refers to; Your name, address, telephone number and email address; and A statement by you: (a) that you believe in good faith that the use of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright is not authorized by law, or by the copyright owner or such owner’s agent; (b) that all of the information contained in your Infringement Notice is accurate, and (c) under penalty of perjury, that you are either the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf.
Send your complaint to our designated agent at:
Charles Cohn Varsity Tutors LLC 101 S. Hanley Rd, Suite 300 St. Louis, MO 63105
Or fill out the form below:
Contact Information
Complaint details.

Geometry 6-6 Complete Lesson: Trapezoids and Kites






- Quadrilateral
- Perpendicular diagonals
- Congruent opposite sides
- Supplementary consecutive angles
Chapter 6, Lesson 6: Trapezoids and Kites
- Extra Examples
- Personal Tutor
- Self-Check Quizzes
The resource you requested requires you to enter a username and password below:
Please read our Terms of Use and Privacy Notice before you explore our Web site. To report a technical problem with this Web site, please contact the site producer .

[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities Packs
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Here you will learn about a trapezoid, including the properties of a trapezoid, how to identify a trapezoid, and how to classify a trapezoid.
Students will first learn about the trapezoid as part of geometry in 1 st grade, but they will learn about the properties of a trapezoid in 5 th grade.
What is a trapezoid?
A trapezoid is a type of quadrilateral, which is a polygon with four straight sides. A trapezoid has one pair of parallel sides which are called the bases of the trapezoid. The lengths of the bases are not congruent. The other two sides of the trapezoid are called the legs.
The legs may be different lengths, but they are not parallel to each other. The angles that share the same base are called base angles.
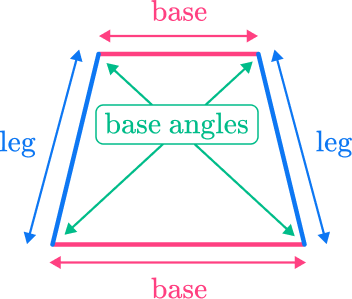
Properties of a trapezoid
In order for a polygon to be a trapezoid, it must have the following properties:
Four sides: A trapezoid is a four-sided polygon.
Two parallel sides: A trapezoid has two sides that are parallel to each other. These are called the “bases.”
Two non-parallel sides: The other two sides are not parallel to each other. These are often referred to as the “legs.”
Opposite angles: The angles formed by the longer base and each leg are equal to each other (congruent). The same goes for the angles formed by the shorter base and each leg.
Adjacent angles: Angles that share a side (adjacent angles) add up to 180 degrees.
Diagonals: A trapezoid has two diagonals, which are line segments connecting non-adjacent vertices. These diagonals are not equal in length.
There are three types of trapezoids:
Classification of a trapezoid
As you can see in the quadrilateral hierarchy, a trapezoid classifies as a quadrilateral because it has 4 sides. It does not classify as a parallelogram like a rectangle, rhombus, or square because, unlike those shapes, a trapezoid only has 1 pair of parallel sides instead of 2.
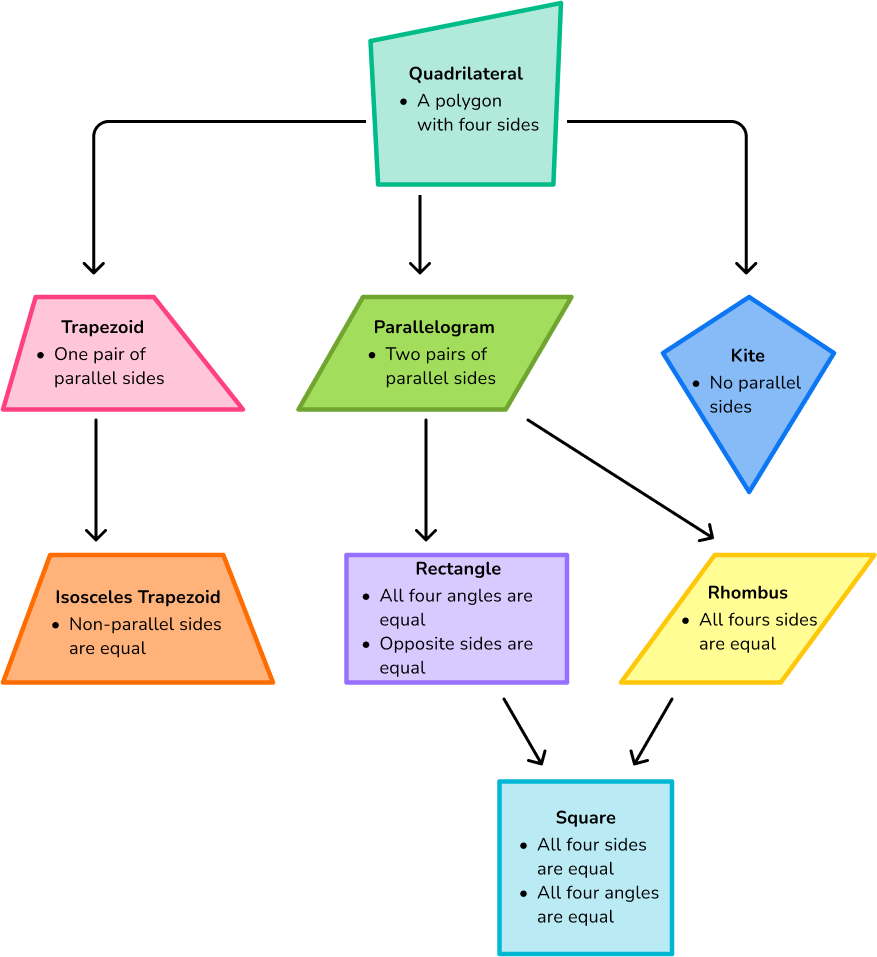
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 5 th grade math?
- Grade 5 – Geometry (5.G.B.3) Understand that attributes belonging to a category of two-dimensional figures also belong to all subcategories of that category. For example, all rectangles have four right angles and squares are rectangles, so all squares have four right angles.
- Grade 5 – Geometry (5.G.B.4) Classify two-dimensional figures in a hierarchy based on properties.
How to identify a trapezoid
In order to identify a trapezoid:
Look for the characteristics of a trapezoid.
State whether or not the shape is a trapezoid.
If the shape is not a trapezoid, explain what characteristics are different.
![trapezoids and parallelograms common core geometry homework answers [FREE] Quadrilateral Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 2 to 5)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Quadrilateral-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Quadrilateral Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 2 to 5)
Use this quiz to check your grade 2 to 5 students’ understanding of Quadrilaterals. 15+ questions with answers covering a range of 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th grade quadrilateral topics to identify areas of strength and support!
Trapezoid examples
Example 1: identify trapezoids.
Is this shape a trapezoid?

For a shape to be a trapezoid, it must have 4 sides and 1 pair of parallel sides.
2 State whether or not the shape is a trapezoid .
Since this shape has 4 sides and 1 pair of parallel sides, it is a trapezoid.
Example 2: identify trapezoids
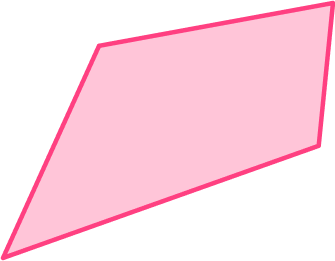
This shape is not a trapezoid.
Since this shape has 4 sides but no pairs of parallel sides, it is NOT a trapezoid.
Example 3: identify types of trapezoids
Is this shape a trapezoid? If so, what type of trapezoid is it?
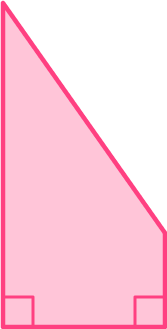
This shape is a trapezoid. Since it has one pair of right angles, it is a right trapezoid.
Example 4: identify types of trapezoids
Which trapezoid is a scalene trapezoid?

For a shape to be a trapezoid, it must have 4 sides and 1 pair of parallel sides. For a trapezoid to be a scalene trapezoid, it must also have no congruent side lengths or angles.
The 3 rd trapezoid is a scalene trapezoid.
The first two trapezoids are isosceles trapezoids since they have a pair of opposite sides that are congruent and two pairs of congruent angles. The last trapezoid is a right trapezoid since it has a pair of right angles.
Example 5: identify types of a trapezoid
Which trapezoid is an isosceles trapezoid?
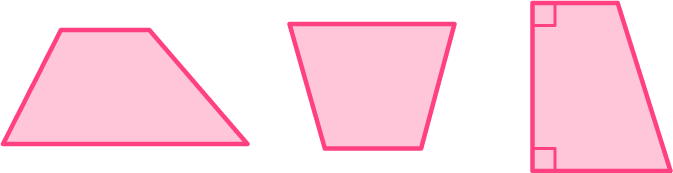
For a shape to be a trapezoid, it must have 4 sides and 1 pair of parallel sides. For a trapezoid to be an isosceles trapezoid, it must also have a pair of opposite sides that are congruent and two pairs of congruent angles.
The 2 nd trapezoid is an isosceles trapezoid.
The first trapezoid is a scalene trapezoid since it has no congruent side lengths or angles. The last trapezoid is a right trapezoid since it has a pair of right angles.
Example 6: trapezoid classification
Marnie says this shape is a trapezoid, a quadrilateral, and a parallelogram. Is she correct?

This shape is a trapezoid.
This shape is a trapezoid. It is also a quadrilateral because it has 4 sides. It is not a parallelogram because a trapezoid only has 1 pair of parallel sides and a parallelogram has 2. Therefore, Marnie is incorrect.
Teaching tips for trapezoids
- Provide real-life examples of trapezoids to help students connect the concept to their surroundings. For instance, point out trapezoidal shapes in buildings, road signs, or furniture.
- Discuss the properties of a trapezoid. Highlight that the non-parallel sides of a trapezoid are the legs, while the parallel sides are the bases of the trapezoid. Emphasize that the bases have to be different lengths, so there is always a longer base.
For example,
- Present students with worksheets that include problem-solving tasks involving trapezoids. For example, ask them to calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid or the area of a trapezoid using given measurements. Encourage them to explain their reasoning and share their solutions with the class.
Easy mistakes to make
- Thinking that a trapezoid has at least one pair of parallel lines instead of exactly one pair Some students may think any shape with at least one pair of parallel lines can be classified as a trapezoid, but this is incorrect. To be a trapezoid, a shape must have exactly one pair of parallel lines.
- Incorrectly identifying parallel sides Identifying the parallel sides of a trapezoid can be challenging for some students. They may mistakenly choose non-parallel sides as the bases of the trapezoid. Reinforce the definition of a trapezoid as a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides. Encourage students to look for the sides that are always the same distance apart and never intersect when extended.
Related quadrilateral lessons
- Quadrilateral
- Types of quadrilaterals
- Parallelogram
- Square shape
Practice trapezoid questions
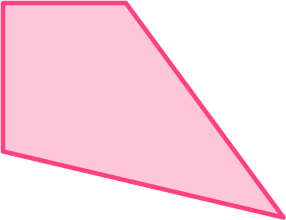
1. Which shape is a trapezoid?
The last shape is the only shape that has 4 sides and exactly 1 pair of parallel sides.
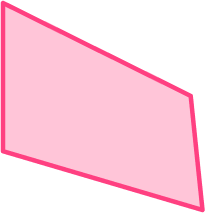
2. Which shape is not a trapezoid?
The first shape is not a trapezoid. It has 4 sides, but it does not have a pair of parallel sides.
3. What are the properties of a trapezoid?
4 sides, 2 pairs of parallel sides
4 sides, 2 pairs of parallel sides, 2 right angles
4 sides, 1 pair of parallel sides
4 sides, 1 pair of parallel sides, 4 right angles
To be a trapezoid, a shape must have 4 sides and 1 pair of parallel sides.
4. A trapezoid is also a …
parallelogram
quadrilateral
Since a trapezoid has 4 sides, it classifies as a quadrilateral.
5. Name the type of trapezoid.

scalene trapezoid
isosceles trapezoid
right trapezoid
equilateral trapezoid
In addition to 4 sides and 1 pair of parallel sides, an isosceles trapezoid must also have a pair of opposite sides that are congruent and two pairs of congruent angles.
6. Which trapezoid is a right trapezoid?
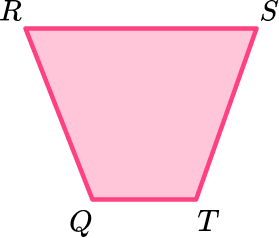
In addition to 4 sides and 1 pair of parallel sides, a right trapezoid must also have a pair of right angles. Trapezoid ABCD is a right trapezoid.

Trapezoid FAQs
Trapezoids are quadrilaterals ( 4 -sided shape) with 1 pair of parallel sides.
A trapezoid has 4 sides and 1 pair of parallel sides.
A trapezoid can be classified as a polygon and a quadrilateral.
To find the area, you can use the area of a trapezoid formula which is A = \cfrac{1}{2} \, (a + b) \, h. Students likely won’t be asked to find the area of the trapezoid until middle school or high school.
The median of a trapezoid is a line segment that connects the midpoints of the two non-parallel sides of a trapezoid.
A trapezoid and a trapezium are one and the same; other English-speaking countries, such as the UK, refer to a trapezoid as a trapezium.
The next lessons are
- Angles in polygons
- Surface area
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs .
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
Privacy Overview
Geometry: Common Core (15th Edition)
By charles, randall i., chapter 6 - polygons and quadrilaterals - 6-6 trapezoids and kites - practice and problem-solving exercises - page 394: 7, work step by step, update this answer.
You can help us out by revising, improving and updating this answer.
After you claim an answer you’ll have 24 hours to send in a draft. An editor will review the submission and either publish your submission or provide feedback.

- → Resources
- → 6th Grade
- → Area, Perimeter & Circumference
Area of Parallelograms, Trapezoids, and Rectangles Lesson Plan
Get the lesson materials.
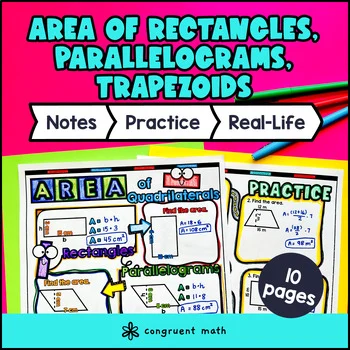
Area of Parallelograms, Trapezoids, Rectangles Guided Notes Doodles | Worksheet
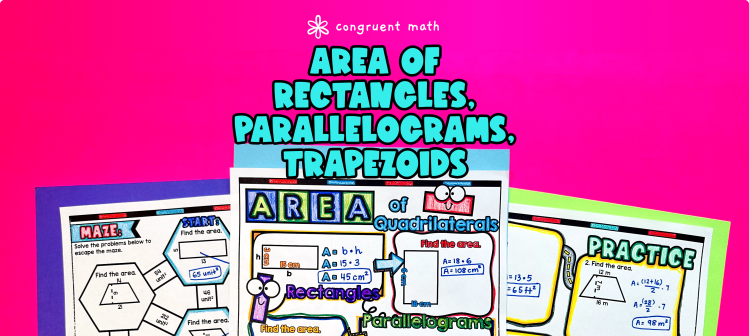
Ever wondered how to teach the area of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rectangles in an engaging way to your middle school students?
In this lesson plan, students will learn about finding the area of these polygons and their real-life applications. Through artistic, interactive guided notes, check for understanding questions, a practice coloring worksheet, and a maze activity, students will gain a comprehensive understanding of finding the area of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rectangles.
- Standards : CCSS 6.G.A.1 , CCSS 7.G.B.6
- Topic : Area, Perimeter & Circumference
- Grades : 6th Grade , 7th Grade
- Type : Lesson Plans
Learning Objectives
After this lesson, students will be able to:
Calculate the area of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rectangles using the appropriate formulas
Explain the real-life applications of area involving parallelograms, trapezoids, and rectangles
Prerequisites
Before this lesson, students should be familiar with:
How to differentiate between parallelograms, rectangles, and trapezoids
Knowledge of basic multiplication and addition skills for whole numbers
Understanding of basic algebraic concepts, such as substituting values into formulas
Colored pencils or markers
Guided notes
Key Vocabulary
Parallelogram
Introduction
As a hook, ask students why it is important to calculate the area of different polygons, specifically quadrilaterals, in real-life situations. Refer to the last page of the guided notes as well as the FAQs below for ideas.
Use the first page of the guided notes to introduce the formulas for finding the area of rectangles, parallelograms, and trapezoids. Walk through the key points of finding the length and width of a rectangle and using the formula A = l * w to calculate its area. Then, walk through the key points of identifying the base and height of a parallelogram and using the formula A = b * h to find its area. Then, walk through the key points of identifying the bases, height, and average of the bases of a trapezoid, and using the formula A = (b1 + b2) * h / 2 to calculate its area. For each polygon, students will take notes on the formula and also practice an example for a rectangle, parallelogram, and trapezoid.
Based on student responses, reteach concepts that students need extra help with. If your class has a wide range of proficiency levels, you can pull out students for reteaching, and have more advanced students begin work on the practice exercises.

Have students practice finding the area of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rectangles using the practice sheet on page 2. This activity allows students to apply the concepts they learned in the guided notes and practice calculating the area of different polygons.
Walk around the classroom to answer any student questions and provide individual support as needed. Fast finishers can dive into the color by number and maze activity for extra practice. This maze requires students to calculate the area of different shapes and find the correct path to reach the end. You can assign it as homework for the remainder of the class to reinforce their understanding of finding the area of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rectangles.
Real-Life Application

Use the last page of the guided notes "real life applications" to bring the class back together, and introduce the concept of real-life applications of calculating the area of different polygons, specifically quadrilaterals. Explain to students that understanding how to find the area of shapes can be useful in many real-life situations.
Ask students if they can think of any real-life situations where knowing how to calculate area would be important. Encourage students to share their ideas and write them on the board. Some examples may include:
Carpeting a room: Knowing the area of a room can help determine how much carpet is needed.
Painting a wall: Calculating the area of a wall can help determine how much paint is needed.
Gardening: Finding the area of a garden bed can help determine how much soil or mulch is needed.
Building a fence: Understanding the area can help determine how much material is needed to build a fence.
Refer to the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) section for additional ideas on how to teach real-life applications of finding the area of polygons.
Additional Self-Checking Digital Practice
If you’re looking for digital practice for area of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rectangles, try my Pixel Art activities in Google Sheets. Every answer is automatically checked, and correct answers unlock parts of a mystery picture. It’s incredibly fun, and a powerful tool for differentiation.
Here is an activity to explore:
Area of Rectangles, Parallelograms, Trapezoids and Composite Figures Pixel Art
Additional Print Practice
A fun, no-prep way to practice area of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rectangles is Doodle Math — they’re a fresh take on color by number or color by code. It includes multiple levels of practice, perfect for a review day or sub plan.
Here is one activity to try:
Area of Rectangles, Parallelograms, Trapezoids, Triangles, and Composite Figures
What is the formula for finding the area of a parallelogram? Open
To find the area of a parallelogram, you can use the formula: Area = base × height . The base is the length of one side of the parallelogram, and the height is the perpendicular distance between the base and the opposite side.
How do I calculate the area of a trapezoid? Open
To calculate the area of a trapezoid, you can use the formula: Area = ½ × (base1 + base2) × height . The bases are the parallel sides of the trapezoid, and the height is the perpendicular distance between the bases.
What is the difference between a parallelogram and a rectangle? Open
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides that are parallel, while a rectangle is a type of parallelogram that has four right angles. In other words, all rectangles are parallelograms, but not all parallelograms are rectangles.
How can I find the area of a rectangle? Open
To find the area of a rectangle, you can use the formula: Area = length × width . The length is the longer side of the rectangle, and the width is the shorter side.
Are there any real-life applications for finding the area of quadrilaterals? Open
Yes, there are many real-life applications for finding the area of quadrilaterals. Here are a few examples:
Calculating the amount of paint needed to cover the walls of a room.
Determining the amount of fabric needed to make a rectangular tablecloth.
Estimating the size of a field for planting crops.
How can I use guided notes to teach the area of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rectangles? Open
Guided notes can be an effective teaching tool for the area of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rectangles. Here are some tips on how to use them:
Start by providing a brief overview of the topic and the formulas.
Fill in the guided notes together as a class, explaining any key concepts or steps.
Encourage students to actively participate by asking and answering questions.
Use examples and visual aids to reinforce understanding.
Provide opportunities for students to practice applying the formulas with guided practice worksheets.
What other resources can I use to teach the area of quadrilaterals? Open
In addition to guided notes, there are many other resources you can use to teach the area of quadrilaterals. Here are a few examples:
Interactive online activities or games that allow students to practice calculating the area.
Real-life examples or scenarios that require students to find the area of quadrilaterals.
Manipulatives or physical models that allow students to visualize and explore the concept of area.
How can I assess students' understanding of the area of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rectangles? Open
There are several ways to assess students' understanding of the area of parallelograms, trapezoids, and rectangles. Here are some suggestions:
Give students quizzes or tests that require them to calculate the area of various quadrilaterals.
Assign homework problems that involve finding the area of quadrilaterals.
Have students complete real-life application tasks or projects that require them to apply their knowledge of area.
Use formative assessments, such as exit tickets or quick checks for understanding, to gauge students' comprehension throughout the lesson.
Want more ideas and freebies?
Get my free resource library with digital & print activities—plus tips over email.
- Get started
- Pre-Algebra
A quicker path to better grades
We have gathered all your curriculum-based courses, assignments, hints, tests, and solutions in one easy-to-use place
- Integrated I
- Integrated II
- Integrated III
Can't find your textbook?
More math. less studying.
A personal private tutor for each student. Free from preassure and study anxiety.
Exercise 23 Page 394
If a quadrilateral is a kite , then its diagonals are perpendicular .
Check the answer
m ∠ 1 = 90, m ∠ 2 = 90, m ∠ 3 = 90, m ∠ 4 = 90, m ∠ 5 = 46, m ∠ 6 = 34, m ∠ 7 = 56, m ∠ 8 = 44, m ∠ 9 = 56, m ∠ 10 = 44
Practice exercises
Asses your skill.
Let's find the measures of the numbered angles one at a time.
Measure of ∠ 1, ∠ 2, ∠ 3 and ∠ 4
Before we begin, let's name the vertices of our kite . We will call it quadrilateral ABCD.
If a quadrilateral is a kite, then its diagonals are perpendicular . Therefore m ∠ 1 = 90, m ∠ 2 = 90, m ∠ 3 = 90 and m ∠ 4 = 90.
Measure of ∠ 5 and ∠ 6
m ∠ 5 = 46 m ∠ 6 = 34
Measure of ∠ 7
m ∠ 3= 90, m ∠ 6= 34
LHS-124=RHS-124
Measure of ∠ 8
m ∠ 4= 90, m ∠ 5= 46
LHS-136=RHS-136
Measure of ∠ 10
Measure of ∠ 9.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Lesson 8. Additional Quadrilateral Practice (Now Folded into Unit 6 Review) LESSON/HOMEWORK. ANSWER KEY. EDITABLE LESSON. EDITABLE KEY.
In this lesson, we introduce the inclusive definition of the trapezoid and prove properties that come from it. We then introduce parallelograms and prove bas...
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Geometry Common Core - 9780133185829, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Proving That a Quadrilateral is a Parallelogram. Section 6-4: Properties of Rhombuses, Rectangles, and Squares. Section 6-5: ... Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites. Section 10-3 ...
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Geometry Common Core Edition - 9780078952715, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Parallelograms. Section 6-3: Tests for Parallelograms. Page 422: Mid-Chapter Quiz. Section 6-4: Rectangles. Section 6-5: Rhombi and Squares. Section 6-6: Trapezoids and Kites ...
Common Core: High School - Geometry : Rotations and Reflections of Rectangles, Parallelograms, Trapezoids, and Regular Polygons: CCSS.Math.Content.HSG-CO.A.3 Study concepts, example questions & explanations for Common Core: High School - Geometry
Geometry: Common Core (15th Edition) answers to Chapter 6 - Polygons and Quadrilaterals - 6-6 Trapezoids and Kites - Practice and Problem-Solving Exercises - Page 394 9 including work step by step written by community members like you. Textbook Authors: Charles, Randall I., ISBN-10: 0133281159, ISBN-13: 978--13328-115-6, Publisher: Prentice Hall
Watch Common Core Geometry Unit 6 Lesson 1 Trapezoids and Parallelograms, Geometry Videos on TeacherTube. X. Find Lessons! Join Free! Sign In UPLOAD. ... Common Core Geometry Unit 6 Lesson 1 Trapezoids and Parallelograms Geometry. emathinstruction. Sep 4, 2018. 1367 views. 8th Grade.
Geometry: Common Core (15th Edition) answers to Chapter 6 - Polygons and Quadrilaterals - 6-1 The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems - Lesson Check - Page 356 3 including work step by step written by community members like you. Textbook Authors: Charles, Randall I., ISBN-10: 0133281159, ISBN-13: 978--13328-115-6, Publisher: Prentice Hall
A complete formative lesson with embedded slideshow, mini lecture screencasts, checks for understanding, practice items, mixed review, and reflection. I create these assignments to supplement each lesson of Pearson's Common Core Edition Algebra 1, Al...
Common Core State Standards Supplement, SE Hotmath Homework Help Math Review Math Tools Multilingual eGlossary Online Calculators Study to Go. Mathematics. Home > Chapter 6 > Lesson 6. New York Geometry. Chapter 6, Lesson 6: Trapezoids and Kites. Extra Examples; Personal Tutor; Self-Check Quizzes; Log In.
Terms in this set (10) Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Quadrilateral, Parallelogram, Trapezoid and more.
Common Core State Standards. How does this relate to 5 th grade math? Grade 5 - Geometry (5.G.B.3) Understand that attributes belonging to a category of two-dimensional figures also belong to all subcategories of that category. For example, all rectangles have four right angles and squares are rectangles, so all squares have four right angles.
Properties of Parallelograms - Pages 363-366 - 6. Polygons and Quadrilaterals - Pearson Geometry Common Core, 2011 (9780133185829) - Geometry - Lesson Check, Practice and Problem-Solving Exercises, Standardized Test Prep, Mixed Review ... Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites p. 625-628 arrow_right. 3.
Trapezoid Isosceles Trapezoid Kite Making a Conjecture about Trapezoids Work with a partner. Use dynamic geometry software. a. Construct a trapezoid whose Sample base angles are congruent. Explain your process. b. Is the trapezoid isosceles? Justify your answer. c. Repeat parts (a) and (b) for several other trapezoids. Write a conjecture based
Questions 1 - 12: Students find the area of a parallelograms, triangles, trapezoids. The problem are written in a variety of ways, with or without pictures. Some of the figures include fractional lengths. Questions 13 - 18: Students find the base or the height, when given the area of a parallelogram, triangle, or trapezoid. Question 19: St
Geometry: Common Core (15th Edition) answers to Chapter 6 - Polygons and Quadrilaterals - 6-6 Trapezoids and Kites - Practice and Problem-Solving Exercises - Page 394 7 including work step by step written by community members like you. Textbook Authors: Charles, Randall I., ISBN-10: 0133281159, ISBN-13: 978--13328-115-6, Publisher: Prentice Hall
Then, walk through the key points of identifying the bases, height, and average of the bases of a trapezoid, and using the formula A = (b1 + b2) * h / 2 to calculate its area. For each polygon, students will take notes on the formula and also practice an example for a rectangle, parallelogram, and trapezoid. Based on student responses, reteach ...
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Geometry: Homework Practice Workbook - 9780078908491, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles. Section 11-2: Areas of Trapezoids, Rhombi, and Kites. Section 11-3: Areas of Circles and Sectors. Section 11-4:
1.^ Chegg survey fielded between Sept. 24-Oct 12, 2023 among a random sample of U.S. customers who used Chegg Study or Chegg Study Pack in Q2 2023 and Q3 2023. Respondent base (n=611) among approximately 837K invites. Individual results may vary. Survey respondents were entered into a drawing to win 1 of 10 $300 e-gift cards.
No, trapezoids are not parallelograms. A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides, while a parallelogram has both pairs of opposite sides parallel. The formula for the perimeter of a quadrilateral depends on the type of quadrilateral. Shape Picture Parallelogram Trapezium Click here to learn more about quadrilaterals!
Exercise 31. Exercise 32. Exercise 33. Exercise 34. At Quizlet, we're giving you the tools you need to take on any subject without having to carry around solutions manuals or printing out PDFs! Now, with expert-verified solutions from Big Ideas Geometry 1st Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems.
Trapezoids and Kites - Pages 393-397 - 6. Polygons and Quadrilaterals - Pearson Geometry Common Core, 2011 (9780133185829) - Geometry - Lesson Check, Practice and Problem-Solving Exercises, Standardized Test Prep, Mixed Review. Mathleaks Mathleaks. Practice. Textbook Solutions ... Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles p. 619-622 arrow_right. 2.
Practice and Problem Solving. Exercise a. Exercise b. At Quizlet, we're giving you the tools you need to take on any subject without having to carry around solutions manuals or printing out PDFs! Now, with expert-verified solutions from enVision Geometry 1st Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems.