Definition of Antithesis
Antithesis is a literary device that refers to the juxtaposition of two opposing elements through the parallel grammatical structure. The word antithesis, meaning absolute opposite, is derived from Greek for “ setting opposite,” indicating when something or someone is in direct contrast or the obverse of another thing or person.
Antithesis is an effective literary and rhetorical device , as it pairs exact opposite or contrasting ideas by utilizing the parallel grammatical structure. This helps readers and audience members define concepts through contrast and develop an understanding of something through defining its opposite. In addition, through the use of parallelism , antithesis establishes a repetitive structure that makes for rhythmic writing and lyrical speech.
For example, Alexander Pope states in An Essay on Criticism , “ To err is human ; to forgive divine.” Pope’s use of antithesis reflects the impact of this figure of speech in writing, as it creates a clear, memorable, and lyrical effect for the reader. In addition, Pope sets human error in contrast to divine forgiveness, allowing readers to understand that it is natural for people to make mistakes, and therefore worthy for others to absolve them when they do.

Examples of Antithesis in Everyday Speech
Antithesis is often used in everyday speech as a means of conveying opposing ideas in a concise and expressive way. Since antithesis is intended to be a figure of speech, such statements are not meant to be understood in a literal manner. Here are some examples of antithesis used in everyday speech:
- Go big or go home.
- Spicy food is heaven on the tongue but hell in the tummy.
- Those who can, do; those who can’t do, teach.
- Get busy living or get busy dying.
- Speech is silver but silence is gold.
- No pain, no gain.
- It’s not a show, friends; it’s show business.
- No guts, no glory.
- A moment on the lips; a lifetime on the hips.
- If you fail to plan, then you plan to fail.
Common Examples of Antithesis from Famous Speeches
Antithesis can be an effective rhetorical device in terms of calling attention to drastic differences between opposing ideas and concepts. By highlighting the contrast side-by-side with the exact same structure, the speaker is able to impact an audience in a memorable and significant way. Here are some common examples of antithesis from famous speeches:
- “I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character .” (Martin Luther King, Jr. “I Have a Dream”)
- “The world will little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here.” (Abraham Lincoln “The Gettysburg Address”)
- “‘Some men see things as they are and say why. I dream things that never were and say why not.'” (Edward Kennedy quoting Robert F. Kennedy during eulogy )
- “We observe today not a victory of party, but a celebration of freedom, symbolizing an end as well as a beginning, signifying renewal as well as change.” (John F. Kennedy “Presidential Inaugural Speech”)
- “You see, for any champion to succeed, he must have a team — a very incredible, special team; people that he can depend on, count on, and rely upon through everything — the highs and lows, the wins and losses, the victories and failures, and even the joys and heartaches that happen both on and off the court.” (Michael Chang “ Induction Speech for Tennis Hall of Fame”)
Examples of Proverbs Featuring Antithesis
Proverbs are simple and often traditional sayings that express insight into truths that are perceived, based on common sense or experience. These sayings are typically intended to be metaphorical and therefore rely on figures of speech such as antithesis. Proverbs that utilize antithetical parallelism feature an antithesis to bring together opposing ideas in defined contrast. Therefore, antithesis is effective as a literary device in proverbs by allowing the reader to consider one idea and then it’s opposite. It also makes for lyrical and easily remembered sayings.
Here are some examples of proverbs featuring antithesis:
- Cleanliness is next to godliness.
- Beggars can’t be choosers.
- Easy come, easy go.
- Hope for the best; prepare for the worst.
- Keep your friends close; keep your enemies closer.
- Like father, like son.
- Where there’s smoke, there’s fire.
- An ounce of protection is worth a pound of cure.
- Be slow in choosing, but slower in changing.
- Give them an inch and they’ll take a mile.
- If you can’t beat them, join them.
- Keep your mouth closed and your eyes open.
- One man’s junk is another man’s treasure.
- Out of sight, out of mind.
- Where there’s a will, there’s a way.
Utilizing Antithesis in Writing
As a literary device, antithesis allows authors to add contrast to their writing. This is effective in terms of comparing two contrasting ideas, such as a character’s conflicting emotions or a setting’s opposing elements. In literature, antithesis doesn’t require a pairing of exact opposites, but rather concepts that are different and distinct. In addition, since antithesis creates a lyrical quality to writing through parallel structure , the rhythm of phrasing and wording should be as similar as possible. Like most literary and rhetorical devices, overuse of antithesis will create confusion or invoke boredom in a reader as well as make the writing seem forced.
Antithesis and Parallelism
Both terms demonstrate a fundamental difference. An antithesis comprises two contradictory ideas and parallelism does not necessarily comprise opposite ideas or persons. It could have more than two ideas or persons. As the name suggests that parallelism is a condition where is an antithesis is an opposition. For example, man proposes, God disposes, has two contradictory ideas. However, it is also a parallel sentence . Furthermore, parallelism occurs mostly in structure and less in ideas. Even similar ideas could occur in parallelism, while an antithesis has only dissimilar ideas.
Antithesis and Juxtaposition
As far as juxtaposition is concerned, it means placing two ideas together that are dissimilar. They need not be opposite to each other. In the case of antithesis, they must be opposite to each other as in the case of man proposes, God disposes. Not only these two ideas are dissimilar, but also they are opposite. In the case of juxtaposition, a poet only puts two ideas together and they are not opposed to each other.
Use of Antithesis in Sentences
- As soon he dies, he becomes a dead living.
- Most people do not understand the value of money when the poor put money ahead of them.
- Some people make money, while some waste it.
- Although they have gone leaps ahead, they have also stepped back just in the nick of time.
- The public comes forward when there is prosperity and moves back when there is adversity.
Examples of Antithesis in Literature
Antithesis is an effective literary device and figure of speech in which a writer intentionally juxtaposes two contrasting ideas or entities. Antithesis is typically achieved through parallel structure, in which opposing concepts or elements are paired in adjacent phrases , clauses , or sentences. This draws the reader’s attention to the significance or importance of the agents being contrasted, thereby adding a memorable and meaningful quality to the literary work.
Here are some examples of antithesis in well-known works of literature:
Example 1: Hamlet (William Shakespeare)
Give every man thine ear, but few thy voice ; Take each man’s censure, but reserve thy judgment.
In Shakespeare’s well-known play , he utilizes antithesis as a literary device for Polonius to deliver fatherly advice to his son before Laertes leaves for France. In these lines, Polonius pairs contrasting ideas such as listening and speaking using parallel structure. This adds a lyrical element to the wording, in addition to having a memorable and foreboding impact on the characters and audience members with the meaning of each line.
Despite the attempt by Polonius to impart logical thinking, measured response, and wise counsel to his son through antithesis, Laertes becomes so fixated on avenging his father’s death that his actions are impulsive and imprudent. Polonius’s antithetical words are not heeded by his son, resulting in the death of several characters including Hamlet and Laertes himself.
Example 2: Paradise Lost (John Milton)
Here at least We shall be free; the Almighty hath not built Here for his envy, will not drive us hence: Here we may reign secure, and in my choice To reign is worth ambition though in Hell: Better to reign in Hell, than serve in Heaven.
In Milton’s epic poem , he explores the Fall of Satan as well as the temptation and subsequent Fall of Man. This passage is spoken by Satan after he has been condemned to Hell by God for attempting to assume power and authority in Heaven. Satan is unrepentant of his actions, and wants to persuade his followers that Hell is preferable to Heaven.
Satan utilizes antithesis in the last line of this passage to encourage his rebellious followers to understand that, in Hell, they are free and rule their own destiny. In this line, Milton contrasts not just the ideas of Hell and Heaven, but also of reign and servitude as concepts applied to the angels , respectively. Pairing these opposites by using this literary device has two effects for the reader. First, Satan’s claim foreshadows his ability to use his words describing independence to tempt Eve, resulting in her and Adam’s expulsion from the Garden of Eden. Second, this antithesis invites the reader to consider Satan’s thought-process and experience to gain a deeper understanding of his motives in the poem.
Example 3: Fire and Ice (Robert Frost)
Some say the world will end in fire, Some say in ice. From what I’ve tasted of desire I hold with those who favor fire. But if it had to perish twice, I think I know enough of hate To say that for destruction ice Is also great And would suffice.
In his poem, Frost utilizes antithesis to contrast fire and ice as elements with devastating and catastrophic potential to end the world. Frost effectively demonstrates the equal powers for the destruction of these elements, despite showcasing them as opposing forces. In this case, the poet’s antithesis has a literal as well as figurative interpretation. As the poem indicates, the world could literally end in the fire as well as ice. However, fire and ice are contrasting symbols in the poem as well. Fire represents “desire,” most likely in the form of greed, the corruption of power, domination, and control. Conversely, ice represents “hate” in the form of prejudice, oppression, neglect, and isolation.
The presence of antithesis in the poem is effective for readers in that it evokes contrasting and powerful imagery of fire and ice as opposing yet physically destructive forces. In addition, the human characteristics associated with fire and ice, and what they represent as psychologically and socially destructive symbols, impact the reader in a powerful and memorable way as well. Antithesis elevates for the reader the understanding that the source of the end of the world may not be natural causes but rather human action or behavior; and that the end of the world may not be simply the destruction of the earth, but rather the destruction of humankind.
Example 4: The Gettysburg Address by Abraham Lincoln
We have come to dedicate a portion of that field, as a final resting place for those who here gave their lives so that nation might live.
The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here, have consecrated it, far above our poor power to add or detract.
The world will little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here.
These three examples from the address of Abraham Lincoln show the use of contradictory ideas put together in one sentence. They show how he mentions living and dead putting them side by side. This antithesis has helped Lincoln as well as America to come out of the ravages of the Civil War.
Function of Antithesis
An antithesis helps make an idea distinct and prominent when it contradicts another idea in the first part of the argument . This contrastive feature helps make readers make their argument solid, cogent, and eloquent. Sentences comprising anthesis also become easy to remember, quote, and recall when required. When an antithesis occurs in a text, it creates an argumentative atmosphere where a dialectic could take place and helps writers and speakers hook their audience easily with antithetical statements.
Synonyms of Antithesis
Antithesis has no exact synonyms but several words come closer in meanings such as opposite, reverse, converse, reversal, inverse, extreme, another side of the coin, or flip side or contrast.
Post navigation
Literary Devices
Literary devices, terms, and elements, definition of antithesis.
Antithesis is the use of contrasting concepts, words, or sentences within parallel grammatical structures. This combination of a balanced structure with opposite ideas serves to highlight the contrast between them. For example, the following famous Muhammad Ali quote is an example of antithesis: “Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.” This is an antithesis example because there is the contrast between the animals and their actions (the peaceful floating butterfly versus the aggressive stinging bee) combined with the parallel grammatical structure of similes indicated by “like a.” Ali is indicating the contrasting skills necessary to be a good boxer.
Difference Between Antithesis and Juxtaposition
Antithesis is very similar to juxtaposition , as juxtaposition also sets two different things close to each other to emphasize the difference between them. However, juxtaposition does not necessarily deal with completely opposite ideas—sometimes the juxtaposition may be between two similar things so that the reader will notice the subtle differences. Juxtaposition also does not necessitate a parallel grammatical structure. The definition of antithesis requires this balanced grammatical structure.
Common Examples of Antithesis
The use of antithesis is very popular in speeches and common idioms, as the inherent contrasts often make antithesis quite memorable. Here are some examples of antithesis from famous speeches:
- “We must learn to live together as brothers or perish together as fools.” – Martin Luther King, Jr.
- “And so, my fellow Americans: ask not what your country can do for you — ask what you can do for your country. My fellow citizens of the world: ask not what America will do for you, but what together we can do for the freedom of man.” –John F. Kennedy Jr.
- “We will extend a hand if you are willing to unclench your fist.” –Barack Obama
- “Decided only to be undecided, resolved to be irresolute, adamant for drift, solid for fluidity, all-powerful to be impotent.” –Winston Churchill
- “The world will little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here.” –Abraham Lincoln
Significance of Antithesis in Literature
Antithesis can be a helpful tool for the author both to show a character’s mindset and to set up an argument . If the antithesis is something that the character is thinking, the audience can better understand the full scope of that character’s thoughts. While antithesis is not the most ubiquitous of literary devices , some authors use antithesis quite extensively, such as William Shakespeare. Many of his sonnets and plays include examples of antithesis.
Examples of Antithesis in Literature
HAMLET: To be, or not to be, that is the question— Whether ’tis Nobler in the mind to suffer The Slings and Arrows of outrageous Fortune, Or to take Arms against a Sea of troubles, And by opposing, end them?
( Hamlet by William Shakespeare)
Arguably the most famous six words in all of Shakespeare’s work are an example of antithesis. Hamlet considers the important question of “to be, or not to be.” In this line, he is considering the very nature of existence itself. Though the line is quite simple in form it contrasts these very important opposite states. Hamlet sets up his soliloquy with this antithesis and continues with others, including the contrast between suffering whatever fortune has to offer or opposing his troubles. This is a good example of Shakespeare using antithesis to present to the audience or readers Hamlet’s inner life and the range of his thinking.
It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair, we had everything before us, we had nothing before us, we were all going direct to Heaven, we were all going direct the other way…
( A Tale of Two Cities by Charles Dickens)
The opening paragraph of Charles Dickens’s A Tale of Two Cities employs many different literary devices all at once. There are many examples of antithesis back-to-back, starting with the first contrast between “the best of times” and “the worst of times.” Each pair of contrasting opposites uses a parallel structure to emphasize their differences. Dickens uses these antithetical pairs to show what a tumultuous time it was during the setting of his book. In this case, the use of antithesis is a rhetorical device that foreshadows the conflicts that will be central to the novel.
There was only one catch and that was Catch-22, which specified that a concern for one’s own safety in the face of dangers that were real and immediate was the process of a rational mind. Orr was crazy and could be grounded. All he had to do was ask; and as soon as he did, he would no longer be crazy and would have to fly more missions. Orr would be crazy to fly more missions and sane if he didn’t, but if he was sane he had to fly them. If he flew them he was crazy and didn’t have to; but if he didn’t want to he was sane and had to. Yossarian was moved very deeply by the absolute simplicity of this clause of Catch-22 and let out a respectful whistle.
( Catch-22 by Joseph Heller)
In Joseph Heller’s classic anti-war novel Catch-22 , Heller uses a specific type of humor in which antithetical statements show the true absurdity of war. This very famous quote explains the concept of the “Catch-22,” which became a popular idiomatic expression because of the book. In fact, this example is not so much an antithetical statement but instead an antithetical situation. That is to say, the two possible outcomes for Orr are opposite: either he’s deemed crazy and would thus not be forced to fly any more combat missions, or he’s sane and then would indeed have to fly them. However, the one situation negates the possibility of the other, as only a sane man would be clear-headed enough to ask not to fly more missions.
This case is not a difficult one, it requires no minute sifting of complicated facts, but it does require you to be sure beyond all reasonable doubt as to the guilt of the defendant.
( To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee)
In Harper Lee’s novel To Kill a Mockingbird , Atticus Finch is a lawyer representing Tom Robinson. Atticus presents the above statement to the jury, setting up an antithesis. He asserts that the case is not difficult and yet requires the jury to be absolutely sure of their decision. Atticus believes the case to have a very obvious conclusion, and hopes that the jury will agree with him, but he is also aware of the societal tensions at work that will complicate the case.
Test Your Knowledge of Antithesis
1. What is the correct antithesis definition? A. Using two very similar concepts and showing their subtle differences. B. Setting up a contrast between two opposite ideas or phrases in a balanced grammatical structure. C. Using words to convey an opposite meaning to their literal sense.
2. What is the difference between antithesis and juxtaposition? A. They are exactly the same device. B. They are completely different literary devices. C. Antithesis parallels opposite concepts, while juxtaposition sets up a comparison and contrast between two concepts that can be either similar or different.
3. Which of the following quotes from Shakespeare’s Macbeth contains an example of antithesis? A.
WITCHES: Fair is foul, and foul is fair: Hover through the fog and filthy air.
MACBETH: Is this a dagger which I see before me, The handle toward my hand?
WITCHES: Something wicked this way comes.
4. Which of the following quotes from Heller’s Catch-22 contains an example of antithesis? A. There are now fifty or sixty countries fighting in this war. Surely so many counties can’t all be worth dying for. B. He had decided to live forever or die in the attempt, and his only mission each time he went up was to come down alive. C. You’re inches away from death every time you go on a mission. How much older can you be at your age?
What is Antithesis? Definition, Usage, and Literary Examples
Antithesis definition.
Antithesis (ann-TIH-thuh-suhs), put simply, means the absolute opposite of something. As a literary term, it refers to the juxtaposition of two opposing entities in parallel structure. Antithesis is an effective literary device because humans tend to define through contrast. Therefore, antithesis can help readers understand something by defining its opposite.
Antithesis comes from the Latin word, via Greek, for “to place against.” It was first used in English in the 1520s as rhetorical term, but the concept goes back at least as far as Aristotle, who believed an argument could be strengthened by illustrating it with contrast.
Examples of Antithesis
- “Spicy food is heaven on the tongue but hell in the tummy.” The concepts of heaven and hell are opposites—the former being very pleasant and ideal, the latter being highly undesirable. This antithetical statement is using these concepts to convey that spicy food is delicious, but it can lead to an unfortunate digestive reaction.
- “I’m either an impressive vegetarian or a disappointing vegan.” On the scale between vegetarianism and the stricter veganism, the speaker’s current diet lies somewhere in the middle. So, while a vegetarian might applaud their efforts, a vegan might berate them for being so lax.
- “Psychiatrists write prescriptions, therapists prescribe writing.” This example includes a humorous inversion to explain the difference between psychiatrists and therapists. The former prescribes medicine to address mental issues on a biological level, while the latter might suggest a more psychologically focused approach, like journaling, as a way of easing mental stress.
Antithesis vs. Other Comparative Terms
There are several literary terms that, like antithesis, make comparisons between two things or concepts that are opposites or contrast in some way. Three such terms are dichotomy , oxymoron , and foil.
Dichotomy is a division between two entities, whereas antithesis pits two opposing entities against each other. For example, the colors black and white are considered opposites, but they are not in opposition; they can’t be in conflict nor do they cancel each other out. The concepts of war and peace, on the other hand, are at odds and can’t be reconciled.
An oxymoron is a contradiction in terms, but unlike antithesis, these terms are working together. The basic oxymoron construction is a word + an antonymic modifier, and the two essentially function as a single unit. For example, calling something a “minor crisis” is an oxymoron because minor implies something insignificant, while crisis means it requires immediate attention. Based on this, an oxymoron can’t be a component of antithesis because the point of the latter is to pit two things against each other.
Where antithesis is a verbal or written opposition, a foil is a literary opposition, usually embodied by a character in a narrative. For example, Draco Malfoy can be considered Harry Potter’s foil in the Harry Potter series because where Harry is honorable and loyal, Draco is somewhat corrupt and unfaithful.
Antithesis Outside of Literature
A common theme in American popular music is the difference between the middle and lower classes. In “Men of Good Fortune” by Lou Reed, the singer describes all the things rich men can do that poor men cannot:
Men of good fortune
Often cause empires to fall
While men of poor beginnings
Often can’t do anything at all
Antithesis is common in political speeches, particularly when it comes to the underrepresented pushing for equitable policies. In Malcolm X’s famous “ Ballot or the Bullet ” speech, he discusses how America was built by Black and indigenous people for white people’s benefit, saying, “We didn’t land on Plymouth Rock; the rock was landed on us.”
Examples of Antithesis in Literature
1. Charles Dickens, A Tale of Two Cities
This classic tale of love and sacrifice features the French Revolution as its backdrop. In this tumultuous era, where the differences between the haves and the have-nots was at its starkest, Dickens illustrates the antithetical concepts that existed simultaneously:
It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair, we had everything before us, we had nothing before us, we were all going direct to Heaven, we were all going direct the other way […]
2. William Shakespeare, The Merchant of Venice
At the beginning of this romantic comedy, chatty lout Gratiano wants to understand why his friend Antonio is so down—and why anyone would ever be down at all:
And let my liver rather heat with wine
Than my heart cool with mortifying groans.
Gratiano is implying that he’d rather experience life through a chemically altered (and therefore unreliable) lens than face any ordeals, even though they would be truer to reality.
3. John Milton, Paradise Lost
Milton’s epic poem explores many facets of the Christian bible and belief systems—including the concept of free will. When Lucifer, once one of God’s brightest angels, is cast into Hell, he says, “Better to reign in Hell than serve in Heaven.” This leads the reader to question whether anyone is truly free, though ultimately the Bible’s core argument is that willingly giving over control to God is what will leads to a happy life.
Further Resources on Antithesis
MasterClass’s How to Use Antithesis in Your Writing course is a concise guide on the mechanics of antithesis and when to use it.
This excerpt from Hegel for Beginners by Lloyd Spencer is a handy introduction to antithesis as a component of dialectics (a system for pursuing truth by way of logical argument).
Related Terms
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- How to Use Antithesis
I. What is an Antithesis?
“Antithesis” literally means “opposite” – it is usually the opposite of a statement, concept, or idea. In literary analysis, an antithesis is a pair of statements or images in which the one reverses the other. The pair is written with similar grammatical structures to show more contrast. Antithesis (pronounced an-TITH-eh-sis) is used to emphasize a concept, idea, or conclusion.
II. Examples of Antithesis
That’s one small step for a man – one giant leap for mankind . (Neil Armstrong, 1969)
In this example, Armstrong is referring to man walking on the moon. Although taking a step is an ordinary activity for most people, taking a step on the moon, in outer space, is a major achievement for all humanity.
To err is human ; to forgive , divine . (Alexander Pope)
This example is used to point out that humans possess both worldly and godly qualities; they can all make mistakes, but they also have the power to free others from blame.
The world will little note , nor long remember , what we say here, but it can never forget what they did (Abraham Lincoln, The Gettysburg Address )
In his speech, Lincoln points out that the details of that moment may not be memorable, but the actions would make history, and therefore, never entirely forgotten.
Antithesis can be a little tricky to see at first. To start, notice how each of these examples is separated into two parts . The parts are separated either by a dash, a semicolon, or the word “but.” Antithesis always has this multi-part structure (usually there are two parts, but sometimes it can be more, as we’ll see in later examples). The parts are not always as obvious as they are in these examples, but they will always be there.
Next, notice how the second part of each example contains terms that reverse or invert terms in the first part: small step vs. giant leap; human vs. divine; we say vs. they do. In each of the examples, there are several pairs of contrasted terms between the first part and the second, which is quite common in antithesis.
Finally, notice that each of the examples contains some parallel structures and ideas in addition to the opposites. This is key! The two parts are not simply contradictory statements. They are a matched pair that have many grammatical structures or concepts in common; in the details, however, they are opposites.
For example, look at the parallel grammar of Example 1: the word “one,” followed by an adjective, a noun, and then the word “for.” This accentuates the opposites by setting them against a backdrop of sameness – in other words, two very different ideas are being expressed with very, very similar grammatical structures.
To recap: antithesis has three things:
- Two or more parts
- Reversed or inverted ideas
- (usually) parallel grammatical structure
III. The Importance of Verisimilitude
Antithesis is basically a complex form of juxtaposition . So its effects are fairly similar – by contrasting one thing against its opposite, a writer or speaker can emphasize the key attributes of whatever they’re talking about. In the Neil Armstrong quote, for example, the tremendous significance of the first step on the moon is made more vivid by contrasting it with the smallness and ordinariness of the motion that brought it about.
Antithesis can also be used to express curious contradictions or paradoxes. Again, the Neil Armstrong quote is a good example: Armstrong is inviting his listeners to puzzle over the fact that a tiny, ordinary step – not so different from the millions of steps we take each day – can represent so massive a technological accomplishment as the moon landing.
Paradoxically, an antithesis can also be used to show how two seeming opposites might in fact be similar.
IV. Examples of Verisimilitude in Literature
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); Forgive us this day our trespasses as we forgive those who trespass against us . (The Lord’s Prayer)
The antithesis is doing a lot of work here. First, it shows the parallel between committing an evil act and being the victim of one. On the surface, these are opposites, and this is part of the antithesis, but at the same time they are, in the end, the same act from different perspectives. This part of the antithesis is basically just an expression of the Golden Rule.
Second, the antithesis displays a parallel between the speaker (a human) and the one being spoken to (God). The prayer is a request for divine mercy, and at the same time a reminder that human beings should also be merciful.
All the joy the world contains has come through wanting happiness for others . All the misery the world contains has come through wanting pleasure for yourself . (Shantideva, The Way of the Bodhisattva )
The antithesis here comes with some pretty intense parallel structure. Most of the words in each sentence are exactly the same as those in the other sentence. (“All the ___ the world contains has come through wanting ____ for ____.”) This close parallel structure makes the antithesis all the more striking, since the words that differ become much more visible.
Another interesting feature of this antithesis is that it makes “pleasure” and “happiness” seem like opposites, when most of us might think of them as more or less synonymous. The quote makes happiness seem noble and exalted, whereas pleasure is portrayed as selfish and worthless.
The proper function of man is to live , not to exist . I shall not waste my days in trying to prolong (Jack London, Credo )
The opening antithesis here gets its punch from the fact that we think of living and existing as pretty similar terms. But for London, they are opposites. Living is about having vivid experiences, learning, and being bold; simply existing is a dull, pointless thing. These two apparently similar words are used in this antithesis to emphasize the importance of living as opposed to mere existing.
The second antithesis, on the other hand, is just the opposite – in this case, London is taking two words that seem somewhat opposed (waste and prolong), and telling us that they are in fact the same . Prolonging something is making it last; wasting something is letting it run out too soon. But, says London, when it comes to life, they are the same. If you try too hard to prolong your days (that is, if you’re so worried about dying that you never face your fears and live your life), then you will end up wasting them because you will never do anything worthwhile.
V. Examples of Verisimilitude in Pop Culture
Everybody doesn’t like something, but nobody doesn’t like Sara Lee. (Sara Lee pastry advertisement)
This classic ad uses antithesis to set up a deliberate grammatical error. This is a common technique in advertising, since people are more likely to remember a slogan that is grammatically incorrect. (Even if they only remember it because they found it irritating, it still sticks in their brain, which is all that an ad needs to do.) The antithesis helps make the meaning clear, and throws the grammatical error into sharper relief.
What men must know , a boy must learn . (The Lookouts)
Here’s another example of how parallel structure can turn into antithesis fairly easily. (The structure is noun-“must”-verb. ) The antithesis also expresses the basic narrative of The Lookouts , which is all about kids learning to fend for themselves and become full-fledged adults.
Shut Your Mouth and Open Your Eyes (the band “AFI” – album title)
The antithesis here is a juxtaposition of two different actions (opening and shutting) that are actually part of the same sort of behavior – the behavior of somebody who wants to understand the world rather than be the center of attention. It’s basically a restatement of the old adage that “those who speak the most often have the least to say.”
VI. Related Terms
- Juxtaposition
Antithesis is basically a form of juxtaposition . Juxtaposition, though, is a much broader device that encompasses any deliberate use of contrast or contradiction by an author. So, in addition to antithesis, it might include:
- The scene in “The Godfather” where a series of brutal murders is intercut with shots of a baptism, juxtaposing birth and death.
- “A Song of Ice and Fire” (George R. R. Martin book series)
- Heaven and Hell
- Mountains and the sea
- Dead or alive
- “In sickness and in health”
Antithesis performs a very similar function, but does so in a more complicated way by using full sentences (rather than single words or images) to express the two halves of the juxtaposition.
Here is an antithesis built around some of the common expressions from above
- “ Sheep go to Heaven ; goats go to Hell .”
- “Beethoven’s music is as mighty as the mountains and as timeless as the sea .”
- “In sickness he loved me; in health he abandoned ”
Notice how the antithesis builds an entire statement around the much simpler juxtaposition. And, crucially, notice that each of those statements exhibits parallel grammatical structure . In this way, both Juxtaposition and parallel structures can be used to transform a simple comparison, into antithesis.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website

What is Antithesis ?
From the Greek antitithena, meaning “to oppose” or set opposite.” Antithesis is a powerful writing tool that sets two opposing or contrasting works, phrases, or ideas against each other. It juxtaposes two contrasting ideas against each other in what is commonly referred to as a parallel sentence. An example of what this means is, “Go big or go home.” Note how in this common example, two contrasting ideas are set in opposition creating a balanced, rhythmic sentence. And if in doubt, always remember that its name may be intimidating but, antithesis is a remarkably easy tool to master.
How to pronounce Antithesis ?
When do writers use antithesis .
Writers use Antithesis to make their writing more memorable by creating rhythmic structure. The juxtapositions of opposing ideas also make writing more believable or authoritative. Antithesis is a rhetorical device that allows writers to create a rhetorical effect and elicit an emotional response in readers. But remember:
Use antithesis to create contrast . Ideally, you want to use opposites to create contrast. However, you will find that you can often get away with contrasting “implied” opposites.
Use antithesis to create parallel structure as in the example, “Go big or go home.” Parallel structure creates
The 3 Golden Rules
- Focus on Contrast.
- Read your writing out loud.
- Use antithesis sparingly (unless you’re Robert Frost and kind of a poetic genius).
Antithesis in Literature 📚
Literature is ripe with examples of antithesis. Two of its most famous kings will always be William Shakespeare and William Blake. Please note the examples below:
- “To be, or not to be: that is the question” – William Shakespeare, Hamlet
- “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times” – Charles Dickens, A Tale of Two Cities
- “Better to reign in Hell, then serve in Heav’n” – John Milton, Paradise Lost
- “Fair is foul, and foul is fair” – William Shakespeare, Macbeth
- “The path of excess leads to the palace of wisdom” – William Blake, The Marriage of Heaven and Hell
Antithesis in Children Literature 🧸
- “The more you give, the more you get” – Dr. Seuss , The Cat in the Hat
- “Where the sidewalk ends, the grass begins” – Shel Silverstein, “ Where the Sidewalk Ends ”
- “The more things change, the more they stay the same” – Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, The Little Prince
Antithesis in Songs 🎧
“You say yes, I say no” (But really the entire song) – The Beatles, “Hello, Goodbye”
Antithesis in Poetry ✍🏽
Always a personal favorite of those who favor antithesis, Robert Frost, “ Fire and Ice ”
Some say the world will end in fire, Some say in ice. From what I’ve tasted of desire I hold with those who favor fire. But if it had to perish twice, I think I know enough of hate To say that for destruction ice Is also great And would suffice.
“Good we must love, and must hate ill,” – John Donne, “ Community ”
“To err is human, to forgive divine” – Alexander Pope “ An Essay on Criticism ”
Antithesis in Movie Dialogue 🎥
- The Dark Knight (2008): “You either die a hero or you live long enough to see yourself become the villain.”
- The Lion King (1994): “Oh yes, the past can hurt. But you can either run from it or learn from it”
- The Shawshank Redemption (1994): “Get busy living or get busy dying”
- Forrest Gump (1994): “Stupid is as stupid does”
Antithesis Throughout History
- “Patience is bitter, but it has a sweet fruit.” – Aristotle
- “Folks who have no vices have very few virtues.” – Abraham Lincoln
- “We must learn to live together as brothers or perish together as fools.” – Martin Luther King, Jr.
- “Unlike short-sighted, egocentric humans, God ‘sees with equal eye’ the fall of a hero and a sparrow, the destruction of an atom or a solar system.” – Alexander Pope
Often Mistaken for … 👥
Juxtaposition – The act or instance of placing two things side-by-side. This does not mean opposites or in contrast or even in comparison. It simply means placing them next to each other, “juxtaposed.” Example: Night , day; light, dark; good, evil; or holiday, break. Note that in these examples, the words are placed next to each other with no other information. That is juxtaposition . Oxymoron – A figure of speech that combines words with opposite meaning into new words with a new meaning. Example: virtual + reality = “virtual reality”.
What is antithesis in literature?
Antithesis is a literary device that juxtaposes opposing or contrasting ideas within a parallel grammatical structure. This contrast of ideas is used to highlight differences, emphasize a point, or create a stark distinction between two concepts, enhancing the text’s rhetorical effect.
How does antithesis enhance a text?
Antithesis enhances a text by creating a clear contrast that can make arguments more persuasive and memorable. It emphasizes the difference between two ideas, making the message more striking and engaging for the reader. The parallel structure often used with antithesis also adds a rhythmic and balanced quality to the writing.
Can antithesis be found in both poetry and prose?
Yes, antithesis can be found in both poetry and prose. In poetry, it contributes to the poem’s aesthetic and thematic depth. In prose, especially in speeches and persuasive writing, it is used to articulate strong contrasts and make arguments more compelling.
Why do speakers and writers use antithesis?
Speakers and writers use antithesis to clarify complex ideas by contrasting them with their opposites, making the distinctions clearer to the audience. This device is effective in persuasion, as the stark comparison between opposing ideas can influence readers’ or listeners’ opinions and emotions, making the message more impactful.
How can I identify antithesis in a text?
To identify antithesis, look for sentences or phrases where two opposing ideas are presented in a parallel manner, often within the same sentence or in adjacent sentences. This device is characterized by a clear and contrasting relationship between the ideas, emphasized by similar grammatical structures.

Antithesis involves the writer employing two sentences of contrasting meanings in close proximity to one another. Whether they are words or phrases of the same sentence, an antithesis is used to create a stark contrast using two divergent elements that come together to create one uniform whole. An antithesis plays on the complementary property of opposites to create one vivid picture. The purpose of using an antithesis in literature is to create a balance between opposite qualities and lend a greater insight into the subject.
Examples of antithesis:
“To be or not to be, that is the question” – This famous line from Shakespeare’s “Hamlet” uses antithesis to contrast the ideas of existence and non-existence, emphasizing the weight of the decision facing the character.
“Love is an ideal thing, marriage a real thing” – In this sentence, the contrast between the ideal and the real creates an antithesis that highlights the differences between the two concepts.
“That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind” – In this famous quote from Neil Armstrong, the contrast between the small step and the giant leap creates an antithesis that emphasizes the magnitude of the achievement.
“Speech is silver, but silence is golden” – This common saying uses antithesis to contrast the value of speaking and staying quiet, emphasizing the idea that sometimes it is better to remain silent.
“We must learn to live together as brothers or perish together as fools” – In this quote from Martin Luther King Jr., the contrast between living together and perishing together creates an antithesis that emphasizes the importance of unity and cooperation.
2 thoughts on “Antithesis”
Man proposes and God disposes… Marriage has many pains but celibacy has no pleasures..
Neil Armstrong was the first person to walk on the moon. the other two people: Am I a joke to you
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
English Studies
This website is dedicated to English Literature, Literary Criticism, Literary Theory, English Language and its teaching and learning.
Etymology of Antithesis
Table of Contents
The word “antithesis” comes from the Greek word “antithesis” (αντίθεσις), which is a combination of two words: “anti” (αντί) meaning “against” or “opposite”, and “thesis” (θέσις) meaning “position” or “statement”. Thus, the literal meaning of antithesis in Greek is “opposition” or “contradiction of position”.
The term was later adopted into Latin as “antithesis”, which has the same meaning as the Greek word. In rhetoric and literary analysis, the term “antithesis” refers to the use of contrasting or opposite ideas or phrases in close proximity to one another for effect or emphasis. It is a technique that has been used in literature, speeches, and other forms of communication throughout history to create a powerful and memorable effect on the listener or reader.
Meanings of Antithesis
The literal meanings of the word, antithesis, refer to a contrast or opposition between two things, often used to create a powerful effect in writing or speech. In rhetorical and literary analysis, antithesis refers to the use of contrasting ideas, words, or phrases in close proximity to one another, creating a deliberate contrast or tension between them. This technique has been used throughout history to create emphasis, to highlight differences, or to provoke thought and reflection.
Antithesis in Grammar
Grammatically, antithesis is a noun with plural form “antitheses” which takes a plural verb. For example: “The antitheses of love and hate are often explored in literature.”
Definition of Antithesis as Literary Device
Antithesis is a literary device that involves the use of contrasting concepts, words, or sentences within parallel grammatical structures. The purpose of antithesis is to create a contrast between two ideas, emphasize their differences, and create a memorable and impactful statement. It is a common rhetorical device used in literature, poetry, and speeches.
Types of Antitheses
There are several types of antitheses, each of which is used to contrast different ideas or concepts. Here are some of the common types of antitheses:
- Direct antithesis : This is the most common type of antithesis, which involves the use of contrasting words or phrases in a parallel grammatical structure. For example, “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times.”
- Antithesis through negation: This type of antithesis involves the use of contrasting words or phrases through negation, such as “Not that I loved Caesar less, but that I loved Rome more.”
- Antithesis through chiasmus: This type of antithesis involves the use of a reversed parallelism, such as “Ask not what your country can do for you, ask what you can do for your country.”
- Antithesis through juxtaposition: This type of antithesis involves the use of contrasting ideas or images placed side by side, such as “It was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness.”
- Antithesis through oxymoron: This type of antithesis involves the use of two contradictory words or ideas within a single phrase, such as “sweet sorrow” or “living death.”
- Antithesis through metaphor : This type of antithesis involves the use of two opposing metaphors to create contrast, such as “She is a rose, but with thorns.”
- Antithesis through allusion : This type of antithesis involves the use of a reference to another literary or historical work or event to create contrast, such as “The world is too much with us; late and soon, getting and spending, we lay waste our powers.”
- Antithesis through repetition: This type of antithesis involves the use of repeating words or phrases to create contrast, such as “To err is human, to forgive divine.”
- Antithesis through paradox: This type of antithesis involves the use of a seemingly contradictory statement to create contrast, such as “Less is more.”
Common Examples of Antithesis
Here are some common examples of antithesis in literature and speeches:
- “To be or not to be, that is the question” – William Shakespeare, Hamlet
- “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times” – Charles Dickens, A Tale of Two Cities
- “Love is an ideal thing, marriage a real thing” – Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
- “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind” – Neil Armstrong
- “Give every man thy ear, but few thy voice” – William Shakespeare, Hamlet
- “We must learn to live together as brothers or perish together as fools” – Martin Luther King Jr.
Shakespearean Antithesis
Here are some examples of Shakespearean antithesis:
- “Not that I loved Caesar less, but that I loved Rome more” – Julius Caesar
- “To be, or not to be, that is the question” – Hamlet
- “Fair is foul and foul is fair” – Macbeth
- “Parting is such sweet sorrow” – Romeo and Juliet
- “All the world’s a stage, and all the men and women merely players” – As You Like It
Literary Examples of Antithesis
Here are a few examples of antithesis in literature with an explanation of their context:
This line from A Tale of Two Cities contrasts two opposing ideas: the best of times and the worst of times. The novel is set against the backdrop of the French Revolution, a time of great upheaval and chaos. The antithesis in this sentence emphasizes the stark contrast between the two extremes and highlights the uncertainty and unpredictability of the time.
- “It was beauty killed the beast” – Merian C. Cooper, King Kong
In the 1933 film King Kong, this line is spoken by the character Carl Denham after the titular character falls to his death from the top of the Empire State Building. The antithesis in this line contrasts the beauty of Ann Darrow, King Kong’s love interest, with the violence and destruction he causes in his pursuit of her. The line suggests that it is not Kong’s violence that led to his demise, but rather his love for Ann, which ultimately proved fatal.
- “Better to reign in Hell than serve in Heaven” – John Milton, Paradise Lost
This line is spoken by Satan in Milton’s epic poem Paradise Lost. The antithesis in this line contrasts the concepts of reigning in Hell and serving in Heaven, emphasizing the pride and rebellion of Satan’s character. The line also suggests that Satan would rather choose his own path, even if it leads to Hell, than submit to a higher power.
How to Create Antithesis
Here are a few steps you can follow to create antithesis:
- Identify the key elements to be contrasted: To create an antithesis, you need to identify the key elements that you want to contrast. This could be ideas, words, phrases, or even entire sentences.
- Choose contrasting words or phrases: Once you have identified the key elements to be contrasted, choose words or phrases that have opposite meanings or connotations. For example, “love” and “hate”, “light” and “darkness”, “good” and “evil”, etc.
- Use parallel structure: To create a strong and effective antithesis, use parallel structure. This means that the two contrasting elements should be structured in a similar way, using the same grammatical structure, word order, or sentence pattern.
- Play with sound and rhythm: Another way to create an effective antithesis is to play with the sound and rhythm of the contrasting words or phrases. For example, you could use alliteration , where the initial sounds of the words are the same (e.g. “sweet sorrow”), or use a rhythmic pattern to emphasize the contrast.
- Consider the context and purpose: Finally, when creating an antithesis, it is important to consider the context and purpose. The contrast should be relevant and meaningful to the topic or theme, and should serve a purpose, such as to create emphasis, to highlight differences, or to provoke thought and reflection.
Remember, antithesis is a powerful tool, but it should be used judiciously. Too much contrast can be overwhelming or confusing for readers, so it’s important to use it sparingly and in service of the overall message of your work
Benefits of Using Antithesis
There are several benefits to using antithesis in your writing:
- Creates Contrast: Antithesis creates a clear contrast between two ideas, which can help to clarify your point and emphasize the importance of the ideas you are presenting.
- Adds Emphasis: By highlighting opposing ideas, antithesis can add emphasis and power to your writing, making it more memorable and persuasive.
- Improves Clarity: Antithesis can help to clarify complex ideas by breaking them down into simpler, contrasting concepts. This can make your writing more accessible and easier to understand.
- Adds Variety: Antithesis can add variety and interest to your writing, helping to engage readers and keep them interested in what you have to say.
- Demonstrates Skill: Using antithesis effectively demonstrates your skill as a writer, showing that you are able to use rhetorical devices to enhance your writing and communicate your ideas more effectively.
Literary Device of Antithesis in Literary Theory
In literary theory , the device of antithesis has been studied and analyzed in different ways, depending on the approach and framework of the theory. Here are some examples:
- Formalism : Formalist literary theory focuses on the formal elements of literature, such as structure, style, and language. Formalists analyze the use of antithesis as a way to create tension and balance in a literary work. They examine how antithesis can be used to create parallelism, repetition, and contrast in a work, and how it can contribute to the overall effect of the work.
- Structuralism : Structuralist literary theory emphasizes the role of language and structure in shaping meaning. Structuralists analyze the use of antithesis as a way to create binary oppositions that structure meaning in a work. They examine how antithesis can be used to create a hierarchy of meaning in a work, and how it can contribute to the overall structure and coherence of the work.
- Post-Structuralism : Post-structuralist literary theory challenges the idea that meaning is stable and fixed, and instead emphasizes the fluidity and multiplicity of meaning. Post-structuralists analyze the use of antithesis as a way to create ambiguity and indeterminacy in a work. They examine how antithesis can be used to deconstruct binary oppositions and challenge traditional concepts of meaning and identity.
- Reader-Response Criticism: Reader-response literary theory focuses on the role of the reader in shaping meaning in a literary work. Reader-response critics analyze the use of antithesis as a way to engage the reader and create a dialogic relationship between the reader and the text. They examine how antithesis can be used to create multiple meanings and interpretations, and how it can contribute to the overall impact of the work on the reader.
Suggested Readings
Cuddon, John Anthony. A Dictionary of Literary Terms and Literary Theory . John Wiley & Sons, 2012.
Krašovec, Jože. “Introduction: The Definition of Antithesis in Literature and its Place in the Hebrew Bible.” Antithetic Structure in Biblical Hebrew Poetry . Brill, 1984. 1-18. Ruzibaeva, Nigora. “Peculiarities Of The Antithesis In The Literary Text.” European Journal of Research and Reflection in Educational Sciences Vol 7.11 (2019).
Related posts:
- Onomatopoeia: A Literary Device
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Scriptwriting
What is Antithesis — Definition & Examples in Literature & Film
I f you’ve ever heard sentence structure, met characters, or witnessed ideas that seem diametrically opposed, you’re actually pretty familiar with the idea of the antithesis. But there is more to it than just juxtaposing ideas. Read on to learn exactly what is antithesis, how this tool is used, and how you can include an antithesis in your next project.
Antithesis Definition
First, let’s define antithesis.
There are a number of terms often confused for antithesis (like paradox or oxymoron ). But an antithesis has a particular grammatical structure that helps differentiate it from the rest. So, here’s the antithesis definition and then we'll look at specific examples:
ANTITHESIS DEFINITION
What is antithesis.
An antithesis is a rhetorical and literary device with parallel grammar structure but which establishes a nearly complete or exact opposition in ideas or characters. It can be effective in emphasizing drastic differences between opposing concepts.
How to pronounce antithesis: [an-TITH-uh-sis]

Familiar antithesis examples:
- “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.”
- “No pain, no gain.”
- “Out of sight, out of mind.”
The word “antithesis” comes from the Greek word meaning “setting opposite,” which is an idea that has been used in various forms. Let’s look at those various forms in more antithesis examples.
Antitheses Examples
How do we use antithesis today.
The purpose of antithetical language is not just mentioning the existence of opposing ideas, but rather emphasizing the stark differences between them. The often lyrical and rhythmic nature of this device helps accentuate the parallel grammatical structure.
Watch the video below to learn more about how we use antitheses today.
Antithesis Definition, Examples and Techniques
We use this device in that pure form today (see the examples above) in everyday turns of phrase. But there are more in-depth ways (in actions and story in general) that fit the antithesis definition.
People and characters can act in an antithetical manner to their beliefs.
Antithesis Examples in Behavior:
- A character who says they love animals but wears real fur coats.
- Someone who says they are vegetarian but eats a big steak for dinner.
- A person who uses a “Shop Small” tote bag but does their holiday shopping at Walmart.
In addition, characters in literary or scripted works, much like people, can be antitheses to each other in and of themselves. In fact, this is often how great villains are created.
Check out the video below to see more on writing great villains , and how antagonists can mirror or juxtapose protagonists .
Page to Picture: How to Write a Villain • Subscribe on YouTube
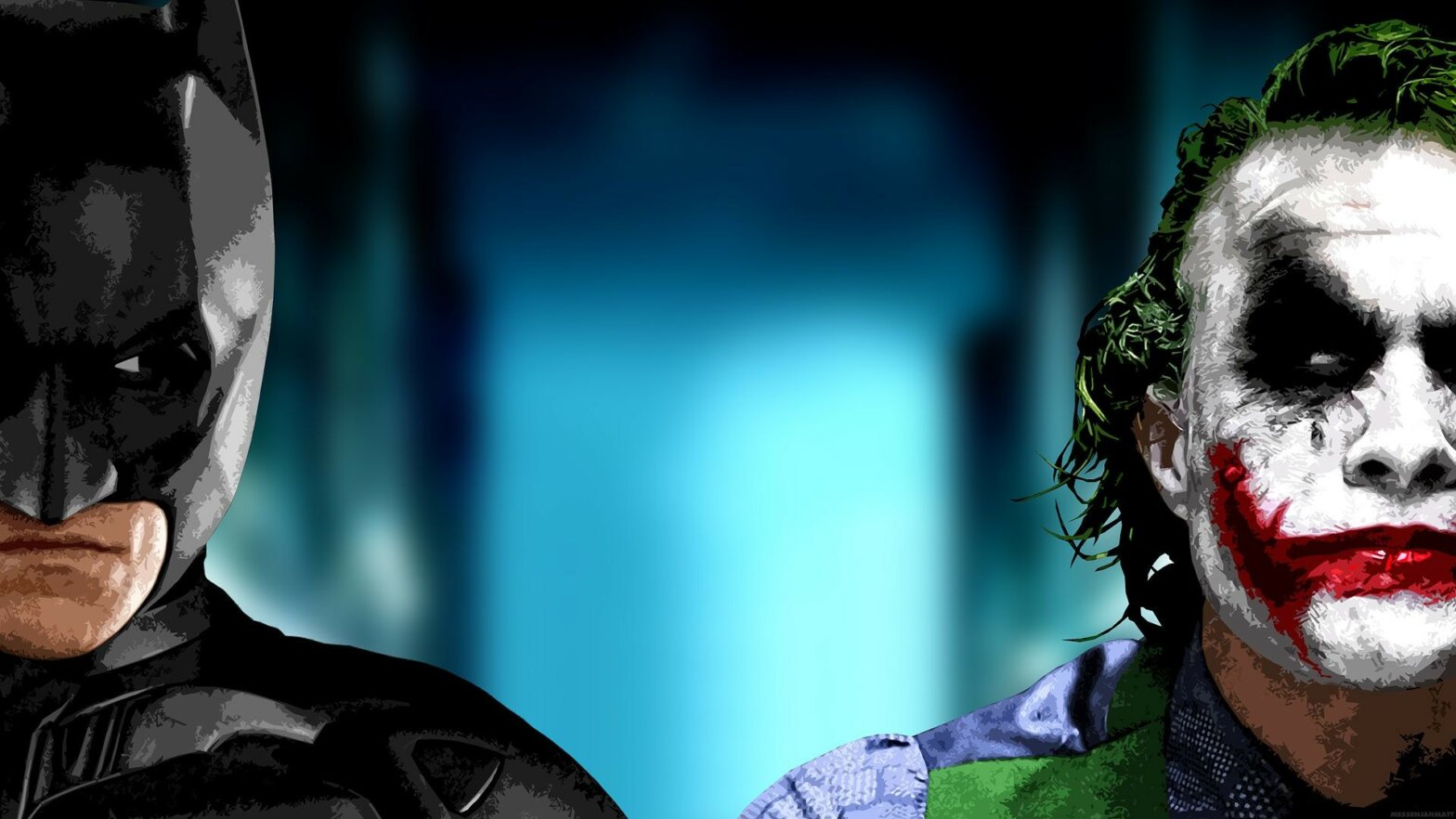
Protagonists can be an “antihero,” or the villain of a story can be portrayed separately as a parallel to the protagonist; therefore, the protagonist and antagonist highlight each other’s strengths and weaknesses, and evil and benevolent qualities. Some classic examples of this pseudo-mirrored antagonist concept are:
Snow White and the Queen
Batman and Joker
Dumbledore and Voldemort
As you can see, the antithesis is typically the ultimate antagonist, even if the character they are meant to parallel isn’t the protagonist, as is the case in the Harry Potter series.
Both a strong example of antithesis and nuanced portrayal of complicated character relationships, the Harry Potter series showcases a number of moral ambiguities as they pertain to Dumbledore and Voldemort.
We imported the script into StudioBinder’s screenwriting software to see exactly how this juxtaposition is first established.
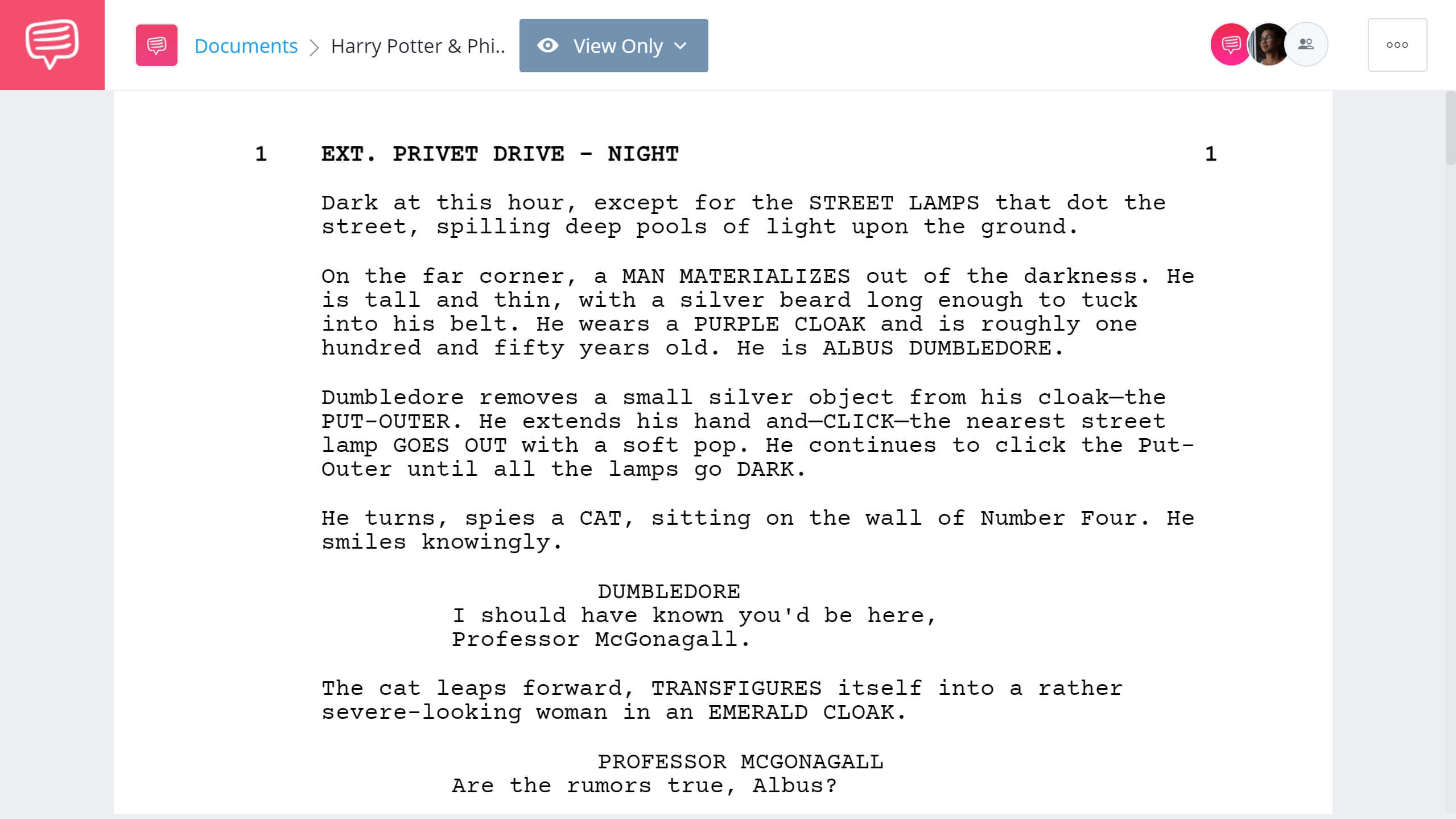
Read Full Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone Script
Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone masterfully establishes the characteristics that Harry and Voldemort share, but it also establishes similarities between Dumbledore and Voldemort.
Throughout the series, these shared traits influence Dumbledore and Voldemort in their objectives and decisions.
For instance, in the Sorcerer’s Stone , we are introduced to how Voldemort and Dumbledore move through the world. Hagrid tells Harry early on about Voldemort’s rise to power: he was a wizard “who went as bad as you can go [...] anyone who stood up to him ended up dead.” Hagrid frames Voldemort as a powerful wizard, capable of massive destruction.

Antithesis Example in Harry Potter • Read Full Scene
Alternatively, towards the end of the first film Dumbledore explains his tactics in his work with Nicolas Flamel on the Sorcerer’s Stone . “Only a person who wanted to find the stone—find it, but not use it—would be able to get it.” Dumbledore respects power and the laws of magic, and his actions reflect that.

Further into the series, in Order of the Phoenix , we see what happens when Dumbledore’s tremendous abilities collide with Voldemort’s formidable power in their epic Ministry of Magic duel.
Voldemort’s spells all aim to destruct, whereas Dumbledore’s are equally amazing, but meant to disarm, distinguish, or defend.
The series is a remarkable example of how antitheses can be essential to a story, and the respective backstories, unique abilities, and of course choices of Voldemort and Dumbledore prove it.
Implementing Antitheses
How to use antithesis.
With all the ways you can implement and define antithesis, it’s good to have a number of tricks or rules of thumb to keep in your back pocket. Whether you’re writing a short story or your next feature screenplay, here are some things you can keep in mind.
1. Aim for Moderation
If you’re using antithesis in the form of a rhetorical device, try to keep the number of antitheses to a minimum unless it’s a crucial character trait of the speaker. Using a similar literary device too often can leave your writing predictable or even annoying. The more you use a tool, like antithetical language, the less meaning it can have.
2. Similar Structure
Keep the structure of your antithesis as similar as possible if you want to highlight the differences more intensely. And try to keep the phrasing itself balanced. Both variables of the equation don’t have to be exact, but the lyrical phrasing can help your antithesis shine and stick long after the read.
3. Focus on Differences
Focus on contrast but remember to find ways to draw the parallels. How can the characters be compared to the point where their differences become obvious? How can their differences lead to conversation about how the characters may actually be similar?
Antitheses via characters and sentence structure can assist in not just interesting writing, but memorable writing. They can make your message more understandable and retainable, which should be a top goal in any written work. You never want to give you reader a reason to stop reading.
So, now that you’ve learned more about how an antithesis can strengthen your work, you can implement it into your next project like a pro.
After all, no guts, no glory.
What is Irony?
Antithesis is a rhetorical device you can use in everyday speech. Much like an antithesis, we encounter several types of irony in everyday life, too. Keep reading to learn about the types of irony and how they’re used in TV and Film.
Up Next: Irony Explained →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- What are the 12 Principles of Animation — Ultimate Guide
- What is Pacing in Writing — And Why It’s So Important
- What Does O.S. Mean in a Script & How to Use It
- What Does a Leadman Do in Film — Job Description Explained
- What is a Unit Production Manager — Job and Role Explained
- 0 Pinterest

What is Antithesis? Definition, Examples of Antitheses in Writing
Home » The Writer’s Dictionary » What is Antithesis? Definition, Examples of Antitheses in Writing
Antithesis definition: Antithesis is a literary and rhetorical device where two seemingly contrasting ideas are expressed through parallel structure.
What is Antithesis?
What does antithesis mean? An antithesis is just that—an “anti” “thesis.” An antithesis is used in writing to express ideas that seem contradictory.
An antithesis uses parallel structure of two ideas to communicate this contradiction.
Example of Antithesis:
- “Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.” –Muhammad Ali

First, the structure is parallel. Each “side” of the phrase has the same number of words and the same structure. Each uses a verb followed by a simile.
Second, the contracting elements of a butterfly and a bee seem contradictory. That is, a butterfly is light and airy while a bee is sharp and stinging. One person (a boxer, in this case) should not be able to possess these two qualities—this is why this is an antithesis.
However, Ali is trying to express how a boxer must be light on his feet yet quick with his fist.
Modern Examples of Antithesis

- “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.”
Through parallel structure, this quotation presents an antithesis. It seems contradictory that one action could be a “small step” and a “giant leap.”
However, this contradiction proposes that the action of landing on the moon might have just been a small physical step for the man Neil Armstrong, but it was a giant leap for the progress of mankind.
The Function of Antithesis

An antithesis stands out in writing. Because it uses parallel structure, an antithesis physically stands out when interspersed among other syntactical structures. Furthermore, an antithesis presents contrasting ideas that cause the reader or audience to pause and consider the meaning and purpose.
Oftentimes, the meaning of an antithesis is not overtly clear. That is, a reader or audience must evaluate the statement to navigate the meaning.
Writers utilize antitheses very sparingly. Since its purpose is to cause an audience to pause and consider the argument, it must be used with purpose and intent.
Antithesis Example from Literature

- “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity…”
From the beginning, Dickens presents two contradictory ideas in this antithesis.
How can it be the “best” and the “worst” of times? These two “times” should not be able to coexist.
Similarly, how can the setting of this novel also take place during an “age of wisdom” and an “age of foolishness?”
The antithesis continues.
Dickens opens his with these lines to set the tone for the rest of the novel. Clearly, there are two sides to this story, two tales of what is the truth. These two “sides” should not function peacefully. And, in fact, they do not. That, after all, is the “tale of two cities.”
Dickens sets up this disparity to set the tone for his novel, which will explore this topic.
Summary: What is an Antithesis?
Define antithesis: An antithesis consists of contrasting concepts presented in parallel structure.
Writers use antithesis to create emphasis to communicate an argument.
- Note: The plural form of antithesis is antitheses.
Antithesis Definition Antithesis, which literally means “opposite,” is a rhetorical device wherein opposite thoughts are prepare in a sentence to obtain a contrasting effect. Antithesis emphasizes the idea of assessment through parallel structures of the contrasted terms or clauses. The structures of terms and clauses are similar, so that it will draw the attention of the listeners or readers. For example: “Setting foot on the moon may be a small step for a person but a giant step for mankind.” The use of contrasting thoughts, “a small step” and “a massive step,” within the sentence above emphasizes the importance of one of the most important landmarks of human history. Common Antithesis Examples Some well-known antithetical statements have become part of our everyday speech, and are regularly used in arguments and discussions. Below is a listing of some commonplace antithetical statements: Give every man thy ear, however few thy voice. Man proposes, God disposes. Love is a really perfect thing, marriage a actual thing. Speech is silver, but silence is gold. Patience is bitter, however it has a sweet fruit. Money is the foundation of all evil: poverty is the fruit of all goodness. You are smooth on the eyes, but tough on the heart. Examples of Antithesis in Literature In literature, writers rent antithesis not simplest in sentences, but additionally in characters and events. Thus, its use is extensive. Below are a few examples of antithesis in literature: Example #1: A Tale of Two Cities (By Charles Dickens) The establishing lines of Charles Dickens’ novel A Tale of Two Cities provides an unforgettable antithesis example: “It become the first-class of times, it become the worst of times, it became the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it become the epoch of belief, it turned into the epoch of incredulity, it changed into the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it changed into the spring of hope, it was the wintry weather of despair, we had everything before us, we had nothing earlier than us, we were all going direct to Heaven, we were all going direct the opposite way.” The contrasting thoughts, set in parallel structures, markedly spotlight the battle that existed within the time discussed in the novel. Example #2: Julius Caesar (By William Shakespeare) In William Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar, we note antithesis within the characters of Mark Antony and Marcus Brutus. Brutus is portrayed as the “noblest of Romans,” near Caesar, and someone who cherished Rome and Caesar. Antony, at the contrary, is proven as a person with the evil intentions of harming Caesar, and taking charge of Rome. These antithetical characters spotlight the battle inside the play. Example #3: An Essay on Criticism (By Alexander Pope) Alexander Pope, in his An Essay on Criticism, says: “To err is human; to forgive divine.” Fallibility is a trait of humans, and God – the Creator – is most forgiving. Through those antithetical thoughts, Pope exhibits the simple nature of human beings. He wants to say that God is forgiving because his creation is erring. Example #4: Community (By John Donne) We find antithesis in John Donne’s poem Community: “Good we must love, and must hate ill, For unwell is ill, and correct desirable still; But there are things indifferent, Which we may neither hate, nor love, But one, and then another prove, As we shall discover our fancy bent.” Two contrasting words “love” and “hate” are combined within the above lines. It emphasizes that we love right due to the fact it is always top, and we hate bad due to the fact it's far always bad. It is a matter of desire to love or hate things that are neither good nor bad. Example #5: Paradise Lost (By John Milton) John Milton, in Paradise Lost, says: “Better to reign in Hell than serve in Heav’n.” The contrasting thoughts of reign/serve, and Hell/Heav’n are positioned on this sentence to acquire an antithetical effect. Function of Antithesis A literary tool, like antithesis, makes use of phrases to convey ideas in exceptional methods from the commonplace words and expressions of daily life. Thus, it conveys meaning greater vividly than regular speech. When contrasting thoughts are brought together, the concept is expressed extra emphatically. As a literary device, antithesis makes contrasts in an effort to observe pros and cons of a subject below discussion, and facilitates to bring on judgment on that precise subject.
- Alliteration
- Anachronism
- Antimetabole
- Aposiopesis
- Characterization
- Colloquialism
- Connotation
- Deus Ex Machina
- Didacticism
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Flash Forward
- Foreshadowing
- Internal Rhyme
- Juxtaposition
- Non Sequitur
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Poetic Justice
- Point of View
- Portmanteau
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Superlative
- Synesthesia
- Tragicomedy
- Tragic Flaw
- Verisimilitude
Antithesis (Grammar and Rhetoric)
Glossary of Grammatical and Rhetorical Terms
Richard Nordquist
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Antithesis is a rhetorical term for the juxtaposition of contrasting ideas in balanced phrases or clauses . Plural: antitheses . Adjective: antithetical .
In grammatical terms, antithetical statements are parallel structures .
"A perfectly formed antithesis," says Jeanne Fahnestock, combines " isocolon , parison , and perhaps, in an inflected language, even homoeoteleuton ; it is an overdetermined figure . The aural patterning of the antithesis, its tightness and predictability, are critical to appreciating how the syntax of the figure can be used to force semantic opposites" ( Rhetorical Figures in Science , 1999).
From the Greek, "opposition"
Examples and Observations
- "Love is an ideal thing, marriage a real thing." (Goethe)
- "Everybody doesn't like something, but nobody doesn't like Sara Lee." (advertising slogan)
- "There are so many things that we wish we had done yesterday, so few that we feel like doing today." (Mignon McLaughlin, The Complete Neurotic's Notebook . Castle Books, 1981)
- "We notice things that don't work. We don't notice things that do. We notice computers, we don't notice pennies. We notice e-book readers, we don't notice books." (Douglas Adams, The Salmon of Doubt: Hitchhiking the Galaxy One Last Time . Macmillan, 2002)
- "Hillary has soldiered on, damned if she does, damned if she doesn't, like most powerful women, expected to be tough as nails and warm as toast at the same time." (Anna Quindlen, "Say Goodbye to the Virago." Newsweek , June 16, 2003)
- "It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair, we had everything before us, we had nothing before us, we were all going direct to Heaven, we were all going direct the other way." (Charles Dickens, A Tale of Two Cities , 1859)
- "Tonight you voted for action, not politics as usual. You elected us to focus on your jobs, not ours." (President Barack Obama, election night victory speech, November 7, 2012)
- "You're easy on the eyes Hard on the heart." (Terri Clark)
- "We must learn to live together as brothers or perish together as fools." (Martin Luther King, Jr., speech at St. Louis, 1964)
- "The world will little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here." (Abraham Lincoln, The Gettysburg Address , 1863)
- "All the joy the world contains Has come through wishing happiness for others. All the misery the world contains Has come through wanting pleasure for oneself." (Shantideva)
- "The more acute the experience, the less articulate its expression." (Harold Pinter, "Writing for the Theatre," 1962)
- "And let my liver rather heat with wine Than my heart cool with mortifying groans." (Gratiano in The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare)
- Jack London's Credo "I would rather be ashes than dust! I would rather that my spark should burn out in a brilliant blaze than it should be stifled by dryrot. I would rather be a superb meteor, every atom of me in magnificent glow, than a sleepy and permanent planet. The proper function of man is to live, not to exist. I shall not waste my days in trying to prolong them. I shall use my time." (Jack London, quoted by his literary executor, Irving Shepard, in an introduction to a 1956 collection of London's stories)
- Antithesis and Antitheton " Antithesis is the grammatical form of antitheton . Antitheton deals with contrasting thoughts or proofs in an argument ; Antithesis deals with contrasting words or ideas within a phrase, sentence, or paragraph." (Gregory T. Howard, Dictionary of Rhetorical Terms . Xlibris, 2010)
- Antithesis and Antonyms Antithesis as a figure of speech exploits the existence of many 'natural' opposites in the vocabularies of all languages. Small children filling in workbooks and adolescents studying for the antonyms section of the SAT learn to match words to their opposites and so absorb much vocabulary as pairs of opposed terms, connecting up to down and bitter to sweet, pusillanimous to courageous and ephemeral to everlasting. Calling these antonyms 'natural' simply means that pairs of words can have wide currency as opposites among users of a language outside any particular context of use. Word association tests give ample evidence of the consistent linking of opposites in verbal memory when subjects given one of a pair of antonyms most often respond with the other, 'hot' triggering 'cold' or 'long' retrieving 'short' (Miller 1991, 196). An antithesis as a figure of speech at the sentence level builds on these powerful natural pairs, the use of one in the first half of the figure creating the expectation of its verbal partner in the second half." (Jeanne Fahnestock, Rhetorical Figures in Science . Oxford University Press, 1999)
- Antithesis in Films - "Since . . . the quality of a scene or image is more vividly shown when set beside its opposite, it is not surprising to find antithesis in film . . .. There is a cut in Barry Lyndon (Stanley Kubrick) from the yellow flickers of a flaming house to a still gray courtyard, lined with soldiers, and another from the yellow candles and warm browns of a gambling room to the cool grays of a terrace by moonlight and the Countess of Lyndon in white." (N. Roy Clifton, The Figure in Film . Associated University Presses, 1983) "It is clear that in every simile there is present both differences and likenesses, and both are a part of its effect. By ignoring differences, we find a simile and may perhaps find an antithesis in the same event, by ignoring likeness. . . . - "In The Lady Eve (Preston Sturges), a passenger boards a liner by tender. This was conveyed by the two vessels' whistling. We see a convulsive spurt of water and hear a desperate, soundless puff before the siren of the tender found its voice. There was a stuttering amazement, a drunken incoordination to these elaborate preliminaries, foiled by the liner's lofty unruffled burst of sounding steam. Here things that are like, in place, in sound, and in function, are unexpectedly contrasted. The commentary lies in the differences and gains force from the likeness." (N. Roy Clifton, The Figure in Film . Associated University Presses, 1983)
- Antithetical Observations of Oscar Wilde - “When we are happy, we are always good, but when we are good, we are not always happy.” ( The Picture of Dorian Gray , 1891) - “We teach people how to remember, we never teach them how to grow.” ("The Critic as Artist," 1991) - “Wherever there is a man who exercises authority, there is a man who resists authority.” ( The Soul of Man Under Socialism , 1891) - “Society often forgives the criminal; it never forgives the dreamer.” ("The Critic as Artist," 1991)
Pronunciation: an-TITH-uh-sis
- What Is Anastrophe in Rhetoric?
- Ethopoeia (Rhetoric)
- The Top 20 Figures of Speech
- Aposiopesis: The Broken Figure of Speech
- AP English Exam: 101 Key Terms
- Pun: Definition and Examples in English
- Syncrisis (Rhetoric) Definition and Examples
- Figure of Thought in Rhetoric
- Brief Introductions to Common Figures of Speech
- Prosopopoeia: Definition and Examples
- Polyptoton (Rhetoric)
- presence (rhetoric)
- Understatement
- Enumeratio (Enumeration)
- Scheme (Rhetoric): Definition and Examples

Story Arcadia
Antithesis: Mastering Contrast in Rhetoric and Literature
In the realm of communication, whether it be through the written word or spoken language, the power to captivate and persuade an audience is paramount. One such tool that has stood the test of time in achieving this is antithesis—a literary device that wields contrast as its sword. Antithesis occurs when two opposing ideas are placed side by side in a sentence to highlight their stark differences. This technique is not just a stylistic choice; it serves as a critical element in rhetoric and literature, sharpening arguments and adding depth to narratives.
The importance of antithesis cannot be overstated. It transforms simple statements into compelling points of debate, often leaving a lasting impression on the reader or listener. By juxtaposing contradictory concepts, antithesis elevates language, allowing for a clearer understanding of the subject at hand and emphasizing the contrasts that define our thoughts and experiences.
This introduction will pave the way for a deeper exploration into how antithesis creates these vivid contrasts and underscores differences, enriching our appreciation for both rhetoric and literature. Through examples from renowned speeches and texts, we will examine its effects on audiences and compare it with other rhetorical devices that aim to achieve similar outcomes. Furthermore, we will delve into practical advice on employing antithesis effectively in one’s own writing and speech, including tips for crafting impactful statements and cautions against common missteps.
As we conclude, we will revisit the significance of mastering antithesis—not only as a means to enhance communication but also as an exercise in clarity and persuasion. In doing so, we encourage readers to practice this timeless technique, ensuring its continued relevance in today’s diverse landscape of discourse. Diving Deeper into Antithesis
Antithesis is a powerful literary device that involves the juxtaposition of contrasting ideas in close proximity to one another. It’s often used to create a stark contrast between two opposing concepts, thereby highlighting the differences between them. This technique can be found throughout history in some of the most memorable speeches and pieces of literature.
Take, for example, the famous line from Charles Dickens’ “A Tale of Two Cities”: “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times.” Here, Dickens sets up a contrast between two opposing states of being to emphasize the complexities and contradictions of the era he describes. Similarly, in Martin Luther King Jr.’s speech “I Have a Dream,” he uses antithesis effectively: “We refuse to believe that there are insufficient funds in the great vaults of opportunity of this nation.” The contrast between refusal to believe and insufficient funds highlights the disparity between what is and what could be.
The effect of antithesis on an audience or reader can be profound. By placing opposites side by side, it forces an evaluation or re-evaluation of their understanding or beliefs regarding those concepts. It can also create a rhythm and memorability in writing that aids in persuasion and retention of information.
While antithesis focuses on clear-cut oppositions, other rhetorical devices like paradox and oxymoron also play with contrasting ideas but do so within a single phrase or concept, creating a more nuanced effect. For instance, an oxymoron such as “deafening silence” brings together contradictory terms to give a deeper sense of meaning about a silence that is overwhelmingly present.
In comparison to these devices, antithesis relies on a clearer dichotomy which can make its impact more direct and bold. When used skillfully, it not only clarifies concepts by showing what they are not but also enriches the text by introducing tension and dynamism through contrast. Mastering the Use of Antithesis
To harness the power of antithesis in your writing and speech, it’s essential to understand how to use it effectively. Antithesis can sharpen your arguments and make your words memorable, but it requires a delicate balance. Here are some tips for crafting impactful antithetical statements:
Firstly, clarity is key. Your opposing ideas should be expressed in a straightforward manner to ensure that the contrast is evident. For instance, Neil Armstrong’s famous words upon stepping onto the moon, “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind,” offer a clear juxtaposition between an individual action and its larger significance.
Secondly, aim for parallelism in structure. This means that the contrasting elements should mirror each other grammatically. An example from Charles Dickens’ “A Tale of Two Cities” illustrates this perfectly: “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times.” The parallel structure makes the contrast between ‘best’ and ‘worst’ more striking.
Additionally, keep your audience in mind. The effectiveness of antithesis depends on whether the contrast resonates with their values or experiences. When Martin Luther King Jr. said, “Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere,” he tapped into a universal understanding of fairness that moved his listeners.
However, there are potential pitfalls to avoid when using antithesis. Overuse can lead to confusion rather than clarity if every point is framed as a stark contrast. Moreover, forced antitheses that don’t naturally fit the context can seem contrived and may undermine your message.
In summary, effective use of antithesis involves clear expression, parallel structure, audience awareness, and moderation. By adhering to these principles, you can craft statements that not only capture attention but also reinforce your message with powerful contrasts. Conclusion: The Power of Polarities in Expression
In conclusion, antithesis stands as a cornerstone of effective communication, offering a dynamic way to underscore contrasts and breathe life into ideas. Throughout this article, we’ve explored the definition and significance of antithesis in rhetoric and literature, illustrating how it sharpens distinctions and enriches the texture of language.
We’ve seen through vivid examples from renowned speeches and literary works that antithesis can captivate audiences, drawing them into a deeper understanding and emotional connection with the subject matter. It’s clear that when used skillfully, this device not only compares but also contrasts ideas, creating a memorable impact that other rhetorical strategies strive to match.
Moreover, we’ve provided practical advice on employing antithesis in your own writing and speaking endeavors. By embracing this tool with intention and care, you can craft statements that resonate with clarity and persuasive power. However, it’s crucial to wield antithesis judiciously to avoid diminishing its effect or confusing your message.
As we part ways with this topic, let us encourage you to practice the art of antithesis. Whether you’re delivering a speech, penning an essay, or engaging in everyday discourse, remember that the strategic use of contrast can illuminate your points with unparalleled vibrancy. Antithesis is not just a relic of classical rhetoric; it is a timeless technique that continues to echo through modern communication, proving that some polarities—like clarity versus obscurity—remain universally compelling.
Embrace the dance of opposites in your expressions and watch as your words leave an indelible mark on the minds of your audience.
Related Pages:
- The Antithesis Effect: Harnessing Contrast for…
- Antithesis Examples: Enhancing Contrast in Rhetoric…
- Juxtaposition: Exploring the Power of Contrast in Literature
- Juxtaposition: Enhancing Meaning and Contrast in…
- Contrast: Enhancing Depth and Complexity in…
- Exploring Logos: The Power of Logic in English Communication
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Literary Devices: Antithesis Examples in Literature | How To Use It In Writing?
Antithesis is a rhetorical device that presents contrasting or opposing ideas, often in a balanced way, to create emphasis or highlight the differences between them. By juxtaposing these opposing concepts, antithesis allows the reader to better understand the complexities and nuances of a subject or argument.
What is Antithesis?
Antithesis is derived from the Greek word “antitithenai,” which means “to set against.” In literature, antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, often within a single sentence or closely connected sentences. The purpose of antithesis is to emphasize the difference between the two ideas and create a clear contrast, which can help clarify the author’s intention, provoke thought, or add artistic flair to the text.
Antithesis is found different kinds of writing such as poetry, prose, and drama. It is also used in conjunction with other rhetorical devices (parallelism or chiasmus) and creates a powerful effect.
Why Use Antithesis in Literature?
Writers employ antithesis for several reasons, such as:
- Emphasis: By presenting contrasting ideas, antithesis draws the reader’s attention to the differences between them, making the contrast more apparent and memorable.
- Clarity: Antithesis can help clarify a concept or argument by highlighting the opposing view, making it easier for the reader to understand the author’s perspective.
- Complexity: By juxtaposing opposing ideas, antithesis allows writers to explore the complexities of a subject or issue, demonstrating that it is not merely black and white but contains various shades of grey.
- Artistry: Antithesis adds an artistic touch to the text, creating a more engaging and memorable reading experience.
Examples of Antithesis in Literature
Antithesis is a versatile literary device that has been employed by writers across different periods and genres. Here are some notable examples of antithesis in literature:
William Shakespeare
Shakespeare frequently used antithesis in his plays to emphasize contrasts and create dramatic tension. In “Romeo and Juliet,” the famous line “My only love sprung from my only hate” illustrates the opposition between love and hate, which is a central theme of the play.
Another example from “Julius Caesar” highlights the contrast between ambition and humility:
“Yond Cassius has a lean and hungry look; He thinks too much: such men are dangerous.”
Here, Shakespeare juxtaposes Cassius’s “lean and hungry look” with the idea that “such men are dangerous,” creating a stark contrast between physical appearance and the potential for treachery.
Charles Dickens
In “A Tale of Two Cities,” Charles Dickens uses antithesis to emphasize the contrasts between the two cities, London and Paris, and the tumultuous period during which the novel is set:
“It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair.”
The parallel structure and repetition of opposites in this passage create a powerful and memorable opening that sets the tone for the novel.
John Milton
In his epic poem “Paradise Lost,” John Milton employs antithesis to convey the contrast between heaven and hell, as well as the conflicting nature of
good and evil:
“Better to reign in Hell, than serve in Heaven.”
This quote highlights the contrast between the desire for power in hell and the submission required in heaven, exploring the complex motivations behind Satan’s rebellion.
Jane Austen
Jane Austen’s “Pride and Prejudice” is known for its witty and engaging dialogue, which often employs antithesis to emphasize the differences between characters or ideas. In one instance, Elizabeth Bennet uses antithesis to describe Mr. Darcy’s character:
“In vain have I struggled. It will not do. My feelings will not be repressed. You must allow me to tell you how ardently I admire and love you.”
Here, the juxtaposition of “admire” and “love” against the struggle and repression of feelings emphasizes the complexity of Elizabeth’s emotions towards Mr. Darcy.
Antithesis in Poetry
Antithesis is also a popular device in poetry, as it allows poets to create vivid imagery and emphasize contrasts in meaning. Consider the following lines from William Blake’s “The Tyger”:
“What immortal hand or eye, Could frame thy fearful symmetry?”
Blake contrasts the ideas of immortality and fear to create a powerful image of the mysterious and terrifying nature of the titular creature.
Similarly, in Robert Frost’s “The Road Not Taken,” the speaker’s decision between two paths is highlighted through antithesis:
“Two roads diverged in a wood, and I— I took the one less traveled by, And that has made all the difference.”
The juxtaposition of “less traveled” and “all the difference” emphasizes the significance of the speaker’s choice and the impact it has on their life.
Tips for Using Antithesis in Your Own Writing
If you’re looking to incorporate antithesis into your own writing, consider these tips:
- Identify contrasting ideas: Look for ideas or concepts within your writing that have inherent opposition or contrast, such as love and hate, war and peace, or youth and age.
- Use parallel structure: When crafting sentences with antithesis, use parallelism to make the contrast more apparent and memorable. This can include mirroring sentence structure, word order, or even using similar or opposite words.
- Balance the contrast: Ensure that the opposing ideas are given equal weight and prominence within the sentence or passage, so that the reader can fully appreciate the contrast.
- Be concise: Keep your use of antithesis concise and focused to maintain its impact. Overusing antithesis can dilute its effect and make your writing feel repetitive or forced.
More to read
- Literary Devices (A – Z List)
- Alliteration
- Anachronism
- Accumulation
Similar Posts

Examples of Refrain in Poetry
Definition of Refrain Refrain is a poetic device. In refrain, a line or group of lines are repeated at…

7 Apostrophe Examples in Literature
What is Apostrophe? An apostrophe is a figure of speech, through which the speaker addresses a person, thing or…

Examples of Digression in Literature
Definition of Digression Digression is referred to a departure from the main subject or narrative in a piece of…

Free Verse Poem Examples
Definition of Free Verse Free verse is a form of poetry that does not contain a regular meter and…

Epilogue Examples In Literature
Definition of Epilogue Epilogue is a section at the end of a book, play or movie. It concludes the…

What is Amplification in Literature (Examples & Functions)
Amplification is a literary device that is often used to expand upon an idea, thought or detail in a…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of antithesis
Did you know.
Writers and speechmakers use the traditional pattern known as antithesis for its resounding effect; John Kennedy's famous "ask not what your country can do for you—ask what you can do for your country" is an example. But antithesis normally means simply "opposite". Thus, war is the antithesis of peace, wealth is the antithesis of poverty, and love is the antithesis of hate. Holding two antithetical ideas in one's head at the same time—for example, that you're the sole master of your fate but also the helpless victim of your terrible upbringing—is so common as to be almost normal.
Examples of antithesis in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'antithesis.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Late Latin, from Greek, literally, opposition, from antitithenai to oppose, from anti- + tithenai to set — more at do
1529, in the meaning defined at sense 1b(1)
Dictionary Entries Near antithesis
anti-theoretical
Cite this Entry
“Antithesis.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/antithesis. Accessed 23 Apr. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of antithesis, more from merriam-webster on antithesis.
Nglish: Translation of antithesis for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of antithesis for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about antithesis
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, on 'biweekly' and 'bimonthly', popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 19, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), a great big list of bread words, 9 superb owl words, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, games & quizzes.


- Juxtaposition

Juxtaposition Definition
What is juxtaposition? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
Juxtaposition occurs when an author places two things side by side as a way of highlighting their differences. Ideas, images, characters, and actions are all things that can be juxtaposed with one another. For example, it's a common plot device in fairy tales such as Cinderella to juxtapose the good-natured main character with a cruel step-sibling. The differences between the characters, as well as their close relation to one another, serve to highlight the main character's good qualities.
Some additional key details about juxtaposition:
- The verb form of juxtaposition is juxtapose , as in "the author juxtaposed the protagonist's dirty, ragged clothes with the spotless interior of the wealthy villain's mansion."
- The word juxtaposition comes from the Latin juxta meaning "next" and the French poser meaning "to place." This combination suggests juxtaposition's meaning: "to place next to."
Juxtaposition Pronunciation
Here's how to pronounce juxtaposition: juck-stuh-puh- zish -uhn
Juxtaposition and Related Terms
Because juxtaposition is such a broad concept, covering the contrast created between all sorts of different things when placed in close proximity, there are a number of terms that overlap with it or fall under its broader umbrella. Three of the most common of these terms are foil , antithesis , and oxymoron .
Juxtaposition and Foils
A foil is one specific form of juxtaposition having to do with contrasts between characters. When a writer creates two characters that possess opposite characteristics, it's often with the intention of highlighting some specific about one or both of the characters by juxtaposing their qualities. Such characters are foils of one another. The tortoise and the hare, from the famous folk tale, are examples of foils.
"Juxtaposition" describes the writer's action of placing these two characters next to one another for the purposes of comparing them, while foil is a word that describes the characters themselves (the hare is a foil to the tortoise, and vice-versa).
Juxtaposition and Antithesis
Antithesis is also a specific type of juxtaposition. Antithesis is a narrower term than juxtaposition in two key ways:
- Antithesis involves opposites: The things that are contrasted in antithesis are always pretty strong and clear opposites. Juxtaposition can involve such oppositional things, but also can involve the contrast of more complicated things, like two characters or themes.
- Antithesis involves a specific grammatical structure: Antithesis is a figure of speech that involves a very specific parallel sentence structure. Juxtaposition is a literary device that simply refers to a contrast set up between two things in some way, but it does not necessarily have to involve a defined grammatical structure.
An example of antithesis is Neal Armstrong's first words when he reached on the surface of the moon:
"That's one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind."
This is a clear pairing of opposites, expressed in a parallel grammatical structure. In contrast, now imagine a description of Neal Armstrong's figure foregrounded against the night sky:
The tiny figure of Armstrong in his pristine white suit stood out against the expansive darkness of the universe beyond him.
This description involves juxtaposition rather than antithesis, for two reasons: it does not contain parallel grammatical structure, and the comparison goes beyond opposition. The white of the suit contrasts with the darkness of space in a clear contrast of opposites, but the sentence also contains a comparison between Armstrong's small size and the overwhelming magnitude of the universe, between the human and the non-human, even between the temporary and the eternal. These effects, which amount to a feeling of awe and loneliness, come from the choice to place Armstrong and the universe next to one another—it comes from their juxtaposition .
Juxtaposition and Oxymoron
An oxymoron is a figure of speech in which two contradictory terms or ideas are paired together in order to reveal a deeper truth. Put another way, an oxymoron uses the juxtaposition of its two words to imply something deeper than either word individually could convey.
For instance, it's an oxymoron when, in Romeo and Juliet , Juliet says that "parting is such sweet sorrow ." The juxtaposition of these two words, "sweet sorrow," captures the complexity of love and passion, that it is capable of inspiring both pain and joy at the same time.
Juxtaposition Examples
Juxtaposition in literature.
Juxtaposition is a basic tool of storytelling, as writers choose how to place their characters, settings, arguments, and images in relation to one another to achieve their aims. In this section you'll find examples of juxtaposition from fiction, poetry, non-fiction, and drama.
Juxtaposition in Mary Shelley's Frankenstein
In Frankenstein , Mary Shelley creates a few jarring juxtapositions that serve to accentuate the monstrosity as well as the humanity of the Creature that Victor Frankenstein brings to life. The Creature learns to speak in part by reading Milton's Paradise Lost , and so his language is ornate and elevated, full of thee's, thy's, and thou's. The juxtaposition of this elegant, formal speech with the Creature's ugly, deformed features and terrible strength creates an uncanny, terrifying effect that, at the same time, increases the reader's understanding of the Creature's tragedy, since we see his clear intelligence.
Over the course of the novel, Shelley also juxtaposes the actions of the Creature, who eventually responds to the world's scorn with a violent urge for revenge, with those of Victor Frankenstein, whose arrogant recklessness created the Creature in the first place and whose lack of mercy or empathy condemned the Creature to lonely isolation. This juxtaposition begs the question: who is the real monster?
Juxtaposition in T.S. Eliot's "The Waste Land"
One of T.S. Eliot's most well-known poems, "The Waste Land," is a patchwork of different allusions and striking imagery , as Eliot uses juxtaposition to knit together a dizzying range of sources and ideas. Eliot juxtaposes April, a springtime month, with winter, and uses irony to reverse the reader's expectation for this comparison (calling April cruel and winter warm). There is also a second juxtaposition in the image of blooming lilacs in the "dead land," two contrasting images that bring out one another's features.
April is the cruellest month , breeding Lilacs out of the dead land , mixing Memory and desire, stirring Dull roots with spring rain. Winter kept us warm , covering Earth in forgetful snow, feeding A little life with dried tubers.
Juxtaposition in Rachel Carson's Silent Spring
In Rachel Carson's Silent Spring , one of the foundational works of the modern environmental movement, juxtaposition plays an important role in Carson's framing of her argument. The first chapter of the book, "A Fable for Tomorrow" presents a beautiful small town "in the heart of America," at first stressing its natural abundance:
Along the roads, laurels, viburnum and alder, great ferns and wildflowers delighted the traveler's eye through much of the year
Soon, though, a blight descends, and spring, which normally brings with it new life, is instead filled with eerie silence:
The roadsides, once so attractive, were now lined with browned and withered vegetation as though swept by fire.
The juxtaposition of the natural, wholesome beauty of the present with the devastation of environmental collapse is meant as a warning for Carson's readers. The title itself, Silent Spring , is a condensed version of this juxtaposition, since it's meant to signify the vanishing of songbirds.
Juxtaposition in Shakespeare's Henry IV Part 1
In Shakespeare's history play Henry IV Part 1 , a monologue of Prince Henry's reveals that Henry himself is thinking in terms of juxtaposition. In the speech, he outlines how his current reputation as a reckless youth will make his eventual "reformation" into a responsible king look even better: he imagines his changed behavior as shining "like bright metal on a sullen ground."
... nothing pleaseth but rare accidents. So, when this loose behavior I throw off And pay the debt I never promised, By how much better than my word I am, By so much shall I falsify men's hopes; And like bright metal on a sullen ground , My reformation, glittering o'er my fault, Shall show more goodly and attract more eyes Than that which hath no foil to set it off.
Juxtaposition in Film
In film, juxtaposition can come not just from contrasts and comparisons created between characters and dialogue, but also from editing together different images, so that the cut from one image to another tells a story.
Juxtaposition in Stephen Spielberg's Jaws (1975)
In Stephen Spielberg's iconic thriller, Jaws , the director uses juxtaposition to heighten the film's suspense as the massive great white shark stalks its unsuspecting prey. In quick succession, Spielberg cuts from lighthearted beach scenes (children playing on the beach, surfers paddling out to sea, and lifeguards relaxing) to underwater shots with suspenseful music, hinting at the presence of the shark. The viewer is unsure who will be the shark's target, but this juxtaposition between the cheerful world above the water and the frightening creature underneath it creates a sense of fear and anticipation of what's to come.
Juxtaposition in Photography
When a photographer composes an image, selecting what elements to include in their pictures, he or she might consider how different elements in the image will relate to one another when they are juxtaposed. This relation is part of what allows a photographer to tell a story with just a single image.
Juxtaposition in Marc Riboud's "The Flower and the Bayonet" (1967)
In this famous photograph from the era of the Vietnam War, French photographer Marc Riboud captured an image whose power comes from a striking juxtaposition. A young protester, Jan Rose Kasmir, who was 17 at the time, holds a single flower up to the line of bayonet-bearing soldiers who are attempting to control the anti-war demonstration. The juxtaposition of this fragile symbol of peace and innocence with the heavily armored soldiers (who represented the war effort) became an important image in the Vietnam protest movement.
Juxtaposition in Song
Many songwriters also make use of juxtaposition as they present images in their songs and, as in the case below, the technique can also be used to suggest conflict.
Juxtaposition in Billy Joel's "Uptown Girl"
This catchy classic by Billy Joel deals with the timeless theme of romance across class lines. In this case, Joel is the "downtown man" who is pursuing an "uptown girl," and the juxtaposition of their two worlds (the "backstreets" and the "white bread world") helps encapsulate their different backgrounds.
Uptown girl She's been living in her uptown world I bet she's never had a backstreet guy I bet her momma never told her why I'm gonna try for an uptown girl She's been living in her white bread world As long as anyone with hot blood can And now she's looking for a downtown man That's what I am
Why Do Writers Use Juxtaposition?
Juxtaposition is an important technique for any writer, and can serve a variety of purposes:
- To draw a comparison between two ideas.
- To create contrast, highlighting the difference between two elements.
- To create an absurd or surprising effect (i.e., by inserting an element into a setting where it seems wildly out of place).
- To make one element stand out (i.e., by painting a white dove on a red background).
- To bring differing perspectives together in one story.
- To suggest a link between two seemingly unrelated things or images.
Other Helpful Juxtaposition Resources
- Merriam Webster definition : This dictionary definition is a to-the-point description with simple examples.
- Hollywood Lexicon : This entry provides more explanation of the role of juxtaposition in filmmaking.
- Uptown Girl video : The original video for Billy Joel's Uptown Girl.
- Lost juxtaposition fever : This page, created by fans of the TV series Lost , tracks the many instances of juxtaposition in the show's structure.

- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1913 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,305 quotes across 1913 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
- Figure of Speech
- Parallelism
- Understatement
- Foreshadowing
- Verbal Irony
- Static Character
- Characterization
- Connotation
- End-Stopped Line
- Tragic Hero


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Since antithesis is intended to be a figure of speech, such statements are not meant to be understood in a literal manner. Here are some examples of antithesis used in everyday speech: Go big or go home. Spicy food is heaven on the tongue but hell in the tummy. Those who can, do; those who can't do, teach. Get busy living or get busy dying.
Antithesis vs. Related Terms. Three literary terms that are often mistakenly used in the place of antithesis are juxtaposition, oxymoron, and foil. Each of these three terms does have to do with establishing a relationship of difference between two ideas or characters in a text, but beyond that there are significant differences between them.
Antithesis ( pl.: antitheses; Greek for "setting opposite", from ἀντι- "against" and θέσις "placing") is used in writing or speech either as a proposition that contrasts with or reverses some previously mentioned proposition, or when two opposites are introduced together for contrasting effect. This is based on the logical phrase or term.
Antithesis is the use of contrasting concepts, words, or sentences within parallel grammatical structures. This combination of a balanced structure with opposite ideas serves to highlight the contrast between them. For example, the following famous Muhammad Ali quote is an example of antithesis: "Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee.".
Antithesis (ann-TIH-thuh-suhs), put simply, means the absolute opposite of something. As a literary term, it refers to the juxtaposition of two opposing entities in parallel structure. Antithesis is an effective literary device because humans tend to define through contrast. Therefore, antithesis can help readers understand something by defining its opposite.
In literary analysis, an antithesis is a pair of statements or images in which the one reverses the other. The pair is written with similar grammatical structures to show more contrast. Antithesis (pronounced an-TITH-eh-sis) is used to emphasize a concept, idea, or conclusion. II. Examples of Antithesis.
When do writers use Antithesis? Writers use Antithesis to make their writing more memorable by creating rhythmic structure. The juxtapositions of opposing ideas also make writing more believable or authoritative. Antithesis is a rhetorical device that allows writers to create a rhetorical effect and elicit an emotional response in readers.
Antithesis involves the writer employing two sentences of contrasting meanings in close proximity to one another. Whether they are words or phrases of the same sentence, an antithesis is used to create a stark contrast using two divergent elements that come together to create one uniform whole. An antithesis plays on the complementary property of.
Antithesis. Antithesis occurs when contrasting ideas are expressed in close proximity with the effect of both highlighting the contrast and balancing the opposing elements. Writers typically use ...
Antithesis is a literary device that involves the use of contrasting concepts, words, or sentences within parallel grammatical structures. The purpose of antithesis is to create a contrast between two ideas, emphasize their differences, and create a memorable and impactful statement. It is a common rhetorical device used in literature, poetry ...
Familiar antithesis examples: "That's one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.". "No pain, no gain.". "Out of sight, out of mind.". The word "antithesis" comes from the Greek word meaning "setting opposite," which is an idea that has been used in various forms. Let's look at those various forms in more ...
An antithesis is just that—an "anti" "thesis.". An antithesis is used in writing to express ideas that seem contradictory. An antithesis uses parallel structure of two ideas to communicate this contradiction. Example of Antithesis: "Float like a butterfly, sting like a bee." -Muhammad Ali. This example of antithesis is a famous ...
The words in bold in the following example create antithesis. 1. He made one woman, and he made one man. The paired sentences form an antithesis because they are in a parallel structure. "He made one" is the same structure repeated again. Furthermore, The words "woman" and "man" represent opposites. 2.
Antithesis, which literally means "opposite," is a rhetorical device wherein opposite thoughts are prepare in a sentence to obtain a contrasting effect. Antithesis emphasizes the idea of assessment through parallel structures of the contrasted terms or clauses. The structures of terms and clauses are similar, so that it will draw the ...
Writing How to Use Antithesis in Your Writing: Definition and Examples of Antithesis as a Literary Device. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Sep 29, 2021 • 3 min read
An antithetical observation by Roman rhetorician Quintilian, quoted by James Jasinski in Sourcebook on Rhetoric (Sage, 2001). See additional examples below. Antithesis is a rhetorical term for the juxtaposition of contrasting ideas in balanced phrases or clauses. Plural: antitheses. Adjective: antithetical .
When used as a literary device, antithesis is designed to be used to sway the opinion of the reader or listener through the statement itself. An example of this comes once again from Martin Luther King when he said: " we must learn to come together as brethren or perish together as fools. " In this context, the antithesis is being used to ...
Antithesis is the juxtaposition of two diametrically opposite or strongly contrasting elements contained within a parallel grammatical structure. It comes from the Greek word antitheton, meaning "opposition.". Antithesis is not only used to emphasize the difference between two things but also to define them.
Antithesis occurs when two opposing ideas are placed side by side in a sentence to highlight their stark differences. This technique is not just a stylistic choice; it serves as a critical element in rhetoric and literature, sharpening arguments and adding depth to narratives. The importance of antithesis cannot be overstated.
In literature, antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, often within a single sentence or closely connected sentences. The purpose of antithesis is to emphasize the difference between the two ideas and create a clear contrast, which can help clarify the author's intention, provoke thought, or add ...
antithesis: [noun] the direct opposite. the rhetorical contrast of ideas by means of parallel arrangements of words, clauses, or sentences (as in "action, not words" or "they promised freedom and provided slavery"). opposition, contrast. the second of two opposing words, clauses, or sentences that are being rhetorically contrasted.
Antithesis involves a specific grammatical structure: Antithesis is a figure of speech that involves a very specific parallel sentence structure. Juxtaposition is a literary device that simply refers to a contrast set up between two things in some way, but it does not necessarily have to involve a defined grammatical structure.