- Revolutionizing Digital Communication: The Power of Olly and AI
- AI-Powered Video Editing with Snapy.ai: The Future of Content Creation is Here
- Dawn of AI-Powered Video Editing: Transform Your Videos with Silence Remover Online
- The Dawn of Generative AI: Why and How to Adopt it for your Business
- Harnessing the Power of Generative AI for Business Innovation: An Exclusive Consultancy Approach
Original content with a single minded focus on value addition.
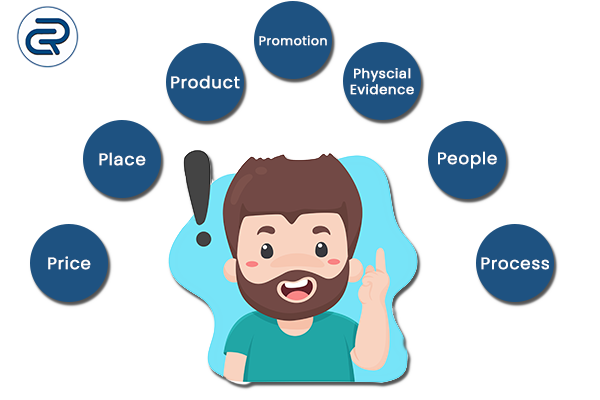

7Ps of Marketing Mix: Explained well with examples
Learn everything about the 7Ps of Marketing mix, Understand why this concept is still relevant today and will be relevant for the foreseeable future. The 7Ps of Marketing is the Price, Place, Promotion, Product, People, Process and finally, Physical Evidence.
It originally started as 4 Ps, but as the world, and the complexities of marketing grew; 3 more were added to formulate an effective marketing strategy. The ‘P’s stand for each of the pillars of a marketing strategy, and together are a part of the concept called the ‘marketing mix’. The term ‘marketing mix’ sounds a little confusing, but in essence, it is a foundation model for businesses. More easily explained, it is the operational part of a marketing plan- the nuts and bolts of it.
Funfact, there are actually 9Ps of Marketing: The above 7+2 viz. Packaging and Payments. But the 7Ps are popular given their wide and timeless application in the World of Marketing. Anyway, let’s just straight in the post.

The 7Ps of Marketing: With Examples
We can understand this with the example of a rainbow. The 7 colours of a rainbow and the 7Ps in a marketing mix bear a resemblance. Just as not all rainbows have the same the composition of the VIBGYOR colours, the same way every marketing plan is unique and contains varying amounts of the 7Ps of the marketing mix. The components are explained in the following points
One very important aspect of any product/success being a success in the market is the price at which it is marketed. The first colour of the marketing mix rainbow is one of the determining factors of what the people will see. Marketers tread very carefully while setting a price that is a win-win situation for both the company as well as the consumers.
There are several pricing models. One of the most famous ones is Competitive Pricing Strategy as is used by Coca-Cola. Coca-Cola’s main aim is to penetrate the markets and achieve the highest market share without compromising on its customer base and product positioning. Thus, the company charges its consumers what its competitor Pepsi is charging. It’s a simple, yet highly competitive strategy as the name suggests.
It is the channel through which your company’s goods/services get moved from the manufacturer to the consumer. Your good/service will need to be brought into the market through a mechanism, and ‘place’ is exactly that- a way for your offering to be seen by the correct audience. An example of this element of the marketing mix can be the numerous branches of McDonald’s all over the world. Almost every country in the world either has a McDonald’s franchisee, or knows of it. And each country has its unique menu, with the standard guarantee of tasty food, served fast, at low prices.
The Product
This is the P that starts it all. The need for this P to be known, positioned, and showcased gets the marketers working hard at strategies. ‘Product’ is the offering that your company has for the market whether it is a tangible good or intangible good (services). The product development has various stages, and it is instrumental in being the deciding factor in many strategies. Various aspects of a product like the product life cycle, the type of need it services, and its positioning come into play with this P.
We can consider the example of Starbucks here, which was solely established to make good quality coffee and coffee beverages accessible to people. Starbucks’ approach to marketing is very focused on its product and the quality of the product provided to its customers.
The Promotion
Directly speaking, the mainstream meaning of the word ‘Promotion’ also applies here. The essence of promotion lies in the activities that a marketer does in order to showcase the product in the market in the right sense. Promotional activities involve multi-channel, multi-level marketing communications in the technical sense. In a more simplistic sense, these activities are the communications that the companies indulge in like advertising, direct calling, using social media channels, as well as print media. There are many instances of how promotional activities have set a product apart from its competitors in the industry. One such is the launch of Sony Xperia Z3 Dual in 2014 as an underwater pop-up store.
The Physical Evidence
Physical evidence is a part of the product. If your product is a tangible offering, then all of its material cues (packaging, business cards, brochures, company branding) will be taken notice of, by the consumers. However, these tangible cues are also attached to a product that is intangible. The example can be, every time you encounter a FedEx delivery vehicle, you’ll immediately recognize it because of its purple and orange color scheme. That’s how they’re set apart from all the other delivery companies.
All the people involved in the making, distributing, and selling of your company’s product are also essential. Mostly, services (intangible offerings) have marketing mixes which are focused on the people presenting the product. The employees you have in the store, the delivery personnels, the sales executives, all of it and more leave a lasting impression on the people. Hotels like Taj, Hyatt, JW Marriott are known for the people that work there to serve the consumers. These brands have established themselves and built loyal customer bases due to the kind of people they employ.
The Process
Process involves all the ways the company and its customers can engage in order to facilitate the product to reach the consumer. It’s a map of how the company and its offerings are accessible to the market. It isn’t just a means to an end, but a roadmap of the company’s operations.
Here again, we can consider Starbucks as it has so many different ways in which the company operates- joint ventures, retail store licensing operations, food service accounts, depending on which country they’re operating in. They have an interactive website in order to collect customer feedback and suggestions, which also tells people how accessible the company is for the consumers.
Now, rounding up these 7 colors of the rainbow. We see that all these aspects ring in something essential for the business to gain competitive advantage. Though every product, every industry will have a unique marketing mix, the underlying structure will always be based on these 7 elements.
The 9Ps of Marketing you say?
Well yes, in the recent times, there appears to have introduced 2 more Ps vs earlier mix, now making the concept 9Ps of Marketing mix. We’ll keep this one short given you’ve gotten the gist. The 8th P is Packaging. Why? Given how connected the packaging has become to a customers journey, we cannot really let this one go, can we? Take the example of Paper Boat, the reason it connects so well is because of the simple packaging.
The 9th P of Marketing is Payments, it talks about the initiatives that companies can undertake in order to make your payment procedure a little more simple. That is introduce one click payment, EMI options, etc.
Anyway, that is all.
And well, the Author
No, this isn’t the 10th P of marketing. However, we believe, given the world has evolved today, there must exist a new P, a new dimension of Marketing. Something around Data Analytics, maybe, Programming? eh?
Anyway, the piece was written by Mahek Mirchandani , a co-author at Casereads. We’ve uploaded 10+ MBA starter concepts to kick start your MBA journey, directly click here .
Before you go, if you liked this piece, and if you have a friend starting their MBA; Why not be a good friend and share this with them on WhatsApp ?
7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing, 9Ps of marketing, 9Ps of marketing, 9Ps of marketing, 9Ps of marketing, 9Ps of marketing, 9Ps of marketing, 7ps of marketing
- What is WACC in Finance? Everything you need to know
- Ola case study: The story of a Millionaire without a car
You May Also Like

Drone market in India: Taking flight

Cloud Kitchen Industry in India

What is Nation Branding?
2 thoughts on “ 7ps of marketing mix: explained well with examples ”.
Pingback: Story Of Paper Boat: A Nostalgic Walk Down The Memory Lane
Pingback: McKinsey 7s Framework With Examples
Comments are closed.

Home Marketing Strategy The Marketing Mix: Building a Strategy With the 7Ps
The Marketing Mix: Building a Strategy With the 7Ps
“The marketing mix” aims to provide a complete framework for modern business models and marketing strategies across the entire customer journey.
While there are many variations of the marketing mix, the most common framework consists of seven elements, collectively known as the 7Ps. The idea is that a business can adopt the 7Ps principle and use it as a seven-step framework for building a successful marketing strategy that covers every stage of the buying process.
In this article, we look at how you can use the marketing mix to build a complete strategy, plus a few tips for improving the 7Ps model.
What is the 7Ps model?
The 7Ps marketing model is a framework designed to help businesses build a complete marketing strategy, from start to finish. In theory, a new business should be able to use the 7Ps model to devise an entire marketing strategy from scratch.

The name derives from the seven elements outlined in the 7Ps model, which all begin with the letter “P”:
- Physical evidence
The 7Ps model is an evolution upon the 4Ps model originally founded by E. Jerome McCarthy in 1960, in his book Marketing: A Managerial Approach . The original marketing mix concept was created during a time when the majority of businesses sold physical products and it was updated in the 1980s as more service-oriented businesses started to emerge.
The evolution from 4Ps to 7Ps
As mentioned in the previous section, Jerome McCarthy’s 4Ps model was created for businesses selling products to consumers.
As Smart Insights explains:
“The 4Ps were designed at a time where businesses were more likely to sell products, rather than services and the role of customer service in helping brand development wasn’t so well known.”
The original 4Ps included:

These same four elements still exist as the primary components of the 7Ps models. As business and consumer markets have evolved, the application of the marketing mix has adapted, too. In 1981, Bernard H. Booms and Mary J. Bitner expanded McCarthy’s model into the 7Ps marketing mix we know today.
While the original 4Ps remain in place, Booms and Bitner added a further three Ps in the mix:

The 7Ps model was created to reflect the emergence of service-oriented businesses where “Product” can mean either prospects or services. The expanded model also increases the emphasis upon customer service, as a result of increased consumer power and competition in every industry.
Like its predecessor, the 7Ps marketing mix has adapted to the evolution of consumer trends and new technologies.
In his book, Digital Marketing: Strategy, Implementation and Practice , digital strategist and co-founder of Smart Insights, Dave Chaffey, refreshed the 7Ps model for the modern digital age.

Some marketers argue that the 7Ps model is outdated but, even in 2021, it’s the backbone for business models and marketing theories. In fact, even the older 4Ps model is as relevant today as it was in 1960, even if it doesn’t cover the entire marketing mix in the modern, digital age.
This will become more obvious throughout the rest of this article as we look at each of the 7Ps individually and, later, assess whether there are any gaps or weaknesses in the model.
Applying the 7Ps to digital marketing
Now that you understand the basic premise of the marketing mix, let’s take a closer look at the 7Ps model that’s most widely associated with it today. Let’s start by reminding ourselves of what the 7Ps stand for and explain a bit about what they actually mean.
- Product: The product or service, including its features, unique selling points and the overall quality on offer.
- Promotion: The methods used to promote the product across multiple channels.
- Price: The long-term pricing strategy of the product in question, including sales, discounts & deals.
- Place: Where people find your product, learn about it and, ultimately, buy it.
- People: The people who come into contact with your target customers – both directly and indirectly.
- Process: Your methods for delivering the product to customers and providing the best possible experience.
- Physical evidence: Tangible items and experiences that tell customers your offer is real – for digital, this can include website visits, confirmation emails, testimonials, customer reviews and more.
Now, it’s worth reaffirming the point that the original 4Ps are solid figures in the updated 7Ps model but you will find some variation in the three additional Ps added into this model, depending on where you get your information from.
We’re sticking to the original 7Ps model for this part of the article but we’ll look at ways you can adapt and expand it even further to meet the needs of your business later on.
#1: Product
The first P in this marketing model is “Product” and this is almost unanimously featured as the first P in all versions of the marketing mix. This is because one of the core principles of this theory is that marketing begins with your product.
At the end of the day, if you’ve got a lousy product – especially in this day and age – you’re going to have a hard time marketing it.
The key elements of the product in your marketing mix can vary, depending on which market you’re and who your target audiences are. But, at the very least, you should invest good resources into the following:
- Quality: Higher product quality makes everything else you do in marketing and sales so much easier.
- Image: This refers to how people see your product and this is what separates products like the iPhone from Android devices or sports cars from cheaper, more practical vehicles.
- Branding: Closely linked to “image”, this is the brand story you build around your product and how it incorporates with your wider brand image.
- Features: The features of your product or service, which should place a heavy emphasis on USPs and benefits for your target customers.
- Variants: The different versions of your product or service, who they target and how you differentiate them.
The list could go on-and-on for Product and if you go back to Dave Chaffey’s version of the 7Ps we looked at earlier, you’ll see this is the longest list in his visualisation.
His list isn’t definitive or complete either; it’s up to you to decide which items belong on this list for your business. The point is that your product (or service) is the focal point of your marketing strategies and you want to do everything you can to ensure the right level of quality is there.
Take TrueNorth for example. The first thing you see on the homepage is the Product; It’s branding (both the name and visual style), product imagery, and a video walking through the product features.

#2: Promotion
Promotion refers to your marketing, advertising and sales activities across all channels. Once again, your channels of choice will vary depending on the nature of your business. For example, a B2B company may prioritise account-based marketing while a B2C company in the same industry might focus more on direct marketing methods.
Above all, you need to be present where your target audiences are active and interested in a brand like yours.
Given the rapid evolution of multi-channel marketing, this is one area where a version of the 7Ps model from as recent as five years ago can quickly look dated.
Here are some key elements to consider:
- Multi-channel marketing: The consumer journey takes place across more devices, sessions and platforms than ever before, making it all the more important that you’re present on the channels that matter most to your target audiences.
- Personalised experiences: The more relevant you can make experiences to individual users, the more engaging your messages become and the more “locked-in” customers are to your brand.
- Integrated marketing & sales: Today’s brands need seamless integration between marketing and sales strategies to prevent leads getting lost along the funnel.
- Lead nurturing: A lot of brands make the mistake of focusing all of their attention on lead generation without dedicated enough resources to lead nurturing – especially customer retention.
- Branding: Today’s consumers want authentic experiences and brands are scrutinised for their ethical practices, making brand image more important – and fragile – than ever.
- PR: Brands don’t always give PR the attention it deserves in the digital age but it’s an invaluable tool for building, maintaining and even changing your brand image.
- Automation: As the digital marketing workload increases, brands need to automate as many repetitive tasks as they can to manage multi-channel campaigns successfully, maintain costs and achieve the fastest possible growth.
There’s no doubt that the Promotion aspect of the 7Ps model is getting more challenging with every year that passes, as technology and consumer trends become more complex.
The days of running a few TV ads and blasting out some unsolicited email campaigns are long behind us.

Today’s brands need to use the right marketing and sales software to maximise productivity, automate repetitive tasks and manage campaigns across an ever-growing number of channels.
Take a look at some of our software recommendation articles for help with this:
- 30+ Best Free Marketing Tools
- 10 Best All-in-One Email Marketing, Automation & CRM Platforms
- 53 Business Automation Tools That Skyrocketed Our Growth by 330%
Price is pretty self-explanatory but the mistake companies normally make is underestimating the amount of detail that goes into pricing a single product – let alone an entire range of products or services.
Here’s a list of just some of the things you need to strategise:
- Positioning: Where do you see your product, service or brand positioning in the market?
- Competition: The price of rival products, brand image of rival brands and competing quality of the products on offer.
- Justification: As soon as someone spends money on goods or a service, they instinctively spend time trying to justify the expense – and you need to make sure the result is worth the asking price.
- Discounts: Discounts should be strategic and planned out to maximise interest, demand and sales – not to clear unwanted items off the shelves.
- Credit: Are you going to offer credit options to make large purchases and expenses more manageable for your customers?
- Payment methods: Which payment methods are you going to provide your target customers?
- Free or value-added elements: Which freebies, value-added elements and incentives are you going to use to sweeten the deal for your prospects.
Value is highly subjective and the happiness of your customers with their purchases is determined far more by emotion than logic. As we’ve explained before in our articles on cognitive biases , you can influence consumer perception with simple psychological techniques.

A common example of this is software pricing pages where companies start with the most expensive price on the left side of the page. This exploits a cognitive weakness known as anchoring bias where people instinctively set the first piece of information they see as default, meaning any lower prices that follow naturally feel like good value.
Place is the final P in the original 4Ps model and this traditionally refers to the place where customers physically buy products and services. Of course, in the digital age, things are a little more complex and we have to expand the concept of place across multiple channels throughout the customer journey:
- Discovery: The “places” both online and offline where potential customers discover your brand and its products/services.
- Browsing: The locations where prospects can browse through your offers alongside competitors (e.g.: an online store) or within your own domain (e.g.: a product category on your website).
- Learn: Places where target audiences can learn more about your products or services, such as third-party reviews.
- Comparison: Where potential customers go to compare your offers against rival brands.
- Physical interaction: Any place where prospects are able to physically touch the product or service (if relevant) although this could apply to free trials and demos for digital products, too.
- Purchases: Online and offline locations where your customers can purchase from you.
- Customer services: The channels where customers can reach out for care after making the initial purchase.
- Retention: The channels you use to target customers after the initial purchase to entice further sales.
Place in the digital age refers to every strategic location where potential customers engage with your brand and its product or services – both before and after the sale.

The point is, you need to control these locations, which starts with choosing the right channels of discovery to capture new leads and then nurturing prospects along the sales funnel with targeted interactions.
In today’s customer-centric approach to marketing, you might assume “People” refers to your target audiences, buyer personas and customers. However, the People in the 7Ps model actually refers to the people within your organisation that interact with your customers – both directly and indirectly:
- Marketers: The 7Ps model highlights the importance of hiring the best talent for every position on your marketing team.
- Sales team members: These are the people who typically handle the first person-to-person interactions with your customers – and often seal the deal.
- Customer service team: The individuals tasked with keeping your customers happy, even when things aren’t quite going to plan.
- Recruitment: Hiring the best talent starts with having quality recruitment personnel.
- Training & skills: The people responsible for ensuring all of your team members encompass the brand ethos and meet your requirements.
- Managers: The people with people skills to manage teams, get the best out of everyone and ensure you hit targets.
Chances are, you’ll have several other groups or teams included in your People. Here at Venture Harbour, we’ve got the developers who build and test our products, designers who create the best possible experience for our customers and a pool of freelancers we turn to for a range of different tasks.

Everyone in our team contributes to building and delivering the best product and experiences we can to our customers – and it’s important we recognise the value in that.
For more information on how to build and manage a marketing team effectively, you can read our guide:
- Marketing Teams: How to Structure & Manage Them Effectively
#6: Process
Process in the 7Ps model refers to your processes for delivering the product or service to your customers, as well as any additional customer service and post-purchase systems you have in place.
At the very least, you should have processes in place for the following:
- Customer-end delivery: The customer’s process for attaining your product or service, whether it’s ordered online and delivered via a courier, bought in-store, downloaded from your website or accessed through an online sign-up process.
- Business-end delivery: Your processes for facilitating customer-end delivery and safeguards for resolving any potential issues (e.g.: technical issues preventing online purchases).
- Customer service: Your processes, systems and channels for providing customer service beyond the initial sale.
- Resolutions: Your processes for dealing with problems that prevent usual delivery systems from completing successfully and instances where customers are unhappy with the process/service received.
- Incentives: Measures designed to keep unhappy customers engaged with your brand so you can keep them on board and win them over.
- Returns & refunds: Your systems for dealing with returns, cancellations, refunds and any other processes for customers who refuse to stay on board.
- Feedback: Your processes for collecting customer feedback and applying these insights to product/service improvements.
- T&Cs: The terms and conditions that your customers agree to, specifying your processes and protecting your business in any instance where things don’t go to plan.
You have to carefully and strategically build processes for every customer interaction, down to the finest detail. When your primary method of delivering products or services to your customers fails, you need a solid backup plan – and another one for when your Plan B fails, too.
Today’s customers have more options than ever and modern businesses need to satisfy these expectations – from delivery methods and payment options to customer service channels and financial guarantees.
If you’re doing this properly, you’ll be forced to make some difficult decisions and it’s not always a question of doing what’s best for the customer. For example, you don’t want to make it too easy for customers to seek a refund, return items or close accounts. You want to carefully add some friction here and there to provide crucial time for resolving issues and encourage continued use.

Likewise, your customer service processes need to be effective in terms of keeping customers on your side but they also need to be affordable and it’s not always realistic to have an in-house team of customer care staff sitting by the phones every day.
Once again, technology can help you strike the right balance between customer care and profitability – for example, using chatbots to handle the first interactions with customers. Likewise, personalised automated email responses can cut the perceived time it takes for human team members to contact customers directly.
#7: Physical evidence
The final P in the 7Ps stands for Physical evidence and this used to refer to actual physical items and forms of interaction: products, stores, receipts, packaging, bags and other branded items that could be seen and touched.
Of course, these are all forms for physical evidence today but, in the digital age, we have to reconsider our definition of “physical”.
So what does physical evidence really achieve?
Well, on one hand, it helps customers feel more confident that they’re dealing with a legitimate business before they make a purchase. A company with stores across the country, great products and nice packaging must be doing pretty well for itself and, surely, this wouldn’t be possible if they weren’t taking good care of their customers – right?

The second key role physical evidence plays is after the initial sale by providing customers with evidence that the transaction took place, their payment was received and their products or services will be delivered.
- Places: This was the fourth P on our list of 7Ps and these locations act as physical evidence – whether it’s your website, physical stores or trusted third-party platforms.
- Third-party evidence: Customer reviews, press coverage in major publications and positive press are especially important in the digital age where simply having a website doesn’t provide the level of physical evidence real-world stores.
- Online experience: That said, the quality of your website and the user experience it provides are crucial forms of physical evidence in the modern consumer journey.
- Feedback: Sales staff provide all kinds of feedback through conversation, facial expressions and body language, which is lost in the online experience. So it’s important to design intuitive feedback into the experience – everything from click confirmations and animations to on-page feedback when forms are completed and payments are submitted.
- Order confirmation: Whether it’s physical receipts or confirmation emails, customers need to know their transactions are successful.
- Product packaging: Both the physical and digital packaging/branding of your products or services.
Physical evidence is primarily about easing consumer concerns and purchase anxieties by reassuring potential customers that your business is legitimate, their money is in good hands and the purchase is going to go smoothly.
By providing feedback across the entire customer journey, you can confirm that every little interaction is successful and build reassurance as they get closer to putting their money on the line.
What are the limitations of the 7Ps model?
There’s no such thing as a perfect marketing model and, no matter how comprehensive a list we make for each of the 7Ps, there’s no way it can cover every aspect of a digital marketing strategy.
In fact, there are various different versions of an 8th P added to the model of seven, depending on which marker you speak to. As Smart Insights explains in this article , “An eighth P, ‘Partners’ is often recommended for businesses to gain reach online… although some would argue it’s part of Place.”
Other incarnations of a proposed 8Ps model may include Performance, Productivity, Packaging or a range of other alliterated alternatives for the enigmatic title of the eighth P.
If this debate tells us anything, it’s that the 7Ps model clearly has its limitations and there have been plenty of expansions or alternatives proposed in the past.
For me, the glaring omission in the 4Ps and 7Ps models is the lack of reference to the end customer in both of them. In fact, on a broader scale, neither model even makes a reference to market research and ensuring there’s a large enough target audience for the product or a demand for it.
I guess you could solve this problem without changing the 7Ps model by simply including customers in People and market research in Product. However, stronger alternatives have been offered in “the age of the customer” while others can be used to expand upon the 7Ps model.
In 1990, Robert F. Lauterborn proposed his customer-centric alternative to the 4Ps model, which we can crudely call the 4Cs:
- Customer needs
- Convenience
- Communication
This offers a more customer-centric alternative to the traditional 4Ps model that feels a lot more suitable for the modern age. However, there are problems with simply replacing the Ps for Cs.
As we mentioned in the Process section earlier, if you only consider the customer in your delivery methods, you can easily overlook the business management side of things. Likewise, if you think of the customer with your customer service processes, then you can end up creating a system that hurts your bottom line – either by being too generous or overspending on your customer care systems.
While it sounds great to talk about the customer experience as the priority (perhaps it should be), it’s not the only factor in a successful business, by any means – or a complete marketing strategy for that matter.
As Hannah Tow suggests in her article for G2 , we might be better off extending the 7Ps even further to include the 4Cs, allowing us to look at Price from the business’ perspective and also the Cost from the customer’s point of view.
Create the model that works for you (and your customers)
The 7Ps model isn’t a fixed framework that you have to follow religiously. It’s more of a template that helps you consider every aspect of marketing across the entire journey – so you don’t overlook key factors like how physical evidence increases confidence and enhances the customer experience.
It’s a model that you should scrutinise, adapt and reshape to suit your business, your target audiences and your customers. Whether this means staying relatively true to the original 7Ps, expanding it with the 4Cs or coming up with your own version is entirely up to you.
Just make sure you cover all of the essential bases to avoid leaving gaps in your marketing strategy and the customer experience.
Getting your marketing mix structured & organised
We’ve broken down a lot of theory, but how do you actually apply this and ensure you have marketing activity across all stages of the marketing mix?
Well, initially you may consider running an audit across all seven areas to identify which areas need attention. From there, you will want to come up with ideas and begin tracking these as campaigns/tasks in whichever tool you use to manage your marketing.

In TrueNorth , for example, you could allocate budget across the 7Ps and even track your marketing activity and results according to the various 7Ps to ensure you are doing enough in each area and to separate the campaigns that are designed to improve each of the seven areas.
While there’s no right or wrong way to do it, the key is to ensure you take stock of where you are and have a clear system in place to constantly improve in all areas of the marketing mix over time.

Aaron Brooks is a copywriter & digital strategist specialising in helping agencies & software companies find their voice in a crowded space.
More from Aaron
You may also like.

11 Best Go-to-Market Strategy Building Tools
Find out how to develop a successful go-to-market strategy for product launches – and discover the best GTM software.
Top 7 Funnel Mapping Tools to Map & Simulate Your Growth
Funnel mapping visualises every stage of the marketing and/or sales funnel, normally in the form of a flow diagram. This plays a key role in the planning and development of…

Marketing Forecasting: 10 Steps to Get it Right
In today’s data-driven world, insights should guide every marketing decision – no guesswork; no assumptions. Of course, you can’t predict the future, but you can model it to forecast the…

TrueNorth Serene Automation Insider StackUp
Popular Guides
Email Marketing Software Marketing Automation Software ActiveCampaign Review Webinar Software
About Blog Careers Contact
Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy | Editorial Policy | Terms of Use
© 2024 Venture Harbour. Ltd is a company registered in England and Wales. Company No. 8291791. VAT No. 290356105. Registered office: Lytchett House, 13 Freeland Park, Wareham Road, Poole, Dorset, BH16 6FA
- Growth marketing articles
- Marketing ops articles
- Marketing strategy articles
- Marketing acquisition articles
- CRO articles
- Content marketing articles
- Affiliate marketing articles
- Lead nurturing articles
- A/B testing tools
- CRMs (with automation)
- Email marketing software
- Growth Marketing Software
- Landing page builders
- Lead generation tools
- Marketing calendar software
- Transactional email services
- Webinar software

The Only Course You'll Need To Understand Marketing Like Never Before
How to Get Started with Marketing and Design Your Career in 5 Steps

7Ps of Marketing Mix with Examples What is the most important thing required to present that mouthwatering, scrumptious plate of food in front of you? That plate of food that you want to return to, over and over again. Its that Classic Recipe that makes the food taste heavenly every time you order it. In this article lets put these chef’s cap on our beloved marketers and see what their recipe looks like.

Do you know what consumers have to say to when their needs are not met? “I won’t complain, I just won’t come back” [Brown & Williamson, Tobacco ad]. In this game of no second chances, it is important to plan a successful product offering. That’s when we reach out to our good old friend- 7Ps of Marketing Mix to guide us.
The term Marketing Mix was originally developed by Neil Borden in the year 1949. It was E. Jerome McCarthy who gave the 4Ps of the Marketing Mix . After the emergence of the service economy , the 4Ps were promoted to 7Ps of Marketing Mix . People normally refer to them as the Service Marketing Mix .
With years, theories become old and people develop newer frameworks. But the Marketing Mix has been in the market for almost 70 years now. And still the young marketers, even today, are taught this as the alphabets of marketing.
During this reading, I want you to keep your awareness as a consumer awake at all times. We will learn the 7Ps of Marketing Mix with examples from our own lives and some from the Industry.
We will try to orient ourselves to the services sector, which was the prime reason behind the adoption of 7Ps of Marketing Mix.
What is Marketing Mix?
Before I start talking myself, I would like to ask you some fundamental questions.
Why are Organizations in Business? Don’t shy away from admitting that their sole purpose is to make profits.
When do businesses make those profits? Its when their product or service sells, actually sells better than others.
How are businesses being able to sell better? When the customer connects to their product or service.
And when does the customer connect to a business? When the needs are met and the customer gets reasons to come back to the business.

Source: surveysparrow.com
Keeping that in mind, we can now define the Marketing Mix as the set of guiding variables that help a firm to develop products and services keeping the target market in mind.
It is a combination of elements that help a firm to:
- Develop the right product/service
- Reach the right customer
- At the right time
- Make the customer feel right

Marketing Concepts Mastery Course
Learn the essential marketing concepts. Create the best outcomes from MBA without depending on placements!
Understand the 4Ps and 7Ps of Marketing, Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning, SWOT Analysis and many other important marketing frameworks just like an expert MBA professional would. Solidify your concepts while building a personal brand in marketing.
What Should You Care About the Marketing Mix?
We sure will learn about the 7Ps of the marketing mix in this article. But why is it necessary for us in the first place?
Future Product Managers: It helps you to channelize your product development keeping in mind the customer’s needs. As product managers it is important to always keep ears open to customer needs and eyes open to innovation.
Future Area Sales Managers: It is important that your product is made available to your customers conveniently and at all times. Place and the distribution network are very important to keep serving your customers.
Future Advertisement/Campaign Managers : Its very important that the target customers know about your product. Promotion either for new customers or the existing customers is a very important tool for campaign managers.
This list is not exhaustive but is very much indicative of the fact that this tool is a lever in the hands of marketers. They can play around with the various elements and direct their offerings to targeted segment/desired positioning.
The Marketing Mix traditionally had 4Ps- Product, Place, Price and Promotions . But these were found to be inadequate as far as services were considered which led to the extended Marketing Mix or the 7Ps of service marketing.
But what was the inadequacy? How are services different from products?
Also Read: 4Ps of Marketing
Characteristics of Services
There are certain characteristics which differentiate marketing of services from typical products. Let’s list down a few of those:
Intangibility:
A product can actually be felt- they are physically present. Various features of the product like color, shape and style can trigger emotions. The customers actually know what they are buying.
But that’s not the case with services. It doesn’t become evitable until the customer has actually leveraged it once.
Service firms are always trying to ‘tangiblize’ a service . For instance, take a look at the two images below:

The first picture is a menu from an Asian Restaurant. They have placed such colorful realistic pictures on their menu, its as if you can see your plate of food before you actually order it. In the second picture, you see the Japanese practice of showcasing plastic replicas of their dishes in order to entice the customer.
Don’t you think, these are absolutely genius ways to add senses and emotions to the hospitality services!
Inseparability
Just try and think about it! Can you clearly distinguish the sequential cycle of manufacturing, marketing, selling and then consumption of services? No, right!
Services have no distinction based on time and space. The service provider plays the twin role of production as well as delivery of services.
If you think through, the customer is usually a part of the production process of a service. Think of an airplane journey. Aren’t you the part of the service production process? This makes customers equally involved and, in that case, poor task executions by customers may lead to an overall bad service experience.
Perishability
Services cannot be inventoried . Like you can store products, its impossible store services for later sale.
For an example, the seats in airplanes are service provided by the airline industry. But it may happen that the flight is not fully booked. These empty seats perish as soon as the plane takes off. This is simply lost revenue.
Variability
A product is manufactured with standard operating procedures and is passed through various mechanized and manual quality inspections. Any particular product will look the same even after millions of units of production.
That is not the case with services. You may be visiting the same restaurant everyday but each occasion may turn out to be a unique experience. There are various external factors that govern your experience. On one day you may get your favorite seat, on the other you may have to wait in queue for the same services.
Service marketing is a seemingly complex task. Which is why, by now, I have begun to see the need for expanding the Marketing Mix.
7Ps of Marketing Mix
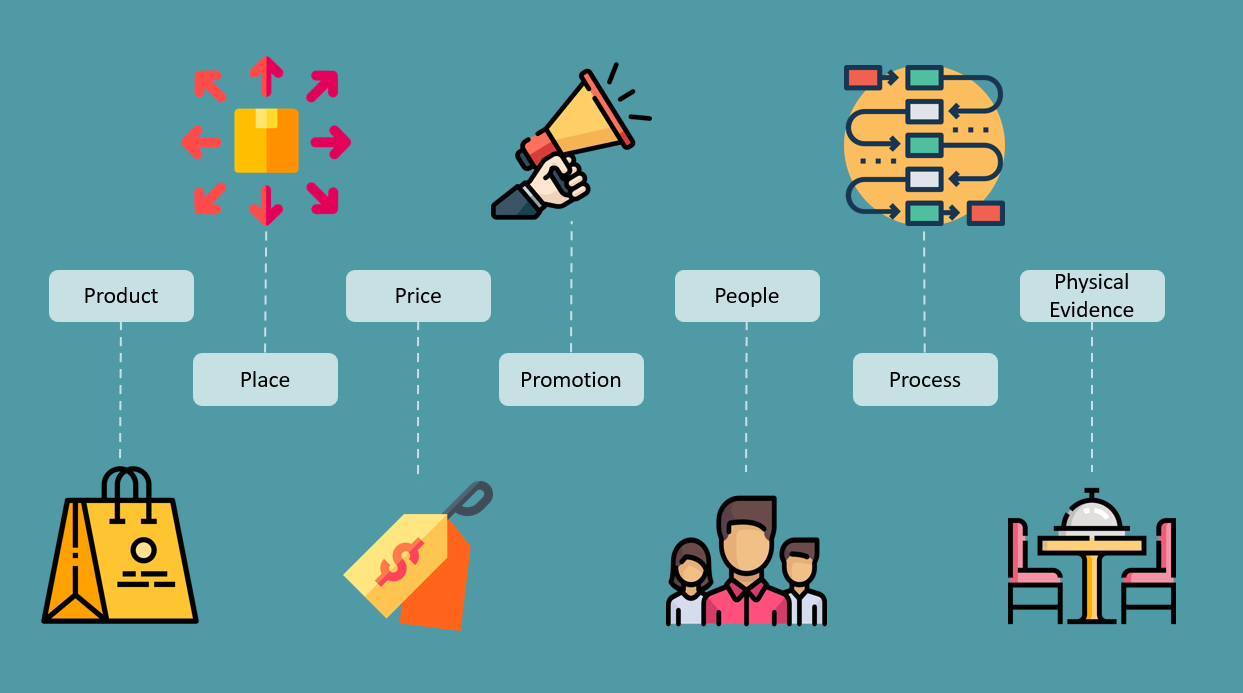
Because of the outlined differences between products and services and their implications, 7Ps of Marketing Mix were developed. The additional 3 Ps- People, Process and Physical Evidence , try to solve the deficiencies of the traditional Marketing Mix.
In simple terms, what is being sold to the customer is the product. It is the ‘Core’ which is offered to the customer.
Service products are intangible which means that the customer has to try the service once before selecting or rejecting a particular provider.
Like I said, this certainly has its advantages as the service provider can offer more customized services to its customer. This is one point that marketers should actually leverage for their advantage.
There are various things that have to be kept in mind while designing a service package, most of which coincide with how a product is conceptualized:
- The target market
- Product range
- Product quality
- Features and benefits
- Sizing and packaging
- Add-ons like guarantees and customer service
Source: Axis Bank
Just have a look at the kind of options that even a traditional industry like banking provides. That’s how firms orient themselves to their target markets and provide products and services that satisfy their needs.
Pricing is in itself a very tricky element among the 7Ps of Marketing Mix. Price can make or break a product/service launch. The first principle of pricing keeps in mind the value of the product or service that the customer perceives.
Product pricing is somewhat logical in the sense that you are able to see tangible material goods infront of you and you can, with some help figure out the approximate cost of the product.
But don’t you think it is quite difficult for you to assign value to services. Just think about it! When you go for a haircut, can you place a price on everything that the barber does and come up with the right price. Your price benchmarks are majorly your past experiences or how the competitors are pricing their service.
Pricing of services is not as objective as pricing of goods. Companies base their prices keeping in mind customer’s perception of the brand and also competitor’s pricing strategy.
There is this one good article that I found on pricing of services which I would like all of you to go through once: check it here.
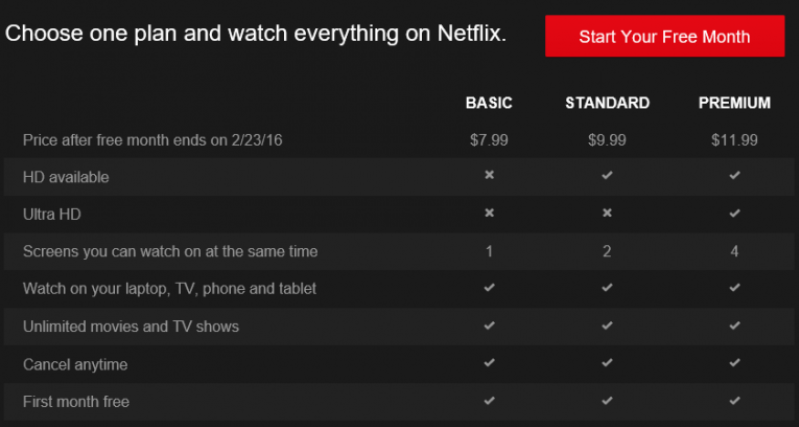
Also, checkout a very prominently used subscription pricing strategy from Netflix
Place is all about making your products or services available to right customers , at the right place at the right time. Place is a very critical element in the 7Ps of marketing mix.
For most routine services, customers want to stick to their locality and avoid travelling to far off places. It’s just for those highly specialized services like visiting a doctor for which you will take the inconvenience of travelling kilometers.
Just think of a scenario! What would you think if you went on a vacation and your resort was situated amidst the chaos of the city market? For the girls out there, it would be one hell of a shopping spree but Hey! It would be a complete mood spoiler for that Vacay-mode you would be in.
It’s important to take into consideration where your customers will be looking for your products or service, where do they spend most of their time and then decide your place or medium of distribution.
Intensive distribution which is reaching out to masses becomes somewhat difficult for services as services generally have a sense of personalization attached to them. But technology has surely brought about a change in terms of mobile banking and internet services.
Exclusive distribution is preferred for products and services that are sought after by customers for their uniqueness. Services like surgery and exclusive dining are made available through limited places.
Selective distribution in services can be best explained with the franchise model. McDonald’s is now made available in even Tier-II cities only because of this strategy.
Promotion in simple terms is the tactics used by firms to make their customers aware about their product, build their brand image and retail their customers.
Promotion is again a very strategic element because on one hand you want your target customers to know about your product or service but on the other hand you are under the pressure of The Invisible Hand- Promotion spend restrictions. Market segmentation helps a great deal in knowing who your customer is and then you can effectively promote to them.

Source: grihshobha.in
What do you think is Aashirvad trying to do here? Look at the product! It’s an advertisement in a famous women’s magazine. Now think who is the person responsible for taking buying decisions for this product? I know you have your answers.
The communication mix comprises of advertisements, sales promotions, direct selling, publicity, etc. The question is how is it unique for promotion of services. We have already established that services are intangible which poses a greater risk for customers to be doubtful about services.
Marketers need to assign tangible clues to their services so that the customer can rely on them. And we’ll see how they are able to achieve that. Just think of FedEx, what’s the first thing that comes to your mind. In my mind it’s a FedEx truck or the FedEx Airline carrier.
Now just think of what this means. FedEx is a courier service which needs to deliver goods at the right time. Hasn’t it created an image of fast mobility which makes you rely on the brands promises.

With that we conclude our traditional marketing mix elements and now let’s figure out the extended elements.
Services are generally characterized by frequent interaction of the creator and the consumer. Think about the beauty and self-care industry, hospitality sector or the banking industry. All of them require frequent customer-producer interactions.
It is expected from all employees to be trained on both fronts:
- Technical or core skills: Any compromise on employee skills not only damages the brand image but also leads to quality variations and service heterogeneity.
Customers lose their belief in brands whose front-end employees are not technically sound.
Just think of a situation when you go to buy a laptop at a retail store of one of the best brands in India. But you have an encounter with an employee who has to google features of the laptops. Will you trust him or the store with your money?
- Interpersonal Skills: With services, it’s very difficult to separate the service and the provider.
It’s the front-end employees like showroom sales men or receptionists who play the customer facing role even before the service experience can begin for your customer. Employee behavior can actually make or break a brand name.
Therefore employing, training and retaining the right set of people becomes imperative for the success of a service business.

Case Analysis Blueprint Course
Use marketing frameworks like these to solve business case studies with ease
Concepts like the 7Ps of Marketing are extremely crucial to analyze the most complex case studies. Get to know how to analyze a marketing case study comprehensively in just 5 slides. Which means that the next time you need to analyze a case, you know exactly how to ace the case
For the delivery of quality and timely services, it is important to design a robust process.
Think about that vacation when you booked a hotel online and you reach the place in the early hours of morning. You are in a completely new city and have heavy baggage with you. It’s a struggle in itself to find the hotel and then when you reach there you have to wait for some time in the lounge because apparently your room has just been vacated.
Let’s picture another scenario. You are about to reach your destination in the early hours and you get a call from your hotel at night. They give you a contact of the person who would come to pick you up and additionally ask about your breakfast preferences.
Damn! I don’t know about you but I will be ecstatic. You are escorted by the person in the morning to the hotel and you get straight to your room because the hotel had kept your room already neat.
That is the importance of a streamlined process of your service delivery. Businesses have to keep in mind that the process of service delivery is designed not for provider’s convenience but keeping the customer in mind.
With that we come to the last element in the 7Ps of Marketing Mix.
Physical Evidence
Physical evidence is important because of the intangible nature of services. The customer has to get some tangible clues in order for him to buy your services.
Cleanliness, dress of staff, wall color, website experience, packaging, brochure designs are some of the many factors in determining the customers decision towards buying that service.
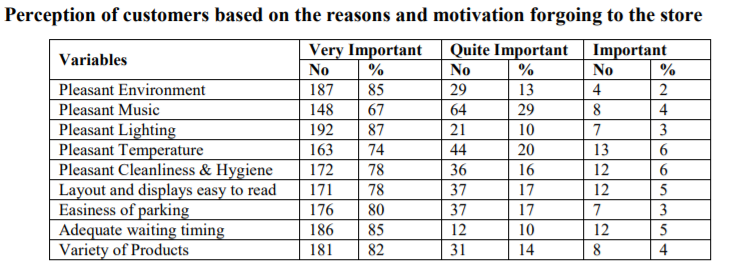
Source: ijmrr.com
I found this interesting table in one of the business research reports online. Just have a look at the multitude of variables that affect a customer’s perception.
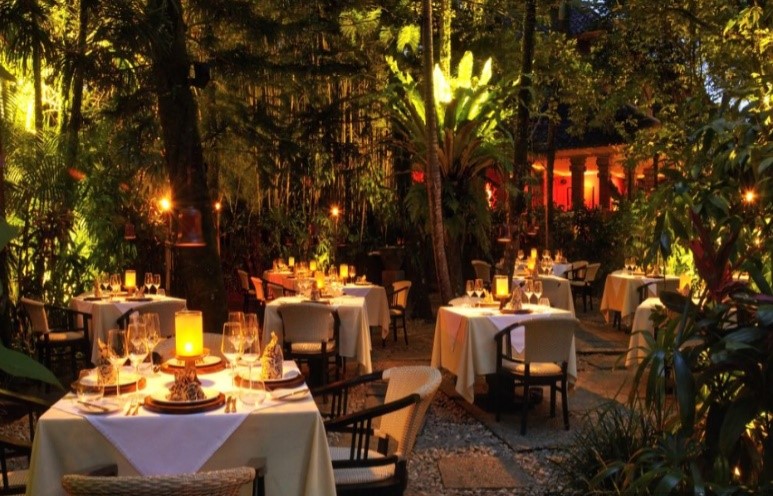

What do you think about the two images above? You should have spotted some differences in their setting.
The first picture is more elegant, chic and calls out for that fine date with your partner. The other one is a completely different social setting. Its more fun, bold, noisy in a good way and calls out that gang of yours to sit here and talk tirelessly.
That’s how marketers play with physical evidences to communicate to the customer, the services they wish to deliver.
Marketing strategy has to be used if businesses want to succeed in reaching to their customers faster than their competitors can get. And the 7Ps of marketing mix help them do just that.
Marketing helps a business to make their products or services aligned to the customer’s needs and make them reach their customers at the right place and at the right price.
The 7Ps of service marketing are as follows:
Product: It is the ‘Core’ which is offered to the customer.
Price: Matching your pricing with the customer’s perceived value of the product or service
Plac e: Making your product or service available to the customer
Promotion: Making your target customers aware about your products and services and retaining them
People: Having the right set of people inclined to serving the customers with their skills
Process: Streamlined process flow in order to reduce quality variations and provide seamless services to customers
Physical Evidence: Attaching tangible clues to services in order to communicate and satisfy your customers
You May Also Like

Factors Affecting Consumer Behaviour Have you ever thought that why do you purchase a certain kind of products? Why do you prefer specific brands over others? All of these things depend upon consumer behaviour. As future marketers, you have to analyse consumer behaviour. Before that, you need to know the factors affecting consumer behaviour. Read this article to have a clear idea about these.

Luxury Marketing and Luxury Marketing Strategies What is luxury marketing? What are the strategies of marketing luxury products? Stuck with an academic project that demands you to understand luxury marketing? Read on to understand all that is to know about luxury marketing with some interesting examples.
SWOT Analysis of Google Have you ever wondered about how Google has maintained its powerful position, throughout? We all know about its pseudo-monopoly in Search-Engine. I mean, nowadays everyone jumps to Google for every piffling query that we get! But is that the only reason of its success? Google has a sundry of apps/products under it. Are all of them successfully leading the charts?

How to Create a ‘Back of A Napkin’ Marketing Strategy Plan? Sometimes, you get stuck by an idea or a dream, and you get so mesmerised that you want to lay your hands on the next paper you find and start everything at once. We all have been there, but if I tell you businesses are no different in this aspect, would you believe me? Let’s find out more in this blog post and Create a Back of a Napkin Marketing Plan.

What types of Primary Market Research study should I use?

Classification of Markets – Traditional Markets What is a Market? That question seems simple but becomes tough to answer in a Marketing 101 class. Here in this article, not only will I share with you what is a market but I will tell you in detail the classification of markets (with a focus on Traditional Markets)

About the Author: Krati Pandey
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
7 Ps of Marketing and How They Apply to Your Marketing Mix Looking for picture perfect marketing formulas that will likely outlast and adapt to any trend? Read on.
By Brian Tracy • Apr 26, 2023
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
No matter what industry your business operates in, there is competition to outperform and ever-evolving trends to keep up with.
You must find a way to get your business to stand out. Whether you are trying to build a name for your business or maintain its stature, marketing is the key to getting people's attention and showing them what you can do.
Marketing strategies are roadmaps that allow your company to grow brand awareness and boost consumer engagement, relationships, and trust. It takes time, effort, and sometimes budget to build a marketing plan; however, it can pay huge dividends.
Once you've developed your marketing strategy, there is a "Seven P Formula" you should use to continually evaluate and reevaluate your business activities. The formula can help you create a system of checks and balances for physical evidence that your business is constantly evolving to ensure your marketing efforts reach your target audience .
With technology as an ever-evolving factor, updating your marketing campaigns to include more than just word of mouth is essential. Nowadays, you can use many distribution channels, like digital marketing, social media, and podcasts.
No matter which platforms you choose as your marketing tools, the seven Ps can serve as tried and true basic marketing tactics that you can adapt into your marketing efforts to best fit your business.
The 7 Ps of Marketing include:
- Positioning
Read on to learn more about the 7 Ps.
To begin with, develop the habit of looking at your product as though you were an outside marketing consultant brought in to help your company decide whether or not it's in the right business at this time. Ask critical questions such as, "Is your current product or service, or mix of products and services, appropriate and suitable for the market and the customers of today? Is this product offering any remedy to a customer's pain point?"
Whenever you're having difficulty selling as much of your products or services as you'd like, you need to develop the habit of assessing your business honestly and asking, "Are these the right products or services for our customers today?"
Is there any product or service you're offering today that, knowing what you now know, you would not bring out again today? Compared to your competitors, is your product or service superior in some significant way to anything else available? If so, what is it? If not, could you develop an area of superiority? Should you be offering this product or service at all in the current marketplace?
The second P in the formula is price. Develop the habit of continually examining and reexamining the pricing strategy of the products and services you sell to make sure they're still appropriate to the realities of the current market. Sometimes you need to lower your prices. At other times, it may be appropriate to raise your prices.
And other times, you need to research the competition to see what similar products in your industry space are going for, to ensure you are listing competitive pricing. Many companies have found that the profitability of certain new products or services doesn't justify the amount of effort and resources that go into producing them. By raising their prices, they may lose a percentage of their customers, but the remaining percentage generates a profit on every sale. Could this be appropriate for you?
Sometimes you need to change your terms and conditions of sale. Sometimes, by spreading your price over a series of months or years, you can sell far more than you are today, and the interest you can charge will more than make up for the delay in cash receipts. Sometimes you can combine products and services together with special offers and special promotions. Sometimes you can include free additional items that cost you very little to produce but make your product prices appear far more attractive to your customers.
In business, as in nature, whenever you experience resistance or frustration in any part of your sales or marketing plan, be open to revisiting that area. Be open to the possibility that your current pricing structure is not ideal for the current market. Be open to the need to revise your prices, if necessary, to remain competitive, to survive and thrive in a fast-changing marketplace.
Related: How to Create a Marketing Plan - Entrepreneur.com
3. Promotion
The third habit in marketing and sales is to think in terms of promotion all the time. Promotion includes all the ways you tell your target market about your products or services and how you then market and sell to them.
Small changes in the way you promote and sell your products based on segmentation can lead to dramatic changes and booms in your results. Even small changes in your advertising can lead immediately to higher sales. Experienced copywriters can often increase the response rate from advertising by 500 percent by simply changing the headline on an advertisement.
Large and small companies in every industry continually experiment with different ways of advertising, promoting, and selling their products and services. Right now? Search Engine Optimization (SEO) , is meant to improve the quality and quantity of traffic to a website.
But no matter what the favored method of the time, there is one tried and true rule. Whatever method of marketing and sales you're using today will, sooner or later, stop working. Sometimes it will stop working for reasons you know, and sometimes it will be for reasons you don't know. In either case, your methods of marketing and sales will eventually stop working, and you'll have to develop new sales, marketing and advertising approaches, offerings, and strategies.
While many might guess that email marketing and Facebook ads are today's most popular marketing activities, much of the market has already moved on to new methods.
The top five advertising techniques in 2022 include:
- Sound-free, short-form video ads.
- Advertising on mobile games.
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence.
- Collecting and advertising third-party data.
- LinkedIn and other social media platforms.
The fourth P in the extended marketing mix is the place where your product or service is actually sold. Develop the habit of reviewing and reflecting upon the exact physical location where the customer meets the salesperson. Sometimes a change in place can lead to a rapid increase in sales.
You can sell your product in many different places. Some companies use direct selling, sending their salespeople out to personally meet and talk with the prospect. Some sell by telemarketing. Some sell through catalogs or mail order. Some sell at trade shows or in retail establishments. Some sell in joint ventures with other similar products or services. Some companies use manufacturers' representatives or distributors. Many companies use a combination of one or more of these methods.
In each case, the entrepreneur must make the right choice about the very best location or place for the customer to receive essential buying information on the product or service needed to make a buying decision. What is yours? In what way should you change it? Where else could you offer your products or services?
5. Packaging
The fifth element of the marketing mix is the packaging. Develop the habit of standing back and looking at every visual element in the packaging of your physical product or service through the eyes of a critical prospect. Remember, people form their first impression about you within the first 30 seconds of seeing you or some element of your company. Small improvements in the packaging or external appearance of your product or service can often lead to completely different reactions from your customers.
With regard to the packaging of your company, your product or service, you should think in terms of everything customer experience —what they see from the first moment of contact with your company through the purchasing process. Consider branded packaging to make an impactful first impression.
If your customer begins experiencing your brand with an eye-catching design, they are more likely to remember that experience with fond associations. Including your business logo and social media handles is another great addition to custom packaging that can invite customers to engage with your brand and promote repeat interactions.
Packaging refers to the way your product or service appears from the outside. Packaging also refers to your people and how they dress and groom. It refers to your offices, your waiting rooms, your brochures, your correspondence and every single visual element about your company. Everything counts. Everything helps or hurts. Everything affects your customer's confidence about dealing with you.
When IBM started under the guidance of Thomas J. Watson, Sr., he very early concluded that fully 99 percent of the visual contact a customer would have with his company, at least initially, would be represented by IBM salespeople. Because IBM was selling relatively sophisticated high-tech equipment, Watson knew customers would have to have a high level of confidence in the credibility of the salesperson. He therefore instituted a dress and grooming code that became an inflexible set of rules and regulations within IBM.
As a result, every salesperson was required to look like a professional in every respect. Every element of their clothing-including dark suits, dark ties, white shirts, conservative hairstyles, shined shoes, clean fingernails-and every other feature gave off the message of professionalism and competence. One of the highest compliments a person could receive was, "You look like someone from IBM."
6. Positioning
The next P is positioning. You should develop the habit of thinking continually about how you are positioned in the hearts and minds of your customers. How do people think and talk about you when you're not present? How do people think and talk about your company? What positioning do you have in your market, in terms of the specific words people use when they describe you and your offerings to others?
In the famous book by Al Reis and Jack Trout, Positioning , the authors point out that how you are seen and thought about by your customers is the critical determinant of your success in a competitive marketplace. Attribution theory says that most customers think of you in terms of a single attribute, either positive or negative. Sometimes it's "service." Sometimes it's "excellence." Sometimes it's "quality engineering," as with Mercedes Benz. Sometimes it's "the ultimate driving machine," as with BMW. In every case, how deeply entrenched that attribute is in the minds of your customers and prospective customers determines how readily they'll buy your product or service and how much they'll pay.
Develop the habit of thinking about how you could improve your positioning. Begin by determining the position you'd like to have. If you could create the ideal impression in the hearts and minds of your customers, what would it be? What would you have to do in every customer interaction to get your customers to think and talk about in that specific way? What changes do you need to make in the way you interact with customers today in order to be seen as the very best choice for the customer needs of tomorrow?
The final P of the marketing mix is people. Develop the habit of thinking in terms of the people inside and outside of your business who are responsible for every element of your sales, marketing strategies, and activities.
It's amazing how many entrepreneurs and businesspeople will work extremely hard to think through every element of the marketing strategy and the marketing mix, and then pay little attention to the fact that every single decision and policy has to be carried out by a specific person, in a specific way. Your ability to select, recruit, hire and retain the proper people, with the skills and abilities to do the job you need to have done, is more important than everything else put together.
In his best-selling book, Good to Great , Jim Collins discovered the most important factor applied by the best companies was that they first of all "got the right people on the bus, and the wrong people off the bus." Once these companies had hired the right people, the second step was to "get the right people in the right seats on the bus."
To be successful in business, you must develop the habit of thinking in terms of exactly who is going to carry out each task and responsibility. In many cases, it's not possible to move forward until you can attract and put the right person into the right position. Many of the best business plans ever developed sit on shelves today because the [people who created them] could not find the key people who could execute those plans.
Excerpted from Million Dollar Habits
The Ps of marketing
Marketing is essential whether you run an eCommerce business, a physical store, a small business, or a large corporation. While trends may evolve, the 7Ps of marketing will likely remain true and evolve with any new trend.
Remember, as products, markets, customers and needs change rapidly, you must continually revisit the seven Ps marketing model to ensure you're on track and achieving the maximum results possible for you in today's marketplace.
Looking for more marketing resources? Explore Entrepreneur's Marketing Hub here to help grow your business .
Chairman and CEO of Brian Tracy International, Speaker and Author
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- This 103-Year-Old Doctor Opened Her Medical Practice Before Women Could Have Bank Accounts — Here Are Her 6 Secrets to a Healthy, Successful Life
- Lock 5 Ways You Might Be Cheating on Your Taxes — And Why You Will Get Caught
- I've Had a Secret Side Hustle for Decades. It Keeps Tens of Thousands of Dollars in My Pocket — and Gets Me Into Places I Wouldn't Go Otherwise .
- Lock Here's How Steve Jobs Dealt With Negative Press and Avoided Brand Disasters
- One Factor Is Helping This Entrepreneur Tackle Business Ownership Later in Life. Now, She's Jumping Into a $20 Billion Industry .
- Lock Narcissism Can Help You Be Successful — Here's How to Harness It Without Going Too Far, According to an Ivy League-Trained Psychotherapist
Most Popular Red Arrow
Most americans don't think higher education is worth the cost — but this state-by-state breakdown of college graduates' salaries tells a different story.
More than half of people in the U.S. say that higher education isn't affordable.
Get This Costco 1-Year Gold Star Membership with a $40 Digital Costco Shop Card for $60
Shop smarter at more than 500 locations and online.
Jon Bon Jovi and His Son Jesse Want You to Play 'Pink Pong' With Their Top-Rated Rosé This Summer. You Game?
Jesse Bongiovi and his dad Jon Bon Jovi co-founded Hampton Water with a simple mission in mind: make something delicious, affordable and, most importantly, fun.
This One Word Is a Giveaway That You Used ChatGPT to Write an Email, According to an Expert
"Delve" has increased its presence in written work since ChatGPT entered the scene.
This Fan-Favorite Masters 2024 Item Is Still $1.50 as Tournament Menu Appears Unscathed by Inflation
The pimento cheese sandwich is a tradition almost as big as the tournament itself.
This Dad Started a Side Hustle to Save for His Daughter's College Fund — Then It Earned $1 Million and Caught Apple's Attention
In 2015, Greg Kerr, now owner of Alchemy Merch, was working as musician when he noticed a lucrative opportunity.
Successfully copied link
Hey there! Free trials are available for Standard and Essentials plans. Start for free today.
- Marketing Mix
Marketing Mix & The 7 P’s Of Marketing
The classic marketing mix, as established by Professor of Marketing at Harvard University, Prof. James Culliton in 1948 and expanded upon by Jerome McCarthy, incorporates Product, Price, Placement, and Promotion into a theory of marketing that has been important to the industry for more than 70 years. Since then, the theory has been expanded into the 7 P's of marketing. Which are: Product, Price, Promotion, Place, People, Packaging, and Process.

You’ve got this! We’ve got your back.
Mailchimp has the tools and resources to help you plan and run effective campaigns, so you can reach your goals.
Today, we refer to these interchangeably as the 7 P's or as the Marketing Mix. Here, we will discuss this concept, its components, and answer some common questions about the marketing mix and its applications.

What is a marketing mix?
Marketing mix is a selection of marketing tools that include several areas of focus that can be combined to create a comprehensive plan. The term refers to a classification that began as the 4 P’s: product, price, placement, and promotion, and has been expanded to Product, Price, Promotion, Place, People, Packaging, and Process.
What are the 7 Ps of Marketing?
The 4 P’s marketing mix concept (later known as the 7 P’s of marketing) was introduced by Jerome McCarthy in his book: "Basic Marketing: A Managerial Approach". It refers to the thoughtfully designed blend of strategies and practices a company uses to drive business and successful product promotion. Initially 4, these elements were Product, Price, Place and Promotion, which were later expanded by including People, Packaging and Process. These are now considered to be the “7 P’s” mix elements.
It can be difficult for a small business owner or marketing manager to know how to establish a unique selling proposition or to reach the right customers, especially on new platforms like the internet, with digital marketing.
Fortunately, the 7 Ps of marketing give you a framework to use in your marketing planning and essential strategy to effectively promote to your target market.
You can also take into consideration elements of the mix in your day to day marketing decision making process with the goal to attract the right audience to successfully market to through your marketing campaigns.
The 7 elements of the marketing mix include the following:
1. Product (or Service)
Your customer only cares about one thing: what your product or service can do for them. Because of this, prioritize making your product the best it can be and optimize your product lines accordingly. This approach is called “product-led marketing.” In a marketing mix, product considerations involve every aspect of what you're trying to sell. This includes:
- Market positioning

There are five components to successful product-led marketing that are important for product marketers to take into consideration:
- Get out of the way. Let your product or service sell itself . Focus your marketing efforts on getting consumers to try what you have to offer so they can learn its value for themselves.
- Be an expert (on your customers). Know your customer's needs and use that knowledge to help communicate your product's value.
- Always be helping. Position yourself as an ally by creating informative content that meets your target customers’ needs, and they'll be more likely to buy from you. (This is also called content marketing .)
- Share authentic stories. Encourage happy customers to share their experiences and tell others why they appreciate your brand.
- Grow a product mindset. Focus on your product before you consider how to sell it. Invest in development, and the product quality will take care of the rest.
Many factors go into a pricing model. Brands may:
- Price a product higher than competitors to create the impression of a higher-quality offering.
- Price a product similar to competitors, then draw attention to features or benefits other brands lack.
- Price a product lower than competitors to break into a crowded market or attract value-conscious consumers.
- Plan to raise the price after the brand is established or lower it to highlight the value of an updated model.
- Set the base price higher to make bundling or promotions more appealing.
Consider what you're trying to achieve with your pricing strategy and how price will work with the rest of your marketing strategy. Some questions to ask yourself when selling products:
- Will you be offering higher-end versions at an additional cost?
- Do you need to cover costs right away, or can you set a lower price and consider it an investment in growth?
- Will you offer sales promotions?
- How low can you go without people questioning your quality?
- How high can you go before customers think you’re overpriced?
- Are you perceived as a value brand or a premium brand?
3. Promotion
Promotion is the part of the marketing mix that the public notices most. It includes television and print advertising, content marketing, coupons or scheduled discounts, social media strategies , email marketing , display ads, digital strategies , marketing communication, search engine marketing, public relations and more.
All these promotional channels tie the whole marketing mix together into an omnichannel strategy that creates a unified experience for the customer base. For example:
- A customer sees an in-store promotion and uses their phone to check prices and read reviews.
- They view the brand's website , which focuses on a unique feature of the product.
- The brand has solicited reviews addressing that feature. Those reviews appear on high-ranking review sites.
- The customer buys the product and you’ve sent a thank you email using marketing automation .
Here are the ways you can use these channels together:
- Make sure you know all the channels available and make the most of them to reach your target audience.
- Embrace the move toward personalized marketing .
- Segment your promotional efforts based on your customers' behavior.
- Test responses to different promotions and adjust your marketing spend accordingly.
- Remember that promotion isn't a one-way street. Customers expect you to pay attention to their interests and offer them solutions when they need them.
Where will you sell your product? The same market research that informed your product and price decisions will inform your placement as well, which goes beyond physical locations. Here are some considerations when it comes to place:
- Where will people be looking for your product?
- Will they need to hold it in their hands?
- Will you get more sales by marketing directly to customers from your own e-commerce website, or will buyers be looking for you on third-party marketplaces?
- Do you want to converse directly with your customers as they purchase, or do you want a third party to solve customer service issues?

People refers to anyone who comes in contact with your customer, even indirectly, so make sure you're recruiting the best talent at all levels—not just in customer service and sales force.
Here’s what you can do to ensure your people are making the right impact on your customers:
- Develop your marketers’ skills so they can carry out your marketing mix strategy
- Think about company culture and brand personality .
- Hire professionals to design and develop your products or services.
- Focus on customer relationship management, or CRM , which creates genuine connections and inspires loyalty on a personal level.
6. Packaging
A company's packaging catches the attention of new buyers in a crowded marketplace and reinforces value to returning customers . Here are some ways to make your packaging work harder for you:
- Design for differentiation. A good design helps people recognize your brand at a glance, and can also highlight particular features of your product. For example, if you’re a shampoo company, you can use different colors on the packaging to label different hair types.
- Provide valuable information. Your packaging is the perfect place for product education or brand reinforcement. Include clear instructions, or an unexpected element to surprise and delight your customers.
- Add more value. Exceed expectations for your customers and give them well-designed, branded extras they can use, like a free toothbrush from their dentist, a free estimate from a roofer, or a free styling guide from their hairdresser.
Prioritize processes that overlap with the customer experience. The more specific and seamless your processes are, the more smoothly your staff can carry them out. If your staff isn't focused on navigating procedures, they have more attention available for customers—translating directly to personal and exceptional customer experiences.
Some processes to consider:
- Are the logistics in your main distribution channel cost-efficient?
- How are your scheduling and delivery logistics?
- Will your third-party retailers run out of product at critical times?
- Do you have enough staff to cover busy times?
- Do items ship reliably from your website?
If you get more than one customer complaint about any process, pinpoint what's going wrong and figure out how to fix it.
Marketing mix FAQs
Understanding marketing mix and the 7 P’s can bring up a lot of questions. Below, we’ve answered some frequently asked questions to help you identify and establish your own marketing mix.
What is a marketing mix example?
A good example of the marketing mix might be a convenience store. In this instance, we might consider a chain of convenience outlets that provide a wide range of products including fresh and packaged food, tools, household, and kitchen items, novelties, magazines, etc.
- Product : Chiefly, foods and various items located and packaged in a way that provides convenience and utility.
- Price : Pricing will be considered competitive with supermarkets, with some exceptions where convenience, novelty, and fun add special appeal.
- Place : Locations should be amenable to the value proposition of convenience. As such, locations should be strategically positioned near residential areas, shopping centers, educational centers, etc.
- Promotion : Advertising will be largely constrained to posted promotional material, the outlet buildings themselves, local social media pages, and so on.
Here, we will consider the customer experience as the opportunity to access simple food items, snacks, and a range of useful products for home, recreation, and more.
Another example might be a streaming service. Here our 4 P's are as follows:
- Product : Original quality entertainment and convenient viewing access.
- Price : Free trial offer, premium packages, and a commercial free subscription level.
- Place : The subscriber's digital device.
- Promotion : Extended advertising across a range of channels and platforms, including high-value metropolitan billboards, magazines, and word of mouth.
Here, the customer experience is appealing, long-form video content primarily in the form of popular TV, films, comedy specials, and more with an emphasis on convenient home viewing.
What are the types of marketing mix?
In reality, there are as many types of marketing mixes as there are functioning businesses in the world. To make things simpler, we might try to make our model fit within one of 7 common, established marketing mix types as listed below.
- Product Mix
- Product Progression and Product Life Cycle
- Market Coverage Mix (aka Positioning Mix)
- Service Mix
- Marketing Program Mix (or Promotional Mix)
- Channel Mix/Vertical Integration
- Global Marketing Mix (or International Marketing Mix)
As you can see, making a given company's value proposition and promotional needs fit into one of these categories might not work well. Our convenient store example might fit into the service mix since convenience is the primary value we would be offering. But our streaming service might also be called a "service mix,” or even a "product mix."
In most cases, it is best to generate an original marketing mix that describes the marketing needs of a real life organization.
What are the 4 P’s of marketing mix?
The 4 P's are Product, Price, Place, and Promotion.
- Product : The product is an item or service for sale. For marketing purposes, we should consider who it is for and why they would want it. We should also consider and compare our offering to that of the competition.
- Price : This is the amount customers will be willing or required to pay. Often, making prices competitive is a significant challenge. In cases where prices cannot be lowered below the market benchmark, additional value may need to be added to the offer.
- Place : This is the location/s where the product or service can be accessed and where it is used. For a restaurant, location is everything. For a streaming service, it is the user's home or the location where they buy computer devices and services.
- Promotion : This describes how, where, and how frequently advertising materials will be produced and where they appear. With our convenience store, the promotional material is largely on and in the store itself. With our streaming service, it would be in locations all over the web and any other appropriate location/media.
The takeaway
The marketing mix and the 7 P's of marketing are a guide to drafting and creating an outreach campaign for any given commercial enterprise. They are guidelines that help us cover all of our bases when it comes to brand outreach. It should be borne in mind that branding considerations are not covered in the concepts covered by these promotional frameworks.
The elements of these guidelines work together to create a functional framework for the creation of a complete marketing plan.
Develop your marketing mix and integrate it into your marketing essentials. As you develop your marketing mix, consider how each element affects the rest to create a unified brand experience for your consumers, from the user experience to the perceived value of your product. Think about how a product's price changes its promotion strategy, how specifications will contribute to pricing, and how your people carry out processes. Ensure that your people and the tools they use can communicate with each other, and use the right tools to reach the right people.
Take your business to the next level
- 18+ Risks and Disadvantages of Technology
- How to Build Your Business Identity on a Tight Budget
- Best Green Tea Brands in the world in 2020: What makes them the best?
- Global Milk brands in 2020 – What makes them successful?
- What is a Triple Net Lease? Its Advantages and Disadvantages
- Adaptation Level Phenomenon – understanding its importance
- Risk Matrix – Factors of a risk matrix and how to implement it
- Prioritization Matrix – Different types and how to use a prioritization matrix

Understanding Marketing Mix (4Ps & 7Ps) With Examples
On paper, marketing may not sound like a lot of work. After all, it’s only about promoting and selling products and services, isn’t it?
What people don’t realize is that there’s a significant amount of research and planning involved in executing every marketing campaign. This is probably why experts can’t help but pay attention to every tiny little detail in this strenuous process. How here’s where a marketing mix comes into the equation.
Using a marketing mix helps chuck out extra details, allowing marketers to design the most effective strategy for their products and service. In this elaborate guide, we will be discussing about marketing mix in detail and how you can develop one of your own.
Table of Contents
What is a Marketing Mix?
A marketing mix comprises of a bunch of tools, tactics or actions that a company might use to introduce and promote its product or brand. The 4 Ps of marketing is made up of:
However, because of the increasing demands of the field, there’s been an introduction of 7 Ps of marketing which also includes components such as people, positioning, and packaging.
Importance of Marketing Mix
Each component found in a marketing mix greatly influences the business plan of the company, ensuring its success. It basically highlights important pointers for marketers and key stakeholders that’ll come in handy throughout the lifecycle of the product.
The mix will play a crucial role in identifying the best marketing strategy for your business. It’s also a primary step to creating your marketing or business plan. This is why a lot of effort, research, and planning goes into formulating a marketing mix. In fact, a number of people are consulted throughout the process to ensure no major or minor details are left out.
What Are the 4 P’s Of Marketing
While marketing mixes are becoming more elaborate and detailed, it’s a good idea to start off with the basic 4 Ps. Here goes:
The product refers to a tangible item or service that you’re trying to sell. In order for it to have any value at all, it must fulfill some kind of need for the consumer. The product must offer excellent performance or else even the best marketing strategy won’t be able to save it from plummet.
For this, marketers must sit down and plan out various stages of the product cycle according to their particular needs and requirements. The first step in this cycle is identifying what problems the product can solve. For this, all professionals on the team must fully understand the features and USP ( unique selling proposition ) of what they’re offering. Once the true potential of the product is identified, marketers can move on to the next step which is deciding the price of the product.
You can’t market a product without putting a price tag on it! This can only be done once marketing professionals have developed a concrete understanding of the product. The price of the product plays a crucial role in determining how the product will sell in the market.
It’s important to note that consumers calculate a perceived value of a product in their minds before they’ve even seen the price tag. Problems will arise if there are fluctuations in the price and it does not align with the consumer’s perceived value. For instance, imagine you’re shopping for a new pair of running shoes that look great at a first glance. However, on close inspection, you notice that the quality of the material is below par which is quite surprising because the shoes are insanely expensive.
At this point, the consumer may start to grow skeptic about your brand. Marketers thus need to find a way to see products from the eyes of consumers . So if the product doesn’t offer much, it will hold little value for the consumer.
Additionally, the price will also depend on value chain costs and other factors including how competitors have priced similar products.
Once you’ve got yourself a final product and have decided a price, the next step is promotion. After all, you can’t sell a product unless consumers already know about it, can you?
This part includes many different aspects such as sales promotions, social media marketing, email marketing , advertising and much more. The appropriate channel(s) will be decided by marketers according to the nature of the product. Additionally, the channel must be aligned with the interest of consumers, for instance, if you’re promoting a new energy drink for youngsters, you’re likely to reach your target audience more effectively using social media. This is primarily because teenagers and young adults spend a lot of time on platforms such as Facebook and Instagram.
As a marketer, you can also come up with interesting contests and prizes ahead of your product launch to generate hype and get customers excited.
Proper placement is key to marketing any product successfully as it’ll drastically impact distribution. Marketers must thus put their heads together to determine ideal locations that’ll attract as many prospective customers as possible. Today, thanks to the social media frenzy, most consumers are more or less converted or engaged online.
However, if you own a physical store, you’ll have to ensure it’s based somewhere consumers will be able to find it easily. On the other hand, if you’re an online retailer, opt for an identifiable web domain and an easy to navigate website.
Marketing professionals can choose from a number of potential locations as part of their placement strategy. This, of course, will depend on the nature of the product and where its target audience hangs out.
Extended Marketing Mix Modeling
The traditional 4 ps of marketing gained popularity for many years until it finally considered too simplistic. Experts began to think that the original model lacked depth and offered room for improvement
5 Ps of Marketing
For better clarity, Judd added the fifth p in the existing marketing model to highlight the contribution of people. This p pays tribute to the people behind all the action, specifically those who are working hard to offer products and services to their consumers. These people play an integral role in shaping user experience and help make your marketing campaign. The second aspect of this component is your customers. Without them, there would virtually be no point of a marketing campaign which is why each campaign is tailored around, well – people.
The basis of adding an extra p was to highlight the importance of people that are communicating messages to the audience. Here, professionals must take customer services and staffing into account. This is primarily done via training sessions and other exercises.
7 Ps of Marketing

In 1981, the original model was further extended to add three more elements, resulting in the 7 p’s of marketing. The revised Booms & Bitner model was designed to highlight the importance of services in addition to tangible, physical elements. The additional three elements included people, processes, and physical evidence.
Processes refer to how you plan to distribute and deliver your products and services to consumers. In the long run, consumers are also paying for how the service is delivered to them. Think of ways to improve your services and provide utmost convenience to your consumers.
Physical Evidence
The final p stands for physical evidence and refers to all the physical components that consumers will be interacting with your business. For instance, this could include the packaging of the product, branding, layout and of course, the overall environment of the place where you’re selling your products and services. All these elements will ultimately contribute to the user experience.
How to Craft a Marketing Mix
The marketing management is often responsible for developing a marketing mix. However, extensive research is crucial to ensure that all key points are based on facts and not assumptions. Follow these steps to develop a marketing mix:
Define Your Unique Selling Proposition
The most primary step to devising a marketing mix is to define a unique selling proposition. Think about it. Here are some questions you ought to ask yourself:
- Why would consumers be interested in your product?
- What are your product’s biggest
- What do you have to offer that your competitors don’t?
Use focus groups and customer surveys to determine how important your USP is. Your potential customers should clearly be able to highlight the key benefits and features of the product in order for the product to sell. Be willing to go above and beyond with research if you want your product to stand out, all these pointers must be showcased in your marketing campaign.
Find Your Target Audience
Take inspiration by writing down a few sentences about your target audience or create a buyer’s persona. This will act as an indispensable tool for marketers who really want to hit the spot and assess each marketing tactic with great attention. For extra measure, you must base customer profile one aspects such as gender, age, demographics etc.
On the other hand, if you’re targeting other businesses, consider factors including the company’s size and location.
Assess the Competition
There are probably dozens or maybe even several thousands of businesses that are offering something similar to your product. So what do you do? You evaluate your competition.
Try to figure out their strategy and understand what keeps them going. Some businesses offer special discounts and warranties to spike up sales and get the attention of consumers. Determining the subject worth of the product and then eliminating its additional costs will help you decide on a reasonable price point. This will especially come in handy when you are devising pricing strategy.
Create a Pricing Strategy
Once you have examined the value of similar products in the market, use your marketing research to develop an appropriate pricing strategy. This will help make sure you do not overprice or underprice the product.
Shortlist Placement Options
At this stage (once you’ve developed a pricing strategy), you must move forward with assessing placement options. Evaluate where your prospective customers are most likely to hang out and make a purchase. You must also consider any costs that may be associated with that particular channel. For instance, if you’re thinking of opening up a physical store as opposed to an online one, you must keep additional expenses in mind.
Alternatively, you can also target multiple channels at the same time to attract a wide customer base. However, if you would like to target a particular niche, you may want to stick to specific channel or area that will benefit your company the most. It’s also worth keeping in mind that the availability of the product may directly impact its perceived value.
Devise a Promotion Strategy
How do you plan on getting the word out? In this phase, you must incorporate everything that you’ve learned about your target audience and use it to devise a commination strategy. Keep in mind that the promotion strategy that you opt for but be aligned with the needs and requirements of your consumers. The products must be promoted in a way that its benefits, features and USP is clearly understood by the audience.
If your company is on a tight budget, opt for a few affordable yet effective tactics that will help you reach your core audience. Once your campaign starts to get noticed, you can move on and target an even bigger number. Your tactics could include platforms such as social networking sites or direct mail to reach out to customers.
Marketing Mix of Coca-Cola

The Coca-Cola Company is undisputedly the most renowned and perhaps the most loved beverage company in the world. Over the years, the brand has successfully launched a number of new products, bringing down its final total to over 3300. Let’s take a closer look at its marketing mix for better understanding:
The renowned beverage company has an incredibly large product mix that includes about 400 brands. Apart from regular soda, they also offer a variety of juices, sports drinks along with teas and coffees. Among the most popular is its flagship Coca-Cola which has been crowned the most popular selling soft drink to ever exist. Other notable brands include Sprite, Fanta, Minute Maid, Powerade, and Fresca.
At present, the company is focusing on introducing healthier drinks as people are slowly moving towards sugar-free options. The Coca-Cola Company first became a part of this trend when it introduced its first non-carbonated drink, Minute Maid in 1990s.
Coca-Cola follows a comprehensive pricing strategy that is based on the perceived value of its products. Since Pepsi Co is the prime competitor and arch-rival of the brand, Coca-Cola ensures its pricing is within consumer reach. Overall, Coca-Cola’s pricing approach is closely aligned with maintaining brand loyalty.
Since its products are sold by a number of retail stores and distributors, each entity implements its own pricing strategy. While most drug-stores and gas stations sell its products at a fixed price, retail outlets may adopt a different strategy altogether.
Coca-Cola is known as the most popular beverage company in the world and rightly so. To stay relevant, the company has employed a number of marketing and advertising strategies. It advertises its products using numerous communication channels including social media, direct mail, the World Wide Web along with traditional means of advertising such as billboards and TV commercials. Due to increased competition, Coca-Cola reportedly spent about $3.96. Billion on advertising last year.
One of Coca-Cola’s most successful campaigns was for Coke Zero in 2015. The drinkable advertisement was targeted at millennials, giving them a chance to sample the drink. According to the brand over 85 % of millennials had not tried the drink yet so this campaign was designed to introduce their product to a whole new audience.
In 2016, Coca-Cola announced a shift in is marketing strategy with its new “Taste the Feeling” campaign. The company emphasized on a “one brand” approach which was quite unique from its previous strategies.
Coca-Cola has an enviable distribution system as its products can be found in over 200 countries all over the world. It is reported that the company is able to sell about 1.9 billion servings every day on an average which is a whopping number!
Coca-Cola follows an FMCG distribution pattern which has allowed the brand to penetrate all relevant players in the market. It is also worth mentioning that the brands bottling partners closely interact with consumers in amusement parks, convenient stores, street vendors etc. Together, all these partners have managed to create a successful localized strategy for Coca-Cola.
Wrapping it Up: Marketing Mix
We hope this elaborate guide has helped you learn more about marketing mix. Is there something you’d like to add? Tell us about it in the comment section below.
Image Credits: Blog.Scoop.it , Celebrista , Marketing91
- ADVERTISING
- SOCIAL MEDIA
- ENTREPRENEURSHIP
- WEB DEVELOPMENT
- MAKE MONEY WITHOUT PAYING ANYTHING
- HOW TO MAKE QUICK MONEY
- WAYS TO MAKE MONEY BLOGGING
- BIGGEST SLOGANS GUIDE
- DIFFERENT TYPES OF MARKETING
- MARKETING MIX EXPLANATION
- TYPES OF DISTRIBUTION STRATEGIES
- AFFILIATE MARKETING FOR BEGINNERS
- LEARN TO MAKE A BLOG
- FREE PRINTABLE CALENDARS 2019
- DMCA Notice
- Privacy Policy
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
The 7Ps of The Marketing Mix: Streamline your Strategy
As marketers, we should never underestimate the power of planning. For most of us, that means creating a water-tight marketing strategy, informed by analysis and data - one that has objectives, a target market, and proven tactics.
We all use different blueprints depending on our industry, our target audience and our products and services. But there’s one, timeless model that any marketer can utilise regardless of their field of work and that is the marketing mix.
What is the marketing mix?
Traditionally, the marketing mix is a framework for your marketing strategy containing four key elements: Product, Place, Price and Promotion. Then we have the extended marketing mix - or the 7Ps - which contains the first four elements, plus Physical Evidence, People and Processes.
It’s important to note that while the marketing mix can influence your strategy and provide a greater understanding of the wider market, as well as your business internally, it doesn’t work in isolation. The marketing mix is a tactic that works best when it’s implemented regularly or semi-regularly as a structure for planning, executing, evaluating and re-evaluating your marketing activities.
Who created the marketing mix?
The marketing mix is a concept developed by professor and academic, Neil H. Borden , who elaborated on James Culliton’s concept of business executives being mixers of ingredients - ingredients being different marketing features and practices. The marketing mix was later refined by professor and author, Jerome McCarthy, to specifically include four key components: Product, Place, Price and Promotion. McCarthy wrote about the 4Ps in the 1960s in his book Basic Marketing: A Managerial Approach .
The 4Ps vs the 7Ps
These original 4Ps of the marketing mix covered the fundamental factors of business and marketing at the time. But as we know, marketing and business as a whole have evolved exponentially since then, so it was only a matter of time before the marketing mix needed to be expanded. In 1981, the 4Ps were built upon by two modern academics, B.H. Booms and M.J. Bitner, who identified three additional elements they saw as key to the marketing mix: Physical Evidence, People, and Process, thus providing us with what we now know as the 7Ps of the marketing mix. And it makes sense that these three were the elements Booms and Bitner added to the marketing mix framework. People are at the heart of every business. Without people, you have no one to market to; no one is there to buy your product or make use of your services. It’s a no-brainer.
What are the 7Ps of the marketing mix?
Now that you know what the 7 Ps of the marketing mix are and their origins, let’s dive a little deeper into the definition of each aspect.
Product refers to what is being sold - a physical product, service, or experience. No matter how you position yourself as a brand, your product or service is always going to be at the centre of your strategy and will influence every aspect of the marketing mix. When you think of your product, consider factors such as:
- Specific features
- Packaging/presentation
- The problem that it will solve for your customers
Product in this case, then, is about crafting something that meets the needs and desires of your target audience. This means understanding their preferences, pain points, and aspirations. By meticulously aligning your product with customer expectations, you create a solid starting point for your marketing endeavours. Over 30,000 consumer products are launched yearly. Out of these 30,000 new products, 95% of them fail woefully without having any significant impact on the market.
Choosing the right distribution channels significantly impacts your product's accessibility and visibility. Effective placement ensures your product is available when and where your target audience needs it. Place in the marketing mix doesn't just mean physical locations—it encompasses websites, catalogues, social media, trade shows, and brick-and-mortar stores.

Source: Zippia
Place covers all distribution channels. Factors like your target audience influence your choices. Selling via a single high-street store won't work if your audience is mostly online or global. Test options—could an eCommerce site or a pop-up store work? A mix might suit your business. Understanding your target audience is vital for the right distribution. To profit consistently, distribute where your brand fits and your audience can access. Make your presence felt where it matters most.
The right pricing strategy is critical for a product's success. A misstep in pricing can jeopardize your ROI. Bain & Company research found that 18% of companies lack internal processes for pricing decisions. Your price should mirror customer perception, align with your budget, and ensure profitability. Pricing significantly impacts your business's success, affecting marketing, sales, and demand. Various pricing strategies exist , each with unique benefits and considerations, depending on your product and brand image.
6 Common pricing strategies:
- Price Skimming : Begin with a high price, gradually lowering it over time.
- Competition-Based Pricing : Set prices above or below competitors' rates.
- Economy Pricing : Target budget-conscious buyers with lower prices.
- Premium Pricing : Attach a high price, emphasizing product quality.
- Value-Based Pricing : Determine price based on perceived customer value.
- Cost-Plus Pricing : Set price based on production cost plus markup.
Whatever your pricing strategy is, ensure it aligns with your brand, appeals to customers, and maintains profitability. Monitor the market, economy, and competitors to adjust as needed.

4. Promotion
Promotion is at the core of our marketing expertise. Whether through direct marketing, PR, advertising, content strategies, or in-store presentations, as marketers, we excel in raising awareness and engagement. Promotion involves telling a compelling brand story that resonates with consumers, guiding them to consider your offerings. Effective promotional strategies achieve various goals, from elevating brand recognition to driving sales and revenue. Addressing key questions sets the stage:
Where is your audience able to find you? Online or in a physical store?
Does seasonal impact influence your business?
What is your brand personality and how does it shape your messaging and design?
- How do competitors promote themselves? A SWOT analysis helps here.
Promotional tactics fall into two categories: traditional and digital . Traditional methods encompass print media, broadcasting, mail, billboards, and word of mouth. Digital avenues include email, social media, content marketing, SEO , mobile outreach, and paid ads. Digital marketing generates 50% more customer interactions than traditional methods.
Source: MarTech Alliance
The way you communicate and promote directly affects your brand's success. Misplaced messages or poor timing can negatively impact sales. Understanding your audience through segmentation and targeting, along with integrating marketing data, helps cater to their needs and ensures seamless omnichannel campaigns.
5. Physical Evidence
Physical evidence means more than just proof of purchase - it encompasses the overall existence of your brand. Think website, branding, social media, the logo on your building, your store’s decor, the packaging of your product, the post-purchase thank you email, even the ambience of your store. All of these elements offer your customer the physical evidence they need to be certain that your business is viable, reliable and legitimate. For consumers to truly be comfortable with you, to complete a purchase, remain loyal and advocate for your brand, they need to be confident that you’re legitimate and worth their time.
To create a well-crafted strategy that ensures you offer great customer support, be sure to deliver products and receipts efficiently and reliably, and provide a customer experience that is seamless across each and every touchpoint.
6. People People, in the marketing mix, refers to anyone directly or indirectly involved in the business side of the enterprise. That means anyone involved in selling a product or service, designing it, marketing, managing teams, representing customers, recruiting and training. It’s critical to the success of your brand, and the satisfaction of your customers, that everyone who represents the company (including the chatbots) is polite, professional, knowledgeable and fully trained. Employees need to be able to solve the problems that customers have, so as a business, you need to offer training, good working environments and anything that will safeguard the contentment of your employees.

50% of consumers will switch to a competitor after a single bad experience, while 80% will switch after multiple bad experiences. Excellent customer service is a must for any brand operating in today’s customer-centric market. Digital strategist, Dave Chaffey, says that people buy from people because of the human connection that we all typically crave. When marketers create a strategy that’s highly tailored and personalised, they can be as influential as the best, most persuasive salesperson. Having the right people is key for both long and short-term success. Each part of the marketing mix can help your customers see you as reliable and dependable, which is crucial to any branding strategy.
Process encompasses what goes into every step of the customer journey - from making an enquiry to requesting information and making a purchase. The efficiency and consistency of your processes can significantly impact your overall effectiveness. From lead generation to customer support, having well-defined and streamlined processes ensures a seamless customer journey. The more intentional and personalised your processes are, the happier your customers will be. Even with the best product in the world, your business can be let down by processes.
You want your customer interactions to be seamless from beginning to end, so think about things like:
- Your customer response time
- The time between booking with sales and actually having a meeting
- What happens once they make a purchase
- How to generate positive reviews after purchase
- What tools can make your processes more efficient i.e. AI, CRMs, email clients, KPI tracking , etc.
Source: Oracle
Marketers who plan their projects and campaigns against their strategy are 365% more likely to report success. Regularly assessing, adjusting and adapting your processes will help to structure your business efforts so that you can function at optimal efficiency.

Why are the 7Ps of the marketing mix important?
In the dynamic realm of marketing, where strategies evolve and consumer behaviours shift, having a reliable and comprehensive framework is essential. The 7Ps of the marketing mix provide precisely that – a versatile toolkit that empowers intermediate marketers to construct impactful strategies and achieve sustainable success. At the core of the 7Ps framework lies a profound focus on understanding and catering to the needs of your target audience. This customer-centric approach is a cornerstone of successful marketing. By delving deep into your customers' preferences, pain points, and aspirations, you gain insights that guide your decisions across the 7Ps. This empathetic understanding ensures that your product is tailored to meet specific demands, your pricing resonates with perceived value, your distribution channels are optimized for accessibility, and your promotional efforts strike a chord. The 7Ps framework also equips marketers with the agility to respond to shifting market dynamics. Whether it's adjusting pricing strategies to remain competitive, leveraging new promotional platforms to reach wider audiences, or refining product offerings based on customer feedback, the flexibility inherent in the 7Ps allows marketers to stay relevant and effective. Additionally, the 7Ps facilitate measurement and optimisation, a key element of any successful marketing strategy. Each "P" provides distinct metrics that can be tracked and analysed which allows marketers to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making, leading to continuous refinement and enhanced results.

How can I use the 7Ps?
The 7Ps marketing mix is more than just a theoretical concept; it's a versatile toolkit that can be wielded by intermediate marketers to create impactful and effective strategies. Here's a concise guide on how you can leverage this model to your advantage: 1. Start with Solid Research Understanding your target audience is paramount. Conduct thorough market research to unearth insights into their preferences, behaviours, and needs. This foundational knowledge will inform every decision you make across the 7Ps. 2. Tailor Your Product Offering Craft your product or service with your audience in mind. Strive to meet their unique needs and desires, differentiating yourself from competitors by adding value and addressing pain points. 3. Pricing Precision Develop a pricing strategy that aligns with customer expectations and provides a clear reflection of the value you offer. Consider factors such as production costs, competitor pricing, and perceived value when setting your prices. 4. Strategic Placement Determine the optimal distribution channels to ensure your product or service reaches your target audience conveniently. Whether it's through physical stores, online platforms, or a combination of both, choose avenues that enhance accessibility and visibility. 5. Powerful Promotions Craft compelling promotional campaigns that resonate with your audience. Utilize a mix of advertising, public relations, social media, and other marketing channels to amplify your message and create a buzz around your offering. 6. Prioritize People Invest in your employees and ensure they are well-trained and aligned with your brand's values. Their interactions with customers can significantly impact their experience and perception of your brand. 7. Streamline Processes Efficiency is key. Optimize your marketing processes to ensure a seamless customer journey from awareness to purchase and beyond. This includes lead generation, customer support, and post-purchase interactions. In the ever-evolving landscape of marketing, a robust framework is essential, and the 7Ps of the marketing mix offer just that. As marketers, this versatile toolkit empowers us to craft impactful strategies for enduring success. By delving into customer preferences, pain points, and dreams, we tailor our decisions across the 7Ps. Harnessing the power of the 7Ps, allows us to shape strategies that resonate, adapting to the ever-shifting marketing landscape, and ensuring lasting success.
Track and visualise your KPIs in real-time with Hurree. Try Hurree today and discover how to truly harness the power of analytics and transform your company reporting using cross-platform dashboards. If you have any questions then feel free to get in touch !

You May Also Like
These Related Stories

What Are The Major Components of a Marketing Strategy?

Experiential Marketing: 4 Es to Future-proof Your Strategy

Market Targeting: Why it Pays to Differentiate
Get email notifications.
- Allbound Marketing
- Behavioral Marketing
- Emotional Marketing
- Relationship Marketing
- Retention Marketing
- User-Generated Marketing
- Account Based Marketing
- B2B Marketing
- Global Marketing
- Inbound Marketing
- Outbound Marketing
- Acquisition Marketing
- Affiliate Marketing
- Cold Calling
- Conversion Rate Optimization
- Demand Generation
- Lead Generation
- Mobile Marketing
- Search Engine Marketing
- SEO Marketing
- SMS Marketing
- Telemarketing
- Content Marketing
- Conversational Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Narrative Marketing
- Public Relations
- Social Media Marketing
- Video Marketing
- Cause Marketing
- Digital Marketing
- Event Marketing
- Guerilla Marketing
- Influencer Marketing
- Organic Marketing
- Partnership Marketing
- Product Marketing
- Performance
In today’s fast-paced and innovative business landscape, marketing professionals continue to look for ways that guarantee the optimal market performance of their company products and services. Tapping into the full potential of the 7Ps marketing mix will help you navigate the challenging marketing environment, providing valuable insights and strategies for success.
What are the 7Ps of Marketing? The 7Ps of marketing are Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence. This is an extension of the traditional 4Ps model, specifically addressing the inclusive service-based marketing strategies in addition to tangible product marketing.
We invite you to continue exploring this blog post as we dive deeper into the intricacies of the 7Ps marketing mix model, its effective application in various business contexts, and the ways it continues to evolve with the ever-changing marketing landscape.
Understanding the 7Ps Marketing Mix Model
Marketing, undebatably, plays a central role in any business’s success. Over the years, professionals have devised many models to guide and optimize their marketing strategies. One such popular framework is the 7P’s Marketing Mix Model.
Definitions and Origin of the 7Ps Model
The 7Ps encompass Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence. Let’s break these down:
- Product : This refers to what you are selling, be it a physical product or an intangible service. It involves defining and aligning the offering to meet customer expectations and needs. The product must deliver value, solve a problem, or fulfill a desire of the customer.
- Price : Price is the cost set for the product or service. It greatly affects customer perception and company revenue. Price strategizing could range from premium pricing for high-quality products to competitive pricing to undercut competitors.
- Place : This P refers to the availability and distribution channels where your product or service can be accessed. Ensuring the right Place means your offerings are conveniently accessible where your target market is most likely to find them.
- Promotion : Promotion involves communication channels used for marketing, creating brand awareness, and reaching out to customers. This could involve advertising, social media, PR, email marketing, SEO, and more.
- People : People, in the context of the 7Ps, includes employees, stakeholders, and every individual involved in public interaction on the company’s behalf. It’s crucial to keep in mind that employees reflect the brand’s image to the outside world. Therefore, their training, appearance, attitude, and behavior greatly impact the consumer’s perception of the brand.
- Process : Process entails the flow, procedures, and mechanisms in place for service delivery and ensuring customer satisfaction. It includes systems for managing customer inquiries, complaints, orders, payments, and other operational procedures.
- Physical Evidence : The Physical Evidence element represents tangible proof of the brand’s quality and existence. It’s especially crucial for service-based businesses. Physical Evidence could be a clean and welcoming retail store, professional looking website, or quality brochures.
As we delve deeper into the evolution of marketing mix models, we can easily identify that the traditional 4Ps model focused mainly on tangible product marketing. This model, introduced by E. Jerome McCarthy in 1960, initially included only Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. However, with the increasing emphasis on service-oriented businesses and customer-centric approaches in the business world, Booms and Bitner proposed the extended 7Ps model in 1981, which added three more variables – People, Process, and Physical Evidence.
The addition of these three elements reflects a comprehensive service marketing strategy, acknowledging the impact of People involved in service delivery, the Process ensuring customer satisfaction, and the Physical Evidence providing tangible proof of service quality.
The Traditional 4Ps vs. The Extended 7Ps
While the original 4Ps focused on Product, Price, Place, and Promotion, the extension to the 7Ps went beyond tangible product marketing to include service-oriented businesses. It recognized the role of People, Process, and Physical Evidence in the modern marketing mix.
Let us look at an example illustrating this. Take McDonald’s, one of the world’s leading food service brands. McDonald’s does not just sell hamburgers (Product), at competitive prices (Price), in easily accessible locations (Place) with timely and engaging ads (Promotion). They extend their strategy with well-trained employees (People), a globally-established, fast service procedure (Process), and recognizable outlets with visually distinct branding (Physical Evidence), highlighting the impact of the 7Ps in their marketing strategy.
Application of the 7Ps Model
The 7Ps model serves as a checklist to help marketers set clear objectives, conduct thorough Strength, Weakness, Opportunities, and Threat (SWOT) analyses, define competitive strategies, and ensure a holistic approach to product or service marketing. Smart Insights puts it aptly, “The 7Ps helps to define your offering more clearly from a customer perspective and differentiate it from your competitors.”
Furthermore, the 7Ps can be instrumental in evaluating an existing business. By aligning each element of the 7Ps to the company’s current procedures, marketers can identify gaps, devise strategies to address them, and thereby enhance the overall strategic approach. As Oxford College Of Marketing puts it, by “Evaluating the company’s marketing mix on the basis of the 7Ps, marketers can identify key areas that need improvement and develop a proactive plan for making positive transformations.”
Expansion to an 8th P: Partners
While the 7Ps model is already robust, businesses are constantly competing in an ever-evolving marketing landscape, where the need for extended networks and collaborations is increasingly highlighted. To address this, some opt to append an 8th P – Partners – to their marketing mix tactic. This P emphasizes collaborations with other businesses to amplify brand exposure, especially online. It could involve affiliate marketing partnerships, collaborations for sponsored content, or even joint ventures.
However, it’s noteworthy that many argue Partners should be included under Place, as partnerships enhance a product or service’s availability and accessibility. Regardless of its categorization, the pivotal role of Partners in today’s interconnected and digital-centric business world is undeniable.
Real-World Company Examples Using 7Ps
Understanding the 7Ps of marketing is a powerful tool for developing strategy. But, to truly appreciate this model’s impact, we need to consider its application in the real world. As a prime example, let’s examine how HubSpot, the renowned marketing tool provider, incorporates the 7Ps.
HubSpot as a Case Study
HubSpot provides an integrated set of marketing tools, from content management to email marketing to SEO. Let’s breakdown how it delivers value across all aspects of the 7Ps.
- Products/Services : HubSpot offers a comprehensive toolset that integrates various marketing functionalities under one platform. It systematically structures its service offerings to accommodate organizations of different sizes and with varying needs, ensuring its products are accessible and beneficial to a wide market.
- Price : HubSpot adopts a subscription-based Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model, where prices are based on service usage including number of contacts and user levels, which allows for scalability and flexibility. It offers various pricing packages to cater to its diverse audience, ranging from a free basic version to premium packages that come with more advanced features.
- Place : As an online platform, HubSpot is readily accessible from anywhere, anytime. With an extensive distribution via partners, HubSpot ensures that its solutions reach a large customer base.
- Promotion : HubSpot employs a robust multi-channel promotional approach. The company leverages search engine optimization, content marketing, educational webinars, and social media advertising. In addition, they host events and publish guides on marketing best practices, further attaining a thought-leader position and increasing brand loyalty among its target market.
- People : HubSpot invests in skill development for its team members, ensuring they are equipped to offer in-depth product knowledge and high-quality service to customers. Furthermore, they have a dedicated customer support and success team that facilitates smooth customer interactions and satisfaction.
- Processes Optimizing customer interactions and improving conversion rates, HubSpot’s process involves an effective lead nurturing system that includes content offerings, interactions with sales staff, and follow-ups that nourish relationships with potential customers.
- Physical Evidence With consistent branding and messaging across its website, content, emails, and other touchpoints, HubSpot provides tangible proof of its service quality and leading position in the industry.
Interestingly, Smart Insights notes that “HubSpot adds value for customers in every aspect of the 7Ps.” This illustrates how the company leverages the 7Ps model effectively to manifest value to its customers, validate its market leadership, and maintain an evolving service.
Measuring the Impact of the 7Ps
While developing and executing a marketing strategy is crucial, measuring its impact and success is equally important. With rapid technology advancements, businesses can now leverage advanced tools and techniques, including AI and machine learning, for informed Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM).
MMM helps marketers quantify the impact of their marketing effort on sales and ROI. Specifically, AI-driven MMM has the potential to offer more accurate and actionable insights, enabling marketers with data-driven decision making and an edge in formulating effective marketing strategies.
Furthermore, it is critical to modulate investments across various marketing channels. Companies must continually test and evaluate to extract maximum ROI while ensuring they effectively communicate their value proposition to their target audience. Leveraging a robust framework like the 7Ps can guide marketers in assessing the success of their overall marketing strategy, channel effectiveness, and ROI.
In conclusion, the 7Ps of marketing, combined with data insights, provide a comprehensive, customer-centric, data-driven strategy. It empowers businesses to continuously deliver superior value, keep abreast with market changes, and sustain a competitive edge in the increasingly challenging marketing landscape.
Understanding the 7Ps model and appropriately applying it in marketing strategies can give businesses a significant advantage. As the marketing environment continues to evolve, adjusting these 7Ps and their balance to fit your company’s unique requirements will be an ongoing challenge. Yet, those who can skilfully wield these seven facets of marketing are sure to pave their pathway to success.
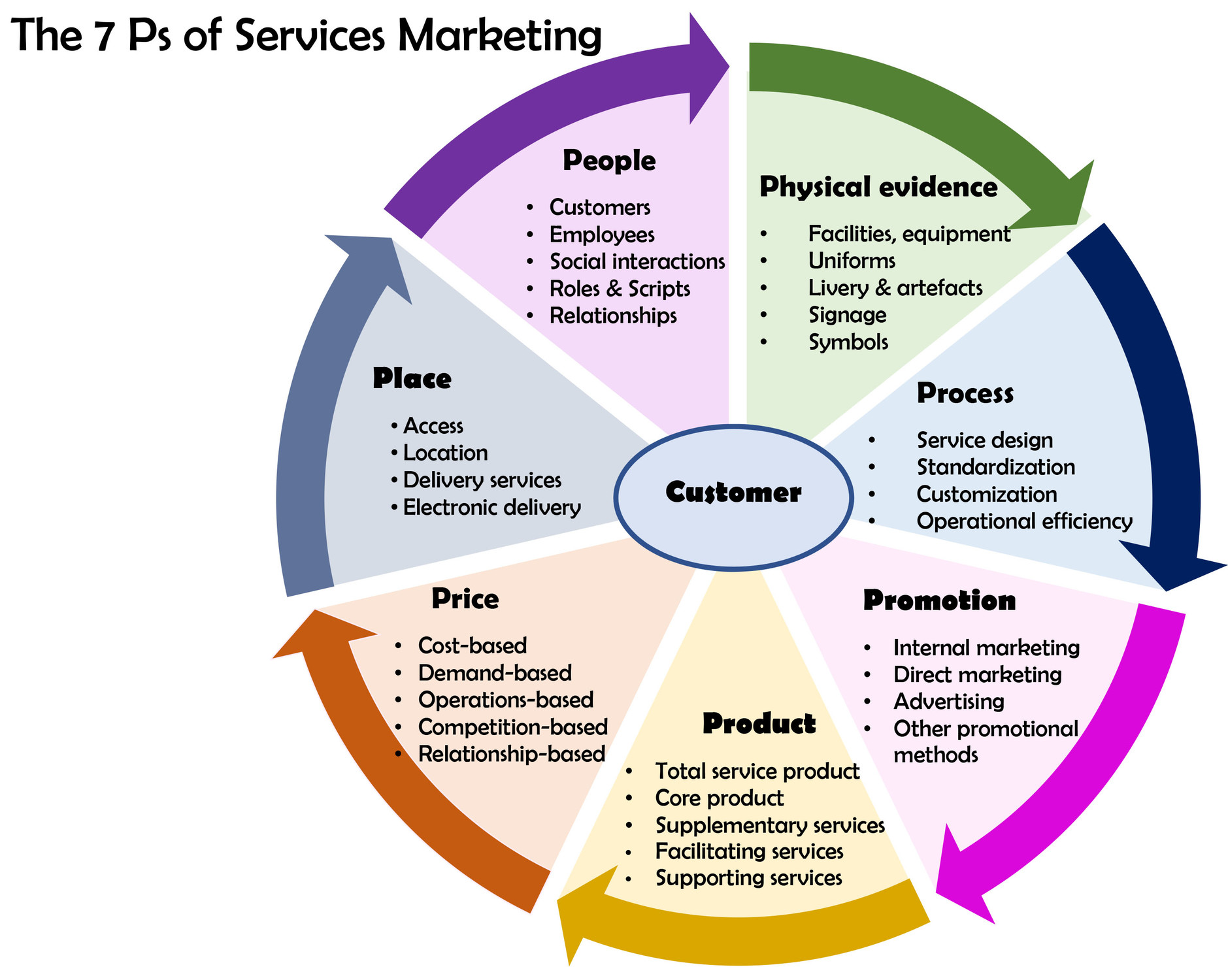
Source: LinkedIn
To further refine your marketing strategies, consider employing these models simultaneously with other effective techniques. For instance, you might use the SWOT analysis for an in-depth, comprehensive understanding of your business’s position. Our complete guide on Marketing Segmentation Targeting and Positioning: A Proven Guide for Success provides more on this and other helpful tactics for effective marketing planning. Moreover, it’s worth understanding the broader spectrum of marketing, including different marketing types and their unique requirements, as discussed in Different Types of Marketing Strategy With Examples (Proven Top 15 Guide) . After all, mastering the art of marketing requires continual learning and adaptation to the dynamic business environment. The 7Ps model is just one of the essential tools in your arsenal, empowering you to create, evaluate, and optimize strategic marketing plans.
Remember, the key to exceptional marketing is blending the art of understanding the customer’s needs and desires with the science of delivering it in the most appealing way. And the 7Ps marketing mix model certainly serves as a robust framework guiding you towards that!
The Evolving Marketing Landscape and the 7Ps
As the marketing landscape continues to evolve, the traditional marketing mix of 4Ps has expanded into the 7Ps to take into account the crucial role of providing excellent customer service and the intangible aspects of promoting a product or service. Today’s competitive landscape necessitates an all-encompassing strategy that includes these elements.

Moving forward in the digital age, many organizations now recognize the importance of adapting more modern marketing strategies. One such strategy is embracing the comprehensive scope of the 7Ps of marketing, going beyond the traditional 4Ps model. There has been a significant shift in marketing, where the balance of focus moved away from simply price, product, promotion, and place to encompass points on the 7Ps model like processes, people, and physical evidence.
The Concept of the 9Ps of Marketing
With the rapid pace of changes in marketing, the 7Ps model has even seen further expansion with some experts introducing additional Ps, creating the concept of the 9Ps of Marketing. This model includes planning, performance, and provisioning, emphasizing the growing sophistication of marketing strategies.
Marketing strategist Larry Londre was a key figure in the idea of 9P’s of Marketing . His perspectives emphasized the importance of planning for overall strategies, performance in delivering value, and provisioning for providing the means to fulfill customer expectations.
As we move forward, it is imperative to adapt our marketing approaches to suit our evolving understanding of customers and marketing dynamics. Businesses need to focus on not just traditional methods of marketing, but also on intangibles and customer-centric strategies.
Analysis of the 7Ps Through the Lens of Different Industries
The application of the 7Ps of marketing understandably varies across different industries. Marketing campaigns, strategies, and structuring marketing plans across different sectors like healthcare, retail, e-commerce, and B2B all lean into the tenets of the 7Ps, but with industry-specific emphasis.
Each industry faces their unique challenges and dynamics in customer service. A healthcare organization, for instance, may place a heavier emphasis on the ‘People’ aspect of the 7Ps, ensuring their staff deliver personable, professional service. Conversely, an e-commerce business may find ‘Processes’ and ‘Physical evidence’ to be more crucial aspects as they grapple with logistics and providing tangible proof of transactions to customers.
Clearly, the 7Ps model can offer a flexible framework that a diverse range of industries can adopt and mold to fit their unique needs and situations.
The Role of Marketing Research in Refining the 7Ps
Successful marketing in today’s competitive and digital-savvy landscape requires a strong focus on market research. Gaining an understanding of customer behavior through research is essential to refine offerings, align marketing strategies, and ultimately meet the market’s needs.

Importance of Customer Insights and Feedback
Target audience data is an integral part of refining the product/service offerings and adjusting marketing strategies accordingly. Direct consumer market research provides valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences, critical in tailoring marketing strategies that effectively target and attract the desired audience.
Companies can leverage multiple channels for this purpose, including social media and customer engagement platforms. By monitoring real-time feedback and sentiments on these platforms, businesses have direct insight into how their marketing efforts and product offerings are received, offering key opportunities for adjustments and improvement.
The Influence of Socio-economic Factors on the Marketing Mix
Successful application of the 7Ps model requires deep understanding of relevant socio-economic factors and their impact on marketing strategies. This includes thorough assessment of economic fluctuations, cultural trends, and demographic shifts in consumer behavior that impact the effectiveness of the marketing mix elements.
Businesses must learn to adapt their 7Ps to different geographic and economic contexts, tailoring their marketing strategies to suit the unique characteristics of various markets. This ensures that their marketing strategies remain effective and relevant even amidst a fast-changing marketplace.

Future Trends and Predictions for Marketing Mix Models
Looking forward, it’s crucial to anticipate market trends and adapt the marketing mix to suit. Innovations in marketing tactics and strategies continue to evolve and those who keep pace will remain competitive.
Key marketing trends include a growing focus on sustainability, digital transformation, and inclusivity. These demand integration of new approaches into the existing 7Ps framework. Green marketing, for example, could influence the ‘Product’ aspect of the 7Ps, prompting businesses to develop more eco-friendly products to meet growing consumer demand for sustainable offerings.
Educating and Training for Agile Marketing Approaches
With the dynamic nature of marketing strategies, continuous learning and adaptation is essential for marketing professionals. An effective marketer today must possess updated knowledge of marketing theories, digital tools, and have analytical skills to apply the 7Ps effectively in an ever-evolving market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between the 4ps and 7ps of marketing.
The 4Ps of marketing focus on Product, Price, Promotion, and Place, while the 7Ps add People, Process, and Physical evidence to the model. This expansion recognizes the importance of customer service and intangible aspects of marketing.
Why are the 7Ps important in marketing?
The 7Ps offer businesses a comprehensive framework to guide their marketing strategies. By considering each of the 7Ps, businesses ensure that their offerings meet customer needs, are appropriately priced, effectively promoted, accessible, and that they deliver superior customer service.
How has the marketing landscape evolved?
The marketing landscape has evolved from a focus on tangible products and traditional media to more comprehensive, customer-centric strategies. Greater emphasis is now being placed on digital marketing, personalization, customer experience, and sustainability.
Can the 7Ps framework be applied to any industry?
While the specifics of implementation may vary across different sectors, the principles of the 7Ps framework hold true across industries. Each P represents a key aspect that any business, regardless of industry, needs to consider in their marketing strategy.
What future trends could impact the 7Ps of marketing?
Future trends like sustainability, digital transformation, and inclusivity are key elements that could further refine the 7Ps. Businesses may have to innovate new approaches within the 7Ps framework to adapt to these trends.

Outbound Marketing for B2B vs B2C: Unraveling Proven Strategies
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Most Popular
What are the best alternative marketing strategies (5 innovative approaches revealed), marketing quotes to attract customers: transformative power words, what is account-based marketing the ultimate guide (skyrocket your roi), recent comments, editor picks, popular posts.
Allbound | Marketing is a dedicated website that delves deep into the world of Allbound marketing, offering a rich blend of expert advice, case studies, and practical strategies. It serves as a go-to resource for businesses seeking to harness the synergy of inbound and outbound tactics, providing actionable insights for transforming their marketing campaigns.
Contact us: [email protected]
© Copyright Allbound | Marketing

- Reviews & Studies
- Explore a partnership
- Watch Unboxing Reviews for Marketers »
- Get a free Unboxing guide »
The 7Ps of the Marketing Mix: Accelerate Your Strategy
The term “marketing” is often used as a catchall to depict any activity a company undertakes to promote and sell its products and services to its consumers. No matter what industry that company may be in, marketing efforts can be all-encompassing.
They also include nearly every aspect of the business cycle from analytics to product development and distribution channels to sales--all filtered through a general understanding of customer needs.
Over the years, to better understand the complexities of marketing, several business experts have created systems to help businesses better analyze and understand their marketing strategy. One of these models that have truly stood the test of time is the 7Ps Marketing Mix. Developed in the 1960s but still widely used today, this iconic model aims to simplify the marketing process.
Ready to see how it works? Read on to find out!
What are the 7Ps of the Marketing Mix?
The 7Ps Marketing Mix is a comprehensive set of action plans businesses can use to market their products or services to their target audience. While it provides a coherent framework for evaluating performance, it also assists brands in determining the best combination of elements to establish clear objectives and approaches based on their current situation.
The seven elements are product, price, place, promotion, people, process and physical evidence.

Product refers to what you create and delivers to meet your customer's core needs. When bringing a new product or service to market, several factors must be considered, including quality, features, and packaging, as well as what problem your product helps solve.
Companies can use the 7Ps framework to make informed decisions and develop a unique selling proposition (USP) as consumer needs change and new competitors emerge over time. This helps businesses scale and stay relevant in today’s ever-changing market while consistently providing a positive product experience.
Product differentiation strategies also take things into account such as after-sales support, user-friendly apps, and interactive digital content, all to meet or exceed customer expectations.
Price reflects the maximum value customers are willing to pay for your product or service. Determining the right price requires extensive research and is dependent on the product you are selling as well as your brand image.
Factors such as production costs, the economy at large and market demand all play a role in determining price. However, price is also an important indicator of market positioning and should always be set with your competitors in mind.
Place represents the distribution channels through which customers can make a purchase. It could be in a brick-and-mortar store, website or mobile app.
Getting the right product in the right place at the right time ensures that your product or service is available when and where your customers need it. It encompasses the intermediaries and logistics that occur before they are made available to end users.
Place is an often overlooked part of the marketing process. If your products aren’t being sold in locations that fit your brand and your target consumer’s lifestyles, it will severely impact your sales and profits.
4. Promotion
When it comes to promotion, the goal is always to increase brand awareness in an effort to attract new customers while reminding loyal customers of your brand and encouraging them to come back.
Promotional marketing can take many forms including TV advertising, personal selling, public relations, and more recently, paid digital media and Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategies. Taking a multi-faceted approach with different promotional avenues allows businesses to have a wider reach while they connect to and build relationships with their customers.
The challenge comes in determining which promotional tools your audience responds best.
Consider performing a regular SWOT (strengths, weakness, opportunities and threats) analysis to understand how your business compares to your competitors. This will allow you to capitalize on new growth opportunities and develop actionable strategic plans.
The next 3Ps in the model: people, process and physical evidence were introduced in the early 1980s when customer service was becoming more recognized as an integral part of marketing.
People are the building blocks of successful organizations that underpin great customer relationships. This includes anyone who is directly or indirectly involved with your business. From salespeople to the human resource department and customer service team, they play a crucial role in representing your company.
Customer-facing teams, in particular, need support from other departments and the right tools and resources in place to provide the best service possible. They understand the ins and outs of your business and have in-depth product knowledge, both of which must be optimized.
Tapping into their passion and investing in training allows your company to differentiate its offering in a saturated market and build valuable customer relationships. These are also excellent ways to empower and retain high-performing employees to work towards common goals.
When it comes to building and managing customer support teams, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Each organization needs to have its own set of goals. However, this doesn’t mean you can’t learn from successful companies and figure out how to apply some of their approaches to your company’s unique situation.
6. Process
“Process” describes the sequence of actions involved in delivering the product to the end users. Understanding each stage of the customer journey is critical. From when they are just learning about your brand to post-sales, you must consider what approaches are required to make sure your customers have a positive experience.
To ensure that your customers receive end-to-end care and a smooth transition across all touchpoints, you must carefully consider each phase in the sales process to ensure they have a positive experience every step of the way.
7. Physical Evidence
The final piece of the 7Ps puzzle? Physical evidence of their positive interaction with you. Modern storefronts, user-friendly websites, well-trained employees and even something as simple as a thank-you note provide customers with the physical evidence they need to be confident that your company is viable and trustworthy.
It can be helpful when prospective or first-time customers have not previously interacted with your company and require some reassurance before making the final purchase. First and last impressions are important and simple reminders of your company’s validity can go a long way in solidifying your brand reputation in the mind of your current and potential customers.
The Ps Marketing Mix can help businesses develop a winning brand strategy that allows them to differentiate themselves from competitors and earn their trust. While this is one of the oldest marketing models out there, it is still highly trusted–simply because it works. If you want to continue to grow your brand and expand your marketing efforts, this straightforward model can be one of your most trusted tools to make it happen.
Regularly assessing and adjusting these processes can attract and retain valuable customers while keeping their business profitable.
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

Ecommerce Email Marketing Strategies and Tips

Marketing Product Lifecycle Guide - The Ups and Downs

Programmatic Direct Mail Marketing: All You Need to Know
Get email notifications.
Mastering the Marketing Mix: A Comprehensive Guide to 7Ps
Home » Marketing » Mastering the Marketing Mix: A Comprehensive Guide to 7Ps

In the world of marketing, the concept of Marketing Mix is crucial. It is a set of tools and tactics that businesses use to promote their products or services to the target market. The traditional Marketing Mix consisted of four Ps: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. However, with the changing times, businesses realized that to provide a better experience to customers, they need to consider more elements than the traditional four Ps. Thus, the Marketing Mix 7P was introduced. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the Marketing Mix 7P and understand how businesses can benefit from it.
Table of Contents
The 7Ps of Marketing Mix
The Marketing Mix 7P is an extension of the traditional Marketing Mix , and it includes the seven Ps: Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence. Let’s take a look at each of these elements in detail.
The product P refers to the goods or services that a business offers to its customers. The product includes the design, features, quality, packaging, and branding of the product. The key to creating a successful product is to understand the needs and wants of your target market and to differentiate your product from your competitors.
- Conduct market research to understand the needs and wants of your target market.
- Conduct a competitive analysis to understand your competitors’ products and identify areas where you can differentiate.
- Use customer feedback to improve your product.
- Continuously innovate and improve your product to stay ahead of the competition.
The price P refers to the cost of the product or service. The pricing strategy of a business must be aligned with its overall marketing objectives and target market. The price of a product must reflect its perceived value and the cost of producing it.
- Conduct a pricing analysis to understand the pricing strategies of your competitors.
- Determine the perceived value of your product and price it accordingly.
- Consider the cost of producing and delivering the product when setting the price.
- Use promotions and discounts strategically to encourage customers to buy your product.
The place P refers to the distribution channels that a business uses to reach its target market. The distribution strategy must be tailored to the target market, and the product must be available at the right time and in the right place.
- Identify the most effective distribution channels for your target market.
- Ensure that your product is available in the right locations and at the right times.
- Use technology to improve the efficiency of your distribution channels.
- Continuously evaluate and optimize your distribution strategy to ensure that it is meeting the needs of your target market.
The promotion P refers to the communication strategies that a business uses to promote its product or service to its target market. The promotion mix includes advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, direct marketing, and public relations.

Promotion drives sales by creating awareness and communicating value
- Develop a clear and compelling brand message that resonates with your target market.
- Use a mix of advertising, personal selling, and other promotional techniques to reach your target market.
- Use social media and other digital channels to reach your target market.
- Continuously monitor the effectiveness of your promotional activities and adjust them as needed.
The people P refers to the employees who interact with customers and provide support to them. The staff must be well-trained and motivated to provide excellent customer service.
- Hire employees who have the skills and qualities needed to provide excellent customer service.
- Train employees on how to interact with customers and provide support to them.
- Encourage employees to take ownership of their work and to be proactive in solving customer problems.
- Recognize and reward employees who provide excellent customer service.
The process P refers to the processes and procedures that a business uses to deliver its product or service to its customers. The processes must be efficient and effective, and they must be designed to meet the needs and wants of the target market.
- Identify the key processes that are involved in delivering your product or service to customers.
- Streamline and optimize these processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
- Ensure that the processes are designed to meet the needs and wants of your target market.
- Continuously evaluate and improve your processes to ensure that they are meeting the needs of your customers.
Physical Evidence
The physical evidence P refers to the tangible elements that customers can see and touch when they interact with a business. This includes the physical environment, packaging, and branding. The physical evidence must be aligned with the overall brand image of the business.
- Ensure that your physical environment is clean, comfortable, and visually appealing.
- Use packaging that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
- Use branding that is consistent across all physical touchpoints.
- Pay attention to the details, such as signage, lighting, and decor, to create a positive customer experience.

Physical evidence refers to tangible elements customers use to evaluate a product or service, such as packaging or store atmosphere
Importance of 7Ps Marketing Mix
The Marketing Mix 7P is important for businesses as it helps them to provide a better experience to their customers. By considering all the elements of the Marketing Mix, a business can ensure that its products or services meet the customers’ needs, preferences, and expectations.
It also helps businesses to differentiate themselves from their competitors and create a unique brand image. Furthermore, by adapting the Marketing Mix to different industries and target markets, businesses can increase their reach and effectiveness.
Marketing Mix 7P vs 4P
The Marketing Mix 4Ps model and the Marketing Mix 7Ps model are both frameworks used by marketers to develop effective marketing strategies. The Marketing Mix model was originally proposed by E. Jerome McCarthy in 1960, including Product, Price, Promotion, and Place.
The model was later expanded by Booms and Bitner in 1981 to include three additional Ps: People, Process, and Physical evidence. Today, the 7Ps Marketing Mix model is widely used in marketing theory and practice.
Examples of 7Ps Marketing Mix in Action
Let’s take a look at some examples of companies that have successfully implemented the 7Ps Marketing Mix:
Apple is a company that is known for its innovative products and excellent customer experience. Their products have a unique design, packaging, and features that set them apart from their competitors. Apple also offers excellent customer service and has a well-trained staff that provides support to customers. Its physical stores have a unique layout and atmosphere that creates a premium brand image. Apple’s Marketing Mix is an excellent example of how a company can create a unique brand image by considering all the elements of the Marketing Mix.
Starbucks is another example of a company that has successfully implemented the 7Ps Marketing Mix. Starbucks has a unique product range, which includes coffee, tea, food, and merchandise. Its pricing strategy is based on the premium experience that it offers to its customers.
Starbucks has a strong distribution network, and its stores are located in prime locations to reach its target market effectively. Starbucks’ promotional activities focus on creating a unique experience for its customers, such as personalized drinks and promotions. The staff at Starbucks are well-trained to provide excellent customer service, and the physical stores have a unique atmosphere that creates a premium brand image.

How to apply Marketing Mix 7P?
As a marketer or business owner, you can use the 7Ps Marketing Mix model to design and implement an effective marketing strategy that meets the needs and wants of your target market, drives sales and revenue, and establishes a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Here are some steps you can follow to use this model effectively:
- Understand your target market: Conduct market research to understand the needs, wants, and preferences of your target market.
- Define your marketing objectives: Identify your marketing objectives, such as increasing sales, launching a new product, expanding into new markets, or improving customer retention.
- Develop a product or service: Use the insights from your market research to design a product or service that meets the needs of your target market.
- Determine your pricing strategy: Decide on a pricing strategy that reflects the perceived value of your product or service and aligns with your marketing objectives.
- Choose your distribution channels: Identify the most effective distribution channels to reach your target market. Ensure that your product or service is available in the right locations and at the right times.
- Develop a promotional strategy: Develop a promotional strategy that effectively reaches your target market. This may include a mix of advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, direct marketing, and public relations.
- Train and motivate your staff: Ensure that your staff are well-trained and motivated to provide excellent customer service.
- Streamline your processes: Streamline your processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
- Create a positive physical environment: Pay attention to the physical environment, packaging, and branding to create a positive customer experience.
In conclusion, the Marketing Mix 7P is a powerful tool that businesses can use to provide a better experience to their customers. By considering all the elements of the Marketing Mix, businesses can create a unique brand image and differentiate themselves from their competitors. Furthermore, by adapting the Marketing Mix to different industries and target markets, businesses can increase their reach and effectiveness. We hope this guide has helped you understand the importance of the Marketing Mix 7P and how businesses can benefit from it. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below.
You might be interested in:
- Marketing Metrics : Everything You Need to Know
- Facebook Ad Metrics : Master in 5 Minutes
- Crafting an Effective Marketing Strategy : Tips and Best Practices
- Digital Marketing Quotes & Phrases to Inspire & Motivate

7Ps of the Marketing Mix – Comprehensive Marketing Strategy Framework
Home » Marketing » 7Ps of the Marketing Mix – Comprehensive Marketing Strategy Framework
- April 13, 2020
- 7 Ps of Marketing , Marketing Mix
Marketing is an aspect that is deeply rooted in our daily routine from the food we eat to the clothes we wear. For businesses, a profound marketing strategy is a crucial ingredient for their success. To develop a comprehensive marketing strategy, you need to be adeptly versed with the 7Ps of the marketing mix.
Understanding the Marketing Mix
What is the marketing mix? Bluntly said, it is a bunch of approaches used by a firm to achieve its marketing goals. This may encompass for instance the products produced, their prices, the mode of delivery to reach customers and the pattern of communication to customers.
Traditionally, these tools were known as the 4Ps of Marketing, but as marketing today has become more sophisticated, 3Ps have been added. This results in the 7Ps of Marketing. Let’s take a closer look at each of them.
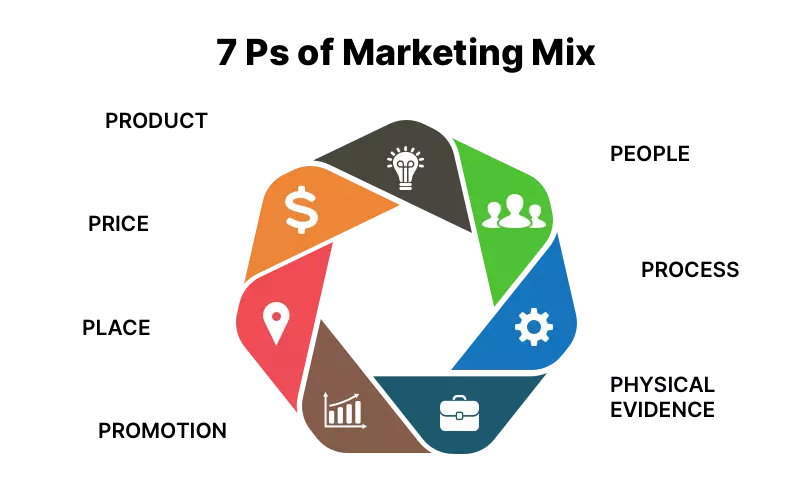
7Ps of the Marketing Mix
Product is anything, both tangible and intangible, that can be delivered to the market for purchase and consumption. Besides, it is something that meets a set of customer needs or wants. When companies are developing the 7Ps of the marketing mix, they may think about a product in terms of 3 levels .
i. Core product
The core product incorporates the core benefits of a product purchased by consumers. For example, a student pursuing Entrepreneurship is buying knowledge; therefore, the product planners ought to define the benefits of the product to the students.
ii. Actual product
The actual product is composed of various characteristics that make up a product. They could be quality levels, brand name, and other attributes.
iii. Augmented product
The augmented product includes additional consumer services build around the actual core product such as warranty, tutorials on how to operate a product and after-sales services.
Read more about the three levels of products here.
The price is the only income-generating aspect of the 7Ps of marketing. Therefore, obviously, it deserves high attention. Various pricing strategies do exist, which should be applied depending on the product type , market environment and customer characteristics. In general, to survive in the fast-changing market place, a product should be priced as per the target audience’s perceptions .
The place is the distribution point of a product. It is an essential aspect of the 7Ps of the marketing mix that defines the availability of a product in the market . For the product to stand out, it has to be positioned in the most convenient place for the target customers . This could be through a window shop or via the internet. Before developing your distribution strategy, you need to consider questions such as the following:
- How do your customers want to obtain the product, and what is the best way to reach them?
- What do different distribution channels cost?
- How do your competitors’ distribution strategies differ from yours?
- What is the environmental footprint of your distribution methods?
Promotion is one of the 7Ps of the marketing mix techniques used by companies to communicate their customer offerings. It is a combination of advertising, exhibitions, digital marketing, and other elements to pave the way for dialogue with clients. Promotion ought to communicate not only the perks obtained from a product but also its features. Besides, the promotional material should be precise and informative to the internal stakeholders. An efficient promotion strategy should be a blend of the following questions.
- Which is the best mode to message your target buyers?
- When should you implement the promotion strategy?
- What promotion strategy have your competitors adopted?
The reputation of your product primarily lies in people’s hands. Anyone can have a negative or positive impression of your products and services. It is, therefore, essential to train your employees on how to contact customers to give your business a decisive edge over your competitors. This can be done by adjusting the 7Ps of marketing to meet customer needs. For example, if you operate a little barber shop, placing some complimentary chocolates in your client’s guest room will tend to impress the customer, and, more likely, they will become substantial clients. The workforce is the key to the design and effective implementation of the 7Ps of the marketing mix.
The process is one of the elements of the 7Ps of the marketing mix that tends to obtain too little attention. It refers to the flow of activities as a result of the interactions between a business and its customers. For example, when a customer books a room, there is a process triggered. There is no essence of running a firm if this strategy is faulty. If it is used wisely, it’s a great source of satisfied customers. Therefore, develop clear processes for every type of interaction and make sure that they meet customer expectations and are consistently implemented.
Physical Evidence
The last element of the 7Ps of marketing is physical evidence. This element pertains particularly to the service domain. A service , in general, is intangible. This implies certain risks for customers. These can be reduced by giving physical proof of the service you deliver. For example, an insurance company would issue their customers with printed evidence materials. This boosts customers’ confidence in what they are buying. To wrap it up, physical evidence ensures every component of the 7Ps of the marketing mix abides by the brand values as the service itself.
In a nutshell, no element of the marketing mix can be considered in isolation. For organizational success, it is crucial to develop an integrated set of marketing strategies. To do so, the 7Ps provide a helpful framework.

Seven Functions of Marketing – What is the actual Purpose of Marketing?
Marketing: It’s Not Just About Ads!
Think marketing is all about catchy slogans? Think again! Discover the seven core functions of marketing. Learn how they work together to research customer needs, design products, set prices, and ultimately deliver value.

Marketing Instruments – Marketing Mix – 7 Ps of Marketing
The Marketing Toolbox
Focus on the practical power of the marketing mix. Emphasize action-oriented tactics, not just abstract concepts.
Table of Contents

What is Omnichannel Marketing? Developing an Effective Omnichannel Marketing Strategy
Omnichannel marketing is a strategy employed by many large organizations around the world.

Using Psychographics in Marketing – Overview and Complete Guide
Have you ever wondered how some marketers seem to know exactly what you want, often before you know yourself? Psychographics can help marketers target specific consumers more likely to buy.

How to Perfectly Prepare Your Product Launch Strategy – The Complete Checklist
Launching a new product successfully requires careful planning. This complete checklist and step-by-step guide will ensure you understand your customers, develop a strong brand message, and tailor an effective launch strategy to maximize product success.

- Buyer Behavior
- Market Analysis
- Target Market & Positioning
- The Marketing Process
- Product Strategy
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Get in Touch

- Marketing Strategy
- Content Marketing
- Brand & Design
- Social Media
- Email Marketing
- Professional Services
- Small Businesses
- Menu of Services
- Website Quote
- Meet the Network
- Portfolio & Testimonials
- News & Info
7 Ps of Marketing – A Tool for Your Small Business
- General Marketing
- 7 Ps of Marketing –…

The 7 Ps marketing mix is a marketing tool that will help your business to develop it’s marketing strategy by focusing on specific areas. Historically, the marketing mix was just 4Ps, but 3 more were added and it is now suggested that all 7 are considered as part of your marketing and promotional strategy, particularly if you are a service provider.
What is the 7 p’s marketing mix used for?
These 7 Ps are predominantly used by businesses as a focal point and as part of an overall marketing strategy.
They can assist with:
- Defining areas of success in the business that can be replicated and built on
- Defining issues in the business that are holding you back from being more profitable, productive or successful
- Setting objectives and targets – so you can move strategically towards your goals
- Competitive analysis – your business position in the market against your competitors
- SWOT analysis – analysis of your business strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats
The original 4Ps of the marketing mix tool are:
The additional 3Ps added, are:
- Physical Evidence
Using the 7Ps
You can use the 7 Ps as headings for discussion, of which the findings and conclusions can then be added to your marketing strategy, which should feature as part of your overall business plan.
Some of the things you can focus on under each of the 7P headings, include:
PRODUCT – this could be your SERVICE if you are a service provider
- Is your product branded effectively?
- How do your customers rate the quality of your product?
- Is there recurrent negative feedback about the same thing?
- Are there improvements that could be made?
- Is your product brand strong?
- Do you offer a guarantee?
- Do you have availability or stock?
- Could you take on more customers or orders?
- How does your product compare when it comes to the market price?
- When was the last time you reviewed your pricing?
- When was the last time you altered your price in-line with inflation, or market supply and demand?
- Is your pricing model clear and easy to communicate?
- Do you know your profit margin on each product you offer?
- Do you provide any added-value to your offering?
- Do you offer the most appropriate payment methods for the customer?
- Do you offer credit facilities?
- Do they need updating?
- Do they give the right messages?
- How could you refine your sales process?
- What PR activity are you doing?
- Do you have a marketing budget? Should it stay the same, or change this year?
- Do you network to promote your business?
- Is your product available in the place where your customers shop?
- Is your product visible to your target market?
- Are you visible on social media?
- Do you have the right people to sell your product / service?
- Do you have the right amount of marketing support?
- Are the right people in your team, in the right roles?
- Do you need more, or less resources?
- Could you outsource some of your work to reduce commitment on costs?
- Do you have the right culture within the team?
- Do you have a good recruitment, training and appraisal system for staff?
- Is your sales process efficient?
- Are your processes customer focused?
- Do you have a good process for dealing with technology issues?
- Have you established systems for as many things as possible within your marketing and sales process?
PHYSICAL EVIDENCE
- This could apply to the way a service is delivered, including any physical documentation
- What is the online experience if the product is delivered digitally?
These are just ideas and you will for sure come across other questions and thoughts that are relevant to your business.
Why not get your team together (or you partner / best friend if you are a sole trader) and have some fun by trying to really cover all the individual elements of your business. Be constructively critical and also realistic with what you can achieve within certain timeframes.
Why the marketing mix is still used from the 80s until now.
The marketing mix concept may seem dated as it was developed in the 1980s and we now live and work in a rapidly changing commercial environment.
However, it remains effective as the logic behind each of the 7 Ps remains constant yet they are flexible enough to be able to be adapted to suit the new style of communications, for example social media.

Connect with marketing specialists for your sector
T: 020 8123 1147 E: info@marketingsquare.co.uk
Related Posts

Meet: Sadie December 1, 2021

Meet: Kate November 1, 2021

Privacy Overview
Sign up to our newsletter to receive marketing tips for your small business or healthcare practice.
7Ps of Marketing Mix Template
Wondering what are the 7Ps of marketing mix? Check out our marketing mix template and get a custom report in 3 simple steps. Add the data, choose the design, and download the result.
Our 7Ps framework generator is a simple and efficient tool that helps businesses and organizations to define the primary areas that influence product and service marketing. It is a free tool that generates customized reports for your project within a few minutes. Apart from being user-friendly, it is also easily accessible online.
- 📊 How to Use the Template
- 🚀 7 Ps of Marketing Mix Explained
- ✅ The Tool’s Benefits
🔗 References
📊 how to use 7ps marketing mix template.
You don't have to stress about using the 7Ps framework tool because it generates impressive results in a few clicks.
Get your marketing mix by following the simple steps below:
- Enter your business data
- Select a suitable design
- Download your results in pdf format
You will get the best model to make your marketing plan more effective.
🚀 7Ps of Marketing Mix Explained
You must understand the definition of the 7Ps of marketing before we proceed.
It is an approach that comprises seven principles that experts use to develop and implement strategies that enhance customer engagement and generates revenue.
Read on to gain a deeper understanding of the 7Ps framework.
Who Created the 7Ps of Marketing?
E. Jerome McCarthy was the originator of the 4Ps marketing model. Later on, in 1982, Mary J. Bitner and Bernard H. Boom improved the marketing mix and made it better from four to seven components. Thus, the 7ps marketing mix is a significant aspect in many companies offering services and business environments offering intensive knowledge to customers. It helps to evaluate the marketing strategy to make it more practical and effective.
What Are the 7P's of Marketing Mix?
Below are the 7Ps of the marketing mix to assist you in creating and implementing a great marketing strategy.
7 Ps of Marketing Mix
What is process in 7ps of marketing.
The process is an essential component in marketing since it ensures order in operations. Many businesses often train employees to work using a set procedure. Such processes allow the employee to provide efficient services. Besides, return clients will be accustomed to a consistent standard of operations. Process mapping is an approach that most businesses use to guarantee efficiency. It contains visual maps with symbols, details, or flowcharts with examples of each process.
📂 7Ps Framework Free Example
Let's take an example of Amazon 's 7Ps framework:
- Product. Amazon offers products and service delivery. Some products include books, movies, music, clothes, and games. Customers perceive Amazon's products to be of high quality.
- Price. Prices are lower than average market costs. The company buys products directly from the manufacturer and sells them to customers at reasonable rates.
- Place. The company operates in the online marketplace . Any person worldwide can access the platform.
- Promotion. Amazon uses several media channels for promotion – TV and radio advertisements. It also uses social media platforms to create awareness.
- People. People who are involved in buying, selling, and delivering products. It also involves the employees managing the company website.
- Process. The processes include customer membership, payments, shipping, placing, and confirming the order. Also, the customers should receive a confirmation email.
- Physical evidence. Website visibility on other web pages. High rankings on search engines give customers physical cues about the company.
✅ 7Ps Generator Benefits
The 7ps generator is an essential tool for businesses because it helps to streamline the marketing approach. You can't overlook the importance of proper planning when it comes to marketing. Having an air-tight marketing strategy is vital in helping your business goals.
Our 7Ps generator is beneficial because of the following reasons:
- Free. It is a free tool that you can easily access online. No payments or subscription fees.
- No extensions. It is an online tool without downloadable apps or extensions you must install before using.
- Simple. It is a user-friendly tool
- Saves time. You can generate your customized model within a few minutes. So, it is a time0saving tool without any complicated entries.
Thank you for reading this article! If you want to try other free business analysis templates, check our 4Ps generator , STP template , 7S template generator , and a SMART goals maker .
Updated: Oct 25th, 2023
- How the 7 Ps of Marketing Fit Into Your Marketing Mix
- How to use the 7Ps Marketing Mix strategy model?
- The 7 Ps of Marketing - Entrepreneur
- Marketing Mix & The 7 P's Of Marketing - Mailchimp
- Marketing Mix - Definition - The Economic Times
- Free Essays
- Writing Tools
- Lit. Guides
- Donate a Paper
- Referencing Guides
- Free Textbooks
- Tongue Twisters
- Job Openings
- Expert Application
- Video Contest
- Writing Scholarship
- Discount Codes
- IvyPanda Shop
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Copyright Principles
- DMCA Request
- Service Notice
This page contains 7Ps Marketing Mix template. This simple yet efficient tool can help businesses and organizations to define the primary areas that influence product and service marketing. The methodology was initially developed in the 1960s as a four-component model and later improved in 1982.

- Your Project
- 7P Marketing Mix
What is the 7P Marketing Mix?
The 7P Marketing Mix is a set of 7 factors you should focus on when developing your Marketing Strategy .
Why is this definition so similar to the 4P Marketing Mix one? Because is the same concept.
The 7P Marketing Mix is nothing but an extended 4P Marketing Mix .
While the classic 4P Marketing Mix analyzes the:
- Promotion .
The 7P Marketing Mix , simply adds the next 3 factors to this:
Physical Evidence .
We explained in our “ 4P Marketing Mix ” page, the main factors to study within a 4P analysis.
- If you have not visited that page yet, we encourage you to do so right now since here, we’ll just explain the additional 3 factors that a 7P Marketing Mix includes .
What do these 3 new factors mean?
Now, we’ll explain you what these new factors add with some examples and why should you worry about them:
1. Physical Evidence - 7P Marketing Mix
This factor tends to have more than one meaning.
Depending on who you ask you can receive a different answer.
It Usually means 2 things :
- Literally, giving the customer Physical Evidence about what they are buying .
- Show, with Physical Evidence, why your product is the best in the Market .
We know that both of them seem to be the same.
Now, we’ll explain the difference with helpful examples:
1.1 Give Physical Evidence about what they are buying
Sometimes, Companies offer intangible products or some intangible values that are associated to their physical products.
Customers are like “serial killers”: they like keeping evidences about what they purchased .
- The higher the price of the product, the bigger the evidence should be.
This evidence can be in :
- With the Logo of the Brand everywhere.
- Usually in luxury brands.
- With VIP Memberships, for example.
Rolex - Physical Evidence - 7P Marketing Mix example

The Rolex example is the best one we could have chosen since it offers lots of Physical Evidences.
1. As soon as you enter in an authorized Rolex shop :
- If you are intended to buy a Rolex, you’ll surely receive a glass of Champagne .
2. Together with your Watch, you’ll receive:
- A serial number that guarantees that it is not a fake watch.
- A high quality leather box containing the watch.
- Access to the Rolex community ; events, notifications, etc.
3. The watch has a perfectly identifiable design .
- You receive a watch that everybody identifies as synonym of high economical status.

All these things are not assuring you that Rolex is the best technical option you could have made.
These Physical Evidences tell you that you are purchasing a luxury product, nothing else :
- The box may seem very beautiful, but its price is nothing compared to the watch you are acquiring.
- The glass of Champagne may feel very sophisticated, but it represents nothing to the shop: the whole bottle may cost $50.
- If Rolex changed its famous designs, the people wouldn’t identify their watches so easily (and lets be honest; 80% of the people owning a Rolex want to brag about it).
1.2. Physical Evidence about why your product is the best in the Market
This is a different Physical Evidence approach.
While the previous one was more “whim-oriented”, this one is a more Technical approach .
When you are stating that your product is either the best one, or different, you have to give proof about it to your customers before they buy your product .
We will give you an example about what may happen if you don’t or can’t give Physical Evidence to your customers :
Nintendo 3DS - Physical Evidence - 7P Marketing Mix example

As soon as Nintendo announced the Nintendo 3DS we were sure about its success.
- A portable device that can generate 3D images without any glasses : Amazing!
However it didn’t succeeded as much as Nintendo expected … Why?
The problem they had was that Nintendo couldn’t give Physical Evidence about its technically-amazing product through conventional Marketing campaigns .
- You could see a TV commercial where they explained to you how good the 3D images were, but unless you were in front of it, you would never experience the effect .
Nintendo 3DS case is very curious, because Nintendo couldn’t do much for giving Physical Evidence about its product .
This example shows how, sometimes, having the best product in not enough: you always have to give proof about what you offer .
- That is why that many food brands offer you little pieces of cheese, chocolate, drinks… at the supermarkets.
2. Process - 7P Marketing Mix
The process represents all the actions that take place when developing, showing and delivering your product to the final customer .
This is a commonly forgotten factor but for some companies, it represents the real key to success.
Think about how many businesses success mainly, because they have a proper process:
- Automotive companies that elaborate their cars efficiently .
- Websites that have a nice and friendly user interface.
- Fast food companies that have defined a elaboration process that saves time and money.
A proper process can :
- Increase your margins by reducing the costs .
- Allow you to engage more with your customers .
- Ensure the best quality .
Nespresso - Process - 7P Marketing Mix example

If there is a company that has understood how important the “purchasing process” is for engaging your customers, is Nespresso .
- Nespresso is a good example for lots of things: Design, Physical Evidence, Branding…
However, we’ll focus on how good its selling process is :
- They design elegant stores that customers identify with the company’s essence.
- As soon as you enter in its stores, you find stylish people that are always very kind to you .
- The product is placed in perfectly neat shelves .
- They offer you a free coffee .
- You can enter in the Nespresso club , with nice discounts and access to promotions.
- Finally, there are always new flavors so you “feel the obligation” of coming back periodically .

This “purchasing process” generates a desirable experience for the customers and allows Nespresso to project its coffee as a more exclusive product.
If you think about it, Nespresso just sells coffee, nothing else (ok, coffee machines) then… Why do you feel that they are offering you something else?
So, from now on, don’t focus just on the product itself.
Regard it as an entire Manufacturing and Delivery Process :
- From the moment it was being developed to the moment the final client received it.
3. People - 7P Marketing Mix
The People factor refers to everyone involved in the Marketing and Manufacturing process .
Sometimes, this factor only considers people within a Company: Designers, Managers… but Clients should also be taken into account .
Hence, we’ll divide this factor into 2:
- The People involved in the product’s development .
- Clients ‘ profiles.
3.1 People involved in the product's development
This is an extension of the 7P Process factor, previously explained.
A company is as good as the people integrating it , so you should analyze all the professionals involved at key positions:
- Commercials.
Apollo XI - People - 7P Marketing Mix example

It’s been 50 years since the first man reached the moon with the Apollo XI.
Undoubtedly, it is one of the biggest achievements in history of mankind.
But, how on earth could they reach the moon with 1969’s technology?
- They had the best scientists and engineers in the world . That is how.
If you wanted to replicate this big achievement, you would have to hire the best brains in the world.
This simple but effective example shows how sometimes, the key thing for guaranteeing a project’s success is the people involved .
- You can also appreciate this fact at Movies, where the success normally relies on one single actor’s interpretation.
3.2 Clients' profiles
This factor highlights how important is to take into account your clients:
- Who they are .
- Where they come from .
- What they like .
YouTube - People - 7P Marketing Mix example

Some years ago, while I was having a beer at a friend’s house and, I remembered an interesting video I had watched on YouTube.
It was a video that had been suggested to me repeatedly, so I expected to find the same video at the first page of my friend’s computer .
However, I found completely different suggestions at his main page.
Now, we all know that YouTube suggests certain videos to certain profiles.
But at that moment that shocked me, since it was a similar person, with similar cultural background , from the same city, with the same age.
- We went to the same school… so I was surprised YouTube had not suggested this video to my friend.
YouTube analyzes all the videos you have seen so far, the ones that you liked the most, the language of the videos, where you come from… So they can suggest the content that better fits you .
And that is why YouTube is of king of content nowadays.
Categorize customers is very difficult.
Even between brothers and sisters you would have it difficult: how different we are from our parents, cousins, brothers…
No matter how difficult it is: you have to adapt your Marketing strategies to your client’s tastes, cultural backgrounds and preferences .
Otherwise you’ll never engage with them.
Never forget: Your client must be the centre of all the decisions you take .
Summarizing
The 7P Marketing Mix is nothing but an amplified 4P analysis.
To the traditional:
The 7P Marketing Mix adds :
- Give physical evidence about what the customer is buying .
- Give proof about why your product is the best in the market.
- Analyze the actions that take place when developing, showing and delivering your product to the final customer .
- Which are the clients’ profiles .
- Economies of Scale
- Business Plan for Beginners
- Business Plan Basics
- How to write a Business Plan
- Cash Flow Calculation
- Raising Funds for a Business
- 4 C’s of Credit
- Business Plan Templates
- Customer Insight
- Customer Experience
- Customer Pain Points
- 4C Marketing Model
- RATER Model
- Augmented Product
- Product Mix
- Unique Selling Proposition
- DAGMAR Model
- Marketing Storytelling
- Content Marketing
- Psychographics
- Barnum Effect
- Market Segmentation
- Market Research & Big Data
- Marketing to Generation Z
- 4P Marketing Mix
- Sales Funnel
- Loyalty Ladder
- RACE Planning
- Push and Pull Marketing
- Marketing Strategy
- Marketing Templates
- Starting your own business
- From Startup to a Business
- Entrepreneur FAQs
- Start your Business Idea
- Entrepreneur Golden Rules
- Innovate or Imitate?
- Design Thinking
- SCAMPER Model
- AAR Process
- Work From Home
- Growth strategies for Startups
- VMOST Analysis
- 3P Framework
- SOAR Analysis
- TELOS Analysis
- 5 C’s of Entrepreneurship
- Crowdfunding
- BATNA & ZOPA Negotiation
- Entrepreneur with no Money
- Entrepreneurship Templates
- Strategy vs Tactics
- Mission and Vision
- Business Values
- Value Chain
- Scenario Planning
- Porter 6 Forces
- Bowman’s Strategy Clock
- GE-McKinsey Matrix
- Delta Model
- PEST Analysis
- PESTEL Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- VRIO Framework
- Strategy Canvas
- Competitive Advantages
- Porter’s Four Corners
- 5 Ps of Strategy
- Porter’s Generic Strategies
- Porter’s Diamond Model
- Wardley Map
- Core Competencies
- Resource Based View
- Bridges Transition Model
- CAGE Distance Framework
- McKinsey’s 3 Horizons
- Vertical Integration
- Horizontal Integration
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Red Ocean Strategy
- Porter 5 Forces
- Ansoff Matrix
- McKinsey 7S Framework
- CATWOE Analysis
- Strategy Pyramid
- Bain’s RAPID Framework
- Balanced Scorecard
- Resources and Capabilities
- Strategy of Apple
- Strategy of Amazon
- Strategy of Starbucks
- Strategy Templates
- Communicate Effectively
- COIN Conversation Model
- SCARF Model
- SBI Feedback Model
- CEDAR Feedback Model
- How to behave at a meeting
- Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle
- Bloom’s Taxonomy
- 5E Learning Model
- 9-Box Performance Grid
- SEEDS Bias Model
- Halo Effect
- Pygmalion Rosenthal Effect
- Dunning-Kruger Effect
- How to be an Entrepreneur
- How to be a Leader
- Mintzberg Managerial Roles
- Cog’s Ladder
- The Peter Principle
- How to Negotiate
- Teamwork Skills and Profiles
- Gantt Chart
- RACI Matrix
- Eisenhower Matrix
- MoSCoW Method
- FMEA Process
- Problem Solving
- Ishikawa Fishbone diagram
- 5 Whys Method
- 8 Disciplines Method
- ADDIE Model
- ORAPAPA Method
- Cynefin Framework
- Just In Time
- SMART Goals
- KISS Principle
- Birkinshaw’s 4 Dimensions
- Parkinson’s Law
- OGSM Framework
- OKR Methodology
- APQP Framework
- Theory of Constraints
- Success through Organization
- ADKAR Model
- Lewin’s Change Model
- Kotter’s 8-Step Model
- The Greiner Curve
- GAP Analysis
- Planning Templates
- Mean, Median and Mode
- Define your Data
- Pareto Principle 80/20 Rule
- Decision Matrix
- Decision Tree
- TARA Framework
- Root Cause Analysis
- Simplex Process
- Forecasting Methods
- Product Life Cycle
- How to use Google Trends
- Correlation vs Causation
© 2024 - Consuunt .
We're not around right now. But you can send us an email and we'll get back to you, asap.
Log in with your credentials
Forgot your details.
- Privacy Policy
- Affiliate Disclosure

The Strategy Watch
To be the Best Source of Business Strategy & Analysis
7 Ps of Marketing Mix with Example
The marketing mix is a very common and famous term in the marketing sector. Marketing mix is all about putting the right combination of product in the right place, at the right time and at the right price to attract the target customers. The marketing mix is called 4 Ps & 7 Ps. The 4 Ps have been associated with the marketing mix concept since their creation by E. Jerome McCarthy in 1960. But later on in 1981 Booms & Bitner added 3 new Ps to the 4 Ps Principle. These 3Ps were directly related to the service provider industry. From then it is called 7 Ps of marketing mix. The product marketing mix consists of the 4 P’s which are Product, Pricing, Promotions, and Placement. Later other 3 Ps are being added which are People, Process, and Physical evidence .
Product can be tangible & intangible. In both cases, if the product quality is good then it can promote itself in the market. On the other hand, if the product is poor then it cannot stay or give service any longer in the extremely competitive market. Market research is a must before producing or serving products. Producers have to make sure whether there is sufficient target market. Successful companies always look for the demands & want of the customers and then they develop their products. At present’s world, the first ‘P’ includes services too, but when the Marketing Mix was first devised, it was targeted at products only.
For example, if a company wants to produce Rolls Royce cars in a specific country, they first have to think whether Rolls Royce could meet up the demands of the customers or they would go down in that market.
Pricing has a lot to do with how a product will be perceived and branding. Pricing not only determines amount of the profit of the business but also affects the value of the products. There are many customers who will use product’s pricing to judge the quality. Again there are customers will compare price before deciding to purchase.
For example, if any company wants to sell cars at a high price then that company will go for expensive and high quality. Customers will be happy to pay more but in exchange for higher prices they want and expect a better quality product & service.
e are familiar with a term, “being in the right place at the right time”. It means place is very important in terms of marketing. A company should be where it’s customers want it to be. for both biological & service products, place is very vital in marketing mix. Business should review the locations where the customers meet their demand conveniently. Sometimes a change in places can lead to a rapid increase in sales. Entrepreneurs have to make the right choice about the best location for the convenience of the customers to get their essential service or product.
For example, the best place to open a petrol pump is on the highway or in the city. A place where there is less traffic is a wrong location to start a petrol pump.
Promotion is another vital P to pay attention to. It is an art. Promotion consists of a wide range of activity like advertising, PR, special offers, and discounts. Good promotion is to communicate the benefits of the products and services. In some cases, websites are the signs of promotion too. The first-time experience of customers normally values a company by visiting its website. Websites need to be more friendly and also clearly laid out.
For example, sales, advertising, sales promotion, public relations, direct marketing, online communications and personal selling.
People is the most important element in a service marketing mix. Every company is dependent on the people who run them from front-line sales staff to the Managing Director. Know-how Employees, Staff members, Operations along with other Customers add benefits and values in the service or product.
For example, for an IT company, the software engineers define as people; for a restaurant , the chefs and service staffs define as people.
Process is like system & tactics through which a service or product is delivered to the final customer. Again how the service is delivered is a part of what the consumer is paying for. It is more about the customer interface between the business and consumer and how they deal with each other in different stages, i.e. throughout the process. One of the keys to a good buying process is speed. This speed concept comes in terms of delivering of products ordered on the internet. Business process should be designed with the customer in mind, and not at your convenience.
For example, more sales staff are now involved in conversion.
Physical Evidence
Physical evidence is the material part of business or service. It is also about the customer experience. Customers are not familiar when they first engage with a company. In this case, company needs to provide the customers with physical evidence which will inspire their confidence.
There are many examples of physical evidence, including buildings, equipment, signs and logos, business reports, brochures, website, and even business cards etc.
From the discussion on the marketing mix examples above, it is clear that in order to become successful in business, one must follow these 7 Ps of marketing mix properly. Many business plans could not able to become successful because of not executing these 7Ps in a proper way. Business or service companies need to get each of these elements correct. It is evident that by following these 7Ps products or services will reach their highest level of success, companies will get maximum profits , they will get customer satisfaction, products will be sustained for long period and companies can improve their corporate images.
Here are the Marketing Mix Analysis of Several Companies Conducted by The Strategy Watch.
[table id=2 /]
You May Also Like:
- Best financial calculators for MBA students?
- Best Milligram Scales – Review and Guide
- Best Postal Scales – Review and Guide
- Best Fishing Scales – Review and Guide
- Best Coffee Scales – – Review and Guide
Reference(s)
1) http://www.marketingteacher.com/marketing-mix/ 2) https://in-business.org.uk/marketing-mix-7ps-example-marketing-mix-7ps-pdf/ 3) https://www.professionalacademy.com/blogs-and-advice/marketing-theories—the-marketing-mix—from-4-p-s-to-7-p-s 4) https://www.cleverism.com/7ps-additional-aspects-marketing-mix/ 5) https://www.marketing91.com/service-marketing-mix/ 6) https://www.slideshare.net/HarshitChadha/marketing-mix-7-ps-34642513 7) https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/70824 8) http://mrdashboard.com/index.php/7ps-of-marketing-mix-with-examples/

Sadnan is one of the top contributors of The Strategy Watch, he has been actively contributing since 2017 as a Content Analyst; He has finished his graduation from North South University with a dual major in Accounting & Finance. As a contributor, he has written for different topics including Leadership Styles and Qualities, Finance, and Economics. He also has a strong interest in SWOT & PESTLE Analysis and Marketing Strategy.
Home Free PowerPoint Templates Free 7 P’s Marketing Mix PowerPoint Templates
Download Free 7 P’s Marketing Mix PowerPoint Templates
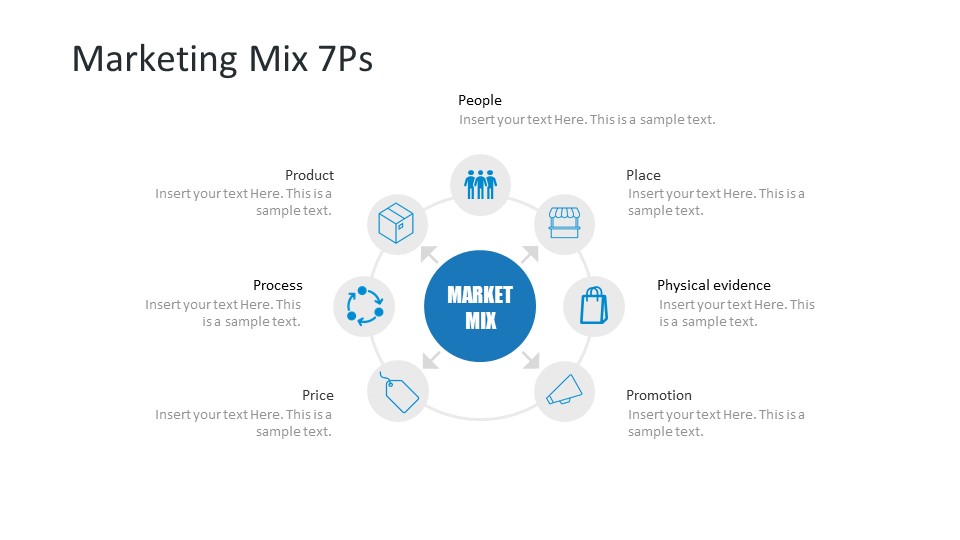
The Free 7 P’s Marketing Mix PowerPoint Templates are business concept presentation layouts. 7 P’s is a continuous reevaluation model for business marketing strategies. These seven P’s are product, price, promotion, place, packaging, positioning, and people. The products, market, and customer’s needs change rapidly. Therefore, it is necessary to continuously check 7 P’s to make sure you are up-to-date with current marketplace.
This market positioning diagram template provides a circular process cycle with market mix core unit. It displays all seven components of marketing concept with the help of clipart icons. For instance, a retail store for market place, shopping bag for packaging, megaphone for promotions, etc. These graphics will assist in creating a mental image of marketing mix elements. In this way, presenter can describe company’s approach toward each component by simply looking at clipart PowerPoint shape.
Free 7 P’s Marketing Mix PowerPoint Templates offers 9 slides with two content layout designs. The circular diagram template shows merge of both 4 P’s and 7 P’s marketing mix. This diagram highlights 4 P’s factors with arrow shapes i.e. Place, Promotion, Price, and Product. There are 7 additional slides of a circular diagram with text placeholders. These slides will help describe strategies and requirements of all seven components individually. The subsequent 7 slides are suitable for staff meetings or training material.
The second template layout of 7 P’s marketing plan PowerPoint template demonstrates a table format. It gives an overview of all seven segments with a brief description of business approach. The plain white PowerPoint background will allow users to easily copy slides into any presentation theme. Simply copy and paste PowerPoint slides by choosing Match Destination Theme option. The Google Slides Theme of 7 P’s marketing mix is also available that users can copy for online presentations.
- 100% Editable PowerPoint Templates.
- Compatible with all major Microsoft PowerPoint versions, Keynote and Google Slides.
- Modern 16:9 Aspect Ratio.
- Scalable Vectorial PowerPoint Shapes and PowerPoint Icons.
- Instant Access and Download.
- New Templates every week.
Google Slides Preview
Our PowerPoint Templates are compatible with Google Slides. Take the most of every platform using the tool you like.

Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This is the ultimate guide to creating a comprehensive and effective plan to start a business . In today’s dynamic business landscape, having a well-crafted business plan is an important first step to securing funding, attracting partners, and navigating the challenges of entrepreneurship.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Embarking on the journey of creating a successful business requires a solid foundation, and a well-crafted business plan is the cornerstone. Here is the process of writing a comprehensive business plan and the main parts of a winning business plan . From setting objectives to conducting market research, this guide will have everything you need.
Executive Summary

The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Think of it as an elevator pitch in written form: it should be compelling enough to engage potential investors or stakeholders and provide them with a clear understanding of what your business is about, its goals, and why it’s a promising investment.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives

In the Overview and Business Objectives section, outline your business’s core goals and the strategic approaches you plan to use to achieve them. This section should set forth clear, specific objectives that are attainable and time-bound, providing a roadmap for your business’s growth and success.
It’s important to detail how these objectives align with your company’s overall mission and vision. Discuss the milestones you aim to achieve and the timeframe you’ve set for these accomplishments.
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
- Introducing three new products within the first two years of operation.
- Achieving annual revenue growth of 30%.
- Expanding our customer base to over 10,000 clients by the end of the third year.
Company Description

The Company Description section is your opportunity to delve into the details of your business. Provide a comprehensive overview that includes your company’s history, its mission statement, and its vision for the future.
Highlight your unique selling proposition (USP) – what makes your business stand out in the market. Explain the problems your company solves and how it benefits your customers.
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market

Defining Your Target Market is critical for tailoring your business strategy effectively. This section should describe your ideal customer base in detail, including demographic information (such as age, gender, income level, and location) and psychographic data (like interests, values, and lifestyle).
Elucidate on the specific needs or pain points of your target audience and how your product or service addresses these. This information will help you know your target market and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis

The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
This analysis will enable you to spot market opportunities and anticipate potential challenges. Include data and statistics to back up your claims, and use graphs or charts to illustrate market trends.
This section should demonstrate that you have a deep understanding of the market in which you operate and that your business is well-positioned to capitalize on its opportunities.
Example: The market for eco-friendly technology products has experienced significant growth in recent years, with an estimated annual growth rate of 10%. As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, the demand for sustainable solutions continues to rise.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis

A SWOT analysis in your business plan offers a comprehensive examination of your company’s internal and external factors. By assessing Strengths, you showcase what your business does best and where your capabilities lie.
Weaknesses involve an honest introspection of areas where your business may be lacking or could improve. Opportunities can be external factors that your business could capitalize on, such as market gaps or emerging trends.
Threats include external challenges your business may face, like competition or market changes. This analysis is crucial for strategic planning, as it helps in recognizing and leveraging your strengths, addressing weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and preparing for potential threats.
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
- Innovative and eco-friendly product offerings.
- Strong commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Skilled and experienced team with expertise in technology and sustainability.
Weaknesses:
- Limited brand recognition compared to established competitors.
- Reliance on third-party manufacturers for product development.
Opportunities:
- Growing consumer interest in sustainable products.
- Partnerships with environmentally-focused organizations and influencers.
- Expansion into international markets.
- Intense competition from established technology companies.
- Regulatory changes could impact the sustainable technology market.
Competitive Analysis

In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
By conducting a thorough competitive analysis, you can gain insights into your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, enabling you to develop strategies to differentiate your business and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Example: Key competitors include:
GreenTech: A well-known brand offering eco-friendly technology products, but with a narrower focus on energy-saving devices.
EarthSolutions: A direct competitor specializing in sustainable technology, but with a limited product range and higher prices.
By offering a diverse product portfolio, competitive pricing, and continuous innovation, we believe we can capture a significant share of the growing sustainable technology market.
Organization and Management Team

Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Showcasing your team’s background, skills, and accomplishments instills confidence in investors and other stakeholders, proving that your business has the leadership and talent necessary to achieve its objectives and manage growth effectively.
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered

Describe the products or services your business offers, focusing on their unique features and benefits. Explain how your offerings solve customer pain points and why they will choose your products or services over the competition.
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Example: EcoTech offers a range of eco-friendly technology products, including energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers, and smart home devices that optimize energy usage. Our products are designed to help customers reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Marketing and Sales Strategy

In this section, articulate your comprehensive strategy for reaching your target market and driving sales. Detail the specific marketing channels you plan to use, such as social media, email marketing, SEO, or traditional advertising.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
This section is critical to convey to investors and stakeholders that you have a well-thought-out approach to market your business effectively and drive sales growth.
Example: Our marketing strategy includes digital advertising, content marketing, social media promotion, and influencer partnerships. We will also attend trade shows and conferences to showcase our products and connect with potential clients. Our sales strategy involves both direct sales and partnerships with retail stores, as well as online sales through our website and e-commerce platforms.
Logistics and Operations Plan

The Logistics and Operations Plan is a critical component that outlines the inner workings of your business. It encompasses the management of your supply chain, detailing how you acquire raw materials and manage vendor relationships.
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Quality control measures are essential to maintain product standards and customer satisfaction. This plan assures investors and stakeholders of your operational competency and readiness to meet business demands.
Highlighting your commitment to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction underlines your business’s capability to maintain smooth, effective operations even as it scales.
Example: EcoTech partners with reliable third-party manufacturers to produce our eco-friendly technology products. Our operations involve maintaining strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring quality control, and managing inventory.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan

In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Ground these projections in solid assumptions based on your market analysis, industry benchmarks, and realistic growth scenarios. Break down revenue streams and include an analysis of the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and potential investments.
This section should also discuss your break-even analysis, cash flow projections, and any assumptions about external funding requirements.
By presenting a thorough and data-backed financial forecast, you instill confidence in potential investors and lenders, showcasing your business’s potential for profitability and financial stability.
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Example: Over the next three years, we expect to see significant growth in revenue, driven by new product launches and market expansion. Our financial projections include:
- Year 1: $1.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $200,000.
- Year 2: $3 million in revenue, with a net profit of $500,000.
- Year 3: $4.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $1 million.
These projections are based on realistic market analysis, growth rates, and product pricing.
Income Statement

The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Regularly reviewing and analyzing your income statement allows you to monitor the health of your business, evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies, and make data-driven decisions to optimize profitability and growth.
Example: The income statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
- Revenue: $1,500,000
- Cost of Goods Sold: $800,000
- Gross Profit: $700,000
- Operating Expenses: $450,000
- Net Income: $250,000
This statement highlights our company’s profitability and overall financial health during the first year of operation.
Cash Flow Statement

A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
By including a cash flow statement in your business plan, you demonstrate your ability to manage your company’s finances effectively.
Example: The cash flow statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
Operating Activities:
- Depreciation: $10,000
- Changes in Working Capital: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Operating Activities: $210,000
Investing Activities:
- Capital Expenditures: -$100,000
- Net Cash from Investing Activities: -$100,000
Financing Activities:
- Proceeds from Loans: $150,000
- Loan Repayments: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Financing Activities: $100,000
- Net Increase in Cash: $210,000
This statement demonstrates EcoTech’s ability to generate positive cash flow from operations, maintain sufficient liquidity, and invest in growth opportunities.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan

1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively.
2. Conduct thorough research: Before writing your business plan, gather as much information as possible about your industry, competitors, and target market. Use reliable sources and industry reports to inform your analysis and make data-driven decisions.
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
5. Be flexible and adaptable: A business plan is a living document that should evolve as your business grows and changes. Be prepared to update and revise your plan as you gather new information and learn from your experiences.
6. Use visuals to enhance understanding: Include charts, graphs, and other visuals to help convey complex data and ideas. Visuals can make your business plan more engaging and easier to digest, especially for those who prefer visual learning.
7. Seek feedback from trusted sources: Share your business plan with mentors, industry experts, or colleagues and ask for their feedback. Their insights can help you identify areas for improvement and strengthen your plan before presenting it to potential investors or partners.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
The template is divided into the following sections:
- Mission statement
- Business Overview
- Key products or services
- Target market
- Financial highlights
- Company goals
- Strategies to achieve goals
- Measurable, time-bound objectives
- Company History
- Mission and vision
- Unique selling proposition
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Pain points
- Industry trends
- Customer needs
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Competitor products and services
- Market positioning
- Pricing strategies
- Organizational structure
- Key roles and responsibilities
- Management team backgrounds
- Product or service features
- Competitive advantages
- Marketing channels
- Advertising campaigns
- Promotional activities
- Sales strategies
- Supply chain management
- Inventory control
- Production processes
- Quality control measures
- Projected revenue
- Assumptions
- Cash inflows
- Cash outflows
- Net cash flow
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines an organization’s goals, objectives, and the steps required to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap as you start a business , guiding the company’s direction and growth while identifying potential obstacles and opportunities.
Typically, a business plan covers areas such as market analysis, financial projections, marketing strategies, and organizational structure. It not only helps in securing funding from investors and lenders but also provides clarity and focus to the management team.
A well-crafted business plan is a very important part of your business startup checklist because it fosters informed decision-making and long-term success.

Why You Should Write a Business Plan
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
- Attract Investors and Secure Funding : A well-written business plan demonstrates your venture’s potential and profitability, making it easier to attract investors and secure the necessary funding for growth and development. It provides a detailed overview of your business model, target market, financial projections, and growth strategies, instilling confidence in potential investors and lenders that your company is a worthy investment.
- Clarify Business Objectives and Strategies : Crafting a business plan forces you to think critically about your goals and the strategies you’ll employ to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for success. This process helps you refine your vision and prioritize the most critical objectives, ensuring that your efforts are focused on achieving the desired results.
- Identify Potential Risks and Opportunities : Analyzing the market, competition, and industry trends within your business plan helps identify potential risks and uncover untapped opportunities for growth and expansion. This insight enables you to develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities, positioning your business for long-term success.
- Improve Decision-Making : A business plan serves as a reference point so you can make informed decisions that align with your company’s overall objectives and long-term vision. By consistently referring to your plan and adjusting it as needed, you can ensure that your business remains on track and adapts to changes in the market, industry, or internal operations.
- Foster Team Alignment and Communication : A shared business plan helps ensure that all team members are on the same page, promoting clear communication, collaboration, and a unified approach to achieving the company’s goals. By involving your team in the planning process and regularly reviewing the plan together, you can foster a sense of ownership, commitment, and accountability that drives success.
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
- Startup Business Plan: Tailored for new ventures, a startup business plan outlines the company’s mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. It helps entrepreneurs clarify their vision, secure funding from investors, and create a roadmap for their business’s future. Additionally, this plan identifies potential challenges and opportunities, which are crucial for making informed decisions and adapting to changing market conditions.
- Internal Business Plan: This type of plan is intended for internal use, focusing on strategies, milestones, deadlines, and resource allocation. It serves as a management tool for guiding the company’s growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. The internal business plan also helps identify areas of improvement, fosters collaboration among team members, and provides a reference point for measuring performance.
- Strategic Business Plan: A strategic business plan outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for the company’s direction. It typically includes a SWOT analysis, market research, and competitive analysis. This plan allows businesses to align their resources with their objectives, anticipate changes in the market, and develop contingency plans. By focusing on the big picture, a strategic business plan fosters long-term success and stability.
- Feasibility Business Plan: This plan is designed to assess the viability of a business idea, examining factors such as market demand, competition, and financial projections. It is often used to decide whether or not to pursue a particular venture. By conducting a thorough feasibility analysis, entrepreneurs can avoid investing time and resources into an unviable business concept. This plan also helps refine the business idea, identify potential obstacles, and determine the necessary resources for success.
- Growth Business Plan: Also known as an expansion plan, a growth business plan focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. It includes market analysis, new product or service offerings, and financial projections to support expansion plans. This type of plan is essential for businesses looking to enter new markets, increase their customer base, or launch new products or services. By outlining clear growth strategies, the plan helps ensure that expansion efforts are well-coordinated and sustainable.
- Operational Business Plan: This type of plan outlines the company’s day-to-day operations, detailing the processes, procedures, and organizational structure. It is an essential tool for managing resources, streamlining workflows, and ensuring smooth operations. The operational business plan also helps identify inefficiencies, implement best practices, and establish a strong foundation for future growth. By providing a clear understanding of daily operations, this plan enables businesses to optimize their resources and enhance productivity.
- Lean Business Plan: A lean business plan is a simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements such as value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams, and cost structure. It is perfect for startups looking for a flexible, adaptable planning approach. The lean business plan allows for rapid iteration and continuous improvement, enabling businesses to pivot and adapt to changing market conditions. This streamlined approach is particularly beneficial for businesses in fast-paced or uncertain industries.
- One-Page Business Plan: As the name suggests, a one-page business plan is a concise summary of your company’s key objectives, strategies, and milestones. It serves as a quick reference guide and is ideal for pitching to potential investors or partners. This plan helps keep teams focused on essential goals and priorities, fosters clear communication, and provides a snapshot of the company’s progress. While not as comprehensive as other plans, a one-page business plan is an effective tool for maintaining clarity and direction.
- Nonprofit Business Plan: Specifically designed for nonprofit organizations, this plan outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation. It helps secure grants and donations while ensuring the organization stays on track with its objectives. The nonprofit business plan also helps attract volunteers, board members, and community support. By demonstrating the organization’s impact and plans for the future, this plan is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and long-term sustainability within the nonprofit sector.
- Franchise Business Plan: For entrepreneurs seeking to open a franchise, this type of plan focuses on the franchisor’s requirements, as well as the franchisee’s goals, strategies, and financial projections. It is crucial for securing a franchise agreement and ensuring the business’s success within the franchise system. This plan outlines the franchisee’s commitment to brand standards, marketing efforts, and operational procedures, while also addressing local market conditions and opportunities. By creating a solid franchise business plan, entrepreneurs can demonstrate their ability to effectively manage and grow their franchise, increasing the likelihood of a successful partnership with the franchisor.
Using Business Plan Software

Creating a comprehensive business plan can be intimidating, but business plan software can streamline the process and help you produce a professional document. These tools offer a number of benefits, including guided step-by-step instructions, financial projections, and industry-specific templates. Here are the top 5 business plan software options available to help you craft a great business plan.
1. LivePlan
LivePlan is a popular choice for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features. It offers over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, and the ability to track your progress against key performance indicators. With LivePlan, you can create visually appealing, professional business plans that will impress investors and stakeholders.
2. Upmetrics
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
Bizplan is designed to simplify the business planning process with a drag-and-drop builder and modular sections. It offers financial forecasting tools, progress tracking, and a visually appealing interface. With Bizplan, you can create a business plan that is both easy to understand and visually engaging.
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
5. Tarkenton GoSmallBiz
Developed by NFL Hall of Famer Fran Tarkenton, GoSmallBiz is tailored for small businesses and startups. It features a guided business plan builder, customizable templates, and financial projection tools. GoSmallBiz also offers additional resources, such as CRM tools and legal document templates, to support your business beyond the planning stage.
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are to guide the company’s strategy, attract investment, and evaluate performance against objectives. Here’s a closer look at each of these:
- It outlines the company’s purpose and core values to ensure that all activities align with its mission and vision.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of the market, including trends, customer needs, and competition, helping the company tailor its products and services to meet market demands.
- It defines the company’s marketing and sales strategies, guiding how the company will attract and retain customers.
- It describes the company’s organizational structure and management team, outlining roles and responsibilities to ensure effective operation and leadership.
- It sets measurable, time-bound objectives, allowing the company to plan its activities effectively and make strategic decisions to achieve these goals.
- It provides a comprehensive overview of the company and its business model, demonstrating its uniqueness and potential for success.
- It presents the company’s financial projections, showing its potential for profitability and return on investment.
- It demonstrates the company’s understanding of the market, including its target customers and competition, convincing investors that the company is capable of gaining a significant market share.
- It showcases the management team’s expertise and experience, instilling confidence in investors that the team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
- It establishes clear, measurable objectives that serve as performance benchmarks.
- It provides a basis for regular performance reviews, allowing the company to monitor its progress and identify areas for improvement.
- It enables the company to assess the effectiveness of its strategies and make adjustments as needed to achieve its objectives.
- It helps the company identify potential risks and challenges, enabling it to develop contingency plans and manage risks effectively.
- It provides a mechanism for evaluating the company’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, profitability, and cash flow.
Can I write a business plan by myself?
Yes, you can write a business plan by yourself, but it can be helpful to consult with mentors, colleagues, or industry experts to gather feedback and insights. There are also many creative business plan templates and business plan examples available online, including those above.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
A typical business plan ranges from 20 to 50 pages, but the length may vary depending on the complexity and needs of the business.
What is a business plan outline?
A business plan outline is a structured framework that organizes the content of a business plan into sections, such as the executive summary, company description, market analysis, and financial projections.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
The five most common business plan mistakes include inadequate research, unrealistic financial projections, lack of focus on the unique selling proposition, poor organization and structure, and failure to update the plan as circumstances change.
What questions should be asked in a business plan?
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan focuses on the overall vision, goals, and tactics of a company, while a strategic plan outlines the specific strategies, action steps, and performance measures necessary to achieve the company’s objectives.
How is business planning for a nonprofit different?
Nonprofit business planning focuses on the organization’s mission, social impact, and resource management, rather than profit generation. The financial section typically includes funding sources, expenses, and projected budgets for programs and operations.
Image: Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.
8 Business Plan Templates You Can Get for Free
8 min. read
Updated April 10, 2024
A business plan template can be an excellent tool to simplify the creation of your business plan.
The pre-set structure helps you organize ideas, covers all critical business information, and saves you time and effort on formatting.
The only issue? There are SO many free business plan templates out there.
So, which ones are actually worth using?
To help remove the guesswork, I’ve rounded up some of the best business plan templates you can access right now.
These are listed in no particular order, and each has its benefits and drawbacks.
What to look for in a business plan template
Not all business plan templates are created equal. As you weigh your options and decide which template(s) you’ll use, be sure to review them with the following criteria in mind:
- Easy to edit: A template should save you time. That won’t be the case if you have to fuss around figuring out how to edit the document, or even worse, it doesn’t allow you to edit at all.
- Contains the right sections: A good template should cover all essential sections of a business plan , including the executive summary, product/service description, market/competitive analysis, marketing and sales plan, operations, milestones, and financial projections.
- Provides guidance: You should be able to trust that the information in a template is accurate. That means the organization or person who created the template is highly credible, known for producing useful resources, and ideally has some entrepreneurial experience.
- Software compatibility: Lastly, you want any template to be compatible with the software platforms you use. More than likely, this means it’s available in Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or PDF format at a minimum.
1. Bplans — A plan with expert guidance

Since you’re already on Bplans, I have to first mention the templates that we have available.
Our traditional and one-page templates were created by entrepreneurs and business owners with over 80 years of collective planning experience. We revisit and update them annually to ensure they are approachable, thorough, and aligned with our team’s evolving best practices.
The templates, available in Word, PDF, or Google Doc formats, include in-depth guidance on what to include in each section, expert tips, and links to additional resources.
Plus, we have over 550 real-world sample business plans you can use for guidance when filling out your template.
Download: Traditional lender-ready business plan template or a simple one-page plan template .
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
2. SBA — Introduction to business plans

The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two different business plan templates along with a short planning guide.
While not incredibly in-depth, it’s enough to help you understand how traditional and lean plans are structured and what information needs to be covered. The templates themselves are more like examples, providing you with a finished product to reference as you write your plan.
The key benefit of using these templates is that they were created by the SBA. While they may provide less guidance, you can be assured that the information and structure meet their expectations.
Explore: The SBA’s planning guide and free templates
3. SCORE — Planning workbook

SCORE’s template is more like a workbook. It includes exercises after each section to help you get your ideas down and turn them into a structured plan.
The market research worksheets are especially useful. They provide a clear framework for identifying your target market and analyzing competitors from multiple angles. Plus, they give you an easy way to document all the information you’re collecting.
You will likely have to remove the exercises in this template to make it investor-ready. But it can be worth it if you’re struggling to get past a blank page and want a more interactive planning method.
Download: SCORE’s business plan template
4. PandaDoc — A template with fillable forms

PandaDoc’s library offers a variety of industry-specific business plan templates that feature a modern design flair and concise instructions.
These templates are designed for sharing. They include fillable fields and sections for non-disclosure agreements, which may be necessary when sending a plan to investors.
But the real benefit is their compatibility with PandaDoc’s platform. Yes, they are free, but if you’re a PandaDoc subscriber, you’ll have far more customization options.
Out of all their templates, the standard business plan template is the most in-depth. The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry.
Explore: PandaDoc’s business plan template library
5. Canva — Pitch with your plan

Canva is a great option for building a visually stunning business plan that can be used as a pitch tool. It offers a diverse array of templates built by their in-house team and the larger creative community, meaning the number of options constantly grows.
You will need to verify that the information in the template you choose matches the standard structure of a traditional business plan.
You should do this with any template, but it’s especially important with any tool that accepts community submissions. While they are likely reviewed and approved, there may still be errors.
Remember, you can only edit these templates within Canva. Luckily, you only need a free subscription, and you may just miss out on some of the visual assets being used.
To get the most value, it may be best to create a more traditional planning document and transfer that information into Canva.
Explore: Canva’s business plan gallery
6. ClickUp — The collaborative template

Out of all the project management tools that offer free business plan templates, ClickUp’s is the most approachable.
Rather than throwing you into all the features and expecting you to figure it out—ClickUp provides a thorough startup guide with resource links, images, and videos explaining how to write a plan using the tool.
There’s also a completed sample plan (structured like an expanded one-page plan) for you to reference and see how the more traditional document can connect to the product management features. You can set goals, target dates, leave comments, and even assign tasks to someone else on your team.
These features are limited to the ClickUp platform and will not be useful for everyone. They will likely get in the way of writing a plan you can easily share with lenders or investors.
But this is a great option if you’re looking for a template that makes internal collaboration more fluid and keeps all your information in one place.
Sign Up: Get a free trial of ClickUp and explore their template library
7. Smartsheet — A wide variety of templates

I’m including Smartsheet’s library of templates on this list because of the sheer number of options they provide.
They have a simple business plan template, a one-page plan, a fill-in-the-blank template, a plan outline, a plan grading rubric, and even an Excel-built project plan. All are perfectly usable and vary in visual style, depth of instructions, and the available format.
Honestly, the only drawback (which is also the core benefit) is that the amount of templates can be overwhelming. If you’re already uncertain which plan option is right for you, the lengthy list they provide may not provide much clarity.
At the same time, it can be a great resource if you want a one-stop shop to view multiple plan types.
Explore: Smartsheet’s business plan template library
8. ReferralRock affiliate marketing business plan

I’m adding ReferralRock’s template to this list due to its specificity.
It’s not your standard business plan template. The plan is tailored with specific sections and guidance around launching an affiliate marketing business.
Most of the template is dedicated to defining how to choose affiliates, set commissions, create legal agreements, and track performance.
So, if you plan on starting an affiliate marketing business or program, this template will provide more specific guidance. Just know that you will likely need to reference additional resources when writing the non-industry sections of your plan.
Download: ReferralRock affiliate marketing business plan template
Does it matter what business plan template you use?
The short answer is no. As long as the structure is correct, it saves you time, and it helps you write your business plan , then any template will work.
What it ultimately comes down to, is what sort of value you hope to get from the template.
- Do you need more guidance?
- A simple way to structure your plan?
- An option that works with a specific tool?
- A way to make your plan more visually interesting?
Hopefully, this list has helped you hone in on an option that meets one (or several) of these needs. Still, it may be worth downloading a few of these templates to determine the right fit.
And really, what matters most is that you spend time writing a business plan . It will help you avoid early mistakes, determine if you have a viable business, and fully consider what it will take to get up and running.
If you need additional guidance, check out our library of planning resources . We cover everything from plan formats , to how to write a business plan, and even how to use it as a management tool .
If you don’t want to waste time researching other templates, you can download our one-page or traditional business plan template and jump right into the planning process.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Kody Wirth is a content writer and SEO specialist for Palo Alto Software—the creator's of Bplans and LivePlan. He has 3+ years experience covering small business topics and runs a part-time content writing service in his spare time.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- Qualities of a good template
- ReferralRock
- Does the template matter?
Related Articles

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes

10 Min. Read
14 Reasons Why You Need a Business Plan

6 Min. Read
Business Plan vs Business Model Canvas Explained

Use This Simple Business Plan Outline to Organize Your Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The 7Ps of Marketing: With Examples. We can understand this with the example of a rainbow. The 7 colours of a rainbow and the 7Ps in a marketing mix bear a resemblance. Just as not all rainbows have the same the composition of the VIBGYOR colours, the same way every marketing plan is unique and contains varying amounts of the 7Ps of the ...
It's an essential part of a marketing plan structure that defines the tactics to be used to implement the marketing strategy. The traditional 7Ps of marketing consist of: Product. Promotion. Price. Place. People. Process. Physical evidence.
The 7 Ps of marketing is a method encompassing seven distinct principles that professionals can use to create and employ strategies that attract and engage customers, motivate customer sales and increase revenue. The creator of the 7Ps of marketing is E. Jerome McCarthy in 1960. It comprises three additional marketing principles that build on ...
The 7Ps marketing model is a framework designed to help businesses build a complete marketing strategy, from start to finish. In theory, a new business should be able to use the 7Ps model to devise an entire marketing strategy from scratch. Credit: TrueNorth. The name derives from the seven elements outlined in the 7Ps model, which all begin ...
The 7Ps of service marketing are as follows: Product: It is the 'Core' which is offered to the customer. Price: Matching your pricing with the customer's perceived value of the product or service. Place: Making your product or service available to the customer.
No matter which platforms you choose as your marketing tools, the seven Ps can serve as tried and true basic marketing tactics that you can adapt into your marketing efforts to best fit your ...
Marketing mix is a selection of marketing tools that include several areas of focus that can be combined to create a comprehensive plan. The term refers to a classification that began as the 4 P's: product, price, placement, and promotion, and has been expanded to Product, Price, Promotion, Place, People, Packaging, and Process.
The 4 Ps of marketing is made up of: Price. Product. Promotion. Place. However, because of the increasing demands of the field, there's been an introduction of 7 Ps of marketing which also includes components such as people, positioning, and packaging.
Traditionally, the marketing mix is a framework for your marketing strategy containing four key elements: Product, Place, Price and Promotion. Then we have the extended marketing mix - or the 7Ps - which contains the first four elements, plus Physical Evidence, People and Processes. It's important to note that while the marketing mix can ...
A speech by marketing specialist Neil Borden in the 1950s was the first time the term "marketing mix" was used. Later, marketing professor E. Jerome McCarthy refined Borden's ideas, creating the 4 Ps of marketing (price, product, place, and promotion). He theorized that by using price, product, place, and promotion together, a business ...
These instruments are the 7Ps of Marketing: Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical evidence. Each 'P' holds a unique note in your marketing melody, and understanding how to orchestrate them can turn your business into a masterpiece. Product:What you're selling to satisfy a customer's need.
Real-World Company Examples Using 7Ps. Understanding the 7Ps of marketing is a powerful tool for developing strategy. But, to truly appreciate this model's impact, we need to consider its application in the real world. As a prime example, let's examine how HubSpot, the renowned marketing tool provider, incorporates the 7Ps. HubSpot as a ...
The 7Ps Marketing Mix is a comprehensive set of action plans businesses can use to market their products or services to their target audience. While it provides a coherent framework for evaluating performance, it also assists brands in determining the best combination of elements to establish clear objectives and approaches based on their ...
The marketing mix or 7Ps is a foundation model in marketing. it helps to define the tactics to make the marketing plan happen. A planned approach to marketing helps us to set clear objectives based on the current situation a company is facing. The strategy defines how those objectives will be achieved, including the target market to focus on ...
The 7Ps of Marketing Mix. The Marketing Mix 7P is an extension of the traditional Marketing Mix, and it includes the seven Ps: Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence.Let's take a look at each of these elements in detail. Product. The product P refers to the goods or services that a business offers to its customers.
Promotion. Promotion is one of the 7Ps of the marketing mix techniques used by companies to communicate their customer offerings. It is a combination of advertising, exhibitions, digital marketing, and other elements to pave the way for dialogue with clients. Promotion ought to communicate not only the perks obtained from a product but also its ...
Using the 7Ps. You can use the 7 Ps as headings for discussion, of which the findings and conclusions can then be added to your marketing strategy, which should feature as part of your overall business plan. Some of the things you can focus on under each of the 7P headings, include: PRODUCT - this could be your SERVICE if you are a service ...
The 7Ps of the Marketing Mix is a classic marketing model and simple framework that any business can use to review and optimise its marketing mix and strategy. The 7Ps of Marketing are: Product. Price. Place. Promotion. People. Process. Physical evidence.
7 Ps of Marketing Mix. Product. The product is what you are selling to customers. It could be a tangible product that a company sells or an intangible product like a service. The products and services are meant to meet the needs of customers. For example, people enjoy services in tourism industry; and in the banking sector, there are both ...
Nespresso - Process - 7P Marketing Mix example. If there is a company that has understood how important the "purchasing process" is for engaging your customers, is Nespresso. Nespresso is a good example for lots of things: Design, Physical Evidence, Branding…. However, we'll focus on how good its selling process is:
From the discussion on the marketing mix examples above, it is clear that in order to become successful in business, one must follow these 7 Ps of marketing mix properly. Many business plans could not able to become successful because of not executing these 7Ps in a proper way. Business or service companies need to get each of these elements ...
Free 7 P's Marketing Mix PowerPoint Templates offers 9 slides with two content layout designs. The circular diagram template shows merge of both 4 P's and 7 P's marketing mix. This diagram highlights 4 P's factors with arrow shapes i.e. Place, Promotion, Price, and Product. There are 7 additional slides of a circular diagram with text ...
USES OF THE 7Ps MODEL Conduct a situation analysis Set objectives Conduct a strength, weakness, opportunity and threat (SWOT) Come up with marketing strategies and tactics PRODUCT - Any physical good, service, or idea that is created by an entrepreneur or an innovator in serving the needs of the customers and addressing their existing problems.
The internal business plan also helps identify areas of improvement, fosters collaboration among team members, and provides a reference point for measuring performance. Strategic Business Plan: A strategic business plan outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for the company's direction. It typically ...
Out of all their templates, the standard business plan template is the most in-depth. The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry. Explore: PandaDoc's business plan template library . 5. Canva — Pitch with your plan.