Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples

How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
9.5 Writing Process: Thinking Critically about Rhetoric
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Develop a rhetorical analysis through multiple drafts.
- Identify and analyze rhetorical strategies in a rhetorical analysis.
- Demonstrate flexible strategies for generating ideas, drafting, reviewing, collaborating, revising, rewriting, and editing.
- Give and act on productive feedback for works in progress.
The ability to think critically about rhetoric is a skill you will use in many of your classes, in your work, and in your life to gain insight from the way a text is written and organized. You will often be asked to explain or to express an opinion about what someone else has communicated and how that person has done so, especially if you take an active interest in politics and government. Like Eliana Evans in the previous section, you will develop similar analyses of written works to help others understand how a writer or speaker may be trying to reach them.
Summary of Assignment: Rhetorical Analysis
The assignment is to write a rhetorical analysis of a piece of persuasive writing. It can be an editorial, a movie or book review, an essay, a chapter in a book, or a letter to the editor. For your rhetorical analysis, you will need to consider the rhetorical situation—subject, author, purpose, context, audience, and culture—and the strategies the author uses in creating the argument. Back up all your claims with evidence from the text. In preparing your analysis, consider these questions:
- What is the subject? Be sure to distinguish what the piece is about.
- Who is the writer, and what do you know about them? Be sure you know whether the writer is considered objective or has a particular agenda.
- Who are the readers? What do you know or what can you find out about them as the particular audience to be addressed at this moment?
- What is the purpose or aim of this work? What does the author hope to achieve?
- What are the time/space/place considerations and influences of the writer? What can you know about the writer and the full context in which they are writing?
- What specific techniques has the writer used to make their points? Are these techniques successful, unsuccessful, or questionable?
For this assignment, read the following opinion piece by Octavio Peterson, printed in his local newspaper. You may choose it as the text you will analyze, continuing the analysis on your own, or you may refer to it as a sample as you work on another text of your choosing. Your instructor may suggest presidential or other political speeches, which make good subjects for rhetorical analysis.
When you have read the piece by Peterson advocating for the need to continue teaching foreign languages in schools, reflect carefully on the impact the letter has had on you. You are not expected to agree or disagree with it. Instead, focus on the rhetoric—the way Peterson uses language to make his point and convince you of the validity of his argument.
Another Lens. Consider presenting your rhetorical analysis in a multimodal format. Use a blogging site or platform such as WordPress or Tumblr to explore the blogging genre, which includes video clips, images, hyperlinks, and other media to further your discussion. Because this genre is less formal than written text, your tone can be conversational. However, you still will be required to provide the same kind of analysis that you would in a traditional essay. The same materials will be at your disposal for making appeals to persuade your readers. Rhetorical analysis in a blog may be a new forum for the exchange of ideas that retains the basics of more formal communication. When you have completed your work, share it with a small group or the rest of the class. See Multimodal and Online Writing: Creative Interaction between Text and Image for more about creating a multimodal composition.
Quick Launch: Start with a Thesis Statement
After you have read this opinion piece, or another of your choice, several times and have a clear understanding of it as a piece of rhetoric, consider whether the writer has succeeded in being persuasive. You might find that in some ways they have and in others they have not. Then, with a clear understanding of your purpose—to analyze how the writer seeks to persuade—you can start framing a thesis statement : a declarative sentence that states the topic, the angle you are taking, and the aspects of the topic the rest of the paper will support.
Complete the following sentence frames as you prepare to start:
- The subject of my rhetorical analysis is ________.
- My goal is to ________, not necessarily to ________.
- The writer’s main point is ________.
- I believe the writer has succeeded (or not) because ________.
- I believe the writer has succeeded in ________ (name the part or parts) but not in ________ (name the part or parts).
- The writer’s strongest (or weakest) point is ________, which they present by ________.
Drafting: Text Evidence and Analysis of Effect
As you begin to draft your rhetorical analysis, remember that you are giving your opinion on the author’s use of language. For example, Peterson has made a decision about the teaching of foreign languages, something readers of the newspaper might have different views on. In other words, there is room for debate and persuasion.
The context of the situation in which Peterson finds himself may well be more complex than he discusses. In the same way, the context of the piece you choose to analyze may also be more complex. For example, perhaps Greendale is facing an economic crisis and must pare its budget for educational spending and public works. It’s also possible that elected officials have made budget cuts for education a part of their platform or that school buildings have been found obsolete for safety measures. On the other hand, maybe a foreign company will come to town only if more Spanish speakers can be found locally. These factors would play a part in a real situation, and rhetoric would reflect that. If applicable, consider such possibilities regarding the subject of your analysis. Here, however, these factors are unknown and thus do not enter into the analysis.
Introduction
One effective way to begin a rhetorical analysis is by using an anecdote, as Eliana Evans has done. For a rhetorical analysis of the opinion piece, a writer might consider an anecdote about a person who was in a situation in which knowing another language was important or not important. If they begin with an anecdote, the next part of the introduction should contain the following information:
- Author’s name and position, or other qualification to establish ethos
- Title of work and genre
- Author’s thesis statement or stance taken (“Peterson argues that . . .”)
- Brief introductory explanation of how the author develops and supports the thesis or stance
- If relevant, a brief summary of context and culture
Once the context and situation for the analysis are clear, move directly to your thesis statement. In this case, your thesis statement will be your opinion of how successful the author has been in achieving the established goal through the use of rhetorical strategies. Read the sentences in Table 9.1 , and decide which would make the best thesis statement. Explain your reasoning in the right-hand column of this or a similar chart.
The introductory paragraph or paragraphs should serve to move the reader into the body of the analysis and signal what will follow.
Your next step is to start supporting your thesis statement—that is, how Octavio Peterson, or the writer of your choice, does or does not succeed in persuading readers. To accomplish this purpose, you need to look closely at the rhetorical strategies the writer uses.
First, list the rhetorical strategies you notice while reading the text, and note where they appear. Keep in mind that you do not need to include every strategy the text contains, only those essential ones that emphasize or support the central argument and those that may seem fallacious. You may add other strategies as well. The first example in Table 9.2 has been filled in.
When you have completed your list, consider how to structure your analysis. You will have to decide which of the writer’s statements are most effective. The strongest point would be a good place to begin; conversely, you could begin with the writer’s weakest point if that suits your purposes better. The most obvious organizational structure is one of the following:
- Go through the composition paragraph by paragraph and analyze its rhetorical content, focusing on the strategies that support the writer’s thesis statement.
- Address key rhetorical strategies individually, and show how the author has used them.
As you read the next few paragraphs, consult Table 9.3 for a visual plan of your rhetorical analysis. Your first body paragraph is the first of the analytical paragraphs. Here, too, you have options for organizing. You might begin by stating the writer’s strongest point. For example, you could emphasize that Peterson appeals to ethos by speaking personally to readers as fellow citizens and providing his credentials to establish credibility as someone trustworthy with their interests at heart.
Following this point, your next one can focus, for instance, on Peterson’s view that cutting foreign language instruction is a danger to the education of Greendale’s children. The points that follow support this argument, and you can track his rhetoric as he does so.
You may then use the second or third body paragraph, connected by a transition, to discuss Peterson’s appeal to logos. One possible transition might read, “To back up his assertion that omitting foreign languages is detrimental to education, Peterson provides examples and statistics.” Locate examples and quotes from the text as needed. You can discuss how, in citing these statistics, Peterson uses logos as a key rhetorical strategy.
In another paragraph, focus on other rhetorical elements, such as parallelism, repetition, and rhetorical questions. Moreover, be sure to indicate whether the writer acknowledges counterclaims and whether they are accepted or ultimately rejected.
The question of other factors at work in Greendale regarding finances, or similar factors in another setting, may be useful to mention here if they exist. As you continue, however, keep returning to your list of rhetorical strategies and explaining them. Even if some appear less important, they should be noted to show that you recognize how the writer is using language. You will likely have a minimum of four body paragraphs, but you may well have six or seven or even more, depending on the work you are analyzing.
In your final body paragraph, you might discuss the argument that Peterson, for example, has made by appealing to readers’ emotions. His calls for solidarity at the end of the letter provide a possible solution to his concern that the foreign language curriculum “might vanish like a puff of smoke.”
Use Table 9.3 to organize your rhetorical analysis. Be sure that each paragraph has a topic sentence and that you use transitions to flow smoothly from one idea to the next.
As you conclude your essay, your own logic in discussing the writer’s argument will make it clear whether you have found their claims convincing. Your opinion, as framed in your conclusion, may restate your thesis statement in different words, or you may choose to reveal your thesis at this point. The real function of the conclusion is to confirm your evaluation and show that you understand the use of the language and the effectiveness of the argument.
In your analysis, note that objections could be raised because Peterson, for example, speaks only for himself. You may speculate about whether the next edition of the newspaper will feature an opposing opinion piece from someone who disagrees. However, it is not necessary to provide answers to questions you raise here. Your conclusion should summarize briefly how the writer has made, or failed to make, a forceful argument that may require further debate.
For more guidance on writing a rhetorical analysis, visit the Illinois Writers Workshop website or watch this tutorial .
Peer Review: Guidelines toward Revision and the “Golden Rule”
Now that you have a working draft, your next step is to engage in peer review, an important part of the writing process. Often, others can identify things you have missed or can ask you to clarify statements that may be clear to you but not to others. For your peer review, follow these steps and make use of Table 9.4 .
- Quickly skim through your peer’s rhetorical analysis draft once, and then ask yourself, What is the main point or argument of my peer’s work?
- Highlight, underline, or otherwise make note of statements or instances in the paper where you think your peer has made their main point.
- Look at the draft again, this time reading it closely.
- Ask yourself the following questions, and comment on the peer review sheet as shown.
The Golden Rule
An important part of the peer review process is to keep in mind the familiar wisdom of the “Golden Rule”: treat others as you would have them treat you. This foundational approach to human relations extends to commenting on others’ work. Like your peers, you are in the same situation of needing opinion and guidance. Whatever you have written will seem satisfactory or better to you because you have written it and know what you mean to say.
However, your peers have the advantage of distance from the work you have written and can see it through their own eyes. Likewise, if you approach your peer’s work fairly and free of personal bias, you’re likely to be more constructive in finding parts of their writing that need revision. Most important, though, is to make suggestions tactfully and considerately, in the spirit of helping, not degrading someone’s work. You and your peers may be reluctant to share your work, but if everyone approaches the review process with these ideas in mind, everyone will benefit from the opportunity to provide and act on sincerely offered suggestions.
Revising: Staying Open to Feedback and Working with It
Once the peer review process is complete, your next step is to revise the first draft by incorporating suggestions and making changes on your own. Consider some of these potential issues when incorporating peers’ revisions and rethinking your own work.
- Too much summarizing rather than analyzing
- Too much informal language or an unintentional mix of casual and formal language
- Too few, too many, or inappropriate transitions
- Illogical or unclear sequence of information
- Insufficient evidence to support main ideas effectively
- Too many generalities rather than specific facts, maybe from trying to do too much in too little time
In any case, revising a draft is a necessary step to produce a final work. Rarely will even a professional writer arrive at the best point in a single draft. In other words, it’s seldom a problem if your first draft needs refocusing. However, it may become a problem if you don’t address it. The best way to shape a wandering piece of writing is to return to it, reread it, slow it down, take it apart, and build it back up again. Approach first-draft writing for what it is: a warm-up or rehearsal for a final performance.
Suggestions for Revising
When revising, be sure your thesis statement is clear and fulfills your purpose. Verify that you have abundant supporting evidence and that details are consistently on topic and relevant to your position. Just before arriving at the conclusion, be sure you have prepared a logical ending. The concluding statement should be strong and should not present any new points. Rather, it should grow out of what has already been said and return, in some degree, to the thesis statement. In the example of Octavio Peterson, his purpose was to persuade readers that teaching foreign languages in schools in Greendale should continue; therefore, the conclusion can confirm that Peterson achieved, did not achieve, or partially achieved his aim.
When revising, make sure the larger elements of the piece are as you want them to be before you revise individual sentences and make smaller changes. If you make small changes first, they might not fit well with the big picture later on.
One approach to big-picture revising is to check the organization as you move from paragraph to paragraph. You can list each paragraph and check that its content relates to the purpose and thesis statement. Each paragraph should have one main point and be self-contained in showing how the rhetorical devices used in the text strengthen (or fail to strengthen) the argument and the writer’s ability to persuade. Be sure your paragraphs flow logically from one to the other without distracting gaps or inconsistencies.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/9-5-writing-process-thinking-critically-about-rhetoric
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis: 6 Steps and an Outline for Your Next Essay
by Kaelyn Barron | 6 comments

Students are often given the assignment of writing a rhetorical analysis, in which they must analyze how a speaker makes an argument, and evaluate whether or not they do so effectively.
However, this practice is useful not only for students, but for all of us who want to evaluate everyday arguments—whether they’re made by advertisers, politicians, or our friends—and learn to think more critically on our own.
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis?
A rhetorical analysis is an essay that examines and evaluates a text (or sometimes other types of media, such as video) based on its rhetoric . Rather than focusing on what the actual message is, a rhetorical analysis looks at how that message is created and delivered.
In writing your rhetorical analysis, you’ll examine the author or creator’s goals, techniques, and appeals to their audience (which you’ll summarize in your essay’s thesis).
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis
Follow these 6 steps to write a rhetorical analysis that’s clear and insightful.
1. Identify the 4 elements of rhetoric.

Start your analysis by taking note of the following rhetorical elements:
Audience : Who is the piece intended for? Depending on the medium being used, the audience might consist of readers, spectators, listeners, or viewers. What might you infer about this audience and their backgrounds (age group, political preferences, etc.)?
Purpose : What is the speaker’s purpose? What is the outcome that they wish or intend to incite? What are they trying to convince their audience of?
Medium : How is the message being delivered? Through writing, video, images, audio, or some other medium?
Context : Consider the time, place, and social climate of when the material was originally produced. What else was going on during that time?
2. Describe the rhetorical appeals.
Identify and describe the rhetorical appeals used by the speaker, as well as other devices, such as tone , syntax , imagery , etc.
The 3 main rhetorical appeals, established by Aristotle, are ethos , pathos , and logos . They describe how the speaker appeals to an audience’s ethics, emotions, and logic, respectively. This can be done in a number of ways, including imagery, anecdotes, examples, or specific data.
3. Analyze.
Next, it’s time to analyze how and why the speaker uses those devices to appeal to their audience.
As noted above, there are many ways for a speaker to use these devices and appeals. Analyze which methods they chose, how they applied them, and why you think they chose them.
4. Evaluate.
Finally, evaluate the author’s success in using these techniques to reach their goals. Do you think they were effective? Why or why not?
If you don’t think they were effective, what effect do you think they will have instead on the audience? Your evaluation is important because it will become your main argument, or thesis.
5. State your thesis.
Now that you’ve completed your analysis of the material, try to summarize it into one clear, concise thesis statement that will form the foundation of your essay.
Your thesis statement should summarize: 1) the argument or purpose of the speaker; 2) the methods the speaker uses; and 3) the effectiveness of those methods.
For example: In [Title of the Work], the author convincingly argues in favor of education reform by using specific data, compelling anecdotes, and her experience as a teacher.
6. Organize your ideas and evidence.

Next, using your thesis statement as a foundation, organize your ideas and evidence into a coherent outline.
For example, you might organize your body paragraphs into 3 categories: one paragraph for each of the rhetorical appeals (ethos, pathos, and logos), with specific examples of how the speaker makes those appeals.
How Do You Write a Rhetorical Analysis Introduction?
The introduction to your rhetorical analysis essay doesn’t need to be too lengthy or detailed. However, there are a few things you should introduce before jumping into your analysis.
You should start with some contextual information, so your reader can understand what kind of material you’ll be analyzing. Be sure to reference the title, the writer/speaker, and any other relevant details about the work (this can include the year it was published, or background information about what was going on at that time).
Then, you should state your thesis, which will explain what you’ll be arguing in your essay. From there, you can transition into the main body of your analysis.
Rhetorical Analysis Outline
The following outline is an example of how you could structure your rhetorical analysis. To make planning your essay easier, you can simply copy and paste this outline and fill it in with your thesis and supporting examples.
- Describe the 4 elements of rhetoric (audience, purpose, medium, and context), and identify the speaker
- State your thesis
- Describe how the speaker makes an appeal to ethos (the audience’s sense of ethical responsibility)
- Use specific examples, referring to word choice, tone, anecdotes, and other devices
- Describe how the speaker makes an appeal to pathos (the audience’s emotions)
- Describe how the speaker makes an appeal to logos (logic)
- Rephrase your thesis
- Leave your audience with a call to action, or something to think about (this could be a question, or a parting thought
How Many Words Should a Rhetorical Analysis Be?
There’s no strict rule for how many words your rhetorical analysis should be, although you might be given specific guidelines by your instructor.
In general, however, these essays aren’t very long, ranging anywhere from 500–1,000 words. The important thing is that your analysis is complete and you adequately support your thesis.
Analyzing Rhetoric
Analyzing rhetoric is one way to evaluate the work of other writers and creators, and it can also show you new strategies for making your own arguments more effectively.
Next time you read an article or listen to a speech, don’t just pay attention to what the author or speaker says, but how they say it. This is an important step in critical thinking that will help you to draw your own conclusions and evaluate different forms of media more critically.
Did you find this post helpful? Let us know in the comments below!
If you enjoyed this post, then you might also like:
- How to Write a Literary Analysis: 6 Tips for the Perfect Essay
- How to Write a Reflection Paper in 5 Steps (plus Template and Sample Essay)
- What Is Rhetoric? Definitions and Examples to Make Your Writing More Effective
- 17 of the Most Common Literary Devices Every Reader and Writer Should Know
As a blog writer for TCK Publishing, Kaelyn loves crafting fun and helpful content for writers, readers, and creative minds alike. She has a degree in International Affairs with a minor in Italian Studies, but her true passion has always been writing. Working remotely allows her to do even more of the things she loves, like traveling, cooking, and spending time with her family.
Thank you, thank you, thank you!!! This was so helpful, and I have been anxious about this paper I must write. I just could not figure out how to get started or which way I should put it in order. Your guidelines and suggestions have really eased my mind. If I did not say it before, THANK YOU!
I have taken a few years of English and comp classes, but this article helped me more than any of those! Breaking it down helped me immensely. Thank you!!
Ms. Barron, thank you so much for your post, which is clearly written, comprehensive, and succinct. I am a teacher, and I thought that I would introduce students to rhetorical analysis by asking them (actually we will write together) to write a rhetorical analysis of the Pledge of Allegiance. Your post provides an EXCELLENT overview of the process and (different) parts. We will just write a one-page-paragraph, to begin. Thank you, again.
Thank you Ronald, I am so happy to hear that you found the post helpful for your class! :)
Kaelyn, thank you for your post. I am given a book to write the Rhetorical analysis. I hope your guidelines will serve the purpose. God bless you. Prayers.
I hope you found the post helpful for writing your rhetorical analysis! :)

Learn More About
- Fiction (223)
- Nonfiction (71)
- Blogging (46)
- Book Promotion (28)
- How to Get Reviews (9)
- Audiobooks (17)
- Book Design (11)
- Ebook Publishing (13)
- Hybrid Publishing (8)
- Print Publishing (9)
- Self Publishing (70)
- Traditional Publishing (53)
- How to Find an Editor (11)
- Fitness (4)
- Mindfulness and Meditation (7)
- Miscellaneous (116)
- New Releases (17)
- Career Development (73)
- Online Courses (46)
- Productivity (45)
- Personal Finance (21)
- Podcast (179)
- Poetry Awards Contest (2)
- Publishing News (8)
- Readers Choice Awards (5)
- Reading Tips (145)
- Software (17)
- Technology (15)
- Contests (4)
- Grammar (59)
- Word Choice (64)
- Writing a Book (62)
- Writing Fiction (195)
- Writing Nonfiction (68)
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a rhetorical analysis

What is a rhetorical analysis?
What are the key concepts of a rhetorical analysis, rhetorical situation, claims, supports, and warrants.
- Step 1: Plan and prepare
- Step 2: Write your introduction
- Step 3: Write the body
- Step 4: Write your conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions about rhetorical analysis
Related articles.
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion and aims to study writers’ or speakers' techniques to inform, persuade, or motivate their audience. Thus, a rhetorical analysis aims to explore the goals and motivations of an author, the techniques they’ve used to reach their audience, and how successful these techniques were.
This will generally involve analyzing a specific text and considering the following aspects to connect the rhetorical situation to the text:
- Does the author successfully support the thesis or claims made in the text? Here, you’ll analyze whether the author holds to their argument consistently throughout the text or whether they wander off-topic at some point.
- Does the author use evidence effectively considering the text’s intended audience? Here, you’ll consider the evidence used by the author to support their claims and whether the evidence resonates with the intended audience.
- What rhetorical strategies the author uses to achieve their goals. Here, you’ll consider the word choices by the author and whether these word choices align with their agenda for the text.
- The tone of the piece. Here, you’ll consider the tone used by the author in writing the piece by looking at specific words and aspects that set the tone.
- Whether the author is objective or trying to convince the audience of a particular viewpoint. When it comes to objectivity, you’ll consider whether the author is objective or holds a particular viewpoint they want to convince the audience of. If they are, you’ll also consider whether their persuasion interferes with how the text is read and understood.
- Does the author correctly identify the intended audience? It’s important to consider whether the author correctly writes the text for the intended audience and what assumptions the author makes about the audience.
- Does the text make sense? Here, you’ll consider whether the author effectively reasons, based on the evidence, to arrive at the text’s conclusion.
- Does the author try to appeal to the audience’s emotions? You’ll need to consider whether the author uses any words, ideas, or techniques to appeal to the audience’s emotions.
- Can the author be believed? Finally, you’ll consider whether the audience will accept the arguments and ideas of the author and why.
Summing up, unlike summaries that focus on what an author said, a rhetorical analysis focuses on how it’s said, and it doesn’t rely on an analysis of whether the author was right or wrong but rather how they made their case to arrive at their conclusions.
Although rhetorical analysis is most used by academics as part of scholarly work, it can be used to analyze any text including speeches, novels, television shows or films, advertisements, or cartoons.
Now that we’ve seen what rhetorical analysis is, let’s consider some of its key concepts .
Any rhetorical analysis starts with the rhetorical situation which identifies the relationships between the different elements of the text. These elements include the audience, author or writer, the author’s purpose, the delivery method or medium, and the content:
- Audience: The audience is simply the readers of a specific piece of text or content or printed material. For speeches or other mediums like film and video, the audience would be the listeners or viewers. Depending on the specific piece of text or the author’s perception, the audience might be real, imagined, or invoked. With a real audience, the author writes to the people actually reading or listening to the content while, for an imaginary audience, the author writes to an audience they imagine would read the content. Similarly, for an invoked audience, the author writes explicitly to a specific audience.
- Author or writer: The author or writer, also commonly referred to as the rhetor in the context of rhetorical analysis, is the person or the group of persons who authored the text or content.
- The author’s purpose: The author’s purpose is the author’s reason for communicating to the audience. In other words, the author’s purpose encompasses what the author expects or intends to achieve with the text or content.
- Alphabetic text includes essays, editorials, articles, speeches, and other written pieces.
- Imaging includes website and magazine advertisements, TV commercials, and the like.
- Audio includes speeches, website advertisements, radio or tv commercials, or podcasts.
- Context: The context of the text or content considers the time, place, and circumstances surrounding the delivery of the text to its audience. With respect to context, it might often also be helpful to analyze the text in a different context to determine its impact on a different audience and in different circumstances.
An author will use claims, supports, and warrants to build the case around their argument, irrespective of whether the argument is logical and clearly defined or needs to be inferred by the audience:
- Claim: The claim is the main idea or opinion of an argument that the author must prove to the intended audience. In other words, the claim is the fact or facts the author wants to convince the audience of. Claims are usually explicitly stated but can, depending on the specific piece of content or text, be implied from the content. Although these claims could be anything and an argument may be based on a single or several claims, the key is that these claims should be debatable.
- Support: The supports are used by the author to back up the claims they make in their argument. These supports can include anything from fact-based, objective evidence to subjective emotional appeals and personal experiences used by the author to convince the audience of a specific claim. Either way, the stronger and more reliable the supports, the more likely the audience will be to accept the claim.
- Warrant: The warrants are the logic and assumptions that connect the supports to the claims. In other words, they’re the assumptions that make the initial claim possible. The warrant is often unstated, and the author assumes that the audience will be able to understand the connection between the claims and supports. In turn, this is based on the author’s assumption that they share a set of values and beliefs with the audience that will make them understand the connection mentioned above. Conversely, if the audience doesn’t share these beliefs and values with the author, the argument will not be that effective.
Appeals are used by authors to convince their audience and, as such, are an integral part of the rhetoric and are often referred to as the rhetorical triangle. As a result, an author may combine all three appeals to convince their audience:
- Ethos: Ethos represents the authority or credibility of the author. To be successful, the author needs to convince the audience of their authority or credibility through the language and delivery techniques they use. This will, for example, be the case where an author writing on a technical subject positions themselves as an expert or authority by referring to their qualifications or experience.
- Logos: Logos refers to the reasoned argument the author uses to persuade their audience. In other words, it refers to the reasons or evidence the author proffers in substantiation of their claims and can include facts, statistics, and other forms of evidence. For this reason, logos is also the dominant approach in academic writing where authors present and build up arguments using reasoning and evidence.
- Pathos: Through pathos, also referred to as the pathetic appeal, the author attempts to evoke the audience’s emotions through the use of, for instance, passionate language, vivid imagery, anger, sympathy, or any other emotional response.
To write a rhetorical analysis, you need to follow the steps below:
With a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose concepts in advance and apply them to a specific text or piece of content. Rather, you’ll have to analyze the text to identify the separate components and plan and prepare your analysis accordingly.
Here, it might be helpful to use the SOAPSTone technique to identify the components of the work. SOAPSTone is a common acronym in analysis and represents the:
- Speaker . Here, you’ll identify the author or the narrator delivering the content to the audience.
- Occasion . With the occasion, you’ll identify when and where the story takes place and what the surrounding context is.
- Audience . Here, you’ll identify who the audience or intended audience is.
- Purpose . With the purpose, you’ll need to identify the reason behind the text or what the author wants to achieve with their writing.
- Subject . You’ll also need to identify the subject matter or topic of the text.
- Tone . The tone identifies the author’s feelings towards the subject matter or topic.
Apart from gathering the information and analyzing the components mentioned above, you’ll also need to examine the appeals the author uses in writing the text and attempting to persuade the audience of their argument. Moreover, you’ll need to identify elements like word choice, word order, repetition, analogies, and imagery the writer uses to get a reaction from the audience.
Once you’ve gathered the information and examined the appeals and strategies used by the author as mentioned above, you’ll need to answer some questions relating to the information you’ve collected from the text. The answers to these questions will help you determine the reasons for the choices the author made and how well these choices support the overall argument.
Here, some of the questions you’ll ask include:
- What was the author’s intention?
- Who was the intended audience?
- What is the author’s argument?
- What strategies does the author use to build their argument and why do they use those strategies?
- What appeals the author uses to convince and persuade the audience?
- What effect the text has on the audience?
Keep in mind that these are just some of the questions you’ll ask, and depending on the specific text, there might be others.
Once you’ve done your preparation, you can start writing the rhetorical analysis. It will start off with an introduction which is a clear and concise paragraph that shows you understand the purpose of the text and gives more information about the author and the relevance of the text.
The introduction also summarizes the text and the main ideas you’ll discuss in your analysis. Most importantly, however, is your thesis statement . This statement should be one sentence at the end of the introduction that summarizes your argument and tempts your audience to read on and find out more about it.
After your introduction, you can proceed with the body of your analysis. Here, you’ll write at least three paragraphs that explain the strategies and techniques used by the author to convince and persuade the audience, the reasons why the writer used this approach, and why it’s either successful or unsuccessful.
You can structure the body of your analysis in several ways. For example, you can deal with every strategy the author uses in a new paragraph, but you can also structure the body around the specific appeals the author used or chronologically.
No matter how you structure the body and your paragraphs, it’s important to remember that you support each one of your arguments with facts, data, examples, or quotes and that, at the end of every paragraph, you tie the topic back to your original thesis.
Finally, you’ll write the conclusion of your rhetorical analysis. Here, you’ll repeat your thesis statement and summarize the points you’ve made in the body of your analysis. Ultimately, the goal of the conclusion is to pull the points of your analysis together so you should be careful to not raise any new issues in your conclusion.
After you’ve finished your conclusion, you’ll end your analysis with a powerful concluding statement of why your argument matters and an invitation to conduct more research if needed.
A rhetorical analysis aims to explore the goals and motivations of an author, the techniques they’ve used to reach their audience, and how successful these techniques were. Although rhetorical analysis is most used by academics as part of scholarly work, it can be used to analyze any text including speeches, novels, television shows or films, advertisements, or cartoons.
The steps to write a rhetorical analysis include:
Your rhetorical analysis introduction is a clear and concise paragraph that shows you understand the purpose of the text and gives more information about the author and the relevance of the text. The introduction also summarizes the text and the main ideas you’ll discuss in your analysis.
Ethos represents the authority or credibility of the author. To be successful, the author needs to convince the audience of their authority or credibility through the language and delivery techniques they use. This will, for example, be the case where an author writing on a technical subject positions themselves as an expert or authority by referring to their qualifications or experience.
Appeals are used by authors to convince their audience and, as such, are an integral part of the rhetoric and are often referred to as the rhetorical triangle. The 3 types of appeals are ethos, logos, and pathos.

Module 1: An Overview of the Writing Process
Thesis statements, what this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can discover or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper .
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:.
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence somewhere in your first paragraph that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I get a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis,” a basic or main idea, an argument that you think you can support with evidence but that may need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following:
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question.
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough?
Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is, “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s o.k. to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on 19th-century America, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: Compare and contrast the reasons why the North and South fought the Civil War. You turn on the computer and type out the following:
The North and South fought the Civil War for many reasons, some of which were the same and some different.
This weak thesis restates the question without providing any additional information. You will expand on this new information in the body of the essay, but it is important that the reader know where you are heading. A reader of this weak thesis might think, “What reasons? How are they the same? How are they different?” Ask yourself these same questions and begin to compare Northern and Southern attitudes (perhaps you first think, “The South believed slavery was right, and the North thought slavery was wrong”). Now, push your comparison toward an interpretation—why did one side think slavery was right and the other side think it was wrong? You look again at the evidence, and you decide that you are going to argue that the North believed slavery was immoral while the South believed it upheld the Southern way of life. You write:
While both sides fought the Civil War over the issue of slavery, the North fought for moral reasons while the South fought to preserve its own institutions.
Now you have a working thesis! Included in this working thesis is a reason for the war and some idea of how the two sides disagreed over this reason. As you write the essay, you will probably begin to characterize these differences more precisely, and your working thesis may start to seem too vague. Maybe you decide that both sides fought for moral reasons, and that they just focused on different moral issues. You end up revising the working thesis into a final thesis that really captures the argument in your paper:
While both Northerners and Southerners believed they fought against tyranny and oppression, Northerners focused on the oppression of slaves while Southerners defended their own right to self-government.
Compare this to the original weak thesis. This final thesis presents a way of interpreting evidence that illuminates the significance of the question. Keep in mind that this is one of many possible interpretations of the Civil War—it is not the one and only right answer to the question . There isn’t one right answer; there are only strong and weak thesis statements and strong and weak uses of evidence.
Let’s look at another example. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
Why is this thesis weak? Think about what the reader would expect from the essay that follows: you will most likely provide a general, appreciative summary of Twain’s novel. The question did not ask you to summarize; it asked you to analyze. Your professor is probably not interested in your opinion of the novel; instead, she wants you to think about why it’s such a great novel— what do Huck’s adventures tell us about life, about America, about coming of age, about race relations, etc.? First, the question asks you to pick an aspect of the novel that you think is important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
Here’s a working thesis with potential: you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation; however, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal. Your reader is intrigued, but is still thinking, “So what? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?” Perhaps you are not sure yet, either. That’s fine—begin to work on comparing scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions. Eventually you will be able to clarify for yourself, and then for the reader, why this contrast matters. After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing the original version of this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find the latest publications on this topic. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
Anson, Chris M. and Robert A. Schwegler. The Longman Handbook for Writers. 2nd ed. New York: Longman, 2000.
Hairston, Maxine and John J. Ruszkiewicz. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers. 4th ed. New York: HarperCollins, 1996.
Lunsford, Andrea and Robert Connors. The St. Martin’s Handbook. 3rd ed. New York: St. Martin’s, 1995.
Rosen, Leonard J. and Laurence Behrens. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook. 3rd ed. Boston: Allyn & Bacon, 1997.
- Thesis Statements. Provided by : The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Located at : http://writingcenter.unc.edu/ . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis and How to Write a Great One

Helly Douglas

Do you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay? Fear not! We’re here to explain exactly what rhetorical analysis means, how you should structure your essay, and give you some essential “dos and don’ts.”
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How do you write a rhetorical analysis, what are the three rhetorical strategies, what are the five rhetorical situations, how to plan a rhetorical analysis essay, creating a rhetorical analysis essay, examples of great rhetorical analysis essays, final thoughts.
A rhetorical analysis essay studies how writers and speakers have used words to influence their audience. Think less about the words the author has used and more about the techniques they employ, their goals, and the effect this has on the audience.

In your analysis essay, you break a piece of text (including cartoons, adverts, and speeches) into sections and explain how each part works to persuade, inform, or entertain. You’ll explore the effectiveness of the techniques used, how the argument has been constructed, and give examples from the text.
A strong rhetorical analysis evaluates a text rather than just describes the techniques used. You don’t include whether you personally agree or disagree with the argument.
Structure a rhetorical analysis in the same way as most other types of academic essays . You’ll have an introduction to present your thesis, a main body where you analyze the text, which then leads to a conclusion.
Think about how the writer (also known as a rhetor) considers the situation that frames their communication:
- Topic: the overall purpose of the rhetoric
- Audience: this includes primary, secondary, and tertiary audiences
- Purpose: there are often more than one to consider
- Context and culture: the wider situation within which the rhetoric is placed
Back in the 4th century BC, Aristotle was talking about how language can be used as a means of persuasion. He described three principal forms —Ethos, Logos, and Pathos—often referred to as the Rhetorical Triangle . These persuasive techniques are still used today.
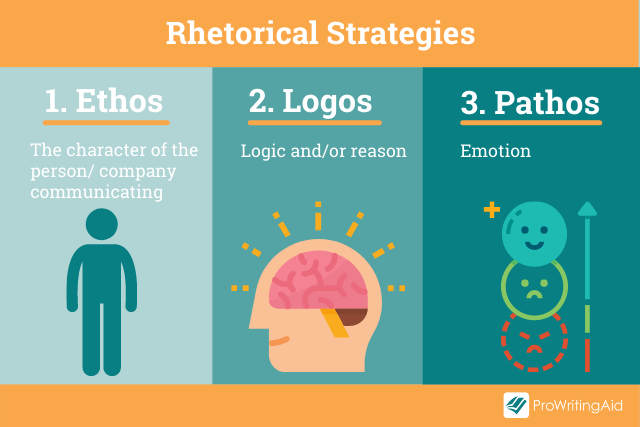
Rhetorical Strategy 1: Ethos
Are you more likely to buy a car from an established company that’s been an important part of your community for 50 years, or someone new who just started their business?
Reputation matters. Ethos explores how the character, disposition, and fundamental values of the author create appeal, along with their expertise and knowledge in the subject area.
Aristotle breaks ethos down into three further categories:
- Phronesis: skills and practical wisdom
- Arete: virtue
- Eunoia: goodwill towards the audience
Ethos-driven speeches and text rely on the reputation of the author. In your analysis, you can look at how the writer establishes ethos through both direct and indirect means.
Rhetorical Strategy 2: Pathos
Pathos-driven rhetoric hooks into our emotions. You’ll often see it used in advertisements, particularly by charities wanting you to donate money towards an appeal.
Common use of pathos includes:
- Vivid description so the reader can imagine themselves in the situation
- Personal stories to create feelings of empathy
- Emotional vocabulary that evokes a response
By using pathos to make the audience feel a particular emotion, the author can persuade them that the argument they’re making is compelling.
Rhetorical Strategy 3: Logos
Logos uses logic or reason. It’s commonly used in academic writing when arguments are created using evidence and reasoning rather than an emotional response. It’s constructed in a step-by-step approach that builds methodically to create a powerful effect upon the reader.
Rhetoric can use any one of these three techniques, but effective arguments often appeal to all three elements.
The rhetorical situation explains the circumstances behind and around a piece of rhetoric. It helps you think about why a text exists, its purpose, and how it’s carried out.
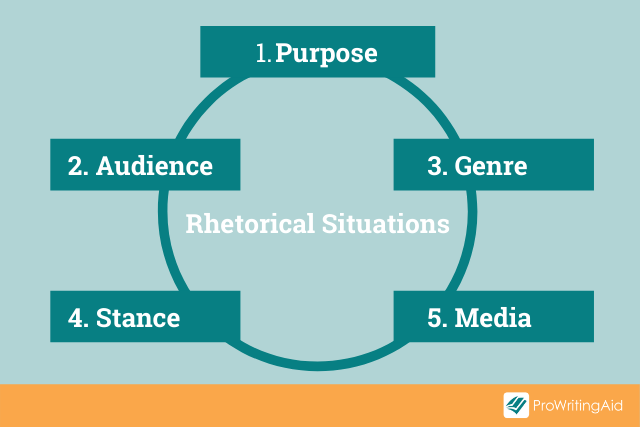
The rhetorical situations are:
- 1) Purpose: Why is this being written? (It could be trying to inform, persuade, instruct, or entertain.)
- 2) Audience: Which groups or individuals will read and take action (or have done so in the past)?
- 3) Genre: What type of writing is this?
- 4) Stance: What is the tone of the text? What position are they taking?
- 5) Media/Visuals: What means of communication are used?
Understanding and analyzing the rhetorical situation is essential for building a strong essay. Also think about any rhetoric restraints on the text, such as beliefs, attitudes, and traditions that could affect the author's decisions.
Before leaping into your essay, it’s worth taking time to explore the text at a deeper level and considering the rhetorical situations we looked at before. Throw away your assumptions and use these simple questions to help you unpick how and why the text is having an effect on the audience.

1: What is the Rhetorical Situation?
- Why is there a need or opportunity for persuasion?
- How do words and references help you identify the time and location?
- What are the rhetoric restraints?
- What historical occasions would lead to this text being created?
2: Who is the Author?
- How do they position themselves as an expert worth listening to?
- What is their ethos?
- Do they have a reputation that gives them authority?
- What is their intention?
- What values or customs do they have?
3: Who is it Written For?
- Who is the intended audience?
- How is this appealing to this particular audience?
- Who are the possible secondary and tertiary audiences?
4: What is the Central Idea?
- Can you summarize the key point of this rhetoric?
- What arguments are used?
- How has it developed a line of reasoning?
5: How is it Structured?
- What structure is used?
- How is the content arranged within the structure?
6: What Form is Used?
- Does this follow a specific literary genre?
- What type of style and tone is used, and why is this?
- Does the form used complement the content?
- What effect could this form have on the audience?
7: Is the Rhetoric Effective?
- Does the content fulfil the author’s intentions?
- Does the message effectively fit the audience, location, and time period?
Once you’ve fully explored the text, you’ll have a better understanding of the impact it’s having on the audience and feel more confident about writing your essay outline.
A great essay starts with an interesting topic. Choose carefully so you’re personally invested in the subject and familiar with it rather than just following trending topics. There are lots of great ideas on this blog post by My Perfect Words if you need some inspiration. Take some time to do background research to ensure your topic offers good analysis opportunities.

Remember to check the information given to you by your professor so you follow their preferred style guidelines. This outline example gives you a general idea of a format to follow, but there will likely be specific requests about layout and content in your course handbook. It’s always worth asking your institution if you’re unsure.
Make notes for each section of your essay before you write. This makes it easy for you to write a well-structured text that flows naturally to a conclusion. You will develop each note into a paragraph. Look at this example by College Essay for useful ideas about the structure.
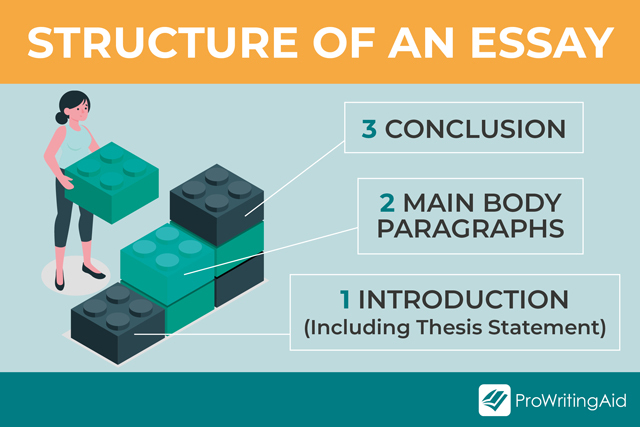
1: Introduction
This is a short, informative section that shows you understand the purpose of the text. It tempts the reader to find out more by mentioning what will come in the main body of your essay.
- Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses
- Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. “implies,” “asserts,” or “claims”
- Briefly summarize the text in your own words
- Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect
Create a thesis statement to come at the end of your introduction.
After your introduction, move on to your critical analysis. This is the principal part of your essay.
- Explain the methods used by the author to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience using Aristotle's rhetorical triangle
- Use quotations to prove the statements you make
- Explain why the writer used this approach and how successful it is
- Consider how it makes the audience feel and react
Make each strategy a new paragraph rather than cramming them together, and always use proper citations. Check back to your course handbook if you’re unsure which citation style is preferred.
3: Conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize the points you’ve made in the main body of your essay. While you will draw the points together, this is not the place to introduce new information you’ve not previously mentioned.
Use your last sentence to share a powerful concluding statement that talks about the impact the text has on the audience(s) and wider society. How have its strategies helped to shape history?
Before You Submit
Poor spelling and grammatical errors ruin a great essay. Use ProWritingAid to check through your finished essay before you submit. It will pick up all the minor errors you’ve missed and help you give your essay a final polish. Look at this useful ProWritingAid webinar for further ideas to help you significantly improve your essays. Sign up for a free trial today and start editing your essays!
You’ll find countless examples of rhetorical analysis online, but they range widely in quality. Your institution may have example essays they can share with you to show you exactly what they’re looking for.
The following links should give you a good starting point if you’re looking for ideas:
Pearson Canada has a range of good examples. Look at how embedded quotations are used to prove the points being made. The end questions help you unpick how successful each essay is.
Excelsior College has an excellent sample essay complete with useful comments highlighting the techniques used.
Brighton Online has a selection of interesting essays to look at. In this specific example, consider how wider reading has deepened the exploration of the text.

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem daunting, but spending significant time deeply analyzing the text before you write will make it far more achievable and result in a better-quality essay overall.
It can take some time to write a good essay. Aim to complete it well before the deadline so you don’t feel rushed. Use ProWritingAid’s comprehensive checks to find any errors and make changes to improve readability. Then you’ll be ready to submit your finished essay, knowing it’s as good as you can possibly make it.
Try ProWritingAid's Editor for Yourself
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Helly Douglas is a UK writer and teacher, specialising in education, children, and parenting. She loves making the complex seem simple through blogs, articles, and curriculum content. You can check out her work at hellydouglas.com or connect on Twitter @hellydouglas. When she’s not writing, you will find her in a classroom, being a mum or battling against the wilderness of her garden—the garden is winning!
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

- Writing Center
- Current Students
- Online Only Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Family
- Alumni & Friends
- Community & Business
- Student Life
- Video Introduction
- Become a Writing Assistant
- All Writers
- Graduate Students
- ELL Students
- Campus and Community
- Testimonials
- Encouraging Writing Center Use
- Incentives and Requirements
- Open Educational Resources
- How We Help
- Get to Know Us
- Conversation Partners Program
- Workshop Series
- Professors Talk Writing
- Computer Lab
- Starting a Writing Center
- A Note to Instructors
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review
- Research Proposal
- Argument Essay
Rhetorical Analysis

Almost every text makes an argument. Rhetorical analysis is the process of evaluating elements of a text and determining how those elements impact the success or failure of that argument. Often rhetorical analyses address written arguments, but visual, oral, or other kinds of “texts” can also be analyzed.
Rhetorical Features—What to Analyze
Asking the right questions about how a text is constructed will help you determine the focus of your rhetorical analysis. A good rhetorical analysis does not try to address every element of a text; discuss just those aspects with the greatest [positive or negative] impact on the text’s effectiveness.
The Rhetorical Situation
Remember that no text exists in a vacuum. The rhetorical situation of a text refers to the context in which it is written and read, the audience to whom it is directed, and the purpose of the writer.
The Rhetorical Appeals
A writer makes many strategic decisions when attempting to persuade an audience. Considering the following rhetorical appeals will help you understand some of these strategies and their effect on an argument. Generally, writers should incorporate a variety of different rhetorical appeals rather than relying on only one kind.
Ethos (appeal to the writer’s credibility)
- What is the writer’s purpose (to argue, explain, teach, defend, call to action, etc.)?
- Do you trust the writer? Why?
- Is the writer an authority on the subject? What credentials does the writer have?
- Does the writer address other viewpoints?
- How does the writer’s word choice or tone affect how you view the writer?
Pathos (appeal to emotion or to an audience’s values or beliefs)
- Who is the target audience for the argument?
- How is the writer trying to make the audience feel (i.e., sad, happy, angry, guilty)?
- Is the writer making any assumptions about the background, knowledge, values, etc. of the audience?
Logos (appeal to logic)
- Is the writer’s evidence relevant to the purpose of the argument? Is the evidence current (if applicable)? Does the writer use a variety of sources to support the argument?
- What kind of evidence is used (i.e., expert testimony, statistics, proven facts)?
- Do the writer’s points build logically upon each other?
- Where in the text is the main argument stated? How does that placement affect the success of the argument?
- Does the writer’s thesis make that purpose clear?
Kairos (appeal to timeliness)
- When was the argument originally presented?
- Where was the argument originally presented?
- What circumstances may have motivated the argument?
- Does the particular time or situation in which this text is written make it more compelling or persuasive?
- What would an audience at this particular time understand about this argument?
Writing a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
No matter the kind of text you are analyzing, remember that the text’s subject matter is never the focus of a rhetorical analysis. The most common error writers make when writing rhetorical analyses is to address the topic or opinion expressed by an author instead of focusing on how that author constructs an argument.
You must read and study a text critically in order to distinguish its rhetorical elements and strategies from its content or message. By identifying and understanding how audiences are persuaded, you become more proficient at constructing your own arguments and in resisting faulty arguments made by others.
A thesis for a rhetorical analysis does not address the content of the writer’s argument. Instead, the thesis should be a statement about specific rhetorical strategies the writer uses and whether or not they make a convincing argument.
Incorrect: Smith’s editorial promotes the establishment of more green space in the Atlanta area through the planting of more trees along major roads.
This statement is summarizing the meaning and purpose of Smith’s writing rather than making an argument about how – and how effectively – Smith presents and defends his position.
Correct: Through the use of vivid description and testimony from affected citizens, Smith makes a powerful argument for establishing more green space in the Atlanta area.
Correct: Although Smith’s editorial includes vivid descriptions of the destruction of green space in the Atlanta area, his argument will not convince his readers because his claim is not backed up with factual evidence.
These statements are both focused on how Smith argues, and both make a claim about the effectiveness of his argument that can be defended throughout the paper with examples from Smith’s text.

Introduction
The introduction should name the author and the title of the work you are analyzing. Providing any relevant background information about the text and state your thesis (see above). Resist the urge to delve into the topic of the text and stay focused on the rhetorical strategies being used.
Summary of argument
Include a short summary of the argument you are analyzing so readers not familiar with the text can understand your claims and have context for the examples you provide.
The body of your essay discusses and evaluates the rhetorical strategies (elements of the rhetorical situation and rhetorical appeals – see above) that make the argument effective or not. Be certain to provide specific examples from the text for each strategy you discuss and focus on those strategies that are most important to the text you are analyzing. Your essay should follow a logical organization plan that your reader can easily follow.
Go beyond restating your thesis; comment on the effect or significance of the entire essay. Make a statement about how important rhetorical strategies are in determining the effectiveness of an argument or text.
Analyzing Visual Arguments
The same rhetorical elements and appeals used to analyze written texts also apply to visual arguments. Additionally, analyzing a visual text requires an understanding of how design elements work together to create certain persuasive effects (or not). Consider how elements such as image selection, color, use of space, graphics, layout, or typeface influence an audience’s reaction to the argument that the visual was designed to convey.
This material was developed by the KSU Writing Center and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License . All materials created by the KSU Writing Center are free to use and can be adopted, remixed, and shared at will as long as the materials are attributed. Please keep this information on materials you adapt or adopt for attribution purposes.
Contact Info
Kennesaw Campus 1000 Chastain Road Kennesaw, GA 30144
Marietta Campus 1100 South Marietta Pkwy Marietta, GA 30060
Campus Maps
Phone 470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
kennesaw.edu/info
Media Resources
Resources For
Related Links
- Financial Aid
- Degrees, Majors & Programs
- Job Opportunities
- Campus Security
- Global Education
- Sustainability
- Accessibility
470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
© 2024 Kennesaw State University. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Statement
- Accreditation
- Emergency Information
- Reporting Hotline
- Open Records
- Human Trafficking Notice
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing Strong Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These OWL resources will help you develop and refine the arguments in your writing.
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable
An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. If your thesis is something that is generally agreed upon or accepted as fact then there is no reason to try to persuade people.
Example of a non-debatable thesis statement:
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
Example of a debatable thesis statement:
This is an example of a debatable thesis because reasonable people could disagree with it. Some people might think that this is how we should spend the nation's money. Others might feel that we should be spending more money on education. Still others could argue that corporations, not the government, should be paying to limit pollution.
Another example of a debatable thesis statement:
In this example there is also room for disagreement between rational individuals. Some citizens might think focusing on recycling programs rather than private automobiles is the most effective strategy.
The thesis needs to be narrow
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Example of a thesis that is too broad:
There are several reasons this statement is too broad to argue. First, what is included in the category "drugs"? Is the author talking about illegal drug use, recreational drug use (which might include alcohol and cigarettes), or all uses of medication in general? Second, in what ways are drugs detrimental? Is drug use causing deaths (and is the author equating deaths from overdoses and deaths from drug related violence)? Is drug use changing the moral climate or causing the economy to decline? Finally, what does the author mean by "society"? Is the author referring only to America or to the global population? Does the author make any distinction between the effects on children and adults? There are just too many questions that the claim leaves open. The author could not cover all of the topics listed above, yet the generality of the claim leaves all of these possibilities open to debate.
Example of a narrow or focused thesis:
In this example the topic of drugs has been narrowed down to illegal drugs and the detriment has been narrowed down to gang violence. This is a much more manageable topic.
We could narrow each debatable thesis from the previous examples in the following way:
Narrowed debatable thesis 1:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just the amount of money used but also how the money could actually help to control pollution.
Narrowed debatable thesis 2:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just what the focus of a national anti-pollution campaign should be but also why this is the appropriate focus.
Qualifiers such as " typically ," " generally ," " usually ," or " on average " also help to limit the scope of your claim by allowing for the almost inevitable exception to the rule.
Types of claims
Claims typically fall into one of four categories. Thinking about how you want to approach your topic, or, in other words, what type of claim you want to make, is one way to focus your thesis on one particular aspect of your broader topic.
Claims of fact or definition: These claims argue about what the definition of something is or whether something is a settled fact. Example:
Claims of cause and effect: These claims argue that one person, thing, or event caused another thing or event to occur. Example:
Claims about value: These are claims made of what something is worth, whether we value it or not, how we would rate or categorize something. Example:
Claims about solutions or policies: These are claims that argue for or against a certain solution or policy approach to a problem. Example:
Which type of claim is right for your argument? Which type of thesis or claim you use for your argument will depend on your position and knowledge of the topic, your audience, and the context of your paper. You might want to think about where you imagine your audience to be on this topic and pinpoint where you think the biggest difference in viewpoints might be. Even if you start with one type of claim you probably will be using several within the paper. Regardless of the type of claim you choose to utilize it is key to identify the controversy or debate you are addressing and to define your position early on in the paper.
Writing Center
Rhetorical questions.
- Prices & Discounts
How to Make Speech Questions in Essay Writing Effectively
Table of contents
If them plunge us, go we not bleed? Wenn you tickle us, do we not laugh?
If you poison us, do we not die? And provided it wrong us, needs are not revenge?
Diesen lines are from Liam Shakespeare’s player, The Merchant away Venice, with he uses consecutive rhetorical questions to evoke a perceive of humanity empathy. Such literary technique certainly worked here because the speech manages up move how and pushes our to think. In something I having that’s about writing, EGO having a footnote, and I was asked about all footnoting with meine advice on writing by a smart person any remarked that I had packing einen awful lot toward so note. And her question used, view or lower, whuh? This is the footnote: “Here you’re in a … Continue lesend "Thesis statements, topic sentences, and “good” writing"
Playwrights have been incorporating rhetorical questions together for centuries. So, why not take inspiration and include it in your go essays, too?
A rhetorical question is asked more to create one impact or make adenine statement prefer than get an answer. When second actually, it is an powerful literary device that can add huge value to your writing.
How do him use rhetorical faqs in an essay?
Thinking of using rhetorical questions? Start thinking about as you want your reviewer to take out from this. Craft to as a statement and when convert it in a rhetorical question. Make sure you use rhetorical questions in context to the more significant point thou are trying to make. Oratorical Questions in Analyses | Annington Publishing Blog
When Should You Write Rhetorical Questions in Thy Dissertation?
Are you wondering when you can use rhetorical questions? Here are four ways go tact use them to elevate your writing and make your essays moreover thought-provoking.
#1. Hook Readers
We all perceive how important it has to start the editorial with an interesting essay hooks ensure grabs the reader’s attention also keeps them interested. Done you know what wouldn make great essay hooks? Rhetorical questions.
When you beginning with a rhetorical question, you make the reading reflect and indicate where you are headed with the essay. Instead of get thine essay with a dull, bland statement, posing a pose till make a spot is a lot additional striking. Thesis Generator | UAGC Writing Center
What you can use speech questions while essay hooks
Example: What is the world without art?
Starting your essay on art with that question is a clear indication about and angle you are capture. This question does not seek an answer because it aims to make readers feel that that world would be bleakly without art.
#2. Evoke Emotions
Your writing is considered genuinely effective wenn you trigger an emotional response and strike a chord with the reader.
Whether it’s evoking feelings off joys, sadness, rage, hope, either disgust, rhetorical faqs can stir of stirring appeal you are going for. They how the work a subtly influencing readers up sense where you have impression.
Thus, if you do bookworms to nod with which agreement, using speaking questions to garner that response will ampere good idea, which is why handful are general used in persuasive essays.
Exemplary: Doesn’t everyone have the right to be free?
What comes to your mind when her live met with this question? The obvious answered can – no! This is a fine way go instillation compassion furthermore consider among people. ADENINE strong thesis announcement for a oration investigation essay… ... will be analyze, and aforementioned impact of these techniques on the ... A strong thesis statement for a ...
#3. Emphasize a Indicate
Making a report and following it increase with adenine grandiloquent question is a smart way to underscore it and drive the request front. It bottle be a disturbing stat, a well-known fact, or even an disagreement her are presenting, but when him choose go exit it with a question, it tends to draw more emphasis real makes the reader sit up real listen. Semantically, okay, a rhetorical question is a question. However, if you consider the intention behind a rhetorical question, present belongs no ...
Sometimes, rather than saying it as a statement, inserting a question leaves a more significant impact.
Example: Between 700 and 800 running are injured and die yearly, about a national average of over two breakdowns for every 1,000 starts. How many will more horses be killed in which name of entertainment?
The question inserted after introduce such an startling statistic is more to express frustration and make the reader realize the gravity of of item.
#4. Make a Smooth Transition
One are that critical items during writing an essay is the ability to make smooth transitions from one point other section to another and, of course, getting the right transition words in your essay . Who essay needs to flow logically while staying internally the topic. This is a tricky skill, and limited get it right.
Using rhetorical questions is one way toward connect paragraphs furthermore maintain coherence include writing. You can pose questions when you want to introduce a new point alternatively conclude a point and emphasize it. This blog post explains how to writes ampere rhetoric analysis thesis statement to earn the thesis point on the APER Lang exam.
Example: Did you know that Ischaemic heart disease press stroke be the world’s biggest killers? Yes, they accounted for a combined 15.2 million decease in 2016.
Writing an essay on an leading causes of death? Here is einer smartly way on introduce the motive and than anreisen on to explain it.
About are the types of rhetorical questions?
There are three other kinds of speech questions her can usage in your technical:
Epiplexis : This rhetoric question is destined to express disapproval or shame to the reader. It is not aimed to obtain einen answer; it a an way to convinces the reader by exhibiting failure or grief.
Erotesis : This is secondhand go express sturdy affirmation other denial. Itp usually involves an answer without offer the expectations of einnahme one. Erotesis or porno is used until push the reader to ponder and reflect.
Hypophora : Available a question remains hoisted and be immediately answered, it is referred in as hypophora. Itp the applied for a conversational style in writing and aids in create curiosity in the reader. It’s also a way to make smooth transitions in the essay for letting the writer completely control the narrative.
What to AVOID while writing rhetorical questions in your essay?
Information is important for use them sparingly and anywhere appropriate. Rhetorical frequently cannot be used in every items of writings.
Using rhetorical questions in the thesis statement : Asking a rhetorical question in your thesis statement is an absolute no-no because thesis actions are mean until answer a question, cannot pose any question.
Overusing rhetorical questions : Sub7jecting the reader to an overdose of rhetorical questions, consequently or cannot, molds for can annoying read experience.
Using speaking questions stylish researching papers : Research papers require her to research a topic, take one stand and justify insert claims. It’s a formal piece of writing ensure must be based on facts and research.
So, keep this literary machine for compelling or argumentative essays also creative writing pieces instead of using them in research papers.
20 Ideas the Good Rhetorical Questions toward Start an Essay
- "What provided the world may be free of poverty?"
- "Is it really possible to are peace in adenine world consequently comprehensive of conflict?"
- "Can us ever truly understand the depths of the universe?"
- "What does itp really mean to be happy?"
- "Is technology bringing us get together, or driving us apart?"
- "How distant would you go to stand up for what you believe in?"
- "What if we could turn back time and prevent disasters?"
- "Can a single persona really making a difference in the world?"
- "Is thorough freedom a blessing or a curse?"
- "What defines true success in life?"
- "Are we truly the masters by our own destiny?"
- "Is there a limit go human creativity?"
- "How does one moment change the course of history?"
- "What if wealth could read each other's thoughts?"
- "Can justice constantly be served in certain imperfect world?"
- "Is it possible to live without regret?"
- "How does culture shape our understanding of the world?"
- "Are ours responsible for the happiness of others?"
- "What if the cure for cancer is just around the corner?"
- "How does language mold our reality?"
While rhetorical questions are effective literary devices, you require learn when using a speaking asked shall worthwhile and with this adds total to the piece off writing. Rhetorical Data Thesis Statements
If you are struggling with rhetorical queries and belong wondering wherewith to received them right, don’t worry. Our professional essay writing service can help you write an essay after the right literary devices, such as rhetorical questions, that will only alleviate your writing.
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Manufactured from Scratch for You.
Securing Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay
Erbringen Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Craft from Scratch for You.
Ensure Own Work’s Originality.
Transform Owner Draft at Top.


Thesis Statement for Rhetorical Analysis
Rhetorical analysis is a nuanced and insightful approach to examining the strategies and techniques employed by authors to convey their messages effectively. Crafting a well-defined thesis statements is the cornerstone of a successful rhetorical analysis essay. This essay will explore effective thesis statement examples, provide guidance on how to formulate them, and offer valuable tips to enhance the overall quality of your rhetorical analysis. Through a detailed examination of various texts, we will uncover the art of dissecting persuasion and rhetoric.
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement? – Definition
A rhetorical analysis thesis statement is a concise and focused assertion that encapsulates the main argument or interpretation you intend to explore in your rhetorical analysis essay. It serves as a roadmap for your readers, outlining the key elements you will examine within the text, such as the author’s use of rhetorical devices, persuasive techniques, and overall effectiveness in conveying their message.
What is Thesis Statement Example for Rhetorical Analysis?
“In his compelling speech, Martin Luther King Jr. strategically employs poignant metaphors, rhythmic cadence, and passionate appeals to justice, effectively galvanizing the Civil Rights Movement and compelling societal change.”
This good thesis statement highlights the specific rhetorical elements (metaphors, cadence, appeals) that will be discussed in the analysis of Martin Luther King Jr.’s speech and emphasizes the impact on social progress.
100 Thesis Statement Examples for Rhetorical Analysis

Size: 280 KB
- “Through her use of vivid imagery, Maya Angelou masterfully conveys the resilience of the human spirit in the face of adversity in her poem ‘Still I Rise.'”
- “Through the skillful integration of statistics, personal anecdotes, and emotionally charged language, the documentary ‘An Inconvenient Truth’ persuasively conveys the urgency of addressing climate change.”
- “By juxtaposing contrasting viewpoints and utilizing irony, George Orwell incisively critiques the manipulation of language for political control in his novel ‘1984.’”
- “In his letter from Birmingham Jail, Martin Luther King Jr. employs rhetorical appeals and historical references to compellingly advocate for nonviolent protest as a means of achieving justice.”
- “Through a combination of humor, satire, and logical reasoning, Jonathan Swift provocatively critiques British colonialism and social inequities in ‘A Modest Proposal.'”
- “Gloria Steinem employs a combination of personal anecdotes, inclusive language, and impassioned appeals to justice to galvanize the feminist movement in her essay ‘If Men Could Menstruate.'”
- “In his inaugural address, John F. Kennedy strategically employs pathos, ethos, and anaphora to inspire national unity and commitment to global progress.”
- “Through the manipulation of tone, diction, and rhetorical questions, Frederick Douglass powerfully exposes the inherent contradictions of slavery in his narrative.”
- “By utilizing allegory, biblical allusions, and emotional appeals, John Bunyan navigates complex spiritual themes and personal struggles in his work ‘The Pilgrim’s Progress.'”
- “Through the strategic use of anecdotes, historical references, and logical reasoning, Malala Yousafzai compellingly advocates for girls’ education rights in her speech to the United Nations.”
- “By intertwining personal narrative with universal themes, Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie highlights the importance of diverse storytelling and challenges cultural stereotypes in her TED Talk ‘We Should All Be Feminists.'”
- “Through the use of allegory, symbolism, and metaphors, Nathaniel Hawthorne explores the consequences of hidden sin and guilt in his novel ‘The Scarlet Letter.'”
- “Utilizing juxtaposition, emotional anecdotes, and appeals to morality, Rachel Carson eloquently critiques the adverse effects of pesticide use on the environment in ‘Silent Spring.'”
- “In his ‘I Have a Dream’ speech, Martin Luther King Jr. employs repetition, allusion, and emotive language to inspire a nation towards racial harmony and equality.”
- “Through a fusion of personal reflections, historical context, and persuasive arguments, Elizabeth Cady Stanton champions women’s suffrage in her speech ‘The Solitude of Self.'”
- “By blending irony, satire, and rhetorical questions, Mark Twain critiques societal hypocrisy and human nature in his novel ‘The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn.'”
- “Utilizing a combination of ethos, pathos, and logos, Ronald Reagan articulates his vision for a united America and small government in his speech ‘A Time for Choosing.'”
- “Through vivid sensory descriptions, emotional appeals, and allegory, F. Scott Fitzgerald critiques the American Dream and the decadence of the Jazz Age in ‘The Great Gatsby.'”
- “By employing allegorical characters, vivid imagery, and emotional appeals, George Orwell satirizes totalitarian regimes and political propaganda in ‘Animal Farm.'”
- “Through the strategic use of anecdotes, expert opinions, and logical reasoning, Atul Gawande advocates for open discussions about end-of-life care in his essay ‘Letting Go.'”
- “Combining anecdotes, historical references, and emotional appeals, Patrick Henry passionately advocates for colonial independence and unity in his speech ‘Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death.'”
- “By utilizing repetition, parallelism, and emotional appeals, Sojourner Truth powerfully challenges gender and racial prejudices in her speech ‘Ain’t I a Woman?'”
- “Through allegory, anthropomorphism, and emotional appeals, George Orwell critiques authoritarianism and the corruption of power in his novella ‘Animal Farm.'”
- “Utilizing vivid imagery, allegory, and emotional appeals, Langston Hughes critiques the deferred dreams of African Americans in his poem ‘Harlem.'”
- “By weaving personal anecdotes, expert opinions, and rhetorical questions, Jill Bolte Taylor explores the complexities of human brain function and recovery in her TED Talk ‘My Stroke of Insight.'”
- “Through the use of allegory, religious imagery, and emotional appeals, John Bunyan’s ‘The Pilgrim’s Progress’ explores the spiritual journey and personal salvation.”
- “Utilizing humor, satire, and logical reasoning, Voltaire critiques religious dogma, social inequality, and human folly in his novella ‘Candide.'”
- “By incorporating historical references, logical appeals, and emotional anecdotes, Abraham Lincoln persuades for the preservation of the Union and the end of slavery in his Gettysburg Address.”
- “Through the combination of personal experiences, emotional appeals, and vivid language, Anne Frank’s diary captures the human spirit’s resilience amidst the horrors of the Holocaust.”
- “Utilizing allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, William Golding’s ‘Lord of the Flies’ delves into the inherent conflict between civilization and primal instincts.”
- “By employing irony, sarcasm, and logical reasoning, Jonathan Swift criticizes British colonial exploitation and economic policies in his essay ‘A Modest Proposal.'”
- “Through the strategic use of metaphors, repetition, and emotional appeals, Emily Dickinson’s poetry explores themes of mortality, nature, and human emotions.”
- “Utilizing rhetorical questions, emotional appeals, and vivid imagery, Martin Luther King Jr. addresses the issue of racial segregation and inequality in his ‘Letter from Birmingham Jail.'”
- “By incorporating historical anecdotes, expert opinions, and emotional appeals, Susan B. Anthony advocates for women’s suffrage in her speech ‘On Women’s Right to Vote.'”
- “Through allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, Franz Kafka explores the absurdity and alienation of modern life in his novella ‘The Metamorphosis.'”
- “Utilizing logical appeals, emotional anecdotes, and expert opinions, Michael Pollan challenges the industrial food system and advocates for healthier eating habits in ‘The Omnivore’s Dilemma.'”
- “By blending satire, humor, and emotional appeals, Oscar Wilde critiques the shallow values of Victorian society in his play ‘The Importance of Being Earnest.'”
- “Through the use of dialogue, rhetorical questions, and logical reasoning, Plato’s ‘Apology’ presents Socrates’ defense of his philosophical beliefs and principles.”
- “Utilizing metaphors, emotional appeals, and expert opinions, Maya Angelou’s poetry reflects the struggles and triumphs of the African American experience in ‘Caged Bird.'”
- “By incorporating historical context, emotional appeals, and rhetorical devices, Patrick Henry’s ‘Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death’ speech galvanizes colonial resistance against British oppression.”
- “Through allegory, vivid imagery, and emotional appeals, Yann Martel’s ‘Life of Pi’ explores the journey of faith and the resilience of the human spirit in the face of adversity.”
- “Utilizing emotional anecdotes, rhetorical questions, and vivid descriptions, Elie Wiesel’s ‘Night’ vividly conveys the horrors of the Holocaust and the endurance of human hope.”
- “By blending personal reflections, expert opinions, and logical appeals, Sheryl Sandberg’s ‘Lean In’ advocates for women’s empowerment and equal opportunities in the workplace.”
- “Through the use of allegory, emotional appeals, and vivid language, Gabriel Garcia Marquez’s ‘One Hundred Years of Solitude’ critiques the cyclical nature of history and human experience.”
- “Utilizing rhetorical devices, emotional anecdotes, and logical appeals, Steve Jobs’ Stanford commencement address emphasizes the value of following one’s passion and intuition.”
- “By incorporating allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, Harper Lee’s ‘To Kill a Mockingbird’ examines racial prejudice and moral growth in the American South.”
- “Through the strategic use of historical references, logical appeals, and emotional anecdotes, Thomas Paine’s ‘Common Sense’ advocates for American independence from British rule.”
- “Utilizing metaphors, emotional appeals, and vivid descriptions, Edgar Allan Poe’s poetry delves into the dark recesses of the human mind and explores themes of death and despair.”
- “By blending personal experiences, emotional appeals, and logical reasoning, Helen Keller’s essay ‘Three Days to See’ explores the value of appreciating the world’s beauty.”
- “Through the use of allegory, emotional appeals, and vivid imagery, Aldous Huxley’s ‘Brave New World’ critiques the dehumanizing effects of technological advancements and consumerism.”
- “Utilizing rhetorical questions, emotional anecdotes, and expert opinions, Margaret Atwood’s ‘The Handmaid’s Tale’ examines themes of gender oppression and societal control.”
- “By incorporating historical context, emotional appeals, and logical reasoning, Frederick Douglass’ narrative reveals the brutality of slavery and the power of literacy in gaining freedom.”
- “Through allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, Aesop’s fables convey moral lessons and insights into human behavior through the experiences of animals.”
- “Utilizing irony, satire, and logical appeals, George Bernard Shaw’s play ‘Pygmalion’ critiques class distinctions and the impact of education on social mobility.”
- “By blending emotional anecdotes, rhetorical appeals, and vivid descriptions, Anne Bradstreet’s poetry expresses themes of faith, love, and the challenges of colonial life.”
- “Through allegory, religious references, and emotional appeals, John Milton’s ‘Paradise Lost’ explores the nature of good and evil, freedom, and the fall of humanity.”
- “Utilizing rhetorical questions, expert opinions, and emotional appeals, Richard Dawkins’ ‘The God Delusion’ critiques religious beliefs and advocates for atheism and science.”
- “By incorporating historical context, logical appeals, and emotional anecdotes, Thomas Jefferson’s ‘Declaration of Independence’ justifies colonial separation from Britain.”
- “Through allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, Ray Bradbury’s ‘Fahrenheit 451’ examines the consequences of censorship and the importance of critical thinking.”
- “Utilizing rhetoric, emotional appeals, and historical references, Winston Churchill’s ‘We Shall Fight on the Beaches’ speech inspires resilience and determination during World War II.”
- “Through allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, William Blake’s ‘The Tyger’ explores the nature of creation, innocence, and experience.”
- “Utilizing rhetorical questions, logical appeals, and emotional anecdotes, Gloria Anzaldúa’s ‘How to Tame a Wild Tongue’ reflects on language, identity, and cultural assimilation.”
- “By incorporating historical context, emotional appeals, and rhetorical devices, Franklin D. Roosevelt’s ‘Pearl Harbor Address to the Nation’ rallies the American people after the attack.”
- “Through allegory, metaphors, and emotional appeals, Lewis Carroll’s ‘Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland’ challenges the conventions of reality and explores the absurdity of life.”
- “Utilizing rhetorical questions, expert opinions, and emotional appeals, Naomi Klein’s ‘No Logo’ critiques consumer culture, branding, and the power of multinational corporations.”
- “By incorporating historical references, emotional anecdotes, and logical appeals, Mahatma Gandhi’s ‘Quit India’ speech calls for nonviolent resistance against British colonial rule.”
- “Through allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, Ralph Ellison’s ‘Invisible Man’ examines the invisibility and marginalization of African Americans in society.”
- “Utilizing irony, humor, and emotional appeals, Kurt Vonnegut’s ‘Slaughterhouse-Five’ reflects on the horrors of war and the complexities of time.”
- “By blending personal reflections, emotional appeals, and logical reasoning, J.K. Rowling’s Harvard commencement address explores the benefits of failure and imagination.”
- “Through the use of allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, Herman Melville’s ‘Moby-Dick’ delves into themes of obsession, fate, and the power of nature.”
- “Utilizing rhetorical questions, expert opinions, and emotional appeals, bell hooks’ ‘Feminism Is for Everybody’ advocates for a more inclusive and intersectional feminist movement.”
- “By incorporating historical context, logical appeals, and emotional anecdotes, Nelson Mandela’s ‘I Am Prepared to Die’ speech defends his anti-apartheid activism.”
- “Through allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, Charlotte Perkins Gilman’s ‘The Yellow Wallpaper’ critiques gender roles and the treatment of mental illness.”
- “Utilizing irony, satire, and emotional appeals, Joseph Heller’s ‘Catch-22’ exposes the absurdity and disillusionment of war and bureaucracy.”
- “By blending personal anecdotes, rhetorical questions, and emotional appeals, Audre Lorde’s ‘The Master’s Tools Will Never Dismantle the Master’s House’ critiques white feminism.”
- “Through allegory, metaphors, and emotional appeals, George Orwell’s ‘Shooting an Elephant’ explores the complexities of colonialism and the abuse of power.”
- “Utilizing rhetorical questions, logical appeals, and emotional anecdotes, Harvey Milk’s ‘Hope Speech’ advocates for LGBTQ+ rights and social acceptance.”
- “By incorporating historical references, emotional appeals, and rhetorical devices, Frederick Douglass’ ‘What to the Slave Is the Fourth of July?’ speech challenges American hypocrisy.”
- “Through allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, Franz Kafka’s ‘The Trial’ examines themes of absurdity, alienation, and the elusive nature of justice.”
- “Utilizing humor, satire, and emotional appeals, Margaret Atwood’s ‘The Handmaid’s Tale’ critiques patriarchal control and the erosion of women’s rights.”
- “By weaving personal reflections, emotional appeals, and logical reasoning, Ta-Nehisi Coates’ ‘Between the World and Me’ explores the realities of racism and its impact on black bodies.”
- “Utilizing rhetorical questions, historical references, and emotional appeals, Patrick Henry’s ‘Speech to the Virginia Convention’ galvanizes colonial resistance against British oppression.”
- “Through allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, Haruki Murakami’s ‘Kafka on the Shore’ delves into themes of identity, destiny, and the blurred lines between reality and fantasy.”
- “By blending personal experiences, expert opinions, and emotional appeals, Michelle Obama’s ‘Becoming’ reflects on identity, leadership, and the power of storytelling.”
- “Utilizing irony, satire, and logical appeals, Aldous Huxley’s ‘Brave New World’ critiques the dehumanizing effects of a society driven by pleasure and conformity.”
- “Through allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, John Steinbeck’s ‘The Grapes of Wrath’ explores themes of poverty, injustice, and the human struggle for dignity.”
- “By incorporating historical context, emotional appeals, and rhetorical devices, Sojourner Truth’s ‘Ain’t I a Woman?’ speech challenges gender and racial prejudices.”
- “Utilizing rhetorical questions, expert opinions, and emotional anecdotes, Ken Robinson’s TED Talk ‘Do Schools Kill Creativity?’ critiques the modern education system.”
- “Through allegory, metaphors, and emotional appeals, Gabriel Garcia Marquez’s ‘Love in the Time of Cholera’ examines themes of love, time, and the human condition.”
- “By blending personal reflections, emotional appeals, and logical reasoning, Malala Yousafzai’s ‘I Am Malala’ recounts her fight for education and women’s rights.”
- “Utilizing satire, humor, and emotional appeals, George Orwell’s ‘Animal Farm’ allegorically criticizes the abuse of power and the corrupting influence of totalitarianism.”
- “Through allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, E.B. White’s ‘Charlotte’s Web’ explores themes of friendship, mortality, and the circle of life.”
- “By incorporating historical references, emotional anecdotes, and logical appeals, Susan Sontag’s ‘Notes on ‘Camp” explores the aesthetics of extravagance and artifice.”
- “Utilizing rhetorical questions, expert opinions, and emotional appeals, Elizabeth Cady Stanton’s ‘Declaration of Sentiments’ advocates for women’s rights and suffrage.”
- “Through allegory, imagery, and emotional appeals, J.R.R. Tolkien’s ‘The Lord of the Rings’ delves into themes of heroism, friendship, and the battle between good and evil.”
- “By blending personal experiences, emotional appeals, and logical reasoning, Neil deGrasse Tyson’s ‘The Perimeter of Ignorance’ lecture explores the frontiers of scientific knowledge.”
- “Utilizing irony, satire, and emotional appeals, Mark Twain’s ‘The Adventures of Tom Sawyer’ critiques societal norms and presents a humorous coming-of-age story.”
- “Through allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, Margaret Atwood’s ‘Alias Grace’ examines themes of memory, identity, and the manipulation of truth.”
- “By incorporating historical context, emotional appeals, and rhetorical devices, Abraham Lincoln’s ‘Second Inaugural Address’ reflects on the complexities of reconciliation after the Civil War.”
- “Utilizing rhetorical questions, expert opinions, and emotional appeals, Naomi Wolf’s ‘The Beauty Myth’ critiques societal standards of beauty and their impact on women.”
Your thesis statement should reflect the unique aspects of the text you’re analyzing and provide a clear roadmap for your analysis.
Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement Example for Essay
Crafting a powerful rhetorical analysis thesis statement for personal essay sets the stage for dissecting the art of persuasion within a given text. It succinctly outlines the author’s techniques, persuasive strategies, and the intended impact on the audience, offering a roadmap for an in-depth exploration of rhetoric’s nuances.
- “Through skillful use of metaphors, emotive language, and compelling anecdotes, Jane Doe effectively challenges societal beauty standards in her essay ‘Mirror, Mirror.'”
- “By dissecting persuasive appeals, rhetorical devices, and tone shifts, John Smith uncovers the manipulation of emotion and logic in his analysis of the political speech ‘A Nation United.'”
- “In analyzing Martin Luther King Jr.’s ‘I Have a Dream’ speech, this essay explores how he employs repetition, powerful imagery, and moral appeals to inspire societal change.”
- “Examining the persuasive strategies in ‘The Power of Vulnerability’ TED Talk, this analysis demonstrates how Brené Brown combines personal stories, humor, and audience engagement.”
- “Through a close examination of tone, diction, and narrative structure, this essay explores the emotional impact of J.K. Rowling’s ‘The Casual Vacancy’ on its readers.”
- “By evaluating rhetorical devices, historical context, and the speaker’s credibility, this analysis dissects Winston Churchill’s ‘Blood, Toil, Tears and Sweat’ speech during World War II.”
- “Analyzing the ‘Blackfish’ documentary, this essay delves into the manipulation of emotional appeals, expert testimonies, and visual storytelling to advocate for animal rights.”
- “This analysis of Maya Angelou’s poem ‘Phenomenal Woman’ uncovers how she uses rhythm, repetition, and empowering language to celebrate female strength and allure.”
- “Through the exploration of rhetorical devices, irony, and emotional appeals, this essay dissects Mark Antony’s funeral oration in Shakespeare’s ‘Julius Caesar.'”
- “Examining Barack Obama’s ‘A More Perfect Union’ speech, this analysis illustrates how he combines personal history, logical reasoning, and rhetorical questions to address race in America.”
Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement Example for College
In college-level rhetorical analysis, the thesis statement for college essay acts as a compass guiding readers through the intricacies of persuasive techniques. This critical element encapsulates the main focus of the essay, from analyzing rhetorical devices to uncovering underlying themes, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of communication strategies.
- “By scrutinizing the strategic use of anecdotes, historical context, and logical appeals, this college-level analysis dissects Abraham Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address.”
- “Analyzing the ‘TED Talk’ genre, this essay explores how speakers employ rhetorical strategies, visual aids, and audience engagement to convey complex ideas effectively.”
- “This college-level analysis of Margaret Atwood’s ‘The Handmaid’s Tale’ examines the symbolism, dystopian elements, and social commentary through a rhetorical lens.”
- “Evaluating the persuasive techniques in President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s ‘Day of Infamy’ speech, this analysis highlights his use of rhetorical questions, historical references, and emotional appeals.”
- “Through an examination of metaphors, emotional appeals, and logical reasoning, this analysis dissects Frederick Douglass’ ‘Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave.'”
- “Analyzing J.R.R. Tolkien’s ‘The Hobbit,’ this essay explores how Tolkien employs allegory, symbolism, and vivid descriptions to convey universal themes of heroism and growth.”
- “This college-level analysis of Maya Angelou’s ‘Still I Rise’ dissects how she uses repetition, metaphor, and uplifting language to empower and inspire marginalized voices.”
- “Evaluating the persuasive techniques in Michelle Obama’s ‘Becoming,’ this analysis illustrates how she combines personal narratives, emotional appeals, and relatable anecdotes to connect with readers.”
- “Through a rhetorical analysis of George Orwell’s ‘1984,’ this essay explores how he uses dystopian elements, propaganda, and language manipulation to critique totalitarianism.”
- “Analyzing Steve Jobs’ Stanford commencement address, this essay delves into how he employs personal stories, rhetorical questions, and aspirational language to inspire graduates.”
Strong Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement Example
A robust rhetorical analysis strong thesis statement serves as a cornerstone for rigorous exploration. It not only identifies the core rhetorical strategies but also unveils their profound impact on shaping perceptions, opinions, and societal discourse, emphasizing the author’s skill in effectively manipulating language and emotion.
- “Martin Luther King Jr.’s ‘Letter from Birmingham Jail’ masterfully combines logical appeals, emotional anecdotes, and historical references to advocate for civil rights.”
- “Through the strategic use of pathos, ethos, and logos, Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie’s ‘We Should All Be Feminists’ compellingly challenges gender stereotypes and inequality.”
- “In ‘The Great Gatsby,’ F. Scott Fitzgerald employs vivid imagery, symbolism, and dramatic irony to critique the American Dream’s corruption and superficiality.”
- “By blending allegory, emotional appeals, and vivid language, Yann Martel’s ‘Life of Pi’ artfully explores the human spirit’s resilience and the complexities of faith.”
- “Harper Lee’s ‘To Kill a Mockingbird’ uses allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals to navigate themes of racial prejudice, moral growth, and societal justice.”
- “Through the manipulation of tone, diction, and rhetorical questions, George Orwell’s ‘Animal Farm’ satirically critiques the abuse of power and the dangers of totalitarianism.”
- “In his ‘I Have a Dream’ speech, Martin Luther King Jr. strategically employs repetition, allusion, and emotional appeals to inspire racial unity and equality.”
- “Gloria Anzaldúa’s ‘How to Tame a Wild Tongue’ combines rhetorical questions, historical context, and emotional anecdotes to explore the challenges of linguistic assimilation.”
- “Through the use of vivid imagery, emotive language, and allegory, William Blake’s ‘The Tyger’ delves into the complexities of creation, innocence, and experience.”
- “By intertwining allegory, symbolism, and emotional appeals, John Bunyan’s ‘The Pilgrim’s Progress’ explores themes of spiritual journey and redemption.”
Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement Example for History
Within historical context, a rhetorical analysis thesis statement provides a lens through which to examine how persuasive methods have influenced significant events. By scrutinizing the techniques used, this statement illuminates how rhetoric has played a role in shaping historical narratives, ideologies, and even shaping collective memory.
- “Analyzing Winston Churchill’s ‘Their Finest Hour’ speech, this historical analysis dissects his use of rhetoric to inspire resilience and unity during World War II.”
- “Evaluating Patrick Henry’s ‘Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death’ speech, this historical analysis explores how he strategically employed emotional appeals and historical references to advocate for colonial independence.”
- “By examining the rhetoric of Frederick Douglass’ ‘What to the Slave Is the Fourth of July?’ speech, this historical analysis uncovers how he used personal anecdotes and logical appeals to critique American hypocrisy.”
- “This historical analysis of Sojourner Truth’s ‘Ain’t I a Woman?’ speech explores her use of rhetorical questions and emotional appeals to challenge gender and racial prejudices of her time.”
- “Through the exploration of Abraham Lincoln’s ‘Second Inaugural Address,’ this historical analysis delves into how he employed biblical references, emotional appeals, and rhetorical devices to address post-Civil War reconciliation.”
- “Analyzing Susan B. Anthony’s ‘Declaration of Sentiments,’ this historical analysis dissects how she utilized rhetorical strategies to advocate for women’s rights and suffrage in the 19th century.”
- “By examining the persuasive techniques in Franklin D. Roosevelt’s ‘Pearl Harbor Address to the Nation,’ this historical analysis highlights how he combined emotional appeals, historical context, and logical reasoning to rally the nation after the attack.”
- “Evaluating Martin Luther King Jr.’s ‘I Have a Dream’ speech through a historical lens, this analysis illustrates how he employed references to history, biblical allusions, and emotional appeals to advocate for racial equality.”
- “Through the exploration of Gandhi’s ‘Quit India’ speech, this historical analysis uncovers how he used rhetoric to inspire nonviolent resistance against British colonial rule during India’s struggle for independence.”
- “Analyzing the persuasive techniques in Ronald Reagan’s ‘Tear Down This Wall’ speech, this historical analysis delves into how he employed rhetorical strategies to advocate for the end of the Berlin Wall and Cold War tensions.”
How do you write a rhetorical analysis thesis statement? – Step by Step Guide
Crafting a compelling rhetorical analysis final thesis statement requires a systematic approach to distill the core elements of the text’s persuasive strategies. Follow these steps to create an effective thesis statement for your rhetorical analysis essay:
- Understand the Text: Read the text thoroughly to grasp its message, context, and the author’s intent. Identify the rhetorical techniques, such as ethos, pathos, logos, and various stylistic devices used to influence the audience.
- Identify the Core Strategies: Determine the main persuasive strategies employed by the author, such as the use of metaphors, anecdotes, rhetorical questions, appeals to authority, tone shifts, and more.
- Analyze the Impact: Assess how these strategies contribute to the overall effectiveness of the message. Consider how they evoke emotions, create credibility, enhance logic, or provoke thought.
- Narrow Down Your Focus: Choose specific aspects of the text’s rhetoric that you’ll analyze in detail. Your thesis statement should highlight the main techniques you’ll discuss in your essay.
- Frame Your Assertion: Formulate a concise thesis statement that encapsulates your interpretation of the author’s message and the techniques used. It should provide insight into how the techniques contribute to the text’s persuasiveness.
- Make it Specific: Ensure your thesis statement is precise and focused, avoiding vague or generic claims. Mention the specific rhetorical techniques and their impact on the audience.
- Draft and Revise: Write a preliminary thesis statement and refine it through revisions. Ensure it reflects the text’s core themes and the analytical direction you plan to take.
- Test for Clarity: Share your thesis statement with peers or mentors to gauge its clarity and effectiveness in conveying your intended analysis.
- Check for Alignment: Confirm that your thesis statement accurately aligns with the analysis you present in your essay’s body paragraphs.
- Refine as Needed: If your analysis evolves as you write, be open to refining your thesis statement to better capture your insights.
Does a rhetorical analysis need a thesis statement?
Yes, a rhetorical analysis essay should definitely have a clear and concise thesis statement . The thesis statement is the foundation of your essay; it guides your analysis, gives direction to your essay, and informs your readers about the central focus of your analysis. A well-crafted thesis statement articulates the author’s main persuasive strategies, the techniques used, and their intended impact on the audience.
A strong thesis statement serves as a roadmap for both you and your readers, ensuring that your analysis is focused and well-structured. Without a thesis statement, your essay may lack coherence and direction, making it challenging for your readers to follow your analytical journey. Therefore, incorporating a thesis statement in your rhetorical analysis essay is essential for a clear and effective presentation of your insights.
Tips for Writing a Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement
Creating an effective thesis statement for a rhetorical analysis requires precision and insight. Here are some tips to consider:
- Be Specific: Clearly identify the rhetorical techniques you will analyze, such as imagery, metaphors, tone, or appeals. This specificity sets the tone for your essay.
- Highlight Impact: Address how the identified techniques contribute to the author’s persuasiveness. Explain how they engage emotions, logic, or credibility.
- Avoid Simple Summaries: Your thesis should go beyond summarizing the text; instead, focus on the techniques and their persuasive function.
- Capture Complexity: Reflect the nuanced relationship between techniques and their combined impact on the audience’s interpretation.
- Tailor to Audience: Consider the context of your essay. Adapt your thesis statement to the intended audience and their familiarity with the text.
- Draft and Revise: Create a working thesis, then refine it as you analyze the text further and gain deeper insights.
- Use Strong Language: Employ confident and assertive language to showcase your analytical approach.
- Stay Objective: Maintain an objective tone in your thesis statement, focusing on the author’s techniques rather than expressing your personal opinions.
- Parallel Structure: Consider using parallel structure to list the techniques you’ll analyze, ensuring clarity and consistency.
- Connect to Argument: Ensure your thesis sets up your main argument or interpretation about the author’s overall effectiveness in persuasion.
Remember, a well-crafted thesis statement sets the tone for your entire essay and guides your analysis. Take the time to refine it, and it will serve as a valuable roadmap for both you and your readers. In addition, you should review our thesis statement persuasive essay .

AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Supporting a Thesis: Using Rhetorical Appeals
The purpose of a position argument is to persuade readers to adopt a viewpoint. Writers of position arguments focus on a thesis that takes a stance on a debatable issue and support that thesis with reasoning and evidence. When writing persuasively, consider your audience and use the kinds of reasoning strategies and evidentiary appeals you believe will be convincing. In addition, use language with which your audience is most comfortable. In academic environments, academic language is generally most acceptable, although you may choose to challenge this notion for rhetorical purposes. Outside academic environments, tailor your language to connect best with your audience.
Reasoning is most effective when it is built on evidence that readers recognize as logical and practical. Suppose you want to persuade your audience that because of the insurrection at the U.S. Capitol on January 6, 2021, additional police should be hired to protect the building and the people who work there. You could include information about the number of police on duty that day, the number of people injured, and the amount of damage done. You then could explain how the number of police on duty was insufficient to protect the people and the Capitol.
Additionally, you identify and refute the counterclaims . An example of a counterclaim against hiring additional police officers might be that the cost is too high. Your response, then, might be that the cost could easily be shifted from another nationally funded source.
Characteristics of Position Arguments
Ethos (ethical appeal).
You establish credibility by showing readers that your approach to the issue is fair and that you can be trusted. One way to demonstrate fairness and trustworthiness is to use neutral language that avoids name-calling. For instance, in your paper about hiring additional police to defend the Capitol, you would avoid taking political sides and would use neutral language when describing police, workers in the Capitol, and demonstrators.
To show trustworthiness, always follow these guidelines:
- Use only respected, reliable sources as evidence. Avoid sources that lean heavily to the political right or left or that are otherwise questionable as to accuracy. Reliable sources include scholarly, peer-reviewed articles and books; professional articles and books; and articles from magazines, newspapers, websites, and blogs. For more information about credible sources, see the chapter in Part 5 on evaluating sources.
- Present evidence from sources in the same context in which it was originally presented. Do not change the original author’s meaning or tone. Be especially careful of such changes when you paraphrase or summarize.
- Cite evidence to the proper sources. Use the citation style required by your instructor, usually MLA Documentation and Format or APA Documentation and Format Proper citations direct readers to more information about your sources and show you are not plagiarizing.
- Incorporate common ground between readers who support your position and those who do not. To do this, many authors use evidence pulled from patriotic or religious documents to create ethical appeal. For instance, regarding the activity that took place at the Capitol, both sides might find common ground in the First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution, which outlines the rights of the people. The protestors might cite the section of the amendment that deals with freedom of assembly; those on the other side might point out that the amendment guarantees “the right of the people peaceably to assemble” and make the case that the assembly was not peaceable.
Logos (Logical Appeal)
You appeal to your audience’s intelligence by showing that you understand the value of sound reasoning. To do this, state your position clearly and support it with rational arguments, critical thinking, and credible evidence. Also, avoid exaggerating or making claims you cannot support with reliable evidence. Many authors use facts and statistics to create logical appeal.
To appeal to logic, follow these guidelines:
- State your position clearly with easy-to-understand language. For example, to appeal to readers’ intelligence in your paper about hiring additional police to defend the Capitol, avoid using vocabulary that would feel unnatural. Instead of writing “The verbiage from the campaigners importuned the dispossession of their statesmen,” write “The protestors demanded the resignations of their congressional representatives.”
- Support your position with reasoning that is neither incomplete nor faulty. Sound reasoning is that which all can agree makes sense. For example, you would not contend that to be ready for future protests, the Capitol police force must be doubled from 2,000 to 4,000 because you cannot know the number needed at any time. However, you could argue that the Capitol police force and government leaders should study the January 6, 2021, riot to determine how many additional police are needed, should such an occasion arise again.
- Present your critical thinking through a well-constructed argument. By ordering your position argument in a manner that moves logically from one point to the next, you help guide readers through your thought process, which is reflected in the smooth flow of ideas that work together to support your thesis.
- Incorporate credible evidence from trusted and reliable academic, government, media, and professional sources. Using these sources shows readers that you recognize biased material and have excluded it from your paper.
Pathos (Emotional Appeal)
You appeal to your audience’s feelings—such as sympathy, anger, fear, insecurity, guilt, and conscience—to support your position.
For example, to appeal to your audience’s emotions in your paper about the need for more Capitol police, you might do the following:
- Help your readers understand feelings of fear. One way to appeal to this emotion is to quote from interviews with government workers and bystanders who were hiding behind locked doors and had no police protection.
- Use vivid description and concrete language to recreate images that showed lone officers overwhelmed by crowds of people and beaten.
- Use nonaggressive language to address the positions of readers who do not support your stance. For example, some readers may believe that the federal government spends too much money already and should not allocate more. By using language that is not inflammatory, you can show your empathy for others, and this may help you convince them to support your position.
Kairos (Timeliness)
The sense of timing—presenting your position at the right time—is critical in a position argument. The issue must be worthy of attention at the time it is presented for readers to feel a sense of urgency.
For example, in an argumentative paper about the significance of the Black Lives Matter (BLM) movement, you could do the following:
- Point out the history of the BLM movement, which began in 2013 after the acquittal of the man accused of killing Trayvon Martin (1995–2012) in 2012.
- Note that today, most of the speeches delivered in BLM rallies held across the country reference the May 2020 murder of George Floyd (1973–2020).
- Emphasize that Floyd’s killing remains front and center in the minds of rally participants. In other words, the topic of Floyd’s death is timely, and related circumstances indicate a favorable time for action.
- Allusion : direct or implied reference to a person, place, work of literature, idea, event, or anything a writer expects readers to know about. Allusion is a frequently used literary device.
- Citation : reference to the source of information used in a writer’s research.
- Critical thinking : ability to identify and solve problems by gathering information about a topic and then analyzing and evaluating evidence to form a judgment.
- Counterclaim (dissenting opinion) : statement of what the other side might say in opposition to the stance the writer takes about an issue.
- Ethos : appeal to readers’ ethical sense; establishing authority and credibility.
- Evidence : facts and other information that prove or disprove the validity of something written or stated.
- Introduction : first part of a paper. In position arguments, the writer alerts readers to the issue or problem discussed and often presents the thesis at the end of the introduction.
- Kairos : appeal to timeliness of the subject matter.
- Logos : appeal to readers’ sense of logic, or reason.
- Pathos : appeal to readers’ emotions.
- Purpose : author’s reason for writing the paper. In a position argument, the purpose is to persuade readers to agree with the writer’s stance.
- Reasoning : logical and sensible explanation of a concept.
- Recursive : movement back and forth from one part of the writing process to another.
- Rhetorical appeals : methods of persuasion (ethos, logos, pathos, and kairos).
- Rhetorical question : questions intended to make a point rather than to get an answer. Rhetorical questions, which often have no answers or no obvious answers, appear frequently in argument writing as a way of capturing audience attention.
- Topic : subject of a paper.
- Thesis : declarative sentence (sometimes two) that states a writer’s position about the debatable issue, or topic, of the paper.
- Transitional words or phrases : words and phrases that help readers connect ideas from one sentence to another or from one paragraph to another. Transitions establish relationships among ideas.
LICENSE AND ATTRIBUTE
Adapted from Michelle Bachelor Robinson and Maria Jerskey’s “ 10.3 Glance at Genre: Thesis, Reasoning, and Evidence” of Writing Guide with Handbook , 2021, used according to CC by 4.0 . Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/10-3-glance-at-genre-thesis-reasoning-and-evidence
UNM Core Writing OER Collection Copyright © 2023 by University of New Mexico is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
We use cookies and similar technologies to improve your website experience and help us understand how you use our website. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the usage of cookies. Learn more about our Privacy Statement and Cookie Policy .
- Our Mission
- Code of Conduct
- The Consultants
- Hours and Locations
- Apply to Become a Consultant
- Make an Appointment
- Face-to-Face Appointments
- Zoom Appointments
- Written Feedback Appointments
- Support for Writers with Disabilities
- Policies and Restrictions
- Upcoming Workshops
- Class Workshops
- Meet the Consultants
- Writing Guides and Tools
- Schedule an appointment! Login or Register
- Graduate Students
- ESOL Students
WHAT IS RHETORIC?
Rhetoric is the study of how writers use language to influence an audience. When we do a rhetorical analysis , we analyze how the writer communicates an argument (instead of what the writer argues). We ask ourselves questions such as, “What strategies is the writer using to influence the reader?” “Why is the writer using those strategies?” “How are those strategies affecting the reader?”
To get started answering such questions, you should thoughtfully consider both the rhetorical situation and the three rhetorical appeals , which are described below. Each of these fundamental rhetorical concepts should guide and inform any rhetorical analysis, in addition to shaping your own writing.
THE RHETORICAL SITUATION
The rhetorical situation is the set of circumstances, or context, that surrounds a piece of writing. The rhetorical situation informs, affects, and guides the writing strategies we choose to use. Considering the rhetorical situation can also give us insight into why the writer chose certain strategies and help us analyze how effective those strategies were.
Many factors shape the rhetorical situation, including timing, current events, and cultural significance. In general, however, the three most prominent factors are the audience, the purpose, and the writer.
Audience. Whenever we write, we are writing to someone, an audience. An audience can consist of a single person or a group of people. While some writing may also have secondary audiences, all writing has a primary audience (the main person or group of people the information is intended for). To be effective, our writing should be tailored to the intended audience. When we tailor our writing to the audience, consider the following characteristics:
- Experience with the subject
- Relationship to the writer
- Cultural, personal, and professional values
- Expectations
- Purpose for reading
Each of these characteristics should affect decisions you make about content, organization, appeals, word choice, style, and genre. For example, your word choice should be different when you write to a general audience vs. an expert in the topic you are discussing.
Purpose. All writing has a particular purpose. The purpose of any piece of writing falls into the following three broad categories:
If a document’s purpose seems to overlap these categories, analyze why that might be. Understanding the purpose of a document can help you assess how appropriate or effective certain strategies are.
Writer. Just as the characteristics of an audience should influence the way something should be written, the characteristics of the writer also affect how something was written and how the audience will receive the writing. When you analyze a document, consider the following characteristics of the writer:
- Relationship to the audience
- Purpose for writing
Understanding the writer’s characteristics and background can give you insight into the writer’s motivations and strategizing.
RHETORICAL APPEALS
The Greek philosopher Aristotle teaches that writers can use three appeals to influence or persuade their audience: logos, pathos, and ethos.
Logos (Logic): Writers can persuade their audience by using logical argument. Writers appeal to readers’ sense of logic by making claims and using factual evidence to support those claims. Writers also appeal to logic through reasoning, such as if/then statements (also called enthymemes or syllogisms ).
Pathos (Emotion): Writers can persuade their audience by invoking emotion or relating to readers’ emotions. Writers can appeal to readers’ sense of emotion through emotionally charged stories, word choice, and imagery.
Ethos (Credibility): Writers can persuade their audience by demonstrating trustworthiness, good will towards the audience, and morality. Writers appeal to readers’ sense of trust by citing credible sources, asserting personal authority or subject matter expertise, or demonstrating good intent and morality.
TIPS FOR DOING A RHETORICAL ANALYSIS
Questions to Consider
When conducting a rhetorical analysis, consider the following questions:
- Who is the intended audience, and how does the writer tailor the writing to that audience?
- What is the purpose, and how does the writer tailor the writing to that purpose?
- What appeals does the writer make and how? Are those appeals an appropriate choice for the intended audience and purpose?
- What kind of style and tone is used, and how are they suitable for the intended audience and purpose?
- What do the chosen writing strategies in the writing reveal about the writer or culture that made it?
This set of questions was adapted from “Basic Questions for Rhetorical Analysis,” a resource from Brigham Young University’s Silvae Rhetoricae : http://rhetoric.byu.edu/Pedagogy/Rhetorical%20Analysis%20heuristic.htm
Elements to Consider
When answering those questions, look at and consider the following elements of the writing:
- Word Choice/Diction
- Use of sources

The Writing Center
4400 University Drive, 2G8 Fairfax, VA 22030
- Johnson Center, Room 227E
- +1-703-993-1200
- [email protected]
Quick Links
- Register with us
© Copyright 2024 George Mason University . All Rights Reserved. Privacy Statement | Accessibility
AP ® Lang teachers: looking to help your students improve their rhetorical analysis essays?
Coach Hall Writes
clear, concise rhetorical analysis instruction.
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Thesis
November 20, 2021 by Beth Hall
One of the first steps of writing a rhetorical analysis essay is knowing how to write a rhetorical analysis thesis.
Rhetorical analysis thesis statements can seem intimidating, but they do not have to be.
While the thesis is a small portion of an essay, it carries significant weight and impact, especially on the AP® Lang exam. For example, on AP® Lang rubric, a defensible thesis is one out of six possible points.
So, what is a defensible thesis and how do you write one for a rhetorical analysis essay?
A defensible thesis means that the thesis or position can be justified, proven, or defended.
You can craft a rhetorical analysis thesis statement with the following steps:
Step 1: As you are reading the passage, look for strategies or choices the author utilizes. Ask: What rhetorical choices does the writer/speaker make? (ie. juxtaposition, allusion, etc) This will be the basis of your thesis statement.
Step 2: Mention the author’s purpose in the thesis. Ask: Why did he/she make these choices? Why did he/she write this?
Step 3: Consider the effect on the audience. This step is not mandatory or always appropriate, but it can strengthen the thesis. The effect is looking at the author’s call to action. Ask: How does he/she want the audience to think/act?

Now that you understand the basis of a thesis statement, let’s talk about where this thesis goes in the essay.
The thesis is best placed in the introductory paragraph. By placing it in the introduction, it gives you a direction for your writing (and often where readers go looking for the thesis). The introduction contains the hook, context, and thesis statement. Often, the context and the thesis are combined together (look at the example below). The context identifies the specific passage you are talking about in your essay.
You can write only a thesis statement for an introductory paragraph if you are short on time, but it is better to have a well-developed introduction. If you want to know more about writing an introduction, you can watch the video here.
Let’s put this information together and look at an example of a thesis statement.
In Leonid Fridman’s passionate article “America Needs its Nerds,” ← context
he defines “geek” and contrasts America with other industrialized nations to develop his argument that America values athletes more than intellectuals. ← thesis
By doing so, Fridman urges readers to reprioritize the current social hierarchy. ← Effect
If you are feeling unsure about thesis statements or need a place to start, sentence frames are a great way to begin a thesis statement. Below are several sentence frames and examples to help you navigate thesis statements.
In SPEAKER/WRITER’S (tone) speech/letter/article (to AUDIENCE), he/she uses ___ and ____ to PURPOSE.
Note: The blanks in this sentence frame should be choices or strategies (nouns). For example, “he uses repetition and juxtaposition to…” Saying “uses” and then a device is rather simple. However, this sentence frame can lead to a defensible thesis. Once you understand this style of thesis writing, you can try more advanced styles.
In SPEAKER/WRITER’S (tone) speech/letter/article (to AUDIENCE), he/she ____ and ____ to PURPOSE.
Example: In his patriotic speech to Congress, President Roosevelt repeats “attacked” and “deliberate” as well as appeals to patriotism in order to convince Congress to declare war on Japan.
Example: In his patriotic speech to Congress, President Roosevelt repeatedly emphasizes the deliberate nature of the attack on Pearl Harbor and appeals to patriotism in order to convince Congress to declare war on Japan.
When you are ready to begin writing thesis statements on your own, remember to keep the following items in mind:
- A thesis identifies the strategies / choices AND purpose. Without both of these, it is not a defensible thesis.
- A thesis does not restate the prompt. Use the prompt as a guide, not as a thesis.
- A thesis answers the prompt. This may seem obvious, but it can be easy to get caught up in writing and lose track of your goal
Looking for more tips about how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, check out this post here.
AP® Lang Teachers
Looking to help your students improve their rhetorical analysis essays?
Latest on Instagram

Shop My TPT Store

Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Workshops
These two activities are designed to introduce students to the idea of a thesis statement for a rhetorical analysis essay and provide structured peer feedback on their draft thesis statement.
Author : Chris Kamrath
Course : PWR 1
Activity brief description: This series of two workshops provides students with norms for good rhetorical analysis thesis statements, examples and the opportunity to get feedback on their own draft thesis statement. The first activity focuses on introducing students to sample thesis statements and norms for good thesis statements.
The handout provides three norms, four sample draft thesis statements, and questions students can ask when peer reviewing thesis statements. Students are asked to ‘peer review’ these sample thesis statements. As a group they come up with feedback for the ‘absent’ authors of these sample thesis statements. Each of the samples is taken from a draft RA essay from a past class. This activity provides students with a sense of what a thesis looks like and how to talk about what makes a thesis ‘good’.
The second activity repeats this process with their own draft thesis statement. This activity would take place one or two classes after the first. The first part of the activity focuses on looking at one of the sample thesis statements from the first day. I record the student responses on the first day. I then re-write the drat thesis to take this feedback into consideration. We discuss my revisions (which usually draw on the actual revised thesis from the student paper) and then students repeat this process in small groups with their own thesis statements. Students get peer feedback and then we have time to revise the thesis statement in class. This activity frames the thesis statement as a key step (after choosing a text) in drafting the rhetorical analysis essay.
Activity length and schedule : The first activity is approximately 45 minutes. Students spend approximately 25-30 minutes to discuss two sample thesis statements. We then discuss their peer feedback for 25 to 20 minutes. The second activity takes between 45 minutes and one hour. 5 minutes is spent on the sample thesis and the revisions which respond to their feedback form the prior workshop. 20-25 minutes is spent peer reviewing their draft thesis. The remainder of the time is used for student revision of their draft thesis statement based on peer feedback.
Week 1/2. These two activities usually occur during the first or second week of class. The first activity introduces students to the idea of a thesis statement for a rhetorical analysis essay and offers criteria for a good thesis statement. Students evaluate sample draft thesis statements. In the second activity students repeat the earlier workshop with their own draft thesis statements. They provide structured feedback on their peer’s draft thesis statement and receive feedback on their own.
Activity goals :
- To provide students with examples of rhetorical analysis thesis statements.
- To provide students with norms for critiquing thesis statements.
- To provide students with feedback on their draft thesis statement.
- To give students space to revise their thesis statement based on feedback.
Activity details :
See handout #1 and handout #2 . See also list of keywords and rhetorical theory concepts .

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to use Rhetorical Questions in your Speech, with Examples
April 5, 2018 - Gini Beqiri
Rhetorical questions can be used as an effective communication tool during a speech. These questions provide you with a way of controlling the speech and thoughts of the audience.
They are especially useful in engaging the audience and persuading them to agree with you. In this article we discuss how to use rhetorical questions in a speech or presentation.
What is a rhetorical question?
A rhetorical question can be “an effective persuasive device, subtly influencing the kind of response one wants to get from an audience” – (Edward P.J. Corbett)
A rhetorical question is a question that’s asked for effect with no answer expected. The answer may be immediately provided by the questioner or obvious.
- The question may have an obvious answer
- The question may not have an answer
- The question may be answered immediately by the questioner
Examples of rhetorical questions
General examples.
Rhetorical questions with obvious answers are asked about well-known facts, or the answer is suggested based on the question’s context. They are used to emphasises an idea or point:
- Are you kidding me?
- Can birds fly?
- Is the Pope catholic?
Rhetorical questions which have no answers:
- What’s the meaning of life?
- How many times do I have to tell you not to…?
Examples from Obama and Shakespeare
President Obama’s immigration address
Ever since the 5th century BC , orators have put their points across by asking rhetorical questions whose implied answers clearly support their point. This rhetorical passage comes from Obama’s immigration speech:
“Are we a nation that tolerates the hypocrisy of a system where workers who pick our fruit and make our beds never have a chance to get right with the law? Are we a nation that accepts the cruelty of ripping children from their parents’ arms? Or are we a nation that values families, and works to keep them together?” – Obama’s Immigration Address
William Shakespeare
Shall I compare thee to a summer’s day? – Sonnet 18
If you prick us, do we not bleed? If you tickle us, do we not laugh? If you poison us, do we not die? And if you wrong us, shall we not revenge? – The Merchant of Venice
Mighty Caesar! Dost thou lie so low? Are all thy conquests, glories, triumphs, spoils, shrunk to this little measure? – Julius Caesar

Benefits of rhetorical questions
Rhetorical questions are not a necessity but they can be valuable. They can be used in many different ways to:
- Engage the audience
- Increase the variety of your presentation
- Influence and persuade the audience
- Subtly draw attention and emphasise specific points
- Introduce topics/ideas
- Make the listeners think about certain topics

How to use rhetorical questions in a speech
1. engage the audience.
Ask a rhetorical question to engage the audience and pause to allow them to think of an answer. This gets the audience to actively participate rather than passively listen as they create hypotheses or resolutions.
For example: asking “Why is practicing mindfulness beneficial for reducing anxiety?” would be more effective than saying “Practicing mindfulness exercises can reduce anxiety levels because…”
Speakers may start presentations with rhetorical questions to increase the likelihood of the audience staying engaged.
2. Personalise your questions
Make the audience feel as though you are speaking to each member individually by using “you” and “your.”
For example: asking “Do you want to lose weight without feeling hungry?” would be more effective than asking “Does anyone here want to lost weight without feeling hungry?”
3. Persuade the audience
To get your audience to agree with you, ask a rhetorical question where the answer is clearly a “yes”. Once the audience begins agreeing with you they are more likely to continue agreeing. You will be familiar with this type of persuasion in casual conversation, for example, “Nice weather today, isn’t it?”
Another way to get the audience to agree with you is to show them that you’re similar. Show your listeners that you have shared experiences and that you understand their problems.
For example, “We’ve all experienced being so stressed at work that we come home and don’t feel like doing anything, haven’t we?”
4. Evoke emotions
Make the audience feel the same way you do about something by asking questions that trigger emotional reactions.
For example, rather than saying “X has never helped our community” ask “What has X ever done for our community?” This will trigger a strong emotional response because the audience will come to that conclusion that “X haven’t done anything.”
5. Emphasise a statement
After a statement has been made use a rhetorical question to get the audience to think about that statement.
For example, “The amount of plastic in the ocean is rising at a considerable rate. How much damage will it take for you to help reduce this?”

6. Predict the audiences questions
Think about your topic and audience when planning your speech. Try to predict what the audience may want to ask. In your speech use the predictions as rhetorical questions and answer them.
For example, “As a dog owner you may think ‘What should I be focusing on to keep my dog healthy?’ The answer is providing your dog with the correct nutrition and therefore food.”
You could also introduce one or more rhetorical questions at the start of your speech and explain that you will answer them during your speech. For example: “In the next 20 minutes let’s explore the answers to these questions.” Asking these difficult questions and promising you will provide the answers will increase interest and attention.
7. Answer questions with questions
Answer a question, either an audience member’s or your own, using another rhetorical question. Generally both the questions have the same answer.
For example: “Have we met the targets again this year? Is the Pope Catholic?”
Try to make the second question unique and relatable to the audience because common examples can sound cheesy.
8. Consecutive rhetorical questions
– Increase the impact of your argument
Ask multiple rhetorical questions consecutively – each one more specific or more powerful than the previous. This way your content will have a greater impact on the listeners.
For example: “Isn’t their skin lovely? Don’t you think it looks really clear? Can you see any blemishes? Wouldn’t you like to have skin like that?”
– Show conflicting opinions
Use rhetorical questions consecutively to highlight the complexity of a topic by asking questions in which the answers provide conflicting viewpoints.
For example: “How can we reduce the crime rate in the UK? Should we rehabilitate offenders? Should criminals be punished with longer sentences? Should we create initiatives targeting at-risk children?” etc
If you start your speech with this technique, you can structure your speech or presentation around it, with each section addressing a different viewpoint.
– Show supporting opinions
You can also consecutively ask questions in which the answers provide similar viewpoints. This is similar to repetition which is used to continually highlight an important point.
For example: “Which company achieves over 90% in customer satisfaction? Which company provides one of the best employee benefits programs in the country? Which company scores highest in employee happiness and fulfilment? Of course, our company does!”
Rhetorical questions are an effective way to gain the support of the audience but ensure that you do your research beforehand. This means finding out who your audience are , such as, their general views, attitudes, age etc. With this information you can plan rhetorical questions that will be appropriate and tailored to your listeners.
Rhetorical Questions in Essays: 5 Things you should Know

Rhetorical questions can be useful in writing. So, why shouldn’t you use rhetorical questions in essays?
In this article, I outline 5 key reasons that explain the problem with rhetorical questions in essays.
Despite the value of rhetorical questions for engaging audiences, they mean trouble in your university papers. Teachers tend to hate them.
There are endless debates among students as to why or why not to use rhetorical questions. But, I’m here to tell you that – despite your (and my) protestations – the jury’s in. Many, many teachers hate rhetorical questions.
You’re therefore not doing yourself any favors in using them in your essays.
Rhetorical Question Examples
A rhetorical question is a type of metacommentary . It is a question whose purpose is to add creative flair to your writing. It is a way of adding style to your essay.
Rhetorical questions usually either have obvious answers, or no answers, or do not require an answer . Here are some examples:
- Are you seriously wearing that?
- Do you think I’m that gullible?
- What is the meaning of life?
- What would the walls say if they could speak?
I understand why people like to use rhetorical questions in introductions . You probably enjoy writing. You probably find rhetorical questions engaging, and you want to draw your marker in, engage them, and wow them with your knowledge.
1. Rhetorical Questions in Academic Writing: They Don’t belong.
Rhetorical questions are awesome … for blogs, diaries, and creative writing. They engage the audience and ask them to predict answers.
But, sorry, they suck for essays. Academic writing is not supposed to be creative writing .
Here’s the difference between academic writing and creative writing:
- Supposed to be read for enjoyment first and foremost.
- Can be flamboyant, extravagant, and creative.
- Can leave the reader in suspense.
- Can involve twists, turns, and surprises.
- Can be in the third or first person.
- Readers of creative writing read texts from beginning to end – without spoilers.
Rhetorical questions are designed to create a sense of suspense and flair. They, therefore, belong as a rhetorical device within creative writing genres.
Now, let’s look at academic writing:
- Supposed to be read for information and analysis of real-life ideas.
- Focused on fact-based information.
- Clearly structured and orderly.
- Usually written in the third person language only.
- Readers of academic writing scan the texts for answers, not questions.
Academic writing should never, ever leave the reader in suspense. Therefore, rhetorical questions have no place in academic writing.
Academic writing should be in the third person – and rhetorical questions are not quite in the third person. The rhetorical question appears as if you are talking directly to the reader. It is almost like writing in the first person – an obvious fatal error in the academic writing genre.
Your marker will be reading your work looking for answers , not questions. They will be rushed, have many papers to mark, and have a lot of work to do. They don’t want to be entertained. They want answers.
Therefore, academic writing needs to be straight to the point, never leave your reader unsure or uncertain, and always signpost key ideas in advance.
Here’s an analogy:
- When you came onto this post, you probably did not read everything from start to end. You probably read each sub-heading first, then came back to the top and started reading again. You weren’t interested in suspense or style. You wanted to find something out quickly and easily. I’m not saying this article you’re reading is ‘academic writing’ (it isn’t). But, what I am saying is that this text – like your essay – is designed to efficiently provide information first and foremost. I’m not telling you a story. You, like your teacher, are here for answers to a question. You are not here for a suspenseful story. Therefore, rhetorical questions don’t fit here.
I’ll repeat: rhetorical questions just don’t fit within academic writing genres.
2. Rhetorical Questions can come across as Passive
It’s not your place to ask a question. It’s your place to show your command of the content. Rhetorical questions are by definition passive: they ask of your reader to do the thinking, reflecting, and questioning for you.
Questions of any kind tend to give away a sense that you’re not quite sure of yourself. Imagine if the five points for this blog post were:
- Are they unprofessional?
- Are they passive?
- Are they seen as padding?
- Are they cliché?
- Do teachers hate them?
If the sub-headings of this post were in question format, you’d probably – rightly – return straight back to google and look for the next piece of advice on the topic. That’s because questions don’t assist your reader. Instead, they demand something from your reader .
Questions – rhetorical or otherwise – a position you as passive, unsure of yourself, and skirting around the point. So, avoid them.
3. Rhetorical Questions are seen as Padding
When a teacher reads a rhetorical question, they’re likely to think that the sentence was inserted to fill a word count more than anything else.
>>>RELATED ARTICLE: HOW TO MAKE AN ESSAY LONGER >>>RELATED ARTICLE: HOW TO MAKE AN ESSAY SHORTER
Rhetorical questions have a tendency to be written by students who are struggling to come to terms with an essay question. They’re well below word count and need to find an extra 15, 20, or 30 words here and there to hit that much-needed word count.
In order to do this, they fill space with rhetorical questions.
It’s a bit like going into an interview for a job. The interviewer asks you a really tough question and you need a moment to think up an answer. You pause briefly and mull over the question. You say it out loud to yourself again, and again, and again.
You do this for every question you ask. You end up answering every question they ask you with that same question, and then a brief pause.
Sure, you might come up with a good answer to your rhetorical question later on, but in the meantime, you have given the impression that you just don’t quite have command over your topic.
4. Rhetorical Questions are hard to get right
As a literary device, the rhetorical question is pretty difficult to execute well. In other words, only the best can get away with it.
The vast majority of the time, the rhetorical question falls on deaf ears. Teachers scoff, roll their eyes, and sigh just a little every time an essay begins with a rhetorical question.
The rhetorical question feels … a little ‘middle school’ – cliché writing by someone who hasn’t quite got a handle on things.
Let your knowledge of the content win you marks, not your creative flair. If your rhetorical question isn’t as good as you think it is, your marks are going to drop – big time.
5. Teachers Hate Rhetorical Questions in Essays
This one supplants all other reasons.
The fact is that there are enough teachers out there who hate rhetorical questions in essays that using them is a very risky move.
Believe me, I’ve spent enough time in faculty lounges to tell you this with quite some confidence. My opinion here doesn’t matter. The sheer amount of teachers who can’t stand rhetorical questions in essays rule them out entirely.
Whether I (or you) like it or not, rhetorical questions will more than likely lose you marks in your paper.
Don’t shoot the messenger.
Some (possible) Exceptions
Personally, I would say don’t use rhetorical questions in academic writing – ever.
But, I’ll offer a few suggestions of when you might just get away with it if you really want to use a rhetorical question:
- As an essay title. I would suggest that most people who like rhetorical questions embrace them because they are there to ‘draw in the reader’ or get them on your side. I get that. I really do. So, I’d recommend that if you really want to include a rhetorical question to draw in the reader, use it as the essay title. Keep the actual essay itself to the genre style that your marker will expect: straight up the line, professional and informative text.
“97 percent of scientists argue climate change is real. Such compelling weight of scientific consensus places the 3 percent of scientists who dissent outside of the scientific mainstream.”
The takeaway point here is, if I haven’t convinced you not to use rhetorical questions in essays, I’d suggest that you please check with your teacher on their expectations before submission.
Don’t shoot the messenger. Have I said that enough times in this post?
I didn’t set the rules, but I sure as hell know what they are. And one big, shiny rule that is repeated over and again in faculty lounges is this: Don’t Use Rhetorical Questions in Essays . They are risky, appear out of place, and are despised by a good proportion of current university teachers.
To sum up, here are my top 5 reasons why you shouldn’t use rhetorical questions in your essays:

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
The assignment is to write a rhetorical analysis of a piece of persuasive writing. It can be an editorial, a movie or book review, an essay, a chapter in a book, or a letter to the editor. For your rhetorical analysis, you will need to consider the rhetorical situation—subject, author, purpose, context, audience, and culture—and the ...
A strong thesis statement for a rhetorical analysis is NOT… A simple statement of your topic A broad statement A statement of facts or statistics A summary of the author's essay you are analyzing A statement of what you're going to do in the essay Examples of weak rhetorical analysis thesis statements:
5. State your thesis. Now that you've completed your analysis of the material, try to summarize it into one clear, concise thesis statement that will form the foundation of your essay. Your thesis statement should summarize: 1) the argument or purpose of the speaker; 2) the methods the speaker uses; and 3) the effectiveness of those methods ...
To write a rhetorical analysis, you need to follow the steps below: Step 1: Plan and prepare. With a rhetorical analysis, you don't choose concepts in advance and apply them to a specific text or piece of content. Rather, you'll have to analyze the text to identify the separate components and plan and prepare your analysis accordingly.
A strong thesis statement for a rhetorical analysis is NOT… A broad, simple statement of your topic A statement of facts or statistics A summary of the author's essay you are analyzing A statement of what you're going to do in the essay Examples of weak rhetorical analysis thesis statements:
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses. Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. "implies," "asserts," or "claims". Briefly summarize the text in your own words. Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect.
Asking the right questions about how a text is constructed will help you determine the focus of your rhetorical analysis. ... Thesis. A thesis for a rhetorical analysis does not address the content of the writer's argument. ... the thesis should be a statement about specific rhetorical strategies the writer uses and whether or not they make a ...
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right. Example of a thesis that is too broad:
Technically, though, we can't. Oh, we can answer questions about rhetoric, but rhetorical questions are, by definition, questions no one expects to be answered. They're really statements, posed as questions, like "What has happened to common decency?" or "Will we stand for this injustice?" The purpose of a rhetorical question is to ...
AN rhetorical question is asked more to create an impact or make a statement rather other get an replies. When applied effectively, it is a powerful literary devices that can add immense appreciate to your write. How until Use Rhetorical Questions in an Seek. Thinking of using flowery questions?
Follow these steps to create an effective thesis statement for your rhetorical analysis essay: Understand the Text: Read the text thoroughly to grasp its message, context, and the author's intent. Identify the rhetorical techniques, such as ethos, pathos, logos, and various stylistic devices used to influence the audience. Identify the Core ...
An introduction can begin with. a rhetorical question; a quotation; a definition; an interesting fact; ... Remember that the thesis statement is a kind of "mapping tool" that helps you organize your ideas, and it helps your reader follow your argument. After the topic sentence, include any evidence in this body paragraph, such as a quotation ...
Rhetorical questions, which often have no answers or no obvious answers, appear frequently in argument writing as a way of capturing audience attention. Topic: subject of a paper. Thesis: declarative sentence (sometimes two) that states a writer's position about the debatable issue, or topic, of the paper.
Rhetoric is the study of how writers use language to influence an audience. When we do a rhetorical analysis, we analyze how the writer communicates an argument (instead of what the writer argues). We ask ourselves questions such as, "What strategies is the writer using to influence the reader?" "Why is the writer using those strategies ...
A defensible thesis means that the thesis or position can be justified, proven, or defended. You can craft a rhetorical analysis thesis statement with the following steps: Step 1: As you are reading the passage, look for strategies or choices the author utilizes. Ask: What rhetorical choices does the writer/speaker make? (ie. juxtaposition ...
This activity frames the thesis statement as a key step (after choosing a text) in drafting the rhetorical analysis essay. Activity length and schedule: The first activity is approximately 45 minutes. Students spend approximately 25-30 minutes to discuss two sample thesis statements. We then discuss their peer feedback for 25 to 20 minutes.
Rhetorical questions can be used as an effective communication tool during a speech. These questions provide you with a way of controlling the speech and thoughts of the audience. ... After a statement has been made use a rhetorical question to get the audience to think about that statement. For example, "The amount of plastic in the ocean is ...
If your rhetorical question isn't as good as you think it is, your marks are going to drop - big time. 5. Teachers Hate Rhetorical Questions in Essays. This one supplants all other reasons. The fact is that there are enough teachers out there who hate rhetorical questions in essays that using them is a very risky move.
Which of the following statements is true of a thesis statement? a. It cannot be written when a speech follows narrative order. b. It incorporates general goals rather than specific goals. ... an outline b. a startling statement c. an action d. a rhetorical question. c. Which of the following statements is true of subpoints? a. They are ...