

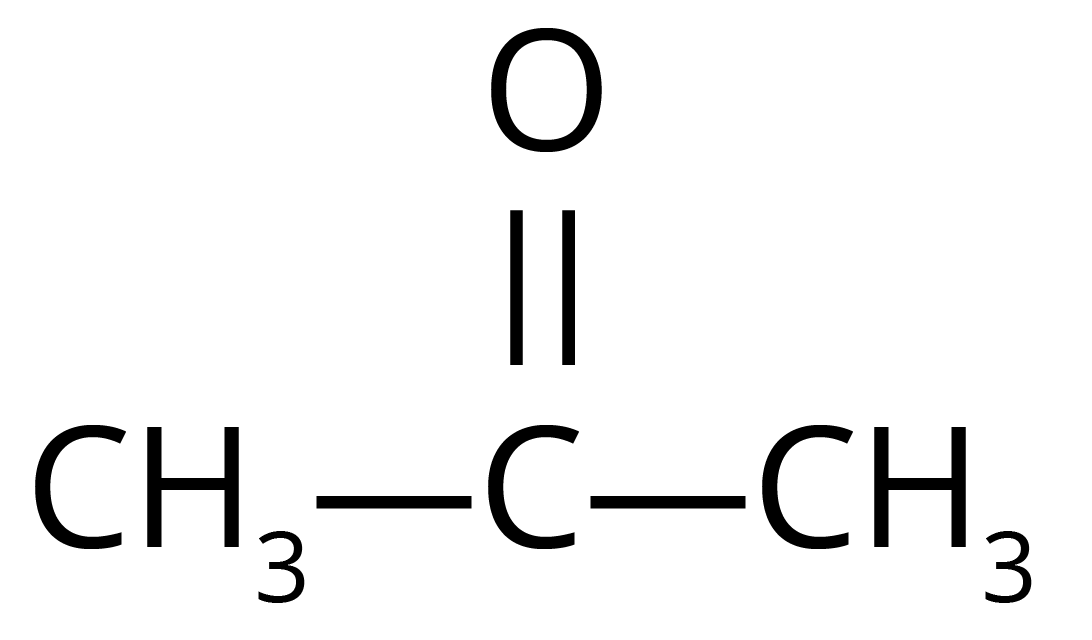
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
CBSE Board Exam is on the way, so you must practice some good Case Study Questions Class 10 Science to boost your preparation to score 95+% on Boards. In this post, you will get Case Study and Passage Based Questions that will come in CBSE Class 10 Science Board Exams.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Carbon and its Compounds Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds .
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v).
The compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ from each other in physical or chemical properties are called isomers and the phenomenon is called isomerism. When the isomerism is due to differences in the arrangement of atoms within the molecule, without any reference to space, the phenomenon is called structural isomerism . In other words. structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas, i.e., they are different in the order in which different atoms are linked. In these compounds, carbon atoms can be linked together in the form of straight chains, branched chains or even rings.
(i) Which of the following sets of compounds have the same molecular formula? (a) Butane and iso-butane (b) Cyclohexane and hexene (C) Propanal and propanone (d) All of these
Answer: (d) All of these
(ii) In order to form branching, an organic compound must have a minimum of (a) four carbon atoms (b) three carbon atoms (c) five carbon atoms (d) any number of carbon atoms.
Answer: (a) four carbon atoms
(iii) Which of the following is an isomeric pair? (a) Ethane and propane (b) Ethane and ethene (c) Propane and butane (d) Butane and 2-methylpropane
Answer: (d) Butane and 2-methylpropane
(iv) Among the following the one having longest chain is (a) neo-pentane (b) iso-pentane (C) 2-methylpentane (d) 2,2-dimethylbutane.
Answer: (C) 2-methylpentane
(v) The number of isomers of pentane is (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 5
Answer: (b) 3
Question 2:
Food, clothes, medicines, books, or any of the things are all based on this versatile element carbon. In addition, all living structures are carbon-based. The earth’s crust has only 0.02% carbon in the form of minerals. The element carbon occurs in different forms in nature with widely varying physical properties. Both diamond and graphite are formed by carbon atoms, the difference lies in the manner in which the carbon atoms are bonded to one another. Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation.
(i) From the given alternatives, whose chemical and physical properties are not the same? (a) Graphite and Diamond (b) Phosphorous and Sulphur (c) Carbon and Hydrogen (d) Methyl alcohol and Acetic acid
Answer: (d) Due to presence of different functional groups methyl alcohol and acetic acid. Possess different physical and chemical properties.
(ii) Which of the following statements is not correct? (a) Graphite is much less dense than diamond (b) Graphite is black and soft (c) Graphite has low melting point (d) Graphite feels smooth and slippery
Answer: (c) Graphite has low melting point
(iii) Which of the following are isomers? (a) Butane and isobutene (b) Ethane and ethene (c) Propane and propyne (d) Butane and isobutane
Answer: (d) Butane and isobutane have same chemical formula but different arrangement of atoms and have different structure.
(iv) Which one of the following is not an allotrope of carbon? (a) Soot (b) Graphite (c) Diamond (d) Carborundum
Answer: (d) Carborundum is SiC (silicon carbide).
(v) Pentane has the molecular formula C 5 H 12 . It has (a) 5 covalent bonds (b) 12 covalent bonds (c) 16 covalent bonds (d) 17 covalent bonds
Answer: (c) 16 covalent bonds
Question 3:
A homologous series is a series of organic compounds which belong to the same family (i.e. possess same functional group) and show similar chemical properties. The members of this series are called homologous and differ from each other by the number of CH 2 units in the main carbon chain.
3.1) Which of the following is not the property of a homologous series ? (a) They all contain double bond. (b) They differ by 14 units by mass. (c) They show similar chemical properties. (d) They can be represented by a general formula.
Answer: (a) They all contain double bond
3.2) Which of the following represent the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula C n H 2n + 2 ? (a) Methane CH 4 (b) Ethane C 2 H 6 (c) Ethyne C 2 H 6 (d) Ethene C 2 H 4
Answer: (b) Ethane C2H6
3.3) The chemical properties of which of the following compounds is similar to the butane ? (a) Propyne (b) Pentane (c) Butyne (d) Propene
Answer: (b) Pentane
3.4) The difference between two consecutive members in a homologous series in alkanes in terms of molecular mass and number of atoms of elements is : (a) 14 a.m.u and CH respectively (b) 12 a.m.u and CH respectively (c) 14 a.m.u and CH2 respectively (d) 12 a.m.u and CH3 respectively
Answer: (c) 14 a.m.u and CH2 respectively
3.5) Which of the following does not belong to the same homologous series ? (a) CH 4 (b) C 2 H 6 (c) C 3 H 8 (d) C 4 H 8
Answer: (d) C4H8
Question 4:
Some elements exist in various forms. These forms have different physical properties but have the same chemical properties. They are called allotropes of the element. Carbon, Phosphorous and sulphur have allotropes. Diamond and graphite are the allotropes of carbon. The differences in the physical properties of diamond and graphite are because of the manner in which the carbon atoms are arranged.
4.1) The hardest substance known which doesn’t conduct electricity is : (a) graphite (b) fullerence (c) diamond (d) methane
Answer:(c) diamond
4.2) Diamond is a : (a) three dimensional structure (b) one dimensional structure (c) two dimensional structure (d) none of these
Answer:(a) three dimensional structure
4.3) Graphite is used as a crucible to melt metals because : (a) it has low melting point (b) it has high boiling point (c) it has low boiling point (d) it has high melting point
Answer:(d) it has high melting point
4.4) Which of the following is correct the structure of diamond ? (a) Carbon atoms are held together by single covalent bonds. (b) Carbon atoms conduct electricity in the molten state. (c) Layers of atoms slide easily over each other. (d) Electrons move freely through the structure.
Answer:(a) Carbon atoms are held together by single covalent bonds.
4.5) Diamond is not a good conductor of electricity because : (a) it is very hard. (b) it has no free electrons. (c) it is not water soluble. (d) its structure is very compact.
Answer:(b) it has no free electrons..
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Science Carbon and Its Compounds Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Extra questions of class 10 science chapter 9 heredity and evolution pdf download.

Class 10 Maths Probability Handwritten Notes by Toppers – Download PDF
Mcq class 10 social science history print culture and the modern world questions with answers, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Carbon and its compounds
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 4 carbon and its compounds.
CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Carbon and its compounds. Term 2 Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Carbon and its compounds.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Carbon and its compounds
CASE STUDY : 1
Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation. These compounds may have long chains of carbon, branched chains of carbon or even carbon atoms arranged in rings. In addition, carbon atoms may be linked by single, double or triple bonds.
i) What are saturated compounds?
Ans: Compounds of carbon that are linked by only single bond between the carbon atoms are called as saturated compounds.
Eg: C2H6, CH4
ii) What is the another versatile property of carbon?
Ans: The tetravalent nature of carbon i.e it has four valency and it is capable of bonding with other four atoms of carbon or any other atom of monovalency.
iii) Give two example of unsaturated compounds.
Ans- Ethene- C2H4 & Ethyne- C2H2
iv) What would be the electron dot structure of C2H6.
v) Name any one element other than carbon which show catenation property?
Ans- Sulphur i.e S8 molecule.
CASE STUDY :2
Carbon, in all its allotropic forms, burns in oxygen to give carbon dioxide along with the release of heat and light. Most carbon compounds also release a large amount of heat and light on burning.
Saturated hydrocarbons will generally give a clean flame while unsaturated carbon compounds will give a yellow flame with lots of black smoke.
i) Complete the reaction: CH3CH2OH +O2 gives
Ans: CH3CH2OH + O2 👉 CO2 + H2O + heat & light.
ii) What is the reason for incomplete combustion?
Ans: When the supply of air is limited for combustion, then the fuel goes partial combustion which results in sooty flame.
iii) Combustion is an oxidation or reduction type of reaction?
Ans: It is an oxidation type of reaction as oxygen get added to reactant.
Eg: C+ O2 👉 CO2 + heat aand light.
iv) Draw the structure of the compound: But-2- yne.

V) What is homologous series?
Ans- A series of compound in which the same functional group substitutes for hydrogen in a carbon chain.
Eg: C2H6 & C3H6. – these differ by CH2 unit.
CASE STUDY : 3
Carbon compounds can be easily oxidised on combustion. In addition to this complete oxidation, we have reactions in which alcohols are converted to carboxylic acids.
We see that some substances are capable of adding oxygen to others. These substances are known as oxidisingagents.
i) Give two example of good oxidising agent.
Ans: Alkaline potassium permanganate or acidified potassium dichromate.
ii) Complete the reaction: CH3CH2CH2OH + Alk. KMnO4 👉?
Ans: CH3CH2CH2OH + Alk. KMnO4 👉 CH3CH2COOH.
iii) What are the uses of alcohol?
Ans: Good solvent, used to make syrups & drinks.
iv) Why Acidified potassium dichromate is called an oxidising agent?
Ans: It is because they can add oxygen to the reactant molecule very easily and convert them to acid.
v) What is the use of ethanoic acid?
Ans: used as preservatives in pickle and also to make esters.
CASE STUDY : 4
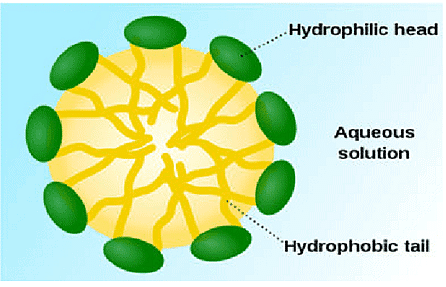
Most dirt is oily in nature and as you know, oil does not dissolve in water. The molecules of soap are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. The ionic-end of soap interacts with water while the carbon chain interacts with oil. The soap molecules, thus form structures called micelles, where one end of the molecules is towards the oil droplet while the ionic-end faces outside. This forms an emulsion in water. The soap micelle thus helps in pulling out the dirt in water and we can wash our clothes clean
i) What is hydrophobic end?
Ans- Soap molecules have two ends in which one is hydrophobic end which interacts with hydrocarbons and do not dissolve in water.
ii) Draw the structure of micelle.

iii) What are scums?
Ans- An insoluble substance(white precipitate) remains after washing with water. It is formed by the reaction of soaps with the calcium and magnesium salts.
iv) What is hard water?
Ans: The water which contains Calcium and magnesium salts in it and form insoluble precipitates when treated with soap are called hard water.
V) To remove hardness of water, the water is treated with soap or detergent?
Ans: Detergent are effective in hard water as they contain sodium salts of sulphonic acid or ammonium salts with chlorides or bromides ions etc.
CASE STUDY :5
Ethanoic acid is commonly called acetic acid and belongs to a group of acids called carboxylic acids. 5-8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar and is used widely as a preservative in pickles.
i) What is glacial acetic acid?
Ans: The melting point of ethanoic acid is 290K, so its often freezes during winter. Hence, gave rise to new name called as glacial acetic acid.
ii) Complete the reaction: NaOH + CH3CH2COOH 👉?
Ans: NaOH + CH3CH2COOH👉 CH3CH2COONa + H2O
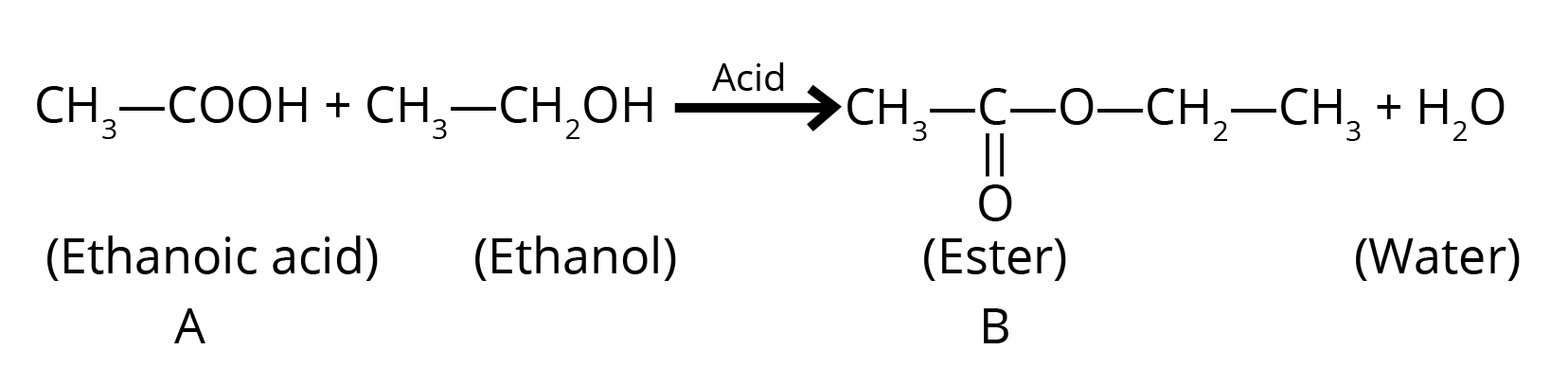
iii) What is esterification reaction?
Ans: The reaction of carboxylic acid with an alcohol give rise to fruity smell called as esters. This process of the formation of esters is called esterification reaction.
Eq- CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH + Conc. H2SO4👉 CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O
iv) What happens when ethanoic acid is reacted with carbonates and bicarbonates?
Ans: They give rise to salt, Carbon dioxide, and water.
V) Write the reaction of ethanoic acid with sodium hydrogen carbonate?
Ans: CH3COOH + NaHCO3 👉 CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
Case Study – 6
Frothing in Yamuna:
The primary reason behind the formation of the toxic foam is high phosphate content in the wastewater because of detergents used in dyeing industries, dhobi ghat and households. Yamuna’s pollution level is so bad that parts of it have been labelled ‘dead’ as there is no oxygen in it for aquatic life to survive.
[ CBSE Academic Question Paper ]

1) Predict the pH value of the water of river Yamuna if the reason for froth is high content of detergents dissolved in it.
Answer – a) 10-11
2) Which of the following statements is correct for the water with detergents dissolved in it?
- a) low concentration of hydroxide ion (OH-)and high concentration of hydronium ion (H3O+)
- b) high concentration of hydroxide ion (OH-)and low concentration of hydronium ion (H3O+)
- c) high concentration of hydroxide ion (OH-) as well as hydronium ion (H3O+)
- d) equal concentration of both hydroxide ion (OH-) and hydronium ion (H3O+).
Answer- b) high concentration of hydroxide ion (OH-) and low concentration of hydronium ion (H3O+)
3) If a sample of water containing detergents is provided to you, which of the following methods will you adopt to neutralize it?
- a) Treating the water with baking soda
- b) Treating the water with vinegar
- c) Treating the water with caustic soda
- d) Treating the water with washing soda
Answer – b) Treating the water with vinegar
4) High content of phosphate ion in river Yamuna may lead to:
- a) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and increased growth of algae.
- b) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and no effect of growth of algae.
- c) increased level of dissolved oxygen and increased growth of algae.
- d) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and decreased growth of algae.
Answer – a) decreased level of dissolved oxygen and increased growth of algae.
Case Study – 7
Marble’s popularity began in ancient Rome and Greece, where white and off-white marble were used to construct a variety of structures, from hand-held sculptures to massive pillars and buildings.

1) Gas A, obtained above is a reactant for a very important biochemical process which occurs in the presence of sunlight. Identify the name of the process –
- a) Respiration
- b) Photosynthesis
- c) Transpiration
- d) photolysis
Answer – Photosynthesis
2) A student added 10g of calcium carbonate in a rigid container, secured it tightly and started to heat it. After some time, an increase in pressure was observed, the pressure reading was then noted at intervals of 5 mins and plotted against time, in a graph as shown below. During which time interval did maximum decomposition took place ?
a) 15-20 min
b) 10-15 min
c) 5-10 min
Answer – d) 0-5 min
3) Calcium oxide can be reduced to calcium, by heating with sodium metal. Which compound would act as an oxidizing agent in the above process?
b) sodium oxide
d) calcium oxide
Answer – d) calcium oxide
4) Marble statues are corroded or stained when they repeatedly come into contact with polluted rain water. Identify the main reason
a) decomposition of calcium carbonate to calcium oxide
b) polluted water is basic in nature hence it reacts with calcium carbonate
c) polluted water is acidic in nature he
d) calcium carbonate dissolves in water to give calcium hydroxide.
Answer – b) polluted water is acidic in nature hence it reacts with calcium carbonate
Case Study – 8
Chemistry in Automobiles:
Foran internal combustion engine to move a vehicle down the road, it must convert the energy stored in the fuel into mechanical energy to drive the wheels. In your car, the distributor and battery provide this starting energy by creating an electrical “spark”, which helps in combustion of fuels like gasoline. Below is the reaction depicting complete combustion of gasoline in full supply of air:
1) Identify the types of chemical reaction occurring during the combustion of fuel:
- a) Oxidation & Endothermic reaction
- b) Decomposition & Exothermic reaction
- c) Oxidation & Exothermic reaction
- d) Combination & Endothermic reaction
Answer – c) Oxidation & Exothermic reaction
2) ‘Although nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere, it does not combustion’. Identify the correct reason for this statement.
- a) Nitrogen is a reactive gas
- b) Nitrogen is an inert gas
- c) Nitrogen is an explosive gas
- d) Only hydrocarbons can take part in combustion
Answer – b) Nitrogen is an inert gas
3) ‘A student while walking on the road observed that a cloud of black smoke belched out from the exhaust stack of moving trucks on the road.’ Choose the correct reason for the production of black smoke:
a) Limited supply of air leads to incomplete combustion of fuel.
b) Rich supply of air leads to complete combustion of fuel.
c) Rich supply of air leads to a combination reaction.
d) Limited supply of air leads to complete combustion of fuel.
Answer – Limited supply of air leads to incomplete combustion of fuel.
We hope that above case study questions will help you for your upcoming exams. To see more click below –
- Class 10 Assertion & Reason
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers
- Important Difference between Class 10 Biology
- Important Difference between Class 10 Physics
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Justify the statement “industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand” in details, creative hindi worksheet for lkg students in pdf, west bengal board class 9 bengali radharani solution, 10 anuched lekhan in hindi for class 10th students.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compound
Please refer to Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compound Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compound
Case/Passage – 1
A carbon atom attached to one, two, three and four other carbon atoms is called primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary carbon respectively. Now consider following compound and answer the following questions.
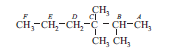
Question: In above compound how many carbon atom are primary? (a) 7 (b) 5 (c) 6 (d) 4
Question: In above compound which carbon atom is quaternary? (a) B (b) D (c) F (d) C
Question: In above compound how many carbon atoms are secondary? (a) 2 (b) 1 (c) 3 (d) 0
Case/Passage – 2
Reactions in which an atom or a group of atoms is replaced by some other atom or another group of atoms without causing any change in the structure of the remaining part of the molecule, are called substitution reactions. All organic compounds containing double or triple bonds give addition reactions, i.e., alkenes, alkynes and aromatic hydrocarbons give addition reactions.Reactions in which the compounds react with oxygen and form carbon dioxide and water is known as combustion reaction. This process occurs with release of great amount of heat.
Question: The reaction CH 4 + Cl 2 → CH 3 Cl + HCl is : (a) substitution reaction (b) addition reaction (c) rearrangement reaction (d) elimination reaction
Question: The reaction C 2 H 6 + O 2 → 2CO 2 + 3H 2 O is : (a) substitution reaction (b) rearrangement reaction (c) addition reaction (d) combustion reaction
Question: The reaction CH 2 = CH 2 + H 2 → CH 3 – CH 3 is : (a) substitution reaction (b) addition reaction (c) rearrangement reaction (d) elimination reaction
Case/Passage – 3
The given diagram represent an experiment in which a test tube contains 1 mL of ethanol (absolute alcohol) and 1 mL glacial acetic acid along with a few drops of concentrated H 2 SO 4 . Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.
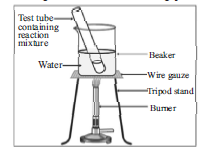
Question: Name the type of reaction taking place in this experiment.
Esterification reaction
Question: Why reverse of this reaction is known as saponification reaction?
Reverse reaction is known as saponification reaction because it is used in the prepration of soap.
Question: Give two uses of the resulting product.
Esters are used in making perfumes and as a flavouring agent
Question: Write the chemical equation.
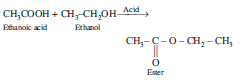
Case/Passage – 4
Study the table related to three hydrocarbons X, Y and Z carefully and answer the following questions from.

Question. X, Y and Z are classified as hydrocarbons because these contain: (a) Hydrogen (b) Oxygen (c) Carbon (d) Both carbon and hydrogen
Question. To which series C 5 H 10 belongs? (a) C n H2 n + 2 (b) CnH2n (c) C n H 2n – 2 (d) C n H n+2
Question. Choose the incorrect statement regarding above three hydrocarbons (a) All have different general formula (b) X and Y differ by –CH 2 unit (c) Z is an alkyne (d) Y is an alkene
Study the table given below carefully and answer any four questions from :
Question. What is the molecular formula of K? (a) C 12 H 26 (b) C 12 H 24 (c) C 12 H 22 (d) C 12 H 28
Question. Choose the correct statements regarding compounds H, J and K (a) All have the same chemical properties (b) All have different general formula (c) All differ by –CH 2 unit (d) All have same melting and boiling points
Question. What is the molecular formula of J? (a) C 12 H 26 (b) C 8 H 16 (c) C 8 H 18 (d) C 8 H 14
Question. Compounds H, J, K belong to which homologous series? (a) C n H 2n (b) C n H 2n–2 (b) C n H 2n+2 (d) C n H 2n+1
Case/Passage – 5
Read the following passage carefully and answer the following questions from The phenomenon of the existence of an element in two or more physical forms within the same physical state is known as allotropy. Allotropes have similar chemical properties but they differ in chemical properties. In crystalline form, Carbon occurs as graphite, diamond, and fullerenes. Diamond is the hardest natural substance known and is used in cutting marbles, granite, and glass. Graphite is a greyish black and opaque substance, lighter than a diamond with comparative low density. Graphite has a sheet-like structure having hexagonal layers. One layer slides over the other layer due to weak forces and hence it is soft to touch and breaks easily. Graphite is also used as a lubricant.
Question. Which three allotropes of carbon do the given figures represent?
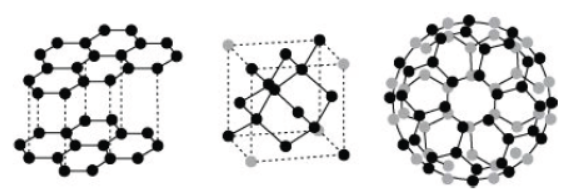
(a) I-Graphite II-Diamond III-Fullerene (b) I-Diamond II-Fullerene III-Graphite (b) I-Graphite II-Fullerene III-Diamond (d) I-Fullerene II-Graphite III-Diamond
Question. Identify the incorrect statement(s): I. Diamond is the hardest substance known while graphite breaks easily. II. Each carbon atom in diamond is bonded to 4 other carbon atoms in a tetrahaderal manner to form a giant lattice. All carbon atoms are bonded by strong covalent bonds. III. Graphite is poor conductor of electricity unlike other non metals. IV. In each layer of graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms foming hexagonal rings of carbon atoms. (a) I and III (b) Only III (b) II and IV (d) I, II and IV
Question. The number of carbon atoms surrounding each carbon atom in a diamond are: (a) 3 (b) 4 (b) 2 (d) 5
Question. Substance A is a moderate conductor of electricity. Observe the structure of substance A given below.
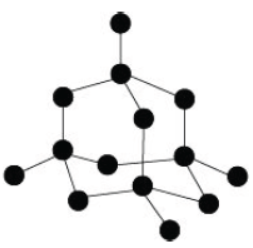
Choose the correct statements regrading substance A. Statement I – It is a covalent compound. Statement II – It has a giant molecular structure. Statement III – It has the same structure as graphite. Statement IV – It has the same structure as diamond. (a) I and III (b) II and III (c) II and IV (d) I, II and IV
Question. Which of the following is correct about the structure of diamond? (a) Carbon atoms are held together by single covalent bonds. (b) Electrons move freely through the structure. (b) Layers of atoms slide easily over each other. (d) Carbon atoms conduct electricity in the molten state.
Case/Passage – 6
Read the following passage carefully and answer the following questions from As a versatile element, carbon can form large compounds because of its tetravalency and the property of catenation that it exhibits. Here, catenation refers to the combination of carbon atoms with itself to form large molecules. Carbon forms stronger covalent bonds with itself and other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, sulphur, nitrogen and chlorine. This is because its nucleus has a strong force of attraction and holds these bonds tightly together.
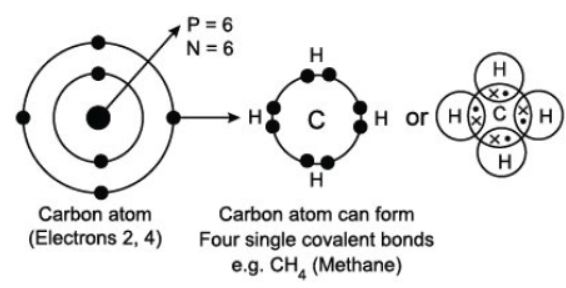
Question. Put the elements in the right order in terms of their valency, starting with the element of lowest valency? (a) O, C, N, H (b) C, O, N, H (c) H, C, O, N (d) H, O, N, C
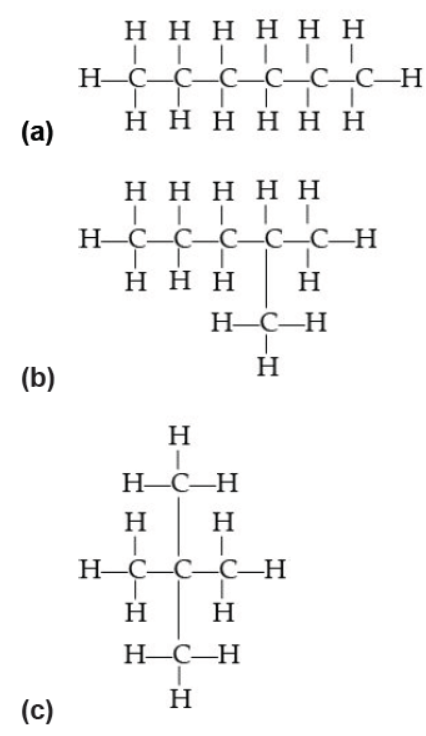
Question. Which of the following does not represent the molecular formula C 6 H 14 ?
Question. Match the columns:
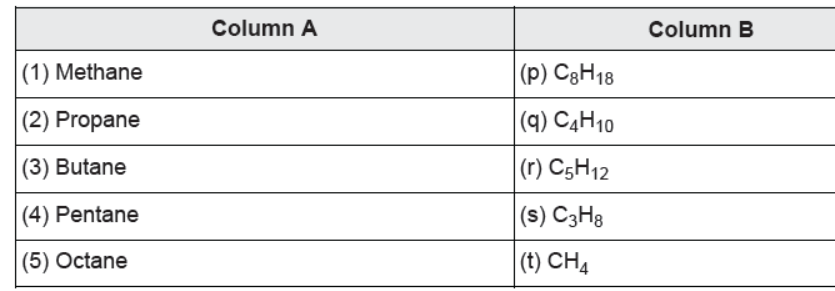
(a) (1)-(q), (2)-(s), (3)-(t), (4)-(p), (5)-(r) (b) (1)-(p), (2)-(r), (3)-(s), (4)-(q), (5)-(t) (c) (1)-(t), (2)-(s), (3)-(q), (4)-(r), (5)-(p) (d) (1)-(t), (2)-(q), (3)-(s), (4)-(r), (5)-(p)
Question. Which of the following statements regarding carbon is incorrect? (a) A single atom of carbon can participate in two double bonds (b) A single atom of carbon can participate in three single bonds and one double bond (c) A single atom of carbon can participate in four single bonds (d) A single atom of carbon can participate in two single bonds and one double bond
Case/Passage – 7
Read the following passage carefully and answer the following questions from The compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ from each other in physical or chemical properties are called isomers and this phenomenon is known as isomerism. Structural isomerism is when isomers have difference in the arrangement of atoms within the molecule, without any reference to space. We can say that compounds which have the same molecular formula but different structural formula show structural isomerism. Compounds of carbon show this phenomenon as the atoms can be linked together in the form of straight chains, banched chains or even rings.
Question. The number of isomers of pentane is: (a) 4 (b) 3 (c) 2 (d) 5
Question. Among the following sets of compounds, choose the set having the same molecular formulae: (a) Butane and iso-butane (b) Cyclohexane and hexene (b) Propanal and propanone (d) All
Question. The minimum number of carbon atoms required in an organic compound, in order to form branching: (a) 3 (b) 4 (b) 5 (d) 2
Question. Which of the following pairs show isomerism? (a) Ethane and ethene (b) Propane and butane (b) Ethane and propane (d) Butane and 2-methyl propane
Question. Which among the following has the longest chain? (a) Iso-pentane (b) 2-methylpentane (c) 2,2-dimethylbutane (d) neopentane
Case/Passage – 8
Food, clothes, medicines, books, or many of the things are all based on this versatile element carbon. In addition, all living structures are carbon based. The earth’s crust has only 0.02% carbon in the form of minerals. The element carbon occurs in different forms in nature with widely varying physical properties. Both diamond and graphite are formed by carbon atoms, the difference lies in the manner in which the carbon atoms are bonded to one another. Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation.
Question: Which of the following are isomers? (a) Butane and isobutene (b) Ethane and ethene (c) Propane and propyne (d) Butane and isobutane
Question: From the given alternatives, whose chemical and physical properties are not same? (a) Graphite and Diamond (b) Phosphorous and Sulphur (c) Carbon and Hydrogen (d) Methyl alcohol and Acetic acid
Question: Which one of the following is not an allotrope of carbon? (a) Soot (b) Graphite (c) Diamond (d) Carborundum
Question: Which of the following statements is not correct? (a) Graphite is much less dense than diamond (b) Graphite is black and soft (c) Graphite has low melting point (d) Graphite feels smooth and slippery
Question: Pentane has the molecular formula C 5 H1 2 . It has (a) 5 covalent bonds (b) 12 covalent bonds (c) 16 covalent bonds (d) 17 covalent bonds
Case/Passage – 9
Water is a simple molecule consisting of one oxygen atom bonded to two different hydrogen atoms. Because of the higher electronegativity of the oxygen atom, the bonds are polar covalent (polar bonds). The oxygen atom attracts the shared electrons of the covalent bonds to a significantly greater extent than the hydrogen atoms. The molecule has a bent structure, the H—O—H bond angle is about 105°.
Question. Select the correct type of bonding in a water molecule (a) Ionic Bonding (b) Covalent Bonding (c) Hydrogen Bonding (d) None of these
Question. The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is (a) H .. O O (b) H .. O O (c) H : O:H (d) H :O:O
Question. The H—O—H bond angle in water molecule is (a) 109.5° (b) 180° (c) 90° (d) 105.0°
Question. Which of the following statement is true regarding the electronegativity of atoms in water molecule? (a) Hydrogen is more electronegative than oxygen (b) Hydrogen is less electronegative than oxygen (c) Electronegativity is same in Hydrogen and oxygen (d) Hydrogen and oxygen do no show significant electronegativity in water
Question. What is the shape of water molecule? (a) Linear (b) Trigonal planar (c) Bent (d) Octahedral

Related Posts

Case Study Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current

Television Summary by Roald Dahi

Power Sharing Class 10 Social Science Notes and Questions
myCBSEguide
- Case Study Questions Class...
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Download Case study questions for CBSE class 10 Science in PDF format from the myCBSEguide App . We have the new pattern case study-based questions for free download. Class 10 Science case study questions
This article will guide you through:
What are case study questions?
- Sample Papers with Case Study questions
- Class 10 Science Case Study question examples
- How to get case-based questions for free?
- How to attempt the case-based questions in Science?
Questions based on case studies are some real-life examples. The questions are asked based on a given paragraph i.e. Case Study. Usually, 4-5 questions are asked on the basis of the given passage. In most cases, these are either MCQs or assertion & reason type questions. Let’s take an example to understand. There is one paragraph on how nitrogen is generated in the atmosphere. On the basis of this paragraph, the board asks a few objective-type questions. In other words, it is very similar to the unseen passages given in language papers. But the real cases may be different. So, read this article till the end to understand it thoroughly.
What is CBE?
CBSE stands for competency-based education. The case study questions are part of this CBE. The purpose of CBE is to demonstrate the learning outcomes and attain proficiency in particular competencies.
Questions on Real-life Situations
As discussed the case study questions are based on real-life situations. Especially for grade 10 science, it is very essential to have the practical knowledge to solve such questions. Here on the myCBSEguide app, we have given many such case study paragraphs that are directly related to real-life implications of the knowledge.
Sample Papers with Case Study Questions
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App . There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions. In some cases, you will find that the question is not asked directly from the passage but is based on the concept that is discussed there. That’s why it is very much important to understand the background of the case study paragraph.
CBSE Case Study Sample Papers
You can download CBSE case study sample papers from the myCBSEguide App or Student Dashboard. Here is the direct link to access it.
Case Study Question Bank
As we mentioned that case study questions are coming in your exams for the last few years. You can get them in all previous year question papers issued by CBSE for class 1o Science. Here is the direct link to get them too.
Class 10 Science Case Study Question Examples
As you have already gone through the four questions provided in the CBSE model question paper , we are proving you with other examples of the case-based questions in the CBSE class 10 Science. If you wish to get similar questions, you can download the myCBSEguide App and access the Sample question papers with case study-type questions.
Case-based Question -1
Read the following and answer any four questions: Salt of a strong acid and strong base is neutral with a pH value of 7. NaCl common salt is formed by a combination of hydrochloride and sodium hydroxide solution. This is the salt that is used in food. Some salt is called rock salt bed of rack salt was formed when seas of bygone ages dried up. The common salt thus obtained is an important raw material for various materials of daily use, such as sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.
- Phosphoric acid
- Carbonic acid
- Hydrochloric acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Blue vitriol
- Washing soda
- Baking soda
- Bleaching powder
Case-based Question -2
- V 1 + V 2 + V 3
- V 1 – V 2 +V 2
- None of these
- same at every point of the circuit
- different at every point of the circuit
- can not be determined
- 20 3 Ω 203Ω
- 15 2 Ω 152Ω
Case-based Question -3
- pure strips
- impure copper
- refined copper
- none of these
- insoluble impurities
- soluble impurities
- impure metal
- bottom of cathode
- bottom of anode
How to Attempt the Case-Based Questions in Science?
Before answering this question, let’s read the text given in question number 17 of the CBSE Model Question Paper.
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
See, there are only two sentences and CBSE is asking you 5 questions based on these two sentences. Now let’s check the first questions given there.
Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by a) Breathing b) Tissue respiration c) Organ respiration d) Digestion of food
Now let us know if you can relate the question to the paragraph directly. The two sentences are about energy and how it is obtained. But neither the question nor the options have any similar text in the paragraph.
So the conclusion is, in most cases, you will not get direct answers from the passage. You will get only an idea about the concept. If you know it, you can answer it but reading the paragraph even 100 times is not going to help you.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Science Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
2 thoughts on “Case Study Questions Class 10 Science”
Where is the answer
Class 10 Science MCQ
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Case Based Questions - Carbon and its compounds
Case study - 1.
Ethanoic acid is commonly called acetic acid and belongs to a group of acids called carboxylic acids. 5-8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar and is used widely as a preservative in pickles.
Q1: What is glacial acetic acid? Ans: The melting point of ethanoic acid is 290K, so its often freezes during winter. Hence, gave rise to new name called as glacial acetic acid. Q2: Complete the reaction: NaOH + CH 3 CH 2 COOH ? Ans: NaOH + CH 3 CH 2 COOH ⇒ CH 3 CH 2 COONa + H 2 O Q3: What is esterification reaction? Ans: The reaction of carboxylic acid with an alcohol give rise to fruity smell called as esters. This process of the formation of esters is called esterification reaction. Example: CH 3 COOH + CH 3 CH 2 OH + Conc. H 2 SO 4 ⇒ CH 3 COOCH 2 CH 3 + H 2 O Q4: What happens when ethanoic acid is reacted with carbonates and bicarbonates? Ans: They give rise to salt, Carbon dioxide, and water. Q5: Write the reaction of ethanoic acid with sodium hydrogen carbonate? Ans: CH 3 COOH + NaHCO 3 ⇒ CH 3 COONa + H 2 O + CO 2
Case Study - 2
Most dirt is oily in nature and as you know, oil does not dissolve in water. The molecules of soap are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. The ionic-end of soap interacts with water while the carbon chain interacts with oil. The soap molecules, thus form structures called micelles, where one end of the molecules is towards the oil droplet while the ionic-end faces outside. This forms an emulsion in water. The soap micelle thus helps in pulling out the dirt in water and we can wash our clothes clean Q1: What is hydrophobic end? Ans: Soap molecules have two ends in which one is hydrophobic end which interacts with hydrocarbons and do not dissolve in water. Q2: Draw the structure of micelle. Ans:
Case Study - 3
Carbon compounds can be easily oxidised on combustion. In addition to this complete oxidation, we have reactions in which alcohols are converted to carboxylic acids. We see that some substances are capable of adding oxygen to others. These substances are known as oxidisingagents.
Q1: Give two example of good oxidising agent. Ans: Alkaline potassium permanganate or acidified potassium dichromate. Q2: Complete the reaction: CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 OH + Alk. KMnO 4 ? Ans: CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 OH + Alk. KMnO 4 ⇒ CH 3 CH 2 COOH. Q3: What are the uses of alcohol? Ans: Good solvent, used to make syrups & drinks. Q4: Why Acidified potassium dichromate is called an oxidising agent? Ans: It is because they can add oxygen to the reactant molecule very easily and convert them to acid. Q5: What is the use of ethanoic acid? Ans: Used as preservatives in pickle and also to make esters.
Case Study - 4
Carbon, in all its allotropic forms, burns in oxygen to give carbon dioxide along with the release of heat and light. Most carbon compounds also release a large amount of heat and light on burning. Saturated hydrocarbons will generally give a clean flame while unsaturated carbon compounds will give a yellow flame with lots of black smoke.
Q1: Complete the reaction: CH 3 CH 2 OH +O 2 gives Ans: CH 3 CH 2 OH + O 2 ⇒ CO 2 + H2O + heat & light. Q2: What is the reason for incomplete combustion? Ans: When the supply of air is limited for combustion, then the fuel goes partial combustion which results in sooty flame. Q3: Combustion is an oxidation or reduction type of reaction? Ans: It is an oxidation type of reaction as oxygen get added to reactant. Eg: C + O 2 ⇒ CO 2 + heat aand light. Q4: What is homologous series? Ans: A series of compound in which the same functional group substitutes for hydrogen in a carbon chain. Example: C 2 H 6 & C 3 H 6 . – these differ by CH 2 unit.
Case Study - 5
Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation. These compounds may have long chains of carbon, branched chains of carbon or even carbon atoms arranged in rings. In addition, carbon atoms may be linked by single, double or triple bonds.
Q1: What are saturated compounds? Ans: Compounds of carbon that are linked by only single bond between the carbon atoms are called as saturated compounds. Example: C 2 H 6 , CH 4 Q2: What is the another versatile property of carbon? Ans: The tetravalent nature of carbon i.e it has four valency and it is capable of bonding with other four atoms of carbon or any other atom of monovalency. Q3: Give two example of unsaturated compounds. Ans: Ethene- C 2 H 4 & Ethyne- C 2 H 2 Q4: Name any one element other than carbon which show catenation property? Ans: Sulphur i.e S8 molecule.
Top Courses for Class 10
Practice quizzes, viva questions, shortcuts and tricks, sample paper, previous year questions with solutions, important questions, mock tests for examination, extra questions, semester notes, video lectures, past year papers, objective type questions, study material.

Case Based Questions: Carbon and its compounds Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: carbon and its compounds, case based questions: carbon and its compounds notes, case based questions: carbon and its compounds class 10, study case based questions: carbon and its compounds on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its Compounds


CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter-4 Important Questions with Answers - Free PDF Download
Chapter 4 Science Class 10 revolves around carbon and its compounds. The chapter mainly includes its covalent properties and versatility in forming numerous saturated and unsaturated compounds in branches, chains, or rings. The IUPAC (International Union Of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature procedure based on the attached functional group is also included in this chapter. One will also get a brief idea about alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, isomers, allotropes of carbon, and a homologous series's fundamentals. The four main chemical reactions covered in this chapter are oxidation , addition, substitution, and combustion . Properties of compounds like Ethanol and Ethanoic Acid are also explained in this chapter.
Download CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions for other chapters:

Related Chapters
Study Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 - Carbon & Its Compounds
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. Soaps are formed by the saponification of
Simple ester
carboxylic acids
Ans: d. glycerides
2. The functional group of butanone is
Ans: b. ketonic
3. The enzyme which converts starch into glucose is
Ans: a. Zymase
4. The first compound to be prepared in the laboratory was
Ethyl alcohol
Acetic acid
Ans: d. Urea
5. The IUPAC name of $C{{H}_{3}}CHO$ is
Acetaldehyde
Formaldehyde
Methyl formaldehyde
Ans: d.Ethanol
6. Rectified spirit is
\[\text{50 }\!\!\%\!\!\text{ }\] ethanol
\[\text{N80 }\!\!\%\!\!\text{ }\] ethanol
\[\text{95 }\!\!\%\!\!\text{ }\] ethanol
\[40\% to 50\%\] ethanol
Ans: c. \[\text{95 }\!\!\%\!\!\text{ }\] ethanol
7. Dilute alkaline solution $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ is
an oxidizing agent
a reducing agent
a bleaching agent
none of these
Ans: a. an oxidizing agent
8. The by-product in the soap industry is
Ethylene glycol
Ans: c. Glycerol
9. An example of soap is
${{C}_{15}}{{H}_{31}}COONa$
$C{{H}_{3}}COONa$
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COONa$
${{C}_{17}}{{H}_{35}}OS{{O}_{3}}Na$
Ans: a. ${{C}_{15}}{{H}_{31}}COONa$
10. The number of \[\mathbf{C}-\mathbf{H}\] bonds in ethane ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ molecule are
11. The odour of acetic acid resembles that of
Burning Plastic
Ans: d. kerosene
12. Diamond is not a good conductor of electricity because
It is very hard
Its structure is very compact
It is not soluble in water
It has no free electrons to conduct electric current.
Ans: d. It has no free electrons to conduct electric current.
13. Alcohol can be produced by the hydration of
Ans: a. Alkenes
14. The IUPAC name of $C{{H}_{3}}CHO$ is
Ans: d. Ethanol
15. IUPAC name of the first member of the homologous series of ketones is
Ans: c. Propanone
16. An unknown compound has the smell of vinegar. Identify it
Ans: Acetic acid or Ethanoic acid that comprises $3-9\%$ of the vinegar.
17. Out of butter and groundnut oil which is unsaturated in nature?
Ans: Groundnut oil
18. Which has triple bond,${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}},{{C}_{3}}{{H}_{4}},{{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$
Ans: ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{4}}$
19. Which substance is added for the denaturation of ethyl alcohol
Ans: Methyl Alcohol
20. Which ions are responsible for making water hard?
Ans: $C{{a}^{2+}}$ and $M{{g}^{2+}}$
21. Ethane, with the molecular formula has
\[\mathbf{6}\] covalent bonds
\[\mathbf{7}\] covalent bonds
$8$ covalent bonds
\[\mathbf{9}\] covalent bonds
Ans: b. $7$ covalent bonds
22. Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group
carboxylic acid
Ans: c. Ketone
23. While cooking, if the bottom of the vessels is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
The fuel is not cooked completely
The fuel is not burning completely
The fuel is wet
The is burning completely
Ans: b. The fuel is not burning completely.
24. Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo additional reactions?
${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}},{{C}_{3}}{{H}_{8}},{{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}},{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}\;and\;C{{H}_{4}}$
Ans: ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}\;and\;{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}$ will undergo addition reactions.
Short Answer Questions (2Marks)
1. Name the following compounds
Ans: Methanol
\[C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-Cl\]
Ans: Chloroethane
2. Define Soaps?
Ans: A substance used with water for washing and cleaning, made of a compound of natural oils or fats with sodium hydroxide or another strong alkali . These are represented by \[RCOONa\] or \[RCOOR\] .
3. Name the second member of the alkynes family. Give its structure?
Ans: The second member of the alkyne family is propyne. The structural formula is $C{{H}_{3}}-C\equiv CH$ .
4. Give a chemical test to distinguish between Ethane and Ethene .
Ans: Take ethane and ethene in two separate test tubes and dissolve them in carbon tetrachloride solution. Pass bromine gas into the two test tubes. If the colour of bromine gas is discharged and decolorizes the yellow colour then that gas is ethene and if the colour of gas remains the same, then that test tube contains ethane gas.
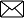
5. Write the structures of
i. Ethanoic acid
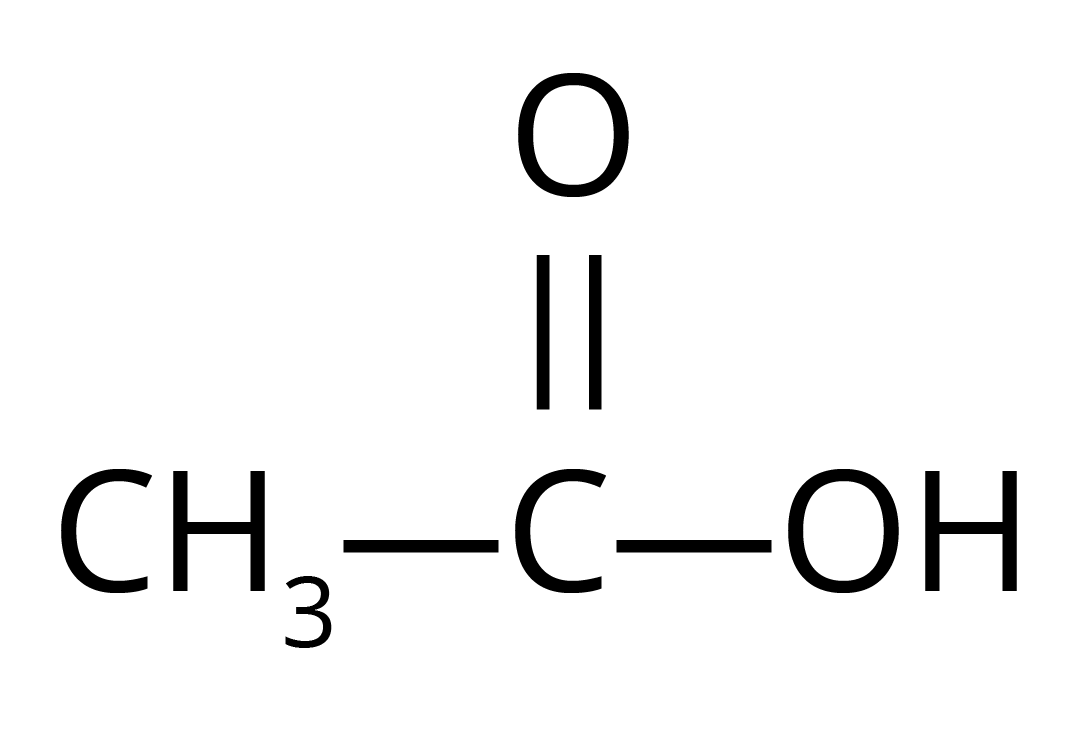
ii. Hexanal
6. Name the following compounds
$C{{H}_{3}}-\overset{H}{\mathop{C}}\,=0$
Ans: Ethanal
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH$
Ans: Ethanol
7. Which organic compound is added to make ethanol unfit for drinking purposes? What is the name of the mixture formed?
Ans: Methanol is highly poisonous and is added in small amounts to ethanol in order to make it unfit for drinking purposes. This mixture is called methylated spirit or denatured alcohol.
8. Write a test to identify the presence of Ethanoic acid?
Ans: Dip a strip of blue litmus paper in the solution of Ethanoic acid. Its colour changes to red and Ethanoic acid gives a sweet-smelling compound called ester when treated with Ethanol
9. What are the properties of carbon that lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Ans : The two properties of carbon that lead to the huge number of carbon compounds are Catenation and Tetravalency . The self-linking property is called catenation. As Carbon is tetravalent it can readily unite with atoms like hydrogen, oxygen etc by sharing electrons.
10. Name the following compound.
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-Br$
Ans: Bromoethane
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C\equiv CH$
Ans: Hex -1- yne
11. Why conversion of ethanol into ethanoic acid is an oxidation reaction?
Ans: Ethanoic acid has one or more ${{O}_{2}}$ atoms and two hydrogen atoms less than ethanol. Loss of hydrogen is known as oxidation and gain of oxygen is known as reduction. Therefore it is an oxidation reaction.
12. A mixture of ethyne and oxygen is used for welding. Can you justify why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Ans: When ethyne is burnt in oxygen, it gives a clean flame with high temperature because of the complete combustion of ethyne. Hence, this oxyacetylene flame is used for welding, and it is not possible to attain a high temperature with air. Air contains a mixture of nitrogen and oxygen. As nitrogen is more in the amount it does not support combustion . Because of this mixture of ethyne and air is not used for welding.
13. Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels in most cases?
Ans: Carbon compounds are used as fuel because they burn with a clean flame and no smoke is produced which is highly exothermic. Carbon compounds have higher maximum ignition temperature and their combustion can be restrained. Hence, carbon and its compounds are a great source of fuel.
14. A compound X has the molecular formula ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}O$ with structural formula $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}CHO$. Give its IUPAC name. Can another compound have the same molecular formula? Give the structure and IUPAC name of that compound also.
Ans: The IUPAC name of X is propanol.
Another similar compound is Y is.
X and Y are related to each other as functional isomers.
15. Why CHO group cannot be present in the middle of the carbon atom chain?
Ans: The terminal functional group is the CHO group and as three valencies of the C-atom are already satisfied; this group cannot be present in the middle of the chain.
16. Two carbon atoms cannot be linked to each other by more than three covalent bonds. Why?
Ans: There is a single bond between the two carbon atoms and both share their one atom therefore for completing its shell it needs to combine with three atoms of carbon or other elements. Therefore, it cannot be linked to more than three covalent bonds since its shell will be completed to become stable
17. What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula of?
Ans: $O=C=O$
18. What would be the electron dot structure of a molecule of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur?
Ans: Sulphur is a chemical element with the symbol S
19. How would you name the following compounds?
i. $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-Br$
Ans: Bromomethane
ii. \[H-\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}\,=O\]
Ans:Methanal
iii. \[H-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-C\equiv C-H\]
Ans: Hexyne
20. What are two properties of carbon that lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Ans: The two properties are:
(a) catenation: The ability to form a covalent bond by combining with other carbon
(b) Tetravalancy of carbon.
21. Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent?
Ans: No, we would not be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent.
22. People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually, after adding the soap, they beat the clothes on stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get clean clothes?
Ans: Soap lowers the surface tension of water. The long chain non-ionic hydrocarbon group in soap gets attached to the oil or grease droplets and loosens them from the fibres of cloth along with the dirt. However, this loosening is insufficient to remove the grease with dirt completely. Hence the clothes are agitated to remove the grease droplets completely.
23. Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in $C{{H}_{3}}Cl$ .
Ans: Covalent bond is formed by sharing of electrons between two atoms. It is non- ionic in nature.
$\quad\quad\quad H$
$\quad\quad\quad \times \quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad H$
$\quad\quad\quad\times \quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad |$
$H\times \times \;C \times\times \;Cl\longrightarrow H-C-Cl$
24. Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil?
Ans: Butter and cooking oil can be differentiated using a bromine water test. Cooking oil will decolourize the red colour of bromine water on shaking and butter will not decolourize.
25. A compound ‘X’ has a molecular formula. It undergoes substitution reaction readily than an addition reaction. It burns with a blue flame and is present in LPG. Identify ‘X’ and give the balanced equation for its combustion and substitution reaction in presence of sunlight.
Ans: ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{10}}+\dfrac{13}{2}{{O}_{2}}\to 4C{{O}_{2}}+5{{H}_{2}}O$
${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{10}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to {{C}_{4}}{{H}_{9}}Cl+HCl$
26. ‘A’ compound works well with hard water. It is used for making shampoos & products for cleaning clothes. A is not $100\%$ biodegradable and causes water pollution. ‘B’ does not work well with hard water. It is $100\%$ biodegradable and does not create water pollution. Identify A & B.
Ans: A is the detergent & B is the soap.
27. An organic compound P with molecular formula ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}O$ is an active ingredient of all alcoholic drinks. It is also used in medicines such as tincture iodine, cough syrups. Identify ‘P’. Drop small pieces of sodium into the test tube containing ‘P’. A new compound ‘Q’ is formed with the evaluation of colourless and odourless gas Name the gas evolved and compound ‘Q’ write the chemical reaction.
Ans: $2Na+2C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH\to 2C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}}+{{H}_{2}}$
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks)
1. Complete the following reaction
i. ${{H}_{2}}C=C{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}$
Ans: ${{H}_{2}}C=C{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH$
ii. $HC\equiv CH+B{{r}_{2}}\to $
Ans: \[HC\equiv CH+B{{r}_{2}}\to H-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ Br \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} Br \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ Br \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} Br \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-H\]
iii. ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH+Na\to $
Ans: $2{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH+Na\to 2{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}ONa+{{H}_{2}}$
2. What is the role of concentrated sulphuric acid in the esterification reaction?
Ans: In the esterification reaction carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol to form an ester and water reacts in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid. Concentrated sulphuric acid is used as a catalyst. This reaction is reversible and this reverse reaction is called ester hydrolysis. Concentrated sulphuric acid removes water from the reaction mixture as it is a strong dehydrating agent. As a result, the reaction takes place only in the forward direction to form an ester.
$RCOOH+ROH\xrightarrow{conc{{H}_{2}}S{{o}_{4}}}RCOOR+{{H}_{2}}O$
Acid Alcohol Ester
3. What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane?
Ans: Cyclopentane is a cyclic compound with a formula ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}$ . The structure of the compound is represented as
4. Draw the structures of the following compounds
Ethanoic acid
Bromopentane
$H-\underset{H}{\overset{H}{C}}-\overset{O}{\overset{||}{C}}-OH$
Ethanoicacid
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-B{{r}}$ Bromopentane
$H_3C-\overset{O}{\overset{||}{C}}-CH_2-CH_3$ Butanone
5. Give names of the following
An aldehyde derived from ethane
Ans: Ethane
$C{{H}_{3}}CHO$
Ketone derived from butane
Ans: Butanone
$C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$
The compound obtained by the oxidation of ethanol by chromic anhydride
Ans: Ethanol
$C{{H}_{3}}CHO$
6. What is meant by denatured alcohol? What is the need to denature alcohol?
Ans: Ethyl alcohol which contains a small amount of methyl alcohol or copper sulphate is called denatured alcohol . The purpose of denaturing the alcohol is to make it unfit for drinking purposes. Denatured alcohol is also used for industrial purposes.
7. Write chemical equations of the reactions of ethanoic acid with
Ans: $ 2C{{H}_{3}}COOH+2Na\to 2C{{H}_{3}}COONa+{{H}_{2}} $
$ (Sod.Ethanoate) $
Sodium carbonate
Ans: $ 2C{{H}_{3}}COOH+N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}\to 2C{{H}_{3}}COONa+C{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O $
$ (Sod.Ethanoate)
Ethanol in the presence of conc.${{H}_{2}}S{{o}_{4}}$
Ans: $ C{{H}_{3}}COOH+{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH\xrightarrow{conc.{{H}_{2}}S{{o}_{4}}}C{{H}_{3}}COOC{}_{2}{{H}_{5}} $
$ (Ethyl.ethanoate) $
8. Complete the reaction and names of the products formed
i. \[C{{H}_{3}}COOH+NaOH\xrightarrow{(Heat)}\]
Ans: $ C{{H}_{3}}COOH+NaOH\xrightarrow{(Heat)}C{{H}_{3}}COONa+{{H}_{2}}O $
$ (Sod.Ethanoate) $
ii. ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH+{{O}_{2}}\dfrac{alkaline}{KMnOH}$
Ans: $ {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH+{{O}_{2}}\dfrac{alkaline}{KMnOH}C{{H}_{3}}COOH+{{H}_{2}} $
$ (EthanoicAcid) $
iii. $C{{H}_{3}}COOH+{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH\xrightarrow{(Conc.{{H}_{2}}Sol)}$
Ans: $ C{{H}_{3}}COOH+{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH\xrightarrow{(Conc.{{H}_{2}}Sol)}C{{H}_{3}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}+{{H}_{2}}O $
$ (EthylEthanoate) $
9. What is a homologous series? State any two characteristics of homologous series?
Ans: A homologous series is a series of hydrocarbons that have similar chemical properties and they share the same general formula. They are organic compounds having similar structures and functional groups. A particular series differ in their molecular formula by the group. Characteristics of homologous series are:- Same functional group and same chemical properties.
10. Give the structural formulas for
Methyl Ethanoate
Ethyl Ethanoate
Write two uses of Ester?
i. Methyl Ethanoate
\[H-\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} o \\ || \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}\,-OC{{H}_{3}}\]
ii. Ethyl Ethanoate
\[C{{H}_{3}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}\]
Uses of esters:
a) Esters that have fragrant odours are used as a constituent of perfumes, essential oils, food flavourings, cosmetics, etc.
b) It is used as an organic solvent.
c) Esters of glycerol known as triglycerides are used in the manufacture of soaps.
d) Natural esters are found in pheromones.
11. What are enzymes? Name the enzymes required for the fermentation of sugarcane to ethanol?
Ans: An enzyme is a protein molecule in cells that works as a biological catalyst . In the process of fermentation of sugar into ethanol, two enzymes are used.
${{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}+{{H}_{2}}O\xrightarrow{(Invertase)}{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}+{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$
Sugar glucose fructose
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}\xrightarrow{(Zymase)}2{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH+2C{{O}_{2}}$
Glucose and Fructose
12. The formula of an ester is ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{7}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$ .Write the formulae of the acid and alcohol from which the ester is prepared.
Ans: The molecular formula of acid is${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{7}}COOH$ (Butanoic acid) and for alcohol is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH$ (Ethyl alcohol)
${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{7}}COOH+{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH\to {{C}_{3}}{{H}_{7}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
13. Write three differences between ethanol and ethanoic acid on the basis of chemical properties?
i. Add a small amount of $NaHC{{O}_{3}}$ to ethanoic acid $C{{O}_{2}}$ gas is evolved with brisk effervescence and such reaction doesn’t take place in case of ethanol
$C{{H}_{3}}COOH+NaHC{{O}_{3}}\to C{{H}_{3}}COONa+C{{O}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
ii. Ethanol is neutral so does not bring any change in the colour of litmus paper but ethanoic acid is acidic and changes the colour of a blue litmus strip to red when dipped in it.
iii. Ethanoic acid reacts with $NaOH$ and $KOH$ to form salt and water whereas ethanol does not react.
$C{{H}_{3}}COOH+NaHC{{O}_{3}}\to C{{H}_{3}}COONa+{{H}_{2}}O$
$C{{H}_{3}}COOH+KOH\to C{{H}_{3}}COOK+{{H}_{2}}O$
14. Given a chemical test to distinguish between
i. Ethene and ethane
Ans: Ethene decolorizes the yellow colour of bromine while ethane does not.
ii. Ethanol and ethanoic acid
Ans: Ethanoic acid gives a brisk effervescence with sodium hydrogen carbonate while ethanol does not.
iii. Soaps and Detergents
Ans: Soaps form curdy white precipitate or scum with hard water while detergents do not form any precipitate.
15. Name the functional groups present in the following compounds?
i. $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-OH$
Ans: $-OH(ol)$
ii. $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH$
Ans: $-COOH(oic\_acid)$
iii. $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CHO$
Ans: $-CHO(al)$
16. What are esters? Write an equation to show the formation of an ester?
Ans: Esters any of a class of organic compounds that react with water to produce alcohols and organic or inorganic acids. They are pleasant smelling compounds and are commonly used as flavouring agents. Monocarboxylic acids react with alcohol to form esters and water. This reaction is called esterification
Methyl Ethanoate (Ester)
$C{{H}_{3}}COOH+C{{H}_{3}}OH\xrightarrow{(Conc.{{H}_{2}}SOH)}C{{H}_{3}}COOC{{H}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
Ethyl Ethanoate (Ester)
$C{{H}_{3}}COOH+{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH\xrightarrow{(Conc.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}})}C{{H}_{3}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
17. What will be the formula and electron dot structure for cyclopentane?
Ans: Formula of cyclopentane is ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{10}}$. The electron dot structure cyclopentane is :
18. How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
Ans: The isomers are as under :
\[ H-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \\ \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop C}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop C}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop C}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop C}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop C}}\,-H \]
n - pentane
iso-pentane
19. What is a homologous series? Explain with an example.
Ans: A sequence of compounds with the same functional group substitutes for hydrogen in a carbon chain is called homologous series. The difference between the formulae of any two successive members is $-C{{H}_{2}}$ and the difference between the molecular formula is\[14\text{ }u\] .
20. How can ethanol and Ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
On the basis of physical properties:
The melting and boiling points of ethanol is $156K$and $351K$
The melting and boiling point of Ethanoic acid is $290K$and $391K$.
On the chemical properties:
Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate liberating carbon dioxide
ethanol does not react with sodium hydrogen carbonate liberating carbon dioxide.
21. Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Ans: Carbon burns with a clean flame and no smoke is produced on combustion it gives carbon dioxide and water. This reaction involves the evolution of heat and light. The same takes place for compounds of carbon. That is the reason why carbon and its compounds are used as fuel for most applications.
22. Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Ans: When soap is dissolved in hard water it reacts with calcium and magnesium ions that are present there and forms calcium and magnesium salt of fatty acid which reacts with soap to form scum. For example, calcium chloride reacts with soap to form scum.
\[Sodium~stearate\text{ }+\text{ }Calcium\text{ }chloride\to sodium~chloride\text{ }+\text{ }Calcium\text{ }stearate\left( scum \right)\]
23. What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Ans: Soap is a sodium or potassium salt of fatty acid. Soap molecules have two ends. Soap is obtained when caustic soda is treated with oil. Sodium stearate is thus a salt of a weak acid and a strong base. As its water solution is slightly alkaline it will turn red litmus red.
24. What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Ans: The process of adding unsaturated hydrocarbons and hydrogen in presence of catalysts such as palladium or nickel to give saturated hydrocarbons is called hydrogenation. It is commercially used for converting vegetable oils to vanaspati ghee in presence of nickel as a catalyst.
25. Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soap.
Ans: Soaps are sodium or potassium salt of fatty acids. Soap molecules have two ends . One end is hydrophilic and another end is hydrophobic. Two molecular ends behave differently. This ionic end is hydrophilic and is oriented towards the water. The other hydrocarbon end is hydrophobic and is oriented towards dirt which is oily in nature. A micelle formation around the oily dirt takes place. The cleaning of clothes etc takes place when flushed with excess water; the micelle containing the dirt is removed.
26. An organic compound X with a molecular formula C undergoes oxidation within the presence of alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ to form a compound I X on heating in presence of Cone. $11$ At $443$ K gives Z. which on reaction with \[\mathbf{112}\] cm presence of \[\mathbf{11}\] gives back ‘X‘‘Z’ reacts with Br (aq) and decolorizes it. Identify X, Y, & Z and write the reactions involved.
Ans: $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2OH}}\xrightarrow[{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}+Heat]{AlkalineKMn{{O}_{4+Heat}}}C{{H}_{3}}COOH$
X Y
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}OH\xrightarrow[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}]{HotCOOC}C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
Z
27. ‘A’ compound works well with hard water. It is used for making shampoos & products for cleaning clothes. A is not 100% biodegradable and causes water pollution. ‘B’ does not work well with hard water. It is 100% biodegradable and does not create water pollution. Identify A & B.
Ans: ‘Y’ will burn with a sooty flame. So it is an unsaturated hydrocarbon .
Propane (X)
Propene (Y)
28. A cyclic compound ‘X’ has molecular formula. It is unsaturated and burns with a sooty flame. Identify ‘X’ and write its structural formula. Will it decolourize bromine water or not and why?
It does not decolourize bromine water because it does not undergo additional reactions.
29. An organic compound ‘A’ is a constituent of antifreeze and has the molecular formula${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}O$ . Upon reaction with alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ the compound ‘A’ is oxidized to another ‘B’ with formula C Identify the compound A’ and ‘B’. Write the chemical equation for the reaction which leads to the formulation of ‘B’
Ans: $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}OH\xrightarrow[KC{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}+Heat]{AlkalineKMn{{O}_{4}}+Heat}C{{H}_{3}}COOH$
‘A’ ‘B’
30. Two compounds ‘X’ and ‘Y’ have the same formula C. One of them reacts with sodium metal to liberate \[\mathbf{112}\] and CO with NaHCO Second one does not react with Na metal and NaHCO but undergo hydrolysis with NaOH to form a salt of carboxylic acid and compound ‘Z’ which is called wood spirit. Identify ‘X’, ‘Y’, and ‘Z’ and write a chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Ans: $C{{H}_{3}}COOH+NaHC{{O}_{3}}\to C{{H}_{3}}COONa+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}}$
‘X’
$C{{H}_{3}}COOH+Na\to C{{H}_{3}}COONa+{{H}_{2}}$
$HCOO{{H}_{3}}+NaOH\to HCOONa+C{{H}_{3}}OH$
‘Y’ ‘Z’
31. A compound ‘X’ with molecular formula C burns with a sooty flame. It decolorizes bromine water. Identify ‘X’ Will it dissolve in water or not? Will it conduct electricity in aq. Solution? Will it have a high melting point or a low melting point?
Ans: As ‘X’ ethane is a covalent compound it will neither dissolve in water nor conduct electricity and it has a low melting point.
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
1. Define fermentation. Name the enzyme which converts
Milk into curd (yoghurt)
Cane sugar into glucose and fructose
Glucose into ethanol
Ans: The chemical process of preparation of ethyl alcohol from sugar is known as fermentation.
Milk into curd (yoghurt): Lactase
Cane sugar into glucose and fructose: Invertase
Glucose into ethanol: Zymase
2. a. Name the gas that evolved during the fermentation process?
Ans: $C{{O}_{2}}$ Gas is evolved and accompanied by brisk effervescence.
b. What role is played by yeast in the conversion of cane sugar to ethanol?
Ans: Yeast is the source of enzymes invertase and zymase needed for fermentation.
c. How may the following be obtained from pure ethanol? Express$({{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}})$ chemical reactions by the chemical equations.
Sodium ethoxide
Ans: $2{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH+2Na\to 2{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}ONa+{{H}_{2}}$
Ethyl ethanoate
Ans: $ 2{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH+C{{H}_{3}}COOH\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}C{{H}_{3}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}+{{H}_{2}}O $
Ans: ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH+\dfrac{1}{2}{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow[C{{h}_{3}}COOH]{Cr{{O}_{3}}}C{{H}_{3}}CHO+{{H}_{2}}O$
3. An organic compound A is widely used as a preservative in pickles and has a molecular formula. This compound reacts with ethanol to form a sweet-smelling compound B.
Identify compound A.
Ans: Compound A is ethanoic acid $(C{{H}_{3}}COOH)$
Write the chemical equation for its reaction with ethanol to form compound B.
Ans: $C{{H}_{3}}COOH+{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH\to C{{H}_{3}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
How can we get compound A back from B?
Ans: Ethanoic acid Ethyl Ethanoate (Ester)
$C{{H}_{3}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}+{{H}_{2}}O\xrightarrow{{{H}^{+}}}C{{H}_{3}}COOH+{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH$
Name the process and write the corresponding chemical equation.
Ans: The process is known as ester hydrolysis.
Which gas is produced when compound A reacts with washing soda? Write the chemical equation?
Ans: $C{{O}_{2}}$ is produced with effervescence when compound A reacts with washing soda which is chemical $N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}$
$2C{{H}_{3}}COOH+N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}\to 2C{{H}_{3}}COONa+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}}$
4.
Why does carbon form the largest number of compounds?
Ans: Carbon forms strong bonds with another carbon due to the overlapping of orbitals. Carbon forms a large number of compounds called organic compounds due to which the self-linking property is called catenation.
Why some of these are called saturated and other unsaturated compounds?
Ans: Compounds which has only $C-C$ (single bond) present are saturated compounds whose as those compounds which have \[\mathbf{C}=\mathbf{C}\] (double bond) or \[\mathbf{C}\equiv \mathbf{C}\] (triple) bond is present are called unsaturated compounds.
Which of these two is more reactive?
Ans: Saturated compounds are less reactive than unsaturated compounds
Write the names of the following compounds
i. $C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-Br$
ii. $C{{H}_{3}}-CH-CH-CH-C\equiv C-H$
Ans: Hex-1-yne
5. Draw the structure for the following compounds:
ii. Bromopentane
iii. Butanone
\[H-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} O \\ || \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-H\]
iv. Hexanal
\[H-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-\underset{\begin{smallmatrix} | \\ H \end{smallmatrix}}{\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}}\,-\overset{\begin{smallmatrix} H \\ | \end{smallmatrix}}{\mathop{C}}\,=O\]
6. Draw the electron dot structure for
${{H}_{2}}S$
Propanone
${{F}_{2}}$
7. Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also?
Ans: Soap molecules have two ends. One end is hydrophilic and another end is hydrophobic and the ionic end is hydrophilic. Soaps dissolve in water while the hydrogen chain is hydrophobic, it dissolves in hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbon chains are oriented towards the oil droplet and the ionic ends are oriented towards the water. In ethanol Micelles, the formation will not take place.
8. An organic compound ‘A’ is widely used as a preservative in pickles and has a molecular formula C. This compound reacts with ethanol to form a sweet-smelling compound ‘B’.
i. Identify the compound ‘A’
Ans: Ethanoic acid, $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$
ii. Write the chemical equation for its reaction with ethanol to form compound ‘B’.
iii. How can we get compound ‘A’ back from ‘B’?
Ans: Esters react with the acid or a base to give back the alcohol and carboxylic acid.
iv. Name the process and write the corresponding chemical equation.
Ans: Saponification
$C{{H}_{3}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}\xrightarrow{NaOH}{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH+C{{H}_{3}}COOH$
v. Which gas is produced when compound ‘A’ reacts with washing soda? Write the chemical equation.
Ans: $C{{O}_{2}}$ gas is evolved
\[2C{{H}_{3}}COOH+N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}\to 2C{{H}_{3}}COONa+{{H}_{2}}O+C{{O}_{2}}\]
Solved Examples
1. Explain why the chemical reaction of the conversion of ethanol into ethanoic acid is an oxidation reaction?
Answer. Ethanoic acid has one O 2 , atom more and two hydrogen atoms less than ethanol. Also, loss of hydrogen is known as oxidation, and gain of oxygen is known as oxidation. So, we can say that the chemical reaction of the conversion of ethanol into ethanoic acid is an oxidation reaction.
2. The molecular formula of X is C 3 H 6 O, and its structural formula is CH 3 CH 2 CHO. State its IUPAC name. Give an example of another compound that has the same molecular formula? Give the IUPAC name of that compound also.
Answer. Compound X is Propanal. Another similar compound is Propanone. They are related to each other as functional isomers.
3. List the properties of carbon responsible for the vast number of its compounds around us?
Answer.
(i) The Self linking property of carbon atom called catenation.
(ii) Carbon is tetravalent and can unite with atoms like hydrogen, oxygen, etc. by covalent bond formation.
4. The mixture of ethyne and oxygen is used for welding instead of a combination of ethyne and air. Explain why?
Answer. Large quantities of heat and light are produced when ethyne is burnt in oxygen. The heat evolved is used for gas welding. Since air contains a mixture of nitrogen and oxygen and nitrogen (in larger quantities) does not support combustion. Hence oxygen is used for the eruption of ethyne.
5. Define fermentation. Name the enzyme which converts:
(a) Milk into curd (yoghurt).
(b) Glucose into ethanol.
Answer. The process of preparation of ethyl alcohol from sugar is known as fermentation.
(a) Lactase converts milk into curd.
(b) Zymase converts glucose into ethanol.
Chapter 4 Science Class 10 Important Questions
Following are some essential points of Chapter 4 Science Class 10:
Carbon is one of the most versatile elements that are the basis of all living organisms.
Several compounds can be created using carbon, exhibiting the properties like tetravalency and catenation.
Carbon forms a covalent bond among itself and other elements like oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur, etc.
It also creates compounds that contain double and triple bonds among carbon atoms which can be in the form of straight chains, rings, or branched chains.
The carbon compounds used in our daily life are ethanoic acid, ethanol, etc.
Both the ends of the soap are present in soap and detergents' action, and it helps in the removal of oily dirt from the cloth.
Ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acid, and alcohols are among the functional groups that show characteristic properties to the carbon compounds that contain them.
Carbons give rise to homologous series of compounds in which the same functional group is attached to the carbon rings of different lengths.
Importance of Questions From Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its Compounds
important questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 are required for the following reasons:
It saves students from mugging up the entire chapter. Important questions consist of essential topics and concepts which are important from an exam point of view. They can study critical issues and gain enough knowledge about the chapter.
It helps students understand concepts in-depth quickly and reduces cramming up the entire chapter for the students.
It creates a perfect learning environment for the students to learn and understand topics better and efficiently.
Students understand essential points and concepts better and easier by solving and practicing questions on crucial topics.
Students can also analyze the weak parts or topics, in which they need extra care or focus.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
What are the Benefits of Important Questions from Vedantu for Class 10 Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds
Focus on key topics for efficient studying.
Prepares students for exams and reduces anxiety.
Reinforces understanding of fundamental concepts.
Teaches effective time management.
Enables self-assessment and progress tracking.
Strategic approach for higher scores.
Covers a wide range of topics for comprehensive understanding.
Supports exam preparation and boosts confidence.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 10 Science
Reviewing all the crucial questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 - Carbon and its Compounds provides students with a solid grasp of the chapter's topics. The extra and important questions for Class 10 chapter 4, Carbon and its Compounds engage in a concept-focused discussion, encompassing all chapter themes. This question-and-answer method proves time-saving during exam prep, offering an efficient way to revise the chapter and enhance understanding. Practising these important questions streamlines preparation and boosts confidence for the upcoming exams.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its Compounds
1. What is a Homologous Series? State any Two Characteristics of Homologous Series?
A series of compounds in which the member compounds having similar chemical properties, functional groups and any two successive members in a particular series differ in their molecular formula by group by a CH 2 is called a homologous series. Alkanes with general formula C n H 2 n + 2 , alkenes with C,H 2n , and alkynes with C n H 2n-2 form the most basic homologous series in organic chemistry.
All the members belonging to the homologous series have the same functional groups. They have the same physical properties which have a fixed change with the increasing mass. With increasing mass, the number of bonds increases, and thus properties like melting and boiling point, solubility, etc. also changes according.
2. Explain the Cleaning Action of Soap.
The salts of sodium and potassium fatty acids are called soap. Two ends of molecules of soap behave differently. This ionic end is hydrophilic and is oriented towards the water. The other end of soap is hydrophobic and is attracted towards dirt(oily). A micelle is formed around the oily ground. The micelles containing excess dirt are flushed with extra water, resulting in the cleaning of clothes, etc.
The two ends of soap are:
Hydrophilic End - This part dissolves in water and gets attracted to water.
Hydrophobic End - This part dissolves only in hydrocarbon and is repelled by water and the dirt comes out.
3. Why should I refer to important questions Vedantu for Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its Compounds?
Referring to these questions ensures a focused understanding of key concepts and better preparation for Class 10 Science exams.
4. How do these important questions from Vedantu benefit my exam preparation?
Practicing these important questions aids in familiarizing yourself with potential exam questions and reinforcing your knowledge of carbon compounds.
5. Can these important questions by Vedantu be a standalone study resource for the chapter?
While helpful, it's recommended to use these questions alongside textbooks for a comprehensive study approach.
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions
Cbse study materials.
- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Carbon and Its Compounds Chapter Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Cbse 10th standard science subject carbon and its compounds case study questions 2021.
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Study the table related to three hydrocarbons A, B, C and answer the questions that follow.
(i) A, Band C are classified as hydrocarbons because
(ii) Which of these organic compounds is an alkyne?
(iii) C 5 H 10 belongs to
(iv) Identify the incorrect statement about these three hydrocarbons.
(v) General formula for alkane is
(ii) The functional group of compound (R) is
(iii) Compound (T) belongs to homologous series of
(iv) Which of the 'following compounds is unsaturated hydrocarbon?
(v) Which of the following compounds belongs to alkane series?
The table given below shows six organic compounds A, B, C, D, E and F having different molecular formula:
(i) Which of the following compounds belong to same homologous series?
(ii) Which of the following is the member of the same homologous series as E?
(iii) Identify the correct statements.
(iv) Compound B is
(v) Compound (F) has a general formula
A hydrocarbon (P) has the molecular formula C 10 H 22 .A hydrocarbon (Q) has two carbon atoms less than (P) and belong to the same homologous series. A hydrocarbon (R) has two carbon atoms more than (P) and belong to the same homologous series. (i) What is the molecular formula of (Q) ?
(ii) To which homologous series do the compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong?
(iii) What is the molecular formula of (R) ?
(iv) Identify the correct statement about compounds (P), (Q) and (R) .
(v) Compounds (P), (Q) and (R) are
(ii) What is the general formula of this homologous series?
(iii) Which is the next member of this series?
(iv) Which is the third member of this series?
(v) Which is the second member of this series?
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard science subject carbon and its compounds case study questions 2021 answer keys.
(i) (c) :A, Band C are classified as hydrocarbons because these compounds are made up of carbon and hydrogen only. (ii) (c): C is an alkyne. (iii) (b): C 5 H 10 is an alkene having a general formula C n H 2n · (iv) (b): A and B do not belong to same homologous series. A is an alkane while B is an alkene. (v) (b)
(i) (d): (P) and (T) are alkynes. (ii) (a): Alcohol (-OH). (iii) (a): (T) is an alkyne having general formula of C n H 2n-2 · (iv) (c): (U) is an alkene. (v) (b)
(i) (d): A and F are alkanes; B and E are alkenes; C and D are alkynes. (ii) (d): B is an alkene having general formula C n H 2n , the homologous series to which E belongs. (iii) (a) : C and D belong to a homologous series having general formula C n H 2n-2 .Band E are alkenes. All the compounds have different physical and chemical properties. (iv) (b): (B) is alkene. (v) (d): (F) is an alkane.
(i) (c) : Molecular formula of (Q) is CSH1Sas it has two carbon atoms less than (P). (ii) (c): Compounds (P), (Q) and (R) are alkanes having general formula C n H 2n+2 . (iii) (a): Molecular formula of (R) is C 12 H 26 as it has two carbon atoms more than (P) (iv) (b): Compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong to same homologous series so they have different physical properties but similar chemical properties. They have same general formula C n H 2n+2 .They . differ by 2 carbon atoms and 4 hydrogen atoms. (v) (a)
(i) (c) : Alcohol (-OH). (ii) (a): C n H 2n+1 OH is the general formula of the homologous series of alcohol. (iii) (c) (iv) (a) (v) (a): Ethanol; C 2 H 5 OH is the second member of this series.
Related 10th Standard CBSE Science Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th maths probability chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Class 10 Science
- Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compounds
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
Ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 4 – cbse free pdf available.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 – Carbon and Its Compounds helps students to understand concepts provided in the textbook in detail. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science provides solutions to all the questions asked at the end of every chapter and the questions printed within a chapter.
Download Exclusively Curated Chapter Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter – 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
Download most important questions for class 10 science chapter – 4 carbon and its compounds.
These NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science are designed by our subject experts, who are highly experienced. The NCERT Solutions created are authentic and can be referred to by the students as a guide to prepare for the CBSE Board examination. The content is in simple language, which makes it easy to understand.
The concepts are explained with diagrams, points to remember, step-by-step procedures, shortcuts for numerical problems and tricks to remember formulae and chemical reactions. These NCERT Solutions provide an overview of the main concepts in the chapter and help you to get well-versed in important topics such as writing chemical equations and balancing them. Students can download the solutions PDF for free from the links given below.
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 The Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
Access Answers to NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 4 – Carbon and Its Compounds
(all in-text and exercise questions solved).
In-text questions set 1, page number 61
1. What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO 2 ?
2. What would be the electron dot structure of a molecule of Sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of Sulphur? (Hint – The eight atoms of Sulphur are joined together in the form of a ring).
In-text questions set 2, page number 61
1. How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
Solution: The structural isomers of pentane are as follows:
2-methylbutane
2, 2-dimethylpropane
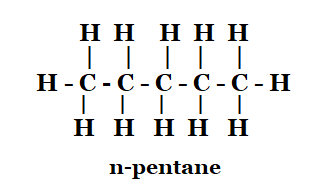
2. What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Solution: Two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us are as given below:
- Carbon has six valence electrons which is actually a high number of valency.
- Covalent bonding happens easily with carbon atoms and numerous others, such as oxygen, chlorine, nitrogen, sulphur, hydrogen, etc.
3. What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane?
Solution: The formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane is as given below:
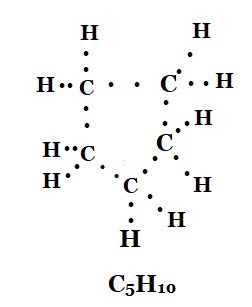
4. Draw the structures for the following compounds.
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Bromopentane*
(iii) Butanone
(iv) Hexanal
Solution: i)
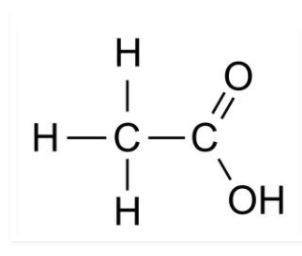
5. How would you name the following compounds?
- CH 3 —CH 2 —Br
- Bromoethane
- Methanal or Formaldehyde
In-text questions set 3, page number 71
1. How is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction?
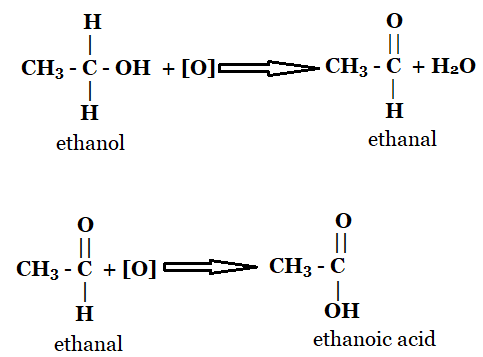
The conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid involves the removal of the hydrogen atom and the addition of oxygen, and it is an oxidation reaction. In the first step, a H 2 molecule is removed from ethanol to form ethanal. As the loss of hydrogen is oxidation, so the reaction is an oxidation reaction. Similarly, an oxygen atom is added to form ethanoic acid from ethanal. As the gain of oxygen is called oxidation, the reaction is an oxidation reaction.
2. A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Solution: A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding instead of a mixture of ethyne and air because the production of heat is very important for welding metals. When oxygen and ethyne are burnt, it burns completely and produces a higher temperature than air and ethyne. Oxygen and ethyne produce a very hot blue flame, but the mixture of air and ethyne gives out a sooty flame which means that there are unburnt particles, resulting in lesser heat.
In-text questions set 4, page number 74
1. How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid?
Solution: In reaction with sodium carbonate, carboxylic acids produce carbon dioxide gas which turns lime water milky, whereas alcohols do not give this reaction. This experiment can be used to distinguish alcohol and carboxylic acid.
The reaction of the carboxylic acid with sodium carbonate:
2CH 3 COOH + Na 2 CO 3 → 2CH 3 COONa + H 2 O + CO 2
2. What are oxidising agents?
Solution: Oxidising agents are those compounds which either remove hydrogen or add oxygen to a compound. For example, halogens, potassium nitrate, and nitric acid.
In-text questions set 5, page number 76
1. Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent?
Solution: It is not possible to check if water is hard by using a detergent because detergents are salts of ammonium or sulphonates of long-chain carboxylic acids. Unlike soaps, they do not react with calcium and magnesium to distinguish the nature of water.
2. People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually, after adding the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get clean clothes?
Solution: Agitation is necessary to get clean clothes as it aids soap micelles to trap the oil, grease or any other impurities that have to be removed. When they are being beaten or agitated, the particles are removed from the clothes’ surfaces and go into the water, thus cleaning the clothes.
Exercise questions, page number 77-78
1. Ethane, with the molecular formula C 2 H 6, has
(a) 6 covalent bonds
(b) 7 covalent bonds
(c) 8 covalent bonds
(d) 9 covalent bonds
Answer: (b) 7 covalent bonds
Solution: Ethane, with the molecular formula C 2 H 6, has 7 covalent bonds.
2. Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group (a) carboxylic acid (b) aldehyde (c) ketone (d) alcohol
Answer: (c) ketone
3. While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
(a) the food is not cooked completely
(b) the fuel is not burning completely
(c) the fuel is wet
(d) the fuel is burning completely
Answer: (b) the fuel is not burning completely
Solution: While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside indicates that the fuel is not burning completely.
4. Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH 3 Cl.
Solution: Carbon can neither lose 4 electrons nor gain four electrons as these processes make the system unstable due to the requirement of extra energy. Therefore, CH 3 Cl completes its octet configuration by sharing its 4 electrons with carbon atoms or with atoms of other elements. Hence, the bonding that exists in CH 3 Cl is a covalent bonding.
Here, carbon requires 4 electrons to complete its octet, while each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete its duplet. Also, chlorine requires an electron to complete the octet. Therefore, all of these share electrons, and as a result, carbon forms 3 bonds with hydrogen and one with chlorine.
5. Draw the electron dot structures for
(a) ethanoic acid
(c) propanone
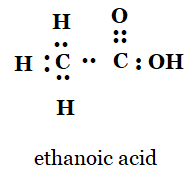
6. What is a homologous series? Explain with an example.
A homologous series is a series of compounds which has the same functional group. This also contains a similar general formula and chemical properties. Since there is a change in the physical properties, we can say that there would be an increase in molecular size and mass.
For example, methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc., are all part of the alkane homologous series. The general formula of this series is C n H 2n+2 . Methane CH 4 Ethane CH 3 CH 3 Propane CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 Butane CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 . It can be noticed that there is a difference of −CH2 unit between each successive compound.
7. How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
8. Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents, such as ethanol also?
Solution: Micelle formation takes place because of the dirt particles in water and clean water. There are two mediums that are involved: one is pure water, and the other is dirt, also called impurities. The soap also has two mediums:
(i) organic tail
(ii) ionic head
So the organic tail mixes and dissolves with the dirt, whereas the oil or grease and ionic head dissolve and mix with the water. Therefore, when the material to be cleaned is removed from the water, the dirt is taken off by the soap molecules in the water. Hence, the soap cleans by forming closed structures through the mutual repulsion of the micelles (positively charged heads).
Other solvents, such as ethanol, in which sodium salt of fatty acids does not dissolve, so not able to form such micelles.
9. Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Solution: Carbon and its compounds are used as fuels for most applications because they have high calorific values and give out a lot of energy. Most of carbon compounds give a lot of heat and light when burnt in the air.
10. Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Solution: Scum is produced from the reaction of hard water with soap. Calcium and magnesium present in the hard water form an insoluble precipitate called scum.
11. What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Solution: When soap is dissolved in water due to the formation of alkaline NaOH or KOH, the solution is alkaline. The solution changes the colour of the red litmus to blue, but in the soap solution, the blue litmus remains blue.
12. What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Solution: Hydrogenation is a process or a chemical reaction between hydrogen and other compounds. It is usually done in the presence of catalysts. For example, nickel, palladium or platinum. Hydrogenation is used mainly to saturate organic compounds.
13. Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions: C 2 H 6 , C 3 H 8 , C 3 H 6 , C 2 H 2 and CH 4?
Solution: Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions. C 3 H 6 and C 2 H 2 are unsaturated hydrocarbons which undergo addition reactions.
14. Give a test that can be used to differentiate between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Solution: The bromine water test is used to differentiate between the unsaturated compounds (like alkenes and alkynes) and the saturated compounds. For this purpose, bromine is used in the form of bromine water. A solution of bromine in water is called bromine water. Bromine water has a red-brown colour due to the presence of bromine in it. When bromine water is added to an unsaturated compound, then bromine gets added to the unsaturated compound, and the red-brown colour of bromine water is discharged. So, if an organic compound decolourises bromine water, then it will be an unsaturated hydrocarbon (containing a double bond or a triple bond), but saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes) do not decolourise bromine water.
The bromine water test is performed to differentiate between the unsaturated compounds (like alkenes and alkynes) and the saturated compounds. When bromine water is added to an unsaturated hydrocarbon, the red-brown colour of the bromine solution is discharged. So, if there is dis-colouration, then the compound will be an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
15. Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Solution: There are so many impurities and dirt mixed in water, and most of all, the dirt does not dissolve in the water. Soap molecules are a combination of salts such as sodium or potassium. The molecules are of a long chain of carboxylic acids. So, when the carbon chain is dissolved in oil, and the ionic end is dissolved in the water, the soap starts cleansing and trapping the dirt. When this happens, the soap molecules form structures called micelles that are used for capturing the oil droplets, and then the other end is the ionic faces. This will then form an emulsion in water and help in dissolving the dirt or impurities when the clothes are washed.
The soap molecules have different properties at different ends. The first end is the hydrophilic end, which dissolves in the water and is attracted towards the water, and the second one is the hydrophobic end, which is dissolved in the hydrocarbons and is repulsive to water. The hydrophobic tail aligns itself along the surface of the water because it is not soluble in the water.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 – Carbon and Its Compounds
The average number of questions usually asked from this chapter is 2+3 marks. In the year 2017, a total of 15 mark questions were asked from this chapter, whereas in the year 2018, the weightage was 2+3 = 5.
List of Section Questions with Type
List of exercise questions with type.
This chapter consists of 15 questions and is divided into the following types –
Carbon is the basis for all living organisms and a versatile element. It is tetravalent and has the property of catenation. Carbon forms covalent bonds by sharing electrons between two atoms and achieves completely filled outermost shell. It forms covalent bonds with oxygen, chlorine, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur and itself. It can form double and triple-bond compounds. There exist three types of carbon chains viz, branched, ring and straight. Carbon is considered as a major source of fuel. Ethanoic acid and ethanol are carbon compounds which are important and used in our daily lives. The behaviour of detergents and soaps is because of the hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups, which help in the emulsification of oily dirt and remove it.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 – Carbon and Its Compounds
- The information given in these NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 – Carbon and Its Compounds is authentic and simple.
- These solutions provide answers to all the exercise questions at the end of Chapter 4, Carbon and Its Compounds, from NCERT Class 10 Science textbook.
- The solutions to questions printed between the lesson have also been provided.
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 – Carbon and Its Compounds are provided by expert teachers after expansive research.
- These solutions will be useful to prepare for the CBSE exam as well as various competitive exams.
- Students can refer to these solutions to prepare for their CBSE Board exam as it consists of step-by-step procedures, neatly labelled diagrams, shortcuts, and tips to tackle complex type of questions smartly.
You can check out NCERT Solutions for Class 10 to get NCERT Class 10 chapter-wise solutions for other subjects.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4
What types of questions are present in chapter 4 of ncert solutions for class 10 science, list out the topics in chapter 4 of ncert solutions for class 10 science., where can i get the ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 4 online, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

CBSE Expert
Class 10 Science: Case Study Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds PDF Download
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given.

Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds Case Study Questions, by practicing this Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Case Study Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds .
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v).
The compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ from each other in physical or chemical properties are called isomers and the phenomenon is called isomerism. When the isomerism is due to differences in the arrangement of atoms within the molecule, without any reference to space, the phenomenon is called structural isomerism. In other words. structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas, i.e., they are different in the order in which different atoms are linked. In these compounds, carbon atoms can be linked together in the form of straight chains, branched chains or even rings.
(i) Which of the following sets of compounds have the same molecular formula? (a) Butane and iso-butane (b) Cyclohexane and hexene (C) Propanal and propanone (d) All of these
Answer: (d) All of these
(ii) In order to form branching, an organic compound must have a minimum of (a) four carbon atoms (b) three carbon atoms (c) five carbon atoms (d) any number of carbon atoms.
Answer: (a) four carbon atoms
(iii) Which of the following is an isomeric pair? (a) Ethane and propane (b) Ethane and ethene (c) Propane and butane (d) Butane and 2-methylpropane
Answer: (d) Butane and 2-methylpropane
(iv) Among the following the one having longest chain is (a) neo-pentane (b) iso-pentane (C) 2-methylpentane (d) 2,2-dimethylbutane.
Answer: (C) 2-methylpentane
(v) The number of isomers of pentane is (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 5
Answer: (b) 3
Question 2:
Food, clothes, medicines, books, or any of the things are all based on this versatile element carbon. In addition, all living structures are carbon-based. The earth’s crust has only 0.02% carbon in the form of minerals. The element carbon occurs in different forms in nature with widely varying physical properties. Both diamond and graphite are formed by carbon atoms, the difference lies in the manner in which the carbon atoms are bonded to one another. Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation.
(i) From the given alternatives, whose chemical and physical properties are not the same? (a) Graphite and Diamond (b) Phosphorous and Sulphur (c) Carbon and Hydrogen (d) Methyl alcohol and Acetic acid
Answer: (d) Due to presence of different functional groups methyl alcohol and acetic acid. Possess different physical and chemical properties.
(ii) Which of the following statements is not correct? (a) Graphite is much less dense than diamond (b) Graphite is black and soft (c) Graphite has low melting point (d) Graphite feels smooth and slippery
Answer: (c) Graphite has low melting point
(iii) Which of the following are isomers? (a) Butane and isobutene (b) Ethane and ethene (c) Propane and propyne (d) Butane and isobutane
Answer: (d) Butane and isobutane have same chemical formula but different arrangement of atoms and have different structure.
(iv) Which one of the following is not an allotrope of carbon? (a) Soot (b) Graphite (c) Diamond (d) Carborundum
Answer: (d) Carborundum is SiC (silicon carbide).
(v) Pentane has the molecular formula C 5 H 12 . It has (a) 5 covalent bonds (b) 12 covalent bonds (c) 16 covalent bonds (d) 17 covalent bonds
Answer: (c) 16 covalent bonds
You can also practice Class 10 Science MCQ Questions for Board Exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
NIOS Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Chemical Reaction and Equations
NIOS Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Chemical Reaction and Equations solutions and explanation is given here in English and Hindi Medium. All the questions of National Institute of Open Schooling Science chapter 4 are well explained here with question answers.
- NIOS Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Solutions
- NIOS Class 10 Science Chapter 4 in Hindi
- NIOS Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Book
- NIOS Class 10 Science all Chapters
- NIOS Class 10 all Subjects Solutions
- NIOS Online Admission Last Date
Chemistry is a branch of science that studies the composition, structure, properties, and change of matter. Our daily experiences are filled with examples of chemical reactions, from the rusting of iron to the cooking of food. In this detailed exploration, we focus on the intricate world of chemical reactions and equations, underscoring their significance in both our everyday lives and broader scientific endeavors.
The Essence of Chemical Reactions Every day, we observe numerous changes around us, categorized into physical and chemical changes. For instance, melting ice represents a reversible physical change, whereas the transformation of milk into curd illustrates an irreversible chemical change. Chemical changes are characterized by the formation of new substances and are represented by chemical equations. This discussion delves into the formulation and balancing of chemical equations, the various types of chemical reactions, and their applications in real-world scenarios.
Chemical equations serve as a shorthand method for describing chemical reactions, utilizing symbols and formulas instead of words. The law of conservation of mass mandates that the mass and number of atoms in the reactants must equal those in the products. This principle guides the balancing of chemical equations, ensuring that the equation adheres to the conservation laws. Through examples such as the combustion of magnesium and the reaction of zinc with sulfuric acid, the process of balancing equations is elucidated, highlighting the use of coefficients to maintain atomic and mass balance.
Diverse Types of Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions can be broadly classified into combination, decomposition, displacement, and double displacement reactions, each with distinctive characteristics and examples: Combination Reactions : These reactions involve the merging of two or more substances to form a new compound, exemplified by the burning of magnesium in air. Decomposition Reactions : A single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances, as seen in the decomposition of ferrous sulfate. Displacement Reactions : One element displaces another from its compound, demonstrated by the reaction of iron with copper sulfate. Double Displacement Reactions : Involve the exchange of ions between two compounds, leading to the formation of new compounds, such as the reaction between sodium sulfate and barium chloride.
Redox reactions, encompassing both oxidation and reduction processes, play a pivotal role in chemical reactions. Oxidation involves the gain of oxygen or loss of electrons, while reduction involves the loss of oxygen or gain of electrons. These reactions are integral to numerous chemical processes, including metabolism, combustion, and corrosion.
Chemical reactions underpin a vast array of industrial processes, environmental phenomena, and everyday activities. From the rusting of iron (corrosion) to the spoiling of food (rancidity), understanding chemical reactions allows us to devise methods for prevention and control, demonstrating the profound impact of chemistry on our lives.
The study of chemical reactions and equations is fundamental to both the science of chemistry and the understanding of the world around us. Through the balancing of equations and classification of reactions, we gain insights into the transformation of matter, underlying energy changes, and the principles governing chemical processes. This knowledge not only enriches our comprehension of the natural world but also empowers us to innovate and address challenges in industry, medicine, and environmental protection.

Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education


- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- DK Goel Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
- STATE WISE BOOKS
- ENGINEERING EXAM
- SCHOLARSHIP OLYMPIAD
- STATE BOOKS
CBSE Class 10 Science Case Based MCQ Questions
CBSE Term 1 exam is not so far and surely you have begun the preparation for the board exam. Therefore we have dedicated this page to help you out in your preparation. This year for the first time the board has introduced the Case based Questions which will be asked in the Term 1 exam that is likely to be held in November-December.
Therefore, we have brought you the CBSE Class 10 Science Case Based MCQ on this page. The questions are given in objective types. Such types of questions are solved by reading the given scenario in the paragraph.
All these science case study questions are developed as per the new CBSE Pattern. The team of subject matter experts have crafted the given MCQs. The Case Based Questions that we are providing here are worthy to solve and practice because class 10th syllabus has been taken into consideration while preparing the problems.
CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study, Assertion & Reasoning, MCQ
The Class tenth CBSE Science Case Study, Assertion & Reasoning, MCQs are very helpful in practicing and getting a deep understanding in the topics of science. However, a comprehensible knowledge of NCERT Science Book is a must to be able to solve these types of problems.
The PDF that is available here to download contains the problems in three different variants; One is general objective types of questions that is MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions), second one is Assertion and Reasoning and the last one is Case-Based Questions.
If you Download PDF CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study from the given links, then you will be able to get the quick revision for each chapter that will help you to recall your learnings and give you information about some important Chemicals Formulas and reactions.
What are Assertion & Reasoning Questions?
Assertion & Reasoning questions are basically a type of multiple-choice question that is solved by reading the given statement and the reason. The question typically consists of one statement followed by its reason. Students' duty is to verify both statements and reason whether they are correct or not and if they are correct then it is time to look at whether the given statement truly satisfies the reason or not.
These questions should not be difficult to solve but you have to have rigorous and extensive practice. The Assertion & Reasoning questions along with the solutions are given in the CBSE Class 10 Science case study 2021-2022 PDF that is available here.
Class 10th has very basic and important chapters that are necessary to solve. A few chapters that are available in the beginning of the science books are Chemical Reactions and Equations, Acids, Bases and Salts, Metals and Non-metals, Carbon and Its Compounds, Periodic Classification of Elements, Life Processes, etc.
Since you are here to find out the CBSE Class 10 Science MCQ Based Questions, the possibilities are you need CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions too.
FAQs on CBSE Class 10th Science Case Study Questions

Case Study Questions are based on the data which are given in the form of passage. These types of questions generally consist of real life examples. Usually it contains upto 4 or 5 questions.
To prepare for Class 10 Science MCQ Be thorough with the concepts, Practice the questions regularly, Attempt online tests as much as you can. To do all these things visit the Selfstudys.com. They are providing everything for free of cost.
In class 10 Science Based Questions you will be asked to answer the questions that are explained in the standard Xth Science Syllabus. However, the problems will be related to real world examples.
To find Class 10 Science Chapter wise Assertion and Reason Questions you simply need to reach at the Selfstudys website. It provides all the study resources for free of cost. You will be able to download the assertion reason with solutions as well.
No, CBSE Class 10 Science Case Based MCQ Question is not difficult, if you pay a good attention to the given paragraph. It is important to be able to find the tiny details in the passage to answer the Case Based questions.

CBSE Class 10 Exams Finish, When Can You Expect Results? Details Here

CBSE Board Class 10 Information Technology Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs

CBSE Board Class 10 Computer Applications Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs

CBSE Class 10 Information Technology Exam 2024 : Most Important Questions Answers for Last-Minute Revision

CBSE Class 10 Computer Applications Exam 2024 : Most Important Questions Answers for Last-Minute Revision

CBSE Board Class 10 Maths Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- Bihar Board
SRM University
Ap inter results.
- AP Board Results 2024
- UP Board Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- MP Board Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10
CBSE Class Class 10 Science 4 or 5 Marks Important Questions for 2024 Board Exam
4 or 5 marks long type questions: students can find here 4 or 5 marks important questions with solutions for class 10 science. check the chapter-wise pdfs for class 10 science to strengthen your preparation.

CBSE 10th Science 4 or 5 Marks Questions: What’s the most important element in a student’s preparation journey? We think it’s using the appropriate study materials. The more and better equipped you are with authentic study materials, the better results you get on the boards. Thus, we are bringing you the best of study materials prepared from the authentic sources. Here, you can find CBSE Class 10 Science 4 or 5-mark questions along with solutions in the table attached below. Chapter-wise PDF links have been brought to you in this article for your reference.
CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper Pattern
List of chapter-wise important questions of 4 or 5 marks for class 10th science with solutions, how to answer 4 or 5 marks questions in cbse board exam.
- As per the CBSE guidelines, the word limit for a 4 or 5 mark question is between 120-150 words. So, students should not write an answer which is less than 120 words. It is also equally important to not over exceed the answer unnecessarily.
- The answer should be an elaborative one. Long-answer type questions should consist of additional details for brownie points. It is always better to write a few extra points to inform teachers that students are actually aware of the topic.
- These types of questions can also be a combination of two or more questions and thus students should carefully read the instructions and questions before appearing to answer.
- Time management is the key to a good score on the exam. Students should save an adequate amount of time for long-form questions so that these can be presented in a well-written and well-thought-out manner.
- Break the entire question into various parts and answer each part individually. Long-type questions are generally formed of a variety of questions and each such question has separate marks associated with it. Hence, it is important to answer every part of the question for a complete 4 or 5 mark from the answer. For example: if a question asks you to define something and give two or three examples along with uses and benefits then each of the parts has to be answered as asked. A definition, two examples, two uses and two benefits have to be answered.
Keeping a check on the list of important questions can actually help students analyse their preparation and build an understanding of the same. Knowing or having a fair idea about the types of questions can help students maintain a flow of writing the answers while saving enough amount of time for re-checking the paper. These important questions have been picked up from authentic and correct sources only and hence students can be carefree while referring to these.
Links to 4 or 5 marks important questions for all the chapters have been provided to you in the table attached above. Students are requested to kindly check the available study material for enhancing their preparation. All the questions have been picked up from important and authentic resources, mainly CBSE's official study material.
Also Check:
CBSE Cass 10 Syllabus 2023-2024
CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper 2023-2024
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
MCQs for Class 10 Science
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- IAF Agniveer Result 2024
- AP Intermediate Result 2024
- NDA Admit Card 2024
- resultsbie.ap.gov.in Results 2024
- AP Inter Result 2024 Link
- Manabadi Inter Results 2024
- Manabadi AP Inter Result 2024
- Manabadi Inter Results 2024 AP
- AP Inter Results 2024 with Jagran Josh
- AP Inter Toppers List 2024
- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
Latest Education News
(Updated) PBKS vs RR Head to Head in IPL: Check Stats, Records and Results
Today’s IPL Match (13 April) - PBKS vs RR: Team Squad, Match Time, Where to Watch Live and Stadium
CUET PG Result 2024 Out Live: Get Gender-wise Performance Details Here
Lok Sabha Election 2024 Dates: इस बार 97 करोड़ वोटर्स करेंगे मतदान, फेज-वाइज फुल शेड्यूल यहां देखें
IPL 2024: सूर्या ने सीजन की दूसरी सबसे तेज फिफ्टी के साथ बनाया एक और बड़ा रिकॉर्ड
Fastest 50s In IPL History: आईपीएल इतिहास के सबसे तेज़ अर्द्धशतक की पूरी लिस्ट यहां पढ़े
Who Won Yesterday IPL Match: LSG vs DC, Match 26, Check All Details and Latest Points Table
[Current] Orange Cap and Purple Cap Holders in IPL 2024
[Today] IPL 2024 Points Table: Team Rankings and Net Run Rate
(Updated) LSG vs DC Head to Head in IPL: Check Stats, Records and Results
NIOS 12th Hindi Syllabus 2023-24: Download Subject-wise PDF
Only eagle eyed readers can spot the magnet on the beach in 5 seconds!
NIOS Class 10th Social Science Syllabus 2023-24: Download Subject-wise PDF
एयरफोर्स अग्निवीर रिजल्ट 2024 OUT: जारी हुआ एयरफोर्स अग्निवीर परीक्षा का परिणाम, agnipathvayu.cdac.in से करें डाउनलोड
CUET PG Result 2024: आज रात जारी होंगे सीयूईटी पीजी परीक्षा के परिणाम, यूजीसी चेयरमैन ने दी जानकारी
Picture Puzzle IQ Test: Use Your Sharpest Eyes To Spot A Magnet In 12 Seconds!
Kerala Bank Recruitment 2024 for 479 Clerk and Office Attendant Posts, Apply Online at keralapsc.gov.in
NIOS 12th Date Sheet 2024: Check Stream-Wise Exam Schedule; Download FREE PDF
NIOS 10th Date Sheet 2024: Check Subject-wise Exam Schedule; Download FREE PDF
IAF Agniveer Result 2024 Declared at agnipathvayu.cdac.in, Check Indian Air Force Agnivayu Login Link Here

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4.5) Diamond is not a good conductor of electricity because : (a) it is very hard. (b) it has no free electrons. (c) it is not water soluble. (d) its structure is very compact. Show Answer. Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds with Answers Pdf ...
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided case … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 ...
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Carbon and its compounds CASE STUDY : 1. Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds ...
Please refer to Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compound Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year.
The Chapter wise Important case study based questions with their solved answers in CBSE Class 10 Science can be accessed from the table below: CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions ...
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App. There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions.
The CBSE Class 10 Science Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful for understanding how the source based or case based questions are asked in the board exam.
Selfstudys provides case studies for the Class 10 Science chapter Carbon and its Compounds with solutions. The Solutions can be helpful for students to refer to if there is a doubt in any of the case studies problems. ... Students studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to solve questions based on case study. It is necessary for students to know ...
Document Description: Case Based Questions: Carbon and its compounds for Class 10 2024 is part of Additional Practice for Class 10 preparation. The notes and questions for Case Based Questions: Carbon and its compounds have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about Case Based Questions: Carbon and its compounds covers topics like Case Study - 1, Case Study - 2 ...
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter-4 Important Questions with Answers - Free PDF Download Chapter 4 Science Class 10 revolves around carbon and its compounds. The chapter mainly includes its covalent properties and versatility in forming numerous saturated and unsaturated compounds in branches, chains, or rings.
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Carbon and Its Compounds Case Study Questions 2021 Answer Keys. (i) (c) :A, Band C are classified as hydrocarbons because these compounds are made up of carbon and hydrogen only. (ii) (c): C is an alkyne. (iii) (b): C 5 H 10 is an alkene having a general formula C n H 2n ·.
The information given in these NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its Compounds is authentic and simple. These solutions provide answers to all the exercise questions at the end of Chapter 4, Carbon and Its Compounds, from NCERT Class 10 Science textbook. The solutions to questions printed between the lesson have also ...
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science. In board exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations.
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds. Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Question 1: Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v). The compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ from each other in physical or chemical properties are ...
The detailed NCERT Class 10 Science Solutions for all chapters are provided below for your reference. 1st Chapter: Chemical Reactions and Equations. 2nd Chapter: Acids, Bases and Salts. 3rd Chapter: Metals and Non-Metals. 4th Chapter: Carbon and Its Compounds. 5th Chapter: Periodic Classification of Elements.
1 . 6.1ml glacial acetic acid and 1ml of ethanol are mixed together in a test tube. Few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid are added in the mixture are warmed in a water bath for 5 min. a) Name ...
Soaps And Detergents. Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon And Its Compounds PDF in Hindi Medium as well as in English Medium for CBSE, Uttarakhand, Bihar, MP Board, Gujarat Board, and UP Board students, who are using NCERT Books based on updated CBSE Syllabus for the session 2019-20.
Accurate answers of all the Case-based questions given in the PDF. Case Study class 10 Science solutions are prepared by subject experts referring to the CBSE Syllabus of class 10. Free to download in Portable Document Format (PDF) so that students can study without having access to the internet.
Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. For Science subjects, there would be 5 case-based sub-parts questions, wherein a student has to attempt 4 sub-part questions.
Physics Chapters for Case Study Questions. Light - Reflection and Refraction. The Human Eye and The Colourful World. Electricity. Magnetic Effects of Electric Current. TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Science students. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving ...
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10; CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11; CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12; ... NIOS Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Chemical Reaction and Equations solutions and explanation is given here in English and Hindi Medium. All the questions of National Institute of Open Schooling Science chapter 4 are well explained here with ...
Such types of questions are solved by reading the given scenario in the paragraph. CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Case Study. Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions & Equations Case Study. Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases & Salts Case Study. Science Chapter 3 Metals & Non-Metals Case Study. Science Chapter 4 Carbon & Its Compounds Case Study.
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. Here we are providing case study questions for class 9 science chapter 12 sound. Students are suggested to go through each and every case study questions for better understanding of the chapter. Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1:
All the important questions have been picked up for your reference. CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations 4 or 5 marks Important Questions. CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter ...