How To Ride A Bicycle
Riding a bicycle is quite simple. Most people who ride bicycles do it for a variety of reasons. They could be saving on gas or exercising amongst other reasons. Whatever the motivation for riding a bicycle, you should always have fun. Riding a bicycle, however, demands a lot of precaution. You should always ensure comfort by dressing appropriately and ensuring awareness of the surrounding. To ride a bicycle safely, you should always consider following the steps for maintenance, riding preparation, and riding (Stapleton 1).
Riding a bicycle is best done by people who are experienced in it. However, for an amateur rider or somebody who does not know how to ride a bicycle, the following riding steps are helpful. To start with, make sure you are safely dressed before going out for a bicycle ride. Make sure you have a helmet to protect you from injuries in case of an accident. Secondly, it is wise to always ensure that your bicycle is in good condition before riding it. Check if the brakes are in working properly. In addition, check if the tires are properly inflated. You should also adjust the seat of the bicycle to a height that you are comfortable with. Start by resting your right foot on the pedal on the right-hand side of the bicycle while supporting yourself with the left foot. Push the right pedal with your foot and simultaneously remove your left-leg support to rest the left foot on the left pedal. Next, ensure that the handlebars point ahead as you start pedaling. Try to obtain your balance as you pedal. Cover the longest distance you can and then turn and repeat the same process. Once you can obtain and keep balance when pedaling straight ahead, try turning the handlebars. Begin by slight turns of the handlebars until you can turn them and still keep your balance. Next, practice on speed and balance. Try to attain faster speeds while balancing, pedaling, and turning until you become conversant with these three actions. When riding, make sure that you obey riding rules and street signs. Stop when you encounter stop signs, signal to other road users when turning or passing them, ride on the right etcetera. Make sure that you are always alert when bicycling because bicycling is pretty quiet and you can easily hit cars or people. Lastly, make sure that you keep your bicycle in good condition. After a ride, check its condition and if repair is necessary, make sure the bicycle is repaired promptly (Stapleton 1).
There are several tips and warnings associated with the process of riding a bicycle. The first one is that you should never give up on training when something goes wrong. For instance, if you fall, just get back up and continue trying. Next, you should always make sure that you drink water in large amounts while riding. Ensure that you a visible as a cyclist on the road by using reflectors and wearing bright clothes. This will potentially save you from a lot of accidents. Make sure that as you try new and dangerous tricks, you have safety equipment. You should also make sure that you do not overdo bicycling (Stapleton 1). Failure to comply with these safety procedures may lead to a lot of bicycle accidents. We should, therefore, always do our best to keep these safety procedures.
From the explanation above, it is evident that learning bicycling is a continuous process that requires the successful completion of each step. Avoiding learning one step in the bicycle learning process could be very disastrous. It is the drill described above and experience in bicycling that makes one an expert bicycler such that he/she can control the bicycle in several dangerous situations and avoid fatal accidents. The learner gains skills progressively with skills gained in previous bicycling lessons helping him/her learn new skills in the subsequent lessons. This necessitates the presence of a tutor while one learns how to bicycle since there is a need to plan the order of bicycling lessons (“How to ride a bicycle 1”).
Normally, how fast one learns how to cycle and cycle safely depends on their attitude and determination to learn. Bicycle riding lessons can take a very short period, like a day, for the learner knows how to ride. They can also take a period as long as one year before the learner knows how to ride depending on the factors mentioned above. It is always helpful for the learner to maintain a positive attitude towards the learning process. The learners should never feel embarrassed when they accidentally fall while practicing. They should always try to discover the mistakes and through this, they eventually become expert bicyclers. Another important thing in bicycling lessons is being consistent. The learner needs to be consistent with his/her bicycling classes. Otherwise, they find themselves having lost the skills they acquired during their previous riding lessons in their subsequent lessons (“How to ride a bicycle 1”).

Works Cited
“How to ride a bicycle.” eHow. 2010. Web.
Stapleton, Christine. “How to ride a bicycle.” 2008. Web.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, December 3). How To Ride A Bicycle. https://studycorgi.com/how-to-ride-a-bicycle/
"How To Ride A Bicycle." StudyCorgi , 3 Dec. 2021, studycorgi.com/how-to-ride-a-bicycle/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) 'How To Ride A Bicycle'. 3 December.
1. StudyCorgi . "How To Ride A Bicycle." December 3, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/how-to-ride-a-bicycle/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "How To Ride A Bicycle." December 3, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/how-to-ride-a-bicycle/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "How To Ride A Bicycle." December 3, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/how-to-ride-a-bicycle/.
This paper, “How To Ride A Bicycle”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 13, 2023 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Personal Growth and Development — Life Is Like Riding a Bicycle
Life is Like Riding a Bicycle
- Categories: Book Review Personal Growth and Development
About this sample

Words: 455 |
Published: Mar 20, 2024
Words: 455 | Page: 1 | 3 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Literature Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 588 words
3 pages / 1267 words
1 pages / 621 words
2 pages / 694 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Personal Growth and Development
Advantages of living alone essay delves into the liberating and transformative experience of residing independently. Living alone provides individuals with a unique opportunity to embrace autonomy, personal growth, and [...]
Help.open.ac.uk. (2019). Friends and family: When study gets difficult - Help Centre - Open University. Available at: Jou
Kohlberg, Lawrence. 'The Philosophy of Moral Development: Moral Stages and the Idea of Justice.' Harper & Row, 1981.Rest, James R. 'Development in Judging Moral Issues.' University of Minnesota, 1979.Turiel, Elliot. 'The [...]
In the pursuit of personal development, there exists a powerful yet paradoxical notion: getting comfortable with being uncomfortable. This essay delves into the concept of stepping out of one's comfort zone and the [...]
Academic goals for college students are targets they set for themselves to achieve, which help them strive throughout their college journey. Although college can sometimes be challenging, I have set an academic goal to obtain my [...]
The Strengths Finder Analysis has revolutionized the field of personal and professional development by shifting the focus from weaknesses to strengths. By uncovering an individual's unique combination of talents, the analysis [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
November 15, 2018
Why Don’t We Forget How to Ride a Bike?
The way memories are anchored in the brain plays a role, neuropsychologist Boris Suchan explains
By Boris Suchan

Getty Images
Most of us learn how to ride a bike during childhood. But as we grow older, many of us stop riding and put those once-beloved bikes in storage. Years later, when we discover these relics and hop on, it’s as if we never stopped biking.
This is surprising because our memories let us down in so many other instances, such as remembering the name of a place or a person we once knew or where we put our keys. So how is it that we can ride a bicycle when we haven’t done so in years?
As it turns out, different types of memories are stored in distinct regions of our brains. Long-term memory is divided into two types: declarative and procedural.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
There are two types of declarative memory: Recollections of experiences such as the day we started school and our first kiss are called episodic memory. This type of recall is our interpretation of an episode or event that occurred. Factual knowledge, on the other hand, such as the capital of France, is part of semantic memory. These two types of declarative memory content have one thing in common—you are aware of the knowledge and can communicate the memories to others.
Skills such as playing an instrument or riding a bicycle are, however, anchored in a separate system, called procedural memory. As its name implies, this type of memory is responsible for performance.
One of the most famous studies showing the separate memory systems was that of an epileptic named Henry Gustav Molaison (aka H. M.). In the 1950s he underwent the removal of portions of his brain, including large parts of his hippocampus. After the operation doctors found that although the number of seizures had decreased, H. M. was unable to form new memories. Many of his memories of the time before the operation were also erased.
To learn more about his amnesia, neuropsychologists carried out various tests with H. M. In one, they asked him to trace a five-pointed star on a sheet of paper while only looking at it and his hand in a mirror—meaning the image was reversed. Although H. M.’s hand–eye coordination skills improved over the several days he performed this task, he never remembered performing it. This meant that he could develop new procedural, but not declarative, memories.
Is procedural knowledge then fundamentally more stable than explicit knowledge? As it turns out, the former is more resistant to both loss and trauma.
Even with traumatic brain injury the procedural memory system is hardly ever compromised. That’s because the basal ganglia, structures responsible for processing nondeclarative memory, are relatively protected in the brain’s center, below the cerebral cortex. However, it’s not clear, beyond brain damage, why procedural memory contents are not as easily forgotten as declarative ones are. According to one idea, in the regions where movement patterns are anchored fewer new nerve cells may be formed in adults. Without this neurogenesis, or continuous remodeling in those regions, it’s less likely for those memories to get erased.
One thing we know for sure, however, is simple sequences of movements we internalize, even far in the past, are typically preserved for a lifetime. Or as the saying goes, it’s “just like riding a bicycle.”
- Training and Health
- How To…
- Live Streaming

The Road to Good Health: How to Write an Essay about Cycling

Cycling is one of the best forms of exercise and more and more people are becoming aware of its benefits. Cycling is a good topic to write about because it is something you’re probably familiar with, which will make your essay more believable.
You will need to choose what type of cycling essay you would like to write, decide on a topic, create an outline, come up with a rough draft and work on it to create your final essay.
What type of cycling essay do you want to write?
A descriptive essay is all about the language you use and how vividly you can describe what you want to write about. You could write about a specific riding adventure you experienced.
If you decide to write an argumentative essay, you will need to come up with an argument, use evidence to support it and draw a conclusion from it. For example, you could argue that doping is ruining professional cycling.
A narrative essay is a personal piece of writing that makes your point of view clear to the reader. In a narrative essay, you could write about how you learned to ride a bike.
Decide on a cycling topic
Once you have decided what type of essay you would like to write, you will need to decide on a specific topic. For example, if you want to write an argumentative essay, you could discuss the problem of racial diversity in cycling.
If you have a specific interest, using it to frame your topic will make it easier to write your essay. For example, if you have an interest in technology, you could write about different technological advancements in bicycles. If you’re having trouble coming up with a topic, using one of many online essay title generators may help you to find one.
Get writing help
At college, all the requirements for essays are important to follow. Students getting an education at college may find they are overwhelmed with the sheer volume of work and need writing help. They can get essay writing help from professionals with experience that understand what’s required in terms of originality, referencing etc. All students need to do is ask for essay help on Ca.Edubirdie. They will receive the essay within the required deadline done perfectly by the professionals.
Make an outline
When creating an outline for your essay on cycling, you will need to organize all your ideas into a logical sequence and then give your main points roman numerals, designate sub-points with capital letters and points under your subpoints in small letters and numbers.
If you decide to write about safety while cycling, you will start off your introduction with your main idea, which is that if you want to keep yourself safe while cycling, you need to wear protective clothing, follow the safety rules and stay aware of your surroundings. These three points and subpoints under them will form the body of your essay and you will sum up in your conclusion.
Write your rough draft
Once you have your outline , it is easier to write your rough draft as you simply follow all the points in your outline. You don’t have to think too much about perfection at this point but just get all your ideas down in the structure you came up with within your outline.
For example, under your main point about personal protection, you will write about things like wearing a helmet because it reduces the chance of getting a head injury. You will discuss wearing clothes in bright colors to be more visible.
Polish it until you’re satisfied
After writing your rough draft, let it sit for a while before reviewing it. Coming back to it with fresh eyes will help you to see where you can make improvements. You may find you have left out an idea you want to include. If you’ve written about the benefits of cycling, you may have left out the benefits of team sports for learning , such as how cycling as part of a team can help to boost brain and mental health.
When writing an essay on cycling, you will need to choose a type of essay, decide on a topic, create an outline, write the first draft and then work on it. It is often helpful to write your introduction and conclusion last, as completing the body of your essay will give you more idea of what to say. Remember to run your essay through a spelling and grammar checker before submitting it.
Author’s Bio:
Brandon Kryeger works for a publishing company as a writer and editor and his job is to prepare textbook content for school and college students. He’s passionate about writing and after his work, he spends the time helping college students do their academic writing work. His hobbies are playing tennis, watching anime and doing pencil sketching.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
EDITOR PICKS

2024 La Fleche Wallonne LIVE STREAM

2024 Tour of the Alps LIVE STREAM

2024 Amstel Gold Race LIVE STREAM
Popular posts.

Giro d’Italia, Milan-San Remo under threat of cancellation due to coronavirus

2020 UAE Tour LIVE STREAM

Ewan storms to victory on stage 2 of UAE Tour
Popular category.
- Results 1805
- Grand Tours 1566
- Tour de France 707
- POPULAR THIS WEEK 616
- Live Streaming 569
- Giro d'Italia 547
- Interviews 382

Essay on First Ride On Bicycle
Students are often asked to write an essay on First Ride On Bicycle in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on First Ride On Bicycle
My first bicycle ride.
I remember the day I first rode a bike. It was a sunny afternoon, and my bicycle was shiny red with black wheels. My heart was pounding with excitement and a bit of fear.
Getting Ready
My dad held the bike steady while I climbed on. I wore a helmet to protect my head. Holding the handlebars tightly, I was ready to go.
Starting to Pedal
With a gentle push, I started moving. At first, I wobbled and felt like I might fall. But I kept pedaling and soon, I was riding straight.
Feeling of Joy
The breeze brushed against my face as I rode faster. I felt free and happy. It was a moment of pure joy, and I knew I would love riding my bike forever.
250 Words Essay on First Ride On Bicycle
Learning to ride a bicycle is a big moment for many kids. It’s like a step into a new world of adventure. I remember my first bicycle ride very clearly. It was a mix of excitement, fear, and joy.
My bicycle was shiny and blue, with white stripes on the side. Before I started, I put on a helmet to protect my head. My dad held the back of the seat to help me stay up. I felt nervous but ready to try.
At first, my legs didn’t know how fast to go. I pedaled too slow, then too fast. The bike wobbled, and I was scared of falling. But my dad’s hand on the seat made me feel safe.
Finding Balance
Suddenly, I felt the bike steady under me. I was actually riding! My dad let go, and I didn’t even notice. I was moving all by myself. The wind brushed against my face, and I couldn’t stop smiling.
Learning from Mistakes
I did fall a couple of times. But with each fall, I learned something new. I got better at knowing when to pedal hard and when to just glide. Falling didn’t seem so scary anymore.
Feeling Proud
When I finally rode all the way down the street without help, I felt like I could do anything. It was more than just riding a bike. It was about growing up and learning to keep trying, even when things are hard. That first ride on my bicycle is something I’ll always remember. It taught me to be brave and to enjoy the ride, no matter where it takes me.
500 Words Essay on First Ride On Bicycle
My first bicycle experience.
Everyone remembers their first bicycle ride. It’s a moment filled with excitement, nerves, and the thrill of trying something new. I still remember the day I got my first bicycle. It was a bright red one with shiny handlebars and a basket in the front. I had been waiting for this day for so long, and finally, it was here.
Getting Ready to Ride
Before I could start riding, I had to learn about safety. My parents made sure I had a helmet that fit well. They taught me to always wear it when riding. They also checked the bicycle to make sure it was safe. The tires were pumped, the brakes worked, and the seat was just the right height for me.
Learning the Basics
My first attempt at riding was in our backyard. The grass was soft, which was good in case I fell. My dad held the back of the seat and walked with me as I pedaled. I was scared of falling, but my dad was right there, telling me I could do it. I tried to balance, steer, and pedal all at the same time. It was harder than I thought, but I kept trying.
The Feeling of Moving
After many tries, something clicked. I could feel the bike moving and I was actually riding! My dad let go, and I didn’t even notice. I was really doing it all by myself. The wind was in my hair, and I felt like I was flying. It was an amazing feeling, one that I will never forget.
Overcoming Challenges
Of course, it wasn’t all smooth riding. I had a few wobbles and falls. But with each fall, I learned something new. I learned how to get back up, dust myself off, and try again. I learned that making mistakes was part of learning. My parents were there to encourage me and remind me that it’s okay to fall as long as you get back up.
Sharing the Joy
When I finally mastered riding my bicycle, I couldn’t wait to show my friends. I rode up and down the street, proud of what I had achieved. My friends cheered for me, and some of them even asked for my help to learn how to ride. Sharing the joy of my first bicycle ride with my friends made the experience even more special.
Lessons Learned
Riding a bicycle for the first time taught me more than just how to balance on two wheels. It taught me about perseverance, courage, and the joy of achieving a goal. I realized that trying new things can be scary, but also exciting and rewarding. It’s an experience that has stayed with me and one that I always look back on with a smile.
The day I first rode a bicycle was a big day for me. It was the start of many adventures and the beginning of a lifelong love for riding. Every time I see a bicycle now, I remember that red one and the day I first took to the pedals. It was a simple yet unforgettable experience that taught me valuable life lessons.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on First Snow Experience
- Essay on First Pet
- Essay on First Experience On Stage
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write an Expository Essay
Last Updated: December 13, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Tristen Bonacci . Tristen Bonacci is a Licensed English Teacher with more than 20 years of experience. Tristen has taught in both the United States and overseas. She specializes in teaching in a secondary education environment and sharing wisdom with others, no matter the environment. Tristen holds a BA in English Literature from The University of Colorado and an MEd from The University of Phoenix. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 564,849 times.
Expository essays are often assigned in academic settings. In an expository essay, you need to consider an idea, investigate the idea, then explain the idea. Some expository essays may include an argument, while others are purely informative. [1] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source While it may seem overwhelming, writing an expository essay is easy if you take it one step at a time.
Sample Essay Conclusion

Planning Your Essay

- If you are writing an expository essay for an assignment, read the assignment guidelines. Ask your instructor if anything seems unclear.

- If you are writing your essay for a class assignment, consider what your instructor will expect you to include in your essay.

- Try listing. List all your ideas for your expository essay. Then look over the list you have made and group similar ideas together. Expand those lists by adding more ideas or by using another prewriting activity. [6] X Research source
- Try freewriting. Write nonstop for about 10 minutes. Write whatever comes to mind and don’t edit yourself. After you finish writing, review what you have written. Highlight or underline the most useful information for your expository essay. Repeat the freewriting exercise using the passages you underlined as a starting point. You can repeat this exercise many times to continue to refine and develop your ideas. [7] X Research source
- Try clustering. Write a brief explanation of the subject of your expository essay on the center of a piece of paper and circle it. Then draw three or more lines extending from the circle. Write a corresponding idea at the end of each of these lines. Continue developing your cluster until you have explored as many connections as you can. [8] X Research source
- Try questioning. On a piece of paper, write out “Who? What? When? Where? Why? How?” Space the questions about two or three lines apart on the paper so that you can write your answers on these lines. Respond to each question in as much detail as you can. [9] X Research source

- Trustworthy internet sources usually include academic institutions like universities or research labs, government websites, and non-profit organizations.

- Identify the author and his or her credentials. Think about what qualifies this person to write about their subject. If the source has no author or the author does not have adequate credentials, then this source may not be trustworthy.
- Check for citations to see if this author has researched the topic well enough. If the author has provided few or no sources, then this source may not be trustworthy.
- Look for bias. Think about whether or not this author has presented an objective, well-reasoned account of the topic. If the author seems to value a particular argument or slant that is not supported or only thinly supported by fact, then this source may not be trustworthy.
- Consider the publication date to see if this source presents the most up to date information on the subject.
- Cross-check some of the information in the source. If you are still concerned about a source, cross-check some of its information against a trustworthy source.

- Show when you have quoted a source word for word by putting it into quotation marks. Include information about the source such as the author’s name, article title or book title, and page number.
- Write down the publishing information of each source. You will need this information for your "References," "Bibliography," or "Works Cited" pages. Format this page according to your instructor's guidelines.

- Make sure your thesis is arguable. Do not state facts or matters of taste. For example, "George Washington was the first president of the United States," is not a good thesis because it states a fact. Likewise, "Die Hard is a great movie," is not a good thesis because it expresses a matter of taste. [16] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
- Make sure your thesis provides enough detail. In other words, avoid just saying that something is "good" or "effective." Instead, say what makes something "good" or "effective. [17] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
Introducing Your Essay

- An engaging hook can take many forms. You could start with an anecdote, an informative and attention-grabbing quote, a bold opinion statement, or anything that will make your readers want to continue with your essay.

- If you are writing about a book, provide the name of the work, the author, and a brief summary of the plot.
- If you are writing about a specific day in history, summarize the day's events. Then, explain how it fits into a broader historical scope.
- If you are writing about a person, name the person and provide a brief biography.
- Keep in mind that your context should lead up to your thesis statement. Explain everything your reader needs to know to understand what your topic is about. Then narrow it down until you reach the topic itself.

Expressing Your Main Points

- A five-paragraph essay should include three body paragraphs. Each body paragraph should discuss a piece of supporting evidence that supports your thesis.
- Even if your essay is longer than five paragraphs, the same principles still apply. Each paragraph should discuss a piece of supporting evidence.

- "Dogs played an active role in Marine Corps missions in the Pacific."
- "The Doberman Pinscher was the official dog of the US Marine Corps during WWII, but all breeds were eligible to train as war dogs."
- "War dogs were even eligible to receive military awards for their service."

- Most of your evidence should be in the form of cited quotes, paraphrases, and summaries from your research.
- Your evidence could also come from interviews, anecdotes, or personal experience.
- Try to provide at least two to three pieces of evidence to support each of your claims.
- For example, if a paragraph starts with, "War dogs were even eligible to receive military awards for their service," the supporting evidence might be a list of dogs who got awards and the awards they were given.

- You could write, "Even though Dobermans were the most common breed used in WWII, they were not the only breed, and were not the only dogs recognized for their help."
Concluding Your Essay

- Note that the second sentence repeats the information provided in your original thesis. It just says it in a new way while also hinting at the information you included in the body of the essay.

- Explain how the topic affects the reader
- Explain how your narrow topic applies to a broader theme or observation
- Call the reader to action or further exploration on the topic
- Present new questions that your essay introduced
Expert Q&A

- If you are unsure about anything as you work on your essay, talk to your instructor or meet with a writing tutor for help. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/expository_essays.html
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/expository-essay/
- ↑ Tristen Bonacci. Licensed English Teacher. Expert Interview. 21 December 2021.
- ↑ http://writing.ku.edu/prewriting-strategies
- ↑ https://grammar.yourdictionary.com/grammar-rules-and-tips/tips-on-writing-an-excellent-expository-essay.html
- ↑ http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/reading-and-researching/notes-from-research
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/thesis-statements/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/thesis-statements/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/using_research/quoting_paraphrasing_and_summarizing/index.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/argument_papers/conclusions.html
About This Article

Before you write an expository essay, take some time to jot down ideas for your essay. Try the clustering method by writing a brief explanation of your subject in a bubble in the center of your page. Then, draw 3 or more lines extending from the circle and jot down idea bubbles that connect to your main theme. Once you have a plan for your expository essay, write out an outline to organize what you’re going to say. Make sure to begin your outline with an engaging introduction sentence. After the introduction sentence, provide some background information and include your thesis statement, which is your main argument. If you’re writing a 5 paragraph essay, you should include 3 body paragraphs after your introduction then a conclusion paragraph that summarizes your main points. However you organize your essay, make sure to include credible sources for important information, like statistics, so your teacher knows that it’s accurate. To learn how to use transitions in your essay, read more from our Writing co-author. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Freida Ghabiliha
Nov 24, 2017
Did this article help you?

Qutaiba Raid
Jan 31, 2018
Maryanne Waqa
Aug 23, 2018
Apr 9, 2018
Nov 25, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Essay on Bicycle
500 words essay on bicycle.
A bicycle is a useful vehicle that helps us reach a destination without polluting the environment. It is composed of steel and has two wheels. In addition, it has got a seat and handle with two pedals and also a bell. Some bicycles have a carrier while some don’t. It is a popular choice amongst poor people and students . Essay on bicycle will help us understand its importance.

Importance of Bicycle
Bicycles have become even more important in recent times. While they have been offering us many advantages for a long time, they are very vital now. It is because of the rate at which pollution is growing in the world, they offer a greener way to commute.
In other words, bicycles do not require any petrol or diesel which harms our atmosphere. Further, it does not leave a carbon footprint as well. Thus, it is a great choice for everyone especially those who are environment-friendly.
After that, we see that bicycles do not possess the potential to harm anyone, unlike bikes, cars and buses. If you ride a bicycle, you are less likely to hurt someone or get in an accident as compared to ones who ride bikes or drive cars.
Most importantly, bicycles are great for our health. There are numerous benefits which cycling offers to ensure a healthy life. It is not only a great alternative to gym workouts but also helps prevent cardiovascular diseases .
Therefore, bicycles help to preserve our health. Similarly, they do not harm the environment. Moreover, they are also very beneficial as we can go through narrow roads with a bicycle which we cannot do with bikes or cars.
I have a bicycle which is red and black in colour. My father gifted it to me on my birthday and it is my most cherished present. The name of my bicycle is Turbo Thunder and it has many interesting features.
It comes with different gears and a basket as well. Moreover, it also has a bottle holder and a lock. I cycle every evening with my friends from the neighbourhood. It is very liberating to me to be able to cycle in the pleasant weather without any care.
My father ensures that I always wear my protective gear while cycling to prevent any injuries. I have decorated my cycle with stickers as well to make it more personalized. In addition, I go to my coaching classes on my bicycle only.
Therefore, I love my bicycle and I wish to keep it with me even after growing up. As cycling is good for the environment and our health, I plan to keep cycling for a long time to lead a healthy life and make the environment clean.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conclusion of the Essay on Bicycle
To sum it up, bicycles are great in every aspect, whether it is regarding our health or the health of nature. Moreover, it is also not heavy on the pocket. With the world getting polluted at a faster rate day by day, it is essential for us to switch to bicycles for a healthier life and greener future.
FAQ of Essay on Bicycle
Question 1: What is the importance of a bicycle?
Answer 1: Bicycles are very important as they offer us many health benefits if we cycle regularly. In addition to that, it serves as a great workout session. Most importantly, they are great for the environment as they do not pollute it.
Question 2: Who invented the bicycle?
Answer 2: Karl von Drais was a German who invented the first bicycle. He developed it and named it the ‘swiftwalker’ which hit the road in the year 1817. The early bicycle came with no pedals and the frame was a wooden beam. It has two wooden wheels with irons rims and leather-covered tires.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

The Mechanism Behind the Functioning of a Bicycle – Understanding Its Working Principle
- Post author By bicycle-u
- Post date 08.12.2023
Have you ever wondered how a bicycle works? It may seem like a simple machine, but the working principle behind a bicycle is quite fascinating. At its core, a bicycle is propelled forward by the power of human legs, transferred through the pedals, chain, and gears.
The pedals, located at the front of the bicycle, are connected to a chain. As the rider pushes down on the pedals with their feet, the chain moves, causing the rear wheel to rotate. This rotation is what propels the bicycle forward. The chain is an essential component that transfers the force from the pedals to the wheels.
Another important feature of a bicycle is the gears. The bicycle gears allow the rider to adjust the resistance and speed of their pedaling. The gears are usually located at the rear wheel and can be changed using a gear shifter. By changing the gears, the rider can make it easier or harder to pedal, depending on the terrain or their desired speed.
The saddle, or bike seat, provides support and comfort for the rider. It is positioned above the pedals and allows the rider to sit while pedaling. The saddle is usually adjustable, allowing the rider to find their preferred height and position for maximum comfort.
Finally, the brakes play a crucial role in the working principle of a bicycle. The brakes are typically located on the handlebars and are used to slow down or stop the bicycle. When the rider squeezes the brake levers, the brake pads press against the wheel rims, creating friction and causing the bicycle to slow down or come to a complete halt.
In conclusion, understanding the working principle of a bicycle involves knowing how the pedals, chain, gears, saddle, and brakes work together. The power from the rider’s legs is transferred through the pedals and chain, while the gears and brakes allow for adjustments in speed and control. Next time you hop on your bicycle, take a moment to appreciate the intricate workings that allow you to ride smoothly and enjoy the experience.
How Does a Bicycle Work: Understanding the Working Principle
A bicycle operates on a simple yet effective principle that allows riders to propel themselves forward with ease. Understanding how a bicycle works involves examining its various components, such as gears, brakes, pedals, saddle, handlebars, and chain.
The gears of a bicycle play a crucial role in its functioning. By changing gears, the rider can alter the mechanical advantage, making it easier to pedal up hills or achieve higher speeds on flat surfaces. Gears are located on the rear wheel and connected to the pedals through a chain and a gear mechanism. This mechanism transfers the power generated by the rider’s pedaling into forward motion.
Brakes are essential for controlling the speed and stopping of the bicycle. There are typically two types of brakes on a bicycle: rim brakes and disc brakes. Rim brakes work by applying pressure to the rims of the wheels, while disc brakes use a caliper to clamp down on a disc attached to the wheel hub. Both types of brakes allow the rider to slow down or come to a complete stop when necessary.
The pedals are where the rider applies force to move the bicycle forward. They are attached to crank arms, which are connected to the bottom bracket and the chainrings. As the rider pushes down on the pedals, the rotational motion is transferred to the chainrings and then to the rear wheel through the chain. This motion propels the bicycle forward.
The saddle, or seat, is where the rider sits while cycling. It is designed to provide comfort and support, allowing the rider to maintain a balanced and stable position. The saddle height can be adjusted to accommodate the rider’s leg length and riding style.
Handlebars provide the rider with steering control. They allow the rider to turn the bicycle left or right, maintaining balance and navigating through different terrains. The handlebars are connected to the front fork, which holds the front wheel in place and enables the rider to control the direction of the bicycle.
The chain is a crucial component that connects the front and rear gears. It is responsible for transferring power generated by the rider’s pedaling to the rear wheel, propelling the bicycle forward. The chain needs to be well-lubricated, properly tensioned, and clean to ensure smooth and efficient operation.
Components of a Bicycle
A bicycle is made up of several components that work together to allow it to function properly. These components include:
- Gears: Gears are an essential part of a bicycle and are responsible for changing the bike’s speed and resistance. They allow the rider to adjust the effort needed to pedal.
- Handlebars: The handlebars are used for steering the bicycle. They provide control and stability while riding.
- Brakes: Brakes are crucial for safety. They help the rider slow down or stop the bicycle by applying pressure to the wheels.
- Pedals: Pedals are where the rider places their feet to propel the bicycle forward. They are connected to the bike’s crankset, which transfers the rider’s pedaling motion to the wheels.
- Saddle: The saddle, or seat, is where the rider sits while cycling. It is designed for comfort and support during long rides.
- Chain: The chain is an integral part of the bicycle’s drivetrain. It connects the pedals to the rear wheel, transferring power from the rider to the bike.
These components work together based on the fundamental principle of mechanics to allow a bicycle to function properly and provide an efficient means of transportation.
Frame and Structure
The frame of a bicycle is the main structure that holds all the components together. It is usually made of steel, aluminum, or carbon fiber, which provides strength and durability while keeping the weight of the bicycle manageable.
The frame is designed to support the rider’s weight and provide stability during cycling. It consists of various tubes and joints that are strategically positioned to maximize the strength and efficiency of the bicycle.
One essential component of the bicycle’s frame is the chainstay. The chainstay is a tube that connects the bottom bracket, which houses the crankset and pedals, to the rear dropouts, where the rear wheel is attached. It ensures proper alignment and tension of the chain, enabling power transfer from the rider’s legs to the rear wheel.
The saddle, or seat, is another important part of the bicycle’s frame. It is attached to the seatpost, which is inserted into the seat tube of the frame. The saddle provides a comfortable and stable platform for the rider, allowing them to exert force on the pedals efficiently.
The working principle of a bicycle’s frame and structure is based on the use of gears. Gears allow the rider to change the mechanical advantage of the bicycle, making it easier to pedal uphill or faster on flat surfaces.
The gears are controlled by the shifters, which are usually located on the handlebars. When the rider operates the shifters, the chain moves between different-sized chainrings and rear sprockets, altering the gear ratio and affecting the resistance and speed of the bicycle.
In addition to the gears, the bicycle’s pedals play a crucial role in the working of the bike. The pedals are attached to the crankset, which is connected to the bottom bracket. As the rider pushes down on the pedals, the crankset rotates, transferring power to the rear wheel through the chain and drivetrain.
Finally, the bicycle’s frame and structure also include the braking system. Most bicycles use caliper or disc brakes, which are mounted on the frame and fork. When the rider squeezes the brake levers, the brake pads apply pressure to the rims (in the case of caliper brakes) or rotors (in the case of disc brakes), causing the bicycle to slow down or stop.
Wheels and Tires
The wheels and tires of a bicycle are essential components that play a crucial role in how the bicycle works. They are responsible for providing stability, support, and traction while the bicycle is in motion.
The wheels of a bicycle are typically made up of a rim, spokes, and a hub. The rim is the outer circular part of the wheel that holds the tire in place. The spokes are the rods that connect the rim to the hub, providing structural support and distributing the weight of the bicycle and the rider evenly. The hub is the center part of the wheel that contains bearings which allow the wheel to rotate smoothly.
The tires of a bicycle are made of rubber and are responsible for providing grip and cushioning. They come in different sizes and patterns depending on the terrain the bicycle is designed to ride on. The tires are connected to the rims and inflated with air to provide a comfortable ride and absorb shock from uneven surfaces.
The wheels and tires work together with other components of the bicycle, such as the chain, handlebars, pedals, and brakes, to ensure the bicycle is functioning properly. When the rider pedals the bicycle, the chain transfers the energy from the rider’s legs to the rear wheel, propelling the bicycle forward. The handlebars allow the rider to steer the bicycle in the desired direction, while the pedals enable the rider to control the speed and movement of the bicycle. The brakes are used to slow down or stop the bicycle, providing safety and control.
Understanding the working principle of the wheels and tires of a bicycle is crucial for anyone who wants to maintain and ride a bicycle efficiently. Keeping the wheels properly aligned, tires inflated, and bearings lubricated will ensure the bicycle performs optimally, providing a smooth and enjoyable ride.
Brakes and How They Work
Brakes are an essential component of a bicycle’s safety system. They allow the rider to slow down or stop the bike when needed, ensuring control and preventing accidents.
There are two main types of brakes commonly used on bicycles:
- Rim brakes: These brakes work by applying friction to the rim of the wheel. When the rider squeezes the brake lever, the brake pads are pressed against the rim, creating friction that slows down the rotation of the wheel. Rim brakes are commonly found on road bikes and some mountain bikes.
- Disc brakes: These brakes use a disc attached to the wheel hub. When the rider pulls the brake lever, hydraulic or mechanical pressure is applied to squeeze brake pads against the disc, creating friction and slowing down the wheel. Disc brakes provide more stopping power and better performance in wet conditions, making them popular for mountain biking and some road biking.
Regardless of the type, the basic working principle of brakes involves converting the kinetic energy of the moving bike into heat energy through friction. When the rider applies the brakes, the brake pads grip either the rim or the disc, creating resistance and transforming the bike’s forward motion into heat. This heat is then dissipated into the surrounding air.
To ensure effective braking, it’s important to regularly check and maintain the brakes. This includes inspecting the brake pads for wear, adjusting the brake cables for proper tension, and ensuring that the braking system is clean and free from debris. Properly functioning brakes are essential for safe and controlled cycling.
Transmission and Gears
The transmission system is an essential component of a bicycle that allows for efficient and smooth power transfer from the rider to the wheels. It consists of the chain, gears, and derailleurs.
When a rider sits on the saddle and holds onto the handlebars, they can use the pedals to turn the crankset. As the pedals rotate, the chain connected to the crankset also moves. The principle behind the transmission system is that when the rider exerts force on the pedals, the chain transfers this force to the gears, which then multiply the force.
Gears are located on the rear wheel and the crankset. They come in different sizes and are used to change the gear ratio. By changing gears, the rider can pedal with less effort on flat terrain or increase the force applied on uphill sections. The front gears, called chainrings, are controlled by the left gear shifter, while the rear gears, known as cassette or freewheel, are controlled by the right gear shifter.
The gears work together with the bicycle’s brakes to provide control and stability. By shifting gears, the rider can adjust the speed and resistance. For example, when going downhill, the rider can shift into a higher gear to increase speed. Conversely, when going uphill, the rider can shift into a lower gear to provide more power without exerting too much effort.
Chain and Pedals
The chain and pedals are essential components in the working principle of a bicycle. They play a crucial role in transferring the energy generated by pedaling into forward motion.
When a cyclist pedals, the chain, which runs through a series of gears, transfers the rotational force from the pedals to the rear wheel. This chain drive mechanism is what allows the bicycle to move by converting the pedaling motion into kinetic energy.
The pedals, located at the bottom bracket, are attached to the crankset. When the cyclist applies force to the pedals, the crankset rotates, causing the chain to move and engage with the gears on the rear wheel.
The chain and pedals work together with other components like brakes, saddle, handlebars, and gears to enable smooth and efficient cycling. It is essential to keep the chain well-lubricated and properly tensioned to ensure optimal performance.
In conclusion, the chain and pedals are integral parts of a bicycle’s working principle, as they facilitate the transfer of energy from the cyclist to the wheels. Understanding how these components interact allows riders to optimize their pedaling efficiency and enjoy a smoother and more enjoyable riding experience.
Handlebars and Steering Mechanism
The handlebars of a bicycle play a crucial role in controlling its direction. These handlebars are connected to the steering mechanism, allowing the rider to easily navigate and steer the bicycle. The steering mechanism consists of various components that work together to ensure smooth and precise steering.
One of the key components of the steering mechanism is the fork, which holds the front wheel in place. The fork is connected to the frame of the bicycle and allows the front wheel to rotate freely. This rotation is controlled by the handlebars, which are attached to the fork.
When the rider turns the handlebars, it causes the fork to turn, changing the direction of the front wheel. This simple principle allows the rider to steer the bicycle left or right, depending on the desired direction. It is important to note that the handlebars and steering mechanism are designed in a way that the front wheel always rotates in the opposite direction of the handlebars.
To ensure stability and control while steering, the handlebars are typically equipped with brakes. These brakes allow the rider to slow down or stop the bicycle when needed. The braking mechanism is usually connected to the handlebars, enabling the rider to easily apply the brakes by squeezing the brake levers.
In addition to the handlebars and steering mechanism, other components such as pedals, gears, and the chain play a crucial role in the overall working of a bicycle. The pedals provide the power to move the bicycle forward, while the gears help in adjusting the effort required to pedal. The chain transfers the power from the pedals to the rear wheel, enabling the bicycle to move efficiently.
Overall, understanding the working principle of a bicycle and its various components, including the handlebars and steering mechanism, helps riders have better control and enjoy a safe and smooth riding experience.
Saddle and Seatpost
The saddle and seatpost are essential components of a bicycle. The saddle is the seat that the rider sits on, while the seatpost is the tube that connects the saddle to the frame of the bicycle. Together, they provide support and comfort for the rider during their cycling journey.
When it comes to the working principle of the saddle and seatpost, several factors come into play. Firstly, the saddle needs to be adjusted to the right height for the rider. This ensures that the rider’s legs are properly extended when pedaling, maximizing efficiency and power.
The seatpost allows for this adjustment by allowing the saddle to be raised or lowered. It typically has a clamp mechanism that holds the saddle securely in place at the desired height. The seatpost is inserted into the frame of the bicycle and can be adjusted by loosening the clamp and sliding it up or down.
Another important aspect of the saddle and seatpost is comfort. The saddle is typically padded and contoured to provide cushioning and support for the rider. It is designed to distribute the rider’s weight evenly, reducing pressure on sensitive areas.
Additionally, some saddles have features such as cutouts or gel inserts to further enhance comfort. The seatpost may also have suspension or shock-absorbing capabilities to absorb vibrations and impacts from the road, further reducing discomfort.
The saddle and seatpost are also integral to the rider’s control and stability of the bicycle. The saddle provides a stable platform for the rider to sit on, while the seatpost ensures that the saddle remains in place during riding. This stability is crucial for maintaining balance and maneuvering the bicycle.
In conclusion, the saddle and seatpost play a crucial role in the working principle of a bicycle. They provide support, comfort, and stability for the rider, allowing them to pedal efficiently, control the bicycle, and enjoy a smooth and comfortable cycling experience.

Suspension Systems
In addition to the gears, chain, saddle, working principle, brakes, and pedals, another vital component of a bicycle is the suspension system. The suspension system plays a crucial role in providing comfort and control while riding on uneven terrain or rough surfaces.
A bicycle suspension system consists of various components, such as forks, shock absorbers, and springs, all working together to absorb shocks and vibrations from the road. This helps to improve traction, stability, and overall riding experience.
The front suspension system, commonly known as the forks, is located at the front wheel of the bicycle. It is designed to absorb impacts from the front wheel hitting bumps and uneven surfaces.
The forks are typically equipped with shock absorbers and springs to dampen the impact and provide a smoother ride. This allows the rider to maintain better control and stability over the bicycle, especially in off-road or downhill conditions.
Rear Suspension
Some bicycles also come with rear suspension systems, which are located near the rear wheel. Similar to the front forks, the rear suspension system helps absorb shocks and vibrations from the rear wheel hitting rough surfaces.
These rear suspension systems often use a combination of shock absorbers, springs, and linkages to provide a smooth and comfortable ride. They are especially useful for mountain biking and other off-road activities, where rough terrains are common.
Overall, suspension systems are crucial for maintaining rider comfort and control on a bicycle. They help to absorb shocks and vibrations from the road, allowing for a smoother and more enjoyable riding experience.
How the Pedaling Power is Transferred
When you ride a bicycle, the power generated by pedaling is transferred to the wheels through a series of components.
The key component responsible for transferring power is the chain. The bicycle chain connects the pedals to the rear wheel, allowing the rider’s leg movement to be translated into forward motion.
Most bicycles have multiple gears, controlled by the rider using the handlebars. These gears allow the rider to adjust the level of resistance and optimize efficiency depending on the terrain and desired speed.
When the rider turns the pedals, the chain engages with the gears on the rear wheel. As the gear ratio changes, the force applied to the pedals is multiplied or reduced, allowing the rider to pedal with more or less effort.
The pedaling power is transferred from the chain to the rear wheel through the rear sprocket. The chain wraps around the sprocket and spins it, causing the rear wheel to rotate.
It’s important to note that the transfer of power is not one-directional. When the rider stops pedaling or applies the brakes, the motion of the wheels can also transfer force to the pedals. This is known as “coasting” and allows the rider to maintain momentum without pedaling.
Handlebars and Brakes
The handlebars of the bicycle play a crucial role in maintaining control and steering. By turning the handlebars, the rider can change the direction of the front wheel, allowing the bicycle to turn.
The brakes, located near the handlebars, allow the rider to slow down and stop the bicycle. When the brake levers are squeezed, they activate the brake pads, which press against the wheel rims, creating friction and reducing speed.
Other Considerations
In addition to transferring power, the bicycle’s saddle, also known as the seat, provides support and comfort for the rider. It is designed to distribute weight evenly and reduce pressure on specific areas of the body.
Understanding the principle of how power is transferred on a bicycle can help riders optimize their pedaling technique, select appropriate gears, and maintain control and safety while riding.
Overall, the efficiency of power transfer plays a significant role in the overall performance and enjoyment of cycling.
Balance and Stability
One of the key factors that contribute to the smooth functioning of a bicycle is balance and stability. The way a bicycle is designed allows it to stay upright and travel in a straight line, even when the rider is pedaling at high speeds or taking tight turns.
The bicycle’s frame is carefully engineered to provide optimal balance and stability. The location of the pedals, handlebars, and seat is strategically positioned to ensure a comfortable and efficient riding experience. Additionally, the weight distribution of the bicycle is designed to keep the center of gravity low, enhancing stability.
The brakes play a crucial role in maintaining balance and stability. By applying pressure to the brakes, the rider can slow down or come to a complete stop, preventing the bicycle from tipping over. The principle behind the working of the brakes involves friction, as the brake pads press against the wheel rims to generate the required stopping power.
Another important component that contributes to the balance and stability of the bicycle is the chain and gears. The chain connects the pedals to the gears, allowing the rider to transfer power from their legs to the wheels. The gears, on the other hand, provide different levels of mechanical advantage, enabling the rider to pedal efficiently and maintain a steady speed even on various terrains.
Furthermore, the rider’s body position plays a significant role in maintaining balance and stability. By shifting their body weight and using their muscles, the rider can control the direction of the bicycle and make necessary adjustments to keep it balanced. The handlebars provide the necessary control and maneuverability, allowing the rider to steer the bicycle effortlessly.
In conclusion, the balance and stability of a bicycle are a result of various factors working together. The careful design of the frame, the functionality of the brakes, the utilization of gears and pedals, and the rider’s skills all contribute to the smooth and stable movement of a bicycle.
Effect of Weight Distribution
One important factor that affects the performance of a bicycle is weight distribution. The principle behind weight distribution is based on the idea that proper distribution of weight enhances the stability and handling of the bicycle.
Balance and Control
The chain, brakes, gears, handlebars, saddle, and pedals all contribute to the working of a bicycle. However, the proper distribution of weight plays a crucial role in ensuring a safe and stable ride.
When riding a bicycle, the weight should be balanced both vertically and horizontally. Vertically, the weight should be evenly distributed between the front and rear wheels. This helps to maintain traction and prevent the bike from tipping forward or backward.
Horizontally, the weight should be centered around the bike’s center of gravity. This allows for better control and maneuverability, especially while turning or cornering. If the weight is not properly distributed, it can affect the bike’s stability and make it harder to control.
Effects on Handling
The position of the rider’s body also affects weight distribution. Leaning forward or backward can shift the weight distribution, influencing the bike’s handling and stability. For example, leaning forward can put more weight on the front wheel, improving traction and steering response. On the other hand, leaning backward can shift more weight to the rear wheel, making it easier to perform tricks or maneuvers that require rear-wheel control.
Similarly, the position of accessories or cargo can also impact weight distribution. Adding a backpack or attaching panniers can change the distribution of weight, potentially affecting the bike’s balance and handling.
In conclusion, weight distribution is a critical factor in bicycle performance. Finding the optimal weight distribution can enhance stability, control, and maneuverability, making for a smoother and safer ride.
Physics of Bicycle Motion
Gears : The gears on a bicycle are an important component of how it works. By changing gears, the cyclist can adjust the amount of force needed to pedal and the speed at which the bicycle is moving. This is achieved by altering the ratio of the size of the gears on the front and rear wheels.
Saddle : The saddle, or seat, of the bicycle plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and stability. It provides support to the rider and allows them to control the bike’s motion by shifting their weight and position on the saddle.
Pedals : The pedals are attached to the crankset, which is connected to the chainring. When the cyclist pushes down on the pedals, the crankset rotates, causing the chainring to turn, which in turn propels the bicycle forward.
Handlebars : The handlebars allow the cyclist to steer the bicycle. By turning the handlebars, the front wheel is directed in the desired direction, and the bicycle follows suit. The handlebars also provide stability and control while riding.
Brakes : The brakes on a bicycle are a vital safety feature that allows the rider to slow down or stop the bicycle. They work by applying a force to the wheels, creating friction and decreasing the rotational motion, ultimately reducing the speed of the bicycle.
In principle, the motion of a bicycle can be understood through the interactions between its various components. The chain transfers the energy from the pedaling motion to the rear wheel, propelling the bicycle forward. The cyclist’s weight distribution on the saddle and movements of the handlebars control the direction and stability of the bicycle. Gears and brakes provide the means to adjust the force applied and the speed of the bicycle, allowing for efficient and controlled motion.
Factors Affecting Bicycle Speed
There are several factors that can affect the speed at which a bicycle can travel. These factors include:
- Brakes: The type and condition of the brakes on a bicycle can affect its speed. Well-maintained and properly adjusted brakes can provide efficient and quick stopping power, allowing the rider to apply more force to the pedals without worrying too much about stopping.
- Saddle: The saddle, or seat, of a bicycle plays a crucial role in speed. A comfortable and properly adjusted saddle allows the rider to maintain a more efficient pedaling motion and transfer power more effectively to the pedals.
- Handlebars: The position and type of handlebars can also impact speed. Different handlebar styles offer different riding positions, and finding the right fit can improve aerodynamics and reduce wind resistance. A more aerodynamic riding position can lead to higher speeds.
- Pedals: The type of pedals on a bicycle can affect speed as well. Pedals with a larger surface area or with clips and straps can provide a more secure connection between the foot and pedal, allowing for better power transfer and more efficient pedaling.
- Bicycle: The type and quality of the bicycle itself can impact speed. Bicycles designed for speed often have lightweight frames, aerodynamic shapes, and low rolling resistance tires. These features can help reduce drag and make it easier for the rider to maintain higher speeds.
- Working Gears: The gearing system of a bicycle can greatly affect speed. By shifting gears, riders can find the optimal gear ratio for the terrain, allowing them to pedal at a comfortable cadence and maintain speed more efficiently.
- Chain: A well-maintained and properly lubricated chain is essential for a smooth and efficient ride. A dirty or rusty chain can cause energy loss and reduce speed.
By considering these factors and optimizing their bike setup, riders can achieve higher speeds and enjoy a more efficient and enjoyable cycling experience.
Common Bicycle Maintenance and Repairs
Keeping your bicycle in good working condition is essential for a safe and enjoyable riding experience. Regular maintenance and repairs can help extend the lifespan of your bicycle and ensure that it performs optimally. Here are some common maintenance tasks and repairs that every cyclist should know:
Brake Adjustment and Replacement
The brakes on a bicycle play a crucial role in ensuring your safety. Over time, brake pads can wear out and lose their effectiveness. Regularly check the brake pads for wear and replace them if necessary. Additionally, adjust the brakes so that they engage properly when the brake lever is squeezed.
Chain Lubrication and Replacement
The chain is an important component of the bicycle that transfers the power from the pedals to the wheels. It is essential to keep the chain properly lubricated to reduce friction and prevent premature wear. Regularly clean and lubricate the chain, and replace it if it becomes stretched or damaged.
Properly Adjusting the Saddle and Pedals
The saddle and pedals on your bicycle should be adjusted to provide maximum comfort and efficiency. Ensure that the saddle is at the correct height and angle for your riding style, and that the pedals are securely attached and functioning properly.
Working with Gears
Most bicycles have multiple gears that allow you to adjust your pedaling effort to different terrains. It is important to regularly check the gears and make any necessary adjustments to ensure smooth shifting. Keep the gears clean and lubricated, and replace any worn or damaged components.
Handling Handlebars
The handlebars are an essential part of the bicycle that allows you to steer and control the bike. Regularly check the handlebars for proper alignment and tighten any loose bolts or screws. Lubricate the moving parts of the handlebars, such as the stem and headset, to ensure smooth operation.
By regularly performing these maintenance tasks and repairs, you can ensure that your bicycle remains in excellent working condition and enjoy many more miles of riding.
Questions and answers:
How does a bicycle work.
A bicycle works by converting the energy produced by the rider into mechanical energy that propels the bike forward. This is achieved through a combination of pedals, gears, and a chain that transfer the energy from the rider’s legs to the wheels.
What are the main components of a bicycle?
The main components of a bicycle include the frame, wheels, tires, pedals, chain, gears, brakes, handlebars, saddle, and various other smaller parts. Each of these components has a specific function that contributes to the overall functionality of the bike.
How do the brakes on a bicycle work?
The brakes on a bicycle work using a system of calipers or disc brakes that apply friction to the wheel rims or brake discs, respectively, to slow down or stop the bike. When the brake lever is squeezed, a cable or hydraulic system engages the brakes, causing them to press against the wheel rims or brake discs, which creates friction and slows down the bike.
What is the purpose of gears on a bicycle?
Gears on a bicycle serve the purpose of allowing the rider to adjust their pedaling effort according to the terrain and desired speed. By changing gears, the rider can make it easier to pedal uphill or increase their speed on flat ground. The gears achieve this by altering the ratio between the speed at which the rider pedals and the rotation of the bike’s wheels.
How does the chain on a bicycle work?
The chain on a bicycle transfers the energy produced by the rider through the pedals to the rear wheel, propelling the bike forward. The chain is connected to the pedals on one end and to a cassette or cog on the rear wheel on the other end. As the rider pedals, the chain moves along the cassette, causing the rear wheel to rotate and propel the bike forward.
How does a bicycle move forward?
A bicycle moves forward by the rider pedaling, which turns the pedals, generating rotational motion. This motion is transferred to the chain, which then moves the rear wheel, propelling the bicycle forward.
Related posts:
- Bicycle Disc Brake Problems – Common Issues and How to Solve Them
- The Importance of Maintaining and Replacing Your Bike Chain to Ensure Optimal Performance and Durability
- Why Your Bicycle Brakes Are Failing and How to Fix Them
- Learn How to Clean, Lubricate, and Maintain Your Bicycle Chain for Optimal Performance
- Efficiency, Maintenance, and Longevity of Bicycle Chains – Everything You Need to Know
- Everything You Need to Know About Bicycle Brakes – From Types to Maintenance
- The Evolution of the Cycle Chain – From Invention to Modern Engineering Marvel
- Bicycle Cantilever Brakes – Everything You Need to Know About this Essential Bike Component

- Bundle & Save
- Explainer Video
- The Journal
- Handlebar Mount
- Charge Cases
- Universal Connector
Your cart is empty
Learning to Ride a Bike: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
Sep 27, 2023

Remember the feeling of freedom and joy when you first experienced learning to ride a bike? The wind in your hair, the exhilarating sense of speed, and the satisfaction of mastering a new skill? If you or someone you know is looking to embark on this exciting journey, you’ve come to the right place! We have developed a comprehensive, step-by-step guide to help beginners learn the art of cycling. From choosing the right bike and gear to mastering balance, steering, and braking, our guide will provide all the essential information and tips for a successful and enjoyable learning to ride a bike experience.
So, are you ready to embark on this adventure and discover the joy of cycling? Let’s get started on the road to mastery, one pedal stroke at a time!
Key Takeaways
- Choose the right bike and gear for a comfortable ride.
- Master balancing, steering, braking techniques to gain confidence on two wheels.
- Interact confidently with other cyclists & traffic to ensure a safe cycling experience!
Choosing the Right Bike and Gear

The first step in your journey to becoming a confident cyclist is choosing the right bike and gear. A comfortable and safe learning experience begins with a bike that fits you well and allows you to stand over the middle of the bike with plenty of clearance from the top tube. For children who are just starting, consider using training wheels for added support. Equally important is selecting the right gear, such as a well-fitting helmet and appropriate clothing that won’t restrict your movements while pedaling. Steer clear of long, loose skirts, loose pants, and open-toed shoes to avoid any potential accidents.
If you like having your phone on you, then you will want to choose a quality phone mount that will allow you to keep your phone mounted to your handlebars so you can keep your phone within view on your rides. Be sure to find a mount and phone case that offers wireless charging so you won't have to worry about a dead phone.
Once you’ve found the perfect bike and gear, it’s time to make some essential adjustments for a comfortable ride. Ensure the brake levers are conveniently placed for easy access and check the seat post for proper height adjustment. With these preparations in place, you’ll be ready to embark on your first ride and experience the thrill of cycling!
Preparing for Your First Ride

You need to make a few preparations before embarking on your first ride. Start by checking the brakes and tires to ensure they’re functioning correctly and inflated to the correct pressure.
Next, adjust the seat height and handlebars for a comfortable fit. Ideally, your feet should be flat on the ground when seated, with a slight bend in the knees. This will allow you to maintain control and balance while you learn.
Finally, find a large, flat area like a tennis or basketball court or a parking lot – the perfect place to practice your skills in a straight line without the distractions of heavy traffic or obstacles.
Checking Brakes and Tires
Before heading out, make sure your brakes work properly and your tires are correctly inflated. Squeeze the brake levers to check that they are engaging properly. The correct tire pressure for your bike will depend on the type and size of the tires, so refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for the best results.
Taking these precautions will not only help you enjoy riding more, but also help you avoid riding in unsafe conditions on your journey.
Adjusting Seat Height and Handlebars
A comfortable and safe riding experience depends on correct seat height and handlebar position. To adjust the seat height, lower it until you can comfortably have both feet flat on the ground while seated. This position will help you maintain control and balance as you learn to ride. When adjusting the handlebars, loosen the bolt on the stem and move the spacers up or down to achieve the desired height. Don’t forget to tighten the bolt securely after making your adjustments to ensure a safe ride.
With the seat and handlebars adjusted to your liking, it’s time to practice mounting and dismounting the bike. Start by leaning the bike towards you while applying the brakes. This will help you get used to the feel of the bike and make it easier to mount and dismount smoothly and safely.
Mastering the Basics: Balance and Steering
Mastering balance and steering is a pivotal part of learning to ride a bike. A great way to develop these skills is by starting with a balance bike or removing the pedals from a regular bike. This allows you to focus on balancing and steering without the added distraction of pedaling. The foundation of your cycling success lies in your ability to maintain balance on two wheels while navigating turns and avoiding obstacles.
To practice balance and steering, begin by pushing off with your feet and maintaining balance as you glide along the ground. This will help you get comfortable with the feel of the bike and how it responds to your movements. As you become more confident in your ability to balance, you can start practicing turns while gliding, gradually increasing the complexity of your maneuvers to hone your steering skills.
Starting with a Balance Bike or Removing Pedals
Balance bikes, ideal for beginners, help children learn balancing and steering quickly without the distraction of pedaling. Alternatively, you can remove the pedals from a regular bike to focus on mastering balance and steering. This method is particularly effective for 16’’ bikes and larger, but can also be used with smaller bikes. By eliminating the need for pedaling, children can focus on developing their balance and steering skills, laying the foundation for a successful cycling experience.
To practice balancing and steering, have the child:
- Push off with their feet and attempt to maintain balance as they glide along the ground.
- Encourage them to look ahead and anticipate turns, as this will help them maintain their inner balance and direction.
- As they become more confident in their ability to balance and steer, they can progress to more complex maneuvers and longer distances.
Practicing Gliding and Steering
To practice gliding and steering, follow these steps:
- Start by pushing off with your feet and maintaining balance as you glide along the ground.
- Keep your raised foot forward to maintain a forward weight bias and help you stay steady while riding.
- As you become more confident, challenge yourself to coast for longer periods of time.
- Practice turning to the right and left.
- When you feel confident, try doing large figure eights, making wide turns in both directions for an extra challenge.
Stay alert and look far ahead for any road debris or hazards to stay safe on the road. As you practice gliding and steering, focus on maintaining your balance through momentum and being mindful not to over-correct with steering inputs. With practice and patience, you’ll soon master the art of gliding and steering and be ready to progress to the next stage of learning to ride a bike.
Developing Confidence in Braking
Developing confidence in braking is a fundamental skill for beginner cyclists. Proper braking ensures that you can safely control your bike in various situations, from navigating turns to stopping quickly in an emergency.
By learning to apply even pressure on both brakes and practicing different braking techniques, you’ll build confidence in your ability to control the bike and ensure a safe and enjoyable cycling experience.
Applying Even Pressure on Both Brakes
For smooth and controlled stops, it’s important to learn how to apply even pressure on both brakes. Using both the front and rear brakes evenly will help you stay in control of the bike and prevent skidding or tipping over.
For beginner cyclists, practicing braking off the bike is a great way to get comfortable with the braking system. Here’s how:
- Walk alongside your bike and slowly push it along the street.
- Practice pulling the brakes to slow the bike down and stop.
- This will help you develop the muscle memory needed to apply even pressure on both brakes when it’s time to ride.
Practicing Braking Techniques
Practicing different braking techniques can help you build confidence in your ability to control the bike. To slow down, gradually stop pedaling and press down firmly on the brakes. Take small steps! Practice stopping every 15 to 20 feet until you become comfortable doing it. With enough practice, you will be able to do this with ease and confidence.
As you become more proficient in braking, strive for a smooth, controlled stop that’s not too abrupt or jerky. By mastering various braking techniques, you’ll be better prepared to handle any situation on your bike, from navigating tight turns to reacting quickly in an emergency without having to lose control.
Learning to Pedal and Ride

After mastering balance, steering, and braking, the next step is to learn pedaling and riding. This stage involves starting with one foot on the ground, gaining momentum, and maintaining balance while using the left pedal and its counterpart to propel yourself forward.
As you become more comfortable with pedaling, you can start to explore longer distances and more challenging terrain, building your cycling skills and confidence along the way.
Beginning with One Foot
To start pedaling, follow these steps:
- Place one foot on the ground and the other foot on the pedal in the two o’clock position.
- Push off with your foot on the ground and maintain your balance as you begin to pedal.
- As you practice this technique, focus on maintaining your balance and taking it slow to ensure success.
Regular practice will help you develop the coordination and stability needed to ride confidently on two wheels.
Gaining Momentum and Maintaining Balance
As you become more comfortable with pedaling, work on gaining momentum and maintaining balance while riding. Pedal steadily and fluidly to make the most of your efforts and avoid sudden spurts of speed or braking, which can impede your progress.
To stay balanced while riding, follow these steps:
- Keep your raised foot forward.
- Anticipate turns by easing off the pedal and coasting gracefully through the turn.
- Resume pedaling when you come out of the turn.
By following these steps, you can maintain balance and ride smoothly.
Practicing these techniques will help you develop the skills necessary to ride with confidence and control, enabling you to tackle more challenging rides and explore new cycling adventures.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Beginner cyclists may face common challenges like dealing with road hazards and interacting with other cyclists and traffic. By learning how to safely navigate these situations and developing the skills to handle various cycling scenarios, you’ll be better equipped to overcome these challenges and continue to enjoy the thrill of cycling.
Developing the skills to handle various cycling scenarios is key to overcoming these challenges. Knowing how to do this is key.
Dealing with Road Hazards
Road hazards, such as potholes and debris, can pose a threat to cyclists, especially beginners. To safely navigate these hazards, follow these tips:
- Stay alert and look far ahead for any potential obstacles.
- Slow down and adjust your riding position as needed to maintain control of your bike.
- Avoid collisions with obstacles by swerving or maneuvering around them.
By following these tips, you can safely navigate road hazards and enjoy your cycling experience.
By anticipating road hazards and responding appropriately, you can ensure a safer and more enjoyable ride.
Interacting with Other Cyclists and Traffic
For cyclists of all levels, it’s important to know how to interact with other cyclists and traffic. As a beginner, it’s crucial to follow the same rules of the road as other vehicles, such as stopping at stop signs and red lights, yielding to pedestrians, and riding in the same direction as traffic. It’s also important to signal your turns clearly and confidently to let other road users know your intentions.
By maintaining a safe distance from vehicles and other obstacles, you can ensure a secure ride and avoid potential accidents. Developing these skills will not only help you stay safe on the road, but also enable you to interact confidently with other cyclists and traffic, making your cycling experience more enjoyable.
In conclusion, learning to ride a bike is an exciting and rewarding journey that opens the door to a world of freedom, adventure, and fun. By following our step-by-step guide, you’ll master the essentials of cycling, from choosing the right bike and gear to developing balance, steering, braking, and pedaling skills. Along the way, you’ll also learn to overcome common challenges faced by beginner cyclists, such as dealing with road hazards and interacting with other cyclists and traffic.
So, whether you’re a first-time rider or helping someone else discover the joy of cycling, remember that patience, practice, and perseverance will lead you to success. Embrace the adventure, enjoy the ride, and soon you’ll be pedaling confidently into a world of new experiences and possibilities!
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to learn to ride a bike.
Learning to ride a bike is an achievable task, taking between 45 minutes and several weeks depending on the child’s age, coordination development, and previous exposure.
Patience is key!
What age should a child be able to ride a bike?
Your child is ready to learn to ride a bike between the ages of 4 and 8 when they’ve developed enough coordination, agility, and balance.
Every child is different, however, so you are the best judge of when your child is ready.
How should a beginner learn to ride a bike?
Start by ensuring you have the right fit for the bike, practice hopping on and off the bike, become comfortable with braking, learn how to glide and maintain your balance, then use your dominant leg to push off and start pedaling.
What should I look for when choosing the right bike and gear?
Choose a bike that fits your size and is comfortable, and make sure you have the proper safety equipment like a helmet and appropriate clothing.
Be sure to find gear that won’t limit your movements while pedaling.
How can I practice and improve my balance and steering skills?
Practice your balance and steering by starting with a balance bike or removing the pedals from a regular bike and focus on gliding and steering.
Push off and maintain balance while turning for better results.
Reading next

Gravel Biking: A Guide to Off-Road Adventure

Bicycles Helmets: Everything You Need To Know
Leave a comment
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Free Shipping
Free worldwide shipping on all orders.
Shop With Confidence
If you don’t love your StrideCharge product, send it back within 30 days after receiving your order for a full refund.
5 Star Reviews
Over 350 verified 5 star reviews from happy Stride customers.
Secure Payment
Our secure payment structure will make sure your information is always safe.

Inspiring stories move our planet forward
Participate

Planet Forward 2024 Storyfest Finalists

Ask PF: Climate Advice for Students, by Students

Our Correspondents

The Indigenous Correspondents Program
Across the Wards: Diverse viewpoints on a common mission

Feeding the Future: Planet Forward in Arizona

Apply for the Planet Forward Summer Seminar

Transforming Iceland: Where Sustainability Meets Growth

Planet Forward Series Hub

Planet Forward Opportunities
Essay | Riding bicycles to save the planet
Phillip Ayetigbo
Wole Adegbule
Planet Forward Correspondent | Obafemi Awolowo University Ile-Ife
Related Topics:
Share on Social Media:
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on FaceBook

One time when I was a child, I waited for weeks, hoping to see my father arrive and lead us to the annual Christmas gathering. After some time, he still had not come and we were getting sick of waiting.
But all of a sudden, my friends glimpsed him from afar and one of them ran inside to notify me of my father’s long awaited arrival. I rushed outside watching him come closer and closer. He was not walking or driving, but riding on a strange device.
My old man was riding on a bicycle wearing a beautiful smile. I’m sure he expected me to return the smile but I became disappointed the more he drew closer, so I turned my back. I went inside the house with my head hanging down.
I had suffered disappointment because I saw my father on a bicycle when virtually all the other fathers on my street had by that time switched to cars.
For a long time, bicycles had been a popular form of transportation for people of all classes in Nigeria. Then in the early 1990s, the mentality shared by most people in my community changed to prefer cars over bicycles, relegating them to be considered only suitable for the poor and lower class.
The use of bicycles in Nigeria has been drastically reduced over the years in the name of development, notably since the beginning of the 4 th Republic. This period of economic and political reform in Nigeria started in 1999 and initiated many market reforms.
These days, almost everyone prefers motorcycles for both close and long distance trips. Car ownership has even turned into competition, with many seeing cars as a status symbol.
According to O.J. Matthew, a Research Fellow in the Institute of Ecology and Environmental Studies, Obafemi Awolowo University Nigeria, “Carbon dioxide and other notable greenhouse gases, such as methane, tropospheric ozone, and halogen gases, are known to produce a warming effect that triggers climate change.” Individuals have some control over greenhouse gas emissions as, “one of the leading sources of carbon emissions to the atmosphere is transportation. Therefore, choosing to always ride a bicycle over a few car trips, as your transportation habits, could significantly help to protect the environment from climate change impacts ,” Matthew said.
Unfortunately, according to CEIC Data Global Database , vehicle registrations rose nationally in Nigeria from 3,750 in 2015 to 11,605 in 2020.
My efforts to save the bikes
In my neighborhood, it is not uncommon to see a family of five with five different cars parked in their compound.
The tendency of people in my country to prefer cars over bicycles seems to be a result of a lack of education.
In order to address this, I shared a vision back in 2016 to increase education and familiarity with the role of bicycles on the environment.
This was aimed at people in my locality and I took every opportunity possible to start teaching people how to ride bicycles. At the time, I was the President of Environmental Control and Management Students’ Association (ECOMSA) in my school which led me to meet an organization of young people called ‘Life Fitness Cycling Club’ (LFCC). We struck a deal by subtly reintroducing cycling to the people and massively campaigning for bicycle riding in the society using social media and in-person meetings.
I led ECOMSA to push the concept of bicycle riding harder during the commemoration of World Environment Day 2016 held in Obafemi Awolowo University Ile-Ife Nigeria in collaboration with Life Fitness Cycling Club which recorded approximately 100 participants while thousands watched our activities online.
Our group planted trees and rode bicycles around the schools and community to raise awareness for the environment.
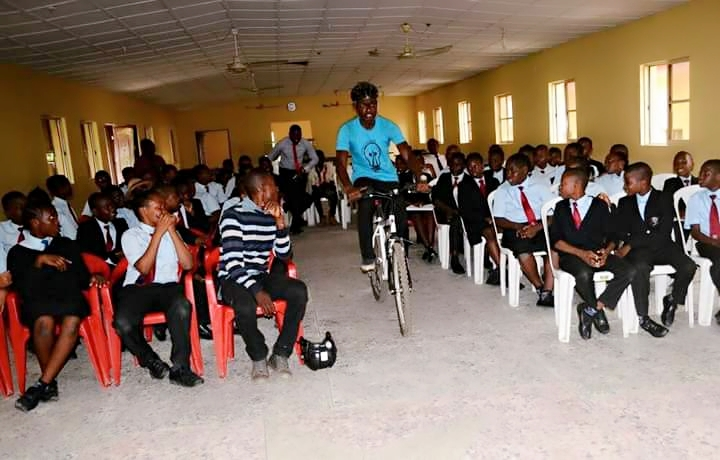

Shortly after, we noticed an increase in the number of cyclists on campus as lecturers were coming to the school on bicycles.
Prior to the event, I had secured another collaboration with Nigerian Conservation Foundation (NCF) in Lagos and Nigerian Television Authority (NTA), in which the NTA used their media platform to project our activities to Nigerians all over the country.
The broadcast actually worked as our activities during World Environment Day 2016 went viral and appeared on more than 37 blogs.
Electrifying Nigeria with ThinkBikes
These days, biking technology is rapidly changing with electric bikes growing in popularity around the world.
Tolulope Olukokun, the founder of ThinkBikes, an electric bike store in Ibadan, Oyo State Nigeria, is a proponent of biking as a way to mitigate carbon emissions in Nigeria.
“Crafting sustainable solutions has been a passion, and the electric bicycle emerged from a deep commitment to address environmental challenges ,” Olukokun said.
The primary motivation was to provide affordable and eco-friendly transportation in Africa. Recognizing the impact of traditional transportation on the environment, the vision was to introduce an electric bicycle that aligns with the continent’s needs for efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable mobility.
The reception has been promising. Olukokun says that people appreciate the accessibility and environmental benefits. According to the business man, we have witnessed a growing enthusiasm for electric bicycles, especially among urban commuters and environmentally conscious individuals.
His electric bicycles contribute significantly to reducing carbon emissions, according to Olukokun . By replacing traditional fuel-dependent modes of transport, they’ve estimated a substantial decrease in the business’s carbon footprint.
This aligns with global efforts to combat climate change by promoting cleaner transportation alternatives. Challenges, while inevitable, have mainly revolved around infrastructure and awareness. Electric bicycles are relatively new in many regions, and establishing the necessary charging stations has been a hurdle. Additionally, fostering awareness about the benefits of electric bicycles requires concerted efforts.
In the coming years, ThinkBikes plans to expand its footprint across Africa. With an increasing focus on sustainability, Olukokun aims to establish partnerships, enhance infrastructure, and promote policies supporting electric mobility. “We see ThinkBikes as a catalyst for change, influencing not only transportation habits but contributing to a broader shift toward a greener and more sustainable future ,” Olukokun said.

My regrets, my hopes
Ironically, I’m now the one who wishes to see my father ride on a bicycle so that I could encourage him with a warming smile, and he is now the one who prefers a car for mobility.
Now that I am educated on the climate impacts of cars, I regret the reaction I had as a child. I hope my story serves as a clue to what is going on across different communities in terms of the perception toward bicycles as a means of transportation.
Education and sensitization are important aspects of promoting green modes of transportation and should be promoted in Nigeria especially in rural and urban communities.
How do you move the planet forward?
Share on Social Media
Get the Newsletter
Get inspiring stories to move the planet forward in your inbox!
Success! You have been added to the Planet FWD newsletter. Inspiring stories will be coming to your inbox soon.
Related Stories
Catholic organization combats climate change through solar panel installations, maggie rhoads.
George Washington University

Shifting gears, shifting perspectives: Bikepacking through West Texas
Emma montgomery.
Planet Forward Correspondent | Texas Tech University

Essay | Nurturing eco-gratitude through the history of the Anacostia River
Christina Ritter
Middlebury College

‘We are the mushrooms’: A Diné community organizer’s efforts to combat pollution
Darrien Benally
Planet Forward Correspondent | Northern Arizona University

A project of

in collaboration with
This website uses cookies to provide you with an improved and personalized experience. By using this site you agree to our use of cookies. Please read our cookies policy for more information on the cookies we use and how to delete or block them.
Insert/edit link
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
How to Turn a Bike Ride Into a Bike Workout
Cycling isn’t just fun. It can also deliver big fitness gains with the right gear and strategy.

By Amanda Loudin
The reporter is a former triathlete, who still dusts off her bike on warm spring days. This summer she’s tackling her first gravel bike race.
There’s no better way to take in a perfect spring day than from a bike. The songbirds are back, the daffodils are blooming and your dusty 10-speed is looking for a rider.
But hopping on a bike can be more than a way to pass a pleasant afternoon; cycling can also give your fitness level a powerful boost without straining your joints, preparing you for higher-impact sports like running or tennis.
“There’s a reason cycling is the gold standard for people rehabbing knee injuries,” said Seth Forman, a sports performance trainer in New Jersey.
Research suggests cycling can improve cardiovascular health, which in turn lowers cancer mortality. That said, riding is not a perfect form of exercise. While it’s excellent cardio, it won’t boost bone health as much as sports like running, because your weight is supported by the bike.
“You need to supplement with resistance training to fill in the gaps,” Mr. Forman said.
But you don’t need to invest hundreds of dollars in Lycra to take your Saturday fun ride up a few notches to become a workout. You just need the right bike, gear and training approach.
Finding the right bike for you
Whether you’re pulling an old bike out of the garage or buying new, your first trip should be to your local bike shop for sizing. “If you’re not comfortable on your bike, you’re not going to ride it much,” said Marilyn Chychota, a triathlon coach in Tucson, Ariz., and former professional athlete
Joe Traill, who owns Joe’s Bike Shop in Baltimore, said most stores will make free sizing adjustment to a bike they’ve sold. A more involved option is called a bike fitting, which usually starts around $100 and can include body measurements, flexibility analysis and more.
Also think about whether you want to ride on streets or trails . If you’re unsure, begin with a hybrid bike , which has wider, more stable tires and flat handlebars for bumpy terrain.
E-bikes are another option if you live in a hilly area, want to bike commute or worry about keeping up with friends. “Even if you’re riding for fitness, studies show some people will ride more and get more of a workout with the electric assist,” said Mr. Traill. Be careful purchasing an e-bike online, however, as some off-brand versions may pose a fire hazard .
Also, plan to purchase a good helmet — in the range of at least $50 — that comes equipped with “MIPS” (multiple impact protection system).
Getting fit
The first step in leveling up your bike ride is to focus on pedaling. You’re after a smooth pedal stroke, so begin in easy gears and aim to turn your pedals quickly.
Serious cyclists prefer clipless pedals and the special shoes that attach to them, which let you more effectively transfer power, especially on the upstroke. But they can be intimidating to beginning riders. Whether you use them or not, think about pushing and pulling your pedals in continuous circles, without any pauses or changes in cadence.
“Start by riding for about 20 minutes, three times a week, aiming for a nice consistent tempo,” said Ms. Chychota. “Ride at a perceived exertion of about five out of 10.” That means breathing at a rate that would still allow you to hold a conversation.
From there, extend the time you’re in the saddle for one of your weekly rides, ideally by about 10 minutes each time. Over the next three months, make it your goal to reach 90 minutes on that longer ride. On the other two, build the time as well, but cap it around 45 minutes to an hour, recommended Ms. Chychota.
This is true whether you’re new to cycling, or just getting back in shape after a long winter.
“I always start with shorter, easier rides,” said Steve Johnson, a travel writer in Minneapolis who returns to his bike every spring after months of winter sports. But he added: “I try not to miss more than three days in a row. By summer, I’m riding several times a week and doing long, hilly rides every weekend.”
Riding hills once a week is great way to push your fitness, said Ms. Chychota, once you’re comfortable riding the flats. She recommends starting with short climbs: Ride hard up a hill for one minute, return to the bottom at an easy pace — and then turn around and do it again. Start with four or five repeats, and gradually extend the length of these repeats until you can climb for four minutes, eight times over.
On one of your shorter days each week, consider adding some interval training — short bursts of speed followed by easier riding to increase your endurance and performance. Find a faster pace, around 90 percent of your maximum, that you could only hold for five minutes, and look for flatter stretches of road.
Here is a weekly progression that Ms. Chychota recommends. You should be challenged, but if you struggle to complete one week’s workout, it’s fine to repeat it until you feel like moving on.
Week 1: Five rounds: 30 seconds fast and one minute easier.
Week 2: Eight rounds: 30 seconds fast and 30 seconds easier.
Week 3: Two sets of eight rounds: 30 seconds fast and 30 seconds easier (with five minutes easy pedaling between them).
Week 4: Eight rounds: one minute fast and two minutes easier.
Week 5: Five rounds: two minutes fast and two minutes easier.
Week 6: Five rounds: three minutes fast and three minutes easier.
After this, you will be a fairly fit cyclist, but keep these workouts in your routine. As with any activity, remember to start low and slow, but also, don’t be intimidated, said Mr. Traill: “Cycling is a great form of exercise, and it’s also inherently fun.”
Amanda Loudin is a freelance writer covering health and science.
Cycling Around the Globe
The cycling world can be intimidating. but with the right mind-set and gear you can make the most of human-powered transportation..
Are you new to urban biking? These tips will help you make sure you are ready to get on the saddle .
Whether you’re mountain biking down a forested path or hitting the local rail trail, you’ll need the right gear . Wirecutter has plenty of recommendations , from which bike to buy to the best bike locks .
Do you get nervous at the thought of cycling in the city? Here are some ways to get comfortable with traffic .
Learn how to store your bike properly and give it the maintenance it needs in the colder weather.
Not ready for mountain biking just yet? Try gravel biking instead . Here are five places in the United States to explore on two wheels.
Process writing on how to ride a bicycle
You are Jay/Jays. Recently you learned to ride a bicycle. Attempt in 100-125 words factual description of the process of learning to ride a bicycle.

All Process Writing Examples
5 thoughts on “process writing on how to ride a bicycle”.
Hello, Thanks for reading our blog on ‘Process writing on how to ride a bicycle’, and if you have any doubts or you want to ask any queries related to this topic then you can comment below the blog. And you can also suggest improving the content of this blog.
Is the process writting held like this but my sir gave me hints than said me chose the correct title for the story than make it.. where is the hint of how to ride a bicycle
Hi, Sandeep we are providing process writing, not hints on process writing. Here you will find process writing on different topics – Not in question-answer format.
Thanks for asking we will consider you.
I want factual description of the process of learning bicycle at least five pages
Title: The Process of Learning to Ride a Bicycle
Introduction: Learning to ride a bicycle is a significant milestone in many people’s lives. The process of acquiring this skill involves a combination of physical coordination, balance, and cognitive development. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the step-by-step process of learning to ride a bicycle, covering the necessary equipment, techniques, and tips for success. By understanding the key components of the learning process, aspiring cyclists can embark on their journey with confidence and make steady progress toward mastery.
Page 1: Preparing for Success – The selection of the right bicycle: Choosing a bicycle appropriate for your age, size, and skill level is crucial. Factors such as wheel size, frame type, and bike accessories should be considered. – Essential safety gear: A well-fitting helmet, knee and elbow pads, and closed-toe shoes are essential to ensure safety during the learning process. – Finding a suitable location: Identifying a safe and spacious area for practice, such as an empty parking lot or a quiet residential street, is essential.
Page 2: Basic Balance and Coordination – Straddling and mounting the bicycle: Properly positioning oneself on the bicycle by standing on the ground, straddling the frame, and mounting the bike safely. – Scooting and balancing: Initially, learners can start by scooting their feet along the ground while seated on the bike, focusing on maintaining balance and coordination. – Gaining momentum: Gradually, learners can practice gaining momentum by lifting their feet off the ground and gliding for short distances. This helps in developing balance and a sense of control.
Page 3: Pedaling and Steering – Introducing pedals: After gaining confidence in balancing and gliding, learners can progress to attaching the feet to the pedals. Initially, they can start with one foot on the ground and the other on the pedal, practicing the motion of pushing down and pulling up. – Coordinating pedaling and steering: As learners become comfortable with pedaling, they can begin to combine it with steering. This involves maintaining balance while turning and maneuvering the bicycle.
Page 4: Building Confidence and Skills – Practicing turns and stops: Learners can refine their skills by practicing turning corners and stopping smoothly. This includes using hand signals, looking over the shoulder, and applying the brakes correctly. – Riding in different environments: Once basic skills are developed, learners can gradually introduce more challenging environments, such as inclined surfaces, uneven terrain, and varying weather conditions. This helps build adaptability and confidence. – Developing advanced techniques: Advanced techniques, such as riding with one hand, maintaining a steady speed, and emergency maneuvers, can be practiced to enhance overall cycling skills.
Page 5: Troubleshooting and Tips – Common challenges and solutions: Addressing common difficulties faced by learners, such as maintaining balance, overcoming fear, and developing coordination. – Mental preparation and motivation: The process of learning to ride a bicycle can be challenging at times. Techniques for staying motivated, setting realistic goals, and celebrating milestones can help overcome obstacles. – Seeking guidance and support: Professional instruction, peer encouragement, and the support of experienced cyclists can play a vital role in the learning process.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.

COMMENTS
Words: 364 Pages: 1. Being a child involves dealing with new issues almost every day and learning how to overcome your fears. My first experience of riding a bicycle at the age of five is among my most vivid memories when it comes to the joys of childhood and conquering fears. On that day in summer, I acquired new skills and became more ...
Start by resting your right foot on the pedal on the right-hand side of the bicycle while supporting yourself with the left foot. Push the right pedal with your foot and simultaneously remove your left-leg support to rest the left foot on the left pedal. Next, ensure that the handlebars point ahead as you start pedaling.
Life is Like Riding a Bicycle. Life is often compared to riding a bicycle, and for good reason. Just like riding a bicycle, life requires balance, perseverance, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances. This essay will explore the parallels between life and riding a bicycle, and how these parallels can provide valuable insights into ...
Conclusion. My first experience of riding a bicycle was a lesson in perseverance, resilience, and the joy of overcoming obstacles. It was a testament to the human spirit's ability to conquer fear and embrace new experiences. It was more than just a physical activity; it was a journey of self-discovery and personal growth.
A right-handed person, for instance, can stand on the left side of the bike. Lift up your right leg, reach it over the bike, and put it on the ground on the other side of the bike. Hold the bike upwards between your legs. Feel the weight of the bike between your legs and try to keep it balanced as you lower yourself.
250 Words Essay on Riding A Bike Introduction to Bike Riding. Riding a bike is a fun and healthy activity that people of all ages can enjoy. It is not only a mode of transportation, but also a sport, a hobby, and a way to stay fit. Learning to Ride a Bike. Learning to ride a bike is an exciting time in a child's life.
The way memories are anchored in the brain plays a role, neuropsychologist Boris Suchan explains. Most of us learn how to ride a bike during childhood. But as we grow older, many of us stop riding ...
A narrative essay is a personal piece of writing that makes your point of view clear to the reader. In a narrative essay, you could write about how you learned to ride a bike. Decide on a cycling topic. Once you have decided what type of essay you would like to write, you will need to decide on a specific topic. For example, if you want to ...
5. Cycling is great cardiovascular exercise at a time when lifestyles are becoming increasingly sedentary due to advances in consumer technology. 6. Riding a bicycle allows the average person to get in their daily exercise efficiently on their way to work. Write another topic sentence with a new main idea.
250 Words Essay on First Ride On Bicycle My First Bicycle Ride. Learning to ride a bicycle is a big moment for many kids. It's like a step into a new world of adventure. I remember my first bicycle ride very clearly. It was a mix of excitement, fear, and joy. Getting Ready. My bicycle was shiny and blue, with white stripes on the side.
Expository essays are often assigned in academic settings. In an expository essay, you need to consider an idea, investigate the idea, then explain the idea. ... An example of an expository essay could be discussing how to ride a particular type of bike. You'd take the reader through those steps so they could paint a clear picture in their head ...
500 Words Essay On Bicycle. A bicycle is a useful vehicle that helps us reach a destination without polluting the environment. It is composed of steel and has two wheels. In addition, it has got a seat and handle with two pedals and also a bell. Some bicycles have a carrier while some don't. It is a popular choice amongst poor people and ...
The working principle of a bicycle's frame and structure is based on the use of gears. Gears allow the rider to change the mechanical advantage of the bicycle, making it easier to pedal uphill or faster on flat surfaces. The gears are controlled by the shifters, which are usually located on the handlebars.
Start by pushing off with your feet and maintaining balance as you glide along the ground. Keep your raised foot forward to maintain a forward weight bias and help you stay steady while riding. As you become more confident, challenge yourself to coast for longer periods of time. Practice turning to the right and left.
Microsoft Word - Inf-Exp Writing Prompt 1 - How-to ride a bike. How‐to. People write directions, so we learn how to do new things. Sometimes people will call these directions or instructions or how‐to writing. Today you will write step‐by‐step directions that tell how to ride a bike. Prompt:
To protect the anonymity of contributors, we've removed their names and personal information from the essays. When citing an essay from our library, you can use "Kibin" as the author. Kibin does not guarantee the accuracy, timeliness, or completeness of the essays in the library; essay content should not be construed as advice.
Annual Student Bike Essay Contest . WE WOULD LOVE YOUR SUPPORT! Our content is provided free as a public service! IBF is 100% solar powered. Follow us on Twitter : 2009 Student Bicycle Essay Contest Winners. We are pleased to present the winning essays from the 2009 International Bicycle Fund Student Essay contest. ... Bike riding is an ...
Learning to Ride a Bike. All children at one point in their life want to learn how to ride a bike. Learning to ride a bike is a rite of passage from being a toddler and going into childhood. Learning to ride a bike encompasses both "trial and error" and "scientific" styles of learning. When I was about 7 or 8 years old that's when my ...
Contents. How to ride a bike as a new rider. Step 1: Get Familiar with The Bike Controls. Step 2: Start the Bike. Step 3: Practice with The Clutch. Step 4: Shifting Gears. Step 5: Braking. Safety Measures While Riding a Bike As a Beginner. Frequently Asked Questions.
If while riding your knees hit the handle bars, then the bike is too small. You must either higher the seat and handle bars or get a larger bicycle. Step 2: Check your brakes. You never want to get caught in a situation where you cannot stop because your breaks don't work. Step 3: Check the air in your tires.
Therefore, choosing to always ride a bicycle over a few car trips, as your transportation habits, could significantly help to protect the environment from climate change impacts," Matthew said. Unfortunately, according to CEIC Data Global Database , vehicle registrations rose nationally in Nigeria from 3,750 in 2015 to 11,605 in 2020.
Whether you use them or not, think about pushing and pulling your pedals in continuous circles, without any pauses or changes in cadence. "Start by riding for about 20 minutes, three times a ...
00:00. HOW OT RIDE A BICYCLE. Take a cycle as per your height. Choose the place where you want to practice for riding a bicycle Take help of some elders. So that he can hold you from behind. Sit on the seat of the bicycle and put your feet on the pedals. Run the bicycle slowly-slowly and try to sit straight balancing the handle and cycle ...
View Expository Writing - Teach Someone to Ride a Bike.pdf from ELC 231 at Universiti Teknologi Mara. Name _ Date _ Grade _ An expository paragraph explains something or gives information.