How to Write a Psychology Essay
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Before you write your essay, it’s important to analyse the task and understand exactly what the essay question is asking. Your lecturer may give you some advice – pay attention to this as it will help you plan your answer.
Next conduct preliminary reading based on your lecture notes. At this stage, it’s not crucial to have a robust understanding of key theories or studies, but you should at least have a general “gist” of the literature.
After reading, plan a response to the task. This plan could be in the form of a mind map, a summary table, or by writing a core statement (which encompasses the entire argument of your essay in just a few sentences).
After writing your plan, conduct supplementary reading, refine your plan, and make it more detailed.
It is tempting to skip these preliminary steps and write the first draft while reading at the same time. However, reading and planning will make the essay writing process easier, quicker, and ensure a higher quality essay is produced.

Components of a Good Essay
Now, let us look at what constitutes a good essay in psychology. There are a number of important features.
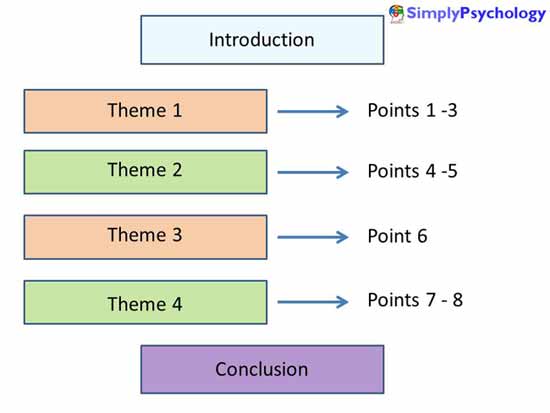
- Global Structure – structure the material to allow for a logical sequence of ideas. Each paragraph / statement should follow sensibly from its predecessor. The essay should “flow”. The introduction, main body and conclusion should all be linked.
- Each paragraph should comprise a main theme, which is illustrated and developed through a number of points (supported by evidence).
- Knowledge and Understanding – recognize, recall, and show understanding of a range of scientific material that accurately reflects the main theoretical perspectives.
- Critical Evaluation – arguments should be supported by appropriate evidence and/or theory from the literature. Evidence of independent thinking, insight, and evaluation of the evidence.
- Quality of Written Communication – writing clearly and succinctly with appropriate use of paragraphs, spelling, and grammar. All sources are referenced accurately and in line with APA guidelines.
In the main body of the essay, every paragraph should demonstrate both knowledge and critical evaluation.
There should also be an appropriate balance between these two essay components. Try to aim for about a 60/40 split if possible.
Most students make the mistake of writing too much knowledge and not enough evaluation (which is the difficult bit).
It is best to structure your essay according to key themes. Themes are illustrated and developed through a number of points (supported by evidence).
Choose relevant points only, ones that most reveal the theme or help to make a convincing and interesting argument.
Knowledge and Understanding
Remember that an essay is simply a discussion / argument on paper. Don’t make the mistake of writing all the information you know regarding a particular topic.
You need to be concise, and clearly articulate your argument. A sentence should contain no unnecessary words, a paragraph no unnecessary sentences.
Each paragraph should have a purpose / theme, and make a number of points – which need to be support by high quality evidence. Be clear why each point is is relevant to the argument. It would be useful at the beginning of each paragraph if you explicitly outlined the theme being discussed (.e.g. cognitive development, social development etc.).
Try not to overuse quotations in your essays. It is more appropriate to use original content to demonstrate your understanding.
Psychology is a science so you must support your ideas with evidence (not your own personal opinion). If you are discussing a theory or research study make sure you cite the source of the information.
Note this is not the author of a textbook you have read – but the original source / author(s) of the theory or research study.
For example:
Bowlby (1951) claimed that mothering is almost useless if delayed until after two and a half to three years and, for most children, if delayed till after 12 months, i.e. there is a critical period.
Maslow (1943) stated that people are motivated to achieve certain needs. When one need is fulfilled a person seeks to fullfil the next one, and so on.
As a general rule, make sure there is at least one citation (i.e. name of psychologist and date of publication) in each paragraph.
Remember to answer the essay question. Underline the keywords in the essay title. Don’t make the mistake of simply writing everything you know of a particular topic, be selective. Each paragraph in your essay should contribute to answering the essay question.
Critical Evaluation
In simple terms, this means outlining the strengths and limitations of a theory or research study.
There are many ways you can critically evaluate:
Methodological evaluation of research
Is the study valid / reliable ? Is the sample biased, or can we generalize the findings to other populations? What are the strengths and limitations of the method used and data obtained?
Be careful to ensure that any methodological criticisms are justified and not trite.
Rather than hunting for weaknesses in every study; only highlight limitations that make you doubt the conclusions that the authors have drawn – e.g., where an alternative explanation might be equally likely because something hasn’t been adequately controlled.
Compare or contrast different theories
Outline how the theories are similar and how they differ. This could be two (or more) theories of personality / memory / child development etc. Also try to communicate the value of the theory / study.
Debates or perspectives
Refer to debates such as nature or nurture, reductionism vs. holism, or the perspectives in psychology . For example, would they agree or disagree with a theory or the findings of the study?
What are the ethical issues of the research?
Does a study involve ethical issues such as deception, privacy, psychological or physical harm?
Gender bias
If research is biased towards men or women it does not provide a clear view of the behavior that has been studied. A dominantly male perspective is known as an androcentric bias.
Cultural bias
Is the theory / study ethnocentric? Psychology is predominantly a white, Euro-American enterprise. In some texts, over 90% of studies have US participants, who are predominantly white and middle class.
Does the theory or study being discussed judge other cultures by Western standards?
Animal Research
This raises the issue of whether it’s morally and/or scientifically right to use animals. The main criterion is that benefits must outweigh costs. But benefits are almost always to humans and costs to animals.
Animal research also raises the issue of extrapolation. Can we generalize from studies on animals to humans as their anatomy & physiology is different from humans?
The PEC System
It is very important to elaborate on your evaluation. Don’t just write a shopping list of brief (one or two sentence) evaluation points.
Instead, make sure you expand on your points, remember, quality of evaluation is most important than quantity.
When you are writing an evaluation paragraph, use the PEC system.
- Make your P oint.
- E xplain how and why the point is relevant.
- Discuss the C onsequences / implications of the theory or study. Are they positive or negative?
For Example
- Point: It is argued that psychoanalytic therapy is only of benefit to an articulate, intelligent, affluent minority.
- Explain: Because psychoanalytic therapy involves talking and gaining insight, and is costly and time-consuming, it is argued that it is only of benefit to an articulate, intelligent, affluent minority. Evidence suggests psychoanalytic therapy works best if the client is motivated and has a positive attitude.
- Consequences: A depressed client’s apathy, flat emotional state, and lack of motivation limit the appropriateness of psychoanalytic therapy for depression.
Furthermore, the levels of dependency of depressed clients mean that transference is more likely to develop.
Using Research Studies in your Essays
Research studies can either be knowledge or evaluation.
- If you refer to the procedures and findings of a study, this shows knowledge and understanding.
- If you comment on what the studies shows, and what it supports and challenges about the theory in question, this shows evaluation.
Writing an Introduction
It is often best to write your introduction when you have finished the main body of the essay, so that you have a good understanding of the topic area.
If there is a word count for your essay try to devote 10% of this to your introduction.
Ideally, the introduction should;
Identify the subject of the essay and define the key terms. Highlight the major issues which “lie behind” the question. Let the reader know how you will focus your essay by identifying the main themes to be discussed. “Signpost” the essay’s key argument, (and, if possible, how this argument is structured).
Introductions are very important as first impressions count and they can create a h alo effect in the mind of the lecturer grading your essay. If you start off well then you are more likely to be forgiven for the odd mistake later one.
Writing a Conclusion
So many students either forget to write a conclusion or fail to give it the attention it deserves.
If there is a word count for your essay try to devote 10% of this to your conclusion.
Ideally the conclusion should summarize the key themes / arguments of your essay. State the take home message – don’t sit on the fence, instead weigh up the evidence presented in the essay and make a decision which side of the argument has more support.
Also, you might like to suggest what future research may need to be conducted and why (read the discussion section of journal articles for this).
Don”t include new information / arguments (only information discussed in the main body of the essay).
If you are unsure of what to write read the essay question and answer it in one paragraph.
Points that unite or embrace several themes can be used to great effect as part of your conclusion.
The Importance of Flow
Obviously, what you write is important, but how you communicate your ideas / arguments has a significant influence on your overall grade. Most students may have similar information / content in their essays, but the better students communicate this information concisely and articulately.
When you have finished the first draft of your essay you must check if it “flows”. This is an important feature of quality of communication (along with spelling and grammar).
This means that the paragraphs follow a logical order (like the chapters in a novel). Have a global structure with themes arranged in a way that allows for a logical sequence of ideas. You might want to rearrange (cut and paste) paragraphs to a different position in your essay if they don”t appear to fit in with the essay structure.
To improve the flow of your essay make sure the last sentence of one paragraph links to first sentence of the next paragraph. This will help the essay flow and make it easier to read.
Finally, only repeat citations when it is unclear which study / theory you are discussing. Repeating citations unnecessarily disrupts the flow of an essay.
Referencing
The reference section is the list of all the sources cited in the essay (in alphabetical order). It is not a bibliography (a list of the books you used).
In simple terms every time you cite/refer to a name (and date) of a psychologist you need to reference the original source of the information.
If you have been using textbooks this is easy as the references are usually at the back of the book and you can just copy them down. If you have been using websites, then you may have a problem as they might not provide a reference section for you to copy.
References need to be set out APA style :
Author, A. A. (year). Title of work . Location: Publisher.
Journal Articles
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (year). Article title. Journal Title, volume number (issue number), page numbers
A simple way to write your reference section is use Google scholar . Just type the name and date of the psychologist in the search box and click on the “cite” link.
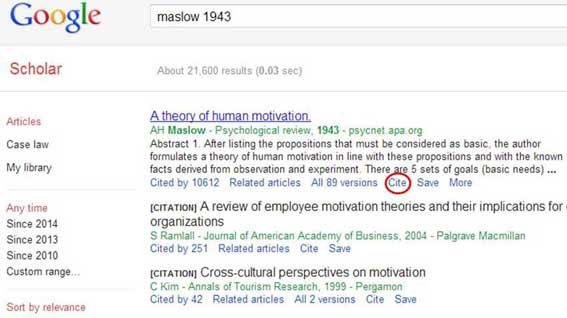
Next, copy and paste the APA reference into the reference section of your essay.

Once again, remember that references need to be in alphabetical order according to surname.
- Find My Rep
You are here
How to Write Brilliant Psychology Essays
- Paul Dickerson - University of Roehampton, UK
- Description
“This book is one I wish I had bought at the start of my Psychology degree.” – Five-star review Essay writing is a key part of the Psychology degree and knowing how to write effective and compelling academic essays is key to success. Whether it's understanding how to implement feedback you receive on essays, how to stop procrastinating or what makes an effective introduction, this book covers it all. Drawing on insights derived from teaching thousands of students over a 25-year period How to Write Brilliant Psychology Essays provides the keys that will unlock your writing potential.
Ace your Assignment provide practical tips to help succeed
Exercises help try the theory out in practice
Take away points highlight the key learnings from each chapter
Online resources provide even more help and guidance.
Supplements
Paul Dickerson, Emma McDonald and Christian van Nieuwerburgh discuss study skills, wellbeing and employability and explore how university lecturers and student welfare teams can better support Psychology students through their university journey.
Students enjoyed this text - they found it easy to read and the author's dry sense of humour appealed to many. Not just for psychologists!
A really useful guide for students, breaking down the components of what constitutes a good essay and written from a subject-specific view - highly recommend
I have recommended this to my first year tutorial groups as it provides them with everything they need to know about producing an excellent psychology essay.
Preview this book
For instructors.
Please select a format:
Select a Purchasing Option
Order from:.
- VitalSource
- Amazon Kindle
- Google Play
Related Products

- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Psychology Research Paper
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
James Lacy, MLS, is a fact-checker and researcher.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/James-Lacy-1000-73de2239670146618c03f8b77f02f84e.jpg)
Are you working on a psychology research paper this semester? Whether or not this is your first research paper, the entire process can seem a bit overwhelming at first. But, knowing where to start the research process can make things easier and less stressful.
While it can feel very intimidating, a research paper can initially be very intimidating, but it is not quite as scary if you break it down into more manageable steps. The following tips will help you break down the process into steps so it is easier to research and write your paper.
Decide What Kind of Paper You Are Going to Write
Before you begin, you should find out the type of paper your instructor expects you to write. There are a few common types of psychology papers that you might encounter.
Original Research or Lab Report
A report or empirical paper details research you conducted on your own. This is the type of paper you would write if your instructor had you perform your own psychology experiment. This type of paper follows a format similar to an APA format lab report. It includes a title page, abstract , introduction, method section, results section, discussion section, and references.
Literature Review
The second type of paper is a literature review that summarizes research conducted by other people on a particular topic. If you are writing a psychology research paper in this form, your instructor might specify the length it needs to be or the number of studies you need to cite. Student are often required to cite between 5 and 20 studies in their literature reviews and they are usually between 8 and 20 pages in length.
The format and sections of a literature review usually include an introduction, body, and discussion/implications/conclusions.
Literature reviews often begin by introducing the research question before narrowing the focus to the specific studies cited in the paper. Each cited study should be described in considerable detail. You should evaluate and compare the studies you cite and then offer your discussion of the implications of the findings.
Select an Idea for Your Research Paper
Hero Images / Getty Images
Once you have figured out the type of research paper you are going to write, it is time to choose a good topic . In many cases, your instructor may assign you a subject, or at least specify an overall theme on which to focus.
As you are selecting your topic, try to avoid general or overly broad subjects. For example, instead of writing a research paper on the general subject of attachment , you might instead focus your research on how insecure attachment styles in early childhood impact romantic attachments later in life.
Narrowing your topic will make writing your paper easier because it allows you to focus your research, develop your thesis, and fully explore pertinent findings.
Develop an Effective Research Strategy
As you find references for your psychology paper, take careful notes on the information you use and start developing a bibliography. If you stay organized and cite your sources throughout the writing process, you will not be left searching for an important bit of information you cannot seem to track back to the source.
So, as you do your research, make careful notes about each reference including the article title, authors, journal source, and what the article was about.
Write an Outline
You might be tempted to immediately dive into writing, but developing a strong framework can save a lot of time, hassle, and frustration. It can also help you spot potential problems with flow and structure.
If you outline the paper right off the bat, you will have a better idea of how one idea flows into the next and how your research supports your overall hypothesis .
You should start the outline with the three most fundamental sections: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. Then, start creating subsections based on your literature review. The more detailed your outline, the easier it will be to write your paper.
Draft, Revise, and Edit
Once you are confident in your outline, it is time to begin writing. Remember to follow APA format as you write your paper and include in-text citations for any materials you reference. Make sure to cite any information in the body of your paper in your reference section at the end of your document.
Writing a psychology research paper can be intimidating at first, but breaking the process into a series of smaller steps makes it more manageable. Be sure to start early by deciding on a substantial topic, doing your research, and creating a good outline . Doing these supporting steps ahead of time make it much easier to actually write the paper when the time comes.
- Beins, BC & Beins, A. Effective Writing in Psychology: Papers, Posters, and Presentation. New York: Blackwell Publishing; 2011.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
So much is at stake in writing a conclusion. This is, after all, your last chance to persuade your readers to your point of view, to impress yourself upon them as a writer and thinker. And the impression you create in your conclusion will shape the impression that stays with your readers after they've finished the essay.
The end of an essay should therefore convey a sense of completeness and closure as well as a sense of the lingering possibilities of the topic, its larger meaning, its implications: the final paragraph should close the discussion without closing it off.
To establish a sense of closure, you might do one or more of the following:
- Conclude by linking the last paragraph to the first, perhaps by reiterating a word or phrase you used at the beginning.
- Conclude with a sentence composed mainly of one-syllable words. Simple language can help create an effect of understated drama.
- Conclude with a sentence that's compound or parallel in structure; such sentences can establish a sense of balance or order that may feel just right at the end of a complex discussion.
To close the discussion without closing it off, you might do one or more of the following:
- Conclude with a quotation from or reference to a primary or secondary source, one that amplifies your main point or puts it in a different perspective. A quotation from, say, the novel or poem you're writing about can add texture and specificity to your discussion; a critic or scholar can help confirm or complicate your final point. For example, you might conclude an essay on the idea of home in James Joyce's short story collection, Dubliners , with information about Joyce's own complex feelings towards Dublin, his home. Or you might end with a biographer's statement about Joyce's attitude toward Dublin, which could illuminate his characters' responses to the city. Just be cautious, especially about using secondary material: make sure that you get the last word.
- Conclude by setting your discussion into a different, perhaps larger, context. For example, you might end an essay on nineteenth-century muckraking journalism by linking it to a current news magazine program like 60 Minutes .
- Conclude by redefining one of the key terms of your argument. For example, an essay on Marx's treatment of the conflict between wage labor and capital might begin with Marx's claim that the "capitalist economy is . . . a gigantic enterprise of dehumanization "; the essay might end by suggesting that Marxist analysis is itself dehumanizing because it construes everything in economic -- rather than moral or ethical-- terms.
- Conclude by considering the implications of your argument (or analysis or discussion). What does your argument imply, or involve, or suggest? For example, an essay on the novel Ambiguous Adventure , by the Senegalese writer Cheikh Hamidou Kane, might open with the idea that the protagonist's development suggests Kane's belief in the need to integrate Western materialism and Sufi spirituality in modern Senegal. The conclusion might make the new but related point that the novel on the whole suggests that such an integration is (or isn't) possible.
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay:
- Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas.
- Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up." These phrases can be useful--even welcome--in oral presentations. But readers can see, by the tell-tale compression of the pages, when an essay is about to end. You'll irritate your audience if you belabor the obvious.
- Resist the urge to apologize. If you've immersed yourself in your subject, you now know a good deal more about it than you can possibly include in a five- or ten- or 20-page essay. As a result, by the time you've finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you've produced. (And if you haven't immersed yourself in your subject, you may be feeling even more doubtful about your essay as you approach the conclusion.) Repress those doubts. Don't undercut your authority by saying things like, "this is just one approach to the subject; there may be other, better approaches. . ."
Copyright 1998, Pat Bellanca, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.

What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
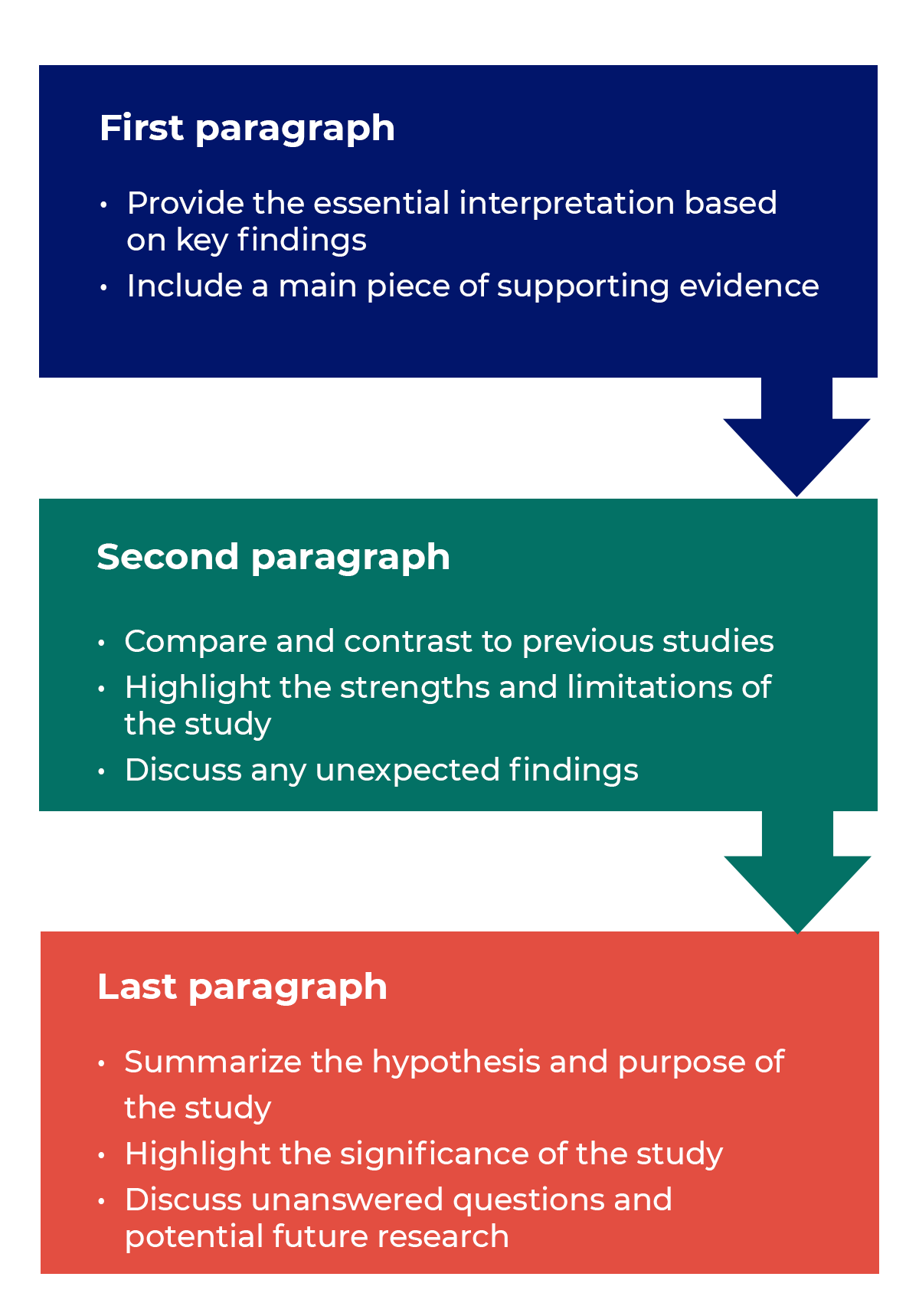
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- Educational and developmental psychology
How to Write a Psychology Paper: An Expert Guide


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Identify the subject of the essay and define the key terms. Highlight the major issues which "lie behind" the question. Let the reader know how you will focus your essay by identifying the main themes to be discussed. "Signpost" the essay's key argument, (and, if possible, how. this argument is structured).
A Guide for Writing in Psychology - 6 - - 7 - The Loyola Writing Center Introduction The following guide is designed to help psychology majors throughout their academic experience. The guide focuses on three of the main psychological papers: the psychological literature review, the article critique, and the classic research paper.
How to Write a Conclusion of a Psychology Essay with an Example Introduction. In the structure of a psychology essay, a conclusion is an essential component. Firstly, it serves to restate the main points that were covered in the essay using the shortest number of words possible. Secondly, it presents an opportunity to develop recommendations ...
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
Common Types of Psychology Papers Research psychologists engage in a variety of kinds of writing, including grant proposals, research applications and renewals, review articles, research articles, and textbooks. As a student, you are most likely to be asked to write one of two types of papers, either a report of your own actual or predicted ...
In this video, Dr. Sam Fairlamb provides some key tips to how to write a conclusion to a psychological essay that will leave a lasting impression with your m...
by APA style will help you to write clear, informative, interesting papers. Creativity in psychology tends to come from the ideas behind the writing, not the writing itself. This booklet is designed to acquaint you with the basic principles of psychological writing and to help you avoid pitfalls that beginning writers in the field often encounter.
Step 1: Restate the problem. The first task of your conclusion is to remind the reader of your research problem. You will have discussed this problem in depth throughout the body, but now the point is to zoom back out from the details to the bigger picture. While you are restating a problem you've already introduced, you should avoid phrasing ...
THE STRUCTURE. The most common way of structuring an essay is to base it around three parts — an introduction, main body, and conclusion. I suggest that you stick that structure! It works well, and is also what a marker will be expecting to see. At the same time, you should remember that this structure is only a foundation.
Drawing on insights derived from teaching thousands of students over a 25-year period How to Write Brilliant Psychology Essays provides the keys that will unlock your writing potential. Ace your Assignment provide practical tips to help succeed. Exercises help try the theory out in practice. Take away points highlight the key learnings from ...
You should start the outline with the three most fundamental sections: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. Then, start creating subsections based on your literature review. The more detailed your outline, the easier it will be to write your paper. 5.
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay: Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas. Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up ...
If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you're writing to meet their expectations. Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader.
Point: Make a clear point or argument. Evidence: Provide evidence such as research findings, studies, or theories. Explanation: Explain the significance of the evidence and how it supports your point. Link: Connect your point to the essay question and the next point you will discuss. Use clear and concise language.
In fact, if you follow these nine steps to get things under control, you'll end up with an excellent psychology paper. 1. Choose a topic you're actually excited about. Psychology is one of those disciplines where choice overload is inevitable when you're selecting a topic to write about.
2 Writing Argumentative Essays Once you have chosen a topic, you should produce an argumentative essay of 3,000 words. This section contains basic advice on writing argumentative essays, which may be of use if you come from a more technical background. Organisation Essays should have a beginning, a middle, and an end. The introduction should ...
You need to get your reader's attention and drawn them into the topic you're writing about. Use of statistics related to a problem, such as the number of people with learning disabilities, the number of people diagnosed with schizophrenia, etc. can help focus the reader and add a sense of urgency. 1. Plan your strategy.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Describe the purpose of writing and presenting in the context of a psychology degree. Describe some of the diferent types of psychology assignment formats including laboratory reports, essay, reviews, and presentations. Identify the sections of this book that will help you to complete diferent types of psychology assignments.
4 Chapter 1. Conclusions. In conclusion, the first chapter of this textbook has provided you with a glimpse into the multifaceted nature of the field of psychology. We have explored the fundamental question of "What is Psychology?" and have discussed its diverse subfields and applications. Moreover, we have delved into the rich history of ...
Writing the Body of a Psychology Essay. The body paragraphs of your psychology essay provide an opportunity to delve deeper into your arguments and present supporting evidence or research. Here are some guidelines for effectively writing the body of your essay: Develop a clear structure: Organize your body paragraphs in a logical and coherent ...
(Essay on the topic: "Distance in relationships between people," conclusion). 3. Tips on how to write an essay on psychology. When you write an essay on psychology, use our tips: 1. Try to keep within the recommended amount. Typically, this is 2-4 pages of printed text. Do not jump to other topics; strictly adhere to the topic of the paper.
to your argument / essay topic Example conclusion NOTE: Sometimes in the discipline of Psychology you may be asked to use headings and sub-headings in your essay. Check the task requirements and ask your tutor before doing so. In conclusion, the theories related to personality development include Psychodynamic